- FRONT MATTER
- TABLE OF CONTENTS

Oral Presentation and Powerpoint
I once attended a talk where the speaker held everyone’s attention for a key five minutes by pulling the Seinfeld trick—putting on "a show about nothing." An engineer at a small, struggling company, he was near the end of a slick Powerpoint presentation about whether the design for a critical machine should be modernized to speed up production, and he presented three options:
- Retool the machine in-house, which would sacrifice a month of production time but result in faster output in the long run.
- Buy a new machine from a known distributor, which would involve a hefty up-front expense but save labor costs and time;
- Do nothing.
That’s right—do nothing. Continue with production and learn to live with the sacrifices.
To dramatize this third point, the speaker filled the presentation screen—which up to then had held colorful Powerpoint slides employing slick transitions and graphics—with nothing. He simply left the screen blank, proposed the option of taking no action, and then shut off the projector. For the next five minutes, he engaged the audience members—which included the company president and the company accountant—by switching to a lecture format, moving around the room without so much as a pointer or note card, and arguing his case: that it was smarter for the company to maintain status quo, especially since it was struggling financially. Ultimately, he impressed his point on the audience not with the magic of presentation software, but with reasoning, creativity, common sense, and the bottom line. As the speaker hoped, the company bought into option number 3.
As this example demonstrates, effective oral presentation is more about creative thinking on your feet and basic skills than about wearing good shoes and knowing how to turn on the computer projector. Companies have long cried for graduates who can give dynamic talks, and they have long relied on talks as a key way to sway concerned parties towards a desired outcome. But many presenters make the mistake of trying to let the computer, bells and whistles blaring, do all the work for them. They forget the fundamentals of oral presentation, and thus whatever polish they have quickly loses its luster.
To become a modern speaker worth listening to, whether you’re serving as a company representative or presenting at a conference, you must come fully prepared, engage your audience’s attention and memory, attend to some visual design basics, and take stock of how you come across as a speaker.
Preparing for a Talk
There’s a rule-of-thumb in carpentry: Measure twice, cut once. The tenets behind this principle should be obvious—once a mistake is made, it’s difficult or impossible to undo. Though the carpenter can usually spackle or glue to repair, as a speaker you simply cannot get back those three minutes you just wasted in a fifteen-minute presentation. The following preparation principles will keep you right on plumb.
- Practice your talk straight through, and as you go jot quick notes to yourself about how to improve it. If you cannot manage to practice your talk straight through, perhaps you are not yet ready to offer it.
- Ideally, practice your talk under conditions similar to those in which you will give it, considering such factors as acoustics, distance from the audience, lighting, and room size. Lighting becomes especially important when computer equipment is involved. Be mentally prepared to adapt to the environmental conditions.
- As a draft, present your talk to a friend or two first and have them critique it. If you’re really gutsy and can tolerate the unforgiving lens of the camcorder, videotape your practice talk and critique it afterwards.
- View all of your visuals from your audience’s perspective prior to your talk. Be sure that your audience can easily see all that you want them to see, especially material that appears in the lower half of the screen.
- When you give a talk professionally, always request presentation guidelines from any relevant organizations and conform to them explicitly. It would be embarrassing for you if you were expected to present units in metric, for example, and you did otherwise because you failed to request or follow the available guidelines.
- As part of your preparation, choose an appropriately snappy and helpful title. You are expected not to come off as stodgy. Which talk would you rather attend: "Specific Geometrical Objects with Fractional Dimensions and Their Various Applications to Nature in General and The Universe At Large as we Know it" or "And On The Eighth Day, God Created Fractals"?
- Become highly familiar with any technology you’ll be using. Practice with the actual hardware or type of hardware you’ll be working with, making sure that compatibility or speed issues don’t get in your way. I’ve seen students go to present at a conference with a zip disk of their talk confidently in hand, only to find that the computer they were using didn’t have a zip drive. To facilitate faster computer speed, load your presentation onto the desktop if possible rather than run it from a CD or flash drive. If websites are needed as part of your presentation, check connection speeds and make sure all URLs are up and running.
Helping Your Audience Remember Your Key Points
Andy Warhol is known for the comment that everyone will be famous for 15 minutes. If your 15 minutes of fame is during your oral presentation, you want to be sure not to blow it. I’m amazed at how many times I’ve sat through a talk and come away with only a vague sense of what it was about. There are many reasons for this—some speakers view their talk as simply a format for reading a paper, while others fill the air with many words but little substance—but the most common reason is the simplest one: the speaker showed uncertainty about the talk's alleged subject. If you don’t spell out your premise, highlight your key points, and make it easy for your audience to remember the thrust of your presentation, you can’t expect your listeners to come away with understanding and investment.
To ensure an engaged audience for your talk, follow these practices:
- Introduce and Conclude . Use a formal introduction at the beginning of your talk and a summary afterwards to highlight your major points. Make sure your audience can remember your key points by keeping them simple and straightforward—even enumerated.
- Present in Sections . Give your talk "parts" —usually no more than three major parts for practical purposes—and let us know when we’re transitioning from one part to the next. This will help your audience to remain interested and focused.
- Spell out the Objective . Give the talk’s objective and even a hint of the conclusion right up front. Articulate the objective on its own slide so we can’t miss it. Revisit the objective at the end if necessary to underscore how it was realized.
- Use Props . Consider the use of some simple, meaningful props—even pass them around. Props can generate audience interest and, especially if they represent the actual work you did, they make the nature of that work more concrete. I’ve been to great talks where an experimental sample or photographs representing production sites were passed around, and they often generated focused questions from the audience members afterwards.
- Use Handouts . If appropriate, give a handout. As long as it’s well-designed, a concise written summary with bulleted points on a handout will ensure that your talk can be followed throughout. Such a handout should ideally be just one or two pages long, and be sure to time and manage its distribution so that it doesn’t take away attention from you as you speak. One possibility for handouts is an actual printout of your slides through the "Handouts" option in Powerpoint, but be certain that your audience actually needs all of your slides before electing this option.
- Offer Q&A . If question and answer is involved as part of the end of the talk, don’t let any questions deflect our interest. Some audience members might try to draw the attention to themselves, or focus on a mistake or uncertainty in your presentation, or even undermine your authority directly with an intimidating challenge. (I recall one speaker at a professional conference being tossed the strange question, "Your data is crap, isn’t it?") Remember that the stage and agenda are yours, and it’s your job to keep it that way and end your talk with a bang, not a whimper. If you don’t know the answer to a question, admit it or offer to discuss it privately after the presentation, then move on. One savvy way to handle questions is to turn back to your presentation slides as you answer them—call up a slide that will help repeat or explain the relevant point—and this will remind your audience that your talk had substance.
Mastering the Basics of Slide Design
Powerpoint helps us to think of each projected page as a "slide" in a slideshow. But just as someone else’s home movies can be thoroughly uninteresting if they’re grainy, poor in quality, and irrelevant, Powerpoint slides that are too flashy, cluttered, meaningless, or poorly designed can quickly turn a darkened room full of smart people into a mere gathering of snoozers. As you design your slides, consider these factors:
- Templates . Even though Powerpoint helps you design your slides, don’t assume that someone else’s template will always match your needs. Take charge of slide design by considering first the most efficient way to transmit the necessary information.
- Simplicity . Keep slides as simple and uncluttered as possible, and if the information must be complex, prioritize it for your audience as you present it (e.g., if presenting a ten-column table, direct your audience to the most significant columns). Offer only one major point per illustration. If you need to focus on more than one point, re-present the illustration in another form on a separate slide with the different point emphasized.
- Titles . Give most slides titles, with a font size of at least 36 points, and body text with a font size of at least 24 points. If you need to cite a source of information, include the citation in a smaller font size at the bottom of your slide.
- Rule of 8s. Apply the "rule of 8s": include no more than 8 words per line and 8 lines per slide.
- Bullets . When using bulleted lists in slides, present each bulleted line in parallel fashion—i.e., if the first line is a fragment, the others should be as well; if the first line opens with a verb, so should the others.
- Design . Design slides so that their longest dimension is horizontal rather than vertical. Use both uppercase and lowercase letters and orient pictures left to right. Avoid the overuse of animations and transitions, especially audio-based transitions, which can be distracting and downright silly.
- Color . Make sure the color for both the background and text are highly readable, especially under less than optimal lighting conditions. There’s nothing wrong with basic dark lettering and white background for your slides, particularly if they’re text-based. If you do choose a background theme or color, enhance continuity and viewability by keeping it consistent and subtle.
- Images . When possible, replace words with images. Use images in particular when presenting data, demonstrating trends, simplifying complex issues, and visualizing abstractions.
- Spelling. Spelling does count, and you can’t rely on Powerpoint to be an effective proofreader. Be sure your slides are free of grammatical and spelling errors. As Will Rogers quipped, "Nothing you can’t spell will ever work."
Maintaining the Look and Sound of a Professional Speaker
Public speaking is often cited by people as their number one fear (with death, ironically, as number two. Clearly, no one overcomes such fear overnight, and no one set of tips can transmogrify you into a polished speaker. However, you can work through that fear by learning from the successes of others. As Christopher Lasch once noted, "Nothing succeeds like the appearance of success." Good speakers attend first to their wardrobe, dressing as well as their "highest ranking" audience member is likely to dress. An equally important part of looking and sounding like a professional speaker is how you handle your body language and your voice. You must exude confidence if you want to be taken seriously, and remember that a high percentage of your audience’s perception is not about what you say but about how you look when you say it. The following guidelines will help you to look good and sound good as you give a talk:
- Take care not to stand in the way of your own slides—many speakers do this without even realizing it. Especially when using an overhead projector, point to the projected image of your slide (ideally, use a stick pointer or laser pointer) rather than the original source. This helps you avoid covering up more of the image than you intended and keeps our focus on the projected image rather than your accidental hand shadow puppet.
- Ideally, use the mouse pointer, a stick pointer, or a laser pointer to draw our attention to a particular item on the screen. One simple circle drawn briefly around the selected information is enough to draw our attention. Beware of slapping a stick pointer loudly against a screen, or leaving a laser pointer on for so long that its bright dot shakes all over the screen as a blazing red mirror of your nervousness.
- When you are not using a slide directly, keep it out of sight or out of your audience’s line of attention. Turn off the projector or create a dark screen when no visuals are relevant; literally invite your audience to turn its attention away from one thing to another.
- When working with computer projection, do not trust that hardware will always perform as you anticipate. Sometimes equipment fails midstream, or what worked fine for one speaker in a group doesn’t work for the next. If necessary, take backup transparencies of your slides ready for use on an overhead projector. Be certain that an overhead projector is available beforehand as a fallback.
- Don’t forget the value of a good old-fashioned easel or chalkboard. Not only do they offer variety, they are especially good for writing down basic information that you also want your audience to muse over or write down, or for presenting a picture as it evolves via its individual pieces (e.g., a flow chart, schematic, or simple experimental set-up).
- Maintain eye contact with at least a few people—especially those who are being the most responsive—in various parts of the room. Conversely, if you’re especially nervous about one or two audience members or you note some audience members looking sour or uninterested, avoid eye contact with them.
- Refer to time as an organizational tool: "For the next two minutes, I will summarize the city’s housing problem, then I will move on to . . . " This keeps both you and your audience anchored.
- Use the "point, turn, talk" technique. Pause when you have to turn or point to something, then turn back towards the audience, then talk. This gives emphasis to the material and keeps you connected with audience members. Strictly avoid talking sideways or backwards at your audience.
- Use physical gestures sparingly and with intention. For instance, raise three fingers and say "thirdly" as you make your third point; pull your hands toward your chest slightly as you advocate the acceptance of an idea. Beware, though, of overusing your body, especially to the point of distraction. Some speakers habitually flip their hair, fiddle with their keys, or talk with their hands. I’ve heard some people recommend that speakers keep one hand in a pocket to avoid overusing physical gestures.
- Minimize the amount of walking necessary during your talk, but do stand rather than sit because it commands more authority. As you speak, keep your feet firmly rooted and avoid continual shuffling of your weight. Intentionally leaning slightly on one leg most of the time can help keep you comfortable and relaxed.
- Take care to pronounce all words correctly, especially those key to the discipline. Check pronunciation of ambiguous words beforehand to be certain. It would be embarrassing to mispronounce "Euclidian" or "Möbius strip" in front of a group of people that you want to impress. I once mispronounced the word "banal" during a speech to English professors and one of the audience members actually interrupted to correct me. Most of that speech was—as you might guess—banal.
- Dead air is much better than air filled with repeated "ums," "likes," and "you knows." Get to know your personal "dead air" fillers and eliminate them. Out of utter boredom during a rotten speech a few years ago, I counted the number of times the speaker (a professor) used the word "basically" as an empty transition—44 times in just five minutes. Don’t be afraid to pause occasionally to give your listeners time to digest your information and give yourself a moment for reorientation. To quote Martin Fraquhar, "Well-timed silence hath more eloquence than speech."
- If you know that you have a mannerism that you can’t easily avoid—such as stuttering or a heavy accent—and it distracts you from making a good speech, consider getting past it by just pointing it out to the audience and moving on. I’ve been to several talks where the speaker opened by saying "Please accept the fact, as I have, that I’m a stutterer, and I’m likely to stutter a bit throughout my speech." One such speaker even injected humor by noting that James Earl Jones, one of his heroes, was also once a stutterer, so he felt in good company. As you might guess, the following speeches were confidently and effectively delivered, and when the mannerism arose it was easy to overlook.
- Avoid clichés, slang, and colloquialisms, but don’t be so formal that you’re afraid to speak in contractions or straightforward, simple terms. Use visual language, concrete nouns, active single-word verbs. When using specialized or broad terms that might be new or controversial to some audience members, be sure to define them clearly, and be prepared to defend your definition.
- Be animated and enthusiastic, but carefully so—many notches above the "just-the facts" Joe Friday, but many notches below the over-the-top Chris Rock.
For more advice on giving oral presentations and the use of Powerpoint, visit these websites:
"Powerpoint Presentations That are Not so Pretty" from about.com
"Rethinking the Design of Presentation Slides" Powerpoint by author Michael Alley
- Program Design
- Peer Mentors
- Excelling in Graduate School
- Oral Communication
- Written communication
- About Climb
Creating a 10-15 Minute Scientific Presentation
In the course of your career as a scientist, you will be asked to give brief presentations -- to colleagues, lab groups, and in other venues. We have put together a series of short videos to help you organize and deliver a crisp 10-15 minute scientific presentation.
First is a two part set of videos that walks you through organizing a presentation.
Part 1 - Creating an Introduction for a 10-15 Minute Scientfic Presentation
Part 2 - Creating the Body of a 10-15 Minute Presentation: Design/Methods; Data Results, Conclusions
Two additional videos should prove useful:
Designing PowerPoint Slides for a Scientific Presentation walks you through the key principles in designing powerful, easy to read slides.
Delivering a Presentation provides tips and approaches to help you put your best foot forward when you stand up in front of a group.
Other resources include:
Quick Links
Northwestern bioscience programs.
- Biomedical Engineering (BME)
- Chemical and Biological Engineering (ChBE)
- Driskill Graduate Program in the Life Sciences (DGP)
- Interdepartmental Biological Sciences (IBiS)
- Northwestern University Interdepartmental Neuroscience (NUIN)
- Campus Emergency Information
- Contact Northwestern University
- Report an Accessibility Issue
- University Policies
- Northwestern Home
- Northwestern Calendar: PlanIt Purple
- Northwestern Search
Chicago: 420 East Superior Street, Rubloff 6-644, Chicago, IL 60611 312-503-8286

How to Create Effective Speaking PowerPoint Presentations
- Carolyn Manion Kinnie
- January 23, 2023
Table of Contents
Introduction.
On your path to becoming a speaker, you overcome a lot of hurdles. You find your niche, you market yourself, you land a few local gigs, and then your first big keynote. You’ve finally “made it” in your industry and you’ll be speaking to thousands at a conference. During your last check-in with the event planner, they ask: “can you send your slides to our A/V guy before the talk?” You freeze. Nobody ever taught you how to create effective speaking powerpoint presentations! Will the same powerpoint template you used for that final project in high school suffice?
While that may not be exactly how this scenario plays out for you, at some point, probably early on in your speaking career, the question will arise. How do you create effective speaking PowerPoint presentations? Do they really matter? Can you just copy some sentences from your talk onto slides and call it a day?
We get questions about this a lot, and we’re here to help. We’ve covered the topic of speaking PowerPoint presentations a few times on the TSL podcast, specifically on episodes 190 – 191 and 262 . Today, we’ll go over when and why you should use slides (and if you really should)! Then we’ll cover some of the essential strategies for creating effective slides to go with your talk.
Do you really need slides?
A lot of aspiring speakers over-emphasize the role PowerPoint plays in their speaking engagements. Before we get into how to create your slides, let’s get one fundamental principle out of the way.
You can’t rely on your PowerPoint.
Slides are an enhancement , not a replacement for good content or your presence onstage. If your talk can’t stand on its own, even the most beautifully formatted PowerPoint can’t cover up for you. You should always be able to give your talk just as compellingly without a slideshow, video, photos, etc. Practice and hone your talk first, then create slides to go with it.
Preparedness is absolutely essential to the art of speaking, and even the best PowerPoint cannot cover for your unpreparedness. Slides exist to help the audience, not as a reminder for you. If you’re trying to make up for poor speaking skills with a fancy slide deck, that time is better spent working on your content and on-stage presentation. The order of importance is content first, delivery next, and only then your PowerPoint.
After all, you could be that unlucky speaker who walks on stage just before a power outage happens. Or the event planning intern loses your flash drive. Or the battery on the mac connected to the projector dies. Sure, those are all worst case scenarios. But anybody who’s been around in the conference space for a while will tell you they do happen. Unfortunately, many speakers treat their PowerPoint as a crutch, and fumble around if something goes wrong on the technical end. The ability to deliver your talk seamlessly without slides in such a situation will set you apart and endear you to event planners and audience members alike.
OK, so a PowerPoint isn’t absolutely essential. But when slides do enhance, they can be powerful! Some examples of their use include:
- Adding structure e.g. showing when you’re moving onto a new topic or reviewing points you’ve already made.
- Orienting your audience toward your message by highlighting key words or points that they should listen for.
- Presenting data, statistics, and research conclusions, especially if your field has a commonly used “visual shorthand”.
Your PowerPoint should work alongside your storytelling to keep your audience engaged and to the point. In our next section, we will dig deeper into how you can make your slides as effective and impactful as possible.
Free Download: 6 Proven Steps to Book More Paid Speaking Gigs in 2024
Download our 18-page guide and start booking more paid speaking gigs today!
Creating effective content in speaking PowerPoint Presentations
You should approach your speaking PowerPoint with an attitude of intentionality and minimalism. The number of slides is irrelevant–it’s how you present information on them that counts. Craft your words beautifully, and it will be easy to create slides alongside them.
When it comes to text on the screen, less is almost always more. Avoid redundancy–those blocks of text that you are going to say out loud anyway can go. Use big, readable fonts in a high-contrast color. Often, a single word to keep the audience on track is more compelling than a long block quote that would only distract them.
Minimalism doesn’t mean you should do away with images, but you must use them wisely! Two of the best uses for images are as an illustration or a visualization of a step-by-step process. Only images of the highest quality belong in your presentation, so ditch the grainy screenshots and dimly-lit photos. Free resources like Pixabay , Pexels , and Unsplash will provide you with great high-res stock images. For charts and diagrams, TSL friend Nancy Duarte offers a free PowerPoint-ready tool called Diagrammer . You can hear Nancy’s advice for slides and storytelling on Episode 262 of the Speaker Lab Podcast.
As we’ve mentioned before , reminding people that you are a professional speaker is essential to building your network and brand recognition. Don’t underestimate the possibilities your slides offer for self-promotion! Do you offer additional services such as courses or coaching? Integrate stories of past client work with images alongside. Have you spoken for audiences similar to those that your listeners are part of? Include a picture from one of those events. Here’s one way to gain fans and followers with your speaking PowerPoint that you can implement anytime: at the end of your talk, display your social media handle or a QR code that leads to an email subscriber form. If you give away a free resource to email subscribers ( as you should ), this is a great chance to mention it.
You shouldn’t create an entirely new PowerPoint every time you speak. Once you develop a signature talk, develop an easily adaptable PowerPoint template to go along with it. Use the same color scheme, fonts, and voice as your website and other business materials (more tips here for developing your speaker brand ).
It’s also in your own brand’s interest to design your slides with the client in mind. If there is a color, logo, or hashtag that unites your PowerPoint to an overarching event theme, it will be a big hit with audience and planners alike. Consider asking your point of contact if there’s a theme you should be aware of ahead of time. Integrating the theme into your template in small or subtle ways will take no time at all–and neither will your content if you follow our principles of intentionality and minimalism! Learn more about making the most of minimalist slides on Episode 190 of our podcast.
Presenting your speaking PowerPoint: technical tips
Once you’ve nailed down your content, you should run through your speech alongside your slides at least once. Knowing how to create effective speaking PowerPoint presentations is half the battle; presenting them onstage presents its own set of challenges. Here are some tips for jumping through technical hoops and making sure nothing in your control goes wrong.
When it comes to the template we mentioned in the previous section, you’ll have the option of creating it in a 4:3 or 16:9 aspect ratio. Always ask your client if they know the projector dimensions, but 4:3 is the safest by default. It’s far better to have smaller slides centered on a widescreen projector than unexpected cropping! Once you have the time, creating two templates will allow you to make the most of widescreen projectors when they are available.
If music or video is an absolutely essential part of your message, it can totally have a place in your PowerPoint. But if it’s not essential, leave it out! The A/V team will be relieved and it’s one less thing that can go wrong. If you must include animations, videos, music, etc., do so in the way that creates the least friction by requiring the least technical support. Have a game plan for smoothly moving on if it doesn’t work. If you’ve focused properly on crafting your talk, it will still have the same impact.
Here’s one tip we can’t stress enough: always bring backup. Even if you sent your slides to the client a week ago, bring a flash drive. If you’re supposed to project from your own device, send the file to the client or upload it to google slides just in case. And this tip doesn’t just apply to your PowerPoint! Put together a little tech bag stocked with cables, clickers, microphones, adaptors, and chargers. Many speakers even bring an ethernet cord.
Preparedness is key when it comes to effectively presenting your speaking PowerPoint. Ask about deadlines and technical requirements well in advance. At the same time, you can’t prepare for every scenario, so being easy to work with is equally important. If you can roll with the punches, event planners and A/V teams alike will look forward to seeing your name on the program. Those good relationships are essential to the referrals that will ensure you future gigs down the road.
If you’re looking for more details of technical success with your speaking PowerPoints, head over to episode 191 of the TSL podcast.
What Type Of Speaker Are You?
Click below to discover your Speaker Archetype and how to start getting booked and paid to speak!
Some speakers, like TSL founder Grant Baldwin or famous keynoter Simon Sinek avoid using slides whenever possible.
Others, like our friend Melanie Deziel , love creating effective speaking PowerPoints that help maximize their message.
Wherever you fall on the question of slides, it’s important to use them intentionally and without overwhelming the audience. While every speaker will have their own characteristic style, these tips should set you well on your way to creating amazing speaking slides!
- Last Updated: February 29, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.

Search Utah State University:
Oral presentations.
An oral presentation is usually more than just reading a paper or set of slides to an audience (though in some disciplines, this is the expectation). How you deliver your presentation is as important in communicating your message as what you say. Use these guidelines to learn simple tools that help you prepare and present an effective presentation, and design PowerPoint slides that support and enhance your talk.
Download Oral Presentation Template
Preparation Tips
An effective presentation is more than just standing up and giving information. A presenter must consider how best to communicate the information to the audience. Use these tips to create a presentation that is both informative and interesting:
- Organize your thoughts. Start with an outline and develop good transitions between sections. Emphasize the real-world significance of your research.
- Have a strong opening. Why should the audience listen to you? One good way to get their attention is to start with a question, whether or not you expect an answer.
- Define terms early. If you are using terms that may be new to the audience, introduce them early in your presentation. Once an audience gets lost in unfamiliar terminology, it is extremely difficult to get them back on track.
- Don't get lost in the details. It's natural to be excited about your research and want to tell your audience all about it, but they don't need to know every detail. Focus on giving them enough information to broadly understand how you arrived at your conclusion, what your findings are, and why they matter.
- Finish with a bang. Find one or two sentences that sum up the importance of your research. How is the world better off as a result of what you have done?
- Design PowerPoint slides to introduce important information. Consider doing a presentation without PowerPoint. Then consider which points you cannot make without slides. Create only those slides that are necessary to improve your communication with the audience.
- Time yourself. Do not wait until the last minute to time your presentation. Different conferences will allow for different amounts of time. At on-campus events hosted by the Office of Research, you only have 8 minutes to speak, so you want to know, as soon as possible, if you are close to that limit.
- Create effective notes for yourself. Have notes that you can read. Do not write out your entire talk; use an outline or other brief reminders of what you want to say. Make sure the text is large enough that you can read it from a distance.
- Practice, practice, practice. The more you practice your presentation, the more comfortable you will be in front of an audience. Practice in front of a friend or two and ask for their feedback. Record yourself and listen to it critically. Make it better and do it again.
Powerpoint Tips
Microsoft PowerPoint is a tremendous tool for presentations. It is also a tool that is sometimes not used effectively. If you are using PowerPoint, use these tips to enhance your presentation:
- Use a large font. As a general rule, avoid text smaller than 24 point.
- Use a clean typeface. Sans serif typefaces, such as Arial, are generally easier to read on a screen than serifed typefaces, such as Times New Roman.
- Use bullet points, not complete sentences. The text on your slide provides an outline to what you are saying. If the entire text of your presentation is on your slides, there is no reason for the audience to listen to you. A common standard is the 6/7 rule: no more than six bulleted items per slide and no more than seven words per item.
- Use contrasting colors. Use a dark text on a light background or a light text on a dark background. Avoid combinations of colors that look similar. Avoid red/green combinations, as this is the most common form of color blindness.
- Use special effects sparingly. Using animations, cool transition effects, sounds and other special effects is an effective way to make sure the audience notices your slides. Unfortunately, that means that they are not listening to what you are saying. Use special effects only when they are necessary to make a point.
Presentation Tips
When you start your presentation, the audience will be interested in what you say. Use these tips to help keep them interested throughout your presentation:
- Be excited. You are talking about something exciting. If you remember to be excited, your audience will feel it and automatically become more interested.
- Speak with confidence. When you are speaking, you are the authority on your topic, but do not pretend that you know everything. If you do not know the answer to a question, admit it. Consider deferring the question to your mentor or offer to look into the matter further.
- Make eye contact with the audience. Your purpose is to communicate with your audience, and people listen more if they feel you are talking directly to them. As you speak, let your eyes settle on one person for a few seconds before moving on to somebody else. You do not have to make eye contact with everybody, but make sure you connect with all areas of the audience equally.
- Avoid reading from the screen. First, if you are reading from the screen, you are not making eye contact with your audience. Second, if you put it on your slide, it is because you wanted them to read it, not you.
- Blank the screen when a slide is unnecessary. A slide that is not related to what you are speaking about can distract the audience. Pressing the letter B or the period key displays a black screen, which lets the audience concentrate solely on your words. Press the same key to restore the display.
- Use a pointer only when necessary. If you are using a laser pointer, remember to keep it off unless you need to highlight something on the screen.
- Explain your equations and graphs. When you display equations, explain them fully. Point out all constants and dependent and independent variables. With graphs, tell how they support your point. Explain the x- and y-axes and show how the graph progresses from left to right.
- Pause. Pauses bring audible structure to your presentation. They emphasize important information, make transitions obvious, and give the audience time to catch up between points and to read new slides. Pauses always feel much longer to speakers than to listeners. Practice counting silently to three (slowly) between points.
- Avoid filler words. Um, like, you know, and many others. To an audience, these are indications that you do not know what to say; you sound uncomfortable, so they start to feel uncomfortable as well. Speak slowly enough that you can collect your thoughts before moving ahead. If you really do not know what to say, pause silently until you do.
- Relax. It is hard to relax when you are nervous, but your audience will be much more comfortable if you are too.
- Breathe. It is fine to be nervous. In fact, you should be—all good presenters are nervous every time they are in front of an audience. The most effective way to keep your nerves in check—aside from a lot of practice beforehand—is to remember to breathe deeply throughout your presentation.
- Acknowledge the people who supported your research. Be sure to thank the people who made your research possible, including your mentor, research team, collaborators, and other sources of funding and support.
Sharing your work can help you expand your network of contacts who share your research interests. For undergraduate researchers who intend to complete a graduate degree, presenting can be an invaluable experience. We recommend discussing your interest in sharing your research with your faculty advisor. They can help match your interests with the appropriate venue.
See guide for Poster Presentations
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- How to prepare and...
How to prepare and deliver an effective oral presentation
- Related content
- Peer review
- Lucia Hartigan , registrar 1 ,
- Fionnuala Mone , fellow in maternal fetal medicine 1 ,
- Mary Higgins , consultant obstetrician 2
- 1 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin, Ireland
- 2 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin; Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Medicine and Medical Sciences, University College Dublin
- luciahartigan{at}hotmail.com
The success of an oral presentation lies in the speaker’s ability to transmit information to the audience. Lucia Hartigan and colleagues describe what they have learnt about delivering an effective scientific oral presentation from their own experiences, and their mistakes
The objective of an oral presentation is to portray large amounts of often complex information in a clear, bite sized fashion. Although some of the success lies in the content, the rest lies in the speaker’s skills in transmitting the information to the audience. 1
Preparation
It is important to be as well prepared as possible. Look at the venue in person, and find out the time allowed for your presentation and for questions, and the size of the audience and their backgrounds, which will allow the presentation to be pitched at the appropriate level.
See what the ambience and temperature are like and check that the format of your presentation is compatible with the available computer. This is particularly important when embedding videos. Before you begin, look at the video on stand-by and make sure the lights are dimmed and the speakers are functioning.
For visual aids, Microsoft PowerPoint or Apple Mac Keynote programmes are usual, although Prezi is increasing in popularity. Save the presentation on a USB stick, with email or cloud storage backup to avoid last minute disasters.
When preparing the presentation, start with an opening slide containing the title of the study, your name, and the date. Begin by addressing and thanking the audience and the organisation that has invited you to speak. Typically, the format includes background, study aims, methodology, results, strengths and weaknesses of the study, and conclusions.
If the study takes a lecturing format, consider including “any questions?” on a slide before you conclude, which will allow the audience to remember the take home messages. Ideally, the audience should remember three of the main points from the presentation. 2
Have a maximum of four short points per slide. If you can display something as a diagram, video, or a graph, use this instead of text and talk around it.
Animation is available in both Microsoft PowerPoint and the Apple Mac Keynote programme, and its use in presentations has been demonstrated to assist in the retention and recall of facts. 3 Do not overuse it, though, as it could make you appear unprofessional. If you show a video or diagram don’t just sit back—use a laser pointer to explain what is happening.
Rehearse your presentation in front of at least one person. Request feedback and amend accordingly. If possible, practise in the venue itself so things will not be unfamiliar on the day. If you appear comfortable, the audience will feel comfortable. Ask colleagues and seniors what questions they would ask and prepare responses to these questions.
It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don’t have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
Try to present slides at the rate of around one slide a minute. If you talk too much, you will lose your audience’s attention. The slides or videos should be an adjunct to your presentation, so do not hide behind them, and be proud of the work you are presenting. You should avoid reading the wording on the slides, but instead talk around the content on them.
Maintain eye contact with the audience and remember to smile and pause after each comment, giving your nerves time to settle. Speak slowly and concisely, highlighting key points.
Do not assume that the audience is completely familiar with the topic you are passionate about, but don’t patronise them either. Use every presentation as an opportunity to teach, even your seniors. The information you are presenting may be new to them, but it is always important to know your audience’s background. You can then ensure you do not patronise world experts.
To maintain the audience’s attention, vary the tone and inflection of your voice. If appropriate, use humour, though you should run any comments or jokes past others beforehand and make sure they are culturally appropriate. Check every now and again that the audience is following and offer them the opportunity to ask questions.
Finishing up is the most important part, as this is when you send your take home message with the audience. Slow down, even though time is important at this stage. Conclude with the three key points from the study and leave the slide up for a further few seconds. Do not ramble on. Give the audience a chance to digest the presentation. Conclude by acknowledging those who assisted you in the study, and thank the audience and organisation. If you are presenting in North America, it is usual practice to conclude with an image of the team. If you wish to show references, insert a text box on the appropriate slide with the primary author, year, and paper, although this is not always required.
Answering questions can often feel like the most daunting part, but don’t look upon this as negative. Assume that the audience has listened and is interested in your research. Listen carefully, and if you are unsure about what someone is saying, ask for the question to be rephrased. Thank the audience member for asking the question and keep responses brief and concise. If you are unsure of the answer you can say that the questioner has raised an interesting point that you will have to investigate further. Have someone in the audience who will write down the questions for you, and remember that this is effectively free peer review.
Be proud of your achievements and try to do justice to the work that you and the rest of your group have done. You deserve to be up on that stage, so show off what you have achieved.
Competing interests: We have read and understood the BMJ Group policy on declaration of interests and declare the following interests: None.
- ↵ Rovira A, Auger C, Naidich TP. How to prepare an oral presentation and a conference. Radiologica 2013 ; 55 (suppl 1): 2 -7S. OpenUrl
- ↵ Bourne PE. Ten simple rules for making good oral presentations. PLos Comput Biol 2007 ; 3 : e77 . OpenUrl PubMed
- ↵ Naqvi SH, Mobasher F, Afzal MA, Umair M, Kohli AN, Bukhari MH. Effectiveness of teaching methods in a medical institute: perceptions of medical students to teaching aids. J Pak Med Assoc 2013 ; 63 : 859 -64. OpenUrl
Search form

Search This Site
Recipient Directory
- Getting Started
- Policies for Grants
- Double Hoo Award
- Harrison Undergraduate Research Awards
- Kenan Award
- University Undergraduate Award for Arts Projects
- URN Conference Grants
- USOAR Program
- UVA Summer Programs
- Other Opportunities
- Faculty Support
- USOAR Mentor
- Presentation Format Details
- Information For Mentors
Oral Presentation Tips
- Poster Presentations
- Research Journals
How To Make an Oral Presentation of Your Research
You’ve been working on your research for months, and now that it’s finished, or almost there, you need to make an oral presentation. Perhaps you are applying to attend the ACC Meeting of the Minds undergraduate research conference. Maybe you would like to participate in the Undergraduate Research Symposium in the spring semester here at UVA. Here are some tips to help you bring order to the ideas swirling in your head—and communicate the key points about your research to an audience.
Timing. Find out how long your talk should be. As you decide what to present, keep in mind that a ten-minute talk is very different from a 45-minute lecture. If you only have ten minutes, you’ll need to focus on the most important points. With more time, you’ll still need to focus on those points, but you’ll be able to present additional supporting detail. Time yourself giving your talk, and make cuts if you need to. It is fine to end a bit early. Going overtime shows your lack of preparation.
Audience. Find out what sort of audience will listen to your talk. Specialists in your field will bring a different sort of understanding to your presentation from a general audience; you may be able to use certain technical terms without defining them, but always beware of jargon and acronyms. With a general audience, you need to ask yourself what educated people not in your field will know, define any terms that may be unfamiliar to them, and make an effort to explain the significance of your research in terms the listeners are likely to understand.
Content. Students often think they need to explain every single thing they know or be perceived as knowing too little. This is not true. Giving a talk is a great opportunity to think about the big picture rather than focusing on details. This can be hard if you are immersed in the specifics of your project.
Step back for a moment to before you became the expert on your particular topic. What piqued your interest? Why did you start asking the questions you asked? Now step into the future. When you look back on this research, what will you remember as the most interesting or compelling thing you learned? Were there surprises?
Now you are ready to ask yourself: What are the points I want to convey? What do I want the audience to learn? When audience members remember my talk the following day, what main point do I want them to remember?
- introduce yourself;
- present your research question and why it matters;
- describe how you conducted your research,
- explain what you found out and what it means; and
- conclude with a summary of your main points.
Depending on your topic, you may need to provide background information so that the audience understands the significance of your inquiry. Be judicious in the amount of information you give, and do not let this discussion get you off track. Once you’ve provided sufficient background, bring the focus back to your research by reminding the audience of your research question.
Do not even think of opening PowerPoint until you have organized your ideas and decided on your main points. If you need guidance, see below for a sample oral presentation outline.
PowerPoint. You should treat PowerPoint as a useful tool. You can use it to incorporate images into your presentation , to emphasize important points , and to guide your audience in following your argument . You should not use it for anything else.
This means:
Don’t present too much information on the slides. The audience cannot read a long section of text and simultaneously listen to you speak about it. If you really must provide a long quotation, then highlight the words and phrases you want to emphasize, and read the quote out loud, slowly, so the audience can absorb it.
Do explain to your audience what each chart or graph indicates. Use charts and graphs to convey information clearly, not simply to show that you did the work.
Don’t spend extra time on making a fancy PowerPoint presentation with moving images and graphics unless they are vital for communicating your ideas.
Do be prepared to give your talk even if technology fails. If your charts don’t look quite right on the screen, or you forget your flash drive, or there’s a power outage, or half the audience can’t see the screen, you should still be able to make an effective presentation. (Bring a printout to speak from, just in case any of these disasters befalls you.)
Tone. It is best to approach your prepared talk as a somewhat formal occasion. Treat your audience—and your topic—with respect. Even if you know everyone in the room, introduce yourself. Don’t address audience members as “you guys.” Dress neatly. Most of all, share your enthusiasm for your subject.
Practice speaking slowly and clearly. If you want to emphasize an important point, repeat it. Practice speaking slowly and clearly.
You don’t need to read your talk, and in fact you should avoid doing so. But you should speak it out loud enough times that you know when there are points that tend to trip you up, where you might have a tendency to throw in something new and get off track, and whether some of your transitions are not smooth enough.
And, of course, time yourself. Make cuts if you need to.
Practice again.
Sample Oral Presentation Outline
Introduction Hello, my name is ____. I am a ___-year student at the University of Virginia majoring in ____. I’m going to talk to you today about my research on _____.
Context of research
- I had the opportunity to join Professor ____’s lab, where the research focus is____.
- This is research for my Distinguished Majors thesis….
- I got interested in this area because ….
Research question and significance
- I wanted to find out _______[insert your research question].
- This is an important question because _____. OR This question interested me because ______.
Research methods/design
- I thought the best way to answer this question would be by ______.
- I chose this method because….
Research activity Here’s what I did: _______.
Results Here’s what I found out: ______.
Significance of results/where this research might lead
- This result matters because….
- Now that I’ve learned this, I see that some other questions to ask are….
Conclusion/Summary of main points I set out to answer ______ [research question] by _______ [research methods]. And I discovered that ______ [brief statement of results]. This was interesting because _____ [significance]/This will help us understand ____.<
Acknowledgments
- I am grateful to my advisor, Professor _____, for her guidance.…
- My work was supported by a _____ award. OR I’d like to thank the ____ Family for their generosity.
Questions I would be happy to take your questions.
Student Academic Success Center
Powerpoint / oral presentation slide design.
Microsoft PowerPoint and its brand of slide design have dominated the market for decades. By some measures, PowerPoint is installed on over a billion computers around the world . Even if you use one of PowerPoint's competitors, like Google Slides, you probably still follow the same basic design model PowerPoint carved out in the 1980s. For all the millions of PowerPoint-style presentations given every day, however, many fail to assist speakers’ basic purposes: to be clear and engaging.
This handout will teach you a research-backed model to efficiently redesign your slides for maximum effectiveness. Specifically, you’ll learn:
- The “Assertion-Evidence” model of slide design
- How to convert text-heavy slides into a more visual format
This method can be applied to many fields by following these three steps:
- Clearly assert the slide’s main idea in a complete sentence
- Reinforce the argument with visual evidence
- Simplify slide design
To see these principles in action, click the link in the sidebar to watch the videos or view, download, and print the PDF.
Need one-on-one help with your presentation? Schedule an appointment with one of our consultants now!
Related Resources
- Download the PDF
- Watch the video
- Edit the slides for the video
- Watch our workshop (part 1)
- Watch our workshop (part 2)
Designing Effective PowerPoint Presentations
Designing Effective Slide Presentations
Download the practice slides for this video
Designing Effective PowerPoint Presentations, Part 1 (recorded workshop)
Designing Effective PowerPoint Presentations, Part 2 (recorded workshop)
Quick Links
- Academic Calendar
- Academic Integrity
- Bias Reporting and Response
- Statement of Assurance
- Documents, Forms, and News [Internal Staff Only]
Other Helpful Departments
- Disability Resources
- Center for Student Diversity & Inclusion
- Graduate Education
- Office of International Education
- University Health Services

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
August 3, 2018 - Dom Barnard
For many people the thought of delivering a presentation is a daunting task and brings about a great deal of nerves . However, if you take some time to understand how effective presentations are structured and then apply this structure to your own presentation, you’ll appear much more confident and relaxed.
Here is our complete guide for structuring your presentation, with examples at the end of the article to demonstrate these points.
Why is structuring a presentation so important?
If you’ve ever sat through a great presentation, you’ll have left feeling either inspired or informed on a given topic. This isn’t because the speaker was the most knowledgeable or motivating person in the world. Instead, it’s because they know how to structure presentations – they have crafted their message in a logical and simple way that has allowed the audience can keep up with them and take away key messages.
Research has supported this, with studies showing that audiences retain structured information 40% more accurately than unstructured information.
In fact, not only is structuring a presentation important for the benefit of the audience’s understanding, it’s also important for you as the speaker. A good structure helps you remain calm, stay on topic, and avoid any awkward silences.
What will affect your presentation structure?
Generally speaking, there is a natural flow that any decent presentation will follow which we will go into shortly. However, you should be aware that all presentation structures will be different in their own unique way and this will be due to a number of factors, including:
- Whether you need to deliver any demonstrations
- How knowledgeable the audience already is on the given subject
- How much interaction you want from the audience
- Any time constraints there are for your talk
- What setting you are in
- Your ability to use any kinds of visual assistance
Before choosing the presentation’s structure answer these questions first:
- What is your presentation’s aim?
- Who are the audience?
- What are the main points your audience should remember afterwards?
When reading the points below, think critically about what things may cause your presentation structure to be slightly different. You can add in certain elements and add more focus to certain moments if that works better for your speech.

What is the typical presentation structure?
This is the usual flow of a presentation, which covers all the vital sections and is a good starting point for yours. It allows your audience to easily follow along and sets out a solid structure you can add your content to.
1. Greet the audience and introduce yourself
Before you start delivering your talk, introduce yourself to the audience and clarify who you are and your relevant expertise. This does not need to be long or incredibly detailed, but will help build an immediate relationship between you and the audience. It gives you the chance to briefly clarify your expertise and why you are worth listening to. This will help establish your ethos so the audience will trust you more and think you’re credible.
Read our tips on How to Start a Presentation Effectively
2. Introduction
In the introduction you need to explain the subject and purpose of your presentation whilst gaining the audience’s interest and confidence. It’s sometimes helpful to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped to help filter down your topic:
- Introduce your general topic
- Explain your topic area
- State the issues/challenges in this area you will be exploring
- State your presentation’s purpose – this is the basis of your presentation so ensure that you provide a statement explaining how the topic will be treated, for example, “I will argue that…” or maybe you will “compare”, “analyse”, “evaluate”, “describe” etc.
- Provide a statement of what you’re hoping the outcome of the presentation will be, for example, “I’m hoping this will be provide you with…”
- Show a preview of the organisation of your presentation
In this section also explain:
- The length of the talk.
- Signal whether you want audience interaction – some presenters prefer the audience to ask questions throughout whereas others allocate a specific section for this.
- If it applies, inform the audience whether to take notes or whether you will be providing handouts.
The way you structure your introduction can depend on the amount of time you have been given to present: a sales pitch may consist of a quick presentation so you may begin with your conclusion and then provide the evidence. Conversely, a speaker presenting their idea for change in the world would be better suited to start with the evidence and then conclude what this means for the audience.
Keep in mind that the main aim of the introduction is to grab the audience’s attention and connect with them.
3. The main body of your talk
The main body of your talk needs to meet the promises you made in the introduction. Depending on the nature of your presentation, clearly segment the different topics you will be discussing, and then work your way through them one at a time – it’s important for everything to be organised logically for the audience to fully understand. There are many different ways to organise your main points, such as, by priority, theme, chronologically etc.
- Main points should be addressed one by one with supporting evidence and examples.
- Before moving on to the next point you should provide a mini-summary.
- Links should be clearly stated between ideas and you must make it clear when you’re moving onto the next point.
- Allow time for people to take relevant notes and stick to the topics you have prepared beforehand rather than straying too far off topic.
When planning your presentation write a list of main points you want to make and ask yourself “What I am telling the audience? What should they understand from this?” refining your answers this way will help you produce clear messages.
4. Conclusion
In presentations the conclusion is frequently underdeveloped and lacks purpose which is a shame as it’s the best place to reinforce your messages. Typically, your presentation has a specific goal – that could be to convert a number of the audience members into customers, lead to a certain number of enquiries to make people knowledgeable on specific key points, or to motivate them towards a shared goal.
Regardless of what that goal is, be sure to summarise your main points and their implications. This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there.
Follow these steps:
- Signal that it’s nearly the end of your presentation, for example, “As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…”
- Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation – “In this speech I wanted to compare…”
- Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions
- Indicate what is next/a call to action/a thought-provoking takeaway
- Move on to the last section
5. Thank the audience and invite questions
Conclude your talk by thanking the audience for their time and invite them to ask any questions they may have. As mentioned earlier, personal circumstances will affect the structure of your presentation.
Many presenters prefer to make the Q&A session the key part of their talk and try to speed through the main body of the presentation. This is totally fine, but it is still best to focus on delivering some sort of initial presentation to set the tone and topics for discussion in the Q&A.

Other common presentation structures
The above was a description of a basic presentation, here are some more specific presentation layouts:
Demonstration
Use the demonstration structure when you have something useful to show. This is usually used when you want to show how a product works. Steve Jobs frequently used this technique in his presentations.
- Explain why the product is valuable.
- Describe why the product is necessary.
- Explain what problems it can solve for the audience.
- Demonstrate the product to support what you’ve been saying.
- Make suggestions of other things it can do to make the audience curious.
Problem-solution
This structure is particularly useful in persuading the audience.
- Briefly frame the issue.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it ‘s such a problem. Use logos and pathos for this – the logical and emotional appeals.
- Provide the solution and explain why this would also help the audience.
- Call to action – something you want the audience to do which is straightforward and pertinent to the solution.
Storytelling
As well as incorporating stories in your presentation , you can organise your whole presentation as a story. There are lots of different type of story structures you can use – a popular choice is the monomyth – the hero’s journey. In a monomyth, a hero goes on a difficult journey or takes on a challenge – they move from the familiar into the unknown. After facing obstacles and ultimately succeeding the hero returns home, transformed and with newfound wisdom.
Storytelling for Business Success webinar , where well-know storyteller Javier Bernad shares strategies for crafting compelling narratives.
Another popular choice for using a story to structure your presentation is in media ras (in the middle of thing). In this type of story you launch right into the action by providing a snippet/teaser of what’s happening and then you start explaining the events that led to that event. This is engaging because you’re starting your story at the most exciting part which will make the audience curious – they’ll want to know how you got there.
- Great storytelling: Examples from Alibaba Founder, Jack Ma
Remaining method
The remaining method structure is good for situations where you’re presenting your perspective on a controversial topic which has split people’s opinions.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it’s such a problem – use logos and pathos.
- Rebut your opponents’ solutions – explain why their solutions could be useful because the audience will see this as fair and will therefore think you’re trustworthy, and then explain why you think these solutions are not valid.
- After you’ve presented all the alternatives provide your solution, the remaining solution. This is very persuasive because it looks like the winning idea, especially with the audience believing that you’re fair and trustworthy.
Transitions
When delivering presentations it’s important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it’s all relevant. This can be done using speech transitions which are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified.
Transitions can be one word, a phrase or a full sentence – there are many different forms, here are some examples:
Moving from the introduction to the first point
Signify to the audience that you will now begin discussing the first main point:
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- First, let’s begin with…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
Shifting between similar points
Move from one point to a similar one:
- In the same way…
- Likewise…
- Equally…
- This is similar to…
- Similarly…
Internal summaries
Internal summarising consists of summarising before moving on to the next point. You must inform the audience:
- What part of the presentation you covered – “In the first part of this speech we’ve covered…”
- What the key points were – “Precisely how…”
- How this links in with the overall presentation – “So that’s the context…”
- What you’re moving on to – “Now I’d like to move on to the second part of presentation which looks at…”
Physical movement
You can move your body and your standing location when you transition to another point. The audience find it easier to follow your presentation and movement will increase their interest.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Key slides for your presentation
Slides are a useful tool for most presentations: they can greatly assist in the delivery of your message and help the audience follow along with what you are saying. Key slides include:
- An intro slide outlining your ideas
- A summary slide with core points to remember
- High quality image slides to supplement what you are saying
There are some presenters who choose not to use slides at all, though this is more of a rarity. Slides can be a powerful tool if used properly, but the problem is that many fail to do just that. Here are some golden rules to follow when using slides in a presentation:
- Don’t over fill them – your slides are there to assist your speech, rather than be the focal point. They should have as little information as possible, to avoid distracting people from your talk.
- A picture says a thousand words – instead of filling a slide with text, instead, focus on one or two images or diagrams to help support and explain the point you are discussing at that time.
- Make them readable – depending on the size of your audience, some may not be able to see small text or images, so make everything large enough to fill the space.
- Don’t rush through slides – give the audience enough time to digest each slide.
Guy Kawasaki, an entrepreneur and author, suggests that slideshows should follow a 10-20-30 rule :
- There should be a maximum of 10 slides – people rarely remember more than one concept afterwards so there’s no point overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
- The presentation should last no longer than 20 minutes as this will leave time for questions and discussion.
- The font size should be a minimum of 30pt because the audience reads faster than you talk so less information on the slides means that there is less chance of the audience being distracted.
Here are some additional resources for slide design:
- 7 design tips for effective, beautiful PowerPoint presentations
- 11 design tips for beautiful presentations
- 10 tips on how to make slides that communicate your idea
Group Presentations
Group presentations are structured in the same way as presentations with one speaker but usually require more rehearsal and practices. Clean transitioning between speakers is very important in producing a presentation that flows well. One way of doing this consists of:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what health anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Elnaz will talk about the prevalence of health anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Elnaz”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Joe.”
From this example you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
Example of great presentation structure and delivery
Having examples of great presentations will help inspire your own structures, here are a few such examples, each unique and inspiring in their own way.
How Google Works – by Eric Schmidt
This presentation by ex-Google CEO Eric Schmidt demonstrates some of the most important lessons he and his team have learnt with regards to working with some of the most talented individuals they hired. The simplistic yet cohesive style of all of the slides is something to be appreciated. They are relatively straightforward, yet add power and clarity to the narrative of the presentation.
Start with why – by Simon Sinek
Since being released in 2009, this presentation has been viewed almost four million times all around the world. The message itself is very powerful, however, it’s not an idea that hasn’t been heard before. What makes this presentation so powerful is the simple message he is getting across, and the straightforward and understandable manner in which he delivers it. Also note that he doesn’t use any slides, just a whiteboard where he creates a simple diagram of his opinion.
The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout – by Rick Rigsby
Here’s an example of a presentation given by a relatively unknown individual looking to inspire the next generation of graduates. Rick’s presentation is unique in many ways compared to the two above. Notably, he uses no visual prompts and includes a great deal of humour.
However, what is similar is the structure he uses. He first introduces his message that the wisest man he knew was a third-grade dropout. He then proceeds to deliver his main body of argument, and in the end, concludes with his message. This powerful speech keeps the viewer engaged throughout, through a mixture of heart-warming sentiment, powerful life advice and engaging humour.
As you can see from the examples above, and as it has been expressed throughout, a great presentation structure means analysing the core message of your presentation. Decide on a key message you want to impart the audience with, and then craft an engaging way of delivering it.
By preparing a solid structure, and practising your talk beforehand, you can walk into the presentation with confidence and deliver a meaningful message to an interested audience.
It’s important for a presentation to be well-structured so it can have the most impact on your audience. An unstructured presentation can be difficult to follow and even frustrating to listen to. The heart of your speech are your main points supported by evidence and your transitions should assist the movement between points and clarify how everything is linked.
Research suggests that the audience remember the first and last things you say so your introduction and conclusion are vital for reinforcing your points. Essentially, ensure you spend the time structuring your presentation and addressing all of the sections.
Trends in Medicine
Seven tips for creating powerful oral presentations.

The next time you set out to develop a professional presentation, you might want to look to the theatrical world for inspiration. This advice comes from Erika Bailey , a professional dialect coach and the Head of Voice and Speech at American Repertory Theater. She recently shared her expertise with scholars in Harvard Medical School’s Effective Writing for Health Care certificate program.
Bailey explains that using a theatrical lens can provide a valuable framework through which to organize information for your presentation. In fact, she thinks about preparing her own presentations in two steps: first she crafts as a playwright, and then she presents as a performer. Mastering both roles can be essential to achieving success.
Here are some of her favorite tips to create powerful presentations:
Tip #1: Craft a good story to engage your audience.
Whether you are sharing research findings or talking about a new service or need, it’s always a good idea to think about the story you want to tell. “The story is a powerful way to share ideas and bring people and communities together,” Bailey says. You can think about the plotline, the characters involved and their needs, the setting and the back story.
The story could be a mystery (a problem occurs, and you need to solve it), a romance (you have two problematic ideas that come together in a marriage), a revolution (fighting against an established idea) or a crisis (tragedy may occur if you don’t act now).
Once you have your story, you might memorize the full script, or use a teleprompter, or have cards with an outline and speak in more free form. Regardless of how you present your information, just remember that the story should be at the center of your efforts to engage your reader in the experience.
Tip #2: Use simple language that is easy for people to follow.
The words you select, and how you use them, will make a big difference in how well people hear—and remember—what you tell them. This is especially true in oral presentations. “When we write sentences for people to read, we can add more complexities. But when writing for presentations, we need to simplify, since the listener has only one time to hear what you are saying,” Bailey explains. This makes it important to craft ideas and sentences that are short and succinct (preferably with more periods and fewer commas for ease of listening).
For example, Bailey works with Harvard faculty who are filming on-demand courses and often must help them adapt their well-crafted essays to work for an oral presentation.
She helps them to make sentences shorter and more active, add pauses, slow down the pace, and insert gestures to make the material more engaging. She says that these same tweaks can also translate to many types of presentations and settings.
Tip #3: Use cues to guide your readers through your speech.
In writing, people can go back and read something twice. But in a presentation, they only listen once. Therefore, you need to guide them with strategic cues, so they don’t have to work so hard to follow you. This can be adding simple language, such as, “This is what I am going to talk about today,” so they will know what to expect and what you want them to take away from your presentation.
You can also use repetition to make sure they will hear—and remember—your main points. For instance, she suggests saying: “I am going to talk about public speaking. You can look at yourself as a playwright and a performer.” Then repeat these ideas three times throughout your presentation to make sure people grasp the idea and will be able to recall it later.
Finally, you can give a signal of where you are in your speech to grab people’s attention as you wind down your presentation. “For example, I suggest saying, ‘In conclusion,’ to let your audience know when you are finishing up.” This signals them to listen carefully because you will be summarizing the takeaways again and you don’t want them to miss it.
Tip #4: Use non-verbal clues strategically.
“Make sure you use your body for inflections and gestures and think about how to move your body in space,” Bailey says. “Think about standing tall, lengthening your spine and stretching your tailbone and you will be perceived by your audience as more energized.”
She also recommends using non-verbal clues to punctuate (literally) your words.
“You can use pauses in your speech, and use gestures to act out periods, commas and semi-colons when you talk,” she points out.
“Gesture fully. I encourage as much use of movement as possible,” she says. With many presentations taking place over Zoom these days, she says that thinking of using your space more fully (extending your movements beyond the small box you show up in on the screen) can help you be perceived as more confident and more engaging, too.
Tip #5: Develop stage presence to be more memorable.
Some presenters stick with you longer after the presentation ends.
“In my role at American Repertory Theater, I would go across the country and see 50 people a day audition. Then I would look at their headshots later and I could not even remember seeing some of them. But others, I can still remember now exactly what they did in that room. They were able to come alive in the moment,” she says, crediting their stage presence to making their performances so memorable.
While stage presence comes more easily to some people than others, Bailey says there are three things you can do to increase your presence:
- Be really connected to your subject matter—be interested, curious and want to share what you know.
- Connect to your audience in the moment.
- See the audience and let them see you.
This commitment to connect with the audience and awareness of self can be especially essential to making that lasting impression, she stresses, and can truly set you apart from everyone else in the room.
Tip #6: Prepare for success.
“When we write or edit, we edit until 5 minutes before a paper is due. But as a performer, you first need to write and edit your script days before the presentation so you can rehearse it,” she says.
Before any presentation, Bailey says she reads her script out loud at home and plays around with vocal variety, including the volume, the pacing and the pitch. This helps her feel more comfortable and allows her to determine the right mix for her presentation in advance.
If you want to increase your comfort level, she recommends joining an organization like Toast Masters to get more practice.
Tip #7: Cut yourself some slack.
“If you find public speaking nerve-racking, it’s okay. It does not have to be perfect. Just find a way to be as expressive as possible (within your comfort zone) to engage your audience,” Bailey says.
Also, remember that you don’t have to suddenly become a performer. It is okay to start off small by adopting some of these tips and continuing to build on them over time as your confidence grows.
Written by Lisa D. Ellis
Related Articles

Uniting Quality Writing with Dynamic Speaking in Health Care Communications
For people working in the health care field, developing their writing skills can help them do their…


Improving Care for Autistic Adults
When autistic children transition into early adulthood, they lose access to many of the services and…

Physicians at the Forefront of Health Care Technology Innovation
The technology age has ushered in a new era for the medical field. With the rapid advancement of…
© 2024 by the President and Fellows of Harvard College
Search form
- Speaking exams
- Typical speaking tasks
Oral presentation
Giving an oral presentation as part of a speaking exam can be quite scary, but we're here to help you. Watch two students giving presentations and then read the tips carefully. Which tips do they follow? Which ones don’t they follow?
Instructions
Watch the video of two students doing an oral presentation as part of a speaking exam. Then read the tips below.
Melissa: Hi, everyone! Today I would like to talk about how to become the most popular teen in school.
Firstly, I think getting good academic results is the first factor to make you become popular since, having a good academic result, your teacher will award you in front of your schoolmates. Then, your schoolmates will know who you are and maybe they would like to get to know you because they want to learn something good from you.
Secondly, I think participating in school clubs and student unions can help to make you become popular, since after participating in these school clubs or student union, people will know who you are and it can help you to make friends all around the school, no matter senior forms or junior forms.
In conclusion, I think to become the most popular teen in school we need to have good academic results and also participate in school clubs and student union. Thank you!
Kelvin: Good evening, everyone! So, today I want to talk about whether the sale of cigarettes should be made illegal.
As we all know, cigarettes are not good for our health, not only oneself but also other people around. Moreover, many people die of lung cancer every year because of smoking cigarettes.
But, should the government make it illegal? I don’t think so, because Hong Kong is a place where people can enjoy lots of freedom and if the government banned the sale of cigarettes, many people would disagree with this and stand up to fight for their freedom.
Moreover, Hong Kong is a free market. If there's such a huge government intervention, I think it’s not good for Hong Kong’s economy.
So, if the government wants people to stop smoking cigarettes, what should it do? I think the government can use other administrative ways to do so, for example education and increasing the tax on cigarettes. Also, the government can ban the smokers smoking in public areas. So, this is the end of my presentation. Thank you.
It’s not easy to give a good oral presentation but these tips will help you. Here are our top tips for oral presentations.
- Use the planning time to prepare what you’re going to say.
- If you are allowed to have a note card, write short notes in point form.
- Use more formal language.
- Use short, simple sentences to express your ideas clearly.
- Pause from time to time and don’t speak too quickly. This allows the listener to understand your ideas. Include a short pause after each idea.
- Speak clearly and at the right volume.
- Have your notes ready in case you forget anything.
- Practise your presentation. If possible record yourself and listen to your presentation. If you can’t record yourself, ask a friend to listen to you. Does your friend understand you?
- Make your opinions very clear. Use expressions to give your opinion .
- Look at the people who are listening to you.
- Write out the whole presentation and learn every word by heart.
- Write out the whole presentation and read it aloud.
- Use very informal language.
- Only look at your note card. It’s important to look up at your listeners when you are speaking.
Useful language for presentations
Explain what your presentation is about at the beginning:
I’m going to talk about ... I’d like to talk about ... The main focus of this presentation is ...
Use these expressions to order your ideas:
First of all, ... Firstly, ... Then, ... Secondly, ... Next, ... Finally, ... Lastly, ... To sum up, ... In conclusion, ...
Use these expressions to add more ideas from the same point of view:
In addition, ... What’s more, ... Also, ... Added to this, ...
To introduce the opposite point of view you can use these words and expressions:
However, ... On the other hand, ... Then again, ...
Example presentation topics
- Violent computer games should be banned.
- The sale of cigarettes should be made illegal.
- Homework should be limited to just two nights a week.
- Should school students be required to wear a school uniform?
- How to become the most popular teen in school.
- Dogs should be banned from cities.
Check your language: ordering - parts of a presentation
Check your understanding: grouping - useful phrases, worksheets and downloads.
Do you think these tips will help you in your next speaking exam? Remember to tell us how well you do in future speaking exams!

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.
Home Blog Presentation Ideas How To Do a Proper Thesis Defense Using the Right PowerPoint Presentation
How To Do a Proper Thesis Defense Using the Right PowerPoint Presentation

Writing a thesis is stressful, but preparing an oral defense can be even more painful. But it doesn’t have to be; with proper preparation and a good presentation, you will be able to better equip yourself comes time to present your thesis defense.
But what makes a good thesis defense?
A proper presentation helps you with your thesis defense because it helps you capture the panels’ attention and gives you cues and reminders on what to say as well.
It also helps keep your data organized while visually looking good and provides a flow structure for the rest of your presentation.
In today’s article, we will be giving you The Right PowerPoint Templates for Your Thesis Defense and a powerful outline composed of best practices and layouts specifically designed to help you defend your thesis in both written and oral presentations.
In the next segments of this article, we’ll walk you through the most feasible process on how to ace this kind of presentation.
Let’s dive into the outline of what makes a great thesis defense.
Thesis Defense Overview
Similarities.
- Type of Degree
Thesis and Dissertation Distinction Varies on Location
Three most common thesis defense myths, how to use chatgpt to structure your thesis.
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Methodology
- Acknowledgements
- Questions and Answers
- Contact Information
- Tips During Your Oral Defense
- More Quick Tips on How to Present
A thesis defense is composed of two parts – a thesis and a defense.
The thesis, according to Grad School Hub , represents a student’s collective understanding of his or her program and major.
Universities often include a thesis in every course as one of the final requirements to earn a particular graduate or postgraduate degree.
The thesis, however, isn’t just a mere requirement.
It helps the students to grow out of their shell from their respective discipline and give them the opportunity to present all the findings of their study.
Moreover, some people think a thesis is just a long essay, but it’s not. Unlike an essay, a thesis needs to assert something.
This can be considered one of the most crucial research documents that a student makes during their academic schooling .
On the other hand, defense is the presentation of the pieces of evidence to support and prove your research.
It’s the most essential part of the thesis process.
Your presentation has to be prepared to answer questions from members of the committee and any other panel present, and it’s your job to convince them and defend your thesis with ample proof.
Prior to presenting, you have to carefully determine what appropriate evidence should be presented before the panel, depending on what thesis you have to defend.

Thesis and Dissertation Distinguished
A thesis or dissertation is usually required to complete a particular graduate degree. These two words are often used interchangeably by most students when referring to research studies.
But while being almost similar in format or structure, it’s worth noting that they have significant differences that set them apart from each other.
The very reason why thesis and dissertation are treated the same is that these two are both extensive papers. Not just merely long essays like what others are claiming.
Both of these papers are extensive. This is why students are given ample time, usually the entire last semester of the last year of study, to complete all the requirements and finally acquire their degree.
With regards to structure, both papers are very similar with few differences.
Differences Between Thesis and Dissertation
One of the significant differences between the two is to whom the paper is assigned. A thesis is usually required for those students earning a bachelor’s or master’s degree. While a dissertation is for those, who want to obtain a doctorate degree.
However, not all students taking a master’s degree are required to make a thesis. Prior to their enrollment, they have been given a choice of whether they’ll go for a non-thesis program or with a thesis.
Those who have a plan to escalate their degree to a doctorate eventually should take the path of a thesis. This is to prepare themselves for a more extensive dissertation requirement as doctorate students. Otherwise, they will be only limited to earning a master’s degree.

But above all, the most significant difference between the two papers is the purpose for which it is written.
A thesis, like what has been mentioned above, is being done by students obtaining a bachelor’s or master’s degree and has the purpose of testing their understanding of the discipline they’re engaged with.
A thesis is focused on obtaining technical expertise.
On the other hand, a dissertation is made for students to come up with an original study that other researchers haven’t already studied.

USA: In the United States of America, they consider a thesis shorter than a dissertation. In fact, aside from being a requirement to graduate in college, a thesis is now also inculcated in master’s degree programs. And since the dissertation is more extensive, the thesis is treated as preliminary in gaining a doctorate degree.
Europe: The distinction between the two papers is almost opposite to that of the USA. In Europe, a dissertation is only a broader research study from a post-graduate program and not the making of original research. Instead, educational systems in the said continent treat the doctoral thesis as a more elaborate paper writing.

The difference between a thesis and a dissertation might not seem that big, but it’s important that we know what makes them different.
If your upcoming defense gives you pressure and uneasiness, it could be cause you are not sure what to expect. Today we will dispel three common thesis defense myths that will help you be more confident in your presentation.
“Answer all the questions correctly. Otherwise, your thesis won’t get approved.”
You are expected to have a focus on your research.
That being said, you have to study each part of your thesis, every detail, and even your sources.
You have to study and practice how to effectively deliver your presentation.
But don’t overthink to the extent that you’re stressing yourself to know everything perfectly.
Don’t overstress if you can’t answer one of the questions, this doesn’t necessarily mean the committee won’t approve your thesis.
You should know that research is a continuous study.
So you should expect that your committee will always be able to find a gap in your study to fill in future related research .
So in times you don’t exactly know the answer, admit it, and you’ll learn as they give their sides or suggestions.
Making up an answer will only displease your committee, so it’s to be upfront, honest, and transparent.
“The committee is just there to find holes in your study. They don’t care about you.”
One of the typical descriptions students have of the committee is that they are just there to poke holes in your thesis.
Going in with this perspective makes standing before them a nerve-wracking experience.
They’re not your enemy.
In fact, they are there to help you polish your study.
They might challenge you with difficult suggestions and tricky questions.
In the end, they will walk you through the process to come up with better results that won’t only benefit you but also your research.
They care about you and your study, and they’re ultimately there to make your thesis and the research better. Separate yourself from your work look at it objectively, and don’t take their comments personally .
“If your thesis defense isn’t successful, you have to start your thesis all over again”
An unsuccessful defense is one of the worst-case fears most students have.
One thing that you should be aware of is when you aren’t able to please your committee, you don’t need to start a new thesis again or go back to square one with your existing paper.
It’s unusual that your committee will ask you to change your topic and start from scratch again.
The fact that you’ve been permitted to defend your study means your research is almost complete.
They might suggest further details or ask you for minor revisions, and that’s normal.
But overall, you need to go into this defense thinking that your presentation will be successful. Otherwise, you are already setting yourself up for failure with the wrong mindset.
Remember that positive thoughts attract positive results.
Thesis Defense Presentation Structure and Slides Content
We can use language learning models like ChatGPT to help us curate the structure of our thesis presentation. Let’s see a step-by-step solution on how to apply this.
Step 1: Define the thesis topic and research questions
You can set the environment for ChatGPT to work by explaining what your thesis is going to cover and which specific questions you aim to address through the course of that document. This gives ChatGPT the context from which it shall formulate the structure. A prompt can be written like this:
“Take the role of an academic professional who shall help me to write my thesis. This thesis is going to cover the topic of (insert topic), and through its course, I want to answer these questions: Question 1 – Question 2 – Question 3 – Consider this information as the starting point for this chat.”
Step 2: Ask for an outline
With the previously provided information, ask ChatGPT to generate an outline for your presentation. If some of the points listed in the output don’t convince you, then chat with the interface until you reach a final outline. Then, ask to elaborate on each specific point for information or cues you may have overlooked.
Step 3: Ask ChatGPT which content should you place per slide
Instead of debating how are you going to trim your thesis into a presentation format, ask ChatGPT to do the decision process for you. You can be as specific as asking how many words per slide, how many slides should the presentation have, if you need any visual element, etc.
N.B.: We don’t recommend using ChatGPT to retrieve academic references as, in some cases, it can provide faulty results. You can ask if any facts on this presentation need to be checked or similar questions. ChatGPT is a powerful tool, but it shouldn’t be considered a bible, so be extra cautious about grabbing content directly from its outputs.
1. Title Page
This slide should contain the information that is provided on the title page of your hard copy . Here is an example of title page or cover slide for your title defense or thesis presentation.

- The title of your research paper
- Where you are studying
- Name and details of your course
- Name of Adviser
2. Introduction Slide
Your introduction slide should provide the committee with an idea of the following:

- What is the topic area that you are investigating ?
- What are the specific research questions that you set out to answer?
- Why is this question important to answer?
- What were the objectives of your research?
3. Literature Review Slide
It’s not necessary to cover everything that’s currently understood in the available literature. You may want to present the following content under a Literature Review slide:

- Relevant current research that is close to your topic
- Different theories that may apply to your specific area of research
- Areas of weakness that are currently highlighted
4. Methodology Slide
Make sure to touch the factors below within your process, and include the following in the Methodology slide:

- The type of study you have conducted: qualitative, quantitative, or mixed
- The methods that you chose and why
- Details of the population, sampling methods, and other information
- Provide information regarding how you have analyzed the data that you have collected
5. Results Slide
This part should give the committee/audience a good understanding of what you’ve discovered during your research. The statistics & results slide could include the final results of your analysis, here is an example:

- An overall description of the data that you collected during your research
- The results of the analysis that you have done on that data
- What were the most significant findings from your data
6. Discussion Slide
Highlight here the meaning of the findings in relation to your discipline program and the research that you have done:

- What are the major findings, and what do they mean with regard to your research
- How do these findings relate to what others have found in the past
- How can you explain any unusual or surprising result
7. Conclusions Slide
You have to end your presentation with a conclusion summarizing all that you have found within your research. Here is an example of a Conclusion slide in a Thesis presentation:

- Restate your research questions
- Show how your results answer these questions
- Show what contribution you have made
- State any limitations to the work you have done
- Suggest future research
- Make any recommendations
See Also: How to Create a Great Investors Pitch Deck and Close the Deal
8. Acknowledgements Slide
Express gratitude to your advisor, committee members, peers, and others who supported your research journey. This slide provides a moment to acknowledge the collaborative nature of academic work.
9. Questions and Answers Slide
Dedicate a slide for audience questions at the end of your presentation.
Encourage engagement by inviting questions from the audience.
Be prepared to provide clear and concise responses to inquiries.
10. References Slide
Include a slide listing your cited sources throughout your presentation.
Use a consistent citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
The References slide demonstrates your thorough engagement with existing literature.
11. Contact Information Slide
If you’re open to further inquiries or collaborations, consider adding your contact information.
Include your email address or relevant professional social media handles.
How to use SlideModel AI Presentation Maker for your Thesis Presentation
If you want to save hours of manual time, you can leverage AI tools to make your thesis presentation. The best part of integrating AI tools into our workflow is that we can pair them to get even better results than we expected. With SlideModel’s AI presentation maker , users can create an entire slide deck by introducing these variables:
- Topic of your thesis
- Number of slides to include in your thesis presentation
- Outline checkup
And that’s it! Download the AI-generated presentation in PPTX format or for Google Slides, and edit it if you require adding some extra content. The core elements are already done, and you can save countless hours of hard work.
Tips During Your Oral Defense!
Review your materials.
Even if you already feel confident with your upcoming presentation, you still need to review your materials.
You can bring the hard copy of your thesis with you during the defense, but you don’t want to get lost in your presentation when you forget some specific details and have to scan your papers.
You should know your paper in and out.
Rehearse Your Presentation
It’s not wrong if it sounds like a script when you speak in your oral defense. It’s expected and understandable.
You need to practice your presentation, especially when there’s a time restriction given to every presenter.
You only need to prepare enough slides that would fit your time limit. A hundred slides aren’t suitable for a 15 to 20-minute presentation, nor 10 slides for an hour of defense.
Your rehearsal will be more effective if you practice it in front of an audience.
Note: You will experience complete silence in the defense room. You might feel awkward because, most of the time, you’re the only one speaking out loud. This is completely fine, and it’s something you should practice in rehearsal should you be afraid.
Narrow the Presentation of Ideas
Regarding your slides, you don’t have to include everything that’s in your paper. You should narrow down your ideas to the main points and the most important details, such as the statistics and findings.
If the members of your committee think you lack details or they want to hear a further explanation, they won’t hesitate to ask you.
Prepare for the Unexpected Questions
The panel tends to challenge the presenters, usually through some hard questions.
Its aim is how well do you you have done your research and how prepared you are.
But as long as you know the ins and outs of your paper, you shouldn’t lose your confidence regardless of which questions they ask.
Just keep in mind that what you’re saying in your oral defense is not in conflict with what is written on the hard copy you provided them.
What To Do When You Don’t Know the Answer
If the committee asks you a question and you don’t know the answer, don’t make up a baseless answer.
Baseless means out-of-context answers or something without proof or backup.
How To Deal With The Nervousness
The committee expects you to be nervous. Of course, it’s normal.
However, one effect of being nervous is the changes in your behavior.
There’s a tendency for you’ll talk fast, which will make it hard for the committee to understand you.
It might also cause you to have a mental block.
So try to slow down. Take a deep breath.
Inhale, exhale. Remember to breathe!
It’s OK to pause, and it’s OK to take your time; it’s more important that the committee clearly understands what you are trying to articulate.
More Quick Tips on How to Present!
- Introduce yourself at the beginning
- Introduce the title of the presentation
- Don’t read your notes if possible
- Don’t speak too fast
- Put an emphasis on what you’re saying so you don’t sound monotonous
- Look at your adviser once in a while for possible signs
- Stand on the right of the white screen if you are right-handed so you can easily refer to the slide without giving your back to the committee
- Face the audience when you talk
- Keep an eye contact
- Make sure to keep attention to the reactions of the committee and don’t forget to react in turn
We hope you enjoyed this article on how to do a proper thesis defense and how to best prepare for one using proven tips and techniques to help you get through this. Hopefully, after your defense, you will be set as the one in your class to deliver an inspiring graduation speech for your peers. If you have value, please remember to share this article. We also recommend you read these Thesis Statement Examples for inspiration to create your own professionally.
1. MasterDoc PowerPoint Template

Creating a Thesis presentation should be a straight forward task; based on your thesis document and following the tips described above you have a high level structure already outlined. The MasterDoc PowerPoint template provides professional layouts with texts and image placeholders; so you can create document like slides using your thesis defense as your content. This template is ideal for a highly detailed documents, where visuals and words unite to illustrate one concept per page. The result is an asset that can be read and digested more quickly than either your thesis document or a presentation created for assisting a speech. A document created with the MasterDoc PowerPoint templates is meant to be printed or distributed, read on screen without the accompaniment of a presenter or used in an e-learning platform as pure learning content.
Use This Template
2. Thesis Presentation PowerPoint Template

You had invested a considerable time researching, testing hypothesis and confirming your thesis. Craft your thesis presentation with the same level of detail you applied in your work. Using the Thesis Presentation PowerPoint Template you will focus only in your content and your message. The layouts, images,design and structure will be taken care by the template.
3. Master Thesis PowerPoint Template

The Master Thesis PowerPoint Template is a professional document designed for postgraduate degrees presentations. It provides simple sections that follow the structure and best practices of traditional research thesis presentations. Starting with the introduction to the theory and state of the art scenario; following with hypothesis research and its findings and concluding with the confirmation or negation of the initial thesis statement.
4. Essay Outline PowerPoint Template

Your thesis defense can be accompanied by an essay, that states your thesis and argues about it using several supporting paragraphs. This kind of document is ideal to be an intermediate step between reading assisting to the thesis presentation and reading the complete thesis documentation. It has more information that your thesis defense abstract, but does summarizes the supporting evidence and examples that allows the argument of each idea behind the thesis. You can use the Essay Outline Template to present your Essay outline and create an essay linked to your thesis defense documentation.

Like this article? Please share
Academics, Degree, Dissertation, Doctorate, Education, Faculty, Master, PhD, Student, Thesis Filed under Presentation Ideas
Related Articles

Filed under Presentation Ideas • November 9th, 2023
How to Create and Deliver a Research Presentation
Presentation is one of the final steps of a research endeavor. Learn how to make and deliver a research presentation using our templates and tips.

Filed under Education • September 10th, 2023
How To Write An Essay? – Where to start?
Do you wonder How to write an essay ? Start with the essay structure. This post describes the standard essay structure with its content, and which essay types are popular. Develop your writing skills using the best practices of Essay Structure.

Filed under Education • September 2nd, 2023
Thesis Statement Examples
What makes a good thesis statement? Simple answer, precision and enough evidence to support your statement. In this article we analyze what are good thesis statements with examples.
36 Responses to “How To Do a Proper Thesis Defense Using the Right PowerPoint Presentation”
Great job! This has made my thesis presentation a whole lot easier.
Excellent !!!!!
Now I feel I’m quite confident on how to do my dissertation presentation properly and how to defend it. I will share that with other friends and colleagues.
Thank you so much for your kind help.
Best regards, Awad
Thank you for such a valuable guide.
it was very helpful
Thanks a bunch for the general summary for thesis defense with all related information that we might have to know. Great job!
Great tips.
i have proposal defense in two days and im so nervous right now! reading this is helpful in some ways thankyou!
It’s very helpful and understandable. Easy steps to follow.
I found it very helpful to refresh and make my self ready for my defense!
Thank you a lot this article. It’s really helpful!
Naveen Kumar S: Thank you its very Helpful. I appreciate all your effort this is very useful.
Very important and interesting so go on thank you
I really like it. In the near future I am going to present for the MA thesis. Therefore, it will guide me a lot. If you can please attach with this email the detail.
I do like the article as it proves to be valuable and worthy. I enjoyed reading every single note. It helped me feel at ease and have confidence when my viva day takes place. THANK YOU SO MUCH.
Appreciate your Assistance
Thanks a lot for the gist
Thank you so much, I got full information and knowledge.
This has made me look forward to my thesis defense. Thanks a lot
Very useful
thank you very much for your best information
Thank you very much the article is full of knowledge on Thesis as well as dissertation defense. Big Up!
I am appreciative. Well informative and educative.
Thanks immensely for these wonderful tips on presentation during defense. I personally found more useful to me as I prepare to defend my Master Dissertation.
Thank you very much! I now feel more confident.
Thanks for your good self overall usability of the Participations motivated points and contribute significantly in thesis defense practices. Best wishes to one and All
Happy To Help.
Thank you very much. As I am pursuing for my PhD in Leadership, I got it so meaningful and worth having.
Your tips on What a Thesis and Dissertation are, are on point. I have fully understood their differences and similarities. I have also noted the killer way of summaring a Power Point Presentation. Slidemodel.com…you are just a force to reckon with. I need more information…in case you have models you can share with me and those interested in this subject covered.
Thanks a million times for your timely guidance. Just preparing to do my PhD Thesis defense.
this was very, very helpful…Thank you!
Highly appreciate your effort to deliver what a student is looking for. I find your article really helpful and to the point. Thanks !
Regarding to my P.P, I’ve understood so many issues from this. Thankyou!
i got it as it is so important for my deffence presentation, thanky you very much
This Material was very hopeful and encourage any student who prepare any presentation relation with thesis. It also combined more encauragable and it enhance presentation!
Thought provoking content Thank you.
Great comments. very helpful
Leave a Reply

- Oral Presentations
- Popular Categories
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Powerpoint Templates and Google slides for Oral Presentations
Save your time and attract your audience with our fully editable ppt templates and slides..

Presenting Goods Oral Presentation Ideas In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase four stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Goods Oral Presentation Ideas. This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

Presenting Business Related Topics Oral Presentation In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase two stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Business Related Topics Oral Presentation. This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

Presenting our Oral Presentation Types In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases four stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Oral Presentation Types This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.

Presenting Most Important Part Preparing Oral Presentation In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase three stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Most Important Part Preparing Oral Presentation. This well-structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

Presenting Good Oral Presentation Ideas In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase four stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Good Oral Presentation Ideas. This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

Presenting Oral Presentation Topics In Powerpoint And Google Slides Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase four stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Oral Presentation Topics This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

Presenting this set of slides with name - Oral Presentation Skills Personal Development Skills Decision Making Communication Cpb. This is an editable five stages graphic that deals with topics like Oral Presentation Skills, Personal Development Skills, Decision Making Communication to help convey your message better graphically. This product is a premium product available for immediate download, and is 100 percent editable in Powerpoint. Download this now and use it in your presentations to impress your audience.

Presenting this set of slides with name Effective Oral Communication Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Portfolio Ideas Cpb. This is an editable Powerpoint four stages graphic that deals with topics like Effective Oral Communication to help convey your message better graphically. This product is a premium product available for immediate download and is 100 percent editable in Powerpoint. Download this now and use it in your presentations to impress your audience.
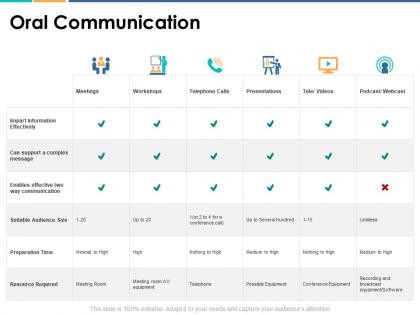
Presenting this set of slides with name Oral Communication Resource Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Pictures Graphics. The topics discussed in these slides are Marketing, Business, Management, Planning, Strategy. This is a completely editable PowerPoint presentation and is available for immediate download. Download now and impress your audience.
Presenting this set of slides with name Oral System Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Layouts Examples. The topics discussed in these slides are Oral System. This is a completely editable PowerPoint presentation and is available for immediate download. Download now and impress your audience.

Presenting Oral Language Development Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Outline Smartart Cpb slide which is completely adaptable. The graphics in this PowerPoint slide showcase four stages that will help you succinctly convey the information. In addition, you can alternate the color, font size, font type, and shapes of this PPT layout according to your content. This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Oral Language Development. This well-structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG. So, without any delay, click on the download button now.

Presenting our Face To Face Conversation Oral Communication Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Styles Influencers Cpb PowerPoint template design. This PowerPoint slide showcases five stages. It is useful to share insightful information on Face To Face Conversation Oral Communication This PPT slide can be easily accessed in standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also available in various formats like PDF, PNG, and JPG. Not only this, the PowerPoint slideshow is completely editable and you can effortlessly modify the font size, font type, and shapes according to your wish. Our PPT layout is compatible with Google Slides as well, so download and edit it as per your knowledge.

Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

palm sunday
5 templates

14 templates

solar eclipse
25 templates

26 templates

28 templates

13 templates
Communication Presentation templates
When we use the word "communication", we can be referring to many things. good or bad communication as a social skill, exchanging information between one or more people or we can also be alluding to the media such as television or radio that are responsible for transmitting the information. well, we have something to communicate to you: we have a set of google slides themes and powerpoint templates for these types of communication and many others..

Media and Communications Thesis
Are you about to finish your dissertation on Media and Communications? Prepare your thesis defense using this presentation. It includes a lot of illustrations over a teal background. Explain your objectives, methodology, results and conclusions and edit the pie charts, tables and infographics that we offer.

Pictograms for Communication with Children
Download the Pictograms for Communication with Children presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different...

Cross Cultural Communication Master's Degree
Communication can be the bridge that connects different cultures. This has a name: cross-cultural communication! Although if we start from the idea that every culture is a different way of conceiving the world, how does communication happen? Enter the exciting world of cross-cultural communication with a master's degree about it,...

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access
Career Technical Subject for Middle School - 6th Grade: Arts, Audio-Visual Technology, and Communications
Technology is the future. However, without incredible human creators behind it, its use would not be possible. Behind technological tools, such as audiovisual content creation or graphic design, there is a great mind with a great imagination. Indeed, if you are a creative person, with a constant desire to create...

Communications Major for College: Print Journalism
Newspapers never go out of style, so if you like journalism you might be interested in this area of communication: print journalism! With this formal template of gray and red slides you can speak about the content of this interesting major like what it is about, how it is organized,...

Mastering the Basics of Communication for College
Good communication is the ticket that will get you where you want to go. With this template you can prepare a workshop to prepare students to up their communication game at university. Take advice from the best orators in the world and sum up their tips in these editable slides!...

Brutalist Visual Communications Portfolio
Are you looking for a way of making your works as a visual communicator reach new audiences, clients and recruiters? Slidesgo has a solution for you: this brutalist design! Well, it surely will have a brutal impact on everyone who reads it, but as you probably already know, brutalism is...

Alexander Graham Bell Day
Download the Alexander Graham Bell Day presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different graphic...

Healthy Relationships and Communication Skills - 8th Grade
Download the Healthy Relationships and Communication Skills - 8th Grade presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. If you’re looking for a way to motivate and engage students who are undergoing significant physical, social, and emotional development, then you can’t go wrong with an educational template designed for Middle School by...

Food and Beverage Office Gathering
Download the Food and Beverage Office Gathering presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Gone are the days of dreary, unproductive meetings. Check out this sophisticated solution that offers you an innovative approach to planning and implementing meetings! Detailed yet simplified, this template ensures everyone is on the same page, contributing...

Healthy Relationships and Communication Skills - 11th Grade
Download the Healthy Relationships and Communication Skills - 11th Grade presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. High school students are approaching adulthood, and therefore, this template’s design reflects the mature nature of their education. Customize the well-defined sections, integrate multimedia and interactive elements and allow space for research or group...

Public Speaking Academy
With around 75% of the world’s population being afraid of public speaking, it is ranked as the number one fear in humans! Luckily, your public speaking academy is here to significantly reduce that number. And you won’t be bothering with useless “Imagine your audience not wearing clothes” tips either, but...

Business Meeting to Improve Communication Skills
Communication is a key soft skill, and this template provides a fantastic way to deliver some lessons on how to improve them in the context of a business meeting. Its clean and friendly design makes every slide attractive and uncluttered, and the upbeat illustrations and photos of people communicating in...

Language Arts Subject for Middle School: Communication and its Elements
Communication is not only about speaking, there are many aspects involved to make communication possible. Do you know them all? Present communication and its elements for your next language arts subject for middle school! What kinds of communication are there, what are its elements, what factors affect them, what gaps...

Effective Communications Meeting
You've been told that there will be a meeting next Friday. There's still time to create a slideshow in which you can detail the objectives of such meeting, along with a report of your project and other essential information. Fear not, this new template is quite the eye-catching one. Actually,...

Building Positive Relationships and Conflict Resolution - 3rd Grade
Download the Building Positive Relationships and Conflict Resolution - 3rd Grade presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and easily edit it to fit your own lesson plan! Designed specifically for elementary school education, this eye-catching design features engaging graphics and age-appropriate fonts; elements that capture the students' attention and make...

Debate and Persuasive Communication - Spanish - Foreign Language - 11th Grade
Download the Debate and Persuasive Communication - Spanish - Foreign Language - 11th Grade presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. As university curricula increasingly incorporate digital tools and platforms, this template has been designed to integrate with presentation software, online learning management systems, or referencing software, enhancing the overall efficiency...
- Page 1 of 15
New! Make quick presentations with AI
Slidesgo AI presentation maker puts the power of design and creativity in your hands, so you can effortlessly craft stunning slideshows in minutes.

Register for free and start editing online

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Oral presentations typically involve three important steps: 1) planning, 2) practicing, and 3) presenting. 1. Planning Oral presentations require a good deal of planning. Scholars estimate that approximately 50% of all mistakes in an oral presentation actually occur in the planning stage (or rather, lack of a planning stage). Make sure to ...
As this example demonstrates, effective oral presentation is more about creative thinking on your feet and basic skills than about wearing good shoes and knowing how to turn on the computer projector. Companies have long cried for graduates who can give dynamic talks, and they have long relied on talks as a key way to sway concerned parties ...
First is a two part set of videos that walks you through organizing a presentation. Part 1 - Creating an Introduction for a 10-15 Minute Scientfic Presentation. Part 2 - Creating the Body of a 10-15 Minute Presentation: Design/Methods; Data Results, Conclusions. Two additional videos should prove useful: Designing PowerPoint Slides for a ...
Put together a little tech bag stocked with cables, clickers, microphones, adaptors, and chargers. Many speakers even bring an ethernet cord. Preparedness is key when it comes to effectively presenting your speaking PowerPoint. Ask about deadlines and technical requirements well in advance.
Oral Presentations. An oral presentation is usually more than just reading a paper or set of slides to an audience (though in some disciplines, this is the expectation). How you deliver your presentation is as important in communicating your message as what you say. Use these guidelines to learn simple tools that help you prepare and present an ...
Delivery. It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don't have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
If you need guidance, see below for a sample oral presentation outline. PowerPoint.You should treat PowerPoint as a useful tool. You can use it to incorporate images into your presentation, to emphasize important points, and to guide your audience in following your argument. You should not use it for anything else. This means:
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. So, you've been tasked with organizing an oral presentation skills workshop. Don't sweat it! We've got just the thing to make your next workshop stand out from the rest - this duotone design presentation template. It's professional, simple, and chock-full of features that will make your audience ...
PowerPoint / Oral Presentation Slide Design Download the handout Watch the videos. Microsoft PowerPoint and its brand of slide design have dominated the market for decades. By some measures, PowerPoint is installed on over a billion computers around the world. Even if you use one of PowerPoint's competitors, like Google Slides, you probably ...
9 tips for a great oral presentation. 1. Practise, practise, practise. Practice is essential to presenting and speaking well. Rehearsals will give you a chance to try out different techniques. Most importantly practising your talk will help you to know your material well, and to allow you to stay on point and keep to a time limit. 2.
Follow these steps: Signal that it's nearly the end of your presentation, for example, "As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…". Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation - "In this speech I wanted to compare…". Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions.
Difference between Normal View & Slide Show View, Presenting Keyboard ShortcutsHow you design and use visual/audio aids in an oral presentation like a speech...
Oral-Presentation Format. Getting your thoughts onto presentation software can happen in several . ways. For example, you can • read through your paper and highlight (or bold or underline) key points, • summarize the main points of each paper section (e.g., introduction, method), ©SAGE Publications
Tip #2: Use simple language that is easy for people to follow. The words you select, and how you use them, will make a big difference in how well people hear—and remember—what you tell them. This is especially true in oral presentations. "When we write sentences for people to read, we can add more complexities.
Make sure each slide has one key idea and that idea is important to your message. Write the key point to make for each slide (often the heading) If the slide doesn't have a point, eliminate it!!! Tips for preparing your talk (cont.) Have only 1 idea per slide. Use the header to state the main idea of the slide, and use the body of the slide ...
Personal online tutoring. EnglishScore Tutors is the British Council's one-to-one tutoring platform for 13- to 17-year-olds. Giving an oral presentation as part of a speaking exam can be quite scary, but we're here to help you. Watch two students giving presentations and then read the tips carefully.
In this example, the presenter of this conference about 5G technologies combines starting a presentation with facts plus powerful graphics to deliver the message. Design created using our Key Company Highlights PowerPoint Template. For more tips and insights on how to start a presentation, we invite you to check this article.
Myth #1. "Answer all the questions correctly. Otherwise, your thesis won't get approved.". You are expected to have a focus on your research. That being said, you have to study each part of your thesis, every detail, and even your sources. You have to study and practice how to effectively deliver your presentation.
This PPT presentation can be accessed with Google Slides and is available in both standard screen and widescreen aspect ratios. It is also a useful set to elucidate topics like Business Related Topics Oral Presentation. This well structured design can be downloaded in different formats like PDF, JPG, and PNG.
In our example, we've used three icons accompanied by a short title and text. Conclusions slide. Following that, reiterate the important points of your research results you want your audience to take away from your thesis defense presentation. You can do so by expanding the next slide to have more icons and points, for example. Review slide
Download the Healthy Relationships and Communication Skills - 11th Grade presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. High school students are approaching adulthood, and therefore, this template's design reflects the mature nature of their education. Customize the well-defined sections, integrate multimedia and interactive elements and allow ...
Free Oral Powerpoint Templates And Google Slides Themes. Designing an eyecatching presentation template is time-consuming. Download the following free and ready-to-use Oral powerpoint templates and Google slides themes for the upcoming presentation. You only need to change text, logo or colors on the professional PPT templates. Filter by. Style.