
PMCLounge.com
Simplifying Project Management

Resource Assignments (Physical Resource and Project Team) – Outputs of Acquire Resources

Hold on a second and ask yourself, what could be the outputs of the Acquire Resources process?

It should be obvious, getting the resources assigned! Let’s look into both assignments.
1. Physical Resource Assignments
Physical resources include equipments, supplies, materials and even locations. This output is basically the documentation confirming the assignment of all the physical resources which would be used in your project
2. Project Team Assignments
As obvious as this is, the documentation of team members or human resources for your project, there is some extra information at play here. With this output, the team member names are updated in the project management plan and other relevant documents like schedules, RACI matrix etc
You are already aware of the other outputs of Acquire Resources process like,
- Resource Calendars
- Change Requests
Check more articles on Resource Management
Share this:
Continue reading, related posts.

Which form of Power should you use?
August 27, 2019 May 22, 2020

Conflicts are Good! Here are the 4 Reasons Why
August 26, 2019 September 26, 2019

Vroom’s Expectancy Theory | McClelland’s Human Motivation Theory | McKinsey’s 7S Framework
August 23, 2019 September 26, 2019
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Pass your PMP Exam in 50 days!

Project Resource Management – Everything You Must Know to PASS Your CAPM & PMP Exam
Capm exam & pmp exam study notes: project resource management.
Written By: Alvin the PM | Last Updated: June 12, 2021 Topic : CAPM Exam & PMP Exam Certification Study Notes
Listed below are my CAPM Exam & PMP Exam Study Notes for Project Resource Management that I’ve used to pass my own CAPM Exam, and which I also intend to use for my 2021 PMP Exam Preparation .
If you find any of my website notes and Youtube Videos helpful to pass your CAPM Exam or PMP Exam, considering supporting me by buying me a cup of “virtual” coffee by clicking the below link. ❤️ SUPPORT Alvin the PM by buying me “virtual” coffee ❤️
Please Note: These notes are meant to be a supplementary aid, and not as your primary study material for your CAPM Exam and/or PMP Exam. This is meant to help clarify any confusing topics and explain the most challenging concepts which are difficult to understand & remember. Please reference your own Exam Prep Book or your PMBOK Guide for further detail.
I’ve listed the Knowledge Area below, with an explanation of the following: 1) Overview of each Process Group 2) Reference Section & Page in PMBOK 6th Edition 3) ITTO Summary & Analysis (Input, Tool, Technique, Output) >> Any items marked with an * asterisk are the unique ones & critical topics to master 4) Key Concepts & Helpful Exam Prep Information
Overview of Resource Management
Resource Management is split up into the following six (6) Process Groups: 1) Plan Resource Management (PL) 2) Estimate Activity Resources (PL) 3) Acquire Resources (EX) 4) Develop Team (EX) 5) Manage Team (EX) 6) Control Resources (M&C)
Purpose: Understanding what resources are needed to successfully execute your project, and acquiring & managing these resources
>> Alvin’s Exam Tip: This Knowledge Area can be confusing and really easy to mix up with Procurement Management and Stakeholder Management … So, just think of Resource Management as: What resources do you need ( physical or personnel ) and how will you procure & manage them? Remember… Resource Management is focused on BOTH the Team and Physical Resources. Alvin the PM
Key Concepts: 1. What is the difference between Physical and Team Resources? – Physical Resources = Supplies, Materials, tools, equipment, facilities, software, cloud/IT, databases – Personnel / Team Resources = Human resources (e.g. Engineers, Supply Chain Buyers, Analysts, Manufacturing Specialists) 2. What are the factors which can influence the management & development of a team ? – Environment and locations of your Team members – Organization’s change management, culture, and politics – How stakeholders communicate with each other
Process #1: Plan Resource Management
1.1 Resource Management: Plan Resource Management (PL) – Pg. 312, PMBOK 6th Edition Purpose : Developing the Resource Management Plan for how to manage your resources. Think of this as the first step for Planning your Resources…
How will you make sure that you have enough resources to launch your project to 100% completion? In other words, what process will you follow to estimate/determine the resources needed, and ultimately, to procure and manage these resources?
ITTO Analysis: Plan Resource Management 1) What do You Need? ( Input ) – Project Charter , Project Management Plan, Project Documents, EEF/OPA >> Project Management Plan : Quality Management Plan, Scope Baseline >> Project Documents : Project Schedule, Requirements Documentation, Risk Register, Stakeholder Register 2) What is the Result? ( Output ) – * Resource Management Plan , * Team Charter, Updates to Project Documents 3) How Do You Accomplish It? (Tool/Technique) – *Organizational Theory; Expert Judgment; Meetings; Data Representation >> Data Representation : *Responsibility Assignment Matrix, *Hierarchical Charts, and *Text-oriented Formats
Key Concepts: Resources are limited, and oftentimes, may compete for priority. This of course, impacts your project’s costs, schedule, and risks, and are all critical factors to consider when you’re planning your project. As a Project Manager, it’s your responsibility to determine if you have enough resources to support your project’s work, and to plan accordingly for the availability and/or scarcity of these resources.
Key Terms to Remember: 1. Data Representation Techniques Hierarchical Charts – This is a graphical, top-down graphic showing positions and responsibilities of each team member, or a hierarchical list of team & physical resources based upon category and resource type. >>Example: Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS), and Resource Breakdown Structure Text-oriented Formats – Outlined descriptions of the job positions and responsibilities of each team member Responsibility Assignment Matrix, RAM – Shows the connection between Work Packages/ActivitIes and Team Members. >> The most commonly used RAM is known as a RACI Chart RACI Chart Example
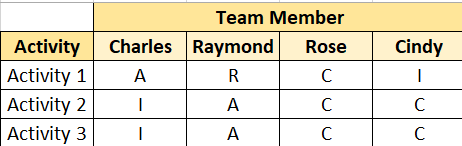
R = Responsible : Who is the one actually performing the work? A = Accountable : Typically, only one person is held Accountable for the completion of an activity. For example, the Engineer’s Manager. C = Consult : Who are Subject Matter Experts or other team members you can reach out to while working on the execution of this task? I = Inform : Who do you notify that the work is being completed? 2. Organizational Theory – This explains how people and teams behave and interact with each other. 3. Resource Management Plan – This Plan contains information for how we will identify, procure and manage our resources.
What’s inside the Resource Management Plan? 1 – How resources will be determined and acquired 2 – Roles & Responsibilities 3 – Organization Charts 4 – Guidance for how resources will be managed and released from the project 5 – Development and training of the team 6 – Description of how team members will be rewarded and recognized for their efforts 7 – Controlling of Resources – How do we make sure that resources are available when needed? Alvin the PM
4. Team Charter – This defines the expectations of what is accepted from each team member, and in so doing, helps increase the team’s cohesiveness and productivity >> What are the team’s guidelines (communications & etiquette for holding meetings), values (code of conduct), principles, and processes to follow (making decisions, and resolving conflict)
Process #2: Estimate Activity Resources
1.2 Resource Management: Estimate Activity Resources (PL) – Pg. 320, PMBOK 6th Edition Purpose : Determining the resources you need (staff, material, supplies, equipment) to execute the project. During this process, you’ll be creating a Resource Breakdown Structure outlining the resources (qty and type) you need to perform your project’s activities, as well as a list of your Resource Requirements and your Basis of Estimates .
ITTO Analysis: Estimate Activity Resources 1) What do You Need? ( Input ) – Project Management Plan, Project Documents, OPA/EEF >> Project Management Plan: Resource Management Plan , Scope Baseline >> Project Documents: Activity Attributes & List, Logs (Assumption and Risk Register), Resource Calendars, Cost Estimates 2) What is the Result? ( Output ) – *Resource Requirements, *Resource Breakdown Structure, *Basis of Estimates , Updates to Project Documents 3) How Do You Accomplish It? (Tool/Technique) **Key Tools: Estimation Techniques (Bottom-up, Analogous, Parametric) Other Tools : Expert Judgment, Data Analysis, PMIS, and Meetings >> Data Analysis: Alternatives Analysis
Key Concepts: This Process Group is performed simultaneously with Estimate Costs. If for example, you need additional resources, you may want to hire a contractor to obtain the required technical knowledge, and you’ll also need to determine what those additional costs would be. Or, providing training to your Engineer so he/she can have the skillset needed to perform the more complex work. (1) Estimation Techniques: Bottom-up – Estimating resources at the activity level and then rolling this up to the Work Package Level) Analogous – Leverage previous project’s for comparison Parametric – Estimation technique that uses a statistical relationship between historical data. For example, it takes X # hours to complete work. (2) Alternatives Analysis – Evaluate different options (e.g. make vs buy, using internal vs external resources, different equipment manufacturers, using different materials) and evaluating impact on project’s objectives (quality, cost, risk, and scope)
Key Terms to Remember: 1. Resource Requirements – What resources do you need to complete each activity? Qty & type? 2. Resource Breakdown Structure – Top-down graphical representation showing the resource categories needed to perform your project’s work, such as Labor, Material, Equipment, and Supplies 3. Resource Histogram – Compares the resources you need to their availability
Process #3: Acquire Resources
1.3 Resource Management: Acquire Resources (EX) – Pg. 328, PMBOK 6th Edition Purpose : This is the process for obtaining all the project’s required resources (personnel, equipment, material, supplies, tools). It’s during this process group that you’ll be assigning team members to their roles & responsibilities.
ITTO Analysis: Acquire Resources 1) What do You Need? ( Input ) – Project Management Plan, Project Documents, OPA/EEF >> Project Management Plan: Resource Management Plan, Procurement Management Plan, Cost Baseline >> Project Documents: Project Schedule, Resource Calendars & Requirements, Stakeholder Register 2) What is the Result? ( Output ) – *Physical Resource Assignments, *Team Assignments, *Resource Calendars, *Change Requests , Updates to Project Management Plan & Project Documents, Updates to OPA & EEF 3) How Do You Accomplish It? (Tool/Technique) – * Virtual Teams, *Pre-assignment , Decision making, and Interpersonal & Team Skills >> Decision Making; Multicriteria Decision Analysis >> Interpersonal and Team Skills: Negotiation
Key Concepts: 1. Remember that resources you procure can be from either inside OR outside your company. >> Internal Resources are obtained by Negotiating , using your Interpersonal and Team Skills , and working with the respective functional manager >> External Resources are obtained through the procurement process.
Key Terms to Remember: 1. Pre-assignment – This is when you assign your stakeholders to your project IN ADVANCE 2. Virtual Teams – Team members who do NOT meet in-person and work remotely from each other. 3. Multicriteria Decision Analysis – This technique uses criteria to rate potential resources and which ones will be procured. Factors to consider include: Availability, cost, experience, location, skill level 4. Assignments: Team & Physical Resource Assignments Physical Resource Assignments – This captures which physical resources will be used during the project: Equipment, materials, supplies Project Team Assignments – Assigning the roles & responsibilities of your team members 5. Resource Calendars – What are the actual working business days that resources are available?
Process #4: Develop Team
1.4 Resource Management: Develop Team (EX) – Pg. 336, PMBOK 6th Edition Purpose : This is the process where you will improve your team dynamics, the team member’s competencies, and how they interact with each other. What is the goal of Developing the Team ? Promote teamwork, increase team morale and productivity, create an environment of team spirit
(1) Enhance the team’s technical knowledge (Helps drive project to successful completion) (2) Create an environment of trust and openness (Less conflict and increased collaboration) (3) Drive accountability and ownership from the team so they feel empowered to make decisions (Each person will want to do his/her best to contribute to the project’s success)
ITTO Analysis: Develop Team 1) What do You Need? ( Input ) – Project Management Plan, Project Documents, OPA/EEF >> Project Management Plan: Resource Management Plan >> Project Documents: Project Schedule, Team Assignments, Resource Calendars, Lessons Learned, Team Charter 2) What is the Result? ( Output ) *Team Performance Assessments, *Change Requests , Updates to Project Management Plan & Project Documents, Updates to OPA & EEF 3) How Do You Accomplish It? (Tool/Technique) – * Colocation , * Communication Technology , * Individual & Team Assessments , * Recognition & Rewards, *Training, * Virtual Teams , Meetings, Interpersonal and Team Skills >> Interpersonal and Team Skills: Conflict management, influencing, motivation, negotiation, team building
Key Concepts: Tuckman Ladder – 5 Stages of Development 1) Forming – The ‘introduction’ . Your Team Members meet each other and learn about the project and their assigned responsibilities & roles. Everyone is a little ‘shy’ in the beginning. 2) Storming – You are STARTING to work on the project now! Everyone starts looking into the work required for the project, and you begin taking technical decisions. >> This is where the ‘storm’ hits, and people disagree, since the team members may not be collaborative or open to each other’s ideas. This makes the environment counterproductive. 3) Norming – This is the period where the team dynamics goes to ‘ normal ’ and everyone builds a normal relationship with each other. >> Your Team now starts being collaborative and supporting & trusting each other. Your goal is to move from Storming to Norming as soon as possible, so that everyone trusts each other and works effectively. 4) Performing – This is when you have the DREAM TEAM and everyone is ‘performing’ at their best, like a well oiled machine! All issues are worked through independently. Think, Peak Performance! 5) Adjourning – Closing out the project and releasing the team members from the project.
Key Terms to Remember: 1. Team Charter – Outlines the guidelines for how the team will operate 2. Colocation : Place team members in the SAME location 3. Communication Technology – Shared portals, Audio/Video Tools, Email & Chat 4. Team Performance Assessments – These assessments are a way to evaluate your team’s performance – how well are we doing, collectively as a group? Note that this is the KEY output of the Develop Team process. >> Use this evaluation to identify ways to improve your team’s behavior & performance. This could be coaching, training, and mentorship. 5. Individual and Team Assessments – These are tools to give you an idea of the strengths and weaknesses of your team members. Examples of assessments include: surveys, assessments, interviews, and ability tests. 6. Recognition and Rewards – Always consider cultural backgrounds when giving out rewards & recognition to your team members
Process #5: Manage Team
1.5 Resource Management: Manage Team (EX) – Pg. 345, PMBOK 6th Edition Purpose : Optimizing the the project’s performance by tracking each person’s performance, giving feedback, helping solve issues, and managing team changes. In this process, you’re influencing the behavior of your Team through leadership, conflict management, and communication. This focuses more on the HUMAN side of things.
ITTO Analysis: Manage Team 1) What do You Need? ( Input ) – *Work Performance Reports, *Team Performance Assessments, Project Management Plan, Project Documents, OPA/EEF >> Project Management Plan: Resource Management Plan >> Project Documents: Logs (Issue Log, Lessons Learned), Team Assignments, Team Charter 2) What is the Result? ( Output ) *Change Requests , Updates to Project Management Plan & Project Documents, Updates to EEF 3) How Do You Accomplish It? (Tool/Technique) – * Interpersonal and Team Skills, PMIS >> Interpersonal and Team Skills: Conflict management, influencing, leadership, emotional intelligence, decision making
Key Concepts: Work Performance Report s – These reports are the results/visual representation of the analyzed Work Performance Information – Helps determine future resource requirements, recognition & rewards, and updates to resource management plan Conflict Resolution Techniques – How do you resolve Conflict? (1) Withdraw/Avoid – Avoiding and backing away from the situation. You’re retreating from a conflict, postponing the issue, and you’d like someone else to resolve the issue. >> Example: Not responding to an email or phone call; Having another Manager help resolve conflict (2) Smooth/Accommodate – Highlights the areas that everyone agrees upon and considers everyone’s viewpoint to maintain the relationship. >> Goal is to maintain relationships within the team. More cooperative & less assertive. >> Example: Repeating the areas that everyone agrees to (3) Compromise/Reconcile – Keep everyone happy! This is a ‘middle-ground’ or neutral zone. Brings some satisfaction to everyone. – Might temporarily solve the problem in the near-term, but could lead to problems in the future. Leads to ‘ lose-lose ’ outcome. >> Example: Agree to one solution that was recommended by all teams. (4) Force/Direct – Being an autocrat, where you force your view onto others. – Leads to a win / lose situation. One person will feel like they lost. >> Example: In a team discussion, deciding to follow the strategy from Management/HIPPO (i.e. the Highest Paid Person’s Opinion). (5) Collaborate/Problem Solve – Best approach to solve conflicts. You need to have open dialogue in order to incorporate different viewpoints, and address everyone’s points. Leads to ‘ win-‘win >> Reaching a consensus What are the sources of Conflict ? 7 Sources of conflict in order from highest to lowest: >>Schedule, Project priorities, Resources, Technical opinions, Administrative procedures, Cost, Personality
Key Terms to Remember: 1. Emotional Intelligence – Understanding your own emotions, as well as those around you on your team 2. Influencing – Project Managers have little to no authority over team members in a matrix-style organization; therefore, be persuasive, articulate your points, and build trust with your team 3. Leadership – Motivate your team for high performance
Process #6: Control Resources
1.6 Resource Management: Control Resources (M&C) – Pg. 352, PMBOK 6th Edition Purpose : Were the resources you planned actually available during the execution of the project? Do any corrective actions need to be implemented if there aren’t sufficient resources available? And, how does the actual usage of the resources compare to the planned resources? . In contrast to Develop and Manage Team , which is focused on employee/staffing resources, Control Resources is focused on the availability of physical resources .
ITTO Analysis: Control Resources 1) What do You Need? ( Input ) – Work Performance Data, Agreements, Project Management Plan, Project Documents, OPA >> Project Management Plan: Resource Management Plan >> Project Documents: Logs (Issue Log, Lessons Learned, Risk Register ) , Physical resource assignments, Project Schedule, and Resource Breakdown Structure & Requirements 2) What is the Result? ( Output ) *Work Performance Information, Change Requests , Updates to Project Management Plan & Project Documents 3) How Do You Accomplish It? (Tool/Technique) *Problem Solving , * Interpersonal and Team Skills, *PMIS , and Data Analysis >> Data Analysis: Alternatives Analysis, Cost-benefit Analysis, Performance Reviews, Trend Analysis >> Interpersonal and Team Skills: *Negotiation, *Influencing
Key Terms to Remember: 1. Resource Requirements – What are the physical resources which you need in your project? 2. Physical Resource Assignments – What is your planned usage for each physical resource? 3. Trend Analysis – How is our project performing with respect to time? Are we getting better or worse? 4. Work Performance Information – By examining the resource requirements and how the resources were allocated for your project, how is the project going? Are all correct resources being used at the correct time for the correct tasks?
I hope you found the above information helpful with your Project Management Exam Prep Journey! If you found this useful, please feel free to SHARE and RECOMMEND this website with a friend. My goal is to help other Project Managers pass their own CAPM Exam and PMP Exam, and become Certified in Project Management.
Cheers, Alvin
You Might Also Like
New pmp exam 2021 most frequently asked questions, project risk management – everything you must know to pass your capm & pmp exam, what areas should i study for the new pmp exam 2021, privacy overview.

PMEducation

Physical Resource Management
Physical Resources are: Equipment, Materials, Supplies, Facilities, and Infrastructure that are utilized by your project, or become a part of your project deliverable. Physical Resources are different from Human Resources, which we discuss HERE

The importance of good Physical Resource management is to ensure you have the right Physical Resources at the right place in the right time, in order for your project to proceed as planned. Due to the temporary nature of projects, the Physical Resources you need for your project often belong to someone else and are utilized elsewhere.
Your organization might have adopted resource philosophies such as: lean, just-in-time, kaisen, total productive maintenance, or theory of constraints. if so, you need to manage your project taking these philosophies into account., management of physical resources consists of four processes: plan physical resource management, estimate time and cost of physical resources, acquire the physical resources, and monitor & control the physical resources. these are described below:, a) plan physical resource management, firstly identify what physical resources will be required for your project. look at your work breakdown structure (wbs) for thoughts about the physical resource requirements., for larger and more complex projects you will want to write a resource management plan (rmp). your rmp will describe:, > how the resources will be acquired,, > how they will be managed, and, > how they will be used., as an example, for the equipment shown in the photo above, your rmp could describe that these machines will be acquired through rental, for a specific phase of the project. they would be managed by performing the periodic maintenance which is prescribed by the equipment maintenance manual. they will be used on 12 hour shifts by our staff operators, for example., your resource management plan should also describe the methods you will use to ensure sufficient resources are available where and when they are needed., your resource management plan provides input information to your project's assumptions log (if you have one) and your risk register. (scroll down on the linked page), remember to consider resource leveling and resource smoothing (both found on this page) when making your resource management plan., b) estimate time and cost of physical resources, if not already done when planning time and cost, you will now want to estimate the time and the cost of physical resources for your project. consider the types, and quantities, of physical resources needed. equipment rental companies often charge by the number of hours a machine is used, so for this type of rental equipment you would estimate the number of hours of intended use to arrive at a cost estimate. other rentals such as scaffolding and power tools will be rented on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis., the use of physical resources that belong to your organization might not impact your project cost but likely impact availability for some other project or operation. for this reason, it is important to estimate the time requirement for the physical resources., we have already seen methods for estimating under time and cost. click here to review these ideas., if the physical resources will require a purchasing activity, give your purchasing team as much "heads-up" time as possible to prepare., c) acquire the physical resources, at the appropriate time you will acquire the physical resources and assign them to their respective activities. too early acquisition adds unnecessary cost and prevents others from using shared resources. too late acquisition, of course, impacts project schedule. for similar reasons, timely release of acquired physical resources is also important., acquiring external physical resources might require a purchasing process, some delivery time, or other lead time. action the acquisition in sufficient time, allowing for these activities., pay extra attention to special physical resources that are unique and/or critical to your project's success. special equipment and materials, for example, can greatly impact your project schedule if not delivered on time., some physical resources might already be pre-assigned to your project so check for possible duplication and for suitability of what has been assigned to you., you can place the availability of resources on a resource calendar, simply a calendar format modified for this purpose. the availability of resources may impact your time plan, so consider this carefully. for example, working in smaller sized facilities might take longer than with those which are more adequately sized. scarce resources might only be available at certain times. your resource calendar will be very useful in managing physical resources., d) monitor & control the physical resources, after planning, you will want to begin monitoring and controlling the outcomes of your project. this process involves ensuring the physical resources assigned and allocated to your project (as in your resource management plan) are available as planned; as well as monitoring the planned vs actual utilization of these resources and taking corrective action as necessary. click here and follow the links to find out how to monitor and control physical resources., the following web page provides insights that reinforce the ideas we have discussed:, https://www.designingbuildings.co.uk/wiki/resource_management_in_construction.
#resource #physical #equipment #materials #supplies #facilities #infrastructure #RMP #estimate #acquire
Recent Posts
WHY ? The first Question
WHO ? Stakeholders
Initiating Your Project - First Steps

4squareviews
Recent posts.
- CompTIA A+ Study Resources
- IT Certification and the Feynman Technique–Part 2 and 3
- IT Certification and the Feynman Technique–Part 1
- Chicago’s Rollout–The Pros and Cons of Small Businesses
- Chicago’s Rollout–A Change of Habit (10)
- September 2023
- February 2020
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- September 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- February 2012
- January 2012
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address:
- Uncategorized
- Entries feed
- Comments feed
- WordPress.com
6th Edition PMBOK® Guide–Process 9.3 Acquire Resources: Outputs
This post covers the outputs for the process 9.3 Acquire Resources. Remember that in the 6th Edition of the PMBOK® Guide, “resources” now covers two categories: both physical resources (material, equipment, supplies, locations) and human resources.
9.3.3 Acquire Resources: Outputs
9.3.3.1 Physical Resource Assignments
Documentation of the physical resource assignments that will be used during the project.
9.3.3.2 Project Team Assignments
Documentation of team assignments which records the project team members and their roles and responsibilities for the project. Such documentation may include
- Project team directory
- Project organization chart
9.3.3.3 Resource Calendar
A resource calendar identifies the times when each specific resource is available, taking into account the normal business hours for the organization as a whole and the specific schedule of each resource (accounting for vacation days, etc.). In this way, the project manager will know when and for how long identified resources will be available during the project.
9.3.3.4 Change Requests
If the Acquire Resources process results in a change such as an impact on the schedule, the project manager needs to submit a change request which is then handled in the process 4.6 Perform Integrated Change Control. If there are changes to the Resource Management Plan that are needed, then this will also require a change request.
9.3.3.5 Project Management Plan Updates
- Resource Management plan–any changes to the resource management plan resulting from this process will cause the plan to be updated.
- Cost baseline–the acquisition of resources for the project may affect the cost baseline.
9.3.3.6 Project Documents Updates
- Lessons learned register–the lessons learned register during the process of acquiring resources for the project may be updated to reflect experience which may impact how resources are acquired later in the project.
- Project schedule–the availability of resources (see Resource Calendar) may affect changes to the timing of some of the activities in the project schedule.
- Resource breakdown structure–any resources acquired during this process will be recorded in the RBS.
- Resource requirements–this is updated to reflect resources acquired for the project.
- Risk register–new risks identified during this process relating to the acquisition of resources are recorded in the risk register and managed using the risk management processes.
- Stakeholder register–this is updated with information on existing stakeholders that may have been gained as a result of this process.
9.3.3.7 Enterprise Environmental Factor Updates
- Resource availability within the organization will be affected by their utilization as resources on this project.
9.3.3.8 Organizational Process Assets Updates
- Documentation related to acquiring, assigning and allocating resources.
Share this:
Filed under: Uncategorized |
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Recent tweets.
Create a free website or blog at WordPress.com. WP Designer.

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
PMP: 8. Project Resource Management
- Study Again
- Physical resources include equipment, materials, facilities, and infrastructure. - Human resources include Team resources or personnel. - The project manager is responsible for the team formation as an effective group. - The project manager as a leader should be responsible for proactively developing team skills and competencies while retaining and improving team satisfaction and motivation. - Modern project resource management approaches seek to optimize resource utilization. - Trends in resource management lean management, just in time (JIT), manufacturing, Kaizen, total productive maintenance (TPM), theory of constraints (TOC). - Project manager should invest in personal emotional intelligence (EI) by improving inbound (self-management, self-awareness) and outbound (relationship management). - Research suggests that project teams that succeed in developing team EI or become an emotionally competent group are more effective. Additionally, there is a reduction in staff turnover - Agile approaches have improved self-organizing teams, where the team functions with an absence of centralized control. - The globalization of projects has promoted the need for virtual teams that work on the same project, but are not collocated at the same site. The availability of communication technology has made virtual teams feasible - Collaboration is intended to boost productivity and facilitate innovative problem solving - Projects with high variability benefit from team structures that maximize focus and collaboration - Planning for physical and human resources is much less predictable in projects with high variability
Plan Resource Management (Planning Process Group) Plan Resource Management is the process of defining how to estimate, acquire, manage, and use team and physical resources. Key benefit of this process is that it establishes the approach and level of management effort needed for managing project resources based on the type and complexity of the project. - This process is performed once or at predefined points in the project. - Resource planning is used to determine and identify an approach to ensure that sufficient resources are available for the successful completion of the project - Project resources include team members, supplies, materials, equipment, services and facilities - resources can be obtained from the organization’s internal assets or from outside the organization through a procurement process. - Other projects may be competing for the same resources required for the project at the same time and location which may impact project costs, schedules, risk and quality.
Plan Resource Management Inputs: 1- Project Charter 2- Project Management plan - Includes (Quality management plan and Scope baseline) 3- Project Documents - Includes (Project schedule, Requirements documentation, Risk register and Stakeholder register) 4- Enterprise Environmental Factors 5- Organizational Process Assets
Plan Resource Management Tools & Techniques: 1- Expert Judgment 2- Data Representation - Includes Charts (Hierarchical, Matrix and text oriented). - The Objective is to ensure that each work package has an unambiguous owner and that all team members have a clear understanding of their roles and responsibilities - Hierarchical format may be used to represent high-level roles, while a text-based format may be better suited to document the detailed responsibilities - Hierarchical charts: The traditional organizational chart structure can be used to show positions and relationships in a graphical, top-down format. - Work breakdown structure (WBS): designed to show how project deliverables are broken down into work packages and provide a way of showing high-level areas of responsibility. - Organizational breakdown structure (OBS) : is arranged according to an organization’s existing departments, units, or teams, with the project activities or work packages listed under each department. You may see all project responsibilities by looking at OBS - Resource breakdown structure: hierarchical list of team and physical resources related by category and resource type that is used for planning, managing and controlling project. Each descending (lower) level represents an increasingly detailed description of the resource until the information is small enough to be used in conjunction with the work breakdown structure (WBS) to allow the work to be planned, monitored, and controlled. - Assignment Matrix: - Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) shows the project resources assigned to each work package. It is used to illustrate the connections between work packages, or activities, and project team members - On larger projects, RAMs can be developed at various levels (High and Low) - High-level RAM can define the responsibilities of a project team, group, or unit within each component of the WBS - Lower-level RAMs are used within the group to designate roles, responsibilities, and levels of authority for specific activities - Matrix shows all activities associated with one person and all people associated with one activity. To ensure that there is only one person assigned to one task to avoid confusion
- Example of RAM is a RACI (responsible, accountable, consult and inform) chart
- RACI chart is a useful tool to use to ensure clear assignment of roles and responsibilities when the team consists of internal and external resources A RACI chart is a matrix of all the activities or decision making authorities undertaken in an organisation set against all the people or roles. At each intersection of activity and role it is possible to assign somebody responsible, accountable, consulted or informed for that activity or decision.
6 Steps To Create A RACI Chart Step 1: Identify Project Roles. Step 2: Identify Project Tasks Or Deliverables. Step 3: Assign The RACI To Each Role And Task. Step 4: Agree on This With Your Team. Step 5: Agree on This With The Core Project Stakeholders. Step 6: Make It Useful Throughout The Life Of The Project.
- Text-oriented Formats: Team member responsibilities that require detailed descriptions can be specified in text-oriented formats. Document provides information like responsibilities, authority, competencies, and qualifications. This document may be called (position description and role-responsibility) and it may be used as template for future projects.
3- Organizational theory - Provides information regarding the way in which people, teams, and organizational units behave. - Effective use of common techniques identified in organizational theory can shorten the amount of time, cost and effort needed to create the Plan Resource Management process outputs and improve planning efficiency 4- Meetings
Plan Resource Management Outputs:
1- Resource Management Plan - provides guidance on how project resources should be categorized, allocated, managed, and released. It may be divided between the team management plan and physical resource management plan according to the specifics of the project. This include - Resource Identification: Includes methods for identifying and quantifying team and physical resources needed - Acquire resources: Includes guidance how to acquire team and physical resources - Includes Roles and responsibilities such as - Role: function assumed by, or assigned to, a person in the project - Authority: The rights to apply project resources, make decisions, sign approvals, accept deliverables, and influence others to carry out project work - Responsibility: assigned duties and work that a project team member is expected to perform in order to complete the project’s activities - Competence: skill and capacity required to complete assigned activities within the project constraints. If project member doesn’t have required competencies, proactive response such as training, hiring, schedule changes, or scope changes are initiated. - Project organization charts: graphic display of project team members and their reporting relationships. It can be formal or informal based on the need of the project - Project team resource management: Guidance on how project team resources should be defined, staffed, managed, and eventually released - Training: Training strategies for team members - Team development: Methods for developing the project team. - Resource control: Methods for ensuring adequate physical resources are available as needed and that the acquisition of physical resources is optimized for project needs. - Recognition plan: Which recognition and rewards will be given to team members and when,
2- Team Charter - Document that establishes the team values, agreements, and operating guidelines for the team - Includes (Team values, Communication guidelines, Decision-making criteria and process, Conflict resolution process, meeting guidelines and Team agreements) - Establishes clear expectations regarding acceptable behavior by project team members (Ground Rules) - Early commitment to clear guidelines decreases misunderstandings and increases productivity - Team charter works best when the team develops it, or at least has an opportunity to contribute to it - Team charter can be reviewed and updated periodically
3- Project Document Updates - Includes (Assumption log and Risk register)
Estimate Activity Resources (Planning Process Group) Estimate Activity Resources is the process of estimating team resources and the type and quantities of materials, equipment, and supplies necessary to perform project work. Key benefit of this process is that it identifies the type, quantity, and characteristics of resources required to complete the project. - This process is performed periodically throughout the project as needed - The Estimate Activity Resources process is closely coordinated with other processes, such as the Estimate Costs
Estimate Activity Resources Inputs: 1- Project Management plan - Includes (Resource management plan and Scope baseline) 2- Project Documents - Includes (Activity attributes, Activity list, Assumption log, Cost estimates, Resource calendars and Risk register) 3- Enterprise Environmental Factors 4- Organizational Process Assets
Estimate Activity Resources Tools & Techniques: 1- Expert Judgment - Specialized knowledge or training in team and physical resource planning and estimating 2- Bottom-Up Estimating - Team and physical resources are estimated at the activity level and then aggregated to develop the estimates for work packages, control accounts, and summary project levels 3- Analogous Estimating - Uses information regarding resources from a previous similar project as the basis for estimating a future projects. It is used as quick estimating method and can be used when the project manager can only identify a few top levels of the WBS 4- Parametric Estimating - Uses an algorithm or a statistical relationship between historical data and other variables to calculate resource quantities needed for an activity. 5- Data Analysis - Alternative analysis: used to evaluate identified options in order to select the options or approaches to use to execute and perform the work of the project. Alternatives analysis assists in providing the best solution to perform the project activities, within the defined constraints 6- Project Management Information System (PMIS) - Includes resource management software that can help plan, organize, and manage resource 7- Meetings - The project manager may hold planning meetings with functional managers to estimate the resources needed per activity, level of effort (LoE), skill level of the team resources, and the quantity of the materials needed
Estimate Activity Resources Outputs: 1- Resources Requirements - Identify the types and quantities of resources required for each work package or activity - can be aggregated to determine the estimated resources for each work package, each WBS branch, and the project as a whole. 2- Basis of Estimates - The amount and type of additional details supporting the resource estimate vary by application area - It provides a clear and complete understanding of how the resource estimate was derived. 3- Resource Breakdown Structure - Hierarchical representation of resources by category and type - Categories include labor, material, equipment, and supplies. - Resource types may include the skill level, grade level, required certifications - It is used to guide the categorization for the project. In this process it is a completed document that will be used to acquire and monitor resources. 4- Project Documents Updates - Includes (Activity attributes, Assumption log and Lessons learned register)
Acquire Resources (Executing Process Group) Acquire Resources is the process of obtaining team members, facilities, equipment, materials, supplies, and other resources necessary to complete project work Key benefit of this process is that it outlines and guides the selection of resources and assigns them to their respective activities. - This process is performed periodically throughout the project as needed - Resources can be internal or external - Internal resources are acquired (assigned) from functional or resource managers - External resources are acquired through the procurement processes. - The project management team may or may not have direct control over resource - The project manager or project team should effectively negotiate and influence others who are in a position to provide the required team and physical resources for the project. - Failure to acquire the necessary resources for the project affect project schedules, budgets, customer satisfaction, and risks and it decreases the probability of success or result in cancellation - If the team resources are not available due to constraints such as economic factors or assignment to other projects, the project manager or team may be required to assign alternative resources, perhaps with different competencies or costs. Alternative resources are allowed provided there is no violation of legal, regulatory, mandatory, or other specific criteria - These factors should be considered and accounted for in the planning stages of the project
Acquire Resources Inputs: 1- Project Management Plan - Includes (Resource management plan, Procurement management plan and Cost baseline) 2- Project Documents - Includes (Project schedule, Resource calendars, Resource requirements and Stakeholder register) 3- Enterprise Environmental Factors 4- Organizational Process Assets
Acquire Resources Tools & Techniques: 1- Decision Making - Multicriteria decision: criteria are developed and used to rate or score potential resources. The criteria are weighted according to their relative importance and values can be changed for different types of resources. Examples of selection criteria for resources includes (Availability, Cost, Team ability, Experience, Knowledge, Skills, Attitude and international factors). 2- Interpersonal and Team Skills - Negotiation: Many projects need to negotiate for required resources. The team ability to influence others is an important role in negotiating resource allocation. The project management team may need to negotiate with - Functional Manager: Ensure that the project receives the best resources possible in the required timeframe and until their responsibilities are complete - Other project management teams within the performing organization - External organizations and suppliers: Provide appropriate, scarce, specialized, qualified, certified, or other specific team or physical resources. 3- Pre-Assignment - When physical or team resources are determined in advance, they are considered pre-assigned - This occur if the project is the result of specific resources being identified as part of a competitive proposal or if the project is dependent upon the expertise of particular persons - Pre-assignment might also include the team members who have already been assigned in Develop Project Charter Process or other processes before the initial Resource Plan has been completed 4- Virtual Teams - The use of virtual teams creates new possibilities when acquiring project team members - Virtual teams are defined as groups of people with a shared goal who fulfill their roles with little or no time spent meeting face to face - The availability of communication technology has made virtual teams feasible - Communication planning becomes increasingly important in a virtual team environment
Acquire Resources Outputs: 1- Physical Resources Assignments - Documentation of the physical resource assignments records the material, equipment, supplies, locations, and other physical resources that will be used during the project. 2- Project Team Assignments - Documentation of team assignments records the team members and their roles and responsibilities for the project. Documentation can include a project team directory and names inserted into the project management plan, such as the project organization charts and schedules 3- Resource Calendars - Identifies the working days, shifts, start and end of normal business hours, weekends, and public holidays when each specific resource is available - Information on which resour ces are potentially available during a planned activity period is used for estimating resource utilization - Resource calendars also specify when and for how long identified team and physical resources will be available during the project - The information may be at the activity or project level 4- Change Requests 5- Project Management Plan Updates - Includes (Resource management plan, Cost baseline) 6- Project Documents Updates - Includes (Lessons learned register, Project schedule, Resource breakdown structure, Resource requirements, Risk register and Stakeholder register) 7- Enterprise Environmental Factors Updates - Includes (Resource availability and Amount of the organization’s consumable resources used) 8- Organizational Process Assets Updates - Includes (documentation related to acquiring, assigning and allocating resources)
Develop Team (Executing Process Group) Develop Team is the process of improving competencies, team member interaction, and the overall team environment to enhance project performance Key benefit of this process is that it results in improved teamwork, enhanced interpersonal skills and competencies, motivated employees, reduced attrition, and improved overall project performance. - This process is performed throughout the project - Project managers require skills to identify, build, maintain, motivate, lead, and inspire project teams to achieve high team performance and meet the project’s objectives - Teamwork is a critical factor for project success, and developing and effective team is the project manager’s responsibility - In a climate of mutual trust . Developing the project team improves the people skills, technical competencies, and overall team environment and project performance - Objective of developing a project team include (Improve the team knowledge and skill to achieve project’s objective and lower cost and reduce time, improve trust among the team to raise morale and lower conflict, create dynamic collaborative team to improve productivity and allow cross-training to share knowledge and expertise and empower decision making) - One of the models to describe team development is “Tuckman ladder” which includes five stages of development the team may go through. Projects with team members who worked together in the past may skip a stage - Forming: a phase where the team members meet and learn about the project and their formal roles. Team members tend to be independent and not as open in this phase - Storming: the team begins to address the project work, technical decisions, and the project management approach. If team members are not collaborative or open to differing ideas and perspectives, the environment can become counterproductive - Norming : team members begin to work together and adjust their work habits and behaviors to support the team. The team members learn to trust each other - Performing: Teams that reach the performing stage function as a well-organized unit. They are interdependent and work through issues smoothly and effectively - Adjourning: the team completes the work and moves on from the project. This typically occurs when staff is released from the project as deliverables are completed or as part of the Close Project or Phase process - The duration of a particular stage depends upon team dynamics, team size, and team leadership
Develop Team Inputs: 1- Project Management Plan - Includes (Resource management plan) 2- Project Documents - Includes (Lessons learned register, Project schedule, Project team assignments, Resource calendars and Team charter) 3- Enterprise Environmental Factors 4- Organizational Process Assets
Develop Team Tools & Techniques: 1- Colocation - Colocation involves placing many or all of the most active project team members in the same physical location to enhance their ability to perform as a team - Colocation can be temporary or can continue for the entire project - Colocation strategies can include a team meeting room or common places to post schedules 2- Virtual Teams - Virtual teams can bring benefits such as the use of more skilled resources, reduced costs, less travel and relocation expenses 3- Communication Technology - Address team development issues in collocated and virtual teams and help in building harmonious environment for the collocated team and a better understanding for the virtual team - Examples of communication technology (Shared portal (shared repository like websites or intranet which is effective for virtual teams), Video conferencing, Audio conferencing and Email/Chat. 4- Interpersonal and Team Skills - Conflict management: The project manager needs to resolve conflicts in a timely manner and in a constructive way in order to achieve a high-performing team - Influencing: An influencing skill used in this process is gathering relevant and critical information to address important issues and reach agreements while maintaining mutual trust. - Motivation: Providing a reason for someone to act. Teams are motivated by empowering them to participate in decision making and encouraging them to work independently - Negotiation: Negotiation among team members is used to reach consensus on project needs. Negotiation can build trust and harmony among the team members - Team Building - Team building is conducting activities that enhance the team’s social relations and build collaborative approach and cooperative working environment - Team building activities can vary from a 5-minute agenda item in a status review meeting to an offsite, professionally facilitated event - Objective of team-building activities is to help individual team members work together effectively. - While team building is essential during the initial stages of a project, it should be a continuous process. Changes in a project environment are inevitable, and to manage them effectively, a continuous or renewed team-building effort may be applied - The project manager should continually monitor team functionality and performance to determine if any actions are needed to prevent or correct various team problems 5- Recognition and Rewards - Part of the team development process involves recognizing and rewarding desirable behavior - The original plan for rewarding people is developed during the Plan Resource Management process - Reward decisions are made, formally or informally during the process of managing the project team - Money is viewed as a tangible aspect of any reward system, but intangible rewards could be equally or even more effective - Good strategy for project managers is to give the team recognition throughout the life cycle 6- Training - Training includes all activities designed to enhance the competencies of the project team members - Examples of training include classroom, online, computer-based, training from another project team - Scheduled training takes place as stated in the resource management plan - Unplanned training takes place as a result of observation, conversation, and project performance - Training costs could be included in the project budget or supported by the performing organization if the added skills may be useful for future projects - It may be performed by in-house or by external trainers. 7- Individual and Team Assessments - Gives the project manager and the project team insight into areas of strengths and weaknesses - Helps project managers assess team members’ preferences, aspirations and how they process - Various tools can be used such as attitudinal surveys, specific assessments, structured interviews, ability tests, and focus groups 8- Meetings - Example: project orientation meetings, team-building meetings and team developments meetings
Develop Team Outputs: 1- Team Performance Assessments - As project team development efforts such as training, team building, and colocation are implemented, the project management team makes formal or informal assessments of the project team’s effectiveness. - Effective team development strategies are expected to increase the team’s performance, which increases the likelihood of meeting the project objectives. - As a result of conducting evaluation of the team’s overall performance, the project team can identify the specific training, coaching or changes required to improve the team performance 2- Change Requests 3- Project Management Plan Updates - Includes (resource management plan) 4- Project Document Updates - Includes (Lessons learned register, Project schedule, Project team assignments, Resource calendars and Team charter) 5- Enterprise Environmental Factors Updates - Includes (Employee development plan record and skill assessments) 6- Organizational Process Assets Updates - Includes (Training requirements and Personnel assessment)
Manage Team (Executing Process Group) Manage Team is the process of tracking team member performance, providing feedback, resolving issues, and managing team changes to optimize project performance Key benefit of this process is that it influences team behavior, manages conflict, and resolves issues. - This process is performed throughout the project - Team management involves a combination of skills with special emphasis on communication, conflict management, negotiation, and leadership - Project managers should provide challenging assignments to team members and provide recognition for high performance - The project manager needs to be sensitive to both the willingness and the ability of team members to perform their work and adjust their management and leadership styles accordingly
Manage Team Inputs: 1- Project Management Plan - Includes (Resource management plan) 2- Project Documents - Includes (Issue log, Lessons learned register, Project team assignments and Team charter) 3- Work Performance Reports - Physical or electronic representation of work performance information intended to generate decisions, actions, or awareness. - Project reports that can help with team management include results from (Schedule control, Cost control, Quality control and scope validation) - The information in the reports assists in determining future team resource requirements, recognition and rewards and update the resource management plan 4- Team Performance Assessments - Formal or informal assessments of the project team performance. Which helps in resolving issues, modify communication address conflict and improve the team interaction 5- Enterprise Environmental Factors 6- Organizational Process Assets
Manage Team Tools & Techniques:
1- Interpersonal and Team Skills - Conflict management - Conflict is inevitable in a project environment. Sources of conflict include scarce resources, scheduling priorities, and personal work styles - Team ground rules, group norms, and solid project management practices, like communication planning and role definition, reduce the amount of conflict - Successful conflict management r esults in greater productivity and positive working relationships. When managed, differences of opinion can lead to increased creativity and better decision making - Conflict should be addressed early and usually in private, using a direct, collaborative approach. If disruptive conflict continues, formal procedures may be used, including disciplinary actions
- There are five general techniques in resolving the conflict: - Withdraw/avoid: Retreating from an actual or potential conflict situation; postponing the issue to be better prepared or to be resolved by others - Smooth/accommodate Emphasizing areas of agreement rather than areas of difference; conceding one’s position to the needs of others to maintain harmony and relationships. - Compromise/reconcile: Searching for solutions that bring some degree of satisfaction to all parties in order to temporarily or partially resolve the conflict. This approach occasionally results in a lose-lose situation. - Force/direct: Pushing one’s viewpoint at the expense of others; offering only win-lose solutions, usually enforced through a power position to resolve an emergency. This approach often results to a win-lose situation - Collaborate/problem solve: Incorporating multiple viewpoints and insights from differing perspectives, requires a cooperative attitude and open dialogue that typically leads to consensus and commitment. This approach can result in a win-win situation. - Decision making: Ability to negotiate and influence the organization and the project management team, rather than the set of tools described in the decision making tool set - Emotional Intelligence: Ability to identify, assess, and manage the personal emotions of oneself and other people. The team may use it to reduce tension and increase cooperation by identifying, assessing, and controlling the sentiments of project team members and follow up on their issues. - Influencing: Because project managers often have little or no direct authority over team members in a matrix environment, their ability to influence stakeholders on a timely basis is critical to project success. Key skills include (Ability to be persuasive, Articulate points and positions, Effective listening skills, Awareness in any situation and Gather information to address issues) - Leadership: Successful projects require leaders with strong leadership skills. Leadership is the ability to lead a team and inspire them to do their jobs well. It encompasses a wide range of skills, abilities and actions. Leadership is important through all phases of the project life cycle.
2- Project Management Information System (PMIS) - Includes (resource management scheduling software that can be used to managing and coordinating team members across the project activities)
Manage Team Outputs: 1- Change Requests - Example (Staffing changes whether made by choice or by uncontrollable events, can disrupt the project team. This disruption can cause the schedule to slip or the budget to be exceeded. Staffing changes include moving people to different assignments, outsourcing some of the work, or replacing team members who leave) 2- Project Management Plan Updates - Includes (Resource management plan, Schedule baseline, Cost baseline) 3- Project Documents Updates - Includes (Issue log, Lessons learned register and Project team assignments) 4- Enterprise Environmental Factors Updates - Includes (Input to organizational performance appraisals and Personnel skill)
Control Resources (Monitor & Controlling Process Group) Control Resources is the process of ensuring that the physical resources assigned and allocated to the project are available as planned, as well as monitoring the planned versus actual utilization of resources and taking corrective action as necessary Key benefit of this process is ensuring that the assigned resources are available to the project at the right time and in the right place and are released when no longer needed - Control Resources process should be performed continuously in all project phases and throughout the project life cycle - The resources needed for the project should be assigned and released at the right time, right place, and right amount for the project to continue without delays - The Control Resources process is concerned with physical resources such as equipment, materials and facilities. Team members are addressed in the Manage Team process. - Updating resource allocation requires knowing what actual resources have been used to date and what is still needed
Control Resources Inputs: 1- Project Management Plan - Includes (Resource management plan) 2- Project Documents - Includes (Issue log, Lessons learned register and physical resource assignments, Project schedule, Resource breakdown structure, Resource requirements and Risk register) 3- Work Performance Data - Contains data on project status such as the number and type of resources that have been used 4- Agreements - Agreements made within the context of the project are the basis for all resources external to the organization and should define procedures when new, unplanned resources are needed or when issues arise with the current resources 5- Organizational Process Assets
Control Resources Tools & Techniques: 1- Data Analysis - Alternative analysis: Alternatives can be analyzed to select the best resolution for correcting variances in resource utilization - Cost-benefit analysis: helps to determine the best corrective action in terms of cost in case of project deviations - Performance reviews: Performance reviews measure, compare, and analyze planned resource utilization to actual resource utilization. Cost and schedule work performance information can also be analyzed to help pinpoint issues that can influence resource utilization - Trend Analysis: As the project progresses, the project team may use trend analysis, based on current performance information, to determine the resources needed at upcoming stages of the project. Trend analysis examines project performance over time and can be used to determine whether performance is improving or deteriorating. 2- Problem Solving - Set of tools that helps the project manager to solve problems during the control resource process - The problem can be inside or outside the organization - The methodical steps to deal with a problem include (Identify the problem, Define the problem, Investigate, Analyze, Solve and Check the solution) 3- Interpersonal and Team Skills (Soft Skills) - Negotiation: Project manager may need to negotiate for additional physical resources, changes in physical resources, or costs associated with th e resources. - Influencing: Influencing can help the project manager solve problems and obtain the resources needed in a timely manner 4- Project Management Information System (PMIS) - Includes resource management scheduling software that can be used to monitor resource utilization
Control Resources Outputs: 1- Work Performance Information - includes information on how the project work is progressing by comparing resource requirements and resource allocation to resource utilization across the project activities. - This comparison can show gaps in resource availability that need to be addressed 2- Change Requests 3- Project Management Plan Updates - Includes (Resource management plan, Scheduling baseline and Cost baseline) 4- Project Documents Updates - Includes (Assumption log, Issue log, Lessons learned register, Physical resource assignments, Resource breakdown structure and Risk register)
PMBOK Formulas (14 Item/s)
Pmp - project management professional test (66 item/s), project management basics knowledge test (30 item/s), pmp- cram (161 item/s), pmp glossary (554 item/s), class 9 history map work: the french revolution, google analytics certification questions & answers, comptia a+ core certification: the basics of it hardware part 1 - basic cable types and their connectors, features, and purposes, pance exam: eyes, ears, nose, throat (eent) review questions & answers, national registry paramedic exam: gynecological emergencies, obstetrics, and newborn resuscitation.

250+ Top Skills To Find & Keep A Job

500+ Pages of Distilled Wisdom
250+ easy-to-follow guides 5000+ proven tips 13 types of essential skills the world's first & only encyclopedia of self help, self improvement & career advice, welcome to fatskills, join 4 million+ people from around the world who have taken our online quizzes to test & improve their basic knowledge of what they are studying..
❤ If you liked Fatskills , you can support us by checking out Tiny Skills - 250+ Top Work & Persoal Skills Made Easy Our mission is to help improve your scores in any subject and exam using 28500+ online quizzes, practice tests & study guides.
21.5k practice tests / practice exams and online quizzes. 1.85 million+ multiple choice test questions / practice questions 700+ subjects covering all test prep, competitive exams, certification exams, entrance exams, & school / college exams., about | explore | user guide | topics | subjects | career aptitude tests | community | resources | what should we know privacy | terms |, without work one finishes nothing. - ralph waldo emerson © the simple project 2024.
©2024 The Simple Project .
Project Resource Management
Locked lesson.
- Lesson resources Resources
- Quick reference Reference
About this lesson
The Resource Management processes provide guidance for managing the project team and the management and deployment of physical resources to support the project activities.
Exercise files
Download this lesson’s related exercise files.
Quick reference
The Resource Management processes provide guidance for managing the physical resources and the project team including the core team, extended team and any project staff.
When to use
Many of these processes will need to be used frequently throughout the lifecycle of the project. Different physical resources become available at different times during the project. Team members change, roles change, outside factors can influence internal team performance and relationships. If there are people involved (and there are always people involved) these processes apply.
Instructions
"Project Resource Management includes the processes to identify, acquire, and manage the resources needed for the successful completion of the project.” PMBOK ® Guide
These processes apply to physical resources such as facilities and equipment and to the project team and team issues. The project may use few physical resources and have a very small team who know each other well. The project may be controlling massive amounts of equipment and physical resources with a large multi-location, multi-cultural team that have never met each other before. In either case these processes should be used, but the amount of time and effort to achieve the process outputs and the number of tools and techniques needed may change dramatically. In some cases the project team, or a portion of it, may report directly to the project manager. In most cases, they do not. When that is the case, the value of these processes is heightened. Although it should go without saying, I will repeat it anyway. Ethical behavior is essential to maintain effectiveness with your project team. If they ever suspect you of lying, stealing, or cheating, it is virtually impossible to ever regain their confidence.
Project Resource Management Processes
There are four Project Human Resources Management Processes. They relate to each other as shown in the diagram below. The four processes are:
- 9.1 Plan Resource Management : “The process defining how to estimate, acquire, manage, and utilize physical and team resources.” PMBOK ® Guide
- 9.2 Estimate Activity Resources : “The process of estimating team resources and the type and quantity of material, equipment and supplies necessary to perform project work.” PMBOK ® Guide
- 9.3 Acquire Resources : “The process of obtaining team members, facilities, equipment, material, supplies and other resources necessary to complete project work.” PMBOK ® Guide
- 9.4 Develop Team : “The process of improving competencies, team member interaction, and overall team environment to enhance project performance.” PMBOK ® Guide
- 9.5 Manage Team : “The process of tracking team member performance, providing feedback, resolving issues, and managing team changes to optimize project performance.” PMBOK ® Guide
- 9.6 Control Resources : “The process of ensuring that the physical resources assigned and allocated to the project are available as planned as well as monitoring the planned versus actual use of the resources, and performing corrective action as necessary.” PMBOK ® Guide
Definitions are taken from the Glossary of the Project Management Institute, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, ( PMBOK ® Guide ) – Sixth Edition, Project Management Institute, Inc., 2017, Pages 698, 702, 705, 706, 710, 713, and 717. PMBOK is a registered mark of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
Project Team Management
There are many tools and techniques that can be used to assist the project manager in the management of the project team. One of the most commonly cited tools and techniques is Interpersonal and Team Skills. In addition to the personal interactions, the project manager will normally need to get the team working together. He or she can not do all the communication and interactions, the team will need to connect and function together. There are several techniques that are very useful to the management of the team interactions.
If the project has more than just three or four team members, you should plan on using a Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM), often referred to as a RACI matrix. In addition, as the team starts to work together it often goes through stages of team development interactions: Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing, and Adjourning.
Just as a side note, most project teams cycle back and forth between Storming and Norming, only occasionally getting to Performing. That is due to the temporary and unique nature of the project. Normally some of the team members have never worked together before, so they need to storm and then norm. Just about the time they get the teams “norms” worked out, a new team member joins, or the project moves to a new phase, the responsibilities change.
Which leads to the last tool I want to discuss. Teams often face conflict. When that occurs, first and foremost strive to keep it on a level of professional disagreement and not personal attacks. The Thomas Kilman Model is a great technique for determining a strategy to pursue to resolve the conflict. Just remember, projects may not have time to find the collaborative answer and will need to fall back to a compromise solution.
- 00:04 Hi, I'm Ray Sheen.
- 00:06 I'd now like to look at the project resource management knowledge area.
- 00:11 The project management body of knowledge, the PMBOK guide, defines this as
- 00:15 Project Resource Management includes the processes to identify, acquire, and
- 00:19 manage the resources needed for the successful completion of the project.
- 00:23 This project management process went through a significant overhaul with the of
- 00:28 the PMBOK.
- 00:28 It now includes the management of physical resources like equipment, facilities, and
- 00:33 raw material along with the management of the project team members.
- 00:37 The process must be exercised often as team members on a project team will
- 00:41 often change.
- 00:42 Some team members are only part time,
- 00:44 where an individual is being moved regularly from project to project.
- 00:47 Even if the team is stable, the team dynamics can change.
- 00:50 So the team leader needs to be watching for
- 00:52 signs of trouble throughout the project life cycle.
- 00:55 There are six project resource management processes.
- 00:58 The first one is to plan resource management.
- 01:01 This will create the resource management plan that contains policies and
- 01:04 procedures that the project will follow with respect to acquisition and management
- 01:08 of physical resources, and with respect to project team and staffing the project.
- 01:14 Another planning process is estimate activity resources, which determines which
- 01:18 resources are needed to complete each of the project activities.
- 01:22 Next is acquire resources.
- 01:24 This process is just what it says.
- 01:26 It's finding the people and physical resources needed for the project,
- 01:30 confirming their availability, and getting them onto the team.
- 01:34 Develop Team focuses on improving the competencies of team members
- 01:37 with respect to team behavior and project management activities.
- 01:41 This should lead to a project team that is working well together.
- 01:44 A third process focused on the team is manage team.
- 01:48 Teams will inevitably face conflict.
- 01:50 In addition, people may be joining or leaving the project, and
- 01:53 many people are over allocated which often leads to underperforming on the project.
- 01:58 The project manager must assess the team and individual performance and
- 02:02 take appropriate action to ensure the project's goal are met.
- 02:06 The last process is Control Resources.
- 02:08 This process focuses mostly on the physical resources to ensure that they
- 02:12 are being used in the appropriate manner and
- 02:14 taking corrective action when there are problems.
- 02:17 There are several techniques that the project manager can use to develop and
- 02:20 manage the project team.
- 02:22 One of these is the Responsibility Accountability Matrix,
- 02:25 sometimes called the RACI matrix.
- 02:28 It clarifies roles and responsibilities and
- 02:30 can assist the project manager when acquiring project team members
- 02:34 to ensure that they recruit someone with the needed skills.
- 02:37 The matrix has the WBS task on one side and the project team members on the other.
- 02:42 It then assigns specific roles for the appropriate individual on each task.
- 02:47 The assignment clarifies expectations for each team member.
- 02:51 The next technique is team building.
- 02:53 There are many approaches to team building, and
- 02:55 this is one of the more common ones used in project management.
- 02:58 A team goes through the stages of forming, storming, norming, performing, and
- 03:01 then adjourning.
- 03:03 A challenge of project teams is that the team members are often changing, and
- 03:07 as soon as the project team begins to work together through the forming, storming,
- 03:10 and norming stages, a new person joins the team or
- 03:13 someone leaves, and responsibilities change.
- 03:16 Then the project team drops back down and must start over.
- 03:20 The third technique is a framework for addressing conflict management.
- 03:23 There are number of different conflict management approaches.
- 03:26 I like the Skillmann model shown here, and it's referenced in the PMBO Guide.
- 03:30 Project teams will face conflict at some point.
- 03:33 I'm not saying that there will be yelling and screaming and fist fights.
- 03:36 But there will be different opinions on how a should be done, or
- 03:39 whether a result meets the requirements.
- 03:42 In this model, the manager should assess the situation and
- 03:44 choose an interaction strategy that best fits the needed outcome.
- 03:49 So let's take a look at how resource management processes interact
- 03:52 with each other.
- 03:53 We start with the Plan Resource Management process.
- 03:56 We see a familiar pattern.
- 03:58 This process creates a resource management plan
- 04:01 that is incorporated into the overall project management plan.
- 04:04 The project management plan is an input to all the other processes and
- 04:08 is an input back to this process.
- 04:10 In addition,
- 04:11 this process creates team charters, which are maintained as a project document.
- 04:15 Note this is not the project charter, this is a team charter and addresses how
- 04:20 the team members will interact during the conduct of the project.
- 04:24 The estimate activity resources process creates three of our project documents.
- 04:29 The resource requirements, basis of estimates, and
- 04:31 a resource breakdown structure,
- 04:33 which is a hierarchical organization of resources by categories or types.
- 04:38 Acquire resources also creates three project documents.
- 04:42 These are physical resource assignment, project team assignments, and
- 04:45 resource calendars.
- 04:47 All six of the processes will periodically provide project document updates and
- 04:52 acquire resources, develop team, manage team, and
- 04:56 control resources will provide updates back to the project management plan.
- 05:01 Of course, we need resources to do the work of the project.
- 05:05 And depending upon your available resources, this set of project management
- 05:09 processes will either be the easiest part of your job or your biggest headache.
Lesson notes are only available for subscribers.
PMI, PMP, CAPM and PMBOK are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
Twitter LinkedIn WhatsApp Email
How is your GoSkills experience?
Your feedback has been sent
© 2024 GoSkills Ltd. Skills for career advancement
- Recent Topics
- Forum Policy
TOPIC: Physical Resource Assignments (PMBOK section 9.3.3.1)
Physical resource assignments (pmbok section 9.3.3.1) 3 years 8 months ago #22394, physical resource assignments (pmbok section 9.3.3.1) 3 years 8 months ago #22399.
- Our Mission
- Our Partners
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Notice
- Corporate Project Management Training
- Group Discounts
- PM PrepCast Discount Coupon
- Scholarships
- Free PMP® Newsletter
- Free PMP® Questions
- Free PMI-ACP® Questions
- Free CAPM® Simulator
- Project Management Basics
- Mastering Business Analysis
- PMP® Exam Simulator
- PMP® Formulas
- PMI-ACP® Exam Training
- CAPM® Exam Training
- PMP® Exam Prep
- PrepCast PMP® Practice Exam
- Forgot your password?
- Forgot your username?
- Order The PM PrepCast
- PM PrepCast Product Details
- PMP Exam Agile Booster Course
- The PMP® Exam Simulator
- The PM Formulas
- The PM StudyCoach (recorded)
- The PM StudyCoach Guidebook
- The PM FlashCards
- All PMP® Products Overview
- PM Basics Course
- Corporate PMP Training
- Order the Agile PrepCast
- Agile PrepCast Product Details
- The ACP StudyCoach Guidebooks
- The PMI-ACP® Exam Simulator
- Corporate PMI-ACP Training
- Order The PM PrepCast for CAPM
- The PM PrepCast for CAPM®
- The CAPM® Exam Simulator
- 60 PMP PDUs - From The PM PrepCast
- 60 PMP PDUs - From The PDU Podcast
- 15 PMP Power Skills PDUs
- 17 PMP Leadership PDUs
- 30 PMI-ACP PDUs
- 17 PMI-ACP Leadership PDUs
- 15 CAPM PDUs
- 5 PDUs Business Analysis Course
- Artificial Intelligence for Project Managers
- Free PM PrepCast Training
- Free PM PrepCast Exam Simulator
- Free PMP® Practice Exam
- The Free PM PrepCast
- Free PMP® Exam Guides
- Free PMP® Exam Newsletter
- Free PMP® Webinars
- All Free PMP® Exam Resources...
- The Free Agile PrepCast
- Free PMI-ACP® Exam Newsletter
- All Free PMI-ACP® Exam Resources...
- Free CAPM® Exam Newsletter
- All Free PDU Resources...
- Explore Corporate Training Offers
- Unlocking Corporate Efficiency
- How PM Training Transform Businesses
- PM Training for Shifting Market Demands
- PM Training for Your Business
- Student Success with PMP Simulation
- PMP® Study Guide
- PMP® Certification Cost
- 35 Hours of Project Management Education
- Knowledge Areas & Process Groups
- How to Fill in the PMP Application
- PMP® Certification Exam
- How to get PMP Certification
- PMP® Exam Questions
- PMP® Certification Bangalore
- Failed PMP Exam
- PMI-ACP Certification Study Guide
- CAPM Certification Study Guide
- 12 Project Management Principles Explained by Experts
- Project Management Certifications Career Advancement
- PMP vs Certifications
- Project Management Organization Company Benefits
- Project Management Organizations Importance
- PM PrepCast Reviews
- PM PrepCast Reviews on Google
- PM Exam Simulator Reviews
- Agile PrepCast Reviews
- PMP® Exam Coaching Reviews
- Exam Prep Essentials eBook Reviews
- Add Your Review
- Student Profiles
- Successful Students
- PMP® Exam Discussion
- PMP® Exam Lessons Learned
- Free PMP® Exam Questions
- PMI-ACP® Exam Discussion
- PMI-ACP® Exam Lessons Learned
- CAPM® Exam Discussion
- CAPM® Exam Lessons Learned
- PDU Questions and Answers
- CIPP/E® Exam Discussion
- CIPP/E® Exam Lessons Learned
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Resource Requirements in Project Management: A Quick Guide

When a project is planned, a set of steps are outlined to deliver a product or service. Resource requirements need to be identified and allocated for those steps to be executed. Think of resource requirements as the fuel that drives all project activities.
Once one understands what resource requirements are in project management, next there is estimating what those resources will be and managing them. To help with this process, we’ll define resource requirements and link to a free resource plan template.
What Are Resource Requirements in Project Management?
Resources are anything you need to complete a project including teams, equipment, raw materials and so on. These are called the resource requirements. Being able to know ahead of initiating the project which resources you’ll need is essential.
Resource requirements in project management allow project managers to know what they’ll need to execute their tasks and deliver the project on time and within their budget. Knowing one’s resource requirements will also help project managers to get the most out of their resources.
This can be done more effectively with project management software. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software that allocates and schedules project resources through multiple views. Managers can use our robust Gantt charts to schedule resources and their costs. The sheet view gives you a customizable grid to track individual project resources or a portfolio of projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.
How to Estimate & Manage Project Resource Requirements
Resource requirements differ from project to project, of course, but also on how productive your team can be and even project switching, which is as team members pass tasks to one another. There’s also the feedback loop as comments or changes come from stakeholders, clients, etc. That’s a lot of variables. The following steps will help you narrow the forecast to be as accurate as possible.
1. Define Your Project Scope
The first step is to understand the scope of your project. That is knowing the project’s goals, deadlines and deliverables. There are many ways to determine the scope of a project. Using the project teams to mine their knowledge of the work and historical data can also play a role in estimating the project scope. More time-consuming, but accurate, is a work breakdown structure, or a hierarchical tree diagram that helps you to identify the project deliverables and tasks.
2. Write a Scope of Work
The scope of work is a project document that defines all the work that’s done over the project’s life cycle. That includes the project deliverables, timeline, milestones, how reporting will be done and more. The importance of this step goes beyond estimating your project resource requirements and helps manage them to avoid scope creep, such as adding tasks to the project during its execution. A scope of work document will help you have a more accurate idea of the project and, in so doing, its resource requirements.
3. Make a Resource Breakdown Structure
Just as you use a work breakdown structure to identify deliverables, a resource breakdown structure can help you identify the project resource requirements. It’ll help you to identify resource types, such as people and tangible and intangible assets before the start of the project. This will not only help estimate your resource requirements but also help with scheduling and managing them, such as resource allocation.
4. Estimate the Costs Related to Your Project Resources
Resources aren’t just team members, raw materials, equipment and so forth. It’s also money. One must consider costs when estimating and managing project resource requirements. This means you must forecast the cost for each resource that will be used in your project. This will also inform your budget. Accurately forecasting the related costs for your project resources helps to save money without negatively affecting the project quality of your deliverables.
5. Create a Resource Schedule
Identify resource requirements for the project and allocate them on a timeline to create a resource schedule . To do this, you’ll need to know the availability of your team members and the start and end dates of their assigned tasks. This will make your project more efficient and save money by having the right resources allocated at the right time.
6. Create a Resource Management Plan
The next step is to develop a resource management plan that details the acquisition, development, usage, management, control and release of the project resources. This will provide a guide or roadmap for the project manager and project team to allocate, manage and control resources needed to complete the project as efficiently as possible.
7. Use Resource Tracking Tools
Anyone who’s made a resource management plan knows that there will be changes during execution. Therefore, a project manager must use resource-tracking tools to monitor and control resource requirements. Whatever resource tracking tool you use should provide a clear view of where and how those resources are being used. This will enhance the resource management plan and allocation of those resources as you can adjust to respond to changes in your project.
Types of Resource Requirements in Project Management
We’ve mentioned resource requirements and have briefly written about what project resources are, but to better understand them and their place in project management it’s important to define what we’ve been talking about. Below we list the main categories that make up resource requirements in project management and define each with examples.
- Labor: These are the people who work on the project’s production and deliver its goods and services. They can be part-time or full-time employees and anyone on the project team with the various skills required to deliver the project.
- Materials: This is what’s used to assemble the product or in the creation of whatever deliverables are being made in the project. Included in this category are supplies and other consumable items, such as wood, metal, glue, etc.
- Equipment: Sometimes bunched together with materials in defining resource requirements, equipment is what machinery is used to complete the project on schedule . This can be tools or software and heavy machinery.
- Property, Land or Infrastructure: This is another category that some fold into equipment, but deserves its distinct definition. Here we’re talking about the place where the work is happening or the underlying framework of features of a system or organization. That might be the job site on a construction project or roadways, sewers, railways and powerlines.
- Cash/Funding: Lastly, are the financial resources that pay for the project. This includes the budget, funding sources and cost allocations.
Resource Requirements vs. Resource Constraints
Resource requirements, as noted above, are the people, materials and equipment necessary to complete the project. Resource constraints are factors that can limit the supply of those resources to the project. Therefore, resource requirements are what you want to complete the project and resource constraints are anything that might prevent that from happening.
Resource constraints are a kind of risk associated with the resources you have allocated to the project. It’s something you’ll have to factor in as you create your resource requirements plan. Some examples of a resource constraint include inadequate financial capital, unavailability of needed resources and a new deadline for completion of the project due to a request from the client.
Resource Plan Template
Identifying your resource requirements will inform your resource plan , which then lists and organizes those resources over the life cycle of your project. It also helps one determine the amount of resources and their cost.
Use our free resource plan template for Excel to schedule your resources. With it, you can list all your human resources, which department they work in, their total effort, rate and the cost of that resource for your project. There’s even a weekly calendar to schedule them.
More Free Resource Requirements Management Templates
The free resource plan template is only one of over 100 free project management templates for Excel and Word that you can download right now. They cover every aspect of managing a project across several industries. Here are a few that relate to resource requirements.
Work Breakdown Structure Template
A work breakdown structure (WBS) is essential in identifying all your resource requirements. Our free work breakdown structure template for Excel has two sheets. One is a WBS list that’s broken down into phases of the projects and the deliverables due, the other is a WBS tree diagram that visually shows the breakdown of the project deliverables from top to bottom.
Scope of Work Template
A scope of work document is also important when determining the resource requirements for a project. It includes deliverables, but also what’s in and out of scope for the project, a timeline, milestone and project costs.
Project Estimate Template
Another part of resource requirements is estimating their cost to the project. Our free project estimate template for Excel will help you make a more accurate forecast of those costs. With this free template, you can estimate labor costs, but also materials, for each phase in your project.

ProjectManager Helps You Manage Project Resource Requirements
While all of our free resource requirement templates can help you identify and plan your project resources, they’re not an efficient tool to manage and track them throughout the life cycle of your project. Templates are static documents that must be manually updated and are not great for collaboration. ProjectManager is award-winning project and portfolio management software that helps you track and allocate resources in real time.
Track Resource Utilization With Real-Time Dashboards
If you’re not monitoring your project resource requirements throughout the project, you’re in danger of going over budget or not having the resources you need when you need to allocate them. To optimize resource utilization, use our real-time dashboards , which track your costs, time, workload and more so you can catch issues and respond to them quickly to stay on schedule and keep to your budget.
Use Workload Charts to Allocate Resources Effectively
Teams are a project’s most valuable resource. Without a project team, no amount of raw materials, equipment, etc., will deliver your project. The ability to keep teams productive without eroding morale is critical to a successful project. First, you can set your team’s availability, such as vacation time, PTO and even global holidays for remote workers, which makes it easier to assign them to tasks. Then toggle over to the color-coded workload chart and balance their workload to keep them working at capacity.
Related Resource Management Content
Resource management is a topic much bigger than just resource requirements. If you’re interested in learning more about resources as they relate to project management our site is an online hub for that and much more. We publish weekly blogs, tutorial videos and, of course, free templates. Here are some of the pieces we’ve published on resource management.
- What Is Resource Optimization? Techniques & Best Practices
- Best Resource Management Software: Free & Paid Options Ranked
- 5 Must-Have Resource Management Tools
- Identifying and Overcoming Resource Constraints
- Resource Forecasting in Project Management: A Quick Guide
ProjectManager is online project and portfolio management software that connects teams in the office, out in the field and anywhere in between. They can share files, comment at the task level and stay updated with email and in-app notifications. Join teams at Avis, Nestle and Siemens who are using our software to deliver successful projects. Get started with ProjectManager today for free.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.

Project Resource Management

Managing the project resources is how the project manager spends most of their time. From ordering supplies, to training team members, to paying bills, the project resources are a seemingly bottomless pit of active management. Meanwhile, the project team is one of the most important components of project success – Having confidence that your team is going to get the job done right, on time, and under budget, is virtually priceless. This is included in the Project Management Body of Knowledge ( PMBOK ) Project Resource Management knowledge area.
The 6 processes in this knowledge area are:
Plan Resource Management
Estimate activity resources.

Develop Team
Manage team, control resources.
Before any project can proceed, the project resource requirements need to be defined. The main part of this initial planning step involves identifying the type and quantity of resources that are required, including people. Some resources have a grade or skill level associated with them, such as experience level of people, or size of crane. Job descriptions are created for the project team members. The Project Resource Management Plan, a component of the overall Project Management Plan , summarizes this resource planning step.
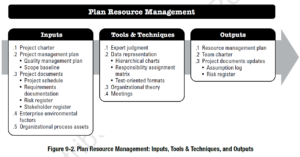
- Quality management plan
- Scope baseline
- Project schedule
- Requirements documentation
- Risk register
- Stakeholder register
- Enterprise environmental factors
- Organizational process assets
Tools & Techniques
- Expert judgment
- Hierarchical charts
- Responsibility assignment matrix
- Text-oriented formats
- Organizational theory
- Resource management plan
- Team charter
- Assumption log
The resources required to carry out the project must almost always be estimated during the planning stage. Resources are classified into type and quantity, as well as other factors that might affect the cost or schedule, such as grade, quality, availability, and so on. The three primary methods of estimating, Analogous, Parametric, and Three point, are used in conjunction with bottom up or top down estimating to determine the resource requirements.
- Activity attributes
- Activity list
- Cost estimates
- Resource calendars
- Bottom-up estimating
- Analogous estimating
- Parametric estimating
- Alternatives analysis
- Project management information system
- Resource requirements
- Basis of estimates
- Resource breakdown structure
- Lessons learned register
Acquire Resources
Once the project execution phase is underway, the resources identified in the Resource Management Plan must be acquired. The project schedule is consulted to determine when the resources are needed. The Procurement Management Plan, a separate component of the Project Management Plan, guides the purchasing process for tools and equipment that must be purchased. Project team positions are advertised and the workers are hired.
- Procurement management plan
- Cost baseline
- Multi-criteria decision analysis
- Negotiation
- Pre-assignment
- Virtual teams
- Physical resource assignments
- Project team assignments
- Change requests
- Enterprise environmental factors updates
- Organizational process assets updates
Most projects require additional knowledge to complete their deliverables. The project team must obtain this knowledge at the appropriate point in the project timeline. Unlike tools and equipment, project team members require rewarding work, future opportunities, and career development, or they will leave.
- Communication technology
- Conflict management
- Influencing
- Team building
- Recognition and rewards
- Individual and team assessments
- Team performance assessments
The project team is one of the most important components of project success (actually, any organization’s success). Project team assignments tend to change as team members learn different project tasks and project managers assess their strengths and weaknesses. Project issues need to be dealt with by the appropriate project team members, and project work needs to be actively managed.
- Work performance reports
- Decision making
- Emotional intelligence
- Schedule baseline
The project resources require regular, ongoing control procedures to ensure they are being used most efficiently, that they are performing the required tasks, and so on. The Resource Management Plan must be consulted regularly to ensure that project resource usage is according to plan. Cost-benefit analysis and alternatives analysis are utilized to optimize the use of resources.
- Work performance information
- Cost-benefit analysis
- Performance reviews
- Trend analysis
- Problem solving
Tutorial Navigation
- Previous Page: Project Quality Management
- Next Page: Project Communications Management
- Tutorial Home: PMP Exam Tutorial

- Project Initiation
- Project Planning
- Project Execution
- Monitoring and Controlling
- Project Closure
- Project Management Tutorial
- Project Scheduling Tutorial
- Earned Value Tutorial
- PMP Exam Tutorial
- Find Talent
- PRINCE2 Foundation
- PRINCE2 Practitioner
- PRINCE2 Professional
- IPMA Level A
- IPMA Level B
- IPMA Level C
- IPMA Level D
- Learning Videos
Certification
Recent posts.
- PMI Project Knowledge Areas, Intro
- PMI Project Knowledge Areas, Video 1: Project Integration
- Project Risk Checklist
- Creating a Risk Register
- 50 SMART Goals
- Reporting Earned Value
- Analogous Estimating
- Variance at Completion (Earned Value Analysis)
- TCPI (Earned Value Analysis)
FIND IT HERE
Subscibe to ProjectEngineer.NET channel – YouTube
- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Support Forums
- 04. Project Integration Management
- 05. Project Scope Management
- 06. Project Schedule Management
- 07. Project Cost Management
- 08. Project Quality Management
- 09. Project Resource Management
- 10. Project Communications Management
- 11. Project Risk Management
- 12. Project Procurement Management
- 13. Project Stakeholder Management
- 49 Processes in Project Management
- Comment Create task
9. Resource Management
9.1 plan resource management - planning process group.
The processes of defining how to estimate, acquire, manage, and utilize physical and tem resources.
- Project Charter
- Project Management Plan
- Project Documents
- Enterprise Environmental Factors
- Organizational Process Assets
- Expert Judgment
- Data Representation
- Organizational Theory
- Resource Management Plan
- Team Charter
- Project Documents Updates
9.2 Estimate Activity Resources - Planning Process Group
The process of estimating team resources and the type and quantities of material, equipment, and supplies necessary to perform project work
- Bottom-up Estimating
- Analogous Estimating
- Parametric Estimating
- Data Analysis
- Project Management Information Systems
- Resource Requirements
- Basis of Estimates
- Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
9.3 Acquire Resources - Execution Process Group
The process of obtaining team members, facilities, equipment, materials, supplies, and other resources necessary to complete the project
- Project Management plan
- Decision Making
- Interpersonal & team skills
- Pre-Assignment
- Virtual Teams
- Physical Resource Assignments
- Project Team Assignments
- Resource Calendars
- Change Requests
- Project Management Plan Updates
- Enterprise Environmental Factors Updates
9.4 Develop Team - Execution Process Group
Process of improving competencies, team member interaction, and the overall team environment to enhance project performance
- Communication Technology
- Interpersonal & Team Skills
- Recognition and Rewards
- Individual and Team Assessments
- Team Performance Assessments
- Project documents Updates
- Organizational Process Assets Updates
9.5 Manage Team - Execution Process Group
Tracking team member performance, providing feedback, resolving issues, and managing changes to optimize project performance
- Work Performance Reports
- Interpersonal and Team Skills
- Project Management Information System
- Project Management plan Updates
9.6 Control Resources - Monitoring & Control Process Group
Ensuring that the physical resources assigned and allocated to the project are available as planned, as well as monitoring the planned versus actual use of resources, and performing corrective action as needed.
- Work Performance Data
- Problem Solving
- Work Performance Information
Cancel Save
Move page to under this page
Contact us lovepmp.com
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you accept and understand our Privacy Policy .
9.6 Control Resources
by Nate Brummer | May 19, 2021
- Project management plan
- Resource management plan
- Project documents
- Lessons learned register
- Physical resource assignments
- Project schedule
- Resource breakdown structure
- Resource requirements
- Risk register
- Work performance data
- Organizational process assets
Tools & Techniques
- Data analysis
- Alternatives analysis
- Cost-benefit analysis
- Performance reviews
- Trend analysis
- Problem solving
- Interpersonal and team skills
- Negotiation
- Influencing
- Project mgt. information system
- Work performance information
- Change requests
- Project mgt. plan updates
- Schedule baseline
- Cost baseline
- Project document updates
- Assumption log
Account Settings
- Account Information

Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Introduction to PMP Certification
- PMP Exam – All You Need To Know Regarding PMP Certification
- Top 10 Reasons To Get PMP® Certified
- What is PMP®Certification? – All you need to know about PMP®
- PMP Certification – Become A Certified Project Management Professional®
PMBOK Guide 6
- PMBOK 6th Edition – 10 Knowledge Areas and 49 Processes
- PMP Exam Prep – Best Way to Prepare for PMP Certification Exam
Project Management Basics
- Project Management – Phases and Methodologies
- Project Management Life Cycle – Everything You Need to Know
- Project Management Tools – Helping Aids of Project Managers
- What is Gantt Chart in Project Management?
Knowledge Areas
- Top 10 Project Management Knowledge Areas (PMBOK)
- Project Integration Management – Know How To Integrate Processes
- Project Scope Management – Know How To Manage Project Efficiently
- Project Cost Management – Know How To Manage Your Budgets
- Project Time Management – How To Optimize Project Schedule
- Project Quality Management – How To Optimize Project Quality
What is Project Resource Management and How to Perform it?
- How To Remove Project Clutter Using Konmari?
- Project Communication Management – What Makes A Project Successful?
- Project Risk Management – Know How to Mitigate Risks
- What Is Project Procurement Management And How To Perform It?
- Learn how to Perform an Effective Project Stakeholder Management
PMP Interview Questions
Top 50 pmp exam questions and answers for 2024.
- Top 30+ Project Manager Interview Questions You Need to Know in 2024
Career Guidance
- Project Manager Salary: How Much Does A Project Manager Earn?
- How to Build an Impressive Project Manager Resume?
- What are the Project Manager Roles and Responsibilities?
- PMP vs PRINCE2 – Which Certification to Choose?
Project Management and Methodologies
In my previous articles, I have covered various aspects of Project Management . Since the project team and material resources are the main catalysts that drive a project toward success, thus it becomes very important to properly manage and utilize these resources. In this article, I would be specifically talking about Project Resource Management, how it is performed and what are the various processes involved in it.
Below are the topics that I will be covering in this Project Resource Management article:
What is Project Resource Management?
Resource management benefits, project resource management processes.
To master all the concepts of Project Management, you can check out our structured PMP Certification Training program, where you will be guided by the PMP certified instructors.
Let’s get started.
Project Resource Management is one of the ten Knowledge Areas of the project management framework that exclusively deals with the resources involved in a project . According to PMBOK ® Guide – Sixth Edition ,
To proceed with a project, it is very important to clearly identify and define the type and amount of resources required. Resource in project management is an umbrella term for physical resources and team resources that are required in order to complete the final deliverable. Physical resources include materials, equipment, facilities, and infrastructure whereas the team resources are human resources. For a project manager , it is very crucial to understand the distinction between the skills and competencies that are needed in order to manage both types of resources.
Project resource management ensures that the project is being executed in accord with the scope and overview that was defined during the planning phase. It also ensures that the right resources are in the right place for the right people at the right time. Not only this, resource management has many other benefits, about which I will be talking in the next section. Enrolling in a PRINCE2 course can significantly enhance your project resource management skills, ensuring successful project execution.
- Optimum Utilization of Resources: With a well-organized project resource management you can use your project resources to their full potential, maximizing their productivity while making sure that they do not feel overworked.
- Increases Revenue: With optimum utilization of resources and balanced workload, the efficiency of a project increases that in turn results in increased revenue and success of a project.
- Helps in Resolving Internal Conflicts: Resource management helps in resolving any kind of internal issues regarding the project resources whether be it human resources or physical resources. In project teams, internal conflicts are very important to resolve; else they may hamper in the project development.
- Avoids Unforeseen Obstacles: A structured resource management will help you in gaining insights into your resources upfront and help in planning how to use them, and troubleshoot gaps or hindrances beforehand.
- Enhances Employee Satisfaction: Project resource management also helps in clearly outlining the right compensation and benefits which ensures that the employees are happy and satisfied.
- Improves Employee Performance: Resource Management helps in defining the project resource requirements and thus recruiting the right resources from the very beginning of the project.
- Helps in Quality Training and Development: The project resource management team solely focuses on the development and growth of the project team. From time to time they organize assessments for determining what type of skills training and programmes are required for the development of the employees.
- Better Control of Budget: With effective resource management, you can easily avoid “overallocation” or “dependency” of resources which will give you better control over your project.
- Builds Transparency: It builds up a transparent framework from where other teams of your organization can see and analyze your team’s bandwidth, and thus help in deciding whether your team is working at their full potential and are available to take on new projects.
This knowledge area consists of six processes which are listed below along with their detailed explanation:
- Plan Resource Management
- Estimate Activity Resources
- Acquire Resources
- Develop Team
- Manage Team
- Control Resources
1. Plan Resource Management
Plan Resource Management is the first and the initial step of the project resource management Knowledge Area . It involves various aspects like defining the process of estimating, acquiring, managing and using physical and human resources. This process is usually performed only once or at few predefined points throughout the project lifecycle to help in establishing the way of approach and level of management required for managing resources. These aspects are majorly influenced by the type and complexity of the project.
This process consists of various inputs, tools & techniques and outputs which I have listed down in the below table:
2. Estimate Activity Resources
Once you are done with planning, the next process is Estimate Activity Resources. In this process, the resources required for the project along with their type and quantity of tools, equipment, raw material, and supplies are being estimated. This process is generally executed after specific time intervals throughout the project lifecycle . With this, you can pinpoint the what type of resources you need, in what amounts and what should be their characteristics in order to finish the project successfully.
There are various inputs, tools & techniques and outputs involved in this process that I have listed in the below table:
3. Acquire Resources
Acquire Resources is the third process of project resource management Knowledge Area that deals with collecting the various human resources, facilities, tools and equipment , supplies and raw materials required to deliver the project. This process helps in outlining and guiding the selection process of the project resources and then assigning them to their specific activities/tasks. Thus, it is performed at periodic intervals throughout the project lifecycle and helps in preventing running out of resources.
This process consists of various inputs, tools & techniques and outputs which I have listed in the below table:
4. Develop Team
Next process of this Knowledge Area is to Develop Team . As the name suggests, this process purely concentrates on the development of team bonding and assigning them with rewarding work, future opportunities, and career development. It helps in enhancing the overall team performance by improving team members competencies, interactions, and the environment. This process is performed throughout the project lifecycle and intensifies teamwork, improves interpersonal skills of the individuals, motivates the team and reduces attrition.
Develop Team process involves various inputs, tools & techniques and outputs that I have listed in the below table:
5. Manage Team
Since the project team is acquired and developed, the next step is to manage them. In this process, each and every team members performance is monitored and tracked, their problem areas are identified and the issues are resolved and feedbacks are given in order to optimize the project performance. This process is generally performed throughout the project lifecycle and helps in influencing team behavior, managing the conflicts and resolving brewing issues.
In the below table I have listed down the various inputs, tools & techniques and outputs that are involved in this process:
6. Control Resources
Control Resources is the final process of the project resource management Knowledge Area . In this process, the project managers ensure that the resources that are assigned and allocated for the project activities are available, monitor their estimated usage vs actual usage and subsequently take corrective actions to keep the project on track. This process is implemented throughout the project lifecycle and helps in ensuring that the necessary project resources are deployed to the correct places at the correct time and are released when the project comes to an end.
With this, we come to the end of this Project Resource Management article. There are 10 Knowledge Areas in the project management framework and Resource Management was just one of them. If you wish to learn more about project management framework or project management exam guide , you can check my other articles as well.
If you found this “Project Resource Management” article relevant, check out the PMP training India by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the globe.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of this Project Resource Management article, and we will get back to you.
Recommended videos for you
The agile way with pmi-acp-i, path to pmp : cracking project integration management – ii, path to pmp, the agile way with pmi-acp – ii, itil foundation : master the art of implementing it service management, introduction to pmp®, itil csi: the age of continual service improvement, path to pmp : cracking project integration management – i, the agile way with pmi-acp®, the agile way with pmi-acp, itil : master the art of implementing it service management – ii, meaning of six sigma: the industry-independent methodology, lean six sigma certification for starters, path to pmp- i, introduction to pmi-acp®, refresh and evaluate your readiness for pmp exam, a beginning to itsm, recommended blogs for you, monitoring and controlling project work, career prospects with pmp® certification, introduction to project quality management, introduction to agile certified practitioner (acp), project communication management: how to ensure success, agile project management – beginners guide to agile project management, scrum vs kanban: battle of the agile frameworks, introduction to agile domain areas, agile methodology and importance of pmi-acp®, pmi-acp® sample questions and answers in 2024, the 7 principles of prince2, themes and processes, project manager roles and responsibilities, what is itil® – one stop solution to it infrastructure library, understanding project selection and its importance, scrum master: what are the roles and responsibilities, top 20 project management tools in 2024, what is pmp certification – all you need to know about pmp® (project management professional) certification, servicenow itsm tools: adding social flavour to itsm, how to set up a project management office in your organization, join the discussion cancel reply, trending courses in project management and methodologies, pmp certification training course.
- 72k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
PRINCE2® Foundation & Practitioner Ce ...
- 12k Enrolled Learners
Certified Scrum Master® (CSM) Certificati ...
- 5k Enrolled Learners
Advanced Executive Certificate in Supply Chai ...
- 1k Enrolled Learners
Six Sigma Green Belt Certification Training
- 4k Enrolled Learners
Executive Development Programme in General Ma ...
Microsoft® project 2013 training.
- 3k Enrolled Learners
PMI® Agile Certified Practitioner Trainin ...
- 8k Enrolled Learners
Professional Scrum Master (PSM) Certification ...
Pmi-rmp® certification training course, browse categories, subscribe to our newsletter, and get personalized recommendations..
Already have an account? Sign in .
20,00,000 learners love us! Get personalised resources in your inbox.
At least 1 upper-case and 1 lower-case letter
Minimum 8 characters and Maximum 50 characters
We have recieved your contact details.
You will recieve an email from us shortly.
Project Resource Management
- First Online: 04 July 2018
Cite this chapter

- Paul Sanghera 2
3855 Accesses
The objectives covered in this chapter make up 8 percent of the CAPM exam, equivalent to about 11 questions. Study the whole chapter in detail.
- Estimate Activity Resources
- Resource Management Plan
- Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
- Manage Team Process
- Organizational Process Assets
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
San Francisco, California, USA
Paul Sanghera
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Paul Sanghera
About this chapter
Sanghera, P. (2019). Project Resource Management. In: CAPM® in Depth. Apress, Berkeley, CA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4842-3664-2_6
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4842-3664-2_6
Published : 04 July 2018
Publisher Name : Apress, Berkeley, CA
Print ISBN : 978-1-4842-3663-5
Online ISBN : 978-1-4842-3664-2
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0) Apress Access Books
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- REST API for Oracle Fusion Cloud Project Management
Expense Resource Assignments REST Endpoints

COMMENTS
Physical resources include equipments, supplies, materials and even locations. This output is basically the documentation confirming the assignment of all the physical resources which would be used in your project. 2. Project Team Assignments. As obvious as this is, the documentation of team members or human resources for your project, there is ...
The project resources require regular, ongoing control procedures to ensure they are being used most efficiently, that they are performing the required tasks, and so on. The Resource Management Plan must be consulted regularly to ensure that project resource usage is according to plan. Cost-benefit analysis and alternatives analysis are ...
1 CAPM Exam & PMP Exam Study Notes:Project Resource Management. 1.1 Overview of Resource Management. 1.2 Process #1: Plan Resource Management. 1.3 Process #2: Estimate Activity Resources. 1.4 Process #3: Acquire Resources. 1.5 Process #4: Develop Team. 1.6 Process #5: Manage Team.
Physical Resources are: Equipment, Materials, Supplies, Facilities, and Infrastructure that are utilized by your project, or become a part of your project deliverable. Physical Resources are different from Human Resources, which we discuss HERE The importance of good Physical Resource management is to ensure you have the right Physical Resources at the right place in the right time, in order ...
Remember that in the 6th Edition of the PMBOK® Guide, "resources" now covers two categories: both physical resources (material, equipment, supplies, locations) and human resources. 9.3.3 Acquire Resources: Outputs. 9.3.3.1 Physical Resource Assignments. Documentation of the physical resource assignments that will be used during the project.
1- Physical Resources Assignments - Documentation of the physical resource assignments records the material, equipment, supplies, locations, and other physical resources that will be used during the project. 2- Project Team Assignments - Documentation of team assignments records the team members and their roles and responsibilities for the project.
The resource breakdown structure (RBS) is a hierarchical structure of resource categories and types required to complete the activities of the project. The RBS can be used to identify and analyze the project team resource assignments and usage of physical resources. Updates to Project Documents.
ProjectManager is a robust project management software with Gantt charts, real-time dashboards and other resource management tools to help you monitor your project resources. Get started with ProjectManager today for free. ProjectManager helps you schedule and manage resources in real time. Learn more!
Download this lesson's related exercise files. Project Resource Management.docx. 64.2 KB Project Resource Management - Solution.docx. Project Quality Management. Project Communication Management. The Resource Management processes provide guidance for managing the project team and the management and deployment of physical resources to support ...
Please look on page 354 in the PMBOK, especially the point 9.6.1.2. Project Documents, at the third bullet, Physical resource assignments:`. "The physical resource assignments describe the expected resource utilization along with details such as types, amount, location and whether the resource is internal to the organization or outsourced".
A resource can be any kind of asset that helps complete a task. There are seven main types of resources in project management: services, labor, equipment, materials, money, time, and space. Each type has its own unique characteristics and must be effectively managed to ensure a successful project.
Resource Requirements in Project Management: A Quick Guide. When a project is planned, a set of steps are outlined to deliver a product or service. Resource requirements need to be identified and allocated for those steps to be executed. Think of resource requirements as the fuel that drives all project activities.
Project Resource Management. Managing the project resources is how the project manager spends most of their time. From ordering supplies, to training team members, to paying bills, the project resources are a seemingly bottomless pit of active management. Meanwhile, the project team is one of the most important components of project success ...
9.6 Control Resources - Monitoring & Control Process Group. Ensuring that the physical resources assigned and allocated to the project are available as planned, as well as monitoring the planned versus actual use of resources, and performing corrective action as needed. Inputs. Project Management Plan. Project Documents.
9.6 Control Resources. Control Resources is the process of ensuring that the physical resources assigned and allocated to the project are available as planned. This includes monitoring the planned vs. actual utilization of resources and taking corrective action as needed.
Executing a project requires resources, and executing a project successfully requires the optimal use of those resources. Therefore, coordinating and managing resources, including both human resources, also called team resources, and physical resources—i.e., material, equipment, facilities, and infrastructure—is an integral part of overall project execution.
Project staff assignments have dropped out. That leaves resource calendars and project management plan updates, plus some new ones. We have: Physical resource assignments: these relate to the non-people resources that you need for the project. Project team assignments: these relate to the people that you need for the project. You should also ...
Resources - " Project management plan Plan updates. . . . . • Resource management plan • Schedule baseline • Cost baseline Direct & Ma rage Project Work,.__.J 5-]] ... Physical resource assignments Project schedule Resource breakdown structure Resource requirements Risk register.
Summary. In the management of a construction project, the supervisor is responsible for the management of the resources that will be utilized to construct the project. The physical resources includes manpower; materials, tools and equipment; the construction site itself; dollars; and time. This chapter begins to develop an understanding of some ...
The process of ensuring that the physical resources assigned and allocated to the project are available as planned, as well as monitoring the planned versus actual utilization of resources and performing corrective action as necessary. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Plan resource management, Estimate Activity ...
3. Acquire Resources. Acquire Resources is the third process of project resource management Knowledge Area that deals with collecting the various human resources, facilities, tools and equipment, supplies and raw materials required to deliver the project.This process helps in outlining and guiding the selection process of the project resources and then assigning them to their specific ...
Build a resource plan and track resource dates. Create resource estimation including percentage allocation, hours, bill and cost rates, and amounts. Create project resource requests and track their assignments. Add resources to a project. Enable time tracking for resources. Control the project access for team members. Project Administrator
resources—and physical resources—i.e., material, equipment, facilities, and infrastructure—is an integral part of overall project execution. Identifying, acquiring, and managing these resources is called resource management. During project planning, you define roles and assign responsibilities to those roles, as
Resource requirements. Resource calendars. Enterprise environmental factors. Existing information on organizational resources. Marketplace conditions. Organizational structure. Geographic locations. Organizational process assets. Policies and procedures for acquiring, allocating, and assigning resources to the project.
Expense Resource Assignments REST Endpoints. An object that includes the attributes that are used to store values while creating or updating expense resource assignments for a project task. For example, hotel expenses can be planned on a project task. Last Updated April 2024 You can use Oracle REST APIs to view and manage data stored in Oracle ...