
How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals

The self presentation theory and how to present your best self

Transform your life
Make meaningful changes and become the best version of yourself. BetterUp's professional Coaches are here to support your personal growth journey.

Jump to section
What does self presentation mean?
What are self presentation goals, individual differences and self presentation.
How can you make the most of the self presentation theory at work?
We all want others to see us as confident, competent, and likeable — even if we don’t necessarily feel that way all the time. In fact, we make dozens of decisions every day — whether consciously or unconsciously — to get people to see us as we want to be seen. But is this kind of self presentation dishonest? Shouldn’t we just be ourselves?
Success requires interacting with other people. We can’t control the other side of those interactions. But we can think about how the other person might see us and make choices about what we want to convey.
Self presentation is any behavior or action made with the intention to influence or change how other people see you. Anytime we're trying to get people to think of us a certain way, it's an act of self presentation. Generally speaking, we work to present ourselves as favorably as possible. What that means can vary depending on the situation and the other person.
Although at first glance this may seem disingenuous, we all engage in self-presentation. We want to make sure that we show up in a way that not only makes us look good, but makes us feel good about ourselves.
Early research on self presentation focused on narcissism and sociopathy, and how people might use the impression others have of them to manipulate others for their benefit. However, self presentation and manipulation are distinct. After all, managing the way others see us works for their benefit as well as ours.
Imagine, for example, a friend was complaining to you about a tough time they were having at work . You may want to show up as a compassionate person. However, it also benefits your friend — they feel heard and able to express what is bothering them when you appear to be present, attentive, and considerate of their feelings. In this case, you’d be conscious of projecting a caring image, even if your mind was elsewhere, because you value the relationship and your friend’s experience.
To some extent, every aspect of our lives depends on successful self-presentation. We want our families to feel that we are worthy of attention and love. We present ourselves as studious and responsible to our teachers. We want to seem fun and interesting at a party, and confident at networking events. Even landing a job depends on you convincing the interviewer that you are the best person for the role.
There are three main reasons why people engage in self presentation:
Tangible or social benefits:
In order to achieve the results we want, it often requires that we behave a certain way. In other words, certain behaviors are desirable in certain situations. Matching our behavior to the circumstances can help us connect to others, develop a sense of belonging , and attune to the needs and feelings of others.
Example: Michelle is a new manager . At her first leadership meeting, someone makes a joke that she doesn’t quite get. When everyone else laughs, she smiles, even though she’s not sure why.
By laughing along with the joke, Michelle is trying to fit in and appear “in the know.” Perhaps more importantly, she avoids feeling (or at least appearing) left out, humorless, or revealing that she didn’t get it — which may hurt her confidence and how she interacts with the group in the future.
To facilitate social interaction:
As mentioned, certain circumstances and roles call for certain behaviors. Imagine a defense attorney. Do you think of them a certain way? Do you have expectations for what they do — or don’t — do? If you saw them frantically searching for their car keys, would you feel confident with them defending your case?
If the answer is no, then you have a good idea of why self presentation is critical to social functioning. We’re surprised when people don’t present themselves in a way that we feel is consistent with the demands of their role. Having an understanding of what is expected of you — whether at home, work, or in relationships — may help you succeed by inspiring confidence in others.
Example: Christopher has always been called a “know-it-all.” He reads frequently and across a variety of topics, but gets nervous and tends to talk over people. When attending a networking event, he is uncharacteristically quiet. Even though he would love to speak up, he’s afraid of being seen as someone who “dominates” the conversation.
Identity Construction:
It’s not enough for us to declare who we are or what we want to be — we have to take actions consistent with that identity. In many cases, we also have to get others to buy into this image of ourselves as well. Whether it’s a personality trait or a promotion, it can be said that we’re not who we think we are, but who others see.
Example: Jordan is interested in moving to a client-facing role. However, in their last performance review, their manager commented that Jordan seemed “more comfortable working independently.”
Declaring themselves a “people person” won’t make Jordan’s manager see them any differently. In order to gain their manager’s confidence, Jordan will have to show up as someone who can comfortably engage with clients and thrive in their new role.
We may also use self presentation to reinforce a desired identity for ourselves. If we want to accomplish something, make a change, or learn a new skill , making it public is a powerful strategy. There's a reason why people who share their goals are more likely to be successful. The positive pressure can help us stay accountable to our commitments in a way that would be hard to accomplish alone.
Example: Fatima wants to run a 5K. She’s signed up for a couple before, but her perfectionist tendencies lead her to skip race day because she feels she hasn’t trained enough. However, when her friend asks her to run a 5K with her, she shows up without a second thought.
In Fatima’s case, the positive pressure — along with the desire to serve a more important value (friendship) — makes showing up easy.
Because we spend so much time with other people (and our success largely depends on what they think of us), we all curate our appearance in one way or another. However, we don’t all desire to have people see us in the same way or to achieve the same goals. Our experiences and outcomes may vary based on a variety of factors.
One important factor is our level of self-monitoring when we interact with others. Some people are particularly concerned about creating a good impression, while others are uninterested. This can vary not only in individuals, but by circumstances. A person may feel very confident at work , but nervous about making a good impression on a first date.
Another factor is self-consciousness — that is, how aware people are of themselves in a given circumstance. People that score high on scales of public self-consciousness are aware of how they come across socially. This tends to make it easier for them to align their behavior with the perception that they want others to have of them.
Finally, it's not enough to simply want other people to see you differently. In order to successfully change how other people perceive you, need to have three main skills:
1. Perception and empathy
Successful self-presentation depends on being able to correctly perceive how people are feeling , what's important to them, and which traits you need to project in order to achieve your intended outcomes.
2. Motivation
If we don’t have a compelling reason to change the perception that others have of us, we are not likely to try to change our behavior. Your desire for a particular outcome, whether it's social or material, creates a sense of urgency.
3. A matching skill set
You’ve got to be able to walk the talk. Your actions will convince others more than anything you say. In other words, you have to provide evidence that you are the person you say you are. You may run into challenges if you're trying to portray yourself as skilled in an area where you actually lack experience.
How can you make the most of the self presentation theory at work?
At its heart, self presentation requires a high-level of self awareness and empathy. In order to make sure that we're showing up as our best in every circumstance — and with each person — we have to be aware of our own motivation as well as what would make the biggest difference to the person in front of us.
Here are 6 strategies to learn to make the most of the self-presentation theory in your career:
1. Get feedback from people around you
Ask a trusted friend or mentor to share what you can improve. Asking for feedback about specific experiences, like a recent project or presentation, will make their suggestions more relevant and easier to implement.
2. Study people who have been successful in your role
Look at how they interact with other people. How do you perceive them? Have they had to cultivate particular skills or ways of interacting with others that may not have come easily to them?
3. Be yourself
Look for areas where you naturally excel and stand out. If you feel comfortable, confident, and happy, you’ll have an easier time projecting that to others. It’s much harder to present yourself as confident when you’re uncomfortable.
4. Be aware that you may mess up
As you work to master new skills and ways of interacting with others, keep asking for feedback . Talk to your manager, team, or a trusted friend about how you came across. If you sense that you’ve missed the mark, address it candidly. People will understand, and you’ll learn more quickly.
Try saying, “I hope that didn’t come across as _______. I want you to know that…”
5. Work with a coach
Coaches are skilled in interpersonal communication and committed to your success. Roleplay conversations to see how they land, and practice what you’ll say and do in upcoming encounters. Over time, a coach will also begin to know you well enough to notice patterns and suggest areas for improvement.
6. The identity is in the details
Don’t forget about the other aspects of your presentation. Take a moment to visualize yourself being the way that you want to be seen. Are there certain details that would make you feel more like that person? Getting organized, refreshing your wardrobe, rewriting your resume, and even cleaning your home office can all serve as powerful affirmations of your next-level self.
Self presentation is defined as the way we try to control how others see us, but it’s just as much about how we see ourselves. It is a skill to achieve a level of comfort with who we are and feel confident to choose how we self-present. Consciously working to make sure others get to see the very best of you is a wonderful way to develop into the person you want to be.
Allaya Cooks-Campbell
With over 15 years of content experience, Allaya Cooks Campbell has written for outlets such as ScaryMommy, HRzone, and HuffPost. She holds a B.A. in Psychology and is a certified yoga instructor as well as a certified Integrative Wellness & Life Coach. Allaya is passionate about whole-person wellness, yoga, and mental health.
Impression management: Developing your self-presentation skills
How to make a presentation interactive and exciting, 6 presentation skills and how to improve them, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, what is self-preservation 5 skills for achieving it, how self-knowledge builds success: self-awareness in the workplace, 8 clever hooks for presentations (with tips), developing psychological flexibility, how to not be nervous for a presentation — 13 tips that work (really), similar articles, how self-compassion strengthens resilience, what is self-efficacy definition and 7 ways to improve it, what is self-awareness and how to develop it, what i didn't know before working with a coach: the power of reflection, manage your energy, not your time: how to work smarter and faster, building resilience part 6: what is self-efficacy, why learning from failure is your key to success, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
IResearchNet
Self-Presentation
Self-presentation definition.
Self-presentation refers to how people attempt to present themselves to control or shape how others (called the audience) view them. It involves expressing oneself and behaving in ways that create a desired impression. Self-presentation is part of a broader set of behaviors called impression management. Impression management refers to the controlled presentation of information about all sorts of things, including information about other people or events. Self-presentation refers specifically to information about the self.
Self-Presentation History and Modern Usage
Early work on impression management focused on its manipulative, inauthentic uses that might typify a used car salesperson who lies to sell a car, or someone at a job interview who embellishes accomplishments to get a job. However, researchers now think of self-presentation more broadly as a pervasive aspect of life. Although some aspects of self-presentation are deliberate and effortful (and at times deceitful), other aspects are automatic and done with little or no conscious thought. For example, a woman may interact with many people during the day and may make different impressions on each person. When she starts her day at her apartment, she chats with her roommates and cleans up after breakfast, thereby presenting the image of being a good friend and responsible roommate. During classes, she responds to her professor’s questions and carefully takes notes, presenting the image of being a good student. Later that day, she calls her parents and tells them about her classes and other activities (although likely leaving out information about some activities), presenting the image of being a loving and responsible daughter. That night, she might go to a party or dancing with friends, presenting the image of being fun and easygoing. Although some aspects of these self-presentations may be deliberate and conscious, other aspects are not. For example, chatting with her roommates and cleaning up after breakfast may be habitual behaviors that are done with little conscious thought. Likewise, she may automatically hold the door open for an acquaintance or buy a cup of coffee for a friend. These behaviors, although perhaps not done consciously or with self-presentation in mind, nevertheless convey an image of the self to others.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.

Although people have the ability to present images that are false, self-presentations are often genuine; they reflect an attempt by the person to have others perceive him or her accurately, or at least consistent with how the person perceives himself or herself. Self-presentations can vary as a function of the audience; people present different aspects of themselves to different audiences or under different conditions. A man likely presents different aspects of himself to his close friends than he does to his elderly grandmother, and a woman may present a different image to her spouse than she does to her employer. This is not to say that these different images are false. Rather, they represent different aspects of the self. The self is much like a gem with multiple facets. The gem likely appears differently depending on the angle at which it is viewed. However, the various appearances are all genuine. Even if people present a self-image that they know to be false, they may begin to internalize the self-image and thereby eventually come to believe the self-pres
entation. For example, a man may initially present an image of being a good student without believing it to be genuine, but after attending all his classes for several weeks, visiting the professor during office hours, and asking questions during class, he may come to see himself as truly being a good student. This internalization process is most likely to occur when people make a public commitment to the self-image, when the behavior is at least somewhat consistent with their self-image, and when they receive positive feedback or other rewards for presenting the self-image.
Self-presentation is often directed to external audiences such as friends, lovers, employers, teachers, children, and even strangers. Self-presentation is more likely to be conscious when the presenter depends on the audience for some reward, expects to interact with the audience in the future, wants something from the audience, or values the audience’s approval. Yet self-presentation extends beyond audiences that are physically present to imagined audiences, and these imagined audiences can have distinct effects on behavior. A young man at a party might suddenly think about his parents and change his behavior from rambunctious to reserved. People sometimes even make self-presentations only for themselves. For instance, people want to claim certain identities, such as being fun, intelligent, kind, moral, and they may behave in line with these identities even in private.
Self-Presentation Goals
Self-presentation is inherently goal-directed; people present certain images because they benefit from the images in some way. The most obvious benefits are interpersonal, arising from getting others to do what one wants. A job candidate may convey an image of being hardworking and dependable to get a job; a salesperson may convey an image of being trustworthy and honest to achieve a sale. People may also benefit from their self-presentations by gaining respect, power, liking, or other desirable social rewards. Finally, people make certain impressions on others to maintain a sense of who they are, or their self-concept. For example, a man who wants to think of himself as a voracious reader might join a book club or volunteer at a library, or a woman who wishes to perceive herself as generous may contribute lavishly to a charitable cause. Even when there are few or no obvious benefits of a particular self-presentation, people may simply present an image that is consistent with the way they like to think about themselves, or at least the way they are accustomed to thinking about themselves.
Much of self-presentation is directed toward achieving one of two desirable images. First, people want to appear likeable. People like others who are attractive, interesting, and fun to be with. Thus, a sizable proportion of self-presentation revolves around developing, maintaining, and enhancing appearance and conveying and emphasizing characteristics that others desire, admire, and enjoy. Second, people want to appear competent. People like others who are skilled and able, and thus another sizable proportion of self-presentation revolves around conveying an image of competence. Yet, self-presentation is not so much about presenting desirable images as it is about presenting desired images, and some desired images are not necessarily desirable. For example, schoolyard bullies may present an image of being dangerous or intimidating to gain or maintain power over others. Some people present themselves as weak or infirmed (or exaggerate their weaknesses) to gain help from others. For instance, a member of a group project may display incompetence in the hope that other members will do more of the work, or a child may exaggerate illness to avoid going to school.
Self-Presentation Avenues
People self-present in a variety of ways. Perhaps most obviously, people self-present in what they say. These verbalizations can be direct claims of a particular image, such as when a person claims to be altruistic. They also can be indirect, such as when a person discloses personal behaviors or standards (e.g., “I volunteer at a hospital”). Other verbal presentations emerge when people express attitudes or beliefs. Divulging that one enjoys backpacking through Europe conveys the image that one is a world-traveler. Second, people self-present nonverbally in their physical appearance, body language, and other behavior. Smiling, eye contact, and nods of agreement can convey a wealth of information. Third, people self-present through the props they surround themselves with and through their associations. Driving an expensive car or flying first class conveys an image of having wealth, whereas an array of diplomas and certificates on one’s office walls conveys an image of education and expertise. Likewise, people judge others based on their associations. For example, being in the company of politicians or movie stars conveys an image of importance, and not surprisingly, many people display photographs of themselves with famous people. In a similar vein, high school students concerned with their status are often careful about which classmates they are seen and not seen with publicly. Being seen by others in the company of someone from a member of a disreputable group can raise questions about one’s own social standing.
Self-Presentation Pitfalls
Self-presentation is most successful when the image presented is consistent with what the audience thinks or knows to be true. The more the image presented differs from the image believed or anticipated by the audience, the less willing the audience will be to accept the image. For example, the lower a student’s grade is on the first exam, the more difficulty he or she will have in convincing a professor that he or she will earn an A on the next exam. Self-presentations are constrained by audience knowledge. The more the audience knows about a person, the less freedom the person has in claiming a particular identity. An audience that knows very little about a person will be more accepting of whatever identity the person conveys, whereas an audience that knows a great deal about a person will be less accepting.
People engaging in self-presentation sometimes encounter difficulties that undermine their ability to convey a desired image. First, people occasionally encounter the multiple audience problem, in which they must simultaneously present two conflicting images. For example, a student while walking with friends who know only her rebellious, impetuous side may run into her professor who knows only her serious, conscientious side. The student faces the dilemma of conveying the conflicting images of rebellious friend and serious student. When both audiences are present, the student must try to behave in a way that is consistent with how her friends view her, but also in a way that is consistent with how her professor views her. Second, people occasionally encounter challenges to their self-presentations. The audience may not believe the image the person presents. Challenges are most likely to arise when people are managing impressions through self-descriptions and the self-descriptions are inconsistent with other evidence. For example, a man who claims to be good driver faces a self-presentational dilemma if he is ticketed or gets in an automobile accident. Third, self-presentations can fail when people lack the cognitive resources to present effectively because, for example, they are tired, anxious, or distracted. For instance, a woman may yawn uncontrollably or reflexively check her watch while talking to a boring classmate, unintentionally conveying an image of disinterest.
Some of the most important images for people to convey are also the hardest. As noted earlier, among the most important images people want to communicate are likeability and competence. Perhaps because these images are so important and are often rewarded, audiences may be skeptical of accepting direct claims of likeability and competence from presenters, thinking that the person is seeking personal gain. Thus, people must resort to indirect routes to create these images, and the indirect routes can be misinterpreted. For example, the student who sits in the front row of the class and asks a lot of questions may be trying to project an image of being a competent student but may be perceived negatively as a teacher’s pet by fellow students.
Finally, there is a dark side to self-presentation. In some instances, the priority people place on their appearances or images can threaten their health. People who excessively tan are putting a higher priority on their appearance (e.g., being tan) than on their health (e.g., taking precautions to avoid skin cancer). Similarly, although condoms help protect against sexually transmitted diseases and unwanted pregnancy, self-presentational concerns may dissuade partners or potential partners from discussing, carrying, or using condoms. Women may fear that carrying condoms makes them seem promiscuous or easy, whereas men may fear that carrying condoms makes them seem presumptuous, as if they are expecting to have sex. Self-presentational concerns may also influence interactions with health care providers and may lead people to delay or avoid embarrassing medical tests and procedures or treatments for conditions that are embarrassing. For example, people may be reluctant to seek tests or treatment for sexually transmitted diseases, loss of bladder control, mental disorders, mental decline, or other conditions associated with weakness or incompetence. Finally, concerns with social acceptance may prompt young people to engage in risky behaviors such as excessive alcohol consumption, sexual promiscuity, or juvenile delinquency.
References:
- Jones, E. E., Pittman, T. S. (1982). Toward a general theory of strategic self-presentation. In J. Suls (Ed.), Psychological perspectives on the self (Vol. 1, pp. 231-260). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
- Leary, M. R. (1996). Self-presentation: Impression management and interpersonal behavior. Boulder, CO: Westview Press.
- Leary, M. R., Tchividjian, L. R., & Kraxberger, B. E. (1994). Self-presentation can be hazardous to your health: Impression management and health risk. Health Psychology, 13, 461-470.
- Schlenker, B. R. (1980). Impression management: The self-concept, social identity, and interpersonal relations. Monterey, CA: Brooks/Cole.
Impression Management: Erving Goffman Theory
Charlotte Nickerson
Research Assistant at Harvard University
Undergraduate at Harvard University
Charlotte Nickerson is a student at Harvard University obsessed with the intersection of mental health, productivity, and design.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
- Impression management refers to the goal-directed conscious or unconscious attempt to influence the perceptions of other people about a person, object, or event by regulating and controlling information in social interaction.
- Generally, people undertake impression management to achieve goals that require they have a desired public image. This activity is called self-presentation.
- In sociology and social psychology, self-presentation is the conscious or unconscious process through which people try to control the impressions other people form of them.
- The goal is for one to present themselves the way in which they would like to be thought of by the individual or group they are interacting with. This form of management generally applies to the first impression.
- Erving Goffman popularized the concept of perception management in his book, The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life , where he argues that impression management not only influences how one is treated by other people but is an essential part of social interaction.

Impression Management in Sociology
Impression management, also known as self-presentation, refers to the ways that people attempt to control how they are perceived by others (Goffman, 1959).
By conveying particular impressions about their abilities, attitudes, motives, status, emotional reactions, and other characteristics, people can influence others to respond to them in desirable ways.
Impression management is a common way for people to influence one another in order to obtain various goals.
While earlier theorists (e.g., Burke, 1950; Hart & Burk, 1972) offered perspectives on the person as a performer, Goffman (1959) was the first to develop a specific theory concerning self-presentation.
In his well-known work, Goffman created the foundation and the defining principles of what is commonly referred to as impression management.
In explicitly laying out a purpose for his work, Goffman (1959) proposes to “consider the ways in which the individual in ordinary work situations presents himself and his activity to others, the ways in which he guides and controls the impression they form of him, and the kind of things he may or may not do while sustaining his performance before them.” (p. xi)
Social Interaction
Goffman viewed impression management not only as a means of influencing how one is treated by other people but also as an essential part of social interaction.
He communicates this view through the conceit of theatre. Actors give different performances in front of different audiences, and the actors and the audience cooperate in negotiating and maintaining the definition of a situation.
To Goffman, the self was not a fixed thing that resides within individuals but a social process. For social interactions to go smoothly, every interactant needs to project a public identity that guides others’ behaviors (Goffman, 1959, 1963; Leary, 2001; Tseelon, 1992).
Goffman defines that when people enter the presence of others, they communicate information by verbal intentional methods and by non-verbal unintentional methods.
According to Goffman, individuals participate in social interactions through performing a “line” or “a pattern of verbal and nonverbal acts by which he expresses his view of the situation and through this his evaluation of the participants, especially himself” (1967, p. 5).
Such lines are created and maintained by both the performer and the audience. By enacting a line effectively, a person gains positive social value or “face.”
The verbal intentional methods allow us to establish who we are and what we wish to communicate directly. We must use these methods for the majority of the actual communication of data.
Goffman is mostly interested in the non-verbal clues given off which are less easily manipulated. When these clues are manipulated the receiver generally still has the upper hand in determining how realistic the clues that are given off are.
People use these clues to determine how to treat a person and if the intentional verbal responses given off are actually honest. It is also known that most people give off clues that help to represent them in a positive light, which tends to be compensated for by the receiver.
Impression Management Techniques
- Suppressing emotions : Maintaining self-control (which we will identify with such practices as speaking briefly and modestly).
- Conforming to Situational Norms : The performer follows agreed-upon rules for behavior in the organization.
- Flattering Others : The performer compliments the perceiver. This tactic works best when flattery is not extreme and when it involves a dimension important to the perceiver.
- Being Consistent : The performer’s beliefs and behaviors are consistent. There is agreement between the performer’s verbal and nonverbal behaviors.
Self-Presentation Examples
Self-presentation can affect the emotional experience . For example, people can become socially anxious when they are motivated to make a desired impression on others but doubt that they can do so successfully (Leary, 2001).
In one paper on self-presentation and emotional experience, Schlenker and Leary (1982) argue that, in contrast to the drive models of anxiety, the cognitive state of the individual mediates both arousal and behavior.
The researchers examine the traditional inverted-U anxiety-performance curve (popularly known as the Yerkes-Dodson law) in this light.
The researchers propose that people are interpersonally secure when they do not have the goal of creating a particular impression on others.
They are not immediately concerned about others’ evaluative reactions in a social setting where they are attempting to create a particular impression and believe that they will be successful in doing so.
Meanwhile, people are anxious when they are uncertain about how to go about creating a certain impression (such as when they do not know what sort of attributes the other person is likely to be impressed with), think that they will not be able to project the types of images that will produce preferred reactions from others.
Such people think that they will not be able to project the desired image strongly enough or believe that some event will happen that will repudiate their self-presentations, causing reputational damage (Schlenker and Leary, 1982).
Psychologists have also studied impression management in the context of mental and physical health .
In one such study, Braginsky et al. (1969) showed that those hospitalized with schizophrenia modify the severity of their “disordered” behavior depending on whether making a more or less “disordered” impression would be most beneficial to them (Leary, 2001).
Additional research on university students shows that people may exaggerate or even fabricate reports of psychological distress when doing so for their social goals.
Hypochondria appears to have self-presentational features where people convey impressions of illness and injury, when doing so helps to drive desired outcomes such as eliciting support or avoiding responsibilities (Leary, 2001).
People can also engage in dangerous behaviors for self-presentation reasons such as suntanning, unsafe sex, and fast driving. People may also refuse needed medical treatment if seeking this medical treatment compromises public image (Leary et al., 1994).
Key Components
There are several determinants of impression management, and people have many reasons to monitor and regulate how others perceive them.
For example, social relationships such as friendship, group membership, romantic relationships, desirable jobs, status, and influence rely partly on other people perceiving the individual as being a particular kind of person or having certain traits.
Because people’s goals depend on them making desired impressions over undesired impressions, people are concerned with the impressions other people form of them.
Although people appear to monitor how they come across ongoingly, the degree to which they are motivated to impression manage and the types of impressions they try to foster varies by situation and individuals (Leary, 2001).
Leary and Kowalski (1990) say that there are two processes that constitute impression management, each of which operate according to different principles and are affected by different situations and dispositional aspects. The first of these processes is impression motivation, and the second is impression construction.
Impression Motivation
There are three main factors that affect how much people are motivated to impression-manage in a situation (Leary and Kowalski, 1990):
(1) How much people believe their public images are relevant to them attaining their desired goals.
When people believe that their public image is relevant to them achieving their goals, they are generally more motivated to control how others perceive them (Leary, 2001).
Conversely, when the impressions of other people have few implications on one’s outcomes, that person’s motivation to impression-manage will be lower.
This is why people are more likely to impression manage in their interactions with powerful, high-status people than those who are less powerful and have lower status (Leary, 2001).
(2) How valuable the goals are: people are also more likely to impress and manage the more valuable the goals for which their public impressions are relevant (Leary, 2001).
(3) how much of a discrepancy there is between how they want to be perceived and how they believe others perceive them..
People are more highly motivated to impression-manage when there is a difference between how they want to be perceived and how they believe others perceive them.
For example, public scandals and embarrassing events that convey undesirable impressions can cause people to make self-presentational efforts to repair what they see as their damaged reputations (Leary, 2001).
Impression Construction
Features of the social situations that people find themselves in, as well as their own personalities, determine the nature of the impressions that they try to convey.
In particular, Leary and Kowalski (1990) name five sets of factors that are especially important in impression construction (Leary, 2001).
Two of these factors include how people’s relationships with themselves (self-concept and desired identity), and three involve how people relate to others (role constraints, target value, and current or potential social image) (Leary and Kowalski, 1990).
Self-concept
The impressions that people try to create are influenced not only by social context but also by one’s own self-concept .
People usually want others to see them as “how they really are” (Leary, 2001), but this is in tension with the fact that people must deliberately manage their impressions in order to be viewed accurately by others (Goffman, 1959).
People’s self-concepts can also constrain the images they try to convey.
People often believe that it is unethical to present impressions of themselves different from how they really are and generally doubt that they would successfully be able to sustain a public image inconsistent with their actual characteristics (Leary, 2001).
This risk of failure in portraying a deceptive image and the accompanying social sanctions deter people from presenting impressions discrepant from how they see themselves (Gergen, 1968; Jones and Pittman, 1982; Schlenker, 1980).
People can differ in how congruent their self-presentations are with their self-perceptions.
People who are high in public self-consciousness have less congruency between their private and public selves than those lower in public self-consciousness (Tunnell, 1984; Leary and Kowalski, 1990).
Desired identity
People’s desired and undesired selves – how they wish to be and not be on an internal level – also influence the images that they try to project.
Schlenker (1985) defines a desirable identity image as what a person “would like to be and thinks he or she really can be, at least at his or her best.”
People have a tendency to manage their impressions so that their images coincide with their desired selves and stay away from images that coincide with their undesired selves (Ogilivie, 1987; Schlenker, 1985; Leary, 2001).
This happens when people publicly claim attributes consistent with their desired identity and openly reject identities that they do not want to be associated with.
For example, someone who abhors bigots may take every step possible to not appear bigoted, and Gergen and Taylor (1969) showed that high-status navel cadets did not conform to low-status navel cadets because they did not want to see themselves as conformists (Leary and Kowalski, 1990).
Target value
people tailor their self-presentations to the values of the individuals whose perceptions they are concerned with.
This may lead to people sometimes fabricating identities that they think others will value.
However, more commonly, people selectively present truthful aspects of themselves that they believe coincide with the values of the person they are targeting the impression to and withhold information that they think others will value negatively (Leary, 2001).
Role constraints
the content of people’s self-presentations is affected by the roles that they take on and the norms of their social context.
In general, people want to convey impressions consistent with their roles and norms .
Many roles even carry self-presentational requirements around the kinds of impressions that the people who hold the roles should and should not convey (Leary, 2001).
Current or potential social image
People’s public image choices are also influenced by how they think they are perceived by others. As in impression motivation, self-presentational behaviors can often be aimed at dispelling undesired impressions that others hold about an individual.
When people believe that others have or are likely to develop an undesirable impression of them, they will typically try to refute that negative impression by showing that they are different from how others believe them to be.
When they are not able to refute this negative impression, they may project desirable impressions in other aspects of their identity (Leary, 2001).
Implications
In the presence of others, few of the behaviors that people make are unaffected by their desire to maintain certain impressions. Even when not explicitly trying to create a particular impression of themselves, people are constrained by concerns about their public image.
Generally, this manifests with people trying not to create undesired impressions in virtually all areas of social life (Leary, 2001).
Tedeschi et al. (1971) argued that phenomena that psychologists previously attributed to peoples’ need to have cognitive consistency actually reflected efforts to maintain an impression of consistency in others’ eyes.
Studies have supported Tedeschi and their colleagues’ suggestion that phenomena previously attributed to cognitive dissonance were actually affected by self-presentational processes (Schlenker, 1980).
Psychologists have applied self-presentation to their study of phenomena as far-ranging as conformity, aggression, prosocial behavior, leadership, negotiation, social influence, gender, stigmatization, and close relationships (Baumeister, 1982; Leary, 1995; Schlenker, 1980; Tedeschi, 1981).
Each of these studies shows that people’s efforts to make impressions on others affect these phenomena, and, ultimately, that concerns self-presentation in private social life.
For example, research shows that people are more likely to be pro-socially helpful when their helpfulness is publicized and behave more prosocially when they desire to repair a damaged social image by being helpful (Leary, 2001).
In a similar vein, many instances of aggressive behavior can be explained as self-presentational efforts to show that someone is willing to hurt others in order to get their way.
This can go as far as gender roles, for which evidence shows that men and women behave differently due to the kind of impressions that are socially expected of men and women.
Baumeister, R. F. (1982). A self-presentational view of social phenomena. Psychological Bulletin, 91, 3-26.
Braginsky, B. M., Braginsky, D. D., & Ring, K. (1969). Methods of madness: The mental hospital as a last resort. New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Buss, A. H., & Briggs, S. (1984). Drama and the self in social interaction. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 47, 1310-1324. Gergen, K. J. (1968). Personal consistency and the presentation of self. In C. Gordon & K. J. Gergen (Eds.), The self in social interaction (Vol. 1, pp. 299-308). New York: Wiley.
Gergen, K. J., & Taylor, M. G. (1969). Social expectancy and self-presentation in a status hierarchy. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 5, 79-92.
Goffman, E. (1959). The moral career of the mental patient. Psychiatry, 22(2), 123-142.
- Goffman, E. (1963). Embarrassment and social organization.
Goffman, E. (1978). The presentation of self in everyday life (Vol. 21). London: Harmondsworth.
Goffman, E. (2002). The presentation of self in everyday life. 1959. Garden City, NY, 259.
Martey, R. M., & Consalvo, M. (2011). Performing the looking-glass self: Avatar appearance and group identity in Second Life. Popular Communication, 9 (3), 165-180.
Jones E E (1964) Ingratiation. Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York.
Jones, E. E., & Pittman, T. S. (1982). Toward a general theory of strategic self-presentation. Psychological perspectives on the self, 1(1), 231-262.
Leary M R (1995) Self-presentation: Impression Management and Interpersonal Behaior. Westview Press, Boulder, CO.
Leary, M. R.. Impression Management, Psychology of, in Smelser, N. J., & Baltes, P. B. (Eds.). (2001). International encyclopedia of the social & behavioral sciences (Vol. 11). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Leary, M. R., & Kowalski, R. M. (1990). Impression management: A literature review and two-component model. Psychological bulletin, 107(1), 34.
Leary M R, Tchvidjian L R, Kraxberger B E 1994 Self-presentation may be hazardous to your health. Health Psychology 13: 461–70.
Ogilvie, D. M. (1987). The undesired self: A neglected variable in personality research. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 52, 379-385.
- Schlenker, B. R. (1980). Impression management (Vol. 222). Monterey, CA: Brooks/Cole.
Schlenker, B. R. (1985). Identity and self-identification. In B. R. Schlenker (Ed.), The self and social life (pp. 65-99). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Schlenker, B. R., & Leary, M. R. (1982). Social anxiety and self-presentation: A conceptualization model. Psychological bulletin, 92(3), 641.
Tedeschi, J. T, Smith, R. B., Ill, & Brown, R. C., Jr. (1974). A reinterpretation of research on aggression. Psychological Bulletin, 81, 540- 563.
Tseëlon, E. (1992). Is the presented self sincere? Goffman, impression management and the postmodern self. Theory, culture & society, 9(2), 115-128.
Tunnell, G. (1984). The discrepancy between private and public selves: Public self-consciousness and its correlates. Journal of Personality Assessment, 48, 549-555.
Further Information
- Solomon, J. F., Solomon, A., Joseph, N. L., & Norton, S. D. (2013). Impression management, myth creation and fabrication in private social and environmental reporting: Insights from Erving Goffman. Accounting, organizations and society, 38(3), 195-213.
- Gardner, W. L., & Martinko, M. J. (1988). Impression management in organizations. Journal of management, 14(2), 321-338.
- Scheff, T. J. (2005). Looking‐Glass self: Goffman as symbolic interactionist. Symbolic interaction, 28(2), 147-166.

- PRESENTATION SKILLS
Self-Presentation in Presentations
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Presentations
- General Presentation Skills
- What is a Presentation?
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- 7 Qualities of Good Speakers That Can Help You Be More Successful
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
When you give a presentation, it is important to remember the whole package, and that means how you present yourself as well as how you present the material.
It is not good to spend hours and hours preparing a wonderful presentation and neglect the effect of your own appearance.
Whether you like it or not, people make judgements about you based on your appearance.
These judgements may be conscious or subconscious, but they all affect how, and whether, your audience is prepared to take on board your message as presenter.
Our pages on Personal Appearance and Personal Presentation explain the importance of presenting yourself effectively, more generally. This page focuses on the impact of self-presentation in presentations.
The Importance of Expectations
When you stand up to give a presentation, the audience already has certain expectations about how you will behave, and what you will say.
These expectations may be based on the event, the marketing, their knowledge of you, or their previous experience more generally.
Expectations may also be based on societal norms, such as business people are expected to wear suits.
You don’t have to match people’s expectations, of course, but you do need to be aware that, if you don’t, they are going to have to spend time processing that difference. This mismatch will take some of their concentration away from your message.
You also need to be aware that people can only take so much discomfort.
A mismatch between expectations and reality can even lead to a situation called cognitive dissonance , where individuals come into contact with something — whether idea, person, or belief — that causes them to question their own internal beliefs and values.
This can be very uncomfortable, and the normal reaction is to try to avoid it. In a presentation situation, that's going to mean either leaving or just not listening, neither of which is ideal.
This is particularly important if you want to say something that your audience will find difficult to hear.
If you want to say something outrageous, wear a suit.
The late Dr Joe Jaina, Organisational Psychologist at Cranfield School of Management.
Aspects of Personal Presentation
Your personal presentation includes:
- Accessories, which in this context means anything that you’re carrying or wearing, including your notes, although it also includes luggage, bags, phones, jewellery, watches, and scarves;
- Body language; and
Your clothes are probably the most obvious aspect of personal presentation.
In deciding what to wear, there are several things to consider:
What does the audience expect?
It’s not actually as simple as ‘wear a business suit’, because this may not always be appropriate.
It does depend what your audience is expecting. On some occasions, or in some industries, smart casual may be much more appropriate. If you’re not sure, ask the organisers about the dress code. You can also ask someone who has been to the event before, or have a look online.
If it’s a regular event, there will almost certainly be photographs of previous occasions and you can see what other people have worn.
Within the audience’s expectations, what will make you feel comfortable?
You will present best if you are fairly relaxed, so you need to find a balance between the audience’s expectations, and feeling comfortable.
For example, you may have a particular suit that you think makes you look good. For women, it’s also worth thinking about shoes: you’re going to have to stand for the duration of the session, so make sure that you can do that.
If you’re not used to heels, don’t wear them.
Your accessories should be consistent with your clothes.
That doesn’t mean that your bag needs to be the same colour as your jacket. However, if you’re wearing a suit, your notes should be in a briefcase or smart bag, and you’re not carrying a backpack or plastic carrier bag. Again, it’s about not distracting your audience from your message.
Likewise, your notes should be part of your thinking. Producing a dog-eared sheaf of paper is not going to help you project a good image. Papers tend to flap about, whereas cue cards can be held on your hand, which is why it is worth considering using cue cards, or even memorising most of what you’re going to say and using your visual aids as cues.
See our page: Managing your Presentation Notes for more on this.
The Importance of Self-Presentation
In 2005, the Conservative Party in the UK faced a leadership election as leader Michael Howard announced that he would step down. The actual election was held between October and December that year. In October, at the Conservative Party Conference, each of the announced candidates was given an opportunity to make a 20-minute speech.
Before the speeches, David Davis was very much the front-runner in the competition. However, his conference speech was considered poor. He spoke from notes, and never really came alive. David Cameron, a more junior member of the party and considered by many an outside chance as leader, made a speech that set the hall alight. He spoke without notes, and with passion, presenting himself as the young, upcoming potential leader who could take the party in a new direction.
By the following morning, the bookies had David Cameron as the front-runner and he went on to win the leadership election.
Self-Presentation also Includes Body Language and Voice.
While there are many important elements of body language, perhaps the most important is to project self-confidence .
You need to demonstrate that you believe in what you’re saying. Otherwise, why would anyone else believe it?
For more about this, and other aspects of body language that may help your communication, see our pages on Managing a Presentation Event and Non-Verbal Communication .
Part of projecting self-belief is being able to control your voice, and speak slowly and clearly. You also need to vary your tone and pace to keep people interested.
For more about this, see our page on Effective Speaking .
In conclusion…
When you are making a presentation, you are presenting a package: you and your message. The more you are aware of the impact of every element, the more effective the package will be as a whole.

Further Reading from Skills You Need
The Skills You Need Guide to Getting a Job
Develop the skills you need to get that job.
This eBook is essential reading for potential job-seekers. Not only does it cover identifying your skills but also the mechanics of applying for a job, writing a CV or resume and attending interviews.
Continue to: Presenting to Large Groups Top Tips for Effective Presentations
See also: Coping with Presentation Nerves Giving a Speech Presenting Data Building a Personal Brand
Self-Presentation Theory: Self-Construction and Audience Pleasing
Cite this chapter.

- Roy F. Baumeister &
- Debra G. Hutton
Part of the book series: Springer Series in Social Psychology ((SSSOC))
Self-presentation is behavior that attempts to convey some information about oneself or some image of oneself to other people. It denotes a class of motivations in human behavior. These motivations are in part stable dispositions of individuals but they depend on situational factors to elicit them. Specifically, self-presentational motivations are activated by the evaluative presence of other people and by others’ (even potential) knowledge of one’s behavior.
- Antisocial Behavior
- Individual Therapy
- Cognitive Dissonance
- Impression Management
- Experimental Social Psychology
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Adler, A (1921). The neurotic constitution: Outlines of a comparative individualistic psychology and psychotherapy . New York: Moffat Yard.
Google Scholar
Aries, P. (1981). The hour of our death . New York: Knopf.
Baumeister, R. F. (1982a). A self-presentational view of social phenomena. Psychological Bulletin, 91 , 3–26.
Article Google Scholar
Baumeister, R. F. (1982b). Self-esteem, self-presentation, and future interaction: A dilemma of reputation. Journal of Personality, 50 , 29–45.
Baumeister, R. F. (1984). Choking under pressure: Self-consciousness and paradoxical effects of incentives on skillful performance. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 46 , 610–620.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Baumeister, R. F. (1985). The championship choke. Psychology Today, 19 (4:April), 48–52.
Baumeister, R. F. (1986). Identity . New York: Oxford University Press.
Baumeister, R F, Hamilton, J. C., & Tice, D. M. (1985). Public versus private expectancy of success: Confidence booster or performance pressure? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 48 , 1447–1457.
Baumeister, R. F., & Jones, E. E. (1978). When self-presentation is constrained by the target’s prior knowledge: Consistency and compensation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 36 , 608–618.
Baumeister, R. F., & Steinhilber, A (1984). Paradoxical effects of supportive audiences on performance under pressure: The home field disadvantage in sports championships. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 47 , 85–93.
Baumeister, R. F., & Tice, D. M. (1984). Role of self-presentation and choice in cognitive dissonance under forced compliance: Necessary or sufficient causes? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 46 , 5–13.
Baumeister, R. F., & Tice, D. M. (1985). Self-esteem and responses to success and failure: Subsequent performance and intrinsic motivation. Journal of Personality, 53 , 450–467.
Bond, C. F. (1982). Social facilitation: A self-presentational view. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 42 , 1042–1050.
Bond, C. F., & Titus, L. J. (1983). Social facilitation: A meta-analysis of 241 studies. Psychological Bulletin, 94 , 265–292.
Braginsky, B. M., Braginsky, D. D., & Ring, K. (1969). Methods of madness: The mental hospital as a last resort . New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Castaneda, C. (1972). Journey to Ixtlan: The lessons of Don Juan . New York: Simon & Schuster.
Deaux, K, & Major, B. (1977). Sex-related patterns in the unit of perception. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 3 , 297–300.
Emmler, N. (1984). Differential involvement in delinquency: Toward an interpretation in terms of reputation management. Progress in Experimental Personality Research, 13 , 174–239.
Festinger, L., & Carlsmith, J. M. (1959). Cognitive consequences of forced compliance. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 58 , 203–210.
Felson, R (1978). Aggression as impression management. Social Psychology Quarterly, 41 , 205–213.
Gollwitzer, P. M. (1986). Striving for specific identities: The social reality of self-symbolizing. In R. Baumeister (Ed.), Public self and private self . New York: Springer-Verlag.
Greenberg, J. (1983). Self-image versus impression management in adherence to distributive justice standards: The influence of self-awareness and self-consciousness. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 44 , 5–19.
Hinkle, L. (1957). [Untitled.] In Methods of forceful indoctrination: Observations and interviews . New York.
Hogan, R (1982). A socioanalytic theory of personality. In M. Page (Ed.), Nebraska symposium on motivation (pp. 55–89). Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press.
Hogan, R, Mankin, D., Conway, J., & Fox, S. (1970). Personality correlates of undergraduate marijuana use. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 35 , 58–63.
Houghton, W. E. (1957). The Victorian frame of mind: 1830–1870 . New Haven: Yale University Press.
Jones, E. E., & Berglas, S. C. (1978). Control of attributions about the self through self-handicapping strategies: The appeal of alcohol and the role of underachievement. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 4 , 200–206.
Jones, E. E., & Pittman, T. S. (1982). Toward a general theory of strategic self-presentation. In J. Suls (Ed.), Psychological perspectives on the self (Vol. 1, pp. 231–262). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Kassin, S. M. (1984) T. V. Cameras, public self-consciousness and mock juror performance. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 20 , 336–349.
Kett, J. F. (1977). Rites of passage: Adolescence in America 1790 to the present . New York: Basic.
Kidder, L. H., Bellettirie, G., & Cohn, E. S. (1977). Secret ambitions and public performances: The effects of anonymity on reward allocations made by men and women. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 13 , 70–80.
Kolditz, T. A, & Arkin, R. M. (1982). An impression management interpretation of the self-handicapping strategy. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 43 , 492–502.
Latané, B., Williams, K, & Harkins, S. (1979). Many hands make light the work: The causes and consequences of social loafing. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 37 , 822–832.
Lifton, R. J. (1957). [Untitled.] In Methods of forceful indoctrination: Observations and interviews . New York.
Major, B., & Adams, J. B. (1983). Role of gender, interpersonal orientation, and self-presentation in distributive-justice behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 45 , 598–608.
Major, B., McFarlin, D. B., & Gagnon, D. (1984). Overworked and underpaid: On the nature of gender differences in personal entitlement. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 47 , 1399–1412.
McFarlin, D. B., Baumeister, R. F., & Blascovich, J. (1984). On knowing when to quit: Task failure, self-esteem, advice, and nonproductive persistence. Journal of Personality, 52 , 138–155.
Morris, C. (1972). The discovery of the individual: 1050–1200 . New York: Harper & Row.
Paulhus, D. (1982). Individual differences, self-presentation, and cognitive dissonance: Their concurrent operation in forced compliance. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 43 , 838–852.
Pennebaker, J. W. (1984). Confiding, ruminating, and psychosomatic disease. In J. W. Pennebaker (Chair), New paradigms in psychology . Symposium conducted at the annual convention of the American Psychological Association, Toronto, Canada, August 1984.
Pennebaker, J. W. (in press). Traumatic experience and psychosomatic disease: Exploring the roles of behavioral inhibition, obsession, and confiding. Canadian Psychology .
Sacco, W. P., & Hokanson, J. E. (1982). Depression and self-reinforcement in a public and private setting. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 42 , 377–385.
Schlenker, B. R. (1980). Impression management: The self-concept, social identity, and interpersonal relations . Monterey, CA: Brooks/Cole.
Schlenker, B. R. (1982). Translating actions into attitudes: An identity-analytic approach to the explanation of social conduct. In L. Berkowitz (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology (Vol. 15 pp. 194–247). New York: Academic Press.
Scott, M. B., & Lyman, S. M. (1968). Accounts. American Sociological Review, 33 , 46–62.
Silverman, I. (1964). Self-esteem and differential responsiveness to success and failure. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 69 , 115–119.
Smith, T. W, Snyder, C. R, & Perkins, S. C. (1983). The self-serving function of hypochondriacal complaints: Physical symptoms as self-handicapping strategies. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 44 , 787–797.
Sweeney, J. (1973). An experimental investigation of the free rider problem. Social Science Research, 2 , 277–292.
Tang, T. L. P., & Baumeister, R. F. (1984). Effects of personal values, perceived surveillance, and task labels on task preference: The ideology of turning play into work. Journal of Applied Psychology, 69 , 99–105.
Tedeschi, J. T., Schlenker, B. R, & Bonoma, T. V. (1971). Cognitive dissonance: Private ratiocination or public spectacle? American Psychologist, 26 , 685–695.
Tice, D. M., & Baumeister, R F. (1985). Self-esteem, self-handicapping, and self-presentation: The benefits of not practicing. Unpublished manuscript, Case Western Reserve University.
Toch, H. (1969). Violent men . Chicago: Aldine.
Wicklund, R. A, & Gollwitzer, P. M. (1982). Symbolic self-completion . Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Zajonc, R (1965). Social facilitation. Science, 149 , 269–274.
Download references
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, Syracuse University, 13210, Syracuse, New York, USA
Brian Mullen
Department of Psychology, Williams College, 01267, Williamstown, Massachusetts, USA
George R. Goethals
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 1987 Springer-Verlag New York Inc.
About this chapter
Baumeister, R.F., Hutton, D.G. (1987). Self-Presentation Theory: Self-Construction and Audience Pleasing. In: Mullen, B., Goethals, G.R. (eds) Theories of Group Behavior. Springer Series in Social Psychology. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-4634-3_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-4634-3_4
Publisher Name : Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN : 978-1-4612-9092-6
Online ISBN : 978-1-4612-4634-3
eBook Packages : Springer Book Archive
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Week 3: Intrapersonal Communication and Self
Self-presentation.
How we perceive ourselves manifests in how we present ourselves to others. Self-presentation is the process of strategically concealing or revealing personal information in order to influence others’ perceptions. [1] We engage in this process daily and for different reasons. Although people occasionally intentionally deceive others in the process of self-presentation, in general we try to make a good impression while still remaining authentic. Since self-presentation helps meet our instrumental, relational, and identity needs, we stand to lose quite a bit if we are caught intentionally misrepresenting ourselves. In May of 2012, Yahoo!’s CEO resigned after it became known that he stated on official documents that he had two college degrees when he actually only had one. In a similar incident, a woman who had long served as the dean of admissions for the prestigious Massachusetts Institute of Technology was dismissed from her position after it was learned that she had only attended one year of college and had falsely indicated she had a bachelor’s and master’s degree. [2] Such incidents clearly show that although people can get away with such false self-presentation for a while, the eventual consequences of being found out are dire. As communicators, we sometimes engage in more subtle forms of inauthentic self-presentation. For example, a person may state or imply that they know more about a subject or situation than they actually do in order to seem smart or “in the loop.” During a speech, a speaker works on a polished and competent delivery to distract from a lack of substantive content. These cases of strategic self-presentation may not ever be found out, but communicators should still avoid them as they do not live up to the standards of ethical communication.
Consciously and competently engaging in self-presentation can have benefits because we can provide others with a more positive and accurate picture of who we are. People who are skilled at impression management are typically more engaging and confident, which allows others to pick up on more cues from which to form impressions. [3] Being a skilled self-presenter draws on many of the practices used by competent communicators, including becoming a higher self-monitor. When self-presentation skills and self-monitoring skills combine, communicators can simultaneously monitor their own expressions, the reaction of others, and the situational and social context. [4] Sometimes people get help with their self-presentation. Although most people can’t afford or wouldn’t think of hiring an image consultant, some people have started generously donating their self-presentation expertise to help others. Many people who have been riding the tough job market for a year or more get discouraged and may consider giving up on their job search. Now a project called “Style Me Hired” has started offering free makeovers to jobless people in order to offer them new motivation and help them make favorable impressions and hopefully get a job offer. [5]

People who have been out of work for a while may have difficulty finding the motivation to engage in the self-presentation behaviors needed to form favorable impressions.
There are two main types of self-presentation: prosocial and self-serving. [6] Prosocial self-presentation entails behaviors that present a person as a role model and make a person more likable and attractive. For example, a supervisor may call on her employees to uphold high standards for business ethics, model that behavior in her own actions, and compliment others when they exemplify those standards. Self-serving self-presentation entails behaviors that present a person as highly skilled, willing to challenge others, and someone not to be messed with. For example, a supervisor may publicly take credit for the accomplishments of others or publicly critique an employee who failed to meet a particular standard. In summary, prosocial strategies are aimed at benefiting others, while self-serving strategies benefit the self at the expense of others.
In general, we strive to present a public image that matches up with our self-concept, but we can also use self-presentation strategies to enhance our self-concept. [7] When we present ourselves in order to evoke a positive evaluative response, we are engaging in self-enhancement. In the pursuit of self-enhancement, a person might try to be as appealing as possible in a particular area or with a particular person to gain feedback that will enhance one’s self-esteem. For example, a singer might train and practice for weeks before singing in front of a well-respected vocal coach but not invest as much effort in preparing to sing in front of friends. Although positive feedback from friends is beneficial, positive feedback from an experienced singer could enhance a person’s self-concept. Self-enhancement can be productive and achieved competently, or it can be used inappropriately. Using self-enhancement behaviors just to gain the approval of others or out of self-centeredness may lead people to communicate in ways that are perceived as phony or overbearing and end up making an unfavorable impression. [8]
“Getting Plugged In”
Self-presentation online: social media, digital trails, and your reputation.
Although social networking has long been a way to keep in touch with friends and colleagues, the advent of social media has made the process of making connections and those all-important first impressions much more complex. Just looking at Facebook as an example, we can clearly see that the very acts of constructing a profile, posting status updates, “liking” certain things, and sharing various information via Facebook features and apps is self-presentation. [9] People also form impressions based on the number of friends we have and the photos and posts that other people tag us in. All this information floating around can be difficult to manage. So how do we manage the impressions we make digitally given that there is a permanent record?
Research shows that people overall engage in positive and honest self-presentation on Facebook. [10] Since people know how visible the information they post is, they may choose to only reveal things they think will form favorable impressions. But the mediated nature of Facebook also leads some people to disclose more personal information than they might otherwise in such a public or semipublic forum. These hyperpersonal disclosures run the risk of forming negative impressions based on who sees them. In general, the ease of digital communication, not just on Facebook, has presented new challenges for our self-control and information management. Sending someone a sexually provocative image used to take some effort before the age of digital cameras, but now “sexting” an explicit photo only takes a few seconds. So people who would have likely not engaged in such behavior before are more tempted to now, and it is the desire to present oneself as desirable or cool that leads people to send photos they may later regret. [11] In fact, new technology in the form of apps is trying to give people a little more control over the exchange of digital information. An iPhone app called “Snapchat” allows users to send photos that will only be visible for a few seconds. Although this isn’t a guaranteed safety net, the demand for such apps is increasing, which illustrates the point that we all now leave digital trails of information that can be useful in terms of our self-presentation but can also create new challenges in terms of managing the information floating around from which others may form impressions of us.
- What impressions do you want people to form of you based on the information they can see on your Facebook page?
- Have you ever used social media or the Internet to do “research” on a person? What things would you find favorable and unfavorable?
- Do you have any guidelines you follow regarding what information about yourself you will put online or not? If so, what are they? If not, why?
- Lauren J. Human et al., “Your Best Self Helps Reveal Your True Self: Positive Self-Presentation Leads to More Accurate Personality Impressions,” Social Psychological and Personality Sciences 3, no. 1 (2012): 23. ↵
- Lauren Webber and Melissa Korn, “Yahoo’s CEO among Many Notable Resume Flaps,” Wall Street Journal Blogs , May 7, 2012, accessed June 9, 2012, http://blogs.wsj.com/digits/2012/05/07/yahoos-ceo-among-many-notable-resume-flaps . ↵
- Lauren J. Human et al., “Your Best Self Helps Reveal Your True Self: Positive Self-Presentation Leads to More Accurate Personality Impressions,” Social Psychological and Personality Sciences 3, no. 1 (2012): 27. ↵
- John J. Sosik, Bruce J. Avolio, and Dong I. Jung, “Beneath the Mask: Examining the Relationship of Self-Presentation Attributes and Impression Management to Charismatic Leadership,” The Leadership Quarterly 13 (2002): 217. ↵
- “Style Me Hired,” accessed June 6, 2012, http://www.stylemehired.com . ↵
- Owen Hargie, Skilled Interpersonal Interaction: Research, Theory, and Practice (London: Routledge, 2011), 99–100. ↵
- John J. Sosik, Bruce J. Avolio, and Dong I. Jung, “Beneath the Mask: Examining the Relationship of Self-Presentation Attributes and Impression Management to Charismatic Leadership,” The Leadership Quarterly 13 (2002): 236. ↵
- Junghyun Kim and Jong-Eun Roselyn Lee, “The Facebook Paths to Happiness: Effects of the Number of Facebook Friends and Self-Presentation on Subjective Well-Being,” Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking 14, no. 6 (2011): 360. ↵
- Natalie DiBlasio, “Demand for Photo-Erasing iPhone App Heats up Sexting Debate,” USA Today , May 7, 2012, accessed June 6, 2012, http://content.usatoday.com/communities/ondeadline/post/2012/05/demand-for-photo-erasing-iphone-app-heats-up-sexting-debate/1 . ↵
- Perceiving and Presenting Self. Authored by : Anonymous. Provided by : Anonymous. Located at : http://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/a-primer-on-communication-studies/s02-03-perceiving-and-presenting-self.html . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of man straightening tie. Authored by : Alex France. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/5UE1JQ . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

12.3: Self-presentation
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 671

Learning Objectives
- Describe social roles and how they influence behavior
- Explain what social norms are and how they influence behavior
- Define script
- Describe the findings of Zimbardo’s Stanford prison experiment
As you’ve learned, social psychology is the study of how people affect one another’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. We have discussed situational perspectives and social psychology’s emphasis on the ways in which a person’s environment, including culture and other social influences, affect behavior. In this section, we examine situational forces that have a strong influence on human behavior including social roles, social norms, and scripts. We discuss how humans use the social environment as a source of information, or cues, on how to behave. Situational influences on our behavior have important consequences, such as whether we will help a stranger in an emergency or how we would behave in an unfamiliar environment.
Social Roles
One major social determinant of human behavior is our social roles. A social role is a pattern of behavior that is expected of a person in a given setting or group (Hare, 2003). Each one of us has several social roles. You may be, at the same time, a student, a parent, an aspiring teacher, a son or daughter, a spouse, and a lifeguard. How do these social roles influence your behavior? Social roles are defined by culturally shared knowledge. That is, nearly everyone in a given culture knows what behavior is expected of a person in a given role. For example, what is the social role for a student? If you look around a college classroom you will likely see students engaging in studious behavior, taking notes, listening to the professor, reading the textbook, and sitting quietly at their desks (See figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). Of course you may see students deviating from the expected studious behavior such as texting on their phones or using Facebook on their laptops, but in all cases, the students that you observe are attending class—a part of the social role of students.

Social roles, and our related behavior, can vary across different settings. How do you behave when you are engaging in the role of son or daughter and attending a family function? Now imagine how you behave when you are engaged in the role of employee at your workplace. It is very likely that your behavior will be different. Perhaps you are more relaxed and outgoing with your family, making jokes and doing silly things. But at your workplace you might speak more professionally, and although you may be friendly, you are also serious and focused on getting the work completed. These are examples of how our social roles influence and often dictate our behavior to the extent that identity and personality can vary with context (that is, in different social groups) (Malloy, Albright, Kenny, Agatstein & Winquist, 1997).
Social Norms
As discussed previously, social roles are defined by a culture’s shared knowledge of what is expected behavior of an individual in a specific role. This shared knowledge comes from social norms. A social norm is a group’s expectation of what is appropriate and acceptable behavior for its members—how they are supposed to behave and think (Deutsch & Gerard, 1955; Berkowitz, 2004). How are we expected to act? What are we expected to talk about? What are we expected to wear? In our discussion of social roles we noted that colleges have social norms for students’ behavior in the role of student and workplaces have social norms for employees’ behaviors in the role of employee. Social norms are everywhere including in families, gangs, and on social media outlets. What are some social norms on Facebook?
CONNECT THE CONCEPTS: Tweens, Teens, and Social Norms
My \(11\)-year-old daughter, Jessica, recently told me she needed shorts and shirts for the summer, and that she wanted me to take her to a store at the mall that is popular with preteens and teens to buy them. I have noticed that many girls have clothes from that store, so I tried teasing her. I said, “All the shirts say ‘Aero’ on the front. If you are wearing a shirt like that and you have a substitute teacher, and the other girls are all wearing that type of shirt, won’t the substitute teacher think you are all named ‘Aero’?”
My daughter replied, in typical \(11\)-year-old fashion, “Mom, you are not funny. Can we please go shopping?”
I tried a different tactic. I asked Jessica if having clothing from that particular store will make her popular. She replied, “No, it will not make me popular. It is what the popular kids wear. It will make me feel happier.” How can a label or name brand make someone feel happier? Think back to what you’ve learned about lifespan development . What is it about pre-teens and young teens that make them want to fit in (See figure \(\PageIndex{2}\))? Does this change over time? Think back to your high school experience, or look around your college campus. What is the main name brand clothing you see? What messages do we get from the media about how to fit in?

Because of social roles, people tend to know what behavior is expected of them in specific, familiar settings. A script is a person’s knowledge about the sequence of events expected in a specific setting (Schank & Abelson, 1977). How do you act on the first day of school, when you walk into an elevator, or are at a restaurant? For example, at a restaurant in the United States, if we want the server’s attention, we try to make eye contact. In Brazil, you would make the sound “psst” to get the server’s attention. You can see the cultural differences in scripts. To an American, saying “psst” to a server might seem rude, yet to a Brazilian, trying to make eye contact might not seem an effective strategy. Scripts are important sources of information to guide behavior in given situations. Can you imagine being in an unfamiliar situation and not having a script for how to behave? This could be uncomfortable and confusing. How could you find out about social norms in an unfamiliar culture?
Zimbardo's Stanford Prison Experiment
The famous Stanford prison experiment , conducted by social psychologist Philip Zimbardo and his colleagues at Stanford University, demonstrated the power of social roles, social norms, and scripts. In the summer of 1971, an advertisement was placed in a California newspaper asking for male volunteers to participate in a study about the psychological effects of prison life. More than \(70\) men volunteered, and these volunteers then underwent psychological testing to eliminate candidates who had underlying psychiatric issues, medical issues, or a history of crime or drug abuse. The pool of volunteers was whittled down to \(24\) healthy male college students. Each student was paid \(\$15\) per day and was randomly assigned to play the role of either a prisoner or a guard in the study. Based on what you have learned about research methods, why is it important that participants were randomly assigned?
A mock prison was constructed in the basement of the psychology building at Stanford. Participants assigned to play the role of prisoners were “arrested” at their homes by Palo Alto police officers, booked at a police station, and subsequently taken to the mock prison. The experiment was scheduled to run for several weeks. To the surprise of the researchers, both the “prisoners” and “guards” assumed their roles with zeal. In fact, on day 2, some of the prisoners revolted, and the guards quelled the rebellion by threatening the prisoners with night sticks. In a relatively short time, the guards came to harass the prisoners in an increasingly sadistic manner, through a complete lack of privacy, lack of basic comforts such as mattresses to sleep on, and through degrading chores and late-night counts.
The prisoners, in turn, began to show signs of severe anxiety and hopelessness—they began tolerating the guards’ abuse. Even the Stanford professor who designed the study and was the head researcher, Philip Zimbardo, found himself acting as if the prison was real and his role, as prison supervisor, was real as well. After only six days, the experiment had to be ended due to the participants’ deteriorating behavior. Zimbardo explained,
At this point it became clear that we had to end the study. We had created an overwhelmingly powerful situation—a situation in which prisoners were withdrawing and behaving in pathological ways, and in which some of the guards were behaving sadistically. Even the “good” guards felt helpless to intervene, and none of the guards quit while the study was in progress. Indeed, it should be noted that no guard ever came late for his shift, called in sick, left early, or demanded extra pay for overtime work. (Zimbardo, 2013)
The Stanford prison experiment demonstrated the power of social roles, norms, and scripts in affecting human behavior. The guards and prisoners enacted their social roles by engaging in behaviors appropriate to the roles: The guards gave orders and the prisoners followed orders. Social norms require guards to be authoritarian and prisoners to be submissive. When prisoners rebelled, they violated these social norms, which led to upheaval. The specific acts engaged by the guards and the prisoners derived from scripts. For example, guards degraded the prisoners by forcing them do push-ups and by removing all privacy. Prisoners rebelled by throwing pillows and trashing their cells. Some prisoners became so immersed in their roles that they exhibited symptoms of mental breakdown; however, according to Zimbardo, none of the participants suffered long term harm (Alexander, 2001).
The Stanford Prison Experiment has some parallels with the abuse of prisoners of war by U.S. Army troops and CIA personnel at the Abu Ghraib prison in 2003 and 2004. The offenses at Abu Ghraib were documented by photographs of the abuse, some taken by the abusers themselves (See fig. 12.2.3).

Human behavior is largely influenced by our social roles, norms, and scripts. In order to know how to act in a given situation, we have shared cultural knowledge of how to behave depending on our role in society. Social norms dictate the behavior that is appropriate or inappropriate for each role. Each social role has scripts that help humans learn the sequence of appropriate behaviors in a given setting. The famous Stanford prison experiment is an example of how the power of the situation can dictate the social roles, norms, and scripts we follow in a given situation, even if this behavior is contrary to our typical behavior.
Contributors and Attributions
Rose M. Spielman with many significant contributors. The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the creative commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University. For questions regarding this license, please contact [email protected] .Textbook content produced by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 license. Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected] .

Dressing for Success: The Psychology Behind Self Presentation
Dressing for success is more than just putting on a power suit. It’s about understanding the psychology behind self-presentation.
When you dress for success, you are sending a message to the world about who you are and what you want to achieve.
And in this blog post, we will discuss the different factors that go into dressing for success, and we’ll provide some tips on how you can start dressing like a winner.
What is self-presentation and why is it important?
Self-presentation is the act of managing how other people perceive and evaluate you. It involves using various cues, such as your appearance, mannerisms, and speech patterns, to create a certain impression in the minds of others.
When it comes to dressing for success, self-presentation is absolutely critical. How you present yourself to the world sends a powerful message about who you are and what you value. From your choice of clothing to your hairstyle and makeup, everything you do to present yourself can impact how others view you.
So what are some key factors to consider when dressing for success?
Factors that go into dressing for success
There are many different factors that go into dressing for success, including your clothing style, color choices, grooming habits, and body language. Let’s take a closer look at each of these factors:
- Clothing style. Your choice of clothing plays an important role in how others perceive you. For example, if you tend to wear trendy and fashionable clothing items, this may communicate that you are creative and stylish (have a look at some examples of fashionable outfits here ). On the other hand, if you prefer more classic and understated styles, this may suggest that you are more reserved and conservative.
- Colour choices. The colours you choose to wear can also have a big impact on how others perceive you. For example, wearing bright and bold colours may convey an outgoing and fun-loving personality, while wearing darker or muted colours may suggest that you are more serious and professional.
- Grooming habits. Your grooming habits are another important aspect of self-presentation. People will often make snap judgments about you based on the way that you look and smell, so it’s important to pay attention to things like your hair, skin, and body odour.
- Body language. Your body language is an equally important factor in self-presentation. How you hold yourself, the way you walk and stand, and your facial expressions all convey a great deal about your personality and character.
How to dress for success in any situation
So if you want to dress for success in any situation, there are some key tips that you should keep in mind.
First and foremost, it is important to pay attention to the expectations and norms of the situation. For example, if you are going for a job interview or meeting with a potential client, it is important to dress in a professional and polished manner.
But at the same time, you also want to make sure that you feel comfortable and confident in what you are wearing. This means choosing clothing that fits well, makes you feel good, and reflects your individual style.
Another important factor to consider when dressing for success is your body type. Different clothing styles and cuts will look better on different body types, so it is important to be mindful of this when choosing what to wear.
For example, if you are petite, you may want to stick with more streamlined and tailored clothing items, while curvier body types can get away with wearing looser, more flowy styles.
Overall, the key to dressing for success is to feel good about yourself and exude confidence in everything you do.
Tips for putting your best foot forward
Now that you know the key factors to consider when dressing for success, here are some tips and tricks for putting your best foot forward in any situation:
First, pay attention to the colours and patterns you choose. Bright, bold colours can be eye-catching and help you stand out in a positive way, while neutral colours are more understated and professional.
Second, think about the cuts and fits of your clothing. Loose or baggy clothing can make you look sloppy and unprofessional, while form-fitting clothes show off your best features and help you feel more confident.
But when it comes to form-fitting clothes, it’s important to find the right balance between being too revealing and looking frumpy.
Third, consider the details of your outfit. Accessories like jewellery, belts, and scarves can add a finishing touch to any look, while well-chosen shoes and bags can help you complete your overall look.
The power of first impressions
One final thing to keep in mind when dressing for success is the power of first impressions.
How you present yourself to others from the very first moment can have a big impact on how they perceive you, so it is important to always put your best foot forward.
Whether you are going for a job interview, networking with potential clients, or just meeting someone new at a social event, it is vital to make a good impression and leave a positive and lasting impression on others.
So what are some things you can do to leave a good first impression? Some key tips include dressing appropriately for the situation, making eye contact and smiling when you meet someone new ( facial expressions are key to first impressions ), and being polite and respectful at all times.
At the same time, remember to be yourself and own your style; by being confident, authentic, and true to yourself, you can always make a positive impression on others.
Final thoughts
In conclusion, dressing for success is about much more than just what you wear or how you look. Rather, it is about understanding the psychology behind self-presentation and using that knowledge to put your best foot forward in any situation.
Whether you are going for a job interview, attending a high-profile party, or meeting someone new in a professional capacity, the key is to feel confident, be authentic, and exude positive energy.
Dennis Relojo-Howell is the managing director of Psychreg.
VIEW AUTHOR’S PROFILE
Related Articles
How workplace discrimination affects our mental well-being and what we can do about it, the key to success: how dental marketing companies boost brand growth and visibility, how to prepare for the pmp certification toronto exam, budget-friendly jobs to increase offers on your home before summer, navigating the maze: common problems and challenges with lab inventory management processes, management techniques to get the best out of your employees, understanding how power dynamics shape our mental well-being, china injection molding: exploring efficiency and safety, feather flags: the ultimate guide to your brand’s visibility, onboard with style: why branded merchandise should be part of onboarding, how do i build confidence at work , study finds that virtual meetings can boost well-being and performance, these uk cities are the most likely to “job hop” according to new study, former blackrock exec jeff smith on how studying psychology can benefit hr professionals, how to prevent virtual meeting fatigue, new report reveals latest borrowing trends, understanding work fulfilment can enhance your professional and personal life, how to support your employees through the cost-of-living crisis, top tips on how to land your first job and get on the career ladder, young people in the uk believe relocation is necessary for better job opportunities, survey reveals job interview red flags – gere’s what a recruiter thinks, how to future-proof your career, flex office space provider workspace saves nearly a million kilowatt hours in london with the big energy race, 48% of employees surveyed said “green benefits” make them feel more motivated at work.

Psychreg is a digital media company and not a clinical company. Our content does not constitute a medical or psychological consultation. See a certified medical or mental health professional for diagnosis.
- Privacy Policy
© Copyright 2014–2034 Psychreg Ltd
- PSYCHREG JOURNAL
- MEET OUR WRITERS
- MEET THE TEAM

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
68 Self-Presentation, Attitudes, and Persuasion
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe social roles and how they influence behavior
- Explain what social norms are and how they influence behavior
- Define script
- Describe the findings of Zimbardo’s Stanford prison experiment
- Define attitude
- Describe how people’s attitudes are internally changed through cognitive dissonance
- Explain how people’s attitudes are externally changed through persuasion
- Describe the peripheral and central routes to persuasion
Self-presentation
As you’ve learned, social psychology is the study of how people affect one another’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. We have discussed situational perspectives and social psychology’s emphasis on the ways in which a person’s environment, including culture and other social influences, affect behavior. In this section, we examine situational forces that have a strong influence on human behavior including social roles, social norms, and scripts. We discuss how humans use the social environment as a source of information, or cues, on how to behave. Situational influences on our behavior have important consequences, such as whether we will help a stranger in an emergency or how we would behave in an unfamiliar environment.
SOCIAL ROLES
One major social determinant of human behavior is our social roles. A social role is a pattern of behavior that is expected of a person in a given setting or group (Hare, 2003). Each one of us has several social roles. You may be, at the same time, a student, a parent, an aspiring teacher, a son or daughter, a spouse, and a lifeguard. How do these social roles influence your behavior? Social roles are defined by culturally shared knowledge. That is, nearly everyone in a given culture knows what behavior is expected of a person in a given role. For example, what is the social role for a student? If you look around a college classroom you will likely see students engaging in studious behavior, taking notes, listening to the professor, reading the textbook, and sitting quietly at their desks ( Figure ). Of course you may see students deviating from the expected studious behavior such as texting on their phones or using Facebook on their laptops, but in all cases, the students that you observe are attending class—a part of the social role of students.

Social roles, and our related behavior, can vary across different settings. How do you behave when you are engaging in the role of son or daughter and attending a family function? Now imagine how you behave when you are engaged in the role of employee at your workplace. It is very likely that your behavior will be different. Perhaps you are more relaxed and outgoing with your family, making jokes and doing silly things. But at your workplace you might speak more professionally, and although you may be friendly, you are also serious and focused on getting the work completed. These are examples of how our social roles influence and often dictate our behavior to the extent that identity and personality can vary with context (that is, in different social groups) (Malloy, Albright, Kenny, Agatstein & Winquist, 1997).
SOCIAL NORMS
As discussed previously, social roles are defined by a culture’s shared knowledge of what is expected behavior of an individual in a specific role. This shared knowledge comes from social norms. A social norm is a group’s expectation of what is appropriate and acceptable behavior for its members—how they are supposed to behave and think (Deutsch & Gerard, 1955; Berkowitz, 2004). How are we expected to act? What are we expected to talk about? What are we expected to wear? In our discussion of social roles we noted that colleges have social norms for students’ behavior in the role of student and workplaces have social norms for employees’ behaviors in the role of employee. Social norms are everywhere including in families, gangs, and on social media outlets. What are some social norms on Facebook?
My 11-year-old daughter, Jessica, recently told me she needed shorts and shirts for the summer, and that she wanted me to take her to a store at the mall that is popular with preteens and teens to buy them. I have noticed that many girls have clothes from that store, so I tried teasing her. I said, “All the shirts say ‘Aero’ on the front. If you are wearing a shirt like that and you have a substitute teacher, and the other girls are all wearing that type of shirt, won’t the substitute teacher think you are all named ‘Aero’?”
My daughter replied, in typical 11-year-old fashion, “Mom, you are not funny. Can we please go shopping?”
I tried a different tactic. I asked Jessica if having clothing from that particular store will make her popular. She replied, “No, it will not make me popular. It is what the popular kids wear. It will make me feel happier.” How can a label or name brand make someone feel happier? Think back to what you’ve learned about lifespan development . What is it about pre-teens and young teens that make them want to fit in ( Figure )? Does this change over time? Think back to your high school experience, or look around your college campus. What is the main name brand clothing you see? What messages do we get from the media about how to fit in?

Because of social roles, people tend to know what behavior is expected of them in specific, familiar settings. A script is a person’s knowledge about the sequence of events expected in a specific setting (Schank & Abelson, 1977). How do you act on the first day of school, when you walk into an elevator, or are at a restaurant? For example, at a restaurant in the United States, if we want the server’s attention, we try to make eye contact. In Brazil, you would make the sound “psst” to get the server’s attention. You can see the cultural differences in scripts. To an American, saying “psst” to a server might seem rude, yet to a Brazilian, trying to make eye contact might not seem an effective strategy. Scripts are important sources of information to guide behavior in given situations. Can you imagine being in an unfamiliar situation and not having a script for how to behave? This could be uncomfortable and confusing. How could you find out about social norms in an unfamiliar culture?
ZIMBARDO’S STANFORD PRISON EXPERIMENT
The famous Stanford prison experiment , conducted by social psychologist Philip Zimbardo and his colleagues at Stanford University, demonstrated the power of social roles, social norms, and scripts. In the summer of 1971, an advertisement was placed in a California newspaper asking for male volunteers to participate in a study about the psychological effects of prison life. More than 70 men volunteered, and these volunteers then underwent psychological testing to eliminate candidates who had underlying psychiatric issues, medical issues, or a history of crime or drug abuse. The pool of volunteers was whittled down to 24 healthy male college students. Each student was paid $15 per day and was randomly assigned to play the role of either a prisoner or a guard in the study. Based on what you have learned about research methods, why is it important that participants were randomly assigned?
A mock prison was constructed in the basement of the psychology building at Stanford. Participants assigned to play the role of prisoners were “arrested” at their homes by Palo Alto police officers, booked at a police station, and subsequently taken to the mock prison. The experiment was scheduled to run for several weeks. To the surprise of the researchers, both the “prisoners” and “guards” assumed their roles with zeal. In fact, on day 2, some of the prisoners revolted, and the guards quelled the rebellion by threatening the prisoners with night sticks. In a relatively short time, the guards came to harass the prisoners in an increasingly sadistic manner, through a complete lack of privacy, lack of basic comforts such as mattresses to sleep on, and through degrading chores and late-night counts.
The prisoners, in turn, began to show signs of severe anxiety and hopelessness—they began tolerating the guards’ abuse. Even the Stanford professor who designed the study and was the head researcher, Philip Zimbardo, found himself acting as if the prison was real and his role, as prison supervisor, was real as well. After only six days, the experiment had to be ended due to the participants’ deteriorating behavior. Zimbardo explained,
At this point it became clear that we had to end the study. We had created an overwhelmingly powerful situation—a situation in which prisoners were withdrawing and behaving in pathological ways, and in which some of the guards were behaving sadistically. Even the “good” guards felt helpless to intervene, and none of the guards quit while the study was in progress. Indeed, it should be noted that no guard ever came late for his shift, called in sick, left early, or demanded extra pay for overtime work. (Zimbardo, 2013)
The Stanford prison experiment demonstrated the power of social roles, norms, and scripts in affecting human behavior. The guards and prisoners enacted their social roles by engaging in behaviors appropriate to the roles: The guards gave orders and the prisoners followed orders. Social norms require guards to be authoritarian and prisoners to be submissive. When prisoners rebelled, they violated these social norms, which led to upheaval. The specific acts engaged by the guards and the prisoners derived from scripts. For example, guards degraded the prisoners by forcing them do push-ups and by removing all privacy. Prisoners rebelled by throwing pillows and trashing their cells. Some prisoners became so immersed in their roles that they exhibited symptoms of mental breakdown; however, according to Zimbardo, none of the participants suffered long term harm (Alexander, 2001).
The Stanford Prison Experiment has some parallels with the abuse of prisoners of war by U.S. Army troops and CIA personnel at the Abu Ghraib prison in 2003 and 2004. The offenses at Abu Ghraib were documented by photographs of the abuse, some taken by the abusers themselves ( Figure ).

Visit this website to hear an NPR interview with Philip Zimbardo where he discusses the parallels between the Stanford prison experiment and the Abu Ghraib prison in Iraq.
Human behavior is largely influenced by our social roles, norms, and scripts. In order to know how to act in a given situation, we have shared cultural knowledge of how to behave depending on our role in society. Social norms dictate the behavior that is appropriate or inappropriate for each role. Each social role has scripts that help humans learn the sequence of appropriate behaviors in a given setting. The famous Stanford prison experiment is an example of how the power of the situation can dictate the social roles, norms, and scripts we follow in a given situation, even if this behavior is contrary to our typical behavior.
Review Questions
A(n) ________ is a set of group expectations for appropriate thoughts and behaviors of its members.
- social role
- social norm
- attribution
On his first day of soccer practice, Jose suits up in a t-shirt, shorts, and cleats and runs out to the field to join his teammates. Jose’s behavior is reflective of ________.
- social influence
- good athletic behavior
- normative behavior
When it comes to buying clothes, teenagers often follow social norms; this is likely motivated by ________.
- following parents’ rules
- saving money
- looking good
In the Stanford prison experiment, even the lead researcher succumbed to his role as a prison supervisor. This is an example of the power of ________ influencing behavior.
- social norms
- social roles
Critical Thinking Questions
Why didn’t the “good” guards in the Stanford prison experiment object to other guards’ abusive behavior? Were the student prisoners simply weak people? Why didn’t they object to being abused?
Describe how social roles, social norms, and scripts were evident in the Stanford prison experiment. How can this experiment be applied to everyday life? Are there any more recent examples where people started fulfilling a role and became abusive?
Personal Application Questions
Try attending a religious service very different from your own and see how you feel and behave without knowing the appropriate script. Or, try attending an important, personal event that you have never attended before, such as a bar mitzvah (a coming-of-age ritual in Jewish culture), a quinceañera (in some Latin American cultures a party is given to a girl who is turning 15 years old), a wedding, a funeral, or a sporting event new to you, such as horse racing or bull riding. Observe and record your feelings and behaviors in this unfamiliar setting for which you lack the appropriate script. Do you silently observe the action, or do you ask another person for help interpreting the behaviors of people at the event? Describe in what ways your behavior would change if you were to attend a similar event in the future?
Name and describe at least three social roles you have adopted for yourself. Why did you adopt these roles? What are some roles that are expected of you, but that you try to resist?
Attitudes and Persuasion
Social psychologists have documented how the power of the situation can influence our behaviors. Now we turn to how the power of the situation can influence our attitudes and beliefs. Attitude is our evaluation of a person, an idea, or an object. We have attitudes for many things ranging from products that we might pick up in the supermarket to people around the world to political policies. Typically, attitudes are favorable or unfavorable: positive or negative (Eagly & Chaiken, 1993). And, they have three components: an affective component (feelings), a behavioral component (the effect of the attitude on behavior), and a cognitive component (belief and knowledge) (Rosenberg & Hovland, 1960).
For example, you may hold a positive attitude toward recycling. This attitude should result in positive feelings toward recycling (such as “It makes me feel good to recycle” or “I enjoy knowing that I make a small difference in reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills”). Certainly, this attitude should be reflected in our behavior: You actually recycle as often as you can. Finally, this attitude will be reflected in favorable thoughts (for example, “Recycling is good for the environment” or “Recycling is the responsible thing to do”).
Our attitudes and beliefs are not only influenced by external forces, but also by internal influences that we control. Like our behavior, our attitudes and thoughts are not always changed by situational pressures, but they can be consciously changed by our own free will. In this section we discuss the conditions under which we would want to change our own attitudes and beliefs.
WHAT IS COGNITIVE DISSONANCE?
Social psychologists have documented that feeling good about ourselves and maintaining positive self-esteem is a powerful motivator of human behavior (Tavris & Aronson, 2008). In the United States, members of the predominant culture typically think very highly of themselves and view themselves as good people who are above average on many desirable traits (Ehrlinger, Gilovich, & Ross, 2005). Often, our behavior, attitudes, and beliefs are affected when we experience a threat to our self-esteem or positive self-image. Psychologist Leon Festinger (1957) defined cognitive dissonance as psychological discomfort arising from holding two or more inconsistent attitudes, behaviors, or cognitions (thoughts, beliefs, or opinions). Festinger’s theory of cognitive dissonance states that when we experience a conflict in our behaviors, attitudes, or beliefs that runs counter to our positive self-perceptions, we experience psychological discomfort (dissonance). For example, if you believe smoking is bad for your health but you continue to smoke, you experience conflict between your belief and behavior ( Figure ).

Later research documented that only conflicting cognitions that threaten individuals’ positive self-image cause dissonance (Greenwald & Ronis, 1978). Additional research found that dissonance is not only psychologically uncomfortable but also can cause physiological arousal (Croyle & Cooper, 1983) and activate regions of the brain important in emotions and cognitive functioning (van Veen, Krug, Schooler, & Carter, 2009). When we experience cognitive dissonance, we are motivated to decrease it because it is psychologically, physically, and mentally uncomfortable. We can reduce cognitive dissonance by bringing our cognitions, attitudes, and behaviors in line—that is, making them harmonious. This can be done in different ways, such as:
- changing our discrepant behavior (e.g., stop smoking),
- changing our cognitions through rationalization or denial (e.g., telling ourselves that health risks can be reduced by smoking filtered cigarettes),
- adding a new cognition (e.g., “Smoking suppresses my appetite so I don’t become overweight, which is good for my health.”).
A classic example of cognitive dissonance is John, a 20-year-old who enlists in the military. During boot camp he is awakened at 5:00 a.m., is chronically sleep deprived, yelled at, covered in sand flea bites, physically bruised and battered, and mentally exhausted ( Figure ). It gets worse. Recruits that make it to week 11 of boot camp have to do 54 hours of continuous training.

Not surprisingly, John is miserable. No one likes to be miserable. In this type of situation, people can change their beliefs, their attitudes, or their behaviors. The last option, a change of behaviors, is not available to John. He has signed on to the military for four years, and he cannot legally leave.
If John keeps thinking about how miserable he is, it is going to be a very long four years. He will be in a constant state of cognitive dissonance. As an alternative to this misery, John can change his beliefs or attitudes. He can tell himself, “I am becoming stronger, healthier, and sharper. I am learning discipline and how to defend myself and my country. What I am doing is really important.” If this is his belief, he will realize that he is becoming stronger through his challenges. He then will feel better and not experience cognitive dissonance, which is an uncomfortable state.
The Effect of Initiation
The military example demonstrates the observation that a difficult initiation into a group influences us to like the group more , due to the justification of effort. We do not want to have wasted time and effort to join a group that we eventually leave. A classic experiment by Aronson and Mills (1959) demonstrated this justification of effort effect. College students volunteered to join a campus group that would meet regularly to discuss the psychology of sex. Participants were randomly assigned to one of three conditions: no initiation, an easy initiation, and a difficult initiation into the group. After participating in the first discussion, which was deliberately made very boring, participants rated how much they liked the group. Participants who underwent a difficult initiation process to join the group rated the group more favorably than did participants with an easy initiation or no initiation ( Figure ).

Similar effects can be seen in a more recent study of how student effort affects course evaluations. Heckert, Latier, Ringwald-Burton, and Drazen (2006) surveyed 463 undergraduates enrolled in courses at a midwestern university about the amount of effort that their courses required of them. In addition, the students were also asked to evaluate various aspects of the course. Given what you’ve just read, it will come as no surprise that those courses that were associated with the highest level of effort were evaluated as being more valuable than those that did not. Furthermore, students indicated that they learned more in courses that required more effort, regardless of the grades that they received in those courses (Heckert et al., 2006).
Besides the classic military example and group initiation, can you think of other examples of cognitive dissonance ? Here is one: Marco and Maria live in Fairfield County, Connecticut, which is one of the wealthiest areas in the United States and has a very high cost of living. Marco telecommutes from home and Maria does not work outside of the home. They rent a very small house for more than $3000 a month. Maria shops at consignment stores for clothes and economizes where she can. They complain that they never have any money and that they cannot buy anything new. When asked why they do not move to a less expensive location, since Marco telecommutes, they respond that Fairfield County is beautiful, they love the beaches, and they feel comfortable there. How does the theory of cognitive dissonance apply to Marco and Maria’s choices?
In the previous section we discussed that the motivation to reduce cognitive dissonance leads us to change our attitudes, behaviors, and/or cognitions to make them consonant. Persuasion is the process of changing our attitude toward something based on some kind of communication. Much of the persuasion we experience comes from outside forces. How do people convince others to change their attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors ( Figure )? What communications do you receive that attempt to persuade you to change your attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors?

A subfield of social psychology studies persuasion and social influence, providing us with a plethora of information on how humans can be persuaded by others.
Yale Attitude Change Approach
The topic of persuasion has been one of the most extensively researched areas in social psychology (Fiske et al., 2010). During the Second World War, Carl Hovland extensively researched persuasion for the U.S. Army. After the war, Hovland continued his exploration of persuasion at Yale University. Out of this work came a model called the Yale attitude change approach , which describes the conditions under which people tend to change their attitudes. Hovland demonstrated that certain features of the source of a persuasive message, the content of the message, and the characteristics of the audience will influence the persuasiveness of a message (Hovland, Janis, & Kelley, 1953).
Features of the source of the persuasive message include the credibility of the speaker (Hovland & Weiss, 1951) and the physical attractiveness of the speaker (Eagly & Chaiken, 1975; Petty, Wegener, & Fabrigar, 1997). Thus, speakers who are credible, or have expertise on the topic, and who are deemed as trustworthy are more persuasive than less credible speakers. Similarly, more attractive speakers are more persuasive than less attractive speakers. The use of famous actors and athletes to advertise products on television and in print relies on this principle. The immediate and long term impact of the persuasion also depends, however, on the credibility of the messenger (Kumkale & Albarracín, 2004).
Features of the message itself that affect persuasion include subtlety (the quality of being important, but not obvious) (Petty & Cacioppo, 1986; Walster & Festinger, 1962); sidedness (that is, having more than one side) (Crowley & Hoyer, 1994; Igou & Bless, 2003; Lumsdaine & Janis, 1953); timing (Haugtvedt & Wegener, 1994; Miller & Campbell, 1959), and whether both sides are presented. Messages that are more subtle are more persuasive than direct messages. Arguments that occur first, such as in a debate, are more influential if messages are given back-to-back. However, if there is a delay after the first message, and before the audience needs to make a decision, the last message presented will tend to be more persuasive (Miller & Campbell, 1959).
Features of the audience that affect persuasion are attention (Albarracín & Wyer, 2001; Festinger & Maccoby, 1964), intelligence, self-esteem (Rhodes & Wood, 1992), and age (Krosnick & Alwin, 1989). In order to be persuaded, audience members must be paying attention. People with lower intelligence are more easily persuaded than people with higher intelligence; whereas people with moderate self-esteem are more easily persuaded than people with higher or lower self-esteem (Rhodes & Wood, 1992). Finally, younger adults aged 18–25 are more persuadable than older adults.
Elaboration Likelihood Model
An especially popular model that describes the dynamics of persuasion is the elaboration likelihood model of persuasion (Petty & Cacioppo, 1986). The elaboration likelihood model considers the variables of the attitude change approach—that is, features of the source of the persuasive message, contents of the message, and characteristics of the audience are used to determine when attitude change will occur. According to the elaboration likelihood model of persuasion, there are two main routes that play a role in delivering a persuasive message: central and peripheral ( Figure ).

The central route is logic driven and uses data and facts to convince people of an argument’s worthiness. For example, a car company seeking to persuade you to purchase their model will emphasize the car’s safety features and fuel economy. This is a direct route to persuasion that focuses on the quality of the information. In order for the central route of persuasion to be effective in changing attitudes, thoughts, and behaviors, the argument must be strong and, if successful, will result in lasting attitude change.
The central route to persuasion works best when the target of persuasion, or the audience, is analytical and willing to engage in processing of the information. From an advertiser’s perspective, what products would be best sold using the central route to persuasion? What audience would most likely be influenced to buy the product? One example is buying a computer. It is likely, for example, that small business owners might be especially influenced by the focus on the computer’s quality and features such as processing speed and memory capacity.
The peripheral route is an indirect route that uses peripheral cues to associate positivity with the message (Petty & Cacioppo, 1986). Instead of focusing on the facts and a product’s quality, the peripheral route relies on association with positive characteristics such as positive emotions and celebrity endorsement. For example, having a popular athlete advertise athletic shoes is a common method used to encourage young adults to purchase the shoes. This route to attitude change does not require much effort or information processing. This method of persuasion may promote positivity toward the message or product, but it typically results in less permanent attitude or behavior change. The audience does not need to be analytical or motivated to process the message. In fact, a peripheral route to persuasion may not even be noticed by the audience, for example in the strategy of product placement. Product placement refers to putting a product with a clear brand name or brand identity in a TV show or movie to promote the product (Gupta & Lord, 1998). For example, one season of the reality series American Idol prominently showed the panel of judges drinking out of cups that displayed the Coca-Cola logo. What other products would be best sold using the peripheral route to persuasion? Another example is clothing: A retailer may focus on celebrities that are wearing the same style of clothing.
Foot-in-the-door Technique
Researchers have tested many persuasion strategies that are effective in selling products and changing people’s attitude, ideas, and behaviors. One effective strategy is the foot-in-the-door technique (Cialdini, 2001; Pliner, Hart, Kohl, & Saari, 1974). Using the foot-in-the-door technique , the persuader gets a person to agree to bestow a small favor or to buy a small item, only to later request a larger favor or purchase of a bigger item. The foot-in-the-door technique was demonstrated in a study by Freedman and Fraser (1966) in which participants who agreed to post small sign in their yard or sign a petition were more likely to agree to put a large sign in their yard than people who declined the first request ( Figure ). Research on this technique also illustrates the principle of consistency (Cialdini, 2001): Our past behavior often directs our future behavior, and we have a desire to maintain consistency once we have a committed to a behavior.

A common application of foot-in-the-door is when teens ask their parents for a small permission (for example, extending curfew by a half hour) and then asking them for something larger. Having granted the smaller request increases the likelihood that parents will acquiesce with the later, larger request.
How would a store owner use the foot-in-the-door technique to sell you an expensive product? For example, say that you are buying the latest model smartphone, and the salesperson suggests you purchase the best data plan. You agree to this. The salesperson then suggests a bigger purchase—the three-year extended warranty. After agreeing to the smaller request, you are more likely to also agree to the larger request. You may have encountered this if you have bought a car. When salespeople realize that a buyer intends to purchase a certain model, they might try to get the customer to pay for many or most available options on the car.
Attitudes are our evaluations or feelings toward a person, idea, or object and typically are positive or negative. Our attitudes and beliefs are influenced not only by external forces, but also by internal influences that we control. An internal form of attitude change is cognitive dissonance or the tension we experience when our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are in conflict. In order to reduce dissonance, individuals can change their behavior, attitudes, or cognitions, or add a new cognition. External forces of persuasion include advertising; the features of advertising that influence our behaviors include the source, message, and audience. There are two primary routes to persuasion. The central route to persuasion uses facts and information to persuade potential consumers. The peripheral route uses positive association with cues such as beauty, fame, and positive emotions.
Attitudes describe our ________ of people, objects, and ideas.
- evaluations
Cognitive dissonance causes discomfort because it disrupts our sense of ________.
- unpredictability
- consistency
In order for the central route to persuasion to be effective, the audience must be ________ and ________.
- analytical; motivated
- attentive; happy
- intelligent; unemotional
- gullible; distracted
Examples of cues used in peripheral route persuasion include all of the following except
- celebrity endorsement
- positive emotions
- attractive models
- factual information
Give an example (one not used in class or your text) of cognitive dissonance and how an individual might resolve this.
Imagine that you work for an advertising agency, and you’ve been tasked with developing an advertising campaign to increase sales of Bliss Soda. How would you develop an advertisement for this product that uses a central route of persuasion? How would you develop an ad using a peripheral route of persuasion?
Cognitive dissonance often arises after making an important decision, called post-decision dissonance (or in popular terms, buyer’s remorse). Describe a recent decision you made that caused dissonance and describe how you resolved it.
Describe a time when you or someone you know used the foot-in-the-door technique to gain someone’s compliance.
[glossary-page] [glossary-term]attitude:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]evaluations of or feelings toward a person, idea, or object that are typically positive or negative[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]central route persuasion:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]logic-driven arguments using data and facts to convince people of an argument’s worthiness[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]cognitive dissonance:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]psychological discomfort that arises from a conflict in a person’s behaviors, attitudes, or beliefs that runs counter to one’s positive self-perception[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]foot-in-the-door technique:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]persuasion of one person by another person, encouraging a person to agree to a small favor, or to buy a small item, only to later request a larger favor or purchase of a larger item[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]peripheral route persuasion:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]one person persuades another person; an indirect route that relies on association of peripheral cues (such as positive emotions and celebrity endorsement) to associate positivity with a message[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]persuasion:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]process of changing our attitude toward something based on some form of communication[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]script:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]person’s knowledge about the sequence of events in a specific setting[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]social norm:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]group’s expectations regarding what is appropriate and acceptable for the thoughts and behavior of its members[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]social role:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]socially defined pattern of behavior that is expected of a person in a given setting or group[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]stanford prison experiment:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]Stanford University conducted an experiment in a mock prison that demonstrated the power of social roles, social norms, and scripts[/glossary-definition] [/glossary-page]
General Psychology Copyright © by Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Self Introduction
- Start Conversation
- Self Introduction Generator
- Introduction in Other Languages

Self Presentation And Self Presentation Theory Explained
What is Self Presentation?
Self presentation is something that everyone needs to learn, but not many do. If you watch television, movies, read magazines, or even visit social networking websites, you’ll see lots of people talking about who they are. However, very few actually talk about how they feel and why they think the way that they do.
One thing most people struggle with when it comes to self presentation is confidence. People often don’t know what to say or what to ask. They worry about what other people might think of them or what others will think if they start to open up to them. So, instead of taking the plunge and starting to share things about yourself, you just stay quiet. This makes no sense because you never get anywhere in life by keeping silent.
But here’s a little secret – sharing who we are can help us grow personally, professionally and financially.
Self-presentation Definition
When you’re trying to get ahead in life, you need to be able to present yourself in the best possible way. If you don’t know how to do this, you might end up looking like an amateur.
Here is a definition of self presentation.
A person’s self presentation is the way that he or she presents himself to other people. This includes things such as his or her clothing, hairstyle, and makeup.
What Is Self Presentation Theory?
Self-presentation theory is a psychological theory that explains how people present themselves to others. Self-presentation can take many forms, including verbal, nonverbal, and behavioral.
It has two parts: the self-concept and the self-schema. The self-concept is how we see ourselves concerning others; the self-schema is how we see ourselves concerning our thoughts and feelings.
The impact of self-presentation theory on organizations has been significant because it helps us understand why people make some choices over others when they are trying to sell something or position themselves for a job interview or promotion.
The theory was originally developed by anthropologist Sherry Turkle in 1977. In her book Life On The Screen, she wrote about how people use technology to try to create an idealized version of themselves for others, and then try to make their idealized selves real through interactions with other people.
This idea has become more popular in recent years as we have become increasingly connected through technology like social media and smartphones. We see examples all around us: people posting selfies on Instagram with their friends or families who aren’t there; people tweeting updates about their lives while they’re at work, and other examples too numerous to name here.

Drew is the creator of myselfintroduction.com, designed to teach everyone how to introduce themselves to anyone with confidence in any situation.
Leave A Reply Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Perceiving and Presenting Self
Just as our perception of others affects how we communicate, so does our perception of ourselves. But what influences our self-perception? How much of our self is a product of our own making and how much of it is constructed based on how others react to us? How do we present ourselves to others in ways that maintain our sense of self or challenge how others see us? We will begin to answer these questions in this section as we explore self-concept, self-esteem, and self-presentation.
Self-Concept

Our self-concept is also formed through our interactions with others and their reactions to us. The concept of the looking glass self explains that we see ourselves reflected in other people’s reactions to us and then form our self-concept based on how we believe other people see us (Cooley, 1902). This reflective process of building our self-concept is based on what other people have actually said, such as “You’re a good listener,” and other people’s actions, such as coming to you for advice. These thoughts evoke emotional responses that feed into our self-concept. For example, you may think, “I’m glad that people can count on me to listen to their problems.”
We also develop our self-concept through comparisons to other people. Social comparison theory states that we describe and evaluate ourselves in terms of how we compare to other people. Social comparisons are based on two dimensions: superiority/inferiority and similarity/difference (Hargie, 2011). In terms of superiority and inferiority, we evaluate characteristics like attractiveness, intelligence, athletic ability, and so on. For example, you may judge yourself to be more intelligent than your brother or less athletic than your best friend, and these judgments are incorporated into your self-concept. This process of comparison and evaluation isn’t necessarily a bad thing, but it can have negative consequences if our reference group isn’t appropriate. Reference groups are the groups we use for social comparison, and they typically change based on what we are evaluating. In terms of athletic ability, many people choose unreasonable reference groups with which to engage in social comparison. If a man wants to get into better shape and starts an exercise routine, he may be discouraged by his difficulty keeping up with the aerobics instructor or running partner and judge himself as inferior, which could negatively affect his self-concept. Using as a reference group people who have only recently started a fitness program but have shown progress could help maintain a more accurate and hopefully positive self-concept.
We also engage in social comparison based on similarity and difference. Since self-concept is context specific, similarity may be desirable in some situations and difference more desirable in others. Factors like age and personality may influence whether or not we want to fit in or stand out. Although we compare ourselves to others throughout our lives, adolescent and teen years usually bring new pressure to be similar to or different from particular reference groups. Think of all the cliques in high school and how people voluntarily and involuntarily broke off into groups based on popularity, interest, culture, or grade level. Some kids in your high school probably wanted to fit in with and be similar to other people in the marching band but be different from the football players. Conversely, athletes were probably more apt to compare themselves, in terms of similar athletic ability, to other athletes rather than kids in show choir. But social comparison can be complicated by perceptual influences. As we learned earlier, we organize information based on similarity and difference, but these patterns don’t always hold true. Even though students involved in athletics and students involved in arts may seem very different, a dancer or singer may also be very athletic, perhaps even more so than a member of the football team. As with other aspects of
We generally want to know where we fall in terms of ability and performance as compared to others, but what people do with this information and how it affects self-concept
varies. Not all people feel they need to be at the top of the list, but some won’t stop until they get the high score on the video game or set a new school record in a track-and-field event. Some people strive to be first chair in the clarinet section of the orchestra, while another person may be content to be second chair. The education system promotes social comparison through grades and rewards such as honor rolls and dean’s lists. Although education and privacy laws prevent me from displaying each student’s grade on a test or paper for the whole class to see, I do typically report the aggregate grades, meaning the total number of As, Bs, Cs, and so on. This doesn’t violate anyone’s privacy rights, but it allows students to see where they fell in the distribution. This type of social comparison can be used as motivation. The student who was one of only three out of twenty-three to get a D on the exam knows that most of her classmates are performing better than she is, which may lead her to think, “If they can do it, I can do it.” But social comparison that isn’t reasoned can have negative effects and result in negative thoughts like “Look at how bad I did. Man, I’m stupid!” These negative thoughts can lead to negative behaviors, because we try to maintain internal consistency, meaning we act in ways that match up with our self-concept. So if the student begins to question her academic abilities and then incorporates an assessment of herself as a “bad student” into her self-concept, she may then behave in ways consistent with that, which is only going to worsen her academic performance. Additionally, a student might be comforted to learn that he isn’t the only person who got a D and then not feel the need to try to improve, since he has company. You can see in this example that evaluations we place on our self-concept can lead to cycles of thinking and acting. These cycles relate to self-esteem and self-efficacy, which are components of our self-concept.
Self-Esteem

How we judge ourselves affects our communication and our behaviors, but not every negative or positive judgment carries the same weight. The negative evaluation of a trait that isn’t very important for our self-concept will likely not result in a loss of self-esteem. For example, I am not very good at drawing. While I appreciate drawing as an art form, I don’t consider drawing ability to be a very big part of my self-concept. If someone critiqued my drawing ability, my self-esteem wouldn’t take a big hit. I do consider myself a good teacher, however, and I have spent and continue to spend considerable time and effort on improving my knowledge of teaching and my teaching skills. If someone critiqued my teaching knowledge and/or abilities, my self-esteem would definitely be hurt. This doesn’t mean that we can’t be evaluated on something we find important. Even though teaching is very important to my self-concept, I am regularly evaluated on it. Every semester, I am evaluated by my students, and every year, I am evaluated by my dean, department chair, and colleagues. Most of that feedback is in the form of constructive criticism, which can still be difficult to receive, but when taken in the spirit of self-improvement, it is valuable and may even enhance our self-concept and self-esteem. In fact, in professional contexts, people with higher self-esteem are more likely to work harder based on negative feedback, are less negatively affected by work stress, are able to handle workplace conflict better, and are better able to work independently and solve problems (Brockner, 1988).
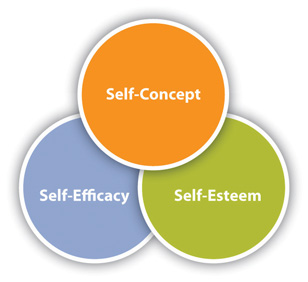
Pedro did a good job on his first college speech. During a meeting with his professor, Pedro indicates that he is confident going into the next speech and thinks he will do well. This skill-based assessment is an indication that Pedro has a high level of self-efficacy related to public speaking. If he does well on the speech, the praise from his classmates and professor will reinforce his self-efficacy and lead him to positively evaluate his speaking skills, which will contribute to his
Self-discrepancy theory states that people have beliefs about and expectations for their actual and potential selves that do not always match up with what they actually experience (Higgins, 1987). To understand this theory, we have to understand the different “selves” that make up our
These different selves can conflict with each other in various combinations. Discrepancies between the actual and ideal/ought selves can be motivating in some ways and prompt people to act for self-improvement. For example, if your ought self should volunteer more for the local animal shelter, then your actual self may be more inclined to do so. Discrepancies between the ideal and ought selves can be especially stressful. For example, many professional women who are also mothers have an ideal view of self that includes professional success and advancement. They may also have an ought self that includes a sense of duty and obligation to be a full-time mother. The actual self may be someone who does OK at both but doesn’t quite live up to the expectations of either. These discrepancies do not just create cognitive unease—they also lead to emotional, behavioral, and communicative changes.

When we compare the actual self to the expectations of ourselves and others, we can see particular patterns of emotional and behavioral effects. When our actual self doesn’t match up with our own ideals of self, we are not obtaining our own desires and hopes, which can lead to feelings of dejection including disappointment, dissatisfaction, and frustration. For
When our actual self doesn’t match up with other people’s ideals for us, we may not be obtaining significant others’ desires and hopes, which can lead to feelings of dejection including shame, embarrassment, and concern for losing the affection or approval of others. For example, if a significant other sees you as an “A” student and you get a 2.8 GPA your first year of college, then you may be embarrassed to share your grades with that person.
When our actual self doesn’t match up with what we think other people think we should obtain, we are not living up to the ought self that we think others have constructed for us, which can lead to feelings of agitation, feeling threatened, and fearing potential punishment. For example, if your parents think you should follow in their footsteps and take over the family business, but your actual self wants to go into the military, then you may be unsure of what to do and fear being isolated from the family.
Finally, when our actual self doesn’t match up with what we think we should obtain, we are not meeting what we see as our duties or obligations, which can lead to feelings of agitation including guilt, weakness, and a feeling that we have fallen short of our moral standard (Higgins, 1987). For
- Actual vs. own ideals. We have an overall feeling that we are not obtaining our desires and hopes, which leads to feelings of disappointment, dissatisfaction, and frustration.
- Actual vs. others’ ideals. We have an overall feeling that we are not obtaining significant others’ desires and hopes for us, which leads to feelings of shame and embarrassment.
- Actual vs. others’ ought. We have an overall feeling that we are not meeting what others see as our duties and obligations, which leads to feelings of agitation including fear of potential punishment.
- Actual vs. own ought. We have an overall feeling that we are not meeting our duties and obligations, which can lead to a feeling that we have fallen short of our own moral standards.
Influences on Self-Perception
We have already learned that other people influence our self-concept and self-esteem. While interactions we have with individuals and groups are definitely important to consider, we must also note the influence that larger, more systemic forces have on our self-perception. Social and family influences, culture, and the media all play a role in shaping who we think we are and how we feel about ourselves. Although these are powerful socializing forces, there are ways to maintain some control over our self-perception.
Social and Family Influences
Various forces help socialize us into our respective social and cultural groups and play a powerful role in presenting us with options about who we can be. While we may like to think that our self-
Parents and peers shape our self-perceptions in positive and negative ways. Feedback that we get from significant others, which includes close family, can lead to positive views of self (Hargie, 2011). In the past few years, however, there has been a public discussion and debate about how much positive reinforcement people should give to others, especially children. The following questions have been raised: Do we have current and upcoming generations that have been overpraised? Is the praise given warranted? What are the positive and negative effects of praise? What is the end goal of the praise? Let’s briefly look at this discussion and its connection to self-perception.

Whether praise is warranted or not is very subjective and specific to each person and context, but in general there have been questions raised about the potential negative effects of too much praise. Motivation is the underlying force that drives us to do things. Sometimes we are intrinsically motivated, meaning we want to do something for the love of doing it or the resulting internal satisfaction. Other times we are extrinsically motivated, meaning we do something to receive a reward or avoid punishment. If you put effort into completing a short documentary for a class because you love filmmaking and editing, you have been largely motivated by intrinsic forces. If you complete the documentary because you want an “A” and know that if you fail your parents will not give you money for your spring break trip, then you are motivated by extrinsic factors. Both can, of course, effectively motivate us. Praise is a form of extrinsic reward, and if there is an actual reward associated with the praise, like money or special recognition, some people speculate that intrinsic
There are cultural differences in the amount of praise and positive feedback that teachers and parents give their children. For example, teachers give less positive reinforcement in Japanese and Taiwanese classrooms than do teachers in US classrooms. Chinese and Kenyan parents do not regularly praise their children because they fear it may make them too individualistic, rude, or arrogant (Wierzbicka, 2004). So the phenomenon of overpraising isn’t universal, and the debate over its potential effects is not resolved.
Research has also found that communication patterns develop between parents and children that are common to many verbally and physically abusive relationships. Such patterns have negative effects on a child’s self-efficacy and self-esteem (Morgan & Wilson, 2007). As you’ll recall from our earlier discussion, attributions are links we make to identify the cause of a behavior. In the case of aggressive or abusive parents, they are not as able to distinguish between mistakes and intentional behaviors, often seeing honest mistakes as intended and reacting negatively to the child. Such parents also communicate generally negative evaluations to their child by saying, for example, “You can’t do anything right!” or “You’re a bad girl.” When children do exhibit positive behaviors, abusive parents are more likely to use external attributions that diminish the achievement of the child by saying, for example, “You only won because the other team was off their game.” In general, abusive parents have unpredictable reactions to their children’s positive and negative behavior, which creates an uncertain and often scary climate for a child that can lead to lower self-esteem and erratic or aggressive behavior. The cycles of praise and blame are just two examples of how the family as a socializing force can influence our self-perceptions.

There are some general differences in terms of gender and self-perception that relate to self-concept, self-efficacy, and envisioning ideal selves. As with any cultural differences, these are generalizations that have been supported by research, but they do not represent all individuals within a group. Regarding self-concept, men are more likely to describe themselves in terms of their group membership, and women are more likely to include references to relationships in their self-descriptions. For example, a man may note that he is a Tarheel fan, a boat enthusiast, or a member of the Rotary Club, and a woman may note that she is a mother of two or a loyal friend.
Regarding self-efficacy, men tend to have higher perceptions of self-efficacy than women (Hargie, 2011). In terms of actual and ideal selves, men and women in a variety of countries both described their ideal self as more masculine (Best & Thomas, 2004). As was noted earlier, gender differences are interesting to study but are very often exaggerated beyond the actual variations. Socialization and internalization of societal norms for gender differences accounts for much more of our perceived differences than do innate or natural differences between genders. These gender norms may be explicitly stated—for example, a mother may say to her son, “Boys don’t play with dolls”—or they may be more implicit, with girls being encouraged to pursue historically feminine professions like teaching or nursing without others actually stating the expectation.
The representations we see in the media affect our self-perception. The vast majority of media images include idealized representations of attractiveness. Despite the fact that the images of people we see in glossy magazines and on movie screens are not typically what we see when we look at the people around us in a classroom, at work, or at the grocery store, many of us continue to hold ourselves to an unrealistic standard of beauty and attractiveness.
Researchers have found that only 12 percent of prime-time characters are overweight, which is dramatically less than the national statistics for obesity among the actual US population (Patzer, 2008). Further, an analysis of how weight is discussed on prime-time sitcoms found that heavier female characters were often the targets of negative comments and jokes that audience members responded to with laughter. Conversely, positive comments about women’s bodies were related to their thinness. In short, the heavier the character, the more negative the comments, and the thinner the character, the more positive the comments. The same researchers analyzed sitcoms for content regarding male characters’ weight and found that although comments regarding their weight were made, they were fewer in number and not as negative, ultimately supporting the notion that overweight male characters are more accepted in media than overweight female characters. Much more attention has been paid in recent years to the potential negative effects of such narrow media representations. The following “Getting Critical” box explores the role of media in the construction of body image.
In terms of self-concept, media representations offer us guidance on what is acceptable or unacceptable and valued or not valued in our society. Mediated messages, in general, reinforce cultural
Advertising in particular encourages people to engage in social comparison, regularly communicating to us that we are inferior because we lack a certain product or that we need to change some aspect of our life to keep up with and be similar to others. For example, for many years advertising targeted to women instilled in them a fear of having a dirty house, selling them products that promised to keep their house clean, make their family happy, and impress their friends and neighbors. Now messages tell us to fear becoming old or unattractive, selling products to keep our skin tight and clear, which will in turn make us happy and popular.

Self-Presentation
How we perceive ourselves manifests in how we present ourselves to others. Self-presentation is the process of strategically concealing or revealing personal information in order to influence others’ perceptions (Human et al., 2012). We engage in this process daily and for different reasons. Although people occasionally intentionally deceive others in the process of self-presentation, in general we try to make a good impression while still remaining authentic. Since self-presentation helps meet our instrumental, relational, and identity needs, we stand to lose quite a bit if we are caught intentionally misrepresenting ourselves. In May of 2012, Yahoo!’s CEO resigned after it became known that he stated on official documents that he had two college degrees when he actually only had one. In a similar incident, a woman who had long served as the dean of admissions for the prestigious Massachusetts Institute of Technology was dismissed from her position after it was learned that she had only attended one year of college and had falsely indicated she had a bachelor’s and master’s degree (Webber & Korn, 2012). Such incidents clearly show that although people can get away with such false self-presentation for a while, the eventual consequences of being found out are dire. As communicators, we sometimes engage in more subtle forms of inauthentic self-presentation.
For example, a person may state or imply that they know more about a subject or situation than they actually do in order to seem smart or “in the loop.” During a speech, a speaker works on a polished and competent delivery to distract from a lack of substantive content. These cases of strategic self-presentation may not ever be found out, but communicators should still avoid them as they do not live up to the standards of ethical communication.
Consciously and competently engaging in self-presentation can have benefits because we can provide others with a more positive and accurate picture ogf who we are. People who are skilled at impression management are typically more engaging and confident, which allows others to pick up on more cues from which to form impressions (Human et al., 2012). Being a skilled self-presenter draws on many of the practices used by competent communicators, including becoming a higher self-monitor. When self-presentation skills and self-monitoring skills combine, communicators can simultaneously monitor their own expressions, the reaction of others, and the situational and

Figure: People who have been out of work for a while may have difficulty finding the
There are two main types of self-presentation: prosocial and self-serving (Sosik, Avolio, & Jung, 2002). Prosocial self-presentation entails behaviors that present a person as a role model and make a person more likable and attractive. For example, a supervisor may call on her employees to uphold high standards for business ethics, model that behavior in her own actions, and compliment others when they exemplify those standards. Self-serving self-presentation entails behaviors that present a person as highly skilled, willing to challenge others, and someone not to be messed with. For example, a supervisor may publicly take credit for the accomplishments of others or publicly critique an employee who failed to meet a particular standard. In summary, prosocial strategies are aimed at benefiting others, while self-serving strategies benefit the self at the expense of others.
In general, we strive to present a public image that matches up with our self-concept, but we can also use self-presentation strategies to enhance our self-concept (Hargie, 2011). When we present ourselves in order to evoke a positive evaluative response, we are engaging in self-enhancement. In the pursuit of self-enhancement, a person might try to be as appealing as possible in a particular area or with a particular person to gain feedback that will enhance one’s self-esteem. For
The video below will discuss the origins of the self-concept.
Bandura, A., Self-Efficacy : The Exercise of Control (New York, NY: W. H. Freeman, 1997).
Best, D. L. and Jennifer J. Thomas, “Cultural versity and Cross-Cultural Perspectives,” in The Psychology of Gender, 2nd ed., eds. Alice H. Eagly, Anne E. Beall, and Robert J. Sternberg (New York, NY: Guilford Press, 2004), 296–327.
Bowles, D. D., “Biracial Identity: Children Born to African-American and White Couples,” Clinical Social Work Journal 21, no. 4 (1993): 418–22.
Brockner, J., Self-Esteem at Work (Lexington, MA: Lexington Books, 1988), 11.
Byrne, B. M., Measuring Self-Concept across the Life Span: Issues and Instrumentation (Washington, DC: American Psychological Association, 1996), 5.
Cooley, C., Human Nature and the Social Order (New York, NY: Scribner, 1902).
DiBlasio, N., “Demand for Photo-Erasing iPhone App Heats up Sexting Debate,” USA Today , May 7, 2012, accessed June 6, 2012, http://content.usatoday.com/communities/ondeadline/post/2012/05/demand-for-photo-erasing-iphone-app-heats-up-sexting-debate/1 .
Dworkin, S. L. and Faye Linda Wachs, Body Panic (New York, NY: New York University Press, 2009), 2.
Hargie, O., Skilled Interpersonal Interaction: Research, Theory, and Practice (London: Routledge, 2011), 261.
Higgins, E. T., “Self-Discrepancy: A Theory Relating Self and Affect,” Psychological Review 94, no. 3 (1987): 320–21.
Human, L. J., et al., “Your Best Self Helps Reveal Your True Self: Positive Self-Presentation Leads to More Accurate Personality Impressions,” Social Psychological and Personality Sciences 3, no. 1 (2012): 23.
Kim, J. and Jong-Eun Roselyn Lee, “The Facebook Paths to Happiness: Effects of the Number of Facebook Friends and Self-Presentation on Subjective Well-Being,” Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking 14, no. 6 (2011): 360.
Loughnan, S., et al., “Economic Inequality Is Linked to Biased Self-Perception,” Psychological Science 22, no. 10 (2011): 1254.
Morgan, W. and Steven R. Wilson, “Explaining Child Abuse as a Lack of Safe Ground,” in The Dark Side of Interpersonal Communication , eds. Brian H. Spitzberg and William R. Cupach (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2007), 341.
Patzer, G. L., Looks: Why They Matter More than You Ever Imagined (New York, NY: AMACOM, 2008), 147.
Sosik, J. J., Bruce J. Avolio, and Dong I. Jung, “Beneath the Mask: Examining the Relationship of
Stockton, M. B., et al., “Self-Perception and Body Image Associations with Body Mass Index among 8–10-Year-Old African American Girls,” Journal of Pediatric Psychology 34, no. 10 (2009): 1144.
Webber, L., and Melissa Korn, “Yahoo’s CEO among Many Notable Resume Flaps,” Wall Street Journal Blogs , May 7, 2012, accessed June 9, 2012, http://blogs.wsj.com/digits/2012/05/07/yahoos-ceo-among-many-notable-resume-flaps .
Wierzbicka, A., “The English Expressions Good Boy and Good Girl and Cultural Models of Child Rearing,” Culture and Psychology 10, no. 3 (2004): 251–78.
- “Style Me Hired,” accessed June 6, 2012, http://www.stylemehired.com . ↵
SPC-101 Kirkwood Copyright © by emcworthy is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Personality
Self-Presentation in the Digital World
Do traditional personality theories predict digital behaviour.
Posted August 31, 2021 | Reviewed by Chloe Williams
- What Is Personality?
- Find a therapist near me
- Personality theories can help explain real-world differences in self-presentation behaviours but they may not apply to online behaviours.
- In the real world, women have higher levels of behavioural inhibition tendencies than men and are more likely to avoid displeasing others.
- Based on this assumption, one would expect women to present themselves less on social media, but women tend to use social media more than men.
Digital technology allows people to construct and vary their self-identity more easily than they can in the real world. This novel digital- personality construction may, or may not, be helpful to that person in the long run, but it is certainly more possible than it is in the real world. Yet how this relates to "personality," as described by traditional personality theories, is not really known. Who will tend to manipulate their personality online, and would traditional personality theories predict these effects? A look at what we do know about gender differences in the real and digital worlds suggests that many aspects of digital behaviour may not conform to the expectations of personality theories developed for the real world.
Half a century ago, Goffman suggested that individuals establish social identities by employing self-presentation tactics and impression management . Self-presentational tactics are techniques for constructing or manipulating others’ impressions of the individual and ultimately help to develop that person’s identity in the eyes of the world. The ways other people react are altered by choosing how to present oneself – that is, self-presentation strategies are used for impression management . Others then uphold, shape, or alter that self-image , depending on how they react to the tactics employed. This implies that self-presentation is a form of social communication, by which people establish, maintain, and alter their social identity.
These self-presentational strategies can be " assertive " or "defensive." 1 Assertive strategies are associated with active control of the person’s self-image; and defensive strategies are associated with protecting a desired identity that is under threat. In the real world, the use of self-presentational tactics has been widely studied and has been found to relate to many behaviours and personalities 2 . Yet, despite the enormous amounts of time spent on social media , the types of self-presentational tactics employed on these platforms have not received a huge amount of study. In fact, social media appears to provide an ideal opportunity for the use of self-presentational tactics, especially assertive strategies aimed at creating an identity in the eyes of others.
Seeking to Experience Different Types of Reward
Social media allows individuals to present themselves in ways that are entirely reliant on their own behaviours – and not on factors largely beyond their ability to instantly control, such as their appearance, gender, etc. That is, the impression that the viewer of the social media post receives is dependent, almost entirely, on how or what another person posts 3,4 . Thus, the digital medium does not present the difficulties for individuals who wish to divorce the newly-presented self from the established self. New personalities or "images" may be difficult to establish in real-world interactions, as others may have known the person beforehand, and their established patterns of interaction. Alternatively, others may not let people get away with "out of character" behaviours, or they may react to their stereotype of the person in front of them, not to their actual behaviours. All of which makes real-life identity construction harder.
Engaging in such impression management may stem from motivations to experience different types of reward 5 . In terms of one personality theory, individuals displaying behavioural approach tendencies (the Behavioural Activation System; BAS) and behavioural inhibition tendencies (the Behavioural Inhibition System; BIS) will differ in terms of self-presentation behaviours. Those with strong BAS seek opportunities to receive or experience reward (approach motivation ); whereas, those with strong BIS attempt to avoid punishment (avoidance motivation). People who need to receive a lot of external praise may actively seek out social interactions and develop a lot of social goals in their lives. Those who are more concerned about not incurring other people’s displeasure may seek to defend against this possibility and tend to withdraw from people. Although this is a well-established view of personality in the real world, it has not received strong attention in terms of digital behaviours.
Real-World Personality Theories May Not Apply Online
One test bed for the application of this theory in the digital domain is predicted gender differences in social media behaviour in relation to self-presentation. Both self-presentation 1 , and BAS and BIS 6 , have been noted to show gender differences. In the real world, women have shown higher levels of BIS than men (at least, to this point in time), although levels of BAS are less clearly differentiated between genders. This view would suggest that, in order to avoid disapproval, women will present themselves less often on social media; and, where they do have a presence, adopt defensive self-presentational strategies.
The first of these hypotheses is demonstrably false – where there are any differences in usage (and there are not that many), women tend to use social media more often than men. What we don’t really know, with any certainty, is how women use social media for self-presentation, and whether this differs from men’s usage. In contrast to the BAS/BIS view of personality, developed for the real world, several studies have suggested that selfie posting can be an assertive, or even aggressive, behaviour for females – used in forming a new personality 3 . In contrast, sometimes selfie posting by males is related to less aggressive, and more defensive, aspects of personality 7 . It may be that women take the opportunity to present very different images of themselves online from their real-world personalities. All of this suggests that theories developed for personality in the real world may not apply online – certainly not in terms of putative gender-related behaviours.
We know that social media allows a new personality to be presented easily, which is not usually seen in real-world interactions, and it may be that real-world gender differences are not repeated in digital contexts. Alternatively, it may suggest that these personality theories are now simply hopelessly anachronistic – based on assumptions that no longer apply. If that were the case, it would certainly rule out any suggestion that such personalities are genetically determined – as we know that structure hasn’t changed dramatically in the last 20 years.
1. Lee, S.J., Quigley, B.M., Nesler, M.S., Corbett, A.B., & Tedeschi, J.T. (1999). Development of a self-presentation tactics scale. Personality and Individual Differences, 26(4), 701-722.
2. Laghi, F., Pallini, S., & Baiocco, R. (2015). Autopresentazione efficace, tattiche difensive e assertive e caratteristiche di personalità in Adolescenza. Rassegna di Psicologia, 32(3), 65-82.
3. Chua, T.H.H., & Chang, L. (2016). Follow me and like my beautiful selfies: Singapore teenage girls’ engagement in self-presentation and peer comparison on social media. Computers in Human Behavior, 55, 190-197.
4. Fox, J., & Rooney, M.C. (2015). The Dark Triad and trait self-objectification as predictors of men’s use and self-presentation behaviors on social networking sites. Personality and Individual Differences, 76, 161-165.
5. Hermann, A.D., Teutemacher, A.M., & Lehtman, M.J. (2015). Revisiting the unmitigated approach model of narcissism: Replication and extension. Journal of Research in Personality, 55, 41-45.
6. Carver, C.S., & White, T.L. (1994). Behavioral inhibition, behavioral activation, and affective responses to impending reward and punishment: the BIS/BAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 67(2), 319.
7. Sorokowski, P., Sorokowska, A., Frackowiak, T., Karwowski, M., Rusicka, I., & Oleszkiewicz, A. (2016). Sex differences in online selfie posting behaviors predict histrionic personality scores among men but not women. Computers in Human Behavior, 59, 368-373.

Phil Reed, Ph.D., is a professor of psychology at Swansea University.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

2.3 Perceiving and Presenting Self
Learning Objectives
- Define self-concept and discuss how we develop our self-concept.
- Define self-esteem and discuss how we develop self-esteem.
- Explain how social comparison theory influences self-perception.
- Discuss how social norms, family, culture, and media influence self-perception.
- Define self-presentation and discuss common self-presentation strategies.
Just as our perception of others affects how we communicate, so does our perception of ourselves. But what influences our self-perception? How much of our self is a product of our own making and how much of it is constructed based on how others react to us? How do we present ourselves to others in ways that maintain our sense of self or challenge how others see us? We will begin to answer these questions in this section as we explore self-concept, self-esteem, and self-presentation.
Self-Concept
Self-concept refers to the overall idea of who a person thinks he or she is. If I said, “Tell me who you are,” your answers would be clues as to how you see yourself, your self-concept. Each person has an overall self-concept that might be encapsulated in a short list of overarching characteristics that he or she finds important. But each person’s self-concept is also influenced by context, meaning we think differently about ourselves depending on the situation we are in. In some situations, personal characteristics, such as our abilities, personality, and other distinguishing features, will best describe who we are. You might consider yourself laid back, traditional, funny, open minded, or driven, or you might label yourself a leader or a thrill seeker. In other situations, our self-concept may be tied to group or cultural membership. For example, you might consider yourself a member of the Sigma Phi Epsilon fraternity, a Southerner, or a member of the track team.

Our self-concept is also formed through our interactions with others and their reactions to us. The concept of the looking glass self explains that we see ourselves reflected in other people’s reactions to us and then form our self-concept based on how we believe other people see us (Cooley, 1902). This reflective process of building our self-concept is based on what other people have actually said, such as “You’re a good listener,” and other people’s actions, such as coming to you for advice. These thoughts evoke emotional responses that feed into our self-concept. For example, you may think, “I’m glad that people can count on me to listen to their problems.”
We also develop our self-concept through comparisons to other people. Social comparison theory states that we describe and evaluate ourselves in terms of how we compare to other people. Social comparisons are based on two dimensions: superiority/inferiority and similarity/difference (Hargie, 2011). In terms of superiority and inferiority, we evaluate characteristics like attractiveness, intelligence, athletic ability, and so on. For example, you may judge yourself to be more intelligent than your brother or less athletic than your best friend, and these judgments are incorporated into your self-concept. This process of comparison and evaluation isn’t necessarily a bad thing, but it can have negative consequences if our reference group isn’t appropriate. Reference groups are the groups we use for social comparison, and they typically change based on what we are evaluating.
We also engage in social comparison based on similarity and difference. Since self-concept is context specific, similarity may be desirable in some situations and difference more desirable in others. Factors like age and personality may influence whether or not we want to fit in or stand out. Although we compare ourselves to others throughout our lives, adolescent and teen years usually bring new pressure to be similar to or different from particular reference groups. Think of all the cliques in high school and how people voluntarily and involuntarily broke off into groups based on popularity, interest, culture, or grade level. But social comparison can be complicated by perceptual influences. As we learned earlier, we organize information based on similarity and difference, but these patterns don’t always hold true. Even though students involved in athletics and students involved in arts may seem very different, a dancer or singer may also be very athletic, perhaps even more so than a member of the football team. As with other aspects of perception, there are positive and negative consequences of social comparison.
We generally want to know where we fall in terms of ability and performance as compared to others, but what people do with this information and how it affects self-concept varies. Not all people feel they need to be at the top of the list, but some won’t stop until they get the high score on the video game or set a new school record in a track-and-field event. The education system promotes social comparison through grades and rewards such as honor rolls and dean’s lists.
Self-Esteem
Self-esteem refers to the judgments and evaluations we make about our self-concept. While self-concept is a broad description of the self, self-esteem is a more specifically an evaluation of the self (Byrne, 1996). If I again prompted you to “Tell me who you are,” and then asked you to evaluate (label as good/bad, positive/negative, desirable/undesirable) each of the things you listed about yourself, I would get clues about your self-esteem. Like self-concept, self-esteem has general and specific elements. Generally, some people are more likely to evaluate themselves positively while others are more likely to evaluate themselves negatively (Brockner, 1988). More specifically, our self-esteem varies across our life span and across contexts.

How we judge ourselves affects our communication and our behaviors, but not every negative or positive judgment carries the same weight. The negative evaluation of a trait that isn’t very important for our self-concept will likely not result in a loss of self-esteem. For example, I am not very good at drawing. While I appreciate drawing as an art form, I don’t consider drawing ability to be a very big part of my self-concept. If someone critiqued my drawing ability, my self-esteem wouldn’t take a big hit. I do consider myself a good teacher, however, and I have spent and continue to spend considerable time and effort on improving my knowledge of teaching and my teaching skills. If someone critiqued my teaching knowledge and/or abilities, my self-esteem would definitely be hurt. This doesn’t mean that we can’t be evaluated on something we find important. Even though teaching is very important to my self-concept, I am regularly evaluated on it. Self-esteem isn’t the only factor that contributes to our self-concept; perceptions about our competence also play a role in developing our sense of self.
Self-Efficacy refers to the judgments people make about their ability to perform a task within a specific context (Bandura, 1997). As you can see in Figure 2.3.1 “Relationship between Self-Efficacy, Self-Esteem, and Self-Concept,” judgments about our self-efficacy influence our self-esteem, which influences our self-concept. The following example also illustrates these interconnections.
Figure 2.3.1: Relationship Between Self-Efficacy, Self-Esteem, and Self-Concept
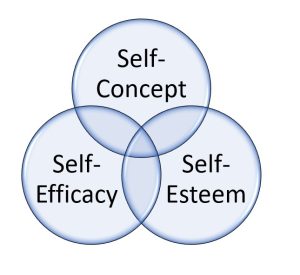
The verbal and nonverbal feedback we get from people affect our feelings of self-efficacy and our self-esteem. As we saw in Pedro’s example, being given positive feedback can increase our self-efficacy, which may make us more likely to engage in a similar task in the future (Hargie, 2011). In general, people adjust their expectations about their abilities based on feedback they get from others. Positive feedback tends to make people raise their expectations for themselves and negative feedback does the opposite, which ultimately affects behaviors and creates the cycle. When feedback from others is different from how we view ourselves, additional cycles may develop that impact self-esteem and self-concept.
Influences on Self-Perception
I am not who I think I am.
I am not who you think I am.
I am who I think you think I am.
We have learned that other people influence our self-concept and self-esteem. While interactions we have with individuals and groups are definitely important to consider, we must also note the influence that larger, more systemic forces have on our self-perception. Social and family influences, culture, and the media all play a role in shaping who we think we are and how we feel about ourselves. Although these are powerful socializing forces, there are ways to maintain some control over our self-perception.
Social and Family Influences
Various forces help socialize us into our respective social and cultural groups and play a powerful role in presenting us with options about who we can be. While we may like to think that our self-perception starts with a blank canvas, our perceptions are limited by our experiences and various social and cultural contexts.
Parents and peers shape our self-perceptions in positive and negative ways. Feedback that we get from significant others, which includes close family, can lead to positive views of self (Hargie, 2011). In the past few years, however, there has been a public discussion and debate about how much positive reinforcement people should give to others, especially children. The following questions have been raised: Do we have current and upcoming generations that have been overpraised? Is the praise given warranted? What are the positive and negative effects of praise? Let’s briefly look at this discussion and its connection to self-perception.

Whether praise is warranted or not is very subjective and specific to each person and context, but in general there have been questions raised about the potential negative effects of too much praise. Motivation is the underlying force that drives us to do things. Sometimes we are intrinsically motivated, meaning we want to do something for the love of doing it or the resulting internal satisfaction. Other times we are extrinsically motivated, meaning we do something to receive a reward or avoid punishment. If you put effort into completing a short documentary for a class because you love filmmaking and editing, you have been largely motivated by intrinsic forces. If you complete the documentary because you want an “A” and know that if you fail your parents will not give you money for your spring break trip, then you are motivated by extrinsic factors. Both can, of course, effectively motivate us. Praise is a form of extrinsic reward, and if there is an actual reward associated with the praise, some people speculate that intrinsic motivation will suffer. But what’s so good about intrinsic motivation? Intrinsic motivation is more substantial and long-lasting than extrinsic motivation and can lead to the development of a work ethic and sense of pride in one’s abilities. Intrinsic motivation can move people to accomplish great things over long periods of time and be happy despite the effort and sacrifices made. Extrinsic motivation dies when the reward stops. Additionally, too much praise can lead people to have a misguided sense of their abilities.
There are cultural differences in the amount of praise and positive feedback that teachers and parents give their children. For example, teachers give less positive reinforcement in Japanese and Taiwanese classrooms than do teachers in US classrooms. Chinese and Kenyan parents do not regularly praise their children because they fear it may make them too individualistic, rude, or arrogant (Wierzbicka, 2004). So the phenomenon of overpraising isn’t universal, and the debate over its potential effects is not resolved.
How people perceive themselves varies across cultures. For example, many cultures exhibit a phenomenon known as the self-enhancement bias , meaning that we tend to emphasize our desirable qualities relative to other people (Loughnan et al., 2011). But the degree to which people engage in self-enhancement varies. A review of many studies in this area found that people in Western countries such as the United States were significantly more likely to self-enhance than people in countries such as Japan. Many scholars explain this variation using a common measure of cultural variation that claims people in individualistic cultures are more likely to engage in competition and openly praise accomplishments than people in collectivistic cultures. The difference in self-enhancement has also been tied to economics, with scholars arguing that people in countries with greater income inequality are more likely to view themselves as superior to others or want to be perceived as superior to others (even if they don’t have economic wealth) in order to conform to the country’s values and norms. This holds true because countries with high levels of economic inequality, like the United States, typically value competition and the right to boast about winning or succeeding, while countries with more economic equality, like Japan, have a cultural norm of modesty (Loughnan, 2011).
Individualism Versus Collectivism
This measure will allow you to assess your own tendency toward individualism or collectivism.
Directions: The following statements are modified from Shulruf, Hattie, and Dixon’s (2007) Auckland collective value tendencies. Please indicate in the space at the left of each item the degree to which you believe the statement applies to you, using the following 5-point scale:
1 = Not at all true of me; 2 = Mostly not true of me; 3 = Neither true nor untrue of me; undecided; 4 = Mostly true of me; 5 = Very true of me
- I discuss job- or study-related problems with my parents.
- I consult my family before making an important decision.
- Before taking a major trip, I consult with most members of my family.
- It is important to consult close friends and get their ideas before making a decision.
- Even when I strongly disagree with my group members, I avoid an argument.
- I hate to disagree with others in my group.
- It is important to make a good impression on one’s manager.
- In interacting with superiors, I am always polite.
- It is important to consider the needs of those who work above me.
- I sacrifice my self-interest for the benefit of my group.
- I consider myself as a unique person separate from others.
- I enjoy being unique and different from others.
- I see myself as “my own person.”
- I take responsibility for my own actions.
- It is important for me to act as an independent person.
- Being able to take care of myself is a primary concern for me.
- I prefer to be self-reliant rather than dependent on others.
- It is my duty to take care of my family, even when I have to sacrifice what I want.
- When faced with a difficult personal situation, it is better to decide for myself than to follow the advice of others.
- I consult with my supervisor on work-related matters.
How did you score? Items 1-10 reflect your tendency toward collectivism, while 11-20 reflect your tendency toward individualism. Add up your total score for items 1-10 and 11-20. Which score is higher? What surprised you about your score? Do you have an individualistic or collectivist value tendency? Be aware of how your individualistic and collectivistic value tendencies influence your communication behaviors across life contexts.
______________________________ ______________________________
1-10 11-20
Source: from “Development of a New Tool for Individualism and Collectivism,” by B. Shulruf, J. Hattie, and R. Dixon, 2007, in Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 25 (4), pp. 385-401.
Race also plays a role in self-perception. For example, positive self-esteem and self-efficacy tend to be higher in African American adolescent girls than Caucasian girls (Stockton et al., 2009). In fact, more recent studies have discounted much of the early research on race and self-esteem that purported that African Americans of all ages have lower self-esteem than whites. Self-perception becomes more complex when we consider biracial individuals—more specifically those born to couples comprising an African American and a white parent (Bowles, 1993). In such cases, it is challenging for biracial individuals to embrace both of their heritages, and social comparison becomes more difficult due to diverse and sometimes conflicting reference groups. Since many biracial individuals identify as and are considered African American by society, living and working within a black community can help foster more positive self-perceptions in these biracial individuals. Such a community offers a more nurturing environment and a buffer zone from racist attitudes but simultaneously distances biracial individuals from their white identity. Conversely, immersion into a predominantly white community and separation from a black community can lead biracial individuals to internalize negative views of people of color and perhaps develop a sense of inferiority. All these challenges lead to a sense of being marginalized from both ethnic groups and interfere in the development of positive self-esteem and a stable self-concept.

There are some general differences in terms of gender and self-perception that relate to self-concept, self-efficacy, and envisioning ideal selves. Regarding self-concept, men are more likely to describe themselves in terms of their group membership, and women are more likely to include references to relationships in their self-descriptions.
Regarding self-efficacy, men tend to have higher perceptions of self-efficacy than women (Hargie, 2011). As was noted earlier, gender differences are interesting to study but are very often exaggerated beyond the actual variations. Socialization and internalization of societal norms for gender differences accounts for much more of our perceived differences than do innate or natural differences between genders. These gender norms may be explicitly stated—for example, a mother may say to her son, “Boys don’t play with dolls”—or they may be more implicit, with girls being encouraged to pursue historically feminine professions like teaching or nursing without others actually stating the expectation.
The representations we see in the media affect our self-perception. The vast majority of media images include idealized representations of attractiveness. Despite the fact that the images of people we see in glossy magazines and on movie screens are not typically what we see when we look at the people around us in a classroom, at work, or at the grocery store, many of us continue to hold ourselves to an unrealistic standard of beauty and attractiveness. Movies, magazines, and television shows are filled with beautiful people, and less attractive actors, when they are present in the media, are typically portrayed as the butt of jokes, villains, or only as background extras (Patzer, 2008). Aside from overall attractiveness, the media also offers narrow representations of acceptable body weight.
Researchers have found that only 12 percent of prime-time characters are overweight, which is dramatically less than the national statistics for obesity among the actual US population (Patzer, 2008). Further, an analysis of how weight is discussed on prime-time sitcoms found that heavier female characters were often the targets of negative comments and jokes that audience members responded to with laughter. Conversely, positive comments about women’s bodies were related to their thinness. Much more attention has been paid in recent years to the potential negative effects of such narrow media representations. The following “Getting Critical” box explores the role of media in the construction of body image.
In terms of self-concept, media representations offer us guidance on what is acceptable or unacceptable and valued or not valued in our society. Mediated messages, in general, reinforce cultural stereotypes related to race, gender, age, sexual orientation, ability, and class. People from historically marginalized groups must look much harder than those in the dominant groups to find positive representations of their identities in media. As a critical thinker, it is important to question media messages and to examine who is included and who is excluded.
Advertising in particular encourages people to engage in social comparison, regularly communicating to us that we are inferior because we lack a certain product or that we need to change some aspect of our life to keep up with and be similar to others. For example, for many years advertising targeted to women instilled in them a fear of having a dirty house, selling them products that promised to keep their house clean, make their family happy, and impress their friends and neighbors. Now messages tell us to fear becoming old or unattractive, selling products to keep our skin tight and clear, which will in turn make us happy and popular.
“Getting Critical”
Body Image and Self-Perception
Take a look at any online content, show, or movie and you will most likely see very beautiful people. When you look around you in your daily life, there are likely not as many glamorous and gorgeous people. Scholars and media critics have critiqued this discrepancy for decades because it has contributed to many social issues and public health issues ranging from body dysmorphic disorder, to eating disorders, to lowered self-esteem.
Much of the media is driven by advertising, and the business of media has been to perpetuate a “culture of lack” (Dworkin & Wachs, 2009). This means that we are constantly told, via mediated images, that we lack something. In short, advertisements often tell us we don’t have enough money, enough beauty, or enough material possessions. Over the past few decades, women’s bodies in the media have gotten smaller and thinner, while men’s bodies have gotten bigger and more muscular. At the same time, the US population has become dramatically more obese. As research shows that men and women are becoming more and more dissatisfied with their bodies, which ultimately affects their self-concept and self-esteem, health and beauty product lines proliferate and cosmetic surgeries and other types of enhancements become more and more popular. From young children to older adults, people are becoming more aware of and oftentimes unhappy with their bodies, which results in a variety of self-perception problems.
- How do you think the media influences your self-perception and body image?
- Describe the typical man that is portrayed in the media. Describe the typical woman that is portrayed in the media. What impressions do these typical bodies make on others? What are the potential positive and negative effects of the way the media portrays the human body?
- Find an example of an “atypical” body represented in the media (a magazine, TV show, or movie). Is this person presented in a positive, negative, or neutral way? Why do you think this person was chosen?
Self-Presentation
How we perceive ourselves manifests in how we present ourselves to others. Self-presentation is the process of strategically concealing or revealing personal information in order to influence others’ perceptions (Human et al., 2012). We engage in this process daily and for different reasons. Although people occasionally intentionally deceive others in the process of self-presentation, in general we try to make a good impression while still remaining authentic. Since self-presentation helps meet our instrumental, relational, and identity needs, we stand to lose quite a bit if we are caught intentionally misrepresenting ourselves. In May of 2012, Yahoo!’s CEO resigned after it became known that he stated on official documents that he had two college degrees when he actually only had one. In another strange case of false presentation, Rachel Dolezal portrayed herself as a black woman who advocated for civil rights issues and even served as the N.A.A.C.P. President in Spokane, WA until her estranged parents made public claims in June 2015, exposing her as a white woman and triggering an international scandal. Such incidents clearly show that although people can get away with such false self-presentation for a while, the eventual consequences of being found out are dire. As communicators, we sometimes engage in more subtle forms of inauthentic self-presentation. For example, during a speech, a speaker works on a polished and competent delivery to distract from a lack of substantive content. These cases of strategic self-presentation may not ever be found out, but communicators should still avoid them as they do not live up to the standards of ethical communication.
Consciously and competently engaging in self-presentation can have benefits because we can provide others with a more positive and accurate picture of who we are. People who are skilled at impression management are typically more engaging and confident, which allows others to pick up on more cues from which to form impressions (Human et al., 2012). Being a skilled self-presenter draws on many of the practices used by competent communicators, including becoming a higher self-monitor. When self-presentation skills and self-monitoring skills combine, communicators can simultaneously monitor their own expressions, the reaction of others, and the situational and social context (Sosik, Avolio, & Jung, 2002).

There are two main types of self-presentation: prosocial and self-serving (Sosik, Avolio, & Jung, 2002). Prosocial self-presentation entails behaviors that present a person as a role model and make a person more likable and attractive. For example, a supervisor may call on her employees to uphold high standards for business ethics, model that behavior in her own actions, and compliment others when they exemplify those standards. Self-serving self-presentation entails behaviors that present a person as highly skilled, willing to challenge others, and someone not to be messed with. For example, a supervisor may publicly take credit for the accomplishments of others or publicly critique an employee who failed to meet a particular standard. In summary, prosocial strategies are aimed at benefiting others, while self-serving strategies benefit the self at the expense of others.
In general, we strive to present a public image that matches up with our self-concept, but we can also use self-presentation strategies to enhance our self-concept (Hargie, 2011). When we present ourselves in order to evoke a positive evaluative response, we are engaging in self-enhancement. In the pursuit of self-enhancement, a person might try to be as appealing as possible in a particular area or with a particular person to gain feedback that will enhance one’s self-esteem. For example, a singer might train and practice for weeks before singing in front of a well-respected vocal coach but not invest as much effort in preparing to sing in front of friends. Although positive feedback from friends is beneficial, positive feedback from an experienced singer could enhance a person’s self-concept. Self-enhancement can be productive and achieved competently, or it can be used inappropriately. Using self-enhancement behaviors just to gain the approval of others or out of self-centeredness may lead people to communicate in ways that are perceived as phony or overbearing and end up making an unfavorable impression (Sosik, Avolio, & Jung, 2002).
Key Takeaways
- Our self-concept is the overall idea of who we think we are. It is developed through our interactions with others and through social comparison that allows us to compare our beliefs and behaviors to others.
- Our self-esteem is based on the evaluations and judgments we make about various characteristics of our self-concept. It is developed through an assessment and evaluation of our various skills and abilities, known as self-efficacy, and through a comparison and evaluation of who we are, who we would like to be, and who we should be (self-discrepancy theory).
- Social comparison theory and self-discrepancy theory affect our self-concept and self-esteem because through comparison with others and comparison of our actual, ideal, and ought selves we make judgments about who we are and our self-worth. These judgments then affect how we communicate and behave.
- Socializing forces like family, culture, and media affect our self-perception because they give us feedback on who we are. This feedback can be evaluated positively or negatively and can lead to positive or negative patterns that influence our self-perception and then our communication.
- Self-presentation refers to the process of strategically concealing and/or revealing personal information in order to influence others’ perceptions. Prosocial self-presentation is intended to benefit others and self-serving self-presentation is intended to benefit the self at the expense of others. People also engage in self-enhancement, which is a self-presentation strategy by which people intentionally seek out positive evaluations.
- Make a list of characteristics that describe who you are (your self-concept). After looking at the list, see if you can come up with a few words that summarize the list to narrow in on the key features of your self-concept. Go back over the first list and evaluate each characteristic, for example noting whether it is something you do well/poorly, something that is good/bad, positive/negative, desirable/undesirable. Is the overall list more positive or more negative? After doing these exercises, what have you learned about your self-concept and self-esteem?
- Discuss at least one time in which you had a discrepancy or tension between two of the three selves described by self-discrepancy theory (the actual, ideal, and ought selves). What effect did this discrepancy have on your self-concept and/or self-esteem?
- Take one of the socializing forces discussed (family, culture, or media) and identify at least one positive and one negative influence that it/they have had on your self-concept and/or self-esteem.
- Getting integrated: Discuss some ways that you might strategically engage in self-presentation to influence the impressions of others in an academic, a professional, a personal, and a civic context.
Bandura, A., Self-Efficacy: The Exercise of Control (New York, NY: W. H. Freeman, 1997).
Best, D. L. and Jennifer J. Thomas, “Cultural Diversity and Cross-Cultural Perspectives,” in The Psychology of Gender, 2nd ed., eds. Alice H. Eagly, Anne E. Beall, and Robert J. Sternberg (New York, NY: Guilford Press, 2004), 296–327.
Bowles, D. D., “Biracial Identity: Children Born to African-American and White Couples,” Clinical Social Work Journal 21, no. 4 (1993): 418–22.
Brockner, J., Self-Esteem at Work (Lexington, MA: Lexington Books, 1988), 11.
Byrne, B. M., Measuring Self-Concept across the Life Span: Issues and Instrumentation (Washington, DC: American Psychological Association, 1996), 5.
Cooley, C., Human Nature and the Social Order (New York, NY: Scribner, 1902).
DiBlasio, N., “Demand for Photo-Erasing iPhone App Heats up Sexting Debate,” USA Today , May 7, 2012, accessed June 6, 2012, http://content.usatoday.com/communities/ondeadline/post/2012/05/demand-for-photo-erasing-iphone-app-heats-up-sexting-debate/1 .
Dworkin, S. L. and Faye Linda Wachs, Body Panic (New York, NY: New York University Press, 2009), 2.
Hargie, O., Skilled Interpersonal Interaction: Research, Theory, and Practice (London: Routledge, 2011), 261.
Higgins, E. T., “Self-Discrepancy: A Theory Relating Self and Affect,” Psychological Review 94, no. 3 (1987): 320–21.
Human, L. J., et al., “Your Best Self Helps Reveal Your True Self: Positive Self-Presentation Leads to More Accurate Personality Impressions,” Social Psychological and Personality Sciences 3, no. 1 (2012): 23.
Kim, J. and Jong-Eun Roselyn Lee, “The Facebook Paths to Happiness: Effects of the Number of Facebook Friends and Self-Presentation on Subjective Well-Being,” Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking 14, no. 6 (2011): 360.
Loughnan, S., et al., “Economic Inequality Is Linked to Biased Self-Perception,” Psychological Science 22, no. 10 (2011): 1254.
Morgan, W. and Steven R. Wilson, “Explaining Child Abuse as a Lack of Safe Ground,” in The Dark Side of Interpersonal Communication , eds. Brian H. Spitzberg and William R. Cupach (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2007), 341.
Patzer, G. L., Looks: Why They Matter More than You Ever Imagined (New York, NY: AMACOM, 2008), 147.
Sosik, J. J., Bruce J. Avolio, and Dong I. Jung, “Beneath the Mask: Examining the Relationship of Self-Presentation Attributes and Impression Management to Charismatic Leadership,” The Leadership Quarterly 13 (2002): 217.
Stockton, M. B., et al., “Self-Perception and Body Image Associations with Body Mass Index among 8–10-Year-Old African American Girls,” Journal of Pediatric Psychology 34, no. 10 (2009): 1144.
Webber, L., and Melissa Korn, “Yahoo’s CEO among Many Notable Resume Flaps,” Wall Street Journal Blogs , May 7, 2012, accessed June 9, 2012, http://blogs.wsj.com/digits/2012/05/07/yahoos-ceo-among-many-notable-resume-flaps .
Wierzbicka, A., “The English Expressions Good Boy and Good Girl and Cultural Models of Child Rearing,” Culture and Psychology 10, no. 3 (2004): 251–78.
The overall idea of who a person thinks they are.
The view of self which is formed based on how we believe other people see us; a reflective process of perceiving self; forming self-concept through our interactions with others and their reactions to us
Developing a sense of self through comparing ourselves to other people
Judgments and evaluations we make about our self-concept; can be positive or negative
An individual’s belief in his/her capacity to execute behaviors necessary to produce specific performance attainments
Being motivated to do something for the love of doing it or the resulting internal satisfaction
Being motivated to do something to receive a reward or to avoid punishment
Tendency to emphasize our desirable qualities relative to other people
A society that values competition and individual achievement more than collective accomplishments
A society that values collective achievements more than individual successes
The process of strategically concealing or revealing personal information in order to influence others’ perceptions
Behaviors that present a person as a role model and make a person more likeable and attractive
Behaviors that present a person in a positive light; for example, as highly skilled, willing to challenge others, and someone not to be messed with
Interpersonal & Small Group Communication Copyright © 2023 by Weber State University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
The Importance of Self-Reflection: How Looking Inward Can Improve Your Mental Health
Sanjana is a health writer and editor. Her work spans various health-related topics, including mental health, fitness, nutrition, and wellness.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SanjanaGupta-d217a6bfa3094955b3361e021f77fcca.jpg)
Dr. Sabrina Romanoff, PsyD, is a licensed clinical psychologist and a professor at Yeshiva University’s clinical psychology doctoral program.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SabrinaRomanoffPhoto2-7320d6c6ffcc48ba87e1bad8cae3f79b.jpg)
Sunwoo Jung / Getty Images
Why Is Self-Reflection So Important?
When self-reflection becomes unhealthy, how to practice self-reflection, what to do if self-reflection makes you uncomfortable, incorporating self-reflection into your routine.
How well do you know yourself? Do you think about why you do the things you do? Self-reflection is a skill that can help you understand yourself better.
Self-reflection involves being present with yourself and intentionally focusing your attention inward to examine your thoughts, feelings, actions, and motivations, says Angeleena Francis , LMHC, executive director for AMFM Healthcare.
Active self-reflection can help grow your understanding of who you are , what values you believe in, and why you think and act the way you do, says Kristin Wilson , MA, LPC, CCTP, RYT, chief experience officer for Newport Healthcare.
This article explores the benefits and importance of self-reflection, as well as some strategies to help you practice it and incorporate it into your daily life. We also discuss when self-reflection can become unhealthy and suggest some coping strategies.
Self-reflection is important because it helps you form a self-concept and contributes toward self-development.
Builds Your Self-Concept
Self-reflection is critical because it contributes to your self-concept, which is an important part of your identity.
Your self-concept includes your thoughts about your traits, abilities, beliefs, values, roles, and relationships. It plays an influential role in your mood, judgment, and behavioral patterns.
Reflecting inward allows you to know yourself and continue to get to know yourself as you change and develop as a person, says Francis. It helps you understand and strengthen your self-concept as you evolve with time.
Enables Self-Development
Self-reflection also plays a key role in self-development. “It is a required skill for personal growth ,” says Wilson.
Being able to evaluate your strengths and weaknesses, or what you did right or wrong, can help you identify areas for growth and improvement, so you can work on them.
For instance, say you gave a presentation at school or work that didn’t go well, despite putting in a lot of work on the project. Spending a little time on self-reflection can help you understand that even though you spent a lot of time working on the project and creating the presentation materials, you didn’t practice giving the presentation. Realizing the problem can help you correct it. So, the next time you have to give a presentation, you can practice it on your colleagues or loved ones first.
Or, say you’ve just broken up with your partner. While it’s easy to blame them for everything that went wrong, self-reflection can help you understand what behaviors of yours contributed to the split. Being mindful of these behaviors can be helpful in other relationships.
Without self-reflection, you would continue to do what you’ve always done and as a result, you may continue to face the same problems you’ve always faced.
Benefits of Self-Reflection
These are some of the benefits of self-reflection, according to the experts:
- Increased self-awareness: Spending time in self-reflection can help build greater self-awareness , says Wilson. Self-awareness is a key component of emotional intelligence. It helps you recognize and understand your own emotions, as well as the impact of your emotions on your thoughts and behaviors.
- Greater sense of control: Self-reflection involves practicing mindfulness and being present with yourself at the moment. This can help you feel more grounded and in control of yourself, says Francis.
- Improved communication skills: Self-reflection can help you improve your communication skills, which can benefit your relationships. Understanding what you’re feeling can help you express yourself clearly, honestly, and empathetically.
- Deeper alignment with core values: Self-reflection can help you understand what you believe in and why. This can help ensure that your words and actions are more aligned with your core values, Wilson explains. It can also help reduce cognitive dissonance , which is the discomfort you may experience when your behavior doesn’t align with your values, says Francis.
- Better decision-making skills: Self-reflection can help you make better decisions for yourself, says Wilson. Understanding yourself better can help you evaluate all your options and how they will impact you with more clarity. This can help you make sound decisions that you’re more comfortable with, says Francis.
- Greater accountability: Self-reflection can help you hold yourself accountable to yourself, says Francis. It can help you evaluate your actions and recognize personal responsibility. It can also help you hold yourself accountable for the goals you’re working toward.
Self-reflection is a healthy practice that is important for mental well-being. However, it can become harmful if it turns into rumination, self-criticism, self-judgment, negative self-talk , and comparison to others, says Wilson.
Here’s what that could look like:
- Rumination: Experiencing excessive and repetitive stressful or negative thoughts. Rumination is often obsessive and interferes with other types of mental activity.
- Self-judgment: Constantly judging yourself and often finding yourself lacking.
- Negative self-talk: Allowing the voice inside your head to discourage you from doing things you want to do. Negative self-talk is often self-defeating.
- Self-criticism: Constantly criticizing your actions and decisions.
- Comparison: Endlessly comparing yourself to others and feeling inferior.
Kristin Wilson, LPC, CCTP
Looking inward may activate your inner critic, but true self-reflection comes from a place of neutrality and non-judgment.
When anxious thoughts and feelings come up in self-reflection, Wilson says it’s important to practice self-compassion and redirect your focus to actionable insights that can propel your life forward. “We all have faults and room for improvement. Reflect on the behaviors or actions you want to change and take steps to do so.”
It can help to think of what you would say to a friend in a similar situation. For instance, if your friend said they were worried about the status of their job after they gave a presentation that didn’t go well, you would probably be kind to them, tell them not to worry, and to focus on improving their presentation skills in the future. Apply the same compassion to yourself and focus on what you can control.
If you are unable to calm your mind of racing or negative thoughts, Francis recommends seeking support from a trusted person in your life or a mental health professional. “Patterns of negative self-talk, self-doubt , or criticism should be addressed through professional support, as negative cognitions of oneself can lead to symptoms of depression if not resolved.”
Wilson suggests some strategies that can help you practice self-reflection:
- Ask yourself open-ended questions: Start off by asking yourself open-ended questions that will prompt self-reflection, such as: “Am I doing what makes me happy?” “Are there things I’d like to improve about myself?” or “What could I have done differently today?” “Am I taking anything or anyone for granted?” Notice what thoughts and feelings arise within you for each question and then begin to think about why. Be curious about yourself and be open to whatever comes up.
- Keep a journal: Journaling your thoughts and responses to these questions is an excellent vehicle for self-expression. It can be helpful to look back at your responses, read how you handled things in the past, assess the outcome, and look for where you might make changes in the future.
- Try meditation: Meditation can also be a powerful tool for self-reflection and personal growth. Even if it’s only for five minutes, practice sitting in silence and paying attention to what comes up for you. Notice which thoughts are fleeting and which come up more often.
- Process major events and emotions: When something happens in your life that makes you feel especially good or bad, take the time to reflect on what occurred, how it made you feel, and either how you can get to that feeling again or what you might do differently the next time. Writing down your thoughts in a journal can help.
- Make a self-reflection board: Create a self-reflection board of positive attributes that you add to regularly. Celebrate your authentic self and the ways you stay true to who you are. Having a visual representation of self-reflection can be motivating.
You may avoid self-reflection if it brings up difficult emotions and makes you feel uncomfortable, says Francis. She recommends preparing yourself to get comfortable with the uncomfortable before you start.
Think of your time in self-reflection as a safe space within yourself. “Avoid judging yourself while you explore your inner thoughts, feelings, and motives of behavior,” says Francis. Simply notice what comes up and accept it. Instead of focusing on fears, worries, or regrets, try to look for areas of growth and improvement.
“Practice neutrality and self-compassion so that self-reflection is a positive experience that you will want to do regularly,” says Wilson.
Francis suggests some strategies that can help you incorporate self-reflection into your daily routine:
- Dedicate time to it: it’s important to dedicate time to self-reflection and build it into your routine. Find a slot that works for your schedule—it could be five minutes each morning while drinking coffee or 30 minutes sitting outside in nature once per week.
- Pick a quiet spot: It can be hard to focus inward if your environment is busy or chaotic. Choose a calm and quiet space that is free of distractions so you can hear your own thoughts.
- Pay attention to your senses: Pay attention to your senses. Sensory input is an important component of self-awareness.
Nowak A, Vallacher RR, Bartkowski W, Olson L. Integration and expression: The complementary functions of self-reflection . J Pers . 2022;10.1111/jopy.12730. doi:10.1111/jopy.12730
American Psychological Association. Self-concept .
Dishon N, Oldmeadow JA, Critchley C, Kaufman J. The effect of trait self-awareness, self-reflection, and perceptions of choice meaningfulness on indicators of social identity within a decision-making context . Front Psychol . 2017;8:2034. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.02034
Drigas AS, Papoutsi C. A new layered model on emotional intelligence . Behav Sci (Basel) . 2018;8(5):45. doi:10.3390/bs8050045
American Psychological Association. Rumination .
By Sanjana Gupta Sanjana is a health writer and editor. Her work spans various health-related topics, including mental health, fitness, nutrition, and wellness.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center
Home Blog Presentation Ideas About Me Slides: How to Introduce Yourself in a Presentation
About Me Slides: How to Introduce Yourself in a Presentation

From conference talks to client demos, it’s always essential to include an About Me slide in any presentation you are giving. Introducing yourself early into the presentation helps build a better rapport with the audience.
You can start with several fun facts about me slide to break the ice or go for a more formal professional bio to explain your background and what makes you qualified to talk about the topic at hand. At any rate, your goal is to get the audience on your side by revealing some of your personality.
How to Introduce Yourself in a Presentation: 4 Approaches
It’s a good practice to include self-introduction slides at the beginning of your presentation. If you are looking to answer how to introduce yourself professionally, typically somewhere after the title, opening slide , and the main agenda. However, the presentation structure will be somewhat different depending on whether you are presenting to a new audience or a group of people familiar with (e.g., your team, clients, or business partners).
Here are four about me slide ideas you can try out, plus an About me template you can use to present yourself in a presentation.

1. Mention Your Name and Affiliations
Start with the introduction basics. State your name, company, title/position, and several quick facts about who you are and what you do. Even if you present to a familiar audience, a brief recap is always welcome.
To keep things a bit more engaging, consider adding some lesser-known facts about yourself. For example:
- Your interests
- Recent accomplishments
- Testimonial/quote from a team member
- Fun nicknames you got
The above can be nice ice breakers for less formal team presentations, project updates, or catch-ups with clients.
Here are several unique About Me examples you can try out:
For a client case study presentation :
“Hi, I’m Lynda, Chief Customer Success Specialist with Acme Corp. (Also, someone you thought was a chatbot for the first few encounters)
47 NPS | 15% Churn Rate | 40% repeat purchase rate”
For a team after-action review presentation :
Mike, Project Manager at Cool Project
(aka Maximizer)
Personal Project stats:
387 Slack messages answered
56 cups of coffee consumed
Project profit gross margin: $1.2 million
2. Work On Your Elevator Pitch
One of the best ways to introduce yourself in a presentation is to share a punchy elevator pitch. This works extra well if you are presenting to a new audience.
An elevator pitch is a concise statement (1-2 sentences) that summarizes your unique strengths, skills, and abilities and explains how these can benefit your listener.
It’s nice to have one ready for your presentations and networking in general since it helps you immediately connect with new people and communicate your value.
Writing a solid elevator pitch may require several attempts and iterations. But the sooner you start — the faster you’ll arrive at the best formula!
To get your creative juices flowing, here are several elevator pitch ideas you can incorporate in an introduction slide about yourself.
For professionals:
“Certified Salesforce Administrator, data visualization specialist, and analytics for top SaaS brands. I help businesses make more sense of their data to drive better outcomes”.
For a mentor :
“Adjunct professor of creative writing at Columbia University, published author, former lifestyle editor at Esquire, the New York Times. I can teach you how to find, shape, pitch, and publish stories for web & print.”
For a student:
“Third-year Marine Biology student at Denver State Uni. Volunteer at Lake Life Protection NGO, climate change activist, looking to expand my research about water conservation”.
3. Answer Popular Questions or Assumptions
If you are a frequent presenter , chances are you get asked a lot of the same “About Me questions” after your speeches and during the networking bits. So why not address a roaster of these in your About Me slide? Select 4-5 most common questions and list them as quick FAQs on your slide deck.
4. Focus on Telling a Story
Strong introductions are personable. They are meant to offer a sneak-peak into your personality and the passion behind your work. That’s why for less formal presentations, you can (and should!) start with a short personal story.
Remember: reliability is important to “click” with your audience.
For instance, neuroscience research of political ads recently found that ads featuring real people performed better than those with genetic stock footage. Among viewers, emotional engagement and memory encoding (recall) increased dramatically when political ads showed relatable people.
The same holds true for commerce. In 2015, GE launched a viral “What’s the Matter With Owen?” video ad series to attract more young talent to the company. The clips featured a relatable protagonist, struggling to explain what his work at GE entails e.g. that the company isn’t building railroads, but actually does some very innovative pilots. Many engineers related to the promo and work applications to GE shoot up by 800% !
As the above examples show, a good relatable story can go a long way. So think about how you can make a PowerPoint presentation about yourself more representative of who you really are as a person.
How to Give a Presentation About Yourself: 4 Fool-Proof Tips
On other occasions, you may be asked to give a full-length “about me” presentation. Typically, this is the case during a second interview, onboarding , or if you are in attending a training program or workshop where everyone needs to present themselves and their work.
Obviously, you’ll need more than one good about me slide in this case. So here’s how to prepare a superb presentation about me.
What to Put in a Presentation About Yourself?
The audience will expect to learn a mix of personal and professional facts about you. Thus, it’s a good idea to include the following information:
- Your name, contact info, website , social media handles, digital portfolio .
- Short bio or some interesting snippets.
- Career timeline (if applicable).
- Main achievements (preferably quantifiable).
- Education, special training.
- Digital badging awards , accolades, and other types of recognition.
- Something more personal — an interest, hobby, aspiration.
The above mix of items will change a bit, depending on whether you are giving an interview presentation about yourself or introduce yourself post-hiring. For example, in some cases a dedicated bio slide may be useful, but other times focusing on main achievements and goals can be better.
That being said, let’s take a closer look at how to organize the above information in a memorable presentation.
P.S. Grab an about me slide template to make the design process easier!

1. Create a List of “Facts About Me”
The easiest way to answer the “tell me about yourself” question is by having an array of facts you can easily fetch from your brain.
When it comes to a full-length about me presentation , it’s best to have a longer list ready. To keep your brainstorming process productive, organize all your ideas in the following buckets:
- Key skills (soft and hard)
- Educational accolades, training
- Accomplishments and other “bragging rights”
- Personal tidbits (a.k.a. fun facts )
Once you have a list, it gets easier to build a series of slides around it.
2. Think Like Your Audience
Most likely you’d be asked to make a presentation about yourself by a recruiter. There’s a good reason why many ask this — they want to determine if you are a good “cultural fit” for their organization.
After all, 33% of people quit within the first 3 months of accepting a new job. Among these:
- 43% of employees quit because their day-to-day role was different than what they were told it would be during the hiring process.
- 32% cite company culture as a factor for leaving within the first three months.
About me presentations often serve as an extra “filter” helping both parties ensure that they are on the same page expectations- and work style-wise. Thus, when you prepare your slide deck, do some background company research. Then try to align the presentation with it by matching the company tone, communication style, and cultural values.
3. Include Testimonials and Recommendations
Use the voice of others to back up the claims you are making in your presentation. After all, trumping your own horn is what you are expected to do in such a presentation. But the voices of others can strengthen the claims you are personally making.
Depending on your role and industry, try to sprinkle some of the following testimonials:
- LinkedIn recommendations
- Quotes from personal or professional references
- Social media comments
- Data metrics of your performance
- Funny assessments from your colleagues/friends
The above not just strengthen your narrative, but also help the audience learn some extras about you and your background. Testimonial slides can be of help for this purpose.
4. Include a Case Study
One of the best ways to illustrate who you are is to show what you are best in. Remember, an about me presentation often needs to “soft sell” your qualifications, experience, and personality.
One of the best ways to do that is to showcase how you can feel in a specific need and solve issues the business is facing.
So if you have the timeframe, use some of the ending slides to deliver a quick case study. You can present:
- Short retrospective of a past successful project
- Before-after transformations you’ve achieved
- Spotlight of the main accomplishments within the previous role
- Main customer results obtained
- Specific solution delivered by you (or the team you’ve worked with)
Ending your presentation on such a high note will leave the audience positively impressed and wondering what results you could achieve for them.
To Conclude
It’s easy to feel stumped when you are asked to talk about yourself. Because there are so many things you could mention (but not necessarily should). At the same time, you don’t want to make your introduction sound like a bragging context. So always think from the position of your audience. Do the facts you choose to share benefit them in any way? If yes, place them confidently on your About Me slides!
1. Personal Self Introduction PowerPoint Template

Use This Template
2. Self Introduction PowerPoint Template

3. Meet the Team PowerPoint Template Slides

4. Introduce Company Profile PowerPoint Template

5. Modern 1-Page Resume Template for PowerPoint

6. Modern Resume Presentation Template
Like this article? Please share
Introduce Yourself, Introduction, Presentation Ideas Filed under Presentation Ideas
Related Articles

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 15th, 2024
How to Create a 5 Minutes Presentation
Master the art of short-format speeches like the 5 minutes presentation with this article. Insights on content structure, audience engagement and more.

Filed under Design • January 24th, 2024
How to Plan Your Presentation Using the 4W1H & 5W1H Framework
The 4W1H and 5W1H problem-solving frameworks can benefit presenters who look for a creative outlook in presentation structure design. Learn why here.

Filed under Presentation Ideas • December 13th, 2023
How To Make a Presentation Interactive
In this article, we will explore the insights behind what makes a presentation interactive. Join us to discover techniques that guarantee a presentation success.
Leave a Reply
12.2 Self-presentation
Learning objectives.
- Describe social roles and how they influence behavior
- Explain what social norms are and how they influence behavior
- Define script
- Describe the findings of Zimbardo’s Stanford prison experiment
As you’ve learned, social psychology is the study of how people affect one another’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. We have discussed situational perspectives and social psychology’s emphasis on the ways in which a person’s environment, including culture and other social influences, affect behavior. In this section, we examine situational forces that have a strong influence on human behavior including social roles, social norms, and scripts. We discuss how humans use the social environment as a source of information, or cues, on how to behave. Situational influences on our behavior have important consequences, such as whether we will help a stranger in an emergency or how we would behave in an unfamiliar environment.
Social Roles
One major social determinant of human behavior is our social roles. A social role is a pattern of behavior that is expected of a person in a given setting or group (Hare, 2003). Each one of us has several social roles. You may be, at the same time, a student, a parent, an aspiring teacher, a son or daughter, a spouse, and a lifeguard. How do these social roles influence your behavior? Social roles are defined by culturally shared knowledge. That is, nearly everyone in a given culture knows what behavior is expected of a person in a given role. For example, what is the social role for a student? If you look around a college classroom you will likely see students engaging in studious behavior, taking notes, listening to the professor, reading the textbook, and sitting quietly at their desks ( Figure 12.8 ). Of course you may see students deviating from the expected studious behavior such as texting on their phones or using Facebook on their laptops, but in all cases, the students that you observe are attending class—a part of the social role of students.
Social roles, and our related behavior, can vary across different settings. How do you behave when you are engaging in the role of son or daughter and attending a family function? Now imagine how you behave when you are engaged in the role of employee at your workplace. It is very likely that your behavior will be different. Perhaps you are more relaxed and outgoing with your family, making jokes and doing silly things. But at your workplace you might speak more professionally, and although you may be friendly, you are also serious and focused on getting the work completed. These are examples of how our social roles influence and often dictate our behavior to the extent that identity and personality can vary with context (that is, in different social groups) (Malloy, Albright, Kenny, Agatstein & Winquist, 1997).
Social Norms
As discussed previously, social roles are defined by a culture’s shared knowledge of what is expected behavior of an individual in a specific role. This shared knowledge comes from social norms. A social norm is a group’s expectation of what is appropriate and acceptable behavior for its members—how they are supposed to behave and think (Deutsch & Gerard, 1955; Berkowitz, 2004). How are we expected to act? What are we expected to talk about? What are we expected to wear? In our discussion of social roles we noted that colleges have social norms for students’ behavior in the role of student and workplaces have social norms for employees’ behaviors in the role of employee. Social norms are everywhere including in families, gangs, and on social media outlets. What are some social norms on Facebook?
Connect the Concepts
Tweens, teens, and social norms.
My 11-year-old daughter, Jessica, recently told me she needed shorts and shirts for the summer, and that she wanted me to take her to a store at the mall that is popular with preteens and teens to buy them. I have noticed that many girls have clothes from that store, so I tried teasing her. I said, “All the shirts say ‘Aero’ on the front. If you are wearing a shirt like that and you have a substitute teacher, and the other girls are all wearing that type of shirt, won’t the substitute teacher think you are all named ‘Aero’?”
My daughter replied, in typical 11-year-old fashion, “Mom, you are not funny. Can we please go shopping?”
I tried a different tactic. I asked Jessica if having clothing from that particular store will make her popular. She replied, “No, it will not make me popular. It is what the popular kids wear. It will make me feel happier.” How can a label or name brand make someone feel happier? Think back to what you’ve learned about lifespan development . What is it about pre-teens and young teens that make them want to fit in ( Figure 12.9 )? Does this change over time? Think back to your high school experience, or look around your college campus. What is the main name brand clothing you see? What messages do we get from the media about how to fit in?
Because of social roles, people tend to know what behavior is expected of them in specific, familiar settings. A script is a person’s knowledge about the sequence of events expected in a specific setting (Schank & Abelson, 1977). How do you act on the first day of school, when you walk into an elevator, or are at a restaurant? For example, at a restaurant in the United States, if we want the server’s attention, we try to make eye contact. In Brazil, you would make the sound “psst” to get the server’s attention. You can see the cultural differences in scripts. To an American, saying “psst” to a server might seem rude, yet to a Brazilian, trying to make eye contact might not seem an effective strategy. Scripts are important sources of information to guide behavior in given situations. Can you imagine being in an unfamiliar situation and not having a script for how to behave? This could be uncomfortable and confusing. How could you find out about social norms in an unfamiliar culture?
Zimbardo’s Stanford Prison Experiment
The famous Stanford prison experiment , conducted by social psychologist Philip Zimbardo and his colleagues at Stanford University, demonstrated the power of social roles, social norms, and scripts. In the summer of 1971, an advertisement was placed in a California newspaper asking for male volunteers to participate in a study about the psychological effects of prison life. More than 70 men volunteered, and these volunteers then underwent psychological testing to eliminate candidates who had underlying psychiatric issues, medical issues, or a history of crime or drug abuse. The pool of volunteers was whittled down to 24 healthy male college students. Each student was paid $15 per day and was randomly assigned to play the role of either a prisoner or a guard in the study. Based on what you have learned about research methods, why is it important that participants were randomly assigned?
A mock prison was constructed in the basement of the psychology building at Stanford. Participants assigned to play the role of prisoners were “arrested” at their homes by Palo Alto police officers, booked at a police station, and subsequently taken to the mock prison. The experiment was scheduled to run for several weeks. To the surprise of the researchers, both the “prisoners” and “guards” assumed their roles with zeal. In fact, on day 2, some of the prisoners revolted, and the guards quelled the rebellion by threatening the prisoners with night sticks. In a relatively short time, the guards came to harass the prisoners in an increasingly sadistic manner, through a complete lack of privacy, lack of basic comforts such as mattresses to sleep on, and through degrading chores and late-night counts.
The prisoners, in turn, began to show signs of severe anxiety and hopelessness—they began tolerating the guards’ abuse. Even the Stanford professor who designed the study and was the head researcher, Philip Zimbardo, found himself acting as if the prison was real and his role, as prison supervisor, was real as well. After only six days, the experiment had to be ended due to the participants’ deteriorating behavior. Zimbardo explained,
At this point it became clear that we had to end the study. We had created an overwhelmingly powerful situation—a situation in which prisoners were withdrawing and behaving in pathological ways, and in which some of the guards were behaving sadistically. Even the “good” guards felt helpless to intervene, and none of the guards quit while the study was in progress. Indeed, it should be noted that no guard ever came late for his shift, called in sick, left early, or demanded extra pay for overtime work. (Zimbardo, 2013)
The Stanford prison experiment demonstrated the power of social roles, norms, and scripts in affecting human behavior. The guards and prisoners enacted their social roles by engaging in behaviors appropriate to the roles: The guards gave orders and the prisoners followed orders. Social norms require guards to be authoritarian and prisoners to be submissive. When prisoners rebelled, they violated these social norms, which led to upheaval. The specific acts engaged by the guards and the prisoners derived from scripts. For example, guards degraded the prisoners by forcing them do push-ups and by removing all privacy. Prisoners rebelled by throwing pillows and trashing their cells. Some prisoners became so immersed in their roles that they exhibited symptoms of mental breakdown; however, according to Zimbardo, none of the participants suffered long term harm (Alexander, 2001).
The Stanford Prison Experiment has some parallels with the abuse of prisoners of war by U.S. Army troops and CIA personnel at the Abu Ghraib prison in 2003 and 2004. The offenses at Abu Ghraib were documented by photographs of the abuse, some taken by the abusers themselves ( Figure 12.10 ).
Link to Learning
Visit this website to hear an NPR interview with Philip Zimbardo where he discusses the parallels between the Stanford prison experiment and the Abu Ghraib prison in Iraq.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Rose M. Spielman, Kathryn Dumper, William Jenkins, Arlene Lacombe, Marilyn Lovett, Marion Perlmutter
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Psychology
- Publication date: Dec 8, 2014
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology/pages/12-2-self-presentation
© Feb 9, 2022 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Greater Good Science Center • Magazine • In Action • In Education
Parenting & Family Articles & More
Can self-compassion help teens with depression, a new study finds that learning to be more supportive and kind to themselves can protect teens who are struggling..
Thirteen year-old Alita told me she knew there was something wrong with her—something that made her “less than.” She felt that, somehow, she was “marked” and deeply unacceptable—even ugly—inside. She was sure everyone else could see what was so blatantly wrong with her, but for the life of her, she couldn’t put her finger on what it was, what made her this way, or what she could do about it. All she knew was that she was not quite like everyone else.
This is all too often how teens feel. Different, alone, apart, unworthy, and undeserving. Like they don’t “belong”—anywhere, to anything or anyone. According to a CDC report , in 2021, 42% of teens—57% of females and 29% of males—experienced persistent feelings of sadness and hopelessness to the degree that they could not engage in regular activities; and 13% of females and 7% of males attempted suicide.
Although navigating the teen years has never been easy, it’s harder now than it was in the past. Today’s teens are still going through the same physical and emotional transitions that they always have, but they are also burdened with pressures from the outside world that we never could have imagined even a few years ago—from fears of school shootings, to the relentless isolation caused by social media and the pandemic, to the terrifying impact of climate change.

In the face of all this, teens no longer have a “safe space”—a place where they can escape to when they’re being bullied, or when the strain of school, friends, and the outside world becomes overwhelming. Heading to their bedroom and closing the door—as teens have done in the past—no longer works. Today, smartphones linger within arm’s reach, abuzz with possibilities, but all too often resulting in disappointment or rejection.
As caring adults, how can we help teens work through and overcome these challenges? Although there are no simple answers to this question, part of the way forward is helping teens learn self-compassion.
How self-compassion helps with depression
Self-compassion means treating yourself with kindness and support when you’re having a hard time, being aware of difficult emotions and recognizing that they are a normal part of life. This may sound like no big deal, but actually most of us do the opposite. When something’s happened that makes us feel badly, for example, we tend to be overly self-critical, often assuming that whatever happened was our fault, or happened because we’re fundamentally flawed—like Alita felt.

Self-Compassion for Educators
Calling all educators and school leaders! Join our free monthly meeting in April to learn more about self-compassion.
In a recently published study , my colleagues and I taught one group of teens the Mindful Self-Compassion for Teens (MSC-T) program, eight sessions designed to help them be more supportive and compassionate to themselves. Another group learned a healthy lifestyles curriculum that included sessions on nutrition, exercise, sleep, and healthy social media use, among other topics.
In the MSC-T program, one of the teens’ favorite practices was a “music meditation.” We played a piece of relaxing instrumental music and instructed teens to simply listen to the music and, when their minds wandered, return to paying attention to the music. Teens found this practice soothing and enjoyed the opportunity to select their own music. One teen said the music practice “made me realize that I can do that every time I listen to music and I always listen to music so that means that, like, 24/7 I can be calm.” While this sounds like a simple mindfulness practice, we were inviting teens to use it as a way to calm and care for themselves.
Another practice that teens were drawn to was using a “comforting gesture” to support themselves and remember to be kind to themselves when feeling anxious or afraid. This could be simply rubbing their two hands together, resting a hand over their heart, or cradling their face in their hands. Here are some downloadable audiorecordings of MSC-T practices .
In our study, all the teens were exhibiting some depressive symptoms to begin with, and these symptoms were expected to increase over time, as they tend to do in teens. The results showed that after six months, teens in the self-compassion group were more than two and a half times less likely to develop full-blown depression compared to teens in the healthy lifestyles group, suggesting that the self-compassion course protected the teens from getting more depressed. In fact, the self-compassion group actually decreased in depression.
Similarly, in a recent study (currently under review), we taught Mindful Self-Compassion for Teens to transgender and gender-diverse teens, a population that experiences high rates of depression and suicidal thinking. These teens had significantly fewer suicidal thoughts two months after the program than before it began.
How does self-compassion work?
Although we can’t determine from these studies how self-compassion is protective, we suspect it has to do with teens developing an understanding of common humanity. In one class, a teen said, “Whatever you’re feeling, you’re not alone in it. Somebody else will feel the same way, will know where you’re coming from, even if you think that no one understands, there will be somebody who does.”
Mindful Self-Compassion for Teens
This program meets weekly (virtually) for 1.5 hours a week for eight weeks and provides teens with the opportunity to engage in activities involving art, music, a few games, some mindful movement, and discussion. All activities are always optional.
Our next class will be held on Mondays, April 15 to June 10 (with no class on May 27), from 4:30-6:00 p.m. PST.
Register for the program
Through taking Mindful Self-Compassion for Teens, teens may realize just this—that, contrary to Alita’s perceptions, they aren’t alone; many others share their experiences of sadness, loneliness, or worry. That experiencing these emotions is part of being a teen.
Research from several meta-analyses (analyzing the results of many studies together) aligns with these findings. For example, teens who are more self-compassionate tend to experience less depression, anxiety, and stress in general than those who are less self-compassionate.
Even more, being more self-compassionate may protect against some of the onslaughts of being a teen. Not only are these self-compassionate teens less likely to become depressed when stressed, but when they are depressed, they’re less likely to self-injure . They’re also less likely to get stressed when academic pressure is high , less likely to get anxious or depressed when using social media , and less likely to get depressed when cyberbullied .
Our first study was just a small initial study of 59 teens, but future work will assess MSC-T in larger groups of teens, and among particular groups, such as those with chronic health conditions. Plans are underway to implement and assess MSC-T in middle and high schools—the subject of my book coming out in June . Also, we’re in the midst of a study implementing a similar program for both children and caregivers together.
Self-compassion isn’t going to solve all teens’ problems. But it will give them a new way to approach their problems—without blaming themselves and with a new perspective, one that can be enormously eye-opening. As one teen said to me after taking a self-compassion course, “You know, it’s changed the way I look at myself and the world.” And that can make all the difference.
About the Author

Karen Bluth
Karen Bluth, Ph.D. , is faculty in the Department of Psychiatry at the University of North Carolina, and a research fellow at the University of North Carolina Frank Porter Graham Child Development Institute, where she conducts research on self-compassion and its influences on the emotional well-being of teens.
You May Also Enjoy

This article — and everything on this site — is funded by readers like you.
Become a subscribing member today. Help us continue to bring “the science of a meaningful life” to you and to millions around the globe.
University of South Florida
Lifelong Learning
Office of University Community Partnerships
Main Navigation

Corporate Training and Professional Education Instructor Jay Powers Gives Insightful Presentation on Leadership and Success
- Tatiana Del Valle
- March 28, 2024
- Leadership and Management
- Text-based Story
The event GROW Pasco 2024 was the backdrop for retired Colonel and University of South Florida instructor Jay Powers, wherein he guided entrepreneurs and leaders toward success earlier this month using the expertise he developed as a U.S. Army Green Beret and leader within Joint Special Operations.
GROW Pasco is an event designed to equip local entrepreneurs and executives for growth in the evolving business landscape. Hosted by the SMARTstart entrepreneurship program at Pasco EDC, it provides educational and networking opportunities for business owners in the area. With a full schedule of speakers, including business and community leaders, and breakout sessions throughout the day, attendees learned how to leverage everything from marketing and social media to artificial intelligence.
USF’s Office of Corporate Training and Professional Education attended to absorb more knowledge, connect with others in the local community, and see unique perspectives on entrepreneurial success.
Weaving Leadership with Self-Care
Powers emphasized key aspects of leadership and organizational growth in his presentation, “Lead Your Way to Entrepreneurial Success,” and coupled these observations with valuable perspectives he’s gained as COO at Tampa Bay Wave, a renowned non-profit accelerator dedicated to tech company growth and the development of Tampa Bay's tech ecosystem.
He honed in on the similarities and differences between the characteristics of successful entrepreneurs and leaders. Good leaders have strengths such as delegation, integrity, empathy, and respect, while entrepreneurs have characteristics such as flexibility, curiosity, persistence, and innovative thinking. Both should have self-awareness to reflect on their actions and how they affect others.
“There’s no single approach to leadership that will work for every person and situation, that's why it's difficult,” Powers said. “It’s important to get feedback to know how you’re truly impacting people.”
He believes people are the critical resource for any organization to succeed, so leaders should strive to create environments where people can thrive.
He also stressed the importance of balancing your business efforts with the other essential areas of your life. Be sure to prioritize sleep, exercise, family, and other parts of your personal life to ensure you bring the best version of yourself to your organization. “If you take the time to invest in it, family can be one of your biggest sources of resilience,” he said.
Ultimately, Powers had two major takeaways:
One: Identify when you need to do less and lead more.
Two: Take a long-term approach to balance.
By getting to know your team, prioritizing feedback, giving people space to take initiative, and taking care of yourself, you can set yourself up with a strong foundation for success both in business and your life.
The impact of his speech was evident in the long line of attendees who patiently waited to chat with him after the presentation. View the full presentation here .
Level Up Your Skills
For a unique opportunity to learn from an experienced leadership practitioner, join Powers for the next session of his course, “Executive Leadership Lessons,” starting Friday, April 5. Designed to accommodate the schedules of busy professionals, this course provides an overview of how to build positive environments, encourage employee input, give and receive feedback, and build trust.
Register here or contact David Hill, associate director of the Office of Corporate Training and Professional Education, at [email protected] for more information.
Return to article listing
Explore More Categories
- Director's Corner
- Hospitality
- Human Resources
- K-12 Education
- Process Improvement
- Professional Development
- Project Management
- Sales and Marketing
About Corporate Training and Professional Education
USF Corporate Training and Professional Education empowers people to craft their future without limits through engaging professional growth learning and certification programs. Its programs focus on an array of topics – human resources, project management, paralegal, process improvement, leadership skills, technology, and much more.
Can I take a photo of the eclipse with my phone? Here's how, plus more info on cellphones.
You can capture Monday's solar eclipse in Wisconsin with your cellphone, according to NASA .
You'll need to use a solar filter to protect your camera, and you'll also need a pair of solar viewing glasses to protect your eyes.
For more information on how to best capture the eclipse, you can visit NASA's website .
While Wisconsin will only see a partial solar eclipse, cell service still could affected by it.
Here's what else to know about cellphones during the eclipse:
Will I have cellphone service during the solar eclipse in Wisconsin?
Solar eclipses can affect the structure and dynamics of Earth's upper atmosphere, otherwise known as the ionosphere, according to NASA . Since the ionosphere contains charged particles and is responsible for reflecting and refracting radio waves, it can possibly affect radio communications and navigation systems.
"While solar eclipses can have noticeable effects on the ionosphere, they are generally temporary and localized to the region experiencing the eclipse," according to NASA.
However, because Wisconsin most likely won't be facing high volumes of crowds traveling to see the partial eclipse, cellular networks won't be as strained across the state as areas in the path of totality.
Will cellular data work during the solar eclipse?
Cellular data should work during the solar eclipse, especially as some networks have expanded since the last solar eclipse in 2017.
AT&T has said it expanded the 5G network to reach millions of people in 24,500 cities across the country. T-Mobile said it has deployed additional cell sites to handle the influx of people traveling to view the eclipse. T-Mobile also said it increased investments in network hardening by more than 30% over the past two years.
More: Wisconsin will be cloudy during the eclipse. Here's where you can travel to see clear skies
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
The Definitive Voice of Entertainment News
Subscribe for full access to The Hollywood Reporter
site categories
Francis ford coppola’s ‘megalopolis’ faces uphill battle for mega deal: “just no way to position this movie”.
The self-funded epic is deemed too “experimental” and “not good” enough for the $100 million marketing spend envisioned by the legendary director.
By Seth Abramovitch , Kim Masters , Pamela McClintock April 8, 2024 3:00pm
- Share this article on Facebook
- Share this article on Twitter
- Share this article on Flipboard
- Share this article on Email
- Show additional share options
- Share this article on Linkedin
- Share this article on Pinit
- Share this article on Reddit
- Share this article on Tumblr
- Share this article on Whatsapp
- Share this article on Print
- Share this article on Comment

NBCUniversal chief content officer Donna Langley was there. So was Sony head Tom Rothman. Bob Iger was one of the few Hollywood heavyweights who couldn’t make it, but at least he had a good excuse, still in the midst of a vicious proxy battle with investor Nelson Peltz.
Related Stories
Shia labeouf ex fka twigs on alleged abuse: "changes the whole of your nervous system", francis ford coppola shares 'the outsiders' audition tapes from tom cruise, patrick swayze.
The project, which Coppola first began writing in 1983, cost a reported $120 million to make — funded in part by the sale of a significant portion of his wine empire (the 2021 deal was reportedly worth over $500 million ). Clocking in at two hours and 15 minutes, the film follows the rebuilding of a metropolis after its accidental destruction, with two competing visions — one from an idealist architect (Adam Driver), the other from its pragmatist mayor (Giancarlo Esposito) — clashing in the process. References to ancient Rome — including Caesar haircuts on the men — abound.
Coppola, 84, has said no decisions will be made regarding a festival bow until a distribution plan is put in place. But while there was no shortage of curious suitors there — in addition to Rothman and Sarandos, Warner Bros.’ Pam Abdy, Disney live-action boss David Greenbaum, Netflix’s Ted Sarandos and Paramount’s Marc Weinstock were all spotted — multiple sources inside the screening tell The Hollywood Reporter that Megalopolis will face a steep uphill battle to find a distribution partner. Says one distributor: “There is just no way to position this movie.”
“Everyone is rooting for Francis and feels nostalgic,” adds another attendee. “But then there is the business side of things.”
But a boutique label like A24 or Neon would likely not have the budget for the grand marketing push Coppola has envisioned. One source tells THR that Coppola assumed he would make a deal very quickly, and that a studio would happily commit to a massive P&A (prints and advertising, including all marketing) spend in the vicinity of $40 million domestically, and $80 million to $100 million globally.
That kind of big-stakes rollout would make Megalopolis a better fit for a studio-backed specialty label like the Disney-owned Searchlight or the Universal-owned Focus. But Universal and Focus have already tapped out of the bidding, sources tell THR .
“I find it hard to believe any distributor would put up cash money and stay in first position to recoup the P&A as well as their distribution fee,” says a distribution veteran. “If [Coppola] is willing to put up the P&A or backstop the spend, I think there would be a lot more interested parties.”
Imax is likely to give the film some support if it gets distribution, sources close to the project say. Like others, however, Imax expected the film to be far more commercial, sources add.
Following the muted response to the March 28 screening, it’s now not even clear if a studio would agree to a negative pickup deal, in which the studio would buy the film outright, or one in which it would distribute the film for a fee. One studio head in attendance described it as “some kind of indie experiment” that might find a home at a streamer.
Most of those who spoke to THR describe a film that is an enormously hard sell to a wide audience. Two people say it’s hard to figure out who is the good guy and who is the bad guy. The big exception is LaBeouf, who they say is the best thing about the film (he’s one of the antagonists).
Several have mentioned an especially cringey sequence involving Jon Voight’s character in bed with what looks like a huge erection; the scene evidently takes quite the turn, but we will not spoil it here.
Another studio head, however, was far less charitable in his assessment: “It’s so not good, and it was so sad watching it. Anybody who puts P&A behind it, you’re going to lose money. This is not how Coppola should end his directing career.”
THR Newsletters
Sign up for THR news straight to your inbox every day
More from The Hollywood Reporter
Monsterverse future looks bright after ‘godzilla x kong’, jackie chan responds to fans concerned over his health: “don’t worry”, george miller on ‘furiosa’ star anya taylor-joy: “there’s something mystical about her”, billy dee williams says actors should be allowed to wear blackface, zendaya says intimacy coordinator was “very helpful” for ‘challengers’: “important that we felt safe”, ‘loki’ actress wunmi mosaku joins michael b. jordan in ryan coogler’s untitled supernatural thriller (exclusive).

SMART: Self-Expanding vs. Balloon-Expandable Valve For TAVR in Patients With Small Valve Annulus
Apr 07, 2024
ACC News Story
The supra-annular self-expanding Evolut PRO/PRO+/FX TAVR device was found to be superior for valve function and noninferior for clinical outcomes at one year compared to the balloon-expandable SAPIEN 3/3 Ultra TAVR device, according to the results of the SMART trial, presented during a Late-Breaking Clinical Trial Session at ACC.24 and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine .
The trial, conducted at 83 international sites across North America, Europe and the Middle East, randomly assigned 716 patients (mean age 80 years, 87% women) who underwent TAVR and had a valve annulus ≤430 mm 2 to either the self-expanding Evolut valve or the balloon-expandable SAPIEN valve. Participants were considered to face a low to intermediate risk, with a mean Society of Thoracic Surgeons Predicted Risk of Mortality of 3.3%.
Results at one year showed that there was no significant between-group difference in the primary composite endpoint of death, disabling stroke or rehospitalization for heart failure – which occurred in 9.4% of patients who received the Evolut valve and 10.6% of those receiving the SAPIEN valve (p<0.001). For the co-primary endpoint of valve function, defined in terms of a composite of structural and nonstructural valve deterioration, blood clotting around the valve, infection of the valve and aortic valve reintervention, the Evolut device was found to be superior; the endpoint occurred in 9.4% of patients who received the Evolut valve and 41.6% of those receiving the SAPIEN valve (p<0.001).
All prespecified secondary endpoints were statistically significant in favor of the self-expanding valve, including blood pressure across the valve and the size of the valve opening. The aortic valve mean gradient at 12 months was 7.7 mm Hg with the self-expanding valve and 15.7 mm Hg with the balloon-expandable valve.
"Clinically, at one year, either valve is reasonable, and the results are pretty similar, although mild valve leaks and some measures of quality of life were better with Evolut," said Howard C. Herrmann, MD, FACC , lead author of the study. "Furthermore, this is the first time we get to identify differences between the devices that might impact later patient outcomes."
Similar results were seen across all subgroups, although the researchers plan to analyze additional subgroups to determine whether valve performance or clinical outcomes may vary among people in different age groups or among people with different comorbidities or annulus size. They also plan to assess measures of valve durability over time, which Herrmann said is becoming more important as younger patients are increasingly undergoing TAVR. Researchers will continue to track outcomes over the next five years.
This was the first trial to focus specifically on informing device selection for patients with small aortic annuli, a patient group that is primarily women and has been underrepresented in previous clinical trials for TAVR. "We think it's important to study this population, which represents up to 40% of all patients getting TAVR, and it's important to study women, who make up the majority of the small annulus population," said Herrmann.
Keywords: ACC Annual Scientific Session, ACC24, Valvular Diseases, Coronary, Peripheral, and Structural Procedures
You must be logged in to save to your library.
Jacc journals on acc.org.
- JACC: Advances
- JACC: Basic to Translational Science
- JACC: CardioOncology
- JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging
- JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions
- JACC: Case Reports
- JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology
- JACC: Heart Failure
- Current Members
- Campaign for the Future
- Become a Member
- Renew Your Membership
- Member Benefits and Resources
- Member Sections
- ACC Member Directory
- ACC Innovation Program
- Our Strategic Direction
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Our History
- Our Bylaws and Code of Ethics
- Leadership and Governance
- Annual Report
- Industry Relations
- Support the ACC
- Jobs at the ACC
- Press Releases
- Social Media
- Book Our Conference Center
Clinical Topics
- Acute Coronary Syndromes
- Anticoagulation Management
- Arrhythmias and Clinical EP
- Cardiac Surgery
- Cardio-Oncology
- Chronic Angina
- Congenital Heart Disease and Pediatric Cardiology
- COVID-19 Hub
- Diabetes and Cardiometabolic Disease
- Dyslipidemia
- Geriatric Cardiology
- Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathies
- Hypertriglyceridemia
- Invasive Cardiovascular Angiography and Intervention
- Noninvasive Imaging
- Pericardial Disease
- Pulmonary Hypertension and Venous Thromboembolism
- Sports and Exercise Cardiology
- Stable Ischemic Heart Disease
- Valvular Heart Disease
- Vascular Medicine
Latest in Cardiology
- Clinical Updates & Discoveries
- Advocacy & Policy
- Perspectives & Analysis
- Meeting Coverage
- ACC Member Publications
- ACC Podcasts
Education and Meetings
- Online Learning Catalog
- Understanding MOC
- Products and Resources
- Image and Slide Gallery
- Certificates and Certifications
- Annual Scientific Session
Tools and Practice Support
- Quality Improvement for Institutions
- CardioSmart
- Accreditation Services
- Clinical Solutions
- Clinician Well-Being Portal
- Mobile and Web Apps
- Advocacy at the ACC
- Cardiology as a Career Path
- Cardiology Careers
- Practice Solutions
Heart House
- 2400 N St. NW
- Washington , DC 20037
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone: 1-202-375-6000
- Toll Free: 1-800-253-4636
- Fax: 1-202-375-6842
- Media Center
- ACC.org Quick Start Guide
- Advertising & Sponsorship Policy
- Clinical Content Disclaimer
- Editorial Board
- Privacy Policy
- Registered User Agreement
- Terms of Service
- Cookie Policy
© 2024 American College of Cardiology Foundation. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Ask a trusted friend or mentor to share what you can improve. Asking for feedback about specific experiences, like a recent project or presentation, will make their suggestions more relevant and easier to implement. 2. Study people who have been successful in your role. Look at how they interact with other people.
Self-presentation refers to how people attempt to present themselves to control or shape how others (called the audience) view them. It involves expressing oneself and behaving in ways that create a desired impression. Self-presentation is part of a broader set of behaviors called impression management. Impression management refers to the ...
Good personal presentation therefore requires good self-esteem and self-confidence. It means that you have to learn about yourself, and understand and accept who you are, both your positives and your negatives, and be comfortable with yourself. This does not, however, mean that you believe that there is nothing that you can improve—but that ...
Self-presentation is the process of strategically concealing or revealing personal information in order to influence others' perceptions. 1 We engage in this process daily and for different reasons. Although people occasionally intentionally deceive others in the process of self-presentation, in general we try to make a good impression while ...
Impression Management in Sociology. Impression management, also known as self-presentation, refers to the ways that people attempt to control how they are perceived by others (Goffman, 1959). By conveying particular impressions about their abilities, attitudes, motives, status, emotional reactions, and other characteristics, people can ...
People often use self-presentation as a way to build their own identity. Many people adopt values, behaviours, and beliefs for which they want others to recognize them. For example, a person might adopt a specific set of religious ideals and want to be identified as a practitioner of that religion. You may present yourself as a firm believer of ...
When you give a presentation, it is important to remember the whole package, and that means how you present yourself as well as how you present the material. It is not good to spend hours and hours preparing a wonderful presentation and neglect the effect of your own appearance. Whether you like it or not, people make judgements about you based ...
Self-presentation is behavior that attempts to convey some information about oneself or some image of oneself to other people. It denotes a class of motivations in human behavior. These motivations are in part stable dispositions of individuals but they depend on situational factors to elicit them. Specifically, self-presentational motivations ...
Self-presentation is the process of strategically concealing or revealing personal information in order to influence others' perceptions. [1] We engage in this process daily and for different reasons. Although people occasionally intentionally deceive others in the process of self-presentation, in general we try to make a good impression ...
This page titled 12.3: Self-presentation is shared under a CC BY 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by OpenStax. social psychology is the study of how people affect one another's thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. We have discussed situational perspectives and social psychology's emphasis on the ….
Self-presentation is the act of managing how other people perceive and evaluate you. It involves using various cues, such as your appearance, mannerisms, and speech patterns, to create a certain impression in the minds of others. When it comes to dressing for success, self-presentation is absolutely critical.
Self-presentation. As you've learned, social psychology is the study of how people affect one another's thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. ... Social psychologists have documented that feeling good about ourselves and maintaining positive self-esteem is a powerful motivator of human behavior (Tavris & Aronson, 2008). In the United States ...
Self-presentational perspectives have been applied to the study of topics such as conformity, aggression, prosocial behavior, leadership, negotiation, social influence, gender, stigmatization, close relationships, emotional experience, and mental and physical health. View chapter Explore book.
What Is Self Presentation Theory? Self-presentation theory is a psychological theory that explains how people present themselves to others. Self-presentation can take many forms, including verbal, nonverbal, and behavioral. It has two parts: the self-concept and the self-schema. The self-concept is how we see ourselves concerning others; the ...
Self-Presentation. How we perceive ourselves manifests in how we present ourselves to others. Self-presentation is the process of strategically concealing or revealing personal information in order to influence others' perceptions (Human et al., 2012). We engage in this process daily and for different reasons.
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
This implies that self-presentation is a form of social communication, by which people establish, maintain, and alter their social identity. These self-presentational strategies can be "assertive ...
Self-esteem refers to the judgments and evaluations we make about our self-concept. While self-concept is a broad description of the self, self-esteem is a more specifically an evaluation of the self (Byrne, 1996). If I again prompted you to "Tell me who you are," and then asked you to evaluate (label as good/bad, positive/negative, desirable/undesirable) each of the things you listed ...
These are some of the benefits of self-reflection, according to the experts: Increased self-awareness: Spending time in self-reflection can help build greater self-awareness, says Wilson. Self-awareness is a key component of emotional intelligence. It helps you recognize and understand your own emotions, as well as the impact of your emotions ...
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
Self Introduction PowerPoint Template by SlideModel. 1. Create a List of "Facts About Me". The easiest way to answer the "tell me about yourself" question is by having an array of facts you can easily fetch from your brain. When it comes to a full-length about me presentation, it's best to have a longer list ready.
12.2 Self-presentation; 12.3 Attitudes and Persuasion; 12.4 Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience; 12.5 Prejudice and Discrimination; 12.6 Aggression; 12.7 Prosocial ... Even the "good" guards felt helpless to intervene, and none of the guards quit while the study was in progress. Indeed, it should be noted that no guard ever came late for ...
1. Start with Your Name and Background Information. Though this is an age-old way of self-introduction, it's always in trend and most preferred by global presenters. State your name, the organization you are representing, the position you hold, and some facts that give a concise idea about your personality.
But as suggested by a theory published by Professor Thomas Lynch in 2018, high self-control may not always be a good thing—and, for some, it could be linked to certain mental health problems. According to Lynch's theory, every single one of us leans more toward one of two personality styles: undercontrol or overcontrol.
Self-compassion isn't going to solve all teens' problems. But it will give them a new way to approach their problems—without blaming themselves and with a new perspective, one that can be enormously eye-opening. As one teen said to me after taking a self-compassion course, "You know, it's changed the way I look at myself and the world."
Good leaders have strengths such as delegation, integrity, empathy, and respect, while entrepreneurs have characteristics such as flexibility, curiosity, persistence, and innovative thinking. Both should have self-awareness to reflect on their actions and how they affect others.
You can capture Monday's solar eclipse in Wisconsin with your cellphone, according to NASA.. You'll need to use a solar filter to protect your camera, and you'll also need a pair of solar viewing ...
Gold's scorching run to an all-time high may seem easy to explain from a distance, given the fractious geopolitical climate and murky outlook for the global economy. The precious metal is ...
The self-funded epic is deemed too "experimental" and "not good" enough for the $100 million marketing spend envisioned by the legendary director. By Seth Abramovitch, Kim Masters, Pamela ...
The supra-annular self-expanding Evolut PRO/PRO+/FX TAVR device was found to be superior for valve function and noninferior for clinical outcomes at one year compared to the balloon-expandable SAPIEN 3/3 Ultra TAVR device, according to the results of the SMART trial, presented during a Late-Breaking Clinical Trial Session at ACC.24 and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of ...