- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
- Image & Use Policy
- Translations
UC MUSEUM OF PALEONTOLOGY

Understanding Evolution
Your one-stop source for information on evolution
Teaching Resources
Natural selection and adaptation slide set.
Grade Level(s):
- UC Museum of Paleontology
Resource type:
Time: 2 minutes
This set of five PowerPoint slides featuring personal response questions (i.e., multiple choice questions that can be used with "clicker" technology) can be incorporated into lectures on natural selection and adaptation in order to actively engage students in thinking about evolution.
Go to this resource »

- Teaching tips
- Teaching background
- [Mechanisms of evolution: Grades 13-16] Evolution results from natural selection acting upon genetic variation within a population.
- [Mechanisms of evolution: Grades 13-16] Organisms cannot intentionally produce adaptive mutations in response to environmental influences.
- [Mechanisms of evolution: Grades 13-16] An individual's fitness (or relative fitness) is the contribution that individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation relative to other individuals in the population.
There are no NGSS/DCI concepts currently linked to this resource.
With increased experience, the instructor will be able to develop new personal response questions, optimizing them for particular applications and topics. To learn more about how personal response questions and other types of active learning activities can be easily incorporated into lecture (and for more downloadable slides!), visit our guide to active learning in the undergraduate classroom .
- Natural Selection
Subscribe to our newsletter
- Teaching resource database
- Correcting misconceptions
- Conceptual framework and NGSS alignment
- Image and use policy
- Evo in the News
- The Tree Room
- Browse learning resources
ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Natural selection.
Natural selection is the process through which species adapt to their environments. It is the engine that drives evolution.
On the Origin of Species
English naturalist Charles Darwin wrote the definitive book outlining his idea of natural selection, On the Origin of Species. The book chronicled his studies in South America and Pacific islands. Published in 1859, the book became a best seller.
Photograph by Ian Forsyth via Getty Images

English naturalist Charles Darwin developed the idea of natural selection after a five-year voyage to study plants, animals, and fossils in South America and on islands in the Pacific. In 1859, he brought the idea of natural selection to the attention of the world in his best-selling book, On the Origin of Species .
Natural selection is the process through which populations of living organisms adapt and change. Individuals in a population are naturally variable, meaning that they are all different in some ways. This variation means that some individuals have traits better suited to the environment than others. Individuals with adaptive traits — traits that give them some advantage—are more likely to survive and reproduce. These individuals then pass the adaptive traits on to their offspring. Over time, these advantageous traits become more common in the population. Through this process of natural selection , favorable traits are transmitted through generations .
Natural selection can lead to speciation , where one species gives rise to a new and distinctly different species . It is one of the processes that drives evolution and helps to explain the diversity of life on Earth.
Darwin chose the name natural selection to contrast with “artificial selection,” or selective breeding that is controlled by humans. He pointed to the pastime of pigeon breeding, a popular hobby in his day, as an example of artificial selection. By choosing which pigeons mated with others, hobbyists created distinct pigeon breeds, with fancy feathers or acrobatic flight, that were different from wild pigeons.
Darwin and other scientists of his day argued that a process much like artificial selection happened in nature, without any human intervention. He argued that natural selection explained how a wide variety of life forms developed over time from a single common ancestor.
Darwin did not know that genes existed, but he could see that many traits are heritable—passed from parents to offspring.
Mutations are changes in the structure of the molecules that make up genes , called DNA . The mutation of genes is an important source of genetic variation within a population. Mutations can be random (for example, when replicating cells make an error while copying DNA ), or happen as a result of exposure to something in the environment, like harmful chemicals or radiation.
Mutations can be harmful, neutral, or sometimes helpful, resulting in a new, advantageous trait. When mutations occur in germ cells (eggs and sperm), they can be passed on to offspring.
If the environment changes rapidly, some species may not be able to adapt fast enough through natural selection . Through studying the fossil record, we know that many of the organisms that once lived on Earth are now extinct. Dinosaurs are one example. An invasive species , a disease organism, a catastrophic environmental change, or a highly successful predator can all contribute to the extinction of species .
Today, human actions such as overhunting and the destruction of habitats are the main cause of extinctions. Extinctions seem to be occurring at a much faster rate today than they did in the past, as shown in the fossil record.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
October 19, 2023
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Biology
Course: ap®︎/college biology > unit 7, introduction to evolution and natural selection.
- Natural selection and the owl butterfly
- Biodiversity and natural selection
- Variation in a species
- Darwin, evolution, & natural selection
- Natural selection
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Video transcript
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

solar eclipse
25 templates

12 templates

north korea

7 templates

21 templates

48 templates
Evolution and Natural Selection Thesis Defense
Evolution and natural selection thesis defense presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
From tiny microorganisms to complex animals like us, all living beings on Earth have evolved over millions of years through a process of natural selection, which essentially means that certain traits or characteristics that aid in an organism's survival are more likely to be passed down to future generations. Slidesgo has been evolving all this time too, and our current templates and many features are a proof of it! Download this green template and prepare the presentation that you'll bring to your thesis defense. It's customizable and has illustrations of plants.
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- Different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides


How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Register for free and start editing online

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Evolution and Natural Selection
Published by Eunice Summers Modified over 4 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Evolution and Natural Selection"— Presentation transcript:
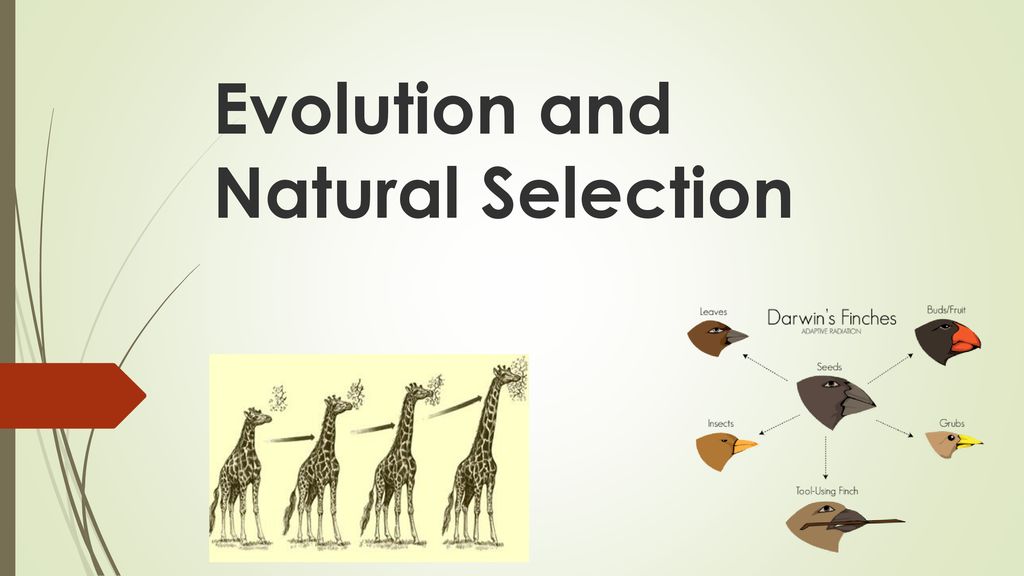
Evolution and Darwin.

7.1 Darwin’s Theory.

Evolution Everything you wanted to learn in the last week of school… You’re welcome! ~Mrs. Boorom

Darwin’s Theory outline notes

Species Change Over Time. What is evolution? Definition: The gradual change in a species over time Takes a Looooong time Results from a change in the.

December, 1831, the HMS Beagle sailed around the world from England for 5 years. Charles Darwin - 22 yr old - ship’s naturalist, studying the natural world.

Evolution Chapters 13, 14, & 15. Earth has millions of other kinds of organisms of every imaginable shape, size, and habitat. The variety of living things.

Evolution. Breaking Down the Definitions Honors 1.Evolution 2.Natural selection 3.Adaptation 4.Fitness 5.Convergent evolution 6.Divergent evolution 7.Adaptive.

Evolution By Aimee Chavez. Species Species: group of organisms that share similar characteristics and can reproduce among themselves to produce fertile.

There are several scientists who observed and predicted the causes behind evolution. Evolution- the development of new organisms from pre-existing.

DARWIN’S THEORY. Charles Darwin ( ) A British scientist who went on a 5 year voyage around the world and studied nature. While travelling Darwin.
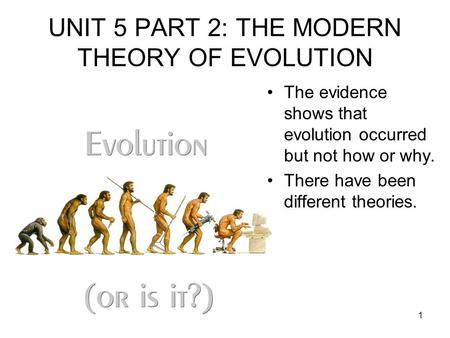
1 UNIT 5 PART 2: THE MODERN THEORY OF EVOLUTION The evidence shows that evolution occurred but not how or why. There have been different theories.

1 History of Evolutionary Thought. 2 Early Ideas On Earth’s Organisms Aristotle believed species were fixed creations arranged by their complexity Aristotle.
8-3 NOTES: DARWIN VS. LAMARCK. BEFORE DARWIN People believed earth was only thousands of years old and organisms did not change.

Unit 1 Lesson 2 Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company.

Unit 1 Lesson 2 Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection

The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection

Darwin & Natural Selection

Evolution: History and Theory
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

Natural Selection, Speciation, and Evolution
Oct 20, 2014
190 likes | 372 Views
Natural Selection, Speciation, and Evolution. Textbook Reference Chapter 14 & 15. Lamarck’s Early Theory on Evolution. Based on 3 ideas 1. Desire (will) to change 2. Use and Disuse 3. Passing on acquired traits (weight lifting) Brought idea of evolution to forefront
Share Presentation
- natural selection
- isolated populations
- evolutionary theory continues
- share common gene pool

Presentation Transcript
Natural Selection, Speciation, and Evolution Textbook Reference Chapter 14 & 15
Lamarck’s Early Theory on Evolution • Based on 3 ideas 1. Desire (will) to change 2. Use and Disuse 3. Passing on acquired traits (weight lifting) • Brought idea of evolution to forefront • Knew nothing of genes or genetics
Charles Darwin • Observations aboard Beagle • Led to his theory of evolution - change in species over time - modern organisms descend from ancient - change in allele frequency in gene pool • Darwin’s mechanism: NATURAL SELECTION • Wrote On the Origin of Species
Influences that Shaped Darwin’s Theory • Charles Lyell, geologist - Earth very old, changed over time • Farmers, artificial selection - choose organisms with desireable traits to produce offspring • Thomas Malthus, economist - Malthusian Doctrine
Evidence for Evolution • Contrasting theories over mechanism for evolution, typically not evolution itself • Evidence of Change: 1.Fossil Record 2. Embryonic Development 3. Anatomical Structures 4. Biochemical Similarities • All pieces support Darwin’s idea of descent from a common ancestor
Evolution by Natural Selection • Darwin’s observations: 1 - wild species show variations 2 - high birthrates & shortage of necessities, causes competition 3 - individuals whose characteristics are well-suited to their environment survive and reproduce, survival of the fittest 4- larger portion of each new generation will have favorable variation 5– over long periods of time, small changes accumulate, population has adapted and natural selection took place The environment selects which characteristics are advantageous Video Clip
Peppered Moths: Natural Selection in Action • Two varieties, population mainly light colored prior to the Industrial Revolution • Soot from burning coal coated trunks • Dark moths now “fit” the best, better suited to survive, birds can’t spot the moths • Relative frequency of alleles for color changed in the gene pool for the population • H.B.D. Kettlewell tested the theory
How do Genes Fit In? • Darwin did not know about genes and genetics • Genes: 1. Responsible for variations 2. Genetic variations arise by mutations 3. Not controlled; no goal in mind • Phenotypic/Genotypic variation 1. Raw material for natural selection 2. One genotype proves to be advantageous example, sickle cell carrier
Modern Evolutionary Theory • Today we define evolutionary fitness as the success an organism has in passing on its genes to the next generation • An adaptation is any genetically controlled trait that increases an organism’s fitness • Think about the weight lifter- big muscles won’t be inherited but gene for the potential to develop large muscles could be
How do new species evolve?
Speciation • Species- individuals that can breed and produce fertile offspring.(share common gene pool) • Niche- habitat and role/job of organism, no 2 can occupy same niche, choices: adapt, move, or go extinct. • Speciation occurs when populations are separated by some barrier • Natural selection can work differently in each group • Groups cannot interbreed develop reproductive isolation • Each group will become fit to the environment they are in • Overtime, two populations cannot breed, new species • Example, Darwin’s finches underwent adaptive radiation
Adaptive Radiation
Darwin’s Finches on the Galapagos Islands Islands isolated populations of finches; natural selection occurred independently in each group Relative frequency for certain traits changed in isolated populations
Divergent One species gives rise to many species Also known as adaptive radiation Many species with common ancestor Many homologous structures Convergent vs. Divergent Evolution
Convergent vs. Divergent Evolution Convergent • Similar looking species that do not have a common ancestor • Similar behavior and appearance • Many analogous structures Video Clip
Evolutionary Theory Continues to Evolve • Gene pools can change in absence of natural selection by: 1. Genetic Drift- allele becomes common by chance 2. Genetic drift implies not all characteristics contribute to fitness • Gene pools can remain unchanged for long periods of time ex. Horseshoe crab, living fossil • Gradual evolutionary change, theory of gradualism • Punctuated equilibrium,long stable periods with spurts of change
- More by User

Evolution/Natural Selection
Evolution/Natural Selection Individual organisms differ and some variation can be inherited (fitness). Fitness is the ability of an organism to survive and reproduce. Organisms produce more offspring than can survive. Compete for limited resources. Survival of the Fittest
628 views • 15 slides

Evolution: Selection and Speciation
Evolution: Selection and Speciation. Vanessa Couldridge Richard Knight . http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Darwin%27s_finches.jpeg. Forms of Selection. Frequency. Trait value. Different selective pressures will cause a population to respond in different ways
1.78k views • 20 slides

Natural Selection and Evolution
Natural Selection and Evolution. Spring 2007 Dobson High School Hope Finzer. Earth’s History. Earth Origins:
1.23k views • 81 slides

Natural selection and Evolution
Natural selection and Evolution. video. What is this all about?. Traits. Traits are passed from one generation to the next That means that all the information to produce all of your traits was contained within the single cell that was you when you were conceived.
1.11k views • 72 slides

EVOLUTION AND NATURAL SELECTION
EVOLUTION AND NATURAL SELECTION. Evolution is defined as the change in species over time. Darwin theorized that evolution occurs through a process known as natural selection . This process is broken down into four parts:. Overproduction Genetic Variation Struggle to Survive
1.04k views • 20 slides

Evolution and Natural Selection
Evolution and Natural Selection. Chapter 5 Pages 96-102. PREMISES OF EVOLUTION. Process by which populations of organisms change over time All modern species arose from earlier forms. Evolutionary history is like a branching tree of life . All life began as first prokaryotes existing 4.
881 views • 68 slides

Evolution and Natural Selection. March 19, 2013. Outline. What is evolution? What is natural selection? What is adaptation? Natural selection simulation. Tree of Life. 1. What is evolution?. Change (in gene frequency) over time. Change over time. Gene frequency in population.
290 views • 14 slides

Natural Selection & Speciation
Natural Selection & Speciation. Science & Society Picture Library. Journal of Researches 1836. 5 – year voyage of the Beagle. On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection(1859).
766 views • 54 slides

Natural Selection and Evolution. Chapter 16: Darwin’s Theory. Darwin’s Epic Journey. Charles Darwin was born in England on February 12, 1809. He grew up at a time when the scientific view of the natural world was shifting dramatically.
995 views • 45 slides

Changes in Populations over Time. Natural Selection and Evolution. Chapter 22 Objectives. 1. Define evolution . 2. Discuss several observations which suggest relatedness between different species. Note observations of both fossil and living organisms .
618 views • 52 slides

Evolution and Natural Selection . Change over time…. Geology. Began to study rock layers called strata George Cuvier Studied fossils Found extinct species and noticed the deeper the fossil the more unique Catastrophism Charles Lyell Believed the earth to be millions of years old
291 views • 17 slides

Evolution and Natural Selection. Introduction to Biology. The “Fog-Basking” Beetle. The “Fog-Basking” Beetle is a species that only lives in the deserts of southwestern Africa. This beetle has an unusual behavior – it stands on its head.
927 views • 71 slides

Evolution and Natural Selection. TRUE Natural selection is not all-powerful; it does not produce perfection If your genes are “good enough,” you’ll get some offspring into the next generation—you don’t have to be perfect. Natural Selection does not produce perfection, just “good enough”.
298 views • 10 slides

Speciation through Natural Selection
NAME: DATE: PERIOD:. Speciation through Natural Selection. Create a series of diagrams that show the 3 steps of speciation, detailing how adaptation includes the proces s of natural selection for Utenstil -beaked hornet-birds (Population) Separation:
126 views • 1 slides

Evolution and Natural Selection. Evolution. “Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution” Theodosius Dobzhansky. Evolution. Evolvere “to unfold or unroll” Central organizing concept of how the world and organism have come to function Builds on accumulating knowledge
694 views • 49 slides

Natural Selection & Speciation. Science & Society Picture Library. Speciation. First, what is a species?. Second: Cladistics , cladograms , clades.
500 views • 38 slides

Natural Selection and Speciation
Natural Selection and Speciation. Stabilizing Selection. favors the average individual reduces variation in a population. Examples. birth weight in humans Siberian husky- muscle mass “living fossils”- organisms that have remained unchanged for millions of years (sharks, crocs).
396 views • 16 slides

Natural Selection and Evolution. Organisms produce more offspring than can survive and they compete for limited resources. Random variations in traits occur among individuals of a population. Variations are heritable (may be passed on to the next generation through reproduction).
437 views • 20 slides

Natural Selection and Speciation. Another way to look at it…. Directional Selection. Fitness. Trait. Trait. Negative Directional Selection. Positive Directional Selection. Stabilizing selection. Fitness. average trait value. Egg laying wasp that eventually kills the cactus.
479 views • 32 slides

Evolution and Natural Selection. How species change over time. Evolution. The theory that organisms today developed from more simple life forms and have changed (evolved) over time. Natural Selection.
227 views • 20 slides

Evolution and Natural Selection. I have called this principle, by which each slight variation, if useful, is preserved, by the term Natural Selection - Charles Darwin, The Origin of Species. Evolution and Natural Selection. We wish to ask:
219 views • 21 slides

Natural Selection and Evolution. In 1835 Charles Darwin traveled to the Galapagos Islands and was intrigued by the various species he observed.
167 views • 14 slides

COMMENTS
This line of thinking led to Darwin's theory of: Natural Selection- mechanism by which individuals that have inherited beneficial adaptations produce more offspring on average than do other individuals. . Nature is the selective agent. . Characteristics are selected only. if. they give advantages to individuals. .
Charles Darwin was a British naturalist who proposed the theory of biological evolution by natural selection. Darwin defined evolution as "descent with modification," the idea that species change over time, give rise to new species, and share a common ancestor. The mechanism that Darwin proposed for evolution is natural selection.
Overview. This set of five PowerPoint slides featuring personal response questions (i.e., multiple choice questions that can be used with "clicker" technology) can be incorporated into lectures on natural selection and adaptation in order to actively engage students in thinking about evolution. [Mechanisms of evolution: Grades 13-16] Evolution ...
Natural selection is the process through which populations of living organisms adapt and change. Individuals in a population are naturally variable, meaning that they are all different in some ways. This variation means that some individuals have traits better suited to the environment than others. Individuals with adaptive traits — traits ...
Transcript. Natural selection is a mechanism of evolution and explains how species adapt to their environment over time through variations in traits. Examples include the peppered moth adapting to industrial pollution, yearly flu virus changes, and antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Understanding natural selection is essential for studying living ...
Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-biology/natural-selection...
sexual selection. group selection. Darwinian fitness. natural selection, process that results in the adaptation of an organism to its environment by means of selectively reproducing changes in its genotype, or genetic constitution. A brief treatment of natural selection follows. For full treatment, see evolution: The concept of natural selection.
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, ... The concept, published by Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in a joint presentation of papers in 1858, ...
Monkeys have two feet and two hands, with prehensile fingers, can grab tools and use them, can throw tantrums when they're angry... Hmmm, maybe he was right after all. Analyze the Theory of Natural Selection in class and, if you need help, get this editable template so that you have a slideshow ready. You'll find illustrations of plants, many ...
The Change Topics Unit covers the topics of Evolution, Natural Selection, Life and Human Origins, Earth System History, and Ecological Succession. This unit includes an interactive and engaging. PowerPoint Presentation of 3,400 slides with built-in class notes (Red Slides), lab activities, project. ideas, discussion questions, assessments (Quiz ...
Download the "Evolution and Natural Selection - Biology - 9th Grade" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. High school students are approaching adulthood, and therefore, this template's design reflects the mature nature of their education. Customize the well-defined sections, integrate multimedia and interactive elements and allow ...
NATURAL SELECTION. YEAR 10 BIOLOGY. TODAYS LESSON. WHAT: Learn about natural selection WHY: To see how Darwin's 5 points of natural selection provides evidence in support of the Theory of Evolution HOW: Class discussion and notes in workbook. CHARLES DARWIN AND THE TREE OF LIFE DVD.
From tiny microorganisms to complex animals like us, all living beings on Earth have evolved over millions of years through a process of natural selection, which essentially means that certain traits or characteristics that aid in an organism's survival are more likely to be passed down to future generations. Slidesgo has been evolving all this ...
2 Evolution vs. Natural Selection. Evolution- Process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms Natural Selection- Process where organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring. 3 Evolution - Early Ideas of Jean-Baptiste Lamarck.
Evolution and Natural Selection Chapter 5 Pages 96-102. PREMISES OF EVOLUTION • Process by which populations of organisms change over time • All modern species arose from earlier forms. • Evolutionary history is like a branching tree of life. • All life began as first prokaryotes existing 4. Charles Darwin and "On the Origin of ...
Charles Darwin and Natural Selection An idea that would change the world. Introduction Charles Darwin developed his theory of evolution by natural selection using four important observations which led him to two deductions. Observations: 1. All organisms produce more offspring than survive to adulthood 2.
Natural Selection, Speciation, and Evolution Textbook Reference Chapter 14 & 15. Lamarck's Early Theory on Evolution • Based on 3 ideas 1. Desire (will) to change 2. Use and Disuse 3. Passing on acquired traits (weight lifting) • Brought idea of evolution to forefront • Knew nothing of genes or genetics. Charles Darwin • Observations ...