- Contact sales
Start free trial

Top 10 Project Management Methodologies: An Overview

Table of Contents
- Waterfall Methodology
- Agile Methodology
- Scrum Methodology
- PMI / PMBOK
- Critical Path Method (CPM)
- Kanban Methodology
- Extreme Programming (XP)
- Lean Methodology
What Is a Project Management Methodology?
A project management methodology is a set of principles, tools and techniques that are used to plan, execute and manage projects. Project management methodologies help project managers lead team members and manage work while facilitating team collaboration.
There are many different project management methodologies, and they all have pros and cons. Some of them work better in particular industries or projects , so you’ll need to learn about project management methodologies to decide which one works best for you.
We’ll go through some of the most popular project management methodologies, which are applied in many sectors such as software development, R&D and product development.
Top 10 Project Management Methodologies
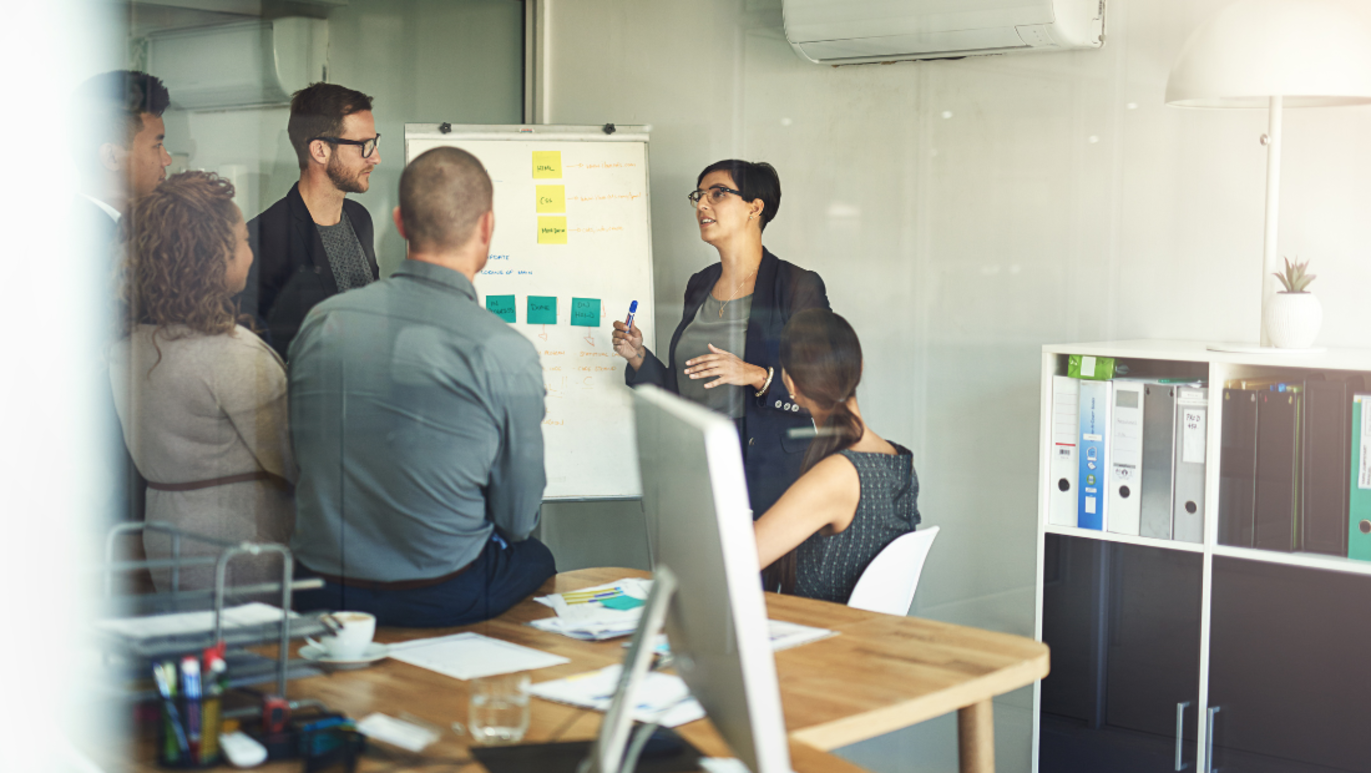
If you manage projects, you need to learn about project management methodologies. Here’s a quick overview of the most commonly used project management methods that you can use.
1. Waterfall Methodology
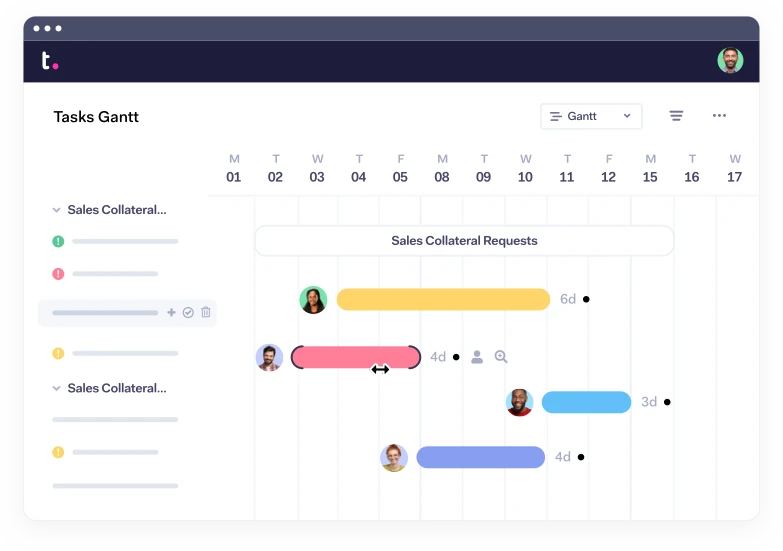
This may be the most straightforward and linear of all the project management methods in this list, as well as the most traditional approach. The name is apt, as the waterfall methodology is a process in which the phases of the project flow downward. The waterfall model requires that you move from one project phase to another only once that phase has been successfully completed.
When to use it: The waterfall approach is great for manufacturing and construction projects , which are highly structured, and when it’s too expensive to pivot or change anything after the fact. The waterfall method makes use of Gantt charts for planning and scheduling.
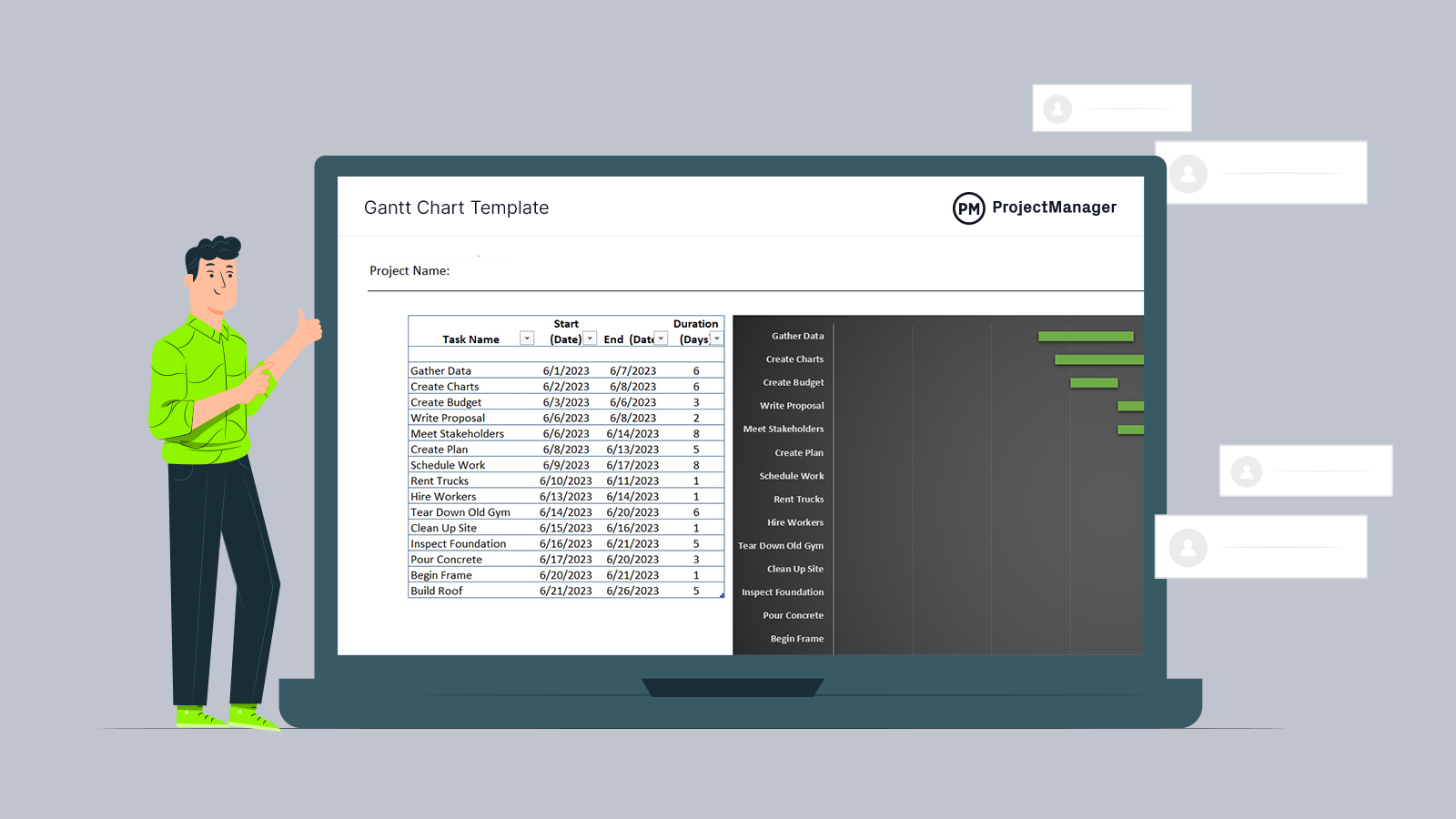
Get your free
Gantt Chart Template
Use this free Gantt Chart Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
2. Agile Methodology
What it is: In a nutshell, Agile project management is an evolving and collaborative way to self-organize across teams. When implementing the agile methodology , project planning and work management are adaptive, evolutionary in development, seeking early delivery and are always open to change if that leads to process improvement. It’s fast and flexible, unlike waterfall project management.
The agile methodology offers project teams a very dynamic way to work and collaborate and that’s why it is a very popular project management methodology for product and software development. That’s because what we think of as agile really appeared in 2001 with the publication of the “Manifesto for Agile Software Development,” authored by 17 software developers.
When to use it: The practice originated in software development and works well in that culture. How do you know if agile is for you? It has been applied to non-software products that seek to drive forward with innovation and have a level of uncertainty, such as computers, motor vehicles, medical devices, food, clothing, music and more. It’s also being used in other types of projects that need a more responsive and fast-paced production schedule , such as marketing.
3. Scrum Methodology
What it is: Scrum is a short “sprint” approach to managing projects. The scrum methodology is It’s ideal for teams of no more than 10 people and often is wedded to two-week cycles with short daily meetings, known as daily scrum meetings . It’s led by what is called a scrum master . Scrum works within an agile project management framework, though there have been attempts to scale Scrum to fit larger organizations.
The term scrum was introduced in a “Harvard Business Review” article from 1986 by Hirotaka Takeuchi and Ikujiro Nonaka. It became a part of agile when Ken Schwaber and Mike Beedle wrote the book “Agile Software Development with Scrum” in 2001. Schwaber formed the Scrum Alliance in 2002, a certified scrum accreditation series. Schwaber left the Scrum Alliance in 2009 to start a parallel accreditation organization called Scrum.org.
When to use it: Like agile, the scrum methodology has been used predominantly in software development, but proponents note it is applicable across any industry or business, including retail logistics, event planning or any project that requires some flexibility. It does require strict scrum roles , however.
4. Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK)
What it is: This is the granddaddy of methodologies if it’s a methodology at all. The Project Management Institute (PMI) is a not-for-profit membership association, project management certification and standards organization.
This organization produces a book called the “Project Management Body of Knowledge” or PMBOK. The PMBOK provides definitions and guidelines for project planning, scheduling, executing and controlling. For example, the project management process groups describe the project life cycle, while the 10 project management knowledge areas explain how to manage a project.

When to use it: Almost any project can benefit from PMBOK, as all projects big and small are going to go through the various stages of the project life cycle outlined in the book. It’s a great way to keep everyone on the same page, so to speak, and offers a clear definition of how a project is managed.
The Project Management Institute it’s also the organization that grants various project management certifications such as the project management professional (PMP) certification, which is the gold standard among project managers and is recognized all over the world. PMBOK is a great traditional framework to run a project.
5. Critical Path Method (CPM)
What it is: In the critical path method (CPM), you build a model of the project, including all the activities listed in a work breakdown structure , the duration of those tasks, what if any task dependencies there are and marking off milestones to indicated larger phases of the project or points in which your project deliverables are due.
With this information, you can identify the longest sequence of tasks to finish the project, which is called the critical path. You’ll need to keep an eye on those tasks because if one of them is delayed, the whole project will be delayed.
The critical path method was developed in the late 1950s by Morgan R. Walker of DuPont and James E. Kelley, Jr., of Remington Rand. DuPont was already using a precursor of CPM as early as the 1940s, and it was applied to the Manhattan Project.
When to use it: CPM works better with smaller or mid-sized projects. The larger the project, the more difficult it can be to take all the data you need to diagram and make sense of it without project management software .
6. Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM)
What it is: In , you’re focusing on resources that you’ll be using to complete the project, such as teams, equipment, office space, etc. It’s a less technical method of project management that doesn’t put as much emphasis on task order or schedule , but rather on balancing resources and keeping them flexible.
First introduced in 1997, in the book “Critical Path” by Eliyahu M. Goldratt, it has been credited with making projects anywhere from 10-50% faster and/or cheaper.
When to use it: CCPM can be applied to both large and small companies, and for projects that include industries such as construction, software development and tech research and development.
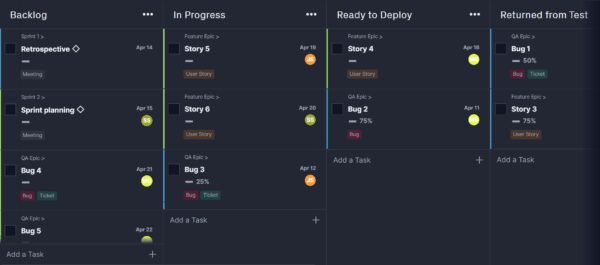
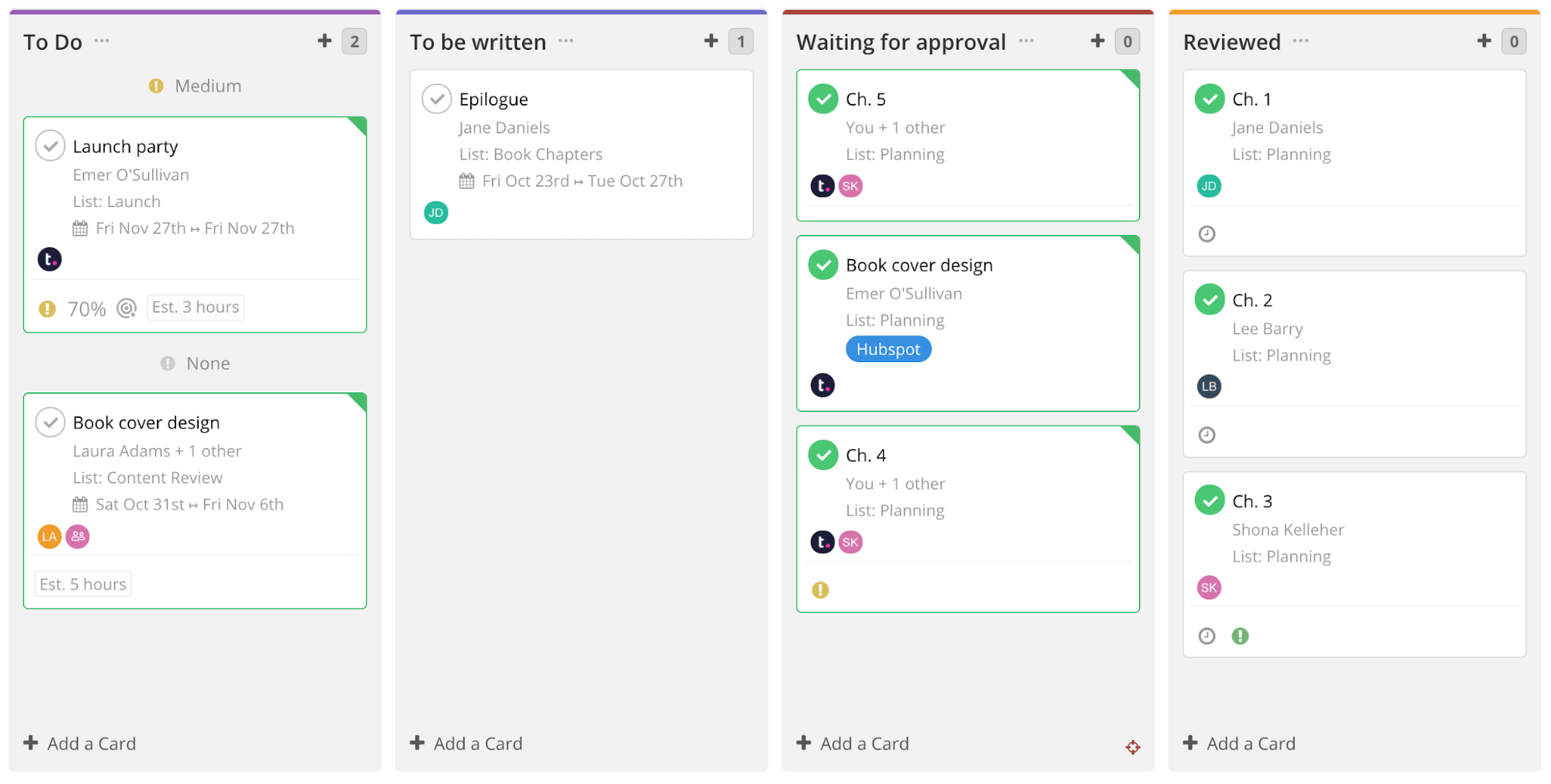
7. Kanban Methodology
What it is: The kanban methodology is a visual approach to project management. The name is literally billboard in Japanese. It helps manage workflow by placing tasks on a kanban board where workflow and progress are clear to all team members. The kanban methodology helps reduce inefficiencies and is a great project management tool for many purposes such as lean manufacturing or agile projects.
Kanban project management has been around since the late 1940s when it was studied by Toyota used the rate of demand to control the rate of production of its vehicles. The car company applied it to its lean manufacturing model, known as the Toyota production system.

With the dawn of visual planning boards in software in our era, like Trello, there are now new uses for kanban tools and kanban methods. Agile teams use kanban boards for story-boarding user stories and for backlog planning in software development.
When to use it: Another process developed initially for manufacturing and for software teams, the kanban method has since expanded and has been used in human resources, marketing, organizational strategy, executive process and accounts receivable and payable. Almost anyone can plan with Kanban boards, adding cards to represent project phases, task deadlines, people, ideas and more. Kanban software makes this methodology especially accessible.
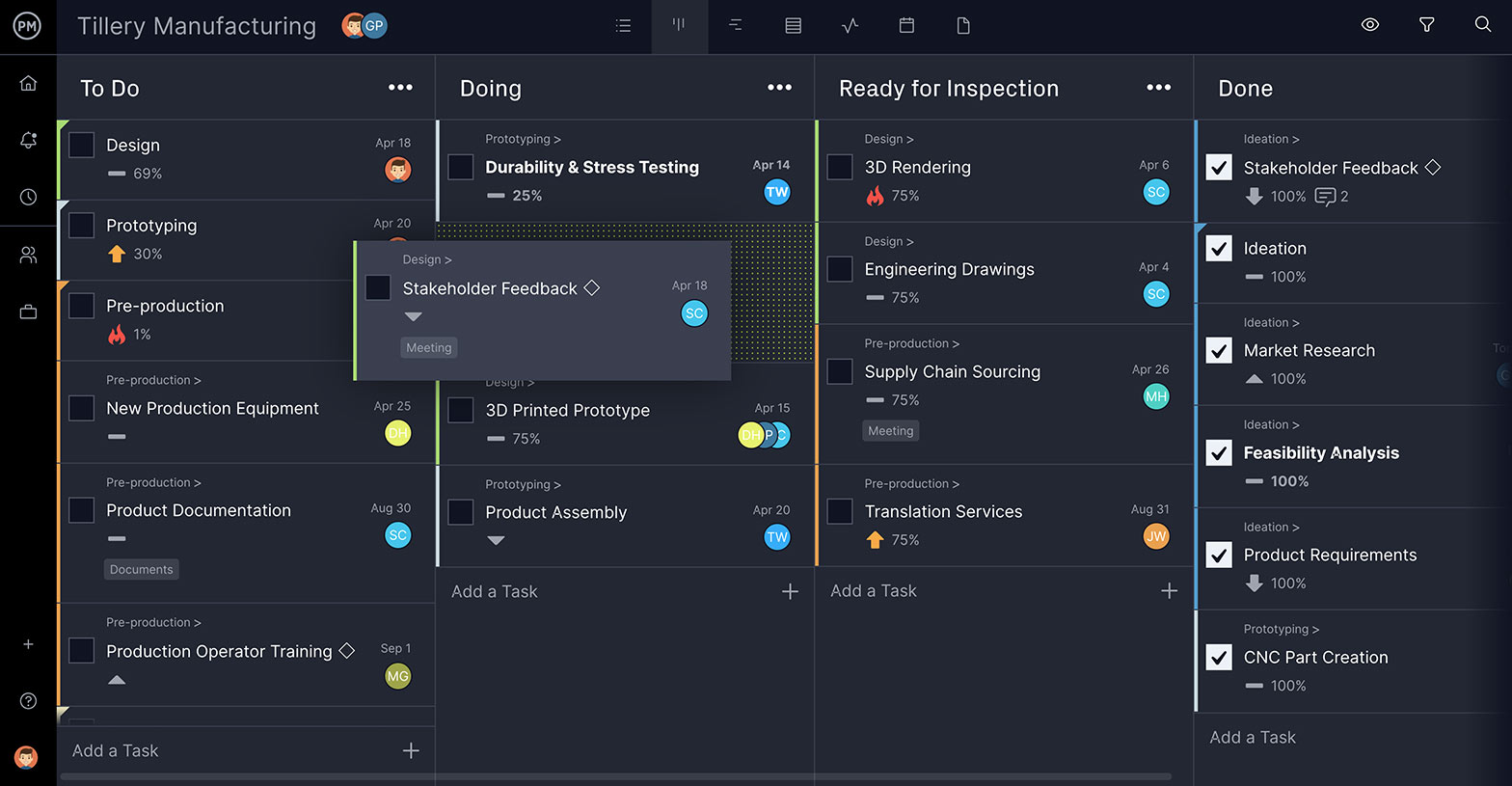
8. Extreme Programming (XP)
What it is: It sounds like some dangerous sport the kids are into, but in fact, XP is a type of agile software development with short development cycles and multiple releases to improve productivity. Customer requirements are sought and can adapt to the course of the project.
Created by Kent Beck while working on the Chrysler Comprehensive Compensation System payroll project, he literally wrote the book (“Extreme Programming Explained”) in 1999. But many of its practices have been around for a while.
When to use it: When requirements change frequently, then you’ll want to use a methodology such as XP. It’s good when your customer doesn’t have a clear idea of what they want.
9. Lean Methodology
What it is: Lean project management is what you’d think it is from its name: a way to cut waste and in so doing increase value in projects and manufacturing processes. So, lean focuses on eliminating waste from key processes to continuously be impacting positively on the value stream. It does this by optimizing separate technologies, assets and verticals.
Lean project management goes back to Henry Ford and his flow production for automating the process of building cars. Toyota picked up on the idea, as well, extending their idea beyond manufacturing to the continuous improvement of the product development process.
Today, software development teams run lean processes to focus on end-user feedback and increased value, which means Lean methodology has taken on a new meaning, particularly with the publishing of Lean Startup, by Eric Ries, who advocates for rapid prototyping, end-user feedback and early and rapid product delivery.
When to use it: Lean project management was first developed by Toyota and is obviously a great methodology for manufacturing. In fact, it’s also referred to as lean manufacturing , but it has been adopted by construction and education industries, among others in the manufacturing space and countless startups and software development firms looking to drive products focused on the end-user.
10. Six Sigma
What it is: Introduced by engineers working at Motorola in the mid-1980s, Six Sigma works to improve quality by identifying what is not working in the project. It applies quality management, including empirical statistics, and employs personnel who are experts in these disciplines. There is also a Lean Six Sigma that adds lean methodology to eliminate waste.
As a doctrine, it says that continued efforts to achieve results that are stable and expected are most important to success. Processes can be refined and improved. It takes the whole organization, from the top down, to sustain quality in a project.
When to use it: This methodology works best in larger organizations. Even companies with a few hundred employees are likely too small to take advantage of its benefits. It requires a certification to practice. Learn about six sigma certification here.
11. PRINCE2
What it is: PRINCE2 stands for Projects IN Controlled Environments and is a structured certified methodology. It was initially created by the UK government for IT projects. PRINCE2 is not like other traditional methods like waterfall, in that it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, but follows seven principles, themes and procedures.
When the UK government adopted standards for IT systems in 1989, they called in PRINCE. PRINCE2 came about in 1996 as a more general project management method. It is now a popular project management methodology throughout all UK governmental agencies and the United Nations.
When to use it: Adopted by many other countries’ governments, PRINCE2, so, as you can imagine, it’s not always suitable for smaller projects.
ProjectManager Works with Any Project Management Methodology
There are almost as many methods to manage as there are projects. But they all share one thing in common: getting deliverables done on time and within budget. No matter which project management methodology you choose ProjectManager is the one software you’ll need to do it.
Tools for Waterfall Project Management
Waterfall is structured. One thing follows the next and it’s all planned out. No problem. ProjectManager has an online Gantt chart . Import your task list to start a new project. Add due dates and the tasks populate a timeline. Link-dependent tasks to avoid bottlenecks. Set milestones to separate the project into phases. You control the project step by step.
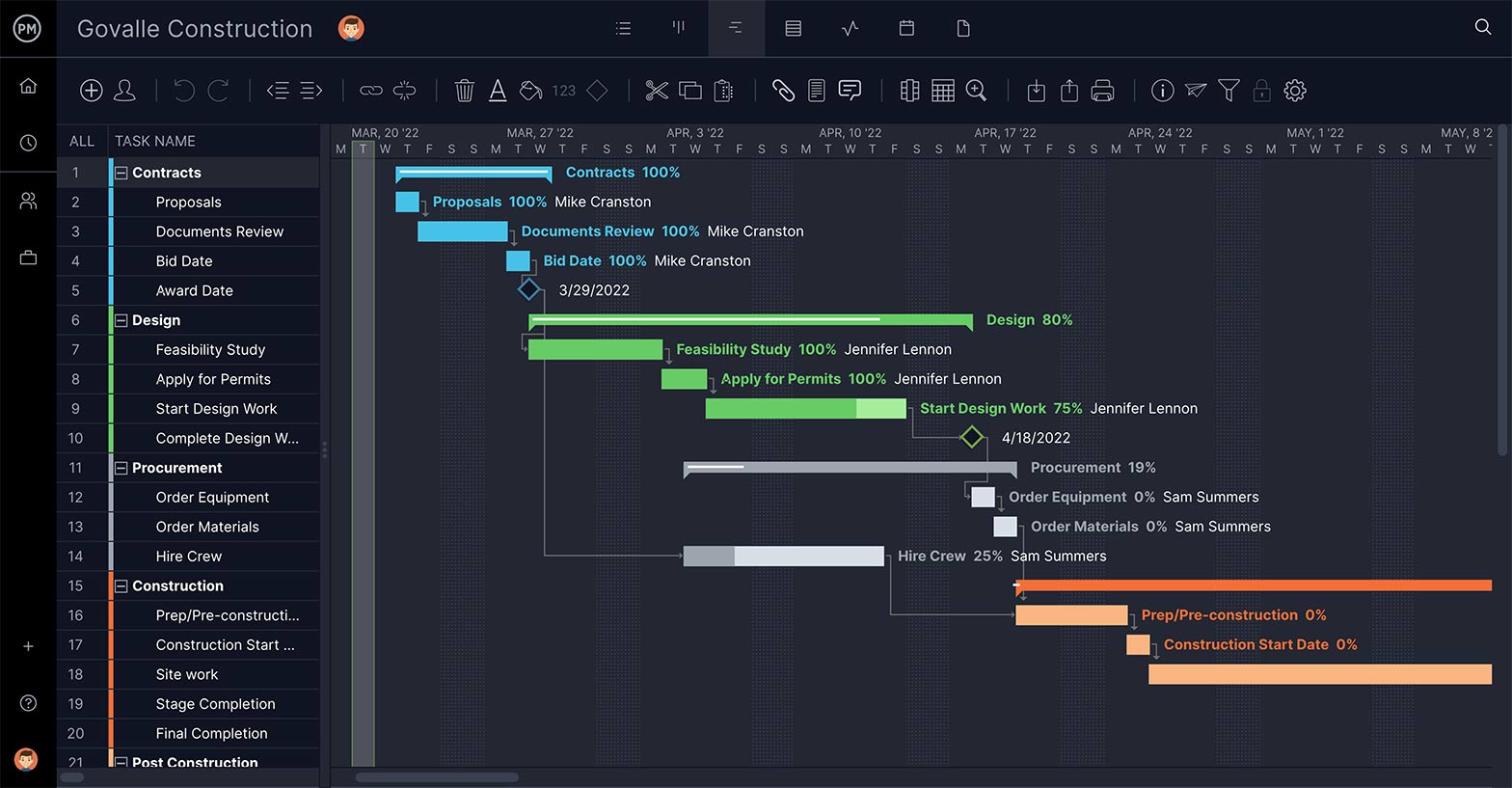
Tools for Agile Project Management
Gantt charts aren’t going to help as much as other project tools if you’re working in an agile framework. That’s true, but ProjectManager is flexible enough to serve scrum teams with multiple project views.
Use the kanban view to map out your sprint. Product backlogs are collected on cards, which can be prioritized for scrum teams to know which user story to work on first. Then the sprint can be archived, so when doing a sprint retrospective, teams can learn from their mistakes and improve the process.
Multiple Views for Diverse Teams
What if your organization is larger, with different divisions, some that work with an agile project management framework and others with a more traditional waterfall methodology? What’s great about ProjectManager is that it can switch from one view to the other, giving IT teams a kanban board view for their scrum sprints and managers a Gantt chart for a bigger project planning overview.
The real-time dashboard and reporting features gather the same data and crunch the same numbers, so whatever project management method you use is tracking the same results.
Yes, ProjectManager is an award-winning project management software for a reason. It’s flexible enough to work in an agile environment, traditional waterfall methodology or a hybrid of the two. You decide, not the software, which means ProjectManager is the one tool to bring in your project, however, you manage it, successfully.
Related Content
- Project Integration Management
- Waterfall Project Management Software
- Agile Project Management Software
- Critical Path Software
There are more project management methodologies, but these are some of the most popular. Regardless of which you use, you need a project management tool to best manage all your processes and projects. ProjectManager is an online PM tool, so whatever methodology is right for you our software will help you apply it to a successful end. Try it free for 30 days and see for yourself.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
- Jira Software
- Jira Work Management
- Jira Service Management
- Atlassian Access
- Company News
- Continuous Delivery
- Inside Atlassian
- IT Service Management
- Work Management
- Project Management

6 popular project management methodologies and what they’re best suited for
You’re a project manager who has just been tasked with managing two very different, yet intertwined projects. It’s up to you to choose the best project management methodology for each project.
One project is with your development team. They need to overhaul your organization’s website to improve the clunky and somewhat confusing user experience—from the moment that a customer lands on the site to after they make a purchase. The development team is super flexible and open to breaking up into smaller teams in order to tackle specific aspects of the website overhaul faster.
The catch with this project? It’s on a time crunch.
The website has to be overhauled before the launch of your second and longer-term project: a large-scale marketing campaign around a new line of products that are launching next quarter.
First of all, you can do this! Breath in, breath out, read on, choose the best project management methodology for each task, and get to work doing what you do best!
How To Choose The Best Project Management Methodology
No two projects are alike.
Some may remind you of a past project (that you absolutely nailed, by the way!) but there’s always a catch, isn’t there? One project may have unlimited budgets, endless resources, and flexible timelines—a walk in the park for you—, while another may have high stakeholder expectations, limited budget, tight timelines, multiple teams, and dozens of dependencies.
Since every project is so different, there are many project management methodologies to choose from that support the various project and team needs. There are so many methodologies, in fact, that new ones may have emerged while you’re reading this!
What Is A Project Management Methodology?
Glad you asked. Methodologies are the systems (or simply, methods) used to do something.
The Project Management Institute defined it as “a system of practices, techniques, procedures, and rules used by those who work in a discipline.”
Choosing the right methodology , as well as project management tools and teams, will set you up for success before your project kicks off. For example, you wouldn’t pick a fast-paced, quick iteration project management methodology for a long-term, large-scale, inflexible, and stakeholder-heavy project. Pair like projects with like systems.
To do that, let’s look at your project factors or considerations, such as constraints and dependents.
What Project Factors Are You Working With?
As mentioned earlier, there are many considerations at play that make each project unique. Some factors to consider what you’re evaluating your project management methodologies include:
- Project budget: How much money is going to be spent on this project? How is it divided up?
- Timeline: When is your project due by?
- Goals: What are the project’s end goals and deliverables? Start there and work backward.
- Values: How do your organizational goals and values apply to this project? Knowing this will help set expectations (and help you hold team members accountable for their commitments ).
- Complexity and Scale: How complex or simple is this project?
- Flexibility: How flexible or rigid is this project and its end goals, timelines, deliverables, and team or stakeholder expectations?
- Project type and industry: Some methodologies work best for certain industries and project types, such as highly creative projects or product development sprints.
- Team: Consider the team size, diversity, flexibility, experience, and individual expertise or strengths and weaknesses, as well as their ability to collaborate and communicate when choosing a methodology.
6 Popular Project Management Methodologies And What They’re Best Suited For
It’s important to learn the similarities and differences of various methodologies available to you. For example, some project management methodologies work best if the end goal is fixed and clear, such as the Waterfall method, whereas others better suit those projects that aren’t, such as Agile and Scrum. Keep your project factors in mind while you read on—and then choose the best method for your team.
Let’s get to the methodologies.
1. Agile: Flexible, Fast, And Short Collaborative Sprint Projects
More than a methodology, agile is a set of principles that would be ideal to follow for your first (hypothetical) project.
Agile is made up of fundamental values that are ideal for small teams to work in short and fast project cycles or sprints without blockers. Blockers include too much documentation, work in progress, meetings, or processes to slow them down. The working team would need to be protected from these blockers so that they can stay focused on the tasks at hand.
Teams who work well together can collaborate on small tasks and adapt and respond to an ever-changing task list. Because agile is an iterative design and build process, teams must be flexible with the outcomes and the path they take to get there.
2. Scrum: Quick And Continuous Development Projects
If agile is a set of principles that teams follow to work quickly and respond adaptively to changes as they arise, then Scrum is a project management methodology and the most popular and simple framework that puts agile principles to use.
Scrum is an ideal methodology for your project with the development team to overhaul the website. It’s ideal for continuous improvement and rolling task lists. Something like improving the customer journey on a website may have a timeline, but will always have room for improvement—especially as customer expectations and the digital space change so quickly.
The goal of Scrum is to develop, build, deliver, and sustain complex products using small collaborative and highly accountable teams and iterative task lists. There are roles, events, and artifacts. Roles include a product owner, development team, and scrum master, while events include sprints, daily scrums, or standup meetings, and artifacts include product and sprint backlogs.
3. Kanban: Visualize Task Progress For Agile Teams
Like Scrum, Kanban is another product management methodology that follows agile principles. Kanban is ideal for projects that are done by small, flexible, and collaborative teams, like Scrum, but there is a highly visual aspect as well.
Tasks are visually displayed in-person on sticky notes or in software such as Trello using columns as they progress. This is called a Kanban board. Tasks move from a backlog through the board’s columns that represent various stages of the process from the backlog, start to finish.

Having a visual representation of backlogged work, work in progress, and completed tasks is a great project management tool for most projects.
This would also be helpful for your second project, in particular, to keep track of tasks’ status as they move throughout the creative process. For example, designing a webpage for the new line of products will have various steps and creative team members involved. Visually seeing how the project is progressing will help you and the team to see how it’s coming along and where blockers are.
4. Lean: Projects That Do More With Less
For those organizations that are looking to transform how they do business, the lean methodology may be one to consider. Lean aims to maximize customer value and minimize waste. This is a great way to put out quality work while increasing efficiencies that minimize unnecessary spending, resources, teams output, or time.
Lean was created in the Japanese manufacturing industry to improve quality control and remove redundancies that may increase the price or value for customers down the line.
Known as the three M’s, Lean methodology defines three types of project waste: muda, mura, and muri.
- Muda is about getting rid of the waste or anything that doesn’t add value.
- Mura streamlines processes, so if one aspect of the project takes too long, for instance, then something further down the task list will have to be completed faster.
- Muri is about removing blockers, such as too many stakeholder meetings.
5. Waterfall: Large-Scale, End-Goal Focused, And Fixed Projects
Tried, tested, and true, the Waterfall methodology has been around since the 1970s. Like a waterfall that cascades downhill, this method is sequential with ordered tasks following one after another as they are completed.
The Waterfall method requires a very solid understanding of the end goal and the necessary steps to get there. As such, it doesn’t leave much room for errors or flexibility. This is great for projects that you’ve done in the past where there is minimal need to adapt on the fly.
This could be something to consider for your large-scale marketing project if you’ve launched new product lines many times in the past and don’t expect any surprises.
With this method, collect and analyze any and all project requirements and deadlines. This requires a lot of up-front work and planning. Then design your approach to meet every stage and their deadline in sequence before reviewing it and putting it into action.
6. Hybrid: Flexible And Fast-Paced Projects With Structured Plans
If agile aims to move fast, adapt quickly, and be flexible, Waterfall is its polar opposite, with fixed deadlines, clear deliverables, and mapped-out categorized project plans.
Hybrid is a methodology that blends the two. Think of it as the best of both worlds. You get the structure and organization of planning milestones out and the flexibility and speed of agile workflows.
It takes the flexible and fast pace of agile principles and blends them with the structured goals and mapped out plans of Waterfall. Take a look at your project requirements, task list, deadlines, and goals. The hybrid methodology uses those as your guidelines, but when it comes to getting the work done, teams should work with some flexibility on rapid iterations.
May The Best Methodology Help You Deliver On Your Projects
There are many more methodologies to name and discuss—and picking the right one for your project can be tricky! In the end, however, it’s all about picking a system that works for you, your project, and your team.
Project management methodologies were created to help you deliver the best possible outcomes based on your project’s circumstances. Take your time to find what works best, try them out, and do a debrief with your team on what worked and what didn’t. If it wasn’t the right methodology for one project, it may be ideal for another—and now you’re armed with that much more knowledge and expertise.
Happy project planning!
Advice, stories, and expertise about work life today.
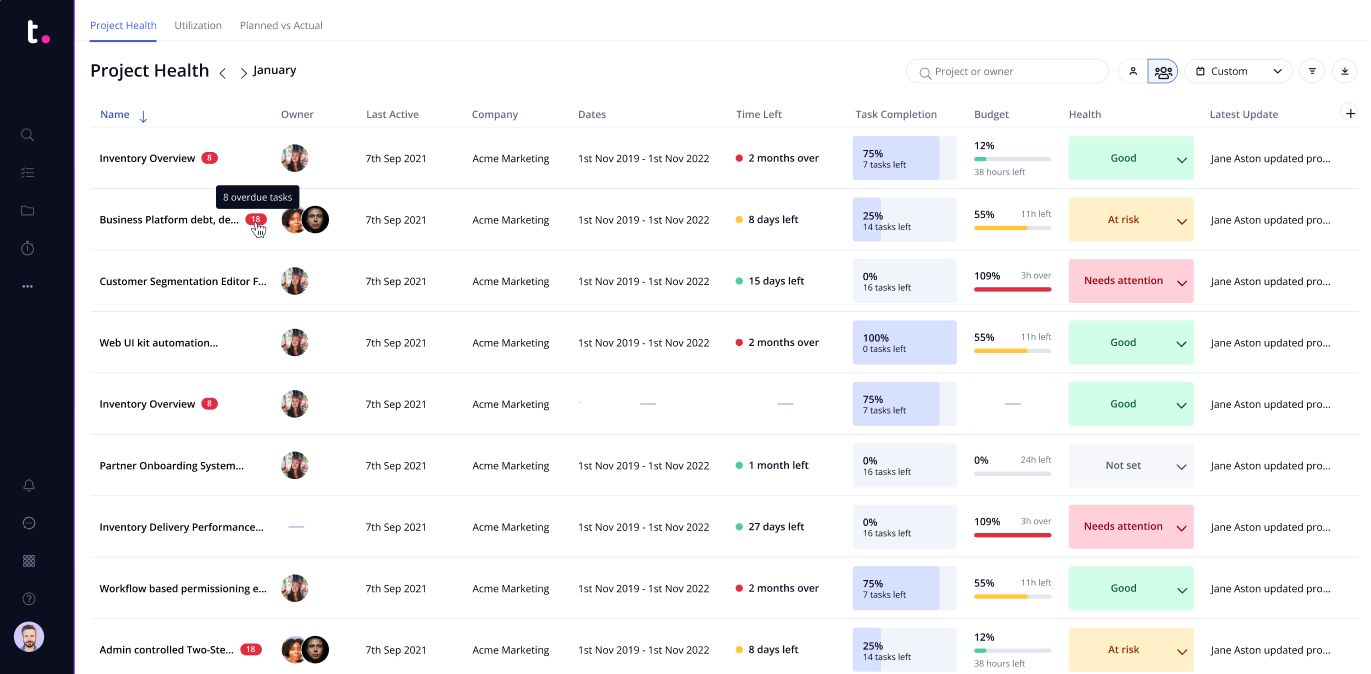
- Project Management Metrics
- Project Portfolio Management
- Proof of Concept Templates
- Punch List Templates
- Requirement Gathering Process
- Requirements Traceability Matrix
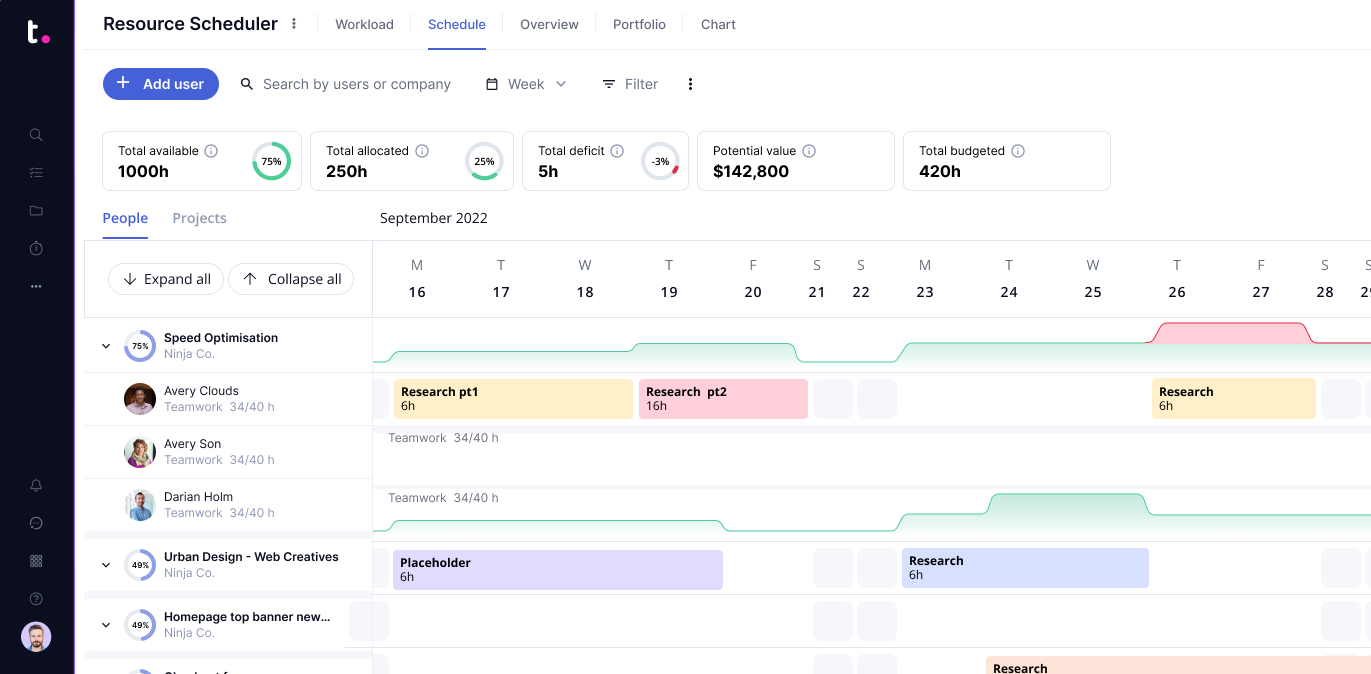
- Resource Scheduling
- Roles and Responsibilities Template
- Stakeholder Mapping
- Team Charter
- Templates for Managers
- What is Project Baseline
- Work Log Templates
- Workback Schedule
- Workload Management
- Work Breakdown Structures
- Agile Team Structure
- Avoding Scope Creep
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts
- Precision VS Accuracy
- Scrum-Spike
- Creating Project Charters
- Guide to Team Communication
- How to Prioritize Tasks
- Mastering RAID Logs
- Overcoming Analysis Paralysis
- Understanding RACI Model
- Eisenhower Matrix Guide
- Guide to Multi Project Management
- Procure-to-Pay Best Practices
- Procurement Management Plan Template to Boost Project Success
- Project Execution and Change Management
- Project Plan and Schedule Templates
- Resource Planning Templates for Smooth Project Execution
- Risk Management and Quality Management Plan Templates
- Risk Management in Software Engineering
- Stage Gate Process
- Stakeholder Management Planning
- Understanding the S-Curve
- Visualizing Your To-Do List
- 30-60-90 Day Plan
- Work Plan Template
- Weekly Planner Template
- Task Analysis Examples
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts for Planning
- Inventory Management Tecniques
- Inventory Templates
- Six Sigma DMAIC Method
- Visual Process Improvement
- Value Stream Mapping
- Creating a Workflow
- Fibonacci Scale Template
- Supply Chain Diagram
- Kaizen Method
- Procurement Process Flow Chart
- UML Activity Diagrams
- Class Diagrams & their Relationships
- Visualize flowcharts for software
- Wire-Frame Benefits
- Applications of UML
- Selecting UML Diagrams
- Create Sequence Diagrams Online
- Activity Diagram Tool
- Archimate Tool
- Class Diagram Tool
- Graphic Organizers
- Social Work Assessment Tools
- Using KWL Charts to Boost Learning
- Editable Timeline Templates
- Guides & Best Practices
- Kinship Diagram Guide
- Graphic Organizers for Teachers & Students
- Visual Documentation Techniques
- Visual Tool for Visual Documentation
- Visualizing a Dichotomous Key
- 5 W's Chart
- Circular Flow Diagram Maker
- Cladogram Maker
- Comic Strip Maker
- Course Design Template
- AI Buyer Persona
- AI Data Visualization
- AI Diagrams
- AI Project Management
- AI SWOT Analysis
- Best AI Templates
- Brainstorming AI
- Pros & Cons of AI
- AI for Business Strategy
- Using AI for Business Plan
- AI for HR Teams
- BPMN Symbols
- BPMN vs UML
- Business Process Analysis
- Business Process Modeling
- Capacity Planning Guide
- Case Management Process
- How to Avoid Bottlenecks in Processes
- Innovation Management Process
- Project vs Process
- Solve Customer Problems
- Startup Templates
- Streamline Purchase Order Process
- What is BPMN
- Approval Process
- Employee Exit Process
- Iterative Process
- Process Documentation
- Process Improvement Ideas
- Risk Assessment Process
- Tiger Teams
- Work Instruction Templates
- Workflow Vs. Process
- Process Mapping
- Business Process Reengineering
- Meddic Sales Process
- SIPOC Diagram
- What is Business Process Management
- Process Mapping Software
- Business Analysis Tool
- Business Capability Map
- Decision Making Tools and Techniques
- Operating Model Canvas
- Mobile App Planning
- Product Development Guide
- Product Roadmap
- Timeline Diagrams
- Visualize User Flow
- Sequence Diagrams
- Flowchart Maker
- Online Class Diagram Tool
- Organizational Chart Maker
- Mind Map Maker
- Retro Software
- Agile Project Charter
- Critical Path Software
- Brainstorming Guide
- Brainstorming Tools
- Visual Tools for Brainstorming
- Brainstorming Content Ideas
- Brainstorming in Business
- Brainstorming Questions
- Brainstorming Rules
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Brainstorming Workshop
- Design Thinking and Brainstorming
- Divergent vs Convergent Thinking
- Group Brainstorming Strategies
- Group Creativity
- How to Make Virtual Brainstorming Fun and Effective
- Ideation Techniques
- Improving Brainstorming
- Marketing Brainstorming
- Rapid Brainstorming
- Reverse Brainstorming Challenges
- Reverse vs. Traditional Brainstorming
- What Comes After Brainstorming
- Flowchart Guide
- Spider Diagram Guide
- 5 Whys Template
- Assumption Grid Template
- Brainstorming Templates
- Brainwriting Template
- Innovation Techniques
- 50 Business Diagrams
- Business Model Canvas
- Change Control Process
- Change Management Process
- NOISE Analysis
- Profit & Loss Templates
- Scenario Planning
- Winning Brand Strategy
- Work Management Systems
- Developing Action Plans
- How to Write a Memo
- Improve Productivity & Efficiency
- Mastering Task Batching
- Monthly Budget Templates
- Top Down Vs. Bottom Up
- Weekly Schedule Templates
- Kaizen Principles
- Opportunity Mapping
- Strategic-Goals
- Strategy Mapping
- T Chart Guide
- Business Continuity Plan
- Developing Your MVP
- Incident Management
- Needs Assessment Process
- Product Development From Ideation to Launch
- Visualizing Competitive Landscape
- Communication Plan
- Graphic Organizer Creator
- Fault Tree Software
- Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
- Decision Matrix Template
- Communities of Practice
- Goal Setting for 2024
- Meeting Templates
- Meetings Participation
- Microsoft Teams Brainstorming
- Retrospective Guide
- Skip Level Meetings
- Visual Documentation Guide
- Weekly Meetings
- Affinity Diagrams
- Business Plan Presentation
- Post-Mortem Meetings
- Team Building Activities
- WBS Templates
- Online Whiteboard Tool
- Communications Plan Template
- Idea Board Online
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Genograms in Social Work Practice
- How to Conduct a Genogram Interview
- How to Make a Genogram
- Genogram Questions
- Genograms in Client Counseling
- Understanding Ecomaps
- Visual Research Data Analysis Methods
- House of Quality Template
- Customer Problem Statement Template
- Competitive Analysis Template
- Creating Operations Manual
- Knowledge Base
- Folder Structure Diagram
- Online Checklist Maker
- Lean Canvas Template
- Instructional Design Examples
- Genogram Maker
- Work From Home Guide
- Strategic Planning
- Employee Engagement Action Plan
- Huddle Board
- One-on-One Meeting Template
- Story Map Graphic Organizers
- Introduction to Your Workspace
- Managing Workspaces and Folders
- Adding Text
- Collaborative Content Management
- Creating and Editing Tables
- Adding Notes
- Introduction to Diagramming
- Using Shapes
- Using Freehand Tool
- Adding Images to the Canvas
- Accessing the Contextual Toolbar
- Using Connectors
- Working with Tables
- Working with Templates
- Working with Frames
- Using Notes
- Access Controls
- Exporting a Workspace
- Real-Time Collaboration
- Notifications
- Meet Creately VIZ
- Unleashing the Power of Collaborative Brainstorming
- Uncovering the potential of Retros for all teams
- Collaborative Apps in Microsoft Teams
- Hiring a Great Fit for Your Team
- Project Management Made Easy
- Cross-Corporate Information Radiators
- Creately 4.0 - Product Walkthrough
- What's New
Project Management Methodologies and Frameworks Every Project Manager Should Know

You might find yourself drowning in information, tools, and processes as a project manager. To stay afloat and thrive, you must choose the right project management methodologies and frameworks that suit your team and project needs.
Many different project management methodologies are available and deciding which one is right for you can be challenging. This article provides an overview of the most popular frameworks to get you started.
What is a Project Management Methodology?
A project management methodology is a set of principles, processes, guidelines, and tools that help to plan, manage, and control a project. The methodology helps to ensure that a project is on schedule, within budget, and that the project goals are met.
A project team or an organization uses a management framework to execute a project. The information generated is usually documented and shared with others. Recording the information is essential as it will help others understand the project requirements and responsibilities.
While most project management methodologies take a standardized approach, some are for specific purposes, i.e., manufacturing or software development.
Project Management Framework vs. Methodology
The terms framework and methodology are often used interchangeably in project management. However, there is a slight yet distinguishable difference between the two approaches.
A framework provides more flexibility and freedom. You can adopt new rules and change or remove existing ones as necessary. As such, a framework provides the structure and direction needed for a project without being too rigid or detailed.
On the other hand, a methodology is a set of principles and processes that guides the management of a project. It is a formal approach that is strictly defined and generally adheres to a strict code complete with steps and rules.
Another way to understand the two approaches is that most of the time, methodologies are for implementing ideas and values, while a framework provides a step-by-step guide to attain that idea or manage that project.
Project Life Cycle Processes
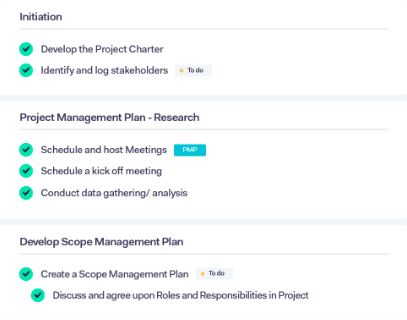
A project management framework includes the whole project management life cycle, which will guide you from the beginning to the end. In a project management life cycle , there are five steps:
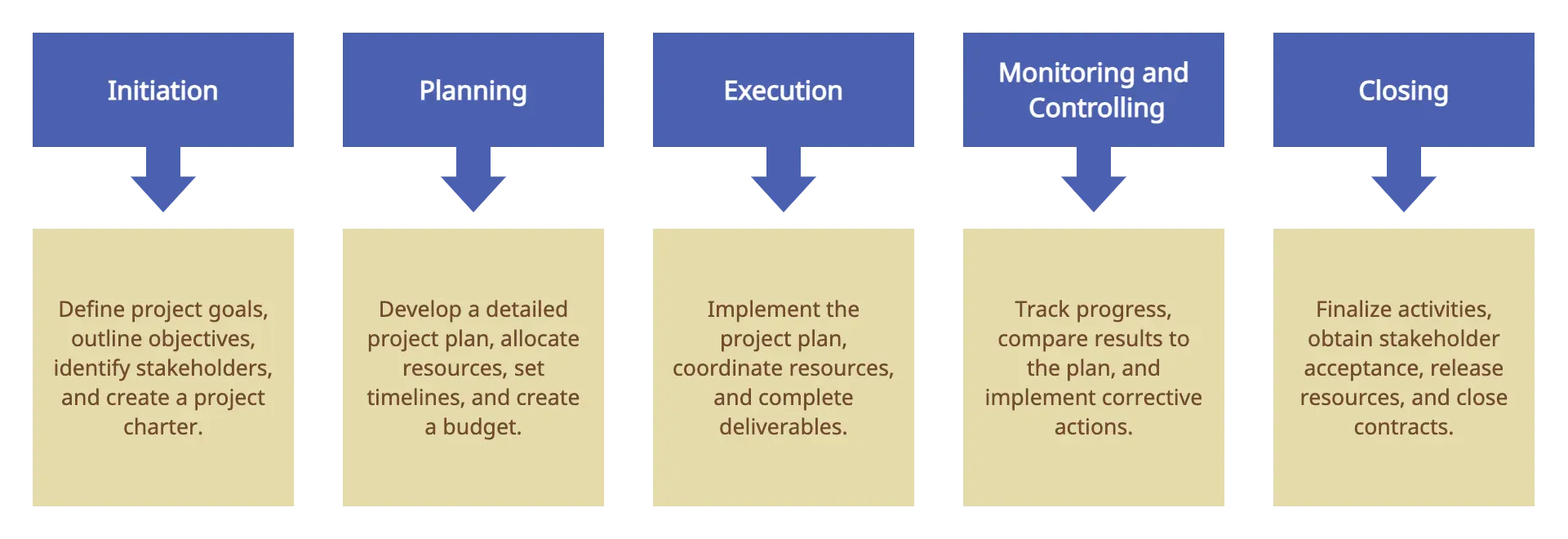
- Initiation : The beginning stage of the project, where the main focus is to narrow down the required key components to kickstart the project. Teams get together to research, brainstorm and conduct analysis and stakeholder mapping/interviews to gather information.
- Planning : Here, the teams and members working on the project are identified along with activities, milestones, risks, management structure, and success benchmarks.
- Execution : During this stage, the project kickstarts and is implemented.
- Management/Monitoring : At each milestone, the progress will be monitored, documented, and reported. Key progress and outputs will be shared with stakeholders as well.
- Review/Closing : This stage marks the end of the project. Project leaders and team members will review and analyze how the project progressed and setbacks to identify future improvements. Updates or replacements will be scheduled if necessary before wrapping up.
5 Key Project Management Methodologies and Frameworks
1. waterfall framework.
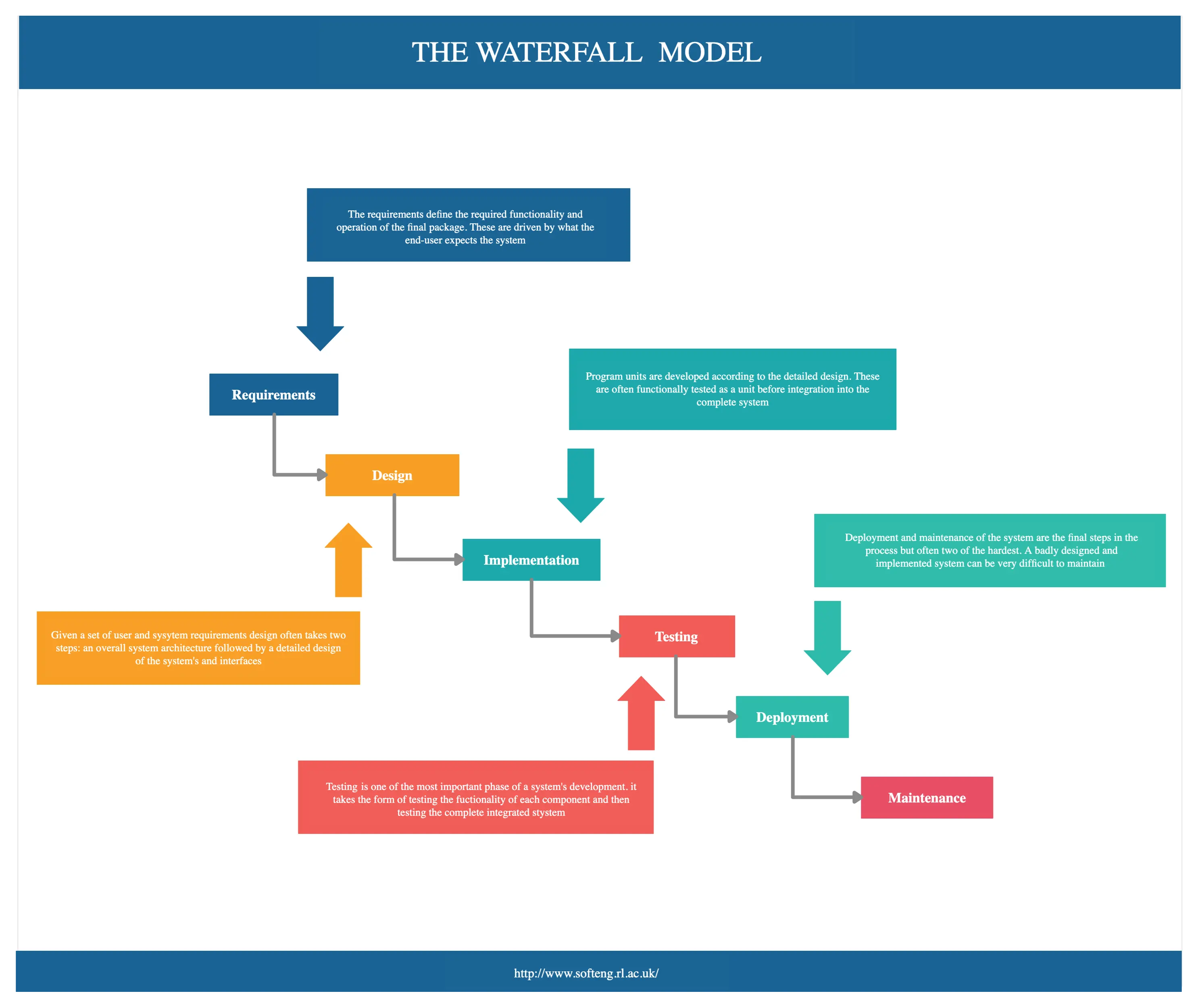
The Waterfall Framework is a linear approach that first gathers stakeholder and customer requirements before creating a sequential project plan to address the identified requirements. Consisting of five main stages, each stage is completed before progressing to the next–similar to a cascading waterfall.
The main stages of the waterfall framework are:
- Requirements : needs and requirements of the business/project are identified, analyzed, and documented.
- Design : possible solutions are explored before a detailed plan is made to achieve the goals.
- Implementation : the project plan and activities are set in motion along with progress measurements.
- Verification/Control : the product is reviewed, and the project plan is compared with the performance to address issues.
- Maintenance/Closure : the end result is shared with clients for feedback and final fixes. Approval is obtained before the project is closed.
- As project and client requirements are identified and agreed in the very first stage, it sets clear client expectations that are easier to plan.
- Extensive documentation ensures that each activity and task is well documented and that no knowledge is lost.
- The project schedule is laid out at the beginning stages. As such, project costs, deadlines, and other resources can be estimated accurately.
- Easier to measure and understand as you progress through each milestone one after the other.
Disadvantages
- Identifying all client/customer requirements at the very beginning is difficult.
- Changes to the product at the end stages are costly and difficult if the customer is unsatisfied.
- Lack of flexibility due to the linear nature of the framework, which provides minimal room for change and adaptation in case of unexpected events.
2. Lean Methodology
Lean methodology originated in the 1950s in Toyota and currently focuses on eliminating waste, maximizing value, and improving efficiencies. Many organizations have opted to adopt the Lean Framework as it can be applied to any business, regardless of size, to achieve objectives in a sustainable manner.
The two main guiding concepts in Lean are respect for people and continuous improvement. Accordingly, necessary training and tools are provided, constant improvement is encouraged, and management takes on a more active role in understanding and meeting the needs of employees to initiate better work performance.
Besides the above two concepts, lean has five core principles that support the methodology:
- Value : customer defines the value of the product offered.
- Value stream : a clear and in-depth understanding of the product’s life cycle from research to development. Each step of the value chain is analyzed to identify waste areas and improvements.
- Flow : every process should be in sync with one another, and the value stream should flow seamlessly.
- Pull : ensures that products are made only when required, leading to shorter delivery cycles and increased flexibility.
- Perfection : always strive for perfection by uncovering quality or waste issues and applying strict measures to address inefficiencies.
- The quality of products is high due to the constant attention to value.
- Reduced costs and increased profits as Lean focuses on providing value and minimizing waste.
- Improved customer relations as the focus is to deliver what the customer requires.
- Regular communications among employees, stakeholders and management pave the way for better decision-making.
- Emphasis on constant improvement leads to continuous learning opportunities.
- Organizations may focus too much on Lean principles that they lose sight of the bigger picture leading to a lack of strategy.
- If there are bottlenecks or resource issues, delivery can be delayed leading to unsatisfied customers.
3. Agile Methodology
Agile is often used in the software industry, though it has spilled into others recently due to its adaptability. It is an iterative approach that promotes collaboration among team members, emphasizing adaptive planning and early delivery of functional products. In an Agile project, development work is carried out in short-term periods called sprints, and the management focuses on continuous improvement throughout the project’s life cycle.
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

Popular frameowkrs such as Scrum and Kanban stem from Agile, which acts as an umbrella term that encompasses several different frameworks. To learn more about Scrum and Kanban, check out The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Scrum and How to Better Manage Your Projects with Kanban Boards .
The Agile Manifesto highlights four core principles that are the building blocks of any agile approach. They are:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
- Agile promotes smaller teams, making it easier to keep up the pace and quickly adapt to necessary changes, leading to faster response times and ample flexibility.
- Faster turnaround times due to the ability to quickly detect and provide solutions to issues.
- Low wastage and costs as tasks are always up-to-date with constant feedback and follow-ups, allowing developers to experiment and test ideas.
- Agile is practiced by many and has a considerable following. Therefore, you can always reach out for help and share knowledge with others if you run into trouble.
- Difficult to measure the progress as it is estimated across several cycles, which may take time.
- Documentation is not given prominence, leading to misunderstandings and difficulty for newer members to be up-to-date.
- At times, there is no clear end date; therefore, the overall project may seem to go on forever. This can also lead to scope changes beyond what was initially agreed (scope creep).
- Due to the short cycle times, the design thinking process may be stinted, leading to a lack of cohesion and fragmentation.
- Teams may tend to avoid key features that may take too long to deliver.
- The need for constant communication can take a toll on team members who have to spend extra energy and time.
4. Critical Chain Project Management Framework
Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) is a project management framework that helps the planning and managing of projects by monitoring the resources required to execute the project tasks. The framework helps project managers to deliver projects in a cost-effective and timely manner.
Buffers are safety margins that ensure all tasks are completed within schedule. CCPM identifies strategic points in the project and inserts buffers to ensure that project milestones are met on time, regardless of constraints or uncertainties. There are several types of buffers used in CCPM.
- Project buffers : this is positioned between the completion date of the project and the last task allowing team members to catch up on any outstanding tasks or delays.
- Feeding buffers : this is positioned between the non-critical chain and the critical chain to prevent delays.
- Resource buffers : resources that are kept aside in case of extra support in terms of resources are required.
- Team members tend to be more efficient and pace themselves rather than working more as the deadline approaches.
- Work is scheduled around resource availability, thereby optimizing resource utilization.
- The insertion of various buffers to address issues on time.
- The minimum time required to finish the project is taken into consideration.
- Major planning packages do not often support the framework.
- If the team does not understand the endpoint, many losses and setbacks could occur.
5. PRINCE2 Framework
PRINCE stands for “PRojects IN Controlled Environments” and is a process-based framework focused on organization and control. The framework started as PRINCE with a particular focus on the IT industry before expanding into others.
PRINCE2 details what each step of the project should look like, deliverables, roles, and responsibilities, and also structure each stage of the project with no loose ends at the point of completion.
- PRINCE2 is a good beginner framework to start project management as it has a defined process with clear steps.
- Due to the detailed and step-by-step guide provided, PRINCE2 is relatively easy to understand and follow. Furthermore, the ability to divide the project into manageable stages is helpful in managing the project.
- PRINCE2 is flexible in nature and can be easily adapted to suit different projects.
- Roles and responsibilities are clearly defined, which improves accountability.
- Lessons learned can be tracked and updated for future reference and improvements.
- PRINCE2 is not ideal for projects in fast-changing environments (i.e., technology-driven) due to the extensive documentation required.
- Requires the buy-in of the senior management for success.
- Requires experience to be managed and delivered successfully.
Key Steps to Follow when Selecting a Methodology or Framework
1. assess the project in terms of size and scope.
Size and scope play a significant role when selecting a suitable project methodology or framework. Some projects may be small, requiring a team of no more than 3-4 people and a short period. In contrast, others would be large, with multiple teams working together for several years.
Larger projects with several cross-functional teams and extended time frames would benefit from adaptive project management frameworks such as agile. In comparison, smaller projects that are less complex would do well with methodologies such as waterfall.
2. Look into the available project management methodologies and frameworks
Once the project scope and size are determined, look into the available methodologies and frameworks. Compare notes, and weigh the pros and cons as to which one would suit your requirements the best while minimizing risks.
3. Obtaining the acceptance and buy-in of your team
Reach out to your team to see their reaction and input. Make sure you listen to their viewpoints and present your side accordingly to obtain their buy-in. Otherwise, conflicts and challenges may hinder the project’s smooth progress.
4. Confirm the selection
Before starting the project, re-confirm the feasibility of your selection by comparing and assessing the success rate of projects delivered using the same framework.
5. Obtain feedback and conduct self-assessments
As the project progresses, ask for feedback from your colleagues regarding the processes followed. Furthermore, make sure to conduct self-assessments to see if the methodology or framework is proceeding according to your expectations and whether it allows you to manage your team successfully.
Tools and Techniques for Project Management Methodologies and Frameworks
There are several tools and techniques relevant to project management methodologies and frameworks. While some specific tools and techniques are similar across multiple frameworks, there are some that may differ. Below are a few commonly used tools and techniques.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Work breakdown structures can be used to break down the larger deliverables of your project into manageable smaller tasks. This is a productivity technique that uses a step-by-step approach to project management.
Gantt Chart
Gantt charts are ideal for tracking tasks' start and end dates and milestones. It helps teams to plan their work and jobs to meet deadlines and allocate resources accordingly.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. For each project, the SWOT identifies the internal (Strengths and Weaknesses) and external (Opportunities and Threats) drivers affecting your ability to meet the goal. For example, suppose your organization is well known for its expertise in customer service. In that case, improving customer service will be a competitive advantage and a meaningful driver for meeting your goals.
RACI Matrix
RACI stands for responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed. RACI matrix is used to describe the roles and responsibilities of team members in a project.
Stakeholder Map
The stakeholder map is a tool to help you understand who your stakeholders are and their needs. Using this tool, you can map stakeholders according to their importance and potential impact on the project.
Decision Tree
A decision tree is used for effective decision-making and predicting potential outcomes when multiple courses of action exist. It allows the team to explore options and outcomes to understand the risks and rewards associated with each possible course of action.
Creately for Project Management
Creately has many tools to make your journey effortless and successful regardless of the type of project methodology or framework you decide to follow.
- Powerful documentation capabilities include doc blocks and attachments and image attachments to create reports and presentations.
- Built-in project management tools including Kanban boards, timelines, multi-role workflows, visual prioritization tools to enable any kind of workflow.
- Whiteboard and freehand drawing capabilities to brainstorm and discuss with colleagues and peers.
- Multiple templates and shapes to prepare project plans and schedules, Gantt charts, roadmaps, and other formats necessary for project management documentation and tracking.
- Multiple access and role levels to manage, share, edit and review, along with multiplayer editing capabilities to collaborate in real-time.
- Comment on anything, with context. Full comment threads and discussions for async collaboration.
- Data, note, and task panels to house information, assign roles and responsibilities, feed in information, and track the progress of activities.
- Integration with other platforms with 2-way syncing to manage data efficiently.
- Spotlight and presentation mode to conduct interactive and dynamic presentations right on the canvas.
Start your project management journey with Creately today!
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.
Project Management Methodologies
Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, Kanban and more. If you’re wondering which methodology you should choose, then you need to read this guide to project management methodologies.
Table of Contents
What is a project management methodology, why are there so many different types of project management methodologies, the project management process: how to choose the right project management methodology, 17 project management methodology examples and frameworks, choosing the right project management methodology.
Once you’ve decided you want to become a project manager , the next step is to figure out which project management methodologies are right for you and your team.
The landscape of project management methodologies can seem a bit overwhelming.
Whether you have a formal project management certification or you’re learning to become a project manager from experience, there’s an absolute smorgasbord of project methodologies to choose from. And they often come with their own rules, lists, principles, and endless acronyms.
We believe that finding the right project management methodology to manage your work shouldn’t be rocket science. So we’ve compiled this list of different project management methodologies to help you figure out which methods, principles and approaches you can use for each team and project.
The only all-in-one platform for client work
Trusted by 20,000 businesses and 6,000 agencies, Teamwork.com lets you easily manage, track, and customize multiple complex projects. Get started with a free 30-day trial.

A project management methodology is a set of principles and practices that guide you in organizing your projects to ensure their optimum performance.
Basically, it’s a framework that helps you to manage your project in the best way possible.
Project management is so important to organizations and teams, but in order for it to be really effective, you need to make sure you’re correctly mapping your project management methodology to your team type, project, organization, and goals.
No two projects are exactly the same (even when you’re using handy features like project templates to replicate your past successes).
And when you factor in the different goals, KPIs and production methods of not only different types of teams but also different types of industries , it makes sense that there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to managing a project.
What works best for one type of team could be an absolute nightmare for another.
For example, many software developers started to find that traditional project management methods were hindering — rather than helping — their workflows and negatively affecting their performance and results.
As a result, software teams began to develop a new type of project management methodology, which was designed to address their particular concerns.
Before long, other teams and industries started to adapt those new project management methods to fit their unique needs and concerns. And on and on, with different project management methodologies being repurposed and adapted for different industries and tweaked to fit specific use cases.
What we’re left with is a ton of different project management methodologies to choose from. So how do you know which project management method (or methods, plural) is right for you and your team?
There are lots of factors that will impact which project management methodology is right for your project, team, and organization. Here’s a quick breakdown of some of the key considerations that can help you decide:
Cost and budget: On a scale of $ to $$$, what sort of budget are you working with? Is there room for that to change if necessary, or is it essential that it stays within these predetermined limits?
Team size: How many people are involved? How many stakeholders? Is your team relatively compact and self-organizing, or more sprawling, with a need for more rigorous delegation?
Ability to take risks: Is this a huge project with a big impact that needs to be carefully managed in order to deliver Very Serious Results? Or is it a smaller-scale project with a bit more room to play around?
Flexibility: Is there room for the scope of the project to change during the process? What about the finished product?
Timeline: How much time is allotted to deliver on the brief? Do you need a quick turnaround, or is it more important that you have a beautifully finished result, no matter how long it takes?
Client/stakeholder collaboration: How involved does the client/stakeholder need — or want — to be in the process? How involved do you need — or want — them to be?
Waterfall methodology
Agile methodology
Scrum methodology
Kanban methodology
Scrumban methodology
eXtreme programming (XP) methodology
Adaptive project framework (APF) methodology
Lean methodology
Critical path method
Critical chain project management
New product introduction (NPI)
Package enabled reengineering (PER)
Outcome mapping
PMI’s PMBOK
PRINCE2 methodology
Rapid application development (RAD) methodology
We’ve compiled a list of 17 effective project management methodologies to help you get to grips with the basics. Let’s dive right in.
1. Waterfall methodology
The Waterfall method is a traditional approach to project management. In it, tasks and phases are completed in a linear, sequential manner, and each stage of the project must be completed before the next begins.
The stages of Waterfall project management generally follow this sequence:
Requirements
Construction
Deployment & maintenance
Progress flows in one direction, like a real waterfall.
Also like a real waterfall, though, this can quickly get dangerous. Since everything is mapped out at the beginning, there’s a lot of room for error if expectations don’t match up with reality. And there’s no going back to a previous stage once it’s completed (just imagine trying to swim against a waterfall — not fun).
Try this project management methodology if:
The end goal of your project is clearly defined — and isn’t going to change.
The stakeholders know exactly what they want (and it isn’t going to change).
Your project is consistent and predictable (i.e. isn’t going to change).
You’re working in a regulated industry that needs extensive project tracking or documentation.
You might need to bring new people into the project midway through and get them up to speed quickly.
This project management methodology might not be for you if:
Your project is liable to change.
You don’t have a full picture of all the requirements before you start.
You need to do continuous testing or adapt to feedback during the process.
2. Agile methodology
Agile project leaders help their team balance at the edge of chaos - some structure, but not too much; adequate documentation, but not too much; some up-front architecture work, but not too much. Finding these balance points is the art of agile leadership." ~ Jim Highsmith, author and software engineer
The agile project management methodology came from a growing dissatisfaction with the linear approach of traditional project management methodologies.
Frustrated with the limitations of project management methods that couldn’t adapt with a project as it progressed, the focus began to shift to more iterative models that allowed teams to revise their project as needed during the process instead of having to wait until the end to review and amend.
The concept of agile project management has gone on to spark several specific sub-frameworks and methodologies, such as scrum, kanban, and lean. But what do they all have in common? The key principles of agile project management methodologies are:
It’s collaborative.
It’s quick.
It’s open to data-driven change.
As such, agile project management methodologies usually involve short phases of work with frequent testing, reassessment, and adaptation throughout.
In many agile methods, all of the work to be done is added to a backlog that teams can work through in each phase or cycle, with project managers or product owners prioritizing the backlog so teams know what to focus on first.
You’re not sure at the outset what the solution will look like.
You need to work quickly, and it’s more important that you see speedy progress than perfect results.
Your stakeholders or client needs (or wants) to be involved at every stage.
This project management methodology isn’t for you if:
You need a lot of documentation (for example, if you’ll be bringing new people on-board during the project).
You need a predictable deliverable, and you need to be crystal clear about what that looks like from the outset.
Your project can’t afford to change during its course.
You don’t have self-motivated people.
You have strict deadlines or deliverables that you need to stay on top of.

The Best Agile Project Management Tools To Use In 2023 & Beyond
It does little good to adopt the Agile method while still using a software that bogs down or complicates your projects. The best agile project management software should go hand-in-hand with the Agile method and make these adaptations smooth, fast, and easy.
3. Scrum methodology
Scrum is a form of agile project management. You can think of it more like a framework than as a project management methodology in itself.
With Scrum, work is split into short cycles known as “sprints”, which usually last about 1-2 weeks. Work is taken from the backlog (see: Agile project management, above) for each sprint iteration,
Small teams are led by a Scrum Master (who is not the same as the project manager ) for the duration of the sprint, after which they review their performance in a “sprint retrospective” and make any necessary changes before starting the next sprint.
You’re striving for continuous improvement.
You don’t have the full commitment from the team needed to make it work.
4. Kanban methodology
"Kanban is not a software development lifecycle methodology or an approach to project management. It requires that some process is already in place so that Kanban can be applied to incrementally change the underlying process." ~ David J. Anderson, Author and pioneer of the Kanban method
Kanban is another method within agile project management.
Originating from the manufacturing industry, the term “kanban” has evolved to denote a framework in which tasks are visually represented as they progress through columns on a kanban board . Work is pulled from the predefined backlog on a continuous basis as the team has capacity and moved through the columns on the board, with each column representing a stage of the process.
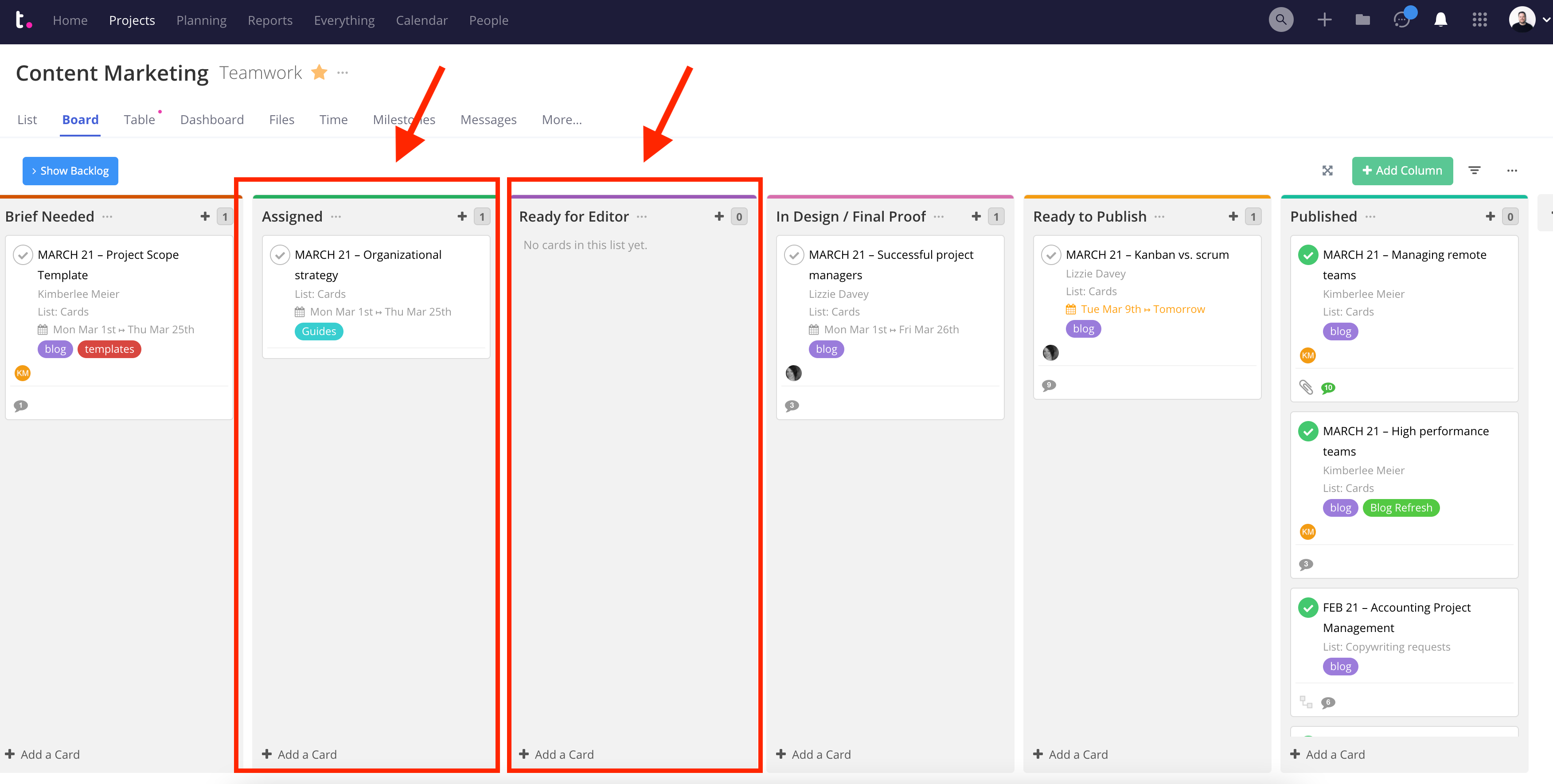
Kanban is great for giving everyone an immediate visual overview of where each piece of work stands at any given time. (You can use kanban boards for everything from your content marketing process to hiring and recruitment .)
It also helps you to see where bottlenecks are at risk of forming — if you notice one of your columns getting clogged, for example, you’ll know that that’s a stage of your process that needs to be examined.
When used as part of an agile project management methodology, it’s also common to implement work in progress (WIP) limits. Work in progress limits restrict the amount of tasks in play at any given time, meaning that you can only have a certain number of tasks in each column (or on the board overall).
This prevents your team from spreading their energy across too many tasks, and instead ensures that they can work more productively by focusing on each task individually.
You’re looking for a visual representation of your project’s progress.
You want at-a-glance status updates.
You want to encourage using WIP limits so your team can stay focused.
You prefer to work on a continuous “pull” basis.
Your process is super complex or has tons of stages.
You want a push system instead of a pull system.
Kanban board view
Use kanban boards in Teamwork.com to map out your workflow, quickly see the status of tasks, and automate your processes.
5. Scrumban methodology
It’s the answer to the age-old question: what if scrum and kanban had a baby?
Scrumban is a hybrid agile project management methodology that has scrum’s nose and kanban’s eyes.
The main benefit of scrumban as a method is that instead of deciding which task from the backlog to work on in each sprint at the outset (like you would in a “traditional” scrum framework), scrumban allows teams to continuously “pull” from the backlog based on their capacity (like they would in a kanban framework).
And using work in progress limits (from kanban) during your sprint cycle (from scrum), you can keep a continuous flow while still incorporating project planning , reviews and retrospectives as needed.
You’ve ever looked at scrum and kanban and thought “I wish those two crazy kids would get together”.
You’ve ever looked wistfully out the window and thought, “Oh, scrum is scrum, and kanban is kanban, and never the twain shall meet”.
6. eXtreme programming (XP) methodology
The eXtreme Programming (XP) methodology is another form of agile project management that was designed for software developmen t.
It emphasizes teamwork and collaboration across managers, customers, and developers, with teams self-organizing. It has a defined set of rules that teams should follow, which are based on its five values: simplicity, communication (face to face is preferred), feedback, respect, and courage.
You want to foster teamwork and collaboration.
You have a small, co-located team.
You’re a rulebreaker.
Your team is spread across different places and time zones.
7. Adaptive project framework (APF) methodology
The adaptive project framework (APF) methodology, also known as adaptive project management (APM), is a type of agile project management methodology that was designed with the inevitability of change in mind.
The adaptive project framework knows that, as John Steinbeck might say, even the best-laid projects of mice and men often go awry. So the fundamental attribute of APF is that teams need to be able to adaptively respond to change.
That means that using adaptive project framework methods, teams must try to anticipate the risks and prepare for the unexpected in their project. They need to understand that key components are constantly in flux, and be able to constantly re-evaluate results and decisions with these moving parts in mind.
This requires lots of communication with all stakeholders and — like other agile project management methodologies — be able to work collaboratively.
You know your ultimate goals (in project management terms, you’ve outlined your Conditions of Satisfaction; or, in Beastie Boys terms, you’re clear about you’re clear about whatcha whatcha whatcha want).
You need predictability.
You don’t have the resources to handle the potential negatives of adaptability (e.g. scope creep, rework, misuse of time).
8. Lean methodology
Lean is another project management methodology that has its origins in manufacturing (and specifically the Toyota Production System). It’s all about applying lean principles to your project management methods to maximize value and minimize waste.
While this originally referred to reducing physical waste in the manufacturing process, it now refers to other wasteful practices in the project management process. These are known as the 3Ms: muda, mura, and muri.
Muda (wastefulness) consumes resources without adding value for the customer.
Mura (unevenness) occurs when you have overproduction in one area that throws all of your other areas out of whack, leaving you with too much inventory (wasteful!) or inefficient processes (also wasteful!).
Muri (overburden) occurs when there is too much strain on resources such as equipment and people, which can often lead to breakdowns — in both machines and humans.
Using the key principles of lean, a project manager can reduce these types of waste to create more efficient workflows.
You’re looking for a set of principles that will help you cut the fat and optimize your flow.
You’re always trying to improve and add value for the customer.
You want to ultimately decrease costs.
You can’t afford to run into supply problems (e.g. you don’t have enough inventory in stock) or lose room for error (e.g. in the case of essential equipment failure).
You don’t have the budget to invest in it (while lean project management aims to reduce costs overall, it can be costly to implement).
You’re a raccoon and you love waste, actually.
9. Critical path method
A project without a critical path is like a ship without a rudder." ~ D. Meyer, Illinois Construction Law
The critical path method (also known as critical path analysis) is a way of identifying and scheduling all of the critical tasks that comprise your project, as well as their dependencies.
That means that you need to:
Identify all of the essential tasks you need to do to achieve your project goal
Estimate how much time each of those tasks will take (bearing in mind that certain tasks will need to be completed before others can be started)
Use all of that information to schedule the “critical path” you’ll need to take in order to get the project done as quickly as possible without missing any crucial steps.
The longest sequence of critical tasks becomes your critical path, and will define the timeframe for your project.
Along the path, you’ll have milestones to meet that will signal when one set of tasks (or phase) is over and you can move on to the next one.
There are lots of ways to visualize the critical path, depending on the complexity of your project, from flow graphs to Gantt charts .
Your project is large-scale and complex.
Your project has a lot of dependencies.
You’re looking for a visual way to map out the sequence of tasks.
You need to identify which tasks are the most important so you can better allocate your resources.
You have a strict plan and deadlines, with no room for silly business.
You love algorithms. Love ‘em!
You don’t need something with a lot of complexity.
You’re unsure about deadlines, timings, or durations.
Your project needs wiggle room to change.
10. Critical chain project management
Critical chain project management (or CCPM) takes the critical path method (CPM) one step further.
While the critical path method defines the length of time needed to get each critical activity done from the beginning of the project to the end, it can often be, well, unrealistic when the time comes to actually put it into practice.
Critical chain project management addresses those issues by allowing a bit more time for the human elements of your project — like delays and resourcing issues.
In critical chain project management, you have a few buffers built in that your critical chain can use without derailing everything else, so that your entire project doesn’t have to go off track just because life happens.
You like the sound of the critical path method, but you want something a little more realistic.
You were already overestimating task durations in CPM to allow for a buffer and you want more accurate data on how long the work is actually taking compared to your projections.
You think buffers are just a safety net for people who didn’t plan it right the first time.
Nothing could possibly go wrong.
11. New product introduction (NPI)
New product introduction is a great project management methodology for when you want to, well, introduce a new product.
Also known as new product development (NPD), the new product introduction process covers everything you need to define, develop and launch a new (or improved) product.
The project follows a single product through the entire development process. This process involves multiple phases or a stage-gate process, which can vary from organization to organization, but usually include things like:
Defining the product spec and project scope
Evaluating the feasibility
Developing the prototype
Validating the prototype via testing and analysis
Manufacturing the product on a larger scale
Evaluating the product’s success in the market after launch
As the requirements for a successful new product introduction span a number of departments across an organization, from leadership to product managers to marketing and more, it requires a lot of cross-functional collaboration and communication.
Project management template
Nail your next project with our project management template. Manage the bigger picture, and turn plans into actionable tasks - without missing a single detail.
You’re bringing a new or improved product to market.
You’re focusing on a single product.
You want to foster key stakeholder and cross-functional alignment right from the beginning.
You’re not bringing a new or improved product to market.
You’re looking for a more agile approach to product development (as NPI is usually sequential rather than iterative).
12. Package enabled reengineering (PER)
Package enabled reengineering (PER) is a project management methodology that aims to help organizations redesign products or processes with fresh eyes. It focuses on facilitating business transformations quickly and strategically, whether through redesign of processes or realignment of people.
Your organization needs an overhaul.
You need a fresh perspective on your products or processes.
You’re not trying to improve an existing system.
13. Outcome mapping
Outcome mapping is a project progress measurement system that was designed by the International Development Research Centre (IDRC). It differs from the other project management methodologies on this list in that it doesn’t focus on measurable deliverables; instead, it focuses on creating lasting behavioural change.
It’s a common project management methodology used in charitable projects in developing countries. As a project management methodology, it’s less about the project itself than the long-term impact of the project and its ability to effect change in the community. As a result, it measures influence rather than other (perhaps more “typical”) measures of project progress.
Outcome mapping consists of a lengthy design phase followed by a record-keeping phase to track the results.
Your project is aimed at changing behaviour rather than producing deliverables.
Your project is related to change and social transformation (e.g. in the fields of international development, charity, communications, research).
Your project is all about finished products rather than behavioural outcomes.
14. Six Sigma
"Measurement is the first step that leads to control and eventually to improvement. If you can't measure something, you can't understand it. If you can't understand it, you can't control it. If you can't control it, you can't improve it." ~ H. James Harrington, author and management mentor
Six Sigma is a method for improving processes with an emphasis on ensuring consistency in output and impeccable quality. (And if it’s good enough for Jack Donaghy… )
There are a few different flavors available, such as Lean Six Sigma and Agile Sigma, but ultimately Six Sigma is a business methodology that aims to eliminate defects and reduce variation by using its defined methodologies.
Six Sigma methods can be used to optimize and improve existing processes or create new ones.
To improve business processes, you can use the Six Sigma DMAIC process, which stands for the phases in the project methodology: D efine, M easure, A nalyze, I mprove, C ontrol.
To create new processes or products, you can use the Six Sigma DMADV process: D efine, M easure, A nalyze, D esign, V erify.
As a set of principles and techniques (sometimes it’s even described as a “philosophy”) rather than a project management methodology in itself, Six Sigma methods can be applied alongside many other project management methodologies, like Lean and Agile.
You’re looking for a set of principles and philosophies you can bring with you to almost every project and organization.
You don’t have a lot of budget to invest in training — it can be expensive to get trained and certified.
You’re looking for a defined process for a particular project rather than a set of guiding rules.
15. PMI’s PMBOK
The Project Management Institute’s Project Management Book of Knowledge (AKA the PMI’s PMBOK) isn’t a project management methodology in and of itself. However, it is a best practices guide — and it forms the basis of the PMI’s Project Management Professional (PMP) certification, one of the leading project management qualifications.
As such, the PMBOK is an industry-standard set of guiding principles that you can use to ensure that your projects across multiple types of teams and organizations meet the PMI’s high standards and comply with best practices.
You have (or want to get) a PMP.
You want to stay up-to-date with industry standards and best practices.
You live and work in a place where the PMP is the standard project management qualification (such as the US).
You need a solid project management methodology to map your project, rather than general (albeit helpful) project management knowledge.
16. PRINCE2 methodology
PRINCE2 ( PR ojects IN C ontrolled E nvironments) is a project management methodology and certification that aims to equip project managers with knowledge of best practices and processes.
Unlike the PMP certification, it doesn’t require a number of prerequisites, making it a good choice for project managers looking to get both a methodological grounding and a qualification.
Also unlike the PMP, PRINCE2 is a methodology in itself. It’s guided by seven principles, which in turn dictate the seven processes a project manager needs to use in each project when using PRINCE2.
You’re looking for a certification to give you an edge.
You live and work in a place where PRINCE2 is the standard project management qualification (such as the UK).
You don’t want to commit to full certification.
The seven-step process doesn’t map to your projects.
You find yourself tailoring (or outright ignoring) the process stages so much that it becomes PINO — “PRINCE in name only”.
17. Rapid application development (RAD) methodology
Rapid application development (RAD) is a type of agile project management methodology that aims to facilitate faster software development .
It uses rapid prototype releases and iterations to gather feedback in a short period of time, and values that user feedback over strict planning and requirements recording.
You want to be able to give customers/clients/stakeholders a working model much sooner (even if it’s not perfect).
You want to create multiple prototypes and work with stakeholders to choose the best one.
Speed is of the essence.
You want to encourage code reuse.
You don’t have an experienced team.
Your clients or stakeholders don’t have the time to commit to such a collaborative process or can’t give feedback within the necessary timeframes.
You have a large team.
You prefer to have a detailed spec that outlines all functional and non-functional requirements.

The right project management methodology can elevate your project and help the project manager to get the best out of each team.
Whether you prefer the agile methods favored in IT project management or the more traditional waterfall project management and critical path methodology used in construction and manufacturing, there’s a project management methodology for every team.
But no matter which methodology you go for, you need a collaborative, flexible, and easy-to-use project management tool to support you every step of the way.
Choosing a team management software that supports multiple methodologies — i.e. that doesn’t lock you into one methodology or way of using it — like Teamwork.com means that every team in your organization has the freedom to work the way that works for them without sacrificing on features or complexity.
No matter how you like to work, Teamwork.com helps your team to replicate their best practices, ensure compliance and consistency, and constantly improve their processes.
What project management methodology allows some of the phases and tasks to overlap?
The project management methodology that allows some of the phases and tasks to overlap is known as "Agile" or "Agile Project Management." Agile is a flexible and iterative approach to project management that tends to be divided into "Sprints", which are time-boxed periods of work. Within each Sprint, cross-functional teams work on various tasks and features, allowing for a degree of overlap between different project phases.
What project management methodology requires the team to complete the previous phase before the next phase starts?
The project management methodology that typically requires the team to complete the previous phase before the next phase starts is the "Waterfall" methodology. Waterfall is a traditional, linear, and sequential approach to project management. In a Waterfall project, each phase must be completed in its entirety before the next phase can begin.
Why do project managers use project management methodologies?
Project managers use project management methodologies to bring structure and organization to their projects, ensuring consistency, risk management, resource allocation, and quality assurance. These methodologies promote effective communication, change management, and scope control, leading to increased efficiency, client and stakeholder satisfaction, and overall project success. They also foster a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability, allowing project managers to navigate changing requirements and uncertainties effectively.
How many project management methodologies are there?
There are numerous project management methodologies, with dozens of well-known approaches like Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, PRINCE2, Kanban, Lean, and Six Sigma, among others. Custom methodologies are also created by organizations to meet specific needs.
What is the difference between agile and scrum?
Agile is a broader project management philosophy that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback, while Scrum is a specific Agile framework. Scrum introduces roles (Scrum Master, Product Owner, Development Team), fixed-time sprints, and defined ceremonies (Sprint Planning, Daily Standup, Sprint Review, Sprint Retrospective) to guide project teams. It also includes key artifacts like the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment.
You may also like...

Get started with Teamwork.com
Start working together beautifully. See how Teamwork.com can help your team with our 30-day free trial.
Chapter 3: Project management methodologies
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
There are many project management methodologies and frameworks out there, designed to assist with different types of projects. But how do you know which one is best for your efforts?
In this section, we’ll walk through the most popular PM methodologies, and share advice for how to choose the best method to fit your needs.
Waterfall or traditional project management
Waterfall or traditional project management is based on a defined set of tasks that are completed sequentially to produce a final deliverable. This method of PM is simple and predictable, but not very flexible.
Waterfall project management is ideal for projects with a single, large deliverable, like a building. While it’s less useful for projects that require a lot of flexibility, are subject to change, or require multiple, dependent tasks to be completed in tandem, like software development.
The main benefits of Waterfall are tight planning and organization, and a high degree of control over each project task and the greater project schedule. That said, using Waterfall can make it difficult to adapt to unexpected events or changes to project scope, which can result in added time, resources, and cost.
Teams often use a Gantt chart , a visual timeline tool that maps out project tasks in succession, in Waterfall-managed projects. Learn more about Gantt charts in Chapter 9 .
To learn more about the phases and pros and cons of Waterfall, visit our in-depth guide to creating and using a Waterfall chart .
The Agile family
The Agile family is a category of project management methodologies that prioritizes flexibility and continuous improvement over rigid, sequential processes. There are many popular methodologies within Agile, and we’ve dug into each below.
Agile project management
In Agile project management , teams complete smaller, incremental tasks, and then continually review, refine, and iterate based on feedback and demands of the end users.
Agile project management was formalized in 2001 by a group of software developers intent on finding a more collaborative, flexible method to complete projects. The group documented their ideas in the Manifesto for Agile Development , which lays out the following four values:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
Agile PM prioritizes a collaborative relationship between the end user and the project team. The customer sets the project objectives, but the deliverables are subject to change as the team incrementally executes each project task. In Agile, each development feature is called a user story , which reflects how the end user will interact with it.
Agile project management was initially intended for software development, but is now commonly used across a variety of industries and types of projects. Learn more about the Agile process and how to implement it by reading our comprehensive guide to Agile PM .
Pros and cons of Agile project management
Agile is a good fit for projects that require a high degree of flexibility and are likely to shift as the project progresses. The top benefits of Agile include the following:
- Less upfront planning
- Increased open communication
- Continual feedback
- Flexible objectives
When used effectively, Agile also often leads to speedier delivery.
However, there are some tradeoffs to this flexible approach:
- Lack of concrete delivery date, which can lead to scope creep
- A high degree of dedication and flexibility from the project team
Is Agile right for you?
Remember, Agile isn’t for everyone. The methodology is likely not right for your team if any of the following apply to you:
- Your project is not very urgent.
- Your client’s expectations don’t support Agile (e.g., they want to give final approval at every stage of the project, or incremental delivery isn’t appropriate for the project specs).
- You or your client’s organization requires detailed documentation at every stage.
- Your current processes are not set up for a more flexible approach.
- Your team or organization doesn’t currently use Agile, and implementing it would be too costly or time consuming.
In the following sections, we’ll go over other methodologies that fall within the Agile family.
Additional Resources
The ultimate agile dictionary, free agile project management templates, best practices for agile project planning.
Scrum , the most popular Agile methodology, involves smaller teams that complete tasks in short, time-bound periods, called sprints , in order to incrementally work through pieces of a larger project or release.
Scrum typically leads to greater responsiveness in customer relationships, lower costs of development, increased job satisfaction, and more immediate returns. Scrum is a fluid practice that takes many moving parts, teams, and goals into consideration as the project progresses.
Scrum teams also engage in four regular meetings, or ceremonies , which provide structure to each sprint:
- Sprint planning: At this meeting, the product is presented and everyone on the Scrum team voices any concerns and feedback. The team designates priorities and estimates the timeline.
- Daily stand-up: The Scrum team meets daily during the sprint to debrief with the team, establish a daily plan, and voice any concerns so the team can address them together.
- Sprint review: Held at the end of each sprint, this meeting is a review of the working product and gives stakeholders transparency into what the team accomplished during the sprint.
- Sprint retrospective: The sprint retrospective is a meeting that occurs after each sprint to discuss team performance and establish ways to improve future efforts.
Each Scrum team has designated members who own specific pieces of the process. These roles include the following:
- Product owner: Possesses a thorough understanding of the product’s business value and serves as the middleman who communicates the stakeholder needs to the development team and writes and prioritizes user stories.
- Development team: Performs the technical development of the product and is responsible for the analysis, design, code writing, testing, and technical communication based on the user stories provided by the product owner.
- Scrum Master: Assists in the progress of the Scrum team by working hand-in-hand with the product owner and the development team to streamline work and eliminate distractions.
As with Agile, Scrum is popular in software development, but it can also be deployed successfully across marketing, design, and other creative projects. Learn more by reading our guide to implementing Scrum with the right tools .
Kanban is an Agile framework that prioritizes continuous improvement , an ongoing effort to improve a product or service incrementally. Kanban teams complete work items based on team capacity and manage resources using a visual kanban board that shows task status.
Kanban originated in Japan in the 1940s. Based on what he had seen in supermarkets, Toyota engineer Taiichi Ohno implemented a supply-and-demand method on the factory floor, which greatly improved the company’s inventory management.
Teams at Toyota created a visual cue (a kanban, which translates to “visual sign” or “card”) to communicate that they were ready to “pull,” or take on, more tasks or materials to complete their work. This approach enabled workers to only take on new tasks when they had capacity for them, which reduced excess work in progress (WIP) . This style of work is now known as the just-in-time (JIT) approach.
How to use a kanban board
The Kanban methodology centers on the kanban board, which is either a physical or digital “board” that includes three columns (or lanes ): to-do, doing, and done. Team members move cards, representing individual tasks, to different columns as a way to track task status. This provides a quick view of how items are progressing and ensures teams have adequate capacity to take on new work.
In recent years, teams have moved to online, digital kanban boards, which helps distributed teams collaborate on projects and gain real-time visibility into the work getting done. You can learn more about setting up a Kanban board with our guide .
Pros and cons of Kanban
Overall, Kanban is great for teams that have many incoming requests, short work cycles, and flexibility with resources and scheduling. However, Kanban can be difficult for teams that work on many interconnected, dependent tasks, or have tight deadlines to adhere to.
To learn more about implementing kanban from the ground up, read our complete guide for newbies .
Critical path method
Critical path method (CPM) is a technique for estimating the total duration of a project by identifying the order in which you must complete all project tasks, and then mapping out your sequenced tasks, called dependencies .
CPM follows the basic steps below:
- Identify all project tasks.
- Identify dependencies among tasks.
- Estimate the duration of each task.
- Add up the durations to calculate the total duration of your project.
- Update the critical path as the project progresses to compare estimated vs. actual timelines.
CPM helps teams reduce project timelines by identifying and scheduling the most important tasks and then scheduling other tasks to happen in parallel. CPM also helps with project planning, as you can easily reference estimated vs. actual project schedules and more accurately estimate how long each task will take on future projects.
Learn more about the steps and advantages of the method with our beginner’s guide to the CPM .
The change management methodologies
Change management is an umbrella term for techniques that help individuals, teams, and organizations implement new processes or achieve organizational change. In this section, we’ll cover event chain and extreme project management.
To learn more, visit our essential guide to change management , or find free change management templates .
Event Chain methodology
In event chain methodology , you identify tasks (events) and their relationships (event chains) in order to properly allocate resources and assess and reduce project risk.
The goal of event chain is to estimate the amount of time and resources you need to complete a project. This method follows some of the same steps as the critical path method — you also break down activities into smaller tasks and outline their dependencies and durations. But, in event chain, you do so to create a realistic timeline and budget, rather than to simply better manage the tasks (and task order).
Event chain can also serve as a modeling technique to create more conservative scheduling estimates, which ultimately improves performance by building in time to address unforeseen risks.
This methodology is often used in change management efforts to eliminate the need to overhaul projects, which can be extremely time consuming and resource-heavy.
Extreme project management
Extreme project management (XP or XPM) is used to manage a massive amount of change in a short period of time. XPM is ideal for fast-paced, complex projects that can handle a trial-and-error approach to successfully pull off the effort.
Think of XPM as the opposite of Waterfall methodology. As opposed to valuing a linear, planned project development process, XPM allows you to change your project plan, budget, and the final deliverable as requirements shift. In XPM, the onus is on the project team to self-correct and shift as necessary.
Extreme project management works well for projects with a high-degree of uncertainty, but is less useful for projects with a clear-cut timeline, budget, and scope.
The process-based methodologies
Process-based methodologies approach work as a collection of processes, rather than a strict methodology that you apply to a single project. These approaches are sometimes used as part of a larger business process management (BPM) strategy.
Lean is an approach aimed at maximizing value while minimizing waste. When deployed properly, Lean helps to identify and eliminate bottlenecks, delays, and other inefficiencies in order to deliver value faster.
Lean originated in manufacturing in the 1950s, but it has evolved over time and is used today across industries. As laid out in the book Lean Thinking , Lean involves the following five core principles and activities:
- Define value: Identify the value of each product or service in the eyes of the customer.
- Map the value stream: Map out the process (aka value stream ) and identify areas of waste, in terms of resources, time, or redundancy.
- Create flow: Create a flow plan that eliminates the waste you identified.
- Employ a pull system: Progress through the plan only as the customer has new needs. Doing so will prevent you from taking on too much at once, or creating a bottleneck at any stage of the process.
- Pursue perfection: Using the idea of continuous improvement, aim to eliminate as much waste as possible from your process.
Visit our comprehensive guide to Lean project management to learn more about different types of Lean methodologies and the best tools for implementing Lean.
Six Sigma is a process improvement methodology that aims to improve quality across projects. Six Sigma takes a statistical approach to measuring and eliminating bugs or defects in project deliverables and raising quality standards.
The basic steps in Six Sigma include finding defects, identifying and eliminating their cause(s), and optimizing processes to increase reliability and accuracy going forward.
Building off the Lean principle of pursuing perfection, Six Sigma aims to eliminate all opportunities for defects by using data-driven improvement cycles to achieve its goal.
There are two main Six Sigma methodologies:
- DMAIC: This stands for define , measure, analyze, improve, control , and is intended to help you improve existing processes.
- DMADV: This stands for define, measure, analyze, improve, verify, and is best for when creating new processes or products.
There is no single, formal certification body for Six Sigma, but many organizations offer training so teams can learn to implement the practice in their organization. Read our article on Six Sigma belts and certifications to learn more.
Six Sigma works well for teams who are interested in implementing data-driven ways to reduce defects and optimize business processes, but is less ideal for those looking for a strict set of steps to follow.
Read our in-depth guide to all things Six Sigma to learn more.
Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma is a hybrid approach to process improvement that combines the Lean principle of no waste and the Six Sigma principle of no defects to improve quality across processes, projects, and products.
Lean Six Sigma offers the following benefits:
- Increased cost savings due to fewer bugs or defects
- Improved quality
- Time savings due to fewer process issues
- Improved data-driven decision making
- Continuous process improvement throughout the organization
While Lean Six Sigma originated in manufacturing, a variety of industries can deploy it to reap benefits. The most common use cases include healthcare, construction, design, and government.
All About Lean Six Sigma
Free lean six sigma templates, other project management methodologies.
Below, you’ll find details on a few more project management methodologies that are gaining traction in the modern PM world.
PRINCE2 , or Projects in Controlled Environments , is a project management methodology that focuses on defining and delivering work against precise requirements. As opposed to Agile PM, PRINCE2 emphasizes intense planning and documentation of work items.
PRINCE2 is a hybrid methodology initially used for information technology (IT) projects to help reduce cost and time overruns. Now, it’s deployed across many different industries.
This approach works well for projects with a clearly defined goal. However, if you need more flexibility, or don’t have time to properly plan and document work, Agile methods might be a better option.
PRiSM , or Projects Integrating Sustainable Methods , is a modern project management methodology that values sustainability over all else. The goal of PRiSM projects is to reduce the environmental impact of a project and drive meaningful social impact.
The PRiSM model is based on the following six principles:
- Commitment and accountability
- Ethical decision making
- Integration and transparency
- Principal and values-based deployments
- Social and ecological equity
- Economic prosperity
Implementing PRiSM is a long term mindset shift that puts sustainability and equity at the center of all processes and projects and aims to maximize value for all involved.
Why you should choose a PM methodology for your organization
Choosing an organization-wide project management method ensures teams have a consistent guideline for how to manage each aspect of their projects, like resources, budget, communication, timeline, and more.
Of course, some teams and projects require different levels of planning, flexibility, and documentation. And, it can be overwhelming to choose one “perfect” approach when there are so many options out there.
But, by assessing the types of projects that you typically take on — as well as your existing processes — you can identify the most effective methodology for you.
In some cases, organizations may select multiple project management types to meet the requirements of different projects and teams.
How to choose the best PM methodology for you
To identify the right project management methodology, first consider the details of your project. Then, assess your existing systems and processes. Look at both what you need as well as what you already have in place to select the best method.
Ask yourself the following questions to evaluate your project needs:
Project basics
- What is the project’s focus?
- What industry are you in?
- How complex is the project?
- Is the project scalable?
Flexibility
- How flexible are your timeline, budget, and deliverables?
- How much planning do you need to do beforehand?
- What is your allotted budget, and how flexible is it?
- What resources do you have, and what additional resources do you need to obtain?
- How flexible is your timeline?
- Are there set start and end dates?
- Does your project have key milestones or a critical path?
Roles and responsibilities
- How many people or teams are working together on this project?
- How specialized is the work?
- What is the level of customer and stakeholder involvement?
After you’ve worked through the project-related questions, follow these steps to identify which methodology aligns best:
- Outline the main variables, like timeline, resources, and budget, that will drive the project.
- Consider how the methodology you choose will impact these variables, such as how a more flexible approach might affect a hard-and-fast deadline.
- Weigh the pros and cons of each methodology against the needs of your project. Think both about which will be the best fit and which will be least disruptive to your current processes.
- Collaborate with other team members to get input.
- Roll out the methodology to the team. This includes educating everyone on the new processes and setting up the necessary tools and documentation systems.
- Apply the methodology to the project and monitor it for success.

Here’s a simplified cheat sheet you can use to identify which methodology will work for your next project:
Discover a better way to streamline workflows and eliminate silos for good.
Shawwal offers - up to 30%
Total with VAT: {{CartWithDetails.cartMaster.total_after_vat}} {{currency}}
Your cart is empty.
12 Project Management Methodologies: Types, Tools, Techniques, And How to Choose
Written By : Bakkah
27 Feb 2024
Table of Content
Definition of Project Management Methodologies:
Types of project management methodologies, project management methodologies tools , project management methodologies techniques, how to choose a project management methodology, explore bakkah's leading courses to boost your skills in project management and business analysis:, popular articles.
PRINCE2 Methodology - 2024 Full Guide About Advantages and Disadvantages
Prosci Methodology - Change Management Methodology
Application of PMO in government entities in Saudi Arabia
Project management methodologies are systematic frameworks and guidelines utilized by organizations to efficiently plan, execute, and complete projects. They offer structured approaches to project management, ensuring adherence to timelines, budgets, and objectives. These methodologies encompass diverse principles, practices, and tools designed to facilitate effective communication and coordination among project-implementing teams.
Project management methodologies vary in their approach, with some emphasizing flexibility and adaptability (e.g., Agile) while others focus on sequential and structured processes (e.g., Waterfall). The appropriate methodology must be selected according to the type of project and its unique circumstances. The goal is to enhance project efficiency, minimize risks, and deliver high-quality results, ultimately contributing to achieving the specified goals and objectives of the project.
Project management methodologies refer to the systematic frameworks, processes, and guidelines organizations follow to plan, execute, monitor, and complete projects. These methodologies provide a structured approach to managing projects, ensuring they are completed on time, within budget, and meet the specified goals and objectives.
Project management methodologies encompass diverse principles, practices, and tools designed to facilitate effective communication and coordination among project-implementing teams.
They can vary in their approach, with some methodologies emphasizing flexibility and adaptability (e.g., Agile), while others focus on sequential and structured processes (e.g., Waterfall). The appropriate methodology must be selected according to the type of project and its unique circumstances.
The goal of Project Management Methodologies is to enhance project efficiency, minimize risks, and deliver high-quality results, ultimately contributing to achieving the specified goals and objectives of the project.
Various tools support their implementation, enhancing collaboration and communication, while diverse techniques facilitate effective project planning, execution, and control.
There are diverse project management methodologies, each with different principles, processes, and approaches. Here are some common types:
1. Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall project management is a traditional approach to project management where tasks are completed sequentially and linearly.
The methodology is called "waterfall" because progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards through phases, like a waterfall. Each phase must be completed before moving on to the next one, and changes to the project are generally not allowed once a phase is closed.
Here are the main phases in the waterfall project management methodology:
- Requirements: Define project scope, objectives, and deliverables.
- Design: Create a detailed plan for how the solution meets requirements.
- Implementation (or Construction): Include coding or construction of the project.
- Testing: Ensure the project meets specified requirements through various testing phases.
- Deployment (or Implementation): Implement the project in the production environment after the success of testing.
- Maintenance and Support: Address issues and user concerns and make updates as needed.
The waterfall methodology is best suited for projects where the requirements are well-understood and unlikely to change significantly during the development process.
It is often used in industries like construction and manufacturing. However, one of its main drawbacks is its inflexibility to adapt to changes once the project has started, as it does not easily accommodate changes in requirements.
2. Agile Methodology
Agile methodology is an iterative and flexible approach to project management that focuses on collaboration, adaptability, and customer satisfaction.
Unlike the linear nature of the waterfall model, agile divides a project into small increments with minimal planning and delivers functional pieces of the project in short time frames, known as iterations or sprints.
Primary principles and practices of agile include:
- Projects are divided into small manageable iterations, delivering potentially shippable product increments.
- Collaboration and communication between team members, stakeholders, and customers are crucial for quick adaptation to changes and alignment with goals.
- Continuous customer feedback allows for adjustments based on changing requirements.
- Agile is flexible and adaptable to changes in requirements or priorities at any stage.
- Continuous delivery aims for a potentially shippable product at the end of each iteration, allowing for early and regular value delivery to the customer.
- Prioritization and timeboxing based on value and importance ensure focus and urgency in delivering value.
- Agile encourages self-organizing, cross-functional team formation that collectively possess the necessary skills to deliver a complete product.
Popular agile frameworks include Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming (XP), each with specific practices and roles.
Agile is widely used in software development and various industries for its adaptability and customer-centric approach.
3. Scrum Framework
Scrum is one of the most widely used agile frameworks for managing complex software development projects. It provides a structured yet flexible approach to product development.
Key elements of the Scrum framework include:
- Roles: Include Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team.
- Artifacts: Comprise the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment.
- Events: Include Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-up, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective.
Scrum's iterative and incremental approach, along with its emphasis on collaboration and adaptability, makes it particularly effective for projects where requirements may change or evolve during development.
4. Kanban Methodology
Kanban is a project management methodology that visualizes workflow using boards, cards, and columns. It also limits tasks that are in progress simultaneously to prevent overloading the team and ensure a steady flow of work.
Emphasizing continuous improvement, Kanban employs feedback loops and a pull system, adapting work based on demand. Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are often used in Kanban to define the expected time frames.
Known for flexibility and adaptability, Kanban suits various industries like architecture, construction, marketing, education, software development, design, and law. Kanban fosters collaboration and shared responsibility and allows incremental process improvements based on specific needs and context.
5. Lean Project Management
Lean Project Management (LPM) is an approach to project management that draws inspiration from Lean principles. The Lean philosophy focuses on minimizing waste, optimizing efficiency, and continuously improving processes.
Lean principles are applied to enhance project delivery, reduce unnecessary activities, and deliver value more effectively.
Principal aspects of Lean Project Management methodology include eliminating waste, using value stream mapping, continuous improvement (Kaizen), customer focus, pull scheduling, visual management, batch size reduction, flexible planning, and cross-functional team use. LPM is suitable for industries like manufacturing, construction, and software development.
Its focus on efficiency and customer value makes it a valuable approach for organizations seeking to optimize their project delivery processes.
6. PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments)
PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is a widely adopted project management methodology developed by the UK government. It provides a structured and process-driven approach to project management, emphasizing flexibility and adaptability.
PRINCE2 divides projects into manageable stages, with defined roles and responsibilities, ensuring organized and controlled project execution.
The methodology consists of seven processes:
- Starting Up a Project (SU): Ensures project prerequisites are in place.
- Initiating a Project (IP): Defines project scope, objectives, and plans.
- Directing a Project (DP): Provides senior management with chief controls.
- Controlling a Stage (CS): Manages day-to-day project activities.
- Managing Product Delivery (MP): Ensures efficient product work.
- Managing a Stage Boundary (SB): Focuses on transitioning between stages.
- Closing a Project (CP): Formally closes the project and ties up loose ends.
PRINCE2 is known for its focus on continuous improvement and adaptability, making it a valuable tool for delivering successful projects within time, cost, and quality constraints.
Boost your career with Bakkah’s PRINCE2 courses:
- PRINCE2® Training Course Online
- PRINCE2® Agile Foundation & Practitioner Online Course and Certification
7. Critical Path Method (CPM)
Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique that identifies the critical path of activities, potential risks, team roles, and the sequence of tasks determining the shortest project duration. Key steps:
- Task Breakdown: Identify and sequence project tasks.
- Duration Estimation: Assign time estimates to tasks.
- Network Diagram: Create a visual representation of task dependencies.
- Critical Path Identification: Find the path critical for project completion.
- Float/Slack Calculation: Determine non-critical task flexibility.
- Resource Allocation: Efficiently allocate resources.
- Monitoring and Control: Monitor progress continuously, update schedules, and take corrective actions., update schedules, and take corrective actions.
CPM is an essential tool for effective project planning and control. It aids in prioritizing critical tasks, managing time constraints, and optimizing project schedules. CMP can be used in several projects, such as engineering, manufacturing, construction, and science.
8. Six Sigma ( Continuous Improvement Methodology)
Six Sigma is a data-driven project management methodology focused on improving process efficiency continuously and reducing defects or errors. Developed by Motorola in the 1980s, Six Sigma seeks to minimize variations and achieve higher levels of quality in processes. It is often applied in manufacturing and process improvement projects. Here is a concise overview of the Six Sigma project management methodology:
- Define (D): Clearly articulate the problem, project goals, scope, and customer requirements.
- Measure (M): Establish metrics, collect data, and measure baseline performance.
- Analyze (A): Use statistical tools to identify root causes of defects or inefficiencies.
- Improve (I): Develop and implement solutions, testing and refining as needed.
- Control (C): Establish measures to sustain improvements and prevent recurrence of defects or issues.
The Six Sigma methodology is often represented by the acronym DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control). Additionally, for more complex or considerable process changes, there is another phase known as DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify).
Bakkah provides certification levels such as Six Sigma Green Belt and Six Sigma Black Belt are available for individuals to demonstrate proficiency in applying Six Sigma principles and methodologies. Organizations implementing Six Sigma often experience enhanced efficiency, reduced defects, and improved customer satisfaction.
9. RAD (Rapid Application Development)
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is a project development methodology that prioritizes quick iterations and prototypes over extensive planning.
It involves user participation throughout the process, parallel development of system components, and a flexible, adaptive approach. Prototyping is a key feature, allowing for continuous refinement based on user feedback. RAD aims to deliver a functional product rapidly, focusing on time and cost efficiency.
Popular RAD tools include Microsoft Visual Basic, PowerBuilder, and OutSystems. The methodology suits projects with changing requirements but may not be ideal for highly structured endeavors.
10. Incremental and Iterative Methodologies
Incremental development involves dividing the project into small increments, each delivering a part of the final product's functionality linearly. User feedback is integrated after each increment, providing ongoing adaptability and the ability to identify and correct issues early. This approach enables early delivery and reduced project risk.
On the other hand, iterative development goes through cycles or iterations, refining the entire system with each iteration. It is highly flexible and accommodates changing requirements throughout the development process.
11. Hybrid Methodologies
Hybrid methodologies in project development involve blending elements from different traditional and agile approaches to create a flexible and tailored solution. That allows teams to adapt practices based on the project's unique requirements, leveraging both structured planning and iterative development.
In a hybrid methodology, the most appropriate elements from each methodology are identified and combined harmoniously. Examples include combining Waterfall and Scrum or integrating lean principles with agile practices.
The goal is to manage risks effectively, enhance flexibility, and address the project-specific needs. Effective communication is crucial to mitigate potential challenges introduced by diverse practices integration.
12. Extreme Programming (XP)
XP is an Agile methodology that emphasizes collaboration, adaptability, and delivering high-quality software through practices such as continuous testing and frequent releases.
Extreme Programming methodology is one of the famous methodologies for managing and developing software and other technical projects. It is based on diverse principles and practices, focusing on increasing software quality and improving team productivity.
A team needs to follow this method if the project is fast-paced or subject to regular change and thus has a dynamic rather than static nature.
The Extreme methodology also aims to achieve productive cooperation between team members and increase the quality of the final product and its flexibility in the face of changes.
Here are the main principles and practices of Extreme Programming:
- XP is built on a set of core values, including communication, simplicity, feedback, and courage.
- Developers work in pairs, one writing code and the other reviewing it in real time. That promotes collaboration, knowledge sharing, and code quality.
- Developers write tests before writing the actual code. That ensures that the code meets specifications and facilitates maintenance and updates.
- Code is integrated frequently to identify and address integration issues early in the development process.
- XP improves code design regularly without changing its functionality.
- XP keeps the design as simple as possible, making it easier to understand, modify, and maintain.
- Frequent and direct interaction with the customer allows for quick adjustments to changing requirements and priorities.
- XP emphasizes continuous improvement through regular reflection on the development process and changes in implementation to enhance efficiency and quality.
Bakkah provides a variety of accredited project management Courses for all professional certificates in project management, risk management, and others.
In brief, choosing the most suitable project management methodology depends on factors such as project size, complexity, industry, and organizational culture. Project managers often customize or combine methodologies to best fit the unique requirements of their projects.
Project management methodologies are often supported and implemented using various tools to enhance efficiency, collaboration, and communication throughout the project lifecycle. Here are some commonly used tools associated with project management methodologies:
1. Project Management Software
Tools like Microsoft Project, Asana, Jira, Trello, and Monday.com provide features for project planning, scheduling, task assignment, and progress tracking.
2. Version Control Systems
Git, SVN (Subversion), and Mercurial help manage changes to source code and documentation, ensuring version control and collaboration in software development projects.
3. Communication and Collaboration Tools
Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Discord facilitate real-time communication, file sharing, and collaboration among team members, supporting Agile and remote work environments.
4. Gantt Charts
Tools like GanttPRO and SmartDraw help create visual representations of project timelines, tasks, and dependencies, commonly used in Waterfall and traditional project management methodologies.
5. Kanban Boards
Trello, KanbanFlow, and LeanKit enable teams to visualize work and optimize workflow, particularly in Agile and Lean methodologies.
6. Scrum Tools
Jira, VersionOne, and Targetprocess support the Scrum framework with features for sprint planning, backlog management, and burndown charts.
7. Resource Management Tools
Workfront, Mavenlink, and TeamGantt assist in resource allocation, workload tracking, and managing team capacity in project management.
8. Risk Management Tools
RiskWatch, RiskyProject, and ProjectManager.com help identify, assess, and manage risks throughout the project lifecycle.
9. Collaborative Document Management
Tools like SharePoint, Google Workspace, and Dropbox Business enable teams to collaborate on documents, share project-related files, and ensure version control.
10. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD) Tools
Jenkins, Travis CI, and GitLab CI/CD automate integration code changes process and deploying software, commonly used in Agile and DevOps methodologies.
11. Time Tracking and Timesheet Tools
Harvest, Toggl, and Clockify assist in tracking project-related activities, allowing for accurate time management and resource allocation.
12. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Tools
Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM support customer-centric projects. That helps teams manage client interactions, feedback, and requirements.
Project managers and teams should carefully select tools that align with their chosen methodologies and project requirements. Integrating these tools can significantly improve project management efficiency and contribute to successful project outcomes.
Project management methodologies involve various techniques to plan, execute, and control projects effectively. Here are some commonly used techniques associated with project management methodologies:
1. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Break a project into smaller, manageable tasks and create a hierarchical structure to define clearly the scope and deliverables.
2. PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) and CPM (Critical Path Method)
Techniques for scheduling and managing tasks by identifying critical paths and dependencies and estimating project duration.
2. SWOT Analysis
Evaluate the project's Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
3. Risk Management
Identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor risks throughout the project lifecycle to minimize potential negative impacts.

4. Stakeholder Analysis
Identify and analyze stakeholders to understand their interests, influence, and expectations and ensure effective communication and engagement.
5. PERT Charts (Program Evaluation and Review Technique)
Graphical representations of project tasks and their dependencies, helping visualize the project schedule and critical path.
6. Scrum Meetings
Daily Standups, Sprint Planning, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective are regular Scrum meetings that facilitate communication and collaboration in Agile projects.
7. Earned Value Management (EVM)
Analyze project performance by measuring the planned value, earned value, and actual cost to assess progress and forecast future performance.
8. Quality Management
Implement techniques such as quality audits, inspections, and control charts to ensure project deliverables meet predefined quality standards.
9. Mind Mapping
Visualize project ideas, requirements, and tasks using mind maps to stimulate creative thinking and organize information in a structured way.
10. Critical Chain Method
Identify and manage resource dependencies to optimize project schedules and improve overall performance.
11. Prototyping
Creating a working model or prototype of a product or system to gather feedback early in the development process is common in Agile and iterative methodologies.
12. Benchmarking
Compare project performance metrics and processes against industry standards or best practices to identify areas for improvement.
13. Dependency Mapping
Identify and visualize dependencies between different tasks or project activities to understand their interrelationships and potential impacts.
14. Agile Estimation Techniques
Use techniques like Planning Poker, Relative Sizing, and Story Points to estimate the effort required for Agile project tasks.
15. Change Management
Implement strategies and techniques to manage and communicate changes effectively, ensuring minimal disruptions to project progress.
16. Communication Plans
Developing plans outlines how project information will be communicated to stakeholders, ensuring clear and consistent communication.
These techniques are often applied based on the specific requirements, characteristics, and principles of the chosen project management methodology. Project managers may tailor and combine these techniques to suit the needs of their projects.
Choosing a suitable project management methodology is crucial for the success of a project. The decision should be based on the project's characteristics, team dynamics, organizational culture, and the nature of the work to be performed. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to choose a project management methodology:
1. Understand Project Requirements
Clearly define the project scope, objectives, and deliverables. Consider the size, complexity, and nature of the project work.
2. Assess Team Skills and Experience
Evaluate the skills and experience of the project team. Consider their familiarity with different methodologies and their adaptability to new approaches.
3. Consider Project Flexibility
Assess the level of flexibility required throughout the project. Some projects may benefit from a more adaptive and iterative approach, while others may require a more structured and sequential process.
4. Examine Project Constraints
Identify any constraints such as budget limitations, time constraints, regulatory requirements, or client preferences that may influence the choice of methodology.
5. Evaluate Organizational Culture
Consider the existing organizational culture and whether it aligns with the principles of certain project management methodologies. Some organizations may prefer traditional, plan-driven approaches, while others may be more receptive to Agile or iterative methods.
6. Define Stakeholder Involvement
Determine the level of involvement and collaboration required from project stakeholders. Some methodologies, like Agile, emphasize continuous stakeholder engagement and feedback.
7. Analyze Project Risks
Evaluate the potential risks associated with the project. Some methodologies, such as Agile, are well-suited for projects with high uncertainty and evolving requirements.
8. Review Industry Standards
Consider industry standards and best practices. Certain industries or project types may have specific guidelines or regulations that align with particular methodologies.
9. Explore Hybrid Approaches
Assess the possibility of combining elements from different methodologies to create a hybrid approach tailored to the project's specific needs.
10. Pilot or Prototype
If feasible, consider running a pilot or prototype using a small-scale version of the project to test how well a methodology fits the team and project requirements.
11. Consult with Stakeholders
Seek input from key stakeholders, including team members, clients, and sponsors. Understand their preferences, expectations, and concerns regarding project management approaches.
12. Training and Transition Plan
Evaluate the readiness of the team to adopt a new methodology. Plan for necessary training and establish a transition plan to smoothly implement the chosen methodology.
13. Continuous Improvement
Be open to evaluating and adjusting the chosen methodology throughout the project. Continuous improvement is essential to address evolving project needs and improve overall project management processes.
Elevate your project management skills with Bakkah Learning's expert-led courses. From PMP to Prince2, Six Sigma to Agile, we offer tailored programs to suit your career goals. With interactive learning, flexible access, and certification preparation, we're your partner for professional growth. Start your journey to mastery today with Bakkah Learning!
Here are some Project Management Courses :
- Certified Associate in Project Management CAPM Course
- PMI-ACP® certification
- PgMP certification
- PMI Scheduling Professional - PMI-SP certification
Risk Management Courses And Certifications:
- Risk Management Professional - PMI-RMP Course
- MoR Certification and course
PRINCE2 Courses
- PRINCE2 Certification
- PRINCE2 Agile.
Project Management Tools:
- Primavera P6 Course
- MSP Course - Managing Successful Programmes
- Microsoft Project training course
Portfolio Management
- P3O Foundation certification
- Management of Portfolios MoP
- The Portfolio Management Professional – PfMP certificate
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Course
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Course
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Course
Ultimately, the choice of a project management methodology should be a thoughtful and informed decision that aligns with the unique characteristics of the project and the organization. Regularly reassess the chosen methodology to ensure its continued effectiveness and make adjustments as needed.
Related Courses
Our learning programs are delivered through a tested and professionally designed methodology.

Exam is included

2,102.5 SAR
Live Online

1,270.75 SAR

2,600.15 SAR

2,712.56 SAR

3,677.7 SAR

Your experience on this site will be improved by allowing cookies.
Added to Cart
{{ convertjson(lastcartitem.course.title) }}, features with this course, total with vat, {{ parsefloat(totalfeatures(lastcartitem)) }} {{currency}}.


How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 11 min read
Project Management Phases and Processes
Structuring your project.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
For all but the smallest projects, experienced project managers use well-established project management methodologies. These are often published systems – such as PMBOK®️ Guide (Project Management Body of Knowledge) or PRINCE2 – but they can also be in-house methodologies that are specific to the organization.
These approaches have some differences in emphasis, and they tend to use slightly different terminology, but they generally share two key features: projects are delivered in stages, and certain common project management processes run across these stages.
This is illustrated in figure 1, below.
Figure 1 – Project Management Structure
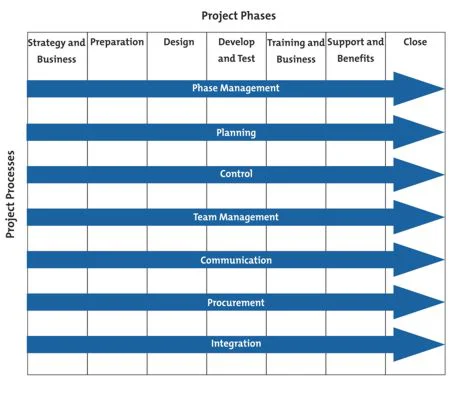
This article explains these phases and processes in more detail. If any of the terms used in this article are unfamiliar to you, refer to our article Words Used in... Project and Program Management .
Deliver your project successfully by breaking it down into these seven key phases.
Project Phases
Phases, or stages, are very important for project managers. By thinking in terms of phases, you can ensure that the deliverables produced at the end of each phase meet their purpose, and that project team members (or sub-teams) are properly prepared for the next phase.
You identify the required deliverables for each phase from the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) for it. The WBS is drafted as part of your preparation activities, and then validated by the rest of the project team. At the end of each phase, someone signs off on the deliverables from that phase. (In your preparation phase, think through who needs to approve each deliverable. Approvers may include the project board, project sponsor, or key stakeholders.) Once the deliverables are approved, the phase is completed and the project team can pass through the "gate" to the next phase. This is why the term "stage/gate" is used so often in project management.
The exact phases, and the order in which they're completed, may vary slightly, depending on what you need to achieve with your project. The phases are as follows:
- Project strategy and business case.
- Preparation.
- Development and testing.
- Training and business readiness.
- Support and benefits realization.
- Project close.
Let's explore each phase in more detail.
Project Strategy and Business Case
In this phase, you define the overall project business requirement , and propose the approach or methodology that you want to use to address it.
The gate at the end of this phase is the approval of your high-level project proposal and of the business case that validates the approach you want to use. You must also show that you can achieve the project's goal within the required timelines and budget.
Make sure that you review the business case at the end of each project phase to ensure that it’s still valid. If anything has changed, revise it as needed.
Preparation
Here, you work with key stakeholders and project team members who have already been identified to establish and start the project:
- Complete a high-level Work Breakdown Structure .
- Determine the project's high-level plan at the milestone level . (Work with appropriate project team members to produce detailed plans at each subsequent phase. This ensures that they have a sense of ownership of these plans.)
- Identify and recruit project members.
- Produce the Project Initiation Document .
- Select third parties to use in the early project phases (for example, IT subcontractors or partners).
- Put actions in place to secure key resources. (For example, reserve rooms for the training phase, and allocate desks and PCs/printers for the project team.)
In this phase you start the work involved with creating the project's deliverables, using the project strategy, business case, and Project Initiation Document as your starting point. Then work with relevant stakeholders to develop the designs of the main deliverables. In larger projects, you may use business analysts to help you with this.
You probably have a project board or project sponsor who is responsible for signing off the overall design, but make sure you also get input from other stakeholders as well. This helps build business ownership of the project deliverables.
If changes to processes are required, use a Flow Chart or Swim Lane Diagram to create a detailed map of how things will work. At this stage, you must do everything you can to think through and deal with project issues before you start to build project deliverables – problems are almost always easier and cheaper to fix at design stage than they are once the detailed work of implementation has started.
Select stakeholders carefully for the detailed design phase. A good detailed design is more likely to lead to a good project deliverable. If the detailed design is poor, the project deliverables are much less likely to meet requirements!
For projects that have significant technical risks and uncertainties, consider including a feasibility or proof-of-concept phase. This increases your certainty that what you're planning (probably at great expense) will work, while allowing you to cancel the project at minimum cost if the proof-of-concept fails.
Development and Testing
With all of the planning and designing complete, the project team can now start to develop and build the components of the project output – whether it's a piece of software, a bridge, or a business process.
As part of this phase, you need to test these components thoroughly to confirm that they work as they should.
Training and Business Readiness
This stage is all about preparing for the project launch or "go live." Do the following things during this phase:
- Train users.
- Put in place ongoing support.
- Transfer data to new systems.
- Identify what's required for the project to be effective from the launch date, and ensure that you adequately address this.
Support and Benefits Realization
Make sure you provide transitional support to the business after the project is launched, and consider what's required before your team members are reassigned. Project teams are often assigned to other work too soon after the project has gone "live", meaning that project benefits are often not fully realized.
Monitor the delivery of project benefits . You can use this to promote your project or to give you information about other actions needed to ensure that the project is successful.
You can monitor benefits as part of "business as usual" activities, and you should (ideally) continue to do so after the project is closed.
Project Close
Closing a project is not the most exciting part of the project lifecycle, but, if you don't do it properly, you may obstruct the ongoing delivery of benefits to the organization. Make sure that you do the following:
- Complete and store documentation.
- Carry out a Post-Implementation Review , so that you and your colleagues can use the experience you've gained in future projects.
- Use your business connections to reassign project team members to appropriate roles in the organization. You don't want to lose the experience and knowledge that they've gained from working on the project.
Project Management Processes
The key project management processes, which run through all of these phases, are:
- Phase management.
- Team management.
- Communication.
- Procurement.
- Integration.
Let's look at each process in more detail.
- Phase management – Here, you ensure that you adequately satisfy the conditions for completing each phase, and for starting the next one. To do this, make sure that you fully understand the "gates", or deliverables that must be completed and approved by the appropriate stakeholders before you can exit a phase. Deliverables and sign-off requirements are usually identified in the Project Initiation Document , so review this appropriately during the project.
- Planning – Carry out high-level planning for the whole project at the start of the project, then do more detailed planning for each phase at the start of each phase. Ensure that you have the right people, resources, methodologies, and supporting tools in place for each planning phase, so that you can deliver the project on time, on budget, and to appropriate quality standards.
- Control – It's essential to control scope , cost , and issues ; and to manage time, risks , and benefits effectively. Create reports that contain the information you need to create an accurate picture of how things are proceeding. A common way of doing this is to use a Project Dashboard .
- Team management – As project manager, you are responsible for managing the project team. Working on a project is often different from most "business as usual" activities, and project work may require a different approach and set of skills. As such, you'll probably need specific project management training and support. And there are additional complexities in managing team members who have project responsibilities as well as other roles at the same time (see our article on Managing Cross-Functional Teams for more on this).
- Communication – Make sure that you're clear about who is responsible for communicating to team members, the project board, the different stakeholders within the business, and relevant third parties. Inadequate communication is a frequent problem area for projects, and it needs considerable attention to communicate well. Our articles on communication skills are a useful starting point for developing these essential skills.
- Procurement – This is a specialist area. Many projects hire third parties to manage purchasing, particularly when it involves IT systems. Managing these third parties is often the role of the project manager. See our articles on Request for Proposal Documents and Procurement Management for more on this.
- Integration – Many projects do not stand on their own within an organization – they often impact other areas of the business. Make sure that you consider how your project will interface with other projects or functions.
Formal project management involves following an established project management methodology. In turn, most of these methodologies follow a set of common project phases, with common processes that run across each phase.
To explore project management further, take our Bite-Sized Training session, What is… Project Management?
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Dyslexia in the workplace.
Supporting People With Dyslexia
How to Use LinkedIn Effectively
Getting the Best from the World's Biggest Networking Site
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Try Mind Tools for FREE
Get unlimited access to all our career-boosting content and member benefits with our 7-day free trial.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Team Briefings

Onboarding With STEPS
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
New pain points podcast - perfectionism.
Why Am I Such a Perfectionist?
Pain Points Podcast - Building Trust
Developing and Strengthening Trust at Work
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Impromptu speaking skills.
Preparing for Last-Minute Opportunities
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The Four Phases of Project Management
- HBR Editors

Planning, build-up, implementation, and closeout.
Whether you’re in charge of developing a website, designing a car, moving a department to a new facility, updating an information system, or just about any other project (large or small), you’ll go through the same four phases of project management: planning, build-up, implementation, and closeout. Even though the phases have distinct qualities, they overlap.
- This story is by the staff at Harvard Business Review.
Partner Center

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
3 The process-based methodologies
Learning Outcomes
- Contextualise key benefits of process-based project management methodologies.
- Exhibit the 7 principles, 7 themes, 7 processes of the PRINCE2 method.
- Articulate the key benefits of Lean Project Management.
- Conceptually map differences and similarities between the Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma approaches.
Process-based project management methodologies follow a systematic process which incorporates creation, management, and improvements. The process aims to align the objectives of the project to those of the organisation, project team, stakeholders, and clients (Goodman 2006). Within this process, all tasks, activities, and objectives must contribute to the outcomes of the project and business strategies. The primary aim is to achieve a common goal, based on collaboration between project team members, stakeholders, and the clients.
Process-based project management ensures that the project team understands the current state, potential improvements, and optimal end-state. This method allows organisations to understand the different requirements of the project to meet the overarching outcomes, and how to best manage the individual processes, tasks, and activities within the project. As per research by Myles and Coats (1995), through process-based project management, organisations are better able to:
- understand the varying client demands, needs and expectations, including how they change over time and in response to environmental factors
- support the response to the identified client expectations
- develop skills and capabilities in the project management domain
- manage their project from end-to-end
- integrate their various projects, programs, and portfolios
- identify and manage the different success and benefit indicators
- link the project outcomes to the organisational goals and objectives.
Within process-based project management, there are 6 commonly identified stages (Myles and Coats 1995), as outlined in Figure 6.
Figure 6. Common phases of process-based project management, by Carmen Reaiche and Samantha Papavasiliou, licensed under CC BY (Attribution) 4.0
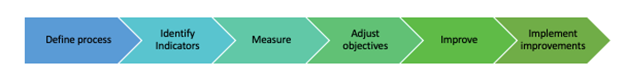
Stage 1: Define the process . Processes need to be clearly identified, precisely documented and shared with the project teams to ensure that they are properly followed and understood. This includes using tools, documentation, stakeholder consultations, agreements, guides for asset management and process diagrams/flow charts. The process should also define the responsibilities and roles of the different team members, including operational needs, reporting requirements and performance expectations.
Stage 2: Identify indicators . Evaluation is a crucial step in the process, including developing, collecting, and monitoring data outlining the performance of the process and team. This ensures that future improvements can be implemented around efficiency, quality, duration, and scheduling. These indicators need to be quantifiable, using comparative data, relevant references, and other supporting data for analysis.
Stage 3: Measure process performance . The current performance of processes needs to be measured to ensure the achievement of objectives and outcomes. This also enables a team to make decisions that support efficiency, evolve over time, and solve complex issues.
Stage 4: Adjust objectives . Check compliance of the process to ensure it is stable and adequate. If it is not, determine how to best improve the processes moving forward.
Stage 5: Improvements. Ongoing improvements and changes will occur to organisational culture, mission and vision statements, and objectives. Therefore, success measurement needs to be considered for all changes.
Stage 6: Implement selected improvements. For improvements as outlined in the previous step, organisational training may be required, as well as ongoing support for team members, and regular monitoring and continuous improvement of processes.
Advantages and disadvantages of process-based project management
There are numerous advantages of applying process-based project management, including improved processes, increased value-adding activities, reduced costs, and strategic alignment to the organisation.
Organisations which follow process-based project management processes see improvements to flexibility, interpersonal relationships between employees, and the reach of the outcomes. Within a process-based methodology, every staff member knows their roles and responsibilities, and they collaborate to achieve the end-state. As a result, use of resources is improved, decreasing overall costs.
Most process-based methods encourage continuous improvements, whereby inefficiencies are identified and removed. Therefore, applying this method to a project and/or an organisation, there is a move away from a hierarchical system. Instead, roles and responsibilities are dictated based on organisational need. Change management also becomes a key area within the planning process. Organisational training needs to be ongoing, ensuring that every employee is part of the process.
Process-based project management methodologies include the following:
- PRINCE2: the main focus is 7 principles, 7 themes, 7 processes.
- Lean Project Management: the main focus is maximum efficiency, minimum waste.
- Six Sigma: the main focus is improvement by eliminating defects/bugs.
- Lean Six Sigma: the main focus is no waste + zero defects.
Let’s explore each of these approaches.
PRINCE2: 7 principles, 7 themes, 7 processes
PRINCE2 is a process-based method for effective project management, and it stands for PR ojects IN C ontrolled E nvironments. The focus of this method is on breaking a project into smaller components and stages (Axelos 2015; PRINCE2 2022). This is achieved by outlining clear roles and responsibilities and applying the project life cycle using the 7 processes outlined in PRINCE2. Projects should also be broken into logical steps, following a framework that is organised and controlled prior to starting the work, and is maintained and followed throughout the execution (Axelos 2015; PRINCE2 2022). PRINCE2 is based on the following 7 key principles, 7 themes and 7 processes.
Seven Principles
The PRINCE2 method is based on the application of 7 principles (also referred to as guidelines) which are not to be altered. PRINCE2 principles are defined as a mindset. If the project does not meet these principles, it should not be managed through PRINCE2 methodology (Lawton 2015; Bennett 2017; Axelos 2018). These principles, as outlined in Lawton (2015), are:
- Continued business justification. The business case is vital and updated throughout the project to ensure that the project remains viable. Through the business case, if the project ceases to provide value, the project can be terminated early.
- Learning from experience. Maintain a lesson learned register for each project and ensure that the project team uses the logs throughout the project (and reviews registers from previous and concurrent projects).
- Defined roles and responsibilities. Within PRINCE2 there are 4 levels of structure in terms of roles and responsibilities, including program or corporate management, project board, project manager and project management team level. Within the project management team, all the primary stakeholders need to be represented (business, user, and suppliers), along with the roles and responsibilities of the team members themselves.
- Managing through stages. Projects are controlled and planned in stages, moving stage by stage. This includes updating documentation as required, including the business case, risk register, project plan and next steps work breakdown structure.
- Management by exception. Projects using the PRINCE2 method have defined tolerances (6 aspects, defined below) for each objective, outlining levels of authority. If these tolerances are exceeded, the decision needs to be extended to a higher delegation.
- Focus on products/outcomes. The project’s primary focus should be the definition and delivery of products or outcomes, including their quality requirements.
- Tailored to suit project environment. PRINCE2 should be tailored to meet the project needs (for example, environment, size, complexity, importance, scheduling, budget, and risk). Within PRINCE2 the first activity is tailoring within the initiation phase (which is then reviewed at each stage).
Not every principle or component outlined with PRINCE2 is applicable to every project. The components are used to guide the project manager and project team on whether these processes are relevant to the project specifics. A primary element of PRINCE2 is tailoring the needs to a particular project (Lawton 2015).
Six aspects
The 6 aspects are also referred to as the project tolerances and/or performance goals. These are used to quantify the project tolerances or performance expectations that need to be followed and considered as part of the decision-making process (Lawton 2015; Bennett 2017; Axelos 2018). Additionally, these can be referred to as Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Table 4 outlines the various aspects within PRINCE2.
Table 4. Six aspects of PRINCE2 (Lawton 2015; Axelos 2018)
Project benefits can be difficult to determine, especially when related to ensuring that the project remains within cost/budget.
Seven Themes
Themes are the activities which need to be completed at the start of a project. They are used to set a baseline and monitor a project throughout its life cycle. Themes are used to guide how the project should be managed (Lawton 2015; Bennett 2017; Axelos 2018). Therefore, themes are tailored to suit the project needs, depending on the environment, scale, budget, and schedule (Lawton 2015). These are outlined in Table 5.
Table 5. Seven themes of PRINCE2 (Lawton 2015; Axelos 2018)
Seven Processes
The 7 processes are used to manage a project and identify the roles and responsibilities of the project team members (Lawton 2015; Bennett 2017; Axelos 2018).
- Project start up. This step determines whether the project is viable and includes the project brief, business case and stepping out a plan of the key milestones. Within this step, the project manager is appointed along with the project team (Axelos 2018). This step should provide a clear scope of work to be completed and support the creation of baselines and performance expectations.
- Project initiation. This step requires the definition of the project aspects (for example, scope, cost, schedule, risk, quality, and benefits) (Axelos 2018).
- Direct a project. This step requires ensuring that the decision-makers are accountable throughout (Axelos 2018).
- Control a stage. This step involves controlling how each individual stage will be managed, following the work breakdown structure, the project plan and schedule. The project manager is responsible for assigning work, and ensuring it is completed and meets the requirements (Axelos 2018). These should be reviewed; ongoing checks need to be in place to verify and compare the progress of the project work against the project plan and consider the issues and risks that have occurred and their resulting impact.
- Manage product/outcome delivery. This step involves managing the delivery of the project product or outcomes, controlling the work being completed and the performance of the project team (Axelos 2018). For the project manager and project team there should be formal requirements for their performance, their acceptance criteria, steps for execution and delivery of the project work.
- Manage stage boundary. This step is broken into 2 parts. First, the project manager is responsible for providing updates to the project boards outlining the performance, updates or changes to documentation, and creating next steps plans (as required) (Axelos 2018). Second, information provided by the project manager to the project board is used to provide understanding of what they are approving or how work is progressing (Axelos 2018). Overall, this step is used to document transitioning or moving between stages.
- Project closure. This step involves the formal closure of the project, transitioning to business as usual and evaluation of the benefits/performance (Axelos 2018).
In sum, PRINCE2 is a commonly used process-based project management methodology. PRINCE2 project management methodology offers significant benefits to project managers, project sponsors, and project team members within an organisation and for the organisation more broadly. These benefits link back to the fact that the project is more controllable using resources and can manage the business and risks associated with the project more efficiently.
Lean project management: maximum efficiency, minimum waste
Lean project management is often referred to as less of a project management tool and more of a mindset for driving continuous improvement. The lean method is based on experiences within the Toyota Production System (TPS) and is often referred to as Toyota’s Lean Method. It is based on applying lean manufacturing principles to managing projects (Womack et al. 1990; Womack and Jones 1996; Moujib 2007). The method focuses on reducing waste across all business processes, resulting in cost and lead-in time reductions and quality improvements.
As the basis of Lean management is continuous improvement, it fits within the broader Agile project management environment. This is due to its overarching flexibility and adaptability to change. The primary focus is delivering value to clients/customers and broader stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing: Toyota Production System
After the 1973 energy crisis, Toyota was the only organisation that managed to resist foreclosure. It did so by changing the way in which it worked to be more efficient and effective. Through implementing a cultural shift within their organisation and empowering its workforce, Toyota was able to undertake a continuous improvement process (Womack et al. 1990; Womack and Jones 1996; Moujib 2007). Encouraging its employees to identify inefficiencies and overcome them through implementing new ways of working (Womack et al. 1990; Womack and Jones 1996; Moujib 2007) led to improvements in its product quality and client satisfaction, and a reduction in cost and lead-times.
This process was a breakthrough for mass production, which started to move towards lean production – from a push system to a pull system.
Lean benefits
The Lean methodology uses less of everything, compared to most other mass production processes (Womack et al. 1990:256). Benefits outlined in the literature include:
- reduced lead-in times
- lower inventory and storage costs (due to less over-production)
- decreased overall costs
- productivity and efficiency improvements
- increased quality
- improved client satisfaction.
3Ms of Lean
‘To be lean is to provide what is needed, when it is needed, with the minimum number of materials, equipment, labor, and space’, (Moujib 2007). Within Lean manufacturing, there are three types of waste: Muda, Muri, and Mura (commonly referred to as the 3Ms) (Moujib 2007).
- Muda includes activities which consume resources without providing additional value.
- Muri includes overuse of equipment or employees.
- Mura outlines operational ‘unevenness’, based on decreased long-term efficiency and productivity.
The overarching aim of Lean project management is to reduce the 3Ms within the project process.
Principles of Lean Thinking
A primary element of Lean project management is the application of 5 principles (outlined in Figure 7). The first step is to understand how to apply the 5 principles to your project (Womack et al. 1990; Womack and Jones 1996; Moujib 2007).
Figure 7. Five Lean Principles, by Carmen Reaiche and Samantha Papavasiliou, licensed under CC BY (Attribution) 4.0
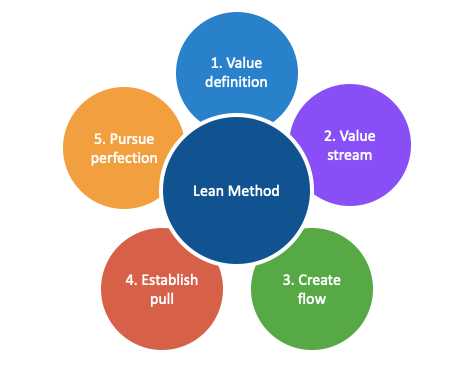
The 5 principles are:
1. specify value in the eyes of the customer.
Specifying value is the first lean principle. This principle requires defining the value of a product, service, or outcome (Womack et al. 1990; Womack and Jones 1996; Shook and Rother 1999; Morgan 2002; Moujib 2007). Value ensures that the outcome is provided to clients at the right time, based on the right price and to the requirements of the client (Womack and Jones 1996). Value should be outlined in the client’s words. The challenge of Principle 1 is being able to focus on what the client is willing to pay and their overarching needs.
2. Identify the value stream for each product
Identifying the value stream is the second lean principle. The value stream can be defined as all the actions within the process that are required to bring about the outcome or product to the client (Womack et al. 1990; Womack and Jones 1996; Shook and Rother 1999; Morgan 2002; Moujib 2007). This includes all steps from design, planning, testing, and launching. The flow should also outline the different value-added and non-value-added processes (Morgan 2002).
The first step in applying Principle 2 is creating a value stream map. This should reflect the current state of how processing is occurring within the organisation, or the steps taken to reach an outcome (Morgan 2002). Once completed, this map needs to be analysed to identify where there is waste and how value can be created. After this has been completed, the future-state map is documented, and it is the representation of how the process needs to operate to reduce waste.
Using these process maps, an improvement plan is generated. This plan will support the transformation from current to future state.
3. Make value flow by eliminating waste
Principle 3 involves the flow of value through the elimination of waste. After defining the value, identifying the value stream and considering the improvement plan, the next step is to create continuous flows (Womack et al 1990; Womack and Jones 1996; Shook and Rother 1999; Morgan 2002; Moujib 2007). This requires eliminating backflows, reworks, wasted work, interruptions, and scrap. The elimination process should involve removing stoppages throughout the process and ensuring that all value streams identified fall within 3 categories:
- Value-Added Work: essential to producing the outcome, product, or service. The aim is to maximise work that fits within this category, as the aim is to provide client value (Form, Fit, Function) (Morgan 2002).
- Value-Enabling Work : work that can be potentially eliminated in the future (based on identified improvements) but cannot be eliminated immediately. In the current state, this work is necessary (Morgan 2002). This incorporates different components, including technology, environment, culture, and others. The aim is to identify waste in this section and minimise work within this category.
- Non-Value-Added Work: work which can be eliminated quickly as it does not flow on to improvements in other areas (Morgan 2002). This section outlines the work that is not needed, defined as pure waste. The aim is to eliminate all work within this category.
In addition to the 3 categories of waste, all the waste (‘pure’ or ‘necessary’) identified can be classified within one of the following 7 types (Womack et al 1990; Womack and Jones 1996; Shook and Rother 1999; Morgan 2002; Moujib 2007):
- Over production: producing more than is necessary before it is required.
- Waiting: non-work time waiting for approval, supplies, parts, etc.
- Transportation: effort wasted on transportation of materials, parts, or finished goods into or out of storage or between processes.
- Over processing: undertaking more work than required (customer requirements) or double the work.
- Inventory: holding excess inventory of raw materials, parts in process or finished goods.
- Motion: wasted motion or actions to pick up or stack parts.
- Defects: reworks or repairs required due to inferior quality.
4. Let the customer pull the flow
Principle 4 is around letting the client pull the flow. This principle presents a challenge, specifically how to avoid delivering value prior to the client’s customer request (Morgan 2002) and ensuring that the outcomes provided do not exceed the initial and agreed upon scope. By letting the client pull the flow, the implementation is based on the just-in-time system, whereby the client signals the need for the item or outcome triggering the next steps required.
5. Continuously improve in the pursuit of perfection
The fifth and final principle is the pursuit of perfection through continuous improvement. This requires a process of improvement built into the business as usual and within the culture (Morgan 2002). The pursuit is endless, and as a result all activities should be questioned as to the value they add. Perfection may never be achievable; however, the aim should be to get as close as possible.
In sum, Lean project management is a process-based project management methodology. This methodology is also referred to as a mindset around the improvements within an organisation. The focus is on improving efficiency, reducing waste, and increasing productivity. There are many benefits associated with the application of Lean methods, including better product outputs and quality and improving the overall organisational efficiency and allocation of resources. Lean methods encourage innovation and quality controls.
Six Sigma: improvement by eliminating defects/bugs
Six Sigma uses a set of techniques and tools for process improvement. The purpose of Six Sigma is to identify improvements to quality in manufacturing through detecting and removing causes of defects, aiming to minimise variability in outputs. To achieve this, Six Sigma uses statistical quality management methodologies (Harry 1988; De Feo and Barnard 2005; Gygi et al. 2005; Kwak and Anbari 2006). Each project follows a set methodology, based on specific value targets (for example, reduction in pollution, improvements to client satisfaction, decreased cost of production).
The term originates from statistical modelling within manufacturing processes, the maturity of which is described through a ‘Sigma rating’ which indicates yield or number of defect-free products (Harry 1988; De Feo and Barnard 2005; Gygi et al. 2005; Coryea et al. 2006; Kwak and Anbari 2006). In technical terms, it relates to how many standard deviations within the normal distribution the percentage of defect-free outcomes equates to.
Six Sigma: Motorola manufacturing
Six Sigma was developed by Motorola, who set Six Sigma as the goal for their manufacturing. The process was developed to promote quality outcomes within an organisation, with a focus on the elimination of defects (Harry 1998). The term was coined in 1985 by Bill Smith and trademarked by Motorola in 1987 (Harry 1998). It has also been defined as an attitude, whereby making outcomes defect-free should be the aim of all employees.
Six Sigma components
This method requires the following components (Harry 1988; Kwak and Anbari 2006):
- Continuous improvements are to be implemented as part of the process, in order to create a stable and predictable output. This stability is vital to business success.
- Characteristics within manufacturing and business processes need to be defined, measured, analysed, improved, and controlled.
- The entire organisation should be committed to achieving ongoing quality improvement – this is especially important for higher level leaders.
There are a number of features within Six Sigma which set it apart from similar methods:
- The focus is on achieving measurable financial returns.
- Leadership and support from management is vital.
- Verifiable data-driven decisions are required to remove guesswork.
The focus of Six Sigma is eliminating defects and reducing variation. The primary goal is to improve processes, so an organisation should determine the appropriate Sigma level for every one of their processes and aim to achieve these. It is important that management is clear on the areas for improvement and how they will be attained.
Methodologies
Six Sigma projects follow two project methodologies (De Feo and Barnard 2005), as follows.
This is used for projects which aim to improve an existing business process. It follows 5 key phases (De Feo and Barnard 2005) (see Figure 8).
Figure 8. DMAIC 5 phases, by Carmen Reaiche and Samantha Papavasiliou, licensed under CC BY (Attribution) 4.0

- Define the system. Document and understand the needs of the client and what they require and use this data to develop the project scope and goals.
- Measure the current process and use it as a baseline.
- Analyse data and identify where possible the different causes and effects. Highlight the relationships between the different factors, then, once all factors have been considered, seek out the root cause of the defects.
- Improve the current process, based on data analysis techniques and mapping future-state processes. It is recommended that organisations use pilot testing to understand the impact of proposed changes.
- Control future-state processes by ensuring deviations from target are corrected before they cause defects. This requires implementing quality control systems (for example, statistical controls), and continuously monitoring the process. This entire process should be ongoing and repeated until desired quality levels are obtained.
This is used for projects which aim to create new outcomes, products, or process designs. The process is also referred to as Design For Six Sigma (DFSS). It follows 5 key phases (De Feo and Barnard 2005) (see Figure 9).
Figure 9. DMADV 5 phases, by Carmen Reaiche and Samantha Papavasiliou, licensed under CC BY (Attribution) 4.0
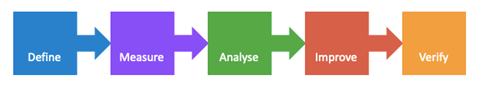
- Define or design project goals which meet the client requirements, and new or existing organisational strategies.
- Measure and identify all the distinctive characteristics which are Critical to Quality, and can be used to measure the outputs, risks, and capabilities.
- Analyse the proposed future state and develop proposals for potential alternatives that can support improvements.
- Design an improved outcome, based on the analysis completed in the analyse step.
- Verify the design using test runs or pilots, implement the process into business as usual and complete the handover.
Benefits to Six Sigma
Organisations can benefit from applying Six Sigma methodology to their business and projects in many ways (Harry 1988; De Feo and Barnard 2005; Gygi et al. 2005; Coryea et al. 2006; Kwak and Anbari 2006), including the following:
- Reduction in operational costs. The application of Six Sigma can provide organisations with a future-state process map which highlights inefficiencies and reduces the exposure to risks, making the organisation more efficient and effective at delivering its outcomes.
- Improved efficiency or timeliness. This methodology improves the efficiency of processes, encouraging timeliness in delivering products or services on time.
- Improved accuracy, controls, and policy compliance. It helps to improve accuracy through reducing Defects-Per-Million-Opportunities (DPMO) across the process value stream. The DPMO is a probabilistic measure of error rate and takes into consideration actual and probable defects in every opportunity.
- Improved customer service. Organisation corporate is significantly impacted by client interactions. By applying Six Sigma, organisations can better understand client experience, understand what is causing different experiences and minimise dissatisfaction.
- Improved cash flow. The primary improvement gained by applying Six Sigma relates to improvements in sales, which results in cash flow improvement.
- Improved regulatory compliance. There are 3 primary types of regulatory compliance: financial and audit, information technology, and legal. The Six Sigma project type will dictate which of these will be the focus and what kinds of defects or efficiencies can be identified.
In sum, Six Sigma is a process-based project management methodology. This method provides organisations and project managers with several tools which support the improvement of business processes and their capability. Like Lean, the purpose is to improve performance of team members including outputs, while decreasing variations in the process to achieving an outcome. This in turn leads to reduction in defects and supports improving profits, team morale and quality outcomes.
Lean Six Sigma: no waste + zero defects
Lean Six Sigma is defined as a collaborative team effort, based on improving overarching performance through the systematic removal of waste (George 2002). It is a combination of Lean project management and the Six Sigma method, which aims to eliminate 8 distinct types of waste (referred to as muda) (George et al. 2003). Therefore, the principles of Lean Six Sigma are aimed at improving both quality processes and efficiency.
Waste can be defined as anything other than the minimum required levels of materials, equipment, parts, space and employees which are essential to complete the product (Summers 2011). The several types of waste are outlined below (Skmot 2017):
- Defects: a product that is unfit for use, requires disposal or reworking. This costs money and time to address.
- Over-production: excess products or those made or purchased before they are required.
- Waiting: delays caused by waiting for material or equipment or conversely unused equipment.
- Non-used talent : wasting human potential and skills, where employees are not empowered to provide feedback or obtain training and skills improvement.
- Transportation: unnecessary or excess movement of people, tools, equipment, products or materials.
- Inventory : excess products and materials that go unprocessed. It could cause items to become unnecessary before the start of its life cycle usage, storage costs increase or damage could occur to the materials.
- Motion: unnecessary movement by people, whereby excessive motion wastes time and can cause injury.
- Extra-processing: doing more work than required to complete a task.
Three key elements of Lean Six Sigma
There are 3 primary elements that need to be understood and considered as part of the application of Lean Six Sigma (George 2002; Summers 2011):
- Customers: These need to be at the centre of everything that an organisation does and support the development of the outcome. Customers are primary stakeholders with a significant interest in obtaining products which are of the highest quality but the cheapest price.
- Processes: Business processes require a rework or evaluation, changing to an outside-in approach based on the value chain. Customers pay for products which are defect-free. Therefore, organisations using Lean Six Sigma focus primarily on high quality products and outputs.
- Employees: Clear business processes are required across all levels of the organisation. Transformation needs to be part of the organisational culture.
Within Lean Six Sigma, innovation stems from need. Need is driven from customer expectations and requirements. Organisations must constantly evolve and this includes developing innovative solutions, with the aim of pre-empting the market needs.
Lean Six Sigma principles
There 5 fundamental principles of Lean Six Sigma (George 2002; Summers 2011) (see Figure 10).
Figure 10. Lean Six Sigma principles, by Carmen Reaiche and Samantha Papavasiliou, licensed under CC BY (Attribution) 4.0
- Customer focus. Define what ‘quality’ and ‘satisfaction’ mean to customers and align business processes with the employees and skills required to achieve the goals.
- Define roadblocks to consistent quality. Undertake an assessment of the organisational priorities which aim to meet customers’ and stakeholders’ expectations. The organisational problems and priorities need to be well defined, and this can be supported by qualitative and quantitative data.
- Eliminate inefficiencies. Remove non-value added and value-added steps within business processes. Through applying Lean Six Sigma, organisations can eliminate waste, simplify processes and offerings, or automate where possible. The aim is to measure the outcomes and improve as needed.
- Communication and employee alignment. Ongoing communication and training should be implemented across the organisation, establishing a cultural change of collective problem-solving. This cultural change should also be encouraged down from the leadership and managerial levels to the employees.
- Be flexible and adaptable. Organisations, including their employees, need to be responsive to change. This should include changes to organisational structure and management strategies, to enable responsiveness to the market.
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma
The implementation of Lean Six Sigma methodology should influence the entire organisation’s approach to delivering customer outcomes (George 2002; Summers 2011). There are a multitude of benefits that the application can provide, including the following:
- Talent and capability development. Using Lean Six Sigma requires ongoing development of employees’ capabilities. As a result, there is an enhanced focus on talent development and continuous learning built into the organisational culture.
- Quality delivery through efficient business processes. Business processes are supported through data-driven decision-making and increased transparency. Quality comes from the client-centric focus which ensures that customer voices are heard and that future designs will meet the changing market.
- Scalable across sectors. Lean Six Sigma can be applied broadly across industries, with successful application seen across retail, IT, healthcare, and other sectors.
- Basis for technology deployment. Lean Six Sigma aims to drive continuous improvement. There are many scenarios where it has supported digital transformation efforts, alongside broader business transformation strategies.
- Enhancement of brand value. Clients trust organisations that respond to their issues and challenges in a timely way. Lean Six Sigma encourages an organisational culture whereby people and processes are based on enhancing brand.
In sum, Lean Six Sigma is another process-based project management methodology. Organisations that use this methodology often identify improvements to their overall client experience and as a result improved client loyalty. These improvements are also evident across the organisation, with improvements to their internal efficiencies, processes and team members, along with increased profitability. Like Lean and Six Sigma, this process-based methodology aims to prevent defects in products or outcomes, reduce costs and remove waste wherever possible.
Test your knowledge
Key Takeaways
- Process-based project management methodologies follow a systematic process which incorporates development, management, and improvements.
- The focus of the PRINCE method is on breaking a project into smaller components and stages.
- Lean project management is often referred to as less of a project management tool, and more of a mindset for driving continuous improvement.
- The purpose of Six Sigma is to identify improvements to quality in manufacturing through identifying and removing causes to defects and aims to minimise variability in outputs.
- Lean Six Sigma is defined as a collaborative team effort, based on improving overarching performance through the systematic removal of waste.
Axelos (2015) Prince2 Agile , Stationary Office, United Kingdom.
Axelos (2018) Directing successful projects with PRINCE2®: the essential guide for project board members (managing successful projects With PRINCE) , Stationary Office, United Kingdom.
Bennett N (2017) PRINCE2 handbook: managing successful projects with PRINCE2 , Stationary Office, United Kingdom.
De Feo JA and Barnard W (2005) JURAN Institute’s Six Sigma breakthrough and beyond: quality performance breakthrough methods , Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited.
George ML, Rowlands D and Kastle B (2003) What is Lean Six Sigma? , McGraw-Hill Education, accessed 3 August 2022. https://archive.org/details/whatisleansixsig00geor
George ML (2002) Lean Six Sigma: combining Six Sigma quality with lean production speed , McGraw-Hill Education.
Goodman AF (2006) Process-based software project management , CRC press, United States.
Gygi C, DeCarlo N and Williams B (2005) Six Sigma for dummies , Wiley Publishing, Hoboken, NJ.
Harry MJ (1988) The nature of six sigma quality , Motorola University Press, Rolling Meadows, Illinois.
Kwak YH and Anbari FT (2006) ‘Benefits, obstacles, and future of six sigma approach’, Technovation , 26.
Lawton I (2015) PRINCE2 made simple , 6th edn, P2MS Press, United Kingdom.
Myles DT and Coats ML (1995) ‘Process-based project management systems’, PM Network , 9(6):10–14.
Morgan J (2002) High performance product development: a systems approach to a lean product development process , Doctoral thesis in Industrial and Operations Engineering, University of Michigan.
Moujib A (2007) ‘Lean Project Management’ [conference presentation], PMI® Global Congress 2007 , EMEA, Budapest, Hungary , Project Management Institute, Newtown Square, PA.
PRINCE2 (2022) What is PRINCE2? , PRINCE2, accessed 3 August 2022. https://www.prince2.com/aus/what-is-prince2
Shook J and Rother M (1999) Learning to see: value stream mapping to add value and eliminate muda , The Lean Enterprise Institute, Brookline, MA.
Skmot N (5 August 2017) ‘ The 8 wastes of lean’, The Lean Way , accessed 02 June 2022. https://theleanway.net/The-8-Wastes-of-Lean
Summers DCS (2011) Lean Six Sigma: process improvement tools and techniques , Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
Womack J and Jones D (1996) Lean thinking: banish waste and create wealth in your corporation , Simon & Schuster, New York.
Womack J, Jones D and Roos D (1990) The machine that changed the world: the story of lean production , HarperCollins, New York.
Management Methods for Complex Projects Copyright © 2022 by Carmen Reaiche and Samantha Papavasiliou is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Project Management Methodology: Definition, Types, Examples

What is a project management methodology ? How can it be defined? In simple terms, it is a must-have to avoid failure and reduce risks because it is one of the critical success factors as well as the core competency of the management team. It is the straightforward way to guide the team through the development and execution of the phases, processes and tasks throughout the project management life-cycle.
What is a Methodology? The Definition in Project Management
The term “ project management methodology ” was first defined in the early 1960s when various business organizations began to look for effective ways that could simplify the realization of business benefits and organize the work into a structured and unique entity (which was called “ project ” later on). Communication and collaboration were the key criteria for establishing productive work relationships between the teams and departments within one and the same organization.
Since that time, the term has been changed and modified many times, new definitions have been created, new elements and functions have been added. Today we consider a project management methodology as a set of broad principles and rules to manage a specific project that has a definite beginning and end. Below is the current definition of methodology .
Project Management Methodology is a strictly defined combination of logically related practices, methods and processes that determine how best to plan, develop, control and deliver a project throughout the continuous implementation process until successful completion and termination. It is a scientifically-proven, systematic and disciplined approach to project design, execution and completion.
The purpose of project methodology is to allow for controlling the entire management process through effective decision making and problem solving, while ensuring the success of specific processes, approaches, techniques, methods and technologies.
Typically, a project management methodology provides a skeleton for describing every step in depth, so that the project manager or program manager will know what to do in order to deliver and implement the work according to the schedule, budget and client specification.
Referring to the above mentioned definition, an appropriately chosen project management methodology paves the way for gaining the following achievements:
- The needs of stakeholders are defined
- A common “language” is established and understood by the team, so they know what’s expected of them
- Cost estimates are complete, accurate and credible
- Every task is done using a common methodological approach
- Most conflicts are spotted and resolved early
- Expected deliverables are produced and handed over
- Lessons are learned and solutions are quickly implemented
Methodology in Project Management Framework
Project management (the acronym “PM”) provides the framework of planning, doing and delivering projects of any kind, size, nature and type. PM framework focuses on the realization of desired change in line with a chosen methodological approach. Actually, change is the core aspect that should be managed. PM framework identifies and defines how to best manage change. And methodology serves as the “way” to systematically realize change in terms of time, cost and quality.
Managing projects means describing and performing the activities required to meet the specific objectives of making change.
For example, writing a book is a kind of project in which the objective is to write a book. This objective can be fulfilled by a series of activities, including defining the topic, collecting material, creating a draft, typing, proofreading, others. So in terms of project management, the author needs to define and then complete all the necessary activities in order to write a book (which means make change).
Here’s a simplified example of how a project methodology can be presented in the management hierarchical structure:
PM Framework precedes Methodology which in turn precedes Lifecycle Stages and determines the project management Processes, Tasks and Activities
Project Management Methodology Types
In project management there are a variety of approaches and methods that can be employed in managing different kinds of project. All the types of project methodology can be conditionally divided into traditional and modern approaches.
Traditional Approach
A traditional approach involves a series of consecutive stages in the project management process. It is a step-by-step sequence to design, develop and deliver a product or service. It entails achieving the succession in the implementation process and provides the benefits of milestone-based planning and team building. In IT and software development, this methodology type is called “ Waterfall ” – one portion of work follows after another in linear sequence.
The following stages are included the traditional project management methodology:
- Initiation (requirements specification)
- Planning and design
- Execution (construction and coding)
- Control and integration
- Validation (testing and debugging)
- Closure (installation and maintenance)
Modern Approaches
Modern methodologies do not focus on linear processes but they provide an alternative look at project management. Some of the methods are best for IT and software development, while others can be implemented in production, process improvement, product engineering, and so on. Modern PM approaches use different models of the management process.
Project Management Methodology Examples
It is the matter of a project’s type, size and nature to select the right methodology. Here are the most popular PM methodologies:
PMBOK® Guide
Although A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge IS NOT a PM methodology in its “ pure state “, many people regard it as the methodological approach to planning, executing, controlling and terminating various projects. Meanwhile, the PMBOK® Guide is a broad inventory of best practices and ideas on planning and implementing projects. Please note that it is just a guide but not a project management methodology.
PRojects IN Controlled Environments 2 ( PRINCE2 ) presents a suite of process-driven methods and documentation-oriented approaches that allow driving various projects in the private sector. It was developed the UK Government, and today this great example of project management methodology is used both in the UK and internationally.
Critical path method (CPM) explores the most important or critical tasks of a project by defining possible activity sequences and estimating the longest duration of each sequence. It helps figure out how long it will take to complete the work and what tasks will compose the scope.
Lean PM methodology intends to maximize customer value and minimize resource waste. Lean project management lets organizations create higher value for their customers with fewer resources. This approach achieves perfection in customer satisfaction and value generation through implementing an optimized process flow that eliminates waste in products, services, transportation, inventories, etc.
The method of Six Sigma was originally developed by Motorola to improve its production processes by eliminating defects (defined as “non-conformity of a product or service to its specifications”). Today Six Sigma is one of the most popular and worldwide trusted examples of project management methodology for ensuring the accuracy and speed of a process’s implementation through eliminating or minimizing waste.
Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) is the way to plan, implement and review various kinds of work in single- and multi-project environments. This management methodology uses Theory of Constraints (TOC) and the concept of buffers to establish improved task durations and manage resource-dependent tasks and activities.
SCRUM is an example of Agile PM methodology that involves teams in producing a software product in 30-day “ sprints ” and monthly “ scrum sessions “. In a SCRUM-driven project, the deliverables are broken down into 30-day intervals. This methodology example is specific and applicable mainly to collaborative, 100%-dedicated teams, with no heavily constrained time and materials budget.
Project Management for Students
Project management for students is a vital part of the education and training process. Students can easily get a project management degree, but it does not mean that it comes as easy as taking the homework. Students need to take into account some important aspects if they want to manage a project properly.
For instance, choosing the best admission essay writing service is of great importance because if for some reason the student cannot deliver a high-quality essay in time, he will most likely fail the course or even worse he will be expelled from the college or university.
Students should prepare well for the project or the essay. They need to research on the topic beforehand, keep track of what is going on, write on time and work within the deadline.
This will allow them to catch up with their fellow students, focusing only on what they have to do and not worrying about what other people are doing.
Worth Reading

How email deliverability affects your B2B marketing success rate and how to increase it
October 14, 2019

Best Management Skills to Be the Best Manager
July 7, 2010

Project Management Plan and Three Angles of PM Triangle
August 23, 2010

The Project Sponsor Role – Selection and Appointment
September 7, 2011

How Tax Works When You’re a Freelancer: 7 Things to Know
April 10, 2023
#ezw_tco-3 .ez-toc-title{ font-size: 120%; ; ; } #ezw_tco-3 .ez-toc-widget-container ul.ez-toc-list li.active{ background-color: #ededed; } Table of Contents Toggle

How-to Guides
How to Write a Feasibility Study Report (FSR)

Integrating Innovative Tech in Project Management

Project initiation stage – Project Initiation Document (PID). Duties of project owner and project team

Organizing Procurement and Purchasing Activities in a Project

Two Common Mistakes in Project Procurement Contracts

Project Sponsor – The Role and Responsibilities
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Discover how today’s most successful IT leaders stand out from the rest. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Read the report .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project management |
- 7 types of process improvement methodol ...
7 types of process improvement methodologies you should know about

Business process improvements are methodologies in which a team evaluates their current processes and adapts them in order to increase profitability. This article highlights seven different process improvements your team can use to reduce inefficiencies and increase profit.
If businesses decided to consistently stay the same over time, many of them would collapse. Innovation requires change, and if businesses don’t change to meet customer demands, they won’t achieve much growth.
This is why many organizations use some form of process improvement methodology to adapt their processes to customer demands.
What is process improvement?
Business process improvements are methodologies in which a team evaluates their current processes and adapts them with the intent to increase productivity, streamline workflows, adapt to changing business needs, or increase profitability.
7 types of process improvement methodologies
There are seven different business process improvement methodologies your team can use to help reduce inefficiencies. In most cases, the methodology you choose depends on why you want to improve your processes and what you’re looking to improve.
1. Six Sigma methodology
Six Sigma is often used in manufacturing, mainly because it helps minimize defects and inconsistencies. The goal here is to optimize for consistency, which in the end leads to customer satisfaction.
There are two main processes used in Six Sigma: DMAIC for existing processes and DMADV for new processes. Since this article focuses specifically on improvements to existing processes, let’s dive into the DMAIC process.
What is the DMAIC process?
DMAIC is a Six Sigma process used to optimize existing processes. DMAIC stands for:
Define the opportunity for improvement.
Measure the performance of your existing processes.
Analyze the process to find defects and root causes.
Improve processes by addressing root causes.
Control any improved processes and assess future process performance to correct deviations.
The bulk of the DMAIC process improvement happens during the analysis stage. During the analysis stage of DMAIC, teams use a fishbone diagram, or an Ishikawa diagram , to visualize the possible causes of a product defect. The head of the fishbone diagram states the initial problem—then as you follow along the spine of the fish, each rib lists different categories of issues that can lead to the initial problem. This type of visual analysis is a good way to identify the different issues one root cause can create.
2. Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total quality management (TQM) is a customer-focused method that involves continuous improvement over time. This technique is often used in supply chain management and customer satisfaction projects.
TQM relies heavily on data-driven decisions and performance metrics. During the problem solving process, you use success metrics to decide how you can improve a process.
Here some key features of TQM:
Customer-focus: The end goal of TQM is always to benefit the end customer. If your team is focused on improving quality, ask yourself how that process change may affect how end consumers experience your product.
Full-team involvement: Unlike other process improvement methodologies TQM involves the entire team—not just production. As a result, you may end up looking for ways to optimize more business-centric processes, such as sales and marketing, to benefit the end consumer.
Continuous improvement: Continuous improvement in business is the idea of making small changes with the goal of continually optimizing processes. There's a lot of variability when it comes to business, and continuous improvement helps your team adapt when outside circumstances change.
Data-driven decision making : In order to apply continuous process improvement, you must continually collect data to analyze how processes are performing. This data can help identify where there may be inefficiencies and where to focus improvement initiatives.
Process-focused: The main goal of implementing TQM is to improve processes. Other process improvement methods like Six Sigma work to minimize the amount of defects, while TQM works to decrease inefficiencies.
3. Lean manufacturing
This form of process improvement goes by many names, with lean manufacturing being the most common. It may also be referred to as Lean production or just-in-time production. Defined by James P. Womack, Daniel Jones, and Daniel Roos in the book "The Machine That Changed the World," Lean highlights five main principles based off of the authors' experiences at Toyota manufacturing.
The 5 principles of lean
Identify value
Value stream mapping
Create flow
Establish pull
Continuous improvement
4. Continuous improvement (kaizen)
The Japanese philosophy of kaizen guides the continuous improvement model . Kaizen was born from the idea that life should be continuously improved so we can lead more satisfying and fulfilling lives.
This same concept can be applied to business—because as long as you are continuously improving, your business can become more successful. The goal of continuous improvement is to optimize for activities that generate value and to get rid of any waste.
There are three types of waste that kaizen aims to remove:
Muda (wastefulness) : Practices that consume resources but don’t add value.
Mura (unevenness): Overproduction that leaves behind waste, like excess product.
Muri (overburden): Too much strain on resources, such as worn out machinery or overworked employees.
5. Plan Do Check Act (PDCA)
The PDCA cycle is an interactive form of problem solving. It's used to improve processes and implement change. PDCA was created by Walter Shewhart when he applied the scientific method to economic quality control. Later, the idea was developed even further by W. Edwards Deming, who expanded on Shewhart's idea and used the scientific method for process improvement in addition to quality control.
There are four main steps to the PDCA cycle:
Plan : Decide on the problem you would like to solve, and create a plan to solve it.
Do: Test and implement the plan at a small scale.
Check: Review how the actions in the Do stage performed.
Act: After reviewing the results of the test, decide whether or not you want to implement the change at a larger scale.
PDCA is an improvement cycle. This means that these steps can be repeated until your team reaches the desired result.
6. 5 Whys analysis
The 5 Whys analysis is a process improvement technique used to identify the root cause of a problem. It's a really simple process in theory: you gather a group of stakeholders who were involved in a failure, and one person asks: "Why did this go wrong?" Repeat this question approximately five times, until you get to the root cause of an issue. The 5 Whys analysis aims to identify the issues within a process, but not human error.
Here's an example:
Problem: There was an increase in customer complaints regarding damaged products.
"Why did this happen?" Because packaging was not sufficient enough to protect the products.
"Why was the packaging not sufficient enough to protect the products?" Because the team testing packaging did not test past a certain level of stress.
"Why did the team not test the packaging further?" Because current standard processes indicated that the testing indicated was sufficient.
"Why did the current standard process indicate that this testing was sufficient?" Because this process was created for a previous product, and not this current product that is coming back damaged.
"Why wasn’t there a new process for the new product?" Because the project template for launching new products doesn’t include stress testing the new packaging.
You can see from this example that the team asked “Why” until they identified the process error that needs to be fixed—in this case, adding a “stress test new packaging” step into their product launch template . When working with stakeholders in processes like this, it's important to identify the issues, and co-create next steps together so that your production can improve.
7. Business process management (BPM)
Business process management, or BPM , is the act of analyzing and improving business processes. Much like any organic being, businesses grow and shift over time. Your team may have implemented processes that worked when your team was small, but as you grow those processes may not scale in a way that allows your team to be as efficient as possible.
Most of the time, BPM helps teams identify bottlenecks, ways to automate manual work, and strategies to improve inefficiencies. There are five main steps to business process management.
Analyze: Look at your current processes and map them from beginning to end. This is commonly known as process mapping.
Model: Draft out what you want the process to look like. Ideally, you'll have found any inefficiencies in the first step, and you can draft how you would like to solve them in this stage.
Implement : Put your model to action. During this stage, it's important to establish key success metrics so you can gauge whether or not the changes made were successful.
Monitor: Decide whether or not your project is successful. Are the success metrics you identified in step three improving?
Optimize: As the process evolves, continue looking for inefficiencies in your process and continuously optimize as you go.
Manage process improvements to increase productivity
As a team lead, one of the most valuable things you can bring to your team are clearer processes and better workflows . When used effectively, process improvement increases your team's productivity and decreases inefficiencies.
To increase clarity and improve processes, try work management. Work management tools like Asana can help you take your team’s productivity to the next level by standardizing processes, streamlining workflows, and keeping your team in sync.
Related resources
Smooth product launches are simpler than you think

What is stakeholder analysis and why is it important?

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning
Understanding dependencies in project management
- Online Degree Explore Bachelor’s & Master’s degrees
- MasterTrack™ Earn credit towards a Master’s degree
- University Certificates Advance your career with graduate-level learning
- Top Courses
- Join for Free
12 Project Management Methodologies: Your Guide
Set your project up for success by choosing the right project management methodology. Your choice of project management methodology defines how you manage a project. Learn about some common options (and how to choose the right one for your project).
![project management process methodology [Featured image] A project manager in a pink dress holds a board with sticky notes at a conference table at which two other people are seated.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/6mQITsFlDQadrInrJrOC2d/dd261784e16bdc8f0be59516a8870ae9/GettyImages-1342254624.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
What is a project management methodology?
The Merriam-Webster Dictionary defines methodology as “a body of methods, rules, and postulates employed by a discipline” or “a particular procedure or set of procedures” [ 1 ]. In the field of project management, this would be a set of rules and processes that define how you manage a project.
When discussing project management methodologies (PMMs), you will most likely encounter a variety of terms—some of them are true methodologies, and others would be more accurately described as principles or philosophies. For the purposes of this discussion, we will consider a variety of terms often referred to as PMMs, even if they do not technically satisfy the definition.
12 popular project management methodologies
Often one of the first decisions you will make as a project manager involves which methodology to follow. As the industry has evolved over the years, so have the PM methodology options. Keep in mind that there is no single option that works best—the best methodology is the one (or combination) that fits your project team and company.
Before we discuss how to choose a methodology, let's take a look at some common options in project management.
1. Waterfall
The waterfall method, first designed by Winston W. Royce in 1970 for software development, is considered a more traditional, linear approach to managing a project. With the waterfall methodology, a project flows through a series of steps or phases. Generally, each must be completed before the next can begin.
Stages of the waterfall model
1. Requirements: In this first phase, you will work with stakeholders in order to clearly define the project's requirements.
2. Design: The critical design phase is when you will plan what the final product will look like and what steps your team needs to take to get there.
3. Implementation: This is where you can picture all your planning into action. For software projects, this is when programmers will write the actual code.
4. Verification: During verification, your team tests the product to ensure it meets the requirements laid out in the first phase.
5. Maintenance: After the project is complete, the development team responds to feedback and makes any necessary modifications.
When to use waterfall
The logical flow of waterfall makes it an excellent option for short, predictable projects where you have a clear vision of the finished product and fixed requirements that are not likely to change. It is best suited for teams and PMs that excel at planning and documentation.
Agile takes an iterative approach to project management. The Agile Manifesto was created by several software development industry leaders as a way to adapt to quickly changing technology at the time.
Although it is technically not a complete methodology — adopting Agile will not give you a comprehensive plan for how to manage your projects — Agile does offer a series of values and principles to promote agility and efficiency in the development process.
Four foundational values of Agile
1. Individuals and interactions over processes and tools: Managing a project around your Agile team rather than your tools can help make your team more responsive and adaptable.
2. Working software over comprehensive documentation: Robust documentation involved in older software development techniques often led to long delays. You will still produce documentation in Agile, but the focus shifts to functionality.
3. Customer collaboration over contract negotiation: Instead of working out every detail of a project at the beginning, this method keeps clients and customers engaged in every stage of the collaborative development process. This is particularly helpful when a customer has unclear or changing requirements.
4. Responding to change over following a plan: Instead of front-loading all the planning of a project, Agile encourages short iterations that help make changes an improvement rather than an expense.
When to use Agile
An Agile approach works well on creative projects where requirements might change along the way and the final details of the product are not yet established. It is also a good option for projects where clients or stakeholders prefer to offer feedback regularly, rather than only when the final product is delivered.
Scrum is a lightweight Agile framework designed to help self-organising teams develop more complex projects. The framework includes a set of roles and meetings centered on the values of commitment, courage, focus, openness, and respect.
To better understand Scrum, let us take a look at some of its roles and practices.
Sprint: Short (usually one month or less) development cycle where a team creates a useable and (hopefully) releasable product increment
Scrum Master: Team leader responsible for coaching the team in the Scrum method, organising Scrum meetings and events, and ensuring team members have the support they need to succeed
Daily Scrum: 15-minute stand-up meeting held each day of a sprint where the team plans work for the next 24 hours
Product backlog: Prioritised list of work still to be done on a product
Product owner: Person responsible for maximising the value of the product by managing the product backlog
Development team: Roles responsible for the actual development work of a project
Sprint review: Informal session where the development team presents their finished iterations to stakeholders for feedback
When to use Scrum
The Scrum method, best for self-managing teams and a culture open to innovation, can help bring products to market more quickly. The short development cycles and frequent stakeholder involvement can often lead to a better-quality product.
Kanban is an Agile method of project management that helps visualise workflow to improve efficiency. The method got its start in the Japanese manufacturing industry before gaining popularity across many fields.
At the center of the Kanban method is a Kanban board—a physical or digital tool that divides workflow into columns organised by development stage, such as to-do, in-progress, and completed tasks. This helps eliminate multi-tasking by encouraging teams to focus on only a few tasks at a time. It also makes it easy for both the team and stakeholders to quickly see where the team is in the development process.
Did you know? The word Kanban means billboard in Japanese. The method was developed by Toyota in the 1940s.
Six Kanban practices
1. Visualise the workflow. The Kanban board visualises a team’s workload in a way that is easy to understand and execute.
2. Limit work in progress. Restricting the number of tasks a team is working on at any given time helps maintain focus.
3. Manage flow. This method switches the focus from managing people to managing a smooth flow of work.
4. Make policies explicit. Keep them simple, visible, and easy to understand.
5. Use feedback loops. Revisiting project goals regularly helps the team respond to changes and take advantage of new opportunities.
6. Improve collaboratively. Teams with a shared vision can work together to achieve continuous improvement. These evolutions should be based on metrics and experimentation.
When to use Kanban
If you want to limit planning and meetings and focus on continuous improvement, Kanban could be a good choice. It is particularly effective in helping teams work through big backlogs or deal with frequent requests from stakeholders.
The Lean methodology focuses on maximising value by reducing waste and improving efficiency. It is another method that came from Toyota and has expanded in popularity well beyond manufacturing.
Five core principles of Lean
The Lean methodology centers on five principles, outlined in the book The Machine that Changed the World and Lean Thinking .
1. Understand value. Think about value from the customer’s perspective. What are they willing to pay?
2. Identify the value stream. Use visual techniques to map out the actions required to develop and launch a product. Use this map to identify areas of waste.
3. Create value flow. You can achieve this by eliminating waste due to things like excess inventory, time spent waiting, or performing more work than is necessary.
4. Use a pull approach. Deliver value as the customer requests it. This keeps the focus on delivering what the customer actually wants while eliminating time spent on features that might not be wanted or needed.
5. Continuously improve. Always seek perfection by assessing the project regularly for ways to reduce waste and enhance value.
When to use Lean
The focus on waste elimination makes Lean a natural fit for more traditional manufacturing projects. But it can also be effective in other industries, particularly when you want to keep the focus of development on the customer first.
6. Critical path method (CPM)
The critical path method defines the longest sequence of tasks that must be completed to successfully complete a project. These are the tasks that, if stalled, could cause delays in the entire project. The method also maps out the dependencies between tasks and an estimate of how long each task will take to complete.
Mapping out these elements can help establish important project deadlines and define a more accurate project schedule.
When to use CPM
CPM is best for projects with a well-defined series of tasks that need to be performed in a set order (construction projects, for example). It is a good option to keep projects with a fixed deadline on schedule.
7. Critical chain management (CCM)
Where CPM focuses on time, the critical chain method (CCM) shifts the focus to the supply chain. This method is used to map out a critical path based on resource availability. These resources could include people, physical space, equipment, or other physical components. Unlike a CPM map, a CCM map includes scheduled buffers to remind a project team that a certain resource is necessary to finish a critical task.
When to use CCM
CCM is well-suited for projects that rely on limited or time-sensitive resources to complete. Overestimating task durations by building in buffers helps teams meet deadlines even in the face of unforeseen circumstances.
PRINCE2 stands for Projects in Controlled Environments. It is a process-based project management methodology used to answer certain basic questions in product development:
What are you trying to achieve?
When will you start?
What do you need to complete it?
Do you need help?
How long will it take?
How much will it cost?
While used primarily by the British government, the PRINCE2 method has been applied to projects in a variety of industries around the world. The method is designed to be scalable to fit a variety of projects.
When to use PRINCE2
PRINCE2 is particularly popular outside the US — it is used in more than 150 different countries. If your project involves multinational stakeholders, it might be worth considering this method. The focus on robust organisation makes it more appropriate for complex yet predictable projects.
The Project Management Body of Knowledge, or PMBOK for short, is not so much a methodology as a collection of best practices and guidelines outlined by the Project Management Institute (PMI).
Did you know? The PMBOK Guide is currently in its seventh edition, published in 2021. The reference was designed to be used alongside the Agile Practice Guide .
The book, regularly updated by PMI, breaks down projects into five stages, often referred to as the lifecycle of a project:
Controlling
While PMBOK is often associated with the waterfall method, its practices can also fit into an Agile framework. For large companies managing multiple projects, PMBOK can help standardise terminology and practices across different departments.
When to use PMBOK
Just about every company and project can benefit from the standardised practices outlined in PMBOK. Project managers who pursue the Project Management Professional (PMP) certification will want to be familiar with the material.
The Projects Integrating Sustainable Methods (PRiSM) model of project management places an emphasis on environmental sustainability. Specifically, the method focuses on minimising the ecological risks and increasing benefits that may impact the five Ps: people, planet, prosperity, process, and products.
Unlike other methodologies, PRiSM looks at projects beyond the scope of development to consider their impact beyond delivery.
Six principles of PRiSM
1. Commitment and accountability: Organisations should take responsibility for a clean environment, employee well-being, and equal opportunities.
2. Ethics and decision making: All decisions should take into account the short and long-term impacts on both society and the environment.
3. Integrated and transparent: Projects should promote financial, environmental, and social benefits at all policy levels.
4. Principal and values-based: Projects should use technology to use resources more efficiently.
5. Social and ecological equity: Project managers should evaluate any impact a project may have on vulnerable populations or environmentally sensitive areas using demographic data.
6. Economic prosperity: Fiscal planning should balance the needs of company stakeholders and future generations.
When to use PRiSM
This approach is best for projects with an established environmental impact, such as real estate and industrial projects. It is not as useful for things like software development, where environmental impact is less of a concern.
11. Six Sigma
Six Sigma, a quality management process developed at Motorola in the 1980s, comprises a set of tools and techniques to eliminate errors in development. This can help reduce costs and customer complaints due to errors.
The method generally takes a five-phase approach to improve existing processes:
Define : Analyse a business problem from a customer perspective.
Measure : Measure the problem in terms of data and define a performance metric.
Analyse : Quantify your goals and determine if your process is efficient and effective.
Improve : Find ways to improve process implementation.
Control : Implement and maintain the solution.
When to use Six Sigma
Six Sigma tends to be most effective in large organisations with several hundred or more employees.
12. Extreme Project Management (XPM)
Doug DeCarlo, the creator of Extreme Project Management (XPM), defines it as “the art and science of facilitating and managing the flow of thoughts, emotions, and interactions in a way that produces valued outcomes under turbulent and complex conditions” [ 2 ].
This flexible approach helps teams adapt to the unknowns that pop up during a project, including frequent changes to requirements and complex project needs. For software development projects, this is sometimes referred to as extreme programming.
When to use XPM
XPM works best for short development cycles with less-defined product specifications. Teams that like to experiment to see what works could thrive with this method.
Hybrid Methodologies
Just as there is no single best method for managing a project, you also do not have to limit yourself to just one option. Project managers have combined various approaches to come up with new hybrid approaches, such as Lean Six Sigma or Scrumban (Scrum and Kanban).
How to choose a project management methodology
The best project management method for you will depend on your project, team organisation, and tools. Let's take a quick look at some things to consider and questions you should ask yourself when choosing a PM methodology.
1. Evaluate the project. Does your project have fixed or flexible requirements? Is the finished product well-defined or will the team take a creative approach to defining it? How complex is it and how long will it take to complete? What physical resources are involved? Will the stakeholders or clients be readily available and how involved would they like to be?
2. Consider your team. Some methods work well with small, self-managing teams. Others lend structure to larger cross-functional teams. Also, take into account what method your team might already be used to. Would the benefits of implementing a new method outweigh the time cost of teaching it?
3. Look at the organisation. What are your company’s goals and values? You will want to choose a methodology that aligns with these elements. Some companies may prefer and employ a particular approach that you will need to adapt to.
4. Think about your tools. Some project management tools are flexible enough to work with various different methodologies. Others might be more specific to a particular approach. Make sure the tools and software you are proficient in are a good match for whatever methodology you select.
If you're considering a career in project management, be ready to learn job-oriented skills with a Professional Certificate in project management from Google . Learn about traditional and Agile methods, access career resources to enhance your resume and interview skills, and get connected with top employers through the Google hiring consortium.
Article sources
Merriam-Webster. " Definition of methodology , https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/methodology." Accessed February 24, 2022.
XPM Group. "Process, https://www.xpmgp.com/process ." Accessed February 24, 2022.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A project management methodology is a set of guiding principles that help you manage a project successfully. ... Cards are moved from one step to the next as they progress through the process ...
12 project management frameworks. Manage projects with one tool. 1. Agile. What it is: The Agile project management methodology is one of the most common project management processes. But the reality is that Agile isn't technically a methodology. Instead, it's best defined as a project management principle. The basis of an Agile approach is ...
Here's a quick overview of the most commonly used project management methods that you can use. 1. Waterfall Methodology. This may be the most straightforward and linear of all the project management methods in this list, as well as the most traditional approach. The name is apt, as the waterfall methodology is a process in which the phases of ...
3. Kanban: Visualize Task Progress For Agile Teams. Like Scrum, Kanban is another product management methodology that follows agile principles. Kanban is ideal for projects that are done by small, flexible, and collaborative teams, like Scrum, but there is a highly visual aspect as well.
Stages of the waterfall model. 1. Requirements: In this first phase, you'll work with stakeholders to clearly define the project scope and requirements. 2. Design: The critical design phase is when you'll plan what the final product will look like and what steps your team needs to take to get there. 3.
A project management methodology is a set of principles, processes, guidelines, and tools that help to plan, manage, and control a project. The methodology helps to ensure that a project is on schedule, within budget, and that the project goals are met. A project team or an organization uses a management framework to execute a project.
1. Waterfall methodology. The Waterfall method is a traditional approach to project management. In it, tasks and phases are completed in a linear, sequential manner, and each stage of the project must be completed before the next begins. The stages of Waterfall project management generally follow this sequence:
Map the value stream: Map out the process (aka value stream) and identify areas of waste, in terms of resources, time, or redundancy. Create flow: Create a flow plan that eliminates the waste you identified. Employ a pull system: Progress through the plan only as the customer has new needs.
Types of Project Management Methodologies. There are diverse project management methodologies, each with different principles, processes, and approaches. Here are some common types: 1. Waterfall Methodology. Waterfall project management is a traditional approach to project management where tasks are completed sequentially and linearly.
Summary. Agile methodology is a project management framework that breaks projects down into several dynamic phases, commonly known as sprints. In this article, get a high-level overview of Agile project management, plus a few common frameworks to choose the right one for your team. Scrum, Kanban, waterfall, Agile.
A project management methodology is a set of principles, rules, and processes for planning, coordinating, and completing a project. The terms "methodology" and "framework" are often used interchangeably, but in the case of project management, there's an important distinction. Framework: The overall philosophy of the management ...
The PMI (Project Management Institute) has defined these five project management process groups, or project management phases, which come together to form the project life cycle. Project Initiation. Project Planning. Project Execution. Project Monitoring & Controlling. Project Closure.
For all but the smallest projects, experienced project managers use well-established project management methodologies. These are often published systems - such as PMBOK®️ Guide (Project Management Body of Knowledge) or PRINCE2 - but they can also be in-house methodologies that are specific to the organization.. These approaches have some differences in emphasis, and they tend to use ...
Here are six project management methodologies and when to best take advantage of them. 1. Waterfall. The waterfall project management process is a traditional approach that follows a sequence of ...
Follow this guide to the different types of project management methodologies available, with information to help you learn which may be most suitable for your organisation. The article gives descriptions of each methodology. ... Six Sigma, a quality management process developed at Motorola in the 1980s, comprises a set of tools and techniques ...
Move Your Project Management Career Forward. With Career Navigator, you can build a personalized career road map in 3 easy steps. Build Your Base Camp — Take inventory of where you are as a professional.. Get Your Career Roadmap — Get personalized action steps from our recommendation engine.. Grow Everyday — Define your professional goals and what you need to achieve them with our new ...
environment using "just enough" process to achieve the desired outcome while maximizing value, managing cost, and enhancing speed. f Each project is unique. f Project success is based on adapting to the unique context of the project to determine the most appropriate methods of producing the desired outcomes.
The Four Phases of Project Management. Planning, build-up, implementation, and closeout. Whether you're in charge of developing a website, designing a car, moving a department to a new facility ...
In sum, Lean project management is a process-based project management methodology. This methodology is also referred to as a mindset around the improvements within an organisation. The focus is on improving efficiency, reducing waste, and increasing productivity. There are many benefits associated with the application of Lean methods, including ...
Project Management Methodology is a strictly defined combination of logically related practices, methods and processes that determine how best to plan, develop, control and deliver a project throughout the continuous implementation process until successful completion and termination. It is a scientifically-proven, systematic and disciplined ...
1. Six Sigma methodology. Six Sigma is a process improvement methodology that aims to minimize the amount of variations within the end product. Developed in 1986 by American engineer and Motorola employee Bill Smith, this process uses statistical data as benchmarks to help business leaders understand how well their processes work.
The project management lifecycle is a step-by-step framework of best practices used to shepherd a project from its beginning to its end. This project management process generally includes four phases: initiating, planning, executing, and closing. Some may also include a fifth "monitoring and controlling" phase between the executing and ...
What is a project management methodology? The Merriam-Webster Dictionary defines methodology as "a body of methods, rules, and postulates employed by a discipline" or "a particular procedure or set of procedures" [].In the field of project management, this would be a set of rules and processes that define how you manage a project.
Survival is one of the most crucial driving forces for many companies today. Once executives recognize that project management is needed to make it happen, changes occur quickly. However, failing to use a project management methodology (PMM) may jeopardize an organisation's efforts and overall effectiveness, in respect to knowledge management, repeatability, comparability, quality, and future ...
Frameworks and Methodologies. Project management frameworks help simplify the project manager's job by providing a standardized, rigorously tested, thoroughly documented, repeatable process that governs a project. In other words, it's a recipe for using your software, creating documents, and gathering reports that you can use over and over. ...
Program management involves a long-term strategy encompassing multiple project tasks ranging from defining success to driving it across different teams. Project management is the process of delivering value that moves a program forward. This often involves organizing projects, coordinating work, and tracking progress.
Location: East Hanover, NJ (Hybrid)#LI-Hybrid The Process Optimization and Program Management Lead will oversee and manage the process redesign and optimization of critical business processes, ensuring smooth execution and alignment with stakeholder requirements. This involves using strong process expertise, project management skills, and effective communication to identify risks, allocate ...