

Energy Resources, Introduction, Sources, Types & Map
The primary energy source on Earth is the sun. Know about Energy Resources, Conventional and non-Conventional Energy Sources & their Maps in this article for the UPSC examination.

Table of Contents
Energy Resources
The traditional definition of energy is the capacity of a system to perform labour, but as energy can take many different forms, it is challenging to come up with a single, all-encompassing definition. It is an attribute of an item that can be changed or transferred from one object to another, but it cannot be created or destroyed. Energy comes from a variety of places.
Mineral fuels are necessary for the production of electricity, which is needed by industry, transportation, and other economic sectors. The traditional energy sources include nuclear energy minerals and fossil fuels including coal, petroleum, and natural gas. These conventional sources are finite, run out and exhaust with time.
Energy Resources Types
Natural sources of energy can be divided into two categories i.e, Conventional Sources of Energy and Non-Conventional Sources of Energy.
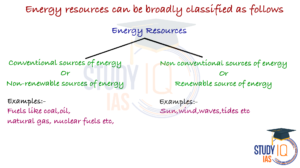
Difference between Conventional Sources of Energy and Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
Conventional energy sources.
One of the vital minerals, coal is primarily employed in the production of thermal energy and the smelting of iron ore. Gondwana and tertiary deposits are the two main geological eras in which coal can be found in rock sequences. In India, bituminous coal accounts for over 80% of the non-coking quality coal reserves.
The Damodar Valley is home to India’s most significant Gondwana coal deposits.They are located in the Jharkhand-Bengal coal belt, which has significant coalfields such as Raniganj, Jharia, Bokaro, Giridih, and Karanpura.The largest coal field is Jharia, followed by Raniganj. The Godavari, Mahanadi, and Sone river valleys are the others that are connected to coal. The most significant coal mining areas are Singrauli in Madhya Pradesh, Singareni in Telangana, Pandur in Andhra Pradesh, Talcher and Rampur in Odisha, Korba in Chhattisgarh, Talcher and Rampur in Odisha, Chanda-Wardha, Kamptee and Bander in Maharashtra.
Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, and Nagaland all have tertiary coal deposits. It is obtained from the Meghalayan regions of Darangiri, Cherrapunji, Mewlong, and Langrin; upper Assamese regions of Makum, Jaipur, and Nazira; the Arunachal Pradesh regions of Namchik-Namphuk; and Kalakot (Jammu and Kashmir). In addition, coastal regions in Gujarat, Jammu and Kashmir, Tamil Nadu, and Pondicherry have brown coal, often known as lignite.
2. Petroleum
Hydrocarbons in liquid and gaseous forms that vary in chemical composition, colour, and specific gravity make up crude petroleum. For all internal combustion engines in automobiles, trains, and aeroplanes, it is a necessary source of energy. Petrochemical industries use its myriad byproducts to make fertiliser, synthetic rubber, synthetic fibre, pharmaceuticals, vaseline, lubricants, wax, soap, and cosmetics. Tertiary-era sedimentary rocks contain crude petroleum.
The Oil and Natural Gas Commission was established in 1956, and since then, oil exploration and production have been actively pursued. The sole oil-producing refinery until 1956 was the Digboi in Assam, but things changed after 1956. New oil reserves have been discovered in the country’s extreme western and eastern regions in recent years.
Digboi, Naharkatiya, and Moran are significant oil-producing regions in Assam. Gujarat has several significant oil reserves, including Ankleshwar, Kalol, Mehsana, Nawagam, Kosamba, and Lunej. Mumbai High, which is located 160 kilometres off the coast of Mumbai, was founded in 1973, and production there started in 1976.
In exploratory wells in the Krishna-Godavari and Kaveri basins on the east coast, oil and natural gas have been discovered. Crude oil, which has numerous contaminants, is the oil that is extracted from the wells. It can’t be used straight up. It requires improvement. India has two different kinds of refineries: (a) market-based and (b) field-based. Field-based refineries are illustrated by Digboi, while market-based refineries are illustrated by Barauni.
3. Natural Gas
In order to transport and market natural gas, the Gas Authority of India Limited was established as a public sector enterprise in 1984. It is found in all oil fields alongside oil, however, there are exclusive reserves in Tripura, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Maharashtra as well as along the eastern coast (Tamil Nadu, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh).
Energy Resources Maps
Below are the Maps of the Energy Resources Maps of India

Non-Conventional Energy Sources
Coal, petroleum, natural gas, and nuclear energy all use finite raw materials as their primary energy source. Only renewable energy sources like sun, wind, hydro geothermal, and biomass are considered sustainable energy sources. These energy sources are more environmentally responsible and evenly dispersed. After the initial cost is covered, non-conventional energy sources will offer more consistent, eco-friendly, and less expensive energy.
1. Nuclear Energy
In recent years, nuclear energy has shown to be a reliable source. Uranium and thorium are significant minerals utilised in the production of nuclear energy. The Dharwar rocks contain uranium reserves. Geographically, it is known that uranium ores can be found along the Singbhum Copper belt in a number of areas. Additionally, it can be found in the districts of Kullu in Himachal Pradesh, Durg in Chhattisgarh, Alwar, and Jhunjhunu in Rajasthan, and Udaipur, Alwar, and Jhunjhunu in Rajasthan. Monazite and ilmenite in the beach sands of Kerala and Tamil Nadu’s coasts are the main sources of thorium. The richest monazite deposits in the world are found in the Keralan districts of Palakkad and Kollam, close to Vishakhapatnam in Andhra Pradesh, and near the Mahanadi river delta in Odisha.
The Atomic Energy Commission was founded in 1948, but advancements couldn’t be achieved until the Atomic Energy Institute in Trombay was founded in 1954 and later renamed the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre in 1967. The significant nuclear energy projects are those at Tarapur in Maharashtra, Rahatbhata near Kota in Rajasthan, Kalpakkam in Tamil Nadu, Narora in Uttar Pradesh, Kaiga in Karnataka, and Kakarapara in Gujarat.
2. Solar Energy
Solar energy is created by harnessing the sun’s rays in photovoltaic cells. Photovoltaics and solar thermal technology are two methods that are thought to be particularly effective in harnessing solar energy. Comparatively speaking, solar thermal energy has some advantages over all other non-renewable energy sources. It is affordable, environmentally friendly, and simple to build.
Solar power is 10% more efficient than nuclear power and 7% more efficient than coal or oil-based systems. Appliances like heaters, crop dryers, cookers, etc. typically use it more. Gujarat and Rajasthan in western India have the most potential for the growth of solar energy.
3. Wind Power
Wind power is a limitless, pollution-free source of electricity. The process of converting wind energy is straightforward. Through the use of turbines, wind energy’s kinetic energy is transformed into electrical energy. As a source of energy, the trade winds, westerlies, and seasonal wind patterns like the monsoon have all been exploited.
Other than these, it is also possible to generate power using local winds, land breezes, and sea breezes. India has already begun producing wind energy. It has an ambitious plan to erect 250 wind turbines with a combined 45 megawatts of power in 12 suitable spots, primarily along the coast. To reduce the cost of oil imports, India’s Ministry of Non-Conventional Sources of Energy is fostering the growth of wind energy.
More than 50,000 megawatts of wind energy can be produced in India, of which only one-fourth is feasible to use. Conditions are favourable for wind energy in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Karnataka.
4. Tidal and Wave Energy
Ocean currents are a never-ending source of energy. Continuous efforts have been made from the beginning of the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries to develop a more effective energy system using constant tidal waves and ocean currents.
The west coast of India is known to experience large tidal waves. As a result, India has a lot of potential for tidal energy production along the coasts, but this potential has not yet been realised.
5. Geothermal Energy
Extreme heat is emitted as magma from the earth’s interior rises to the surface. It is possible to successfully harness and transform this thermal energy into electrical energy. In addition to this, thermal energy is also produced from the hot water that spews from gyser wells. It is commonly referred to as geothermal energy. These days, one of the main energy sources that can be created as a backup supply is thought to be this energy. Since the Middle Ages, people have been using the hot springs and geysers. At Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh, an Indian geothermal energy plant has been put into operation.
6. Bio-energy
Bio-energy is defined as energy produced from biological materials, such as municipal, industrial, and other wastes as well as agricultural residues. A potential source of energy conversion is bioenergy.
It can be transformed into gas for cooking, heat energy, or electrical energy. Along with processing waste and garbage, it will also generate energy. This would boost the quality of life for rural residents in developing nations, lessen environmental pollution, increase independence, and ease the demand for fuel wood. Okhla in Delhi is one such initiative that turns garbage from the city into energy.
Energy Resources Conservation
The difficulty of sustainable development necessitates fusing the pursuit of economic growth with environmental considerations. Traditional resource usage practices generate a significant amount of trash and contribute to other environmental issues. Therefore, conserving resources for future generations is necessary for sustainable growth. The necessity to save resources is critical.
Alternative energy sources including solar, wind, wave and geothermal power provide an endless source of energy. To replace the finite resources, these should be developed. Utilizing scrap metals will allow for the recycling of metals in the case of metallic minerals. Utilizing scrap is particularly important for metals like copper, lead, and zinc, where India has limited deposits. Utilizing alternatives for rare metals may also cut down on usage. Reduced export of strategic and rare minerals is necessary to extend the useful life of the current reserve.
Energy Resources UPSC
Conserving means taking care of and preserving these resources for future generations. As a UPSC aspirant, you should be well aware of the location of various oil refineries and the collaboration of India with various countries in upgrading the refineries. Also, the conservation of energy on an individual level is crucial and switching from conventional to non-conventional energy or alternative energy resources should be encouraged and emphasized. This topic of geography holds immense importance from both Prelims and Mains point of View. The details in the article would help candidates preparing for UPSC 2023.
Energy Resources FAQs
Q) What is the primary sources of energy?
Ans. Sun is the primary source of energy.
Q) What do you mean by conventional sources of energy?
Ans. These resources are exhaustible and run out eventually. Examples are Coal, Petroleum.
Q) Is Nuclear energy conventional or non-conventional resources?
Ans. Nuclear energy is a non-conventional resource Examples are Uranium and Thorium.
Q) Where is the Digboi refinery located?
Ans. It is located in Assam.
Q) What are examples of non-conventional resources?
Ans. Non-conventional resources include solar energy, bioenergy, tidal energy and wind energy.
Other Indian Geography Topics
Other fundamental geography topics.
Sharing is caring!
What is the primary sources of energy?
Sun is the primary source of energy
What do you mean by conventional sources of energy?
These resources are exhaustible and run out eventually. Examples are Coal, Petroleum.

Is Nuclear energy conventional or non-conventional resources?
Nuclear energy is a non-conventional resource Examples are Uranium and Thorium.
Where is the Digboi refinery located?
It is located in Assam.
What are examples of non-conventional resources?
Non-conventional resources include solar energy, bioenergy, tidal energy and wind energy.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- UPSC Online Coaching
- UPSC Exam 2024
- UPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Mains Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPSC Age Limit 2024
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- UPSC Syllabus in Hindi
- UPSC Full Form

Recent Posts
- UPPSC Exam 2024
- UPPSC Calendar
- UPPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPPSC Application Form 2024
- UPPSC Eligibility Criteria 2024
- UPPSC Admit card 2024
- UPPSC Salary And Posts
- UPPSC Cut Off
- UPPSC Previous Year Paper
BPSC Exam 2024
- BPSC 70th Notification
- BPSC 69th Exam Analysis
- BPSC Admit Card
- BPSC Syllabus
- BPSC Exam Pattern
- BPSC Cut Off
- BPSC Question Papers
IB ACIO Exam
- IB ACIO Salary
- IB ACIO Syllabus
CSIR SO ASO Exam
- CSIR SO ASO Exam 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Result 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date
- CSIR SO ASO Question Paper
- CSIR SO ASO Answer key 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Syllabus 2024
Study Material Categories
- Daily The Hindu Analysis
- Daily Practice Quiz for Prelims
- Daily Answer Writing
- Daily Current Affairs
- Indian Polity
- Environment and Ecology
- Art and Culture
- General Knowledge
- Biographies

IMPORTANT EXAMS

- Terms & Conditions
- Return & Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy

Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology
- How to Study Art & Culture?
- What is Art and Culture? What is the difference between the two?
- Indus Civilization
- Evolution of rock-cut architecture in India
- Important rock-cut caves
- The contribution of Pallavas to Rock-cut architecture
- Comparision of art form found at Ellora and Mahabalipuram
- Buddhist Architecture
- Early Temples in India
- Basic form of Hindu temple
- Dravida style of temple architecture
- Nagara Style or North India Temple style
- Vesara style of temple architecture
- Characteristic features of Indo-Islamic form of architecture
- Styles of Islamic architecture in the Indian subcontinent
- Types of buildings in Islamic architecture in the Indian subcontinent
- Evolution of this form of architecture during the medieval period
- Modern Architecture
- Post-Independence architecture
- Indus Civilization Sculpture
- Bharhut Sculptures
- Sanchi Sculptures
- Gandhara School of Sculpture
- Mathura School of Sculpture
- Amaravati School of Sculpture
- Gupta Sculpture
- Medieval School of Sculpture
- Modern Indian Sculpture
- Pre Historic Painting
- Mural Paintings & Cave Paintings
- Pala School
- Mughal Paintings
- Bundi School of Painting
- Malwa School
- Mewar School
- Basohli School
- Kangra School
- Decanni School of Painting
- Madhubani Paintings or Mithila paintings
- Pattachitra
- Kalighat Painting
- Modern Indian Paintings
- Personalities Associated to Paintings
- Christianity
- Zoroastrianism
- Six Schools of Philosophy
- Lokayata / Charvaka
- Hindustani Music
- Carnatic Music
- Folk Music Tradition
- Modern Music
- Personalities associated with Music
- Bharatanatyam
- Mohiniattam
- Folk Dances
- Modern Dance in India
- Sanskrit Theatre
- Folk Theatre
- Modern Theatre
- Personalities associated with Theatre
- History of Puppetry
- String Puppetry
- Shadow Puppetry
- Rod Puppetry
- Glove Puppetry
- Indian Cinema and Circus
- Shankaracharya
- Ramanujacharya (1017-1137AD)
- Madhvacharya
- Vallabhacharya
- Kabir (1440-1510 AD)
- Guru Nanak (1469-1538 AD)
- Chaitanya Mahaprabhu
- Shankar Dev
- Purandaradasa
- Samard Ramdas
- Classical Languages
- Scheduled Languages
- Literature in Ancient India
- Buddhist and Jain Literature
- Tamil (Sangam) Literature
- Malayalam Literature
- Telugu Literature
- Medieval Literature
- Modern Literature
- Important characteristics of Fairs and Festivals of India
- Some of the major festivals that are celebrated in India
- Art & Crafts
- Ancient Science & Technology
- Medieval Science & Technology
- Famous Personalities in Science & Technology
- Tangible Cultural Heritage
- Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Cultural Heritage Sites
- Natural Heritage Sites
- Important Institutions
- Important programmes related to promotion and preservation of Indian heritage
- Ochre Colored Pottery (OCP)
- Black and Red Ware (BRW)
- Painted Grey-Ware (PGW)
- Northern Black Polished Ware (NBPW)
- Origin of Martial arts in India
- Various forms of Martial arts in India
- Situation of Child Labour in India
- Poverty and Child labour- a vicious cycle
- Impact of the pandemic
- Government measures undertaken to eradicate child labour in India
- Challenges before policy makers with respect to child labour.
- Way Forward
- Facts and figures about the prevalence of Child marriage in India
- Factors leading to child marriage in India
- Interlinkages of poverty and child marriages in India
- Impact of child marriage on Indian economy
- Government measures undertaken so far to curb Child Marriages in India
- Measures needed to prevent child marriages
- The Poor state of Hunger and Malnutrition in India
- Multi-dimensional determinants of malnutrition
- Covid-19 impact on malnutrition in children in India
- Government effort to fight malnutrition
- Addressing malnutrition: Measures needed
- Procedure in place to protect children
- Government measures needed
- Role of NCPCR
- Shortcomings of NCPCR
- Way forward
- Key findings of the report in India
- Impact of COVID-19
- Government Measures undertaken
- Measures needed
- Constitutional Provisions to safeguard children
- Child Abuse in India
- Impacts of child abuse
- Government initiatives undertaken
- On children
- On families
- On individual
- Challenges to ban child pornography
- Causes for child mortality
- Government initiatives
- Geographic spread of minorities in India
- Socio-economic status of minorities in India
- Importance of recognition of rights of minorities
- Parameters to define minority in India
- Lack of uniformity in determining minorities
- Prejudice & Discrimination
- Problem of Identity
- Problem of Security
- Problem Relating to Equity
- Problem of Communal Tensions and Riots
- Lack of Representation in Civil Service and Politics
- Problem of Providing Protection
- Failure to Stick on Strictly to Secularism
- Problem of Lack of Representation in Civil Service and Politics
- Key findings related to minorities
- Various factors responsible for under-representation of enrolled minorities
- Problem of Separatism
- Problem Relating to the Introduction of Common Civil Code
- Problems faced by minority women in India
- Factors leading to anger against minorities
- Constitutional Safeguard for Minorities
- Government Welfare Measures for Minorities
- Composition
- Lacunae in NCM
- Measures needed to make NCM more effective
- Major Findings
- Main Recommendations
- Review of the implementation of recommendations of Sachar committee report after Ten Years
- Status of Education in India
- Importance of Education for India
- Contemporary challenges in education sector in India
- Other existing issues
- Measures Needed for Issues related to Education Sector
- Way forward for Issues related to Education Sector
- Feature of Right to Education (RTE) Act, 2009
- Significance of RTE Act, 2009
- Achievements of RTE Act,2009
- Limitations of RTE Act, 2009
- Measures needed foe Right to Education
- Importance of Education as a necessary public good
- Challenges faced by Government schools
- Measures needed for Public Education System in India
- Way forward for Public Education System in India
- Key highlights of the NEP
- Significance of National Education Policy 2020
- Issues with the NEP- 2020
- Measures needed for effective implementation
- Way Forward for New Education Policy
- Three language policy
- Concerns associated over three language formula
- Way forward for Three language formula in India
- Significance of emphasizing native languages in the education system of India
- Way forward for Native language in education
- Significance of ECCE
- NEP 2020 and ECCE
- Challenges for Early Childhood Care and Education
- Way forward for Early Childhood Care and Education
- Need for reforms
- Findings of ASER Report 2019
- Challenges faced – Primary Education in India
- Government Schemes for Elementary Education
- Measures needed for Primary Education in India
- Government Schemes for Secondary Education
- Challenges facing higher education system
- Government schemes for Higher Education
- Measures needed for Higher Education in India
- Way forward for Higher Education in India
- Reasons behind poor quality of teachers
- Opportunities present
- Government Initiative so far
- Way forward for Teacher Education in India
- Present Status
- Advantages of Developing Female Education in India
- Challenges for Gender Imparity in Education
- Way Forward for Gender Imparity in Education
- Crisis of education in India in times of Pandemic
- Impacts on education due to COVID-19 pandemic
- Challenges posed by Online Education
- Online education as a supplement to Traditional Educational Institutes
- Challenges facing medical education in India
- Can private participating alleviate the concerns?
- Government proposal in this regard
- Way forward for Medical Education in India
- Need for value education
- Importance of value education
- Issues related to SC/ST
- Scheduled Caste
- Issues faced by Scheduled Castes
- Major reasons behind miserable conditions of Scheduled Castes
- Constitutional mechanism for upliftment of SC
- Government Initiatives taken for Scheduled Caste development
- Educational Empowerment
- Economic Empowerment
- Social Empowerment
- Evaluation of Government Schemes
- Failure of the Indian judiciary to protect the rights of the people
- Measures needed for Scheduled Caste
- Way forward for Scheduled Caste
- Dalit Women
- Challenges faced by Dalit Women
- Atrocities against Dalit women
- Role of Indian judiciary in protecting sexual violence victims
- Criticism against ignorance of caste-based violence
- Aspects which have improved so far
- Measures needed for Dalit Women
- Way forward for Dalit Women
- National Commission for Scheduled Castes
- Issues related to the role of National Commission for Scheduled Castes
- Measures need to be taken up by NCSC
- Scheduled Tribe
- Definition of Scheduled tribe
- Various problems of tribal communities in India
- Constitutional Safeguards for STs
- Educational & Cultural Safeguards
- Social Safeguard
- Economic Safeguards
- Political Safeguards
- Service Safeguards
- The Fifth Schedule of the Constitution
- The Sixth Schedule of the Constitution
- Need for Sixth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule areas: Benefits of devolving powers
- Issues related to sixth schedule areas
- Legislative measures
- The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006
- Rights under the Act
- Eligibility
- Need for the law
- Issues with the law and its implementation
- Measures needed in FRA’s
- XAXA Committee
- Panchayats (Extension to Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996
- Problems with PESA
- Government Initiatives for ST
- Way Forward in women and health
- Way forward for ST
- Way forward for PVTGs
- Way forward in Violence/crime against Women
- Way forward in sex ratio
Home » Social Justice » Issues related to Health Sector » Universal Health Coverage
Universal Health Coverage
Universal health coverage (UHC) means that all people have access to the health services they need (prevention, promotion, treatment, rehabilitation and palliative care) without the risk of financial hardship when paying for them.
Health accessibility and affordability remain a crucial healthcare problem even in the 21st century. Therefore, World Health Organisation chose “Universal Health Coverage” as the theme for World Health Day 2019. India started working towards the universal problem of affordability and accessibility with the introduction of Ayushman Bharat.
- Universal health coverage has a direct impact on a population’s health and welfare.
- Access and use of health services enables people to be more productive and active contributors to their families and communities.
- It also ensures that children can go to school and learn.
- At the same time, financial risk protection prevents people from being pushed into poverty when they have to pay for health services out of their own pockets.
- Universal health coverage is thus a critical component of sustainable development and poverty reduction, and a key element of any effort to reduce social inequities.
- Universal coverage is the hallmark of a government’s commitment to improve the wellbeing of all its citizens.

- Public sector is severely underfunded.
- Private sector is growing but their rising high cost healthcare service is problematic.
- Our country is also facing serious issues of inadequate quality and coverage.
- Ineffective regulation is a concerned area.
- Combining public and private providers effectively for meeting UHC goals in a manner that avoids perverse incentives, reduces provider induced demand.
- Integrating different types and levels of services—public health and clinical; preventive and promotive interventions along with primary, secondary, and tertiary clinical care.
- The National Health Policy (NHP) 2017 advocated allocating resources of up to two-thirds or more to primary care as it enunciated the goal of achieving “the highest possible level of good health and well-being, through a preventive and promotive healthcare orientation”.
- A 167% increase in allocation this year for the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) — the insurance programme which aims to cover 10 crore poor families for hospitalisation expenses of up to ₹5 lakh per family per annum.
- The government’s recent steps to incentivise the private sector to open hospitals in Tier II and Tier III cities.
- Individual states are adopting technology to support health-insurance schemes. For instance, Remedinet Technology (India’s first completely electronic cashless health insurance claims processing network) has been signed on as the technology partner for the Karnataka Government’s recently announced cashless health insurance schemes.

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
G20 Summit 2023
Last updated on September 12, 2023 by ClearIAS Team

The G20 Summit 2023 just concluded in New Delhi under the Indian Presidency. The PM of India passed the gavel to Brazil, the next G20 President. The 18 th meeting of the Group of Twenty was the first G20 summit to be held in India. Read here to learn about the outcomes of the summit.
The G20 (Group of 20) is an international forum that includes 19 of the world’s largest economies and the European Union.
G20 is a forum for economic, financial, and political cooperation. It addresses the major global challenges and seeks to generate public policies that resolve them.
The Leaders’ Summit is the climax of the G20 process and the work carried out over the year through Ministerial Meetings, Working Groups, and Engagement Groups.
Table of Contents
G20 India Presidency
The G20 is made up of 19 countries and the EU.
- The 19 countries are Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Germany, France, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Mexico, the Russian Federation, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, the UK, and the US.
India holds the Presidency of the G20 from 1 December 2022 to 30 November 2023.
Learn more from: ClearIAS Study Materials
Indonesia held the presidency in 2022, which concluded in the Bali declaration .
Under the Indian Presidency, the G20 in 2023 focussed on the theme, ‘One Earth, One Family, One Future’.
- The theme affirms the value of human, animal, plant, and microorganisms and their interconnectedness on planet Earth and in the wider universe.
- The Indian Presidency will also spotlight Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE), with an emphasis on environmentally sustainable and responsible choices at both the individual lifestyle and the national development level, to achieve a cleaner, greener, and bluer future.
The summit had India showcase its cultural richness through diverse elements like:
- Bharat Mandapam, inspired by Lord Basavaeshwara’s concept of Anubhav mandapam. The “culture corridor,” features a display of diverse traditions from 29 countries, including India and the special invitees to the G20.
- The Chola-style bronze statue of Lord Nataraja.
- Konark Chakra of Odisha’s sun temple and the image of Nalanda University were used as backdrops.
- Showcase of Thanjavur Paintings and Dhokra art
- A brass statue of Lord Buddha under the Bodhi tree.
- Hindustani, Folk, and Carnatic musical heritage of India
Indian Prime Minister formally handed over the G20 presidency to the President of Brazil. India will continue to hold the position until 30 November 2023.
The invited countries for the year were:
- Bangladesh, Egypt, Mauritius, Netherlands, Nigeria, Oman, Singapore, Spain and UAE.
Six agendas were put forth for the G20 Dialogue 2023:
- Green Development, Climate Finance & LiFE
- Accelerated, Inclusive & Resilient Growth
- Accelerating progress on SDGs
- Technological Transformation & Digital Public Infrastructure
- Multilateral Institutions for the 21st Century
- Women-led development
The working groups focused on areas like:
- agriculture, anti-corruption, culture, digital economy, disaster risk reduction, development, education, employment, environment and climate sustainability, energy transitions, health, trade and investment, and tourism.
Major outcomes of the G20 summit 2023
- The African Union joined the G20 as a permanent member.
- A new organization called the Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA) was launched, to promote the development and adoption of sustainable biofuels, and set relevant standards and certification.
- The New Delhi Leaders Declaration was adopted with consensus.
- A group of countries made a joint agreement to build a rail and shipping corridor linking India with the Middle East and Europe called the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor . The group comprises India, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Israel and the European Union.
New Delhi declaration
The G20 2023 joint consensus declaration called the New Delhi Leaders Declaration is an official non-binding declaration that seeks to place emphasis on strong, sustainable, balanced, and inclusive growth.
Global Economic Situation
- To protect the vulnerable, through promoting equitable growth and enhancing macroeconomic and financial stability. Such an approach will help resolve the cost-of-living crisis and unlock strong, sustainable, balanced, and inclusive growth.
- To support the progress towards the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development to achieve strong, sustainable, balanced, and inclusive growth (SSBIG).
- To create inclusive, sustainable, and resilient global value chains, and support developing countries to move up the value chain.
Unlocking Trade for Growth
- To ensure a rules-based, non-discriminatory, fair, open, inclusive, equitable, sustainable, and transparent multilateral trading system, with WTO at its core.
- Recognize challenges MSMEs, particularly in developing countries, face concerning access to information and thus, welcome Jaipur Call for Action for enhancing MSMEs’ access to information to promote the integration of MSMEs into international trade.
Also read: G20 Generic Framework for Mapping Global Value Chains (GVC)
Fighting Corruption
- Strengthening Law Enforcement International Cooperation and Information Sharing for Combating Corruption, Strengthening Asset Recovery Mechanisms for Combating Corruption.
- To enhance global efforts to seize, confiscate, and return criminal proceeds to victims and states, in line with international obligations and domestic legal frameworks, including through support to the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and operationalization of the GlobE Network.
Recommitting to Achieving SDGs
- To accelerate progress on SDGs, we commit to taking collective action for effective and timely implementation of the G20 2023 Action Plan to Accelerate Progress on the SDGs.
Strengthening Global Health and Implementing One Health Approach
- To strengthen the global health architecture, with the World Health Organization (WHO) at its core, and build more resilient, equitable, sustainable, and inclusive health systems to achieve Universal Health Coverage, implement the One Health approach, enhance pandemic preparedness, and strengthen existing infectious diseases surveillance systems.
Designing a Circular Economy World
- Resource Efficiency and Circular Economy Industry Coalition (RECEIC) to enhance environmentally sound waste management, substantially reduce waste generation by 2030, and highlight the importance of zero waste initiatives.
Other major outcomes:
- Overcoming major differences in the Russia-Ukraine war
- Call for full implementation of the Black Sea Grain Initiative
- Action Plan against Fugitive Economic Offenders
- Countering terrorism and money laundering
- Globally fair, sustainable, and modern international tax system
- Digital Public Infrastructure (crypto, Al, etc.)
- Gender equality and women empowerment
- G20 Deccan High-Level Principles on Food Security and Nutrition 2023
G20 Summit 2023 reiterates that cooperation is essential in determining the course the world takes. Headwinds to global economic growth and stability persist.
Years of cascading challenges and crises have reversed gains in the 2030 Agenda and its Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) . Global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions continue to increase, with climate change, biodiversity loss, pollution, drought, land degradation, and desertification threatening lives and livelihoods.
Rising commodity prices, including food and energy prices, are contributing to cost of living pressures. Global challenges like poverty and inequality, climate change, pandemics, and conflicts disproportionately affect women and children, and the most vulnerable.
The G20 Summit 2023 commit to:
- Accelerate strong, sustainable, balanced, and inclusive growth.
- Accelerate the full and effective implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- Pursue low-GHG/low-carbon emissions, climate-resilient, and environmentally sustainable development pathways by championing an integrated and inclusive approach.
- Improve access to medical countermeasures and facilitate more supplies and production capacities in developing countries to prepare better for future health emergencies.
- Promote resilient growth by urgently and effectively addressing debt vulnerabilities in developing countries.
- Scale up financing from all sources for accelerating progress on SDGs
-Article by Swathi Satish

Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For administrative services at the state level, the recruitment is made by the State Public Service Commission (SPSC). The Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) is the central recruiting agency in India. It is an independent constitutional body. The provisions regarding the composition of UPSC, appointment and removal of its members and the ...
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month. Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success. ...
World Health Organisation (WHO) - UPSC Notes. The World Health Organisation (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that looks into matters of public health. Established on April 7th, 1948, its headquarters is located in Geneva, Switzerland. WHO is an important topic for the IAS exam, as it is keeping in news concerning the Covid-19 ...
How to Write Essay in UPSC Exam, Tips for the Essay Paper in IAS Mains exam, Essay for UPSC, UPSC Essay Paper, UPSC Essay Writing, IAS Essay topics, tips to write a good essay in UPSC Exam 2023
Lok Adalat is one of the alternative dispute redressal mechanisms, it is a forum where disputes/cases pending in the court of law or at pre-litigation stage are settled/ compromised amicably. The Lok Adalats are formed to fulfil the promise given by the preamble of the Indian Constitution- securing Justice - social, economic and political ...
It covers a significant part of the Economy subject in the General Studies Paper-3 syllabus and current events of national importance in the UPSC prelims syllabus. In this article, let us look at the concept of national income, its salient features, measurement methods, objectives, advantages, challenges and important facts of national income ...
ADR is a mechanism of dispute resolution that is non adversarial, i.e. working together co-operatively to reach the best resolution for everyone. ADR can be instrumental in reducing the burden of litigation on courts, while delivering a well-rounded and satisfying experience for the parties involved. It provides the opportunity to "expand the ...
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a value-added tax levied on most goods and services sold for domestic consumption. The GST is paid by consumers, but it is remitted to the government by the businesses selling the goods and services.
United Nations: UPSC Notes. The United Nations (UN) is a global organisation tasked with maintaining international peace and security while fostering friendly relations among nations. It is the largest, most recognized and most powerful intergovernmental organisation in the world. The United Nations Organisation is an important topic in the IAS ...
In recent years, India has reportedly shown an improvement at each level of education for boys as well as for girls. 2011 census showed the male literacy rate to be 82.14% while for females it lags behind at 65.46%.; Estimates show that for every 100 girls in rural India only a single one reaches class 12 and almost 40% of girls leave school even before reaching the fifth standard.
Causes of Environmental Degradation. Environmental degradation is the deterioration of the environment caused by the deterioration of resources including soil, water, and air; the loss of ecosystems; and the extinction of wildlife. The main contributors to environmental degradation include modern urbanization, industrialization, population ...
Energy Resources UPSC. Conserving means taking care of and preserving these resources for future generations. As a UPSC aspirant, you should be well aware of the location of various oil refineries and the collaboration of India with various countries in upgrading the refineries. Also, the conservation of energy on an individual level is crucial ...
Universal health coverage (UHC) means that all people have access to the health services they need (prevention, promotion, treatment, rehabilitation and palliative care) without the risk of financial hardship when paying for them. Health accessibility and affordability remain a crucial healthcare problem even in the 21st century. Therefore, World Health Organisation chose "Universal Health ...
Public debt is the total amount borrowed by the government of a country when the government's revenue from taxes and other sources falls short of its spending requirements. In India, public debt includes the total liabilities of the Union government that have to be paid from the Consolidated Fund of India (Article 292).
Preamble declares India to be a sovereign, socialist, secular and democratic republic. The objectives stated by the Preamble are to secure justice, liberty, equality to all citizens and promote fraternity to maintain unity and integrity of the nation. The date is mentioned in the preamble when it was adopted i.e. November 26, 1949.
Global warming is the long-term heating of the Earth's surface observed since the pre-industrial period (between 1850 and 1900) due to human activities. The leading cause was primarily fossil fuel burning, which increases heat-trapping greenhouse gas levels in Earth's atmosphere. This term is not interchangeable with the term " climate ...
Russia - Ukraine Conflict Summary - Russia Ukraine Conflict Timeline, Ukraine Crisis Explained for UPSC 2024 [For more UPSC Notes on International Relations, click here.
World War I (WW I), also known as the Great War, lasted from 28 July 1914 to 11 November 1918. WW I was fought between the Allied Powers and the Central Powers. The main members of the Allied Powers were France, Russia, and Britain. The United States also fought on the side of the Allies after 1917. The main members of the Central Powers were ...
Kushan Empire. Last updated on August 30, 2023 by ClearIAS Team. The Kushan Empire was a major political and cultural power in ancient Central Asia and Northern India. The art and architecture of the Kushan Empire reflect the cultural diversity and interactions of the time. Read here to learn more about the Kushans.
Last updated on September 12, 2023 by ClearIAS Team. The G20 Summit 2023 just concluded in New Delhi under the Indian Presidency. The PM of India passed the gavel to Brazil, the next G20 President. The 18th meeting of the Group of Twenty was the first G20 summit to be held in India. Read here to learn about the outcomes of the summit.
Union Budget 2024 - 25. The Union Budget is the annual budget of the Republic of India. It is presented every year in February generally by the Union Finance Minister. On this page, you can read all about what a budget is, and what the Union Budget 2024-25 talks about. This is a crucial topic for the upcoming UPSC exam.
About: It is the process of implementing land use practices and water management practices to protect and improve the quality of the water and other natural resources within a watershed. Objectives of Watershed Management: Pollution control. Minimising over-exploitation of resources. Water storage, flood control, checking sedimentation.
NABARD is a development bank focussing primarily on the rural sector of the country. It is the apex banking institution to provide finance for Agriculture and rural development. Its headquarter is located in Mumbai, the country's financial capital. It is responsible for the development of the small industries, cottage industries, and any ...