share this!
August 16, 2021

Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
by Sara M Moniuszko

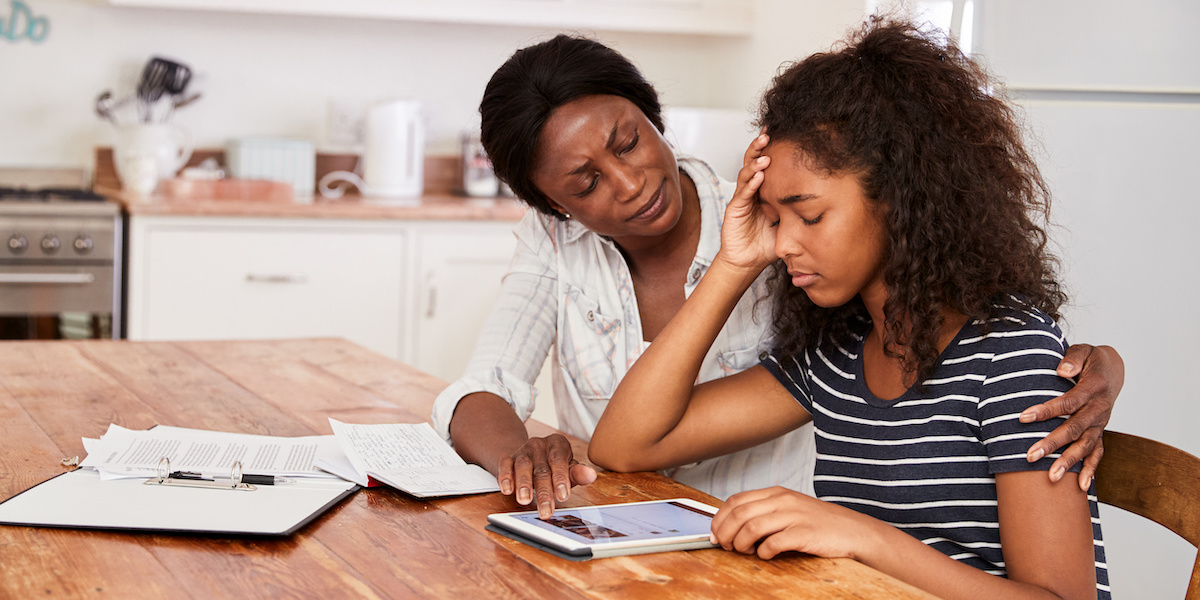
It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors
A cosmic 'speed camera' just revealed the staggering speed of neutron star jets in a world first
4 hours ago
Saturday Citations: 100-year-old milk, hot qubits and another banger from the Event Horizon Telescope project
7 hours ago

Curiosity rover searches for new clues about Mars' ancient water
10 hours ago

Study says since 1979 climate change has made heat waves last longer, spike hotter, hurt more people

Scientist taps into lobsters' unusual habits to conquer the more than 120-year quest to farm them
23 hours ago

Blind people can hear and feel April's total solar eclipse with new technology
Mar 29, 2024

Mapping the best route for a spacecraft traveling beyond the sun's sphere of influence
Researchers outline new approach in search for dark matter through future DUNE research project

Researchers reveal evolutionary path of important proteins
Study identifies protein responsible for gas vesicle clustering in bacteria
Relevant physicsforums posts, how is physics taught without calculus.
20 hours ago
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Mar 24, 2024
The changing physics curriculum in 1961
Suggestions for using math puzzles to stimulate my math students.
Mar 21, 2024
The New California Math Framework: Another Step Backwards?
Mar 14, 2024
Rant about working in the tutoring lab: How should I deal with this?
Feb 25, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you
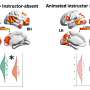
Research reveals significant effects of onscreen instructors during video classes in aiding student learning
Mar 25, 2024

Prestigious journals make it hard for scientists who don't speak English to get published, study finds
Mar 23, 2024

Using Twitter/X to promote research findings found to have little impact on number of citations
Mar 22, 2024

Gender and racial discrimination uncovered in leadership positions at Australia's leading universities
Mar 15, 2024
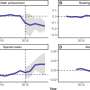
Study finds children in Flint experienced educational declines even if they did not have lead pipes

Could iPhones replace microscopes in early STEM education?
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
Improving lives through learning
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .

Search form
- Find Stories
- For Journalists
Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework
A Stanford researcher found that students in high-achieving communities who spend too much time on homework experience more stress, physical health problems, a lack of balance and even alienation from society. More than two hours of homework a night may be counterproductive, according to the study.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
• Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
• Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
• Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.

Homework Struggles May Not Be a Behavior Problem
Exploring some options to understand and help..
Posted August 2, 2022 | Reviewed by Abigail Fagan
- Mental health challenges and neurodevelopmental differences directly affect children's ability to do homework.
- Understanding what difficulties are getting in the way—beyond the usual explanation of a behavior problem—is key.
- Sleep and mental health needs can take priority over homework completion.
Chelsea was in 10th grade the first time I told her directly to stop doing her homework and get some sleep. I had been working with her since she was in middle school, treating her anxiety disorder. She deeply feared disappointing anyone—especially her teachers—and spent hours trying to finish homework perfectly. The more tired and anxious she got, the harder it got for her to finish the assignments.

One night Chelsea called me in despair, feeling hopeless. She was exhausted and couldn’t think straight. She felt like a failure and that she was a burden to everyone because she couldn’t finish her homework.
She was shocked when I told her that my prescription for her was to go to sleep now—not to figure out how to finish her work. I told her to leave her homework incomplete and go to sleep. We briefly discussed how we would figure it out the next day, with her mom and her teachers. At that moment, it clicked for her that it was futile to keep working—because nothing was getting done.
This was an inflection point for her awareness of when she was emotionally over-cooked and when she needed to stop and take a break or get some sleep. We repeated versions of this phone call several times over the course of her high school and college years, but she got much better at being able to do this for herself most of the time.
When Mental Health Symptoms Interfere with Homework
Kids with mental health or neurodevelopmental challenges often struggle mightily with homework. Challenges can come up in every step of the homework process, including, but not limited to:
- Remembering and tracking assignments and materials
- Getting the mental energy/organization to start homework
- Filtering distractions enough to persist with assignments
- Understanding unspoken or implied parts of the homework
- Remembering to bring finished homework to class
- Being in class long enough to know the material
- Tolerating the fear of not knowing or failing
- Not giving up the assignment because of a panic attack
- Tolerating frustration—such as not understanding—without emotional dysregulation
- Being able to ask for help—from a peer or a teacher and not being afraid to reach out
This list is hardly comprehensive. ADHD , autism spectrum disorder, social anxiety , generalized anxiety, panic disorder, depression , dysregulation, and a range of other neurodevelopmental and mental health challenges cause numerous learning differences and symptoms that can specifically and frequently interfere with getting homework done.

The Usual Diagnosis for Homework Problems is "Not Trying Hard Enough"
Unfortunately, when kids frequently struggle to meet homework demands, teachers and parents typically default to one explanation of the problem: The child is making a choice not to do their homework. That is the default “diagnosis” in classrooms and living rooms. And once this framework is drawn, the student is often seen as not trying hard enough, disrespectful, manipulative, or just plain lazy.
The fundamental disconnect here is that the diagnosis of homework struggles as a behavioral choice is, in fact, only one explanation, while there are so many other diagnoses and differences that impair children's ability to consistently do their homework. If we are trying to create solutions based on only one understanding of the problem, the solutions will not work. More devastatingly, the wrong solutions can worsen the child’s mental health and their long-term engagement with school and learning.
To be clear, we aren’t talking about children who sometimes struggle with or skip homework—kids who can change and adapt their behaviors and patterns in response to the outcomes of that struggle. For this discussion, we are talking about children with mental health and/or neurodevelopmental symptoms and challenges that create chronic difficulties with meeting homework demands.
How Can You Help a Child Who Struggles with Homework?
How can you help your child who is struggling to meet homework demands because of their ADHD, depression, anxiety, OCD , school avoidance, or any other neurodevelopmental or mental health differences? Let’s break this down into two broad areas—things you can do at home, and things you can do in communication with the school.

Helping at Home
The following suggestions for managing school demands at home can feel counterintuitive to parents—because we usually focus on helping our kids to complete their tasks. But mental health needs jump the line ahead of task completion. And starting at home will be key to developing an idea of what needs to change at school.
- Set an end time in the evening after which no more homework will be attempted. Kids need time to decompress and they need sleep—and pushing homework too close to or past bedtime doesn’t serve their educational needs. Even if your child hasn’t been able to approach the homework at all, even if they have avoided and argued the whole evening, it is still important for everyone to have a predictable time to shut down the whole process.
- If there are arguments almost every night about homework, if your child isn’t starting homework or finishing it, reframe it from failure into information. It’s data to put into problem-solving. We need to consider other possible explanations besides “behavioral choice” when trying to understand the problem and create effective solutions. What problems are getting in the way of our child’s meeting homework demands that their peers are meeting most of the time?
- Try not to argue about homework. If you can check your own anxiety and frustration, it can be more productive to ally with your child and be curious with them. Kids usually can’t tell you a clear “why” but maybe they can tell you how they are feeling and what they are thinking. And if your child can’t talk about it or just keeps saying “I don't know,” try not to push. Come back another time. Rushing, forcing, yelling, and threatening will predictably not help kids do homework.

Helping at School
The second area to explore when your neurodiverse child struggles frequently with homework is building communication and connections with school and teachers. Some places to focus on include the following.
- Label your child’s diagnoses and break down specific symptoms for the teachers and school team. Nonjudgmental, but specific language is essential for teachers to understand your child’s struggles. Breaking their challenges down into the problems specific to homework can help with building solutions. As your child gets older, help them identify their difficulties and communicate them to teachers.
- Let teachers and the school team know that your child’s mental health needs—including sleep—take priority over finishing homework. If your child is always struggling to complete homework and get enough sleep, or if completing homework is leading to emotional meltdowns every night, adjusting their homework demands will be more successful than continuing to push them into sleep deprivation or meltdowns.
- Request a child study team evaluation to determine if your child qualifies for services under special education law such as an IEP, or accommodations through section 504—and be sure that homework adjustments are included in any plan. Or if such a plan is already in place, be clear that modification of homework expectations needs to be part of it.
The Long-Term Story
I still work with Chelsea and she recently mentioned how those conversations so many years ago are still part of how she approaches work tasks or other demands that are spiking her anxiety when she finds herself in a vortex of distress. She stops what she is doing and prioritizes reducing her anxiety—whether it’s a break during her day or an ending to the task for the evening. She sees that this is crucial to managing her anxiety in her life and still succeeding at what she is doing.
Task completion at all costs is not a solution for kids with emotional needs. Her story (and the story of many of my patients) make this crystal clear.

Candida Fink, M.D. , is board certified in child/adolescent and general psychiatry. She practices in New York and has co-authored two books— The Ups and Downs of Raising a Bipolar Child and Bipolar Disorder for Dummies.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
The Truth About Homework Stress: What Parents & Students Need to Know
- Fact Checked
Written by:
published on:
- December 21, 2023
Updated on:
- January 9, 2024
Looking for a therapist?
Homework is generally given out to ensure that students take time to review and remember the days lessons. It can help improve on a student’s general performance and enhance traits like self-discipline and independent problem solving.
Parents are able to see what their children are doing in school, while also helping teachers determine how well the lesson material is being learned. Homework is quite beneficial when used the right way and can improve student performance.
This well intentioned practice can turn sour if it’s not handled the right way. Studies show that if a student is inundated with too much homework, not only do they get lower scores, but they are more likely to get stressed.
The age at which homework stress is affecting students is getting lower, some even as low as kindergarten. Makes you wonder what could a five year old possibly need to review as homework?
One of the speculated reasons for this stress is that the complexity of what a student is expected to learn is increasing, while the breaks for working out excess energy are reduced. Students are getting significantly more homework than recommended by the education leaders, some even nearly three times more.
To make matters worse, teachers may give homework that is both time consuming and will keep students busy while being totally non-productive.
Remedial work like telling students to copy notes word for word from their text books will do nothing to improve their grades or help them progress. It just adds unnecessary stress.
Explore emotional well-being with BetterHelp – your partner in affordable online therapy. With 30,000+ licensed therapists and plans starting from only $65 per week, BetterHelp makes self-care accessible to all. Complete the questionnaire to match with the right therapist.
Effects of homework stress at home
Both parents and students tend to get stressed out at the beginning of a new school year due to the impending arrival of homework.
Nightly battles centered on finishing assignments are a household routine in houses with students.
Research has found that too much homework can negatively affect children. In creating a lack of balance between play time and time spent doing homework, a child can get headaches, sleep deprivation or even ulcers.
And homework stress doesn’t just impact grade schoolers. College students are also affected, and the stress is affecting their academic performance.
Even the parent’s confidence in their abilities to help their children with homework suffers due increasing stress levels in the household.
Fights and conflict over homework are more likely in families where parents do not have at least a college degree. When the child needs assistance, they have to turn to their older siblings who might already be bombarded with their own homework.
Parents who have a college degree feel more confident in approaching the school and discussing the appropriate amount of school work.
“It seems that homework being assigned discriminates against parents who don’t have college degree, parents who have English as their second language and against parents who are poor.” Said Stephanie Donaldson Pressman, the contributing editor of the study and clinical director of the New England Center for Pediatric Psychology.
With all the stress associated with homework, it’s not surprising that some parents have opted not to let their children do homework. Parents that have instituted a no-homework policy have stated that it has taken a lot of the stress out of their evenings.
The recommended amount homework
The standard endorsed by the National Education Association is called the “10 minute rule”; 10 minutes per grade level per night. This recommendation was made after a number of studies were done on the effects of too much homework on families.
The 10 minute rule basically means 10 minutes of homework in the first grade, 20 minute for the second grade all the way up to 120 minutes for senior year in high school. Note that no homework is endorsed in classes under the first grade.
Parents reported first graders were spending around half an hour on homework each night, and kindergarteners spent 25 minutes a night on assignments according to a study carried out by Brown University.
Making a five year old sit still for half an hour is very difficult as they are at the age where they just want to move around and play.
A child who is exposed to 4-5 hours of homework after school is less likely to find the time to go out and play with their friends, which leads to accumulation of stress energy in the body.
Their social life also suffers because between the time spent at school and doing homework, a child will hardly have the time to pursue hobbies. They may also develop a negative attitude towards learning.
The research highlighted that 56% of students consider homework a primary source of stress.
And if you’re curious how the U.S stacks up against other countries in regards to how much time children spend on homework, it’s pretty high on the list .
Signs to look out for on a student that has homework stress
Since not every student is affected by homework stress in the same way, it’s important to be aware of some of the signs your child might be mentally drained from too much homework.
Here are some common signs of homework stress:
- Sleep disturbances
- Frequent stomachaches and headaches
- Decreased appetite or changed eating habits
- New or recurring fears
- Not able to relax
- Regressing to behavior they had when younger
- Bursts of anger crying or whining
- Becoming withdrawn while others may become clingy
- Drastic changes in academic performance
- Having trouble concentrating or completing homework
- Constantly complains about their ability to do homework
If you’re a parent and notice any of these signs in your child, step in to find out what’s going on and if homework is the source of their stress.
If you’re a student, pay attention if you start experiencing any of these symptoms as a result of your homework load. Don’t be afraid to ask your teacher or parents for help if the stress of homework becomes too much for you.
What parents do wrong when it comes to homework stress
Most parents push their children to do more and be more, without considering the damage being done by this kind of pressure.
Some think that homework brought home is always something the children can deal with on their own. If the child cannot handle their homework then these parents get angry and make the child feel stupid.
This may lead to more arguing and increased dislike of homework in the household. Ultimately the child develops an even worse attitude towards homework.
Another common mistake parents make is never questioning the amount of homework their children get, or how much time they spend on it. It’s easy to just assume whatever the teacher assigned is adequate, but as we mentioned earlier, that’s not always the case.
Be proactive and involved with your child’s homework. If you notice they’re spending hours every night on homework, ask them about it. Just because they don’t complain doesn’t mean there isn’t a problem.
How can parents help?
- While every parent wants their child to become successful and achieve the very best, it’s important to pull back on the mounting pressure and remember that they’re still just kids. They need time out to release their stress and connect with other children.
- Many children may be afraid to admit that they’re overwhelmed by homework because they might be misconstrued as failures. The best thing a parent can do is make home a safe place for children to express themselves freely. You can do this by lending a listening ear and not judging your kids.
- Parents can also take the initiative to let the school know that they’re unhappy with the amount of homework being given. Even if you don’t feel comfortable complaining, you can approach the school through the parent-teacher association available and request your representative to plead your case.
- It may not be all the subjects that are causing your child to get stressed. Parents should find out if there is a specific subject of homework that is causing stress. You could also consult with other parents to see what they can do to fix the situation. It may be the amount or the content that causes stress, so the first step is identifying the problem.
- Work with your child to create a schedule for getting homework done on time. You can set a specific period of time for homework, and schedule time for other activities too. Strike a balance between work and play.
- Understanding that your child is stressed about homework doesn’t mean you have to allow them not to try. Let them sit down and work on it as much as they’re able to, and recruit help from the older siblings or a neighbor if possible.
- Check out these resources to help your child with their homework .
The main idea here is to not abolish homework completely, but to review the amount and quality of homework being given out. Stress, depression and lower grades are the last things parents want for their children.
The schools and parents need to work together to find a solution to this obvious problem.
Take the stress test!
Join the Find-a-therapist community and get access to our free stress assessment!
Additional Resources
Online therapy.
Discover a path to emotional well-being with BetterHelp – your partner in convenient and affordable online therapy. With a vast network of 30,000+ licensed therapists, they’re committed to helping you find the one to support your needs. Take advantage of their Free Online Assessment, and connect with a therapist who truly understands you. Begin your journey today.
Relationship Counceling
Whether you’re facing communication challenges, trust issues, or simply seeking to strengthen your connection, ReGain’ s experienced therapists are here to guide you and your partner toward a healthier, happier connection from the comfort of your own space. Get started.
Therapist Directory
Discover the perfect therapist who aligns with your goals and preferences, allowing you to take charge of your mental health. Whether you’re searching for a specialist based on your unique needs, experience level, insurance coverage, budget, or location, our user-friendly platform has you covered. Search here.
About the author
You might also be interested in
6 Little Known Things Mindful People Do Differently
Structural Family Therapy: 5 Techniques and Applications
What Does the Ensō Circle Mean?
Disclaimers
Online Therapy, Your Way
Follow us on social media
We may receive a commission if you click on and become a paying customer of a therapy service that we mention.
The information contained in Find A Therapist is general in nature and is not medical advice. Please seek immediate in-person help if you are in a crisis situation.
Therapy Categories
More information
If you are in a life threatening situation – don’t use this site. Call +1 (800) 273-8255 or check these resources to get immediate help.
US South Carolina
Recently viewed courses
Recently viewed.
Find Your Dream School
This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
COVID-19 Update: To help students through this crisis, The Princeton Review will continue our "Enroll with Confidence" refund policies. For full details, please click here.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., how to manage homework stress.
Feeling overwhelmed by your nightly homework grind? You’re not alone. Our Student Life in America survey results show that teens spend a third of their study time feeling worried, stressed, or stuck. If you’re spending close to four hours a night on your homework (the national average), that’s over an hour spent spent feeling panicky and still not getting your work done. Homework anxiety can become a self-fulfilling prophecy: If you’re already convinced that calculus is unconquerable, that anxiety can actually block your ability to learn the material.

Whether your anxiety is related to handling your workload (we know you’re getting more homework than ever!), mastering a particular subject like statistics, or getting great grades for your college application, stress doesn’t have to go hand-in-hand with studying .
In fact, a study by Stanford University School of Medicine and published in The Journal of Neuroscience shows that a student’s fear of math (and, yes, this fear is completely real and can be detectable in scans of the brain) can be eased by a one-on-one math tutoring program. At The Princeton Review this wasn’t news to us! Our online tutors are on-call 24/7 for students working on everything from AP Chemistry to Pre-Calc. Here’s a roundup of what our students have to say about managing homework stress by working one-one-one with our expert tutors .
1. Work the Best Way for YOU
From the way you decorate your room to the way you like to study, you have a style all your own:
"I cannot thank Christopher enough! I felt so anxious and stressed trying to work on my personal statement, and he made every effort to help me realize my strengths and focus on writing in a way that honored my personality. I wanted to give up, but he was patient with me and it made the difference."
"[My] tutor was 1000000000000% great . . . He made me feel important and fixed all of my mistakes and adapted to my learning style . . . I have so much confidence for my midterms that I was so stressed out about."
"I liked how the tutor asked me how was I starting the problem and allowed me to share what I was doing and what I had. The tutor was able to guide me from there and break down the steps and I got the answer all on my own and the tutor double checked it... saved me from tears and stress."
2. Study Smarter, Not Harder
If you’ve read the chapter in your history textbook twice and aren’t retaining the material, don’t assume the third time will be the charm. Our tutors will help you break the pattern, and learn ways to study more efficiently:
"[My] tutor has given me an easier, less stressful way of seeing math problems. It is like my eyes have opened up."
"I was so lost in this part of math but within minutes the tutor had me at ease and I get it now. I wasn't even with her maybe 30 minutes or so, and she helped me figure out what I have been stressing over for the past almost two days."
"I can not stress how helpful it is to have a live tutor available. Math was never and still isn't my favorite subject, but I know I need to take it. Being able to talk to someone and have them walk you through the steps on how to solve a problem is a huge weight lifted off of my shoulder."
3. Get Help in a Pinch
Because sometimes you need a hand RIGHT NOW:
"I was lost and stressed because I have a test tomorrow and did not understand the problems. I fully get it now!"
"My tutor was great. I was freaking out and stressed out about the entire assignment, but she really helped me to pull it together. I am excited to turn my paper in tomorrow."
"This was so helpful to have a live person to validate my understanding of the formulas I need to use before actually submitting my homework and getting it incorrect. My stress level reduced greatly with a project deadline due date."
4. Benefit from a Calming Presence
From PhDs and Ivy Leaguers to doctors and teachers, our tutors are experts in their fields, and they know how to keep your anxiety at bay:
"I really like that the tutors are real people and some of them help lighten the stress by making jokes or having quirky/witty things to say. That helps when you think you're messing up! Gives you a reprieve from your brain jumbling everything together!"
"He seemed understanding and empathetic to my situation. That means a lot to a new student who is under stress."
"She was very thorough in explaining her suggestions as well as asking questions and leaving the changes up to me, which I really appreciated. She was very encouraging and motivating which helped with keeping me positive about my paper and knowing that I am not alone in my struggles. She definitely eased my worries and stress. She was wonderful!"
5. Practice Makes Perfect
The Stanford study shows that repeated exposure to math problems through one-on-one tutoring helped students relieve their math anxiety (the authors’ analogy was how a fear of spiders can be treated with repeated exposure to spiders in a safe environment). Find a tutor you love, and come back to keep practicing:
"Love this site once again. It’s so helpful and this is the first time in years when I don’t stress about my frustration with HW because I know this site will always be here to help me."
"I've been using this service since I was in seventh grade and now I am a Freshman in High School. School has just started and I am already using this site again! :) This site is so dependable. I love it so much and it’s a lot easier than having an actual teacher sitting there hovering over you, waiting for you to finish the problem."
"I can always rely on this site to help me when I'm confused, and it always makes me feel more confident in the work I'm doing in school."
Stuck on homework?
Try an online tutoring session with one of our experts, and get homework help in 40+ subjects.
Try a Free Session
- Tutoring
- College
- Applying to College

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial, what would you score on the mcat today.
Thank you! Look for the MCAT Review Guide in your inbox.
I already know my score.
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- Local Offices
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.

Transforming the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses.
Información en español
Celebrating 75 Years! Learn More >>
- Health Topics
- Brochures and Fact Sheets
- Help for Mental Illnesses
- Clinical Trials
I’m So Stressed Out! Fact Sheet

- Download PDF
- Order a free hardcopy
Feeling overwhelmed? Read this fact sheet to learn whether it’s stress or anxiety, and what you can do to cope.
Is it stress or anxiety?
Life can be stressful—you may feel stressed about performance at school, traumatic events (such as a pandemic, a natural disaster, or an act of violence), or a life change. Everyone feels stress from time to time.
What is stress? Stress is the physical or mental response to an external cause, such as having a lot of homework or having an illness. A stressor may be a one-time or short-term occurrence, or it can happen repeatedly over a long time.
What is anxiety? Anxiety is your body's reaction to stress and can occur even if there is no current threat.
If that anxiety doesn’t go away and begins to interfere with your life, it could affect your health. You could experience problems with sleeping, or with your immune, digestive, cardiovascular, and reproductive systems. You also may be at higher risk for developing a mental illness such as an anxiety disorder or depression. Read more about anxiety disorders .
So, how do you know when to seek help?
Stress vs. Anxiety
It’s important to manage your stress..
Everyone experiences stress, and sometimes that stress can feel overwhelming. You may be at risk for an anxiety disorder if it feels like you can’t manage the stress and if the symptoms of your stress:
- Interfere with your everyday life.
- Cause you to avoid doing things.
- Seem to be always present.
Coping With Stress and Anxiety
Learning what causes or triggers your stress and what coping techniques work for you can help reduce your anxiety and improve your daily life. It may take trial and error to discover what works best for you. Here are some activities you can try when you start to feel overwhelmed:
- Keep a journal.
- Download an app that provides relaxation exercises (such as deep breathing or visualization) or tips for practicing mindfulness, which is a psychological process of actively paying attention to the present moment.
- Exercise, and make sure you are eating healthy, regular meals.
- Stick to a sleep routine, and make sure you are getting enough sleep.
- Avoid drinking excess caffeine such as soft drinks or coffee.
- Identify and challenge your negative and unhelpful thoughts.
- Reach out to your friends or family members who help you cope in a positive way.
Recognize When You Need More Help
If you are struggling to cope, or the symptoms of your stress or anxiety won’t go away, it may be time to talk to a professional. Psychotherapy (also called talk therapy) and medication are the two main treatments for anxiety, and many people benefit from a combination of the two.
If you are in immediate distress or are thinking about hurting yourself, call or text the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or chat at 988lifeline.org .
If you or someone you know has a mental illness, is struggling emotionally, or has concerns about their mental health, there are ways to get help. Read more about getting help .
More Resources
- NIMH: Anxiety Disorders
- NIMH: Caring for Your Mental Health
- NIMH: Child and Adolescent Mental Health
- NIMH: Tips for Talking With a Health Care Provider About Your Mental Health
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Anxiety and Depression in Children
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health NIH Publication No. 20-MH-8125
The information in this publication is in the public domain and may be reused or copied without permission. However, you may not reuse or copy images. Please cite the National Institute of Mental Health as the source. Read our copyright policy to learn more about our guidelines for reusing NIMH content.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Stress and Anxiety Relief: 10 Strategies That Can Help
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
Verywell / Mayur Kakade
Deep Breathing
Mindfulness, write in a journal, watch your caffeine intake, get enough sleep, talk to a loved one, label your emotions, talk to a therapist.
Stress and anxiety are a normal part of life. Sometimes they can even be a good thing. They can inspire you to take action and do your best when it really matters.
The problem is when feelings of stress and anxiety get out of control. Then these feelings cannot only impair your performance—they can also make you sick. Chronic stress can have a number of serious health consequences including decreased immunity, decreased longevity, and a higher risk for anxiety disorders.
Stress is a response to a potential threat, while anxiety is the reaction to that stress. Unfortunately, both are incredibly common among U.S. adults and evidence suggests that recent world events have made the problem worse for many people. Nearly 8 in 10 adults report increased stress levels as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
While you can’t avoid all of the stress in your life, there are stress and anxiety relief strategies that can help you cope more effectively. This article discusses some self-help techniques that can help you get a handle on stress and anxiety. It also covers when to consider talking to a professional.
Exercise can be a highly effective way to deal with things in your life that are causing distress. Research has also found that regular physical activity can protect people against stress and anxiety while also promoting positive emotions.
Exercise can be beneficial for a variety of reasons. It helps to lower the body's stress hormones including adrenaline and cortisol, while also increasing endorphin levels. Endorphins are the body's "feel-good" chemicals. In addition to acting as natural painkillers, they also play a role in inducing feelings of relaxation and boosting mood.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends getting at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity, 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity, or an equivalent combination each week.
Even if you can't meet these benchmarks, any amount or type of exercise is better than nothing and can benefit your mental health and help to decrease anxiety and stress.
Deep breathing can be a highly effective way to deal with feelings of stress and combat symptoms of anxiety. According to the American Institute of Stress, deep breathing combats stress in a number of ways:
- Increased blood flow to the brain stimulates the parasympathetic symptoms and promotes feelings of calmness
- Redirects attention from negative thoughts to the body and physical sensations instead
Fortunately, deep breathing techniques are easy to learn, can be practiced anywhere, and don’t require any special tools.
Try This: Belly Breathing
- Sit in a comfortable position.
- Place one hand on your belly and the other hand on your chest.
- Inhale slowly through your nose, allowing your belly to expand to move your hand outward without expanding your chest.
- Slowly exhale through pursed lips and let your hand on your belly gently help push all of the air out.
- Repeat this move for 3 to 10 breaths.
Experts also suggest that meditation , the ancient practice that involves focused concentration, can be a highly effective tool for stress and anxiety relief. A brief meditation can be helpful as a quick way to induce feelings of calm when you are feeling stressed. Practicing it regularly may help lower your overall stress levels and combat feelings of anxiety.
While the body's stress response can trigger the fight or flight response and put the body into an alert state so you can take action, meditation acts in much the opposite way. It soothes the body's stress response, bringing your heightened physiological and psychological reactions back to a more relaxed state.
Because meditation involves focusing your awareness, it can also help take you out of the distracted, worried thoughts that make you feel stressed or anxious.
Fortunately, there are many different forms of meditation that you can try. Two main types you might consider include concentrative meditation and mindfulness meditation . It pays to experiment and figure out which one you find the most helpful.
Mindfulness is a state of being fully aware and focused on the present moment. It can have a number of positive health effects, including helping to lower stress and anxiety.
Research has found that an approach known as mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), can be helpful for reducing normal everyday stress as well as for coping with other sources of stress such as chronic illness.
This eight-week program utilizes mindfulness along with yoga to address the behaviors, feelings, and thoughts that worsen stress.
While this program is a great option for intensive mindfulness-based training, there are also many quick and easy mindfulness practices you can try to incorporate daily.
When you are feeling stressed out or anxious, you might find it helpful to spend a few moments writing down your feelings. Journaling for stress relief allows you to express your emotions, notice patterns you might have missed, and reflect on the things for which you are grateful.
One 2018 study found that journaling, particularly when it focused on positive emotions, was an effective way to combat the effects of stress and improve overall well-being.
If you decide to try this strategy for stress and anxiety relief, make sure that it doesn’t become an exercise in rumination . This doesn’t mean you should avoid writing about all negative feelings, but consider using it as an opportunity to write about solutions you might try or ways to turn the situation around and make a negative into a positive.
Caffeine might be the most commonly consumed drug in the world, but its psychological effects are often underestimated. While low to moderate doses can make you feel more alert and energetic, too much can leave you feeling jittery and anxious.
It is important to remember, however, that everyone's tolerance for caffeine is different. Some people may be able to drink a moderate amount of coffee each day, around four or five cups a day, without noticing any ill effects.
For other people, just a small amount of caffeine can cause feelings of shakiness or nervousness. If you feel like caffeine might be contributing to feelings of anxiety, consider gradually reducing your intake. Slowly lowering your intake over time can help minimize the unpleasant symptoms of caffeine withdrawal .
Sleep is essential for mental well-being , and research has shown that a lack of sleep may contribute to both the onset and maintenance of a number of mental health conditions, including anxiety.
A poor night of sleep can also leave you feeling stressed and irritable the next day. In addition to feeling exhausted, you might find that even the smallest inconveniences seem unmanageable.
Research has also found that people who experience problems with anxiety are also more likely to struggle with sleep problems. People with sleep difficulties are at a higher risk of developing generalized anxiety disorder , a condition marked by excessive, persistent, and intrusive feelings of worry and anxiety.
Even people who normally don't have problems with anxiety have higher levels of distress and anxiety levels after a night of poor sleep, so finding ways to protect your rest is important.
Tactics like going to bed and waking at the same time, avoiding digital devices before bedtime , and creating a comfortable sleep environment can help you get a better night's rest.
Social support is essential for mental health, particularly when you are facing something that causes you to feel stressed or anxious. Spend some time talking to a good friend or other loved one about how you are feeling.
Social support can come in a variety of forms . Sometimes it can involve validating your feelings (emotional support), while in other cases it involves doing things to help people manage a problem (tangible support). In other instances, it might simply involve sharing information (informational support) or helping you feel supported (belongingness support).
No matter what type of support it is, however, research suggests that feeling supported by others can help lower your blood pressure and better cope with stress.
Also, remember that you are not alone and there are people who understand what it is like to struggle with anxiety and excessive stress. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, nearly 20% of adults in the U.S. have some type of anxiety disorder.
So don't be afraid to share what you are feeling with a friend, or consider reaching out to an anxiety support group , either in person or online.
Research has also found that, in many cases, putting your feelings into words, known as affect labeling, can help reduce the intensity of those emotions. This means that talking to a friend about the things that are causing your stress can actually make those feel less overwhelming.
Try This: Affect Labeling
Focus on labeling your emotions clearly and be as specific as you can be. You might start by saying something general such as “I feel bad,” but work on going further to really identify the source of the distress and how you feel about it.
After some thought, you might realize that you feel bad because you are worried, angry, or disappointed. Acknowledge and accept your emotions without judging them.
It's not always easy to know when it's time to see a professional about your stress and anxiety. It often builds over time, so it can be difficult to recognize when it's become too much because it has simply become your new normal.
If your symptoms of stress and anxiety are causing distress and interfering with your ability to function normally, then it is important to talk to a doctor or therapist. But you also don't have to wait until things feel overwhelmingly out of control to reach out for help.
A therapist can help you identify the sources of stress and anxiety in your life and come up with strategies that will help you cope. They can also determine if you have an anxiety disorder and recommend effective treatments that can help you find relief, including psychotherapy and medications.
A Word From Verywell
Stress and anxiety can take a toll on both your physical and mental well-being. Fortunately, there are a number of things that you can do on your own to improve your ability to cope with stress. By becoming better at managing your stress, you may also be able to lower your risk for anxiety.
If you are still struggling to find stress and anxiety relief, it may be time to talk to your healthcare provider or mental health professional .
American Psychological Association. Stress effects on the body .
American Psychological Association. Stress in America™ 2020 .
Schultchen D, Reichenberger J, Mittl T, et al. Bidirectional relationship of stress and affect with physical activity and healthy eating . Br J Health Psychol . 2019;24(2):315-333. doi:10.1111/bjhp.12355
Harvard Health. How does exercise reduce stress? Surprising answers to this question .
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). How much physical activity do adults need ?.
American Institute of Stress. Take a deep breath .
University of Michigan Health. Stress management: breathing exercises for relaxation .
Sharma H. Meditation: Process and effects . Ayu . 2015;36(3):233–237. doi:10.4103/0974-8520.182756
Hoge EA, Bui E, Marques L, et al. Randomized controlled trial of mindfulness meditation for generalized anxiety disorder: effects on anxiety and stress reactivity . J Clin Psychiatry . 2013;74(08):786-792. doi:10.4088/JCP.12m08083
Smyth JM, Johnson JA, Auer BJ, Lehman E, Talamo G, Sciamanna CN. Online positive affect journaling in the improvement of mental distress and well-being in general medical patients with elevated anxiety symptoms: a preliminary randomized controlled trial . JMIR Ment Health . 2018;5(4):e11290. doi:10.2196/11290
Lara DR. Caffeine, mental health, and psychiatric disorders . J Alzheimers Dis . 2010;20 Suppl 1:S239-48. doi:10.3233/JAD-2010-1378
Scott AJ, Webb TL, Rowse G. Does improving sleep lead to better mental health?. A protocol for a meta-analytic review of randomised controlled trials . BMJ Open . 2017;7(9):e016873. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016873
Shanahan L, Copeland WE, Angold A, Bondy CL, Costello EJ. Sleep problems predict and are predicted by generalized anxiety/depression and oppositional defiant disorder . J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry . 2014;53(5):550–558. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2013.12.029
Bowen KS, Uchino BN, Birmingham W, Carlisle M, Smith TW, Light KC. The stress-buffering effects of functional social support on ambulatory blood pressure . Health Psychol . 2014;33(11):1440–1443. doi:10.1037/hea0000005
National Institute of Mental Health. Any anxiety disorder .
Torre JB, Lieberman MD. Putting feelings into words: affect labeling as implicit emotion regulation . Emotion Review . 2018;10(2):116-124. doi:10.1177/1754073917742706
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Child Program
- Adult Program
- At-Home Program
Take the Quiz
Find a Center
- Personalized Plans
- International Families
- Learning Disorders
- Processing Disorders
- Oppositional Defiant Disorder
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Behavioral Issues
- Struggling Kids
- Testimonials
- The Science Behind Brain Balance
- How It Works
End Homework Anxiety: Stress-Busting Techniques for Your Child

Sometimes kids dread homework because they'd rather be outside playing when they're not at school. But, sometimes a child's resistance to homework is more intense than a typical desire to be having fun, and it can be actually be labeled as homework anxiety: a legitimate condition suffered by some students who feel intense feelings of fear and dread when it comes to doing homework. Read on to learn about what homework anxiety is and whether your child may be suffering from it.
What is Homework Anxiety?
Homework anxiety is a condition in which students stress about and fear homework, often causing them to put homework off until later . It is a self-exacerbating condition because the longer the student puts off the homework, the more anxiety they feel about it, and the more pressure they experience to finish the work with less time. Homework anxiety can cripple some kids who are perfectly capable of doing the work, causing unfinished assignments and grades that slip.

What Causes Homework Anxiety?
There are many causes of homework anxiety, and there can be multiple factors spurring feelings of fear and stress. Some common causes of homework anxiety include:
- Other anxiety issues: Students who tend to suffer anxiety and worry, in general, can begin to associate anxiety with their homework, as well.
- Fear of testing: Often, homework is associated with upcoming tests and quizzes, which affect grades. Students can feel pressure related to being "graded" and avoid homework since it feels weighty and important.
- General school struggle: When students are struggling in school or with grades, they may feel a sense of anxiety about learning and school in general.
- Lack of support: Without a parent, sibling, tutor, or other help at home, students may feel that they won't have the necessary support to complete an assignment.
- Perfectionism: Students who want to perform perfectly in school may get anxious about completing a homework assignment perfectly and, in turn, procrastinate.
Basic Tips for Helping with Homework Anxiety
To help your child with homework anxiety, there are a few basic tips to try. Set time limits for homework, so that students know there is a certain time of the day when they must start and finish assignments. This helps them avoid putting off homework until it feels too rushed and pressured. Make sure your student has support available when doing their work, so they know they'll be able to ask for help if needed. Teaching your child general tips to deal with anxiety can also help, like deep breathing, getting out to take a short walk, or quieting racing thoughts in their mind to help them focus.
How can the Brain Balance Program Help with Homework Anxiety?
Extensive scientific research demonstrates that the brain is malleable, allowing for brain connectivity change and development and creating an opportunity for improvement at any age. Brain Balance has applied this research to develop a program that focuses on building brain connectivity and improving the foundation of development, rather than masking or coping with symptoms.
If you have a child or a teenager who struggles with homework anxiety, an assessment can help to identify key areas for improvement and create an action plan for you and your child. To get started, take our quick, free online assessment by clicking the link below.
Get started with a plan for your child today.
Related posts, what is dyslexia.
By Dr. Rebecca Jackson
Brain-Healthy Chicken Pot Pie
Gluten-Free, Dairy-Free, Brain-Healthy Chicken Pot Pie Recipe
What is ADHD?
Call us at 800.877.5500
Webinar Sign Up
Call 800-877-5500

How to Reduce Homework Stress
If homework is a source of frustration and stress in your home, it doesn’t have to be that way! Read on to learn effective strategies to reduce your child’s homework stress.

Author Katie Wickliff
Published March 2024

If homework is a source of frustration and stress in your home, it doesn’t have to be that way! Read on to learn effective strategies to reduce your child’s homework stress.
- Key takeaways
- Homework stress can be a significant problem for children and their families
- An appropriate amount of quality homework can be beneficial for students
- Parents can help reduce homework stress in several key ways
Table of contents
- Homework stress effects
- How to reduce homework stress
As a parent who has felt the frustration of watching my child be reduced to tears because of her homework each night, I’ve often wondered: do these math worksheets and reading trackers really make a difference to a child’s academic success? Or does homework cause stress without having a positive impact on learning?
If your child experiences a significant amount of homework stress, you may feel at a loss to help. However, there are several things you can do at home to minimize the negative effects of this stress on your child–and you! We’ve put together a list of research-based practices that can help your child better handle their homework load.
The Effects of Homework Stress on Students
Does homework cause stress? Short answer: Yes. It’s been well documented that too much homework can cause stress and anxiety for students–and their parents. However, do the benefits of homework outweigh the costs? Is homework “worth” the frustration and exhaustion that our children experience?
Findings on the benefits of homework at the elementary school level are mixed, with studies showing that homework appears to have more positive effects under certain conditions for certain groups of students.
After examining decades of studies on the relationship between homework and academic achievement, leading homework researcher Harris M. Cooper has proposed the “10-minute rule,” suggesting that homework be limited to 10 minutes per grade level. For example, children in 3rd grade should do no more than 30 minutes of homework daily, while a 1st grader should do no more than 10 minutes of homework. The National Parent Teacher Association and the National Education Association both endorse this guideline as a general rule of thumb.
Because of these research findings, Doodle believes that an appropriate amount of quality homework can help students feel more positive about learning and can provide parents with a critical connection to their child’s school experience . But to keep learning positive, we need to reduce the amount of stress both students and parents feel about homework.
1. Routine, Routine, Routine
Creating an after-school routine and sticking to it helps children feel organized, but with sports, tutoring, or music lessons, many children have varying weekday schedules. As a former classroom teacher and private tutor, I suggest that families post a weekly schedule somewhere visible and communicate that schedule with their child.
At our house, we have a dry-erase calendar posted on the wall. Every Sunday evening, I write both of my children’s schedules for the following week–including homework time. We go through the calendar together, and they reference it often throughout the week. I can tell both my son and daughter feel better when they know when they’ll get their homework done.
2. Create a Homework Space
Ideally, your child should have a dedicated homework space. It doesn’t matter if that space is a desk, a dining room table, or a kitchen countertop. What does matter is that the homework area is tidy, because an unorganized homework area is very distracting.
3. Start Homework Early
Encourage your child to start their homework as early as possible. Help them review their assignments, make a plan for what needs to be completed, and then dive in. Naturally, children are more tired later in the evening which can lead to more stress.
4. Encourage Breaks
If you can see your child becoming frustrated or overwhelmed by their homework, encourage them to take a breather and come back to it later. As a teacher and tutor, I called this a “brain break” and believe these breaks are essential. Taking a short break will give your child a chance to step away from a frustrating problem or assignment.
5. It’s Okay to Ask for Help
Sometimes, homework can become just too stressful and overwhelming. In that case, it really is okay to stop. Children can learn to advocate for themselves by making a list of questions for their teacher and asking for help the next day. Depending on their age, you might need to help role-play how to approach their teacher with their frustrations.
Additionally, parents should never feel afraid to contact their child’s teacher to talk about homework issues. When I was teaching elementary school, I always wanted parents to feel comfortable reaching out about any issues, including homework stress.
6. Get Plenty of Rest
Sleep is critical to a child’s overall wellbeing , which includes their academic performance. Tired kids can’t concentrate as well, which can lead to feeling more overwhelmed about homework assignments. According to the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, kids aged 6-12 should get at least 9 hours of sleep each night.
7. Consider a Homework Group
Organizing a homework group a few times a week is another way for your child to view homework more positively. Working as a group encourages collaboration, while discussions can solidify concepts learned in class.
8. Encourage Positivity
No matter what your school experience was like, it’s important to model a growth mindset for your child. A growth mindset is the belief that your abilities can develop and improve over time. So if your child says something like “ I can’t do this! ” first acknowledge their frustration. Then, encourage them to say, “ I may not understand this yet, but I will figure it out. ” Speaking positively about tough experiences takes practice, but it will go a long way in reducing homework stress for your child.
9. Develop Skills With Fun Games
Feeling stressed about homework is no fun. Completing worksheets and memorizing facts is necessary, but playing games is a great way to inject some excitement into learning. Doodle’s interactive math app is filled with interactive exercises, engaging math games, and unique rewards that help kids develop their skills while having fun.
Lower Math Anxiety with DoodleMath
Does your child struggle with math anxiety? DoodleMath is an award-winning math app f illed with fun, interactive math questions aligned to state standards. Doodle creates a unique work program tailored to each child’s skill level to boost confidence and reduce math anxiety. Try it free today!

FAQs About Homework Stress
Many studies have shown that homework and stress often go hand-in-hand, often because many children feel pressure to perform perfectly or they have trouble managing their emotions–they get overwhelmed or flooded easily.
You can help your child reduce homework stress in several ways, including by establishing a routine, creating a homework space, encouraging breaks, and making homework fun with online games or math apps.

Lesson credits

Katie Wickliff
Katie holds a master’s degree in Education from the University of Colorado and a bachelor’s degree in both Journalism and English from The University of Iowa. She has over 15 years of education experience as a K-12 classroom teacher and Orton-Gillingham certified tutor. Most importantly, Katie is the mother of two elementary students, ages 8 and 11. She is passionate about math education and firmly believes that the right tools and support will help every student reach their full potential.

Parents, sign up for a DoodleMath subscription and see your child become a math wizard!
What we offer
Quick links
All rights reserved.

Are you a parent, teacher or student?
Get started for free!
Maths information pack
We ask for your contact info so we can send our info pack directly to your inbox for your convenience, exam prep information pack, case studies information pack.
Book a chat with our team

I’m new to Doodle

My school is already using Doodle

Information pack
We ask for your contact info so that our education consultants can get in touch with you and let you know a bit more about doodle., student login, which programme would you like to use.
DoodleMaths
DoodleTables
DoodleEnglish
DoodleSpell
If you’d like to use Doodle’s browser version, please visit this page on a desktop.
To log in to Doodle on this device, you can do so through our apps. You can find out how to download them here:
18 Anxiety Worksheets for Adults, Teens & More

And yet, it can also be energizing, focusing our attention and preparing us for action — an evolutionary response to the unexpected, difficult, or downright dangerous (Workman & Reader, 2015).
It is not so much what happens but how we respond that matters the most (Joseph, 2013).
Therapists, counselors, and coaches can help by working with clients to change how they react to anxiety-inducing situations.
In this article, we introduce a collection of free worksheets for use by mental health professionals with their clients or as self-help activities.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises (PDF) for free . These science-based exercises will equip you and your clients with tools to better manage stress and find a healthier balance in your life.
This Article Contains
5 best anxiety worksheets, 4 anxiety worksheets for teens, 3 social anxiety worksheets, 3 anxiety activities for adults, cbt worksheets for anxiety, positivepsychology.com resources, a take-home message.
We can learn to break free from anxiety. With the right approaches, the same situations can have different outcomes (Forsyth & Eifert, 2016).
The following five worksheets encourage clients to recognize that they are not alone in their experiences and can, indeed, learn how to cope with anxiety.
The activities work on their own or can be combined. They support clients by helping them identify situations that cause anxiety, using mindfulness and meditation to restore a balanced perspective, and recognizing that someone should not be defined by the extreme emotions they are experiencing (Forsyth & Eifert, 2016; Southwick & Charney, 2018):
1. Anxiety Hierarchy
Intense fears, phobias, and stressful situations can be highly anxiety provoking. It is helpful to establish a list of challenging situations that result in extreme upset or negative emotions for clients (American Psychological Association, 2016).
Use the Anxiety Hierarchy exercise to list situations that lead to anxiety and rate them on a scale from 1 (mild discomfort) to 10 (extreme emotions such as panic).
Once these anxiety-inducing situations are listed and sorted in order, the practitioner can use graded exposure practices as part of systematic desensitization.
2. Breath Awareness While Waiting
Waiting for an event can leave us excited, concerned, nervous, or anxious. We may notice changes to our physiology (increased heart rate, sweating, and faster breathing), cognition (erratic thinking, poor decision-making, and a failing memory), and emotions (fear, upset, and panic ; Peterson, 2018).
Work with the client to identify times they are waiting during the week — for example, waiting for the bus, at the school gates, at an appointment — and how they expect to feel.
Then use this breath awareness practice for mindful breathing: slowly breathing in through the nose, holding, and slowly breathing out through the mouth. As unhelpful thoughts enter the mind, direct attention back to breathing.
3. Creating a Mindfulness Anxiety Plan
Our behavior often follows patterns, and so does our anxiety. It is possible to anticipate when anxiety might show up, especially when we become more in tune with our bodies and the events around us (Peterson, 2018).
By creating a mindfulness anxiety plan , we can be ready with a list of actions to perform when we begin to recognize our anxiety taking shape and in advance of situations that can be difficult. These actions should aim to improve our wellbeing and leave us less anxious throughout the day
For example, “If my anxiety is getting away from me, I will call my best friend.” Or “Every day, I will go outside for a walk at lunchtime and try to be more mindful.”
4. Who Am I Beyond My Anxiety?
We are not our emotions, but when fearful or anxious, we spend a great deal of time and energy focusing on what is wrong with us, forgetting our strengths (Forsyth & Eifert, 2016).
In this exercise , the client mindful reflects on the following prompts (among others):
I am someone who … I really like … My most important relationship is … I feel my best when …
Reading through the answers helps remind us that anxiety does not define who we are.
5. Funeral Meditation
Often, we stop ourselves from taking on or embracing a challenge for fear of failure or experiencing anxiety.
Despite its foreboding name, the Funeral Meditation is used within Acceptance and Commitment Therapy to help free ourselves from the grip of anxiety (Forsyth & Eifert, 2016).
This powerful meditation helps us reflect on what matters to us, recognizing that, at any time, we can start living in line with how we want to be remembered.
After several calming breaths, we imagine what our funeral would be like, including:
How do people look? Who would be there? What would they say? What would we like people to say about us?
Recognizing our values can help us eliminate anxiety and begin living the way we want.

The following worksheets can also be adapted for adult populations, and mental health practitioners will find them valuable when working with adolescents coping with anxiety.
1. Best and Worst
Children and teens can benefit from stepping back from anxiety-inducing situations to reflect upon how, despite being scary, they can also be exciting.
For example, joining a new class, school, or social group can bring with it feelings of anxiety. When also recognized as exciting, it can be energizing, leading to positive emotions such as hope, curiosity, and gratitude.
Work with your teen client to:
- Identify and capture a situation that makes them feel nervous or scared.
- Use the diagram to capture what is exciting in the left-hand circle and what is scary about the situation in the right-hand circle.
- Write down aspects of the situation that are both scary and exciting in the intersection between the two circles.
Identifying how something fills us with fear while providing energy can help us have a more balanced view regarding how to approach what is ahead.
2. FLARE for Anxiety and Fear
This helpful worksheet helps teach acceptance of difficult feelings (rather than hiding from or rejecting them) through self-acceptance and self-compassion (Khazan, 2019).
The FLARE acronym directs the client to:
- Feel each sensation. Become aware of their heart rate, breath, and body temperature.
- Label the sensations. Do they feel worried, fearful, or anxious?
- Allow the experience to remain as it is. They can say to themselves, “It is OK to feel this way.”
- Respond by refocusing on breathing, taking each breath slowly and making the out-breath longer than the in-breath.
- Expand awareness of their environment and reflect on what they are grateful for that day.
By focusing on positive emotions, the approach builds toward a spiral of positive feelings (Fredrickson, 2010).
3. Radio Doom and Gloom
Teenagers are vulnerable to focusing on the worst events, situations, and outcomes. As a result, it can almost seem like an endless radio program playing in the background, broadcasting negative stories and songs all day long.
While it’s not easy to turn down the volume on the radio (or turn it off completely), we can attend to it less. By learning to treat such negative thinking as background noise and focusing more on current activities, its impact and ability to heighten anxiety are reduced.
4. When I’m Scared
Children and adolescents (and even adults) feel scared sometimes. And that’s OK. It’s a perfectly normal fight-or-flight response to a perceived — or actual — uncomfortable or dangerous situation.
Talking to an adult can help.
When I’m Scared can be used with individual youths or in a group setting.
They are asked to write down what makes them frightened, how it affects their thinking, how it feels physically, and one thing might be that makes them feel better.

Download 3 Free Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will equip you or your clients with tools to manage stress better and find a healthier balance in their life.
Download 3 Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Social anxiety leads to persistent fear and the avoidance of social situations because of concerns about being evaluated by others (Schneier & Goldmark, 2015).
Therapy and the use of interventions enable clients to increase their social engagement and form deep, meaningful relationships (Schneier & Goldmark, 2015).
The following worksheets are valuable for mental health professionals helping clients identify what triggers their anxious thinking and manage them through visualization and mindfulness.
1. A Mountain of Worries
Our worries can mount up. Stresses, concerns, upsets, and things going wrong may seem never-ending, with even the most minor problems blown out of proportion, leaving our anxiety out of control.
This exercise captures situations that bother us and is particularly helpful for social anxiety, where we can begin to identify and reflect on unhelpful thought patterns and learn to expect and plan for how to handle them.
2. Event visualization worksheet
Visualization can feel as real to the mind as experiencing a situation first-hand — especially a social one — and offers a safe and controlled environment to explore and experiment with existing and future challenges (Clough & Strycharczyk, 2015).
Visualizing an event, especially one we are worrying about, can be a powerful and helpful way of reducing concern and anxiety and gaining confidence without the risk of failure or being overwhelmed.
Use the worksheet to:
- Identify an event likely to cause anxiety.
- Visualize the event in as much detail as possible using all the senses.
- Imagine the people and the situation.
- Reflect on how being successful might feel.
Clients can repeat the visualization exercise several times until they feel comfortable and less anxious.
3. The Documentary of You
Anxiety can arise from any environment and is particularly common in social situations (Schneier & Goldmark, 2015).
Mindfulness can help us think about ourselves and our situations with more compassion and forgiveness and less judgment (Forsyth & Eifert, 2016).
In this exercise , the client imagines their life playing out as a movie on a screen. They capture on paper, nonjudgmentally, situations that leave them feeling anxious.
Following a series of grounding breaths, the client considers each one mindfully without becoming too involved.
Finally, they reflect on how reading the story now makes them feel. What is their degree of anxiety?

Changing your relationship with it can help us take charge of our lives (Forsyth & Eifert, 2016).
Try the following three activities to create coping strategies, identify what we can control while learning to accept everything else, and become more comfortable with discomfort.
1. Anxiety Strategy Cards
Preparation is a crucial part of managing anxiety. This sheet contains a list of cards to help clients develop strategies for events and situations where they feel out of control and stressed, with their anxiety building.
Each card offers a valuable reminder of a powerful technique that will help them restore their physical, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral balance.
For example:
When I feel anxious, I could try … controlled breathing. When I feel anxious, I could try … visualization. When I feel anxious, I could try … a grounding technique.
Use them with psychoeducation and technique training to build confidence in the client’s ability to handle and overcome tough times.
2. Control–Influence–Accept Model
We can’t control every situation, so it’s helpful to recognize those that can be influenced by our behavior and those that cannot.
The Control–Influence–Accept Model can stop individuals from feeling overwhelmed and experiencing feelings of hopelessness, frustration, and anxiety when they experience a loss of control or indecision (Thompson & Thompson, 2018).
The client is encouraged to perform each of the following:
- Identify a potentially tricky situation.
- Capture what can be controlled or influenced.
- What cannot be controlled or influenced must be accepted.
- List what needs to be accepted.
Having performed each step, the client reflects on how they now feel about the situation and whether they are left wishing to control or influence anything they have accepted.
3. Interoceptive Exposure
Anxiety has a strong physical element that we can use to increase awareness of panic-related physiological symptoms .
Interoceptive exposure is built on the premise that exposure to such sensations can increase our familiarity with them and our preparedness for future anxiety-inducing situations.
The worksheet uses activities that induce physical, cognitive, and emotional discomfort to replicate the sensations of panic and anxiety.
Note: These should only be used under the guidance of a physician or health professional in a suitably safe environment.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) treats anxiety by restructuring the client’s thinking, with the therapist exploring maladaptive expectations and worries related to upcoming events (Dobson & Dozois, 2021).
1. Anxiety Record
Reflecting on and sharing what makes us anxious can leave us feeling vulnerable, but it is essential. Understanding what leaves us feeling this way allows us to prepare for situations and learn appropriate coping skills.
One of the most powerful techniques is recognizing and, if possible, replacing unhelpful thinking.
Use the simple form in the worksheet to capture the following:
What does the anxiety feel like? When does it happen? What thoughts do you experience? How realistic are these thoughts? What thoughts could you replace them with? Are they more realistic?
Capturing our anxieties is an essential part of reducing them and bringing them under control.
2. Dealing with anxiety: Reverse the Rabbit Hole
The two words “what if?” can be anxiety- inducing, sending our thoughts racing down a rabbit hole of all that could go wrong.
What if I forget the words when I’m on stage? What if my date doesn’t like me?
Reframing an experience helps us experience it differently. We can turn a negative into a positive — reverse the rabbit hole.
In this exercise , we write negative outcomes in the left-hand column and then a corresponding reversed, positive outcome on the right.
What if I nail the speech? What if my date goes really well?
3. Tackling Anxious Thoughts
Anxiety can bias our thinking by making us buy into the likelihood of something terrible happening. As a result, it can be helpful to consider the following three points:
What is the worst potential consequence of this scenario? What is the best possible consequence of this scenario? What do you feel is the most likely consequence of this scenario?
Following these questions, the client thinks about how it would feel in a year’s time if the worst actually happened.
After all, even if the worst outcome becomes a reality, it may be less catastrophic than we imagine.

17 Exercises To Reduce Stress & Burnout
Help your clients prevent burnout, handle stressors, and achieve a healthy, sustainable work-life balance with these 17 Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises [PDF].
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
We have many resources available for therapists to support clients experiencing anxiety.
More extensive versions of the following tools are available with a subscription to the Positive Psychology Toolkit© , but they are described briefly below:
- Replacing Unhelpful Thoughts with Helpful Alternatives CBT is based on the premise that emotions and behaviors result from a person’s interpretation of a situation.
This exercise invites clients to examine the “helpfulness” of a thought they are having about a current challenging situation before formulating a more helpful alternative thought:
- Step one – Describe a challenging situation.
- Step two – Identify the automatic unhelpful thought.
- Step three – Rate the helpfulness of this thought.
- Step four – Come up with a more helpful alternative thought.
- Step five – Rate the helpfulness of this alternative thought.
- Step one – Visualize yourself in a relaxing environment.
- Step two – Add detail to the visualization by exploring all your senses.
- Step three – Enjoy the scene you have created and allow yourself to spend some time taking it all in.
- Step four – Close your eyes and continue taking slow, deep breaths as you visualize the stress leaving your body in waves with each exhale.
This exercise is valuable for stress reduction by connecting the sensations of relaxation with peaceful visual imagery during times of stress.
If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others manage stress without spending hours on research and session prep, check out this collection of 17 validated stress management tools for practitioners. Use them to help others identify signs of burnout and create more balance in their lives.
Anxiety is a normal reaction to life events and can be beneficial in many situations, alerting us to dangers and increasing our attention and readiness for action.
It is often less about our environment or the challenges we face, but how we interpret them.
As a result, anxiety can dramatically impair our ability to function and perform in education, work, and social environments (American Psychological Association, 2016).
Its effects are widespread, impacting 30% of adults at some point in their lives and preventing them from living normally (American Psychiatric Association, 2021). They can find themselves avoiding opportunities and shying away from challenges due to intrusive thoughts or concerns.
Anxiety disorders are treatable. Therapists and counselors can help clients manage anxiety-inducing situations by changing how they view them and learning to cope with stressful conditions.
The anxiety worksheets in this article can be used independently or together as interventions for better managing anxiety. When combined with ongoing therapeutic assessment, it is possible to see how clients bring their feelings under control and return to the lives they wish to lead.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises (PDF) for free .
Ed: Updated March 2023
- American Psychiatric Association. (2021). What are anxiety disorders? Retrieved March 17, 2023, from https://www.psychiatry.org/patients-families/anxiety-disorders/what-are-anxiety-disorders
- American Psychological Association. (2016). Beyond worry: How psychologists help with anxiety disorders . Retrieved March 13, 2023, from https://www.apa.org/topics/anxiety/disorders
- Clough, P., & Strycharczyk, D. (2015). Developing mental toughness: Coaching strategies to improve performance, resilience and wellbeing . Kogan Page.
- Dobson, K. S., & Dozois, D. J. (2021). Handbook of cognitive-behavioral therapies . Guilford Press.
- Forsyth, J. P., & Eifert, G. H. (2016). The mindfulness & acceptance workbook for anxiety: A guide to breaking free from anxiety, phobias & worry using acceptance & commitment therapy (2nd ed.). New Harbinger Publications.
- Fredrickson, B. (2010). Positivity: Groundbreaking research reveals how to release your inner optimist and thrive . Oneworld.
- Joseph, S. (2013). What doesn’t kill us: A guide to overcoming adversity and moving forward . Piatkus.
- Khazan, I. Z. (2019). Biofeedback and mindfulness in everyday life: Practical solutions for improving your health and performance . W.W. Norton & Company.
- Khesht-Masjedi, M. F., Shokrgozar, S., Abdollahi, E., Habibi, B., Asghari, T., Ofoghi, R. S., & Pazhooman, S. (2019). The relationship between gender, age, anxiety, depression, and academic achievement among teenagers. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care , 8 (3), 799–804.
- Peterson, T. J. (2018). The mindfulness workbook for anxiety: The 8-week solution to help you manage anxiety, worry & stress . Althea Press.
- Schneier, F., & Goldmark, J. (2015). Social anxiety disorder. In D. J. Stein & B. Vythilingum (Eds.), Anxiety disorders and gender (pp. 49–67). Springer.
- Southwick, S. M., & Charney, D. S. (2018). Resilience: The science of mastering life’s greatest challenges . Cambridge University Press.
- Thompson, S., & Thompson, N. (2018). The critically reflective practitioner . Macmillan International Higher Education.
- Workman, L., & Reader, W. (2015). Evolutionary psychology: An introduction . Cambridge University Press.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
Thank you. This helps so much I would definitely recommend this article especially for anxious people like me. Very generous of you guys.
I am a mental health professional Mental Health Skill Building and some of this information is very good for my clients. Thank you.
Thank you. So many resources and ideas in one place. We are in New Zealand. It is hard to access quality support here and too many don’t.
I am DYING for the ‘What if’ download. I do this all the time.
Awesome site – thank you!!
what an amazing website, jam packed with FREE and very useful information, thank you so much!!! I am currently working with a teenager and the ‘what-if’ worksheet alone is pure gold and just the thing I was looking for right now.
How do I get the What If worksheet?
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Overcome Languishing & Flourish: A Positive Psychology Guide
Amidst the turmoil of the recent pandemic, one positive psychology construct has captured more attention than any other. As societies worldwide had to endure lockdowns [...]

7 Trauma Response Types & How to Recognize Them
Over-sharing. Over-explaining. Trauma dumping. Hyperindependence. Hypersexualization. People pleasing. Do these sound like common traits your clients have? These may not be character traits but, instead, [...]

6 Best Diaphragmatic Breathing Exercises to Reduce Anxiety
Our brain controls our breathing largely without conscious awareness. We shower, watch football, listen to music, and sleep while our respiratory system functions in the [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (48)
- Coaching & Application (57)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (24)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (45)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (27)
- Positive Communication (20)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (16)
- Positive Psychology (33)
- Positive Workplace (36)
- Productivity (16)
- Relationships (49)
- Resilience & Coping (34)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (37)
- Strengths & Virtues (30)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
3 Stress Exercises Pack
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Should We Get Rid of Homework?
Some educators are pushing to get rid of homework. Would that be a good thing?

By Jeremy Engle and Michael Gonchar
Do you like doing homework? Do you think it has benefited you educationally?
Has homework ever helped you practice a difficult skill — in math, for example — until you mastered it? Has it helped you learn new concepts in history or science? Has it helped to teach you life skills, such as independence and responsibility? Or, have you had a more negative experience with homework? Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes?
Should we get rid of homework?
In “ The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, ” published in July, the Times Opinion writer Jay Caspian Kang argues that homework may be imperfect, but it still serves an important purpose in school. The essay begins:
Do students really need to do their homework? As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?” I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.” The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Mr. Kang argues:
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility. A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
Students, read the entire article, then tell us:
Should we get rid of homework? Why, or why not?
Is homework an outdated, ineffective or counterproductive tool for learning? Do you agree with the authors of the paper that homework is harmful and worsens inequalities that exist between students’ home circumstances?
Or do you agree with Mr. Kang that homework still has real educational value?
When you get home after school, how much homework will you do? Do you think the amount is appropriate, too much or too little? Is homework, including the projects and writing assignments you do at home, an important part of your learning experience? Or, in your opinion, is it not a good use of time? Explain.
In these letters to the editor , one reader makes a distinction between elementary school and high school:
Homework’s value is unclear for younger students. But by high school and college, homework is absolutely essential for any student who wishes to excel. There simply isn’t time to digest Dostoyevsky if you only ever read him in class.
What do you think? How much does grade level matter when discussing the value of homework?
Is there a way to make homework more effective?
If you were a teacher, would you assign homework? What kind of assignments would you give and why?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Jeremy Engle joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2018 after spending more than 20 years as a classroom humanities and documentary-making teacher, professional developer and curriculum designer working with students and teachers across the country. More about Jeremy Engle
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

August 23, 2022 , Filed Under: Uncategorized
How to Manage Homework-Related Stress
Ask students what causes them the most stress, and the conversation will likely turn to homework. Students have complained about homework for practically as long as it has existed. While some dismiss these complaints as students’ laziness or lack of organization, there’s more to it than that. Many students face a lot of pressure to succeed in school, sports, work, and other areas. Also, more teens and young adults are dealing with mental health problems, with up to 40% of college students reporting symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Researchers and professionals debate over whether homework does more harm than good, but at least for now, homework is an integral part of education. How do students deal with heavy homework loads? It’s become common for overwhelmed students to use an essay service to help them complete their assigned tasks. Pulling all-nighters to finish assignments and study for tests is another strategy busy college students use, for better or worse.
If you’re a student that’s struggling to get all your homework done, make sure to take care of your mental health. School is important, but your health is more important. Try the following tips to help you stay on top of your busy schedule.
Make a Schedule
Time management is an important skill, but you can’t learn it without effort. The first step to managing your time more effectively is to make a schedule and stick to it. Use a calendar, planner, or an app to write down everything you need to get done. Set reminders for due dates and set aside time each day for studying. Don’t leave assignments for the last minute. Plan to finish your work well ahead of the due date in case something unexpected happens and you need more time. Make sure your schedule is realistic. Give yourself a reasonable amount of time to complete each task. And schedule time for hobbies and social activities too.
Find a Study Spot
Doing homework in a dedicated workspace can boost your productivity. Studying in bed could make you fall asleep, and doing homework in a crowded, noisy place can be distracting. You want to complete as much work as possible during your study sessions, so choose a place that’s free of distractions. Make sure you have everything you need within arm’s reach. Resist the temptation to check your notifications or social media feeds while you study. Put your phone in airplane mode if necessary so it doesn’t distract you. You don’t need a private office to study efficiently, but having a quiet, distraction-free place to do your homework can help you to get more done.
Get Enough Rest
An all-nighter every once in a while probably won’t do you any lasting harm. But a consistent lack of sleep is bad for your productivity and your health. Most young people need at least 7 hours of sleep every night, so make it your goal to go to bed on time. You’ll feel better throughout the day, have more energy, and improve your focus. Instead of dozing off while you’re doing homework, you’ll be more alert and productive if you get enough sleep.
It’s also important to spend time relaxing and enjoying your favorite activities. Hang out with friends, take a walk, or watch a movie. You’ll feel less stressed if you take some time for yourself.
Don’t Shoot for Perfection
It’s tempting to try to get a perfect grade on every test or assignment. But perfectionism only causes unnecessary stress and anxiety. If you consider yourself a perfectionist, you might spend too much time on less important tasks. Prioritize your assignments and put more time and effort into the most important ones.
Most people struggle with perfectionism because they’ve been taught they should do their best at everything. But you don’t have to go above and beyond for every assignment. That’s not to say you should turn in bad work. But putting in just enough effort to get by isn’t a bad thing. Don’t put pressure on yourself to be the best at everything. Focus on your most important assignments, and don’t spend too much time and effort perfecting the others.
Almost all students deal with the burden of homework-related stress. No one enjoys the anxiety of having a lot of assignments due and not enough time to complete them. But take advantage of this opportunity to learn organization and self-discipline, which will help you throughout your life. Try making a schedule and don’t forget to set aside time to rest. When it’s time to study, choose a quiet place where you can concentrate. Don’t neglect your health; if you’re feeling anxious or depressed, talk to a counselor or your doctor. School stress is hard to avoid, but if you take these steps you can reduce homework anxiety and have better control of your time.
The real voyage of discovery consists not in seeking new landscapes, but in having new eyes — Marcel Proust

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- JMIR Ment Health
- v.4(2); Apr-Jun 2017
Supporting Homework Compliance in Cognitive Behavioural Therapy: Essential Features of Mobile Apps
1 Discipline of Psychiatry, Department of Medicine, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John's, NL, Canada
David Kreindler
2 Division of Youth Psychiatry, Department of Psychiatry, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, ON, Canada
3 Centre for Mobile Computing in Mental Health, Department of Psychiatry, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, ON, Canada
4 Department of Psychiatry, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective psychotherapy modalities used to treat depression and anxiety disorders. Homework is an integral component of CBT, but homework compliance in CBT remains problematic in real-life practice. The popularization of the mobile phone with app capabilities (smartphone) presents a unique opportunity to enhance CBT homework compliance; however, there are no guidelines for designing mobile phone apps created for this purpose. Existing literature suggests 6 essential features of an optimal mobile app for maximizing CBT homework compliance: (1) therapy congruency, (2) fostering learning, (3) guiding therapy, (4) connection building, (5) emphasis on completion, and (6) population specificity. We expect that a well-designed mobile app incorporating these features should result in improved homework compliance and better outcomes for its users.
Homework Non-Compliance in CBT
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is an evidence-based psychotherapy that has gained significant acceptance and influence in the treatment of depressive and anxiety disorders and is recommended as a first-line treatment for both of these [ 1 , 2 ]. It has also been shown to be as effective as medications in the treatment of a number of psychiatric illnesses [ 3 - 6 ]. Homework is an important component of CBT; in the context of CBT, homework can be defined as “specific, structured, therapeutic activities that are routinely discussed in session, to be completed between sessions” [ 7 ]. Completion of homework assignments was emphasized in the conception of CBT by its creator, Aaron Beck [ 8 ]. Many types of homework are prescribed by CBT practitioners, including symptom logs, self-reflective journals, and specific structured activities like exposure and response prevention for obsessions and compulsions. These can be divided into the following 3 main categories: (1) psychoeducational homework, (2) self-assessment homework, and (3) modality-specific homework. Psychoeducation is an important component in the early stage of therapy. Reading materials are usually provided to educate the client on the symptomatology of the diagnosed illness, its etiology, as well as other treatment-relevant information. Self-assessment strategies, including monitoring one’s mood using thought records, teach the patients to recognize the interconnection between one’s feelings, thoughts, and behaviors [ 8 ]. For example, depressed patients may be asked to identify thinking errors in daily life and document the negative influences these maladaptive thinking patterns can produce on their behaviors. Various psychiatric disorders may require different types of modality-specific homework. For example, exposure to images of spiders is a treatment method specific to arachnophobia, an example of a “specific phobia” in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5) [ 9 ]. Homework is strategically created by the therapist to correct and lessen the patient’s psychopathology. The purpose of these exercises is to allow the patients to practice and reinforce the skills learned in therapy sessions in real life.
Homework non-compliance is one of the top cited reasons for therapy failure in CBT [ 10 ] and has remained a persistent problem in the clinical practice. Surveys of practitioners have suggested rates of non-adherence in adult clients of approximately 20% to 50% [ 10 , 11 ] while adherence rates in adolescents have been reported to be approximately 50% [ 12 ]. Many barriers to homework compliance have been identified in the literature; to facilitate discussions, they can be divided into internal and external factors. Internal factors originate from a client’s own psychological environment while external ones are created by external influences. Internal factors that have been identified include lack of motivation to change the situation when experiencing negative feelings, the inability to identify automatic thoughts, disregard for the importance or relevance of the homework, and the need to see immediate results [ 12 - 14 ]. Various external factors have also been identified, including the effort associated with pen-and-paper homework formats, the inconvenience of completing homework because of the amount of time consumed, not understanding of the purpose of the homework, lack of instruction, and failure to anticipate potential difficulties in completing the homework [ 14 - 16 ]. There is strong evidence suggesting that homework compliance is integral to the efficacy of CBT in a variety of psychiatric illnesses. In the treatment of depression with CBT, homework compliance has been correlated with significant clinical improvement and shown to predict decreases in both subjective and objective measures of depressive symptoms [ 17 - 23 ]. Similarly, homework compliance is correlated with short-term and long-term improvement of symptoms in anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social anxiety disorder (SAD), hoarding, panic disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) [ 17 , 24 - 32 ]. Fewer studies have been done on homework compliance in other psychiatric conditions, but better homework compliance has been correlated with significant reductions in pathological behaviors in psychotic disorders [ 33 , 34 ], cocaine dependence [ 35 , 36 ], and smoking [ 37 ]. Two meta-analyses further support the notion that greater homework adherence is associated with better treatment outcomes in depression, anxiety-related disorders, and substance use [ 38 , 39 ].
The Utility of Technology in Enhancing CBT Homework
Despite its demonstrated efficacy, access to CBT (as well as other forms of psychotherapy) remains difficult due to the limited number of practicing psychotherapists and the cost of therapy sessions [ 40 ]. With the rise of mass-market mobile communication devices such as the iPhone or other kinds of mobile devices with app capabilities (smartphones), new solutions are being sought that will use these devices to provide therapy to patients in a more cost-effective manner. Mobile phones with app capabilities are portable devices that combine features of a cellphone and a hand-held computer with the ability to wirelessly access the Internet. Over time, ownership of mobile phones in North America has grown [ 41 , 42 ] and progressively lower prices have further reduced barriers to their use and ownership [ 43 , 44 ]. As more and more people acquire mobile phones, the acceptance of and the demand for mobile health solutions have been on the rise [ 45 ]. Boschen (2008), in a review predating the popularization of the modern mobile phone, identified the unique features of the mobile telephone that made it a potentially suitable vehicle for adjunctive therapeutic applications: portability, acceptability, low initial cost, low maintenance cost, social penetration and ubiquity, “always on,” “always connected,” programmability, audio and video output, keypad and audio input, user-friendliness, and ease of use [ 46 ]. Over the last decade, modern mobile phones have supplanted the previous generation of mobile telephones; progressive increases in their computing power, ongoing advances in the software that they run and interact with (eg, JAVA, HTML5, etc.), common feature sets across different operating systems such as Google Inc.'s Android or Apple Inc.'s iOS, and adoption of common hardware elements across manufacturers (eg, touch screens, high-resolution cameras, etc) have enabled the development of platform-independent apps for mobile phones, or at least apps on different platforms with comparable functionality (eg, apps written for Apple's HealthKit or the apps written for Microsoft's HealthVault).
The popularization of the smartphone presents a unique opportunity to enhance CBT homework compliance using adjunctive therapeutic applications such that well-designed mobile software may be able to diminish barriers to CBT [ 40 ] by making CBT therapists' work more cost-effective. However, there are no guidelines and no existing research that directly address the design of mobile phone apps for this purpose. Given this gap in the literature, we searched MEDLINE (1946 to April 2015) and PsycINFO (1806 to April 2015) for all articles related to “cognitive behavioral therapy”, “homework”, “mobile applications” and “treatment compliance or adherence”, and reviewed articles related to (1) mobile technologies that address homework completion, (2) essential features of therapy, or (3) barriers to homework completion in CBT. In this article, we propose a collection of essential features for mobile phone-based apps that will optimally support homework compliance in CBT.
A Proposed List of Essential Features for Mobile Apps That Optimally Support CBT Homework Compliance
In order to be effective for patients and acceptable to therapists, an optimal mobile phone app to support CBT homework compliance should conform to the CBT model of homework while addressing barriers to homework compliance. Tompkins (2002) provides a comprehensive guideline on the appropriate ways to provide CBT homework such that homework should be meaningful, relevant to the central goals of therapy, salient to focus of the session, agreeable to both therapist and client, appropriate to sociocultural context, practiced in session to improve skill, doable, begin small, have a clear rationale, include written instructions, and include a backup plan with homework obstacles [ 47 ]. In addition, the therapist providing the homework needs to be curious, collaborative, reinforce all pro-homework behavior and successful homework completion, and emphasize completion over outcome [ 47 ]. By combining Tompkins' guidelines with the need to reduce barriers to homework compliance (as described above), we obtained the following list of 6 essential features that should be incorporated into mobile apps to maximize homework compliance: (1) congruency to therapy, (2) fostering learning, (3) guiding therapy, (4) building connections, (5) emphasizing completion, and (6) population specificity.
Congruency to Therapy
Any intervention in therapy needs to be relevant to the central goals of the therapy and salient to the focus of the therapeutic session. A mobile app is no exception; apps have to deliver useful content and be congruent to the therapy being delivered. There are different types of homework in CBT, including (1) psychoeducational homework; (2) self-assessment homework; and (3) modality-specific homework. Which types are assigned will depend on the nature of the illness being treated, the stage of treatment, and the specific target [ 48 ]. An effective app supporting homework compliance will need to be able to adjust its focus as the therapy progresses. Self-monitoring and psychoeducation are major components in the early stage of therapy. Thought records can be used in depression and anxiety while other disorders may require more specific tasks, such as initiating conversation with strangers in the treatment of SAD. Therefore, the treatment modules delivered via mobile phones should meet the specific needs of therapy at each stage of therapy, while also providing psychoeducation resources and self-monitoring capabilities.
Psychoeducational Homework
While there are large amounts of health-related information on the Internet, the majority of information is not easily accessible to the users [ 49 ]. Mobile apps can enhance psychoeducation by delivering clear and concise psychoeducational information linked to the topics being covered in therapy. As psychoeducation is seen as a major component of mobile intervention [ 50 ], it has been incorporated into several mobile apps, some of which have been shown to be efficacious in treating various psychiatric conditions, including stress [ 51 ], anxiety and depression [ 52 ], eating disorders [ 53 ], PTSD [ 54 ], and obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) [ 55 ]. For example, Mayo Clinic Anxiety Coach is a mobile phone app “designed to deliver CBT for anxiety disorders, including OCD” [ 55 ]. The app contains a psychoeducational module that teaches the user on “the use of the application, the cognitive-behavioral conceptualization of anxiety, descriptions of each anxiety disorder, explanations of CBT, and guidance for assessing other forms of treatment” [ 55 ]. The benefits of delivering psychoeducation via a mobile phone app are obvious: the psychoeducational information becomes portable and is easily accessed by the patient. Furthermore, the information is also curated and validated by proper healthcare authorities, which builds trust and reduces the potential for misinformation that can result from patient-directed Internet searches. However, psychoeducation on its own is not optimal. Mobile interventions that also incorporate symptom-tracking and self-help interventions have resulted in greater improvement when used for depression and anxiety symptoms than those that deliver only online psychoeducation [ 50 ].
Self-Assessment Homework
In contrast to conventional, paper-based homework, mobile apps can support in-the-moment self-assessments by prompting the user to record self-report data about the user’s current state [ 56 ]. While information collected retrospectively using paper records can be adversely affected by recall biases [ 57 ], mobile apps enable the patient to document his or her thoughts and feelings as they occur, resulting in increased accuracy of the data [ 58 ]. Such self-assessment features are found in many mobile apps that have been shown to significantly improve symptoms in chronic pain [ 59 , 60 ], eating disorders [ 61 ], GAD [ 62 ], and OCD [ 55 ]. Continuing with the previous example, the Mayo Clinic Anxiety Coach offers a self-assessment module that “measures the frequency of anxiety symptoms” with a self-report Likert-type scale [ 55 ]. The app tracks users’ progress over time based on the self-assessment data; users reported liking the record of daily symptom severity scores that the application provides.
Modality-Specific Homework
Evidence suggests that a variety of modality-specific homework assignments on mobile apps are effective, including relaxation practices, cognitive therapy, imaginal exposure in GAD and PTSD [ 54 , 57 ], multimedia solutions for skill learning and problem solving in children with disruptive behavior or anxiety disorders [ 63 ], relaxation and cognitive therapy in GAD [ 62 ], or self-monitoring via text messages (short message service, SMS) to therapists in bulimia nervosa [ 61 ]. Mayo Clinic Anxiety Coach, for example, has a treatment module for OCD that “guides patients through the use of exposure therapy” [ 55 ]; patients can use this to build their own fear hierarchies according to their unique diagnoses. Users reported liking the app because it contains modality-specific homework that can be tailored to their own needs. Novel formats, such as virtual reality apps to create immersive environments, have been experimented with as a tool for facilitating exposure in the treatment of anxiety disorders with mostly positive feedback [ 64 - 66 ]. Apps that provide elements of biofeedback (such as heart rate monitoring via colorimetry of users' faces using the mobile phone's camera), have recently begun to be deployed. So-called ”serious games,“ (ie, games developed for treatment purposes), are also showing promise in symptom improvement in certain cases [ 51 , 67 , 68 ].
Fostering Learning
Doing CBT homework properly requires time and effort. As noted above, any sense of inconvenience while doing the homework may hamper a patient’s motivation to complete the homework. While patients may appreciate the importance of doing homework, they often find the length of time spent and the lack of clear instructions discouraging, resulting in poor engagement rates [ 49 , 52 ]. Therefore, it makes sense that the tasks should be simple, short in duration to begin with, and include detailed instructions [ 47 ], since homework completion rates have been shown to be correlated with patients’ knowing exactly what to do [ 33 , 69 ]. Many apps incorporate text messaging-based services or personalized feedback to encourage dynamic interactions between the therapist and the client [ 59 ]. However, the types of homework delivered by these apps are fixed. An app that adapts the contents to the user’s progress in learning homework tasks would be more engaging and effective since therapy should be a flexible process by nature. Ideally, the app would monitor and analyze the user’s progress and adjust the homework's content and difficulty level accordingly. While the effectiveness of this type of app has not been studied, a similar app has been described in the literature for treating GAD [ 62 ]. This app, used in conjunction with group CBT, collected regular symptom rating self-reports from patients to track anxiety. Based on patients’ ratings, the app would respond with encouraging comments and invite patients to practice relaxation techniques or prompt the patient to complete specific built-in cognitive therapy modules if their anxiety exceeded a threshold rating. Despite the simple algorithm used to trigger interventions, use of the app with group CBT was found to be superior to group CBT alone.
Guiding Therapy
Therapists have a number of important roles to play in guiding and motivating clients to complete homework. First, the therapist needs to address the rationale of the prescribed homework and work with the client in the development of the treatment plan [ 47 ]. Failure to do this has been identified as a barrier to homework compliance. Second, the therapist should allow the patient to practice the homework tasks during the therapy sessions [ 47 ] in order to build confidence and minimize internal barriers, such as the failing to identify automatic thoughts. Lastly, the therapist has to be collaborative, regularly reviewing homework progress and troubleshooting with the patients [ 47 , 70 ]; this can be done during or in between homework assignments, either in-person or remotely (ie, via voice or text messaging) [ 60 , 71 ].
Reviewing and troubleshooting homework has been seen as a natural opportunity for apps to augment the role of therapists. Individualized guidance and feedback on homework is found in many Internet-based or mobile apps that have been shown to be effective in treating conditions such as PTSD [ 72 ], OCD [ 55 ], chronic pain [ 59 , 60 ], depression and suicide ideation [ 71 ], and situational stress [ 73 ]. Moreover, providing a rationale for homework, ensuring understanding of homework tasks, reviewing homework, and troubleshooting with a therapist have each individually been identified as predictors of homework compliance in CBT [ 74 , 75 ]. However, despite incorporating a variety of features including self-monitoring, psychoeducation, scheduled reminders, and graphical feedback [ 52 ], automated apps with minimal therapist guidance have demonstrated elevated homework non-completion rates of up to 40%, which is less than ideal.
Building Connections
The effects of technology should not interfere with but rather encourage a patient’s ability to build meaningful connections with others [ 76 ]. The therapeutic alliance between the therapist and the client is the strongest predictor of therapeutic outcome [ 77 ] and has been suggested to predict level of homework compliance as well [ 78 ]. While there is no evidence so far to suggest that technology-based interventions have an adverse effect on the therapeutic alliance [ 79 , 80 ], this conclusion should not be generalized to novel technologies as their impact on therapeutic alliance has not been well studied [ 81 ].
An arguably more significant innovation attributable to technology has been its potential to allow patients to form online communities, which have been identified as useful for stigma reduction and constructive peer support systems [ 82 ]. Online or virtual communities provide patients with a greater ability to connect with others in similar situations or with similar conditions than would be possible physically. Internet-delivered CBT that includes a moderated discussion forum has been shown to significantly improve depression symptoms [ 83 ]. Furthermore, professional moderation of online communities increases users’ trust of the service [ 84 ]. Therefore, including social platforms and online forums in a mobile app may provide additional advantages over conventional approaches by allowing easier access to social support, fostering collaboration when completing homework, and enabling communication with therapists.
Emphasizing Completion
A patient’s need to see immediate symptomatic improvement is an impediment to homework compliance since the perception of slow progress can be discouraging to the user [ 35 ]. To address this issue, it is important for both therapists and mobile apps to emphasize homework completion over outcome [ 47 ]. While a therapist can urge the client to finish uncompleted homework during the therapy session to reinforce its importance [ 47 , 85 ], there is little a therapist can do in between therapy sessions to remind clients to complete homework. In contrast, a mobile app can, for example, provide ongoing graphical feedback on progress between sessions to motivate users [ 52 , 86 ], or employ automatic text message reminders, which have been demonstrated to significantly improve treatment adherence in medical illnesses [ 87 ]. These features have previously been incorporated into some technology-based apps for homework adherence when treating stress, depression, anxiety, and PTSD [ 52 , 54 , 88 ] with significant symptom improvement reported in one paper [ 71 ].
Population Specificity
Homework apps should, where relevant or useful, explicitly be designed taking into account the specific characteristics of its target audience, including culture, gender, literacy, or educational levels (including learning or cognitive disabilities). One example of how culture-specific design features can be incorporated can be found in Journal to the West, a mobile app for stress management designed for the Chinese international students in the United States, which incorporates cultural features into its game design [ 89 ]. In this game, breathing activity is associated with the concept of “Qi” (natural energy) in accordance with Chinese traditions; the name of the game itself references to a famous Chinese novel and the gaming environment features inkwash and watercolor schemes of the East Asian style, making the experience feel more “natural” as reported by the users. A different approach to tailoring design is taken by the computer-based games described by Kiluk et al [ 68 ] that combine CBT techniques and multi-touch interface to teach the concepts of social collaboration and conversation to children with autism spectrum disorders. In these games, the touch screen surface offers simulated activities where children who have difficulties with peer engagement can collaborate to accomplish tasks. Children in this study demonstrated improvement in the ability to provide social solutions and better understanding of the concepts of collaboration. Although the population-specific design is intuitively appealing, the degree to which it can enhance homework compliance has yet to be investigated.
Other Considerations
There are several additional issues specific to mobile apps that should be carefully considered when developing mobile apps for homework compliance. Because of screen sizes, input modes, the nature of electronic media, etc, standard CBT homework may need to be translated or modified to convert it into a format optimal for delivery via a mobile phone [ 47 ]. The inclusion of text messaging features remains controversial, in part because of concerns about client-therapist boundary issues outside the therapy sessions [ 90 ]. One potential solution is to use automated text messaging services to replace direct communication between the therapist and the client so the therapist can't be bombarded by abusive messages [ 52 , 61 , 91 , 92 ]. Privacy and security issues are also real concerns for the users of technology [ 93 ], although no privacy breaches related to text messaging or data security have been reported in studies on mobile apps so far [ 88 , 94 - 98 ]. Designers of mobile apps should ensure that any sensitive health-related or personal data is stored securely, whether on the mobile device or on a server.
Finally, while this paper focused on “essential” features of apps, this should not be misunderstood as an attempt to itemize all elements necessary for designing a successful piece of software. Good software design depends on many important elements that are beyond the scope of this paper, such as a well-designed user interface [ 99 ] that is cognitively efficient relative to its intended purpose [ 100 ] and which makes effective use of underlying hardware.
The popularization and proliferation of the mobile phone presents a distinct opportunity to enhance the success rate of CBT by addressing the pervasive issue of poor homework compliance. A variety of barriers exist in traditional, paper-based CBT homework that can significantly hamper clients’ motivation to complete homework as directed. The 6 essential features identified in this paper can each potentially enhance homework compliance. Therapy congruency focuses the features of the app on the central goal of therapy and fostering learning eases engagement in therapy by reducing barriers. Apps should help the therapist guide the client through therapy and not hinder the therapeutic process or interfere with patient’s building connections with others. It is crucial that homework completion be emphasized by the app, not just homework attempting. Population-specific issues should also be considered depending on the characteristics of targeted users.
As an example of how this applies in practice, “Mental Health Telemetry-Anxiety Disorders” (MHT-ANX) is a new mobile app developed by the Centre for Mobile Computing in Mental Health at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto that helps patients monitor their anxiety symptoms using longitudinal self-report. The symptom log is therapy congruent to the practice of CBT since it promotes patients' awareness of their anxiety symptoms and the symptoms’ intensity. The simplicity of the app makes it easy for patients to learn to use, consistent with the need for fostering learning and increasing compliance. The MHT-ANX app was designed to share patient data with their clinicians, helping clinicians guide patients through therapy and more readily engage in discussion about symptom records, thus potentially enhancing the therapeutic relationship. Homework completion is emphasized both by automated text message reminders that the system sends and by questions presented by MHT-ANX that focus on how homework was done. While there are few population-specific design issues obvious at first glance in MHT-ANX, the focus groups conducted as part of our design process highlighted that our target group preferred greater privacy in our app rather than ease of sharing results via social media, and prioritized ease-of-use. While not yet formally assessed, reports from staff and early users suggest that MHT-ANX has been helpful for some patients with promoting homework compliance.
Limitations and Future Challenges
The feature list we have compiled is grounded in current technology; as technology evolves, this list may need to be revised. For example, as artificial intelligence [ 101 ] or emotional sensing [ 102 ] develops further, we would expect that software should be able to dynamically modify its approach to the user in response to users' evolving emotional states.
This paper presents our opinion on this topic, supported by a survey of associated literature. Our original intention was to write a review of the literature on essential features of apps supporting CBT homework compliance, but there was no literature to review. The essential features that are the focus of this article are summaries of key characteristics of mobile apps that are thought to improve homework compliance in CBT, but randomized trials assessing the impact of these apps on homework compliance have not yet been done. We would anticipate synergistic effects when homework-compliance apps are used in CBT (eg, if measures of progress collected from an app were used as feedback during therapy sessions to enhance motivation for doing further CBT work), but the actual impact and efficacy of therapy-oriented mobile apps cannot be predicted without proper investigation.
Abbreviations
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
- How It Works
- Sleep Meditation
- VA Workers and Veterans

- How It Works 01
- Sleep Meditation 02
- Mental Fitness 03
- Neurofeedback 04
- Healium for Business 05
- VA Workers and Veterans 06
- Sports Meditation 07
- VR Experiences 08
- Social Purpose 11
Does Homework Cause Stress? Exploring the Impact on Students’ Mental Health
How much homework is too much?

Jump to: The Link Between Homework and Stress | Homework’s Impact on Mental Health | Benefits of Homework | How Much Homework Should Teacher’s Assign? | Advice for Students | How Healium Helps
Homework has become a matter of concern for educators, parents, and researchers due to its potential effects on students’ stress levels. It’s no secret students often find themselves grappling with high levels of stress and anxiety throughout their academic careers, so understanding the extent to which homework affects those stress levels is important.
By delving into the latest research and understanding the underlying factors at play, we hope to curate insights for educators, parents, and students who are wondering is homework causing stress in their lives?
The Link Between Homework and Stress: What the Research Says
Over the years, numerous studies investigated the relationship between homework and stress levels in students.
One study published in the Journal of Experimental Education found that students who reported spending more than two hours per night on homework experienced higher stress levels and physical health issues . Those same students reported over three hours of homework a night on average.
This study, conducted by Stanford lecturer Denise Pope, has been heavily cited throughout the years, with WebMD eproducing the below video on the topic– part of their special report series on teens and stress :
Additional studies published by Sleep Health Journal found that long hours on homework on may be a risk factor for depression while also suggesting that reducing workload outside of class may benefit sleep and mental fitness .
Lastly, a study presented by Frontiers in Psychology highlighted significant health implications for high school students facing chronic stress, including emotional exhaustion and alcohol and drug use.
Homework’s Potential Impact on Mental Health and Well-being
Homework-induced stress on students can involve both psychological and physiological side effects.
1. Potential Psychological Effects of Homework-Induced Stress:
• Anxiety: The pressure to perform academically and meet homework expectations can lead to heightened levels of anxiety in students. Constant worry about completing assignments on time and achieving high grades can be overwhelming.
• Sleep Disturbances : Homework-related stress can disrupt students’ sleep patterns, leading to sleep anxiety or sleep deprivation, both of which can negatively impact cognitive function and emotional regulation.
• Reduced Motivation: Excessive homework demands could drain students’ motivation, causing them to feel fatigued and disengaged from their studies. Reduced motivation may lead to a lack of interest in learning, hindering overall academic performance.
2. Potential Physical Effects of Homework-Induced Stress:
• Impaired Immune Function: Prolonged stress could weaken the immune system, making students more susceptible to illnesses and infections.
• Disrupted Hormonal Balance : The body’s stress response triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which, when chronically elevated due to stress, can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance and lead to various health issues.
• Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Stress has been known to affect the gastrointestinal system, leading to symptoms such as stomachaches, nausea, and other digestive problems.
• Cardiovascular Impact: The increased heart rate and elevated blood pressure associated with stress can strain the cardiovascular system, potentially increasing the risk of heart-related issues in the long run.
• Brain impact: Prolonged exposure to stress hormones may impact the brain’s functioning , affecting memory, concentration, and cognitive abilities.
The Benefits of Homework
It’s important to note that homework also offers many benefits that contribute to students’ academic growth and development, such as:
• Development of Time Management Skills: Completing homework within specified deadlines encourages students to manage their time efficiently. This valuable skill extends beyond academics and becomes essential in various aspects of life.
• Preparation for Future Challenges : Homework helps prepare students for future academic challenges and responsibilities. It fosters a sense of discipline and responsibility, qualities that are crucial for success in higher education and professional life.
• Enhanced Problem-Solving Abilities: Homework often presents students with challenging problems to solve. Tackling these problems independently nurtures critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
While homework can foster discipline, time management, and self-directed learning, the middle ground may be to strike a balance that promotes both academic growth and mental well-being .
How Much Homework Should Teachers Assign?
As a general guideline, educators suggest assigning a workload that allows students to grasp concepts effectively without overwhelming them . Quality over quantity is key, ensuring that homework assignments are purposeful, relevant, and targeted towards specific objectives.
Advice for Students: How to balance Homework and Well-being
Finding a balance between academic responsibilities and well-being is crucial for students. Here are some practical tips and techniques to help manage homework-related stress and foster a healthier approach to learning:
• Effective Time Management : Encourage students to create a structured study schedule that allocates sufficient time for homework, breaks, and other activities. Prioritizing tasks and setting realistic goals can prevent last-minute rushes and reduce the feeling of being overwhelmed.
• Break Tasks into Smaller Chunks : Large assignments can be daunting and may contribute to stress. Students should break such tasks into smaller, manageable parts. This approach not only makes the workload seem less intimidating but also provides a sense of accomplishment as each section is completed.
• Find a Distraction-Free Zone : Establish a designated study area that is free from distractions like smartphones, television, or social media. This setting will improve focus and productivity, reducing time needed to complete homework.
• Be Active : Regular exercise is known to reduce stress and enhance mood. Encourage students to incorporate physical activity into their daily routine, whether it’s going for a walk, playing a sport, or doing yoga.
• Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques : Encourage students to engage in mindfulness practices, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, to alleviate stress and improve concentration. Taking short breaks to relax and clear the mind can enhance overall well-being and cognitive performance.
• Seek Support : Teachers, parents, and school counselors play an essential role in supporting students. Create an open and supportive environment where students feel comfortable expressing their concerns and seeking help when needed.
How Healium is Helping in Schools
Stress is caused by so many factors and not just the amount of work students are taking home. Our company created a virtual reality stress management solution… a mental fitness tool called “Healium” that’s teaching students how to learn to self-regulate their stress and downshift in a drugless way. Schools implementing Healium have seen improvements from supporting dysregulated students and ADHD challenges to empowering students with body awareness and learning to self-regulate stress . Here’s one of their stories.
By providing students with the tools they need to self-manage stress and anxiety, we represent a forward-looking approach to education that prioritizes the holistic development of every student.
To learn more about how Healium works, watch the video below.
About the Author

Sarah Hill , a former interactive TV news journalist at NBC, ABC, and CBS affiliates in Missouri, gained recognition for pioneering interactive news broadcasting using Google Hangouts. She is now the CEO of Healium, the world’s first biometrically powered immersive media channel, helping those with stress, anxiety, insomnia, and other struggles through biofeedback storytelling. With patents, clinical validation, and over seven million views, she has reshaped the landscape of immersive media.
More From Forbes
Anxiety skyrockets to no. 1 issue among american workers, new study shows.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Anxiety at work reaches number one in mental health issues among the American workforce.
As the workplace headed into 2022—the third year of the pandemic—the incidence of job stress and burnout jumped to an all-time high. The American Psychological Association’s Work and Well-Being study found that 79% of the 1,501 employees surveyed experienced work-related stress in the month before the survey, and 3 in 5 workers said work-related stress caused them to have a lack of interest, motivation and energy at work. Plus, 36% had cognitive weariness, 32% emotional exhaustion, and 44% physical fatigue—a 38% jump from 2019.
Worker Anxiety Going Through The Roof In 2024
When reviewing 2023 survey data, APA psychologists widely agree there is mounting evidence that our society is experiencing the psychological impacts of a collective trauma. Although the pandemic might seem like a distant past, its aftermath along with the psychological impact of global conflict, racism, mass shootings, climate-related disasters and a turbulent economy are weighing on the mental health of the American workforce in 2024.
The latest data analysis from ComPsych analysis —based on a representative sample of more than 300,000 U.S. cases—found that anxiety is now the number one presenting issue among American workers, topping depression, stress, partner/relationship issues, family issues and addiction and grief among other topics people sought help for. In fact, in 2023 nearly a quarter of people (24%) who reached out for mental health assistance did so to get help with anxiety. This jump is especially notable as up until 2017, anxiety didn’t rank in the top five presenting issues for Americans.
According to Dr. Richard Chaifetz, founder, chairman and CEO of ComPsych. “As a society, we’re notably more anxious now than we were just five years ago, and it’s not shocking considering current world events: from the lasting impacts of COVID-19 to civil unrest, an increasingly polarized political landscape, global turmoil, the border crisis and rising crime, the proliferation of AI and an unpredictable economy—there are so many macro issues impacting people’s mental health in addition to interpersonal and personal situations.”
This trend is important for business leaders to be mindful of, particularly as mental health related leaves of absences have exploded in recent years. ComPsych data shows these leaves have increased by 300% since 2017. “For business leaders, there is an imperative to help employees cope with these feelings,” Chaifetz continued. “Companies who invest in resources for employees ultimately benefit by attracting and retaining a healthier and more productive workforce, allowing both employees and companies to thrive.”
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024, amp up your work health to mitigate anxiety.
While employers share some responsibility to create a stress-free workplace, employees also have a responsibility to their work health that is essential for long-term mental and physical viability and the trajectory of their careers. If you toil in a toxic work culture, it’s important to weigh your options and find a workplace that prides itself on employee-centered empathy and care. These work cultures are increasing as a result of the pandemic and The Great Resignation and employee demands for positive change. Even if you work in a healthy environment, chronic anxiety doesn’t give your body a chance to return to its natural resting state. The key is to create an anxiety care plan to offset any potential damage so you can reset your brain and keep it healthy. Here are 10 science-backed steps to help you create your own personalized anxiety care plan to mitigate chronic stress and thrive at work:
- Meditation limits cortisol levels by 25%, according to research, and it reduces mind wandering, free-floating anxiety and mistakes, keeping you on task at work.
- Anxiety prevention foods promote mindful productivity and work health. Aim for protein, Omega-3 fatty acids, eggs, pumpkin seeds, B vitamins and Vitamin D, dark chocolate, turmeric, chamomile, yogurt, green tea and Brazil nuts.
- Regular exercise such as brisk walking re-calibrates a fatigued brain and reduces your risk of developing anxiety by almost 60%.
- Positive self-talk can stop catastrophic mind chatter that causes anxiety and keep you calm in stressful situations.
- Sleep deprivation leads to anxiety, and ample sleep is restorative for calming your mind and contributing to your work health.
- Microbreaks —short breaks of five minutes—throughout the workday mitigate fatigue, reduce anxiety and keep your brain rested and clear.
- Mindful abdominal breathing keeps your mind sharp and focused in the present moment when anxiety tries to steal your breath away.
- An optimistic outlook prevents anxiety from ruling your mind and gives you better memory at work. Plus, looking for the opportunity in the problem helps you scale the career ladder faster and farther than pessimism, according to research.
- Brain scans of people who spend time outdoors show their prefrontal cortex has more gray matter plus a stronger ability to think clearly and self-regulate stress and anxiety.
- Social engagement mitigates cognitive decline, enhances gray matter in the brain and helps reduce anxiety. So it’s important to avoid working in isolation and maintain social connections with coworkers to keep your mind active and healthy.
Our society has become more anxious since the pandemic. The macro events of the nation and world have impacted all of us, compounding the ongoing stressors in the workplace. Most of us can no longer depend on our employers to decide what’s in our best mental health interests. You’re the captain of your ship—not a passenger. You’re in control of your mental health, not your employer. Evaluate your job and life and decide for yourself what reasonable steps you can take to mitigate your anxiety and amp up your work health.
As far as business leaders go, Chaifetz offers sage advice. “It’s vital that employers understand this and invest in their workforce’s well-being. Specifically, I recommend investing in training managers to talk about mental health and to know what their company’s resources are for those struggling with anxiety or other mental health challenges. It’s also important that organizations develop resources and programming that are specific to the unique stressors of the modern world beyond focusing just on mental health alone.”

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health ...
Use a calm voice. When kids feel anxious about homework, they might get angry, yell, or cry. Avoid matching their tone of voice. Take a deep breath and keep your voice steady and calm. Let them know you're there for them. Sometimes kids just don't want to do homework. They complain, procrastinate, or rush through the work so they can do ...
• Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty ...
This list is hardly comprehensive. ADHD, autism spectrum disorder, social anxiety, generalized anxiety, panic disorder, depression, dysregulation, and a range of other neurodevelopmental and ...
"Homework has perennially acted as a source of stress for students, so that piece of it is not new," Galloway says. "But especially in upper-middle-class communities, where the focus is on getting ahead, I think the pressure on students has been ratcheted up." Yet homework can be a problem at the other end of the socioeconomic spectrum as well.
Effects of homework stress at home. Both parents and students tend to get stressed out at the beginning of a new school year due to the impending arrival of homework.. Nightly battles centered on finishing assignments are a household routine in houses with students. Research has found that too much homework can negatively affect children. In creating a lack of balance between play time and ...
5. Practice Makes Perfect. The Stanford study shows that repeated exposure to math problems through one-on-one tutoring helped students relieve their math anxiety (the authors' analogy was how a fear of spiders can be treated with repeated exposure to spiders in a safe environment). Find a tutor you love, and come back to keep practicing ...
Here are 10 tips to help your child learn how to make homework less stressful. 1. Stick to a Schedule. Help your child plan out his or her time, scheduling time for homework, chores, activities, and sleep. Keep this schedule handy so your child knows what he or she should be working on, and when. 2.
What is stress? Stress is the physical or mental response to an external cause, such as having a lot of homework or having an illness. A stressor may be a one-time or short-term occurrence, or it can happen repeatedly over a long time. What is anxiety? Anxiety is your body's reaction to stress and can occur even if there is no current threat.
Exercise. Exercise can be a highly effective way to deal with things in your life that are causing distress. Research has also found that regular physical activity can protect people against stress and anxiety while also promoting positive emotions. Exercise can be beneficial for a variety of reasons.
Homework anxiety is a condition in which students stress about and fear homework, often causing them to put homework off until later. It is a self-exacerbating condition because the longer the student puts off the homework, the more anxiety they feel about it, and the more pressure they experience to finish the work with less time.
Does homework cause stress? Short answer: Yes. It's been well documented that too much homework can cause stress and anxiety for students-and their parents. However, do the benefits of homework outweigh the costs? Is homework "worth" the frustration and exhaustion that our children experience?
CBT Worksheets for Anxiety. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) treats anxiety by restructuring the client's thinking, with the therapist exploring maladaptive expectations and worries related to upcoming events (Dobson & Dozois, 2021).. 1. Anxiety Record. Reflecting on and sharing what makes us anxious can leave us feeling vulnerable, but it is essential.
Homework is associated with some level of stress for most children. However, for youth with an anxiety disorder, the pressure of assignments, tests, and deadlines can provoke panic and can disable ...
Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes? Should we get rid of homework? In " The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, " published ...
Keywords: homework, stress, mental health The outcomes of adolescent mental health is a threat to students' health and wellbeing, more so than it ever has been in the modern era. As of 2019, the CDC reported a nearly 40. percent increase in feelings of sadness or hopelessness over the last ten years, and similar.
Almost all students deal with the burden of homework-related stress. No one enjoys the anxiety of having a lot of assignments due and not enough time to complete them. But take advantage of this opportunity to learn organization and self-discipline, which will help you throughout your life. ... School stress is hard to avoid, but if you take ...
Michaud et al. (2015) also found more hours spent on homework was associated with physical health problems and they have emphasized an extra attention should be paid to stressful mental work due to homework duration. To better measure stress experienced by doing homework, Katz et al. (2012) validated a relevant homework stress scale, in which a ...
Homework Non-Compliance in CBT. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is an evidence-based psychotherapy that has gained significant acceptance and influence in the treatment of depressive and anxiety disorders and is recommended as a first-line treatment for both of these [1,2].It has also been shown to be as effective as medications in the treatment of a number of psychiatric illnesses [3-6].
1. Potential Psychological Effects of Homework-Induced Stress: • Anxiety: The pressure to perform academically and meet homework expectations can lead to heightened levels of anxiety in students. Constant worry about completing assignments on time and achieving high grades can be overwhelming. • Sleep Disturbances: Homework-related stress ...
Anxiety at work reaches number one in mental health issues among the American workforce. getty. As the workplace headed into 2022—the third year of the pandemic—the incidence of job stress and ...
Which neurotransmitter is commonly associated with the regulation of anxiety and stress responses in the brain?a) Dopamineb) Serotoninc) Acetylcholined) GABA (Gamma-aminobutyric acid) This problem has been solved!