Assign a dictionary Key or Value to variable in Python
Last updated: Feb 21, 2023 Reading time · 4 min


# Table of Contents
- Assign a dictionary value to a Variable in Python
- Assign dictionary key-value pairs to variables in Python
- Assign dictionary key-value pairs to variables using exec()
# Assign a dictionary value to a Variable in Python
Use bracket notation to assign a dictionary value to a variable, e.g. first = my_dict['first_name'] .
The left-hand side of the assignment is the variable's name and the right-hand side is the value.
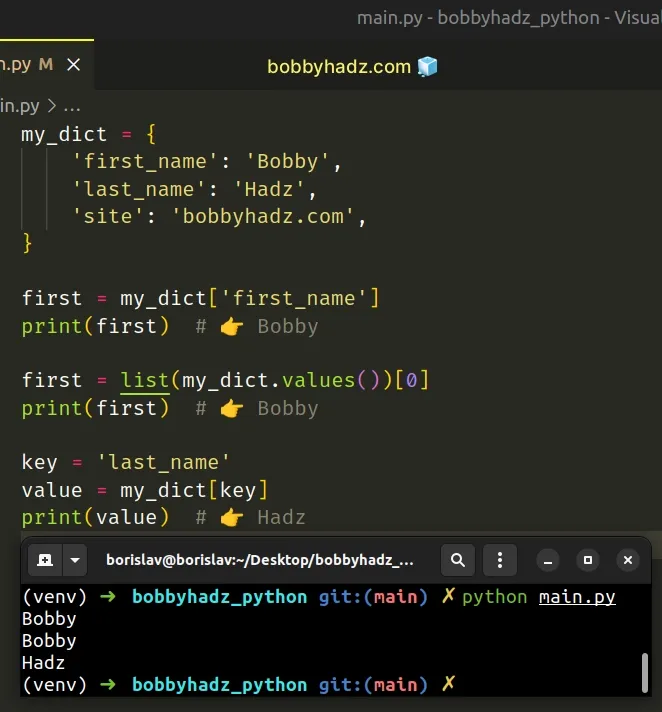
The first example uses square brackets to access a dictionary key and assigns the corresponding value to a variable.
If you need to access the dictionary value using an index , use the dict.values() method.
The dict.values method returns a new view of the dictionary's values.
We had to use the list() class to convert the view object to a list because view objects are not subscriptable (cannot be accessed at an index).
You can use the same approach if you have the key stored in a variable.
If you try to access a dictionary key that doesn't exist using square brackets, you'd get a KeyError .
On the other hand, the dict.get() method returns None for non-existent keys by default.
The dict.get method returns the value for the given key if the key is in the dictionary, otherwise a default value is returned.
The method takes the following 2 parameters:
If a value for the default parameter is not provided, it defaults to None , so the get() method never raises a KeyError .
If you need to assign the key-value pairs of a dictionary to variables, update the locals() dictionary.
# Assign dictionary key-value pairs to variables in Python
Update the locals() dictionary to assign the key-value pairs of a dictionary to variables.
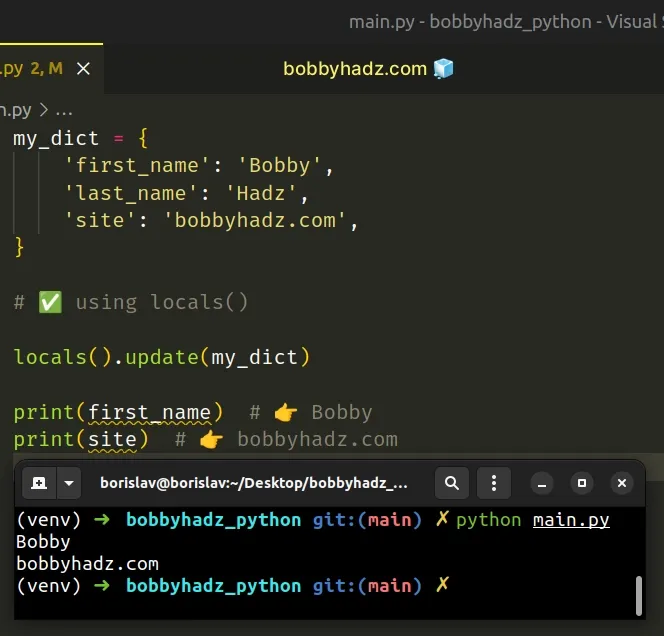
The first example uses the locals() dictionary to assign the key-value pairs of a dictionary to local variables.
The locals() function returns a dictionary that contains the current scope's local variables.
The dict.update method updates the dictionary with the key-value pairs from the provided value.
You can access the variables directly after calling the dict.update() method.
The SimpleNamespace class can be initialized with keyword arguments.
The keys of the dictionary are accessible as attributes on the namespace object.
Alternatively, you can use the exec() function.
# Assign dictionary key-value pairs to variables using exec()
This is a three-step process:
- Iterate over the dictionary's items.
- Use the exec() function to assign each key-value pair to a variable.
- The exec() function supports dynamic execution of Python code.
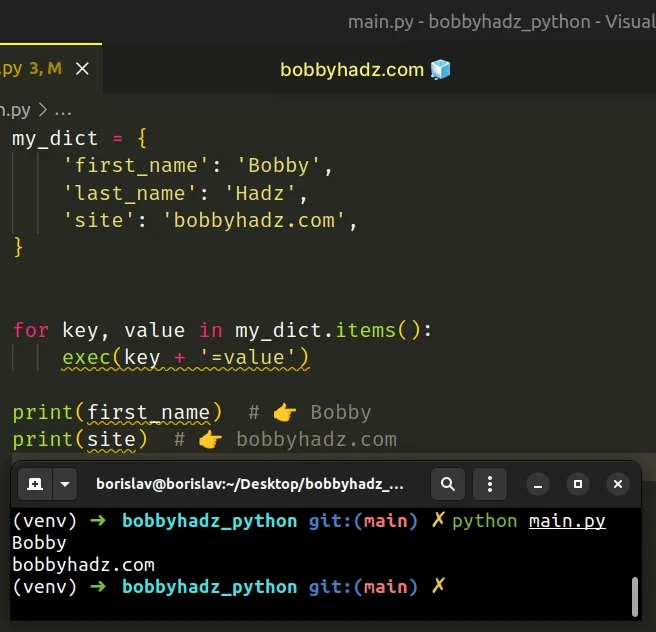
The dict.items method returns a new view of the dictionary's items ((key, value) pairs).
On each iteration, we use the exec() function to assign the current key-value pair to a variable.
The exec function supports dynamic execution of Python code.
The function takes a string, parses it as a suite of Python statements and runs the code.
Which approach you pick is a matter of personal preference. I'd go with the SimpleNamespace class to avoid any linting errors for trying to access undefined variables.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- Check if all values in a Dictionary are equal in Python
- How to Replace values in a Dictionary in Python
- Get multiple values from a Dictionary in Python
- Get random Key and Value from a Dictionary in Python
- Join the Keys or Values of Dictionary into String in Python
- Multiply the Values in a Dictionary in Python
- Print specific key-value pairs of a dictionary in Python
- How to set all Dictionary values to 0 in Python
- Sum all values in a Dictionary or List of Dicts in Python
- Swap the keys and values in a Dictionary in Python

Borislav Hadzhiev
Web Developer

Copyright © 2024 Borislav Hadzhiev
Python: How to access and modify dictionary items
Introduction.
Dictionaries in Python are an essential data structure for storing and accessing data. They work like a real-life dictionary, storing information as key-value pairs. This flexible structure enables storing a wide range of data types and structures, from numbers and strings to lists and even other dictionaries. This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide on accessing and modifying dictionary items, packed with basic to advanced examples to help you navigate through Python dictionaries efficiently.
Preparing a Sample Dict
To begin with, let’s understand the basic structure of a dictionary. A dictionary in Python can be created using curly braces {} with key-value pairs separated by colons. For instance:
Accessing Dictionary Items
Once you have a dictionary, you may want to know how to access its items. Accessing dictionary items can be done by referring to its key name, wrapped in square brackets, or using the get method. Here are examples of both methods:
When using square brackets, if the key does not exist, it will raise a KeyError. The get method, on the other hand, returns None if the key isn’t found, making it a safer option if you’re not sure whether the key exists.
Modifying Dictionary Items
Modifying dictionary items is equally straightforward. You can change the value associated with a specific key simply by assigning a new value to it. Adding new key-value pairs is just a matter of assignment as well. Observe the examples below:
Using the update() Method
Beyond basic access and modification, dictionaries offer several methods and functionalities that make them extremely versatile. For instance, the update method allows you to merge two dictionaries. This can be particularly useful when you need to update multiple items at once or add new items from another dictionary.
Advanced Examples
To further explore the capabilities of Python dictionaries, let’s delve into some advanced applications.
Dictionary Comprehension
This advanced feature allows you to create dictionaries using an iterative approach, akin to list comprehensions. For example, to create a dictionary that maps numbers to their squares:
Using Lambda Functions
You can use lambda functions to filter or sort dictionaries. For instance, to sort a dictionary by its values:
Nested Dictionaries
Sometimes the values within a dictionary are dictionaries themselves. This is perfect for representing hierarchical data. Accessing items in nested dictionaries requires chaining key references:
In summary, dictionaries in Python are highly powerful and versatile. They enable efficient data organization and retrieval through simple syntax and a rich set of functionalities. Whether you’re a beginner or advancing in Python, mastering dictionaries will significantly enhance your coding capabilities. With the examples and explanations provided in this tutorial, you’re well-prepared to utilize dictionaries in your Python projects. Always remember, the best way to learn is by doing. So, dive into coding, experiment with these examples, and discover the powerful potential of Python dictionaries.
Next Article: How to clone a dictionary in Python - Shallow and Deep Copies
Previous Article: Python: Using type hints with NamedTuple – Examples
Series: Working with Dict, Set, and Tuple in Python
Related Articles
- Python Warning: Secure coding is not enabled for restorable state
- Python TypeError: write() argument must be str, not bytes
- 4 ways to install Python modules on Windows without admin rights
- Python TypeError: object of type ‘NoneType’ has no len()
- Python: How to access command-line arguments (3 approaches)
- Understanding ‘Never’ type in Python 3.11+ (5 examples)
- Python: 3 Ways to Retrieve City/Country from IP Address
- Using Type Aliases in Python: A Practical Guide (with Examples)
- Python: Defining distinct types using NewType class
- Using Optional Type in Python (explained with examples)
- Python: How to Override Methods in Classes
- Python: Define Generic Types for Lists of Nested Dictionaries
Search tutorials, examples, and resources
- PHP programming
- Symfony & Doctrine
- Laravel & Eloquent
- Tailwind CSS
- Sequelize.js
- Mongoose.js
How To Add Items To a Python Dictionary?

As a Built-in data type in Python, a dictionary entails key-value pairs. The dictionary, as a whole, is mutable though its keys are immutable and unique. Even though the language doesn’t offer a built-in add feature, you can manually add items to the Python dictionary in multiple ways.
Table of Contents

Python Add to Dictionary: The Assignment Operator
The simplest way to add Python dictionary items is by using = or the assignment operator. The method designates a new value to the key or overwrites the current value. The below example exhibits the assignment operator in action:
In addition, there is also a way to stop the assignment operator from overwriting the key values. The trick is to add an ‘if’ condition to the syntax.
In the example above, the value of ‘c’ remained the same even after the new value definition due to the use of the ‘if’ conditional operator.
Python Add to Dictionary: The Update() Method
Another way to append a Python dictionary or update the current key-value pair is through the update() method. This technique lets you rewrite/overwrite key values with newer ones. The below example illustrates how to use the update() to re-create your Python dictionary.
Python Add to Dictionary: The Merge | Operator
You can also merge two existing Python dictionaries and create a new one using Merge | operator. The example below illustrates how you can use this to create new dictionaries with ease.
Python Add to Dictionary: The Update |= Operator
In addition to the methods above, you can also update Python dictionary items through the update |= operator. The below example illustrates how to update values in two dictionaries and create a new updated one.
The Final Word
Unlike tuples and lists, there is no definite way to add, append, or insert an item in a Python dictionary. So, the trick is to define a new index value to replace the pre-existing one to add or replace Python dictionary items at will.
In this article, we explored multiple ways to use Python’s add-to-dictionary feature with examples. Choose the one that you find the easiest and create better Python dictionaries.
Also Read: How To Use Python Dataclassses?

Full Stack Java Developer | Writer | Recruiter, bridging the gap between exceptional talent and opportunities, for some of the biggest Fortune 500 companies.

Recent Posts
- Top Technology Trends in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide
- AI for Cybersecurity: Evolution for Threat Defense
- A Comprehensive Guide to Initializing Arrays in Java
- Webinar: Mastering Conversational AI in Customer Service: Opportunities, Risks, and Strategies
- Best Databases for Python Projects in 2024
- Press Release
Candidate signup
Create a free profile and find your next great opportunity.
Employer signup
Sign up and find a perfect match for your team.
How it works
Xperti vets skilled professionals with its unique talent-matching process.
Join our community
Connect and engage with technology enthusiasts.

- Hire Developers

© Xperti.io All Rights Reserved
Terms of use
Guide to Dictionaries in Python

- Introduction
Python comes with a variety of built-in data structures, capable of storing different types of data. A Python dictionary is one such data structure that can store data in the form of key-value pairs - conceptually similar to a map. The values in a Python dictionary can be accessed using the keys.
In this guide, we will be discussing Python dictionaries in detail. Firstly, we'll cover the basic dictionary operations (creating a dictionary, updating it, removing and adding elements, etc.) and take a look at a couple more interesting methods afterward.
- How To Create a Dictionary in Python
To create a Python dictionary, we pass a sequence of items (entries) inside curly braces {} and separate them using a comma ( , ). Each entry consists of a key and a value, also known as a key-value pair.
Note: The values can belong to any data type and they can repeat , but the keys must remain unique . Additionally, you can't assign multiple values to the same key, though, you can assign a list of values (as a single value).
Now that we understand what dictionaries are, let's see how to use them in Python. First of all, we need to understand how to create an empty dictionary :
Great! We now have an empty directory. But what if we want to both create and fill a dictionary with some initial data? That's also a pretty easy task in Python - say we have integer keys and string values:
As we said before, it's not necessary that all keys are of the same type:
Alternatively, we can create a dictionary by explicitly calling the Python's dict() constructor :
A dictionary can also be created by passing a list of tuples to the dict() constructor:
Dictionaries can also be nested , which means that we can create a dictionary inside another dictionary:
To print the dictionary contents, we can use Python's print() method and pass the dictionary name as the argument to the method:
This results in:
Note: For concise and readable dictionary creation, consider dictionary comprehensions , especially when deriving from another data source:
- How To Access Elements of a Python Dictionary
To access dictionary items - we pass the key , using the square bracket notation:
This nets us the value associated with the "model" key:
You can store "configuration" items or common constants in a dictionary for ease of centralized access:
This would yield us with:
The dictionary object also provides the get() method , which can be used to access dictionary elements as well. We append the method with the dictionary name using the dot operator and then pass the name of the key as the argument to the method:
Now we know how to access dictionary elements! In the next section, we'll discuss how to add new elements to an already-existing dictionary.
Note: Rather than directly accessing a key, which could result in a KeyError , use the get() method to provide a default value.
- How To Add Elements to a Python Dictionary
There are numerous ways to add new elements to a dictionary. A common way is to add a new key and assign a value to it :
When a key doesn't exist, and we assign a value to it - it gets added to the dictionary:
The new element has Capacity as the key and 1800CC as its corresponding value. It has been added as the first element of the dictionary. Here is another example. First, let's first create an empty dictionary:
Let's verify that it's empty:
The dictionary returns nothing as it has nothing stored yet. Let us add some elements to it, one at a time:
Note: Starting from Python 3.7, dictionaries maintain the order of items based on their insertion. This behavior is guaranteed in Python 3.8+.
To add the elements, we specified keys as well as the corresponding values:
In the above example, 0 is the key while Apples is the value. It is even possible for us to add a set of values to one key as long as that set is referenceable as a single value, such as a collection:
And we have a key with a set as its value:
Other than adding new elements to a dictionary, dictionary elements can also be updated/changed, which we'll go over in the next section.
Advice: Read more about adding new keys to a dictionary in Python in our article "Python: How to Add Keys to a Dictionary" .
- How To Update Dictionary Elements
After adding a value to a dictionary we can then modify the existing dictionary element . You use the key of the element to change the corresponding value:
In this example, we've updated the value for the key year from the old value of 2012 to a new value of 2014 :
- How To Remove Dictionary Elements
The removal of an element from a dictionary can be done in several ways, which we'll discuss one by one in this section.
The del keyword can be used to remove the element with the specified key. We need to call the del keyword followed by the dictionary name. Inside the square brackets that follow the dictionary name, we passed the key of the element we need to delete from the dictionary, let it be the year :
This will remove the entry for the year :
Another way to delete a key-value pair is to use the pop() method and pass the key of the entry to be deleted as the argument to the method:
We invoked the pop() method by appending it with the dictionary name. Running this code will delete the entry for a year in the dictionary:
If you don't specify the key, the popitem() method removes the last item inserted into the dictionary:
The last entry into the dictionary was the year . It has been removed after calling the popitem() method:
But what if you want to delete the entire dictionary ? It would be difficult and cumbersome to use one of these methods on every single key. Instead, you can use the del keyword to delete the entire dictionary:
But, this code will return an error. The reason is that we are trying to access a dictionary that doesn't exist since it has been deleted beforehand:
Depending on the use case, you might need to remove all dictionary elements but not the dictionary itself. This can be achieved by calling the clear() method on the dictionary:
This will give you an empty dictionary (since all the dictionary elements have been removed):
- Other Common Dictionary Methods in Python
Besides methods we've covered so far, Python provides us with a lot of other interesting methods that help us perform operations other than the basic ones described before. In the following subsections, we'll take a look at some other methods you can use alongside dictionaries in Python.
Note: Remember that methods like keys() , values() , and items() return view objects , which are dynamic in nature. This means if the dictionary changes, these views will reflect the change.
- len() Method
With this method, you can count the number of elements in a dictionary:
There are three entries in the dictionary, hence the method will return 3 :
Advice: Read more about calculating the size of dictionaries in Python in our article "Python: Get Size of Dictionary" .
- copy() Method
This method returns a copy of the existing dictionary:
Check out our hands-on, practical guide to learning Git, with best-practices, industry-accepted standards, and included cheat sheet. Stop Googling Git commands and actually learn it!
Let's make sure the copy is properly made and assigned to the variable x :
After printing x in the console, you see that it contains the same elements as those stored in the example_dict dictionary.
Note: This is useful because modifications made to the copied dictionary won't affect the original one.
- items() Method
When called, this method returns an iterable object. The iterable object has key-value pairs for the dictionary, as tuples in a list. This method is primarily used when you want to iterate through a dictionary.
The method is simply called on the dictionary object name:
This will result in:
The object returned by items() can also be used to show the changes that have been implemented in the dictionary:
This code illustrates that when you change a value in the dictionary, the items object is also updated to reflect this change:
- keys() Method
This method also returns an iterable object. The object returned is a list of all keys in the dictionary. And just like with the items() method, the returned object can be used to reflect the changes made to the dictionary.
To use this method, we only call it on the name of the dictionary:
For example:
This will give us:
Often times this method is used to iterate through each key in your dictionary:
This will print each key of the example_dict in a separate line:
- fromkeys() Method
This method returns a dictionary having specified keys and values:
The value for the required keys parameter is iterable and it specifies the keys for the new dictionary. The value for the value parameter is optional and it specifies the default value for all the keys. The default value for this is None .
Suppose we need to create a dictionary of three keys all with the same value, say 25 :
Let's verify that the fromkeys() method created the dictionary we've described:
As expected, the fromkeys() method was able to pick the keys and combine them with the value 25 to create the dictionary we wanted.
The value for the keys parameter is mandatory. The following example demonstrates what happens when the value for the values parameter is not specified:
In this case, None was used as the default value:
- setdefault() Method
This method is applicable when we need to get the value of the element with the specified key. If the key is not found, it will be inserted into the dictionary alongside the specified default value.
The method takes the following syntax:
In this method, the keyname parameter is required. It represents the key name of the item you need to return a value from. The value parameter is optional. If the dictionary already has the key, this parameter won't have any effect. If the key doesn't exist, then the value given in this method will become the value of the key. It has a default value of None :
The dictionary doesn't have the key for color . The setdefault() method has inserted this key and the specified value, that is, Gray , has been used as its value:
The following example demonstrates how the method behaves if the value for the key does exist :
The value Allion has no effect on the dictionary since we already have a value for the key model :
- Dictionary Comprehensions
Dictionary comprehensions, akin to list and set comprehensions, offer a concise way to create dictionaries. Common applications include constructing dictionaries from iterables, transforming existing dictionaries, or filtering dictionary content. This section will guide you through the mechanics and potential uses of dictionary comprehension.
Advice: You can take a deeper dive into the topic of dictionary comprehensions in Python by reading our "Python Dictionary Comprehension: A Fast and Flexible Way to Build Dictionaries" article.
The basic syntax of a dictionary comprehension is pretty similar to the one used for the list comprehension:
The key_expr and value_expr are expressions defining the key-value pairs based on the current item in the iterable .
To illustrate this, let's construct a dictionary that maps numbers to their squares :
Sometimes, you'd like to filter out certain values when creating a dictionary. For that purpose, you can introduce conditions in the dictionary comprehension syntax:
Dictionary comprehension in Python is a powerful mechanism enabling us to do much more than just create simple dictionaries. For example, you can also use it to create and access nested dictionaries :
Combining the zip() function with dictionary comprehension can help you create a dictionary from two lists - one containing keys and one containing values of the newly created dictionary:
The last usage of dictionary comprehension we'll cover in this article is _modifying an existing dictionary. Let's say you want to create a new dictionary from an existing one, where each value is incremented by 1:
- Iterating Through Dictionaries
Iteration is a fundamental operation in programming, and when it comes to dictionaries, Python provides several intuitive methods to traverse through keys, values, or both. Let’s explore the different techniques and scenarios for iterating over dictionaries.
Advice: Read more about iterating through dictionaries in Python in our article "How to Iterate Over a Dictionary in Python" .
- Iterating Over Keys (Default Behavior)
When you loop through a dictionary directly using a for loop, it iterates over its keys by default:
We can achieve the same behavior (but more explicitly) by using the keys() method:
Avoid modifying the size of a dictionary while iterating over it. If you need to remove items, consider iterating over a copy of the dictionary's keys:
- Iterating Over Values Using values()
We'll use the values() method to help us loop through all the values in a dictionary:
- Iterating Over Key-Value Pairs Using items()
This method returns both the key and its corresponding value, which can be unpacked directly within the loop:
This will give us::
- Nested Dictionaries Iteration
If you have dictionaries within dictionaries, you'll need nested loops to traverse them:
We'll get a nicely formatted output:
- Conditional Iteration
You can also integrate conditions within loops for specific requirements:
Since the value of the age key is an integer, it won't be printed out:
- Dictionary and Memory
Dictionaries, while highly versatile and efficient, can also be memory-intensive due to their underlying data structures and mechanisms. This section aims to explore the memory implications of using dictionaries in Python, providing insights and best practices to ensure optimized memory usage.
Advice: In cases where you don't require the functionality of a full dictionary, consider using a list of tuples or a namedtuple .
There are several causes because dictionaries can be memory-intensive. First of all, dictionaries are essentially implemented using hash tables as their under-the-hood. This ensures O(1) average complexity for lookups but requires extra memory to store hashes, table indices, and handle collisions. Other than that, Python dictionaries are designed to resize when they reach a certain load factor. This means that memory might be allocated in advance, even if not immediately used.
If you're interested in checking the memory usage of a dictionary, you can do so by using Python’s sys module:
But what can you do about the size of your dictionaries? Let's take a look at a couple of tips that can help you do a better job of managing your dictionary's size. First of all, if a dictionary grows large and then shrinks (after deletions), it might still retain a large allocated size. In that case, use dict.copy() to create a smaller copy . Additionally, for dictionaries with the same set of keys (like objects of a class), key sharing can save memory. This technique involves using a single memory block to store the keys for multiple dictionaries.
Being conscious of memory implications doesn’t mean you should shy away from dictionaries. Instead, with an informed approach, you can make the most of what dictionaries offer without compromising on system performance.
This marks the end of this guide on Python dictionaries. These dictionaries store data in key-value pairs. The key acts as the identifier for the item while the value is the value of the item. The Python dictionary comes with a variety of methods that can be applied for the retrieval or manipulation of data. In this article, we saw how a Python dictionary can be created, modified, and deleted along with some of the most commonly used dictionary methods.
You might also like...
- Hidden Features of Python
- Python Docstrings
- Handling Unix Signals in Python
- The Best Machine Learning Libraries in Python
- Guide to Sending HTTP Requests in Python with urllib3
Improve your dev skills!
Get tutorials, guides, and dev jobs in your inbox.
No spam ever. Unsubscribe at any time. Read our Privacy Policy.
I am a programmer by profession. I am highly interested in Python, Java, Data Science and Machine learning. If you need help in any of these, don't hesitate to contact me.
In this article

Building Your First Convolutional Neural Network With Keras
Most resources start with pristine datasets, start at importing and finish at validation. There's much more to know. Why was a class predicted? Where was...

Data Visualization in Python with Matplotlib and Pandas
Data Visualization in Python with Matplotlib and Pandas is a course designed to take absolute beginners to Pandas and Matplotlib, with basic Python knowledge, and...
© 2013- 2024 Stack Abuse. All rights reserved.

Create a Dictionary in Python – Python Dict Methods

In this article, you will learn the basics of dictionaries in Python.
You will learn how to create dictionaries, access the elements inside them, and how to modify them depending on your needs.
You will also learn some of the most common built-in methods used on dictionaries.
Here is what we will cover:
- Define an empty dictionary
- Define a dictionary with items
- An overview of keys and values 1. Find the number of key-value pairs contained in a dictionary 2. View all key-value pairs 3. View all keys 4. View all values
- Access individual items
- Add new items
- Update items
- Delete items
How to Create a Dictionary in Python
A dictionary in Python is made up of key-value pairs.
In the two sections that follow you will see two ways of creating a dictionary.
The first way is by using a set of curly braces, {} , and the second way is by using the built-in dict() function.
How to Create An Empty Dictionary in Python
To create an empty dictionary, first create a variable name which will be the name of the dictionary.
Then, assign the variable to an empty set of curly braces, {} .
Another way of creating an empty dictionary is to use the dict() function without passing any arguments.
It acts as a constructor and creates an empty dictionary:
How to Create A Dictionary With Items in Python
To create a dictionary with items, you need to include key-value pairs inside the curly braces.
The general syntax for this is the following:
Let's break it down:
- dictionary_name is the variable name. This is the name the dictionary will have.
- = is the assignment operator that assigns the key:value pair to the dictionary_name .
- You declare a dictionary with a set of curly braces, {} .
- Inside the curly braces you have a key-value pair. Keys are separated from their associated values with colon, : .
Let's see an example of creating a dictionary with items:
In the example above, there is a sequence of elements within the curly braces.
Specifically, there are three key-value pairs: 'name': 'Dionysia' , 'age': 28 , and 'location': 'Athens' .
The keys are name , age , and location . Their associated values are Dionysia , 28 , and Athens , respectively.
When there are multiple key-value pairs in a dictionary, each key-value pair is separated from the next with a comma, , .
Let's see another example.
Say that you want to create a dictionary with items using the dict() function this time instead.
You would achieve this by using dict() and passing the curly braces with the sequence of key-value pairs enclosed in them as an argument to the function.
It's worth mentioning the fromkeys() method, which is another way of creating a dictionary.
It takes a predefined sequence of items as an argument and returns a new dictionary with the items in the sequence set as the dictionary's specified keys.
You can optionally set a value for all the keys, but by default the value for the keys will be None .
The general syntax for the method is the following:
Let's see an example of creating a dictionary using fromkeys() without setting a value for all the keys:
Now let's see another example that sets a value that will be the same for all the keys in the dictionary:
An Overview of Keys and Values in Dictionaries in Python
Keys inside a Python dictionary can only be of a type that is immutable .
Immutable data types in Python are integers , strings , tuples , floating point numbers , and Booleans .
Dictionary keys cannot be of a type that is mutable, such as sets , lists , or dictionaries .
So, say you have the following dictionary:
The keys in the dictionary are Boolean , integer , floating point number , and string data types, which are all acceptable.
If you try to create a key which is of a mutable type you'll get an error - specifically the error will be a TypeError .
In the example above, I tried to create a key which was of list type (a mutable data type). This resulted in a TypeError: unhashable type: 'list' error.
When it comes to values inside a Python dictionary there are no restrictions. Values can be of any data type - that is they can be both of mutable and immutable types.
Another thing to note about the differences between keys and values in Python dictionaries, is the fact that keys are unique . This means that a key can only appear once in the dictionary, whereas there can be duplicate values.
How to Find the Number of key-value Pairs Contained in a Dictionary in Python
The len() function returns the total length of the object that is passed as an argument.
When a dictionary is passed as an argument to the function, it returns the total number of key-value pairs enclosed in the dictionary.
This is how you calcualte the number of key-value pairs using len() :
How to View All key-value Pairs Contained in a Dictionary in Python
To view every key-value pair that is inside a dictionary, use the built-in items() method:
The items() method returns a list of tuples that contains the key-value pairs that are inside the dictionary.
How to View All keys Contained in a Dictionary in Python
To see all of the keys that are inside a dictionary, use the built-in keys() method:
The keys() method returns a list that contains only the keys that are inside the dictionary.
How to View All values Contained in a Dictionary in Python
To see all of the values that are inside a dictionary, use the built-in values() method:
The values() method returns a list that contains only the values that are inside the dictionary.
How to Access Individual Items in A Dictionary in Python
When working with lists, you access list items by mentioning the list name and using square bracket notation. In the square brackets you specify the item's index number (or position).
You can't do exactly the same with dictionaries.
When working with dictionaries, you can't access an element by referencing its index number, since dictionaries contain key-value pairs.
Instead, you access the item by using the dictionary name and square bracket notation, but this time in the square brackets you specify a key.
Each key corresponds with a specific value, so you mention the key that is associated with the value you want to access.
The general syntax to do so is the following:
Let's look at the following example on how to access an item in a Python dictionary:
What happens though when you try to access a key that doesn't exist in the dictionary?
It results in a KeyError since there is no such key in the dictionary.
One way to avoid this from happening is to first search to see if the key is in the dictionary in the first place.
You do this by using the in keyword which returns a Boolean value. It returns True if the key is in the dictionary and False if it isn't.
Another way around this is to access items in the dictionary by using the get() method.
You pass the key you're looking for as an argument and get() returns the value that corresponds with that key.
As you notice, when you are searching for a key that does not exist, by default get() returns None instead of a KeyError .
If instead of showing that default None value you want to show a different message when a key does not exist, you can customise get() by providing a different value.
You do so by passing the new value as the second optional argument to the get() method:
Now when you are searching for a key and it is not contained in the dictionary, you will see the message This value does not exist appear on the console.
How to Modify A Dictionary in Python
Dictionaries are mutable , which means they are changeable.
They can grow and shrink throughout the life of the program.
New items can be added, already existing items can be updated with new values, and items can be deleted.
How to Add New Items to A Dictionary in Python
To add a key-value pair to a dictionary, use square bracket notation.
First, specify the name of the dictionary. Then, in square brackets, create a key and assign it a value.
Say you are starting out with an empty dictionary:
Here is how you would add a key-value pair to my_dictionary :
Here is how you would add another new key-value pair:
Keep in mind that if the key you are trying to add already exists in that dictionary and you are assigning it a different value, the key will end up being updated.
Remember that keys need to be unique.
If you want to prevent changing the value of an already existing key by accident, you might want to check if the key you are trying to add is already in the dictionary.
You do this by using the in keyword as we discussed above:
How to Update Items in A Dictionary in Python
Updating items in a dictionary works in a similar way to adding items to a dictionary.
When you know you want to update one existing key's value, use the following general syntax you saw in the previous section:
To update a dictionary, you can also use the built-in update() method.
This method is particularly helpful when you want to update more than one value inside a dictionary at the same time.
Say you want to update the name and age key in my_dictionary , and add a new key, occupation :
The update() method takes a tuple of key-value pairs.
The keys that already existed were updated with the new values that were assigned, and a new key-value pair was added.
The update() method is also useful when you want to add the contents of one dictionary into another.
Say you have one dictionary, numbers , and a second dictionary, more_numbers .
If you want to merge the contents of more_numbers with the contents of numbers , use the update() method.
All the key-value pairs contained in more_numbers will be added to the end of the numbers dictionary.
How to Delete Items from A Dictionary in Python
One of the ways to delete a specific key and its associated value from a dictionary is by using the del keyword.
The syntax to do so is the following:
For example, this is how you would delete the location key from the my_information dictionary:
If you want to remove a key, but would also like to save that removed value, use the built-in pop() method.
The pop() method removes but also returns the key you specify. This way, you can store the removed value in a variable for later use or retrieval.
You pass the key you want to remove as an argument to the method.
Here is the general syntax to do that:
To remove the location key from the example above, but this time using the pop() method and saving the value associated with the key to a variable, do the following:
If you specify a key that does not exist in the dictionary you will get a KeyError error message:
A way around this is to pass a second argument to the pop() method.
By including the second argument there would be no error. Instead, there would be a silent fail if the key didn't exist, and the dictionary would remain unchanged.
The pop() method removes a specific key and its associated value – but what if you only want to delete the last key-value pair from a dictionary?
For that, use the built-in popitem() method instead.
This is general syntax for the popitem() method:
The popitem() method takes no arguments, but removes and returns the last key-value pair from a dictionary.
Lastly, if you want to delete all key-value pairs from a dictionary, use the built-in clear() method.
Using this method will leave you with an empty dictionary.
And there you have it! You now know the basics of dictionaries in Python.
I hope you found this article useful.
To learn more about the Python programming language, check out freeCodeCamp's Scientific Computing with Python Certification .
You'll start from the basics and learn in an interacitve and beginner-friendly way. You'll also build five projects at the end to put into practice and help reinforce what you've learned.
Thanks for reading and happy coding!
Read more posts .
If this article was helpful, share it .
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Learn Python practically and Get Certified .
Popular Tutorials
Popular examples, reference materials, learn python interactively, python dictionary methods.
Python Dictionary clear()
- Python Dictionary copy()
- Python Dictionary fromkeys()
- Python Dictionary get()
Python Dictionary items()
Python Dictionary keys()
- Python Dictionary popitem()
- Python Dictionary setdefault()
Python Dictionary pop()
Python Dictionary values()
- Python Dictionary update()
Python Tutorials
- Python del Statement
- Python Dictionary Comprehension
- Python Set update()
The items() method returns a view object that displays a list of dictionary's (key, value) tuple pairs.
Syntax of Dictionary items()
The syntax of items() method is:
Note : items() method is similar to dictionary's viewitems() method in Python 2.7.
items() Parameters
The items() method doesn't take any parameters.
Return value from items()
The items() method returns a view object that displays a list of a given dictionary's (key, value) tuple pair.
Example 1: Get all items of a dictionary with items()
Example 2: how items() works when a dictionary is modified.
The view object items doesn't itself return a list of sales items but it returns a view of sales 's (key, value) pair.
If the list is updated at any time, the changes are reflected on the view object itself, as shown in the above program.
Sorry about that.
Python References
Python Library
- Free Python 3 Tutorial
- Control Flow
- Exception Handling
- Python Programs
- Python Projects
- Python Interview Questions
- Python Database
- Data Science With Python
- Machine Learning with Python
- Python Dictionary Methods
- Python Dictionary clear()
- Python Dictionary copy()
- Python Dictionary fromkeys() Method
- Python Dictionary get() Method
Python Dictionary items() method
- Python Dictionary keys() method
- Python Dictionary pop() Method
- Python Dictionary popitem() method
- Python Dictionary setdefault() Method
- Python Dictionary update() method
- Python dictionary values()
Dictionary in Python is an unordered collection of data values, used to store data values like a map, which unlike other Data Types that hold only single value as an element, Dictionary holds key : value pair. In Python Dictionary, items() method is used to return the list with all dictionary keys with values.
Syntax: dictionary.items() Parameters: This method takes no parameters. Returns: A view object that displays a list of a given dictionary’s (key, value) tuple pair.
Example #1:
Output:
Order of these items in the list may not always be same. Example #2: To show working of items() after modification of Dictionary.
If the Dictionary is updated anytime, the changes are reflected in the view object automatically.
Please Login to comment...
- python-dict
- Python-dict-functions
- 10 Best Free Social Media Management and Marketing Apps for Android - 2024
- 10 Best Customer Database Software of 2024
- How to Delete Whatsapp Business Account?
- Discord vs Zoom: Select The Efficienct One for Virtual Meetings?
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Python Tutorial
File handling, python modules, python numpy, python pandas, python matplotlib, python scipy, machine learning, python mysql, python mongodb, python reference, module reference, python how to, python examples, python dictionary items() method.
❮ Dictionary Methods
Return the dictionary's key-value pairs:
Definition and Usage
The items() method returns a view object. The view object contains the key-value pairs of the dictionary, as tuples in a list.
The view object will reflect any changes done to the dictionary, see example below.
Parameter Values
No parameters
More Examples
When an item in the dictionary changes value, the view object also gets updated:

COLOR PICKER

Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, do not hesitate to send us an e-mail:
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
I'm trying to add keys and values to a dictionary by using strings instead of quoted text. So instead of this, dict['key'] = value this: dict[key] = value When I run the command above, I get this error: TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment I think Python is thinking that I'm trying to create a string, not add to a dictionary.
Defining a Dictionary. Dictionaries are Python's implementation of a data structure that is more generally known as an associative array. A dictionary consists of a collection of key-value pairs. Each key-value pair maps the key to its associated value. You can define a dictionary by enclosing a comma-separated list of key-value pairs in ...
Items in a Dictionary Are Ordered. By being ordered, this means that the items in a dictionary maintain the order in which they were created or added. That order cannot change. Prior to Python 3.7, dictionaries in Python were unordered. In the next section, we will see how we can add items to a dictionary. How to Add an Item to a Dictionary
5. Strings in Python are immutable (you cannot change them inplace). What you are trying to do can be done in many ways: Copy the string: foo = 'Hello'. bar = foo. Create a new string by joining all characters of the old string: new_string = ''.join(c for c in oldstring) Slice and copy:
The left-hand side of the assignment is the variable's name and the right-hand side is the value. main.py. ... Iterate over the dictionary's items. Use the exec() function to assign each key-value pair to a variable. ... Swap the keys and values in a Dictionary in Python;
You can use the = assignment operator to add a new key to a dictionary: dict[key] = value. If a key already exists in the dictionary, then the assignment operator updates, or overwrites, the value. The following example demonstrates how to create a new dictionary and then use the assignment operator = to update a value and add key-value pairs ...
A Python dictionary is a collection of items, similar to lists and tuples. However, unlike lists and tuples, each item in a dictionary is a key-value pair (consisting of a key and a value). Create a Dictionary. We create a dictionary by placing key: value pairs inside curly brackets {}, separated by commas. For example,
Method 4: Using The ** Operator. The ** operator helps merge an existing dictionary into a new dictionary and adds additional items. The syntax is: new_dictionary = {**old_dicitonary, **{key:value}} For example, to copy an existing dictionary and append a new item to a new one, see the following code: my_dictionary = {.
Modifying dictionary items is equally straightforward. You can change the value associated with a specific key simply by assigning a new value to it. Adding new key-value pairs is just a matter of assignment as well. Observe the examples below: # Modifying an existing key's value. my_dict['age'] = 31 # Adding a new key-value pair.
Python Add to Dictionary: The Assignment Operator. The simplest way to add Python dictionary items is by using = or the assignment operator. The method designates a new value to the key or overwrites the current value. The below example exhibits the assignment operator in action: dict_example = {'a': 1, 'b': 2} print ("original dictionary ...
To create a Python dictionary, we pass a sequence of items (entries) inside curly braces {} and separate them using a comma (, ). Each entry consists of a key and a value, also known as a key-value pair. Note: The values can belong to any data type and they can repeat, but the keys must remain unique.
Adding items to the dictionary. We can add new items to the dictionary using the following two ways. Using key-value assignment: Using a simple assignment statement where value can be assigned directly to the new key. Using update() Method: In this method, the item passed inside the update() method will be inserted into the dictionary. The item ...
This is the name the dictionary will have. = is the assignment operator that assigns the key:value pair to the dictionary_name. You declare a dictionary with a set of curly braces, {}. ... How to Access Individual Items in A Dictionary in Python . When working with lists, you access list items by mentioning the list name and using square ...
MutableMapping also isn't something that provides item access (it's an Abstract Base Class). You need to write (or inherit) __getitem__ and __setitem__ methods, if you want to implement dictionary- or list-like item assignment and access. -
Dictionary. Dictionaries are used to store data values in key:value pairs. A dictionary is a collection which is ordered*, changeable and do not allow duplicates. As of Python version 3.7, dictionaries are ordered. In Python 3.6 and earlier, dictionaries are unordered. Dictionaries are written with curly brackets, and have keys and values:
Exercise 2: Merge two Python dictionaries into one. Exercise 3: Print the value of key 'history' from the below dict. Exercise 4: Initialize dictionary with default values. Exercise 5: Create a dictionary by extracting the keys from a given dictionary. Exercise 6: Delete a list of keys from a dictionary. Exercise 7: Check if a value exists ...
Lets discuss certain ways in which this task can be performed. Method #1 : Using zip () + loop The combination of above functions can be used to solve this problem. In this, we combine list elements with dictionary using zip () and loop is used to combine iteration logic. Python3. test_list = [{'Gfg': 1, 'id': 2},
Syntax of Dictionary items() The syntax of items() method is:. dictionary.items() Note: items() method is similar to dictionary's viewitems() method in Python 2.7.
Dictionary in Python is an unordered collection of data values, used to store data values like a map, which unlike other Data Types that hold only single value as an element, Dictionary holds key : value pair. In Python Dictionary, items() method is used to return the list with all dictionary keys with values. Syntax: dictionary.items() Parameters: This method takes no parameters.
Definition and Usage. The items() method returns a view object. The view object contains the key-value pairs of the dictionary, as tuples in a list. The view object will reflect any changes done to the dictionary, see example below.