Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center


Assignment ON" EVOLUTION AND HISTORY OF COMPUTER "

Related Papers
Ndidi Opara
Edmund Miller
AJEET TELECOM
ELAIYA SENGUTTUVAN
Tahir Siddique
In this paper, emphasis has been given on the gradual and continuous advancement of computer from on and before 300BC to 2012 and beyond. During this very long period of time, a simple device like computer has witnessed many significant changes in its manufacturing and development. By and large, the changes are conceptual, manufacturing and in ever increasing applications. Abstract-In this paper, emphasis has been given on the gradual and continuous advancement of computer from on and before 300BC to 2012 and beyond. During this very long period of time, a simple device like computer has witnessed many significant changes in its manufacturing and development. By and large, the changes are conceptual, manufacturing and in ever increasing applications.
IEEE Potentials
Cresent Escriber
Fernando A G Alcoforado
This article aims to present how the computer, humanity's greatest invention, evolved and how its most likely future will be. The computer is humanity's greatest invention because the worldwide computer network made possible the use of the Internet as the technology that most changed the world with the advent of the information society. IBM developed the mainframe computer starting in 1952. In the 1970s, the dominance of mainframes began to be challenged by the emergence of microprocessors. The innovations greatly facilitated the task of developing and manufacturing smaller computers - then called minicomputers. In 1976, the first microcomputers appeared whose costs represented only a fraction of those practiced by manufacturers of mainframes and minicomputers. The existence of the computer provided the conditions for the advent of the Internet which is undoubtedly one of the greatest inventions of the 20th century, whose development took place in 1965. At the beginning of the 21st century, cloud computing emerged, which symbolizes the tendency to place all the infrastructure and information available digitally on the Internet. Current computers are electronic because they are made up of transistors used in electronic chips that have limitations given that there will be a time when it will no longer be possible to reduce the size of one of the components of the processors, the transistor. Quantum computers have been shown to be the newest answer in Physics and Computing to problems related to the limited capacity of electronic computers. Canadian company D-Wave claims to have produced the first commercial quantum computer. In addition to the quantum computer, Artificial Intelligence (AI) can reinvent computers.
Suggested Videos
What is a computer.
A computer is an electronic machine that collects information, stores it, processes it according to user instructions, and then returns the result.
A computer is a programmable electronic device that performs arithmetic and logical operations automatically using a set of instructions provided by the user.
Early Computing Devices
People used sticks, stones, and bones as counting tools before computers were invented. More computing devices were produced as technology advanced and the human intellect improved over time. Let us look at a few of the early-age computing devices used by mankind.
Abacus was invented by the Chinese around 4000 years ago. It’s a wooden rack with metal rods with beads attached to them. The abacus operator moves the beads according to certain guidelines to complete arithmetic computations.
- Napier’s Bone
John Napier devised Napier’s Bones, a manually operated calculating apparatus. For calculating, this instrument used 9 separate ivory strips (bones) marked with numerals to multiply and divide. It was also the first machine to calculate using the decimal point system.
Pascaline was invented in 1642 by Biaise Pascal, a French mathematician and philosopher. It is thought to be the first mechanical and automated calculator. It was a wooden box with gears and wheels inside.
- Stepped Reckoner or Leibniz wheel
In 1673, a German mathematician-philosopher named Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz improved on Pascal’s invention to create this apparatus. It was a digital mechanical calculator known as the stepped reckoner because it used fluted drums instead of gears.
- Difference Engine
In the early 1820s, Charles Babbage created the Difference Engine. It was a mechanical computer that could do basic computations. It was a steam-powered calculating machine used to solve numerical tables such as logarithmic tables.
- Analytical Engine
Charles Babbage created another calculating machine, the Analytical Engine, in 1830. It was a mechanical computer that took input from punch cards. It was capable of solving any mathematical problem and storing data in an indefinite memory.
- Tabulating machine
An American Statistician – Herman Hollerith invented this machine in the year 1890. Tabulating Machine was a punch card-based mechanical tabulator. It could compute statistics and record or sort data or information. Hollerith began manufacturing these machines in his company, which ultimately became International Business Machines (IBM) in 1924.
- Differential Analyzer
Vannevar Bush introduced the first electrical computer, the Differential Analyzer, in 1930. This machine is made up of vacuum tubes that switch electrical impulses in order to do calculations. It was capable of performing 25 calculations in a matter of minutes.
Howard Aiken planned to build a machine in 1937 that could conduct massive calculations or calculations using enormous numbers. The Mark I computer was constructed in 1944 as a collaboration between IBM and Harvard.
History of Computers Generation
The word ‘computer’ has a very interesting origin. It was first used in the 16th century for a person who used to compute, i.e. do calculations. The word was used in the same sense as a noun until the 20th century. Women were hired as human computers to carry out all forms of calculations and computations.
By the last part of the 19th century, the word was also used to describe machines that did calculations. The modern-day use of the word is generally to describe programmable digital devices that run on electricity.
Early History of Computer
Since the evolution of humans, devices have been used for calculations for thousands of years. One of the earliest and most well-known devices was an abacus. Then in 1822, the father of computers, Charles Babbage began developing what would be the first mechanical computer. And then in 1833 he actually designed an Analytical Engine which was a general-purpose computer. It contained an ALU, some basic flow chart principles and the concept of integrated memory.
Then more than a century later in the history of computers, we got our first electronic computer for general purpose. It was the ENIAC, which stands for Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer. The inventors of this computer were John W. Mauchly and J.Presper Eckert.
And with times the technology developed and the computers got smaller and the processing got faster. We got our first laptop in 1981 and it was introduced by Adam Osborne and EPSON.
Browse more Topics under Basics Of Computers
- Number Systems
- Number System Conversions
Generations of Computers
- Computer Organisation
- Computer Memory
- Computers Abbreviations
- Basic Computer Terminology
- Computer Languages
- Basic Internet Knowledge and Protocols
- Hardware and Software
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- I/O Devices
- Practice Problems On Basics Of Computers
In the history of computers, we often refer to the advancements of modern computers as the generation of computers . We are currently on the fifth generation of computers. So let us look at the important features of these five generations of computers.
- 1st Generation: This was from the period of 1940 to 1955. This was when machine language was developed for the use of computers. They used vacuum tubes for the circuitry. For the purpose of memory, they used magnetic drums. These machines were complicated, large, and expensive. They were mostly reliant on batch operating systems and punch cards. As output and input devices, magnetic tape and paper tape were implemented. For example, ENIAC, UNIVAC-1, EDVAC, and so on.
- 2nd Generation: The years 1957-1963 were referred to as the “second generation of computers” at the time. In second-generation computers, COBOL and FORTRAN are employed as assembly languages and programming languages. Here they advanced from vacuum tubes to transistors. This made the computers smaller, faster and more energy-efficient. And they advanced from binary to assembly languages. For instance, IBM 1620, IBM 7094, CDC 1604, CDC 3600, and so forth.
- 3rd Generation: The hallmark of this period (1964-1971) was the development of the integrated circuit. A single integrated circuit (IC) is made up of many transistors, which increases the power of a computer while simultaneously lowering its cost. These computers were quicker, smaller, more reliable, and less expensive than their predecessors. High-level programming languages such as FORTRON-II to IV, COBOL, and PASCAL PL/1 were utilized. For example, the IBM-360 series, the Honeywell-6000 series, and the IBM-370/168.
- 4th Generation: The invention of the microprocessors brought along the fourth generation of computers. The years 1971-1980 were dominated by fourth generation computers. C, C++ and Java were the programming languages utilized in this generation of computers. For instance, the STAR 1000, PDP 11, CRAY-1, CRAY-X-MP, and Apple II. This was when we started producing computers for home use.
- 5th Generation: These computers have been utilized since 1980 and continue to be used now. This is the present and the future of the computer world. The defining aspect of this generation is artificial intelligence. The use of parallel processing and superconductors are making this a reality and provide a lot of scope for the future. Fifth-generation computers use ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology. These are the most recent and sophisticated computers. C, C++, Java,.Net, and more programming languages are used. For instance, IBM, Pentium, Desktop, Laptop, Notebook, Ultrabook, and so on.
Brief History of Computers
The naive understanding of computation had to be overcome before the true power of computing could be realized. The inventors who worked tirelessly to bring the computer into the world had to realize that what they were creating was more than just a number cruncher or a calculator. They had to address all of the difficulties associated with inventing such a machine, implementing the design, and actually building the thing. The history of the computer is the history of these difficulties being solved.
19 th Century
1801 – Joseph Marie Jacquard, a weaver and businessman from France, devised a loom that employed punched wooden cards to automatically weave cloth designs.
1822 – Charles Babbage, a mathematician, invented the steam-powered calculating machine capable of calculating number tables. The “Difference Engine” idea failed owing to a lack of technology at the time.
1848 – The world’s first computer program was written by Ada Lovelace, an English mathematician. Lovelace also includes a step-by-step tutorial on how to compute Bernoulli numbers using Babbage’s machine.
1890 – Herman Hollerith, an inventor, creates the punch card technique used to calculate the 1880 U.S. census. He would go on to start the corporation that would become IBM.
Early 20 th Century
1930 – Differential Analyzer was the first large-scale automatic general-purpose mechanical analogue computer invented and built by Vannevar Bush.
1936 – Alan Turing had an idea for a universal machine, which he called the Turing machine, that could compute anything that could be computed.
1939 – Hewlett-Packard was discovered in a garage in Palo Alto, California by Bill Hewlett and David Packard.
1941 – Konrad Zuse, a German inventor and engineer, completed his Z3 machine, the world’s first digital computer. However, the machine was destroyed during a World War II bombing strike on Berlin.
1941 – J.V. Atanasoff and graduate student Clifford Berry devise a computer capable of solving 29 equations at the same time. The first time a computer can store data in its primary memory.
1945 – University of Pennsylvania academics John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert create an Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator (ENIAC). It was Turing-complete and capable of solving “a vast class of numerical problems” by reprogramming, earning it the title of “Grandfather of computers.”
1946 – The UNIVAC I (Universal Automatic Computer) was the first general-purpose electronic digital computer designed in the United States for corporate applications.
1949 – The Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator (EDSAC), developed by a team at the University of Cambridge, is the “first practical stored-program computer.”
1950 – The Standards Eastern Automatic Computer (SEAC) was built in Washington, DC, and it was the first stored-program computer completed in the United States.
Late 20 th Century
1953 – Grace Hopper, a computer scientist, creates the first computer language, which becomes known as COBOL, which stands for CO mmon, B usiness- O riented L anguage. It allowed a computer user to offer the computer instructions in English-like words rather than numbers.
1954 – John Backus and a team of IBM programmers created the FORTRAN programming language, an acronym for FOR mula TRAN slation. In addition, IBM developed the 650.
1958 – The integrated circuit, sometimes known as the computer chip, was created by Jack Kirby and Robert Noyce.
1962 – Atlas, the computer, makes its appearance. It was the fastest computer in the world at the time, and it pioneered the concept of “virtual memory.”
1964 – Douglas Engelbart proposes a modern computer prototype that combines a mouse and a graphical user interface (GUI).
1969 – Bell Labs developers, led by Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie, revealed UNIX, an operating system developed in the C programming language that addressed program compatibility difficulties.
1970 – The Intel 1103, the first Dynamic Access Memory (DRAM) chip, is unveiled by Intel.
1971 – The floppy disc was invented by Alan Shugart and a team of IBM engineers. In the same year, Xerox developed the first laser printer, which not only produced billions of dollars but also heralded the beginning of a new age in computer printing.
1973 – Robert Metcalfe, a member of Xerox’s research department, created Ethernet, which is used to connect many computers and other gear.
1974 – Personal computers were introduced into the market. The first were the Altair Scelbi & Mark-8, IBM 5100, and Radio Shack’s TRS-80.
1975 – Popular Electronics magazine touted the Altair 8800 as the world’s first minicomputer kit in January. Paul Allen and Bill Gates offer to build software in the BASIC language for the Altair.
1976 – Apple Computers is founded by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, who expose the world to the Apple I, the first computer with a single-circuit board.
1977 – At the first West Coast Computer Faire, Jobs and Wozniak announce the Apple II. It has colour graphics and a cassette drive for storing music.
1978 – The first computerized spreadsheet program, VisiCalc, is introduced.
1979 – WordStar, a word processing tool from MicroPro International, is released.
1981 – IBM unveils the Acorn, their first personal computer, which has an Intel CPU, two floppy drives, and a colour display. The MS-DOS operating system from Microsoft is used by Acorn.
1983 – The CD-ROM, which could carry 550 megabytes of pre-recorded data, hit the market. This year also saw the release of the Gavilan SC, the first portable computer with a flip-form design and the first to be offered as a “laptop.”
1984 – Apple launched Macintosh during the Superbowl XVIII commercial. It was priced at $2,500
1985 – Microsoft introduces Windows, which enables multitasking via a graphical user interface. In addition, the programming language C++ has been released.
1990 – Tim Berners-Lee, an English programmer and scientist, creates HyperText Markup Language, widely known as HTML. He also coined the term “WorldWideWeb.” It includes the first browser, a server, HTML, and URLs.
1993 – The Pentium CPU improves the usage of graphics and music on personal computers.
1995 – Microsoft’s Windows 95 operating system was released. A $300 million promotional campaign was launched to get the news out. Sun Microsystems introduces Java 1.0, followed by Netscape Communications’ JavaScript.
1996 – At Stanford University, Sergey Brin and Larry Page created the Google search engine.
1998 – Apple introduces the iMac, an all-in-one Macintosh desktop computer. These PCs cost $1,300 and came with a 4GB hard drive, 32MB RAM, a CD-ROM, and a 15-inch monitor.
1999 – Wi-Fi, an abbreviation for “wireless fidelity,” is created, originally covering a range of up to 300 feet.
21 st Century
2000 – The USB flash drive is first introduced in 2000. They were speedier and had more storage space than other storage media options when used for data storage.
2001 – Apple releases Mac OS X, later renamed OS X and eventually simply macOS, as the successor to its conventional Mac Operating System.
2003 – Customers could purchase AMD’s Athlon 64, the first 64-bit CPU for consumer computers.
2004 – Facebook began as a social networking website.
2005 – Google acquires Android, a mobile phone OS based on Linux.
2006 – Apple’s MacBook Pro was available. The Pro was the company’s first dual-core, Intel-based mobile computer.
Amazon Web Services, including Amazon Elastic Cloud 2 (EC2) and Amazon Simple Storage Service, were also launched (S3)
2007 – The first iPhone was produced by Apple, bringing many computer operations into the palm of our hands. Amazon also released the Kindle, one of the first electronic reading systems, in 2007.
2009 – Microsoft released Windows 7.
2011 – Google introduces the Chromebook, which runs Google Chrome OS.
2014 – The University of Michigan Micro Mote (M3), the world’s smallest computer, was constructed.
2015 – Apple introduces the Apple Watch. Windows 10 was also released by Microsoft.
2016 – The world’s first reprogrammable quantum computer is built.
Types of Computers
- Analog Computers – Analog computers are built with various components such as gears and levers, with no electrical components. One advantage of analogue computation is that designing and building an analogue computer to tackle a specific problem can be quite straightforward.
- Mainframe computers – It is a computer that is generally utilized by large enterprises for mission-critical activities such as massive data processing. Mainframe computers were distinguished by massive storage capacities, quick components, and powerful computational capabilities. Because they were complicated systems, they were managed by a team of systems programmers who had sole access to the computer. These machines are now referred to as servers rather than mainframes.
- Supercomputers – The most powerful computers to date are commonly referred to as supercomputers. Supercomputers are enormous systems that are purpose-built to solve complicated scientific and industrial problems. Quantum mechanics, weather forecasting, oil and gas exploration, molecular modelling, physical simulations, aerodynamics, nuclear fusion research, and cryptoanalysis are all done on supercomputers.
- Minicomputers – A minicomputer is a type of computer that has many of the same features and capabilities as a larger computer but is smaller in size. Minicomputers, which were relatively small and affordable, were often employed in a single department of an organization and were often dedicated to a specific task or shared by a small group.
- Microcomputers – A microcomputer is a small computer that is based on a microprocessor integrated circuit, often known as a chip. A microcomputer is a system that incorporates at a minimum a microprocessor, program memory, data memory, and input-output system (I/O). A microcomputer is now commonly referred to as a personal computer (PC).
- Embedded processors – These are miniature computers that control electrical and mechanical processes with basic microprocessors. Embedded processors are often simple in design, have limited processing capability and I/O capabilities, and need little power. Ordinary microprocessors and microcontrollers are the two primary types of embedded processors. Embedded processors are employed in systems that do not require the computing capability of traditional devices such as desktop computers, laptop computers, or workstations.
FAQs on History of Computers
Q: The principle of modern computers was proposed by ____
- Adam Osborne
- Alan Turing
- Charles Babbage
Ans: The correct answer is C.
Q: Who introduced the first computer from home use in 1981?
- Sun Technology
Ans: Answer is A. IBM made the first home-use personal computer.
Q: Third generation computers used which programming language ?
- Machine language
Ans: The correct option is C.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Basics of Computers
- Computer Abbreviations
- Basic Computer Knowledge – Practice Problems
- Computer Organization
- Input and Output (I/O) Devices
One response to “Hardware and Software”
THANKS ,THIS IS THE VERY USEFUL KNOWLEDGE
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

History of computers: A brief timeline
The history of computers began with primitive designs in the early 19th century and went on to change the world during the 20th century.

- 2000-present day
Additional resources
The history of computers goes back over 200 years. At first theorized by mathematicians and entrepreneurs, during the 19th century mechanical calculating machines were designed and built to solve the increasingly complex number-crunching challenges. The advancement of technology enabled ever more-complex computers by the early 20th century, and computers became larger and more powerful.
Today, computers are almost unrecognizable from designs of the 19th century, such as Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine — or even from the huge computers of the 20th century that occupied whole rooms, such as the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator.
Here's a brief history of computers, from their primitive number-crunching origins to the powerful modern-day machines that surf the Internet, run games and stream multimedia.
19th century
1801: Joseph Marie Jacquard, a French merchant and inventor invents a loom that uses punched wooden cards to automatically weave fabric designs. Early computers would use similar punch cards.
1821: English mathematician Charles Babbage conceives of a steam-driven calculating machine that would be able to compute tables of numbers. Funded by the British government, the project, called the "Difference Engine" fails due to the lack of technology at the time, according to the University of Minnesota .
1848: Ada Lovelace, an English mathematician and the daughter of poet Lord Byron, writes the world's first computer program. According to Anna Siffert, a professor of theoretical mathematics at the University of Münster in Germany, Lovelace writes the first program while translating a paper on Babbage's Analytical Engine from French into English. "She also provides her own comments on the text. Her annotations, simply called "notes," turn out to be three times as long as the actual transcript," Siffert wrote in an article for The Max Planck Society . "Lovelace also adds a step-by-step description for computation of Bernoulli numbers with Babbage's machine — basically an algorithm — which, in effect, makes her the world's first computer programmer." Bernoulli numbers are a sequence of rational numbers often used in computation.

1853: Swedish inventor Per Georg Scheutz and his son Edvard design the world's first printing calculator. The machine is significant for being the first to "compute tabular differences and print the results," according to Uta C. Merzbach's book, " Georg Scheutz and the First Printing Calculator " (Smithsonian Institution Press, 1977).
1890: Herman Hollerith designs a punch-card system to help calculate the 1890 U.S. Census. The machine, saves the government several years of calculations, and the U.S. taxpayer approximately $5 million, according to Columbia University Hollerith later establishes a company that will eventually become International Business Machines Corporation ( IBM ).
Early 20th century
1931: At the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Vannevar Bush invents and builds the Differential Analyzer, the first large-scale automatic general-purpose mechanical analog computer, according to Stanford University .
1936: Alan Turing , a British scientist and mathematician, presents the principle of a universal machine, later called the Turing machine, in a paper called "On Computable Numbers…" according to Chris Bernhardt's book " Turing's Vision " (The MIT Press, 2017). Turing machines are capable of computing anything that is computable. The central concept of the modern computer is based on his ideas. Turing is later involved in the development of the Turing-Welchman Bombe, an electro-mechanical device designed to decipher Nazi codes during World War II, according to the UK's National Museum of Computing .
1937: John Vincent Atanasoff, a professor of physics and mathematics at Iowa State University, submits a grant proposal to build the first electric-only computer, without using gears, cams, belts or shafts.

1939: David Packard and Bill Hewlett found the Hewlett Packard Company in Palo Alto, California. The pair decide the name of their new company by the toss of a coin, and Hewlett-Packard's first headquarters are in Packard's garage, according to MIT .
1941: German inventor and engineer Konrad Zuse completes his Z3 machine, the world's earliest digital computer, according to Gerard O'Regan's book " A Brief History of Computing " (Springer, 2021). The machine was destroyed during a bombing raid on Berlin during World War II. Zuse fled the German capital after the defeat of Nazi Germany and later released the world's first commercial digital computer, the Z4, in 1950, according to O'Regan.
1941: Atanasoff and his graduate student, Clifford Berry, design the first digital electronic computer in the U.S., called the Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC). This marks the first time a computer is able to store information on its main memory, and is capable of performing one operation every 15 seconds, according to the book " Birthing the Computer " (Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2016)
1945: Two professors at the University of Pennsylvania, John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert, design and build the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator (ENIAC). The machine is the first "automatic, general-purpose, electronic, decimal, digital computer," according to Edwin D. Reilly's book "Milestones in Computer Science and Information Technology" (Greenwood Press, 2003).

1946: Mauchly and Presper leave the University of Pennsylvania and receive funding from the Census Bureau to build the UNIVAC, the first commercial computer for business and government applications.
1947: William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain of Bell Laboratories invent the transistor . They discover how to make an electric switch with solid materials and without the need for a vacuum.
1949: A team at the University of Cambridge develops the Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator (EDSAC), "the first practical stored-program computer," according to O'Regan. "EDSAC ran its first program in May 1949 when it calculated a table of squares and a list of prime numbers ," O'Regan wrote. In November 1949, scientists with the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), now called CSIRO, build Australia's first digital computer called the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research Automatic Computer (CSIRAC). CSIRAC is the first digital computer in the world to play music, according to O'Regan.
Late 20th century
1953: Grace Hopper develops the first computer language, which eventually becomes known as COBOL, which stands for COmmon, Business-Oriented Language according to the National Museum of American History . Hopper is later dubbed the "First Lady of Software" in her posthumous Presidential Medal of Freedom citation. Thomas Johnson Watson Jr., son of IBM CEO Thomas Johnson Watson Sr., conceives the IBM 701 EDPM to help the United Nations keep tabs on Korea during the war.
1954: John Backus and his team of programmers at IBM publish a paper describing their newly created FORTRAN programming language, an acronym for FORmula TRANslation, according to MIT .
1958: Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce unveil the integrated circuit, known as the computer chip. Kilby is later awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work.
1968: Douglas Engelbart reveals a prototype of the modern computer at the Fall Joint Computer Conference, San Francisco. His presentation, called "A Research Center for Augmenting Human Intellect" includes a live demonstration of his computer, including a mouse and a graphical user interface (GUI), according to the Doug Engelbart Institute . This marks the development of the computer from a specialized machine for academics to a technology that is more accessible to the general public.

1969: Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie and a group of other developers at Bell Labs produce UNIX, an operating system that made "large-scale networking of diverse computing systems — and the internet — practical," according to Bell Labs .. The team behind UNIX continued to develop the operating system using the C programming language, which they also optimized.
1970: The newly formed Intel unveils the Intel 1103, the first Dynamic Access Memory (DRAM) chip.
1971: A team of IBM engineers led by Alan Shugart invents the "floppy disk," enabling data to be shared among different computers.
1972: Ralph Baer, a German-American engineer, releases Magnavox Odyssey, the world's first home game console, in September 1972 , according to the Computer Museum of America . Months later, entrepreneur Nolan Bushnell and engineer Al Alcorn with Atari release Pong, the world's first commercially successful video game.
1973: Robert Metcalfe, a member of the research staff for Xerox, develops Ethernet for connecting multiple computers and other hardware.
1977: The Commodore Personal Electronic Transactor (PET), is released onto the home computer market, featuring an MOS Technology 8-bit 6502 microprocessor, which controls the screen, keyboard and cassette player. The PET is especially successful in the education market, according to O'Regan.
1975: The magazine cover of the January issue of "Popular Electronics" highlights the Altair 8080 as the "world's first minicomputer kit to rival commercial models." After seeing the magazine issue, two "computer geeks," Paul Allen and Bill Gates, offer to write software for the Altair, using the new BASIC language. On April 4, after the success of this first endeavor, the two childhood friends form their own software company, Microsoft.
1976: Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak co-found Apple Computer on April Fool's Day. They unveil Apple I, the first computer with a single-circuit board and ROM (Read Only Memory), according to MIT .

1977: Radio Shack began its initial production run of 3,000 TRS-80 Model 1 computers — disparagingly known as the "Trash 80" — priced at $599, according to the National Museum of American History. Within a year, the company took 250,000 orders for the computer, according to the book " How TRS-80 Enthusiasts Helped Spark the PC Revolution " (The Seeker Books, 2007).
1977: The first West Coast Computer Faire is held in San Francisco. Jobs and Wozniak present the Apple II computer at the Faire, which includes color graphics and features an audio cassette drive for storage.
1978: VisiCalc, the first computerized spreadsheet program is introduced.
1979: MicroPro International, founded by software engineer Seymour Rubenstein, releases WordStar, the world's first commercially successful word processor. WordStar is programmed by Rob Barnaby, and includes 137,000 lines of code, according to Matthew G. Kirschenbaum's book " Track Changes: A Literary History of Word Processing " (Harvard University Press, 2016).
1981: "Acorn," IBM's first personal computer, is released onto the market at a price point of $1,565, according to IBM. Acorn uses the MS-DOS operating system from Windows. Optional features include a display, printer, two diskette drives, extra memory, a game adapter and more.

1983: The Apple Lisa, standing for "Local Integrated Software Architecture" but also the name of Steve Jobs' daughter, according to the National Museum of American History ( NMAH ), is the first personal computer to feature a GUI. The machine also includes a drop-down menu and icons. Also this year, the Gavilan SC is released and is the first portable computer with a flip-form design and the very first to be sold as a "laptop."
1984: The Apple Macintosh is announced to the world during a Superbowl advertisement. The Macintosh is launched with a retail price of $2,500, according to the NMAH.
1985 : As a response to the Apple Lisa's GUI, Microsoft releases Windows in November 1985, the Guardian reported . Meanwhile, Commodore announces the Amiga 1000.
1989: Tim Berners-Lee, a British researcher at the European Organization for Nuclear Research ( CERN ), submits his proposal for what would become the World Wide Web. His paper details his ideas for Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML), the building blocks of the Web.
1993: The Pentium microprocessor advances the use of graphics and music on PCs.
1996: Sergey Brin and Larry Page develop the Google search engine at Stanford University.
1997: Microsoft invests $150 million in Apple, which at the time is struggling financially. This investment ends an ongoing court case in which Apple accused Microsoft of copying its operating system.
1999: Wi-Fi, the abbreviated term for "wireless fidelity" is developed, initially covering a distance of up to 300 feet (91 meters) Wired reported .
21st century
2001: Mac OS X, later renamed OS X then simply macOS, is released by Apple as the successor to its standard Mac Operating System. OS X goes through 16 different versions, each with "10" as its title, and the first nine iterations are nicknamed after big cats, with the first being codenamed "Cheetah," TechRadar reported.
2003: AMD's Athlon 64, the first 64-bit processor for personal computers, is released to customers.
2004: The Mozilla Corporation launches Mozilla Firefox 1.0. The Web browser is one of the first major challenges to Internet Explorer, owned by Microsoft. During its first five years, Firefox exceeded a billion downloads by users, according to the Web Design Museum .
2005: Google buys Android, a Linux-based mobile phone operating system
2006: The MacBook Pro from Apple hits the shelves. The Pro is the company's first Intel-based, dual-core mobile computer.
2009: Microsoft launches Windows 7 on July 22. The new operating system features the ability to pin applications to the taskbar, scatter windows away by shaking another window, easy-to-access jumplists, easier previews of tiles and more, TechRadar reported .

2010: The iPad, Apple's flagship handheld tablet, is unveiled.
2011: Google releases the Chromebook, which runs on Google Chrome OS.
2015: Apple releases the Apple Watch. Microsoft releases Windows 10.
2016: The first reprogrammable quantum computer was created. "Until now, there hasn't been any quantum-computing platform that had the capability to program new algorithms into their system. They're usually each tailored to attack a particular algorithm," said study lead author Shantanu Debnath, a quantum physicist and optical engineer at the University of Maryland, College Park.
2017: The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is developing a new "Molecular Informatics" program that uses molecules as computers. "Chemistry offers a rich set of properties that we may be able to harness for rapid, scalable information storage and processing," Anne Fischer, program manager in DARPA's Defense Sciences Office, said in a statement. "Millions of molecules exist, and each molecule has a unique three-dimensional atomic structure as well as variables such as shape, size, or even color. This richness provides a vast design space for exploring novel and multi-value ways to encode and process data beyond the 0s and 1s of current logic-based, digital architectures."
2019: A team at Google became the first to demonstrate quantum supremacy — creating a quantum computer that could feasibly outperform the most powerful classical computer — albeit for a very specific problem with no practical real-world application. The described the computer, dubbed "Sycamore" in a paper that same year in the journal Nature . Achieving quantum advantage – in which a quantum computer solves a problem with real-world applications faster than the most powerful classical computer — is still a ways off.
2022: The first exascale supercomputer, and the world's fastest, Frontier, went online at the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF) in Tennessee. Built by Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) at the cost of $600 million, Frontier uses nearly 10,000 AMD EPYC 7453 64-core CPUs alongside nearly 40,000 AMD Radeon Instinct MI250X GPUs. This machine ushered in the era of exascale computing, which refers to systems that can reach more than one exaFLOP of power – used to measure the performance of a system. Only one machine – Frontier – is currently capable of reaching such levels of performance. It is currently being used as a tool to aid scientific discovery.
What is the first computer in history?
Charles Babbage's Difference Engine, designed in the 1820s, is considered the first "mechanical" computer in history, according to the Science Museum in the U.K . Powered by steam with a hand crank, the machine calculated a series of values and printed the results in a table.
What are the five generations of computing?
The "five generations of computing" is a framework for assessing the entire history of computing and the key technological advancements throughout it.
The first generation, spanning the 1940s to the 1950s, covered vacuum tube-based machines. The second then progressed to incorporate transistor-based computing between the 50s and the 60s. In the 60s and 70s, the third generation gave rise to integrated circuit-based computing. We are now in between the fourth and fifth generations of computing, which are microprocessor-based and AI-based computing.
What is the most powerful computer in the world?
As of November 2023, the most powerful computer in the world is the Frontier supercomputer . The machine, which can reach a performance level of up to 1.102 exaFLOPS, ushered in the age of exascale computing in 2022 when it went online at Tennessee's Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF)
There is, however, a potentially more powerful supercomputer waiting in the wings in the form of the Aurora supercomputer, which is housed at the Argonne National Laboratory (ANL) outside of Chicago. Aurora went online in November 2023. Right now, it lags far behind Frontier, with performance levels of just 585.34 petaFLOPS (roughly half the performance of Frontier), although it's still not finished. When work is completed, the supercomputer is expected to reach performance levels higher than 2 exaFLOPS.
What was the first killer app?
Killer apps are widely understood to be those so essential that they are core to the technology they run on. There have been so many through the years – from Word for Windows in 1989 to iTunes in 2001 to social media apps like WhatsApp in more recent years
Several pieces of software may stake a claim to be the first killer app, but there is a broad consensus that VisiCalc, a spreadsheet program created by VisiCorp and originally released for the Apple II in 1979, holds that title. Steve Jobs even credits this app for propelling the Apple II to become the success it was, according to co-creator Dan Bricklin .
- Fortune: A Look Back At 40 Years of Apple
- The New Yorker: The First Windows
- " A Brief History of Computing " by Gerard O'Regan (Springer, 2021)
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Timothy is Editor in Chief of print and digital magazines All About History and History of War . He has previously worked on sister magazine All About Space , as well as photography and creative brands including Digital Photographer and 3D Artist . He has also written for How It Works magazine, several history bookazines and has a degree in English Literature from Bath Spa University .
Error-corrected qubits 800 times more reliable after breakthrough, paving the way for 'next level' of quantum computing
The 7 most powerful supercomputers in the world right now
'Gambling with your life': Experts weigh in on dangers of the Wim Hof method
Most Popular
By Anna Gora December 27, 2023
By Anna Gora December 26, 2023
By Anna Gora December 25, 2023
By Emily Cooke December 23, 2023
By Victoria Atkinson December 22, 2023
By Anna Gora December 16, 2023
By Anna Gora December 15, 2023
By Anna Gora November 09, 2023
By Donavyn Coffey November 06, 2023
By Anna Gora October 31, 2023
By Anna Gora October 26, 2023
- 2 Error-corrected qubits 800 times more reliable after breakthrough, paving the way for 'next level' of quantum computing
- 3 Early humans lived on 'Persian plateau' for 20,000 years after leaving Africa, study suggests
- 4 1,700-year-old Roman fort discovered in Germany was built to keep out barbarians
- 5 Why NASA is launching 3 rockets into the solar eclipse next week
- 2 Early humans lived on 'Persian plateau' for 20,000 years after leaving Africa, study suggests
- 3 'It's had 1.1 billion years to accumulate': Helium reservoir in Minnesota has 'mind-bogglingly large' concentrations
- 4 Bite from toilet rat hospitalizes man in Canada
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
- What is Motherboard?
- Fifth Generation of Computers
- Computer Memory
- How to Add Audio to Powerpoint Presentation
- Different Types of Websites
- Computer Hardware
- Creating Bullet Lists in MS Word
- Text Decoration in MS Word
- Add a Drop Cap in MS Word
- Creating New Styles in MS Word
- Delete Text in Microsoft Word
- Moving Text in Microsoft Word
- Change Page Orientation in MS Word
- What is Internet? Definition, Uses, Working, Advantages and Disadvantages
- What is an Email?
- How to Open a Website using the Web Address?
- Change Paper Size in MS Word
- Change Text Font in Microsoft Word
- How to add Filters in MS Excel?
History of Computers
Before computers were developed people used sticks, stones, and bones as counting tools. As technology advanced and the human mind improved with time more computing devices were developed like Abacus, Napier’s Bones, etc. These devices were used as computers for performing mathematical computations but not very complex ones.
Some of the popular computing devices are described below, starting from the oldest to the latest or most advanced technology developed:
Around 4000 years ago, the Chinese invented the Abacus, and it is believed to be the first computer. The history of computers begins with the birth of the abacus.
Structure: Abacus is basically a wooden rack that has metal rods with beads mounted on them.
Working of abacus: In the abacus, the beads were moved by the abacus operator according to some rules to perform arithmetic calculations. In some countries like China, Russia, and Japan, the abacus is still used by their people.
Napier’s Bones
Napier’s Bones was a manually operated calculating device and as the name indicates, it was invented by John Napier. In this device, he used 9 different ivory strips (bones) marked with numbers to multiply and divide for calculation. It was also the first machine to use the decimal point system for calculation.
It is also called an Arithmetic Machine or Adding Machine. A French mathematician-philosopher Blaise Pascal invented this between 1642 and 1644. It was the first mechanical and automatic calculator. It is invented by Pascal to help his father, a tax accountant in his work or calculation. It could perform addition and subtraction in quick time. It was basically a wooden box with a series of gears and wheels. It is worked by rotating wheel like when a wheel is rotated one revolution, it rotates the neighbouring wheel and a series of windows is given on the top of the wheels to read the totals.
Stepped Reckoner or Leibniz wheel
A German mathematician-philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz in 1673 developed this device by improving Pascal’s invention to develop this machine. It was basically a digital mechanical calculator, and it was called the stepped reckoner as it was made of fluted drums instead of gears (used in the previous model of Pascaline).
Difference Engine
Charles Babbage who is also known as the “Father of Modern Computer” designed the Difference Engine in the early 1820s. Difference Engine was a mechanical computer which is capable of performing simple calculations. It works with help of steam as it was a steam-driven calculating machine, and it was designed to solve tables of numbers like logarithm tables.
Analytical Engine
Again in 1830 Charles Babbage developed another calculating machine which was Analytical Engine. Analytical Engine was a mechanical computer that used punch cards as input. It was capable of performing or solving any mathematical problem and storing information as a permanent memory (storage).
Tabulating Machine
Herman Hollerith, an American statistician invented this machine in the year 1890. Tabulating Machine was a mechanical tabulator that was based on punch cards. It was capable of tabulating statistics and record or sort data or information. This machine was used by U.S. Census in the year 1890. Hollerith’s Tabulating Machine Company was started by Hollerith and this company later became International Business Machine (IBM) in the year 1924.
Differential Analyzer
Differential Analyzer was the first electronic computer introduced in the year 1930 in the United States. It was basically an analog device that was invented by Vannevar Bush. This machine consists of vacuum tubes to switch electrical signals to perform calculations. It was capable of doing 25 calculations in a few minutes.
In the year 1937, major changes began in the history of computers when Howard Aiken planned to develop a machine that could perform large calculations or calculations involving large numbers. In the year 1944, Mark I computer was built as a partnership between IBM and Harvard. It was also the first programmable digital computer marking a new era in the computer world.
Generations of Computers
First Generation Computers
In the period of the year 1940-1956, it was referred to as the period of the first generation of computers. These machines are slow, huge, and expensive. In this generation of computers, vacuum tubes were used as the basic components of CPU and memory. Also, they were mainly dependent on the batch operating systems and punch cards. Magnetic tape and paper tape were used as output and input devices. For example ENIAC, UNIVAC-1, EDVAC, etc.
Second Generation Computers
In the period of the year, 1957-1963 was referred to as the period of the second generation of computers. It was the time of the transistor computers. In the second generation of computers, transistors (which were cheap in cost) are used. Transistors are also compact and consume less power. Transistor computers are faster than first-generation computers. For primary memory, magnetic cores were used, and for secondary memory magnetic disc and tapes for storage purposes. In second-generation computers, COBOL and FORTRAN are used as Assembly language and programming languages, and Batch processing and multiprogramming operating systems were used in these computers.
For example IBM 1620, IBM 7094, CDC 1604, CDC 3600, etc.
Third Generation Computers
In the third generation of computers, integrated circuits (ICs) were used instead of transistors(in the second generation). A single IC consists of many transistors which increased the power of a computer and also reduced the cost. The third generation computers are more reliable, efficient, and smaller in size. It used remote processing, time-sharing, and multiprogramming as operating systems. FORTRON-II TO IV, COBOL, and PASCAL PL/1 were used which are high-level programming languages.
For example IBM-360 series, Honeywell-6000 series, IBM-370/168, etc.
Fourth Generation Computers
The period of 1971-1980 was mainly the time of fourth generation computers. It used VLSI(Very Large Scale Integrated) circuits. VLSI is a chip containing millions of transistors and other circuit elements and because of these chips, the computers of this generation are more compact, powerful, fast, and affordable(low in cost). Real-time, time-sharing and distributed operating system are used by these computers. C and C++ are used as the programming languages in this generation of computers.
For example STAR 1000, PDP 11, CRAY-1, CRAY-X-MP, etc.
Fifth Generation Computers
From 1980 – to till date these computers are used. The ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology is used in fifth-generation computers instead of the VLSI technology of fourth-generation computers. Microprocessor chips with ten million electronic components are used in these computers. Parallel processing hardware and AI (Artificial Intelligence) software are also used in fifth-generation computers. The programming languages like C, C++, Java, .Net, etc. are used.
For example Desktop, Laptop, NoteBook, UltraBook, etc.
Sample Questions
Let us now see some sample questions on the History of computers:
Question 1: Arithmetic Machine or Adding Machine is used between ___________ years.
a. 1642 and 1644
b. Around 4000 years ago
c. 1946 – 1956
d. None of the above
Solution:
a. 1642 and 1644 Explanation: Pascaline is also called as Arithmetic Machine or Adding Machine. A French mathematician-philosopher Blaise Pascal invented this between 1642 and 1644.
Question 2: Who designed the Difference Engine?
a. Blaise Pascal
b. Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
c. Vannevar Bush
d. Charles Babbage
Solution:
d. Charles Babbage Explanation: Charles Babbage who is also known as “Father of Modern Computer” designed the Difference Engine in the early 1820s.
Question 3: In second generation computers _______________ are used as Assembly language and programming languages.
a. C and C++.
b. COBOL and FORTRAN
c. C and .NET
d. None of the above.
b. COBOL and FORTRAN Explanation: In second generation computers COBOL and FORTRAN are used as Assembly language and programming languages, and Batch processing and multiprogramming operating systems were used in these computers.
Question 4: ENIAC and UNIVAC-1 are examples of which generation of computers?
a. First generation of computers.
b. Second generation of computers.
c. Third generation of computers.
d. Fourth generation of computers.
a. First-generation of computers. Explanation: ENIAC, UNIVAC-1, EDVAC, etc. are examples of the first generation of computers.
Question 5: The ______________ technology is used in fifth generation computers .
a. ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration)
b. VLSI( very large scale integrated)
c. vacuum tubes
d. All of the above
a. ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) Explanation: From 1980 -to till date these computers are used. The ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology is used in fifth generation computers.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- School Learning
- School Programming
- 10 Best Todoist Alternatives in 2024 (Free)
- How to Get Spotify Premium Free Forever on iOS/Android
- Yahoo Acquires Instagram Co-Founders' AI News Platform Artifact
- OpenAI Introduces DALL-E Editor Interface
- Top 10 R Project Ideas for Beginners in 2024
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- Random article
- Teaching guide
- Privacy & cookies

A brief history of computers
by Chris Woodford . Last updated: January 19, 2023.
C omputers truly came into their own as great inventions in the last two decades of the 20th century. But their history stretches back more than 2500 years to the abacus: a simple calculator made from beads and wires, which is still used in some parts of the world today. The difference between an ancient abacus and a modern computer seems vast, but the principle—making repeated calculations more quickly than the human brain—is exactly the same.
Read on to learn more about the history of computers—or take a look at our article on how computers work .
Photo: A model of one of the world's first computers (the Difference Engine invented by Charles Babbage) at the Computer History Museum in Mountain View, California, USA. Photo by Cory Doctorow published on Flickr in 2020 under a Creative Commons (CC BY-SA 2.0) licence.
Cogs and Calculators
It is a measure of the brilliance of the abacus, invented in the Middle East circa 500 BC, that it remained the fastest form of calculator until the middle of the 17th century. Then, in 1642, aged only 18, French scientist and philosopher Blaise Pascal (1623–1666) invented the first practical mechanical calculator , the Pascaline, to help his tax-collector father do his sums. The machine had a series of interlocking cogs ( gear wheels with teeth around their outer edges) that could add and subtract decimal numbers. Several decades later, in 1671, German mathematician and philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (1646–1716) came up with a similar but more advanced machine. Instead of using cogs, it had a "stepped drum" (a cylinder with teeth of increasing length around its edge), an innovation that survived in mechanical calculators for 300 hundred years. The Leibniz machine could do much more than Pascal's: as well as adding and subtracting, it could multiply, divide, and work out square roots. Another pioneering feature was the first memory store or "register."
Apart from developing one of the world's earliest mechanical calculators, Leibniz is remembered for another important contribution to computing: he was the man who invented binary code, a way of representing any decimal number using only the two digits zero and one. Although Leibniz made no use of binary in his own calculator, it set others thinking. In 1854, a little over a century after Leibniz had died, Englishman George Boole (1815–1864) used the idea to invent a new branch of mathematics called Boolean algebra. [1] In modern computers, binary code and Boolean algebra allow computers to make simple decisions by comparing long strings of zeros and ones. But, in the 19th century, these ideas were still far ahead of their time. It would take another 50–100 years for mathematicians and computer scientists to figure out how to use them (find out more in our articles about calculators and logic gates ).
Artwork: Pascaline: Two details of Blaise Pascal's 17th-century calculator. Left: The "user interface": the part where you dial in numbers you want to calculate. Right: The internal gear mechanism. Picture courtesy of US Library of Congress .
Engines of Calculation
Neither the abacus, nor the mechanical calculators constructed by Pascal and Leibniz really qualified as computers. A calculator is a device that makes it quicker and easier for people to do sums—but it needs a human operator. A computer, on the other hand, is a machine that can operate automatically, without any human help, by following a series of stored instructions called a program (a kind of mathematical recipe). Calculators evolved into computers when people devised ways of making entirely automatic, programmable calculators.
Photo: Punched cards: Herman Hollerith perfected the way of using punched cards and paper tape to store information and feed it into a machine. Here's a drawing from his 1889 patent Art of Compiling Statistics (US Patent#395,782), showing how a strip of paper (yellow) is punched with different patterns of holes (orange) that correspond to statistics gathered about people in the US census. Picture courtesy of US Patent and Trademark Office.
The first person to attempt this was a rather obsessive, notoriously grumpy English mathematician named Charles Babbage (1791–1871). Many regard Babbage as the "father of the computer" because his machines had an input (a way of feeding in numbers), a memory (something to store these numbers while complex calculations were taking place), a processor (the number-cruncher that carried out the calculations), and an output (a printing mechanism)—the same basic components shared by all modern computers. During his lifetime, Babbage never completed a single one of the hugely ambitious machines that he tried to build. That was no surprise. Each of his programmable "engines" was designed to use tens of thousands of precision-made gears. It was like a pocket watch scaled up to the size of a steam engine , a Pascal or Leibniz machine magnified a thousand-fold in dimensions, ambition, and complexity. For a time, the British government financed Babbage—to the tune of £17,000, then an enormous sum. But when Babbage pressed the government for more money to build an even more advanced machine, they lost patience and pulled out. Babbage was more fortunate in receiving help from Augusta Ada Byron (1815–1852), Countess of Lovelace, daughter of the poet Lord Byron. An enthusiastic mathematician, she helped to refine Babbage's ideas for making his machine programmable—and this is why she is still, sometimes, referred to as the world's first computer programmer. [2] Little of Babbage's work survived after his death. But when, by chance, his notebooks were rediscovered in the 1930s, computer scientists finally appreciated the brilliance of his ideas. Unfortunately, by then, most of these ideas had already been reinvented by others.
Artwork: Charles Babbage (1791–1871). Picture from The Illustrated London News, 1871, courtesy of US Library of Congress .
Babbage had intended that his machine would take the drudgery out of repetitive calculations. Originally, he imagined it would be used by the army to compile the tables that helped their gunners to fire cannons more accurately. Toward the end of the 19th century, other inventors were more successful in their effort to construct "engines" of calculation. American statistician Herman Hollerith (1860–1929) built one of the world's first practical calculating machines, which he called a tabulator, to help compile census data. Then, as now, a census was taken each decade but, by the 1880s, the population of the United States had grown so much through immigration that a full-scale analysis of the data by hand was taking seven and a half years. The statisticians soon figured out that, if trends continued, they would run out of time to compile one census before the next one fell due. Fortunately, Hollerith's tabulator was an amazing success: it tallied the entire census in only six weeks and completed the full analysis in just two and a half years. Soon afterward, Hollerith realized his machine had other applications, so he set up the Tabulating Machine Company in 1896 to manufacture it commercially. A few years later, it changed its name to the Computing-Tabulating-Recording (C-T-R) company and then, in 1924, acquired its present name: International Business Machines (IBM).
Photo: Keeping count: Herman Hollerith's late-19th-century census machine (blue, left) could process 12 separate bits of statistical data each minute. Its compact 1940 replacement (red, right), invented by Eugene M. La Boiteaux of the Census Bureau, could work almost five times faster. Photo by Harris & Ewing courtesy of US Library of Congress .
Bush and the bomb
Photo: Dr Vannevar Bush (1890–1974). Picture by Harris & Ewing, courtesy of US Library of Congress .
The history of computing remembers colorful characters like Babbage, but others who played important—if supporting—roles are less well known. At the time when C-T-R was becoming IBM, the world's most powerful calculators were being developed by US government scientist Vannevar Bush (1890–1974). In 1925, Bush made the first of a series of unwieldy contraptions with equally cumbersome names: the New Recording Product Integraph Multiplier. Later, he built a machine called the Differential Analyzer, which used gears, belts, levers, and shafts to represent numbers and carry out calculations in a very physical way, like a gigantic mechanical slide rule. Bush's ultimate calculator was an improved machine named the Rockefeller Differential Analyzer, assembled in 1935 from 320 km (200 miles) of wire and 150 electric motors . Machines like these were known as analog calculators—analog because they stored numbers in a physical form (as so many turns on a wheel or twists of a belt) rather than as digits. Although they could carry out incredibly complex calculations, it took several days of wheel cranking and belt turning before the results finally emerged.
Impressive machines like the Differential Analyzer were only one of several outstanding contributions Bush made to 20th-century technology. Another came as the teacher of Claude Shannon (1916–2001), a brilliant mathematician who figured out how electrical circuits could be linked together to process binary code with Boolean algebra (a way of comparing binary numbers using logic) and thus make simple decisions. During World War II, President Franklin D. Roosevelt appointed Bush chairman first of the US National Defense Research Committee and then director of the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD). In this capacity, he was in charge of the Manhattan Project, the secret $2-billion initiative that led to the creation of the atomic bomb. One of Bush's final wartime contributions was to sketch out, in 1945, an idea for a memory-storing and sharing device called Memex that would later inspire Tim Berners-Lee to invent the World Wide Web . [3] Few outside the world of computing remember Vannevar Bush today—but what a legacy! As a father of the digital computer, an overseer of the atom bomb, and an inspiration for the Web, Bush played a pivotal role in three of the 20th-century's most far-reaching technologies.
Photo: "A gigantic mechanical slide rule": A differential analyzer pictured in 1938. Picture courtesy of and © University of Cambridge Computer Laboratory, published with permission via Wikimedia Commons under a Creative Commons (CC BY 2.0) licence.
Turing—tested
The first modern computers.
The World War II years were a crucial period in the history of computing, when powerful gargantuan computers began to appear. Just before the outbreak of the war, in 1938, German engineer Konrad Zuse (1910–1995) constructed his Z1, the world's first programmable binary computer, in his parents' living room. [4] The following year, American physicist John Atanasoff (1903–1995) and his assistant, electrical engineer Clifford Berry (1918–1963), built a more elaborate binary machine that they named the Atanasoff Berry Computer (ABC). It was a great advance—1000 times more accurate than Bush's Differential Analyzer. These were the first machines that used electrical switches to store numbers: when a switch was "off", it stored the number zero; flipped over to its other, "on", position, it stored the number one. Hundreds or thousands of switches could thus store a great many binary digits (although binary is much less efficient in this respect than decimal, since it takes up to eight binary digits to store a three-digit decimal number). These machines were digital computers: unlike analog machines, which stored numbers using the positions of wheels and rods, they stored numbers as digits.
The first large-scale digital computer of this kind appeared in 1944 at Harvard University, built by mathematician Howard Aiken (1900–1973). Sponsored by IBM, it was variously known as the Harvard Mark I or the IBM Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator (ASCC). A giant of a machine, stretching 15m (50ft) in length, it was like a huge mechanical calculator built into a wall. It must have sounded impressive, because it stored and processed numbers using "clickety-clack" electromagnetic relays (electrically operated magnets that automatically switched lines in telephone exchanges)—no fewer than 3304 of them. Impressive they may have been, but relays suffered from several problems: they were large (that's why the Harvard Mark I had to be so big); they needed quite hefty pulses of power to make them switch; and they were slow (it took time for a relay to flip from "off" to "on" or from 0 to 1).
Photo: An analog computer being used in military research in 1949. Picture courtesy of NASA on the Commons (where you can download a larger version.
Most of the machines developed around this time were intended for military purposes. Like Babbage's never-built mechanical engines, they were designed to calculate artillery firing tables and chew through the other complex chores that were then the lot of military mathematicians. During World War II, the military co-opted thousands of the best scientific minds: recognizing that science would win the war, Vannevar Bush's Office of Scientific Research and Development employed 10,000 scientists from the United States alone. Things were very different in Germany. When Konrad Zuse offered to build his Z2 computer to help the army, they couldn't see the need—and turned him down.
On the Allied side, great minds began to make great breakthroughs. In 1943, a team of mathematicians based at Bletchley Park near London, England (including Alan Turing) built a computer called Colossus to help them crack secret German codes. Colossus was the first fully electronic computer. Instead of relays, it used a better form of switch known as a vacuum tube (also known, especially in Britain, as a valve). The vacuum tube, each one about as big as a person's thumb (earlier ones were very much bigger) and glowing red hot like a tiny electric light bulb, had been invented in 1906 by Lee de Forest (1873–1961), who named it the Audion. This breakthrough earned de Forest his nickname as "the father of radio" because their first major use was in radio receivers , where they amplified weak incoming signals so people could hear them more clearly. [5] In computers such as the ABC and Colossus, vacuum tubes found an alternative use as faster and more compact switches.
Just like the codes it was trying to crack, Colossus was top-secret and its existence wasn't confirmed until after the war ended. As far as most people were concerned, vacuum tubes were pioneered by a more visible computer that appeared in 1946: the Electronic Numerical Integrator And Calculator (ENIAC). The ENIAC's inventors, two scientists from the University of Pennsylvania, John Mauchly (1907–1980) and J. Presper Eckert (1919–1995), were originally inspired by Bush's Differential Analyzer; years later Eckert recalled that ENIAC was the "descendant of Dr Bush's machine." But the machine they constructed was far more ambitious. It contained nearly 18,000 vacuum tubes (nine times more than Colossus), was around 24 m (80 ft) long, and weighed almost 30 tons. ENIAC is generally recognized as the world's first fully electronic, general-purpose, digital computer. Colossus might have qualified for this title too, but it was designed purely for one job (code-breaking); since it couldn't store a program, it couldn't easily be reprogrammed to do other things.
Photo: Sir Maurice Wilkes (left), his collaborator William Renwick, and the early EDSAC-1 electronic computer they built in Cambridge, pictured around 1947/8. Picture courtesy of and © University of Cambridge Computer Laboratory, published with permission via Wikimedia Commons under a Creative Commons (CC BY 2.0) licence.
ENIAC was just the beginning. Its two inventors formed the Eckert Mauchly Computer Corporation in the late 1940s. Working with a brilliant Hungarian mathematician, John von Neumann (1903–1957), who was based at Princeton University, they then designed a better machine called EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer). In a key piece of work, von Neumann helped to define how the machine stored and processed its programs, laying the foundations for how all modern computers operate. [6] After EDVAC, Eckert and Mauchly developed UNIVAC 1 (UNIVersal Automatic Computer) in 1951. They were helped in this task by a young, largely unknown American mathematician and Naval reserve named Grace Murray Hopper (1906–1992), who had originally been employed by Howard Aiken on the Harvard Mark I. Like Herman Hollerith's tabulator over 50 years before, UNIVAC 1 was used for processing data from the US census. It was then manufactured for other users—and became the world's first large-scale commercial computer.
Machines like Colossus, the ENIAC, and the Harvard Mark I compete for significance and recognition in the minds of computer historians. Which one was truly the first great modern computer? All of them and none: these—and several other important machines—evolved our idea of the modern electronic computer during the key period between the late 1930s and the early 1950s. Among those other machines were pioneering computers put together by English academics, notably the Manchester/Ferranti Mark I, built at Manchester University by Frederic Williams (1911–1977) and Thomas Kilburn (1921–2001), and the EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator), built by Maurice Wilkes (1913–2010) at Cambridge University. [7]
Photo: Control panel of the UNIVAC 1, the world's first large-scale commercial computer. Photo by Cory Doctorow published on Flickr in 2020 under a Creative Commons (CC BY-SA 2.0) licence.
The microelectronic revolution
Vacuum tubes were a considerable advance on relay switches, but machines like the ENIAC were notoriously unreliable. The modern term for a problem that holds up a computer program is a "bug." Popular legend has it that this word entered the vocabulary of computer programmers sometime in the 1950s when moths, attracted by the glowing lights of vacuum tubes, flew inside machines like the ENIAC, caused a short circuit, and brought work to a juddering halt. But there were other problems with vacuum tubes too. They consumed enormous amounts of power: the ENIAC used about 2000 times as much electricity as a modern laptop. And they took up huge amounts of space. Military needs were driving the development of machines like the ENIAC, but the sheer size of vacuum tubes had now become a real problem. ABC had used 300 vacuum tubes, Colossus had 2000, and the ENIAC had 18,000. The ENIAC's designers had boasted that its calculating speed was "at least 500 times as great as that of any other existing computing machine." But developing computers that were an order of magnitude more powerful still would have needed hundreds of thousands or even millions of vacuum tubes—which would have been far too costly, unwieldy, and unreliable. So a new technology was urgently required.
The solution appeared in 1947 thanks to three physicists working at Bell Telephone Laboratories (Bell Labs). John Bardeen (1908–1991), Walter Brattain (1902–1987), and William Shockley (1910–1989) were then helping Bell to develop new technology for the American public telephone system, so the electrical signals that carried phone calls could be amplified more easily and carried further. Shockley, who was leading the team, believed he could use semiconductors (materials such as germanium and silicon that allow electricity to flow through them only when they've been treated in special ways) to make a better form of amplifier than the vacuum tube. When his early experiments failed, he set Bardeen and Brattain to work on the task for him. Eventually, in December 1947, they created a new form of amplifier that became known as the point-contact transistor. Bell Labs credited Bardeen and Brattain with the transistor and awarded them a patent. This enraged Shockley and prompted him to invent an even better design, the junction transistor, which has formed the basis of most transistors ever since.
Like vacuum tubes, transistors could be used as amplifiers or as switches. But they had several major advantages. They were a fraction the size of vacuum tubes (typically about as big as a pea), used no power at all unless they were in operation, and were virtually 100 percent reliable. The transistor was one of the most important breakthroughs in the history of computing and it earned its inventors the world's greatest science prize, the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics . By that time, however, the three men had already gone their separate ways. John Bardeen had begun pioneering research into superconductivity , which would earn him a second Nobel Prize in 1972. Walter Brattain moved to another part of Bell Labs.
William Shockley decided to stick with the transistor, eventually forming his own corporation to develop it further. His decision would have extraordinary consequences for the computer industry. With a small amount of capital, Shockley set about hiring the best brains he could find in American universities, including young electrical engineer Robert Noyce (1927–1990) and research chemist Gordon Moore (1929–). It wasn't long before Shockley's idiosyncratic and bullying management style upset his workers. In 1956, eight of them—including Noyce and Moore—left Shockley Transistor to found a company of their own, Fairchild Semiconductor, just down the road. Thus began the growth of "Silicon Valley," the part of California centered on Palo Alto, where many of the world's leading computer and electronics companies have been based ever since. [8]
It was in Fairchild's California building that the next breakthrough occurred—although, somewhat curiously, it also happened at exactly the same time in the Dallas laboratories of Texas Instruments. In Dallas, a young engineer from Kansas named Jack Kilby (1923–2005) was considering how to improve the transistor. Although transistors were a great advance on vacuum tubes, one key problem remained. Machines that used thousands of transistors still had to be hand wired to connect all these components together. That process was laborious, costly, and error prone. Wouldn't it be better, Kilby reflected, if many transistors could be made in a single package? This prompted him to invent the "monolithic" integrated circuit (IC) , a collection of transistors and other components that could be manufactured all at once, in a block, on the surface of a semiconductor. Kilby's invention was another step forward, but it also had a drawback: the components in his integrated circuit still had to be connected by hand. While Kilby was making his breakthrough in Dallas, unknown to him, Robert Noyce was perfecting almost exactly the same idea at Fairchild in California. Noyce went one better, however: he found a way to include the connections between components in an integrated circuit, thus automating the entire process.
Photo: An integrated circuit from the 1980s. This is an EPROM chip (effectively a forerunner of flash memory , which you could only erase with a blast of ultraviolet light).
Mainframes, minis, and micros
Photo: An IBM 704 mainframe pictured at NASA in 1958. Designed by Gene Amdahl, this scientific number cruncher was the successor to the 701 and helped pave the way to arguably the most important IBM computer of all time, the System/360, which Amdahl also designed. Photo courtesy of NASA .
Photo: The control panel of DEC's classic 1965 PDP-8 minicomputer. Photo by Cory Doctorow published on Flickr in 2020 under a Creative Commons (CC BY-SA 2.0) licence.
Integrated circuits, as much as transistors, helped to shrink computers during the 1960s. In 1943, IBM boss Thomas Watson had reputedly quipped: "I think there is a world market for about five computers." Just two decades later, the company and its competitors had installed around 25,000 large computer systems across the United States. As the 1960s wore on, integrated circuits became increasingly sophisticated and compact. Soon, engineers were speaking of large-scale integration (LSI), in which hundreds of components could be crammed onto a single chip, and then very large-scale integrated (VLSI), when the same chip could contain thousands of components.
The logical conclusion of all this miniaturization was that, someday, someone would be able to squeeze an entire computer onto a chip. In 1968, Robert Noyce and Gordon Moore had left Fairchild to establish a new company of their own. With integration very much in their minds, they called it Integrated Electronics or Intel for short. Originally they had planned to make memory chips, but when the company landed an order to make chips for a range of pocket calculators, history headed in a different direction. A couple of their engineers, Federico Faggin (1941–) and Marcian Edward (Ted) Hoff (1937–), realized that instead of making a range of specialist chips for a range of calculators, they could make a universal chip that could be programmed to work in them all. Thus was born the general-purpose, single chip computer or microprocessor—and that brought about the next phase of the computer revolution.
Personal computers
By 1974, Intel had launched a popular microprocessor known as the 8080 and computer hobbyists were soon building home computers around it. The first was the MITS Altair 8800, built by Ed Roberts . With its front panel covered in red LED lights and toggle switches, it was a far cry from modern PCs and laptops. Even so, it sold by the thousand and earned Roberts a fortune. The Altair inspired a Californian electronics wizard name Steve Wozniak (1950–) to develop a computer of his own. "Woz" is often described as the hacker's "hacker"—a technically brilliant and highly creative engineer who pushed the boundaries of computing largely for his own amusement. In the mid-1970s, he was working at the Hewlett-Packard computer company in California, and spending his free time tinkering away as a member of the Homebrew Computer Club in the Bay Area.
After seeing the Altair, Woz used a 6502 microprocessor (made by an Intel rival, Mos Technology) to build a better home computer of his own: the Apple I. When he showed off his machine to his colleagues at the club, they all wanted one too. One of his friends, Steve Jobs (1955–2011), persuaded Woz that they should go into business making the machine. Woz agreed so, famously, they set up Apple Computer Corporation in a garage belonging to Jobs' parents. After selling 175 of the Apple I for the devilish price of $666.66, Woz built a much better machine called the Apple ][ (pronounced "Apple Two"). While the Altair 8800 looked like something out of a science lab, and the Apple I was little more than a bare circuit board, the Apple ][ took its inspiration from such things as Sony televisions and stereos: it had a neat and friendly looking cream plastic case. Launched in April 1977, it was the world's first easy-to-use home "microcomputer." Soon home users, schools, and small businesses were buying the machine in their tens of thousands—at $1298 a time. Two things turned the Apple ][ into a really credible machine for small firms: a disk drive unit, launched in 1978, which made it easy to store data; and a spreadsheet program called VisiCalc, which gave Apple users the ability to analyze that data. In just two and a half years, Apple sold around 50,000 of the machine, quickly accelerating out of Jobs' garage to become one of the world's biggest companies. Dozens of other microcomputers were launched around this time, including the TRS-80 from Radio Shack (Tandy in the UK) and the Commodore PET. [9]
Apple's success selling to businesses came as a great shock to IBM and the other big companies that dominated the computer industry. It didn't take a VisiCalc spreadsheet to figure out that, if the trend continued, upstarts like Apple would undermine IBM's immensely lucrative business market selling "Big Blue" computers. In 1980, IBM finally realized it had to do something and launched a highly streamlined project to save its business. One year later, it released the IBM Personal Computer (PC), based on an Intel 8080 microprocessor, which rapidly reversed the company's fortunes and stole the market back from Apple.
The PC was successful essentially for one reason. All the dozens of microcomputers that had been launched in the 1970s—including the Apple ][—were incompatible. All used different hardware and worked in different ways. Most were programmed using a simple, English-like language called BASIC, but each one used its own flavor of BASIC, which was tied closely to the machine's hardware design. As a result, programs written for one machine would generally not run on another one without a great deal of conversion. Companies who wrote software professionally typically wrote it just for one machine and, consequently, there was no software industry to speak of.
In 1976, Gary Kildall (1942–1994), a teacher and computer scientist, and one of the founders of the Homebrew Computer Club, had figured out a solution to this problem. Kildall wrote an operating system (a computer's fundamental control software) called CP/M that acted as an intermediary between the user's programs and the machine's hardware. With a stroke of genius, Kildall realized that all he had to do was rewrite CP/M so it worked on each different machine. Then all those machines could run identical user programs—without any modification at all—inside CP/M. That would make all the different microcomputers compatible at a stroke. By the early 1980s, Kildall had become a multimillionaire through the success of his invention: the first personal computer operating system. Naturally, when IBM was developing its personal computer, it approached him hoping to put CP/M on its own machine. Legend has it that Kildall was out flying his personal plane when IBM called, so missed out on one of the world's greatest deals. But the truth seems to have been that IBM wanted to buy CP/M outright for just $200,000, while Kildall recognized his product was worth millions more and refused to sell. Instead, IBM turned to a young programmer named Bill Gates (1955–). His then tiny company, Microsoft, rapidly put together an operating system called DOS, based on a product called QDOS (Quick and Dirty Operating System), which they acquired from Seattle Computer Products. Some believe Microsoft and IBM cheated Kildall out of his place in computer history; Kildall himself accused them of copying his ideas. Others think Gates was simply the shrewder businessman. Either way, the IBM PC, powered by Microsoft's operating system, was a runaway success.
Yet IBM's victory was short-lived. Cannily, Bill Gates had sold IBM the rights to one flavor of DOS (PC-DOS) and retained the rights to a very similar version (MS-DOS) for his own use. When other computer manufacturers, notably Compaq and Dell, starting making IBM-compatible (or "cloned") hardware, they too came to Gates for the software. IBM charged a premium for machines that carried its badge, but consumers soon realized that PCs were commodities: they contained almost identical components—an Intel microprocessor, for example—no matter whose name they had on the case. As IBM lost market share, the ultimate victors were Microsoft and Intel, who were soon supplying the software and hardware for almost every PC on the planet. Apple, IBM, and Kildall made a great deal of money—but all failed to capitalize decisively on their early success. [10]
Photo: Personal computers threatened companies making large "mainframes" like this one. Picture courtesy of NASA on the Commons (where you can download a larger version).
The user revolution
Fortunately for Apple, it had another great idea. One of the Apple II's strongest suits was its sheer "user-friendliness." For Steve Jobs, developing truly easy-to-use computers became a personal mission in the early 1980s. What truly inspired him was a visit to PARC (Palo Alto Research Center), a cutting-edge computer laboratory then run as a division of the Xerox Corporation. Xerox had started developing computers in the early 1970s, believing they would make paper (and the highly lucrative photocopiers Xerox made) obsolete. One of PARC's research projects was an advanced $40,000 computer called the Xerox Alto. Unlike most microcomputers launched in the 1970s, which were programmed by typing in text commands, the Alto had a desktop-like screen with little picture icons that could be moved around with a mouse: it was the very first graphical user interface (GUI, pronounced "gooey")—an idea conceived by Alan Kay (1940–) and now used in virtually every modern computer. The Alto borrowed some of its ideas, including the mouse , from 1960s computer pioneer Douglas Engelbart (1925–2013).
Photo: During the 1980s, computers started to converge on the same basic "look and feel," largely inspired by the work of pioneers like Alan Kay and Douglas Engelbart. Photographs in the Carol M. Highsmith Archive, courtesy of US Library of Congress , Prints and Photographs Division.
Back at Apple, Jobs launched his own version of the Alto project to develop an easy-to-use computer called PITS (Person In The Street). This machine became the Apple Lisa, launched in January 1983—the first widely available computer with a GUI desktop. With a retail price of $10,000, over three times the cost of an IBM PC, the Lisa was a commercial flop. But it paved the way for a better, cheaper machine called the Macintosh that Jobs unveiled a year later, in January 1984. With its memorable launch ad for the Macintosh inspired by George Orwell's novel 1984 , and directed by Ridley Scott (director of the dystopic movie Blade Runner ), Apple took a swipe at IBM's monopoly, criticizing what it portrayed as the firm's domineering—even totalitarian—approach: Big Blue was really Big Brother. Apple's ad promised a very different vision: "On January 24, Apple Computer will introduce Macintosh. And you'll see why 1984 won't be like '1984'." The Macintosh was a critical success and helped to invent the new field of desktop publishing in the mid-1980s, yet it never came close to challenging IBM's position.
Ironically, Jobs' easy-to-use machine also helped Microsoft to dislodge IBM as the world's leading force in computing. When Bill Gates saw how the Macintosh worked, with its easy-to-use picture-icon desktop, he launched Windows, an upgraded version of his MS-DOS software. Apple saw this as blatant plagiarism and filed a $5.5 billion copyright lawsuit in 1988. Four years later, the case collapsed with Microsoft effectively securing the right to use the Macintosh "look and feel" in all present and future versions of Windows. Microsoft's Windows 95 system, launched three years later, had an easy-to-use, Macintosh-like desktop and MS-DOS running behind the scenes.
Photo: The IBM Blue Gene/P supercomputer at Argonne National Laboratory: one of the world's most powerful computers. Picture courtesy of Argonne National Laboratory published on Wikimedia Commons in 2009 under a Creative Commons Licence .
From nets to the Internet
Standardized PCs running standardized software brought a big benefit for businesses: computers could be linked together into networks to share information. At Xerox PARC in 1973, electrical engineer Bob Metcalfe (1946–) developed a new way of linking computers "through the ether" (empty space) that he called Ethernet. A few years later, Metcalfe left Xerox to form his own company, 3Com, to help companies realize "Metcalfe's Law": computers become useful the more closely connected they are to other people's computers. As more and more companies explored the power of local area networks (LANs), so, as the 1980s progressed, it became clear that there were great benefits to be gained by connecting computers over even greater distances—into so-called wide area networks (WANs).
Photo: Computers aren't what they used to be: they're much less noticeable because they're much more seamlessly integrated into everyday life. Some are "embedded" into household gadgets like coffee makers or televisions . Others travel round in our pockets in our smartphones—essentially pocket computers that we can program simply by downloading "apps" (applications).
Today, the best known WAN is the Internet —a global network of individual computers and LANs that links up hundreds of millions of people. The history of the Internet is another story, but it began in the 1960s when four American universities launched a project to connect their computer systems together to make the first WAN. Later, with funding for the Department of Defense, that network became a bigger project called ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network). In the mid-1980s, the US National Science Foundation (NSF) launched its own WAN called NSFNET. The convergence of all these networks produced what we now call the Internet later in the 1980s. Shortly afterward, the power of networking gave British computer programmer Tim Berners-Lee (1955–) his big idea: to combine the power of computer networks with the information-sharing idea Vannevar Bush had proposed in 1945. Thus, was born the World Wide Web —an easy way of sharing information over a computer network, which made possible the modern age of cloud computing (where anyone can access vast computing power over the Internet without having to worry about where or how their data is processed). It's Tim Berners-Lee's invention that brings you this potted history of computing today!
And now where?
If you liked this article..., find out more, on this site.
- Supercomputers : How do the world's most powerful computers work?
Other websites
There are lots of websites covering computer history. Here are a just a few favorites worth exploring!
- The Computer History Museum : The website of the world's biggest computer museum in California.
- The Computing Age : A BBC special report into computing past, present, and future.
- Charles Babbage at the London Science Museum : Lots of information about Babbage and his extraordinary engines. [Archived via the Wayback Machine]
- IBM History : Many fascinating online exhibits, as well as inside information about the part IBM inventors have played in wider computer history.
- Wikipedia History of Computing Hardware : covers similar ground to this page.
- Computer history images : A small but interesting selection of photos.
- Transistorized! : The history of the invention of the transistor from PBS.
- Intel Museum : The story of Intel's contributions to computing from the 1970s onward.
There are some superb computer history videos on YouTube and elsewhere; here are three good ones to start you off:
- The Difference Engine : A great introduction to Babbage's Difference Engine from Doron Swade, one of the world's leading Babbage experts.
- The ENIAC : A short Movietone news clip about the completion of the world's first programmable electronic computer.
- A tour of the Computer History Museum : Dag Spicer gives us a tour of the world's most famous computer museum, in California.
For older readers
For younger readers.
Text copyright © Chris Woodford 2006, 2023. All rights reserved. Full copyright notice and terms of use .
Rate this page
Tell your friends, cite this page, more to explore on our website....
- Get the book
- Send feedback

The Evolution of Computers: Key Resources (July 2013): General Histories and Reference Resources
- The Year of Alan Turing
General Histories and Reference Resources
- Human and Mechanical Computers
- Early Electronic Computers
- Covert Computing and Computer Security
- ARPANET, E-mail, and the World Wide Web
- The Personal Computing Revolution
- The Personalized Web, Mobile, and the Cloud
- Social Networks and Beyond
Works Cited
Numerous titles offer broad accounts of the fascinating history of computing, and more recent publications take the story up to the present. Ian Watson’s comprehensive history published in 2012, The Universal Machine: From the Dawn of Computing to Digital Consciousness , will be particularly appealing to general readers and undergraduate students for its accessible, engaging writing style and many illustrations. Two other notable works published in 2012 are Computing: A Concise History by Paul Ceruzzi (also author of the useful 2003 title, A History of Modern Computing ) and A Brief History of Computing by Gerard O’Regan. Ceruzzi, curator at the National Air and Space Museum, Smithsonian Institution, provides a readable and concise 155-page overview in his book, which is part of the “MIT Press Essential Knowledge” series; this work also contains ample references to the literature in a further reading section and a bibliography. O’Regan’s work offers an encompassing chronological survey, but also devotes chapters to the history of programming languages and software engineering. Also published in 2012 is Peter Bentley’s Digitized: The Science of Computers and How It Shapes Our World , which provides valuable historical coverage and in later chapters reports on the revolutionary developments in artificial intelligence and their impact on society.
Other informative, accessible general histories include Computer: A History of the Information Machine by Martin Campbell-Kelly and William Aspray; Computers: The Life Story of a Technology by Eric Swedin and David Ferro; and Histories of Computing by Michael Sean Mahoney. Mike Hally’s Electronic Brains: Stories from the Dawn of the Computer Age focuses on post-World War II developments, tracing the signal contributions of scientists from the United Kingdom, United States, Australia, and Russia. An excellent pictorial collection of computers is John Alderman and Mark Richards’s Core Memory: A Visual Survey of Vintage Computers Featuring Machines from the Computer History Museum .
The static nature of print reference materials is not the perfect format for the topic of computer innovation; these publications may show their age not just in technical information and jargon but also in a lack of coverage of more contemporary individuals and groups. Nevertheless, several works continue to have lasting value for their excellent and unique coverage. The two-volume Encyclopedia of Computers and Computer History , edited by Raúl Rojas, which was published in 2001, offers comprehensive coverage of historical topics in a convenient format, enhanced with useful bibliographic aids. More serious researchers will find Jeffrey Yost’s A Bibliographic Guide to Resources in Scientific Computing, 1945-1975 valuable for its annotations of earlier important titles and its special focus on the sciences; the volume’s four major parts cover the physical, cognitive, biological, and medical sciences. The Second Bibliographic Guide to the History of Computing, Computers, and the Information Processing Industry , compiled by James Cortada, published in 1996, will also be of value to researchers. For biographical coverage, Computer Pioneers by J. A. N. Lee features entries on well-known and lesser-known individuals, primarily those from the United States and the United Kingdom; however, coverage of female pioneers is limited. Lee also edited the International Biographical Dictionary of Computer Pioneers , which provides broader geographical coverage.
Related and more recent information may be found in several online resources such as the IEEE Global History Network: Computers and Information Processing . Sites featuring interactive time lines and interesting exhibits include the IBM Archives , and Revolution: The First 2000 Years of Computing by the Computer History Museum.
Focusing on women’s contributions to the field is “ Famous Women in Computer Science , available on the Anita Borg Institute website. This site includes nearly eighty short biographies with links to university and other organizational and related websites. A Pinterest board version of the awardees is also available. “ The ADA Project , named in honor of Ada Lovelace (1815-52), who wrote what is considered to be “the first ‘computer program.’” This site is largely based on the Famous Women in Computer Science website but also includes a time line.
In contrast to J. A. N. Lee’s International Biographical Dictionary of Computer Pioneers mentioned previously, the highly recommended Milestones in Computer Science and Information Technology by Edwin Reilly focuses more on technological aspects than individuals. However, this author did not find a more comprehensive one-volume reference resource than Reilly’s. Appendixes include a listing of cited references, classification of entries, “The Top Ten Consolidated Milestones,” and personal name, chronological, and general indexes.
- Second bibliographic guide to the history of computing, computers, and the information processing industry by James W. Cortada (editor) ISBN: 9780313295423 Publication Date: 1996
- << Previous: The Year of Alan Turing
- Next: Human and Mechanical Computers >>
- Last Updated: Jun 20, 2016 2:11 PM
- URL: https://ala-choice.libguides.com/c.php?g=457199
Browse Course Material
Course info.
- Dr. Slava Gerovitch
Departments
- Science, Technology, and Society
As Taught In
- Computer Science
- History of Science and Technology
- Modern History
Learning Resource Types
The history of computing, course meeting times.
Lectures: 1 session / week, 3 hours / session
Description
This course will focus on one particular aspect of the history of computing: the use of the computer as a scientific instrument. The electronic digital computer was invented to do science, and its applications range from physics to mathematics to biology to the humanities. What has been the impact of computing on the practice of science? Is the computer different from other scientific instruments? Is computer simulation a valid form of scientific experiment? Can computer models be viewed as surrogate theories? How does the computer change the way scientists approach the notions of proof, expertise, and discovery? No comprehensive history of scientific computing has yet been written. This seminar will examine scientific articles, participants’ memoirs, and works by historians, sociologists, and anthropologists of science to provide multiple perspectives on the use of computers in diverse fields of physical, biological, and social sciences and the humanities. We will explore how the computer transformed scientific practice, and how the culture of computing was influenced, in turn, by scientific applications.
Requirements
Students are expected to participate in class discussions by reading the assigned materials before class, thinking about the issues and historical patterns suggested in the readings, and relating these issues to their own personal experience. Students will submit a short (one page) reading response paper in the morning before each class. The papers are intended to provoke discussion, rather than give definitive answers. The instructor will provide tentative questions for response papers, but students are encouraged to raise their own questions. The response papers will serve as a basis for subsequent discussion in class.
Assignments for this course also include a final paper (10-15 pages; typed, double-spaced, with 1.25" margins). The final paper is due in class on Session 14. On that day, students will give brief presentations (5-10 min.) of their final papers. A proposal for the final paper (1-2 pages) is due in class on Session 9. It will receive the instructor’s feedback the following week. The proposal should include:
- the central question the final paper will address;
- the historical significance of this question and how it relates to discussions in class;
- a brief outline; and
- a tentative bibliography, including both primary and secondary sources.
The seminar meets only once a week. This means that attendance is particularly important. If you do need to miss class, you must obtain permission from the instructor in advance. Final grades will be determined as follows:

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare

- Computer Fundamentals
- Interview Q
Computer Components
Computer memory.
Computer Network
Computer Virus
Number systems, shortcut keys.
Interview Questions
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share

Learn Latest Tutorials
Transact-SQL
Reinforcement Learning
R Programming
React Native
Python Design Patterns
Python Pillow
Python Turtle
Preparation

Verbal Ability

Company Questions
Trending Technologies
Artificial Intelligence
Cloud Computing
Data Science
Machine Learning
B.Tech / MCA
Data Structures
Operating System
Compiler Design
Computer Organization
Discrete Mathematics
Ethical Hacking
Computer Graphics
Software Engineering
Web Technology
Cyber Security
C Programming
Control System
Data Mining
Data Warehouse


History Of Computers With Timeline [2023 Update]

It’s important to know the history of computers in order to have a good understanding of the field. Computers are one of the most important inventions in human history. Given how fast technology is evolving, you might not expect the history of computers to go back thousands of years. However, that’s exactly the case. But before we go back that far, let’s first understand what a computer actually is.
The First Computers In History
What is a computer.
A computer is simply a machine that follows a set of instructions in order to execute sequences of logical or arithmetic functions. However, when we think of modern computers , we don’t see them as just calculators performing functions. Yet, that’s exactly what they are at their core.
Every time you make a purchase on Amazon or post a picture on Instagram, your computer is executing instructions and processes a massive amount of binary. However, when we consider the definition of a computer, we realize that the history of computers goes far back.
When Was The First Computer Invented?
The history of computers goes back thousands of years with the first one being the abacus . In fact, the earliest abacus, referred to as the Sumerian abacus, dates back to roughly 2700 B.C. from the Mesopotamia region. However, Charles Babbage, the English mathematician and inventor is known as the “Father of Computers.” He created a steam-powered computer known as the Analytical Engine in 1837 which kickstarted computer history.
Digital Vs. Analog Computers
The very first computer, the abacus, is a digital computer because it deals in digits. Today’s computers are also digital because they compute everything using binary: 0’s and 1’s. However, most of the computers between the time of the abacus and modern transistor-based computers were in fact analog computers.
Analog computers, rather than calculating single digits, deal with more complex mathematics and functions. Rather than 1’s and 0’s, analog computers are more often represented by continuously varying quantities. The earliest analog computer, the Antikythera mechanism , is over 2000 years old. These ancient computers paved the way for modern transistor-based computers.
Brief History of Computers
The history of computers goes back as far as 2500 B.C. with the abacus. However, the modern history of computers begins with the Analytical Engine, a steam-powered computer designed in 1837 by English mathematician and “Father of Computers,” Charles Babbage. Yet, the invention of the transistor in 1947, the integrated circuit in 1958, and the microprocessor in 1971 are what made computers much smaller and faster.
In fact, the first personal computer was invented in 1971, the same year as the microprocessor. Then, the first laptop, the Osborne-1 was created a decade later in 1981. Apple and IBM joined the personal computer industry shortly thereafter, popularizing the home PC. Then, when the world wide web came online in 1989, which would eventually serve to connect nearly the whole world.
The 1990s was a booming decade for computer history. IBM produced the first smartphone in 1992 and the first smartwatch was released in 1998. Also, the first-ever quantum computer in history was up and functioning in 1998, if only for a few nanoseconds.
Turn of the Century Computers
The 2000s are the years of social media: the rise and fall of MySpace at the forefront. Facebook took off shortly after and would become one of the popular apps on the iPhone, which was first presented by the legend, Steve Jobs in 2007. It was a pocket-sized computer that was capable of greater computation than the computer which brought mankind to the Moon. The iPad would be released three years later in 2010.
The 2010s seem to have been the decade of Artificial Intelligence and Quantum Computing. Tesla AI-powered self-driving vehicles have made incredible progress toward full autonomy. An AI robot named Sophia was created in 2016 and even gained citizenship in Saudi Arabia in 2017. The world’s first reprogrammable quantum computer was created in 2016, bringing us closer to quantum supremacy.
Timeline Of Computer History
The first digital computer.
2700 B.C: The first digital computer, the Abacus is invented and used around the area of Mesopotamia. Yet, later iterations of the abacus appear in Egypt, Greece, and China, where they’re continually used for hundreds of years. The first abaci were likely used for addition and subtraction which must have been revolutionary for the time. However, the following iterations allowed for more complex calculations.
The First Analog Computer
200 B.C: The first analog computer, the Antikythera mechanism, is created. The Antikythera mechanism was found off the coast of the Greek island of Kythira from which the computer received its name. This find actually baffled most scientists because a computer this advanced wasn’t supposed to exist this long ago. This mechanical analog computer was used by ancient sailors to determine their position in the sea, based on their astrological position.

Binary Number System
1703: Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz developed the binary number system which is at the heart of modern computing. The binary number system is a way to convert a series of 0’s and 1’s into other numbers, letters, and characters. Everything we see on screen and interact with on our computers is converted into binary before the computer can process it. The magic of present-day computers is that they process binary extremely quickly.
First Programmable Loom
1801: Joseph Jacquard creates a punch-card programmable loom which greatly simplified the weaving process. This allowed those with fewer skills to weave more complicated patterns. However, many didn’t like the idea of simplifying and automating the process as it would displace weaving jobs at the time. Yet, technology persisted and the textile industry would eventually change for the better because of it.
First Steam-Driven Computer
1837: Charles Babbage designed the groundbreaking Analytical Engine . The analytical engine was the first major step toward modern computers. Although it was never actually built, its design embodied the major characteristics of modern computers. This included memory, a central processing unit, and the ability for input and output. Charles Babbage is commonly referred to as the “Father of Computers” for his work.
First Computer Algorithm
1843: Ada Lovelace , the daughter of Lord Byron, worked alongside Charles Babbage to design the analytical engine. However, shortly afterward, she developed the first-ever computer algorithm. She carefully considered what computers were capable of when developing her algorithm. The result was a solution to Bernoulli numbers , a significant mathematical advancement.
First U.S. Census Calculator
1890: Herman Hollerith created a tabulating machine to help calculate the U.S. census. The previous decade’s census took eight years to calculate but with the help of Hollerith’s tabulating machine, it took only six years. With the success of his tabulator, Hollerith then began his own company, the Hollerith Electrical Tabulating System. He applied this same technology to the areas of accounting and inventory.
The Turing Machine
1936: Alan Turing invented the Turing Machine and pushed the limits of what a computer could do at the time. A Turing Machine consists of a tape divided by squares that can contain a single digit, often binary digits, or nothing at all. It also consisted of a machine that could read each digit on the tape and change it. This might not sound like much, but computers to this day emulate this functionality of reading simple binary input and computing a logical output. This relatively simple machine enables the computation of any algorithm.
Turing set the standard for computers regarding them as “ Turing complete ” if they met the standards for simulating a Turing machine. Today’s computers are Turing complete because they simulate the same functionality of Turing machines, however with a much greater processing ability.
The Complex Number Calculator
1940: George Stibitz created the Complex Number Calculator for Bell Labs. It consisted of relays that could recognize the difference between ‘0’ and ‘1’ and therefore, could use binary as the base number system. The final version of the Complex Number Calculator used more than 400 relays and took about two years to create.
First Automatic Computer
1941: Konrad Zuse, a German Computer Scientist, invented the Z3 computer . Zuse’s Z3 was the first programmable fully automatic computer in history. It was much larger than the Complex number calculator and contained more than 2,500 relays. Since the Z3 computer didn’t demonstrate any advantage to the Germans during world war II, the government didn’t provide any funding for it and it was eventually destroyed in the war.
First Electric Digital Computer
1942: Professor John Vincent Atanasoff invented the Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC). The ABC was the first automatic electric digital computer in history. It contained over 300 vacuum tubes and solved linear equations but it was not programmable or Turing complete. However, the Atanasoff-Berry Computer will forever hold a place in Computer history.
First Programmable Electronic Digital Computer
1944: British engineer Tommy Flowers and assistants completed the code-breaking Colossus which assisted in decrypting German messages during world war II. It’s held as the first programmable electronic digital computer in history. The Colossus contained more than 1,600 vacuum tubes and thermionic valves in the prototype and 2,400 in the second version, the Mark 2 Colossus.
First General-Purpose Digital Computer
1945: ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) is completed by professors John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert. ENIAC was absolutely massive, consisting of more than 17,000 vacuum tubes, 70,000 resistors, and 10,000 capacitors, filling a 30′ x 50′ room and weighing around 60,000 pounds. It was the first general-purpose digital computer in history and was extremely capable of a computer at the time. It’s said that for the first decade that ENIAC was in operation, it completed more calculations than in all of history previously.

First Computer Transistor
1947: William Shockley of Bell Labs invented the first transistor and drastically changed the course of computing history. The transistor replaced the common vacuum tube which allowed computers to be much more efficient while still greatly reducing their size and energy requirements.
First General-Purpose Commercial Computer
1951: Professors John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert built UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer), the first general-purpose commercial computer in history. The early UNIVAC models utilized 5,000 vacuum tubes but later models in the series adopted transistors. It was a massive computer weighing around 16,000 pounds. However, the massive size allowed for more than 1,000 computations per second.
First Computer Programming Language
1954: A team at IBM led by John Backus created the first commercially available general-purpose computer programming language, FORTRAN. FORTRAN stands for Formula Translation and is still used today. When the language first appeared, however, there were bugs and inefficiencies which led people to speculate on the commercial usability of FORTRAN. Yet, the bugs were worked out many of the programming languages that came after were inspired by FORTRAN.
First Computer Operating System
1956: The first computer operating system in history was released in 1956 and produced by General Motors, called the GM-NAA I/O . It was created by Robert L. Patrick and allowed for direct input and output, hence the name. It also allowed for batch processing: the ability to execute a new program automatically after the current one finishes.
First Integrated Circuit
1958: Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce create the first integrated circuit , commonly known as a microchip. An integrated circuit consists of electronic circuits mounted onto a semiconductor. The most common semiconductor medium is silicon, which is where the name ‘ Silicon Valley ‘ comes from. If not for the integrated circuit, computers would still be the size of a refrigerator, rather than the size of a credit card.
First Supercomputer
1964: History’s first supercomputer, known as the CDC 6600 , was developed by Control Data Corp. It consisted of 400,000 transistors, 100 miles of wiring, and used Freon for internal cooling. Thus, the CDC 6600 was able to reach a processing speed of up to 3 million floating-point operations per second (3 megaFLOPS). Amazingly, this supercomputer was ten times faster than the fastest computer at the time and cost a whopping $8 million.
First Computer Mouse
1964: Douglas Engelbart invented the first computer mouse in history but it wouldn’t accompany the first Apple Macintosh until 1984. The computer mouse allowed for additional control of the computer in conjunction with the keyboard. These two input devices have been the primary source of user input ever since. However, voice commands from present-day smart devices are increasingly becoming the norm.

First Wide Area Computer Network
1969: DARPA created the first Wide Area Network in the history of computers called ARPAnet which was a precursor to the internet . It allowed computers to connect to a central hub and interact in nearly real time. The term “internet” wouldn’t come around until 1973 when computers in Norway and England connect to ARPAnet. Although the internet has continued to advance through the decades, many of the same protocols from ARPAnet are still standards today.
First Personal Computer
1971: The first personal computer in history, the Kenbak-1 , is created by John Blankenbaker, and sold for only $750. However, only around 40 of these computers were ever sold. As small as it was, it was able to execute hundreds of calculations in a single second. Blankenbaker had the idea for the personal computer for more than two decades before completing his first one.
First Computer Microprocessor
1971: Intel releases the first microprocessor in the history of computers, the Intel 4004 . This tiny microprocessor had the same computing power as the ENIAC computer and was the size of an entire room. Even by today’s standards, the Intel 4004 is a small microprocessor, housed on a 2-inch wafer as opposed to today’s 12-inch wafers. That said, the initial model had only 2,300 transistors while it’s not uncommon for today’s microprocessors to have several hundred million transistors.
First Apple Computer
1976: Apple takes the stage and releases its first computer: the Apple-1 . The Apple-1 was different from other computers at the time. It came fully assembled and on a single motherboard. It sold for nearly $700 and had only 4 KB of memory, which is almost laughable compared to today’s standards. However, that was plenty of memory for the applications at the time.
First IBM Personal Computer
1981: IBM launches its first personal computer, the IBM Model-5150 . It only took a year to develop and cost $1,600. However, that was a steep drop from other IBM computers before this that sold for several million dollars. The IBM Model-5150 had only 16 KB of RAM when it was first released, but eventually increased to up to 640 KB maximum RAM.
First Laptop Computer
1981: The first laptop in the history of computers, the Osborne 1 , was released by the Osborne Computer Corporation. It had an incredibly small 5-inch display screen, a bulky fold-out keyboard, 64 KB of main memory, and weighed 24 pounds. Not surprisingly, the Osborne 1 was actually very popular, selling more than 125,000 units in 1982 alone. The going rate for an Osborne 1 was $1,795.
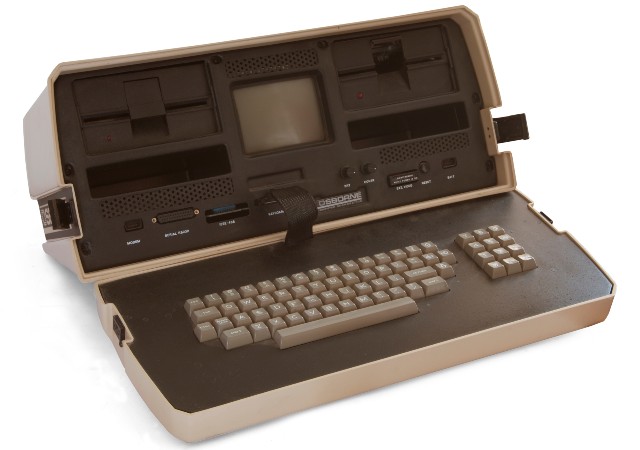

First Windows Operating System
1985: Microsoft released its first version of the Windows operating system, Windows 1.0 . What made Windows 1.0 remarkable was its reliance on the computer mouse which wasn’t standard yet. It even included a game, Reversi, to help users become accustomed to the new input device. Love it or hate it, the Windows 1.0 operating system and its subsequent versions have become commonplace among computers ever since its creation. The development of the original Windows OS was led by none other than Bill Gates himself.
World Wide Web Is Created
1989: The World Wide Web is created by Sir Tim Berners-Lee of CERN . When it was first created, it wasn’t intended to grow into a massive platform that would connect the average person. Rather, it was originally just intended to easily share information between scientists and universities. The first website in the history of computers was actually just a guide to using the world wide web.
First Flash-Based Solid State Drive
1991: The first flash-based solid-state drive was created by SanDisk (at the time it was called SunDisk). These drives presented an alternative option to hard drives and would prove to be very useful in computers, cell phones, and similar devices. This first flash-based SSD had 20 MB of memory and sold for approximately $1,000.
First Smartphone Is Created
1992: IBM created the first-ever smartphone in history, the IBM Simon , which was released two years later in 1994. It was a far cry from the smartphones we’re used to today. However, at the time, IBM Simon was a game-changer. It sold for $1,100 when it was first released and even had a touchscreen and several applications including mail, a calendar, a to-do list, and a few more.
First Platform Independent Language
1995: Sun Microsystems releases the first iteration of the Java programming language . Java was the first computer programming language in history to be platform-independent, popularizing the phrase: “Write once, run anywhere.” Unlike other computer programming languages at the time, a program written with Java could run on any device with the Java Development Kit (JDK).
First Smartwatch Is Released
1998: The first-ever smartwatch , the Ruputer, was released by the watch company Seiko. If you look at the original Ruputer, you’ll see that it really doesn’t look much different than present-day smartwatches with the exception of a better display and minor styling changes. As it wasn’t a touchscreen, a small joystick assisted with navigating the various feature of the watch.
First Quantum Computer
1998: After decades of theory, the first quantum computer is created by three computer scientists. It was only 2 qubits, as opposed to the 16 qubit reprogrammable quantum computers of recent. This first quantum computer didn’t solve any significant problem, as it wasn’t incredibly efficient. In fact, it ran for only a few nanoseconds. However, it was a proof of concept that paved the way for today’s quantum computers.
First USB Flash Drive
2000: The first USB Flash drive in computer history, the ThumbDrive , is released by Trek, a company out of Singapore. However, there were other flash drives that hit the market almost immediately after, such as I.B.M.’s DiskOnKey, a 1.44 MB flash drive. This led to some speculation as to who was actually first. However, as evidenced by the patent application back in 1999, and the fact that Trek’s ThumbDrive made it to market first, the debate was shortly settled.
DARPA Centibots Project
2002: DARPA launched the Centibots project in which they developed 100 identical robots that could work together and communicate with each other. The Centibots could survey an area and build a map of it in real time. Additionally, these robots could identify objects including their companion robots and people, and distinguish between the two. The maps that they make are incredibly accurate. In total, the Centibots project cost around $2.2 million to complete.

MySpace Comes And Goes
2004: MySpace gained over 1 million users within the first month of its official launch and 22 million users just a year later. Soon after in 2005, it was purchased by News Corp for $580 million. However, shortly after the sale of MySpace, it was fraught with scandal after scandal. MySpace helped to popularize social media, with Facebook trailing right behind it, passing MySpace in users in 2008. It eventually laid off about 50% of its workforce in 2011.
Arduino Is Released
2005: Italian designer Massimo Banzi released the Arduino , a credit card-sized development board. The Arduino was intended to help design students who didn’t have any previous exposure to programming and electronics but eventually became a beloved tool for tech hobbyists worldwide. To this day, Arduino boards are increasingly a part of electronics education including self-education.
iPhone Generation-1 Released
2007: Steve Jobs of Apple released the first-ever iPhone , revolutionizing the smartphone industry. The screen was 50% bigger than the popular smartphones of the time, such as the beloved Blackberry and Treo. It also had a much longer-lasting battery. Additionally, the iPhone normalized web browsing and video playback on phones, setting a new standard across the industry. The cost was what you could expect from an iPhone, selling at around $600, more than twice as much as its competitors.
Apple’s iPad Is Released
2010: Only three years after the iPhone is released, Steve Jobs announces the first-ever iPad , Apple’s first tablet computer. It came with a 9.7-inch touchscreen and options for either 16GB, 32GB, or 64GB. The beauty of the iPad is that it was basically a large iPhone, as it ran on the same iOS and offered the same functionality. The original iPad started at $499 with the 64GB Wi-Fi + 3G version selling for $829.
Nest Thermostat Is Released
2011: The Nest Thermostat , a smart thermostat created by Nest Labs, is released as a growing number of household devices make up the “internet of things.” When the Nest Thermostat was first released, not only did it make thermostats smart, it made them beautiful. For only $250 you could buy a thermostat that decreased your energy bill, improved the aesthetic of your home, and is controlled by your phone.
First Raspberry Pi Computer
2012: The first Raspberry Pi computer is released, opening up a world of possibilities for creative coders. These small yet capable computers cost around 25$-$35 when first released and were as small as a credit card. Raspberry Pi’s were similar to the Arduino in size but differed greatly in their capability. The Raspberry Pi is several times faster than the Arduino and has over 100,000 times more memory.
Tesla Introduces Autopilot
2014: Tesla’s Elon Musk introduces the first self-driving features in its fleet of automobiles dubbed: Autopilot. The future of automobiles chauffeuring their passengers with no input from a driver is finally within sight. The first feature of autopilot included not only camera systems but also radar and sonar in order to detect everything within the car’s surroundings. It also included a self-park feature and even a summoning feature that calls the vehicle to you. The computers and technology within Tesla vehicles have essentially turned them into the first advanced personal transportation robots in history.
Sophia The Robot Is Created
2016: Sophia, the artificially intelligent humanoid robot, was created by former Disney Imagineer David Hanson. A year after her creation, Sophia gained citizenship in Saudi Arabia, becoming the first robot in history to gain citizenship. Since she was created, Sophia was taken part in many interviews and even debates. She’s quite a wonder to watch!
First Reprogrammable Quantum Computer
2016: Quantum Computers have made considerable progress and the first reprogrammable quantum computer is finally complete. It’s made up of 5 singular atoms that act as switches. These switches are activated by a laser beam that controls the state of the qubit. This leap has brought us very close to quantum supremacy.
First Brain-Computer Interface
2019: Elon Musk announces Neuralink’s progress of their brain-machine interface that would lend humans the same information processing abilities that computers have while linking to Artificial Intelligence. In this announcement, Neuralink revealed that they had already successfully tested their technology on mice and apes.
Tesla Nears Fully Autonomous Vehicles
2020: In July, Elon Musk declared that a Tesla autopilot update is coming later this year that will bring their vehicles one step closer to complete “level-5” autonomy . Level-5 autonomy would finally allow passengers to reach their destination without any human intervention. The long-awaited software update would likely increase the company’s value massively and Musk’s net worth along with it.
Elon Musk announces Tesla Bot, becomes Time’s Person of the Year

2021: Musk continues to innovate, announcing in August that Tesla is developing a near-life-size humanoid robot. Many are skeptical of the viability of the robot while others claimed this is another of Musk’s inventions that science fiction warned against similar to the Brain-Computer Interface.
Regardless of any opinions, Musk still had a stellar year. Starship has made progress, Tesla sales are on the rise, and Musk managed to earn the title of Time’s Person of the Year. All the while becoming the most wealthy person on the planet, with a net worth exceeding $250 million.
Facebook changes name to Meta, Zuck announces Metaverse
2021: In October, Mark Zuckerberg made a bold and controversial, yet possibly visionary announcement that Facebook would change its name to Meta. Additionally, he explained the new immersive Virtual Reality world they’re creating that would be built on top of the existing social network, dubbed the Metaverse. Zuckerberg elaborated that the technology for the immersive experience he envisions is mostly here but mainstream adoption is still 5 to 10 years out . However, when that time comes, your imagination will be your only limitation within the confines of the Metaverse.
IBM’s “Eagle” Quantum Computer Chip (127 Qubits)
2021: IBM continues to lead the charge in quantum computer development and in November, they showcased their new “Eagle” chip . This is currently the most cutting-edge quantum chip in existence, packing 127 qubits, making it the first to reach over 100 qubits. IBM plans to create a new chip more than three times more powerful than the “Eagle” by next year, 2022.
OpenAI Releases DALL-E 2
2022: DALL-E, developed by OpenAI, is capable of generating high-quality images from textual descriptions. It uses a combination of deep learning techniques and a large database of images to generate new and unique images based on textual input. DALL-E 2, launched in April 2022, is the second generation of this language model that is trained on hundreds of millions of images and is almost magical in its production of high-quality images in a matter of seconds.
IBM’s “Osprey” Quantum Computer Chip (433 Qubits)
2022: In only a year, IBM has nearly tripled the quantum capacity of its previous “Eagle” chip. The new “Osprey” quantum chip, announced in November, greatly surpasses its predecessor. The IBM Osprey quantum computer chip represents a major advancement in quantum computing technology and is expected to pave the way for even more powerful quantum computers in the future.
ChatGPT Released Upon The World
2022: ChatGPT is launched on November 30 and took the world by storm, amassing over 1 million users in only 5 days! Currently, ChatGPT is powered by GPT3.x, which is the latest version of the AI software. The development of ChatGPT was a significant milestone in the field of natural language processing, as it represented a significant improvement in the ability of machines to understand and generate human language.
The Much Hyped GPT4 Is Finally Released
2023: ChatGPT and many other AI apps run on GPT. As powerful as the GPT3.x was, GPT4 is trained on a much more massive data set and is far more accurate and better at understanding the intentions of the user’s prompts. It’s a giant leap forward from the previous version, causing both excitement and concern from the general public as well as tech powerhouses such as Elon Musk who wants to slow the advancement of AI.
Tim Statler
Tim Statler is a Computer Science student at Governors State University and the creator of Comp Sci Central. He lives in Crete, IL with his wife, Stefanie, and their cats, Beyoncé and Monte. When he's not studying or writing for Comp Sci Central, he's probably just hanging out or making some delicious food.
Recent Posts
Programming Language Levels (Lowest to Highest)
When learning to code, one of the first things I was curious about was the difference in programming language levels. I recently did a deep dive into these different levels and put together this...
Is Python a High-Level Language?
Python is my favorite programming language so I wanted to know, "Is Python a High-Level Language?" I did a little bit of research to find out for myself and here is what I learned. Is Python a...

The Evolution Of Computer | Generations of Computer
The development of computers has been a wonderful journey that has covered several centuries and is defined by a number of inventions and advancements made by our greatest scientists. Because of these scientists, we are using now the latest technology in the computer system.
Now we have Laptops , Desktop computers , notebooks , etc. which we are using today to make our lives easier, and most importantly we can communicate with the world from anywhere around the world with these things.
So, In today’s blog, I want you to explore the journey of computers with me that has been made by our scientists.
Note: If you haven’t read our History of Computer blog then must read first then come over here
let’s look at the evolution of computers/generations of computers
COMPUTER GENERATIONS
Computer generations are essential to understanding computing technology’s evolution. It divides computer history into periods marked by substantial advancements in hardware, software, and computing capabilities. So the first period of computers started from the year 1940 in the first generation of computers. let us see…
Table of Contents
Generations of computer
The generation of classified into five generations:
- First Generation Computer (1940-1956)
- Second Generation Computer (1956-1963)
- Third Generation Computer(1964-1971)
- Fourth Generation Computer(1971-Present)
- Fifth Generation Computer(Present and Beyond)
1. FIRST GENERATION COMPUTER: Vacuum Tubes (1940-1956)

The first generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Vacuum tubes” It was developed in 1904 by the British engineer “John Ambrose Fleming” . A vacuum tube is an electronic device used to control the flow of electric current in a vacuum. It is used in CRT(Cathode Ray Tube) TV , Radio , etc.

The first general-purpose programmable electronic computer was the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) which was completed in 1945 and introduced on Feb 14, 1946, to the public. It was built by two American engineers “J. Presper Eckert” and “John V Mauchly” at the University of Pennsylvania.

The ENIAC was 30-50 feet long, 30 tons weighted, contained 18000 vacuum tubes, 70,000 registers, and 10,000 capacitors, and it required 150000 watts of electricity, which makes it very expensive.
Later, Eckert and Mauchly developed the first commercially successful computer named UNIVAC(Univeral Automatic Computer) in 1952 .
Examples are ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer), UNIVAC-1 (Univeral Automatic Computer-1)
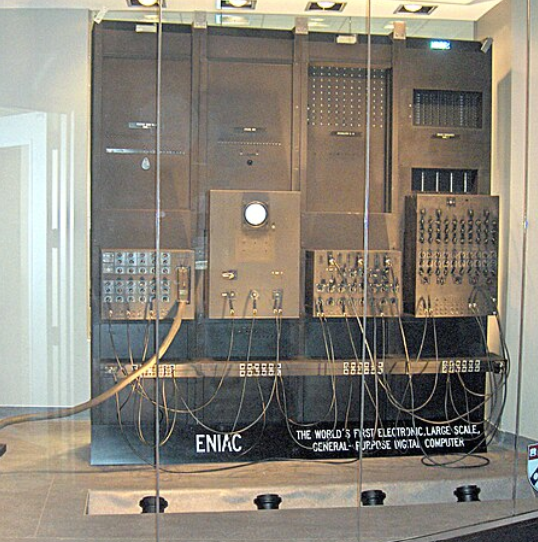

- These computers were designed by using vacuum tubes.
- These generations’ computers were simple architecture.
- These computers calculate data in a millisecond.
- This computer is used for scientific purposes.
DISADVANTAGES
- The computer was very costly.
- Very large.
- It takes up a lot of space and electricity
- The speed of these computers was very slow
- It is used for commercial purposes.
- It is very expensive.
- These computers heat a lot.
- Cooling is needed to operate these types of computers because they heat up very quickly.
2. SECOND GENERATION COMPUTER: Transistors (1956-1963)
The second generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Transistors” and it was developed in 1947 by three American physicists “John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley” .

A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals or open or close a circuit. It was invented in Bell labs, The transistors became the key ingredient of all digital circuits, including computers.
The invention of transistors replaced the bulky electric tubes from the first generation of computers.
Transistors perform the same functions as a Vacuum tube , except that electrons move through instead of through a vacuum. Transistors are made of semiconducting materials and they control the flow of electricity.
It is smaller than the first generation of computers, it is faster and less expensive compared to the first generation of computers. The second-generation computer has a high level of programming languages, including FORTRAN (1956), ALGOL (1958), and COBOL (1959).
Examples are PDP-8 (Programmed Data Processor-8), IBM1400 (International business machine 1400 series), IBM 7090 (International business machine 7090 series), CDC 3600 ( Control Data Corporation 3600 series)
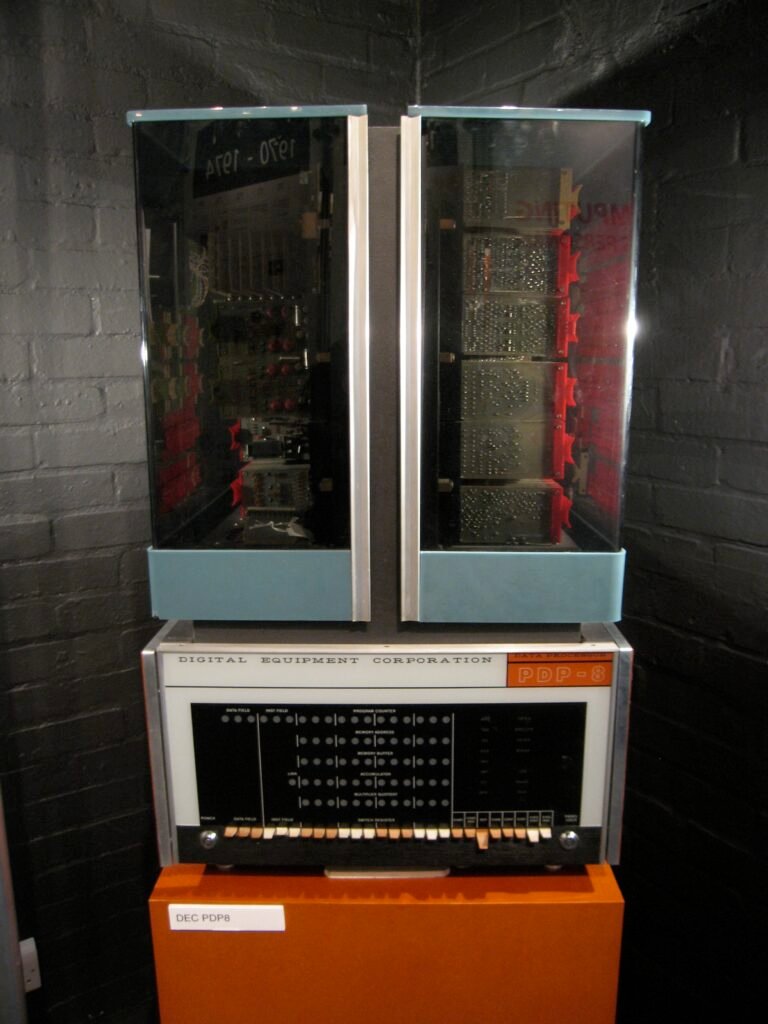

ADVANTAGES:
- It is smaller in size as compared to the first-generation computer
- It used less electricity
- Not heated as much as the first-generation computer.
- It has better speed
DISADVANTAGES:
- It is also costly and not versatile
- still, it is expensive for commercial purposes
- Cooling is still needed
- Punch cards were used for input
- The computer is used for a particular purpose
3. THIRD GENERATION COMPUTER: Integrated Circuits (1964-1971)
The Third generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Integrated Circuits” It was developed in 1958 by two American engineers “Robert Noyce” & “Jack Kilby” . The integrated circuit is a set of electronic circuits on small flat pieces of semiconductor that is normally known as silicon. The transistors were miniaturized and placed on silicon chips which are called semiconductors, which drastically increased the efficiency and speed of the computers.
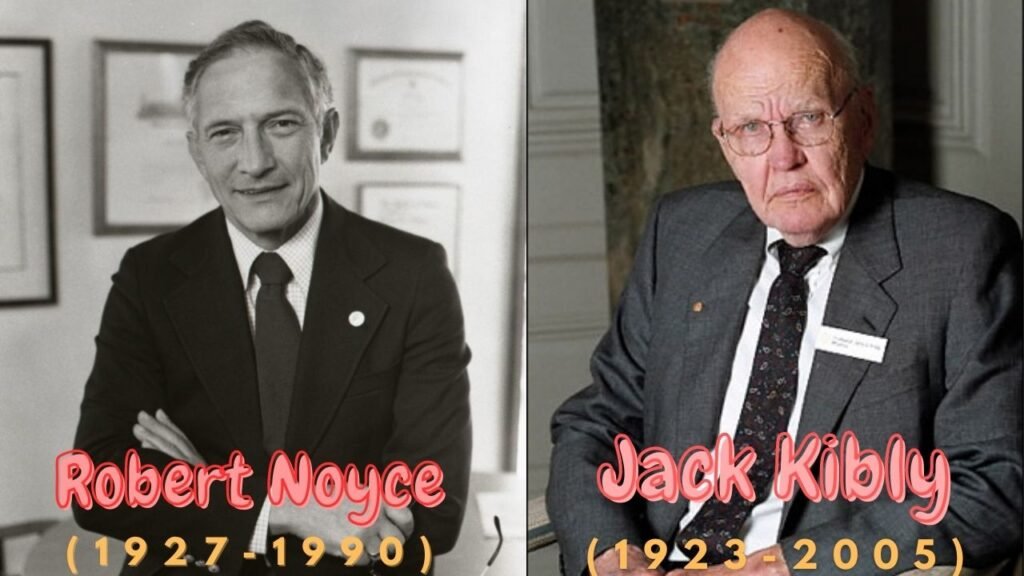
These ICs (integrated circuits) are popularly known as chips. A single IC has many transistors, resistors, and capacitors built on a single slice of silicon.
This development made computers smaller in size, low cost, large memory, and processing. The speed of these computers is very high and it is efficient and reliable also.
These generations of computers have a higher level of languages such as Pascal PL/1, FORTON-II to V, COBOL, ALGOL-68, and BASIC(Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) was developed during these periods.
Examples are NCR 395 (National Cash Register), IBM 360,370 series, B6500

- These computers are smaller in size as compared to previous generations
- It consumed less energy and was more reliable
- More Versatile
- It produced less heat as compared to previous generations
- These computers are used for commercial and as well as general-purpose
- These computers used a fan for head discharge to prevent damage
- This generation of computers has increased the storage capacity of computers
- Still, a cooling system is needed.
- It is still very costly
- Sophisticated Technology is required to manufacture Integrated Circuits
- It is not easy to maintain the IC chips.
- The performance of these computers is degraded if we execute large applications.
4. FOURTH GENERATION OF COMPUTER: Microprocessor (1971-Present)
The fourth generation of computers is characterized by the use of “Microprocessor”. It was invented in the 1970s and It was developed by four inventors named are “Marcian Hoff, Masatoshi Shima, Federico Faggin, and Stanley Mazor “. The first microprocessor named was the “Intel 4004” CPU, it was the first microprocessor that was invented.

A microprocessor contains all the circuits required to perform arithmetic, logic, and control functions on a single chip. Because of microprocessors, fourth-generation includes more data processing capacity than equivalent-sized third-generation computers. Due to the development of microprocessors, it is possible to place the CPU(central processing unit) on a single chip. These computers are also known as microcomputers. The personal computer is a fourth-generation computer. It is the period when the evolution of computer networks takes place.
Examples are APPLE II, Alter 8800

- These computers are smaller in size and much more reliable as compared to other generations of computers.
- The heating issue on these computers is almost negligible
- No A/C or Air conditioner is required in a fourth-generation computer.
- In these computers, all types of higher languages can be used in this generation
- It is also used for the general purpose
- less expensive
- These computers are cheaper and portable
- Fans are required to operate these kinds of computers
- It required the latest technology for the need to make microprocessors and complex software
- These computers were highly sophisticated
- It also required advanced technology to make the ICs(Integrated circuits)
5. FIFTH GENERATION OF COMPUTERS (Present and beyond)
These generations of computers were based on AI (Artificial Intelligence) technology. Artificial technology is the branch of computer science concerned with making computers behave like humans and allowing the computer to make its own decisions currently, no computers exhibit full artificial intelligence (that is, can simulate human behavior).

In the fifth generation of computers, VLSI technology and ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology are used and the speed of these computers is extremely high. This generation introduced machines with hundreds of processors that could all be working on different parts of a single program. The development of a more powerful computer is still in progress. It has been predicted that such a computer will be able to communicate in natural spoken languages with its user.
In this generation, computers are also required to use a high level of languages like C language, c++, java, etc.
Examples are Desktop computers, laptops, notebooks, MacBooks, etc. These all are the computers which we are using.

- These computers are smaller in size and it is more compatible
- These computers are mighty cheaper
- It is obviously used for the general purpose
- Higher technology is used
- Development of true artificial intelligence
- Advancement in Parallel Processing and Superconductor Technology.
- It tends to be sophisticated and complex tools
- It pushes the limit of transistor density.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many computer generations are there.
Mainly five generations are there:
First Generation Computer (1940-1956) Second Generation Computer (1956-1963) Third Generation Computer(1964-1971) Fourth Generation Computer(1971-Present) Fifth Generation Computer(Present and Beyond)
Which things were invented in the first generation of computers?
Vacuum Tubes
What is the fifth generation of computers?
The Fifth Generation of computers is entirely based on Artificial Intelligence. Where it predicts that the computer will be able to communicate in natural spoken languages with its user.
What is the latest computer generation?
The latest generation of computers is Fifth which is totally based on Artificial Intelligence.
Who is the inventor of the Integrated Circuit?
“Robert Noyce” and “Jack Bily”
What is the full form of ENIAC ?
ENIAC Stands for “Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer” .
Related posts:
- The History of Computer Systems and its Generations
- Basic Components of Computer Systems and its Functions
- What is a computer? How is it a useful device?
- 10 Limitations Of Computers System|And its Capabilities?
- Different Applications of Computer Systems in Various Fields | Top 12 Fields
- Explain Von Neumann Architecture?
- What are the input and Output Devices of Computer System with Examples
- What is Unicode and ASCII Code
- What is RAM and its Types?
- What is the difference between firmware and driver? | What are Firmware and Driver?
2 thoughts on “The Evolution Of Computer | Generations of Computer”
It is really useful thanks
Glad to see
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Software Engineering
Title: peer-aided repairer: empowering large language models to repair advanced student assignments.
Abstract: Automated generation of feedback on programming assignments holds significant benefits for programming education, especially when it comes to advanced assignments. Automated Program Repair techniques, especially Large Language Model based approaches, have gained notable recognition for their potential to fix introductory assignments. However, the programs used for evaluation are relatively simple. It remains unclear how existing approaches perform in repairing programs from higher-level programming courses. To address these limitations, we curate a new advanced student assignment dataset named Defects4DS from a higher-level programming course. Subsequently, we identify the challenges related to fixing bugs in advanced assignments. Based on the analysis, we develop a framework called PaR that is powered by the LLM. PaR works in three phases: Peer Solution Selection, Multi-Source Prompt Generation, and Program Repair. Peer Solution Selection identifies the closely related peer programs based on lexical, semantic, and syntactic criteria. Then Multi-Source Prompt Generation adeptly combines multiple sources of information to create a comprehensive and informative prompt for the last Program Repair stage. The evaluation on Defects4DS and another well-investigated ITSP dataset reveals that PaR achieves a new state-of-the-art performance, demonstrating impressive improvements of 19.94% and 15.2% in repair rate compared to prior state-of-the-art LLM- and symbolic-based approaches, respectively
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
department of management sciences, comsats computer for mangment assignment # 1 submitted to: ch. anwar shaukat submitted by: muhammad ahsan tariq (045) abdullah nadeem (006) abdullah nadeen (005) ali sabir (013) "evolution and history of computer" contents introdution:- 4 early history: (williams, 1997) 5 abacus: 5 napier rods: 5 percaline: 5 charlee's babbage's difference engine ...
The word 'computer' has a very interesting origin. It was first used in the 16th century for a person who used to compute, i.e. do calculations. The word was used in the same sense as a noun until the 20th century. Women were hired as human computers to carry out all forms of calculations and computations.
Computer - History, Technology, Innovation: A computer might be described with deceptive simplicity as "an apparatus that performs routine calculations automatically." Such a definition would owe its deceptiveness to a naive and narrow view of calculation as a strictly mathematical process. In fact, calculation underlies many activities that are not normally thought of as mathematical.
The history of computers began with primitive designs in the early 19th century and went on to change the world during the 20th century.
computer, device for processing, storing, and displaying information.. Computer once meant a person who did computations, but now the term almost universally refers to automated electronic machinery.The first section of this article focuses on modern digital electronic computers and their design, constituent parts, and applications. The second section covers the history of computing.
Final Paper Assignment. Write a 10-15 page paper (double-spaced, 1.25" margins, 12 pt font). You may choose any topic that addresses the use of the computer as a scientific instrument. You may choose something close to your own area of expertise, or something completely different.
History of Computers. Before computers were developed people used sticks, stones, and bones as counting tools. As technology advanced and the human mind improved with time more computing devices were developed like Abacus, Napier's Bones, etc. These devices were used as computers for performing mathematical computations but not very complex ones.
Computers truly came into their own as great inventions in the last two decades of the 20th century. But their history stretches back more than 2500 years to the abacus: a simple calculator made from beads and wires, which is still used in some parts of the world today. The difference between an ancient abacus and a modern computer seems vast ...
History of Computers. A computer is an electronic machine that accepts information, stores it, processes it according to the instructions provided by a user and then returns the result. Today, we ...
Course Description. This course focuses on one particular aspect of the history of computing: the use of the computer as a scientific instrument. The electronic digital computer was invented to do science, and its applications range from physics to mathematics to biology to the humanities. What has been the impact of computing on the ….
He was a Visiting Assistant Professor in the Electrical and Computer Engineering Department at George Mason University, Fairfax, Virginia, USA, in Spring 1990. He is currently an Associate Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Computer and Information Science at New Jersey Institute of Technology, Newark, New Jersey, USA.
The last of the three major institutions in the history of computing is the Computer History Museum.7 This holds an exceptional collection of rare and historical computer hardware, including pieces of the ENIAC, an Enigma machine, a SAGE console, a Cray 1 supercomputer, a Xerox Alto, an Altair, and an Apple 1.
Assignment 1 - History of Computer - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Assignment 1 - History of Computer
Numerous titles offer broad accounts of the fascinating history of computing, and more recent publications take the story up to the present. Ian Watson's comprehensive history published in 2012, The Universal Machine: From the Dawn of Computing to Digital Consciousness, will be particularly appealing to general readers and undergraduate students for its accessible, engaging writing style and ...
This course will focus on one particular aspect of the history of computing: the use of the computer as a scientific instrument. The electronic digital computer was invented to do science, and its applications range from physics to mathematics to biology to the humanities. ... Assignments for this course also include a final paper (10-15 pages ...
An abacus is a mechanical device used to aid an individual in performing mathematical calculations. The abacus was invented in Babylonia in 2400 B.C. The abacus in the form we are most familiar with was first used in China in around 500 B.C. It used to perform basic arithmetic operations. Abacus.
The history of computer begins with the birth of abacus which is believed to be the first computer. It is said that Chinese invented Abacus around 4,000 years ago. It was a wooden rack which has metal rods with beads mounted on them. The beads were moved by the abacus operator according to some rules to perform arithmetic calculations.
The history of computer dated back to the period of scientific revolution (i.e. 1543 - 1678). The calculating machine invented by Blaise Pascal in 1642 and. that of Goffried Liebnits marked the ...
The history of computers goes back thousands of years with the first one being the abacus. In fact, the earliest abacus, referred to as the Sumerian abacus, dates back to roughly 2700 B.C. from the Mesopotamia region. However, Charles Babbage, the English mathematician and inventor is known as the "Father of Computers.".
Department: Computer Science Course: Computing Systems Assignment 1: Read up on the history of computers, computing and computer science and submit a 2-page reading report summary of your findings. Background Computer: A computer is an electronic device that accepts raw data as input and processes it with a set of instructions to produce the result as output. Computing: This is any activity ...
A second early electronic machine was Colossus, designed by Alan Turing for the British. military in 1943. The first general purpose programmable electronic computer was the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC), built by J. Presper Eckert and John. V. Mauchly at the University of Pennsylvania.
Computer generations are essential to understanding computing technology's evolution. It divides computer history into periods marked by substantial advancements in hardware, software, and computing capabilities. So the first period of computers started from the year 1940 in the first generation of computers. let us see…
Automated generation of feedback on programming assignments holds significant benefits for programming education, especially when it comes to advanced assignments. Automated Program Repair techniques, especially Large Language Model based approaches, have gained notable recognition for their potential to fix introductory assignments. However, the programs used for evaluation are relatively ...