Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Psychiatry & Mental Health — Depression

Essays About Depression
Depression essay topic examples.
Explore topics like the impact of stigma on depression, compare it across age groups or in literature and media, describe the emotional journey of depression, discuss how education can help, and share personal stories related to it. These essay ideas offer a broad perspective on depression, making it easier to understand and engage with this important subject.
Argumentative Essays
Argumentative essays require you to analyze and present arguments related to depression. Here are some topic examples:
- 1. Argue whether mental health stigma contributes to the prevalence of depression in society.
- 2. Analyze the effectiveness of different treatment approaches for depression, such as therapy versus medication.
Example Introduction Paragraph for an Argumentative Essay: Depression is a pervasive mental health issue that affects millions of individuals worldwide. This essay delves into the complex relationship between mental health stigma and the prevalence of depression in society, examining the barriers to seeking help and the consequences of this stigma.
Example Conclusion Paragraph for an Argumentative Essay: In conclusion, the analysis of mental health stigma's impact on depression underscores the urgent need to challenge and dismantle the stereotypes surrounding mental health. As we reflect on the far-reaching consequences of stigma, we are called to create a society that fosters empathy, understanding, and open dialogue about mental health.
Compare and Contrast Essays
Compare and contrast essays enable you to examine similarities and differences within the context of depression. Consider these topics:
- 1. Compare and contrast the symptoms and risk factors of depression in adolescents and adults.
- 2. Analyze the similarities and differences between the portrayal of depression in literature and its depiction in modern media.
Example Introduction Paragraph for a Compare and Contrast Essay: Depression manifests differently in various age groups and mediums of expression. This essay embarks on a journey to compare and contrast the symptoms and risk factors of depression in adolescents and adults, shedding light on the unique challenges faced by each demographic.
Example Conclusion Paragraph for a Compare and Contrast Essay: In conclusion, the comparison and contrast of depression in adolescents and adults highlight the importance of tailored interventions and support systems. As we contemplate the distinct challenges faced by these age groups, we are reminded of the need for age-appropriate mental health resources and strategies.
Descriptive Essays
Descriptive essays allow you to vividly depict aspects of depression, whether it's the experience of the individual or the societal impact. Here are some topic ideas:
- 1. Describe the emotional rollercoaster of living with depression, highlighting the highs and lows of the experience.
- 2. Paint a detailed portrait of the consequences of untreated depression on an individual's personal and professional life.
Example Introduction Paragraph for a Descriptive Essay: Depression is a complex emotional journey that defies easy characterization. This essay embarks on a descriptive exploration of the emotional rollercoaster that individuals with depression experience, delving into the profound impact it has on their daily lives.
Example Conclusion Paragraph for a Descriptive Essay: In conclusion, the descriptive portrayal of the emotional rollercoaster of depression underscores the need for empathy and support for those grappling with this condition. Through this exploration, we are reminded of the resilience of the human spirit and the importance of compassionate understanding.
Persuasive Essays
Persuasive essays involve arguing a point of view related to depression. Consider these persuasive topics:
- 1. Persuade your readers that incorporating mental health education into the school curriculum can reduce the prevalence of depression among students.
- 2. Argue for or against the idea that employers should prioritize the mental well-being of their employees to combat workplace depression.
Example Introduction Paragraph for a Persuasive Essay: The prevalence of depression underscores the urgent need for proactive measures to address mental health. This persuasive essay asserts that integrating mental health education into the school curriculum can significantly reduce the prevalence of depression among students, offering them the tools to navigate emotional challenges.
Example Conclusion Paragraph for a Persuasive Essay: In conclusion, the persuasive argument for mental health education in schools highlights the potential for early intervention and prevention. As we consider the well-being of future generations, we are called to prioritize mental health education as an essential component of a holistic education system.
Narrative Essays
Narrative essays offer you the opportunity to tell a story or share personal experiences related to depression. Explore these narrative essay topics:
- 1. Narrate a personal experience of overcoming depression or supporting a loved one through their journey.
- 2. Imagine yourself in a fictional scenario where you advocate for mental health awareness and destigmatization on a global scale.
Example Introduction Paragraph for a Narrative Essay: Personal experiences with depression can be transformative and enlightening. This narrative essay delves into a personal journey of overcoming depression, highlighting the challenges faced, the support received, and the lessons learned along the way.
Example Conclusion Paragraph for a Narrative Essay: In conclusion, the narrative of my personal journey through depression reminds us of the resilience of the human spirit and the power of compassion and understanding. As we reflect on our own experiences, we are encouraged to share our stories and contribute to the ongoing conversation about mental health.
Ileana Chivescu Case Study
Depression is depression an actual illness, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Nurse Burnout: Causes, Effects, and Prevention
The epidemic of depression among students and teenagers, the effects of depression in your body and its treatment, the issue of depression and its reality nowadays, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Overview of Biological Predispositions and Risk Factors Associated with Depression
How to overcome depression and anxiety, depression: definition, risks, symptoms and treatment, the best way to help someone who is depressed, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
The Issue of Depression: Mental Battle
What is a depression, living in depression: a firsthand account, teen depression - symptoms and causes, adolescent depression and its contribution to teenage suicides, the issue of depression and its affect in an emerging adulthood, depression: definition and ways of resolving caused problems, depression in teenagers: causes and ways to overcome, depression and its main causes, genetic disorder report: clinical depression, the way teachers can help their students to overcome anxiety and depression, depression and its effects of mind and body, the effectiveness of cognitive behavioural therapy (cbt) for treating individuals with depression and anxiety, how to overcome teenage depression, depression as the reason of serious health problems and suicide, a depressing world with different obstacles, the link between self-esteem and adolescent depression, darwinian psychology and depression: the gender differential hypothesis, prevention of depression, anxiety and burnout in resident doctors – a systematic review, dysregulated processing of negative and positive responses in depression.
Depression, known as major depressive disorder or clinical depression, is a psychological condition characterized by enduring feelings of sadness and a significant loss of interest in activities. It is a mood disorder that affects a person's emotional state, thoughts, behaviors, and overall well-being.
Its origin can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where melancholia was described as a state of sadness and melancholy. In the 19th century, depression began to be studied more systematically, and terms such as "melancholic depression" and "nervous breakdown" emerged. The understanding and classification of depression have evolved over time. In the early 20th century, Sigmund Freud and other psychoanalysts explored the role of unconscious conflicts in the development of depression. In the mid-20th century, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) was established, providing a standardized criteria for diagnosing depressive disorders.
Biological Factors: Genetic predisposition plays a role in depression, as individuals with a family history of the disorder are at a higher risk. Psychological Factors: These may include a history of trauma or abuse, low self-esteem, pessimistic thinking patterns, and a tendency to ruminate on negative thoughts. Environmental Factors: Adverse life events, such as the loss of a loved one, financial difficulties, relationship problems, or chronic stress, can increase the risk of depression. Additionally, living in a socioeconomically disadvantaged area or lacking access to social support can be contributing factors. Health-related Factors: Chronic illnesses, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and chronic pain, are associated with a higher risk of depression. Substance abuse and certain medications can also increase vulnerability to depression. Developmental Factors: Certain life stages, including adolescence and the postpartum period, bring about unique challenges and changes that can contribute to the development of depression.
Depression is characterized by a range of symptoms that affect an individual's emotional, cognitive, and physical well-being. These characteristics can vary in intensity and duration but generally include persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest or pleasure in activities once enjoyed. One prominent characteristic of depression is a noticeable change in mood, which can manifest as a constant feeling of sadness or emptiness. Individuals may also experience a significant decrease or increase in appetite, leading to weight loss or gain. Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or excessive sleepiness, are common as well. Depression can impact cognitive functioning, causing difficulties in concentration, decision-making, and memory recall. Negative thoughts, self-criticism, and feelings of guilt or worthlessness are also common cognitive symptoms. Furthermore, physical symptoms may arise, including fatigue, low energy levels, and a general lack of motivation. Physical aches and pains, without an apparent medical cause, may also be present.
The treatment of depression typically involves a comprehensive approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition. It is important to note that the most effective treatment may vary for each individual, and a personalized approach is often necessary. One common form of treatment is psychotherapy, which involves talking to a mental health professional to explore and address the underlying causes and triggers of depression. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a widely used approach that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with depression. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage depressive symptoms. Antidepressant medications work by balancing neurotransmitters in the brain that are associated with mood regulation. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the right medication and dosage that suits an individual's needs. Additionally, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing depression. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, sufficient sleep, and stress reduction techniques can all contribute to improving mood and overall well-being. In severe cases of depression, when other treatments have not been effective, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be considered. ECT involves administering controlled electric currents to the brain to induce a brief seizure, which can have a positive impact on depressive symptoms.
1. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 264 million people worldwide suffer from depression, making it one of the leading causes of disability globally. 2. Depression can affect people of all ages, including children and adolescents. In fact, the prevalence of depression in young people is increasing, with an estimated 3.3 million adolescents in the United States experiencing at least one major depressive episode in a year. 3. Research has shown that there is a strong link between depression and other physical health conditions. People with depression are more likely to experience chronic pain, cardiovascular diseases, and autoimmune disorders, among other medical conditions.
The topic of depression holds immense significance and should be explored through essays due to its widespread impact on individuals and society as a whole. Understanding and raising awareness about depression is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, depression affects a significant portion of the global population, making it a pressing public health issue. Exploring its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can contribute to better mental health outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals affected by this condition. Additionally, writing an essay about depression can help combat the stigma surrounding mental health. By promoting open discussions and providing accurate information, essays can challenge misconceptions and foster empathy and support for those experiencing depression. Furthermore, studying depression allows for a deeper examination of its complex nature, including its psychological, biological, and sociocultural factors. Lastly, essays on depression can highlight the importance of early detection and intervention, promoting timely help-seeking behaviors and reducing the burden of the condition on individuals and healthcare systems. By shedding light on this critical topic, essays have the potential to educate, inspire action, and contribute to the overall well-being of individuals and society.
1. American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). American Psychiatric Publishing. 2. World Health Organization. (2017). Depression and other common mental disorders: Global health estimates. World Health Organization. 3. Kessler, R. C., Bromet, E. J., & Quinlan, J. (2013). The burden of mental disorders: Global perspectives from the WHO World Mental Health Surveys. Cambridge University Press. 4. Beck, A. T., Rush, A. J., Shaw, B. F., & Emery, G. (1979). Cognitive therapy of depression. Guilford Press. 5. Nierenberg, A. A., & DeCecco, L. M. (2001). Definitions and diagnosis of depression. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 62(Suppl 22), 5-9. 6. Greenberg, P. E., Fournier, A. A., Sisitsky, T., Pike, C. T., & Kessler, R. C. (2015). The economic burden of adults with major depressive disorder in the United States (2005 and 2010). Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 76(2), 155-162. 7. Cuijpers, P., Berking, M., Andersson, G., Quigley, L., Kleiboer, A., & Dobson, K. S. (2013). A meta-analysis of cognitive-behavioural therapy for adult depression, alone and in comparison with other treatments. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 58(7), 376-385. 8. Hirschfeld, R. M. A. (2014). The comorbidity of major depression and anxiety disorders: Recognition and management in primary care. Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders, 16(2), PCC.13r01611. 9. Rush, A. J., Trivedi, M. H., Wisniewski, S. R., Nierenberg, A. A., Stewart, J. W., Warden, D., ... & Fava, M. (2006). Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: A STAR*D report. American Journal of Psychiatry, 163(11), 1905-1917. 10. Kendler, K. S., Kessler, R. C., Walters, E. E., MacLean, C., Neale, M. C., Heath, A. C., & Eaves, L. J. (1995). Stressful life events, genetic liability, and onset of an episode of major depression in women. American Journal of Psychiatry, 152(6), 833-842.
Relevant topics
- Mental Health
- Eating Disorders
- Drug Addiction
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Essays About Depression: Top 8 Examples Plus Prompts
Many people deal with mental health issues throughout their lives; if you are writing essays about depression, you can read essay examples to get started.
An occasional feeling of sadness is something that everyone experiences from time to time. Still, a persistent loss of interest, depressed mood, changes in energy levels, and sleeping problems can indicate mental illness. Thankfully, antidepressant medications, therapy, and other types of treatment can be largely helpful for people living with depression.
People suffering from depression or other mood disorders must work closely with a mental health professional to get the support they need to recover. While family members and other loved ones can help move forward after a depressive episode, it’s also important that people who have suffered from major depressive disorder work with a medical professional to get treatment for both the mental and physical problems that can accompany depression.
If you are writing an essay about depression, here are 8 essay examples to help you write an insightful essay. For help with your essays, check out our round-up of the best essay checkers .
- 1. My Best Friend Saved Me When I Attempted Suicide, But I Didn’t Save Her by Drusilla Moorhouse
- 2. How can I complain? by James Blake
- 3. What it’s like living with depression: A personal essay by Nadine Dirks
- 4. I Have Depression, and I’m Proof that You Never Know the Battle Someone is Waging Inside by Jac Gochoco
- 5. Essay: How I Survived Depression by Cameron Stout
- 6. I Can’t Get Out of My Sweat Pants: An Essay on Depression by Marisa McPeck-Stringham
- 7. This is what depression feels like by Courtenay Harris Bond
8. Opening Up About My Struggle with Recurring Depression by Nora Super
1. what is depression, 2. how is depression diagnosed, 3. causes of depression, 4. different types of depression, 5. who is at risk of depression, 6. can social media cause depression, 7. can anyone experience depression, the final word on essays about depression, is depression common, what are the most effective treatments for depression, top 8 examples, 1. my best friend saved me when i attempted suicide, but i didn’t save her by drusilla moorhouse.
“Just three months earlier, I had been a patient in another medical facility: a mental hospital. My best friend, Denise, had killed herself on Christmas, and days after the funeral, I told my mom that I wanted to die. I couldn’t forgive myself for the role I’d played in Denise’s death: Not only did I fail to save her, but I’m fairly certain I gave her the idea.”
Moorhouse makes painstaking personal confessions throughout this essay on depression, taking the reader along on the roller coaster of ups and downs that come with suicide attempts, dealing with the death of a loved one, and the difficulty of making it through major depressive disorder.
2. How can I complain? by James Blake
“I wanted people to know how I felt, but I didn’t have the vocabulary to tell them. I have gone into a bit of detail here not to make anyone feel sorry for me but to show how a privileged, relatively rich-and-famous-enough-for-zero-pity white man could become depressed against all societal expectations and allowances. If I can be writing this, clearly it isn’t only oppression that causes depression; for me it was largely repression.”
Musician James Blake shares his experience with depression and talks about his struggles with trying to grow up while dealing with existential crises just as he began to hit the peak of his fame. Blake talks about how he experienced guilt and shame around the idea that he had it all on the outside—and so many people deal with issues that he felt were larger than his.
3. What it’s like living with depression: A personal essay by Nadine Dirks
“In my early adulthood, I started to feel withdrawn, down, unmotivated, and constantly sad. What initially seemed like an off-day turned into weeks of painful feelings that seemed they would never let up. It was difficult to enjoy life with other people my age. Depression made typical, everyday tasks—like brushing my teeth—seem monumental. It felt like an invisible chain, keeping me in bed.”
Dirks shares her experience with depression and the struggle she faced to find treatment for mental health issues as a Black woman. Dirks discusses how even though she knew something about her mental health wasn’t quite right, she still struggled to get the diagnosis she needed to move forward and receive proper medical and psychological care.
4. I Have Depression, and I’m Proof that You Never Know the Battle Someone is Waging Inside by Jac Gochoco
“A few years later, at the age of 20, my smile had fallen, and I had given up. The thought of waking up the next morning was too much for me to handle. I was no longer anxious or sad; instead, I felt numb, and that’s when things took a turn for the worse. I called my dad, who lived across the country, and for the first time in my life, I told him everything. It was too late, though. I was not calling for help. I was calling to say goodbye.”
Gochoco describes the war that so many people with depression go through—trying to put on a brave face and a positive public persona while battling demons on the inside. The Olympic weightlifting coach and yoga instructor now work to share the importance of mental health with others.
5. Essay: How I Survived Depression by Cameron Stout
“In 1993, I saw a psychiatrist who prescribed an antidepressant. Within two months, the medication slowly gained traction. As the gray sludge of sadness and apathy washed away, I emerged from a spiral of impending tragedy. I helped raise two wonderful children, built a successful securities-litigation practice, and became an accomplished cyclist. I began to take my mental wellness for granted. “
Princeton alum Cameron Stout shared his experience with depression with his fellow Tigers in Princeton’s alumni magazine, proving that even the most brilliant and successful among us can be rendered powerless by a chemical imbalance. Stout shares his experience with treatment and how working with mental health professionals helped him to come out on the other side of depression.
6. I Can’t Get Out of My Sweat Pants: An Essay on Depression by Marisa McPeck-Stringham
“Sometimes, when the depression got really bad in junior high, I would come straight home from school and change into my pajamas. My dad caught on, and he said something to me at dinner time about being in my pajamas several days in a row way before bedtime. I learned it was better not to change into my pajamas until bedtime. People who are depressed like to hide their problematic behaviors because they are so ashamed of the way they feel. I was very ashamed and yet I didn’t have the words or life experience to voice what I was going through.”
McPeck-Stringham discusses her experience with depression and an eating disorder at a young age; both brought on by struggles to adjust to major life changes. The author experienced depression again in her adult life, and thankfully, she was able to fight through the illness using tried-and-true methods until she regained her mental health.
7. This is what depression feels like by Courtenay Harris Bond
“The smallest tasks seem insurmountable: paying a cell phone bill, lining up a household repair. Sometimes just taking a shower or arranging a play date feels like more than I can manage. My children’s squabbles make me want to scratch the walls. I want to claw out of my own skin. I feel like the light at the end of the tunnel is a solitary candle about to blow out at any moment. At the same time, I feel like the pain will never end.”
Bond does an excellent job of helping readers understand just how difficult depression can be, even for people who have never been through the difficulty of mental illness. Bond states that no matter what people believe the cause to be—chemical imbalance, childhood issues, a combination of the two—depression can make it nearly impossible to function.
“Once again, I spiraled downward. I couldn’t get out of bed. I couldn’t work. I had thoughts of harming myself. This time, my husband urged me to start ECT much sooner in the cycle, and once again, it worked. Within a matter of weeks I was back at work, pretending nothing had happened. I kept pushing myself harder to show everyone that I was “normal.” I thought I had a pattern: I would function at a high level for many years, and then my depression would be triggered by a significant event. I thought I’d be healthy for another ten years.”
Super shares her experience with electroconvulsive therapy and how her depression recurred with a major life event despite several years of solid mental health. Thankfully, Super was able to recognize her symptoms and get help sooner rather than later.
7 Writing Prompts on Essays About Depression
When writing essays on depression, it can be challenging to think of essay ideas and questions. Here are six essay topics about depression that you can use in your essay.

Depression can be difficult to define and understand. Discuss the definition of depression, and delve into the signs, symptoms, and possible causes of this mental illness. Depression can result from trauma or personal circumstances, but it can also be a health condition due to genetics. In your essay, look at how depression can be spotted and how it can affect your day-to-day life.
Depression diagnosis can be complicated; this essay topic will be interesting as you can look at the different aspects considered in a diagnosis. While a certain lab test can be conducted, depression can also be diagnosed by a psychiatrist. Research the different ways depression can be diagnosed and discuss the benefits of receiving a diagnosis in this essay.
There are many possible causes of depression; this essay discusses how depression can occur. Possible causes of depression can include trauma, grief, anxiety disorders, and some physical health conditions. Look at each cause and discuss how they can manifest as depression.

There are many different types of depression. This essay topic will investigate each type of depression and its symptoms and causes. Depression symptoms can vary in severity, depending on what is causing it. For example, depression can be linked to medical conditions such as bipolar disorder. This is a different type of depression than depression caused by grief. Discuss the details of the different types of depression and draw comparisons and similarities between them.
Certain genetic traits, socio-economic circumstances, or age can make people more prone to experiencing symptoms of depression. Depression is becoming more and more common amongst young adults and teenagers. Discuss the different groups at risk of experiencing depression and how their circumstances contribute to this risk.
Social media poses many challenges to today’s youth, such as unrealistic beauty standards, cyber-bullying, and only seeing the “highlights” of someone’s life. Can social media cause depression in teens? Delve into the negative impacts of social media when writing this essay. You could compare the positive and negative sides of social media and discuss whether social media causes mental health issues amongst young adults and teenagers.
This essay question poses the question, “can anyone experience depression?” Although those in lower-income households may be prone to experiencing depression, can the rich and famous also experience depression? This essay discusses whether the privileged and wealthy can experience their possible causes. This is a great argumentative essay topic, discuss both sides of this question and draw a conclusion with your final thoughts.
When writing about depression, it is important to study examples of essays to make a compelling essay. You can also use your own research by conducting interviews or pulling information from other sources. As this is a sensitive topic, it is important to approach it with care; you can also write about your own experiences with mental health issues.
Tip: If writing an essay sounds like a lot of work, simplify it. Write a simple 5 paragraph essay instead.
FAQs On Essays About Depression
According to the World Health Organization, about 5% of people under 60 live with depression. The rate is slightly higher—around 6%—for people over 60. Depression can strike at any age, and it’s important that people who are experiencing symptoms of depression receive treatment, no matter their age.
Suppose you’re living with depression or are experiencing some of the symptoms of depression. In that case, it’s important to work closely with your doctor or another healthcare professional to develop a treatment plan that works for you. A combination of antidepressant medication and cognitive behavioral therapy is a good fit for many people, but this isn’t necessarily the case for everyone who suffers from depression. Be sure to check in with your doctor regularly to ensure that you’re making progress toward improving your mental health.
If you’re still stuck, check out our general resource of essay writing topics .

Amanda has an M.S.Ed degree from the University of Pennsylvania in School and Mental Health Counseling and is a National Academy of Sports Medicine Certified Personal Trainer. She has experience writing magazine articles, newspaper articles, SEO-friendly web copy, and blog posts.
View all posts
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
7 Depression Research Paper Topic Ideas
Nancy Schimelpfening, MS is the administrator for the non-profit depression support group Depression Sanctuary. Nancy has a lifetime of experience with depression, experiencing firsthand how devastating this illness can be.
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
In psychology classes, it's common for students to write a depression research paper. Researching depression may be beneficial if you have a personal interest in this topic and want to learn more, or if you're simply passionate about this mental health issue. However, since depression is a very complex subject, it offers many possible topics to focus on, which may leave you wondering where to begin.
If this is how you feel, here are a few research titles about depression to help inspire your topic choice. You can use these suggestions as actual research titles about depression, or you can use them to lead you to other more in-depth topics that you can look into further for your depression research paper.
What Is Depression?
Everyone experiences times when they feel a little bit blue or sad. This is a normal part of being human. Depression, however, is a medical condition that is quite different from everyday moodiness.
Your depression research paper may explore the basics, or it might delve deeper into the definition of clinical depression or the difference between clinical depression and sadness .
What Research Says About the Psychology of Depression
Studies suggest that there are biological, psychological, and social aspects to depression, giving you many different areas to consider for your research title about depression.
Types of Depression
There are several different types of depression that are dependent on how an individual's depression symptoms manifest themselves. Depression symptoms may vary in severity or in what is causing them. For instance, major depressive disorder (MDD) may have no identifiable cause, while postpartum depression is typically linked to pregnancy and childbirth.
Depressive symptoms may also be part of an illness called bipolar disorder. This includes fluctuations between depressive episodes and a state of extreme elation called mania. Bipolar disorder is a topic that offers many research opportunities, from its definition and its causes to associated risks, symptoms, and treatment.
Causes of Depression
The possible causes of depression are many and not yet well understood. However, it most likely results from an interplay of genetic vulnerability and environmental factors. Your depression research paper could explore one or more of these causes and reference the latest research on the topic.
For instance, how does an imbalance in brain chemistry or poor nutrition relate to depression? Is there a relationship between the stressful, busier lives of today's society and the rise of depression? How can grief or a major medical condition lead to overwhelming sadness and depression?
Who Is at Risk for Depression?
This is a good research question about depression as certain risk factors may make a person more prone to developing this mental health condition, such as a family history of depression, adverse childhood experiences, stress , illness, and gender . This is not a complete list of all risk factors, however, it's a good place to start.
The growing rate of depression in children, teenagers, and young adults is an interesting subtopic you can focus on as well. Whether you dive into the reasons behind the increase in rates of depression or discuss the treatment options that are safe for young people, there is a lot of research available in this area and many unanswered questions to consider.
Depression Signs and Symptoms
The signs of depression are those outward manifestations of the illness that a doctor can observe when they examine a patient. For example, a lack of emotional responsiveness is a visible sign. On the other hand, symptoms are subjective things about the illness that only the patient can observe, such as feelings of guilt or sadness.
An illness such as depression is often invisible to the outside observer. That is why it is very important for patients to make an accurate accounting of all of their symptoms so their doctor can diagnose them properly. In your depression research paper, you may explore these "invisible" symptoms of depression in adults or explore how depression symptoms can be different in children .
How Is Depression Diagnosed?
This is another good depression research topic because, in some ways, the diagnosis of depression is more of an art than a science. Doctors must generally rely upon the patient's set of symptoms and what they can observe about them during their examination to make a diagnosis.
While there are certain laboratory tests that can be performed to rule out other medical illnesses as a cause of depression, there is not yet a definitive test for depression itself.
If you'd like to pursue this topic, you may want to start with the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). The fifth edition, known as DSM-5, offers a very detailed explanation that guides doctors to a diagnosis. You can also compare the current model of diagnosing depression to historical methods of diagnosis—how have these updates improved the way depression is treated?
Treatment Options for Depression
The first choice for depression treatment is generally an antidepressant medication. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are the most popular choice because they can be quite effective and tend to have fewer side effects than other types of antidepressants.
Psychotherapy, or talk therapy, is another effective and common choice. It is especially efficacious when combined with antidepressant therapy. Certain other treatments, such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) or vagus nerve stimulation (VNS), are most commonly used for patients who do not respond to more common forms of treatment.
Focusing on one of these treatments is an option for your depression research paper. Comparing and contrasting several different types of treatment can also make a good research title about depression.
A Word From Verywell
The topic of depression really can take you down many different roads. When making your final decision on which to pursue in your depression research paper, it's often helpful to start by listing a few areas that pique your interest.
From there, consider doing a little preliminary research. You may come across something that grabs your attention like a new study, a controversial topic you didn't know about, or something that hits a personal note. This will help you narrow your focus, giving you your final research title about depression.
Remes O, Mendes JF, Templeton P. Biological, psychological, and social determinants of depression: A review of recent literature . Brain Sci . 2021;11(12):1633. doi:10.3390/brainsci11121633
National Institute of Mental Health. Depression .
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition . American Psychiatric Association.
National Institute of Mental Health. Mental health medications .
Ferri, F. F. (2019). Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2020 E-Book: 5 Books in 1 . Netherlands: Elsevier Health Sciences.
By Nancy Schimelpfening Nancy Schimelpfening, MS is the administrator for the non-profit depression support group Depression Sanctuary. Nancy has a lifetime of experience with depression, experiencing firsthand how devastating this illness can be.

Personalize Your Experience
Log in or create an account for a personalized experience based on your selected interests.
Already have an account? Log In
Free standard shipping is valid on orders of $45 or more (after promotions and discounts are applied, regular shipping rates do not qualify as part of the $45 or more) shipped to US addresses only. Not valid on previous purchases or when combined with any other promotional offers.
Register for an enhanced, personalized experience.
Receive free access to exclusive content, a personalized homepage based on your interests, and a weekly newsletter with topics of your choice.
Home / Parenting, Kids & Teens / Depression in college students: How to help students manage their mental health
Depression in college students: How to help students manage their mental health
Please login to bookmark.

Parents hope college will be a time for their kids to spread their wings and fly. Yet college students are now experiencing record high rates of depression and anxiety. During the 2022-2023 academic year, 41% of students reported experiencing symptoms of depression and 36% said they experienced anxiety, according to the latest Healthy Minds Study . Understandably, parents want to know what they can do to help their college age kids manage their mental health so depression doesn’t dock their wings.
Any single case of depression can have multiple causes involving a mix of biological, genetic or social factors. However, one common cause of depression in college students is the sheer scope of change that comes with moving on from the familiar world of home and high school, according to Paige I. Partain, M.D., a pediatrician at the Mayo Clinic Children’s Center in Rochester, Minnesota, with expertise in child and adolescent mental health.
In addition to changes in housing and social connections, going to college typically accelerates academic expectations. It also scrambles students’ sleep, diet and exercise patterns. For some college students — even those with no history of depression — having so many facets of their lives suddenly challenged and changed can create enough stress to trigger depression, says Dr. Partain
She adds, however, that it’s important “for parents and students alike to recognize that depression can be totally untriggered.” Sometimes students can be on top of their coursework, getting along with new friends and otherwise outwardly crushing college when they sense that their moods have dipped.
If students are baffled about why they’re feeling down, helping them understand that sometimes depression occurs without an identifiable cause is important. It can help relieve the added burden of wondering what’s wrong with them — or blaming themselves — for feeling depressed.
Says Dr. Partain, “I can’t express enough what a difference it makes when I’m talking to teenagers or young adults in their early twenties and I can explain that sometimes it just happens. It can be even more frustrating when you don’t know why depression happens. But I can see the relief in their eyes. They’re like, ‘Yes, you get it.’ To be able to just empathize and label the phenomena can be incredibly powerful.”
Spotting signs of depression in college students
Along with feeling sad and down, common signs of depression in college kids include:
- Changes in appetite such as eating more or less than usual.
- Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or sleeping too much.
- Losing in interest in favorite pastimes including playing sports, making art or hanging out with friends. “Isolation is a really key symptom, particularly for teens and young adults,” says Dr. Partain.
People often experience depression and anxiety at the same time , and college kids are no exception. Determining which one came first can be a “chicken or the egg” question, says Dr. Partain. But big shifts in a student’s mood and behavior may indicate underlying depression.
“If your kid is not one who tends to be anxious, and all of a sudden, there’s worry about everything, that might be an indicator of a problem with mood.” On the flip side, she says, if your kid is usually “a type-A go-getter, and normally a little more anxious, and all of a sudden the work isn’t getting done and grades are slipping, that can also be an indicator that there’s a problem with mood.”
Irritability is another common symptom of depression. “We think a lot about feeling sad or down, and that can certainly be the case for a teenager or a young adult. But there is good medical research to suggest that irritability might be an even better indicator of underlying mood problems,” says Dr. Partain. “It’s another textbook symptom to be aware of.”
What to say if your child seems depressed
Sometimes, parents who think their kids might be depressed are wary of butting into their business. Or they may keep quiet because they’re just not sure how to talk about depression. If parents ask Dr. Partain if they should try talking to their child’s friends or professors about their concerns, she advises them not to go around their child’s back.
Rather, Dr. Partain recommends that parents raise their concerns with their kids in a straightforward way. “As you’re trying to help children develop independence and capability — regardless of the dynamic that you have with your child — I advocate for talking with kids directly.”
To get a better sense of how children are feeling, Dr. Partain says it’s fine to initiate the conversation by text with a simple message like this: Just checking in to say I love you. How are you doing? I want to make sure you’re doing okay.
Let them know that you’re concerned and let them respond in their own time.
If your child shares feelings of being depressed or anxious, make it clear that you’re available to help in whatever way works. “You can ask, ‘Do you want my help, or is this something you want to take care of on your own?’ The biggest thing to avoid is invalidating language: ‘You’ll get over it.’ ‘Going to college is just hard,’ ” says Dr. Partain. “Parents might find a slightly different approach for every kid, but they should feel empowered to speak up because parents can play a powerful role in helping children understand what they’re experiencing.”
Help your college kid develop strategies to cope with depression
With college students experiencing depression or anxiety for the first time, parents can share self-care strategies that have been proved to ease symptoms of depression, including:
- Exercising .
- Connecting with friends.
- Eating healthy foods.
- Spending time in nature.
- Getting adequate sleep, as young adults need between seven and nine hours a night
- Finding a community on campus, whether it be with a group of fellow ultimate Frisbee fans or a religious or political organization.
If students are experiencing any kind of acute or prolonged dip in mood, their parents can also encourage them to seek treatment and help them navigate campus mental health resources. As students’ mental health becomes a central part of the conversation on college and university campuses, Dr. Partain says that more schools are preemptively providing students and parents with information about counseling and medical services.
“I encourage all parents to keep that information handy,” she says. “Even if you have a kid who’s done great and never had difficulty with mental health, it’s helpful to know about available resources, so if your child reaches the point of saying, ‘Mom, Dad, what do I do?’ you can help provide answers.”
Parents can also provide important support to students who have a history of depression, Dr. Partain says. If your child is taking an antidepressant, you can ask the healthcare professional to dispense the prescription in a 90-day supply, with refills that can be obtained at a pharmacy near campus.
As students in Dr. Partain’s care are preparing to transition to college, she has a conversation with them about their specific symptoms of depression. She also reviews the self-care strategies that have helped them feel better in the past. “Depression looks different for everyone, and it’s important for students to do the mental exercise of saying, What does it look like for me? Is it that I’m isolating myself? Is it that I’m less talkative? Is it that I’m more irritable? Is it that I don’t enjoy reading anymore?” says Dr. Partain.
The point of the conversation is to help students become more self-aware about what depression looks like for them, and spot early warning signs so they can act quickly to protect their emotional health. She encourages parents and children to have a version of this conversation together, too, and to develop a shared relapse prevention plan.
Then, if students begin to feel depression coming back while they’re away at college, their parents can reinforce whatever self-care strategies have helped get through rough patches before. For students already seeing therapists, noticing an uptick in symptoms can prompt them to reach out to ask for some extra sessions, with help from parents if needed.
“Almost all therapy providers have the ability to treat people who are in crisis or who feel like they’re significantly worsening. The same goes for healthcare professionals if students are on a medication. If I get a message from a college kid saying, ‘My mood is getting a lot worse,’ I’m going to get them seen within a week, and many other healthcare professionals will too,” says Dr. Partain.
Create a crisis plan
If students have had inpatient treatment or thoughts of suicide in any context in the past, it’s also critically important for them and their parents to have shared emergency safety plans. This can be activated if students ever becomes severely distressed again.
“Sometimes, depending on the family dynamic, the safety plan may not include having the child call the parent. The plan for the child may be calling Aunt Jane, or calling Grandma. But it’s really powerful for the parents to be able to reinforce that and say, ‘That’s OK. I want you to be safe,’ ” says Dr. Partain.
A common worry she hears from parents is that discussing suicide may make it more likely that their child will contemplate or attempt suicide. But, she says, there’s no data showing that talking about suicide makes people more likely to attempt it. In fact, it does the opposite : “Talking about it makes it easier for them to seek help in the moment. The way I phrase it to my patients is, ‘I’m really glad that you’re not having those kinds of thoughts. But I know things can change quickly, and this safety plan is just something we want to have in our back pocket.” Parents don’t have to hammer on the subject,” she adds, “but it’s an important conversation to have, and I wouldn’t avoid it.”

Relevant reading
The Human Body
Take a journey inside the body—as an alien! Hop aboard a flying saucer and travel alongside your alien guides who are on a mission to understand the wonders of human body systems. High-impact graphic art explores the circulatory system, the digestive system, the skeletal system, and more. Lively text introduces…

Discover more Parenting, Kids & Teens content from articles, podcasts, to videos.
Want more children’s health and parenting information? Sign up for free to our email list.
Children’s health information and parenting tips to your inbox.
Sign-up to get Mayo Clinic’s trusted health content sent to your email. Receive a bonus guide on ways to manage your child’s health just for subscribing.
You May Also Enjoy

Privacy Policy
We've made some updates to our Privacy Policy. Please take a moment to review.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- World J Psychiatry
- v.12(7); 2022 Jul 19
Influencing factors, prediction and prevention of depression in college students: A literature review
Xin-qiao liu.
School of Education, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300350, China. nc.ude.ukp@uiloaiqnix
School of Education, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300350, China
Wen-Jie Zhang
Graduate School of Education, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
Wen-Juan Gao
Institute of Higher Education, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
Corresponding author: Xin-Qiao Liu, PhD, Associate Professor, School of Education, Tianjin University, No. 135 Tongyan Road, Jinnan District, Tianjin 300350, China. nc.ude.ukp@uiloaiqnix
The high prevalence of depression among college students has a strong negative impact on individual physical and mental health, academic development, and interpersonal communication. This paper reviewed the extant literature by identifying nonpathological factors related to college students' depression, investigating the methods of predicting depression, and exploring nonpharmaceutical interventions for college students' depression. The influencing factors of college students' depression mainly fell into four categories: biological factors, personality and psychological state, college experience, and lifestyle. The outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 has exacerbated the severity of depression among college students worldwide and poses grave challenges to the prevention and treatment of depression, given that the coronavirus has spread quickly with high infection rates, and the pandemic has changed the daily routines of college life. To predict and measure mental health, more advanced methods, such as machine algorithms and artificial intelligence, have emerged in recent years apart from the traditional commonly used psychological scales. Regarding nonpharmaceutical prevention measures, both general measures and professional measures for the prevention and treatment of college students' depression were examined in this study. Students who experience depressive disorders need family support and personalized interventions at college, which should also be supplemented by professional interventions such as cognitive behavioral therapy and online therapy. Through this literature review, we insist that the technology of identification, prediction, and prevention of depression among college students based on big data platforms will be extensively used in the future. Higher education institutions should understand the potential risk factors related to college students' depression and make more accurate screening and prevention available with the help of advanced technologies.
Core Tip: This study reviewed the extant literature by identifying nonpathological factors related to college students' depression, investigating the methods of predicting depression, and exploring nonpharmaceutical interventions for depression among college students. The influencing factors can be categorized into students’ demographic characteristics, college experience, lifestyle, and social support. For the prediction of depression, methods such as machine algorithms and artificial intelligence have been employed together with the traditional psychological scales. This study summarizes general and professional measures that can be taken for the prevention and treatment of college students' depression.
INTRODUCTION
The prevalence of depression among college students has gradually increased in recent years, even exceeding that of the general public, which has become a global phenomenon[ 1 ]. Mounting research has focused on the topic, and the consensus is that the high prevalence of depression among college students cannot be ignored. For instance, in Asia, a follow-up survey and analysis based on 1401 undergraduates in China over four consecutive years showed that approximately 20% to 40% of undergraduates suffered from depression, anxiety and stress to different degrees, and approximately 35% of them had higher depression levels than the normal population[ 2 ]. An online survey based on 7915 freshmen students at Hong Kong University in China showed that 21%, 41% and 27% of individuals had moderate or higher levels of depression, anxiety and stress, respectively, far exceeding the average in the general population[ 3 ]. The median prevalence rate for depression among 15859 college students in six ASEAN countries (Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam) was 29.4%, and 7% to 8% of students committed suicide; despite the high prevalence of mental illness, their willingness to seek professional help was relatively low[ 4 ]. Among 642 college students in Saudi Arabia, the proportions of moderate depression, anxiety and stress were 53.6%, 65.7% and 34.3%, respectively[ 5 ]. In Africa, among 1206 Nigerian college students, 5.6% had mild depression, and 2.7% suffered severe depressive disorder[ 6 ]. In North America, 53% of 1455 American college students reported that they had experienced depression since the beginning of college, and 9% said they had considered suicide since the beginning of college[ 7 ]. Thirty percent of 7800 Canadian undergraduates reported that their psychological stress increased, and the degree of depression was significantly higher than that of the general population[ 8 ]. In Europe, more than one-third of college students from three higher education institutions in the United Kingdom suffered from long-term mental health diseases, the prevalence rate of which was higher than the average level of national surveys, and the scores of the eight dimensions of mental health, measured by the MOS 36-item short-form health survey, were all significantly lower than those of local peers aged 18 to 34[ 9 ]. In Oceania, 21.8% of 751 Australian college students reported depression, and their depression scores were higher than the standard scores of the general Australian population[ 10 ].
The global outbreak of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic in 2020 brought in additional pressure and challenges for the prevention and treatment of depression among college students. Many reports worldwide voiced that college students had a greater probability of struggling with higher levels of depression after the pandemic. The data show that after the outbreak of the pandemic, acute stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms were widespread among Chinese college students, and the incidence rate was significantly higher than before[ 11 ]. The prevalence rates of moderate depression and suicide-related symptoms among 212 Japanese college students were 11.7% and 6.7%, respectively[ 12 ]. Among 2031 American college students, 48.14% suffered from moderate to severe depression, 38.48% experienced moderate to severe anxiety, 18.04% had suicidal thoughts, and 71.26% reported that their stress/anxiety levels increased during the pandemic[ 13 ]. More than a quarter of Swiss university students had depressive symptoms during the pandemic, which was much higher than that of the general population and higher than that before the pandemic[ 14 ].
The transition from high school to university is full of tension and adaptation. It is a critical period for the shift from late adolescence to adulthood or emerging adulthood, which is neither adolescence nor young adulthood but theoretically and empirically distinct from both periods[ 15 ]. Arnett stressed that this is a stage full of self-exploration, instability, possibility, self-focus, and something in between[ 16 ]. At this phase, individuals will face the challenges of identity and role transformation and more diversification and complexity from families and institutions. Specifically, compared with middle schools, universities put forward higher requirements for freshmen's independence and self-regulation, such as the independence of living in a new place, the autonomy of learning patterns, and the complexity of social networks. However, confronted with these challenges, college students entering the campus for the first time often wander between independence and dependence. On the one hand, they are eager to enjoy new freedoms; on the other hand, it is difficult to eliminate their attachment and economic dependence on their parents; thus, they are often in a state of "pseudo independence"[ 17 ].
In summary, compared with teenagers and adults, college students are the key group at significantly higher risk of poor mental health. A series of factors, including family, college, studies, and social interactions, are likely to induce college students' depression. However, few publications have reviewed the literature on risk factors for college students’ depression. Given that most studies examined individual risk factors based on samples from a certain country or region, this paper reviewed the extant literature related to college students' depression and aimed to systematically present the nonpathological factors, predictions and nonpharmaceutical interventions for college students' depression to provide a reference for stakeholders worldwide.
NONPATHOLOGICAL INFLUENCING FACTORS OF DEPRESSION
The related factors can be roughly divided into four categories: biological factors, personality and psychological state, college experience, and lifestyle. The literature review presented the specific risk factors under four categories in Table Table1. 1 . Subsequently, this paper explained certain factors with controversial research conclusions.
Factors related to depression in college students
Some studies have asserted that the risk of depression in female college students is significantly higher than that in male students[ 24 , 26 , 40 , 41 ]. The possible mechanism lies in physiological differences between the sexes (such as genetic vulnerability, hormone, and cortisol levels), differences in self-concept, and different role expectations from society leading to different emotional responses and behavior patterns. Females are more likely to internalize their negative feelings, whereas males resort to externalizing behaviors such as smoking and alcoholism[ 42 - 44 ]. However, some analyses did not find significant sex differences[ 28 , 45 , 46 ]. Other studies have shown that men have a higher prevalence of depression[ 20 , 47 ]. This may be ascribed to their conservative attitudes toward mental health counseling and treatment under certain social expectations. For instance, women are more help-seeking than men and therefore tend to have more diagnoses and treatment. In particular, gregarious women are more likely to discuss their difficulties with others, such as family and friends, as a form of coping. Nevertheless, considering that societal expectations for men might be different, with those who express vulnerable emotions being regarded as weak, the depressive symptoms of men may manifest as anger and excessive indulgence in smoking and drinking, which are more acceptable masculine expressions in society[ 43 , 44 ].
Year of study
Most studies have found significant differences in the depression level of college students in different years of their education, although some found the difference to be insignificant[ 28 ]. Some research has suggested that undergraduates with lower grades suffer more from depression, which can be attributed to separation from relatives and friends, social adaptation, academic pressure, and increased investment in social activities. A survey of Chinese students showed that the highest scores for depression, anxiety and stress all appeared in the first three years of college, and students’ mental health status was relieved in the fourth year with the passage of time[ 48 ]. A survey of medical students in Saudi Arabia found that students' depression levels continued to rise from the first year of enrollment, reached maximum intensity in the third year, and then dropped significantly with graduation in the last year[ 22 ]. However, other studies found that compared with other undergraduates, senior students had a higher risk of depression. The graduation year is a critical period for individuals to further their studies or go into society, and students are faced with many new stressors, such as graduation pressure, pressure from grades and applications to other institutions, difficulties in future career planning and employment discrimination in the labor market[ 49 ]. Compared with undergraduates, postgraduates may be exposed to greater pressure in obtaining financial security, stable employment, getting married and other aspects of life, which results in a higher risk of depression[ 19 , 41 ].
The depression issues of college students can largely be attributed to their lifestyles. First, the lack of regular physical activities increases the risk of depression[ 11 , 14 ], particularly for individuals whose amount of weekly physical activity fails to meet the standards of the World Health Organization[ 20 ]. Second, substance abuse, such as excessive smoking, alcohol abuse[ 6 , 12 , 21 ], or alcohol intake[ 33 ], can cause depressive disorders, and it should be noted that their relationship might be bidirectional. Studies have shown that individuals with depression are more likely to drink obsessively to relieve their negative emotions due to their poor self-control, which will in turn trap them in a vicious cycle between excessive drinking and depressive disorders[ 32 ]. Third, unhealthy sleeping habits such as daytime sleepiness[ 20 , 34 ], poor sleep quality[ 21 ], and short[ 35 ] or long sleep duration[ 10 ] may lead to depressive symptoms. Fourth, unhealthy nutritional habits are also among the crucial factors that are strongly correlated with depression[ 36 ]. From the perspective of dietary structure and nutritional habits, individuals with depression often report excessive intake of high-fat snacks and margarine/butter/meat fat and inadequate intake of fruits, vegetables, and lean protein[ 30 ]. Overeating[ 14 ] and skipping breakfast[ 10 ], especially for males, are also related to depressive disorders.
Network usage
Relevant studies have indicated that depression in college students is associated with their time spent on the internet[ 50 , 51 ]. Those who suffer from internet addiction and dependence are more likely to struggle with depression[ 52 ], and phubbing (a portmanteau of the words “phone” and “snubbing”) has been proven to be a mediator of the relationship between depression and problematic internet use[ 53 ], mainly focusing on social networking and entertainment[ 54 ].
Social software
Some researchers believe that social software, as a complementary mode of providing social support, can provide more help for people with low social support, thus reducing the occurrence of depression[ 55 ]. However, there is increasing recognition that social networks, especially the excessive use of social media, are closely related to depression[ 56 - 60 ]. Regarding the possible contributing factors, first, individuals who frequently use social software are more likely to have a fear of missing out, and they are always worried that they will miss some important information if they do not refresh the social platform dynamics frequently. This persistent social anxiety will increase the risk of depression[ 61 ]. Second, college students who are addicted to social media are more likely to have a comparison mentality when checking the status updates of others on social network platforms, especially when they feel that others' lives are better than their own, which can result in symptoms of depression[ 62 ]. Third, it is quite impossible for those who struggle with depressive disorders to establish satisfactory interpersonal relationships in virtual space since they usually maintain poor relationships in the real world. The lack of expected support from social networks undoubtedly aggravates their depression[ 63 ].
In addition, because the COVID-19 pandemic has aggravated the depression of college students worldwide, we further analyzed the influencing factors of college students' depression against the background of the COVID-19 pandemic, apart from the general factors mentioned above: (1) Given that COVID-19 is highly contagious and uncertain, the higher risk of becoming infected with COVID-19 is closely related to individuals’ level of depression. Research has indicated that individuals who live in high-risk areas for COVID-19, have close contact with the COVID-19 virus, or have acquaintances or relatives infected with COVID-19[ 19 , 41 ] often have a higher prevalence of depression; (2) Considering that the internet serves as the main channel for college students to obtain information about COVID-19, those who browse the internet for a short time will not suffer from too much anxiety because of the small amount of information they receive. Meanwhile, students surfing the internet for a long time will be able to obtain more accurate details about COVID-19, which can prevent misunderstanding relevant information. Nevertheless, individuals with shorter browsing times often have a higher risk for depression given that they may be easily misled by the rumors and have limited time to verify the authenticity of relevant information[ 64 ]; (3) Academic stress increases the degree of depression of college students with the closure of schools, the challenges of online courses and the risk of graduation delay[ 13 , 65 ]; (4) Financial pressures include the impact of the pandemic on family economic resources[ 49 ] and the increasing uncertainty of individuals about future employment[ 13 ]; (5) Environmental changes, home study, self-isolation, isolation from relatives and friends, decreased exercise frequency, uncertainty of school reopening, regular temperature measurement, wearing masks for a long time, cancellation of package deliveries and take-out supplies and other forced changes in daily study and living habits all increase the risk of depression among college students[ 13 , 49 ]; (6) There is less family support, social support and deteriorating family relations[ 65 ]; and (7) Social confidence wanes. Research has shown that the prevalence of depression also increases when individuals lack confidence in the government[ 66 ].
PREDICTING DEPRESSION
Traditional depression prediction methods are based on various self-rated psychological scales, such as the 21-item depression, anxiety and stress scale (DASS-21) and the self-rating depression scale (SDS). A growing body of research on the reliability and validity of the DASS-21 scale has been published from throughout the world (such as in Britain, Portugal, The Netherlands, Italy, the United States, and Nepal), all of which show that the DASS-21 is a mature tool that can accurately measure the symptoms of depression, anxiety and stress in adult clinical and nonclinical samples and identify and screen people at high risk of depression[ 67 - 70 ]. Similar to the DASS-21, the prediction reliability and validity of the SDS scale for depression have also been confirmed and recognized by relevant studies[ 71 - 73 ]. These are screening tools, and when elevated scores are detected, further evaluation is needed by a clinician. Moreover, the measurement often needs to rely on the patient's own active consultation and cooperation, which is costly, time-consuming, and inaccurate, and there is a risk of social stigma for patients. In recent years, with the progress of science and technology, a series of more advanced methods of depression risk prediction and identification, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, has emerged, which can deeply learn all types of social and behavioral characteristics of people with potential mental illness risk based on big data and then accurately simulate, identify and predict who they are. Typical methods include support vector machines, decision trees, naïve Bayes classifiers, K-nearest neighbor classifiers and logistic regression[ 74 ]. More specifically, support vector machines are applied to classify handwritten digits and organize cancer tissue samples using microarray expression data[ 75 , 76 ]. Decision trees serve as a hierarchical classifier, employing certain rules to divide the predictor space. The naïve Bayes classifier is based on Bayes’ theorem and is employed to predict class membership probabilities. K-nearest neighbor classifiers are instance-based learning classifiers that compare a new datapoint with the k nearest sample datapoints, regarding the class with the nearest neighbors to the new datapoint as the class of the datapoint. Logistic regression, as a probabilistic linear classifier, directly estimates class probabilities with the logit transform[ 74 ].
The gait feature analysis method based on machine learning has been developed as a supplementary tool to identify depression among college students. Relevant research found that the gait of depressed and nondepressed college students showed significant differences. The specific gait performance of depressed patients included reduced walking velocity, arm swing, vertical head movement and stride length, increased body sway and a slumped head posture. When the above series of features were applied to classifiers with different machine learning algorithms, the accuracy of depression screening and recognition reached 91.58%[ 77 ]. A study collected 121 campus behaviors of college students, including basic personal information, academic achievements, poverty subsidies, consumption habits, daily life, library behaviors, and eating habits, and found that 25 campus behaviors are related to depression, such as failing exams, having bad eating habits, increasing night activities, decreasing morning activities, and seldom participating in social activities (such as eating with friends). On this basis, a depression recognition method was developed by combining machine learning algorithms[ 78 ]. There is also research and development of a machine learning method to identify depression based on college students' smartphone and fitness tracker data ( e.g. , Bluetooth, calls, location, campus map, phone usage, steps, sleep), which extracts many features that can effectively identify depression, such as long-term inactivity and restless sleep at night; the recognition accuracy of this method for college students' depression can reach over 80%[ 79 ].
In addition, it is worth noting that social software has increasingly become a nonpathological risk factor for depression among college students. Addiction to social software is often more likely to induce depression, while college students at high risk of depression are more inclined to vent their negative emotions and relieve stress on various online social platforms. In this way, social network behavior analysis was developed based on machine learning as another effective way to identify and predict depression[ 80 , 81 ]. Through mining, emotion analysis and emotion recognition of personal user information data on social network platforms, we can capture the abnormal behavior patterns of people with depression, among which the most frequently used communication methods are text, emoticons, user log-in information and pictures. The selected research usually uses classic off-the-shelf classifiers to analyze the available information and combines words, such as National Research Council Canada (NRC) Word-Emoticon Association Lexicon, WordNet-Affect, Anew, and Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count tool. It is challenging to analyze the combination of temporal information and different types of information[ 82 ]. For example, some studies have conducted text analysis on the Sina Weibo data of Chinese college students. First, the behavioral differences between depressed and nondepressed individuals in language style, emoji usage, number of Weibos, followers and so on were obtained. Then, a deep neural network was applied to feature extraction and dimension reduction for college students with depression, and input data suitable for the classifier were constructed. Finally, a deeply integrated support vector machine was introduced to classify the input data, and more stable and accurate depression identification was realized[ 83 ]. Some studies collected historical behavior data of American college students using Google search and YouTube during the COVID-19 pandemic and found that there were strong correlations between depression and the following online behavior changes: long use sessions (multiple comprehensive activities with short time intervals), more online activities in the middle of the night or even staying up late, and searching for more authentic and realistic topics related to work, money or death, which verifies the feasibility of building a machine learning model based on individual behavior signals to predict college students' depression[ 84 ].
Generally, machine learning has been widely used in a series of mental health risk predictions about college students' depression, stress[ 85 ] and suicidal behavior[ 86 , 87 ]. Big data brings many benefits to the prediction of psychological states by reducing the subjectivity of human judgment or human operations to a certain extent and relieving the concerns of patients about possible social stigma and discrimination. In other words, big data and machine learning result in no prejudice in predictions. Thus, confirming depression through data and behavioral performance may be the developing trend in identifying and predicting depression among college students and an even broader population in the future. However, issues such as data privacy and data protection are unavoidable. The government needs to set stricter privacy protection policies, while a more extensive collection of personal data needs to be confirmed and approved by the collectors.
NONPHARMACEUTICAL PREVENTION OF DEPRESSION
Both general and professional measures for the prevention and treatment of depression were explored in this study. The former emphasizes the importance of multi-subject participation in the prevention and treatment of depression among college students, while the latter focuses on measures with the theoretical support of professional disciplines such as psychology.
General intervention measures
The general interventions are summarized in Table Table2 2 and can be coarsely categorized into support from family, interventions by colleges and universities, cultivation of personal lifestyles, and resilience therapy.
High level of family support
A high level of family support can be used as a buffer against the influence of a high-stress reaction to prevent the development of depression[ 91 ]. In a study of 62 patients who recovered from depression, a high level of perceived emotional support from their families indicated that family support, especially emotional support, was very important for the relief and even rehabilitation of depression[ 92 ]. However, it should be noted that family support and perfect family functioning depend more on objective characteristics related to family socioeconomic status, such as parents' level of education[ 93 ]. In addition, some studies have found that the role family support plays in the prevention and treatment of depression also depends on the levels of perceived stress reactivity of individuals. Specifically, family emotional support can significantly alleviate the symptoms of depression when the perceived stress reactivity is low, but when the individual shows a high level of the perceived stress response, the effect of family emotional support in preventing depression will be greatly reduced[ 94 ].
The intervention from colleges and universities
Prior literature has shown that the faculties, peers, and social clubs on campus can help alleviate the negative effects of online games on depression. Students may seek social support from their teachers, peers, or psychological counseling centers to prevent addiction to online video games that may lead to depressive disorders[ 38 ]. Therefore, colleges and universities should build mental health services involving faculty, students, and psychological counseling centers. In addition, some studies have indicated that the implementation of related courses and projects in universities, such as resilience programs (including goal-building, mindfulness, and resilience skills), might be effective in improving college students' mental health[ 95 ].
Cultivation of healthy lifestyles
Apart from external support from family and intervention by higher education institutions, the prevention of depression also needs to rely on the patient's own efforts. Studies have shown that healthy lifestyles, including proper physical exercise, healthy sleep and diet, and regular sun exposure, can help prevent or reduce the occurrence of depression in college students[ 96 ]. For instance, students with a consistent sleep schedule and sufficient sleep duration are less likely to suffer from depression. Meanwhile, regular sun exposure aids in the synthesis of vitamin D in the body, which is crucial to release fatigue and change the negative moods that individuals with mild or moderate depression may experience[ 46 ]. Proper physical activities are also important for stress and depression relief among college students[ 97 , 98 ]. Additionally, improving diet and overall nutrition is also an effective way to treat depression[ 99 ]. In particular, eating breakfast on time helps reduce the risk of depression[ 46 ]. Certain nutrients, including zinc, magnesium, B vitamins, and cooking fats, have also been proven to be associated with depressive symptoms[ 100 - 102 ]. Therefore, colleges and universities can help prevent the occurrence of depression in college students by providing a regular diet with an adequate intake of vitamins and nutrients[ 103 ].
Resilience therapy
Some research has shown that resilience therapy can help individuals maintain mental health in the face of negative emotions and stressful events, thereby reducing the occurrence of depression[ 104 ]. Others have also found that it can reduce depressive symptoms by modulating the effects of timing and sleep quality on depression[ 105 ].
Professional intervention measures
Cognitive behavioral therapy, which aims to change individual thoughts and behaviors, has been the most widely used treatment method for depression thus far[ 106 - 110 , 113 - 115 ]. Mindfulness intervention programs[ 111 ] based on cognitive behavioral therapy and dialectal behavior group therapy[ 112 ] can effectively alleviate the depressive symptoms of college students.
In recent years, a growing number of online technologies have been applied to the treatment of depression among college students thanks to the rapid development of internet technology and mobile terminal devices[ 116 - 120 ], and some of the technologies were even skillfully combined with cognitive behavioral therapy[ 121 , 122 ]. For example, there are many apps that incorporate elements of cognitive behavioral therapy and mindfulness. A study from Switzerland revealed that apps such as MoodKit, MoodMission and MoodPrismying can successfully deliver ecological momentary interventions (EMIs) based on cognitive behavioral therapy principles to users through smartphones, thereby improving their well-being and effectively reducing the symptoms of depression. The study also noted that EMI has been generally accepted by users of different ages, sex, educational backgrounds and occupations and is expected to provide scalable global mental health solutions[ 123 ]. Compared with behavioral cognitive therapy and online interventions, the efficacy of traditional educational/personalized feedback interventions in the past has been slightly inferior. Some projects have evaluated the effectiveness of mailing personalized standardized alcohol surveys for college students' depression prevention, but unfortunately, there is no obvious improvement[ 124 ].
LIMITATIONS
Limitations of this study include the following. First, this paper analyzed relevant literature written in English, but research in other languages, such as Chinese, Japanese, German, and Italian, was not included. Second, the paper is a narrative review of extensive studies including the influencing factors, prediction, and prevention of depression in college students. We did not undertake explicit methods such as systematic reviews, nor did we involve substantial clinical results and corroborate the evidence in prior literature such as retrospective reviews. The study merely presents studies in the pertinent field by summarizing their main conclusions, which cannot be directly applied to clinical treatment.
This paper reviewed the extant literature by identifying nonpathological factors related to depression among college students, investigating methods of predicting their depressive symptoms, and summarizing nonpharmaceutical interventions. The nonpathological related factors of college students' depression mainly fell into four categories: biological factors, personality and psychological state, college experience, and lifestyle. The outbreak of COVID-19 exacerbated the severity of depression among college students worldwide and posed grave challenges to the prevention and treatment of depression, given that the coronavirus spread quickly with high infection rates, changing the daily routines of college life and creating financial stress, academic stress, and long-term home isolation. Regarding the prediction of vulnerability to depression, machine algorithms and artificial intelligence based on big data have emerged in addition to the commonly used psychological scales. A series of big data, such as text, pictures, video and audio, based on individual social network behaviors was widely discussed and applied to identify and predict college students' depression. Regarding preventive measures, both general measures and professional interventions were discussed for the prevention and treatment of college students' depression, which required not only help from family, professionals, and institutions (cognitive behavioral therapy and online therapy) and society but also the individuals themselves through the cultivation of healthy habits.
Technology based on the internet and big data platforms will become more widely used in the future to identify, predict, and prevent depression among college students. Higher education institutions should clearly understand the potential risk factors related to college students' depression and employ advanced technology for more accurate screening and prevention. They should also work on increasing access to resources and clinical support considering the common difficulties in making appointments and long-term waits for psychological consultation.
Furthermore, this paper proposed two prospects for the future development of nonpharmaceutical interventions for college students' depression. First, the risk of stigma should be minimized. Many traditional precautionary measures are used to help students identify whether they suffer from depression, including e-mail, posters, campus activities, pamphlets, and first aid training courses about mental health. However, these measures may result in further concerns about the risk of stigmatization and psychological worries of students[ 125 ]. Therefore, in the future, we should avoid stigmatizing issues in the prevention of depression among college students and pay more attention to personalization and privacy in the development and application of precautionary measures. Second, the importance of general measures for the prevention and treatment of college students' depression should be combined with professional interventions such as cognitive intervention therapy and other evidence-based treatment. A meta-analysis showed that apart from cognitive behavioral therapy and mindfulness-based interventions, other measures, such as art, exercise, and peer support, are also effective in relieving depressive symptoms in college students[ 126 ].
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank Han T for his contribution to the language editing of the first draft of this study.
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Peer-review started: February 27, 2022
First decision: April 18, 2022
Article in press: June 22, 2022
Specialty type: Psychiatry
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C, C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Kaur M, United States; Radhakrishnan R, New Zealand; Rose AF, United States; Tanabe S, Japan S-Editor: Gao CC L-Editor: A P-Editor: Gao CC
Contributor Information
Xin-Qiao Liu, School of Education, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300350, China. nc.ude.ukp@uiloaiqnix .
Yu-Xin Guo, School of Education, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300350, China.
Wen-Jie Zhang, Graduate School of Education, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China.
Wen-Juan Gao, Institute of Higher Education, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China.
Change Password
Your password must have 8 characters or more and contain 3 of the following:.
- a lower case character,
- an upper case character,
- a special character
Password Changed Successfully
Your password has been changed
- Sign in / Register
Request Username
Can't sign in? Forgot your username?
Enter your email address below and we will send you your username
If the address matches an existing account you will receive an email with instructions to retrieve your username
An Exploratory Study of Students with Depression in Undergraduate Research Experiences
- Katelyn M. Cooper
- Logan E. Gin
- M. Elizabeth Barnes
- Sara E. Brownell
*Address correspondence to: Katelyn M. Cooper ( E-mail Address: [email protected] ).
Department of Biology, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL, 32816
Search for more papers by this author
Biology Education Research Lab, Research for Inclusive STEM Education Center, School of Life Sciences, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85281
Depression is a top mental health concern among undergraduates and has been shown to disproportionately affect individuals who are underserved and underrepresented in science. As we aim to create a more inclusive scientific community, we argue that we need to examine the relationship between depression and scientific research. While studies have identified aspects of research that affect graduate student depression, we know of no studies that have explored the relationship between depression and undergraduate research. In this study, we sought to understand how undergraduates’ symptoms of depression affect their research experiences and how research affects undergraduates’ feelings of depression. We interviewed 35 undergraduate researchers majoring in the life sciences from 12 research-intensive public universities across the United States who identify with having depression. Using inductive and deductive coding, we identified that students’ depression affected their motivation and productivity, creativity and risk-taking, engagement and concentration, and self-perception and socializing in undergraduate research experiences. We found that students’ social connections, experiencing failure in research, getting help, receiving feedback, and the demands of research affected students’ depression. Based on this work, we articulate an initial set of evidence-based recommendations for research mentors to consider in promoting an inclusive research experience for students with depression.
INTRODUCTION
Depression is described as a common and serious mood disorder that results in persistent feelings of sadness and hopelessness, as well as a loss of interest in activities that one once enjoyed ( American Psychiatric Association [APA], 2013 ). Additional symptoms of depression include weight changes, difficulty sleeping, loss of energy, difficulty thinking or concentrating, feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt, and suicidality ( APA, 2013 ). While depression results from a complex interaction of psychological, social, and biological factors ( World Health Organization, 2018 ), studies have shown that increased stress caused by college can be a significant contributor to student depression ( Dyson and Renk, 2006 ).
Depression is one of the top undergraduate mental health concerns, and the rate of depression among undergraduates continues to rise ( Center for Collegiate Mental Health, 2017 ). While we cannot discern whether these increasing rates of depression are due to increased awareness or increased incidence, it is clear that is a serious problem on college campuses. The percent of U.S. college students who self-reported a diagnosis with depression was recently estimated to be about 25% ( American College Health Association, 2019 ). However, higher rates have been reported, with one study estimating that up to 84% of undergraduates experience some level of depression ( Garlow et al. , 2008 ). Depression rates are typically higher among university students compared with the general population, despite being a more socially privileged group ( Ibrahim et al. , 2013 ). Prior studies have found that depression is negatively correlated with overall undergraduate academic performance ( Hysenbegasi et al. , 2005 ; Deroma et al. , 2009 ; American College Health Association, 2019 ). Specifically, diagnosed depression is associated with half a letter grade decrease in students’ grade point average ( Hysenbegasi et al. , 2005 ), and 21.6% of undergraduates reported that depression negatively affected their academic performance within the last year ( American College Health Association, 2019 ). Provided with a list of academic factors that may be affected by depression, students reported that depression contributed to lower exam grades, lower course grades, and not completing or dropping a course.
Students in the natural sciences may be particularly at risk for depression, given that such majors are noted to be particularly stressful due to their competitive nature and course work that is often perceived to “weed students out”( Everson et al. , 1993 ; Strenta et al. , 1994 ; American College Health Association, 2019 ; Seymour and Hunter, 2019 ). Science course instruction has also been described to be boring, repetitive, difficult, and math-intensive; these factors can create an environment that can trigger depression ( Seymour and Hewitt, 1997 ; Osborne and Collins, 2001 ; Armbruster et al ., 2009 ; Ceci and Williams, 2010 ). What also distinguishes science degree programs from other degree programs is that, increasingly, undergraduate research experiences are being proposed as an essential element of a science degree ( American Association for the Advancement of Science, 2011 ; President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology, 2012 ; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine [NASEM], 2017 ). However, there is some evidence that undergraduate research experiences can add to the stress of college for some students ( Cooper et al. , 2019c ). Students can garner multiple benefits from undergraduate research, including enhanced abilities to think critically ( Ishiyama, 2002 ; Bauer and Bennett, 2003 ; Brownell et al. , 2015 ), improved student learning ( Rauckhorst et al. , 2001 ; Brownell et al. , 2015 ), and increased student persistence in undergraduate science degree programs ( Jones et al. , 2010 ; Hernandez et al. , 2018 ). Notably, undergraduate research experiences are increasingly becoming a prerequisite for entry into medical and graduate programs in science, particularly elite programs ( Cooper et al. , 2019d ). Although some research experiences are embedded into formal lab courses as course-based undergraduate research experiences (CUREs; Auchincloss et al. , 2014 ; Brownell and Kloser, 2015 ), the majority likely entail working with faculty in their research labs. These undergraduate research experiences in faculty labs are often added on top of a student’s normal course work, so they essentially become an extracurricular activity that they have to juggle with course work, working, and/or personal obligations ( Cooper et al. , 2019c ). While the majority of the literature surrounding undergraduate research highlights undergraduate research as a positive experience ( NASEM, 2017 ), studies have demonstrated that undergraduate research experiences can be academically and emotionally challenging for students ( Mabrouk and Peters, 2000 ; Seymour et al. , 2004 ; Cooper et al. , 2019c ; Limeri et al. , 2019 ). In fact, 50% of students sampled nationally from public R1 institutions consider leaving their undergraduate research experience prematurely, and about half of those students, or 25% of all students, ultimately leave their undergraduate research experience ( Cooper et al. , 2019c ). Notably, 33.8% of these individuals cited a negative lab environment and 33.3% cited negative relationships with their mentors as factors that influenced their decision about whether to leave ( Cooper et al. , 2019c ). Therefore, students’ depression may be exacerbated in challenging undergraduate research experiences, because studies have shown that depression is positively correlated with student stress ( Hish et al. , 2019 ).
While depression has not been explored in the context of undergraduate research experiences, depression has become a prominent concern surrounding graduate students conducting scientific research. A recent study that examined the “graduate student mental health crisis” ( Flaherty, 2018 ) found that work–life balance and graduate students’ relationships with their research advisors may be contributing to their depression ( Evans et al. , 2018 ). Specifically, this survey of 2279 PhD and master’s students from diverse fields of study, including the biological/physical sciences, showed that 39% of graduate students have experienced moderate to severe depression. Fifty-five percent of the graduate students with depression who were surveyed disagreed with the statement “I have good work life balance,” compared to only 21% of students with depression who agreed. Additionally, the study highlighted that more students with depression disagreed than agreed with the following statements: their advisors provided “real” mentorship, their advisors provided ample support, their advisors positively impacted their emotional or mental well-being, their advisors were assets to their careers, and they felt valued by their mentors. Another recent study identified that depression severity in biomedical doctoral students was significantly associated with graduate program climate, a perceived lack of employment opportunities, and the quality of students’ research training environment ( Nagy et al. , 2019 ). Environmental stress, academic stress, and family and monetary stress have also been shown to be predictive of depression severity in biomedical doctoral students ( Hish et al. , 2019 ). Further, one study found that self-esteem is negatively correlated and stress is positively correlated with graduate student depression; presumably research environments that challenge students’ self-esteem and induce stress are likely contributing to depressive symptoms among graduate students ( Kreger, 1995 ). While these studies have focused on graduate students, and there are certainly notable distinctions between graduate and undergraduate research, the research-related factors that affect graduate student depression, including work–life balance, relationships with mentors, research environment, stress, and self-esteem, may also be relevant to depression among undergraduates conducting research. Importantly, undergraduates in the United States have reported identical levels of depression as graduate students but are often less likely to seek mental health care services ( Wyatt and Oswalt, 2013 ), which is concerning if undergraduate research experiences exacerbate depression.
Based on the literature on the stressors of undergraduate research experiences and the literature identifying some potential causes of graduate student depression, we identified three aspects of undergraduate research that may exacerbate undergraduates’ depression. Mentoring: Mentors can be an integral part of a students’ research experience, bolstering their connections with others in the science community, scholarly productivity, and science identity, as well as providing many other benefits ( Thiry and Laursen, 2011 ; Prunuske et al. , 2013 ; Byars-Winston et al. , 2015 ; Aikens et al. , 2016 , 2017 ; Thompson et al. , 2016 ; Estrada et al. , 2018 ). However, recent literature has highlighted that poor mentoring can negatively affect undergraduate researchers ( Cooper et al. , 2019c ; Limeri et al. , 2019 ). Specifically, one study of 33 undergraduate researchers who had conducted research at 10 institutions identified seven major ways that they experienced negative mentoring, which included absenteeism, abuse of power, interpersonal mismatch, lack of career support, lack of psychosocial support, misaligned expectations, and unequal treatment ( Limeri et al. , 2019 ). We hypothesize negative mentoring experiences may be particularly harmful for students with depression, because support, particularly social support, has been shown to be important for helping individuals with depression cope with difficult circumstances ( Aneshensel and Stone, 1982 ; Grav et al. , 2012 ). Failure: Experiencing failure has been hypothesized to be an important aspect of undergraduate research experiences that may help students develop some the most distinguishing abilities of outstanding scientists, such as coping with failure, navigating challenges, and persevering ( Laursen et al. , 2010 ; Gin et al. , 2018 ; Henry et al. , 2019 ). However, experiencing failure and the stress and fatigue that often accompany it may be particularly tough for students with depression ( Aldwin and Greenberger, 1987 ; Mongrain and Blackburn, 2005 ). Lab environment: Fairness, inclusion/exclusion, and social support within one’s organizational environment have been shown to be key factors that cause people to either want to remain in the work place and be productive or to want to leave ( Barak et al. , 2006 ; Cooper et al. , 2019c ). We hypothesize that dealing with exclusion or a lack of social support may exacerbate depression for some students; patients with clinical depression react to social exclusion with more pronounced negative emotions than do individuals without clinical depression ( Jobst et al. , 2015 ). While there are likely other aspects of undergraduate research that affect student depression, we hypothesize that these factors have the potential to exacerbate negative research experiences for students with depression.
Depression has been shown to disproportionately affect many populations that are underrepresented or underserved within the scientific community, including females ( American College Health Association, 2018 ; Evans et al. , 2018 ), first-generation college students ( Jenkins et al. , 2013 ), individuals from low socioeconomic backgrounds ( Eisenberg et al. , 2007 ), members of the LGBTQ+ community ( Eisenberg et al. , 2007 ; Evans et al. , 2018 ), and people with disabilities ( Turner and Noh, 1988 ). Therefore, as the science community strives to be more diverse and inclusive ( Intemann, 2009 ), it is important that we understand more about the relationship between depression and scientific research, because negative experiences with depression in scientific research may be contributing to the underrepresentation of these groups. Specifically, more information is needed about how the research process and environment of research experiences may affect depression.
Given the high rate of depression among undergraduates, the links between depression and graduate research, the potentially challenging environment of undergraduate research, and how depression could disproportionately impact students from underserved communities, it is imperative to begin to explore the relationship between scientific research and depression among undergraduates to create research experiences that could maximize student success. In this exploratory interview study, we aimed to 1) describe how undergraduates’ symptoms of depression affect their research experiences, 2) understand how undergraduate research affects students’ feelings of depression, and 3) identify recommendations based on the literature and undergraduates’ reported experiences to promote a positive research experience for students with depression.
This study was done with an approved Arizona State University Institutional Review Board protocol #7247.
In Fall 2018, we surveyed undergraduate researchers majoring in the life sciences across 25 research-intensive (R1) public institutions across the United States (specific details about the recruitment of the students who completed the survey can be found in Cooper et al. (2019c) ). The survey asked students for their opinions about their undergraduate research experiences and their demographic information and whether they would be interested in participating in a follow-up interview related to their research experiences. For the purpose of this study, we exclusively interviewed students about their undergraduate research experiences in faculty member labs; we did not consider students’ experiences in CUREs. Of the 768 undergraduate researchers who completed the survey, 65% ( n = 496) indicated that they would be interested in participating in a follow-up interview. In Spring 2019, we emailed the 496 students, explaining that we were interested in interviewing students with depression about their experiences in undergraduate research. Our specific prompt was: “If you identify as having depression, we would be interested in hearing about your experience in undergraduate research in a 30–60 minute online interview.” We did not define depression in our email recruitment because we conducted think-aloud interviews with four undergraduates who all correctly interpreted what we meant by depression ( APA, 2013 ). We had 35 students agree to participate in the interview study. The interview participants represented 12 of the 25 R1 public institutions that were represented in the initial survey.
Student Interviews
We developed an interview script to explore our research questions. Specifically, we were interested in how students’ symptoms of depression affect their research experiences, how undergraduate research negatively affects student depression, and how undergraduate research positively affects student depression.
We recognized that mental health, and specifically depression, can be a sensitive topic to discuss with undergraduates, and therefore we tried to minimize any discomfort that the interviewees might experience during the interview. Specifically, we conducted think-aloud interviews with three graduate students who self-identified with having depression at the time of the interview. We asked them to note whether any interview questions made them uncomfortable. We also sought their feedback on questions given their experiences as persons with depression who had once engaged in undergraduate research. We revised the interview protocol after each think-aloud interview. Next, we conducted four additional think-aloud interviews with undergraduates conducting basic science or biology education research who identified with having depression to establish cognitive validity of the questions and to elicit additional feedback about any questions that might make someone uncomfortable. The questions were revised after each think-aloud interview until no question was unclear or misinterpreted by the students and we were confident that the questions minimized students’ potential discomfort ( Trenor et al. , 2011 ). A copy of the final interview script can be found in the Supplemental Material.
All interviews were individually conducted by one of two researchers (K.M.C. and L.E.G.) who conducted the think-aloud interviews together to ensure that their interviewing practices were as similar as possible. The interviews were approximately an hour long, and students received a $15 gift card for their participation.
Personal, Research, and Depression Demographics
All student demographics and information about students’ research experiences were collected using the survey distributed to students in Fall 2018. We collected personal demographics, including the participants’ gender, race/ethnicity, college generation status, transfer status, financial stability, year in college, major, and age. We also collected information about the students’ research experiences, including the length of their first research experiences, the average number of hours they spend in research per week, how they were compensated for research, who their primary mentors were, and the focus areas of their research.
In the United States, mental healthcare is disproportionately unavailable to Black and Latinx individuals, as well as those who come from low socioeconomic backgrounds ( Kataoka et al. , 2002 ; Howell and McFeeters, 2008 ; Santiago et al. , 2013 ). Therefore, to minimize a biased sample, we invited anyone who identified with having depression to participate in our study; we did not require students to be diagnosed with depression or to be treated for depression in order to participate. However, we did collect information about whether students had been formally diagnosed with depression and whether they had been treated for depression. After the interview, all participants were sent a link to a short survey that asked them if they had ever been diagnosed with depression and how, if at all, they had ever been treated for depression. A copy of these survey questions can be found in the Supplemental Material. The combined demographic information of the participants is in Table 1 . The demographics for each individual student can be found in the Supplemental Material.
a Students reported the time they had spent in research 6 months before being interviewed and only reported on the length of time of their first research experiences.
b Students were invited to report multiple ways in which they were treated for their depression; other treatments included lifestyle changes and meditation.
c Students were invited to report multiple means of compensation for their research if they had been compensated for their time in different ways.
d Students were asked whether they felt financially stable, particularly during the undergraduate research experience.
e Students reported who they work/worked with most closely during their research experiences.
f Staff members included lab coordinators or lab managers.
g Other focus areas of research included sociology, linguistics, psychology, and public health.
Interview Analysis
The initial interview analysis aimed to explore each idea that a participant expressed ( Charmaz, 2006 ) and to identify reoccurring ideas throughout the interviews. First, three authors (K.M.C., L.E.G., and S.E.B.) individually reviewed a different set of 10 interviews and took detailed analytic notes ( Birks and Mills, 2015 ). Afterward, the authors compared their notes and identified reoccurring themes throughout the interviews using open coding methods ( Saldaña, 2015 ).
Once an initial set of themes was established, two researchers (K.M.C. and L.E.G.) individually reviewed the same set of 15 randomly selected interviews to validate the themes identified in the initial analysis and to screen for any additional themes that the initial analysis may have missed. Each researcher took detailed analytic notes throughout the review of an interview, which they discussed after reviewing each interview. The researchers compared what quotes from each interview they categorized into each theme. Using constant comparison methods, they assigned quotes to each theme and constantly compared the quotes to ensure that each quote fit within the description of the theme ( Glesne and Peshkin, 1992 ). In cases in which quotes were too different from other quotes, a new theme was created. This approach allowed for multiple revisions of the themes and allowed the authors to define a final set of codes; the researchers created a final codebook with refined definitions of emergent themes (the final coding rubric can be found in the Supplemental Material). Once the final codebook was established, the researchers (K.M.C. and L.E.G.) individually coded seven additional interviews (20% of all interviews) using the coding rubric. The researchers compared their codes, and their Cohen’s κ interrater score for these seven interviews was at an acceptable level (κ = 0.88; Landis and Koch, 1977 ). One researcher (L.E.G.) coded the remaining 28 out of 35 interviews. The researchers determined that data saturation had been reached with the current sample and no further recruitment was needed ( Guest et al. , 2006 ). We report on themes that were mentioned by at least 20% of students in the interview study. In the Supplemental Material, we provide the final coding rubric with the number of participants whose interview reflected each theme ( Hannah and Lautsch, 2011 ). Reporting the number of individuals who reported themes within qualitative data can lead to inaccurate conclusions about the generalizability of the results to a broader population. These qualitative data are meant to characterize a landscape of experiences that students with depression have in undergraduate research rather than to make claims about the prevalence of these experiences ( Glesne and Peshkin, 1992 ). Because inferences about the importance of these themes cannot be drawn from these counts, they are not included in the results of the paper ( Maxwell, 2010 ). Further, the limited number of interviewees made it not possible to examine whether there were trends based on students’ demographics or characteristics of their research experiences (e.g., their specific area of study). Quotes were lightly edited for clarity by inserting clarification brackets and using ellipses to indicate excluded text. Pseudonyms were given to all students to protect their privacy.
The Effect of Depressive Symptoms on Undergraduate Research
We asked students to describe the symptoms associated with their depression. Students described experiencing anxiety that is associated with their depression; this could be anxiety that precedes their depression or anxiety that results from a depressive episode or a period of time when an individual has depression symptoms. Further, students described difficulty getting out of bed or leaving the house, feeling tired, a lack of motivation, being overly self-critical, feeling apathetic, and having difficulty concentrating. We were particularly interested in how students’ symptoms of depression affected their experiences in undergraduate research. During the think-aloud interviews that were conducted before the interview study, graduate and undergraduate students consistently described that their depression affected their motivation in research, their creativity in research, and their productivity in research. Therefore, we explicitly asked undergraduate researchers how, if at all, their depression affected these three factors. We also asked students to describe any additional ways in which their depression affected their research experiences. Undergraduate researchers commonly described five additional ways in which their depression affected their research; for a detailed description of each way students’ research was affected and for example quotes, see Table 2 . Students described that their depression negatively affected their productivity in the lab. Commonly, students described that their productivity was directly affected by a lack of motivation or because they felt less creative, which hindered the research process. Additionally, students highlighted that they were sometimes less productive because their depression sometimes caused them to struggle to engage intellectually with their research or caused them to have difficulty remembering or concentrating; students described that they could do mundane or routine tasks when they felt depressed, but that they had difficulty with more complex and intellectually demanding tasks. However, students sometimes described that even mundane tasks could be difficult when they were required to remember specific steps; for example, some students struggled recalling a protocol from memory when their depression was particularly severe. Additionally, students noted that their depression made them more self-conscious, which sometimes held them back from sharing research ideas with their mentors or from taking risks such as applying to competitive programs. In addition to being self-conscious, students highlighted that their depression caused them to be overly self-critical, and some described experiencing imposter phenomenon ( Clance and Imes, 1978 ) or feeling like they were not talented enough to be in research and were accepted into a lab by a fluke or through luck. Finally, students described that depression often made them feel less social, and they struggled to socially engage with other members of the lab when they were feeling down.
The Effect of Undergraduate Research Experiences on Student Depression
We also wanted to explore how research impacted students’ feelings of depression. Undergraduates described how research both positively and negatively affected their depression. In the following sections, we present aspects of undergraduate research and examine how each positively and/or negatively affected students’ depression using embedded student quotes to highlight the relationships between related ideas.
Lab Environment: Relationships with Others in the Lab.
Some aspects of the lab environment, which we define as students’ physical, social, or psychological research space, could be particularly beneficial for students with depression.
Specifically, undergraduate researchers perceived that comfortable and positive social interactions with others in the lab helped their depression. Students acknowledged how beneficial their relationships with graduate students and postdocs could be.
Marta: “I think always checking in on undergrads is important. It’s really easy [for us] to go a whole day without talking to anybody in the lab. But our grad students are like ‘Hey, what’s up? How’s school? What’s going on?’ (…) What helps me the most is having that strong support system. Sometimes just talking makes you feel better, but also having people that believe in you can really help you get out of that negative spiral. I think that can really help with depression.”
Kelley: “I know that anytime I need to talk to [my postdoc mentors] about something they’re always there for me. Over time we’ve developed a relationship where I know that outside of work and outside of the lab if I did want to talk to them about something I could talk to them. Even just talking to someone about hobbies and having that relationship alone is really helpful [for depression].”
In addition to highlighting the importance of developing relationships with graduate students or postdocs in the lab, students described that forming relationships with other undergraduates in the lab also helped their depression. Particularly, students described that other undergraduate researchers often validated their feelings about research, which in turn helped them realize that what they are thinking or feeling is normal, which tended to alleviate their negative thoughts. Interestingly, other undergraduates experiencing the same issues could sometimes help buffer them from perceiving that a mentor did not like them or that they were uniquely bad at research. In this article, we use the term “mentor” to refer to anyone who students referred to in the interviews as being their mentors or managing their research experiences; this includes graduate students, postdoctoral scholars, lab managers, and primary investigators (PIs).
Abby: “One of my best friends is in the lab with me. A lot of that friendship just comes from complaining about our stress with the lab and our annoyance with people in the lab. Like when we both agree like, ‘Yeah, the grad students were really off today, it wasn’t us,’ that helps. ‘It wasn’t me, it wasn’t my fault that we were having a rough day in lab; it was the grad students.’ Just being able to realize, ‘Hey, this isn’t all caused by us,’ you know? (…) We understand the stresses in the lab. We understand the details of what each other are doing in the lab, so when something doesn’t work out, we understand that it took them like eight hours to do that and it didn’t work. We provide empathy on a different level.”
Meleana: “It’s great to have solidarity in being confused about something, and it’s just that is a form of validation for me too. When we leave a lab meeting and I look at [another undergrad] I’m like, ‘Did you understand anything that they were just saying?’ And they’re like, ‘Oh, no.’ (…) It’s just really validating to hear from the other undergrads that we all seem to be struggling with the same things.”
Developing positive relationships with faculty mentors or PIs also helped alleviate some students’ depressive feelings, particularly when PIs shared their own struggles with students. This also seemed to normalize students’ concerns about their own experiences.
Alexandra: “[Talking with my PI] is helpful because he would talk about his struggles, and what he faced. A lot of it was very similar to my struggles. For example, he would say, ‘Oh, yeah, I failed this exam that I studied so hard for. I failed the GRE and I paid so much money to prepare for it.’ It just makes [my depression] better, like okay, this is normal for students to go through this. It’s not an out of this world thing where if you fail, you’re a failure and you can’t move on from it.”
Students’ relationships with others in the lab did not always positively impact their depression. Students described instances when the negative moods of the graduate students and PIs would often set the tone of the lab, which in turn worsened the mood of the undergraduate researchers.
Abby: “Sometimes [the grad students] are not in a good mood. The entire vibe of the lab is just off, and if you make a joke and it hits somebody wrong, they get all mad. It really depends on the grad students and the leadership and the mood that they’re in.”
Interviewer: “How does it affect your depression when the grad students are in a bad mood?”
Abby: “It definitely makes me feel worse. It feels like, again, that I really shouldn’t go ask them for help because they’re just not in the mood to help out. It makes me have more pressure on myself, and I have deadlines I need to meet, but I have a question for them, but they’re in a bad mood so I can’t ask. That’s another day wasted for me and it just puts more stress, which just adds to the depression.”
Additionally, some students described even more concerning behavior from research mentors, which negatively affected their depression.
Julie: “I had a primary investigator who is notorious in the department for screaming at people, being emotionally abusive, unreasonable, et cetera. (…) [He was] kind of harassing people, demeaning them, lying to them, et cetera, et cetera. (…) Being yelled at and constantly demeaned and harassed at all hours of the day and night, that was probably pretty bad for me.”
While the relationships between undergraduates and graduate, postdoc, and faculty mentors seemed to either alleviate or worsen students’ depressive symptoms, depending on the quality of the relationship, students in this study exclusively described their relationships with other undergraduates as positive for their depression. However, students did note that undergraduate research puts some of the best and brightest undergraduates in the same environment, which can result in students comparing themselves with their peers. Students described that this comparison would often lead them to feel badly about themselves, even though they would describe their personal relationship with a person to be good.
Meleana: “In just the research field in general, just feeling like I don’t really measure up to the people around me [can affect my depression]. A lot of the times it’s the beginning of a little spiral, mental spiral. There are some past undergrads that are talked about as they’re on this pedestal of being the ideal undergrads and that they were just so smart and contributed so much to the lab. I can never stop myself from wondering like, ‘Oh, I wonder if I’m having a contribution to the lab that’s similar or if I’m just another one of the undergrads that does the bare minimum and passes through and is just there.’”
Natasha: “But, on the other hand, [having another undergrad in the lab] also reminded me constantly that some people are invested in this and meant to do this and it’s not me. And that some people know a lot more than I do and will go further in this than I will.”
While students primarily expressed that their relationships with others in the lab affected their depression, some students explained that they struggled most with depression when the lab was empty; they described that they did not like being alone in the lab, because a lack of stimulation allowed their minds to be filled with negative thoughts.
Mia: “Those late nights definitely didn’t help [my depression]. I am alone, in the entire building. I’m left alone to think about my thoughts more, so not distracted by talking to people or interacting with people. I think more about how I’m feeling and the lack of progress I’m making, and the hopelessness I’m feeling. That kind of dragged things on, and I guess deepened my depression.”
Freddy: “Often times when I go to my office in the evening, that is when I would [ sic ] be prone to be more depressed. It’s being alone. I think about myself or mistakes or trying to correct mistakes or whatever’s going on in my life at the time. I become very introspective. I think I’m way too self-evaluating, way too self-deprecating and it’s when I’m alone when those things are really, really triggered. When I’m talking with somebody else, I forget about those things.”
In sum, students with depression highlighted that a lab environment full of positive and encouraging individuals was helpful for their depression, whereas isolating or competitive environments and negative interactions with others often resulted in more depressive feelings.
Doing Science: Experiencing Failure in Research, Getting Help, Receiving Feedback, Time Demands, and Important Contributions.
In addition to the lab environment, students also described that the process of doing science could affect their depression. Specifically, students explained that a large contributor to their depression was experiencing failure in research.
Interviewer: “Considering your experience in undergraduate research, what tends to trigger your feelings of depression?”
Heather: “Probably just not getting things right. Having to do an experiment over and over again. You don’t get the results you want. (…) The work is pretty meticulous and it’s frustrating when I do all this work, I do a whole experiment, and then I don’t get any results that I can use. That can be really frustrating. It adds to the stress. (…) It’s hard because you did all this other stuff before so you can plan for the research, and then something happens and all the stuff you did was worthless basically.”
Julie: “I felt very negatively about myself [when a project failed] and pretty panicked whenever something didn’t work because I felt like it was a direct reflection on my effort and/or intelligence, and then it was a big glaring personal failure.”
Students explained that their depression related to failing in research was exacerbated if they felt as though they could not seek help from their research mentors. Perceived insufficient mentor guidance has been shown to be a factor influencing student intention to leave undergraduate research ( Cooper et al. , 2019c ). Sometimes students talked about their research mentors being unavailable or unapproachable.
Michelle: “It just feels like [the graduate students] are not approachable. I feel like I can’t approach them to ask for their understanding in a certain situation. It makes [my depression] worse because I feel like I’m stuck, and that I’m being limited, and like there’s nothing I can do. So then I kind of feel like it’s my fault that I can’t do anything.”
Other times, students described that they did not seek help in fear that they would be negatively evaluated in research, which is a fear of being judged by others ( Watson and Friend, 1969 ; Weeks et al. , 2005 ; Cooper et al. , 2018 ). That is, students fear that their mentor would think negatively about them or judge them if they were to ask questions that their mentor thought they should know the answer to.
Meleana: “I would say [my depression] tends to come out more in being more reserved in asking questions because I think that comes more like a fear-based thing where I’m like, ‘Oh, I don’t feel like I’m good enough and so I don’t want to ask these questions because then my mentors will, I don’t know, think that I’m dumb or something.’”
Conversely, students described that mentors who were willing to help them alleviated their depressive feelings.
Crystal: “Yeah [my grad student] is always like, ‘Hey, I can check in on things in the lab because you’re allowed to ask me for that, you’re not totally alone in this,’ because he knows that I tend to take on all this responsibility and I don’t always know how to ask for help. He’s like, ‘You know, this is my lab too and I am here to help you as well,’ and just reminds me that I’m not shouldering this burden by myself.”
Ashlyn: “The graduate student who I work with is very kind and has a lot of patience and he really understands a lot of things and provides simple explanations. He does remind me about things and he will keep on me about certain tasks that I need to do in an understanding way, and it’s just because he’s patient and he listens.”
In addition to experiencing failure in science, students described that making mistakes when doing science also negatively affected their depression.
Abby: “I guess not making mistakes on experiments [is important in avoiding my depression]. Not necessarily that your experiment didn’t turn out to produce the data that you wanted, but just adding the wrong enzyme or messing something up like that. It’s like, ‘Oh, man,’ you know? You can get really down on yourself about that because it can be embarrassing.”
Commonly, students described that the potential for making mistakes increased their stress and anxiety regarding research; however, they explained that how other people responded to a potential mistake was what ultimately affected their depression.
Briana: “Sometimes if I made a mistake in correctly identifying an eye color [of a fly], [my PI] would just ridicule me in front of the other students. He corrected me but his method of correcting was very discouraging because it was a ridicule. It made the others laugh and I didn’t like that.”
Julie: “[My PI] explicitly [asked] if I had the dedication for science. A lot of times he said I had terrible judgment. A lot of times he said I couldn’t be trusted. Once I went to a conference with him, and, unfortunately, in front of another professor, he called me a klutz several times and there was another comment about how I never learn from my mistakes.”
When students did do things correctly, they described how important it could be for them to receive praise from their mentors. They explained that hearing praise and validation can be particularly helpful for students with depression, because their thoughts are often very negative and/or because they have low self-esteem.
Crystal: “[Something that helps my depression is] I have text messages from [my graduate student mentor] thanking me [and another undergraduate researcher] for all of the work that we’ve put in, that he would not be able to be as on track to finish as he is if he didn’t have our help.”
Interviewer: “Why is hearing praise from your mentor helpful?”
Crystal: “Because a lot of my depression focuses on everybody secretly hates you, nobody likes you, you’re going to die alone. So having that validation [from my graduate mentor] is important, because it flies in the face of what my depression tells me.”
Brian: “It reminds you that you exist outside of this negative world that you’ve created for yourself, and people don’t see you how you see yourself sometimes.”
Students also highlighted how research could be overwhelming, which negatively affected their depression. Particularly, students described that research demanded a lot of their time and that their mentors did not always seem to be aware that they were juggling school and other commitments in addition to their research. This stress exacerbated their depression.
Rose: “I feel like sometimes [my grad mentors] are not very understanding because grad students don’t take as many classes as [undergrads] do. I think sometimes they don’t understand when I say I can’t come in at all this week because I have finals and they’re like, ‘Why though?’”
Abby: “I just think being more understanding of student life would be great. We have classes as well as the lab, and classes are the priority. They forget what it’s like to be a student. You feel like they don’t understand and they could never understand when you say like, ‘I have three exams this week,’ and they’re like, ‘I don’t care. You need to finish this.’”
Conversely, some students reported that their research labs were very understanding of students’ schedules. Interestingly, these students talked most about how helpful it was to be able to take a mental health day and not do research on days when they felt down or depressed.
Marta: “My lab tech is very open, so she’ll tell us, ‘I can’t come in today. I have to take a mental health day.’ So she’s a really big advocate for that. And I think I won’t personally tell her that I’m taking a mental health day, but I’ll say, ‘I can’t come in today, but I’ll come in Friday and do those extra hours.’ And she’s like, ‘OK great, I’ll see you then.’ And it makes me feel good, because it helps me take care of myself first and then I can take care of everything else I need to do, which is amazing.”
Meleana: “Knowing that [my mentors] would be flexible if I told them that I’m crazy busy and can’t come into work nearly as much this week [helps my depression]. There is flexibility in allowing me to then care for myself.”
Interviewer: “Why is the flexibility helpful given the depression?”
Meleana: “Because sometimes for me things just take a little bit longer when I’m feeling down. I’m just less efficient to be honest, and so it’s helpful if I feel like I can only go into work for 10 hours in a week. It declutters my brain a little bit to not have to worry about all the things I have to do in work in addition the things that I need to do for school or clubs, or family or whatever.”
Despite the demanding nature of research, a subset of students highlighted that their research and research lab provided a sense of stability or familiarity that distracted them from their depression.
Freddy: “I’ll [do research] to run away from those [depressive] feelings or whatever. (…) I find sadly, I hate to admit it, but I do kind of run to [my lab]. I throw myself into work to distract myself from the feelings of depression and sadness.”
Rose: “When you’re sad or when you’re stressed you want to go to things you’re familiar with. So because lab has always been in my life, it’s this thing where it’s going to be there for me I guess. It’s like a good book that you always go back to and it’s familiar and it makes you feel good. So that’s how lab is. It’s not like the greatest thing in the world but it’s something that I’m used to, which is what I feel like a lot of people need when they’re sad and life is not going well.”
Many students also explained that research positively affects their depression because they perceive their research contribution to be important.
Ashlyn: “I feel like I’m dedicating myself to something that’s worthy and something that I believe in. It’s really important because it contextualizes those times when I am feeling depressed. It’s like, no, I do have these better things that I’m working on. Even when I don’t like myself and I don’t like who I am, which is again, depression brain, I can at least say, ‘Well, I have all these other people relying on me in research and in this area and that’s super important.’”
Jessica: “I mean, it just felt like the work that I was doing had meaning and when I feel like what I’m doing is actually going to contribute to the world, that usually really helps with [depression] because it’s like not every day you can feel like you’re doing something impactful.”
In sum, students highlighted that experiencing failure in research and making mistakes negatively contributed to depression, especially when help was unavailable or research mentors had a negative reaction. Additionally, students acknowledged that the research could be time-consuming, but that research mentors who were flexible helped assuage depressive feelings that were associated with feeling overwhelmed. Finally, research helped some students’ depression, because it felt familiar, provided a distraction from depression, and reminded students that they were contributing to a greater cause.
We believe that creating more inclusive research environments for students with depression is an important step toward broadening participation in science, not only to ensure that we are not discouraging students with depression from persisting in science, but also because depression has been shown to disproportionately affect underserved and underrepresented groups in science ( Turner and Noh, 1988 ; Eisenberg et al. , 2007 ; Jenkins et al. , 2013 ; American College Health Association, 2018 ). We initially hypothesized that three features of undergraduate research—research mentors, the lab environment, and failure—may have the potential to exacerbate student depression. We found this to be true; students highlighted that their relationships with their mentors as well as the overall lab environment could negatively affect their depression, but could also positively affect their research experiences. Students also noted that they struggled with failure, which is likely true of most students, but is known to be particularly difficult for students with depression ( Elliott et al. , 1997 ). We expand upon our findings by integrating literature on depression with the information that students provided in the interviews about how research mentors can best support students. We provide a set of evidence-based recommendations focused on mentoring, the lab environment, and failure for research mentors wanting to create more inclusive research environments for students with depression. Notably, only the first recommendation is specific to students with depression; the others reflect recommendations that have previously been described as “best practices” for research mentors ( NASEM, 2017 , 2019 ; Sorkness et al. , 2017 ) and likely would benefit most students. However, we examine how these recommendations may be particularly important for students with depression. As we hypothesized, these recommendations directly address three aspects of research: mentors, lab environment, and failure. A caveat of these recommendations is that more research needs to be done to explore the experiences of students with depression and how these practices actually impact students with depression, but our national sample of undergraduate researchers with depression can provide an initial starting point for a discussion about how to improve research experiences for these students.
Recommendations to Make Undergraduate Research Experiences More Inclusive for Students with Depression
Recognize student depression as a valid illness..
Allow students with depression to take time off of research by simply saying that they are sick and provide appropriate time for students to recover from depressive episodes. Also, make an effort to destigmatize mental health issues.
Undergraduate researchers described both psychological and physical symptoms that manifested as a result of their depression and highlighted how such symptoms prevented them from performing to their full potential in undergraduate research. For example, students described how their depression would cause them to feel unmotivated, which would often negatively affect their research productivity. In cases in which students were motivated enough to come in and do their research, they described having difficulty concentrating or engaging in the work. Further, when doing research, students felt less creative and less willing to take risks, which may alter the quality of their work. Students also sometimes struggled to socialize in the lab. They described feeling less social and feeling overly self-critical. In sum, students described that, when they experienced a depressive episode, they were not able to perform to the best of their ability, and it sometimes took a toll on them to try to act like nothing was wrong, when they were internally struggling with depression. We recommend that research mentors treat depression like any other physical illness; allowing students the chance to recover when they are experiencing a depressive episode can be extremely important to students and can allow them to maximize their productivity upon returning to research ( Judd et al. , 2000 ). Students explained that if they are not able to take the time to focus on recovering during a depressive episode, then they typically continue to struggle with depression, which negatively affects their research. This sentiment is echoed by researchers in psychiatry who have found that patients who do not fully recover from a depressive episode are more likely to relapse and to experience chronic depression ( Judd et al. , 2000 ). Students described not doing tasks or not showing up to research because of their depression but struggling with how to share that information with their research mentors. Often, students would not say anything, which caused them anxiety because they were worried about what others in the lab would say to them when they returned. Admittedly, many students understood why this behavior would cause their research mentors to be angry or frustrated, but they weighed the consequences of their research mentors’ displeasure against the consequences of revealing their depression and decided it was not worth admitting to being depressed. This aligns with literature that suggests that when individuals have concealable stigmatized identities, or identities that can be hidden and that carry negative stereotypes, such as depression, they will often keep them concealed to avoid negative judgment or criticism ( Link and Phelan, 2001 ; Quinn and Earnshaw, 2011 ; Jones and King, 2014 ; Cooper and Brownell, 2016 ; Cooper et al. , 2019b ; Cooper et al ., unpublished data ). Therefore, it is important for research mentors to be explicit with students that 1) they recognize mental illness as a valid sickness and 2) that students with mental illness can simply explain that they are sick if they need to take time off. This may be useful to overtly state on a research website or in a research syllabus, contract, or agreement if mentors use such documents when mentoring undergraduates in their lab. Further, research mentors can purposefully work to destigmatize mental health issues by explicitly stating that struggling with mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety, is common. While we do not recommend that mentors ask students directly about depression, because this can force students to share when they are not comfortable sharing, we do recommend providing opportunities for students to reveal their depression ( Chaudoir and Fisher, 2010 ). Mentors can regularly check in with students about how they’re doing, and talk openly about the importance of mental health, which may increase the chance that students may feel comfortable revealing their depression ( Chaudoir and Quinn, 2010 ; Cooper et al ., unpublished data ).
Foster a Positive Lab Environment.
Encourage positivity in the research lab, promote working in shared spaces to enhance social support among lab members, and alleviate competition among undergraduates.
Students in this study highlighted that the “leadership” of the lab, meaning graduate students, postdocs, lab managers, and PIs, were often responsible for establishing the tone of the lab; that is, if they were in a bad mood it would trickle down and negatively affect the moods of the undergraduates. Explicitly reminding lab leadership that their moods can both positively and negatively affect undergraduates may be important in establishing a positive lab environment. Further, students highlighted how they were most likely to experience negative thoughts when they were alone in the lab. Therefore, it may be helpful to encourage all lab members to work in a shared space to enhance social interactions among students and to maximize the likelihood that undergraduates have access to help when needed. A review of 51 studies in psychiatry supported our undergraduate researchers’ perceptions that social relationships positively impacted their depression; the study found that perceived emotional support (e.g., someone available to listen or give advice), perceived instrumental support (e.g., someone available to help with tasks), and large diverse social networks (e.g., being socially connected to a large number of people) were significantly protective against depression ( Santini et al. , 2015 ). Additionally, despite forming positive relationships with other undergraduates in the lab, many undergraduate researchers admitted to constantly comparing themselves with other undergraduates, which led them to feel inferior, negatively affecting their depression. Some students talked about mentors favoring current undergraduates or talking positively about past undergraduates, which further exacerbated their feelings of inferiority. A recent study of students in undergraduate research experiences highlighted that inequitable distribution of praise to undergraduates can create negative perceptions of lab environments for students (Cooper et al. , 2019). Further, the psychology literature has demonstrated that when people feel insecure in their social environments, it can cause them to focus on a hierarchical view of themselves and others, which can foster feelings of inferiority and increase their vulnerability to depression ( Gilbert et al. , 2009 ). Thus, we recommend that mentors be conscious of their behaviors so that they do not unintentionally promote competition among undergraduates or express favoritism toward current or past undergraduates. Praise is likely best used without comparison with others and not done in a public way, although more research on the impact of praise on undergraduate researchers needs to be done. While significant research has been done on mentoring and mentoring relationships in the context of undergraduate research ( Byars-Winston et al. , 2015 ; Aikens et al. , 2017 ; Estrada et al. , 2018 ; Limeri et al. , 2019 ; NASEM, 2019 ), much less has been done on the influence of the lab environment broadly and how people in nonmentoring roles can influence one another. Yet, this study indicates the potential influence of many different members of the lab, not only their mentors, on students with depression.
Develop More Personal Relationships with Undergraduate Researchers and Provide Sufficient Guidance.
Make an effort to establish more personal relationships with undergraduates and ensure that they perceive that they have access to sufficient help and guidance with regard to their research.
When we asked students explicitly how research mentors could help create more inclusive environments for undergraduate researchers with depression, students overwhelmingly said that building mentor–student relationships would be extremely helpful. Students suggested that mentors could get to know students on a more personal level by asking about their career interests or interests outside of academia. Students also remarked that establishing a more personal relationship could help build the trust needed in order for undergraduates to confide in their research mentors about their depression, which they perceived would strengthen their relationships further because they could be honest about when they were not feeling well or their mentors might even “check in” with them in times where they were acting differently than normal. This aligns with studies showing that undergraduates are most likely to reveal a stigmatized identity, such as depression, when they form a close relationship with someone ( Chaudoir and Quinn, 2010 ). Many were intimidated to ask for research-related help from their mentors and expressed that they wished they had established a better relationship so that they would feel more comfortable. Therefore, we recommend that research mentors try to establish relationships with their undergraduates and explicitly invite them to ask questions or seek help when needed. These recommendations are supported by national recommendations for mentoring ( NASEM, 2019 ) and by literature that demonstrates that both social support (listening and talking with students) and instrumental support (providing students with help) have been shown to be protective against depression ( Santini et al. , 2015 ).
Treat Undergraduates with Respect and Remember to Praise Them.
Avoid providing harsh criticism and remember to praise undergraduates. Students with depression often have low self-esteem and are especially self-critical. Therefore, praise can help calibrate their overly negative self-perceptions.
Students in this study described that receiving criticism from others, especially harsh criticism, was particularly difficult for them given their depression. Multiple studies have demonstrated that people with depression can have an abnormal or maladaptive response to negative feedback; scientists hypothesize that perceived failure on a particular task can trigger failure-related thoughts that interfere with subsequent performance ( Eshel and Roiser, 2010 ). Thus, it is important for research mentors to remember to make sure to avoid unnecessarily harsh criticisms that make students feel like they have failed (more about failure is described in the next recommendation). Further, students with depression often have low self-esteem or low “personal judgment of the worthiness that is expressed in the attitudes the individual holds towards oneself” ( Heatherton et al. , 2003 , p. 220; Sowislo and Orth, 2013 ). Specifically, a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies found that low self-esteem is predictive of depression ( Sowislo and Orth, 2013 ), and depression has also been shown to be highly related to self-criticism ( Luyten et al. , 2007 ). Indeed, nearly all of the students in our study described thinking that they are “not good enough,” “worthless,” or “inadequate,” which is consistent with literature showing that people with depression are self-critical ( Blatt et al. , 1982 ; Gilbert et al. , 2006 ) and can be less optimistic of their performance on future tasks and rate their overall performance on tasks less favorably than their peers without depression ( Cane and Gotlib, 1985 ). When we asked students what aspects of undergraduate research helped their depression, students described that praise from their mentors was especially impactful, because they thought so poorly of themselves and they needed to hear something positive from someone else in order to believe it could be true. Praise has been highlighted as an important aspect of mentoring in research for many years ( Ashford, 1996 ; Gelso and Lent, 2000 ; Brown et al. , 2009 ) and may be particularly important for students with depression. In fact, praise has been shown to enhance individuals’ motivation and subsequent productivity ( Hancock, 2002 ; Henderlong and Lepper, 2002 ), factors highlighted by students as negatively affecting their depression. However, something to keep in mind is that a student with depression and a student without depression may process praise differently. For a student with depression, a small comment that praises the student’s work may not be sufficient for the student to process that comment as praise. People with depression are hyposensitive to reward or have reward-processing deficits ( Eshel and Roiser, 2010 ); therefore, praise may affect students without depression more positively than it would affect students with depression. Research mentors should be mindful that students with depression often have a negative view of themselves, and while students report that praise is extremely important, they may have trouble processing such positive feedback.
Normalize Failure and Be Explicit about the Importance of Research Contributions.
Explicitly remind students that experiencing failure is expected in research. Also explain to students how their individual work relates to the overall project so that they can understand how their contributions are important. It can also be helpful to explain to students why the research project as a whole is important in the context of the greater scientific community.
Experiencing failure has been thought to be a potentially important aspect of undergraduate research, because it may provide students with the potential to develop integral scientific skills such as the ability to navigate challenges and persevere ( Laursen et al. , 2010 ; Gin et al. , 2018 ; Henry et al. , 2019 ). However, in the interviews, students described that when their science experiments failed, it was particularly tough for their depression. Students’ negative reaction to experiencing failure in research is unsurprising, given recent literature that has predicted that students may be inadequately prepared to approach failure in science ( Henry et al. , 2019 ). However, the literature suggests that students with depression may find experiencing failure in research to be especially difficult ( Elliott et al. , 1997 ; Mongrain and Blackburn, 2005 ; Jones et al. , 2009 ). One potential hypothesis is that students with depression may be more likely to have fixed mindsets or more likely to believe that their intelligence and capacity for specific abilities are unchangeable traits ( Schleider and Weisz, 2018 ); students with a fixed mindset have been hypothesized to have particularly negative responses to experiencing failure in research, because they are prone to quitting easily in the face of challenges and becoming defensive when criticized ( Forsythe and Johnson, 2017 ; Dweck, 2008 ). A study of life sciences undergraduates enrolled in CUREs identified three strategies of students who adopted adaptive coping mechanisms, or mechanisms that help an individual maintain well-being and/or move beyond the stressor when faced with failure in undergraduate research: 1) problem solving or engaging in strategic planning and decision making, 2) support seeking or finding comfort and help with research, and 3) cognitive restructuring or reframing a problem from negative to positive and engaging in self encouragement ( Gin et al. , 2018 ). We recommend that, when undergraduates experience failure in science, their mentors be proactive in helping them problem solve, providing help and support, and encouraging them. Students also explained that mentors sharing their own struggles as undergraduate and graduate students was helpful, because it normalized failure. Sharing personal failures in research has been recommended as an important way to provide students with psychosocial support during research ( NASEM, 2019 ). We also suggest that research mentors take time to explain to students why their tasks in the lab, no matter how small, contribute to the greater research project ( Cooper et al. , 2019a ). Additionally, it is important to make sure that students can explain how the research project as a whole is contributing to the scientific community ( Gin et al. , 2018 ). Students highlighted that contributing to something important was really helpful for their depression, which is unsurprising, given that studies have shown that meaning in life or people’s comprehension of their life experiences along with a sense of overarching purpose one is working toward has been shown to be inversely related to depression ( Steger, 2013 ).

Limitations and Future Directions
This work was a qualitative interview study intended to document a previously unstudied phenomenon: depression in the context of undergraduate research experiences. We chose to conduct semistructured interviews rather than a survey because of the need for initial exploration of this area, given the paucity of prior research. A strength of this study is the sampling approach. We recruited a national sample of 35 undergraduates engaged in undergraduate research at 12 different public R1 institutions. Despite our representative sample from R1 institutions, these findings may not be generalizable to students at other types of institutions; lab environments, mentoring structures, and interactions between faculty and undergraduate researchers may be different at other institution types (e.g., private R1 institutions, R2 institutions, master’s-granting institutions, primarily undergraduate institutions, and community colleges), so we caution against making generalizations about this work to all undergraduate research experiences. Future work could assess whether students with depression at other types of institutions have similar experiences to students at research-intensive institutions. Additionally, we intentionally did not explore the experiences of students with specific identities owing to our sample size and the small number of students in any particular group (e.g., students of a particular race, students with a graduate mentor as the primary mentor). We intend to conduct future quantitative studies to further explore how students’ identities and aspects of their research affect their experiences with depression in undergraduate research.
The students who participated in the study volunteered to be interviewed about their depression; therefore, it is possible that depression is a more salient part of these students’ identities and/or that they are more comfortable talking about their depression than the average population of students with depression. It is also important to acknowledge the personal nature of the topic and that some students may not have fully shared their experiences ( Krumpal, 2013 ), particularly those experiences that may be emotional or traumatizing ( Kahn and Garrison, 2009 ). Additionally, our sample was skewed toward females (77%). While females do make up approximately 60% of students in biology programs on average ( Eddy et al. , 2014 ), they are also more likely to report experiencing depression ( American College Health Association, 2018 ; Evans et al. , 2018 ). However, this could be because women have higher rates of depression or because males are less likely to report having depression; clinical bias, or practitioners’ subconscious tendencies to overlook male distress, may underestimate depression rates in men ( Smith et al. , 2018 ). Further, females are also more likely to volunteer to participate in studies ( Porter and Whitcomb, 2005 ); therefore, many interview studies have disproportionately more females in the data set (e.g., Cooper et al. , 2017 ). If we had been able to interview more male students, we might have identified different findings. Additionally, we limited our sample to life sciences students engaged in undergraduate research at public R1 institutions. It is possible that students in other majors may have different challenges and opportunities for students with depression, as well as different disciplinary stigmas associated with mental health.
In this exploratory interview study, we identified a variety of ways in which depression in undergraduates negatively affected their undergraduate research experiences. Specifically, we found that depression interfered with students’ motivation and productivity, creativity and risk-taking, engagement and concentration, and self-perception and socializing. We also identified that research can negatively affect depression in undergraduates. Experiencing failure in research can exacerbate student depression, especially when students do not have access to adequate guidance. Additionally, being alone or having negative interactions with others in the lab worsened students’ depression. However, we also found that undergraduate research can positively affect students’ depression. Research can provide a familiar space where students can feel as though they are contributing to something meaningful. Additionally, students reported that having access to adequate guidance and a social support network within the research lab also positively affected their depression. We hope that this work can spark conversations about how to make undergraduate research experiences more inclusive of students with depression and that it can stimulate additional research that more broadly explores the experiences of undergraduate researchers with depression.
Important note
If you or a student experience symptoms of depression and want help, there are resources available to you. Many campuses provide counseling centers equipped to provide students, staff, and faculty with treatment for depression, as well as university-dedicated crisis hotlines. Additionally, there are free 24/7 services such as Crisis Text Line, which allows you to text a trained live crisis counselor (Text “CONNECT” to 741741; Text Depression Hotline , 2019 ), and phone hotlines such as the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 1-800-273-8255 (TALK). You can also learn more about depression and where to find help near you through the Anxiety and Depression Association of American website: https://adaa.org ( Anxiety and Depression Association of America, 2019 ) and the Depression and Biopolar Support Alliance: http://dbsalliance.org ( Depression and Biopolar Support Alliance, 2019 ).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are extremely grateful to the undergraduate researchers who shared their thoughts and experiences about depression with us. We acknowledge the ASU LEAP Scholars for helping us create the original survey and Rachel Scott for her helpful feedback on earlier drafts of this article. L.E.G. was supported by a National Science Foundation (NSF) Graduate Fellowship (DGE-1311230) and K.M.C. was partially supported by a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) Inclusive Excellence grant (no. 11046) and an NSF grant (no. 1644236). Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the NSF or HHMI.
- Aikens, M. L., Robertson, M. M., Sadselia, S., Watkins, K., Evans, M., Runyon, C. R. , … & Dolan, E. L. ( 2017 ). Race and gender differences in undergraduate research mentoring structures and research outcomes . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 16 (2), ar34. Link , Google Scholar
- Aikens, M. L., Sadselia, S., Watkins, K., Evans, M., Eby, L. T., & Dolan, E. L. ( 2016 ). A social capital perspective on the mentoring of undergraduate life science researchers: An empirical study of undergraduate–postgraduate–faculty triads . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 (2), ar16. Link , Google Scholar
- Aldwin, C., & Greenberger, E. ( 1987 ). Cultural differences in the predictors of depression . American Journal of Community Psychology , 15 (6), 789–813. Medline , Google Scholar
- American Association for the Advancement of Science . ( 2011 ). Vision and change in undergraduate biology education: A call to action . Retrieved November 29, 2019, from http://visionandchange.org/files/2013/11/aaas-VISchange-web1113.pdf Google Scholar
- American College Health Association . ( 2018 ). Undergraduate reference group executive summary, Fall 2018 . Retrieved November 29, 2019, from www.acha.org/documents/ncha/NCHA-II_Fall_2018_Reference_Group_Executive_Summary.pdf Google Scholar
- American College Health Association . ( 2019 ). Retrieved November 29, 2019, from NCHA-II_SPRING_2019_UNDERGRADUATE_REFERENCE_GROUP_DATA_REPORT.pdf www.acha.org/documents/ncha/NCHA-II_SPRING_2019_UNDERGRADUATE_REFERENCE_GROUP_DATA_REPORT.pdf Google Scholar
- American Psychiatric Association . ( 2013 ). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing. Google Scholar
- Aneshensel, C. S., & Stone, J. D. ( 1982 ). Stress and depression: A test of the buffering model of social support . Archives of General Psychiatry , 39 (12), 1392–1396. Medline , Google Scholar
- Anxiety and Depression Association of America . ( 2019 ). Home page . Retrieved November 29, 2019, from https://adaa.org Google Scholar
- Armbruster, P., Patel, M., Johnson, E., & Weiss, M. ( 2009 ). Active learning and student-centered pedagogy improve student attitudes and performance in introductory biology . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 8 (3), 203–213. Link , Google Scholar
- Ashford, S. J. ( 1996 ). Working with doctoral students: Rhythms of Academic Life: Personal Accounts of Careers in Academia . In Front, P. J.Taylor, M. S. (Eds.), Rhythms of Academic Life: Personal Accounts of Careers in Academia (pp. 153–158). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. Google Scholar
- Auchincloss, L. C., Laursen, S. L., Branchaw, J. L., Eagan, K., Graham, M., Hanauer, D. I. , … & Rowland, S. ( 2014 ). Assessment of course-based undergraduate research experiences: A meeting report . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 13 (1), 29–40. Link , Google Scholar
- Barak, M. E. M., Levin, A., Nissly, J. A., & Lane, C. J. ( 2006 ). Why do they leave? Modeling child welfare workers’ turnover intentions . Children and Youth Services Review , 28 (5), 548–577. Google Scholar
- Bauer, K. W., & Bennett, J. S. ( 2003 ). Alumni perceptions used to assess undergraduate research experience . Journal of Higher Education , 74 (2), 210–230. Google Scholar
- Birks, M., & Mills, J. ( 2015 ). Grounded theory: A practical guide . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. Google Scholar
- Blatt, S. J., Quinlan, D. M., Chevron, E. S., McDonald, C., & Zuroff, D. ( 1982 ). Dependency and self-criticism: Psychological dimensions of depression . Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology , 50 (1), 113. Medline , Google Scholar
- Brown, R. T., Daly, B. P., & Leong, F. T. ( 2009 ). Mentoring in research: A developmental approach . Professional Psychology: Research and Practice , 40 (3), 306. Google Scholar
- Brownell, S. E., Hekmat-Scafe, D. S., Singla, V., Seawell, P. C., Imam, J. F. C., Eddy, S. L. , … & Cyert, M. S. ( 2015 ). A high-enrollment course-based undergraduate research experience improves student conceptions of scientific thinking and ability to interpret data . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 14 (2), ar21. Link , Google Scholar
- Brownell, S. E., & Kloser, M. J. ( 2015 ). Toward a conceptual framework for measuring the effectiveness of course-based undergraduate research experiences in undergraduate biology . Studies in Higher Education , 40 (3), 525–544. Google Scholar
- Byars-Winston, A. M., Branchaw, J., Pfund, C., Leverett, P., & Newton, J. ( 2015 ). Culturally diverse undergraduate researchers’ academic outcomes and perceptions of their research mentoring relationships . International Journal of Science Education , 37 (15), 2533–2554. Medline , Google Scholar
- Cane, D. B., & Gotlib, I. H. ( 1985 ). Depression and the effects of positive and negative feedback on expectations, evaluations, and performance . Cognitive Therapy and Research , 9 (2), 145–160. Google Scholar
- Ceci, S. J., & Williams, W. M. ( 2010 ). Sex differences in math-intensive fields . Current Directions in Psychological Science , 19 (5), 275–279. Medline , Google Scholar
- Center for Collegiate Mental Health . ( 2017 ). Center for Collegiate Mental Health 2017 Annual Report . State College, PA: Penn State Universit. Google Scholar
- Charmaz, K. ( 2006 ). Constructing grounded theory: A practical guide through qualitative research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. Google Scholar
- Chaudoir, S. R., & Fisher, J. D. ( 2010 ). The disclosure processes model: Understanding disclosure decision making and postdisclosure outcomes among people living with a concealable stigmatized identity . Psychological Bulletin , 136 (2), 236. Medline , Google Scholar
- Chaudoir, S. R., & Quinn, D. M. ( 2010 ). Revealing concealable stigmatized identities: The impact of disclosure motivations and positive first-disclosure experiences on fear of disclosure and well-being . Journal of Social Issues , 66 (3), 570–584. Medline , Google Scholar
- Clance, P. R., & Imes, S. A. ( 1978 ). The imposter phenomenon in high achieving women: Dynamics and therapeutic intervention . Psychotherapy: Theory, Research & Practice , 15 (3), 241. Google Scholar
- Cooper, K. M., Ashley, M., & Brownell, S. E. ( 2017 ). A bridge to active learning: A summer bridge program helps students maximize their active-learning experiences and the active-learning experiences of others . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 16 (1), ar17. Link , Google Scholar
- Cooper, K. M., Blattman, J. N., Hendrix, T., & Brownell, S. E. ( 2019a ). The impact of broadly relevant novel discoveries on student project ownership in a traditional lab course turned CURE . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 (4), ar57. Link , Google Scholar
- Cooper, K. M., & Brownell, S. E. ( 2016 ). Coming out in class: Challenges and benefits of active learning in a biology classroom for LGBTQIA students . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 (3), ar37. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.16-01-0074 Link , Google Scholar
- Cooper, K. M., Brownell, S. E., & Gormally, C. C. ( 2019b ). Coming out to the class: Identifying factors that influence college biology instructor decisions about whether to reveal their LGBQ identity in class . Journal of Women and Minorities in Science and Engineering , 25 (3). Google Scholar
- Cooper, K. M., Downing, V. R., & Brownell, S. E. ( 2018 ). The influence of active learning practices on student anxiety in large-enrollment college science classrooms . International Journal of STEM Education , 5 (1), 23. Medline , Google Scholar
- Cooper, K. M., Gin, L. E., Akeeh, B., Clark, C. E., Hunter, J. S., Roderick, T. B. , … & Brownell, S. E. ( 2019c ). Factors that predict life sciences student persistence in undergraduate research experiences . PLoS ONE , 14 (8). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220186 Google Scholar
- Cooper, K. M., Gin, L. E., & Brownell, S. E. ( 2019d ). Diagnosing differences in what introductory biology students in a fully online and an in-person biology degree program know and do regarding medical school admission . Advances in Physiology Education , 43 (2), 221–232. Medline , Google Scholar
- Cooper, K. M., Gin, L. E., & Brownell, S. E. ( In press ). Depression as a concealable stigmatized identity: What influences whether students conceal or reveal their depression in undergraduate research experiences? International Journal of STEM Education , ( in press ). Google Scholar
- Depression and Biopolar Support Alliance . ( 2019 ). Home page . Retrieved November 28, 2019, from www.dbsalliance.org Google Scholar
- Deroma, V. M., Leach, J. B., & Leverett, J. P. ( 2009 ). The relationship between depression and college academic performance . College Student Journal , 43 (2), 325–335. Google Scholar
- Dweck, C. S. ( 2008 ). Mindset: The new psychology of success . New York, NY: Random House Digital. Google Scholar
- Dyson, R., & Renk, K. ( 2006 ). Freshmen adaptation to university life: Depressive symptoms, stress, and coping . Journal of Clinical Psychology , 62 (10), 1231–1244. Medline , Google Scholar
- Eddy, S. L., Brownell, S. E., & Wenderoth, M. P. ( 2014 ). Gender gaps in achievement and participation in multiple introductory biology classrooms . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 13 (3), 478–492. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.13-10-0204 Link , Google Scholar
- Eisenberg, D., Gollust, S. E., Golberstein, E., & Hefner, J. L. ( 2007 ). Prevalence and correlates of depression, anxiety, and suicidality among university students . American Journal of Orthopsychiatry , 77 (4), 534–542. Medline , Google Scholar
- Elliott, R., Sahakian, B. J., Herrod, J. J., Robbins, T. W., & Paykel, E. S. ( 1997 ). Abnormal response to negative feedback in unipolar depression: Evidence for a diagnosis specific impairment . Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry , 63 (1), 74–82. Medline , Google Scholar
- Eshel, N., & Roiser, J. P. ( 2010 ). Reward and punishment processing in depression . Biological Psychiatry , 68 (2), 118–124. Medline , Google Scholar
- Estrada, M., Hernandez, P. R., & Schultz, P. W. ( 2018 ). A longitudinal study of how quality mentorship and research experience integrate underrepresented minorities into STEM careers . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 17 (1), ar9. Link , Google Scholar
- Evans, T. M., Bira, L., Gastelum, J. B., Weiss, L. T., & Vanderford, N. L. ( 2018 ). Evidence for a mental health crisis in graduate education . Nature Biotechnology , 36 (3), 282. Medline , Google Scholar
- Everson, H. T., Tobias, S., Hartman, H., & Gourgey, A. ( 1993 ). Test anxiety and the curriculum: The subject matters . Anxiety, Stress, and Coping , 6 (1), 1–8. Google Scholar
- Flaherty, C. ( 2018 ). New study says graduate students’ mental health is a “crisis.” Retrieved November 29, 2019, from www.insidehighered.com/news/2018/03/06/new-study-says-graduate-students-mental-health-crisis Google Scholar
- Forsythe, A., & Johnson, S. ( 2017 ). Thanks, but no-thanks for the feedback . Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , 42 (6), 850–859. Google Scholar
- Garlow, S. J., Rosenberg, J., Moore, J. D., Haas, A. P., Koestner, B., Hendin, H., & Nemeroff, C. B. ( 2008 ). Depression, desperation, and suicidal ideation in college students: Results from the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention College Screening Project at Emory University . Depression and Anxiety , 25 (6), 482–488. Medline , Google Scholar
- Gelso, C. J., & Lent, R. W. ( 2000 ). Scientific training and scholarly productivity: The person, the training environment, and their interaction . In Brown, S. D.Lent, R. W. (Eds.), Handbook of counseling psychology (pp. 109–139). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons Inc. Google Scholar
- Gilbert, P., Baldwin, M. W., Irons, C., Baccus, J. R., & Palmer, M. ( 2006 ). Self-criticism and self-warmth: An imagery study exploring their relation to depression . Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy , 20 (2), 183. Google Scholar
- Gilbert, P., McEwan, K., Bellew, R., Mills, A., & Gale, C. ( 2009 ). The dark side of competition: How competitive behaviour and striving to avoid inferiority are linked to depression, anxiety, stress and self-harm . Psychology and Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice , 82 (2), 123–136. Medline , Google Scholar
- Gin, L. E., Rowland, A. A., Steinwand, B., Bruno, J., & Corwin, L. A. ( 2018 ). Students who fail to achieve predefined research goals may still experience many positive outcomes as a result of CURE participation . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 17 (4), ar57. Link , Google Scholar
- Glesne, C., & Peshkin, A. ( 1992 ). Becoming qualitative researchers: An introduction . London, England, UK: Longman. Google Scholar
- Grav, S., Hellzèn, O., Romild, U., & Stordal, E. ( 2012 ). Association between social support and depression in the general population: The HUNT study, a cross-sectional survey . Journal of Clinical Nursing , 21 (1–2), 111–120. Medline , Google Scholar
- Guest, G., Bunce, A., & Johnson, L. ( 2006 ). How many interviews are enough? An experiment with data saturation and variability . Field Methods , 18 (1), 59–82. Google Scholar
- Hancock, D. R. ( 2002 ). Influencing graduate students’ classroom achievement, homework habits and motivation to learn with verbal praise . Educational Research , 44 (1), 83–95. Google Scholar
- Hannah, D. R., & Lautsch, B. A. ( 2011 ). Counting in qualitative research: Why to conduct it, when to avoid it, and when to closet it . Journal of Management Inquiry , 20 (1), 14–22. Google Scholar
- Heatherton, T. F., & Wyland, C. L. ( 2003 ). Assessing self-esteem . In Lopez, S. J.Snyder, C. R. (Eds.), Positive psychological assessment: A handbook of models and measures (pp. 219–233). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. https://doi.org/10.1037/10612-014 . Google Scholar
- Henderlong, J., & Lepper, M. R. ( 2002 ). The effects of praise on children’s intrinsic motivation: A review and synthesis . Psychological Bulletin , 128 (5), 774. Medline , Google Scholar
- Henry, M. A., Shorter, S., Charkoudian, L., Heemstra, J. M., & Corwin, L. A. ( 2019 ). FAIL is not a four-letter word: A theoretical framework for exploring undergraduate students’ approaches to academic challenge and responses to failure in STEM learning environments . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 (1), ar11. Link , Google Scholar
- Hernandez, P. R., Woodcock, A., Estrada, M., & Schultz, P. W. ( 2018 ). Undergraduate research experiences broaden diversity in the scientific workforce . BioScience , 68 (3), 204–211. Google Scholar
- Hish, A. J., Nagy, G. A., Fang, C. M., Kelley, L., Nicchitta, C. V., Dzirasa, K., & Rosenthal, M. Z. ( 2019 ). Applying the stress process model to stress–burnout and stress–depression relationships in biomedical doctoral students: A cross-sectional pilot study . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 (4), ar51. Link , Google Scholar
- Howell, E., & McFeeters, J. ( 2008 ). Children’s mental health care: Differences by race/ethnicity in urban/rural areas . Journal of Health Care for the Poor and Underserved , 19 (1), 237–247. Medline , Google Scholar
- Hysenbegasi, A., Hass, S. L., & Rowland, C. R. ( 2005 ). The impact of depression on the academic productivity of university students . Journal of Mental Health Policy and Economics , 8 (3), 145. Medline , Google Scholar
- Ibrahim, A. K., Kelly, S. J., Adams, C. E., & Glazebrook, C. ( 2013 ). A systematic review of studies of depression prevalence in university students . Journal of Psychiatric Research , 47 (3), 391–400. Medline , Google Scholar
- Intemann, K. ( 2009 ). Why diversity matters: Understanding and applying the diversity component of the National Science Foundation’s broader impacts criterion . Social Epistemology , 23 (3–4), 249–266. Google Scholar
- Ishiyama, J. ( 2002 ). Does early participation in undergraduate research benefit social science and humanities students? College Student Journal , 36 (3), 381–387. Google Scholar
- Jenkins, S. R., Belanger, A., Connally, M. L., Boals, A., & Durón, K. M. ( 2013 ). First-generation undergraduate students’ social support, depression, and life satisfaction . Journal of College Counseling , 16 (2), 129–142. Google Scholar
- Jobst, A., Sabass, L., Palagyi, A., Bauriedl-Schmidt, C., Mauer, M. C., Sarubin, N. , … & Zill, P. ( 2015 ). Effects of social exclusion on emotions and oxytocin and cortisol levels in patients with chronic depression . Journal of Psychiatric Research , 60 , 170–177. Medline , Google Scholar
- Jones, K. P., & King, E. B. ( 2014 ). Managing concealable stigmas at work: A review and multilevel model . Journal of Management , 40 (5), 1466–1494. Google Scholar
- Jones, M. T., Barlow, A. E., & Villarejo, M. ( 2010 ). Importance of undergraduate research for minority persistence and achievement in biology . Journal of Higher Education , 81 (1), 82–115. Google Scholar
- Jones, N. P., Papadakis, A. A., Hogan, C. M., & Strauman, T. J. ( 2009 ). Over and over again: Rumination, reflection, and promotion goal failure and their interactive effects on depressive symptoms . Behaviour Research and Therapy , 47 (3), 254–259. Medline , Google Scholar
- Judd, L. L., Paulus, M. J., Schettler, P. J., Akiskal, H. S., Endicott, J., Leon, A. C. , … & Keller, M. B. ( 2000 ). Does incomplete recovery from first lifetime major depressive episode herald a chronic course of illness? American Journal of Psychiatry , 157 (9), 1501–1504. Medline , Google Scholar
- Kahn, J. H., & Garrison, A. M. ( 2009 ). Emotional self-disclosure and emotional avoidance: Relations with symptoms of depression and anxiety . Journal of Counseling Psychology , 56 (4), 573. Google Scholar
- Kataoka, S. H., Zhang, L., & Wells, K. B. ( 2002 ). Unmet need for mental health care among US children: Variation by ethnicity and insurance status . American Journal of Psychiatry , 159 (9), 1548–1555. Medline , Google Scholar
- Kreger, D. W. ( 1995 ). Self-esteem, stress, and depression among graduate students . Psychological Reports , 76 (1), 345–346. Medline , Google Scholar
- Krumpal, I. ( 2013 ). Determinants of social desirability bias in sensitive surveys: A literature review . Quality & Quantity , 47 (4), 2025–2047. Google Scholar
- Landis, J. R., & Koch, G. G. ( 1977 ). An application of hierarchical kappa-type statistics in the assessment of majority agreement among multiple observers . Biometrics , 33 (2), 363–374. Medline , Google Scholar
- Laursen, S., Hunter, A.-B., Seymour, E., Thiry, H., & Melton, G. ( 2010 ). Undergraduate research in the sciences: Engaging students in real science . Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. Google Scholar
- Limeri, L. B., Asif, M. Z., Bridges, B. H., Esparza, D., Tuma, T. T., Sanders, D. , … & Maltese, A. V. ( 2019 ). “Where’s my mentor?” Characterizing negative mentoring experiences in undergraduate life science research . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 (4), ar61. Link , Google Scholar
- Link, B. G., & Phelan, J. C. ( 2001 ). Conceptualizing stigma . Annual Review of Sociology , 27 (1), 363–385. Google Scholar
- Luyten, P., Sabbe, B., Blatt, S. J., Meganck, S., Jansen, B., De Grave, C. , … & Corveleyn, J. ( 2007 ). Dependency and self-criticism: Relationship with major depressive disorder, severity of depression, and clinical presentation . Depression and Anxiety , 24 (8), 586–596. Medline , Google Scholar
- Mabrouk, P. A., & Peters, K. ( 2000 ). Student perspectives on undergraduate research (UR) experiences in chemistry and biology . CUR Quarterly , 21 (1), 25–33. Google Scholar
- Maxwell, J. A. ( 2010 ). Using numbers in qualitative research . Qualitative Inquiry , 16 (6), 475–482. Google Scholar
- Mongrain, M., & Blackburn, S. ( 2005 ). Cognitive vulnerability, lifetime risk, and the recurrence of major depression in graduate students . Cognitive Therapy and Research , 29 (6), 747–768. Google Scholar
- Nagy, G. A., Fang, C. M., Hish, A. J., Kelly, L., Nicchitta, C. V., Dzirasa, K., & Rosenthal, M. Z. ( 2019 ). Burnout and mental health problems in biomedical doctoral students . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 (2), ar27. Link , Google Scholar
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) . ( 2017 ). Undergraduate research experiences for STEM students: Successes, challenges, and opportunities . Washington, DC: National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/24622 Google Scholar
- NASEM . ( 2019 ). The science of effective mentorship in STEMM . Washington, DC: National Academies Press. Retrieved November 29, 2019, from www.nap.edu/download/25568 Google Scholar
- Osborne, J., & Collins, S. ( 2001 ). Pupils’ views of the role and value of the science curriculum: A focus-group study . International Journal of Science Education , 23 (5), 441–467. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500690010006518 Google Scholar
- Porter, S. R., & Whitcomb, M. E. ( 2005 ). Non-response in student surveys: The role of demographics, engagement and personality . Research in Higher Education , 46 (2), 127–152. Google Scholar
- President’s Council of Advisors on Science and Technology . ( 2012 ). Engage to excel: Producing one million additional college graduates with degrees in science, Technology, Engineering, and mathematics . Washington, DC: U.S. Government Office of Science and Technology. Google Scholar
- Prunuske, A. J., Wilson, J., Walls, M., & Clarke, B. ( 2013 ). Experiences of mentors training underrepresented undergraduates in the research laboratory . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 12 (3), 403–409. Link , Google Scholar
- Quinn, D. M., & Earnshaw, V. A. ( 2011 ). Understanding concealable stigmatized identities: The role of identity in psychological, physical, and behavioral outcomes . Social Issues and Policy Review , 5 (1), 160–190. Google Scholar
- Rauckhorst, W. H., Czaja, J. A., & Baxter Magolda, M. ( 2001 ). Measuring the impact of the undergraduate research experience on student intellectual development . Snowbird, UT: Project Kaleidoscope Summer Institute. Google Scholar
- Saldaña, J. ( 2015 ). The coding manual for qualitative researchers . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. Google Scholar
- Santiago, C. D., Kaltman, S., & Miranda, J. ( 2013 ). Poverty and mental health: How do low-income adults and children fare in psychotherapy? Journal of Clinical Psychology , 69 (2), 115–126. Medline , Google Scholar
- Santini, Z. I., Koyanagi, A., Tyrovolas, S., Mason, C., & Haro, J. M. ( 2015 ). The association between social relationships and depression: A systematic review . Journal of Affective Disorders , 175 , 53–65. Medline , Google Scholar
- Schleider, J., & Weisz, J. ( 2018 ). A single-session growth mindset intervention for adolescent anxiety and depression: 9-month outcomes of a randomized trial . Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry , 59 (2), 160–170. Medline , Google Scholar
- Seymour, E., & Hewitt, N. M. ( 1997 ). Talking about leaving: Why undergraduates leave the sciences . Westview Press. Google Scholar
- Seymour, E., & Hunter, A.-B. ( 2019 ). Talking about leaving revisited . New York, NY: Springer. Google Scholar
- Seymour, E., Hunter, A.-B., Laursen, S. L., & DeAntoni, T. ( 2004 ). Establishing the benefits of research experiences for undergraduates in the sciences: First findings from a three-year study . Science Education , 88 (4), 493–534. Google Scholar
- Smith, D. T., Mouzon, D. M., & Elliott, M. ( 2018 ). Reviewing the assumptions about men’s mental health: An exploration of the gender binary . American Journal of Men’s Health , 12 (1), 78–89. Medline , Google Scholar
- Sorkness, C. A., Pfund, C., Ofili, E. O., Okuyemi, K. S., Vishwanatha, J. K., Zavala, M. E. , … & Deveci, A. ( 2017 ). A new approach to mentoring for research careers: The National Research Mentoring Network . BMC Proceedings , 11 , 22. Medline , Google Scholar
- Sowislo, J. F., & Orth, U. ( 2013 ). Does low self-esteem predict depression and anxiety? A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies . Psychological Bulletin , 139 (1), 213. Medline , Google Scholar
- Steger, M. F. ( 2013 ). Experiencing meaning in life: Optimal functioning at the nexus of well-being, psychopathology, and spirituality . In Wong, P. T. P. (Ed.), The human quest for meaning (pp. 211–230). England, UK: Routledge. Google Scholar
- Strenta, A. C., Elliott, R., Adair, R., Matier, M., & Scott, J. ( 1994 ). Choosing and leaving science in highly selective institutions . Research in Higher Education , 35 (5), 513–547. Google Scholar
- Text Depression Hotline . ( 2019 ). Crisis text line . Retrieved November 29, 2019, from www.crisistextline.org/depression Google Scholar
- Thiry, H., & Laursen, S. L. ( 2011 ). The role of student–advisor interactions in apprenticing undergraduate researchers into a scientific community of practice . Journal of Science Education and Technology , 20 (6), 771–784. Google Scholar
- Thompson, J. J., Conaway, E., & Dolan, E. L. ( 2016 ). Undergraduate students’ development of social, cultural, and human capital in a networked research experience . Cultural Studies of Science Education , 11 (4), 959–990. Google Scholar
- Trenor, J. M., Miller, M. K., & Gipson, K. G. ( 2011 ). Utilization of a think-aloud protocol to cognitively validate a survey instrument identifying social capital resources of engineering undergraduates . 118th American Society for Engineering Education Annual Conference and Exposition, Vancouver, BC, Canada . Google Scholar
- Turner, R. J., & Noh, S. ( 1988 ). Physical disability and depression: A longitudinal analysis . Journal of Health and Social Behavior , 29 (1), 23–37. Medline , Google Scholar
- Watson, D., & Friend, R. ( 1969 ). Measurement of social-evaluative anxiety . Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology , 33 (4), 448. Medline , Google Scholar
- Weeks, J. W., Heimberg, R. G., Fresco, D. M., Hart, T. A., Turk, C. L., Schneier, F. R., & Liebowitz, M. R. ( 2005 ). Empirical validation and psychometric evaluation of the Brief Fear of Negative Evaluation Scale in patients with social anxiety disorder . Psychological Assessment , 17 (2), 179. Medline , Google Scholar
- World Health Organization . ( 2018 ). Depression . Retrieved November 29, 2019, from www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression Google Scholar
- Wyatt, T., & Oswalt, S. B. ( 2013 ). Comparing mental health issues among undergraduate and graduate students . American Journal of Health Education , 44 (2), 96–107. Google Scholar
- Carly A. Busch ,
- Tala Araghi ,
- Jingyi He ,
- Katelyn M. Cooper , and
- Colin Harrison, Monitoring Editor
- Emma C. Goodwin ,
- Danielle Pais ,
- Logan E. Gin , and
- Derek Braun, Monitoring Editor
- Baylee A. Edwards ,
- Chloe Bowen ,
- M. Elizabeth Barnes , and
- Tati Russo-Tait, Monitoring Editor
- Sara E. Grineski ,
- Danielle X. Morales , and
- Timothy W. Collins
- Carly A. Busch , and
- Tasneem F. Mohammed ,
- Erika M. Nadile ,
- Madison L. Witt ,
- Cindy Vargas ,
- Missy Tran ,
- Joseph Gazing Wolf ,
- Danielle Brister , and
- Sehoya Cotner, Monitoring Editor
- Katelyn M. Cooper ,
- Sarah L. Eddy , and
- Coping behavior versus coping style: characterizing a measure of coping in undergraduate STEM contexts 14 February 2022 | International Journal of STEM Education, Vol. 9, No. 1
- Lisa A. Corwin ,
- Michael E. Ramsey ,
- Eric A. Vance ,
- Elizabeth Woolner ,
- Stevie Maiden ,
- Nina Gustafson and
- Joseph A. Harsh
- Erin Shortlidge, Monitoring Editor
- K. Supriya ,
- Brian Sato, Monitoring Editor
- Logan E. Gin ,
- Clark Coffman, Monitoring Editor
- Nicholas J. Wiesenthal , and
- Maryrose Weatherton and
- Elisabeth E. Schussler
- Erika Offerdahl, Monitoring Editor
- Eight Recommendations to Promote Effective Study Habits for Biology Students Enrolled in Online Courses Journal of Microbiology & Biology Education, Vol. 23, No. 1
- Fostering professional development through undergraduate research: supporting faculty mentors and student researchers 30 March 2022 | Mentoring & Tutoring: Partnership in Learning, Vol. 30, No. 2
- Jeffrey Maloy ,
- Monika B. Kwapisz , and
- Bryce E. Hughes
- Terrell Morton, Monitoring Editor
- Anxiety and depression among US college students engaging in undergraduate research during the COVID-19 pandemic 14 December 2021 | Journal of American College Health, Vol. 9
- Danielle Brister ,
- Sara E. Brownell ,
- Chade T. Claiborne ,
- Curtis Lunt ,
- Kobe M. Walker ,
- Tamiru D. Warkina ,
- Yi Zheng , and
- Rebecca Price, Monitoring Editor
- Dominant Learning Styles of Interior Design Students in Generation Z 26 July 2021 | Journal of Interior Design, Vol. 46, No. 4
- Linking Emotional Intelligence, Physical Activity and Aggression among Undergraduates 26 November 2021 | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, Vol. 18, No. 23
- Advancing undergraduate synthetic biology education: insights from a Canadian iGEM student perspective Canadian Journal of Microbiology, Vol. 67, No. 10
- Frank A. Guerrero ,
- Sara E. Brownell , and
- Jennifer Momsen, Monitoring Editor
- Nicholas J. Wiesenthal ,
- Isabella Ferreira , and
- Grant Ean Gardner, Monitoring Editor
- Carolyn E. Clark ,
- Deanna B. Elliott ,
- Travis B. Roderick ,
- Rachel A. Scott ,
- Denisse Arellano ,
- Diana Ramirez ,
- Kimberly Velarde ,
- Allyson Aeschliman ,
- Sarah T. Avalle ,
- Jessica Berkheimer ,
- Rachel Campos ,
- Michael Gerbasi ,
- Sophia Hughes ,
- Julie A. Roberts ,
- Quinn M. White ,
- Ehren Wittekind ,
- Rachelle Spell, Monitoring Editor
- Christine Pfund ,
- Janet L. Branchaw ,
- Melissa McDaniels ,
- Angela Byars-Winston ,
- Steven P. Lee ,, and
- Bruce Birren
- Vladimir Anokhin ,
- MacKenzie J. Gray ,
- Daniel E. Zajic ,
- Jason E. Podrabsky , and
- Erin E. Shortlidge
- Depression as a concealable stigmatized identity: what influences whether students conceal or reveal their depression in undergraduate research experiences? 4 June 2020 | International Journal of STEM Education, Vol. 7, No. 1

Submitted: 4 November 2019 Revised: 24 February 2020 Accepted: 6 March 2020
© 2020 K. M. Cooper, L. E. Gin, et al. CBE—Life Sciences Education © 2020 The American Society for Cell Biology. This article is distributed by The American Society for Cell Biology under license from the author(s). It is available to the public under an Attribution–Noncommercial–Share Alike 3.0 Unported Creative Commons License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0).
434 Depression Essay Titles & Research Topics: Argumentative, Controversial, and More
Depression is undeniably one of the most prevalent mental health conditions globally, affecting approximately 5% of adults worldwide. It often manifests as intense feelings of hopelessness, sadness, and a loss of interest in previously enjoyable activities. Many also experience physical symptoms like fatigue, sleep disturbances, and appetite changes. Recognizing and addressing this mental disorder is extremely important to save lives and treat the condition.
In this article, we’ll discuss how to write an essay about depression and introduce depression essay topics and research titles for students that may be inspirational.
- 🔝 Top Depression Essay Titles
- ✅ Essay Prompts
- 💡 Research Topics
- 🔎 Essay Titles
- 💭 Speech Topics
- 📝 Essay Structure
🔗 References
🔝 top 12 research titles about depression.
- How is depression treated?
- Depression: Risk factors.
- The symptoms of depression.
- What types of depression exist?
- Depression in young people.
- Differences between anxiety and depression.
- The parents’ role in depression therapy.
- Drugs as the root cause of depression.
- Dangerous consequences of untreated depression.
- Effect of long-term depression.
- Different stages of depression.
- Treatment for depression.
✅ Prompts for Essay about Depression
Struggling to find inspiration for your essay? Look no further! We’ve put together some valuable essay prompts on depression just for you!
Prompt for Personal Essay about Depression
Sharing your own experience with depression in a paper can be a good idea. Others may feel more motivated to overcome their situation after reading your story. You can also share valuable advice by discussing things or methods that have personally helped you deal with the condition.
For example, in your essay about depression, you can:
- Tell about the time you felt anxious, hopeless, or depressed;
- Express your opinion on depression based on the experiences from your life;
- Suggest a way of dealing with the initial symptoms of depression ;
- Share your ideas on how to protect mental health at a young age.
How to Overcome Depression: Essay Prompt
Sadness is a common human emotion, but depression encompasses more than just sadness. As reported by the National Institute of Mental Health, around 21 million adults in the United States, roughly 8.4% of the total adult population , faced at least one significant episode of depression in 2020. When crafting your essay about overcoming depression, consider exploring the following aspects:
- Depression in young people and adolescents;
- The main causes of depression;
- The symptoms of depression;
- Ways to treat depression;
- Help from a psychologist (cognitive behavioral therapy or interpersonal therapy ).
Postpartum Depression: Essay Prompt
The birth of a child often evokes a spectrum of powerful emotions, spanning from exhilaration and happiness to apprehension and unease. It can also trigger the onset of depression. Following childbirth, many new mothers experience postpartum “baby blues,” marked by shifts in mood, bouts of tears, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. To shed light on the subject of postpartum depression, explore the following questions:
- What factors may increase the risk of postpartum depression?
- Is postpartum depression predictable?
- How to prevent postpartum depression?
- What are the symptoms of postpartum depression?
- What kinds of postpartum depression treatments exist?
Prompt for Essay about Teenage Depression
Teenage depression is a mental health condition characterized by sadness and diminishing interest in daily activities. It can significantly impact a teenager’s thoughts, emotions, and behavior, often requiring long-term treatment and support.
By discussing the primary symptoms of teenage depression in your paper, you can raise awareness of the issue and encourage those in need to seek assistance. You can pay attention to the following aspects:
- Emotional changes (feelings of sadness, anger, hopelessness, guilt, etc.);
- Behavioral changes (loss of energy and appetite , less attention to personal hygiene, self-harm, etc.);
- New addictions (drugs, alcohol, computer games, etc.).
💡 Research Topics about Depression
- The role of genetics in depression development.
- The effectiveness of different psychotherapeutic interventions for depression.
- Anti-depression non-pharmacological and medication treatment .
- The impact of childhood trauma on the onset of depression later in life.
- Exploring the efficacy of antidepressant medication in different populations.
- The impact of exercise on depression symptoms and treatment outcomes.
- Mild depression: pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy .
- The relationship between sleep disturbances and depression.
- The role of gut microbiota in depression and potential implications for treatment.
- Investigating the impact of social media on depression rates in adolescents.
- Depression, dementia, and delirium in older people .
- The efficacy of cognitive-behavioral therapy in preventing depression relapse.
- The influence of hormonal changes on depression risk.
- Assessing the effectiveness of self-help and digital interventions for depression.
- Herbal and complementary therapies for depression .
- The relationship between personality traits and vulnerability to depression.
- Investigating the long-term consequences of untreated depression on physical health.
- Exploring the link between chronic pain and depression.
- Depression in the elderly male .
- The impact of childhood experiences on depression outcomes in adulthood.
- The use of ketamine and other novel treatments for depression.
- The effect of stigma on depression diagnosis and treatment.
- The conducted family assessment: cases of depression .
- The role of social support in depression recovery.
- The effectiveness of online support groups for individuals with depression.
- Depression and cognitive decline in adults.
- Depression: PICOT question component exploration .
- Exploring the impact of nutrition and dietary patterns on depression symptoms.
- Investigating the efficacy of art-based therapies in depression treatment.
- The role of neuroplasticity in the development and treatment of depression.
- Depression among HIV-positive women .
- The influence of gender on depression prevalence and symptomatology.
- Investigating the impact of workplace factors on depression rates and outcomes.
- The efficacy of family-based interventions in reducing depression symptoms in teenagers.
- Frontline nurses’ burnout, anxiety, depression, and fear statuses .
- The role of early-life stress and adversity in depression vulnerability.
- The impact of various environmental factors on depression rates.
- Exploring the link between depression and cardiovascular health .
- Depression detection in adults in nursing practice .
- Virtual reality as a therapeutic tool for depression treatment.
- Investigating the impact of childhood bullying on depression outcomes.
- The benefits of animal-assisted interventions in depression management.
- Depression and physical exercise .
- The relationship between depression and suicidal behavior .
- The influence of cultural factors on depression symptom expression.
- Investigating the role of epigenetics in depression susceptibility.
- Depression associated with cognitive dysfunction .
- Exploring the impact of adverse trauma on the course of depression.
- The efficacy of acceptance and commitment therapy in treating depression.
- The relationship between depression and substance use disorders .
- Depression and anxiety among college students .
- Investigating the effectiveness of group therapy for depression.
- Depression and chronic medical conditions .
Psychology Research Topics on Depression
- The influence of early attachment experiences on the development of depression.
- The impact of negative cognitive biases on depression symptomatology.
- Depression treatment plan for a queer patient .
- Examining the relationship between perfectionism and depression.
- The role of self-esteem in depression vulnerability and recovery.
- Exploring the link between maladaptive thinking styles (e.g., rumination, catastrophizing) and depression.
- Investigating the impact of social support on depression outcomes and resilience.
- Identifying depression in young adults at an early stage .
- The influence of parenting styles on the risk of depression in children and adolescents.
- The role of self-criticism and self-compassion in depression treatment.
- Exploring the relationship between identity development and depression in emerging adulthood.
- The role of learned helplessness in understanding depression and its treatment.
- Depression in the elderly .
- Examining the connection between self-efficacy beliefs and depression symptoms.
- The influence of social comparison processes on depression and body image dissatisfaction .
- Exploring the impact of trauma-related disorders on depression.
- The role of resilience factors in buffering against the development of depression.
- Investigating the relationship between personality traits and depression.
- Depression and workplace violence .
- The impact of cultural factors on depression prevalence and symptom presentation.
- Investigating the effects of chronic stress on depression risk.
- The role of coping strategies in depression management and recovery.
- The correlation between discrimination/prejudice and depression/anxiety .
- Exploring the influence of gender norms and societal expectations on depression rates.
- The impact of adverse workplace conditions on employee depression.
- Investigating the effectiveness of narrative therapy in treating depression.
- Cognitive behavior and depression in adolescents .
- Childhood emotional neglect and adult depression.
- The influence of perceived social support on treatment outcomes in depression.
- The effects of childhood bullying on the development of depression.
- The impact of intergenerational transmission of depression within families.
- Depression in children: symptoms and treatments .
- Investigating the link between body dissatisfaction and depression in adolescence.
- The influence of adverse life events and chronic stressors on depression risk.
- The effects of peer victimization on the development of depression in adolescence.
- Counselling clients with depression and addiction .
- The role of experiential avoidance in depression and its treatment.
- The impact of social media use and online interactions on depression rates.
- Depression management in adolescent .
- Exploring the relationship between emotional intelligence and depression symptomatology.
- Investigating the influence of cultural values and norms on depression stigma and help-seeking behavior.
- The effects of childhood maltreatment on neurobiological markers of depression.
- Psychological and emotional conditions of suicide and depression .
- Exploring the relationship between body dissatisfaction and depression.
- The influence of self-worth contingencies on depression vulnerability and treatment response.
- The impact of social isolation and loneliness on depression rates.
- Psychology of depression among college students .
- The effects of perfectionistic self-presentation on depression in college students.
- The role of mindfulness skills in depression prevention and relapse prevention.
- Investigating the influence of adverse neighborhood conditions on depression risk.
- Personality psychology and depression .
- The impact of attachment insecurity on depression symptomatology.
Postpartum Depression Research Topics
- Identifying risk factors for postpartum depression.
- Exploring the role of hormonal changes in postpartum depression.
- “Baby blues” or postpartum depression and evidence-based care .
- The impact of social support on postpartum depression.
- The effectiveness of screening tools for early detection of postpartum depression.
- The relationship between postpartum depression and maternal-infant bonding .
- Postpartum depression educational program results .
- Identifying effective interventions for preventing and treating postpartum depression.
- Examining the impact of cultural factors on postpartum depression rates.
- Investigating the role of sleep disturbances in postpartum depression.
- Depression and postpartum depression relationship .
- Exploring the impact of a traumatic birth experience on postpartum depression.
- Assessing the impact of breastfeeding difficulties on postpartum depression.
- Understanding the role of genetic factors in postpartum depression.
- Postpartum depression: consequences .
- Investigating the impact of previous psychiatric history on postpartum depression risk.
- The potential benefits of exercise on postpartum depression symptoms.
- The efficacy of psychotherapeutic interventions for postpartum depression.
- Postpartum depression in the twenty-first century .
- The influence of partner support on postpartum depression outcomes.
- Examining the relationship between postpartum depression and maternal self-esteem.
- The impact of postpartum depression on infant development and well-being.
- Maternal mood symptoms in pregnancy and postpartum depression .
- The effectiveness of group therapy for postpartum depression management.
- Identifying the role of inflammation and immune dysregulation in postpartum depression.
- Investigating the impact of childcare stress on postpartum depression.
- Postpartum depression among low-income US mothers .
- The role of postnatal anxiety symptoms in postpartum depression.
- The impact of postpartum depression on the marital relationship.
- The influence of postpartum depression on parenting practices and parental stress.
- Postpartum depression: symptoms, role of cultural factors, and ways to support .
- Investigating the efficacy of pharmacological treatments for postpartum depression.
- The impact of postpartum depression on breastfeeding initiation and continuation.
- The relationship between postpartum depression and post-traumatic stress disorder .
- Postpartum depression and its identification .
- The impact of postpartum depression on cognitive functioning and decision-making.
- Investigating the influence of cultural norms and expectations on postpartum depression rates.
- The impact of maternal guilt and shame on postpartum depression symptoms.
- Beck’s postpartum depression theory: purpose, concepts, and significance .
- Understanding the role of attachment styles in postpartum depression vulnerability.
- Investigating the effectiveness of online support groups for women with postpartum depression.
- The impact of socioeconomic factors on postpartum depression prevalence.
- Perinatal depression: research study and design .
- The efficacy of mindfulness-based interventions for postpartum depression.
- Investigating the influence of birth spacing on postpartum depression risk.
- The role of trauma history in postpartum depression development.
- The link between the birth experience and postnatal depression .
- How does postpartum depression affect the mother-infant interaction and bonding ?
- The effectiveness of home visiting programs in preventing and managing postpartum depression.
- Assessing the influence of work-related stress on postpartum depression.
- The relationship between postpartum depression and pregnancy-related complications.
- The role of personality traits in postpartum depression vulnerability.
🔎 Depression Essay Titles
Depression essay topics: cause & effect.
- The effects of childhood trauma on the development of depression in adults.
- The impact of social media usage on the prevalence of depression in adolescents.
- “Predictors of Postpartum Depression” by Katon et al.
- The effects of environmental factors on depression rates.
- The relationship between academic pressure and depression among college students.
- The relationship between financial stress and depression.
- The best solution to predict depression because of bullying .
- How does long-term unemployment affect mental health ?
- The effects of unemployment on mental health, particularly the risk of depression.
- The impact of genetics and family history of depression on an individual’s likelihood of developing depression.
- The relationship between depression and substance abuse .
- Child abuse and depression .
- The role of gender in the manifestation and treatment of depression.
- The effects of chronic stress on the development of depression.
- The link between substance abuse and depression.
- Depression among students at Elon University .
- The influence of early attachment styles on an individual’s vulnerability to depression.
- The effects of sleep disturbances on the severity of depression.
- Chronic illness and the risk of developing depression.
- Depression: symptoms and treatment .
- Adverse childhood experiences and the likelihood of experiencing depression in adulthood.
- The relationship between chronic illness and depression.
- The role of negative thinking patterns in the development of depression.
- Effects of depression among adolescents .
- The effects of poor body image and low self-esteem on the prevalence of depression.
- The influence of social support systems on preventing symptoms of depression.
- The effects of child neglect on adult depression rates.
- Depression caused by hormonal imbalance .
- The link between perfectionism and the risk of developing depression.
- The effects of a lack of sleep on depression symptoms.
- The effects of childhood abuse and neglect on the risk of depression.
- Social aspects of depression and anxiety .
- The impact of bullying on the likelihood of experiencing depression.
- The role of serotonin and neurotransmitter imbalances in the development of depression.
- The impact of a poor diet on depression rates.
- Depression and anxiety run in the family .
- The effects of childhood poverty and socioeconomic status on depression rates in adults.
- The impact of divorce on depression rates.
- The relationship between traumatic life events and the risk of developing depression.
- The influence of personality traits on susceptibility to depression.
- The impact of workplace stress on depression rates.
- Depression in older adults: causes and treatment .
- The impact of parental depression on children’s mental health outcomes.
- The effects of social isolation on the prevalence and severity of depression.
- The role of cultural factors in the manifestation and treatment of depression.
- The relationship between childhood bullying victimization and future depressive symptoms.
- The impact of early intervention and prevention programs on reducing the risk of postpartum depression.
- Treating mood disorders and depression .
- How do hormonal changes during pregnancy contribute to the development of depression?
- The effects of sleep deprivation on the onset and severity of postpartum depression.
- The impact of social media on depression rates among teenagers.
- The role of genetics in the development of depression.
- The impact of bullying on adolescent depression rates.
- Mental illness, depression, and wellness issues .
- The effects of a sedentary lifestyle on depression symptoms.
- The correlation between academic pressure and depression in students.
- The relationship between perfectionism and depression.
- The correlation between trauma and depression in military veterans.
- Anxiety and depression during childhood and adolescence .
- The impact of racial discrimination on depression rates among minorities.
- The relationship between chronic pain and depression.
- The impact of social comparison on depression rates among young adults.
- The effects of childhood abuse on adult depression rates.
Depression Argumentative Essay Topics
- The role of social media in contributing to depression among teenagers.
- The effectiveness of antidepressant medication: an ongoing debate.
- Depression treatment: therapy or medications ?
- Should depression screening be mandatory in schools and colleges?
- Is there a genetic predisposition to depression?
- The stigma surrounding depression: addressing misconceptions and promoting understanding.
- Implementation of depression screening in primary care .
- Is psychotherapy more effective than medication in treating depression?
- Is teenage depression overdiagnosed or underdiagnosed: a critical analysis.
- The connection between depression and substance abuse: untangling the relationship.
- Humanistic therapy of depression .
- Should ECT (electroconvulsive therapy) be a treatment option for severe depression?
- Where is depression more prevalent: in urban or rural communities? Analyzing the disparities.
- Is depression a result of chemical imbalance in the brain? Debunking the myth.
- Depression: a serious mental and behavioral problem .
- Should depression medication be prescribed for children and adolescents?
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in managing depression.
- Should depression in the elderly be considered a normal part of aging?
- Is depression hereditary? Investigating the role of genetics in depression risk.
- Different types of training in managing the symptoms of depression .
- The effectiveness of online therapy platforms in treating depression.
- Should psychedelic therapy be explored as an alternative treatment for depression?
- The connection between depression and cardiovascular health: Is there a link?
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in preventing depression relapse.
- Depression as a bad a clinical condition .
- Should mind-body interventions (e.g., yoga , meditation) be integrated into depression treatment?
- Should emotional support animals be prescribed for individuals with depression?
- The effectiveness of peer support groups in decreasing depression symptoms.
- The use of antidepressants: are they overprescribed or necessary for treating depression?
- Adult depression and anxiety as a complex problem .
- The effectiveness of therapy versus medication in treating depression.
- The stigma surrounding depression and mental illness: how can we reduce it?
- The debate over the legalization of psychedelic drugs for treating depression.
- The relationship between creativity and depression: does one cause the other?
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy for generalized anxiety disorder and depression .
- The role of childhood trauma in shaping adult depression: Is it always a causal factor?
- The debate over the medicalization of sadness and grief as forms of depression.
- Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or meditation, are effective in treating depression.
- Depression as a widespread mental condition .
Controversial Topics about Depression
- The existence of “chemical imbalance” in depression: fact or fiction?
- The over-reliance on medication in treating depression: are alternatives neglected?
- Is depression overdiagnosed and overmedicated in Western society?
- Measurement of an individual’s level of depression .
- The role of Big Pharma in shaping the narrative and treatment of depression.
- Should antidepressant advertisements be banned?
- The inadequacy of current diagnostic criteria for depression: rethinking the DSM-5.
- Is depression a biological illness or a product of societal factors?
- Literature review on depression .
- The overemphasis on biological factors in depression treatment: ignoring environmental factors.
- Is depression a normal reaction to an abnormal society?
- The influence of cultural norms on the perception and treatment of depression.
- Should children and adolescents be routinely prescribed antidepressants?
- The role of family in depression treatment .
- The connection between depression and creative genius: does depression enhance artistic abilities?
- The ethics of using placebo treatment for depression studies.
- The impact of social and economic inequalities on depression rates.
- Is depression primarily a mental health issue or a social justice issue?
- Depression disassembling and treating .
- Should depression screening be mandatory in the workplace?
- The influence of gender bias in the diagnosis and treatment of depression.
- The controversial role of religion and spirituality in managing depression.
- Is depression a result of individual weakness or societal factors?
- Abnormal psychology: anxiety and depression case .
- The link between depression and obesity: examining the bidirectional relationship.
- The connection between depression and academic performance : causation or correlation?
- Should depression medication be available over the counter?
- The impact of internet and social media use on depression rates: harmful or beneficial?
- Interacting in the workplace: depression .
- Is depression a modern epidemic or simply better diagnosed and identified?
- The ethical considerations of using animals in depression research.
- The effectiveness of psychedelic therapies for treatment-resistant depression.
- Is depression a disability? The debate on workplace accommodations.
- Polysubstance abuse among adolescent males with depression .
- The link between depression and intimate partner violence : exploring the relationship.
- The controversy surrounding “happy” pills and the pursuit of happiness.
- Is depression a choice? Examining the role of personal responsibility.
Good Titles for Depression Essays
- The poetic depictions of depression: exploring its representation in literature.
- The melancholic symphony: the influence of depression on classical music.
- Moderate depression symptoms and treatment .
- Depression in modern music: analyzing its themes and expressions.
- Cultural perspectives on depression: a comparative analysis of attitudes in different countries.
- Contrasting cultural views on depression in Eastern and Western societies.
- Diagnosing depression in the older population .
- The influence of social media on attitudes and perceptions of depression in global contexts.
- Countries with progressive approaches to mental health awareness.
- From taboo to acceptance: the evolution of attitudes towards depression.
- Depression screening tool in acute settings .
- The Bell Jar : analyzing Sylvia Plath’s iconic tale of depression .
- The art of despair: examining Frida Kahlo’s self-portraits as a window into depression.
- The Catcher in the Rye : Holden Caulfield’s battle with adolescent depression.
- Music as therapy: how jazz artists turned depression into art.
- Depression screening tool for a primary care center .
- The Nordic paradox: high depression rates in Scandinavian countries despite high-quality healthcare.
- The Stoic East: how Eastern philosophies approach and manage depression.
- From solitude to solidarity: collective approaches to depression in collectivist cultures.
- The portrayal of depression in popular culture: a critical analysis of movies and TV shows.
- The depression screening training in primary care .
- The impact of social media influencers on depression rates among young adults.
- The role of music in coping with depression: can specific genres or songs help alleviate depressive symptoms?
- The representation of depression in literature: a comparative analysis of classic and contemporary works.
- The use of art as a form of self-expression and therapy for individuals with depression.
- Depression management guidelines implementation .
- The role of religion in coping with depression: Christian and Buddhist practices.
- The representation of depression in the video game Hellblade: Senua’s Sacrifice .
- The role of nature in coping with depression: can spending time outdoors help alleviate depressive symptoms?
- The effectiveness of dance/movement therapy in treating depression among older adults.
- The National Institute for Health: depression management .
- The portrayal of depression in stand-up comedy: a study of comedians like Maria Bamford and Chris Gethard.
- The role of spirituality in coping with depression: Islamic and Hindu practices .
- The portrayal of depression in animated movies : an analysis of Inside Out and The Lion King .
- The representation of depression by fashion designers like Alexander McQueen and Rick Owens.
- Depression screening in primary care .
- The portrayal of depression in documentaries: an analysis of films like The Bridge and Happy Valley .
- The effectiveness of wilderness therapy in treating depression among adolescents.
- The connection between creativity and depression: how art can help heal.
- The role of Buddhist and Taoist practices in coping with depression.
- Mild depression treatment research funding sources .
- The portrayal of depression in podcasts: an analysis of the show The Hilarious World of Depression .
- The effectiveness of drama therapy in treating depression among children and adolescents.
- The representation of depression in the works of Vincent van Gogh and Edvard Munch.
- Depression in young people: articles review .
- The impact of social media on political polarization and its relationship with depression.
- The role of humor in coping with depression: a study of comedians like Ellen DeGeneres.
- The portrayal of depression in webcomics: an analysis of the comics Hyperbole and a Half .
- The effect of social media on mental health stigma and its relationship with depression.
- Depression and the impact of human services workers .
- The masked faces: hiding depression in highly individualistic societies.
💭 Depression Speech Topics
Informative speech topics about depression.
- Different types of depression and their symptoms.
- The causes of depression: biological, psychological, and environmental factors.
- How depression and physical issues are connected .
- The prevalence of depression in different age groups and demographics.
- The link between depression and anxiety disorders .
- Physical health: The effects of untreated depression.
- The role of genetics in predisposing individuals to depression.
- What you need to know about depression .
- How necessary is early intervention in treating depression?
- The effectiveness of medication in treating depression.
- The role of exercise in managing depressive symptoms.
- Depression in later life: overview .
- The relationship between substance abuse and depression.
- The impact of trauma on depression rates and treatment.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness meditation in managing depressive symptoms.
- Enzymes conversion and metabolites in major depression .
- The benefits and drawbacks of electroconvulsive therapy for severe depression.
- The effect of gender and cultural norms on depression rates and treatment.
- The effectiveness of alternative therapies for depression, such as acupuncture and herbal remedies .
- The importance of self-care in managing depression.
- Symptoms of anxiety, depression, and peritraumatic dissociation .
- The role of support systems in managing depression.
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating depression.
- The benefits and drawbacks of online therapy for depression.
- The role of spirituality in managing depression.
- Depression among minority groups .
- The benefits and drawbacks of residential treatment for severe depression.
- What is the relationship between childhood trauma and adult depression?
- How effective is transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) for treatment-resistant depression?
- The benefits and drawbacks of art therapy for depression.
- Mood disorder: depression and bipolar .
- The impact of social media on depression rates.
- The effectiveness of dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) in treating depression.
- Depression in older people .
- The impact of seasonal changes on depression rates and treatment options.
- The impact of depression on daily life and relationships, and strategies for coping with the condition.
- The stigma around depression and the importance of seeking help.
Persuasive Speech Topics about Depression
- How important is it to recognize the signs and symptoms of depression ?
- How do you support a loved one who is struggling with depression?
- The importance of mental health education in schools to prevent and manage depression.
- Social media: the rise of depression and anxiety .
- Is there a need to increase funding for mental health research to develop better treatments for depression?
- Addressing depression in minority communities: overcoming barriers and disparities.
- The benefits of including alternative therapies , such as yoga and meditation, in depression treatment plans.
- Challenging media portrayals of depression: promoting accurate representations.
- Two sides of depression disease .
- How social media affects mental health: the need for responsible use to prevent depression.
- The importance of early intervention: addressing depression in schools and colleges.
- The benefits of seeking professional help for depression.
- There is a need for better access to mental health care, including therapy and medication, for those suffering from depression.
- Depression in adolescents and suitable interventions .
- How do you manage depression while in college or university?
- The role of family and friends in supporting loved ones with depression and encouraging them to seek help.
- The benefits of mindfulness and meditation for depression.
- The link between sleep and depression, and how to improve sleep habits.
- How do you manage depression while working a high-stress job?
- Approaches to treating depression .
- How do you manage depression during pregnancy and postpartum?
- The importance of prioritizing employee mental health and providing resources for managing depression in the workplace.
- How should you manage depression while caring for a loved one with a chronic illness?
- How to manage depression while dealing with infertility or pregnancy loss.
- Andrew Solomon: why we can’t talk about depression .
- Destigmatizing depression: promoting mental health awareness and understanding.
- Raising funds for depression research: investing in mental health advances.
- The power of peer support: establishing peer-led programs for depression.
- Accessible mental health services: ensuring treatment for all affected by depression.
- Evidence-based screening for depression in acute care .
- The benefits of journaling for mental health: putting your thoughts on paper to heal.
- The power of positivity: changing your mindset to fight depression .
- The healing power of gratitude in fighting depression.
- The connection between diet and depression: eating well can improve your mood.
- Teen depression and suicide in Soto’s The Afterlife .
- The benefits of therapy for depression: finding professional help to heal.
- The importance of setting realistic expectations when living with depression.
📝 How to Write about Depression: Essay Structure
We’ve prepared some tips and examples to help you structure your essay and communicate your ideas.
Essay about Depression: Introduction
An introduction is the first paragraph of an essay. It plays a crucial role in engaging the reader, offering the context, and presenting the central theme.
A good introduction typically consists of 3 components:
- Hook. The hook captures readers’ attention and encourages them to continue reading.
- Background information. Background information provides context for the essay.
- Thesis statement. A thesis statement expresses the essay’s primary idea or central argument.
Hook : Depression is a widespread mental illness affecting millions worldwide.
Background information : Depression affects your emotions, thoughts, and behavior. If you suffer from depression, engaging in everyday tasks might become arduous, and life may appear devoid of purpose or joy.
Depression Essay Thesis Statement
A good thesis statement serves as an essay’s road map. It expresses the author’s point of view on the issue in 1 or 2 sentences and presents the main argument.
Thesis statement : The stigma surrounding depression and other mental health conditions can discourage people from seeking help, only worsening their symptoms.
Essays on Depression: Body Paragraphs
The main body of the essay is where you present your arguments. An essay paragraph includes the following:
- a topic sentence,
- evidence to back up your claim,
- explanation of why the point is essential to the argument;
- a link to the next paragraph.
Topic sentence : Depression is a complex disorder that requires a personalized treatment approach, comprising both medication and therapy.
Evidence : Medication can be prescribed by a healthcare provider or a psychiatrist to relieve the symptoms. Additionally, practical strategies for managing depression encompass building a support system, setting achievable goals, and practicing self-care.
Depression Essay: Conclusion
The conclusion is the last part of your essay. It helps you leave a favorable impression on the reader.
The perfect conclusion includes 3 elements:
- Rephrased thesis statement.
- Summary of the main points.
- Final opinion on the topic.
Rephrased thesis: In conclusion, overcoming depression is challenging because it involves a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and environmental factors that affect an individual’s mental well-being.
Summary: Untreated depression heightens the risk of engaging in harmful behaviors such as substance abuse and can also result in negative thought patterns, diminished self-esteem, and distorted perceptions of reality.
We hope you’ve found our article helpful and learned some new information. If so, feel free to share it with your friends. You can also try our free online topic generator !
- Pain, anxiety, and depression – Harvard Health | Harvard Health Publishing
- Depression-related increases and decreases in appetite reveal dissociable patterns of aberrant activity in reward and interoceptive neurocircuitry – PMC | National Library of Medicine
- How to Get Treatment for Postpartum Depression – The New York Times
- What Is Background Information and What Purpose Does It Serve? | Indeed.com
- Thesis | Harvard College Writing Center
- Topic Sentences: How Do You Write a Great One? | Grammarly Blog
725 Research Proposal Topics & Title Ideas in Education, Psychology, Business, & More
414 proposal essay topics for projects, research, & proposal arguments.
Student Essays

Essay on Depression | Depression among Students Essay
Depression is the experience of deep sadness, loss of interest in activities that one usually enjoys, low energy, difficulty concentrating and thoughts about suicide. Read the following written Essay on Depression, what causes it and meaningful ways how to avoid depression in life.
Essay on Depression | Meaning, Causes & Ways how to end Depression in Life
The definition of depression is: a psychological condition in which the subject feels so low and tired that it’s almost impossible to get up and go to work, even when there are things he/she has to do. This can be accompanied by a lack of motivation, fatigue, irritability and a loss of interest in the things he/she used to enjoy.
>>>>> Related Post: Essay on Depression For Students
Types of Depression
- Manic Depression. Bipolar is characterized by extreme mood swings from manic highs (the patient feels “up” and can do anything and has many ambitious plans) to depressive lows (feeling like he/she wants to go back to sleep and stay there forever).
- Secondary Depression: Depression caused by illness (such as cancer) or medical treatment (such as anti-depressant medication), like feeling of worthlessness, suicidal thoughts, lack of interest in daily activities or hobbies, difficulty concentrating or making decisions.
- Childhood Depression – depression that is experienced by children. Most of the time this type of depression occurs in conjunction with conduct disorders
- Clinical Depression: it is usually associated with severe symptoms that interfere seriously with the ability to function. This type of depression lasts for at least two weeks (during which time there are no major signs of improvement).
Impacts of Depression
Five Major Impacts of Depression:
- The person feels very lonely, even when he/she is with friends or loved ones;
- Difficulties making decisions (or indecisiveness) and concentrating;
- Thoughts of suicide (which may lead to suicidal attempts);
- Lack of appetite;
- Low sex drive; low energy; fatigue.
Depression among Students
The most common time of the year when students feel depressed is during final exams, when they are faced with big challenges.
Other causes for depression in this population are: romantic breakups, financial problems, family conflicts or parental abuse, cyberbullying and lack of sleep.
Depression Impacts the work Performance
Yes it does. Depression can greatly reduce our productivity in the workplace since we’re not at our best (mentally speaking). We lose interest in work activities, become easily distracted and make lots of mistakes that end up costing us money or even bringing down company’s profits.
>>>>> Related Post: Essay on Youth Leadership
Ways how to Avoid Depression in Life
Here’s my very own summary of ways to avoid depression:
- Avoid stress as much as possible – learn how to relax, read a book, go out with friends, listen to some nice music… Don’t stay alone for too long or you’ll start feeling lonely and depressed;
- Keep a healthy lifestyle! Exercise regularly (take a walk or go for a run), eat healthy food (fruits and vegetables, whole grains and lean meat);
- Make sure you get enough sleep – about 7 to 8 hours per night;
- Have some time off every month (or week) and relax! Change your environment (if possible) and do something different from the usual routine;
- If you’re feeling depressed – talk to someone! Don’t be shy or embarrassed to have a mental disorder diagnosis. In most countries, depression is very common and also highly treatable. You can visit your doctor or a psychologist for treatment options that fit you best.
>>>>> Related Post: Essay on Compassion For Children & Students
In today’s world, depression is very common and highly treatable. Make sure you get enough sleep, have some time off from work every month or week and talk to someone about your feelings! Don’t stay alone for too long – it’s the best way to avoid depression.
Similar Posts

Paragraph on Grow More Trees
Paragraph on Grow more Trees: Trees are the beauty of our environment. There are great benefits of growing more trees. Trees clean the air and water, provide shade and shelter, conserve energy, and support wildlife. They are also great for the economy. Planting trees more is a simple way to make your community a better…

Paragraph on My Childhood Memories For Students
Paragraph on My Childhood Memories For Students: Childhood is a wonderful part of our life. We all have some wonderful childhood memories that we cherish and remember fondly. In this paragraph, I will share one of my cherished childhood memories with you. One of my favourite childhood memories is when my parents took me to…

Paragraph on My Sister For Students
Paragraph on My Sister: Sisterhood is the great sacred relation created by God. This relationship is so strong that it can never be broken by any means. My sister and I share a really close bond which cannot be described in words. My sister is my best friend, and we always have each other’s back…
![depression students essay 5 Speeches on Yourself – 1,2,5 Minutes Short, Motivating [ 2024 ]](https://mystudentsessays.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Speech-on-Myself-768x432.webp)
5 Speeches on Yourself – 1,2,5 Minutes Short, Motivating [ 2024 ]
Following is the Speech on Myself that tells about Myself Introduction, about my family, My life goals, My life inspiration, what Lessons I have learned. This speech in simple English and in easy to understand words for children and students. 2 Minute Speech on Yourself Greetings! Respected teachers and my dear friends. Today I would…
![depression students essay Essay on Child is the Father of Man [ Explanation with Examples ]](https://mystudentsessays.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Essay-on-child-is-the-father-of-man-768x768.png.webp)
Essay on Child is the Father of Man [ Explanation with Examples ]
There is no denying the fact that the child is the father of man. A child of today is father of tomorrow. The following written essay on topic child is the father of man, gives the complete explanation why child is father of man, meaning, examples, psychology of child etc. This short & long essay,…

Paragraph on My Hobby Dancing for Students
Paragraph on My Hobby Dancing: Dancing is a great art. It is one of the wonderful ways to express your emotions, feelings and expressions. It is the best way to stay physically and mentally healthy. It helps in building confidence and improving concentration. Dancing is my hobby and it has been so since I was…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More From Forbes
High school as a cause of the great depression.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Last year’s economics Nobelist, Claudia Goldin, wrote an influential article in 1998 on the rise of high school in the United States. In 1900, about 10 percent of Americans of proper age attended high school. In 1940, the figure was 70 percent. Most of the growth came over 1920-35. Goldin’s conclusion was the huge increase in secondary education in this period was a chief reason the economy performed so well after 1945.
Shut down the camera, Dorothea, the place actually has "greatest wealth." (Photo by Buyenlarge/Getty ... [+] Images)
Students of the Great Depression of the 1930s will note that at the outset of this horrible event, property taxes increased beyond all precedent and rationality. Property taxes were the source of school financing. They were mainly levied on real estate by states and localities. They had hovered around two percent of GDP for decades. In the early 1930s, they spiked to 7 percent.
Nobody, let alone the mass of property owners in the country as in 1932, can pay 7 percent of their income in property tax. Property tax levies at that stratospheric level will cause a collapse in home values and a raft of foreclosures, sheriff sales, bank failures (mortgages being a principal asset in the banking system), and insolvencies. This is exactly what happened in the early 1930s. The loss of property, homes and farms, is, indeed, along with bread lines, bank runs, and “Brother, Can You Spare a Dime,” the central issue, the heart of the matter, the iconography of the Great Depression.
Why were property taxes so high in the early 1930s? One reason is that they were deductible from the federal income tax. Another is that municipal bond interest was not taxable income—both of these devilish things new since the federal income tax came into being in 1913 and got large (over 50 percent at the top) in the late Teens. Municipalities splurged in the 1920s because the after-tax price of property taxes went down and rich people were throwing money at their tax-exempt bonds.
What did the stolid authorities spend it on? High school, certainly. Goldin:
“Soaring enrollments of the magnitude experienced—increasing by three or four times in the 15 years from 1920 to 1935—meant that school districts, across the United States, had to contend with vastly increased expenditures and corresponding tax burdens. Each high school student cost twice as much to educate per year, in terms of variable costs, than did each elementary school student, and more high-school youths also meant the building of more schools. It should not be surprising, therefore, that the states with the greatest wealth per capita—those of the Far West and Great Plains—were those with the earliest and most rapid education rates.”
New iOS 18 AI Security Move Changes The Game For All iPhone Users
Google issues critical chrome update for all windows users, world war i tactics make a comeback as a ukrainian gunner in the back of a propeller plane shoots down a russian drone.
The Far West and the Great Plains enjoyed “greatest wealth” through 1935—Dorothea Lange, call your office.
Do not let the line in this passage on “tax burdens” fool you. Goldin’s classic article barely mentioned taxation. It noted a few times that local property taxes had to pay for the immense complement of new high school buildings and the extraordinarily high variable costs of high school teacher salaries. At one point she makes the ghastly comment that high school in America was “free.” The article is a celebration of the rise of high school.
The country totally committed itself to high school after 1910, and especially after 1920 (when the bond deduction, she does not note, was extremely valuable with the marginal rate of the income tax at 73 percent). Because of all the building and the masters-degree-toting teachers on payroll prior to 1940, the thesis is, we had a boom for the ages after 1945, especially in the intellectual fields. Without high school, the glorious years after 1945 that were the best and most sophisticated ever could not have happened.
That is the thrust of the article. Again, it was central to the Nobel Prize award of a few months ago. An accountant would have a word. The article is all assets and no liabilities. It is nothing but good things. New high school buildings from 1920-35, new fat teacher salaries over the same years, and the scale is ginormous, from a trifle to accommodating the ample part of the huge 14-18-year-old population. The liabilities, the cost? Not in any direct way considered.
The costs in fact were massive increases in property taxes that especially hit in the early 1930s. States and localities foolishly took out debt beginning in the late Teens because the rich were demanding their tax-free instruments now that the new income tax was over 70 percent at the top. The places spent—and up went the high schools. After ten years, it became apparent that servicing debt interest, and increasingly due principal, was a tough trick. The high-school-building authorities took out more debt to roll over the payments and imposed still more property taxes.
The dip in the economy in 1929, coupled with the increase in property taxes, started to be too much to bear for marginal homeowners. They began defaulting, and in time, in 1930-31, there was enough of this stuff to start resulting in bank failures—by the 1000s. Chicago, that “greatest wealth” Great Plains archetype, high schools now littering the broad-shouldered landscape, paid its teachers 4 out of 24 months in one span in the early 1930s, because there was a spontaneous property tax strike among the city’s legions of breadline desperados.
Such events were embedded in historical scholarship in the 1980s (such as in the landmark work of David Beito). It did not matter in that peer-reviewed warhorse, the Journal of Economic History , in which Goldin’s celebration appeared. To be sure, this article, like all of Goldin’s work, is a joy to read, and is 75 percent instructive, fascinating, and advancing of the frontier of knowledge. But the blind spots; but the blind spots.
This work of the recent Nobelist speaks for the field. As I wrote about the general problem recently , economics, proud rigorous economics, is at sea when it comes to the causes of the Great Depression. Do not tell them that. They will snarl that Milton Friedman showed that the Fed was too tight, and obtuse about banking regulation (all valid), that monetary contraction has been shown beyond any reckoning that it was the culprit, that the gold standard was a fossil—rigor, peer review, lions of the field, seriousness, you-missed-this-in-the-ocean-of-literature….
Almost never does economics squarely discuss taxation as the culprit in the Great Depression, and yet taxation was suddenly enormous on or about 1929. In the future I shall take up why. My hunch is that because it was lay “cranks” like the supply-sider Jude Wanniski who first laid out this potent argument, and well, in the 1970s, the field was too proud and snobbish to follow.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Washington State University
- Go to wsu twitter
- Go to wsu facebook
- Go to wsu linkedin
Polyamorous youth report facing stigma, heightened levels of depression

PULLMAN, Wash. – While increasingly visible among adults, polyamory also exists among adolescents, and as a new study indicates, so does the stigma that can come with it.
A Washington State University study of 323 youth ages 12 to 17 at an LGBTQ+ summer camp found that 54, or about 16.7%, identified as polyamorous or ambiamorous, meaning they were open to either monogamous or polyamorous relationships. These “poly” and “ambi” youth reported higher levels of depressive symptoms than their LGBTQ+ peers.
The study, one of the first to investigate polyamorous relationships in youth, was published in the journal Psychology & Sexuality .
“It was notable that many of the polyamorous teens said they wouldn’t feel safe being out in their home communities,” said study author Traci Gillig, a WSU researcher. “They felt like they would be misunderstood or that people have stereotypes or judgments around what it means for them to be poly, like that they are promiscuous or don’t perceive cheating as a problem.”
Polyamory is a relationship structure that involves having more than one romantic partner at the same time with the consent and knowledge of all the partners, so as with monogamous relationships, the secrecy of cheating is considered a breach of trust. Again similar to monogamy, polyamory is primarily about relationships and does not necessarily have to involve sex at all.
This study was limited to a camp for LGBTQ+ youth called Brave Trails, which likely indicates the adolescents came from more accepting families, Gillig noted. However, 30 adolescents still reported they either would not feel safe, or felt unsure if they would be safe, if they were open about being poly in their home communities.
Gillig said it was encouraging that many also felt they would be supported, and 16 of the 54 poly or ambi campers said they were open about it at home.
Adult polyamory has been gaining attention in the news media and on TV with shows that feature poly people on Netflix and Showtime. It has also been the subject of research, which has found that more than 20% of adults have engaged in consensually non-monogamous relationships like polyamory. Another study also found that some poly adults began to understand their identity as poly when they were adolescents.
For this study, participants filled out questionnaires before and at the end of the camp, which included assessments of anxiety and depressive symptoms. They also answered questions about their preferred relationship structure and how comfortable they felt being open with others about it.
The survey allowed campers to write in explanations, and some who felt less safe said that being poly was “a touchy subject” and that even those who accept their LGBTQ+ identity would not be okay with it.
The poly and ambi kids as well as all the adolescents in the study showed improved mental health after experiencing the accepting environment of the LGBTQ+ camp, and Gillig emphasized that support is key for young people who have a marginalized identity. “Youths’ experience with being polyamorous or ambiamorous is similar to being LGBTQ+ in that if they perceive that they won’t be supported, then they’re not as likely to disclose their identity at home. We know from research with queer youth that this can cause elevated levels of depressive symptoms,” she said. “My hope is that parents would have an open mind, if their child comes to them and expresses that they identify as polyamorous or if they have questions about it.”
Media Contacts
- Sara Zaske , WSU News & Media Relations , 509-335-4846 , [email protected]
- Traci Gillig , WSU Murrow College of Communication , 509-335-1034 , [email protected]

Student-run AI ventures dominate Business Plan Competition
Recent news.

Presidential search: WSU community invited to participate in focus group sessions

Thomas-Brown named dean of the College of Education

Reusable containers a hit with students and the environment

College of Arts and Sciences recognizes outstanding faculty, staff, and students

WSU selects T. Chris Riley-Tillman as next provost
Anxiety and Depression Among College Students Essay
Education is expected to have appositive importance on the student’s life by enhancing their capability to think and improving their competency. However, it often acts as a source of stress that affects students’ mental health adversely. This causation of academic stress often emanates from the need to have high grades, the requirement to change attitude for success, and even pressures put by various school assignments. These pressures introduced by education can make the student undergo a series of anxiety, depression, and stress trying to conform to the forces. The causes of academic stress are well-researched but there is still no explanation why the rate of strain increases despite some measures being implemented to curb student stress. This research explores this niche by using 100 participants who study at my college.
Introduction
Nowadays there are many reasons that cause stress among growing number of students who might not know they are going through the condition most of the time. Hence, undiscovered discouragement or uneasiness can cause understudies to feel that they are continually passing up unique open doors. It prompts substance misuse; self-destruction is the second most typical reason for death among undergrads. The main hypothesis of this article is that college and university students have higher depression rates.
Problem Statement
This proposal undercovers how the problem of anxiety and depression is progressing if not addressed. With such countless youngsters experiencing undiscovered tension, it may be challenging for them to appreciate school. Understudies’ emotional well-being is risked when pressure and trouble go unnoticed, which can prompt social and educational issues (Nelson & Liebel, 2018). Educators might battle to perceive uneasiness since these circumstances manifest themselves contrastingly in different people.
Anxiety and depression are complicated disorders with numerous elements that impact people differently. Teachers and staff must be well trained to deal with these unforeseen events. Understudies coming to college come from various financial foundations, which can prompt an assortment of psychological wellness chances (Li et al., 2021). Additionally, current works will be evaluated to differentiate the risk factors associated with stress among university undergraduates worldwide.
There are various reasons which might cause the onset of anxiety and depression. It can be absence of rest, terrible dietary patterns, and lack of activity add to the gloom in undergrads (Ghrouz et al., 2019). Scholarly pressure, which incorporates monetary worries, strain to track down a decent profession after graduation, and bombed connections, is sufficient to drive a few understudies to exit school or more awful.
Numerous parts of school life add to despondency risk factors. For example, understudies today are owing debtors while having fewer work prospects than prior. Discouraged kids are bound to foster the problems like substance misuse (Lattie et al., 2019). For adaptation to close-to-home trouble, discouraged understudies are more inclined than their non-discouraged companions to knock back the firewater, drink pot, and participate in unsafe sexual practices.
Hypothesis on the Topic
The central hypothesis for this study is that college students have a higher rate of anxiety and depression. The study will integrate various methodologies to prove the hypothesis of nullifying it. High rates of anxiety and depression can lead to substance misuse, behavioral challenges, and suicide (Lipson et al., 2018). Anxiety is one of the most critical indicators of academic success, it shows how students’ attitudes change, reflecting on their overall performance.
Methods Section
Participants.
The study will use college students who are joining and those already in college. The research period is planned to last six months; college students are between the ages of 18 and 21 and life is changing rapidly at this age (Spillebout et al., 2019). This demography will come from the college where I study. The participants will be chosen randomly, the total number will be 100, both female and male, and from all races.
Apparatus/ Materials/ Instruments
Some of the materials to be used in the study will include pencils, papers, and tests. Paper and pencil are typical supplies that students are familiar with, so using them will not cause additional stress. It will be used during the interview with the students and throughout the study will be in effect (Huang et al., 2018). These have been applied in various studies before, and, hence, they will be instrumental in this study.
The study will follow a step-wise procedure to get the required results. First, the students’ pre-depression testing results would be researched and recorded. Second, the students would undergo standardized testing in the same groups. Scholarly accomplishment is impacted by past intellectual performance and standardized testing (Chang et al., 2020). Third, the students’ levels of depression and anxiety would be monitored along with their test results.
The study will use a descriptive, cross-sectional design with categorical and continuous data. The sample demographic characteristics were described using descriptive statistics. Pearson’s proportion of skewness values and common mistake of skewness was utilized to test the ordinariness of the persistent factors. The distinctions in mean scores between sociodemographic variables and stress will be examined using Tests (Lipson et al., 2018). The independent variable will be essential because it will provide the basis of measurement.
The 100 participants had different anxiety levels, as seen from the Test taken and the various evaluations. Forty-five of the participants had high levels, 23 had medium levels, while the remaining 32 had low levels (Lipson et al., 2018). The correlation and ANOVA, which had a degree of era margin of 0.05, were allowed (Lipson et al., 2018). This finding aligns intending to have clear and comprehensive outcomes.
Significance of the Study
If the results would be not significant, it means that students are not subjected to more pressure on average. If the study results in significant outcomes, this would mean that there is much that needs to be done to reduce student’s anxiety. The idea that scholarly accomplishment is indispensable to progress is built up in higher instructive conditions (Nelson & Liebel, 2018). Many colleges devote money to tutoring, extra instruction, and other support services to help students succeed.
APA Ethical Guidelines
The study will have to follow the APA ethical guidelines because it involves experimenting with humans. Some of the policies include having consent from the participant, debriefing the participant on the study’s nature, and getting IRB permission (Nelson & Liebel, 2018). Ethical guidelines should comply with proficient, institutional, and government rules. They habitually administer understudies whom they likewise instruct to give some examples of obligations.
Limitations
The study also had some limitations, making it hard to get the desired outcomes. It was not easy to detect the population-level connections, but not causality. This case hardened the aspect of confounding and getting the relevant random assignment needed for the study had to access (Nelson & Liebel, 2018). For the right individuals for the investigation to be identified, the sampling was not easy.
This study would be essential as it will create a platform for future studies. The result that was gotten shows that many college students are undergoing the problem of anxiety and depression without knowing that it is happening. Educators will have awareness on what aspects of academics they need to modify to ensure their students are not experiencing mental health challenges. Hence, it makes it possible for future researchers to conduct studies to provide possible solutions.
Chang, J., Yuan, Y., & Wang, D. (2020). Mental health status and its influencing factors among college students during the epidemic of COVID-19. Journal of Southern Medical University , 40(2), 171-176.
Ghrouz, A. K., Noohu, M. M., Manzar, D., Warren Spence, D., BaHammam, A. S., & Pandi-Perumal, S. R. (2019). Physical activity and sleep quality in relation to mental health among college students. Sleep and Breathing Journal , 23(2), 627-634.
Huang, J., Nigatu, Y. T., Smail-Crevier, R., Zhang, X., & Wang, J. (2018). Interventions for common mental health problems among university and college students: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Psychiatric Research , 107, 1-10.
Lattie, E. G., Adkins, E. C., Winquist, N., Stiles-Shields, C., Wafford, Q. E., & Graham, A. K. (2019). Digital mental health interventions for depression, anxiety, and enhancement of psychological well-being among college students: A systematic review. Journal of Medical Internet Research , 21(7), e12869.
Li, Y., Zhao, J., Ma, Z., McReynolds, L. S., Lin, D., Chen, Z.,… & Liu, X. (2021). Mental health among college students during the COVID-19 pandemic in China: A 2-wave longitudinal survey. Journal of Affective Disorders , 281, 597-604.
Lipson, S. K., Kern, A., Eisenberg, D., & Breland-Noble, A. M. (2018). Mental health disparities among college students of color. Journal of Adolescent Health , 63(3), 348-356.
Nelson, J. M., & Liebel, S. W. (2018). Anxiety and depression among college students with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): Cross-informant, sex, and subtype differences. Journal of American College Health , 66(2), 123-132.
Spillebout, A., Dechelotte, P., Ladner, J., & Tavolacci, M. P. (2019). Mental health among university students with eating disorders and irritable bowel syndrome in France. Journal of Affective Disorders , 67(5), 295-301.
The following table shows the significant issues that affect the mental health state of most college students. Based on Huang et al.’s research, the biggest concern for most students included stress about their loved ones. Additionally, the authors found that worrying about one’s academics and schooling was the second depressing experience among most college students.
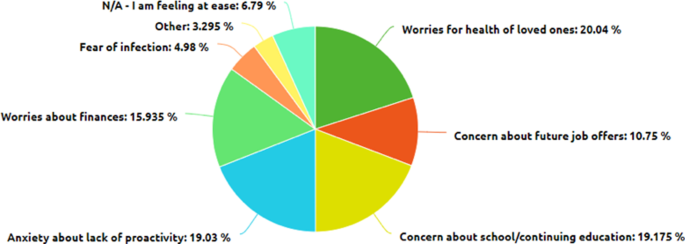
The following figure shows how on top of the current stressors for students, COVID-19 affects their mental health. Li et al.’s research demonstrates that COVID-19 placed more financial burden than before, especially on students with part-time jobs who often face anxiety and stress due to lack of tuition fees (Li et al., 2021). Generally, the research shows that the financial consequences of coronavirus affect the mental state of most college students.
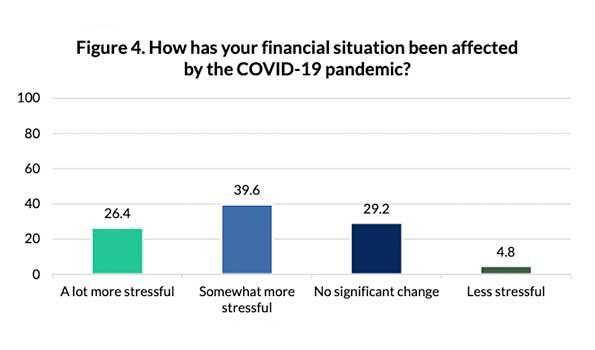
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, April 10). Anxiety and Depression Among College Students. https://ivypanda.com/essays/anxiety-and-depression-among-college-students/
"Anxiety and Depression Among College Students." IvyPanda , 10 Apr. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/anxiety-and-depression-among-college-students/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Anxiety and Depression Among College Students'. 10 April.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Anxiety and Depression Among College Students." April 10, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/anxiety-and-depression-among-college-students/.
1. IvyPanda . "Anxiety and Depression Among College Students." April 10, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/anxiety-and-depression-among-college-students/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Anxiety and Depression Among College Students." April 10, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/anxiety-and-depression-among-college-students/.
- Incorporating Technology in Science Curriculum
- The Targeting Market of the Sustainable Coffee Shop
- Academic Writing: Flipped Classroom Method
- Racism: Healthcare Crisis and the Nurses Role
- The African American Women Leadership in Higher Education
- Undiscovered Killers: The Ineffectiveness of Zero-Tolerance Policies
- Fear associated with sexuality issues in society
- Mean-Variance Skewness Portfolio Performance Gauging
- Medication and Preventive Systems
- How Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Benefits Children
- Defense Mechanisms and Brain Structure
- Coping with Stress and Physical Health Problems
- Quality of Life With Schizophrenia
- Schizophrenia: The Etiology Analysis
- Schizophrenia as a Chronic Mental Disorder
Bruce Drysdale 5th-grade student advances to national finals in DAR's essay contest

Bruce Drysdale fifth grader Lia Martinonis has advanced to the national finals in the Daughters of the American Revolution 2024 Essay Contest, and each time her essay has advanced, her family has celebrated with a cake.
She is anxiously hoping for more cake. Martinonis is one of eight fifth-grade finalists in the nation, and so far, she's won three awards for her essay — one at the local level, one at the state level and the latest for the Southeastern Division.
"I am unbelievably proud. I have felt both shocked and pleased each time I learned that I had won," she said.
And there's prize money involved: $1,000 for first place, $500 for second place and $250 for third place. The winners will be recognized at the National Society Daughters of the American Revolution Continental Congress, which is being held June 26-30 in Washington, D.C.
The topic for the contest was “Stars and Stripes Forever.” Essay writers were asked to imagine they were a newspaper reporter for The Philadelphia Times on May 14, 1897, and the newspaper's editor asked them to attend and report on the first public performance of John Philip Sousa’s new march, “The Stars and Stripes Forever.” The students were to tell about Sousa’s life and the story behind the song.
Lia was with her family on April 20 in Durham to receive the state award, her mother, Andrea, said.
"This essay contest has been an incredible experience for Lia. My daughter aspires to be a writer when she grows up," Andrea Martinonis said. "This opportunity has given her the confidence to pursue that dream. Lia researched the essay subject, learned about American history, honed her writing skills, and read her speech to a large audience at the initial award ceremony.
"As an educator, I couldn't be more pleased that DAR sponsors this contest, encouraging students to write essays and learn about our nation's past. As a parent, I am thrilled that my daughter chooses to spend her free time reading and writing and that her interests and skills are being recognized."
More: North Henderson student one of four grand prize winners in national essay contest
Lia said her teacher, April Summey, assigned the essay contest to her class.
"I remember being frustrated when drafting my essay, but now I am so glad my hard work paid off. I still cannot believe this is all happening," Lia Martinonis said.
This part of her essay describes Sousa talking about composing his new march:
"...Sousa said that he composed the song in his head on his return to America as he grieved the death of his beloved band manager, David Blakely. Sousa said, “In a kind of dreamy way, I used to think over old days at Washington when I was leader of the Marine Band…when we played at all public functions, and I could see the Stars and Stripes flying from the flagstaff.” He also stated, “And that flag of ours became glorified… And to my imagination it seemed to be the biggest, grandest flag in the world, and I could not get back under it quick enough.”
More: Apple Valley Middle student one of four grand prize winners in national contest
Summey called Lia a phenomenal, gifted student who "always goes above and beyond."
"She thrives on a challenge and is an avid learner. Her contagious curiosity shines brightly as she lights up upon acquiring new knowledge," Summey said. "Every year, my fifth grade students work on the DAR essay. They are given a prompt and required to read multiple primary and secondary sources about the topic in order to prepare. I am very passionate about the contest, because it helps students learn history and get excited about it."
Dean Hensley is the news editor for the Hendersonville Times-News. Email him with tips, questions and comments at [email protected]. Please help support this kind of local journalism with a subscription to the Hendersonville Times-News.

Essay on Depression in Youth
Students are often asked to write an essay on Depression in Youth in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Depression in Youth
Understanding depression in youth.
Depression is a serious mental health issue affecting many young people. It’s not just feeling sad, but a constant state of low mood that lasts for weeks or months.
Causes can include school stress, family problems, or bullying. Sometimes, it’s due to chemical imbalances in the brain.
Signs of Depression
Depressed youth may feel hopeless, lose interest in activities they used to enjoy, or have trouble concentrating. They may also sleep too much or too little.
Getting Help
Depression is treatable. If you or a friend are feeling depressed, it’s important to talk to a trusted adult or seek professional help.
250 Words Essay on Depression in Youth
Introduction.
Depression, an often misunderstood mental health disorder, is increasingly prevalent among youth. This psychological condition, characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities, significantly interferes with a young person’s daily life.
Depression in youth is alarmingly common. According to the World Health Organization, depression is the third leading cause of illness and disability among adolescents. The early onset of depression is concerning, as it can lead to detrimental effects on an individual’s personal development, academic performance, and social relationships.
Depression in youth is multifactorial, with genetics, environmental factors, and personal circumstances playing significant roles. Factors such as family history of depression, traumatic life events, bullying, and physical health problems can contribute to its onset. Additionally, the hormonal changes associated with puberty can make teenagers more susceptible to depression.
Depression in youth can have severe implications. It can lead to poor academic performance, substance abuse, risky sexual behaviors, and even suicide. Furthermore, it can affect a young person’s interpersonal relationships and self-esteem, leading to a vicious cycle of isolation and worsening depressive symptoms.
Depression in youth is a pressing public health issue that requires urgent attention. Early detection and appropriate intervention are crucial to mitigate its devastating effects. As a society, we must foster an environment that encourages open dialogue about mental health, reduces stigma, and promotes access to mental health services for young people.
500 Words Essay on Depression in Youth
Depression, a prevalent mental health disorder, has been increasingly recognized among the youth population. Characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest in activities, it is not merely a temporary mood swing but a serious condition that interferes with daily life and normal functioning.
The Prevalence of Depression in Youth
Depression in youth is a global concern, affecting approximately 5.7% of adolescents worldwide. The transition from childhood to adulthood is fraught with numerous physical, emotional, and social changes, making young people particularly susceptible to depression. Factors such as academic pressure, bullying, and the struggle to form an identity can contribute to the onset of depressive symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors
Depression in youth can be attributed to a combination of genetic, biological, environmental, and psychological factors. Genetics play a crucial role, with individuals having a family history of depression being more susceptible. Hormonal changes, particularly during puberty, can also contribute to depression. Environmental factors include traumatic events, family issues, or any form of abuse.
Moreover, the advent of social media has added a new dimension to this issue. The constant comparison, cyberbullying, and the pressure to maintain an ideal online image have been linked to increased levels of anxiety and depression among youth.
Impact of Depression on Youth
Depression can significantly impact a young person’s life, affecting their academic performance, relationships, and overall wellbeing. It can lead to self-harming behaviors, substance abuse, and in severe cases, suicidal thoughts or actions. Moreover, if left untreated, it can lead to chronic mental and physical health issues in adulthood.
Approaches to Treatment
Effective treatment for depression in youth typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has been found particularly effective in helping young people manage their symptoms by changing negative thought patterns. Medication, such as antidepressants, may also be prescribed. However, it’s crucial to approach this with caution due to potential side effects.
Lifestyle changes, including regular exercise, a healthy diet, and adequate sleep, can also play a significant role in managing depression. Additionally, support from family, friends, and school can be instrumental in a young person’s recovery.
Depression in youth is a serious issue that warrants attention. The need for early detection and intervention is paramount to prevent the progression of the disorder and its potential long-term consequences. The stigma associated with mental health issues needs to be challenged, and open conversations about mental health should be encouraged. By doing so, we can create a supportive environment where young people feel comfortable seeking help and discussing their mental health.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Daughter
- Essay on Darjeeling
- Essay on Dam
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
The Most Important Thing I Teach My Students Isn’t on the Syllabus

By Frank Bruni
Mr. Bruni is a contributing Opinion writer and the author of the forthcoming book “The Age of Grievance,” from which this essay is adapted.
I warn my students. At the start of every semester, on the first day of every course, I confess to certain passions and quirks and tell them to be ready: I’m a stickler for correct grammar, spelling and the like, so if they don’t have it in them to care about and patrol for such errors, they probably won’t end up with the grade they’re after. I want to hear everyone’s voice — I tell them that, too — but I don’t want to hear anybody’s voice so often and so loudly that the other voices don’t have a chance.
And I’m going to repeat one phrase more often than any other: “It’s complicated.” They’ll become familiar with that. They may even become bored with it. I’ll sometimes say it when we’re discussing the roots and branches of a social ill, the motivations of public (and private) actors and a whole lot else, and that’s because I’m standing before them not as an ambassador of certainty or a font of unassailable verities but as an emissary of doubt. I want to give them intelligent questions, not final answers. I want to teach them how much they have to learn — and how much they will always have to learn.
I’d been on the faculty of Duke University and delivering that spiel for more than two years before I realized that each component of it was about the same quality: humility. The grammar-and-spelling bit was about surrendering to an established and easily understood way of doing things that eschewed wild individualism in favor of a common mode of communication. It showed respect for tradition, which is a force that binds us, a folding of the self into a greater whole. The voices bit — well, that’s obvious. It’s a reminder that we share the stages of our communities, our countries, our worlds, with many other actors and should conduct ourselves in a manner that recognizes this fact. And “it’s complicated” is a bulwark against arrogance, absolutism, purity, zeal.
I’d also been delivering that spiel for more than two years before I realized that humility is the antidote to grievance.
We live in an era defined and overwhelmed by grievance — by too many Americans’ obsession with how they’ve been wronged and their insistence on wallowing in ire. This anger reflects a pessimism that previous generations didn’t feel. The ascent of identity politics and the influence of social media, it turned out, were better at inflaming us than uniting us. They promote a self-obsession at odds with community, civility, comity and compromise. It’s a problem of humility.
The Jan. 6 insurrectionists were delusional, frenzied, savage. But above all, they were unhumble. They decided that they held the truth, no matter all the evidence to the contrary. They couldn’t accept that their preference for one presidential candidate over another could possibly put them in the minority — or perhaps a few of them just reasoned that if it did, then everybody else was too misguided to matter. They elevated how they viewed the world and what they wanted over tradition, institutional stability, law, order.
It’s no accident that they were acting in the service of Donald Trump, whose pitch to Americans from the very start was a strikingly — even shockingly — unhumble one. “I alone can fix it,” he proclaimed in his 2016 speech accepting the Republican Party’s nomination for president; and at his inauguration in January of the following year, the word “humbled,” which had been present in the first inaugural remarks of both Barack Obama and George W. Bush, was nowhere to be found. Nor were any of its variants. That whole sentiment and politesse were missing, as they had been during a campaign centered on his supposed omniscience.
There are now mini-Trumps aplenty in American politics, but anti-Trumps will be our salvation, and I say that not along partisan or ideological lines. I’m talking about character and how a society holds itself together. It does that with concern for the common good, with respect for the institutions and procedures that protect that and with political leaders who ideally embody those traits or at least promote them.
Those leaders exist. When Charlie Baker, a former Massachusetts governor, was enjoying enormous favor and lofty approval ratings as a Republican in a predominantly Democratic state, he was also stressing the importance of humility. He was fond of quoting Philippians 2:3, which he invoked as a lodestar for his administration. “Do nothing out of selfish ambition or vain conceit,” it says. “Rather, in humility value others above yourself.”
That’s great practical advice for anyone in government, where most meaningful success hinges on teamwork and significant progress requires consensus. Governing, as opposed to demagoguery, is about earning others’ trust and cooperation. Exhibiting a willingness to listen to and to hear them goes a long way toward that.
“Insight and knowledge come from curiosity and humility,” Mr. Baker wrote in a 2022 book, “Results,” coauthored with his chief of staff, Steve Kadish, a Democrat. “Snap judgments — about people or ideas — are fueled by arrogance and conceit. They create blind spots and missed opportunities. Good ideas and interesting ways to accomplish goals in public life exist all over the place if you have the will, the curiosity, and the humility to find them.”
Humble politicians don’t insist on one-size-fits-all answers when those aren’t necessary as a matter of basic rights and fundamental justice. Humble activists don’t either. The campaign for same-sex marriage — one of the most successful social movements of recent decades — showed that progress can be made not by shaming people, not by telling them how awful they are, but by suggesting how much better they could be. Marriage-equality advocates emphasized a brighter future that they wanted to create, not an ugly past that they wanted to litigate. They also wisely assured Americans that gay and lesbian people weren’t trying to explode a cherished institution and upend a system of values, but instead wanted in.
“I don’t want to disparage shouting and demands — everything has its place,” Evan Wolfson, the founder of the pivotal advocacy group Freedom to Marry, told me when we revisited the movement’s philosophy and tactics. At times, he acknowledged, champions of a cause “need to break the silence, we need to push, we need to force.”
“But I used to say, ‘Yes, there’s demanding, but there’s also asking,’” he recalled. “And one is not the enemy of the other. People don’t like being accused, people don’t like being condemned, people don’t like being alienated. It’s a matter of conversation and persuasion.”
That’s consistent with the message delivered by Loretta Ross, a longtime racial justice and human rights advocate, through her teaching, public speaking and writing. Troubled by the frequent targeting and pillorying of people on social media, she urged the practice of calling in rather than calling out those who’ve upset you. “Call-outs make people fearful of being targeted,” she wrote in a guest essay for Times Opinion . “People avoid meaningful conversations when hypervigilant perfectionists point out apparent mistakes, feeding the cannibalistic maw of the cancel culture.” Instead, she advised, engage them. If you believe they need enlightenment, try that route, “without the self-indulgence of drama,” she wrote.
She was preaching humility.
She was also recognizing other people’s right to disagree — to live differently, to talk differently. Pluralism is as much about that as it is about a multiracial, multifaith, multigender splendor. That doesn’t mean a surrender or even a compromise of principles; a person can hold on to those while practicing tolerance, which has been supplanted by grievance. Tolerance shares DNA with respect. It recognizes that other people have rights and inherent value even when we disagree vehemently with them.
We all carry wounds, and some of us carry wounds much graver than others. We confront obstacles, including unjust and senseless ones. We must tend to those wounds. We must push hard at those obstacles. But we mustn’t treat every wound, every obstacle, as some cosmic outrage or mortal danger. We mustn’t lose sight of the struggle, imperfection and randomness of life. We mustn’t overstate our vulnerability and exaggerate our due.
While grievance blows our concerns out of proportion, humility puts them in perspective. While grievance reduces the people with whom we disagree to caricature, humility acknowledges that they’re every bit as complex as we are — with as much of a stake in creating a more perfect union.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Frank Bruni is a professor of journalism and public policy at Duke University, the author of the book "The Age of Grievance" and a contributing Opinion writer. He writes a weekly email newsletter . Instagram Threads @ FrankBruni • Facebook
University of Utah students join pro-Palestine rallies, create encampment on campus
The students set up roughly 20 tents and rallied for hours monday outside the school’s administration building..
(Bethany Baker | The Salt Lake Tribune) A protester carries a Palestinian flag during the pro-Palestine rally at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City on Monday, April 29, 2024.
University of Utah students joined nationwide pro-Palestinian rallies Monday as they set up tents and tarps on the lawn in front of the school’s administration building. Around the perimeter of the encampment, campus police officers paced and carried zip ties.
The students vowed to stay until the leadership of Utah’s flagship university agreed to divest its $1.47 billion endowment from any ties to Israeli companies and weapons manufacturers benefitting from the ongoing Israel-Hamas war.
“Disclose, divest. We will not stop. We will not rest,” they shouted, echoing the same chant heard at Columbia University and Yale , in California and Texas and Wisconsin . Hundreds of students across the country have been arrested for camping in solidarity with Palestinians. Schools have also suspended those participating.
As of 7 p.m. — three hours into their rally — no Utah students had been cited. But a school spokesperson noted a Salt Lake City ordinance that bans camping . Officers also walked around, talking with each other about taking down tents before midnight.
Utah Gov. Spencer Cox posted on X, formerly known as Twitter, about the First Amendment not protecting “violence, threats to public safety, property damage, camping or disruptions to our learning institutions. We will protect protestors and arrest those who violate the law.”
The Utah Department of Public Safety also issued a statement repeating that and said any criminal activity during a protest would be “swiftly addressed.” The insignias for University of Utah police and Salt Lake City police were included on the message.
We fully support everyone’s civil right to express themselves through freedom of speech. Yet, we do not tolerate the acts of any criminal activity, including but not limited to: property damage, unlawful assembly or camping, threats, or violent acts. pic.twitter.com/Lrgs4yzajf — Utah Public Safety (@UtahDPS) April 30, 2024
U. police Capt. Jason Hinojosa added in his own comment: “As heated as the rhetoric has been about the war between Israel and Hamas, we are here, first and foremost, to preserve public safety, and then to make sure people are able to express their opinions.”
At least 800 students at the university, along with some faculty, attended an initial rally on the steps of the Park Building. Inside is U. President Taylor Randall’s office. The students called on him to come out and negotiate. They wrote “Free Palestine” in chalk, in the hope that Randall would see it from his window.
“Our demands are firm and unwavering,” said U. student Alondra. The Salt Lake Tribune agreed not to include her last name as she fears repercussions from the school for speaking out.
She added: “The university owes it to us as a public institution.”
(Bethany Baker | The Salt Lake Tribune) Protesters gather during the pro-Palestine rally at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City on Monday, April 29, 2024.
The University of Utah and its campus police did submit reports in December to prosecutors for criminal charges to be filed against eight students. The school said those students disrupted an event critical of the transgender community being held by a conservative club on campus, forcing officers to shut it down. But the students have contended that the charges were retribution for a previous Palestine rally earlier in the fall; the U. has said that’s not the case.
It was the same student group — Mecha , which is largely led by and for students of color — responsible for those two earlier protests that planned what they called the “emergency” rally and encampment Monday. Some of the students facing misdemeanor charges spoke at the event.
After the speeches, a few students rushed onto the grass with tents, and they popped up the poles. Students circled around, linking arms and chanting.
They held hands and posters. They played hacky sack on the lawn. Inside their circle, they had first-aid kits, granola bars and megaphones. Backpacks were scattered on the surrounding sidewalks, next to signs that said, “Bombs made in Utah are killing kids in Gaza” and “Cut ties to Israel.”
Students waved small and large Palestinian flags as they chanted: “Gaza, Gaza you will rise. Students are by your side.”
Since the Israel-Hamas war started in October — when the militant group Hamas attacked — more than 32,000 Palestinians have been killed and 1,200 Israelis.
The students specifically called on the U. to divest from Lockheed Martin, which has a Utah location, and 47G; both are aerospace and defense companies. The U. also has a research partnership with 47G that was announced in 2023 and which it pays memberships due to be a part of.
The school did not immediately issue a statement Monday about divesting from Israel and weapons companies. A spokesperson referred to a previous 2021 divestment report prepared by faculty that examined what it would take for the school to eliminate holdings in oil and gas companies — which the U. has set goals for.
The students said the university should not only divest from “participating in a genocide” with the Israel-Hamas war — but it should also disclose all of its financial connections with its endowment.
“I’m sorry we have to stand here today to beg our university to divest from an apartheid state,” one student said who declined to give her name.
“Our university is extremely implicated,” added Christopher Loera-Peña, a fourth-year student.
Additionally, the students asked for amnesty for all protesters participating in the event — anticipating later arrests — and for campus police to be permanently disbanded. They passed around papers listing what rights students have and advising them to stay quiet if detained.
More tents were pitched as the hours passed in what they called the “Solidarity Camp.” Some students left after the initial rally. Hundreds remained in the encampment. They wheeled wagons in with food and water, sleeping bags and pillows.
(Chris Samuels | The Salt Lake Tribune) People form an encampment during a demonstration in support of Palestine during a rally at the University of Utah, Monday, April 29, 2024.
They sang, too, and prayed. “This is the people’s university now,” they said. Most wore scarves and masks covering their faces.
Passing cars and a few campus buses honked. There were signs nearby for the U.’s upcoming graduation ceremony.
The rally and encampment is unprecedented for Utah in recent years, which hasn’t seen large student gatherings; many students here live at home and commute to school, which tends to dampen mass protests. And the state is largely conservative.
But the U. has in past decades seen large rallies on campus — with calls to divest from Apartheid in South Africa in the 1980s and against the war in Vietnam in the 1960s. Both of those also came as students at colleges nationwide were speaking out.
“Do not let go of this moment,” said student Julio Irungaray at the rally Monday. “Make it bigger. … You are part of something massive. You are on the right side of history.”
The students said they felt a responsibility to stand up and speak out at their university because the universities that once stood in Palestine are now in rubble.

Donate to the newsroom now. The Salt Lake Tribune, Inc. is a 501(c)(3) public charity and contributions are tax deductible
RELATED STORIES
More than 70 university of utah faculty, staff sign letter supporting students charged for protesting, university of utah students now criminally charged after disrupting conservative club’s event, gov. cox doesn’t want utah colleges commenting on israel-hamas war — or any other political issue, the university of utah withdrew its sponsorship of a student group. the club took over a school office in protest., weber state university takes utah nurse to next level in life, career., phil lyman’s gop lieutenant governor pick not eligible to run in utah, elections office rules, utah high school removes class assignment on student essay titled ‘it is so hard to be trans’, what utah football player aaron lowe’s parents said to the man who killed their son, environmental groups ask judge to keep great salt lake lawsuit alive, featured local savings.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay grade: Good. 2 pages / 978 words. Depression is a disease that afflicts the human psyche in such a way that the afflicted tends to act and react abnormally toward others and themselves. Therefore it comes to no surprise to discover that adolescent depression is strongly linked to teen suicide.
Depression is a disorder characterized by prolonged periods of sadness and loss of interest in life. The symptoms include irritability, insomnia, anxiety, and trouble concentrating. This disorder can produce physical problems, self-esteem issues, and general stress in a person's life. Difficult life events and trauma are typical causes of ...
You may be experiencing depression if you've had some of the below symptoms most of the time for the last 2 weeks: ongoing feelings of sadness. being on-edge or snapping at people. low self ...
While a certain lab test can be conducted, depression can also be diagnosed by a psychiatrist. Research the different ways depression can be diagnosed and discuss the benefits of receiving a diagnosis in this essay. 3. Causes of Depression. There are many possible causes of depression; this essay discusses how depression can occur.
In Mirza et al.'s study, 1/3 of students encounter stress and depression (a subjective mean occurrence of 30.6%) of all participant students, which suggests students have a 9% higher rate of experiencing depression than general people. Depression can destroy life; it greatly impacts living a balanced life.
Depression can take a toll on many aspects of a young person's life, including academic performance, social life, and physical health. It can also increase their risk of substance abuse and co-occurring mental health conditions. For this reason, it is crucial to recognize the signs of depression in college students and provide tools, resources ...
Treatment Options for Depression. The first choice for depression treatment is generally an antidepressant medication. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are the most popular choice because they can be quite effective and tend to have fewer side effects than other types of antidepressants.
Help your college kid develop strategies to cope with depression. With college students experiencing depression or anxiety for the first time, parents can share self-care strategies that have been proved to ease symptoms of depression, including: Exercising. Connecting with friends. Eating healthy foods.
Core Tip: This study reviewed the extant literature by identifying nonpathological factors related to college students' depression, investigating the methods of predicting depression, and exploring nonpharmaceutical interventions for depression among college students.The influencing factors can be categorized into students' demographic characteristics, college experience, lifestyle, and ...
Students are often asked to write an essay on Depression And Anxiety in their schools and colleges. And if you're also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Depression is a form of illness that has diverse types of symptoms. Most people suffering from depression may not experience sadness but experience irritability, or lose interest in most of the activities they were initially engaging in. This illness may interfere with people's daily routine and normal functioning in various aspects of life.
METHODS. This study was done with an approved Arizona State University Institutional Review Board protocol #7247. In Fall 2018, we surveyed undergraduate researchers majoring in the life sciences across 25 research-intensive (R1) public institutions across the United States (specific details about the recruitment of the students who completed the survey can be found in Cooper et al.).
Anxiety disorders are normally brained reactions to stress as they alert a person of impending danger. Most people feel sad and low due to disappointments. Feelings normally overwhelm a person leading to depression, especially during sad moments such as losing a loved one or divorce. When people are depressed, they engage in reckless behaviors ...
500 Words Essay on Depression Among Students Understanding Depression. Depression is a mental health condition that affects how a person feels, thinks, and acts. It can lead to a variety of emotional and physical problems. A person with depression may have trouble doing normal day-to-day activities, and sometimes may feel as if life isn't ...
Students are often asked to write an essay on Depression in their schools and colleges. And if you're also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic. ... 250 Words Essay on Depression Understanding Depression. Depression, a common yet serious mental health disorder, is characterized by ...
1. Our Experts. can deliver a custom essay. for a mere 11.00 9.35/page 304 qualified. specialists online Learn more. Depression is undeniably one of the most prevalent mental health conditions globally, affecting approximately 5% of adults worldwide. It often manifests as intense feelings of hopelessness, sadness, and a loss of interest in ...
This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Cite this essay Download Colleges should offer other ways to help students with depression because their current ways have become ineffective and harmful towards them. The students in general most ...
Abstract. Michael is a 14-year-old boy in the eighth grade from an intact, professional family. He has a 16-year-old brother and a 10-year-old sister who do very well in school and demonstrate no problems. Michael is considered to be very bright, as shown by past grades and achievement test scores.
Essay on Depression | Depression among Students Essay. Leave a Comment. Depression is the experience of deep sadness, loss of interest in activities that one usually enjoys, low energy, difficulty concentrating and thoughts about suicide. Read the following written Essay on Depression, what causes it and meaningful ways how to avoid depression ...
According to the article, some students, faculty and civil liberties groups say that "a university's role is to foster debate — even if it's messy, rude and disruptive — not attempt to ...
Students of the Great Depression of the 1930s will note that at the outset of this horrible event, property taxes increased beyond all precedent and rationality. Property taxes were the source of ...
Students, staff, and faculty are invited to participate in one of three virtual focus group sessions intended to inform the search for WSU's 12th president. ... Polyamorous youth report facing stigma, heightened levels of depression April 29, 2024. While increasingly visible among adults, polyamory also exists among adolescents, and as a new ...
The central hypothesis for this study is that college students have a higher rate of anxiety and depression. The study will integrate various methodologies to prove the hypothesis of nullifying it. High rates of anxiety and depression can lead to substance misuse, behavioral challenges, and suicide (Lipson et al., 2018).
The topic for the contest was "Stars and Stripes Forever." Essay writers were asked to imagine they were a newspaper reporter for The Philadelphia Times on May 14, 1897, and the newspaper's editor asked them to attend and report on the first public performance of John Philip Sousa's new march, "The Stars and Stripes Forever."
Students are often asked to write an essay on Depression in Youth in their schools and colleges. And if you're also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic. ... 500 Words Essay on Depression in Youth Introduction. Depression, a prevalent mental health disorder, has been increasingly ...
The assigned essay had been selected as one of the Top 11 winners in a 2023 student editorial contest through the The Learning Network, a free resource for teachers curated by The New York Times ...
Mr. Bruni is a contributing Opinion writer and the author of the forthcoming book "The Age of Grievance," from which this essay is adapted. I warn my students. At the start of every semester ...
As of 7 p.m. — three hours into their rally — no Utah students had been cited. But a school spokesperson noted a Salt Lake City ordinance that bans camping.Officers also walked around, talking ...