
- High contrast
- Press Centre

Search UNICEF
Education in a post-covid world, towards a rapid transformation.
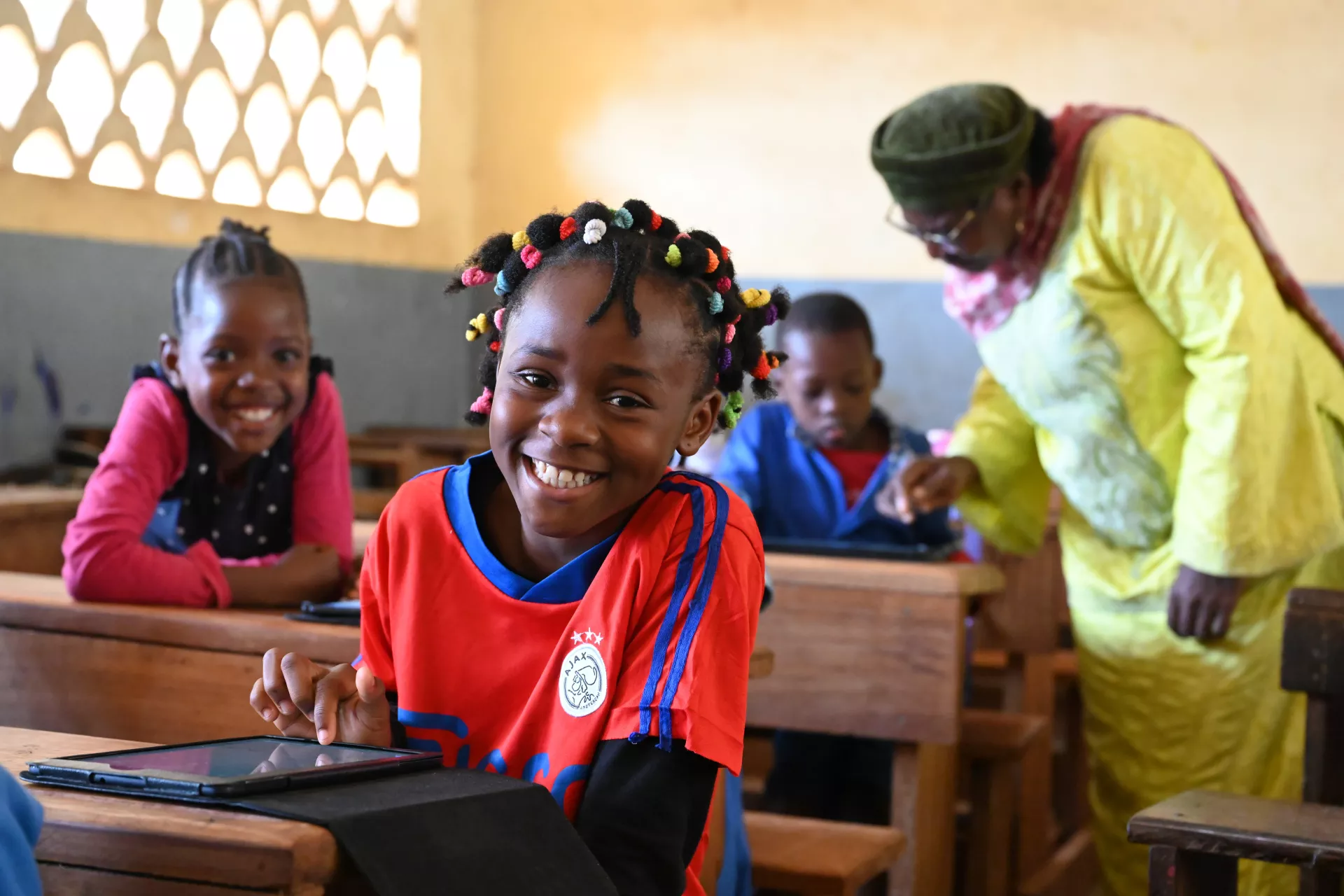

On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a global pandemic, resulting in disruptions to education at an unprecedented scale. In response to the urgent need to recover learning losses, countries worldwide have taken RAPID actions to: R each every child and keep them in school; A ssess learning levels regularly; P rioritize teaching the fundamentals; I ncrease the efficiency of instruction; and D evelop psychosocial health and wellbeing.
Marking three years since the onset of the pandemic, this report looks back at policy measures taken during school closures and reopening based on country survey data, initiatives implemented by countries and regions to recover and accelerate learning, and their emerging lessons within each RAPID action. With schools now reopened worldwide, this report also looks ahead to longer-term education transformation, offering policy recommendations to build more resilient, effective and equitable education systems.

Files available for download
Related topics, more to explore, millions at risk from cholera due to lack of clean water, soap and toilets, and shortage of cholera vaccine, water and the climate crisis: 10 things you should know.
The world needs to get water smart. Everyone has a role to play, and we cannot afford to wait
10 facts about water that might surprise you
How unsafe water, sanitation and hygiene puts children at risk
The urgent need for a child-centred Loss and Damage Fund
The Loss and Damage Fund should put children’s voices at the heart of climate justice
- +1 215 942 8226
- Planning Tools
- Travel Advice
- Email Sign up
Quick Links
- +1 215 942 8226 Call for assistance
- Pandemic Preparedness
- Education and Communication
Short, imaged-based course and posters that do not require high levels of literacy. These are designed to support locations with weaker health systems that are ill-prepared to deal with COVID-19 (2019-novel coronavirus). CONDITIONS OF USE International SOS logo and disclaimers must be retained and visible. Contact International SOS by email for permission to reproduce content (text and images) in a different format.
On this page:
COVID-19 Journey Planner PowerPoint Slides
COVID-19 What you need to know PowerPoint Slides
COVID-19 Vaccination Benefits Infographic
COVID-19 Vaccination and Pregnancy Infographic
COVID-19 What you need to know A3 Infographic Poster
COVID-19 Long-COVID Information Sheet
COVID-19 Long-COVID Infographic
COVID-19 Transmission Infographic
COVID-19 Social Distancing Infographic
COVID-19 Stress Infographic
COVID-19 Hotel Quarantine Tips Infographic
COVID-19 Workplace Posters and a Social Distancing Sticker

COVID-19 Long-COVID Information Sheet - English [ PDF, 43kb ] COVID-19 Long-COVID Information Sheet - Bahasa Indonesian [ PDF, 340kb ] COVID-19 Long-COVID Information Sheet - French [ PDF, 33kb ] COVID-19 Long-COVID Information Sheet - German [ PDF, 42kb ] COVID-19 Long-COVID Information Sheet - Portuguese [ PDF, 33kb ] COVID-19 Long-COVID Information Sheet - Russian [ PDF, 167kb ] COVID-19 Long-COVID Information Sheet - Spanish [ PDF, 42kb ]

COVID-19 Long-COVID Infographic - English [ PDF, 152kb ] COVID-19 Long-COVID Infographic - Bahasa Indonesian [ PDF, 347kb ] COVID-19 Long-COVID Infographic - French [ PDF, 296kb ] COVID-19 Long-COVID Infographic - German [ PDF, 293kb ] COVID-19 Long-COVID Infographic - Portuguese [ PDF, 1.5mb ] COVID-19 Long-COVID Infographic - Russian [ PDF, 1.44mb ] COVID-19 Long-COVID Infographic - Spanish [ PDF, 1.4mb ]

COVID-19 Patients Only A3 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ] COVID-19 Patients Only A4 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ] COVID-19 Patients Only A3 Poster - Bahasa Indonesian [ PDF, 148kb ] COVID-19 Patients Only A3 Poster - Chinese [ PDF, 66kb ] COVID-19 Patients Only A3 Poster - Russian [ PDF, 96kb ]
COVID-19 Please Wait A3 Poster - English [ PDF, 15kb ] COVID-19 Please Wait A4 Poster - English [ PDF, 15kb ] COVID-19 Please Wait A3 Poster - Bahasa Indonesian [ PDF, 180kb ] COVID-19 Please Wait A3 Poster - Chinese [ PDF, 91kb ] COVID-19 Please Wait A3 Poster - Russian [ PDF, 89kb ]
COVID-19 Social Distancing Zone A3 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ] COVID-19 Social Distancing Zone A4 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ] COVID-19 Social Distancing Zone A3 Poster - Chinese [ PDF, 127kb ]
COVID-19 Social Distancing 1.5m A3 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ] COVID-19 Social Distancing 1.5m A4 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ] COVID-19 Social Distancing 1.5m A3 Poster - Chinese [ PDF, 67kb ]
COVID-19 Social Distancing 1-2m/3-6ft A3 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ] COVID-19 Social Distancing 1-2m/3-6ft A4 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ] COVID-19 Social Distancing 1-2m/3-6ft A3 Poster - Bahasa Indonesian [ PDF, 147kb ] COVID-19 Social Distancing 1-2m/3-6ft A3 Poster - Chinese [ PDF, 92kb ]
COVID-19 Social Distancing 2m/6ft A3 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ] COVID-19 Social Distancing 2m/6ft A4 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ]
COVID-19 Social Distancing 6ft/2 arms' A3 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ] COVID-19 Social Distancing 6ft/2 arms' A4 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ] COVID-19 Social Distancing 6ft/2 arms' A3 Poster - Chinese [ PDF, 93kb ]
COVID-19 Symptoms A3 Poster - English [ PDF, 90kb ] COVID-19 Symptoms A4 Poster - English [ PDF, 89kb ] COVID-19 Symptoms A3 Poster - Bahasa Indonesian [ PDF, 434kb ] COVID-19 Symptoms A3 Poster - Chinese [ PDF, 262kb ] COVID-19 Symptoms A3 Poster - Russian [ PDF, 244kb ]
COVID-19 Temperature Check A3 Poster - English [ PDF, 18kb ] COVID-19 Temperature Check A4 Poster - English [ PDF, 28kb ] COVID-19 Temperature Check A3 Poster - Bahasa Indonesian [ PDF, 188kb ] COVID-19 Temperature Check A3 Poster - Chinese [ PDF, 212kb ] COVID-19 Temperature Check A3 Poster - Russian [ PDF, 172kb ]
COVID-19 Waiting Room Capacity A3 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ] COVID-19 Waiting Room Capacity A4 Poster - English [ PDF, 16kb ] COVID-19 Waiting Room Capacity A3 Poster - Bahasa Indonesian [ PDF, 182kb ] COVID-19 Waiting Room Capacity A3 Poster - Chinese [ PDF, 232kb ] COVID-19 Waiting Room Capacity A3 Poster - Russian [ PDF, 88kb ]
COVID-19 Social Distancing Floor Sticker 1.5m - English [ PDF, 8kb ] COVID-19 Social Distancing Floor Sticker 1-2m/3-6ft - English [ PDF, 8kb ] COVID-19 Social Distancing Floor Sticker 6ft/2 arms' - English [ PDF, 8kb ]
Please send any comments or feedback to email .
COVID-19 What you need to know Infographic

COVID-19 - What you need to know A3 Infographic Poster - English [ PDF, 389kb ]

COVID-19 Vaccination and Pregnancy Infographic - English [ PDF, 664kb ]
- Travel restrictions flight operations and screening
- COVID-19 Variants
- Pandemic Home
- Terms and Conditions

Additional data provided by

Please download the file to view it
COVID-19 PowerPoint Presentation on How to Use the Toolkit English
In January 2020 the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak of a new coronavirus disease in Hubei Province, China to be a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. Since then WHO has declared it as a Pandemic affecting more than 115 countries around the globe. India witnessed its first COVID-19 case in Kerala on 30th January 2020. With cases rising steadily, all sections of our society must play a role if we are to stop the spread of this disease and the frontline health worker has the responsibility, the reach and the influence within the community. UNICEF and WHO are supporting the government of India in taking action to contain the COVID-19 outbreak. Towards this UNICEF and WHO developed a training toolkit for training FLWs on COVID response and containment measures. The toolkit consists of this PowerPoint presentation on how to use the FLW Toolkit. This PPT is for Trainers and is a guide on each of the contents that are a part of the FLW Toolkit.
Related Assets
161 downloads

COVID-19 PowerPoint Presentation for FLW Training English
2114 downloads
0 downloads
COVID-19 Pocket Book of Five for ANM, ASHA, AWW English
211 downloads
COVID-19 FACILITATOR GUIDE for Training ANM, ASHA, or AWW English
230 downloads
Request Document
Post feedback.

Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

palm sunday
5 templates

solar eclipse
25 templates

11 templates
weather report
12 templates

26 templates

moon phases
13 templates
Economic Impact of Coronavirus
Economic impact of coronavirus presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
The recent coronavirus pandemic has forced many businesses and industries to stop their activities until society can start resuming a normal life again. This, in turn, is causing an economic impact on most countries. Customize our latest template to present your data on this subject.
Economy is one of the pillars of measuring how good or bad a country is doing. To maximize the understanding of your information, our slides come with an appealing duotone effect for the pictures, granting a modern and up-to-date appearance to the design. You’ll notice that most layouts are based on rectangular shapes, which helps getting everything well organized and into place. The title font is bold and the body copy sans font is also geometric in nature. We wanted to include some actual data on the slides as inspiration for you, so don’t miss out on this chance!
Features of this template
- A duotone-based design with pictures and rectangular shapes
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 23 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics, maps and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the free resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?

Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Register for free and start editing online
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Elsevier - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Impact of COVID-19: a particular focus on Indian education system
Pushpa gothwal.
1 Amity School of Enginnering and Technology, Amity University Rajasthan, Jaipur, India
Bosky Dharmendra Sharma
2 Mayoor Private School, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Nandita Chaube
3 Gujarat Forensic Sciences University, Gandhinagar, India
Nadeem Luqman
4 Ansal University, New Delhi, India
The COVID-19 pandemic has stirred up the world, and its overwhelming impacts can be seen from micro to macro level, that is, from an individual’s day-to-day functioning to the broader level—health sector, finance sector, and off course, the education sector. The younger generation is considered to be the torchbearer of the society. As such, their nutrition, health, safety, and providing education for a holistic development being basic essential needs should be a prime concern for policymakers and all nations worldwide. The present theoretical framework sheds light on the negative as well as the positive impact of COVID-19 on education. It presents a critical analysis of how the education sector experienced a shift from contact teaching to digital learning and got a boost through various online platforms despite having its limitations at the same time including the multidimensional impact of uncertainty and difficulties in sustaining. The chapter also emphasizes the effects of home confinements on students and teachers as well. In this way, the present chapter puts forth the pros and cons of online teaching including various other related aspects.
12.1. Introduction
The word COVID was first discovered in Ontario Cancer Institute in Toronto in 1963. Since then, various mutations were found in different parts of the world, but COVID-19, which was discovered toward the end of 2019, will be written in the history of 2020. The history indicates such incidences every 100 years. Various types of flu infections such as plague (1720), cholera (1817), Spanish flu (1918), and corona virus (2019) have been declared as pandemics. The diagonals of impact or the crater created due to the situation are major concerns today.
The novel corona virus (COVID-19) was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) on March 11, 2020. It is established that this virus influences the aged persons more ( Zhou et al., 2020 ); however, this view was countered ( Bhatnagar et al., 2020 ) and few others have done descriptive and mathematical analysis of COVID spread and made few predictions upon it which are to be observed ( Harjule et al., 2020 , Kumari et al., 2020 , Singh et al., 2020 ). It has globally impacted many sectors like small and large scale businesses, the world economy, health sector, transportation, wages, industries, education, etc. It is evident by the news reports and other reliable sources that this pandemic has majorly brought adverse consequences. However, it is evident that during the global lockdown, a lot of curricular activities, including regular courses, webinars, faculty development programs, lectures, training, and certification programs, have much flourished when it comes to the education sector. Where this online facility has made education easier and comfortable, it has its limitations also. Here, we have emphasized the impact of COVID-19 on the education sector. As per the UNESCO report, the worldwide lockdown has affected over 91% of the world’s student population ( UNESCO, 2019 ). This estimation predicts that the corona virus will adversely impact over 290 million students across 22 countries. The same report estimates that about 32 crore students are affected in India, including those in schools and colleges.
In this chapter we discuss the impact of COVID-19 with a particular focus on education. This chapter is organized as follows: Section 12.1 is introduction; Section 12.2 throws light on impact of COVID-19 on education, which has two subsections—effect of home confinement on children and teachers, and a multidimensional impact of uncertainty. Section 12.3 describes sustaining the education industry during COVID-19 and conclusions are mentioned in the last section.
12.2. Impact of COVID-19 on education
During this pandemic education sector has experienced gross changes such as a shift from regular contact classes to online platforms, modified teaching pedagogy adopted by teachers, conduction of examinations and competitive exams etc. As per the UNESCO report in the education sector, 1,190,287,189 learners have been affected and 150 countrywide closures ( UNESCO, 2019 ). The effect of COVID-19 on the education and mental health of students and academic staff has been explored in the studies ( Cao et al., 2020 , Sahu, 2020 ). It presents some challenges due to COVID-19 on education. First, to protect the traditional teaching system, which is entirely shifted to online teaching, which requires teachers’ training, strong technical support, and high-speed internet, which is not accessible for everyone. Second, the assessment and evaluation system using an online platform does not provide student performance accuracy because the originality of performance cannot be assured ( Ruder, 2019 ). The students may use some other device to take help while answering the questions asked during the assessment. The third is the research platform, including international travel, cancellation, and postponing conferences and seminars. Other research activities have adversely affected the work ( Hutton, Dudley, Horowitz-Kraus, DeWitt, & Holland, 2020 ). However, many such events have shifted to online platforms based on the possibilities, which has increased the participation and popularity of these events ( Cao et al., 2020 ). The fourth concern is student mental health and career, which is grossly affected due to this outbreak ( Sahu, 2020 ).
Studies have been conducted where the impact of COVID-19 on physicians’ education was to be assessed for which they conducted seminars based on self-regulation theory and found significant results ( Clark et al., 1998 , Ferrel and Ryan, 2020 ). Ferral and Ahmad discussed the pandemic’s impact due to which some hospitals in the United Kingdom canceled students’ internship and observations ( Ahmed et al., 2020 , Ferrel and Ryan, 2020 ). This was reassured by another study, which concluded that, as a preventive measure, many hospitals are not permitting students in hospitals, which is adversely influencing their education ( Burgess & Sievertsen, 2020 ).
Edgar discussed the effects of COVID-19 on higher secondary education and the impact of using Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics education. In this study, the authors collected data through the telephonic mode from public school teachers, where they found a significant drop in these students’ academic performance ( Iyer, Aziz, & Ojcius, 2020 ).
COVID-19 has brought the entire education methods from traditional to online modes. There are various online platforms available for learners and professionals. The students can work with peace of mind while staying at their homes where their time, energy, and money are not wasted traveling. They are not fatigued and hence can invest themselves more in comparison to preCOVID conditions. Studying at home has also provided a more significant benefit to the students being directly monitored by parents. When it comes to theory classes, the online platform has given them a vast chance to excel. However, the practical assignments that the students are supposed to conduct in laboratories and fields have seen a major constraint. This has created a significant limitation of teaching for teachers when they cannot provide the demonstrations to the students in the absence of laboratory instruments and other necessary practical materials.
However, this has led to the timely completion of courses despite the complete lockdown but with incomplete knowledge among students whose courses are more practical. Therefore a combination of these pros and cons has brought the education world to a different level.
Several online platforms are available for lectures, training etc., which have made learning easier ( Bambakidis & Tomei, 2020 ). However, in the absence of contact teaching, a one-to-one discussion between a teacher and students is adversely influenced. The chances of filling this lacuna are also not assured because the students will probably be deprived of contact learning before being promoted to the next level. This again leads to next level difficulties that these students may face shortly soon due to unclear concepts of previous standards/grades ( Sintema, 2020 ). Also, in the absence of a formal class environment, the student’s concentration is more likely to be adversely influenced.
Where the online facility has provided the ease of learning through flexi classes, there is no surety that the student himself or herself is attending the class. Due to network troubles, sometimes the teacher and students face many disturbances. Students sometimes get involved in mischievous activities by making fake email IDs, making noises, or giving unnecessary comments etc. The teacher faces difficulty maintaining discipline. However, this online mode is more appropriate for some disciplines than direct contact teachings, such as web designing, etc., where the practical demonstration can be better understood through online presentation and screen sharing options.
On the other hand, students from the low socio-economic class are getting no chance to experience online learning. This creates a huge and unfair social stratification where learners are left deprived of their legitimate right to education. In developing countries like India, where a huge population belongs to rural backgrounds, people are not so technology friendly. This is another challenge for the Indian education system despite the availability of technological facilities. This difficulty is faced by either or both teacher and student. Teachers who are more apt and comfortable in contact teaching cannot give their 100% through online lectures. A very advantageous and constructive aspect that emerged during the lockdown is that many professionals started throwing free online courses, training programs, workshops, webinars, etc., which have given a good chance to all the learners to update their credentials at no expense. People having busy official schedules who are usually not able to invest time in such programs are now getting a chance to upgrade themselves. On the other hand, young professionals are getting a fair chance to present themselves with more confidence.
When it comes to the physiological and cognitive effects, online education has both advantages and disadvantages. Recently, a study was conducted at Harvard Medical School on digital devices’ interference in sleep and creativity. It was found that the use of digital media plays a significant role in making the neural connection for a growing human brain. However, the screen usage of more than the recommended hours can lead to lower brain development. This also leads to the disruption of sleep by undersecretion of the melatonin hormone.
Another major concern is the availability of study resources. Not all the study material is available through online mode. Several offline materials are usually available in the library but not in the online database. A student is being deprived of this material. Furthermore, the educational institutions, which have decided to conduct online examinations, face difficulty in preparing question papers. The question papers are mostly multiple choices that do not give the student a window to write descriptive answers, which are equally crucial for a student to learn. This improves the writing skills of the student.
Where the online conduct of classes and conducting examinations has its challenges, the evaluation, on the other hand, has become more convenient and transparent between the teacher and student, where the students come to know about their performance. There are platforms that allow the faculty to give online assignments and evaluation. Online teaching does not require a large infrastructure for the conduct of classes. Instead, a strong IT team is sufficient to make it workable. In direct contact teaching, the other teaching and stationary materials are required, in the absence of which teaching is likely to suffer. The online teaching platform has covered up this drawback of direct contact teaching. However, online teaching makes people more digitally dependent by reducing direct and one-to-one social interaction. This is gradually making people more technology addicts.
12.2.1. Effect of home confinement on children and teachers
Due to the COVID-19 crisis (in more than 150 countries), all levels of the education system, from preschool to tertiary education, have been affected ( Bjorklund and Salvanes, 2011 , Vahid, 2020 ), wherein gradual closure of schools and universities took place. Similar situations prevailed in the past as well, during the pandemics ( Klaiman, Kraemer, & Stoto, 2011 ). Being confined to home or lockdown has impacted lives and livelihood across different spheres and so the education sector too, though have been able to meet the demands ensuring that via “online learning,” “homeschooling,” “virtual learning,” or “E-learning” children’s educational attainment remains undisrupted mainly ( IAU, 2020 ).
At the tertiary level, almost all universities and colleges have offered online courses and switched to virtual lectures, classes, and webinars ( Strielkowski, 2020 ), since digital learning has emerged as a significant aid for education from just an extracurricular facility. Although the contingencies of digital technologies rendition go past a stop-gap solution during the crisis, it has helped answer a new set of questions entirely about what, how, where, and when students shall learn. With the help of technology, students and teachers can ingress resource materials and not limit just to the text books in different formats, styles at their own pace and time by just going online. Besides teachers, smart digital technologies do not just teach only. Instead, it simultaneously observes, monitors how we study, how we learn, what interests us, the tasks that we involve in, the kind of problems that we face and find difficult to solve and adapt accordingly to meet the needs of the learner with more accuracy, specifications as compared to traditional learning within classrooms ( Kumar, 2020 ).
However, the necessary measures taken are highly applaudable; there are various issues that arise due to prolonged school closures and home confinement ( Cao et al., 2020 ) impacting students’ well-being in COVID time wherein students feel physically less active, sleep irregularities, dietary changes marked by weight gain along with low motivation ( Wickens, 2011 ), boredom to getting more anxious, and irritable as well. Abundant research has been carried out, suggesting having adverse effects on physical and psychological health in school-going children and students pursuing higher education at colleges and universities ( Liu et al., 2019 ). Nevertheless, at the tertiary level, the closing of campuses left them with no choice to leave hostels and dormitories and return to their hometown; however, many got stuck too, leaving them helpless and anxious ( Grubic, Badovinac, & Johri, 2020 ).
The switch to online education ensures minimum loss of studies suffered, and progress and attainment are also closely monitored via timely assessment and evaluations. Internal learning evaluation and assessments are considered to have high significance as it demonstrates the students’ learning needs and support for taking remedial actions ( Pandit, 2020 ). However, having been shifted to online platforms and accessed remotely, a major concern that emerged was the availability of proper internet facility networks and technology, especially in lower socio-economic zones and strata. In many countries, via online portals, TV and radio channels were started and the concern was addressed by the respective governments ( Gyamerah, 2020 ).
Imparting of average grade points based on the course completion for students pursuing higher studies, deferring the exams till further notice, promotion to the next level using “predictive grade,” were announced by few higher education institutions and schools. As per Gonzalez et al. (2020) and Black and Wiliam (2018) , the evaluation method and assessment would also change from traditional high stake to small project-based and activity, assignment-based evaluation shortly as the pandemic continues. At higher education institutes, there is a hold on the ongoing research projects and field works. A virtual internship is provided and various scientific research conferences and symposiums have been postponed and canceled ( Viner et al., 2020 ). They have moved online, whereby these virtual conferences have adversely affected networking opportunities and informal communication, creating a wide gap, especially in case of the inequalities prevailed in accessing technology to educational resources and the absence of proper remedial measures ( Gjoshi & Kume, 2014 ).
It is perceived that higher education can be relatively managed with digital learning or remote schooling ( Srivastava, 2020 ). As such, most of the research carried out to study the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on education discusses the adverse effects in terms of learning and student well-being ( Herold, 2017 ) due to home confinement and digital learning or homeschooling taking place with parental issues and concerns to provide childcare management and guidance required for their distance learning programs, availability of resources, and their socio-economic conditions ( Hiremath, Kowshik, Manjunath, & Shettar, 2020 ).
Despite the ongoing conditions prevailing due to COVID-19, online learning has said to have long-term positive implications that can be expected in comparison to the earlier research studies that suggested that student well-being is affected by the quality of learning ( Mahboob, 2020 ). A recent study sheds light on the significant positive impact of COVID-19 on learning efficiency and performances by adopting online learning strategies. To better understand the teaching and learning process during this crisis, it is imperative to have an education reform made to provide necessary teacher training, making further advancement of the new normal digital learning for functioning smoothly in the future as well ( Stephens, Leevore, Coryell, & Pena, 2017 ).
Furthermore, according to WHO, COVID-19 may never be gone. Instead, people have to learn to live with it. As such, by the policymakers, distance learning is embedded in normal education, so as to help students learn coping skills to deal effectively, minimizing negative impacts in case of crises encountered.
However, as a need of the hour, education shall increasingly embrace online/virtual classrooms, keeping in mind the exposure to students’ screen time in a day, planning of activities wherein parental involvement, assistance, and guidance are considered ( India Today, 2020 ). More physical education, music, dance, home gardening along with art integration should be focussed so as to enhance creativity, and affective domains that advertently shall enhance motivation, physical activities ( Sprang & Silman, 2013 ) and in adolescence too, continuous sitting, eye strains ( Levy & Ramim, 2017 ) and issues like cyber bullying, video game addictions and social media browsing can be put under control. Even for university students, through distance learning, they can collaborate with others, watch lectures prerecorded, and have fruitful discussions. The lecturer can be more of a facilitator rather than an instructor. Distance learning can be as effective as a traditional face-to-face mode of learning. Students have more family time; they can engage at their own pace ( Simonson, Zvacek, & Smaldino, 2019 ).
Moreover, there are barriers to distance learning and are unique to every country. However, its use has worldwide benefits that can be counted on, especially educating, imparting training on various focussed topics to general hobbies ( Bell et al., 2017 ). For educators, having been faced with so many challenges to adjust and get accustomed to the distance learning platform, it is highly commendable to have done so effectively. Still, they find it convincing, and a feel-good factor also persists, as work from home has helped manage home, take care of one’s self and family as mostly the time is spent on daily commuting, travels to reach the workplace, endless department meetings, colloquia or ongoing discussions on one side, and on the contrary, the research evidence ( Goodman, Joshi, Nasim, & Tyler, 2015 ) demonstrated that parents with a low socio-economic background faced difficulties in providing nutritional meals to their children due to school closures, and also the affordability of extra-school activities compared to more advantaged backgrounds.
Nevertheless, to minimize the challenges experienced due to home confinement and school closures, distance learning should be encouraged. Need for updating with modern technology should be introduced with high-speed internet, continuous power supply, cyber security, as well as proper training to educators and students so as to have skills and competencies to operate electronic devices, along with the necessary knowledge and understanding about the method in which the information is imparted.
Clearly, due to our recent experience with the COVID-19 pandemic, many conventional academic life principles have to be reshaped. However, a common goal is being shared by all the education systems, which is to overcome the learning crisis faced and deal effectively with the COVID-19 pandemic.
While talking about the family environment, it has been observed that many faculties are reporting about online teaching difficulties. Especially in children’s cases, it is reported that the families are not cooperating to maintain the class’s decorum. The family members keep disturbing the child for one or the other reason, which promotes the child to continue with disturbing and inattentive behavior. The cognitive skills of the parents also have a significant role in understanding and growth of the child. If the academic and the other assignments are better understood by the parents, the children will have a constant source of support whenever needed without any delay or waiting time for the next interaction with the teacher. In this aspect, India is facing much difficulty because a large population is illiterate or less educated to compliment the contemporary educational demands of their children. Hence, the family has a central role in the learning of the child ( Moon, Kim, & Moon, 2016 ).
12.2.2. A multidimensional impact of uncertainty
The diagonals of impact or the crater that is created due to the situation is a matter of major concern today. If we see the situation and scenario, we will find that this pandemic problem is not just medical or psychological. However, it encompasses a three-dimensional area, that is the bio-psycho-social domain of health psychology, which explains an interconnection between biology, psychology, and socio-environmental factors. This model plays an important role in defining interaction between humans and the environment and puts light on humans’ interaction with their social environment in which we operate within certain domains and norms. When these domains are affected by environmental factors, a lethal combination takes birth. The world is facing the same evidence in the form of various psychological and socio-environmental outcomes, such as financial, mental health, environmental, etc. None of the areas are untouched by the pandemic influences. In the current chapter, the impacts of COVID-19 on education are explained in detail.
Suppose we see the present scenario when uncertainty is prevailing in every sector of society. In that case, it will not be superlative to say that the students of today, despite having their completed degrees, will have a certain and stable career. Such situations are making the students prone to rumination , which means that they are most likely to think about their uncertain future. In the present context, it is in terms of examination outcome and job security. This thought process is likely to affect their overall psyche and, in turn, will lead to a greater rise in major psychological problems.
12.3. Sustaining the education industry during COVID-19
This pandemic situation generates many education losses like postponing the board exams, competitive exams, government exams, schools and colleges closed, etc. To overcome or minimize these losses, the Human Resource Development (HRD) minister released the guideline to all educational institutes to utilize the online platforms for teaching purposes ( Di Pietro, Biagi, Costa, Karpiński, & Mazza, 2020 ). Here, the most popular open-source of online teaching platforms are MS Team, Moodle, Zoom App, Chamilo, Webex, Canvas, Forms, Google Hangouts, and Google Meet. These platforms have helped teachers in online lecture delivery, sharing of notes, assessment, quiz conduction, etc. Several e-learning platforms are also available for students, which offer free certification or audit of the courses. These sources are Coursera, NPTEL, Swayam, edX, WHO, Harvard University, Stanford University, MITs, IITs, NITs, and many more. Therefore, in this situation, students learn at their own pace using digital platforms, while protecting themselves from the corona virus. Hence, the impact of COVID-19 on the education sector is compensated by online teaching platforms ( UNESCO, 2020 ). This online platform also provides teachers and students with various opportunities to interact with experts as per their area of interest without any expenses. Such teaching facilitates students’ effective utilization of time and more online learning activities based on their preferences.
The entire chapter can be summarized in the table mentioned below:
12.4. Conclusion
The pandemic situation has adversely affected several sectors, but the education sector has had both advantages and disadvantages. The virus outbreak has negatively influenced other areas; the education sector has been able to sustain and has shown its advantages. Especially when we talk about digital education, it has proved to be a savior of the entire education system. However, it cannot be avoided that this digitalization has come up with its limitations. It has its pros and cons, such as home confinement, blocked socialization etc. Hence, in this epidemic situation, the fulfilment of course requirements is majorly satisfied. However, the quality of learning and outcome is adversely affected in some teaching areas, which further opens the door to more advanced education reformed by policymakers and government. Therefore, a futuristic approach to implementing such an education system needs much planning to provide a better learning platform. However, to get better results, online teaching techniques and traditional pedagogy may produce highly productive results. Therefore it can be concluded that despite having limitations, this COVID-19 pandemic has got a boost through various online platforms.
- Ahmed, H., Allaf, M., & Elghazaly, H. (2020). COVID-19 and medical education. The Lancet Infectious Diseases . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Bambakidis N.C., Tomei K.L. Impact of COVID-19 on neurosurgery resident training and education. Journal of Neurosurgery. 2020; 1 (aop):1–2. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bell S., Douce C., Caeiro S., Teixeira A., Martín-Aranda R., Otto D. Sustainability and distance learning: A diverse European experience? Open Learning: The Journal of Open, Distance and E-Learning. 2017; 32 (2):95–102. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bhatnagar V., Poonia R.C., Nagar P., Kumar S., Singh V., Raja L., Dass P. Descriptive analysis of COVID-19 patients in the context of India. Journal of Interdisciplinary Mathematics. 2020:1–16. doi: 10.1080/09720502.2020.1761635. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bjorklund, A. & K. Salvanes (2011). Education and family background: Mechanisms and olicies. In E. Hanushek, S. Machin, & L. Woessmann (Eds.), Handbook of the Economics of Education , Vol. 3.
- Black P., Wiliam P. Classroom assessment and pedagogy. Assessment in education: Principles. Policy & Practice. 2018; 25 (6):551–575. [ Google Scholar ]
- Burgess, S. & Sievertsen, H.H. (2020). Schools, skills, and learning: The impact of COVID-19 on education. VoxEu.org, 1.
- Cao W., Fang Z., Hou G., Han M., Xu X., Dong J., Zheng J. The psychological impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on college students in China. Psychiatry Research. 2020; 287 doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.112934. Article 112984. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Clark N.M., Gong M., Schork M.A., Evans D., Roloff D., Hurwitz M., Mellins R.B. Impact of education for physicians on patient outcomes. Pediatrics. 1998; 101 (5):831–836. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Di Pietro, G., Biagi, F., Costa, P., Karpiński Z., & Mazza, J. (2020). The likely impact of COVID-19 on education: Reflections based on the existing literature and recent international datasets, JRC Technical Reports. Available at: https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/handle/JRC121071 .
- Ferrel, M.N., & Ryan, J.J. (2020). The impact of COVID-19 on medical education. Cureus. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Gjoshi R., Kume K. Research on the administrator professional training and its role in the implementation of educational institutions reforms in Kosovo. Interdisciplinary Journal of Research and Development. 2014; 1 :26–30. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gonzalez, T., de la Rubia, M.A., Hincz, K.P., Comas-Lopez, M., Subirats, L., Fort, S., & Sacha, G.M. (2020). Influence of COVID-19 confinement in students’ performance in higher education. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Goodman, A., Joshi, H., Nasim, B., & Tyler, C. (2015). Social and emotional skills in childhood and their long-term effects on adult life. https://www.eif.org.uk/report/social-and-emotional-skills-in-childhood-and-their-longterm-effects-on-adult-life .
- Grubic N., Badovinac S., Johri A.M. Student mental health in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic: A call for further research and immediate solutions. International Journal of Social Psychiatry. 2020; 66 (5):517–518. doi: 10.1177/0020764020925108. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gyamerah, K. (2020). The impacts of COVID-19 on basic education: How can Ghana respond, cope, and plan for recovery ? https://schoolofeducation.blogs.bristol.ac.uk/2020/03/31/the-impacts-of-covid-19-on-basic-education-how-can-ghana-respond-cope-and-plan-for-recovery Accessed 01.04.20.
- Harjule P., Kumar A., Agarwal B., Poonia R.C. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing (PAUC) Springer; 2020. Mathematical modeling and analysis of COVID-19 spread in India. [ Google Scholar ]
- Herold B. (2017). Technology in education: An overview. https://www.edweek.org/ew/issues/technology-in-education/ .
- Hiremath P., Kowshik C.S.S., Manjunath M., Shettar M. COVID 19: Impact of lockdown on mental health and tips to overcome. Asian Journal of Psychiatry. 2020; 51 :102088. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2020.102088. 2 pages. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hutton J.S., Dudley J., Horowitz-Kraus T., DeWitt T., Holland S.K. Associations between screen-based media use and brain white matter integrity in preschool-aged children. JAMA Pediatrics. 2020; 174 (1):e193869. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.3869. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- IAU (2020). The impact of COVID-19 on higher education worldwide. Resources for Higher Education Institutions . International Association of Universities. Retrieved from: https://www.iau-aiu.net/IMG/pdf/covid-19_and_he_resources.pdf .
- India Today (2020). Effect of Covid-19 on campus: Major steps being taken by Colleges to keep education going . https://www.indiatoday.in/educationtoday/featurephilia/story/effect-of-covid-19-on-campus-steps-taken-by-colleges1668156-2020-04-17 .
- Iyer P., Aziz K., Ojcius D.M. Impact of COVID-19 on dental education in the United States. Journal of Dental Education. 2020; 84 (6):718–722. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Klaiman T., Kraemer J.D., Stoto M.A. Variability in school closure decisions in response to 2009 H1N1: A qualitative systems improvement analysis. BMC Public Health. 2011; 11 :73. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-73. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kumar, D.N.S. (2020). Impact of Covid-19 on higher education . Higher Education Digest. https://www.highereducationdigest.com/impact-of-covid-19-on-higher-education .
- Kumari R., Kumar S., Poonia R.C., Singh V., Raja L., Bhatnagar V., Agarwal P. Big Data Mining and Analytics. IEEE; 2020. Analysis and predictions of spread, recovery, and death caused by COVID-19 in India. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Levy, Y. & Ramim, M.M. (2017). The e-learning skills gap study: Initial results of skills desired for persistence and success in online engineering and computing courses. In Proceeding of the Chais 2017 Conference on Innovative and Learning Technologies Research (pp. 57–68).
- Liu C.H., Stevens C., Wong S.H., Yasui M., Chen J.A. The prevalence and predictors of mental health diagnoses and suicide among US college students: Implications for addressing disparities in service use. Depression and anxiety. 2019; 36 (1):8–17. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mahboob, A. (2020). Education in the time of COVID-19. Available at: http://www.flcgroup.net/courses/education101-intro/ .
- Moon J.H., Kim K.W., Moon N.J. Smartphone use is a risk factor for paediatric dry eye disease according to region and age: A case control study. BMC Ophthalmology. 2016; 16 (1):188. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pandit, S. (2020). Sankatma nirantar sikai . Gorkhaparta (May 07). Available at: https://gorkhapatraonline.com/education/2020-05-06-13805 .
- Ruder, D.B. (2019). Retrieved from https://hms.harvard.edu/news/screen-time-brain on June 16, 2010.
- Sahu P. Closure of universities due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Impact on education and mental health of students and academic staff. Cureus. 2020; 12 (4) [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Simonson M., Zvacek S.M., Smaldino S. Teaching and Learning at a Distance: Foundations of Distance Education 7th Edition. IAP; 2019. [ Google Scholar ]
- Singh V., Poonia R.C., Kumar S., Dass P., Agarwal P., Bhatnagar V., Raja L. Prediction of COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic based on time series data using support vector machine. Journal of Discrete Mathematical Sciences & Cryptography. 2020 doi: 10.1080/09720529.2020.1784525. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sintema E.J. Effect of COVID-19 on the performance of grade 12 students: Implications for STEM education. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education. 2020; 16 (7):1851. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sprang G., Silman M. Posttraumatic stress disorder in parents and youth after health-related disasters. Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness. 2013; 7 :105–110. doi: 10.1017/dmp.2013.22. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Srivastava, P. (2020) COVID-19 and the global education emergency . https://oxfamblogs.org/fp2p/covid-19-and-the-global-education-emergency Accessed 18.03.20.
- Stephens, D., Leevore, M., Coryell, D., & Pena, C. (2017). Adult education-related graduate degrees: Insights on the challenges and benefits of online programming .
- Strielkowski, W. (2020), COVID-19 pandemic and the digital revolution in academia and higher education . Preprints 2020, 2020040290, 10.20944/preprints202004.0290.v1. [ CrossRef ]
- UNESCO 2019, < https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse > Accessed 29.0520.
- UNESCO 2020, < https://en.unesco.org/news/covid-19-crisis-Sheds-light-need-new-education-model > Accessed 29.06.20.
- Vahid, F. (2020). A message from a professor to fellow professors and students about at-home learning during COVID-19 .
- Viner, R.M., Russell, S.J., Croker, H., Packer, J., Ward, J., Stansfield, C., & Booy, R. (2020). School closure and management practices during corona virus outbreaks including COVID-19: A rapid systematic review . The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Wickens C.M. In: Higher education: Teaching, internationalization and student issues. Poulsen M.E., editor. Nova Scotia Publishers; 2011. The academic and psychosocial impact of labor unions and strikes on university campuses; pp. 107–133. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z.…Cao B. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult in patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. The Lancet. 2020; 395 (10229):1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30566-3. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

IMAGES
COMMENTS
COVID-19 is an infectious disease of the human respiratory system caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2. The disease is almost always mild and causes fever, dry cough, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Older people and other at-risk populations may develop life-threatening symptoms. There is no vaccine or treatment.
COVID-19 presentation for educators - Google Slides. Parts of this slide didn't load.
Impact on students. The switch to being virtual has lead students to be more distracted, and less focused. Due to lack of motivation, students' grades dropped because they didn't feel obligated to turn in work and a lot of times sleep through zoom. While students were doing school from home, all personal interactions like getting help from ...
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. After a year and a half, has society really learned a lesson about the COVID-19 pandemic? What about in education? These are questions that you can answer by customizing this new template for educational presentations. Teaching and classes in general might be different now, but one thing is ...
Eligible education agenciesinclude state and local agencies (including U.S. Territory and tribal agencies) that oversee prekindergarten,elementary, and/or secondary education. To be eligible, the education agency mustbe implementing anyrecovery program or policy being proposed for study. See the Recommendations. for. a. Strong. Application
The impact of COVID on education. The impact of COVID-19 on education across the world has been unprecedented and devastating. By mid-April 2020, almost 1.6 billion learners in 190 countries had been affected by school closures, which were happening on a scale never seen before. With national governments being forced to make difficult priority decisions regarding public health, the economy and ...
Geo-coded "risk mapping". Floating "cut off" score permits targeted high-risk outreach. Integrated acute danger, disaster/active shooter-terrorism, COVID-19 risk and prior trauma risk indicators in one tool. Parent and student "self-triage" pilot model. WRAP-EM version available at no cost in WA,OR,CA,NV,AZ,UT.
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a global pandemic, resulting in disruptions to education at an unprecedented scale. In response to the urgent need to recover learning losses, countries worldwide have taken RAPID actions to: R each every child and keep them in school; A ssess learning levels regularly; P ...
State of the Current Relevant Literature. Although the scale of the impact of the COVID-19 global pandemic on education overshadows previously experienced nationwide or global crises or disruptions, the phenomenon of schools and higher education institutions having to shift their instruction to online spaces is not totally new to the education community and academia (Johnson et al., 2020).
Introduction. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on education is both unprecedented and widespread in education history, impacting nearly every student in the world (UNICEF 2020; United Nations 2020).The unexpected arrival of the pandemic and subsequent school closures saw massive effort to adapt and innovate by educators and education systems around the world.
The youngest have had to adapt without understanding what was going on. If you want to make COVID-19 understandable for your middle school students, we recommend using this editable template from Slidesgo. With it you can explain the symptoms, prevention measures, how the transmission occurs, what treatments are available, etc.
The transition to an online education during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic may bring about adverse educational changes and adverse health consequences for children and young adult learners in grade school, middle school, high school, college, and professional schools. The effects may differ by age, maturity, and socioeconomic ...
Premium Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. The coronavirus outbreak has become one of the most notorious events of the decade, if not the current century. Every bit of information helps a lot, so let us help you create useful and informative presentations about this virus with our latest template. We've got a serious matter at hand ...
The COVID-19 vaccine has improved the pandemic situation. We are gradually returning to our pre-COVID-19 lifestyle. ... in medical research, particularly in the field of immunology. Highlight these achievements with a Google Slides and PowerPoint presentation! Designed with clear blue hues, this template offers a professional and compelling way ...
This is a PowerPoint presentation from the CDC's Clinician Outreach and Communication Activity (COCA) on the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak. It provides an overview of the epidemiology, clinical features, infection prevention and control, and guidance for clinicians. It also includes links to additional resources and updates from the CDC and the World Health Organization (WHO).
The aim of this survey study is to investigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the education, health, and lifestyle of students from different age-groups. 2.2. Statistical analysis. In this study, we conducted a cross-sectional survey with a sample size of 1182 students from different educational institutions.
Education and Communication. Short, imaged-based course and posters that do not require high levels of literacy. These are designed to support locations with weaker health systems that are ill-prepared to deal with COVID-19 (2019-novel coronavirus). International SOS logo and disclaimers must be retained and visible.
The purpose of this paper is to explore the impact that COVID-19 had on undergraduate nursing education and identify lessons learned as a result. Nursing student perspectives from 2 Midwestern universities were compiled and analyzed to identify challenges, interventions performed, and key lessons learned. In March 2020, college students across ...
In January 2020 the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak of a new coronavirus disease in Hubei Province, China to be a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. Since then WHO has declared it as a Pandemic affecting more than 115 countries around the globe. India witnessed its first COVID-19 case in Kerala on 30th January 2020.
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. The recent coronavirus pandemic has forced many businesses and industries to stop their activities until society can start resuming a normal life again. This, in turn, is causing an economic impact on most countries. Customize our latest template to present your data on this subject.
Abstract. The COVID-19 pandemic has stirred up the world, and its overwhelming impacts can be seen from micro to macro level, that is, from an individual's day-to-day functioning to the broader level—health sector, finance sector, and off course, the education sector. The younger generation is considered to be the torchbearer of the society.