- Essential Grammar
- Nouns, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections.
- English Verbs
- Main and modal auxiliaries, active and passive tenses, phrasal verbs, copulatives, verb order, ordinary verbs and “get”.
- Advanced Grammar
- Articles, prefixes and suffixes, pronouns, emphasis in English, question tags, conditionals and much more!
- Cambridge Courses
- B2 Cambridge First, C1 Cambridge Advanced and C2 Cambridge Proficiency exams.
- Common Mistakes
- Do vs. make, to vs. for, on vs. upon, some vs. any, bring vs. take, and others.
- Punctuation
- Apostrophes, colons, semicolons, commas, hyphens, periods, question and exclamation marks, and quotation marks.
- English Pronunciation
- Introduction to IPA, the suffix «ed», vowels, consonants and common pronunciation errors in English.
- Interesting reads such as English accent, The direct method, Subject inversion, Verbs with “to”…

- Who we are, prices, how the courses work and how much time you should dedicate.
- English Reservoir Method
- Learn about our teaching method.
- Affiliate Programme
- Are you a content creator or teacher? Would you like to become an English Reservoir affiliate and work with us?
- Learn Free on YouTube!
- Learn for free on our YouTube channel!

To do — auxiliary verb

- Base form = do
- Present form = do/does
- Past form = did
- Present participle/gerund = doing
- Past participle = done
To make questions with normal verbs. This also includes question tags
To do is used to make interrogatives in English. We use to do to make interrogatives with all normal verbs, that is, all verbs that aren’t auxiliary or modal auxiliary verbs.
Such normal verbs are, for example, make, clean, study, build, write, play, eat, sing etc. Do is a general-purpose verb for making questions in English. I.e., does she like to play football? Do you own a car? Did they pass their exam?
- Does Sally like to play the piano? Yes, she likes to play.
- Did you do your homework yesterday?
- Does she play soccer?
- George writes poetry, doesn’t he? ( question tag )
- They go to school, don’t they? ( question tag )
If a sentence starts with another auxiliary verb, then the question tag following it must use the same verb as the auxiliary verb. Negative to positive or positive to negative. I.e,
- I can’t see you, can I?
- Question tags
To do is used to form question tags with normal verbs. Question tags are used instead of normal questions when we already assume the answer. For example,
- Christina loves her children, doesn’t she?
‘Doesn’t she’ is the question tag. Because love is a normal verb, it requires the auxiliary verb do in the question tag. Another example of a question tag,
- She didn’t like me, did she?
Did she? is the question tag.
In order to be extra emotive or put more emphasis on the sentence.
To do is used to be extra emotive, that is, we can insert do into our sentences to add more emphasis or emotion. She did call me instead of, she called me. I.e., I did not arrive late yesterday instead of, I didn’t arrive late yesterday.
In this case, the contraction (didn’t) is avoided to give more emphasis. It is only used as an emphasis with ordinary verbs and not other auxiliary verbs.
- Did you do your homework last night? Yes, I did do my homework last night.
- I did not appreciate it when those people spoke loudly.
- They did not have any idea about the situation at all.
- By not using a contraction, the verb ‘do’ is automatically used for emphasis.

To negate, that is, to make sentences or questions negative. But not with other auxiliary verbs.
To do is used to make sentences or questions negative. However, we cannot use do to make other auxiliary or modal auxiliary verbs negative.
We can only use do to negate ordinary verbs. Therefore, it is incorrect to say, I don’t can go. Can is a modal auxiliary verb and takes the adverb not.
Therefore, you would need to say I can’t go. The correct usage of do for negation would be I don’t like cricket. She doesn’t want to come.
- I don’t like tomatoes.
- Do you look up to the sky at night? No, I don’t look up to the sky at night,
- I don’t like maths.
- Did you go out to the party last night?
- Doesn’t he know anyone in the neighbourhood?
- Did you do your assignment?
Therefore, it is wrong to say: ”I don’t can go” or ”She doesn’t must pass the exam”. We use ‘do’ to negate ordinary verbs NOT auxiliary verbs.
Note that in the last example the first ‘to do’ in the sentence functions as an auxiliary verb and the second ‘do’ in the phrase functions as an ordinary verb. So ‘do’ works both as an auxiliary and an ordinary verb.
We use it as a shortened verb form or like a sort of ellipsis
- Did she play tennis last night? Yes, she did . (instead of; ‘yes, she did play tennis…)
- Do you like playing rugby? No, I don’t . (instead of; ‘no, I don’t play…)
- Does he act strangely? Yes, he does . (instead of; ‘yes, he does act strangely)
We already assume the recipient knows what we’re talking about, so it’s not necessary to complete the whole phrase again.

A quick lesson with context and analysis
- Did you catch up 1 with Sophie 2 over the weekend, Maria?
- Yes, I did catch up with her 3 .
- So, what did you guys do then 4 ? Anything special?
- Well, first, we really needed to catch up with each other because it’s been so long since we last spoke. We went out for some drinks in the city centre before finally going to a disco.
- I suppose you two drank a lot then, didn’t you 5 ?
- Well, yes, I guess we shouldn’t have drunk 6 so much, but hey, once in a blue moon 7 doesn’t hurt 8 .
- So, what’s the latest with Sophie? She’s working in consultancy, isn’t she 9,10 ?
- Yes, spot on 11 . Plus, she’s also taking a year off 12 next year to go abroad.
- Wow! Really? Where is she going to go to?
- She said she was going to South America.
- I suppose she’ll be travelling, won’t she 13 ?
- Yes, basically.
- Very interesting. Sounds like you two had a nice time last night. Good to see you’re catching up with everyone.
- Did you catch up with Sophie? The phrasal verb catch up basically means “to see someone that you haven’t seen for a while”. It could be the first time you’re seeing that person in a long time.
- Did you catch up… We use the past form of do in the past, (did) because we’re asking a question about a past action. I.e., did they see you on Tuesday?
- Yes, I did catch up with her. Did is being used to be extra emotive. As a normal answer it would be I caught up with her.
- So, what did you guys do then? Do is both an auxiliary verb and a normal verb. In this example, did is the auxiliary form because did is asking a question in the past. Do functions as an ordinary verb here. In another example you could say, what do you like to do? The first do acts like an auxiliary verb while the latter do works as an ordinary verb.
- I suppose you two drank a lot, didn’t you? This is a question tag. Suppose is an ordinary verb so therefore, it takes the auxiliary verb do in the question tag. With question tags, it’s positive to negative or negative to positive.
- Drink-drank-drunk. The infinitive = drink. The past simple = drank , and the past participle = drunk . I.e., I like to drink wine. I drank some wine. I have drunk some wine.
- Once in a blue moon. An expression meaning that something doesn’t happen very often.
- Once in a blue moon doesn’t hurt. Do is being used to negate/make negative this sentence. Hurt is an ordinary verb, therefore, it needs the auxiliary verb do to be negated.
- She’s working in consultancy. The present continuous is used here because we can use the present continuous in English to talk about actions that happen in the moment, or even permanent states. I.e. I’m working at English Reservoir.
- She’s working in consultancy, isn’t she? ‘s, which is the contracted form of the auxiliary verb be (in third person singular) is used, therefore you can’t use do in the question tag. You must use the auxiliary verb, be.
- Yes, spot on. An expression in English meaning that something or someone is correct.
- Plus, she’s also taking a year off. The present continuous (be + verb + ing) is used here to talk about an action that will happen in the very near future.
- I suppose she’ll be travelling, won’t she? The auxiliary verb will is forming part of the question tag because the auxiliary verb to begin with is will.
Auxiliary verbs:
- Be – auxiliary verb
- Have – auxiliary verb
Modal auxiliary verbs:
- Can and could
- May and might
- Will and shall
- Ought to and should
Advanced grammar:
- Articles (a/an, the, zero article)
- Pronouns: subject, object and possessive
- English conditionals
- Interrogatives in English
- Determiners
- Phrasal verbs
- Prefixes and suffixes
- Reported and direct speech
- Punctuation: apostrophes , colons , semi-colons , commas , dashes , full stops , question marks , exclamation marks , and quotation marks
- Numbers: cardinal, ordinal, and Roman numbers
- The verb: “get”
- ‘Get’ vs. ‘go’ and ‘got’ vs. ‘gotten’
- Copular verbs
- Cleft sentences
- Subjunctive in English
- Vulgar and taboo in English
- Split infinitive
- Emphasis with inversion
- Gerunds in English
- To + infinitive
- Bare infinitive
- British and American spelling

Mastering the Past Tense of Do: Your Ultimate Guide to Fluent English
By: Author ESLBUZZ
Posted on Last updated: September 14, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Learning English grammar can be a challenging task, especially when it comes to understanding the past tense of irregular verbs. One of the most commonly used verbs in English is “do”, and its past tense can be tricky for non-native speakers to grasp. In this article, we will explore the different forms of the past tense of do and provide examples to help you understand how to use them correctly.
Understanding the correct usage of these different forms of the past tense of “do” is essential for effective communication in English. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into each form and provide examples to help you master this important grammatical concept. So, let’s get started!
Past Tense of Do – Image

Understanding the Verb ‘Do’
In English grammar, the past tense refers to the form of a verb that indicates that an action took place in the past.
The verb ‘do’ is one of the most frequently used verbs in the English language. It is used to form questions, negatives, and to emphasize the main verb in a sentence. Understanding the correct usage of the past tense of ‘do’ is essential for effective communication in English.
Simple Past Tense of ‘Do’
The simple past tense of ‘do’ is ‘did’. It is used to talk about completed actions in the past. For example:
- I did my homework yesterday.
- She did not come to the party last night.
- Did you watch the movie last weekend?
Past Continuous Tense of ‘Do’
The past continuous tense of ‘do’ is ‘was/were doing’. It is used to talk about actions that were in progress at a specific time in the past. For example:
- I was doing my homework when my friend called me.
- They were not doing anything when I arrived.
- What were you doing at 5 o’clock yesterday?
Past Perfect Tense of ‘Do’
The past perfect tense of ‘do’ is ‘had done’. It is used to talk about actions that were completed before another action in the past. For example:
- I had done my homework before I went to bed.
- She had not done her laundry when she ran out of clean clothes.
- Had you done your research before the presentation?
Past Perfect Continuous Tense of ‘Do’
The past perfect continuous tense of ‘do’ is ‘had been doing’. It is used to talk about actions that had been in progress for a period of time before another action in the past. For example:
- I had been doing my homework for two hours before I took a break.
- They had not been doing anything productive for weeks before the deadline.
- Had you been doing your exercises regularly before the injury?
In conclusion, understanding the past tense of ‘do’ is crucial for effective communication in English. Practice using the different tenses in various contexts to improve your fluency.
The Past Tense of Do
Form and Usage
In English grammar, the past tense of ‘do’ is ‘did’. ‘Did’ is used to express an action that occurred in the past. The verb ‘do’ is an irregular verb, which means that it does not follow the regular pattern of adding ‘-ed’ to the base form to form the past tense.
To form the past tense of ‘do’, we use ‘did’ as an auxiliary verb followed by the base form of the main verb. For example, “I did my homework” or “He did not eat breakfast this morning”.
Examples in Sentences
Here are some examples of ‘did’ in sentences:
- She did not like the movie.
- They did their best to finish the project on time.
- Did you finish your work before leaving the office?
- He did not want to go to the party.
It is important to note that ‘did’ is used in both affirmative and negative sentences, as well as questions. In questions, ‘did’ is placed at the beginning of the sentence followed by the subject and the base form of the main verb.
Knowing the past tense of ‘do’ is essential for anyone learning English grammar. By using ‘did’ correctly, you can accurately express actions that occurred in the past. Practice using ‘did’ in sentences and questions to improve your understanding of this important verb tense.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
When it comes to using the past tense of “do,” there are a few common mistakes and misconceptions that English learners often encounter. In this section, we’ll explore some of these common issues and provide tips on how to avoid them.
Using “did” Too Much
One common mistake that English learners make when using the past tense of “do” is using “did” too much. While “did” is the correct past tense form of “do,” it’s important to vary your language and use other forms of the past tense as well. For example, instead of always saying “did you do your homework?” try saying “have you finished your homework?” or “completed your homework?”
Forgetting the Auxiliary Verb
Another common mistake is forgetting to use the auxiliary verb “did” in questions and negatives. In English, we use “did” to form questions and negatives in the past tense. For example, instead of saying “you do your homework?” say “did you do your homework?” or instead of saying “I not do my homework,” say “I didn’t do my homework.”
Confusing “Done” and “Did”
A common misconception is that “done” is the past tense of “do.” While “done” is a form of the verb “do,” it’s actually the past participle form, not the past tense form. The past participle is used in perfect tenses, such as “I have done my homework.” The past tense form is “did,” as in “I did my homework yesterday.”
By avoiding these common mistakes and misconceptions, you can improve your use of the past tense of “do” and communicate more effectively in English.

Exercises and Practice
To reinforce your understanding of the past tense of do, we have created several interactive exercises that you can try out. These exercises are designed to help you practice using the past tense of do in different contexts and sentence structures.
Fill in the Blank : In this exercise, you will be given a sentence with a blank space where the past tense of do should be. You will need to select the correct form of the past tense of do to complete the sentence.
Example: Yesterday, I __________ my homework before dinner.
Sentence Scramble : In this exercise, you will be given a scrambled sentence that contains the past tense of do. You will need to unscramble the sentence to make it grammatically correct.
Example: Yesterday, homework I did my.
Multiple Choice : In this exercise, you will be given a sentence with a missing word. You will need to select the correct form of the past tense of do from a list of options.
Example: She __________ her laundry last night. a) do b) did c) does d) doing
We hope these exercises and worksheets will help you master the past tense of do. Keep practicing and you’ll be using it like a pro in no time!
Summary and Conclusion
In this article, we have covered the past tense of “do” in English grammar. We started with an overview of the verb “do” and its various forms in the present tense, before moving on to its past tense forms.
We learned that the past tense of “do” is “did,” and that it is used to talk about actions or events that occurred in the past. We also discussed the different ways in which “did” can be used, including as an auxiliary verb to form questions and negatives.
To help you better understand the past tense of “do,” we provided numerous examples throughout the article. We also included exercises for you to practice using “did” in context.
Overall, mastering the past tense of “do” is an important step in improving your English grammar skills. With practice and persistence, you can become more confident in using this verb tense correctly in your writing and speaking.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the past tense form of the verb ‘do’?
The past tense form of the verb ‘do’ is ‘did’. For example, “Yesterday, I did my homework.”
Can the past tense be used with the verb ‘do’?
Yes, the past tense form of ‘do’ (‘did’) can be used in sentences where the action has already happened in the past. For example, “Did you do your homework?”
What are the different verb forms (V1, V2, V3) for the verb ‘do’?
The different verb forms for ‘do’ are:
- V1 (base form): do
- V2 (past tense): did
- V3 (past participle): done
How is the verb ‘do’ used for emphasis?
The verb ‘do’ can be used for emphasis by adding it before a verb in a sentence. For example, “I do love chocolate!”
The past tense form of the verb 'do' is 'did'. For example, \"Yesterday, I did my homework.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Can the past tense be used with the verb 'do'?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Yes, the past tense form of 'do' ('did') can be used in sentences where the action has already happened in the past. For example, \"He did his best to help me.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the correct past tense for the verb 'learn'?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The correct past tense for the verb 'learn' is 'learned' in American English and 'learnt' in British English. For example, \"I learned a lot from that experience.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are the different verb forms (V1, V2, V3) for the verb 'do'?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The different verb forms for 'do' are:
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"How is the verb 'do' used for emphasis?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The verb 'do' can be used for emphasis by adding it before a verb in a sentence. For example, \"I do love chocolate!\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some examples of using 'do' and 'does' in the present tense?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
- Do: \"Do you like pizza?\"
- Does: \"He does his homework every day.\"
- Recent Posts
- Plural of Species: Rules and Examples - November 8, 2023
- 50th Birthday Wishes to Boost Your English Vocabulary and Writing Skills - October 28, 2023
- Plural of Synopsis: Mastering English Grammar Made Easy! - October 23, 2023
Related posts:
- Arising in the Past: A Complete Guide to the Past Tense of Arise
- Bled or Bleeded? The Past Tense of Bleed
- Past Tense of Buy: How to Use them Correctly in English Grammar
- Past Tense of Cling: A Guide to Mastering English Grammar
Question Tags in English

Question tags are short questions placed at the end of a sentence and they’re used when asking for agreement or confirmation. We mostly use question tags in spoken English.
Regular Question = Did you do your homework yesterday? Question Tag = You did your homework yesterday , didn’t you?
Rule: We don’t use question tags at the end of a question.
Wrong = Did you do your homework yesterday, didn’t you?
Question tags are made using an auxiliary verb and a subject pronoun .
Example: You will be here in ten minutes, won’t you ?
- You : Subject
- Will : Auxiliary Verb
- Be : Main Verb
- Won’t : Auxiliary Verb + not
- You : Subject pronoun
If the main clause is positive, the question tag is negative, and if the main clause is negative, the question tag is positive.
- She is a nurse, isn’t she? = Positive Statement , Negative Question Tag
- She is not a nurse, is she? = Negative Statement , Positive Question Tag
Examples of Question Tags
- His father is a dentist, isn’t he?
- She likes playing tennis, doesn’t she?
- He has got a nice car, hasn’t he?
- Sophia didn’t go to school yesterday, did she?
- You haven’t had breakfast yet, have you?
- You had been to London before, hadn’t you?
- She will come back tomorrow, won’t she?
- John can make his own decision, can’t he?
- They couldn’t come to the party, could they?
- I should see a doctor, shouldn’t I?
- You must call him, mustn’t you?
- She wouldn’t meet with Daniel, would she?
If the statement has a negative meaning, a positive question tag is used. For example;
- He never plays computer games, does he?
- Nobody knows the truth, do they?
There is no contracted form of “am not” so we use “aren’t” in question tag.
- I’m invited to the party, am not I ? = incorrect
- I’m invited to the party, aren’t I ? = correct
Let’s go to the gym, shall we? Don’t stay up late tonight, will you?
Related Posts

What are signal words?

Used to, Be used to, Get used to
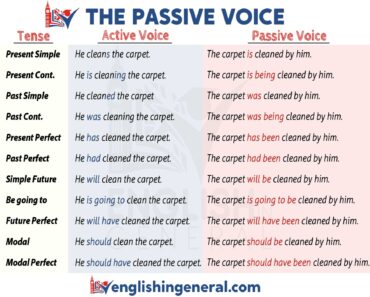
The Passive Voice

Grammar Tips – How To Use Also-Too And As Well In The Right Form?

Imperative Sentence in English

Modal Verbs
Add comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In English grammar, the past tense of ‘do’ is ‘did’. ‘Did’ is used to express an action that occurred in the past. The verb ‘do’ is an irregular verb, which means that it does not follow the regular pattern of adding ‘-ed’ to the base form to form the past tense. To form the past tense of ‘do’, we use ‘did’ as an ...
Regular Question = Did you do your homework yesterday? Question Tag = You did your homework yesterday, didn’t you? Rule: We don’t use question tags at the end of a question. Wrong = Did you do your homework yesterday, didn’t you? Question tags are made using an auxiliary verb and a subject pronoun. Example: You will be here in ten minutes ...