

Direct and Indirect of Past Perfect Tense

We talked about direct and indirect of past progressive tense , in the lesson below I am going to elaborate direct and indirect of past perfect tense. You will learn how to convey a message of someone from past perfect tense. Affirmative, negative, interrogative and negative interrogative sentences along with examples.
For direct and indirect speech complete rules click: Direct and indirect speech complete rules
Tense Change: As a rule, whenever we change a sentence from quoted speech into reported speech, we go one tense back. But if we have past perfect tense in direct speech, we use the same tense in indirect speech.
Affirmatives
- Direct speech: RP, +, + S + had + V3 + ROTS I said to him, “They had played cricket.”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + S + had + V3 + ROTS I told him that they had played cricket.
- Direct speech: RP +, + S + had not + V3 + ROTS He said to me, “We hadn’t played cricket.”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + S + had not + V3 + ROTS He told me that they hadn`t played cricket.
Interrogatives
- Direct speech: RP +, + had + S + V3 + ROTS He asked, “Had you finished playing cricket before the rain started?
- Indirect speech: RP + whether/if + S + had + V3 + ROTS He asked me whether/if we had finished playing cricket before the rain started.
Negative interrogatives
- Direct speech: RP +, + had not + S + V3 + ROTS He asked, “Hadn`t you finished playing cricket before the rain started?”
- Indirect speech: RP + if + S + had not + V3 + ROTS He asked me if we hadn’t finished playing cricket before the rain started.
WH/Information questions
- Direct speech: RP +, + WH + had + S + V3 + ROTS She asked, “Who had you played cricket with before the rain stared?”
- Indirect speech: RP + WH + had + S + V3 + ROTS She wanted to know who I had played cricket with before the rain started.
Check out Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises With Answers
If you would like to know more about direct or quoted speech, or indirect or reported speech, check out more in the book below.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
Related posts
Wh questions in english, simple present tense exercises with answers, indirect speech of imperative sentences, leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Narration Change in Past Tense
Back to: Direct and Indirect Speech (Narration)
Examples of narration change in simple past, past continuous, past perfect, past perfect continuous are given below –
Table of Contents
Direct and Indirect Speech Simple Past Tense Examples
If reported verb is in Past Tense, reported speech will change from Past Indefinite Tense to Past Perfect Tense .
Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech in Past Continuous Tense
If reported verb is in Past Tense, reported speech will change from Past Continuous Tense to Past Perfect Continuous Tense .
Direct and Indirect Speech Past Perfect Tense Examples
If reported verb is in Past Tense & reported speech is in Past Perfect Tense , it will not change. e.g.
Direct and Indirect Speech Past Perfect Continuous Tense Examples
If reported verb is in Past Tense & reported speech is in Past Perfect Continuous Tense , it will not change. e.g.

17 Direct and Indirect Speech Rules for Conversion

Understanding direct and indirect speech conversion rules is crucial for clear and accurate communication. We will explore these rules with detailed examples to master this aspect of the English language in an easy way.
Have you ever found yourself confused about how to accurately report someone else’s speech or statements? If so, you’re not alone. Direct and indirect speech, also known as reported speech, can be tricky to navigate.
But fear not! In this article, we will explore the world of direct and indirect speech conversion rules, guiding you through the intricacies of transforming spoken words into written form.
Let’s now discover the Direct and Indirect Speech Rules in this informative article.
What is Direct Speech or Narration?
Direct speech is a form of reporting that presents someone’s exact words without any alterations. It is commonly enclosed in quotation marks, allowing readers to see the speaker’s statements precisely as they were uttered. For example:
Direct Speech: Riya says, “I shall not go to school.”
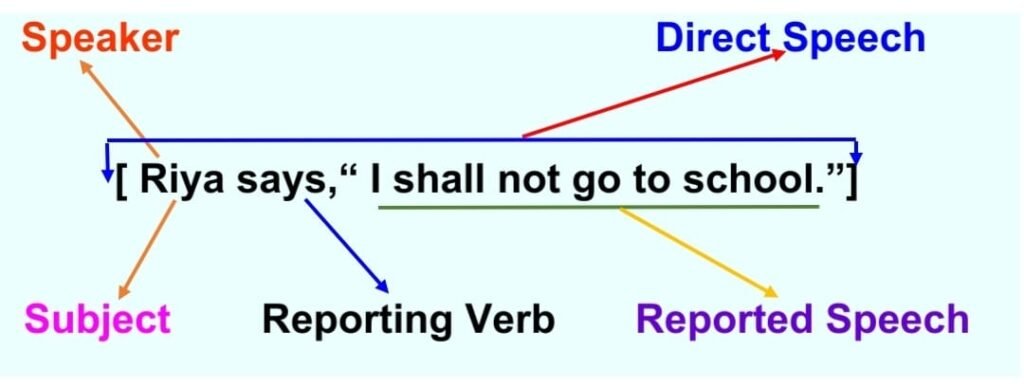
“I shall not go to school. ” – are actual words of Riya. So, it is in the Quotation Marks / Inverted Comma (“ ”) . This format of a sentence with commas and Quotation Marks / Inverted Commas is called Direct Speech where ‘Riya’ is the subject or speaker, ‘ says’ is the reporting verb, and ‘ I shall not go to school’ is called reported speech.
What is Indirect Speech or Narration?
Indirect speech , on the other hand, involves paraphrasing someone’s words and reporting them indirectly, without using quotation marks. It requires a few changes in structure, such as tense and pronoun shifts. Let’s convert the previous example of direct speech into indirect speech:
Indirect Speech: Riya says that she will not go to school.
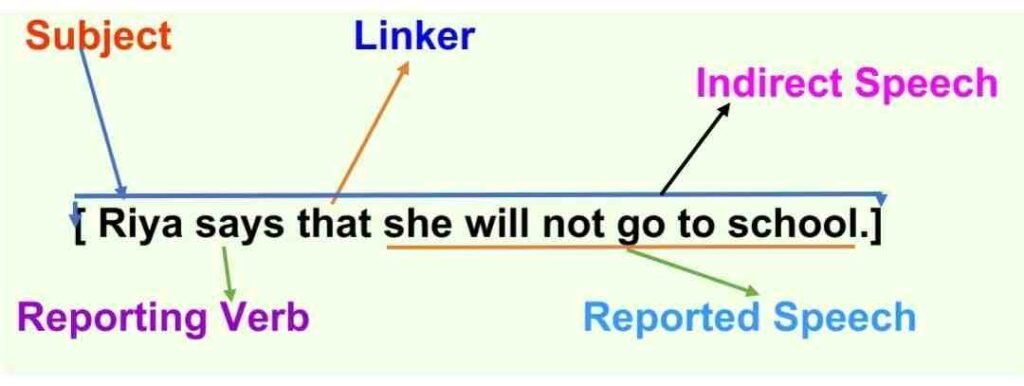
Similarly, we can report the above-mentioned sentence without quoting Riya’s actual words but keeping the meaning the same. This Format of the sentence is called Indirect Speech . In this format, no Comma and no Quotation Mark / Inverted Comma are used. Only Full Stop ( . ) is used at the end of the sentence.
People also ask
Direct and Indirect Speech General Rules
Now, learn the general rules of direct and indirect speech with numerous examples to enhance your language skills. Understand the subtleties of transforming statements, questions, and commands from one form to another effortlessly.
A. Direct and Indirect Speech (Reporting Verbs) Rules
Different reporting verbs are used to introduce indirect speech. The choice of reporting verb can convey the speaker’s attitude towards the reported speech.
Changes in reporting verbs according to tense are one of the most important rules for converting direct speech into indirect speech.
Remember: If the reporting verbs are in the presen t or future tense, the tense of the verb in the reported speech is not changed .
Remember: If the reporting verbs are in the past t ense, the tense of the verb in the reported speech will be in the corresponding past tense.
Here are some commonly used reporting verbs:
Rule 1: Reporting verbs ‘Say’ and ‘Tell’
“Say” and “tell” are two frequently used reporting verbs. “Say” is generally followed by the reported speech, while “tell” is followed by the indirect object (the person being addressed).
Direct: He says , “I am your friend.”
Indirect: He says that he is your friend.
Direct: He said to me, “I’m going to the store.”
Indirect: She told me that he was going to the store.
Rule 2: Reporting Verb ‘Ask’ and ‘Inquire’
When reporting questions , “ask” and “inquire” are commonly employed reporting verbs.
Direct: He said to me, “Where are you going?”
Indirect: He asked where I was going.
Direct: She said , “When will the concert start?”
Indirect: She inquired , “When will the concert start?”
Rule 3: Reporting Verb Request, Advise, Order, and Beg
To report imperative sentences, “Request”, “Advise”, “Order”, and “beg” are often used.
Direct: He said to me, “Go home at once”
Indirect: He ordered me to go home at once.
Direct: She said , “Do not run in the sun”
Indirect: She advised not to run in the sun.”
B. Direct and Indirect Speech ( Tenses ) Rules
The second most important rule is the changes of Tenses for converting direct speech to indirect speech
When transforming direct speech into indirect speech, there are specific rules to follow regarding tense changes:
Rule 4: Reporting Verb Present Tense:
If the Reporting Verb is in the Present Tense, there is no change in the tense in the Reported Verb when Direct Speech is converted into Indirect Narration.
Direct: Arnab says , “The room is dark.”
Indirect: Arnab says that the room is dark.
Direct: Arnab says , “The room was dark.”
Indirect: Arnab says that the room was dark.
Direct: Arnab says , “I shall finish the work.”
Indirect: Arnab says that he will finish the work.
Rule 5: Reporting Verb Future Tense:
If the Reporting Verb is in the Future Tense, there is no change in the tense in the Reported Verb when Direct Speech is converted into Indirect Narration.
Direct: Arnab will say , “The room is dark.”
Indirect: Arnab will say that the room is dark.
Direct: Arnab will say , “The room was dark.”
Indirect: Arnab will say that the room was dark.
Direct: Arnab will say , “I shall finish the work.”
Indirect: Arnab will say that he will finish the work.
Rule 6: Reporting Verb Past Tense:
If the Reporting verb of the Direct Narration is in the Past Tense, the Present Tense of the Verb in the Reported Speech of Direct Narration is changed into the corresponding Past Tense in Indirect Narration.
Direct Speech: Rohan said , “She works hard.”
Indirect Speech: Rohan said that she worked hard.
Direct Speech: Rohan said , “She is singing a song.”
Indirect Speech: Rohan said that she was singing a song.
Direct Speech: The guest said shouting, “We have arrived .”
Indirect Speech: The guest shouted that they had arrived .
Direct Speech: My sister said , “It has been raining hard for 3 days”.
Indirect Speech: My sister said that it had been raining hard for 3 days.
Direct Speech: Father said , “I visited the Taj yesterday.”
Indirect Speech: Father said that he had visited the Taj the previous day.
Direct Speech: The boys said , “They were traveling in the park.”
Indirect Speech: The boys said that they had been traveling in the park.
Direct Speech: The reporters commented, “The Kohinoor had been lost long ago”.
Indirect Speech: The reporters commented that the Kohinoor had been los t long ago.
D i rect Speech: Jyotsna said , “ She had been doing the work for 3 hours”.
Indirect Speech: Jyotsna said that she had been doing the work for 3 hours.
Rule: 7 Direct Indirect Speech (Universal Truth or Habitual Fact) Rules.
The Tense of the Verb remains unchanged in Indirect Narration in cases of General Statements of Facts , Universal Truths , Commonplace Occurrences , and Habitual or Repeated Actions . No real change occurs in these cases. Only there will be present Tense alone.
Direct: The boy said to his mother, “ The sun rises in the East”.
Indirect: The boy told his mother that the sun rises in the East. [ Universal Truth ]
Direct: The monk answered , “ Man is mortal”.
Indirect: The monk answered that man is mortal. [ Universal Truth ]
Direct: The teacher told the students, “ Perseverance always leads to success.”
Indirect: The teacher told the students that perseverance always leads to success.
3. Direct and Indirect Speech ( Changing of Pronouns) Rules
There are certain rules to follow regarding the changes of pronouns from direct speech to indirect speech:
Rule 8: Personal Pronouns
First person.
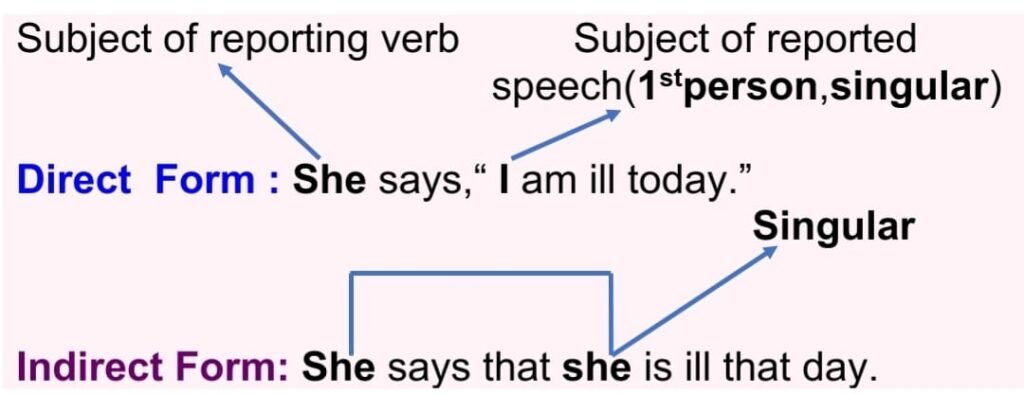
(a) If the subject of the reported speech of direct form is in the first person, the subject of the reported speech will be replaced by the subject of the reporting verb in indirect form, but the number must be the same. [ singular > singular and plural > plural ]
Direct: She says, “ I am ill today.”
Indirect: She says that she is ill that day.
Second Person
(b) If the subject of the reported speech in the Direct Form is in the second person, the subject of the reported speech will be replaced by the object of the reporting verb in the indirect form, but the number must be the same. [ singular > singular and plural > plural ]
Direct: He says to me , ” You can do this work.”
Indirect: He tells me that I can do that work.

Third Person
(c) If the subject of the reported speech of Direct Form is in the third person, there will be no change in the person of the Indirect Form.
Direct: I said, “ He will not wait for his friend.”
Indirect: I said that he would not wait for his friend.

Changing pronouns Chart
Rule 9: demonstrative pronouns.
In the case of demonstrative pronouns, replace them with appropriate pronouns in indirect speech.
Direct: “ This is my book,” she said.
Indirect: She said that it was her book.
4. Direct and Indirect Speech (Punctuation and Quotation Marks ) Rules
Understanding how to punctuate and use quotation marks correctly is crucial when dealing with direct and indirect speech. Here are some guidelines:
Rule 10: Comma and Reporting Verb
When introducing indirect speech with a reporting verb, use a comma to separate the reporting verb from the reported speech.
Example: She said, “I’ll be there on time.”
Rule 11: Question Mark to Full Stop
If the direct speech is a question, change the question mark to a full stop when converting to indirect speech.
Direct: He asked, “Are you coming to the party?”
Indirect: He asked if I was coming to the party.
Rule 12: Exclamation Mark to Full Stop
In cases where the direct speech has an exclamation mark, replace it with a full stop in indirect speech.
Direct: She exclaimed, “What a beautiful day!”
Indirect: She exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
Direct to Indirect speech (Modals and Conditional Sentences) Rules
Indirect speech involving modals and conditional sentences requires careful attention to maintain accuracy:
Rule 13: Modals in Indirect Speech
When dealing with modals like can, could, will, would, may, might, shall, should, must, etc., use the appropriate past form in indirect speech.
Direct: She said , “I can swim.”
Indirect: She said that she could swim.
Rule 14: Conditional Sentences in Indirect Speech
In indirect speech, conditional sentences undergo specific changes, especially when they involve “will” or “would.”
Direct: He said , “I will help you.”
Indirect: He said that he would help me.
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules: (Modifying Words – Time, Place, Manner)
Adding modifying words or phrases can alter the meaning of the reported speech:
Rule 15: Reporting with Adverbs of Time
When using adverbs of time in indirect speech, adjust them to match the new timeframe.
Direct: “I will come tomorrow,” she said.
Indirect: She said that she would come the next day.
Rule 16: Reporting with Adverbs of Place
Similar to adverbs of time, adverbs of place need modification in indirect speech.
Direct: ” I live here,” he said.
Indirect: He said that he lived there.
Rule 17: Reporting with Adverbs of Manner
We can also use Adverbs of manner in indirect speech, requiring appropriate adjustments.
Direct: “He ran quickly,” she said.
Indirect: She said that he ran quickly.
Time, Place, Manner, Distance, and Direction Chart
In Indirect Narration, words denoting Time, Place, Manner, Distance, and Direction used in the quoted speech are correspondingly changed to conform to the point of view of the Reporter. Thus, the sense of nearness is changed into that of Distance, and so on.
Place Chart
Manner chart, distance chart, direction chart, direct and indirect speech advanced rules.
It is necessary to know about the Direct Indirect Speech Advanced Rules to change the mode of narration from direct to indirect speech of different sentences. All five sentences of Direct Indirect Speech Conversion Rules are shown with proper examples below.
A. Assertive Sentence Conversion Rules
To convert Assertive sentences into indirect speech the following rules are applied.
(a) No comma and Inverted comma in Indirect Speech, only full stop at the end.
(b) Reporting Verbs changed from Direct Speech to Indirect Speech ; ‘say – say’, ‘says – says’, ‘said – said’, ‘said to – told’, ‘say to – tell’, ‘says to – tells’.
(c) Connective ‘that’ added before Reported Speech in indirect Narration.
Direct: He said to me, “I am ill.”
Indirect: He told me that he was ill.
B. Interrogative sentences Conversion rules
Forming indirect speech with questions necessitates some adjustments:
Reporting Yes/No Questions
When reporting yes/no questions, use “if” or “whether” and invert the subject and auxiliary verb in indirect speech.
Direct: “Will you be there?” he asked.
Indirect: He asked if I would be there.
Reporting Wh-Questions
For reporting wh-questions, maintain the question word and adjust the word order in indirect speech.
(a) ‘Tell’ and ‘say’ in Direct Narration are changed to ‘ask’, ‘enquire of’, ‘question’, ‘want to know’ etc. in Indirect Narration. (b) In place of introductory ‘that’. ‘if’ or ‘whether’ should be used. (c) In Indirect Narration a full stop (.) must be put in place of a question mark(?) at the end of the sentence. (d) In Direct Narration the Reported Speech begins with W-word or how, in Indirect Narration the same Wh-word or how is retained.
Direct: “Where are you going?” she asked.
Indirect: She asked where I was going.
Direct: The teacher said to me, “Why are you late?”
Indirect: The teacher asked me why I was late.
C. Imperative Sentences Conversion rules
The indirect speech also involves reporting imperatives, which are commands, requests, or advice:
Reporting Commands
When reporting commands, use the reporting verb “tell” and change the imperative verb to the corresponding infinitive.
Direct: The teacher said, “Open your books.”
Indirect: The teacher told the students to open their books.
Reporting Requests
For reporting requests, employ the reporting verb “ask” and convert the imperative verb to the corresponding infinitive.
Direct: She said, “Please help me with this.”
Indirect: She asked for help with that.
(a) Reporting verbs of Direct Speech changed into order or command, advise, or request according to sense in Indirect Speech. (b) ‘To’ is placed before Reported speech in Indirect Narration; for the negative imperative sentence ‘not to’ is used. (c) ‘not to’ can also be replaced by ‘forbid’, or ‘prohibit’. (d) ‘Let’ implies ‘suggestion’ or ‘proposal’; Reporting verb will be ‘suggest’ or ‘propose’ in Indirect Speech. ‘that’ is used before Reported speech in Indirect Narration (e) ‘Let’ without ‘suggestion’ or ‘proposal’; Reporting verb will be ‘tell’, or ‘wish’ according to sense in Indirect Speech. ‘that’ is used before Reported speech in Indirect Narration.
Direct: Mother said to me, “Don’t run in the sun.”
Indirect: Mother advised me not to run in the sun.
Direct: She said to me, “Let us go for a picnic.”
Indirect: She suggested that we should go for a picnic.
D. Optative Sentence Conversion rules
The following rules are used to change an optative sentence from direct speech to indirect speech
(a) Reporting verbs changed to ‘ wish ’, ‘ pray ’, and ‘ bless ’ in Indirect Speech.
(b) Linker, ‘ that ’ is placed before Reported speech in Indirect Narration.
Direct: The monk said to me, “ May God bless you.”
Indirect: The monk wished that God might bless me.
E. Exclamatory Sentences Conversion rules
(a) The reporting verb is changed into exclaim (in joy), exclaim (in grief), cried out (in sorrow), pray, wish, etc. (b) Examinations are turned into statements. (c) Interjections (Alas, Oh, Hurrah) are omitted. (d) ‘What’, and ‘How’ used in exclamation should be replaced by great, great, very, very much, and big.
Direct: The boys said, “Hurrah! we have won the match.”
Indirect: The boy exclaimed in joy that they had won the match.
Solved Exercises Direct and Indirect Speech
Change the following sentences into indirect speech.
Q: Ratan said to Anita, “I don’t like your brother”.
Ans: Ratan told Anita that she did not like her brother.
Q: The hermit said to the boys, “God is present everywhere.”
Ans: The hermit told the boys that God is present everywhere.
Q: :He said to you, “You shouldn’t play in my garden.”
Ans: He told you that you should not play in his garden.
Q: The class teacher said to the students. “The inspector will visit our school today.”
Ans: The class teacher told the students that the inspector would visit their school that day.
Q: He said to me, “I don’t believe you.”
Ans: He told me that he didn’t believe me.
Q: She said to her son, “I’ve often told you not to play with fire.”
Ans: She told her son that she had often told him not to play with fire.
Q: Sitesh said to Lina, “I want you to go to Patna with me.”
Ans: Sitesh told Lina that he wanted her to go to Patna with him.
Q: “We can’t be quite happy in life,” he said.
Ans: He said that they couldn’t be quite happy in life.
Q: He said, “The Muslims bury their dead.”
He said that the Muslims bury their dead.
Q: “You’ve overcooked the steak again, Mary”, he said.
Ans: He told Mary that she had overcooked the steak again.
Q: Ramen said to Bina, “I’m going to your house this, week.”
Ans: Ramen told Bina that he was going to her house that week.
Q: He said, “We will discuss this tomorrow.”
Ans: He said that they would discuss that the next day
Turn the following sentences into direct speech.
Q: He said to me, “You are wicked; so I shall not mix with you.”
Ans: He told me that I was wicked; so he would not mix with me.
Q: He said to you, “I was much struck by your eloquence.”
Ans: He told you that he had been much struck by your eloquence.
Q: We remarked, “God is gracious.”
Ans: We remarked that God is gracious.
Q: I said to my mother, “I shall always obey you.”
Ans: I told my mother that I should always obey her.
Q: He said to Gopal, “You were a mere boy when I saw you last.”
Ans: He told Gopal that he was a mere boy when he had seen him last.
Q: I said to him, “The sky is blue.”
Ans: I told him that the sky is blue.
Q: He said to me, “You will feel the consequences.”
Ans: He told me that I should feel the consequences.
Q: She said to you, “I am not angry with you.”
Ans: She told you that she was not angry with you.
Q: I said to them, “You have done wrong.”
Ans: I told them that they had done wrong.
Q: He said, “I visit the temple every day.”
Ans: He said that he visited the temple every day.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): Direct and Indirect Speech
Q : what is the key difference between direct and indirect speech.
Ans: The main difference lies in the quoting style. Direct speech involves repeating someone’s exact words, while indirect speech reports what was said without quoting verbatim.
FAQ 2: Is it always necessary to backshift the tense in indirect speech?
Ans: While backshifting is common, some exceptions exist, especially in cases where the statement’s truth remains constant.
FAQ 3: How do I handle multiple speakers in indirect speech?
Ans: When reporting multiple speakers, use appropriate reporting verbs and introduce each person’s dialogue in a logical sequence.
FAQ 4: Can I mix direct and indirect speech in the same sentence?
Ans: Combining direct and indirect speech in a sentence is possible, but it requires precision to avoid confusion.
FAQ 5: What are some reporting verbs commonly used in indirect speech?
Ans: Reporting verbs like “said,” “told,” “asked,” “claimed,” and “explained” are frequently employed.
FAQ 6: How can I ensure my writing maintains a natural flow when switching between direct and indirect speech?
Ans: Focus on maintaining consistency in style and verb tense to ensure a smooth transition between direct and indirect speech.
FAQ 7: How do I identify direct and indirect speech in a sentence?
Ans: Direct speech is usually enclosed within quotation marks and directly quotes someone’s words. Indirect speech, on the other hand, reports those words without quotation marks, often using reporting verbs like “said,” “told,” “asked,” etc.
FAQ 8: Can reporting verbs change the meaning of indirect speech?
Ans: Yes, the choice of reporting verbs can convey the speaker’s attitude or emotions towards the reported speech. Different reporting verbs can modify the meaning slightly.
FAQ 9: What are the common reporting verbs for indirect speech?
Ans: Common reporting verbs for indirect speech include “say,” “tell,” “ask,” “inquire,” “explain,” “describe,” and more.
FAQ 10: How do I change tenses in indirect speech?
Ans: The tense in indirect speech is generally shifted back one step. For example, present simple becomes past simple, present continuous becomes past continuous, and so on.
FAQ 11: Is it essential to use quotation marks in indirect speech?
Ans: No, quotation marks are not used in indirect speech as they report the speech without directly quoting it.
FAQ 12: Can you give an example of indirect speech in narratives?
Ans: Certainly! In the story, he said, “I love you,” to which she replied that she loved him too.
FAQ 14: Can we omit the reporting verb in indirect speech?
Ans: It is possible to omit the reporting verb in some cases, especially in informal contexts, but including it adds clarity and structure to the reported speech.
FAQ 15: Do all tenses change in indirect speech?
Ans: Most tenses change in indirect speech, but the changes depend on the context and the tense of the original statement.
FAQ 16: Can you provide more examples of direct and indirect speech transformations?
Ans: Certainly! Here are a few more examples:
Direct: “I am reading a book,” she said. Indirect: She said that she was reading a book.
Direct: “We have completed the project,” they exclaimed. Indirect: They exclaimed that they had completed the project.
FAQ 17: How can I practice using direct and indirect speech effectively?
Ans: Practice by converting direct speech to indirect speech and vice versa using various reporting verbs, tenses, and pronouns. Additionally, read books or articles and identify the reported speech used by the authors.
Related posts:

Reported Speech
Perfect english grammar.

Reported Statements
Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: I like ice cream.
- Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'. (As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you don't use 'that'.)
But , if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
* doesn't change.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
Click here for a mixed tense exercise about practise reported statements. Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.
Reported Questions
So now you have no problem with making reported speech from positive and negative sentences. But how about questions?
- Direct speech: Where do you live?
- Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
- Direct speech: Where is Julie?
- Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
- Direct speech: Do you like chocolate?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
Click here to practise reported 'wh' questions. Click here to practise reported 'yes / no' questions. Reported Requests
There's more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
- Direct speech: Close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
- Direct speech: Please don't be late.
- Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
Reported Orders
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
- Click here for an exercise to practise reported requests and orders.
- Click here for an exercise about using 'say' and 'tell'.
- Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
English With Ashish
Direct and Indirect speech with examples and explanations
Welcome back, smart brains! This article will help you understand how direct speech and indirect speech (narration) work in the English language. What is a direct speech? What is an indirect speech? Why and how do we use direct and indirect speech? How to change direct speech to indirect speech? Going forward, we will know the answers to all these questions.
Whenever someone tells you something or shares something with you, there are two ways to narrate what the person said:
- Direct speech
- Indirect Speech
Let’s suppose you go to a mobile shop to buy a specific mobile phone. On reaching, one of the executives says, “We don’t have this phone.” You go back home. Your elder brother wants to know what happened. There are two ways to convey what the executive said to you.
Direct speech: One of the executives said, “We don’t have this phone.” (Quoting the exact words of the executive)
Indirect speech: One of the executives said that they did not have that phone. (Narrating the executive’s message in your own words)
What is direct speech?
Direct speech definition: It is a way to narrate what someone said using the speaker’s exact words. The reported speech (the speaker’s words) is placed within quotation marks, and it is offset using a comma.
What is indirect speech?
Indirect speech definition: In indirect speech, the original words of the speaker get changed. The pronoun/s, the tense, and the adverbs of time and place in the reported speech (the words of the speaker) get changed. These things, not always but often, are changed as the original message was delivered at some point in time in the past, but we narrate it after some time. That creates a time difference in receiving the message and narrating it to someone. Because of which we have to go back in the past to refer to the right time.
Direct speech: Sandhya said to me, “I love talking to you.” Indirect speech: Sandhya told me that she loved talking to me.
Note: The conjunction ‘ That ’ in the indirect speech can be eliminated too. The sentence is still correct without it.
- Indirect speech: Sandhya told me she loved talking to me.
Note: Changing the tense of the reported speech in indirect speech is called back-shifting.
In the above example, when we are reporting the speaker’s words in indirect speech, we are backshifting the time(tense) of the action to further back. We backshift the tense as the speaker’s words might not fall true or be relevant at the time of narrating it to someone.
She loved talking to me at the time of delivering the message, but now, at the time of narrating to someone, this might not fall true. She might not love talking to me now. That is exactly why the tense is backshifted further back in the past to show the accurate time and action.
But when you are narrating the speaker’s message right after it is being said, you don’t need to backshift the tense as there is almost no difference between the time of receiving the speaker’s message and narrating it to someone.
Let’s suppose we were at a party. Sandhya and I were exchanging words. You were right there too. She said, “I love talking to you.” You didn’t hear it. You come to me and ask, “What did she say to you?”
I tell you that she said that she loves talking to me. It is fairly unlikely for her to change her mind in just a few seconds. 😉
Examples of direct and indirect speech
- Direct speech: She said to me, “It is raining outside.”
- Indirect speech: She told me that it was raining outside.
- Direct speech: “I bought my favorite phone yesterday,” he told me with excitement.
- Indirect speech: He told me with excitement that he had bought his favorite car the previous day.
- Direct speech: Max said, “This is my school.”
- Indirect speech: Max said that that was his house. (You are not there in front of the school.)
- Indirect speech: Max said that this was his house . (You are still there in front of the school.)

How to change direct speech to indirect speech?
Here are the changes you need to make in order to change a direct speech to indirect speech:
1. Remove quotation marks and the comma from the direct speech.
2. use the conjunction that before the reported speech. its use is optional though..
- Direct speech: Sandhya said to me, “I love talking to you.”
- Indirect speech: Sandhya told me that she loved talking to me.
3. Change the pronoun/s of the reported speech.
The subject (pronoun) of the reported speech (indirect speech) is changed according to the subject or the object of the introductory clause, and its object is changed according to the object of the introductory clause.
According to the subject
According to the object
- Direct speech: The students said to me, “You were teaching amazingly well.”
- Indirect speech: The students said that I had been teaching amazingly well.
These are some direct and indirect speech rules we need to master!
3.1 Backshift the tense
3.2 change the adverb of time and place, how to change direct speech to indirect speech in different tenses , 1. present simple to past simple tense.
When the direct speech is in the Present Simple tense , it is changed to the Past Simple tense in the indirect speech.
Direct indirect speech examples:
- Direct speech: “I work with the top CEOs of the world,” he boasted.
- Indirect speech: He boasted that he worked with the top CEOs of the world.
- Direct speech: Sandhya told me, “You look amazing in this dress.”
- Indirect speech: Sandhya told me that I looked amazing in that dress.
- Direct speech: “The sun rises in the east,” my father informed us.
- Indirect speech: My father informed us that the sun rises in the east.
NOTE : When what’s being said is still valid or related or universal, we don’t backshift the tense. In the third example, we have not changed the tense.
2. Present continuous to past continuous tense
When the direct speech is in the Present Continuous tense , it is changed to the Past Continuous tense in the indirect speech.
- Direct speech: “You are making a lot of noise,” the teacher said angrily.
- Indirect speech: The teacher said angrily that we were making a lot of noise.
- Direct speech: She said, “I am getting married next month.”
- Indirect speech: She said that I am getting married next month.
NOTE : The next month has not come yet. She narrated the message before the message gets irrelevant.
3. Present perfect tense to past perfect tense
When the direct speech is in the Present Perfect tense , it is changed to the Past Perfect tense in the indirect speech.
- Direct speech: “I have finished the work,” Max said to me.
- Indirect speech: Max told me that he had finished the work.
- Direct speech: She said, “You have not helped me now.”
- Indirect speech: She said that I had not helped her then.
4. Simple past tense to past perfect tense
When the direct speech is in the Simple Past tense, it is changed to the Past perfect tense in the indirect speech.
Direct and indirect speech examples:
- Direct speech: “We finished the task on time,” he said to me.
- Indirect speech: He told me that they had finished the task on time.
- Direct speech: Rahul said to me, “I enjoyed working with you.”
- Indirect speech: Rahul told me that he had enjoyed working with me.
5. Past continuous tense to past perfect continuous tense
When the direct speech is in the Past Continuous tense, it is changed to the Past Perfect Continuous tense in the indirect speech.
- Direct speech: “He was sleeping here,” the lady told me.
- Indirect speech: The lady told me that he had been sleeping here.
Modal auxiliary verbs in direct and indirect speech
- Direct speech: “ You can’t beat me in a street fight,” He said to me.
- Indirect speech: He told me that I could not beat him in a street fight.
- Direct speech: “We will screw your career,” the company said.
- Indirect speech: The company said that it would screw my career.
- Direct speech: “We might visit you tomorrow, “my friends said to him.
- Indirect speech: My friends said to him that they might visit him the next day.
- Direct speech: “You may get the Job,” Ronny said to me.
- Indirect speech: Ronny told me that I might get the job.
- Direct speech: “I should start working on my communication skills,” He said in frustration.
- Indirect speech: He said in frustration that he should start working on his communication skills.
Important points:
- SAY can’t be followed by an indirect object without the preposition TO . TELL is followed by an indirect object.
- He said me that I teach amazingly well. (Incorrect)
- He said to me that I teach amazingly well. (Correct)
- He told me that I teach amazingly well. (Correct)
- Don’t backshift the tense of the reported speech if what’s been said is universally true or is still relevant at the time of narrating it to someone.
- Direct speech: “He is my father,” Jon informed me.
- Indirect speech: Jon informed me that he is his father.
- Direct speech: “We are going to London in 2022,” She said.
- Indirect speech: She said that they are going to London in 2020. (You are saying it in 2021).
- Direct speech: Rahul said, “India is a democratic country.”
- Indirect speech: Rahul said that India is a democratic country.
Now, we know what a direct and an indirect speech is in English. Feel free to share your question, doubt, or feedback in the comment section, and also, share the post with the people that need it.
For one-on-one classes, contact me at [email protected] .
Here’s my video lesson on the narration!
Click here to learn how to change interrogative sentences into assertive sentences in reported speech!
Ashish Sharma
Ashish found his first love—the English language—a few years back. Since then, he has been immersed in the language, breaking down the language and teaching it to passionate English learners. He has a flair for listening to the English language (podcasts, sitcoms, stories), observing the nuances, and making it easy for English learners. He is known for breaking down complex English topics and making them easy to be understood.
2 thoughts on “Direct and Indirect speech with examples and explanations”
Direct speech: Max said, “This is my school.” Indirect speech: Max said that that was my house. (You are not there in front of the school.) Indirect speech: Max said that this is my house. (You are still there in front of the school.) please check! I think there is an error in indirect sentence as my must be change into his what I believe?!!!!!!\
Hello Imran, Thank you for pointing out the mistake. The verb tense ‘is’ was also needed to be backshifted in the past. It has been taken care of.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
Indirect speech: typical errors.
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
bits and bobs
small things or jobs of different types

Shoots, blooms and blossom: talking about plants

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Search form
- Highest rated
- Verb phrase generator
- Test your grammar
Tense changes in indirect speech
No tense changes.
There are no tense changes in indirect speech if:
Joanna: I have just arrived in Hanoi. Joanna says she has just arrived in Hanoi. (reporting a recent telephone conversation; the reporting verb say is in present simple)
George: I 'm meeting Karen tomorrow. George said he is meeting Karen tomorrow. (reported on the same day, tomorrow still refers to tomorrow)
George said he was meeting Karen the following day. (reported days later, the meeting has already happened)
Copernicus: The planets revolve around the sun. Copernicus stated that the planets revolve around the sun. (it is a general truth)
Once, people believed that the earth was flat. (the reported words are no longer true; people do not believe that the earth is flat)
Mike: I wish I was a year older; then I could enter the race. Mike wished he was a year older, so he could enter the race. (he is not older)

Tense changes
Tenses change in indirect speech if:
Philip in 1980: I have never been to Brunei, but I' m thinking about going there. (the reference point of the present perfect and the present continuous is 1980) When I met Philip in 1980, he said he had never been to Brunei, but he was thinking about going there. (reported years later; the reported words are out of date)
Tim: Sorry, I can't go to work this week. I' m ill. Tim isn't coming to work this week. He said that he was ill.
Tense backshift
As can be seen in the examples above, the verbs in the present perfect, present continuous and present simple tenses in the original statements changed into their corresponding past equivalents (past perfect, past continuous and past simple) in indirect speech. This process is called tense backshift. Note that tense backshift is based on how tenses relate to each other in general:
When I met Philip in 1980, he said he had never been to Brunei. When I arrived at work, I remembered that I hadn't locked the door to my apartment. (two consecutive actions and an earlier action)
When I met Philip in 1980, he said he was thinking about going to Brunei. When I entered the room, I saw that she was studying . (two consecutive actions and a background action in progress)
Tim said that he was ill. I went outside. It was a warm day. (a past action and a past state)
Tense backshift:
The past perfect and past perfect continuous tenses do not change.
In complex sentences, the past simple and past continuous may remain unchanged if the temporal relationship between the events in the clauses is clear from the context:
John: When I got home, I went to bed straight away. John told me that when he got home he went to bed straight away.
Bill: I was reading a book when I heard the crash. Bill said that he was reading a book when he heard the crash.
Helen: When I was writing my thesis, I spent a lot of time at the library. Helen recalled that when she was writing her thesis she spent a lot of time at the library.
Tim: My friends were enjoying themselves playing cards while I was studying in my room. Tim grumbled that his friends were enjoying themselves playing cards while he was studying in his room.
Chris: When I got to her house, she had been waiting for hours. Chris said that when he got to her house she had been waiting for hours.
Rate this page
Related topics.

For timeline diagrams, quotes and exercises, check out our e-book The Grammaring Guide to English Grammar

About | Copyright
Grammaring – A guide to English grammar | Copyright © 2009-2024
Onlymyenglish.com
Learn English
Direct and Indirect Speech
Table of Contents
What is Speech (Narration):
If we want to describe the speech of some other people with other people in our own words, that speech is called a Reported speech or Narration.
Types of Speech
In the English language, there are certain ways to express the spoken words between two people.
The speech has two main types, Direct speech , and Indirect speech , respectively.
These two ways of narration of spoken words are also called Direct and Indirect speech, also known as Direct and Indirect narrations.
Direct and indirect speech is majorly used in any conversations, scripts, or any biographies, etc. where one or more than one person converses with each other.
Direct speech:
It is also called straight speech or quoted speech, which is spoken or written directly in the text by the speaker, writer, or the first person, who is going to speak with anyone with him.
The spoken statements of the speaker normally come under the inverted commas notation, and a speaker who speaks these sentences may come like “he said/he said that.”
The speaker’s words or statements are mentioned in a single phrase pattern or direct discussion.
Indirect speech:
An Indirect speech is also called a reported speech, or secondary speech means the speech, which has spoken indirectly.
It is simply an overlook statement that is used to say about the incident that has happened in the past time.
The actual words of the speaker changed into the past tense and the sentence, and hence the reported speech of the direct speech does not come inside the inverted commas.
Reporting speech:
A person who is going to report the speech or a speech that comes in the first part of the direct speech is called a reporting speech.
- He says , “He cooks food”.
Reported speech:
Reported speech is a speech that is always in an inverted comma or quotation marks.
It is a second part of the direct speech sentence.
- He says, “He cooks food.”
Reporting verb:
The verb, which is used in a reporting speech to report something in a direct speech, is called a reporting verb.
- Zoya said , “I want to go there.”
Reported verb:
The verb which comes inside the reported speech is called reported verb, respectively.
- Zoya said, “I want to go there.”
As we start writing any direct and indirect conversation, we often use reported verbs like “say, tell, ask, inform, instruct, claim, suggest, enquire, etc.”
These reported verbs, whenever used in direct or indirect speech, change into the past simple form like said, told, asked, informed, instructed, claimed, suggested, enquired, etc.
But the verbs used in a speech between the inverted commas will remain as it is.
Examples of direct and indirect speech:
- Indirect speech: John said that she was looking so beautiful.
- Indirect : He said that he was not a culprit.
- Indirect : He said that she was working on that project.
- Indirect : The teacher asked if he completed his homework.
- Indirect : She says that she is an artist.
- Indirect : Sam told me that he was not coming with me.
- Indirect : He says that she is working on that project.

Some basic rules for converting direct speech into indirect speech:
Rule 1 : “no inverted commas.”.
The reported speech does not come into inverted commas or quotation in an indirect speech.
Example: Direct: He said, “I have completed my assignments yesterday.”
Indirect: He said that he had completed his assignments the previous day.
Rule 2: use of “that” conjunction
Using the conjunction word “that” in-between the reporting speech and reported speech in an indirect speech.
Example:
- He said, “I have completed my assignment yesterday.”
- He said that he had completed his assignment the previous day.
Rule 3: Change of tense
While writing a direct speech into an indirect speech, we have to change the tense of the reported speech because whatever we are writing in indirect speech has already happened in the past timing.
- If the tense of a reporting speech of direct speech is in the present tense or future tense , then the tense of the reported speech in indirect speech will not change. It may be in the present tense, past tense, or future tense, respectively.
- Indirect : He says that he is going to school. (no change in tense)
- Indirect : She says that she will not come with me. (no change in tense)
- Indirect : He says that he wrote a letter. (no change in tense)
If the tense of the reporting verb of direct speech is in the past tense, then the tense will change according to these criteria.
For the present tense:
Simple present tense will change into simple past tense..
Direct: He said, “They come to meet me.”
Indirect: He said that they came to meet him.
Present continuous tense will change into past continuous tense.
Direct: She said, “They are coming to meet me.”
Indirect: She said that they were coming to meet her.
Present perfect tense will change into past perfect tense.
Direct: He said, “They have come to meet me.”
Indirect: He said that they had come to meet him.
Present perfect continuous tense will change into past perfect continuous tense.
Direct: She said, “They have been coming to meet me.”
Indirect: She said that they had been coming to meet her.
For the past tense:
Simple past tense will change into the past perfect tense.
Direct: He said, “They came to meet me.”
Indirect: He said that they had come to meet him.
Past continuous tense will change into past perfect continuous tense.
Direct: She said, “They were coming to meet me.”
Indirect: She said that they had been coming to meet her.
Past perfect tense and past perfect continuous tense will remain the same.
Direct: He said, “They had come to meet me.”
Direct: She said, “They had been coming to meet me.”
For the future tense:
There are no changes in the future tense sentences; only shall/will may change into would, can change into could.
- Direct: She said, “Can you come tomorrow.”
Indirect: She said that could he come on the next day
- Direct: He said, “I will never forgive you.”
Indirect: He said that he would never forgive me.
Rule 4: Changing the pronoun
The pronoun used as an indirect subject speech sometimes needs to be changed accordingly in indirect speech as of the reported verb of the direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the first person in reported speech changes based on the subject of the reporting speech in a direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the second person in reported speech changes based on the report’s object in a direct speech.
- The pronoun used for representing the third person remains the same in the reported speech.
- Direct: He said, “ I am going to school.”
- Indirect: He said that he is going to school.
- Direct: She says, “ I will not come with you .”
- Indirect: She says that she will not come with me .
- Direct: They said, “ we are eating our tiffin box.”
- Indirect: They said that they were eating their tiffin box.
Rule 5: Changing the time
The mentioned time (not the timing) in a direct speech sentence will have to change in indirect speech like now becomes then, tomorrow becomes the next day, yesterday becomes the previous day, today becomes that day, later becomes soon.
- Direct: He told, “He is coming from Tokyo today .”
- Indirect: He told me that he was coming from Tokyo that day .
- Direct: She asked, “Will the parcel reach by tomorrow or not?”
- Indirect: She asked whether the parcel will reach by the next day or not.
- Direct: “The teacher has given some assignments yesterday ”, he reminds me.
- Indirect: He reminds me that the teacher had given some assignments on the previous day.
Conversion of statements from direct speech into Indirect speech:
Assertive sentences:.
Assertive sentences are simple statements that may be affirmative or negative.
If we are going to convert assertive sentences from direct speech into indirect speech, we have to replace “said” with “told” sometimes.
Here, the subject in direct speech refers to someone in his talk.
- Direct: He said to me, “she is working on this project.”
Indirect: He told me that she was working on that project.
- Direct: She said to me, “I’m going for a long drive.”
Indirect: She told me that she was going for a long drive.
Imperative sentences:
Imperative sentences are statements that deliver a command, order, request, appeal, or advice.
It depends on the speaker, how he delivers the message to the other person.
- Sit properly!
- Stand by my side!
- Come closer!
While converting these types of sentences cum statements from direct speech to indirect speech, we have to check the type of sentence, whether it is a command, order, request, or else.
- Direct: The teacher said to me, “Sit properly!”
Indirect: The teacher ordered me to sit properly.
- Direct: The Boss said to an office boy, “Bring one coffee for me.”
Indirect: The Boss commanded an office boy to bring a coffee for him.
Indirect: The teacher requested me to sit properly.
- Direct: The bartender said to me, “try this drink.”
Indirect: The bartender advised me to try that drink.
Interrogative sentences:
An interrogative sentence is a sentence which interrogates or ask questions.
Each interrogative sentence ends with an interrogative sign or a question mark sign “?”.
- What is your name?
- Can you do me a favor?
- Why are you laughing in the classroom?
While writing interrogative sentences from direct speech into indirect speech,
- the reporting verb “said” in the direct speech is changed into “asked” in the indirect speech because it asks the question to another person.
- If any reporting verb comes first in the reporting speech, then “If” is used despite “that.”
- In a reporting speech, if any wh-type question words are present, then no other words will be used, and the sentence ends with a full stop sign instead of a question mark.
- Indirect: He asked me what was my name.
- Indirect: She asked if he could do her a favor.
- Indirect: The teacher asked him why he was laughing in the classroom.
Exclamatory sentences:
Exclamatory sentences are those sentences that show emotions, feelings and ends with an exclamation mark!
- Congratulations! You have a baby girl.
- I am extremely sorry for your loss!
- Most welcome!
If any interjection comes in an exclamation sentence, then the exclamation sign removes in an indirect speech, and an exclamatory sentence gets converted into an assertive sentence.
The replacement of reporting verb “said” with exclaimed with (great wonder, sorrow, joy) exclaimed (joyfully, sorrowfully)
Replace with very or very great , if words like how or what comes at the beginning of the reported speech.
- Indirect: He exclaimed with joy that I had a baby girl.
- Indirect: She exclaimed with sorrow that she felt sorry for my loss.
- Indirect: They exclaimed with joy that most welcome.
You might also like

Future Continuous Tense: Definition, Examples, Formula & Rules

Use of ‘Will and Shall’

12th English Grammar | Class 12 English Grammar

Past Perfect Tense: Definition, Examples, Formula & Rules

Past Perfect Continuous Tense: Definition, Examples, Formula, Structure & Rules
Use of would and could with an example.

- Practical Tips
- Spoken English

Direct To Indirect Speech: Complete Rules With Examples

Direct and indirect speech is often a confusing topic for English learners. The basic idea is this:
- In direct speech, we quote a person’s exact words. For example, Meera said, “I can speak English fluently.”
- In indirect speech, we do not quote the person’s exact words but provide a summary of what was said. For example, Meera said that she could speak English fluently.
The critical difference is that direct speech uses the exact words spoken by a person, while indirect speech summarizes what was said. While the definition is simple, the challenge for English language learners is using the proper tenses when converting a phrase from direct to indirect and vice versa.
Why Should You Learn Direct To Indirect Speech Rules?
There are several occasions – in your professional and personal – where you might need to describe an action or event to others. For example, you might have to repeat the team leader’s instructions to your teammates at the workplace. In this scenario, you convert your team leader’s direct to indirect speech.
Knowing conversion rules can help you present or describe the event correctly without making any grammatical errors or spoken English blunders.
In this post, we walk you through the rules of converting direct to indirect speech, helping you speak English fluently online and offline.
How To Use Direct Speech?
The rule is simple: Use direct speech when you want to repeat what someone says as it is, and ensure that the spoken text is sandwiched between quotation (speech) marks.
John said, “I want to learn to speak English fluently.”
It’s common to see the direct speech in newspaper articles and books. For example,
The District Collector announced, “The Chief Minister will inaugurate the city centre next week.”
As you can notice, in direct speech, we use the verb say (said in the past tense) to denote what was spoken. You can also use related verbs like ‘asked,’ ‘replied,’ ‘told,’ ‘informed,’ ‘shouted,’ etc.
How To Use Indirect Speech?
Indirect speech is also reported speech, as we use it to inform/repeat what someone else said. Using the two examples above, we can convert it into indirect speech as follows:
John said that he wanted to learn to speak English fluently.
The District Collector announced that the Chief Minister would inaugurate the city centre the week after.
Another example,
Direct Speech: “I feel cold.”
Indirect Speech: She says that she feels cold.
If you notice these examples carefully, you can see that the tense changes when converting from direct to indirect speech. To illustrate this point, in the following example, direct speech is in the present simple tense, while indirect speech is written in the simple past tense.
Direct Speech: “I live in the city centre.”
Indirect Speech: He said he lived in the city centre.
Tense Change Rules: Direct To Indirect Speech
Similarly, other tenses follow similar rules when changing from direct to indirect speech. Use the following table to help you better understand the tense change rules:
Modal Verbs: Direct To Indirect Speech
When converting direct to indirect speech, you must change modal verbs accordingly. Here are a few examples to help you understand better:
Changing Time Expressions: Direct To Indirect Speech
Sometimes it becomes necessary to change the time expressions when converting from direct to indirect speech. A few examples,
- Direct speech: Sheila said, “I am meeting my brother tomorrow.”
- Indirect speech: Sheila said that she was meeting her brother the following day.
Here are a few examples of other typical time expressions and how they change:
Changing Place Expressions: Direct To Indirect Speech
Like time expressions, you might also have to change words representing places when reporting indirect speech. For example,
- Direct speech: “It’s raining here.”
- Indirect speech: She said that it was raining there.
Here are a few examples of other common place expressions and how they change:
However, the place words only change when you report something from a different location.
Over To You
Now that you’ve seen the rules to convert direct to indirect speech, it’s time to put them into practice. The most efficient way to improve English speaking is to practice what you’ve learned. Join online English-speaking practice classes to gain confidence and mastery in your daily conversations.
Recent Posts
Como usar uma calculadora martingale para melhorar suas estratégias de opções binárias, 35 positive words to describe your best female friend, 20 stylish and popular idioms related to success, how can you teach your child to speak english at home, 40 different ways to say happy birthday.
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- August 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
Related Posts

Broadening Your Vocabulary: Unlocking 40 Altern...

Using Instagram To Learn English: Top 10 Accoun...

50 Commonly Used English Abbreviations For Text...

Never Miss a Blog
Enter your Email ID below to get our insightful blogs into your inbox.

Direct and Indirect speech, Rules, Chart and Exercises
Direct and Indirect speech are ways of narrating the speech of someone to some other person following certain rules. This article covers its types, rules, examples and some exercises on the same.

Table of Contents
Direct and Indirect Speech: In English Grammar, direct and Indirect speech are used in instances when we wish to repeat or convey a speech or statement of some other person. Both direct and indirect speech describes what a third person said or conveyed in the past. Indirect speech is more commonly employed unless it’s a direct quotation, which is consistently enclosed in double quotation marks. Whereas indirect speech is used when you want to convey someone’s statement using your own precise words. It’s worth highlighting that indirect speech is consistently expressed using verbs like “said,” “told,” or “asked.”
Direct and Indirect Speech
There are two types of reported speech in English grammar, they are Direct and Indirect speech. Both speech conveys the speech or statement which was told by some other person. To explain any event, action or scenario we generally convey the sentences quoted by someone in the form of direct and indirect speech. In order to clearly differentiate and make people understand easily, we have detailed the two types of reported speech with examples and exercises below.
Direct Speech
Direct speech is the mode of expression that directly presents the words spoken or quoted by a third person. Generally, direct speech is written inside quotation marks (“”). The quotation is used to differentiate the speech of the third person that has happened in the past. Thus direct speech conveys statements or conversations of someone in the past tense but quoted inside the quotation marks in the present or future tense.
- Kiran said, “I am doing my work.”
- They said, ” We will go for the function.”
- He asked,”Can I make this?”
Indirect Speech
Indirect Speech is used when we convey what someone said in our own words without repeating the actual text of that person. Instead of using quotation marks, the conjunction word, ‘that’ is used. Thus speaker’s words and sentences are reframed into our own words in Indirect speech. Some examples of indirect speech are:
- Direct speech: Kiran said, “I am doing my work.”
- Indirect speech: Kiran said that she is doing her work.
- Direct speech: They said, ” We will go for the function.”
- Indirect speech: They said that they would go to the function.
- Direct speech: He asked, “Can I make this?”
- Indirect speech: He asked whether he can make that.
Rules for Direct and Indirect Speech
There are certain rules and regulations followed while converting a simple direct speech into indirect speech. Certain factors such as Verbs, Tenses, Modals, time, place, and pronouns are also considered while changing. The following are the rules applied when you convert direct speech to indirect speech in English grammar.
Rule-1 : Direct To Indirect Speech Conversion – Reporting Verb
The reporting verb is an important factor to note when changing a direct to an indirect sentence. When the reporting verb is past tense, then the verb inside the quotation is also changed to past when changing a sentence from direct to indirect speech. Examples:
- Direct: He said,’ I am sad.’
- Indirect: He said that he was sad.
An exception is for cases like a universal truth, the tenses remain the same.
- Teena said” The sun rises in the east”.
- Teena said that the sun rises in the east.
If the reporting verb is in present/future tense, then the tense remains the same as in direct speech.
- Direct: She says/will say, ‘I am coming.’
- Indirect: She says/will say she is coming.
Rule 2: Direct Speech to Indirect Speech Conversion – Tenses
If the sentences inside quotes in direct speech are present tense, it is changed to past tense when changed to indirect speech. The rule in the following table is applied while changing tenses from direct speech to reported speech.
Examples of change in Tenses
Rule 4: Direct to Indirect speech Conversion Interrogative sentences
If a sentence starts with a question word like what, when, and why in direct speech, the question word itself acts as the joining class.
- Direct speech: “Where do you live ?” Asked the boy.
- Indirect Speech: The boy enquired where I lived.
Rule 5: Direct to Indirect Speech Conversion Change in Modals
Modal verbs are those verbs that are preceded by another verb, which is the main verb. Can, May, and Must are some examples of Modals. Modals that won’t change are Could, would, should, ought to, might. While changing direct to indirect speech, the Modals change as below:
- Can become could
- May becomes Might
- Must becomes had to (or) would have to
- Direct: She said,” She can sing.”
- Indirect: She said that she could sing.
- Direct: She said,” I should cook the lunch”
- Indirect: She said that she should cook the lunch.
Rule 6: Direct to Indirect speech conversion – pronoun
The first person in Direct speech changes as per the subject of the speech
- Direct: He said, “I am in grade sixth.”
- Indirect: He said that he was in grade sixth.
The second person of Direct speech changes as per the object of the indirect speech.
- Direct: She says to them, “You have achieved your goal.”
- Indirect: She tells them that they have achieved their goal.
If the third person is mentioned in the Direct speech, it does not change in reported speech.
- Direct: He says, “She sings well.”
- Indirect: He says that she sings well.
Rule 7: Direct to indirect speech conversion – Request, Command, Wish and Exclamation.
The imperative words in direct speech change into Infinitives in indirect speech.
- Direct: She said to her ‘Please remove it’.
- Indirect: She requested her to remove that.
Exclamation
- Direct: She said, ‘Alas! I am undone.
- Indirect: She exclaimed sadly that she was broke.
Rule 8: Direct to indirect speech conversion – punctuations
In Direct speech, the words spoken must start with(“) and ends with(.) inside the double inverted commas. All symbols such as question marks, full stops or exclamatory marks should be placed inside the quotes.
- They said. “We are the best”
- She asked, “Can I come with You?”
- He uttered, “Keep Quiet!”
Rule 9: Direct to indirect speech conversion – Change of time
While converting direct speech to Indirect speech, there are certain words to be noted that cannot be used as such in indirect speech. These words get modified into new words which are enlisted below:
- Now becomes Then
- Ago becomes before
- Thus becomes So
- Today becomes That day
- Tomorrow becomes the next day
- Yesterday becomes the day before
- This becomes that
- These become those
- Come becomes go
- Hence becomes thence
- Next week or next month becomes the following week or month
- Direct: He says/will say, ‘My girlfriend came yesterday.’
- Indirect: He says/will say that his girlfriend had come the day before.
Rules for Converting Indirect Speech into Direct Speech:
The following rules should be followed while converting an indirect speech to direct speech:
- Use the reporting verb such as (say, said to) in its correct
- Put a comma before the statement and the first letter of the statement should be in capital
- Insert question marks, quotation marks, exclamation marks and full stops, based on the mood of the
- Remove the conjunctions like (that, too, if or wh ether) wherever necessary .
- Where the reporting verb is in the past tense in indirect, change it to present tense in the direct
- Change the past perfect tense either into the present perfect tense or past tense, as necessary .
Direct and Indirect Speech – Some Exercises
The following are some exercises that students can practice while preparing for their revision tests or board exams.
Q.1. Find out the correct indirect speech for the given sentence.
She said,’ I have cooked this meal.’
- She said that she cooked this meal
- She said that she had cooked that meal.
- She said that I cooked that meal.
- She said that she had cooked this meal.
Answer (2) She said that she had cooked that meal.
Q.2. Choose the correct sentence.
Sanjay said, ‘What a beautiful painting it is’.
- Sanjay exclaimed wonderfully that the painting was very beautiful.
- Sanjay exclaimed with wonder that the painting was very beautiful.
Answer (4) Sanjay exclaimed with wonder that the painting was very beautiful.
Q.3. The correct indirect speech for She asked, “What is the cost of these books?”
- She enquired what was the cost of those books.
- She inquired what was the cost of these books.
- She enquired what is the cost of those books.
- She questioned what was the cost of those books.
Answer (1) She enquired what was the cost of those books.
Q.4. The man said, ‘Oh God! I missed the train today.’
- The man cried that he missed the train that day.
- The man exclaimed in grief that he missed the train today.
- The man said that oh God! he missed that day.
- The man exclaimed with sorrow that he missed the train that day.
Answer (4) The man exclaimed with sorrow that he missed the train that day.
Sharing is caring!
Direct and Indirect speech-FAQs
Q1. what are direct and indirect speech in english.
Ans. Direct speech is a speech that describes what a third person has conveyed or quoted in a direct manner. Generally, direct speech is written inside quotation marks ("").Indirect Speech is used when we convey what someone said in our own words without repeating the actual text of that person.
Q2. In which speech conjunctions are used and what is the purpose?
Ans. The conjunctions are used in Indirect speech. The speaker's words and sentences are reframed into our own words in Indirect speech using conjuctions as connecting words.
Q3. What are modals and what is the significance of using modals?
Ans. Modal verbs are those verbs that are preceded by another verb, which is the main verb. Can, May, and Must are some examples of Modals. While converting direct to indirect speech Can becomes could, May becomes Might, Will becomes Would. Modals that won’t change are Could, would, should, ought to, might.
As Team Lead- Content Writer, I take on leadership within our content creation team, overseeing the development of error-free educational content. My primary responsibility is to produce and analyse high-quality content educating and informing the aspirants about upcoming government exams published on our website. I have more than 6 years experience in content writing wherein 3.5 years of experience in ed-tech content writing.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Board Result 2024
- CBSE 10th Result 2024
- UP Board 10th Result 2024
- MP Board 12th Result 2024
CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 English Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus
CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 10 English Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 SST Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Hindi Syllabus
Exam Date 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- NEET Exam Date 2024
- JEE Mains Exam Date 2024
Latest Posts
Important exams.
- JEE Mains 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- NIMCET 2024
- AP EAMCET 2024
- TS EAMCET 2024
- AP ECET 2024
- TS ECET 2024
- TS PGECET 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- AP Polycet 2024
- TS Polycet 2024
- JEECUP 2024
- Bihar Polytechnic 2024
- Jharkhand Polytechnic 2024
- Responsible Disclosure Program
- Cancellation & Refunds
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Direct and Indirect Speech: Useful Rules and Examples
Are you having trouble understanding the difference between direct and indirect speech? Direct speech is when you quote someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. This can be a tricky concept to grasp, but with a little practice, you’ll be able to use both forms of speech with ease.

Direct and Indirect Speech
When someone speaks, we can report what they said in two ways: direct speech and indirect speech. Direct speech is when we quote the exact words that were spoken, while indirect speech is when we report what was said without using the speaker’s exact words. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I love pizza,” said John. Indirect speech: John said that he loved pizza.
Using direct speech can make your writing more engaging and can help to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion. However, indirect speech can be useful when you want to summarize what someone said or when you don’t have the exact words that were spoken.
To change direct speech to indirect speech, you need to follow some rules. Firstly, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb. Secondly, you need to change the pronouns and adverbs in the reported speech to match the new speaker. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will go to the park,” said Sarah. Indirect speech: Sarah said that she would go to the park.
It’s important to note that when you use indirect speech, you need to use reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked” to indicate who is speaking. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is it?” asked Tom. Indirect speech: Tom asked what time it was.
In summary, understanding direct and indirect speech is crucial for effective communication and writing. Direct speech can be used to convey the speaker’s tone and emotion, while indirect speech can be useful when summarizing what someone said. By following the rules for changing direct speech to indirect speech, you can accurately report what was said while maintaining clarity and readability in your writing.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech
When it comes to reporting speech, there are two ways to go about it: direct and indirect speech. Direct speech is when you report someone’s exact words, while indirect speech is when you report what someone said without using their exact words. Here are some of the key differences between direct and indirect speech:
Change of Pronouns
In direct speech, the pronouns used are those of the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the pronouns have to be changed to reflect the perspective of the reporter. For example:
- Direct speech: “I am going to the store,” said John.
- Indirect speech: John said he was going to the store.
In the above example, the pronoun “I” changes to “he” in indirect speech.
Change of Tenses
Another major difference between direct and indirect speech is the change of tenses. In direct speech, the verb tense used is the same as that used by the original speaker. However, in indirect speech, the verb tense may change depending on the context. For example:
- Direct speech: “I am studying for my exams,” said Sarah.
- Indirect speech: Sarah said she was studying for her exams.
In the above example, the present continuous tense “am studying” changes to the past continuous tense “was studying” in indirect speech.
Change of Time and Place References
When reporting indirect speech, the time and place references may also change. For example:
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” said Tom.
- Indirect speech: Tom said he would meet you at the park the next day.
In the above example, “tomorrow” changes to “the next day” in indirect speech.
Overall, it is important to understand the differences between direct and indirect speech to report speech accurately and effectively. By following the rules of direct and indirect speech, you can convey the intended message of the original speaker.
Converting Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech
When you need to report what someone said in your own words, you can use indirect speech. To convert direct speech into indirect speech, you need to follow a few rules.
Step 1: Remove the Quotation Marks
The first step is to remove the quotation marks that enclose the relayed text. This is because indirect speech does not use the exact words of the speaker.
Step 2: Use a Reporting Verb and a Linker
To indicate that you are reporting what someone said, you need to use a reporting verb such as “said,” “asked,” “told,” or “exclaimed.” You also need to use a linker such as “that” or “whether” to connect the reporting verb to the reported speech.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I love ice cream,” said Mary.
- Indirect speech: Mary said that she loved ice cream.
Step 3: Change the Tense of the Verb
When you use indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verb in the reported speech to match the tense of the reporting verb.
- Indirect speech: John said that he was going to the store.
Step 4: Change the Pronouns
You also need to change the pronouns in the reported speech to match the subject of the reporting verb.
- Direct speech: “Are you busy now?” Tina asked me.
- Indirect speech: Tina asked whether I was busy then.
By following these rules, you can convert direct speech into indirect speech and report what someone said in your own words.
Converting Indirect Speech Into Direct Speech
Converting indirect speech into direct speech involves changing the reported speech to its original form as spoken by the speaker. Here are the steps to follow when converting indirect speech into direct speech:
- Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb used in the indirect speech. This will help you determine the tense of the direct speech.
- Change the pronouns: The next step is to change the pronouns in the indirect speech to match the person speaking in the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “She said that she was going to the store,” the direct speech would be “I am going to the store,” if you are the person speaking.
- Change the tense: Change the tense of the verbs in the indirect speech to match the tense of the direct speech. For example, if the indirect speech is “He said that he would visit tomorrow,” the direct speech would be “He says he will visit tomorrow.”
- Remove the reporting verb and conjunction: In direct speech, there is no need for a reporting verb or conjunction. Simply remove them from the indirect speech to get the direct speech.
Here is an example to illustrate the process:
Indirect Speech: John said that he was tired and wanted to go home.
Direct Speech: “I am tired and want to go home,” John said.
By following these steps, you can easily convert indirect speech into direct speech.
Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech
Direct and indirect speech are two ways to report what someone has said. Direct speech reports the exact words spoken by a person, while indirect speech reports the meaning of what was said. Here are some examples of both types of speech:
Direct Speech Examples
Direct speech is used when you want to report the exact words spoken by someone. It is usually enclosed in quotation marks and is often used in dialogue.
- “I am going to the store,” said Sarah.
- “It’s a beautiful day,” exclaimed John.
- “Please turn off the lights,” Mom told me.
- “I will meet you at the library,” said Tom.
- “We are going to the beach tomorrow,” announced Mary.
Indirect Speech Examples
Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, is used to report what someone said without using their exact words. It is often used in news reports, academic writing, and in situations where you want to paraphrase what someone said.
Here are some examples of indirect speech:
- Sarah said that she was going to the store.
- John exclaimed that it was a beautiful day.
- Mom told me to turn off the lights.
- Tom said that he would meet me at the library.
- Mary announced that they were going to the beach tomorrow.
In indirect speech, the verb tense may change to reflect the time of the reported speech. For example, “I am going to the store” becomes “Sarah said that she was going to the store.” Additionally, the pronouns and possessive adjectives may also change to reflect the speaker and the person being spoken about.
Overall, both direct and indirect speech are important tools for reporting what someone has said. By using these techniques, you can accurately convey the meaning of what was said while also adding your own interpretation and analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is direct and indirect speech?
Direct and indirect speech refer to the ways in which we communicate what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, using quotation marks to indicate that you are quoting someone. Indirect speech, on the other hand, involves reporting what someone has said without using their exact words.
How do you convert direct speech to indirect speech?
To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb, such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.” For example, “I love ice cream,” said Mary (direct speech) can be converted to “Mary said that she loved ice cream” (indirect speech).
What is the difference between direct speech and indirect speech?
The main difference between direct speech and indirect speech is that direct speech uses the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. Direct speech is usually enclosed in quotation marks, while indirect speech is not.
What are some examples of direct and indirect speech?
Some examples of direct speech include “I am going to the store,” said John and “I love pizza,” exclaimed Sarah. Some examples of indirect speech include John said that he was going to the store and Sarah exclaimed that she loved pizza .
What are the rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech?
The rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech include changing the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions. You also need to introduce a reporting verb and use appropriate reporting verbs such as “said,” “told,” or “asked.”
What is a summary of direct and indirect speech?
Direct and indirect speech are two ways of reporting what someone has said. Direct speech involves repeating the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports what someone has said without using their exact words. To convert direct speech to indirect speech, you need to change the tense of the verbs, pronouns, and time expressions and introduce a reporting verb.
You might also like:
- List of Adjectives
- Predicate Adjective
- Superlative Adjectives
Related Posts:

This website is AMNAZING
MY NAAMEE IS KISHU AND I WANTED TO TELL THERE ARE NO EXERCISES AVAILLABLEE BY YOUR WEBSITE PLEASE ADD THEM SSOON FOR OUR STUDENTS CONVIENCE IM A EIGHT GRADER LOVED YOUR EXPLABATIO
sure cries l miss my friend

- All Lessons
- business english
- comprehension
- culture & tips
- expressions
- pronunciation
Learn English Grammar: DIRECT & INDIRECT SPEECH (REPORTED SPEECH)
Test your understanding of this English lesson
15 comments.
I will keep learning.
I made one mistake in quiz Thanks Mrs.Gill for this top-notch clarification of the difference between direct and indirect/reported speech
I made one mistake in this quiz Thank Mrs.Gill for this lesson My mistake was when he asked me to suggest the direct speech and I saw in indirect speech (past perfect), so what I should choose ( the present perfect or past perfect too) for the right as a direct speech
I have 100% accuracy of quiz. Thanks. This was a very interesting lesson.
Thanks Gill ! I got 10 correct out of 10.
Thank you Gill! this was so useful for me. i got 9 out of 10.
10/10 thanks
Thank you Mrs Gill, I’ve got 7 out of 10. I’ve got 2 wrong answer. I did not give my answer for the 1st question but I wrote the correct answer in my paper.
This is going to be a big help for me in improving my English grammar.
By the way, I am a non native English speaker. I hope to see more of you videos about paraphrasing, how to begin to answer questions like how, why identify, describe, outline etc.
Thank you and God bless
I made 1 mistake in the quiz.
Thank you I have got a problem of speaking confidently I always doubt myself 😭
Mrs. Gill, I just want to thank you for these very helpful explanations, Thanks to you, I already know what’s the difference between what we call “Direct speech” and ” Indirect speech. What I keep in mind is: in direct speech, we use quotations and the right personal pronoun whereas, in Indirect, we don’t them, however, we use the third personal pronoun, we use the verb in the past tense as well
Thanks Gill I got 10 correct. I love grammar, without grammar we wouldn’t speak correctly.
Good lesson thank you.
8 out of 10 hehehe
Thank you Gill,this lesson helps me understand the difference between Direct speech and indirect speech.This is going to be a big help for me to improve my grammar in English
about engVid
Learn English for free with 2045 video lessons by experienced teachers. Classes cover English grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, IELTS, TOEFL, and more. Join millions of English learners worldwide who are improving every day with engVid.
- 2-Intermediate
- Privacy Policy
© 2024 LearnVid Inc.
Englishfornoobs.com
English worksheets & lessons for beginners
Direct and Indirect speech: rules and examples
Direct and indirect speech with rules and examples, download all the grammar lessons in one click $27 $19.
In English, to report someone’s words or their own words, you can use direct or indirect speech. These may include statements, questions, orders, advice…
When moving from direct to indirect style, it is often necessary to change personal pronouns, demonstrative and possessive pronouns according to who says what:
- I → he / she
- me → him / her
- my → his / her
- this → that
- mine → his / hers
- ours → theirs
- our → their
Here are some examples:
Note: That is often implied in indirect speech. It is not mandatory to use it, so it is indicated in brackets in this lesson.
Introductory verbs
To relate someone’s words to both direct and indirect speech, you need an introductory verb.
The two most frequent are tell and say, but there are many other possible ones like:
- want to know
Say or tell ?
Be careful to distinguish SAY from TELL . The two verbs may have the same meaning, but their use is different. With TELL, the interlocutor is quoted: the name or pronoun is placed immediately after tell (tell somebody something).
With SAY, the interlocutor is not necessarily quoted; if he is, he is introduced by the preposition to ( say something to somebody ):
- He says (that) he is English.
- He tells me (that) he is English.
However, tell is used in some expressions without mentioning a contact person:
- tell the truth
- tell a story
- tell the time
Note: the wording ‘ He said to me… ‘ is possible but seems clumsy. It is best to use ‘ He told me… ‘.
TIMES MODIFICATIONS
The shift to indirect speech leads to changes in the tense, depending on whether the verb is in the present tense or in the past tense.
If the introductory verb is in the present tense, the tense (or modal) does not change.
- “I’m sorry.” → He says he is sorry.
- “I hate driving” → He says he hates driving.
Be careful, if the statements reported are still true now you must not change the tense!
- He said this morning (that) he hates driving. (= He still hates driving now).
If the introductory verb is in the past, the verb tense changes:
Examples of major changes in time:
The modals could, should, would, might, needn’t, ought to, used to don’t change when used with indirect speech.
Those who change are will → would, can → could, may → might :
- I will come with you. → Tina promised she would come with me.
- I can help you. → He said he could help me.
- It may be a good idea. → I thought it might be a good idea.
* do not change
TIME, PLACE AND DEMONSTRATIVE MARKERS
Expressions of time, place and demonstratives change if the context of indirect speech is different from that of direct speech.
She said “I saw him yesterday.” → She said she had seen him the day before.
Orders and prohibitions to indirect speech
To relate an order or prohibition to indirect speech, verbs such as tell, order or forbid are used… Be careful, remember to replace Don’t by NOT when it is the main verb of the sentence!
For affirmative sentences, use to + infinitive
For negative sentences use not to + infinitive
- Don’t worry! → He told her not to worry.
- He said, “go to bed!” → He ordered the child to go to bed.
- Don’t marry him! → She forbade me to marry him.
- Please don’t be late. → She asked us not to be late.
Questions to the indirect speech
If there is an interrogative word like where/who/when/why… in direct speech, we keep it in indirect speech:
- What are you doing? → She asked me what I was doing.
- Who was that beautifl woman? → He asked me who that beautiful woman had been.
- Where do you live? → He wanted to know where I lived.
- “Why don’t you speak Spanish?” → He asked me why I didn’t speak Spanish.
If it is a closed-ended question or you have to answer yes/no, you use if or whether :
- “Do you like chocolate?” → She asked me if I liked chocolate.
- “Are you living here?” → She asked me if I was living here.
- “Have you ever been to Paris?” → He asked me if I had ever been to Paris.
When the question contains a modal, it is preterite in the reported question:
- How will he react? → He wondered how he would react.
Some examples of indirect questions:
- I wondered what they were talking about.
- I don’t know if they’ll come or not.
OTHER CHANGES
Expressions of advice such as must, should and ought are usually reported using the verbs advise or urge :
- “You must read this book.” → He advised / urged me to read that book.
The expression let’s is usually reported using the verb suggest, with gerund or with should:
- “Let’s go to the cinema.” → He suggested going to the cinema. OR He suggested that we should go to the cinema.
©Englishfornoobs.com
Tags: Grammar
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
English Grammar & Vocabulary
Lessons & Practice Tests
Direct and Indirect Speech – Rules and Examples
13th June 2020 By Edify English Leave a Comment
Any word spoken by a speaker can be written in two different ways. Those two are direct and indirect speech. Direct Speech is when the speaker’s actual words are quoted and these words are put in inverted commas (“…..”) while Indirect Speech is when the speaker’s words are said indirectly with the same meaning without repeating the exact words. For Example, the statement in direct speech She said to me, “I am going to the park” changes into She told me that she was going to the park in indirect speech.

Basic Changes while changing from Direct speech to indirect speech
- The comma ( , )after the reporting verb is removed and the conjunction that is added in the indirect speech.
- If the direct speech contains ‘said to’ , it will be converted into ‘told’ in the indirect speech.
- The quotation marks (Inverted commas) are to be removed in the indirect speech.
- I becomes He/ She
- We becomes they
- You becomes He / She/ They
- Me becomes Him/ he r (Depending on the gender in the direct speech)
- My becomes His/ Her .
- Our becomes their
- Us becomes them
- Your becomes His/ her/ their .
Rules in changing a sentence from Direct and Indirect Speech
- Rule 1: The Verb in the simple present tense in the direct speech changes into the simple past tense in indirect speech
Example: He said to me, “I am happy” becomes He told me that he was happy
(The verb in the direct speech ‘am’ is converted into ‘was’.)
- Rule 2: The verb in the simple past tense becomes past perfect tense in indirect speech.
Example: He said to me, “I was happy” changes into He told me that he had been happy
- Rule 3: A present continuous tense in direct speech becomes past continuous tense in indirect speech.
Example: The peon said, “The professor is teaching in that classroom” changes into The peon said that the professor was teaching in that classroom.
- Rule 4: If the direct speech contains present perfect tense, it changes into the past perfect tense in indirect speech.
Example: She said, “I have passed the test” becomes She said that she had passed the test.
- Rule 5: If the direct speech contains a statement talking about a universal truth or a factual statement, there will be no change of tense in indirect speech.
Example: The teacher said, “The sun rises in the East” becomes The teacher said that the sun rises in the east in indirect speech.
Example: Samuel said, “I know the university’s address.” and the indirect speech for that is Samuel said that he knows the university’s address
Rules for converting Interrogatory sentences
- Rule 6: While converting interrogative sentences, the verb ‘said to’ becomes ‘asked’ and if/ whether will come in the place of ‘that’. The connecting word ‘that’ will not be used in indirect speech. Also, the interrogation mark (?) is not repeated in the indirect speech.
Example: He said to her, “Will you marry me?” changes into He asked her whether she would marry him in the indirect speech.
Rules for Converting Imperative Sentences
- Rule 7: During the conversion of imperative sentences, the verb “said to” is changed into ordered, advised, requested, suggested, proposed, etc. depending on the situation. Also, the connecting word ‘that’ is not used. Instead of that, ‘ to’ is used before the reporting verb.
Example: My father said to me, “prepare well for your examination” . It can be converted to My father advised me to prepare well for my examination.
Rules for Converting Exclamatory Sentences
- Rule 8: For exclamatory sentences, the verb is converted into: exclaimed with joy or sorrow or with surprise, wished, prayed, applauded,/ etc. The exclamatory words and the exclamation are not mentioned anymore in the indirect speech. For example,
Example: The coach said, “Hurrah! we won the match!” is changed as The coach exclaimed with joy that we had won the match.
These are the changes in helping verbs while changing from Direct and Indirect Speech
Note: There is no change in the helping verbs “would, should, could, might, had” in the direct speech and they remain the s ame in indirect speech as well.
Changes in Time and Place
Cha nges in pronoun s
The changes in pronouns in indirect speech depends on the subject and the object of the reporting verb.
- Rule 1: The first person of reported speech changes based on the subject of the reporting verb.
Example: She said, “I watched a movie” can be converted into She said that she had watched a movie . Hence, the first person in the direct speech “I” has become “she” based on the subject.
Had there been “he” instead of “she”, the first person in reported speech changes accordingly into “he”.
- Rule 2: The second person in reported speech changes based on the object of the reporting verb.
Example: She said to me, “You watched a movie” can be converted into She told me that I had watched a movie.
- Rule 3 : The third person in the reported speech remains unchanged.
Example: I said to her, “He will play Chess” can be converted into I told her that he would play Chess.
Stay tuned for more examples of direct and indirect speech.
For an extensive material on tenses, Click here
Follow us on Facebook
Share this:
Subscribe to blog via email.
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
- Athabasca University
- English Grammar Handbook
- Concise ESL Support
Direct and indirect speech
- Write Site - Home
- Staff and contact info
- Write Site dropbox
- RealTime writing coaching
- Writing forum
- Webinar schedule
- Lessons and videos
- Basic grammar: Parts of speech
- Words often confused and misused
- Recognition of sentence parts
- Transitional devices
- Common sentence errors
- Punctuation
- Word mechanics
- Vocabulary and spelling
- Introduction
- Conditional and hypothetical constructions
- Infinitives and gerunds
- Irregular verbs
- Modals and related expressions
- Passive verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Prepositions
- Pronunciation
- Verb tenses
- Supplementary resources
- Critical thinking, reading and writing
- The writing process
- Research writing
- Writing in the disciplines
- Genres common to academic writing
- Argumentative essay
- Argumentation structure
- Expository writing
- Analytical film review process
- Conducting and writing up interviews
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Library basics
- Studying writing at AU
- Writing resources
- Writing courses
- Assess your writing and language skills
- Marking guide for writing assignments
When using indirect or reported speech, the form changes. Usually indirect speech is introduced by the verb said , as in I said , Bill said , or they said . Using the verb say in this tense, indicates that something was said in the past. In these cases, the main verb in the reported sentence is put in the past. If the main verb is already in a past tense, then the tense changes to another past tense; it can almost be seen as moving even further into the past.
Verb tense changes also characterize other situations using indirect speech. Note the changes shown in the chart and see the table below for examples. With indirect speech, the use of that is optional.
The situation changes if instead of the common said another part of the very to say is used. In that case the verb tenses usually remain the same. Some examples of this situation are given below.
Another situation is the one in which modal constructions are used. If the verb said is used, then the form of the modal, or another modal that has a past meaning is used.
While not all the possibilities have been listed here, there are enough to provide examples of the main rules governing the use of indirect or reported speech. For other situations, try to extrapolate from the examples here, or better still, refer to a good grammar text or reference book.
Some other verbs that can be used to introduce direct speech are ask, report, tell, announce, suggest, and inquire. They are not used interchangeably; check a grammar or usage book for further information.
Updated September 11, 2023 by Digital & Web Operations, University Relations ( [email protected] )
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
Direct Indirect Speech
- Verbs and tenses
- Prepositions
- Articles,Vowels and Consonants
- Active Voice and Passive Voice
- Gender-Masculine and Feminine
- Singular and Plural Nouns
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Direct Indirect Speech for Past Perfect Continuous
Last updated at April 2, 2024 by Teachoo

- In this case,there is no change
- Past Perfect Continuous of Direct Speech remains Past Perfect Continuous of Indirect Speech
The teacher said"I had been watching you"
The teacher said I had been watching you
The girl said"I had been going to Aerobics classes"
The girl said I had been going to Aerobics classes
The lady said "She had been getting fat"
The lady said She had been getting fat
The doctor said "You had not been taking medicines"
The doctor said You had not been taking medicines

CA Maninder Singh
CA Maninder Singh is a Chartered Accountant for the past 13 years. He also provides Accounts Tax GST Training in Delhi, Kerala and online.
Get E-filing Return Practice
Watch videos and do assignments
Add more skills to your resume
Get Professional Certification in Accounts and Taxation
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As a rule, whenever we change a sentence from quoted speech into reported speech, we go one tense back. But if we have past perfect tense in direct speech, we use the same tense in indirect speech. Affirmatives. Direct speech: RP, +, + S + had + V3 + ROTS. I said to him, "They had played cricket.". Indirect speech: RP + that + S + had + V3 ...
If reported verb is in Past Tense & reported speech is in Past Perfect Tense, it will not change. e.g. Direct Speech. Indirect Speech. Abhi said to Nidhi, "Had you paid the fee?". Abhi asked Nidhi if she had paid the fee. Mr Roy said, "I had bought a house.". Mr Roy said that he had bought a house.
3. Change the tense of the verb in the reported speech, if needed. If the reporting verb is in the past tense, you should change the tense of the verb inside the reported speech into its past tense. This is not necessary if the reporting verb is in the present or future tense. Examples: Direct Speech: He said, "I am watching a new TV series."
Join Teachoo Black. In this case,there is no changeIn this case,Past Perfect of Direct Speech remains Past Perfect of Indirect SpeechThe teenager said"I had pizza for lunch"-a-The teenager said that he had pizza for lunch-ea-The rich man said"I had 2 private jets-a-The rich man said that he had 2 private jets-ea-Father.
Rule 3: Reporting Verb Request, Advise, Order, and Beg. To report imperative sentences, "Request", "Advise", "Order", and "beg" are often used. Direct: He said to me, "Go home at once". Indirect: He ordered me to go home at once. Direct: She said, "Do not run in the sun". Indirect: She advised not to run in the sun.".
Watch my reported speech video: Here's how it works: We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
3. The tenses of direct speech do not change if the reporting verb is in future tense or present tense. Direct to indirect speech example: Direct: She says/will say, „she is going‟ Indirect: She says/will say she is going. Rule 2 - Direct Speech to Indirect Speech conversion - Present Tense. Present Perfect Changes to Past Perfect.
4. Simple past tense to past perfect tense. When the direct speech is in the Simple Past tense, it is changed to the Past perfect tense in the indirect speech. Direct and indirect speech examples: Direct speech: "We finished the task on time," he said to me. Indirect speech: He told me that they had finished the task on time.
The simple past tense in the direct speech becomes the past perfect tense in the indirect speech. Direct speech: He said, 'The horse died in the night.' Indirect speech: He said that the horse had died in the night. Notes. The tenses may not change if the statement is still relevant or if it is a universal truth. We can often choose whether ...
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Tense backshift. As can be seen in the examples above, the verbs in the present perfect, present continuous and present simple tenses in the original statements changed into their corresponding past equivalents (past perfect, past continuous and past simple) in indirect speech. This process is called tense backshift.
The speech has two main types, Direct speech, and Indirect speech, respectively. These two ways of narration of spoken words are also called Direct and Indirect speech, also known as Direct and Indirect narrations. ... Simple past tense will change into the past perfect tense. Direct: He said, "They came to meet me." ...
If you notice these examples carefully, you can see that the tense changes when converting from direct to indirect speech. To illustrate this point, in the following example, direct speech is in the present simple tense, while indirect speech is written in the simple past tense. Direct Speech: "I live in the city centre."
Direct: She says/will say, 'I am coming.'. Indirect: She says/will say she is coming. Rule 2: Direct Speech to Indirect Speech Conversion - Tenses. If the sentences inside quotes in direct speech are present tense, it is changed to past tense when changed to indirect speech.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech. Change of Pronouns. Change of Tenses. Change of Time and Place References. Converting Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech. Step 1: Remove the Quotation Marks. Step 2: Use a Reporting Verb and a Linker. Step 3: Change the Tense of the Verb. Step 4: Change the Pronouns.
Test your understanding of the English lesson by answering these questions. You will get the answers and your score at the end of the quiz. Which of the following would be the direct speech equivalent of "She said that she hadn't decided when to go swimming.". She said "I can't decide when to go swimming."She said "I didn't decide ...
The shift to indirect speech leads to changes in the tense, depending on whether the verb is in the present tense or in the past tense. If the introductory verb is in the present tense, the tense (or modal) does not change. "I'm sorry." → He says he is sorry. "I hate driving" → He says he hates driving.
Rule 1: The Verb in the simple present tense in the direct speech changes into the simple past tense in indirect speech. Example: He said to me, "I am happy" becomes He told me that he was happy. (The verb in the direct speech 'am' is converted into 'was'.) Rule 2: The verb in the simple past tense becomes past perfect tense in ...
Rule 1 - Direct To Indirect Speech Conversion - Reporting Verb. When the reporting verb of direct speech is in past tense then all the present tenses are changed to the corresponding past tense in indirect speech. Direct to indirect speech example: Direct: She said, 'I am happy'. Indirect: She said (that) she was happy.
AU is Canada's Open University, offering open and flexible distance learning with world-class online courses, undergraduate and graduate degree programs, and professional development options. A look into direct and indirect speech and how its used.
Indirect speech: He said that Sara was going to school. (Tense changed) Rules for change of tense and examples are as follows: Present simple tense into Past simple tense. Present continuous tense into Past continuous tense. Present perfect tense into Past perfect tense. Present perfect continuous tense into Past perfect continuous tense.
Join Teachoo Black. In this case,there is no changePast Perfect Continuous of Direct Speech remains Past Perfect Continuous of Indirect SpeechThe teacher said"I had been watching you"-a-The teacher said I had been watching you-ea-The girl said"I had been going to Aerobics classes"-a-The girl said I had been going to Ae.