
- Publication Recognition

How to Make a PowerPoint Presentation of Your Research Paper
- 4 minute read
- 116.1K views
Table of Contents
A research paper presentation is often used at conferences and in other settings where you have an opportunity to share your research, and get feedback from your colleagues. Although it may seem as simple as summarizing your research and sharing your knowledge, successful research paper PowerPoint presentation examples show us that there’s a little bit more than that involved.
In this article, we’ll highlight how to make a PowerPoint presentation from a research paper, and what to include (as well as what NOT to include). We’ll also touch on how to present a research paper at a conference.
Purpose of a Research Paper Presentation
The purpose of presenting your paper at a conference or forum is different from the purpose of conducting your research and writing up your paper. In this setting, you want to highlight your work instead of including every detail of your research. Likewise, a presentation is an excellent opportunity to get direct feedback from your colleagues in the field. But, perhaps the main reason for presenting your research is to spark interest in your work, and entice the audience to read your research paper.
So, yes, your presentation should summarize your work, but it needs to do so in a way that encourages your audience to seek out your work, and share their interest in your work with others. It’s not enough just to present your research dryly, to get information out there. More important is to encourage engagement with you, your research, and your work.
Tips for Creating Your Research Paper Presentation
In addition to basic PowerPoint presentation recommendations, which we’ll cover later in this article, think about the following when you’re putting together your research paper presentation:
- Know your audience : First and foremost, who are you presenting to? Students? Experts in your field? Potential funders? Non-experts? The truth is that your audience will probably have a bit of a mix of all of the above. So, make sure you keep that in mind as you prepare your presentation.
Know more about: Discover the Target Audience .
- Your audience is human : In other words, they may be tired, they might be wondering why they’re there, and they will, at some point, be tuning out. So, take steps to help them stay interested in your presentation. You can do that by utilizing effective visuals, summarize your conclusions early, and keep your research easy to understand.
- Running outline : It’s not IF your audience will drift off, or get lost…it’s WHEN. Keep a running outline, either within the presentation or via a handout. Use visual and verbal clues to highlight where you are in the presentation.
- Where does your research fit in? You should know of work related to your research, but you don’t have to cite every example. In addition, keep references in your presentation to the end, or in the handout. Your audience is there to hear about your work.
- Plan B : Anticipate possible questions for your presentation, and prepare slides that answer those specific questions in more detail, but have them at the END of your presentation. You can then jump to them, IF needed.
What Makes a PowerPoint Presentation Effective?
You’ve probably attended a presentation where the presenter reads off of their PowerPoint outline, word for word. Or where the presentation is busy, disorganized, or includes too much information. Here are some simple tips for creating an effective PowerPoint Presentation.
- Less is more: You want to give enough information to make your audience want to read your paper. So include details, but not too many, and avoid too many formulas and technical jargon.
- Clean and professional : Avoid excessive colors, distracting backgrounds, font changes, animations, and too many words. Instead of whole paragraphs, bullet points with just a few words to summarize and highlight are best.
- Know your real-estate : Each slide has a limited amount of space. Use it wisely. Typically one, no more than two points per slide. Balance each slide visually. Utilize illustrations when needed; not extraneously.
- Keep things visual : Remember, a PowerPoint presentation is a powerful tool to present things visually. Use visual graphs over tables and scientific illustrations over long text. Keep your visuals clean and professional, just like any text you include in your presentation.
Know more about our Scientific Illustrations Services .
Another key to an effective presentation is to practice, practice, and then practice some more. When you’re done with your PowerPoint, go through it with friends and colleagues to see if you need to add (or delete excessive) information. Double and triple check for typos and errors. Know the presentation inside and out, so when you’re in front of your audience, you’ll feel confident and comfortable.
How to Present a Research Paper
If your PowerPoint presentation is solid, and you’ve practiced your presentation, that’s half the battle. Follow the basic advice to keep your audience engaged and interested by making eye contact, encouraging questions, and presenting your information with enthusiasm.
We encourage you to read our articles on how to present a scientific journal article and tips on giving good scientific presentations .
Language Editing Plus
Improve the flow and writing of your research paper with Language Editing Plus. This service includes unlimited editing, manuscript formatting for the journal of your choice, reference check and even a customized cover letter. Learn more here , and get started today!

- Manuscript Preparation
Know How to Structure Your PhD Thesis

- Research Process
Systematic Literature Review or Literature Review?
You may also like.

What is a Good H-index?

What is a Corresponding Author?

How to Submit a Paper for Publication in a Journal
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- Google Slides Presentation Design
- Pitch Deck Design
- Powerpoint Redesign
- Other Design Services
- Guide & How to's
How to present a research paper in PPT: best practices
A research paper presentation is frequently used at conferences and other events where you have a chance to share the results of your research and receive feedback from colleagues. Although it may appear as simple as summarizing the findings, successful examples of research paper presentations show that there is a little bit more to it.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the basic outline and steps to create a good research paper presentation. We’ll also explain what to include and what not to include in your presentation of research paper and share some of the most effective tips you can use to take your slides to the next level.
Research paper PowerPoint presentation outline
Creating a PowerPoint presentation for a research paper involves organizing and summarizing your key findings, methodology, and conclusions in a way that encourages your audience to interact with your work and share their interest in it with others. Here’s a basic research paper outline PowerPoint you can follow:
1. Title (1 slide)
Typically, your title slide should contain the following information:
- Title of the research paper
- Affiliation or institution
- Date of presentation
2. Introduction (1-3 slides)
On this slide of your presentation, briefly introduce the research topic and its significance and state the research question or objective.
3. Research questions or hypothesis (1 slide)
This slide should emphasize the objectives of your research or present the hypothesis.
4. Literature review (1 slide)
Your literature review has to provide context for your research by summarizing relevant literature. Additionally, it should highlight gaps or areas where your research contributes.
5. Methodology and data collection (1-2 slides)
This slide of your research paper PowerPoint has to explain the research design, methods, and procedures. It must also Include details about participants, materials, and data collection and emphasize special equipment you have used in your work.
6. Results (3-5 slides)
On this slide, you must present the results of your data analysis and discuss any trends, patterns, or significant findings. Moreover, you should use charts, graphs, and tables to illustrate data and highlight something novel in your results (if applicable).
7. Conclusion (1 slide)
Your conclusion slide has to summarize the main findings and their implications, as well as discuss the broader impact of your research. Usually, a single statement is enough.
8. Recommendations (1 slide)
If applicable, provide recommendations for future research or actions on this slide.
9. References (1-2 slides)
The references slide is where you list all the sources cited in your research paper.
10. Acknowledgments (1 slide)
On this presentation slide, acknowledge any individuals, organizations, or funding sources that contributed to your research.
11. Appendix (1 slide)
If applicable, include any supplementary materials, such as additional data or detailed charts, in your appendix slide.
The above outline is just a general guideline, so make sure to adjust it based on your specific research paper and the time allotted for the presentation.
Steps to creating a memorable research paper presentation
Creating a PowerPoint presentation for a research paper involves several critical steps needed to convey your findings and engage your audience effectively, and these steps are as follows:
Step 1. Understand your audience:
- Identify the audience for your presentation.
- Tailor your content and level of detail to match the audience’s background and knowledge.
Step 2. Define your key messages:
- Clearly articulate the main messages or findings of your research.
- Identify the key points you want your audience to remember.
Step 3. Design your research paper PPT presentation:
- Use a clean and professional design that complements your research topic.
- Choose readable fonts, consistent formatting, and a limited color palette.
- Opt for PowerPoint presentation services if slide design is not your strong side.
Step 4. Put content on slides:
- Follow the outline above to structure your presentation effectively; include key sections and topics.
- Organize your content logically, following the flow of your research paper.
Step 5. Final check:
- Proofread your slides for typos, errors, and inconsistencies.
- Ensure all visuals are clear, high-quality, and properly labeled.
Step 6. Save and share:
- Save your presentation and ensure compatibility with the equipment you’ll be using.
- If necessary, share a copy of your presentation with the audience.
By following these steps, you can create a well-organized and visually appealing research paper presentation PowerPoint that effectively conveys your research findings to the audience.
What to include and what not to include in your presentation
In addition to the must-know PowerPoint presentation recommendations, which we’ll cover later in this article, consider the following do’s and don’ts when you’re putting together your research paper presentation:
- Focus on the topic.
- Be brief and to the point.
- Attract the audience’s attention and highlight interesting details.
- Use only relevant visuals (maps, charts, pictures, graphs, etc.).
- Use numbers and bullet points to structure the content.
- Make clear statements regarding the essence and results of your research.
Don’ts:
- Don’t write down the whole outline of your paper and nothing else.
- Don’t put long, full sentences on your slides; split them into smaller ones.
- Don’t use distracting patterns, colors, pictures, and other visuals on your slides; the simpler, the better.
- Don’t use too complicated graphs or charts; only the ones that are easy to understand.
- Now that we’ve discussed the basics, let’s move on to the top tips for making a powerful presentation of your research paper.
8 tips on how to make research paper presentation that achieves its goals
You’ve probably been to a presentation where the presenter reads word for word from their PowerPoint outline. Or where the presentation is cluttered, chaotic, or contains too much data. The simple tips below will help you summarize a 10 to 15-page paper for a 15 to 20-minute talk and succeed, so read on!
Tip #1: Less is more
You want to provide enough information to make your audience want to know more. Including details but not too many and avoiding technical jargon, formulas, and long sentences are always good ways to achieve this.
Tip #2: Be professional
Avoid using too many colors, font changes, distracting backgrounds, animations, etc. Bullet points with a few words to highlight the important information are preferable to lengthy paragraphs. Additionally, include slide numbers on all PowerPoint slides except for the title slide, and make sure it is followed by a table of contents, offering a brief overview of the entire research paper.
Tip #3: Strive for balance
PowerPoint slides have limited space, so use it carefully. Typically, one to two points per slide or 5 lines for 5 words in a sentence are enough to present your ideas.
Tip #4: Use proper fonts and text size
The font you use should be easy to read and consistent throughout the slides. You can go with Arial, Times New Roman, Calibri, or a combination of these three. An ideal text size is 32 points, while a heading size is 44.
Tip #5: Concentrate on the visual side
A PowerPoint presentation is one of the best tools for presenting information visually. Use graphs instead of tables and topic-relevant illustrations instead of walls of text. Keep your visuals as clean and professional as the content of your presentation.
Tip #6: Practice your delivery
Always go through your presentation when you’re done to ensure a smooth and confident delivery and time yourself to stay within the allotted limit.
Tip #7: Get ready for questions
Anticipate potential questions from your audience and prepare thoughtful responses. Also, be ready to engage in discussions about your research.
Tip #8: Don’t be afraid to utilize professional help
If the mere thought of designing a presentation overwhelms you or you’re pressed for time, consider leveraging professional PowerPoint redesign services . A dedicated design team can transform your content or old presentation into effective slides, ensuring your message is communicated clearly and captivates your audience. This way, you can focus on refining your delivery and preparing for the presentation.
Lastly, remember that even experienced presenters get nervous before delivering research paper PowerPoint presentations in front of the audience. You cannot know everything; some things can be beyond your control, which is completely fine. You are at the event not only to share what you know but also to learn from others. So, no matter what, dress appropriately, look straight into the audience’s eyes, try to speak and move naturally, present your information enthusiastically, and have fun!
If you need help with slide design, get in touch with our dedicated design team and let qualified professionals turn your research findings into a visually appealing, polished presentation that leaves a lasting impression on your audience. Our experienced designers specialize in creating engaging layouts, incorporating compelling graphics, and ensuring a cohesive visual narrative that complements content on any subject.
#ezw_tco-2 .ez-toc-widget-container ul.ez-toc-list li.active::before { background-color: #ededed; } Table of contents
- Presenting techniques
- 50 tips on how to improve PowerPoint presentations in 2022-2023 [Updated]
- Keynote VS PowerPoint
- Types of presentations
- Present financial information visually in PowerPoint to drive results

- Design Tips
8 rules of effective presentation

- Business Slides
Employee training and onboarding presentation: why and how
How to structure, design, write, and finally present executive summary presentation?
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Presentations
How to Prepare a Paper Presentation
Last Updated: October 4, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Patrick Muñoz . Patrick is an internationally recognized Voice & Speech Coach, focusing on public speaking, vocal power, accent and dialects, accent reduction, voiceover, acting and speech therapy. He has worked with clients such as Penelope Cruz, Eva Longoria, and Roselyn Sanchez. He was voted LA's Favorite Voice and Dialect Coach by BACKSTAGE, is the voice and speech coach for Disney and Turner Classic Movies, and is a member of Voice and Speech Trainers Association. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 360,870 times.
A paper is bad enough, but presentations are even more nerve-wracking. You've got the writing down, but how do you turn it into a dynamic, informative, enjoyable presentation? Why, here's how!
Guidelines and Audience

- Know how long the speech must be.
- Know how many points you're required to cover.
- Know if you must include sources or visuals.

- If you're presenting to people you know, it'll be easy to know what to break down and what to gloss over. But if you're presenting to unknown stockholders or faculty, for instance, you need to know about them and their knowledge levels, too. You may have to break your paper down into its most basic concepts. Find out what you can about their backgrounds.

- Does the facility have a computer and projector screen?
- Is there a working WiFi connection?
- Is there a microphone? A podium?
- Is there someone who can assist you in working the equipment before your presentation?
Script and Visuals

- Only have one point per notecard -- that way you won't end up searching the notecard for your information. And don't forget to number the cards in case you get mixed up! And the points on your cards shouldn't match your paper; instead of regurgitating information, discuss why the key points of your paper are important or the different points of view on this topic within the field.

- As you go through this outline, remove any jargon if it may not be understood.

- If you won't have access to the proper technology, print visual aids on poster board or foam-core board.
- If using presentation software, use words sparingly, but enough to get your point across. Think in phrases (and pictures!), not sentences. Acronyms and abbreviations are okay on the screen, but when you talk, address them fully. And remember to use large fonts -- not everyone's vision is fantastic. [7] X Research source

- It's okay to be a bit repetitive. Emphasizing important ideas will enhance comprehension and recall. When you've gone full circle, cycle back to a previous point to lead your audience to the right conclusion.
- Minimize the unnecessary details (the procedure you had to go through, etc.) when highlighting the main ideas you want to relay. You don't want to overload your audience with fluff, forcing them to miss the important stuff.
- Show enthusiasm! A very boring topic can be made interesting if there is passion behind it.
Practice, Practice, and More Practice

- If you can grab a friend who you think has a similar knowledge level to your audience, all the better. They'll help you see what points are foggier to minds with less expertise on the topic.

- It'll also help you with volume. Some people get rather timid when in the spotlight. You may not be aware that you're not loud enough!

- Do the same with your conclusion. Thank everyone for their time and open the floor for any questions, if allowed.
- Make eye contact with people in the audience to help build your connection with them.
What Is The Best Way To Start a Presentation?
Community Q&A
- Most people get nervous while public speaking. [10] X Research source You are not alone. [11] X Trustworthy Source Mayo Clinic Educational website from one of the world's leading hospitals Go to source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1
- Visual aids not only help the audience, but they can help jog your memory if you forget where you are in your presentation. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Rehearse in front of a mirror before your presentation. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Answer questions only if it is related to your presentation. Keep these to the end of your talk. Thanks Helpful 76 Not Helpful 14
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://theihs.org/blog/prepare-for-a-paper-presentation-at-an-academic-conference/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/conference-papers/
- ↑ https://www.ncsl.org/legislators-staff/legislative-staff/legislative-staff-coordinating-committee/tips-for-making-effective-powerpoint-presentations.aspx
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4qZMPW5g-v8
- ↑ https://twp.duke.edu/sites/twp.duke.edu/files/file-attachments/paper-to-talk.original.pdf
- ↑ http://www.cs.swarthmore.edu/~newhall/presentation.html
- ↑ https://www.forbes.com/sites/georgebradt/2014/09/10/big-presentation-dont-do-it-have-a-conversation-instead/#6d56a3f23c4b
- ↑ https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/smashing-the-brainblocks/201711/why-are-we-scared-public-speaking
- ↑ https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/specific-phobias/expert-answers/fear-of-public-speaking/faq-20058416
About This Article

To prepare a paper presentation, create an outline of your content, then write your script on note cards or slides using software like PowerPoint. Be sure to stick to one main point per card or slide! Next, design visual aids like graphics, charts, and bullet points to illustrate your content and help the audience follow along. Then, practice giving your presentation in front of friends and family until you feel ready to do it in class! For tips on creating an outline and organizing your information, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Vignesh Sanjeevi
Mar 8, 2016
Did this article help you?

Pulicheri Gunasri
Mahesh Prajapati
Sep 14, 2017
Geraldine Jean Michel
Oct 25, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor’s standpoint. I’ve presented my own research before, but helping others present theirs taught me a bit more about the process. Here are some tips I learned that may help you with your next research presentation:
More is more
In general, your presentation will always benefit from more practice, more feedback, and more revision. By practicing in front of friends, you can get comfortable with presenting your work while receiving feedback. It is hard to know how to revise your presentation if you never practice. If you are presenting to a general audience, getting feedback from someone outside of your discipline is crucial. Terms and ideas that seem intuitive to you may be completely foreign to someone else, and your well-crafted presentation could fall flat.
Less is more
Limit the scope of your presentation, the number of slides, and the text on each slide. In my experience, text works well for organizing slides, orienting the audience to key terms, and annotating important figures–not for explaining complex ideas. Having fewer slides is usually better as well. In general, about one slide per minute of presentation is an appropriate budget. Too many slides is usually a sign that your topic is too broad.

Limit the scope of your presentation
Don’t present your paper. Presentations are usually around 10 min long. You will not have time to explain all of the research you did in a semester (or a year!) in such a short span of time. Instead, focus on the highlight(s). Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
You will not have time to explain all of the research you did. Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
Craft a compelling research narrative
After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story. Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling.
- Introduction (exposition — rising action)
Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story. Introduce the key studies (characters) relevant in your story and build tension and conflict with scholarly and data motive. By the end of your introduction, your audience should clearly understand your research question and be dying to know how you resolve the tension built through motive.
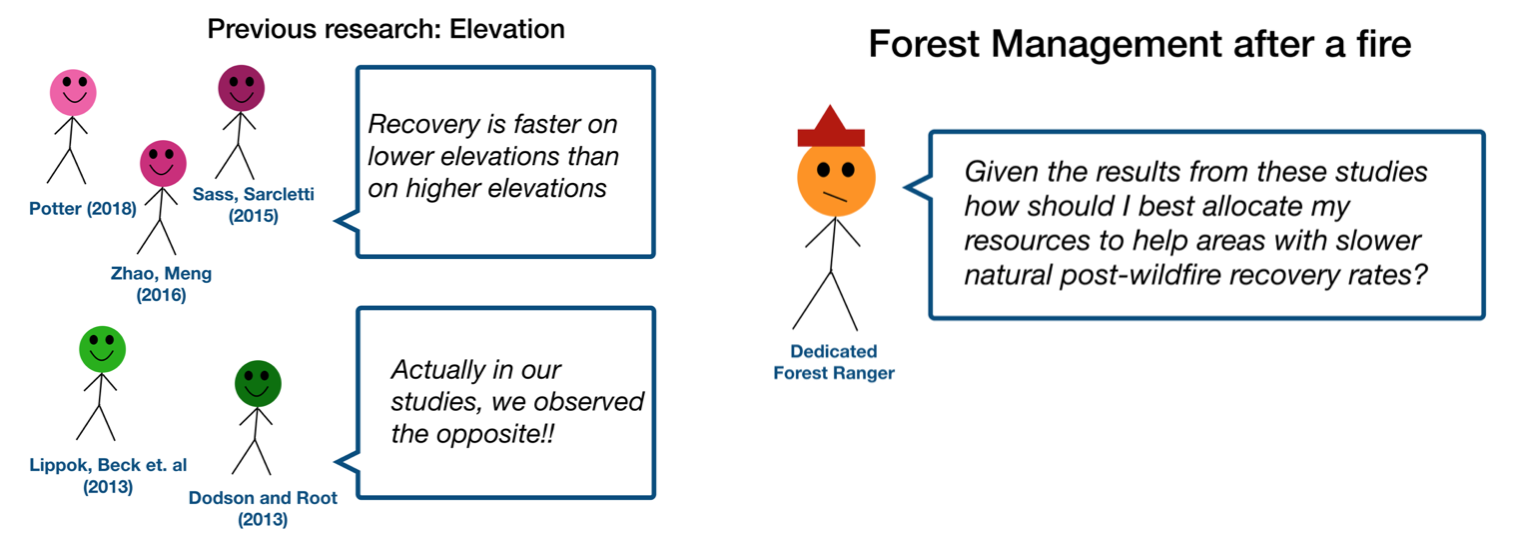
- Methods (rising action)
The methods section should transition smoothly and logically from the introduction. Beware of presenting your methods in a boring, arc-killing, ‘this is what I did.’ Focus on the details that set your story apart from the stories other people have already told. Keep the audience interested by clearly motivating your decisions based on your original research question or the tension built in your introduction.
- Results (climax)
Less is usually more here. Only present results which are clearly related to the focused research question you are presenting. Make sure you explain the results clearly so that your audience understands what your research found. This is the peak of tension in your narrative arc, so don’t undercut it by quickly clicking through to your discussion.
- Discussion (falling action)
By now your audience should be dying for a satisfying resolution. Here is where you contextualize your results and begin resolving the tension between past research. Be thorough. If you have too many conflicts left unresolved, or you don’t have enough time to present all of the resolutions, you probably need to further narrow the scope of your presentation.
- Conclusion (denouement)
Return back to your initial research question and motive, resolving any final conflicts and tying up loose ends. Leave the audience with a clear resolution of your focus research question, and use unresolved tension to set up potential sequels (i.e. further research).
Use your medium to enhance the narrative
Visual presentations should be dominated by clear, intentional graphics. Subtle animation in key moments (usually during the results or discussion) can add drama to the narrative arc and make conflict resolutions more satisfying. You are narrating a story written in images, videos, cartoons, and graphs. While your paper is mostly text, with graphics to highlight crucial points, your slides should be the opposite. Adapting to the new medium may require you to create or acquire far more graphics than you included in your paper, but it is necessary to create an engaging presentation.
The most important thing you can do for your presentation is to practice and revise. Bother your friends, your roommates, TAs–anybody who will sit down and listen to your work. Beyond that, think about presentations you have found compelling and try to incorporate some of those elements into your own. Remember you want your work to be comprehensible; you aren’t creating experts in 10 minutes. Above all, try to stay passionate about what you did and why. You put the time in, so show your audience that it’s worth it.
For more insight into research presentations, check out these past PCUR posts written by Emma and Ellie .
— Alec Getraer, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to make a scientific presentation

Scientific presentation outlines
Questions to ask yourself before you write your talk, 1. how much time do you have, 2. who will you speak to, 3. what do you want the audience to learn from your talk, step 1: outline your presentation, step 2: plan your presentation slides, step 3: make the presentation slides, slide design, text elements, animations and transitions, step 4: practice your presentation, final thoughts, frequently asked questions about preparing scientific presentations, related articles.
A good scientific presentation achieves three things: you communicate the science clearly, your research leaves a lasting impression on your audience, and you enhance your reputation as a scientist.
But, what is the best way to prepare for a scientific presentation? How do you start writing a talk? What details do you include, and what do you leave out?
It’s tempting to launch into making lots of slides. But, starting with the slides can mean you neglect the narrative of your presentation, resulting in an overly detailed, boring talk.
The key to making an engaging scientific presentation is to prepare the narrative of your talk before beginning to construct your presentation slides. Planning your talk will ensure that you tell a clear, compelling scientific story that will engage the audience.
In this guide, you’ll find everything you need to know to make a good oral scientific presentation, including:
- The different types of oral scientific presentations and how they are delivered;
- How to outline a scientific presentation;
- How to make slides for a scientific presentation.
Our advice results from delving into the literature on writing scientific talks and from our own experiences as scientists in giving and listening to presentations. We provide tips and best practices for giving scientific talks in a separate post.
There are two main types of scientific talks:
- Your talk focuses on a single study . Typically, you tell the story of a single scientific paper. This format is common for short talks at contributed sessions in conferences.
- Your talk describes multiple studies. You tell the story of multiple scientific papers. It is crucial to have a theme that unites the studies, for example, an overarching question or problem statement, with each study representing specific but different variations of the same theme. Typically, PhD defenses, invited seminars, lectures, or talks for a prospective employer (i.e., “job talks”) fall into this category.
➡️ Learn how to prepare an excellent thesis defense
The length of time you are allotted for your talk will determine whether you will discuss a single study or multiple studies, and which details to include in your story.
The background and interests of your audience will determine the narrative direction of your talk, and what devices you will use to get their attention. Will you be speaking to people specializing in your field, or will the audience also contain people from disciplines other than your own? To reach non-specialists, you will need to discuss the broader implications of your study outside your field.
The needs of the audience will also determine what technical details you will include, and the language you will use. For example, an undergraduate audience will have different needs than an audience of seasoned academics. Students will require a more comprehensive overview of background information and explanations of jargon but will need less technical methodological details.
Your goal is to speak to the majority. But, make your talk accessible to the least knowledgeable person in the room.
This is called the thesis statement, or simply the “take-home message”. Having listened to your talk, what message do you want the audience to take away from your presentation? Describe the main idea in one or two sentences. You want this theme to be present throughout your presentation. Again, the thesis statement will depend on the audience and the type of talk you are giving.
Your thesis statement will drive the narrative for your talk. By deciding the take-home message you want to convince the audience of as a result of listening to your talk, you decide how the story of your talk will flow and how you will navigate its twists and turns. The thesis statement tells you the results you need to show, which subsequently tells you the methods or studies you need to describe, which decides the angle you take in your introduction.
➡️ Learn how to write a thesis statement
The goal of your talk is that the audience leaves afterward with a clear understanding of the key take-away message of your research. To achieve that goal, you need to tell a coherent, logical story that conveys your thesis statement throughout the presentation. You can tell your story through careful preparation of your talk.
Preparation of a scientific presentation involves three separate stages: outlining the scientific narrative, preparing slides, and practicing your delivery. Making the slides of your talk without first planning what you are going to say is inefficient.
Here, we provide a 4 step guide to writing your scientific presentation:
- Outline your presentation
- Plan your presentation slides
- Make the presentation slides
- Practice your presentation

Writing an outline helps you consider the key pieces of your talk and how they fit together from the beginning, preventing you from forgetting any important details. It also means you avoid changing the order of your slides multiple times, saving you time.
Plan your talk as discrete sections. In the table below, we describe the sections for a single study talk vs. a talk discussing multiple studies:
The following tips apply when writing the outline of a single study talk. You can easily adapt this framework if you are writing a talk discussing multiple studies.
Introduction: Writing the introduction can be the hardest part of writing a talk. And when giving it, it’s the point where you might be at your most nervous. But preparing a good, concise introduction will settle your nerves.
The introduction tells the audience the story of why you studied your topic. A good introduction succinctly achieves four things, in the following order.
- It gives a broad perspective on the problem or topic for people in the audience who may be outside your discipline (i.e., it explains the big-picture problem motivating your study).
- It describes why you did the study, and why the audience should care.
- It gives a brief indication of how your study addressed the problem and provides the necessary background information that the audience needs to understand your work.
- It indicates what the audience will learn from the talk, and prepares them for what will come next.
A good introduction not only gives the big picture and motivations behind your study but also concisely sets the stage for what the audience will learn from the talk (e.g., the questions your work answers, and/or the hypotheses that your work tests). The end of the introduction will lead to a natural transition to the methods.
Give a broad perspective on the problem. The easiest way to start with the big picture is to think of a hook for the first slide of your presentation. A hook is an opening that gets the audience’s attention and gets them interested in your story. In science, this might take the form of a why, or a how question, or it could be a statement about a major problem or open question in your field. Other examples of hooks include quotes, short anecdotes, or interesting statistics.
Why should the audience care? Next, decide on the angle you are going to take on your hook that links to the thesis of your talk. In other words, you need to set the context, i.e., explain why the audience should care. For example, you may introduce an observation from nature, a pattern in experimental data, or a theory that you want to test. The audience must understand your motivations for the study.
Supplementary details. Once you have established the hook and angle, you need to include supplementary details to support them. For example, you might state your hypothesis. Then go into previous work and the current state of knowledge. Include citations of these studies. If you need to introduce some technical methodological details, theory, or jargon, do it here.
Conclude your introduction. The motivation for the work and background information should set the stage for the conclusion of the introduction, where you describe the goals of your study, and any hypotheses or predictions. Let the audience know what they are going to learn.
Methods: The audience will use your description of the methods to assess the approach you took in your study and to decide whether your findings are credible. Tell the story of your methods in chronological order. Use visuals to describe your methods as much as possible. If you have equations, make sure to take the time to explain them. Decide what methods to include and how you will show them. You need enough detail so that your audience will understand what you did and therefore can evaluate your approach, but avoid including superfluous details that do not support your main idea. You want to avoid the common mistake of including too much data, as the audience can read the paper(s) later.
Results: This is the evidence you present for your thesis. The audience will use the results to evaluate the support for your main idea. Choose the most important and interesting results—those that support your thesis. You don’t need to present all the results from your study (indeed, you most likely won’t have time to present them all). Break down complex results into digestible pieces, e.g., comparisons over multiple slides (more tips in the next section).
Summary: Summarize your main findings. Displaying your main findings through visuals can be effective. Emphasize the new contributions to scientific knowledge that your work makes.
Conclusion: Complete the circle by relating your conclusions to the big picture topic in your introduction—and your hook, if possible. It’s important to describe any alternative explanations for your findings. You might also speculate on future directions arising from your research. The slides that comprise your conclusion do not need to state “conclusion”. Rather, the concluding slide title should be a declarative sentence linking back to the big picture problem and your main idea.
It’s important to end well by planning a strong closure to your talk, after which you will thank the audience. Your closing statement should relate to your thesis, perhaps by stating it differently or memorably. Avoid ending awkwardly by memorizing your closing sentence.
By now, you have an outline of the story of your talk, which you can use to plan your slides. Your slides should complement and enhance what you will say. Use the following steps to prepare your slides.
- Write the slide titles to match your talk outline. These should be clear and informative declarative sentences that succinctly give the main idea of the slide (e.g., don’t use “Methods” as a slide title). Have one major idea per slide. In a YouTube talk on designing effective slides , researcher Michael Alley shows examples of instructive slide titles.
- Decide how you will convey the main idea of the slide (e.g., what figures, photographs, equations, statistics, references, or other elements you will need). The body of the slide should support the slide’s main idea.
- Under each slide title, outline what you want to say, in bullet points.
In sum, for each slide, prepare a title that summarizes its major idea, a list of visual elements, and a summary of the points you will make. Ensure each slide connects to your thesis. If it doesn’t, then you don’t need the slide.
Slides for scientific presentations have three major components: text (including labels and legends), graphics, and equations. Here, we give tips on how to present each of these components.
- Have an informative title slide. Include the names of all coauthors and their affiliations. Include an attractive image relating to your study.
- Make the foreground content of your slides “pop” by using an appropriate background. Slides that have white backgrounds with black text work well for small rooms, whereas slides with black backgrounds and white text are suitable for large rooms.
- The layout of your slides should be simple. Pay attention to how and where you lay the visual and text elements on each slide. It’s tempting to cram information, but you need lots of empty space. Retain space at the sides and bottom of your slides.
- Use sans serif fonts with a font size of at least 20 for text, and up to 40 for slide titles. Citations can be in 14 font and should be included at the bottom of the slide.
- Use bold or italics to emphasize words, not underlines or caps. Keep these effects to a minimum.
- Use concise text . You don’t need full sentences. Convey the essence of your message in as few words as possible. Write down what you’d like to say, and then shorten it for the slide. Remove unnecessary filler words.
- Text blocks should be limited to two lines. This will prevent you from crowding too much information on the slide.
- Include names of technical terms in your talk slides, especially if they are not familiar to everyone in the audience.
- Proofread your slides. Typos and grammatical errors are distracting for your audience.
- Include citations for the hypotheses or observations of other scientists.
- Good figures and graphics are essential to sustain audience interest. Use graphics and photographs to show the experiment or study system in action and to explain abstract concepts.
- Don’t use figures straight from your paper as they may be too detailed for your talk, and details like axes may be too small. Make new versions if necessary. Make them large enough to be visible from the back of the room.
- Use graphs to show your results, not tables. Tables are difficult for your audience to digest! If you must present a table, keep it simple.
- Label the axes of graphs and indicate the units. Label important components of graphics and photographs and include captions. Include sources for graphics that are not your own.
- Explain all the elements of a graph. This includes the axes, what the colors and markers mean, and patterns in the data.
- Use colors in figures and text in a meaningful, not random, way. For example, contrasting colors can be effective for pointing out comparisons and/or differences. Don’t use neon colors or pastels.
- Use thick lines in figures, and use color to create contrasts in the figures you present. Don’t use red/green or red/blue combinations, as color-blind audience members can’t distinguish between them.
- Arrows or circles can be effective for drawing attention to key details in graphs and equations. Add some text annotations along with them.
- Write your summary and conclusion slides using graphics, rather than showing a slide with a list of bullet points. Showing some of your results again can be helpful to remind the audience of your message.
- If your talk has equations, take time to explain them. Include text boxes to explain variables and mathematical terms, and put them under each term in the equation.
- Combine equations with a graphic that shows the scientific principle, or include a diagram of the mathematical model.
- Use animations judiciously. They are helpful to reveal complex ideas gradually, for example, if you need to make a comparison or contrast or to build a complicated argument or figure. For lists, reveal one bullet point at a time. New ideas appearing sequentially will help your audience follow your logic.
- Slide transitions should be simple. Silly ones distract from your message.
- Decide how you will make the transition as you move from one section of your talk to the next. For example, if you spend time talking through details, provide a summary afterward, especially in a long talk. Another common tactic is to have a “home slide” that you return to multiple times during the talk that reinforces your main idea or message. In her YouTube talk on designing effective scientific presentations , Stanford biologist Susan McConnell suggests using the approach of home slides to build a cohesive narrative.
To deliver a polished presentation, it is essential to practice it. Here are some tips.
- For your first run-through, practice alone. Pay attention to your narrative. Does your story flow naturally? Do you know how you will start and end? Are there any awkward transitions? Do animations help you tell your story? Do your slides help to convey what you are saying or are they missing components?
- Next, practice in front of your advisor, and/or your peers (e.g., your lab group). Ask someone to time your talk. Take note of their feedback and the questions that they ask you (you might be asked similar questions during your real talk).
- Edit your talk, taking into account the feedback you’ve received. Eliminate superfluous slides that don’t contribute to your takeaway message.
- Practice as many times as needed to memorize the order of your slides and the key transition points of your talk. However, don’t try to learn your talk word for word. Instead, memorize opening and closing statements, and sentences at key junctures in the presentation. Your presentation should resemble a serious but spontaneous conversation with the audience.
- Practicing multiple times also helps you hone the delivery of your talk. While rehearsing, pay attention to your vocal intonations and speed. Make sure to take pauses while you speak, and make eye contact with your imaginary audience.
- Make sure your talk finishes within the allotted time, and remember to leave time for questions. Conferences are particularly strict on run time.
- Anticipate questions and challenges from the audience, and clarify ambiguities within your slides and/or speech in response.
- If you anticipate that you could be asked questions about details but you don’t have time to include them, or they detract from the main message of your talk, you can prepare slides that address these questions and place them after the final slide of your talk.
➡️ More tips for giving scientific presentations
An organized presentation with a clear narrative will help you communicate your ideas effectively, which is essential for engaging your audience and conveying the importance of your work. Taking time to plan and outline your scientific presentation before writing the slides will help you manage your nerves and feel more confident during the presentation, which will improve your overall performance.
A good scientific presentation has an engaging scientific narrative with a memorable take-home message. It has clear, informative slides that enhance what the speaker says. You need to practice your talk many times to ensure you deliver a polished presentation.
First, consider who will attend your presentation, and what you want the audience to learn about your research. Tailor your content to their level of knowledge and interests. Second, create an outline for your presentation, including the key points you want to make and the evidence you will use to support those points. Finally, practice your presentation several times to ensure that it flows smoothly and that you are comfortable with the material.
Prepare an opening that immediately gets the audience’s attention. A common device is a why or a how question, or a statement of a major open problem in your field, but you could also start with a quote, interesting statistic, or case study from your field.
Scientific presentations typically either focus on a single study (e.g., a 15-minute conference presentation) or tell the story of multiple studies (e.g., a PhD defense or 50-minute conference keynote talk). For a single study talk, the structure follows the scientific paper format: Introduction, Methods, Results, Summary, and Conclusion, whereas the format of a talk discussing multiple studies is more complex, but a theme unifies the studies.
Ensure you have one major idea per slide, and convey that idea clearly (through images, equations, statistics, citations, video, etc.). The slide should include a title that summarizes the major point of the slide, should not contain too much text or too many graphics, and color should be used meaningfully.

30+ Best Research Presentation Templates for PowerPoint (PPT)
Finding the right PowerPoint template plays an important part in getting your message across to the audience during a presentation. And it’s especially true for research presentations.
Using the right colors, graphs, infographics, and illustrations in your slides is the key to delivering information more effectively and making your presentation a success.
Today, we handpicked a great collection of research presentation PowerPoint templates for you to make the perfect slideshows for various types of research papers and studies.
Whether you’re preparing for a presentation at a school, event, or conference, there are templates in this list for all purposes. Let’s dive in.
How Does Unlimited PowerPoint Templates Sound?
Download thousands of PowerPoint templates, and many other design elements, with a monthly Envato Elements membership. It starts at $16 per month, and gives you unlimited access to a growing library of over 2,000,000 presentation templates, fonts, photos, graphics, and more.

Pitch Deck Templates
Startup pitch deck.

Animated PPT Templates
Fully animated.

Pitch PowerPoint
Explore PowerPoint Templates
Science & Research Presentation PowerPoint Template

This PowerPoint template is a perfect choice for preparing a research presentation to share your scientific findings and reports.
The template has 30 unique slides with unlimited color options. There are a few infographics included in the slideshow as well.
Why This Is A Top Pick
The presentation has a very modern and creative design where you can showcase your data and information in an attractive way. You won’t be making boring research presentations ever again.
Labvire – Research Presentation PowerPoint Template

Labvire is another modern PowerPoint template you can use for various types of research presentations. It’s also ideal for laboratory-related research presentations. The template has fully customizable slide layouts with editable charts, graphs, and more. You can choose from more than 40 unique slide designs as well.
Novalabs – Science Research PowerPoint Template

Novalabs PowerPoint template features a highly visual and attractive design. The template includes 36 different slides that feature large image placeholders for adding a more visual look to your presentations. There are lots of editable graphics, shapes, and tables included in the template too. Feel free to customize them however you like.
Research & Development PowerPoint Template

The minimal and clean design of this PowerPoint template makes it a great choice for delivering more effective research presentations. With fewer distractions in each slide, you’ll be able to convey your message more easily. The template comes with 30 unique slides. You can change the colors, fonts, and shapes to your preference as well.
Marketing Research Presentation PowerPoint Template

When talking about research presentations, we can’t forget about marketing research. Most sales and marketing meetings usually include a sophisticated marketing research presentation. This PowerPoint template will help you design those research presentations without effort. It includes a total of 150 slides, featuring 30 unique slides in 5 different color schemes.
Free Business Market Research Presentation Template

This is a free PowerPoint template designed for making business market research presentations. It gives you 27 different and fully customizable slides to create professional slideshows for your business meetings.
Free Business Data Analysis & Research Presentation

With this PowerPoint template, you can create colorful and creative business research and data analysis presentation without any design skills. It includes 35 unique slides with lots of infographics and editable shapes. The template is free to use as well.
Lernen – Research Thesis PowerPoint Presentation

Larnen is the ideal PowerPoint template for making research slideshows for your thesis presentations. It includes 30 unique slides that are available in light and dark color themes. It also has editable charts and graphs.
Aristo – Research Academic PowerPoint Presentation
This PowerPoint template is also made with academic research presentations in mind. The template has a professional design with clean layouts and light colors. It comes with more than 30 different slides.
Biosearch – Science Research PowerPoint Template

You can use this PowerPoint template to make professional presentations to present research data and results. It lets you choose from 40 different slides and 90 color themes. The slides are available in both light and dark color themes as well.
Neolabs – Laboratory & Science Research PPT

Neolabs is another science research presentation made with laboratory research teams in mind. You can use it to make effective slideshows to present your research findings. There are 30 unique slides in this template.
Free Business Cost Analysis PowerPoint Template

This is a free PowerPoint and Google Slides template that comes with 35 unique slides. It’s ideal for making research presentations related to business financials.
Research & Case Study PowerPoint Template

Create the perfect case study presentation using your research data with this PowerPoint template. It includes a modern slide design with infographics and charts for effectively presenting your data.
Liron Labs – Laboratory Research PowerPoint Template

Another PowerPoint template for laboratory research presentations. This template includes 15 useful slide layouts with editable graphics, free fonts, and image placeholders. You can edit and customize the colors and text as well.
Research Thesis PowerPoint Template

Make an attractive and creative research thesis presentation using this PowerPoint template. There are over 30 unique slides in this template. You can either use dark or light color themes to create your presentations.
Colorful Thesis Research PowerPoint Template

If you want to make your research presentations look more colorful and creative, this PowerPoint template is for you. It has 15 different slides with fully customizable layouts. It has editable shapes, free fonts, and image placeholders too.
Free Data Analysis Research PowerPoint Template

This PowerPoint template is also free to download. You can also customize it using PowerPoint or Google Slides. This template is ideal for marketing agencies and teams for presenting research and data analysis.
Laboratory & Science Research PowerPoint Template

You can make more convincing and unique lab research presentations using this PowerPoint template. It features a creative design that will easily attract the attention of your audience. You can use it to make various other science and research presentations too. The template includes 30 unique slides.
The Biologist – Research Presentation PowerPoint Template

Just as the name suggests, this PowerPoint template is designed with biology and science-related presentations in mind. It includes many useful slide layouts that can be used to make various types of research presentations. There are 30 different slide designs included in this template with editable shapes and colors.
Modern Science & Research PowerPoint Template

If you’re looking for a PowerPoint template to create a modern-looking research presentation, this template is perfect for you. It features a collection of modern and attractive slides with lots of space for including images, icons, and graphs. There are 30 unique slides in the template with light and dark color themes to choose from.
Marketing Report & Research PowerPoint Template

This PowerPoint template doubles as both a research and report slideshow. You can use it to create various marketing reports as well as marketing research presentations. It comes with 30 slides that feature minimal and clean designs. It includes lots of editable charts, infographics, and tables as well.
Market Research Presentation PowerPoint Template

Another modern PowerPoint template for making market research presentations. This template includes 25 unique slides with master slides, image placeholders, and editable colors. The template is ideal for marketing agencies and corporate businesses.
Free Academic Research Thesis PowerPoint Template

This free PowerPoint template is designed for defending your academic research thesis dissertation. Needless to say, it’s a useful template for academics as well as teachers. The template features 23 unique slide layouts with customizable designs.
Free Economics Research Thesis Presentation Template

You can use this free template to create thesis and research presentations related to economics. It’s useful for academic students and gives you the freedom to choose from 21 slide layouts to make your own presentations.
Labia – Research Presentation Powerpoint Template

Labia is a research presentation template made for professionals. It comes with a set of modern slides with multipurpose designs. That means you can customize them to make many different types of research presentations. There are 30 unique slides included in this template that come in 5 different color themes.
Medical Research Infographics & Powerpoint Slides
You’ll be using lots of charts, graphs, and infographics in your presentations to showcase data in visual form. Not to mention that visuals always work well for attracting the audience’s attention. You can use the infographic slides in this template to create better research presentations. Each slide features a unique infographic with animated designs.
Foreka – Biology Education & Research Presentation PPT

Foreka is a PowerPoint template made for educational presentations, especially for covering topics related to biology. But it can also be customized to present your research presentations. The slides have very useful layouts that are most suitable for making research slide designs. There are 30 slides included with light and dark color themes.
Maua – Aesthetic Business Research PowerPoint Template

This PowerPoint template is suitable for making elegant and stylish business reports and business research presentations. It’s especially great for making background research and competitor research slideshows. The template comes with 30 slides featuring master slides, image placeholders, and more.
World Data Scientist Powerpoint Presentation Template

You can use this PowerPoint template to create research presentations for many different types of topics, industries, and projects. The template includes lots of data-centric slides where you can easily showcase your data in visual form. There are 30 unique slides included with the template as well.
Free SWOT Analysis Infographics PowerPoint Template
SWOT analysis is a commonly used methodology in business research presentations. With this free PowerPoint template, you can create stylish SWOT analysis infographics for your presentations. It includes SWOT infographics in 30 different styles.
Free Market Research Presentation Infographics PPT
This is a collection of free PowerPoint slides that feature various styles of infographics you can use in your business and market research presentations. There are 30 different infographic slides included in this template. You can edit, change colors, and customize them however you like.
Sinara – Science & Research Powerpoint Template

Sinara is a brilliant PowerPoint template you can use to craft a professional presentation for science-related research and reports. It’s available in 3 different color schemes as well as the option to customize the colors to your preference. The template comes in light and dark themes too.
Political Science and Research PowerPoint Template

This PowerPoint template will be quite useful to political science and international relations students. It features a total of 150 slides you can use to create attractive presentations for your research and methodologies. There are slides in 5 different color schemes.
How to Make a Research Poster in PowerPoint
We bet you didn’t know that you could actually design posters in PowerPoint. Well, you can and it’s very easy to do so.
The easiest way to make a poster in PowerPoint is to use a pre-made template like the one above.
You can easily copy one of the slides from a template, and resize the slide dimensions to create a vertical poster. Then add a title with a few lines of text and you’ll have yourself a poster.
Or, if you want to craft a poster from scratch, you can read our complete guide on how to create posters in PowerPoint with step-by-step instructions.
For more useful presentation templates, be sure to check out our best educational PowerPoint templates collection.

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
How to Structure your Presentation, with Examples
August 3, 2018 - Dom Barnard
For many people the thought of delivering a presentation is a daunting task and brings about a great deal of nerves . However, if you take some time to understand how effective presentations are structured and then apply this structure to your own presentation, you’ll appear much more confident and relaxed.
Here is our complete guide for structuring your presentation, with examples at the end of the article to demonstrate these points.
Why is structuring a presentation so important?
If you’ve ever sat through a great presentation, you’ll have left feeling either inspired or informed on a given topic. This isn’t because the speaker was the most knowledgeable or motivating person in the world. Instead, it’s because they know how to structure presentations – they have crafted their message in a logical and simple way that has allowed the audience can keep up with them and take away key messages.
Research has supported this, with studies showing that audiences retain structured information 40% more accurately than unstructured information.
In fact, not only is structuring a presentation important for the benefit of the audience’s understanding, it’s also important for you as the speaker. A good structure helps you remain calm, stay on topic, and avoid any awkward silences.
What will affect your presentation structure?
Generally speaking, there is a natural flow that any decent presentation will follow which we will go into shortly. However, you should be aware that all presentation structures will be different in their own unique way and this will be due to a number of factors, including:
- Whether you need to deliver any demonstrations
- How knowledgeable the audience already is on the given subject
- How much interaction you want from the audience
- Any time constraints there are for your talk
- What setting you are in
- Your ability to use any kinds of visual assistance
Before choosing the presentation’s structure answer these questions first:
- What is your presentation’s aim?
- Who are the audience?
- What are the main points your audience should remember afterwards?
When reading the points below, think critically about what things may cause your presentation structure to be slightly different. You can add in certain elements and add more focus to certain moments if that works better for your speech.

What is the typical presentation structure?
This is the usual flow of a presentation, which covers all the vital sections and is a good starting point for yours. It allows your audience to easily follow along and sets out a solid structure you can add your content to.
1. Greet the audience and introduce yourself
Before you start delivering your talk, introduce yourself to the audience and clarify who you are and your relevant expertise. This does not need to be long or incredibly detailed, but will help build an immediate relationship between you and the audience. It gives you the chance to briefly clarify your expertise and why you are worth listening to. This will help establish your ethos so the audience will trust you more and think you’re credible.
Read our tips on How to Start a Presentation Effectively
2. Introduction
In the introduction you need to explain the subject and purpose of your presentation whilst gaining the audience’s interest and confidence. It’s sometimes helpful to think of your introduction as funnel-shaped to help filter down your topic:
- Introduce your general topic
- Explain your topic area
- State the issues/challenges in this area you will be exploring
- State your presentation’s purpose – this is the basis of your presentation so ensure that you provide a statement explaining how the topic will be treated, for example, “I will argue that…” or maybe you will “compare”, “analyse”, “evaluate”, “describe” etc.
- Provide a statement of what you’re hoping the outcome of the presentation will be, for example, “I’m hoping this will be provide you with…”
- Show a preview of the organisation of your presentation
In this section also explain:
- The length of the talk.
- Signal whether you want audience interaction – some presenters prefer the audience to ask questions throughout whereas others allocate a specific section for this.
- If it applies, inform the audience whether to take notes or whether you will be providing handouts.
The way you structure your introduction can depend on the amount of time you have been given to present: a sales pitch may consist of a quick presentation so you may begin with your conclusion and then provide the evidence. Conversely, a speaker presenting their idea for change in the world would be better suited to start with the evidence and then conclude what this means for the audience.
Keep in mind that the main aim of the introduction is to grab the audience’s attention and connect with them.
3. The main body of your talk
The main body of your talk needs to meet the promises you made in the introduction. Depending on the nature of your presentation, clearly segment the different topics you will be discussing, and then work your way through them one at a time – it’s important for everything to be organised logically for the audience to fully understand. There are many different ways to organise your main points, such as, by priority, theme, chronologically etc.
- Main points should be addressed one by one with supporting evidence and examples.
- Before moving on to the next point you should provide a mini-summary.
- Links should be clearly stated between ideas and you must make it clear when you’re moving onto the next point.
- Allow time for people to take relevant notes and stick to the topics you have prepared beforehand rather than straying too far off topic.
When planning your presentation write a list of main points you want to make and ask yourself “What I am telling the audience? What should they understand from this?” refining your answers this way will help you produce clear messages.
4. Conclusion
In presentations the conclusion is frequently underdeveloped and lacks purpose which is a shame as it’s the best place to reinforce your messages. Typically, your presentation has a specific goal – that could be to convert a number of the audience members into customers, lead to a certain number of enquiries to make people knowledgeable on specific key points, or to motivate them towards a shared goal.
Regardless of what that goal is, be sure to summarise your main points and their implications. This clarifies the overall purpose of your talk and reinforces your reason for being there.
Follow these steps:
- Signal that it’s nearly the end of your presentation, for example, “As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…”
- Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation – “In this speech I wanted to compare…”
- Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions
- Indicate what is next/a call to action/a thought-provoking takeaway
- Move on to the last section
5. Thank the audience and invite questions
Conclude your talk by thanking the audience for their time and invite them to ask any questions they may have. As mentioned earlier, personal circumstances will affect the structure of your presentation.
Many presenters prefer to make the Q&A session the key part of their talk and try to speed through the main body of the presentation. This is totally fine, but it is still best to focus on delivering some sort of initial presentation to set the tone and topics for discussion in the Q&A.

Other common presentation structures
The above was a description of a basic presentation, here are some more specific presentation layouts:
Demonstration
Use the demonstration structure when you have something useful to show. This is usually used when you want to show how a product works. Steve Jobs frequently used this technique in his presentations.
- Explain why the product is valuable.
- Describe why the product is necessary.
- Explain what problems it can solve for the audience.
- Demonstrate the product to support what you’ve been saying.
- Make suggestions of other things it can do to make the audience curious.
Problem-solution
This structure is particularly useful in persuading the audience.
- Briefly frame the issue.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it ‘s such a problem. Use logos and pathos for this – the logical and emotional appeals.
- Provide the solution and explain why this would also help the audience.
- Call to action – something you want the audience to do which is straightforward and pertinent to the solution.
Storytelling
As well as incorporating stories in your presentation , you can organise your whole presentation as a story. There are lots of different type of story structures you can use – a popular choice is the monomyth – the hero’s journey. In a monomyth, a hero goes on a difficult journey or takes on a challenge – they move from the familiar into the unknown. After facing obstacles and ultimately succeeding the hero returns home, transformed and with newfound wisdom.
Storytelling for Business Success webinar , where well-know storyteller Javier Bernad shares strategies for crafting compelling narratives.
Another popular choice for using a story to structure your presentation is in media ras (in the middle of thing). In this type of story you launch right into the action by providing a snippet/teaser of what’s happening and then you start explaining the events that led to that event. This is engaging because you’re starting your story at the most exciting part which will make the audience curious – they’ll want to know how you got there.
- Great storytelling: Examples from Alibaba Founder, Jack Ma
Remaining method
The remaining method structure is good for situations where you’re presenting your perspective on a controversial topic which has split people’s opinions.
- Go into the issue in detail showing why it’s such a problem – use logos and pathos.
- Rebut your opponents’ solutions – explain why their solutions could be useful because the audience will see this as fair and will therefore think you’re trustworthy, and then explain why you think these solutions are not valid.
- After you’ve presented all the alternatives provide your solution, the remaining solution. This is very persuasive because it looks like the winning idea, especially with the audience believing that you’re fair and trustworthy.
Transitions
When delivering presentations it’s important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it’s all relevant. This can be done using speech transitions which are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified.
Transitions can be one word, a phrase or a full sentence – there are many different forms, here are some examples:
Moving from the introduction to the first point
Signify to the audience that you will now begin discussing the first main point:
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- First, let’s begin with…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
Shifting between similar points
Move from one point to a similar one:
- In the same way…
- Likewise…
- Equally…
- This is similar to…
- Similarly…
Internal summaries
Internal summarising consists of summarising before moving on to the next point. You must inform the audience:
- What part of the presentation you covered – “In the first part of this speech we’ve covered…”
- What the key points were – “Precisely how…”
- How this links in with the overall presentation – “So that’s the context…”
- What you’re moving on to – “Now I’d like to move on to the second part of presentation which looks at…”
Physical movement
You can move your body and your standing location when you transition to another point. The audience find it easier to follow your presentation and movement will increase their interest.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Key slides for your presentation
Slides are a useful tool for most presentations: they can greatly assist in the delivery of your message and help the audience follow along with what you are saying. Key slides include:
- An intro slide outlining your ideas
- A summary slide with core points to remember
- High quality image slides to supplement what you are saying
There are some presenters who choose not to use slides at all, though this is more of a rarity. Slides can be a powerful tool if used properly, but the problem is that many fail to do just that. Here are some golden rules to follow when using slides in a presentation:
- Don’t over fill them – your slides are there to assist your speech, rather than be the focal point. They should have as little information as possible, to avoid distracting people from your talk.
- A picture says a thousand words – instead of filling a slide with text, instead, focus on one or two images or diagrams to help support and explain the point you are discussing at that time.
- Make them readable – depending on the size of your audience, some may not be able to see small text or images, so make everything large enough to fill the space.
- Don’t rush through slides – give the audience enough time to digest each slide.
Guy Kawasaki, an entrepreneur and author, suggests that slideshows should follow a 10-20-30 rule :
- There should be a maximum of 10 slides – people rarely remember more than one concept afterwards so there’s no point overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
- The presentation should last no longer than 20 minutes as this will leave time for questions and discussion.
- The font size should be a minimum of 30pt because the audience reads faster than you talk so less information on the slides means that there is less chance of the audience being distracted.
Here are some additional resources for slide design:
- 7 design tips for effective, beautiful PowerPoint presentations
- 11 design tips for beautiful presentations
- 10 tips on how to make slides that communicate your idea
Group Presentations
Group presentations are structured in the same way as presentations with one speaker but usually require more rehearsal and practices. Clean transitioning between speakers is very important in producing a presentation that flows well. One way of doing this consists of:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what health anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Elnaz will talk about the prevalence of health anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Elnaz”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Joe.”
From this example you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
Example of great presentation structure and delivery
Having examples of great presentations will help inspire your own structures, here are a few such examples, each unique and inspiring in their own way.
How Google Works – by Eric Schmidt
This presentation by ex-Google CEO Eric Schmidt demonstrates some of the most important lessons he and his team have learnt with regards to working with some of the most talented individuals they hired. The simplistic yet cohesive style of all of the slides is something to be appreciated. They are relatively straightforward, yet add power and clarity to the narrative of the presentation.
Start with why – by Simon Sinek
Since being released in 2009, this presentation has been viewed almost four million times all around the world. The message itself is very powerful, however, it’s not an idea that hasn’t been heard before. What makes this presentation so powerful is the simple message he is getting across, and the straightforward and understandable manner in which he delivers it. Also note that he doesn’t use any slides, just a whiteboard where he creates a simple diagram of his opinion.
The Wisdom of a Third Grade Dropout – by Rick Rigsby
Here’s an example of a presentation given by a relatively unknown individual looking to inspire the next generation of graduates. Rick’s presentation is unique in many ways compared to the two above. Notably, he uses no visual prompts and includes a great deal of humour.
However, what is similar is the structure he uses. He first introduces his message that the wisest man he knew was a third-grade dropout. He then proceeds to deliver his main body of argument, and in the end, concludes with his message. This powerful speech keeps the viewer engaged throughout, through a mixture of heart-warming sentiment, powerful life advice and engaging humour.
As you can see from the examples above, and as it has been expressed throughout, a great presentation structure means analysing the core message of your presentation. Decide on a key message you want to impart the audience with, and then craft an engaging way of delivering it.
By preparing a solid structure, and practising your talk beforehand, you can walk into the presentation with confidence and deliver a meaningful message to an interested audience.
It’s important for a presentation to be well-structured so it can have the most impact on your audience. An unstructured presentation can be difficult to follow and even frustrating to listen to. The heart of your speech are your main points supported by evidence and your transitions should assist the movement between points and clarify how everything is linked.
Research suggests that the audience remember the first and last things you say so your introduction and conclusion are vital for reinforcing your points. Essentially, ensure you spend the time structuring your presentation and addressing all of the sections.
How To Write A Presentation 101: A Step-by-Step Guide with Best Examples
Jane Ng • 02 Nov 2023 • 8 min read
Is it difficult to start of presentation? You’re standing before a room full of eager listeners, ready to share your knowledge and captivate their attention. But where do you begin? How do you structure your ideas and convey them effectively?
Take a deep breath, and fear not! In this article, we’ll provide a road map on how to write a presentation covering everything from crafting a script to creating an engaging introduction.
So, let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a presentation , what should be in a powerful presentation.
- How To Write A Presentation Script
- How to Write A Presentation Introduction
Key Takeaways
Tips for better presentation.
- How to start a presentation
- How to introduce yourself

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
Presentations are all about connecting with your audience.
Presenting is a fantastic way to share information, ideas, or arguments with your audience. Think of it as a structured approach to effectively convey your message. And you’ve got options such as slideshows, speeches, demos, videos, and even multimedia presentations!
The purpose of a presentation can vary depending on the situation and what the presenter wants to achieve.
- In the business world, presentations are commonly used to pitch proposals, share reports, or make sales pitches.
- In educational settings, presentations are a go-to for teaching or delivering engaging lectures.
- For conferences, seminars, and public events—presentations are perfect for dishing out information, inspiring folks, or even persuading the audience.
That sounds brilliant. But, how to write a presentation?

How To Write A Presentation? What should be in a powerful presentation? A great presentation encompasses several key elements to captivate your audience and effectively convey your message. Here’s what you should consider including in a winning presentation:
- Clear and Engaging Introduction: Start your presentation with a bang! Hook your audience’s attention right from the beginning by using a captivating story, a surprising fact, a thought-provoking question, or a powerful quote. Clearly state the purpose of your presentation and establish a connection with your listeners.
- Well-Structured Content: Organize your content logically and coherently. Divide your presentation into sections or main points and provide smooth transitions between them. Each section should flow seamlessly into the next, creating a cohesive narrative. Use clear headings and subheadings to guide your audience through the presentation.
- Compelling Visuals: Incorporate visual aids, such as images, graphs, or videos, to enhance your presentation. Make sure your visuals are visually appealing, relevant, and easy to understand. Use a clean and uncluttered design with legible fonts and appropriate color schemes.
- Engaging Delivery: Pay attention to your delivery style and body language. You should maintain eye contact with your audience, use gestures to emphasize key points, and vary your tone of voice to keep the presentation dynamic.
- Clear and Memorable Conclusion: Leave your audience with a lasting impression by providing a strong closing statement, a call to action, or a thought-provoking question. Make sure your conclusion ties back to your introduction and reinforces the core message of your presentation.

How To Write A Presentation Script (With Examples)
To successfully convey your message to your audience, you must carefully craft and organize your presentation script. Here are steps on how to write a presentation script:

1/ Understand Your Purpose and Audience:
- Clarify the purpose of your presentation. Are you informing, persuading, or entertaining?
- Identify your target audience and their knowledge level, interests, and expectations.
- Define what presentation format you want to use
2/ Outline the Structure of Your Presentation:
Strong opening: .
Start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience’s attention and introduces your topic. Some types of openings you can use are:
- Start with a Thought-Provoking Question: “Have you ever…?”
- Begin with a Surprising Fact or Statistic: “Did you know that….?”
- Use a Powerful Quote: “As Maya Angelou once said,….”
- Tell a Compelling Story : “Picture this: You’re standing at….”
- Start with a Bold Statement: “In the fast-paced digital age….”
Main Points:
Clearly state your main points or key ideas that you will discuss throughout the presentation.
- Clearly State the Purpose and Main Points: Example: “In this presentation, we will delve into three key areas. First,… Next,… Finally,…. we’ll discuss….”
- Provide Background and Context: Example: “Before we dive into the details, let’s understand the basics of…..”
- Present Supporting Information and Examples: Example: “To illustrate…., let’s look at an example. In,…..”
- Address Counterarguments or Potential Concerns: Example: “While…, we must also consider… .”
- Recap Key Points and Transition to the Next Section: Example: “To summarize, we’ve… Now, let’s shift our focus to…”
Remember to organize your content logically and coherently, ensuring smooth transitions between sections.
Ending:
You can conclude with a strong closing statement summarizing your main points and leaving a lasting impression. Example: “As we conclude our presentation, it’s clear that… By…., we can….”
3/ Craft Clear and Concise Sentences:
Once you’ve outlined your presentation, you need to edit your sentences. Use clear and straightforward language to ensure your message is easily understood.
Alternatively, you can break down complex ideas into simpler concepts and provide clear explanations or examples to aid comprehension.
4/ Use Visual Aids and Supporting Materials:
Use supporting materials such as statistics, research findings, or real-life examples to back up your points and make them more compelling.
- Example: “As you can see from this graph,… This demonstrates….”
5/ Include Engagement Techniques:
Incorporate interactive elements to engage your audience, such as Q&A sessions , conducting live polls , or encouraging participation.
6/ Rehearse and Revise:
- Practice delivering your presentation script to familiarize yourself with the content and improve your delivery.
- Revise and edit your script as needed, removing any unnecessary information or repetitions.
7/ Seek Feedback:
You can share your script or deliver a practice presentation to a trusted friend, colleague, or mentor to gather feedback on your script and make adjustments accordingly.
More on Script Presentation

How to Write A Presentation Introduction with Examples
How to write presentations that are engaging and visually appealing? Looking for introduction ideas for the presentation? As mentioned earlier, once you have completed your script, it’s crucial to focus on editing and refining the most critical element—the opening of your presentation – the section that determines whether you can captivate and retain your audience’s attention right from the start.
Here is a guide on how to craft an opening that grabs your audience’s attention from the very first minute:
1/ Start with a Hook
To begin, you can choose from five different openings mentioned in the script based on your desired purpose and content. Alternatively, you can opt for the approach that resonates with you the most, and instills your confidence. Remember, the key is to choose a starting point that aligns with your objectives and allows you to deliver your message effectively.
2/ Establish Relevance and Context:
Then you should establish the topic of your presentation and explain why it is important or relevant to your audience. Connect the topic to their interests, challenges, or aspirations to create a sense of relevance.
3/ State the Purpose
Clearly articulate the purpose or goal of your presentation. Let the audience know what they can expect to gain or achieve by listening to your presentation.
4/ Preview Your Main Points
Give a brief overview of the main points or sections you will cover in your presentation. It helps the audience understand the structure and flow of your presentation and creates anticipation.
5/ Establish Credibility
Share your expertise or credentials related to the topic to build trust with the audience, such as a brief personal story, relevant experience, or mentioning your professional background.
6/ Engage Emotionally
Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning.
Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations. Aim for clarity and brevity to maintain the audience’s attention.
For example, Topic: Work-life balance
“Good morning, everyone! Can you imagine waking up each day feeling energized and ready to conquer both your personal and professional pursuits? Well, that’s exactly what we’ll explore today – the wonderful world of work-life balance. In a fast-paced society where work seems to consume every waking hour, it’s vital to find that spot where our careers and personal lives harmoniously coexist. Throughout this presentation, we’ll dive into practical strategies that help us achieve that coveted balance, boost productivity, and nurture our overall well-being.
But before we dive in, let me share a bit about my journey. As a working professional and a passionate advocate for work-life balance, I have spent years researching and implementing strategies that have transformed my own life. I am excited to share my knowledge and experiences with all of you today, with the hope of inspiring positive change and creating a more fulfilling work-life balance for everyone in this room. So, let’s get started!”
Check out: How to Start a Presentation?

Whether you’re a seasoned speaker or new to the stage, understanding how to write a presentation that conveys your message effectively is a valuable skill. By following the steps in this guide, you can become a captivating presenter and make your mark in every presentation you deliver.
Additionally, AhaSlides can significantly enhance your presentation’s impact. With AhaSlides, you can use live polls, quizzes, and word cloud to turn your presentation into an engaging and interactive experience. Let’s take a moment to explore our vast template library !
Frequently Asked Questions
1/ how to write a presentation step by step .
You can refer to our step-by-step guide on How To Write A Presentation Script:
- Understand Your Purpose and Audience
- Outline the Structure of Your Presentation
- Craft Clear and Concise Sentences
- Use Visual Aids and Supporting Material
- Include Engagement Techniques
- Rehearse and Revise
- Seek Feedback
2/ How do you start a presentation?
You can start with an engaging opening that grabs the audience’s attention and introduces your topic. Consider using one of the following approaches:
3/ What are the five parts of a presentation?
When it comes to presentation writing, a typical presentation consists of the following five parts:
- Introduction: Capturing the audience’s attention, introducing yourself, stating the purpose, and providing an overview.
- Main Body: Presenting main points, evidence, examples, and arguments.
- Visual Aids: Using visuals to enhance understanding and engage the audience.
- Conclusion: Summarizing main points, restating key message, and leaving a memorable takeaway or call to action.
- Q&A or Discussion: Optional part for addressing questions and encouraging audience participation.

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
More from AhaSlides


Basic Methods Handbook for Clinical Orthopaedic Research pp 227–233 Cite as
How to Prepare a Paper Presentation?
- Timothy Lording 8 , 9 &
- Jacques Menetrey 10 , 11
- First Online: 02 February 2019
2303 Accesses
Presenting your paper at a meeting is an important part of sharing your research with the orthopaedic community. Presentations are generally short and sharp, and careful preparation is key to ensure that the premise, findings, and relevance of your work are successfully conveyed. For most conference papers, the structure will mirror that of a scientific manuscript, with an introduction, materials and methods, results, discussion, and conclusions. Anticipation of potential questions will help to clarify your research for the audience.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Elmansori A, Lording T, Dumas R, Elmajri K, Neyret P, Lustig S. Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25:1598–605.
Article Google Scholar
Lording T, Corbo G, Bryant D, Burkhart TA, Getgood A. Rotational laxity control by the anterolateral ligament and the lateral meniscus is dependent on knee flexion angle: a cadaveric biomechanical study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;90:1922–8.
Google Scholar
Shybut TB, Vega CE, Haddad J, Alexander JW, Gold JE, Noble PC, Lowe WR. Effect of lateral meniscal root tear on the stability of the anterior cruciate ligament-deficient knee. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43:905–11.
Simon RA, Everhart JS, Nagaraja HN, Chaudhari AM. A case-control study of anterior cruciate ligament volume, tibial plateau slopes and intercondylar notch dimensions in ACL-injured knees. J Biomech. 2010;43:1702–7.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Sonnery-Cottet B, Mogos S, Thaunat M, Archbold P, Fayard JM, Freychet B, Clechet J, Chambat P. Proximal tibial anterior closing wedge osteotomy in repeat revision of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42:1873–80.
Stijak L, Herzog RF, Schai P. Is there an influence of the tibial slope of the lateral condyle on the ACL lesion? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;16:112–7.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Melbourne Orthopaedic Group, Windsor, VIC, Australia
Timothy Lording
The Alfred Hospital, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
Centre de Médecine du Sport et de l’Exercice, Hirslanden Clinique la Colline, Geneva, Switzerland
Jacques Menetrey
Service de Chirurgie Orthopédique et Traumatologie de l’Appareil Moteur, University Hospital of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Timothy Lording .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
UPMC Rooney Sports Complex, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
Volker Musahl
Department of Orthopaedics, Sahlgrenska Academy, Gothenburg University, Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Gothenburg, Sweden
Jón Karlsson
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology, Kantonsspital Baselland (Bruderholz, Laufen und Liestal), Bruderholz, Switzerland
Michael T. Hirschmann
McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Olufemi R. Ayeni
Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, NY, USA
Robert G. Marx
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, NorthShore University HealthSystem, Evanston, IL, USA
Jason L. Koh
Institute for Medical Science in Sports, Osaka Health Science University, Osaka, Japan
Norimasa Nakamura
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 ISAKOS
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Lording, T., Menetrey, J. (2019). How to Prepare a Paper Presentation?. In: Musahl, V., et al. Basic Methods Handbook for Clinical Orthopaedic Research. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-58254-1_24
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-58254-1_24
Published : 02 February 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN : 978-3-662-58253-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-662-58254-1
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

solar eclipse
25 templates

11 templates

palm sunday
5 templates

26 templates

8 templates
Paper Presentation templates
What comes to mind when you think about paper books pictures well, paper is the material of an endless list of things, these templates included our designers have used the versatility of this material, that has been around for some centuries now, and created this selection of presentations for your use. get your pen, brush or even your mouse and start creating.

Torn Paper Portfolio
Download the Torn Paper Portfolio presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. When a potential client or employer flips through the pages of your portfolio, they're not just looking at your work; they're trying to get a sense of who you are as a person. That's why it's crucial to curate...

School Subjects and Classroom Objects - French - 2nd Grade
Download the School Subjects and Classroom Objects - French - 2nd Grade presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and easily edit it to fit your own lesson plan! Designed specifically for elementary school education, this eye-catching design features engaging graphics and age-appropriate fonts; elements that capture the students' attention and...

World Literature Major for College: Jose Rizal and The Filibusterism
Download the World Literature Major for College: Jose Rizal and The Filibusterism presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. As university curricula increasingly incorporate digital tools and platforms, this template has been designed to integrate with presentation software, online learning management systems, or referencing software, enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness...

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access
Vintage Paper Style for Middle School Literature Lesson
If you’re going to teach a literature lesson, having a good visual aid will definitely help captivate your class. This is why this vintage paper styled template is going to help you so much in your future classes! Speak about the classic books and authors in elegant, brown slides that...

Vintage Papyrus Minitheme
Imagine stepping into a time machine and being transported back to the land of the pharaohs. In this ancient world, the papyrus is the cornerstone of communication for dynasties upon dynasties. Now, fast forward to the present day, and bring that ancient feel to your modern presentations with a virtual...

Dissertation Writing - Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in History
Download the Dissertation Writing - Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in History presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. As university curricula increasingly incorporate digital tools and platforms, this template has been designed to integrate with presentation software, online learning management systems, or referencing software, enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of...

Formal Research Paper Slideshow
Have you seen these slides? They are perfect for presenting your research paper! First of all, because we have included all the necessary sections of this type of work, such as hypothesis, objectives, methodology, analysis and the conclusions of the paper. The second reason is that the formal style will...

Student Notes Portfolio
Download the Student Notes Portfolio presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. When a potential client or employer flips through the pages of your portfolio, they're not just looking at your work; they're trying to get a sense of who you are as a person. That's why it's crucial to curate...

Papyrus History Lesson
History lessons tend to be boring for students, since they need to remember dates and a bunch of information. Make it entertaining by editing our free presentation template, whose backgrounds based on ancient papyrus rolls take it to the next level.

Graph Paper Style Thesis
Are you familiar with graph paper? Don't you know what it is? We're sure you do, you just didn't know its name. It's paper with a grid, facilitating the representation of graphs or other math-related things. Speaking of which, is your thesis about mathematics? Or maybe not but you just...

World War II - History - 8th Grade
Download the World War II - History - 8th Grade presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. If you’re looking for a way to motivate and engage students who are undergoing significant physical, social, and emotional development, then you can’t go wrong with an educational template designed for Middle School by...

Vintage Torn Paper Aesthetic Agency
If you want to give your agency’s presentations a sophisticated look, this vintage torn paper template might be just the thing. Combining muted tones of blue and brown, every slide is made up pieces of paper that seem to have been ripped from different notebooks. This visual device makes you...

Old Paper Style Bachelor's Thesis
A little vintage touch, which is at the same time elegant? It seems like a good idea, as long as the topic of your thesis fits it. Here's a template that is great for thesis defense slideshows on topics such as literature or history. The typography also plays a part...

Paper Volumes Thesis
Our new template is a good choice for those who are in need of help for their thesis defense. This presentation contains a cut-out effect and rounded shapes. Its layouts and its design are quite minimalist and modern, so after editing the slides with info from your research, you’ll have...

Notebook Lesson
These are the last days before the Summer break! We know that there are some pending lessons that you need to prepare for your students. As they may be thinking about their friends and their holidays, catch their attention with this cool template!

History of Guyana
Download the History of Guyana presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. The education sector constantly demands dynamic and effective ways to present information. This template is created with that very purpose in mind. Offering the best resources, it allows educators or students to efficiently manage their presentations and engage audiences....

Vintage Paper Background for Literature History Class for Middle School
Do you think that we've brought this template from a library? Well, yes, the backgrounds look like old paper, but it's been made in 2022! And now you can download it and transform it however you like. For example, you can use it for literature lessons. There are some examples...

Reconstruction Era and the Gilded Age - History - 11th Grade
In the United States, the Reconstruction Era followed the Civil War and sought to unite the nation and grant civil rights. The Gilded Age brought industrial growth, but also inequality and corruption. Both eras shared the struggle for civil rights and equity. So these are two periods loaded with historical...
- Page 1 of 44
New! Make quick presentations with AI
Slidesgo AI presentation maker puts the power of design and creativity in your hands, so you can effortlessly craft stunning slideshows in minutes.

Register for free and start editing online
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Additional menu
Techooid.com
Create more.

How to Present a Research Paper using PowerPoint [Sample + Tips]
posted on September 30, 2017
- Facebook 831
Spending couple of months or years in research seems less difficult as compared to presenting it. Presenting your research work to a bunch of experts can be very difficult sometimes. Your audience will only like well-crafted presentation.
There are certain things you need to take care of. Presenting a research paper is quite different from a talk or any other presentation. In research paper presentation, you are going to discuss everything that you have done and achieved during your research in limited time.
There is a specific outline that experts recommend that you must follow during your research paper presentation.
Research Paper Presentation Outline
Introduction.
Give the brief introduction of your work. For example, if you are going to work on a disease than describe the
disease. Focus on the things on which you have worked on. If you are working on genes of that disease then it will be important discuss the genetic pathways of the disease in your introduction.
You may discuss the “problem” on which you have worked on during your research.
Things that you need to remember,
- Focus on the relevant information
- Do not more than 3 slides on the introduction
Methodology
It’s about the recipe and spices of your research work. Mention all the materials that were required to do the task and how miraculously you did it. Using flowcharts in your PowerPoint slides can help you to present it in the more engaging way.
Try to fit it in 2 slides only. Emphasis on any special equipment or build that you have used during your work.
Tell your audience about the verifiable objectives you had while doing this research. It doesn’t matter if they vary from your results, it is necessary to tell the audience what were you looking for.
- Consume only one slide
- Make it concise
- You are allowed to use fancy words or good vocabulary here
Results and Discussion
Write down your results, most possibly in the form of the table. Try not to confuse your audience with so much numerical data so charts will work fine. Highlight if you have something novel in your results.
Try to interpret your results in 2-3 points. The conclusion must be very meaningful for audiences. It must not be ambiguous. Usually, a single statement is enough.
Future Recommendations
What can be done more on your particle topic? This is very important if you are going to pursue the same topic in your further studies. It will help you to have a future objective for yourself.
Tips for Research Paper Presentations
- There should be 5*5 rules in each slide. I.e. there are five words in one sentence and there should be five lines on one slide.
- Data should be in the form of small key points or bullets . Data should not be in paragraph form on the slide. It should be precise. Slides are not for the audience it just hints for the presenter. The presenter should explain all terms and every concept that is written on slide.
- Standard heading size is 44 while standard text size is 32.
- Make link of one slide with the second slide during the presentation. For example, tell the audience what they will listen and see in next slide.
- The template of PowerPoint presentation should not have shocking color. Text color should be in contrast with template color. If somewhere in slides text color is same as template audience would not be able to see what is written on it.
- There should be slide number on every slide except title slide.
- All slides should be in homogeneity. The presenter should use either upper case or lower case alphabets in the text of the whole presentation.
- There should be the use of animations but no use of transitions.
- There should be a table of content of presentation on the slide next to title slide. By explaining this presenter should give an overview of the whole presentation.
Paper Presentation Sample
To help our readers, I have made a template for paper presentation. I hope it will be helpful for you. Research paper presentation sample Download.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on StumbleUpon (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
About Haseeb Ahmad
Author is a S&T Journalist and Entrepreneur. He Founded Jaamiah.com - Pakistan's Premier EdTech Startup.
Reader Interactions
September 30, 2017 at 8:31 pm
Simple and useful article. Keep it up, also write about ”Project Report ”
September 30, 2017 at 8:39 pm
Thank you for your kind response. I have pinned your request in our priority to-do list. Keep visiting our site.
May 19, 2018 at 11:56 am
well articulated. thanks for sharing this.
May 19, 2018 at 5:18 pm
Dear Badmus, Thank you for your kind remarks. Please keep visiting and sharing our website
May 25, 2018 at 12:20 am
Hey, nice work.I will love to have a copy of this work sent to my mail, ( [email protected] ),thanks a million
May 25, 2018 at 2:39 pm
Dear keke You can use the “email” share option at the bottom of the article. Thank you for endorsing our work
September 26, 2018 at 8:12 pm
Can you mail it on gmail
September 30, 2018 at 2:59 pm
Dear Vrushikesh, You can download it just by clicking the links. If failed to do so, Please feel free to comment again. I’ll email you
October 22, 2018 at 5:08 am
can you send me the file? the file cant be read. [email protected]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Home Blog Design How to Design a Winning Poster Presentation: Quick Guide with Examples & Templates
How to Design a Winning Poster Presentation: Quick Guide with Examples & Templates

How are research posters like High School science fair projects? Quite similar, in fact.
Both are visual representations of a research project shared with peers, colleagues and academic faculty. But there’s a big difference: it’s all in professionalism and attention to detail. You can be sure that the students that thrived in science fairs are now creating fantastic research posters, but what is that extra element most people miss when designing a poster presentation?
This guide will teach tips and tricks for creating poster presentations for conferences, symposia, and more. Learn in-depth poster structure and design techniques to help create academic posters that have a lasting impact.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
- What is a Research Poster?
Why are Poster Presentations important?
Overall dimensions and orientation, separation into columns and sections, scientific, academic, or something else, a handout with supplemental and contact information, cohesiveness, design and readability, storytelling.
- Font Characteristics
- Color Pairing
- Data Visualization Dimensions
- Alignment, Margins, and White Space
Scientific/Academic Conference Poster Presentation
Digital research poster presentations, slidemodel poster presentation templates, how to make a research poster presentation step-by-step, considerations for printing poster presentations, how to present a research poster presentation, final words, what is a research poster .
Research posters are visual overviews of the most relevant information extracted from a research paper or analysis. They are essential communication formats for sharing findings with peers and interested people in the field. Research posters can also effectively present material for other areas besides the sciences and STEM—for example, business and law.
You’ll be creating research posters regularly as an academic researcher, scientist, or grad student. You’ll have to present them at numerous functions and events. For example:
- Conference presentations
- Informational events
- Community centers
The research poster presentation is a comprehensive way to share data, information, and research results. Before the pandemic, the majority of research events were in person. During lockdown and beyond, virtual conferences and summits became the norm. Many researchers now create poster presentations that work in printed and digital formats.

Let’s look at why it’s crucial to spend time creating poster presentations for your research projects, research, analysis, and study papers.

Research posters represent you and your sponsor’s research
Research papers and accompanying poster presentations are potent tools for representation and communication in your field of study. Well-performing poster presentations help scientists, researchers, and analysts grow their careers through grants and sponsorships.
When presenting a poster presentation for a sponsored research project, you’re representing the company that sponsored you. Your professionalism, demeanor, and capacity for creating impactful poster presentations call attention to other interested sponsors, spreading your impact in the field.
Research posters demonstrate expertise and growth
Presenting research posters at conferences, summits, and graduate grading events shows your expertise and knowledge in your field of study. The way your poster presentation looks and delivers, plus your performance while presenting the work, is judged by your viewers regardless of whether it’s an officially judged panel.
Recurring visitors to research conferences and symposia will see you and your poster presentations evolve. Improve your impact by creating a great poster presentation every time by paying attention to detail in the poster design and in your oral presentation. Practice your public speaking skills alongside the design techniques for even more impact.
Poster presentations create and maintain collaborations
Every time you participate in a research poster conference, you create meaningful connections with people in your field, industry or community. Not only do research posters showcase information about current data in different areas, but they also bring people together with similar interests. Countless collaboration projects between different research teams started after discussing poster details during coffee breaks.
An effective research poster template deepens your peer’s understanding of a topic by highlighting research, data, and conclusions. This information can help other researchers and analysts with their work. As a research poster presenter, you’re given the opportunity for both teaching and learning while sharing ideas with peers and colleagues.
Anatomy of a Winning Poster Presentation
Do you want your research poster to perform well? Following the standard layout and adding a few personal touches will help attendees know how to read your poster and get the most out of your information.

The overall size of your research poster ultimately depends on the dimensions of the provided space at the conference or research poster gallery. The poster orientation can be horizontal or vertical, with horizontal being the most common. In general, research posters measure 48 x 36 inches or are an A0 paper size.
A virtual poster can be the same proportions as the printed research poster, but you have more leeway regarding the dimensions. Virtual research posters should fit on a screen with no need to scroll, with 1080p resolution as a standard these days. A horizontal presentation size is ideal for that.
A research poster presentation has a standard layout of 2–5 columns with 2–3 sections each. Typical structures say to separate the content into four sections; 1. A horizontal header 2. Introduction column, 3. Research/Work/Data column, and 4. Conclusion column. Each unit includes topics that relate to your poster’s objective. Here’s a generalized outline for a poster presentation:
- Condensed Abstract
- Objectives/Purpose
- Methodology
- Recommendations
- Implications
- Acknowledgments
- Contact Information
The overview content you include in the units depends on your poster presentations’ theme, topic, industry, or field of research. A scientific or academic poster will include sections like hypothesis, methodology, and materials. A marketing analysis poster will include performance metrics and competitor analysis results.
There’s no way a poster can hold all the information included in your research paper or analysis report. The poster is an overview that invites the audience to want to find out more. That’s where supplement material comes in. Create a printed PDF handout or card with a QR code (created using a QR code generator ). Send the audience to the best online location for reading or downloading the complete paper.
What Makes a Poster Presentation Good and Effective?
For your poster presentation to be effective and well-received, it needs to cover all the bases and be inviting to find out more. Stick to the standard layout suggestions and give it a unique look and feel. We’ve put together some of the most critical research poster-creation tips in the list below. Your poster presentation will perform as long as you check all the boxes.
The information you choose to include in the sections of your poster presentation needs to be cohesive. Train your editing eye and do a few revisions before presenting. The best way to look at it is to think of The Big Picture. Don’t get stuck on the details; your attendees won’t always know the background behind your research topic or why it’s important.
Be cohesive in how you word the titles, the length of the sections, the highlighting of the most important data, and how your oral presentation complements the printed—or virtual—poster.
The most important characteristic of your poster presentation is its readability and clarity. You need a poster presentation with a balanced design that’s easy to read at a distance of 1.5 meters or 4 feet. The font size and spacing must be clear and neat. All the content must suggest a visual flow for the viewer to follow.
That said, you don’t need to be a designer to add something special to your poster presentation. Once you have the standard—and recognized—columns and sections, add your special touch. These can be anything from colorful boxes for the section titles to an interesting but subtle background, images that catch the eye, and charts that inspire a more extended look.
Storytelling is a presenting technique involving writing techniques to make information flow. Firstly, storytelling helps give your poster presentation a great introduction and an impactful conclusion.
Think of storytelling as the invitation to listen or read more, as the glue that connects sections, making them flow from one to another. Storytelling is using stories in the oral presentation, for example, what your lab partner said when you discovered something interesting. If it makes your audience smile and nod, you’ve hit the mark. Storytelling is like giving a research presentation a dose of your personality, and it can help turning your data into opening stories .
Design Tips For Creating an Effective Research Poster Presentation
The section above briefly mentioned how important design is to your poster presentation’s effectiveness. We’ll look deeper into what you need to know when designing a poster presentation.
1. Font Characteristics
The typeface and size you choose are of great importance. Not only does the text need to be readable from two meters away, but it also needs to look and sit well on the poster. Stay away from calligraphic script typefaces, novelty typefaces, or typefaces with uniquely shaped letters.
Stick to the classics like a sans serif Helvetica, Lato, Open Sans, or Verdana. Avoid serif typefaces as they can be difficult to read from far away. Here are some standard text sizes to have on hand.
- Title: 85 pt
- Authors: 65 pt
- Headings: 36 pt
- Body Text: 24 pt
- Captions: 18 pt

If you feel too prone to use serif typefaces, work with a font pairing tool that helps you find a suitable solution – and intend those serif fonts for heading sections only. As a rule, never use more than 3 different typefaces in your design. To make it more dynamic, you can work with the same font using light, bold, and italic weights to put emphasis on the required areas.
2. Color Pairing
Using colors in your poster presentation design is a great way to grab the viewer’s attention. A color’s purpose is to help the viewer follow the data flow in your presentation, not distract. Don’t let the color take more importance than the information on your poster.

Choose one main color for the title and headlines and a similar color for the data visualizations. If you want to use more than one color, don’t create too much contrast between them. Try different tonalities of the same color and keep things balanced visually. Your color palette should have at most one main color and two accent colors.
Black text over a white background is standard practice for printed poster presentations, but for virtual presentations, try a very light gray instead of white and a very dark gray instead of black. Additionally, use variations of light color backgrounds and dark color text. Make sure it’s easy to read from two meters away or on a screen, depending on the context. We recommend ditching full white or full black tone usage as it hurts eyesight in the long term due to its intense contrast difference with the light ambiance.
3. Data Visualization Dimensions
Just like the text, your charts, graphs, and data visualizations must be easy to read and understand. Generally, if a person is interested in your research and has already read some of the text from two meters away, they’ll come closer to look at the charts and graphs.

Fit data visualizations inside columns or let them span over two columns. Remove any unnecessary borders, lines, or labels to make them easier to read at a glance. Use a flat design without shadows or 3D characteristics. The text in legends and captions should stay within the chart size and not overflow into the margins. Use a unified text size of 18px for all your data visualizations.
4. Alignment, Margins, and White Space
Finally, the last design tip for creating an impressive and memorable poster presentation is to be mindful of the layout’s alignment, margins, and white space. Create text boxes to help keep everything aligned. They allow you to resize, adapt, and align the content along a margin or grid.
Take advantage of the white space created by borders and margins between sections. Don’t crowd them with a busy background or unattractive color.

Calculate margins considering a print format. It is a good practice in case the poster presentation ends up becoming in physical format, as you won’t need to downscale your entire design (affecting text readability in the process) to preserve information.
There are different tools that you can use to make a poster presentation. Presenters who are familiar with Microsoft Office prefer to use PowerPoint. You can learn how to make a poster in PowerPoint here.
Poster Presentation Examples
Before you start creating a poster presentation, look at some examples of real research posters. Get inspired and get creative.
Research poster presentations printed and mounted on a board look like the one in the image below. The presenter stands to the side, ready to share the information with visitors as they walk up to the panels.

With more and more conferences staying virtual or hybrid, the digital poster presentation is here to stay. Take a look at examples from a poster session at the OHSU School of Medicine .
Use SlideModel templates to help you create a winning poster presentation with PowerPoint and Google Slides. These poster PPT templates will get you off on the right foot. Mix and match tables and data visualizations from other poster slide templates to create your ideal layout according to the standard guidelines.
If you need a quick method to create a presentation deck to talk about your research poster at conferences, check out our Slides AI presentation maker. A tool in which you add the topic, curate the outline, select a design, and let AI do the work for you.
1. One-pager Scientific Poster Template for PowerPoint

A PowerPoint template tailored to make your poster presentations an easy-to-craft process. Meet our One-Pager Scientific Poster Slide Template, entirely editable to your preferences and with ample room to accommodate graphs, data charts, and much more.
Use This Template
2. Eisenhower Matrix Slides Template for PowerPoint

An Eisenhower Matrix is a powerful tool to represent priorities, classifying work according to urgency and importance. Presenters can use this 2×2 matrix in poster presentations to expose the effort required for the research process, as it also helps to communicate strategy planning.
3. OSMG Framework PowerPoint Template

Finally, we recommend presenters check our OSMG Framework PowerPoint template, as it is an ideal tool for representing a business plan: its goals, strategies, and measures for success. Expose complex processes in a simplified manner by adding this template to your poster presentation.
Remember these three words when making your research poster presentation: develop, design, and present. These are the three main actions toward a successful poster presentation.

The section below will take you on a step-by-step journey to create your next poster presentation.
Step 1: Define the purpose and audience of your poster presentation
Before making a poster presentation design, you’ll need to plan first. Here are some questions to answer at this point:
- Are they in your field?
- Do they know about your research topic?
- What can they get from your research?
- Will you print it?
- Is it for a virtual conference?
Step 2: Make an outline
With a clear purpose and strategy, it’s time to collect the most important information from your research paper, analysis, or documentation. Make a content dump and then select the most interesting information. Use the content to draft an outline.
Outlines help formulate the overall structure better than going straight into designing the poster. Mimic the standard poster structure in your outline using section headlines as separators. Go further and separate the content into the columns they’ll be placed in.
Step 3: Write the content
Write or rewrite the content for the sections in your poster presentation. Use the text in your research paper as a base, but summarize it to be more succinct in what you share.
Don’t forget to write a catchy title that presents the problem and your findings in a clear way. Likewise, craft the headlines for the sections in a similar tone as the title, creating consistency in the message. Include subtle transitions between sections to help follow the flow of information in order.
Avoid copying/pasting entire sections of the research paper on which the poster is based. Opt for the storytelling approach, so the delivered message results are interesting for your audience.
Step 4: Put it all together visually
This entire guide on how to design a research poster presentation is the perfect resource to help you with this step. Follow all the tips and guidelines and have an unforgettable poster presentation.
Moving on, here’s how to design a research poster presentation with PowerPoint Templates . Open a new project and size it to the standard 48 x 36 inches. Using the outline, map out the sections on the empty canvas. Add a text box for each title, headline, and body text. Piece by piece, add the content into their corresponding text box.

Transform the text information visually, make bullet points, and place the content in tables and timelines. Make your text visual to avoid chunky text blocks that no one will have time to read. Make sure all text sizes are coherent for all headings, body texts, image captions, etc. Double-check for spacing and text box formatting.
Next, add or create data visualizations, images, or diagrams. Align everything into columns and sections, making sure there’s no overflow. Add captions and legends to the visualizations, and check the color contrast with colleagues and friends. Ask for feedback and progress to the last step.
Step 5: Last touches
Time to check the final touches on your poster presentation design. Here’s a checklist to help finalize your research poster before sending it to printers or the virtual summit rep.
- Check the resolution of all visual elements in your poster design. Zoom to 100 or 200% to see if the images pixelate. Avoid this problem by using vector design elements and high-resolution images.
- Ensure that charts and graphs are easy to read and don’t look crowded.
- Analyze the visual hierarchy. Is there a visual flow through the title, introduction, data, and conclusion?
- Take a step back and check if it’s legible from a distance. Is there enough white space for the content to breathe?
- Does the design look inviting and interesting?
An often neglected topic arises when we need to print our designs for any exhibition purpose. Since A0 is a hard-to-manage format for most printers, these poster presentations result in heftier charges for the user. Instead, you can opt to work your design in two A1 sheets, which also becomes more manageable for transportation. Create seamless borders for the section on which the poster sheets should meet, or work with a white background.
Paper weight options should be over 200 gsm to avoid unwanted damage during the printing process due to heavy ink usage. If possible, laminate your print or stick it to photographic paper – this shall protect your work from spills.
Finally, always run a test print. Gray tints may not be printed as clearly as you see them on screen (this is due to the RGB to CMYK conversion process). Other differences can be appreciated when working with ink jet plotters vs. laser printers. Give yourself enough room to maneuver last-minute design changes.
Presenting a research poster is a big step in the poster presentation cycle. Your poster presentation might or might not be judged by faculty or peers. But knowing what judges look for will help you prepare for the design and oral presentation, regardless of whether you receive a grade for your work or if it’s business related. Likewise, the same principles apply when presenting at an in-person or virtual summit.
The opening statement
Part of presenting a research poster is welcoming the viewer to your small personal area in the sea of poster presentations. You’ll need an opening statement to pitch your research poster and get the viewers’ attention.
Draft a 2 to 3-sentence pitch that covers the most important points:
- What the research is
- Why was it conducted
- What the results say
From that opening statement, you’re ready to continue with the oral presentation for the benefit of your attendees.
The oral presentation
During the oral presentation, share the information on the poster while conversing with the interested public. Practice many times before the event. Structure the oral presentation as conversation points, and use the poster’s visual flow as support. Make eye contact with your audience as you speak, but don’t make them uncomfortable.
Pro Tip: In a conference or summit, if people show up to your poster area after you’ve started presenting it to another group, finish and then address the new visitors.
QA Sessions
When you’ve finished the oral presentation, offer the audience a chance to ask questions. You can tell them before starting the presentation that you’ll be holding a QA session at the end. Doing so will prevent interruptions as you’re speaking.
If presenting to one or two people, be flexible and answer questions as you review all the sections on your poster.
Supplemental Material
If your audience is interested in learning more, you can offer another content type, further imprinting the information in their minds. Some ideas include; printed copies of your research paper, links to a website, a digital experience of your poster, a thesis PDF, or data spreadsheets.
Your audience will want to contact you for further conversations; include contact details in your supplemental material. If you don’t offer anything else, at least have business cards.
Even though conferences have changed, the research poster’s importance hasn’t diminished. Now, instead of simply creating a printed poster presentation, you can also make it for digital platforms. The final output will depend on the conference and its requirements.
This guide covered all the essential information you need to know for creating impactful poster presentations, from design, structure and layout tips to oral presentation techniques to engage your audience better .
Before your next poster session, bookmark and review this guide to help you design a winning poster presentation every time.

Like this article? Please share
Cool Presentation Ideas, Design, Design Inspiration Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Design • January 11th, 2024
How to Use Figma for Presentations
The powerful UI/UX prototyping software can also help us to craft high-end presentation slides. Learn how to use Figma as a presentation software here!

Filed under Design • December 28th, 2023
Multimedia Presentation: Insights & Techniques to Maximize Engagement
Harnessing the power of multimedia presentation is vital for speakers nowadays. Join us to discover how you can utilize these strategies in your work.

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • December 15th, 2023
How to Delete a Text Box in Google Slides
Discover how to delete a text box in Google Slides in just a couple of clicks. Step-by-step guide with images.
Leave a Reply
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- IEEE Paper Format | Template & Guidelines
IEEE Paper Format | Template & Guidelines
Published on August 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on April 6, 2023.
IEEE provides guidelines for formatting your paper. These guidelines must be followed when you’re submitting a manuscript for publication in an IEEE journal. Some of the key guidelines are:
- Formatting the text as two columns, in Times New Roman, 10 pt.
- Including a byline, an abstract , and a set of keywords at the start of the research paper
- Placing any figures, tables, and equations at the top or bottom of a column, not in the middle
- Following the appropriate heading styles for any headings you use
- Including a full list of IEEE references at the end
- Not including page numbers
To learn more about the specifics of IEEE paper format, check out the free template below. Note that you may not need to follow these rules if you’ve only been told to use IEEE citation format for a student paper. But you do need to follow them to submit to IEEE publications.
Table of contents
Ieee format template, ieee heading styles, frequently asked questions about ieee.
The template below can be used to make sure that your paper follows IEEE format. It’s set up with custom Word styles for all the different parts of the text, with the right fonts and formatting and with further explanation of key points.
Make sure to remove all the explanatory text in the template when you insert your own.
Download IEEE paper format template
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
IEEE recommends specific heading styles to distinguish the title and different levels of heading in your paper from each other. Styles for each of these are built into the template.
The paper title is written in 24 pt. Times New Roman, centered at the top of the first page. Other headings are all written in 10 pt. Times New Roman:
- Level 1 text headings begin with a roman numeral followed by a period. They are written in small caps, in title case, and centered.
- Level 2 text headings begin with a capital letter followed by a period. They are italicized, left-aligned, and written in title case.
- Level 3 text headings begin with a number followed by a closing parenthesis . They are italicized, written in sentence case, and indented like a regular paragraph. The text of the section follows the heading immediately, after a colon .
- Level 4 text headings begin with a lowercase letter followed by a closing parenthesis. They are italicized, written in sentence case, and indented slightly further than a normal paragraph. The text of the section follows the heading immediately, after a colon.
- Component headings are used for the different components of your paper outside of the main text, such as the acknowledgments and references. They are written in small caps, in title case, centered, and without any numbering.
You should use 10 pt. Times New Roman font in your IEEE format paper .
For the paper title, 26 pt. Times New Roman is used. For some other paper elements like table footnotes, the font can be slightly smaller. All the correct stylings are available in our free IEEE format template .
No, page numbers are not included in an IEEE format paper . If you’re submitting to an IEEE publication, page numbers will be added in the final publication but aren’t needed in the manuscript.
IEEE paper format requires you to include an abstract summarizing the content of your paper. It appears at the start of the paper, right after you list your name and affiliation.
The abstract begins with the word “Abstract,” italicized and followed by an em dash. The abstract itself follows immediately on the same line. The entire section is written in bold font. For example: “ Abstract —This paper discusses … ”
You can find the correct format for your IEEE abstract and other parts of the paper in our free IEEE paper format template .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, April 06). IEEE Paper Format | Template & Guidelines. Scribbr. Retrieved March 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/ieee/ieee-paper-format/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, ieee reference page | format & examples, ieee in-text citation | guidelines & examples, ieee journal citation | guide with examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Conferences
- Call for Papers
- Requirements for Authors
- Instructions for Presenters
- Symposium Organizers
- Past Symposia
- Conference Policies
- Code of Conduct
OSDI '24 Instructions for Presenters
These instructions are for authors of papers accepted for publication at the 18th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI '24) . If you wish to submit a paper to, or deliver a talk at, another upcoming USENIX event, please review the open Calls for Papers and Calls for Participation for our upcoming USENIX conferences .
If you need an invitation letter to apply for a visa to attend the symposium, please contact the Conference Department as soon as possible. Visa applications are reportedly taking more than two months to process. Please identify yourself as a presenter or an author, and include your mailing address in your email request.
Preparing Your Paper for Publication
- Coordinate with your paper shepherd. All papers have an assigned shepherd who will review your paper before the final submission. Please coordinate with your shepherd so they have time for the review, and so you have time to respond to their requests. By default, shepherds are anonymous and you can interact with them via HotCRP. If you are unsure how to proceed, please contact [email protected] .
- Final Papers deadline. A printable PDF of your final paper is due via the submissions system by Tuesday, June 4, 2024 . If you have questions, please contact the Production Department .
- Maximum page length. Final papers should be no longer than 14 pages, including figures and tables, plus as many pages as needed for references.
- Paper format. Papers should be typeset in two-column format using 10-point type on 12-point (single-spaced) leading, in a text block 7" wide x 9" deep, with .33" inter-column space, formatted for 8.5" x 11" paper.
- Embed all fonts in your final paper PDF.
- Apply Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to your final PDF so it is searchable.
- Page numbers must be suppressed on your final paper PDF.
- Looking for templates? Templates and sample first pages (two-column format) for Microsoft Word and LaTeX are available on the USENIX templates page . Please ensure that your final paper is saved as a US letter-sized (8.5" x 11") PDF.
- Artifact Appendix. Authors who pass artifact evaluation are encouraged to add an Artifact Appendix of up to two pages to their paper. The goal of the appendix is to describe and document the artifact in a standard format.
- Certify your final paper's title, author, and abstract in HotCRP. The final PDF's title and author information, including author order and affiliation, and the abstract, must exactly match the information entered into the HotCRP submission system. Please update the information in HotCRP as necessary, then check the certification checkbox. Please note: if you make any changes after you check the certification checkbox, you will need to check the box again.
- Sign the consent to publish form. Each author must sign a consent to publish form, which allows USENIX to publish the paper as well as any slides, audio, and/or video of your presentation. USENIX makes these freely available as part of our commitment to open access. Please review and e-sign the form . If you are the lead author, please be sure all of your co-authors sign a form as well.
- Use of images, audio, and video in your materials. It is very important that you secure permission to use copyright-protected materials in your slide deck, paper, presentation video, or any other materials used at our event or submitted for publication. Even when using an item with a Creative Commons license, you must read and comply with the terms of the license. USENIX receives copyright infringement notices from time to time, resulting from authors or speakers using copyright-protected materials without proper licensing or attribution. When this happens, we have to unpublish the work in question until/unless the issue is resolved. Licensing fees may be incurred, even when the work is unpublished , and USENIX will bill the author or speaker for any costs incurred. When possible, USENIX will refer the complainant directly to the author or speaker, who will be solely responsible for resolving the complaint.
- Embargo requests. All papers will be available online only to registered attendees before the symposium. If your accepted paper should not be published prior to the event, please notify the Production Department . The papers will be made available online to the public beginning on the first day of the symposium.
Preparing Your Paper Presentation
- Designate your paper presenter. The authors of each paper must designate one co-author to present the paper at the symposium via the Presenter Information form provided by the program co-chairs in the acceptance notification email. The deadline to complete this form is Monday, June 17, 2024 . If the paper presenter changes before the event, you are responsible for notifying the Conference Department so they can confirm that the new presenter is registered for the event. This information is required to ensure that all OSDI '24 paper presenters are accounted for on the day of their presentation.
- Registration. Authors presenting their papers must register to attend the symposium. Registration information will be available on the OSDI '24 website in May. Authors will also receive information about registration via email from the Conference Department. Please note: If the symposium registration fee poses a financial hardship for the presenter of the refereed paper, the presenter must contact the Conference Department with a description of their circumstances.
- 1 LCD projector
- 1 wired lavalier microphone
- Cables and extension cords
- Presentation slides. Slides should be set up for a 16:9 aspect ratio. In order to make the content of your presentation available on the USENIX website immediately after the symposium, please email a PDF of your slides to [email protected] as soon as possible after your presentation.
Instructions for Invited Speakers
- Registration. The Conference Department will contact you with instructions for registering for the symposium online. All speakers must be registered to attend the symposium.
- Sign the consent to publish form. All speakers must sign a consent to publish form, which allows USENIX to publish any slides, audio, and/or video of your presentation. USENIX makes these freely available as part of our commitment to open access. Please review and e-sign the form .
If you have questions about the instructions listed above, please contact the OSDI '24 Program Co-Chairs , Ada Gavrilovska and Douglas B. Terry, or the USENIX Production Department .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The presentation layout for pricing plans is a practical slide for B2B or SaaS companies which need to show their different pricing options. Perfect for proposals or product launch presentations. Testimonials. A testimonial from a trusted client gives your brand social proof. Including these in your presentation can make a positive impact.
Here are some simple tips for creating an effective PowerPoint Presentation. Less is more: You want to give enough information to make your audience want to read your paper. So include details, but not too many, and avoid too many formulas and technical jargon. Clean and professional: Avoid excessive colors, distracting backgrounds, font ...
Creating a PowerPoint presentation for a research paper involves several critical steps needed to convey your findings and engage your audience effectively, and these steps are as follows: Step 1. Understand your audience: Identify the audience for your presentation. Tailor your content and level of detail to match the audience's background ...
Free Paper Slide Templates for an Artistic Slideshow. Organize and present your ideas with this paper PowerPoint template. Whether you're a student, teacher, or business professional, these templates are perfect for anyone who wants to make their presentation look professional and organized. With a range of customizable slides, you can easily ...
Make it simple and hassle-free with a collection of well-designed and easy-to-use presentation templates from Canva. To captivate your target audience, you need the proper presentation template design that suits your subject. After all, a pleasing visual, coupled with helpful and relevant content, can go a long way in creating a solid presentation.
To prepare a paper presentation, create an outline of your content, then write your script on note cards or slides using software like PowerPoint. Be sure to stick to one main point per card or slide! Next, design visual aids like graphics, charts, and bullet points to illustrate your content and help the audience follow along.
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor's standpoint. I've presented my own ...
Preparation of a scientific presentation involves three separate stages: outlining the scientific narrative, preparing slides, and practicing your delivery. Making the slides of your talk without first planning what you are going to say is inefficient. Here, we provide a 4 step guide to writing your scientific presentation:
Science & Research Presentation PowerPoint Template. This PowerPoint template is a perfect choice for preparing a research presentation to share your scientific findings and reports. The template has 30 unique slides with unlimited color options. There are a few infographics included in the slideshow as well.
This research paper presentation template uses visual aids, such as pictures and icons to help you communicate clearly and effectively with your audience. You can use this template to present research proposals and papers to faculty staff or the general public. It can be an ideal addition to your funding request. Present your research paper ...
277 templates. Create a blank Research Presentation. Black Modern Technology Keynote Presentation. Presentation by Canva Creative Studio. Pastel Color and Black Aesthetic Group Project Presentation. Presentation by Colllab Supply. Research Proposal Business Presentation in Purple Green Orange Gradients Style.
Follow these steps: Signal that it's nearly the end of your presentation, for example, "As we wrap up/as we wind down the talk…". Restate the topic and purpose of your presentation - "In this speech I wanted to compare…". Summarise the main points, including their implications and conclusions.
6/ Engage Emotionally. Connect emotional levels with your audience by appealing to their aspirations, fears, desires, or values. They help create a deeper connection and engagement from the very beginning. Make sure your introduction is concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations.
In the case of a research presentation, you want a formal and academic-sounding one. It should include: The full title of the report. The date of the report. The name of the researchers or department in charge of the report. The name of the organization for which the presentation is intended.
While PowerPoint long dominated the presentation industry, Visme's free online presentation maker allows you to create even more beautiful and engaging content. With Visme's engaging presentation maker, you can start with a template, dive into one of our themes with various slide ideas, or mix and match slides from different templates to ...
general rule is to have 1 slide per. minute of presentation (may be. excluding the title, competing. interests and acknowledgment. slides). Most conferences allow. the speaker to present paper in ...
Most free paper presentations are 6 min in length. Careful preparation is important, to ensure that that the premise, findings, and relevance of your work are successfully conveyed in this short timeframe. Preparing your talk and preparing your slides go hand in hand and for simplicity are considered here together.
Paper Volumes Thesis. Our new template is a good choice for those who are in need of help for their thesis defense. This presentation contains a cut-out effect and rounded shapes. Its layouts and its design are quite minimalist and modern, so after editing the slides with info from your research, you'll have...
Tips for Research Paper Presentations. There should be 5*5 rules in each slide. I.e. there are five words in one sentence and there should be five lines on one slide. Data should be in the form of small key points or bullets. Data should not be in paragraph form on the slide. It should be precise.
Step 3: Write the content. Write or rewrite the content for the sections in your poster presentation. Use the text in your research paper as a base, but summarize it to be more succinct in what you share. Don't forget to write a catchy title that presents the problem and your findings in a clear way.
IEEE provides guidelines for formatting your paper. These guidelines must be followed when you're submitting a manuscript for publication in an IEEE journal. Some of the key guidelines are: Formatting the text as two columns, in Times New Roman, 10 pt. Including a byline, an abstract, and a set of keywords at the start of the research paper.
46. Creative Brief Presentation. This creative brief presentation template can help you communicate your brand style and design requirements to video editors, graphic designers, creative agencies and freelancers. Swap the existing images, icons, text and colors for your own content and create a branded creative brief.
Paper Format. Consistency in the order, structure, and format of a paper allows readers to focus on a paper's content rather than its presentation. To format a paper in APA Style, writers can typically use the default settings and automatic formatting tools of their word-processing program or make only minor adjustments.
Paper format. Papers should be typeset in two-column format using 10-point type on 12-point (single-spaced) leading, in a text block 7" wide x 9" deep, with .33" inter-column space, formatted for 8.5" x 11" paper. ... It is very important that you secure permission to use copyright-protected materials in your slide deck, paper, presentation ...
Calibre Enabling process control through predictive design and virtual metrology for high product mix manufacturing 2024-03-21T02:56:59.000-0400 Resolution Enhancement Technology (RET) Summary. This is the paper winning the Best Paper & Best Oral Presentation Award at 8th IEEE EDTM Conference 2024. Details. Attachments: ...