
- Publication Recognition

How to Submit a Paper for Publication in a Journal
- 4 minute read
- 81.4K views
Table of Contents
Whether you’ve done it before, or not, submitting a paper for publication in a journal is, to say the least, a process that brings great anxiety and stress. After all your hard work for many months, or even years, recognition is finally at your grasp. That is why there no room for mistakes.
What to Expect of the Scientific Publishing Process
If you are a beginner, you might be struggling to know exactly what to do. After all, it is a step-by-step process, sometimes with a lot of players and paperwork involved; it’s not always evident what to do next. An excellent, high-quality manuscript is the best way to give a good impression from the beginning, putting your paper on the right track for a successful submission. At Elsevier, with our Language Editing services , we not only revise your manuscript, but guarantee there are no text errors.
If, on the other hand, you have already published articles, you might have enough experience to know that each paper submission in a journal is different. Either the journal is different, or the context has changed, or the peers are new. You never know what can go right or wrong, other than the variable that lies under your control – that the manuscript is error-free and spot-on for successful acceptance. In this case, you might consider Elsevier’s professional Language Editing services to amend your text to the target journal’s requirements, helping you focus on other projects.
Scientific Paper Submission. Are you ready? Let’s go!
For many researchers, putting their paper through the professional journal submission process is stressful. Here is a simple to-do list which might help you go through all of it with some peace of mind:
- Use an external editing service, such as Elsevier’s Author Services if you need assistance with language.
- Free e-learning modules on preparing your manuscript can be found on Researcher Academy.
- Mendeley makes your life easier by helping you organize your papers, citations and references, accessing them in the cloud on any device, wherever you are.
- Do not rush submitting your article for publication Carefully re-read and revise your manuscript. Re-reading is essential in the research field and helps identify the most common problems and shortcomings in the manuscript, which might otherwise be overlooked. Often, reading your text out loud will uncover more errors than reading silently to yourself. If you are doubtful about the quality of your text, consider Elsevier’s Professional Language Editing services . Our professional team is trained to provide you with an optimal text for successful submission.
- Read the journal’s aims and scope to make sure they match your paper.
- Check whether you can submit – some journals are invitation only.
- Use the journal’s metrics to measure its impact. In fact, you can also check other additional info – like speed and reach to understand if it’s the right one for you.
- If you’re a post doc, check out our free access program.
- Read the aims and scope and author guidelines of your target journal carefully Once you think your manuscript is ready for submission, the next important step is to read the aims and scope of the journals in your target research area. Doing so will improve the chances of having your manuscript accepted for publishing.
- Submit a cover letter with the manuscript Never underestimate the importance of a cover letter addressed to the editor or editor-in-chief of the target journal. A good cover letter should underline 3 main aspects: the main theme of the paper, its originality/novelty and the relevance of the manuscript to the target journal.
- Make a good first impression with your title and abstract The title and abstract are incredibly important components of a manuscript as they are the first elements a journal editor sees. They create interest and curiosity about the whole work.
Now, what happens if your paper gets rejected by the journal ? It is, by no means, the end of the world. There are very real steps you can take to ultimately get published in a reputable journal.
The Science of Article Publishing
Article publishing is every researcher’s aim. It brings visibility and recognition, essential factors for those who intend to build a full career in research. However, most scientists feel handicapped or lost when it comes to conveying their findings or ideas to others. For many, it can be difficult to re-format a certain type of text to another, be aware of formatting requirements and translate their work into visually appealing outcomes. Additionally, keeping track of all the steps needed to submit an article for publication can be overwhelming and take too much time that could be spent doing new research.
At Elsevier, we believe everyone should be doing what they do best: in this case, leave research for scientists and leave the science of turning the best ideas into excellent quality text to our professionals.
Language Editing Services by Elsevier Author Services:
Find more about How to Submit a Paper for Publication in a Journal on Pinterest:

- Publication Process
How to Write a Journal Article from a Thesis

- Manuscript Review
Looking for Medical Editing Services
You may also like.

How to Make a PowerPoint Presentation of Your Research Paper

What is a Good H-index?

What is a Corresponding Author?
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
For Authors
The sections below provide essential information for authors and we recommend that you take the time to read them before submitting a contribution to Nature . These instructions refer to Articles, Reviews and Perspectives. Separate guidelines are available for Matters Arising and for other types of submission .
Editorial criteria and processes
Please read this section before submitting anything to Nature . This section explains Nature 's editorial criteria, and how manuscripts are handled by our editors between submission and acceptance for publication.
Formatting guide
This section provides a description of all types of contribution published in Nature , and detailed instructions for preparing, formatting and writing all types of manuscripts published by Nature .
Presubmission enquiries
Presubmission enquiries are provided purely as a service to authors to see if a manuscript is likely to be of interest to the journal and are not compulsory.
Initial submission
Please read this section before proceeding with a submission to Nature. Here you can find information on how to prepare and submit your manuscript and any Supplementary Information.
Final submission
This section contains information about how to prepare a final resubmission for publication in Nature .
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information (SI) is peer-reviewed material directly relevant to the conclusion of a paper that cannot be included in the printed version for reasons of space or medium. This section includes information on SI categories and acceptable file formats, size constraints for individual files and how SI should be presented.
Forms and declarations
On this page are the forms to download and complete before publication. These include ‘licence to publish’ forms, manuscript checklists, structure templates and links to reprint order forms.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Submit your paper
Publishing with Elsevier: step-by-step
Learn about the publication process and how to submit your manuscript. This tutorial will help you find the right journal and maximize the chance to be published.
1. Find a journal
Find out the journals that could be best suited for publishing your research. Match your manuscript using the JournalFinder tool, then learn more about each journal.
JournalFinder
Powered by the Elsevier Fingerprint Engine™, Elsevier JournalFinder uses smart search technology and field-of-research-specific vocabularies to match your article to Elsevier journals.
Find out more about a journal
Learn about each journal's topics, impact and submission policies.
Find a journal by name
- Read the journal's aims and scope to make sure it is a match
- Check whether you can submit – some journals are invitation only
- Use journal metrics to understand the impact of a journal
- If available, check the journal at Journal Insights for additional info about impact, speed and reach
- If you're a postdoc, check out our postdoc free access program
2. Prepare your paper for submission
Download our get published quick guide , which outlines the essential steps in preparing a paper. (This is also available in Chinese ). It is very important that you stick to the specific "guide for authors" of the journal to which you are submitting. This can be found on the journal's home page.
You can find information about the publishing process in the understanding the publishing process guide. It covers topics such as authors' rights, ethics and plagiarism, and journal and article metrics.
If you have research data to share, make sure you read the guide for authors to find out which options the journal offers to share research data with your article.
Read more on preparing your paper
Read about publishing in a special issue
- Use an external editing service, such as Elsevier’s Author Services if you need assistance with language
- Free e-learning modules on preparing your manuscript can be found on Researcher Academy
- Mendeley makes your life easier by helping you organize your papers, citations and references, accessing them in the cloud on any device, wherever you are
3. Submit and revise
You can submit to most Elsevier journals using our online systems. The system you use will depend on the journal to which you submit. You can access the relevant submission system via the "submit your paper" link on the Elsevier.com journal homepage of your chosen journal.
Alternatively, if you have been invited to submit to a journal, follow the instructions provided to you.
Once submitted, your paper will be considered by the editor and if it passes initial screening, it will be sent for peer review by experts in your field. If deemed unsuitable for publication in your chosen journal, the editor may suggest you transfer your submission to a more suitable journal, via an article transfer service.
Read more on how to submit and revise
- Check the open access options on the journal's home page
- Consider the options for sharing your research data
- Be accurate and clear when checking your proofs
- Inform yourself about copyright and licensing
4. Track your paper
Track your submitted paper.
You can track the status of your submitted paper online. The system you use to track your submission will be the same system to which you submitted. Use the reference number you received after submission to track your submission.
Unsure about what the submission status means? Check out this video .
In case of any problems contact the Support Center
Track your accepted paper
Once your paper is accepted for publication, you will receive a reference number and a direct link that lets you follow its publication status via Elsevier’s "Track Your Accepted Article" service.
However, even without a notification you can track the status of your article by entering your article reference number and corresponding author surname in Track Your Accepted Article .
Read more about the article tracking service
5. Share and promote
Now that your article is published, you can promote it to achieve a bigger impact for your research. Sharing research, accomplishments and ambitions with a wider audience makes you more visible in your field. This helps you get cited more, enabling you to cultivate a stronger reputation, promote your research and move forward in your career.
Read more on sharing your research After publication, celebrate and get noticed!
Elsevier.com visitor survey
We are always looking for ways to improve customer experience on Elsevier.com. We would like to ask you for a moment of your time to fill in a short questionnaire, at the end of your visit . If you decide to participate, a new browser tab will open so you can complete the survey after you have completed your visit to this website. Thanks in advance for your time.
- SpringerLink shop
Electronic submission
Electronic submission substantially reduced the editorial processing and reviewing times and shortened overall publication times. To submit to the journal of your choice, click the Submit Manuscript button on the journal's homepage.
The link leads you directly to the submission system used by that journal, which is either Editorial Manager, Manuscript Central or Snapp.
Include your ORCID iD
This ID uniquely attaches your identity to your research work, such as your articles and citations. The result: no more confusion because another researcher has the same or a similar name!
To register a new or existing ORCID number, log in to the editorial system and select 'Edit My Account' or 'Update My Information' from the menu.
You can read more about ORCID and its benefits here .
Add your research funding source
It will give your article additional visibility.
Our submission systems will offer the option to include your funding source in a standardized way. In most cases you will be able to choose your funder from the given list. Otherwise, please add it manually.
The funding information will be published as searchable meta-data for the accepted article.
It will be made publicly available through Crossref's funding data search and your article can be found by anyone who looks for your funder’s name.
Further reading: The Crossref Funder Registry
Back to top of Submission
Reviewing and acceptance
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Submission Portal
Submit to the world's largest public repository of biological and scientific information
Type a few words about the sequence data you are submitting and select an option to learn more. You can also browse submission information below.
What do you want to submit?
Enter a few words about your sequence data.
Suggested tools
SRA accepts unassembled reads from high throughput sequencing platforms. Submitted data files should generally be minimally processed and include per-base quality scores.
Submit unassembled reads of SARS-CoV-2 with BioProject, BioSample, metadata and NGS files.
GEO accepts raw data, processed data and metadata for gene expression and epigenomics datasets generated by high-throughput sequencing and microarray technologies.
Submit assembled complete or incomplete/draft prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes. Not for viral, phage, or single locus sequences (for example: 16S rRNA). Submit those to regular GenBank .
Computationally assembled transcribed RNA sequences representing a transcriptome derived from sequence reads submitted to Sequence Read Archive (SRA).
Submit ribosomal RNA (rRNA), rRNA-ITS, SARS-CoV-2, Influenza, Norovirus, Dengue, metazoan COX1 or eukaryotic nuclear mRNA
Submit assembled reads of SARS-CoV-2 with FASTA files and source metadata. Annotation for SARS-CoV-2 is not required.
Eukaryotic nuclear mRNA (fill out CDS and UTR feature annotations in a web form, or upload protein translations for automated CDS annotation; limit 500 sequences)
Eukaryotic nuclear mRNA (provide feature annotations by uploading a feature table), other mRNAs
Submit genomic DNA, organelle, ncRNA, plasmids, other viruses, phages, mRNA and synthetic constructs.
Microarray data from clinical studies that require controlled access.
Information on human sequence variation and relationship to human health.
Submit the electronic version of a peer-reviewed manuscript for inclusion in PubMed Central.
Explore clinicial studies conducted around the world.
Large-scale sequencing projects for an individual loci are taken in GenBank & Sequence Read Archive (SRA).
Submit BioNano maps, Beta-lactamase gene, and PacBio methylation data.
NCBI takes data capturing experimental or inferential results supporting annotation dervied from GenBank primary data.
Small human genomic variation: single nucleotide, insertions, deletions, and microsatellites.
Genetic tests for inherited & somatic genetic variations, including arrays and multiplex panels.
Automatically create a BioProject and BioSample during sequence data submission.
No results found
We need a little more information. Add to your description above, indicating sequence data type and/or whether your data is assembled, unassembled or expression data.
GenBank is the world's largest nucleotide archive containing sequences from all branches of life. The archive is a foundation for medical and biological discovery.
Submit assembled SARS-CoV-2 , Influenza, Norovirus, Dengue virus, rRNA, rRNA-ITS, metazoan COX1, Eukaryotic nuclear mRNA sequences.
Submit genomic DNA, organelle, ncRNA, plasmids, other viruses, phages, mRNA, synthetic constructs.
Submit assembled eukaryotic and prokaryotic genomes (WGS or Complete).
Sequence Read Archive (SRA)
SRA is the largest publicly-available repository of high throughput sequencing data. The archive accepts data from all branches of life as well as metagenomic and environmental surveys.
Submit unassembled, high throughput sequencing reads
SARS-CoV-2 submission instructions
Other Tools
Submit computationally assembled, transcribed RNA sequences after submitting unassembled reads to SRA. Learn more
Submit RNA-seq, ChIP-seq, and other types of gene expression and epigenomics datasets. Learn more
BioProject & BioSample
Choose a tool above if submitting sequence data. Learn more
Sequence Submission FAQ
What is an accession number.
An accession number in bioinformatics is a unique identifier given to a DNA or protein sequence record to allow for tracking of different versions of that sequence record and the associated sequence over time in a single data repository. Because of its relative stability, accession numbers can be utilized as foreign keys for referring to a sequence object, but not necessarily to a unique sequence. All sequence information repositories implement the concept of "accession number" but might do so with subtle variation.
What happens after my data is submitted?
Please read the NLM GenBank and SRA Data Processing document which describes how sequence data are processed and made available to the public, responsibilities of the data submitter, responsibilities of NCBI, and defines data status. You may write to [email protected] if you have questions about your submitted data or if you have questions about the document.
Medical Genetics & Variation Tools
Submit clinical data, small & large human genomics variants, and genotype & phenotype data.
Other Resources
- Clinical Trials
- Manuscripts
The IEEE Article Submission Process
After you have written your article and prepared your graphics, you can submit your article for review. Follow these steps to complete the IEEE Article Submission Process.
Select Your Target Journal
An article may be rejected before peer review if it is outside the scope of the journal. Pick the right journal with these tips.
- Get customized recommendations for your article from the IEEE Publication Recommender tool.
- Conduct a keyword search on IEEE Xplore ® Digital Library for a list of publications with similar content.
- Check your reference list for related journals.
- Ask for suggestions from colleagues and co-authors in your field.
- Read the Aims & Scope of your potential target publications to ensure your article is a good fit. Aims & Scope can be found in the About tab of the journal homepage on IEEE Xplore .
- Keep in mind that some publications only accept certain types of articles. Letters publications will accept brief articles, while Transactions or Journal publications will accept full-length articles.
You can only submit your article to one publication at a time.
Follow All Submission Guidelines
All IEEE journals provide submission guidelines in an “Information for Authors” section, published in the journal or on a society’s website.
To find the guidelines for your target journal:
- find the journal’s home page on IEEE Xplore ;
- click on the About Journal tab;
- click on Publication Details.
Not following guidelines can result in delayed processing of your submission, rejection without review, or errors in your published article.
Submit Your Article
After checking that your article complies with the target journal’s submission guidelines, you are ready to submit. Click the Submit Your Manuscript button on the journal’s home page on IEEE Xplore. You will be taken to the journal’s online submission system, which will walk you through the submission process.
How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal
- Open access
- Published: 30 April 2020
- Volume 36 , pages 909–913, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Clara Busse ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0178-1000 1 &
- Ella August ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5151-1036 1 , 2
268k Accesses
15 Citations
718 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common pitfalls for each section and recommend strategies to avoid them. Further, we give advice about target journal selection and authorship. In the online resource 1 , we provide an example of a high-quality scientific paper, with annotations identifying the elements we describe in this article.
Similar content being viewed by others
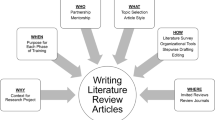
Why, When, Who, What, How, and Where for Trainees Writing Literature Review Articles

Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice


How to design bibliometric research: an overview and a framework proposal
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Writing a scientific paper is an important component of the research process, yet researchers often receive little formal training in scientific writing. This is especially true in low-resource settings. In this article, we explain why choosing a target journal is important, give advice about authorship, provide a basic structure for writing each section of a scientific paper, and describe common pitfalls and recommendations for each section. In the online resource 1 , we also include an annotated journal article that identifies the key elements and writing approaches that we detail here. Before you begin your research, make sure you have ethical clearance from all relevant ethical review boards.
Select a Target Journal Early in the Writing Process
We recommend that you select a “target journal” early in the writing process; a “target journal” is the journal to which you plan to submit your paper. Each journal has a set of core readers and you should tailor your writing to this readership. For example, if you plan to submit a manuscript about vaping during pregnancy to a pregnancy-focused journal, you will need to explain what vaping is because readers of this journal may not have a background in this topic. However, if you were to submit that same article to a tobacco journal, you would not need to provide as much background information about vaping.
Information about a journal’s core readership can be found on its website, usually in a section called “About this journal” or something similar. For example, the Journal of Cancer Education presents such information on the “Aims and Scope” page of its website, which can be found here: https://www.springer.com/journal/13187/aims-and-scope .
Peer reviewer guidelines from your target journal are an additional resource that can help you tailor your writing to the journal and provide additional advice about crafting an effective article [ 1 ]. These are not always available, but it is worth a quick web search to find out.
Identify Author Roles Early in the Process
Early in the writing process, identify authors, determine the order of authors, and discuss the responsibilities of each author. Standard author responsibilities have been identified by The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) [ 2 ]. To set clear expectations about each team member’s responsibilities and prevent errors in communication, we also suggest outlining more detailed roles, such as who will draft each section of the manuscript, write the abstract, submit the paper electronically, serve as corresponding author, and write the cover letter. It is best to formalize this agreement in writing after discussing it, circulating the document to the author team for approval. We suggest creating a title page on which all authors are listed in the agreed-upon order. It may be necessary to adjust authorship roles and order during the development of the paper. If a new author order is agreed upon, be sure to update the title page in the manuscript draft.
In the case where multiple papers will result from a single study, authors should discuss who will author each paper. Additionally, authors should agree on a deadline for each paper and the lead author should take responsibility for producing an initial draft by this deadline.
Structure of the Introduction Section
The introduction section should be approximately three to five paragraphs in length. Look at examples from your target journal to decide the appropriate length. This section should include the elements shown in Fig. 1 . Begin with a general context, narrowing to the specific focus of the paper. Include five main elements: why your research is important, what is already known about the topic, the “gap” or what is not yet known about the topic, why it is important to learn the new information that your research adds, and the specific research aim(s) that your paper addresses. Your research aim should address the gap you identified. Be sure to add enough background information to enable readers to understand your study. Table 1 provides common introduction section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.

The main elements of the introduction section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Methods Section
The purpose of the methods section is twofold: to explain how the study was done in enough detail to enable its replication and to provide enough contextual detail to enable readers to understand and interpret the results. In general, the essential elements of a methods section are the following: a description of the setting and participants, the study design and timing, the recruitment and sampling, the data collection process, the dataset, the dependent and independent variables, the covariates, the analytic approach for each research objective, and the ethical approval. The hallmark of an exemplary methods section is the justification of why each method was used. Table 2 provides common methods section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Results Section
The focus of the results section should be associations, or lack thereof, rather than statistical tests. Two considerations should guide your writing here. First, the results should present answers to each part of the research aim. Second, return to the methods section to ensure that the analysis and variables for each result have been explained.
Begin the results section by describing the number of participants in the final sample and details such as the number who were approached to participate, the proportion who were eligible and who enrolled, and the number of participants who dropped out. The next part of the results should describe the participant characteristics. After that, you may organize your results by the aim or by putting the most exciting results first. Do not forget to report your non-significant associations. These are still findings.
Tables and figures capture the reader’s attention and efficiently communicate your main findings [ 3 ]. Each table and figure should have a clear message and should complement, rather than repeat, the text. Tables and figures should communicate all salient details necessary for a reader to understand the findings without consulting the text. Include information on comparisons and tests, as well as information about the sample and timing of the study in the title, legend, or in a footnote. Note that figures are often more visually interesting than tables, so if it is feasible to make a figure, make a figure. To avoid confusing the reader, either avoid abbreviations in tables and figures, or define them in a footnote. Note that there should not be citations in the results section and you should not interpret results here. Table 3 provides common results section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
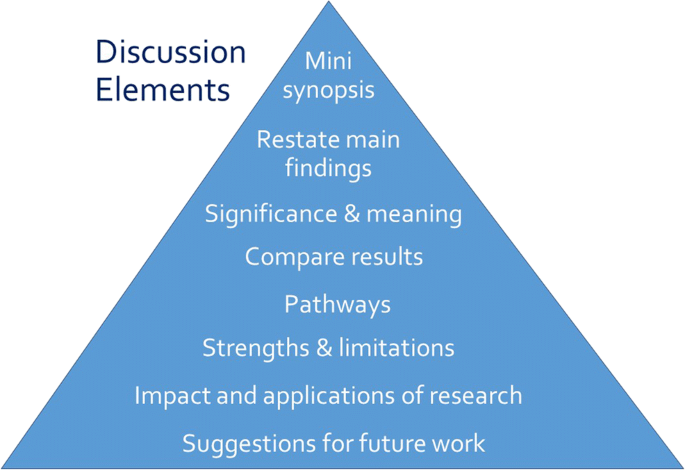
Discussion Section
Opposite the introduction section, the discussion should take the form of a right-side-up triangle beginning with interpretation of your results and moving to general implications (Fig. 2 ). This section typically begins with a restatement of the main findings, which can usually be accomplished with a few carefully-crafted sentences.
Major elements of the discussion section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Next, interpret the meaning or explain the significance of your results, lifting the reader’s gaze from the study’s specific findings to more general applications. Then, compare these study findings with other research. Are these findings in agreement or disagreement with those from other studies? Does this study impart additional nuance to well-accepted theories? Situate your findings within the broader context of scientific literature, then explain the pathways or mechanisms that might give rise to, or explain, the results.
Journals vary in their approach to strengths and limitations sections: some are embedded paragraphs within the discussion section, while some mandate separate section headings. Keep in mind that every study has strengths and limitations. Candidly reporting yours helps readers to correctly interpret your research findings.
The next element of the discussion is a summary of the potential impacts and applications of the research. Should these results be used to optimally design an intervention? Does the work have implications for clinical protocols or public policy? These considerations will help the reader to further grasp the possible impacts of the presented work.
Finally, the discussion should conclude with specific suggestions for future work. Here, you have an opportunity to illuminate specific gaps in the literature that compel further study. Avoid the phrase “future research is necessary” because the recommendation is too general to be helpful to readers. Instead, provide substantive and specific recommendations for future studies. Table 4 provides common discussion section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Follow the Journal’s Author Guidelines
After you select a target journal, identify the journal’s author guidelines to guide the formatting of your manuscript and references. Author guidelines will often (but not always) include instructions for titles, cover letters, and other components of a manuscript submission. Read the guidelines carefully. If you do not follow the guidelines, your article will be sent back to you.
Finally, do not submit your paper to more than one journal at a time. Even if this is not explicitly stated in the author guidelines of your target journal, it is considered inappropriate and unprofessional.
Your title should invite readers to continue reading beyond the first page [ 4 , 5 ]. It should be informative and interesting. Consider describing the independent and dependent variables, the population and setting, the study design, the timing, and even the main result in your title. Because the focus of the paper can change as you write and revise, we recommend you wait until you have finished writing your paper before composing the title.
Be sure that the title is useful for potential readers searching for your topic. The keywords you select should complement those in your title to maximize the likelihood that a researcher will find your paper through a database search. Avoid using abbreviations in your title unless they are very well known, such as SNP, because it is more likely that someone will use a complete word rather than an abbreviation as a search term to help readers find your paper.
After you have written a complete draft, use the checklist (Fig. 3 ) below to guide your revisions and editing. Additional resources are available on writing the abstract and citing references [ 5 ]. When you feel that your work is ready, ask a trusted colleague or two to read the work and provide informal feedback. The box below provides a checklist that summarizes the key points offered in this article.

Checklist for manuscript quality
Data Availability
Michalek AM (2014) Down the rabbit hole…advice to reviewers. J Cancer Educ 29:4–5
Article Google Scholar
International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Defining the role of authors and contributors: who is an author? http://www.icmje.org/recommendations/browse/roles-and-responsibilities/defining-the-role-of-authosrs-and-contributors.html . Accessed 15 January, 2020
Vetto JT (2014) Short and sweet: a short course on concise medical writing. J Cancer Educ 29(1):194–195
Brett M, Kording K (2017) Ten simple rules for structuring papers. PLoS ComputBiol. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005619
Lang TA (2017) Writing a better research article. J Public Health Emerg. https://doi.org/10.21037/jphe.2017.11.06
Download references
Acknowledgments
Ella August is grateful to the Sustainable Sciences Institute for mentoring her in training researchers on writing and publishing their research.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Maternal and Child Health, University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, 135 Dauer Dr, 27599, Chapel Hill, NC, USA
Clara Busse & Ella August
Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan School of Public Health, 1415 Washington Heights, Ann Arbor, MI, 48109-2029, USA
Ella August
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ella August .
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
(PDF 362 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Busse, C., August, E. How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal. J Canc Educ 36 , 909–913 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Download citation
Published : 30 April 2020
Issue Date : October 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Manuscripts
- Scientific writing
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Guide to Getting Published in Journals
- Why publish in journals?
- Identifying potential journals
- Creating a journal comparison spreadsheet
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- How different journals approach peer review
- Different open access models
- Interpreting traditional metrics like the Impact Factor
- Alternative metrics
- Ethics and malpractice statements
- Recognising and avoiding predatory journals
- Instructions for authors
- Submitting your paper
Introduction
You have worked through your list of journals, investigating all your criteria and found the journal that is best suited to your paper and the goals you have for it. It is now time for you to submit!
In this section, we will prepare you for what to expect when submitting to a journal, give some insights into the peer review process, how to respond to requests for revisions and resubmit a paper, and what steps to take should you receive a rejection decision.
Submitting a paper
Make sure you have prepared your paper according to the instructions for authors . Double-check the journal’s requirements with your article to be certain.
If you need to include a cover letter with your submission, you should address the editor by formal name (e.g. Dear Professor Name---) and include the name of the journal but make sure you use the correct one (especially if this is your second-choice journal)!
In the letter, explain why your article is suitable for that journal and how your paper will contribute to furthering its aims & scope. Pitch the value of your article, describing the main theme, the contribution your paper makes to existing knowledge, and its relationship to any relevant articles published in the journal. You should not repeat the abstract in the letter. Include information not typically mentioned in a manuscript.
You may also be requested by the journal to suggest some reviewers for your paper. Good sources for these include authors cited in your references and editorial board members from the journal, or from other journals in the field. You should not suggest anyone that you would have a conflict of interest with, such as co-workers.
You should also make some formal declarations regarding the originality of your work, that you have no conflicts of interest, and that all co-authors (if you have any) agree to the submission.
The review process
As we discussed in the earlier module on peer review , there are a wide range of timeframes over which your review process may be conducted.
It may take several months for the journal to complete the review process, which typically involves:
- Reading the article and deciding whether to send it for review.
- Acquiring sufficient reviewers and receiving all feedback.
- Assessing the reviews and rendering a decision on the paper.
Acquiring reviewers and then receiving those reviews back is the longest part of the process. It is very much dependent on the availability of academics, and is not an especially predictable process.
Journals which use web-based reviewing platforms often feature a status for each submission that authors can check. If this status has not changed for some time, in most cases, you will be able to send the journal administrator or editor an email. Some journals make their review times publicly available, giving you a good idea of how long their process might take, and when it may be appropriate to ask for an update. If you do not know what to expect, we suggest waiting around 2 months before asking for an update.
Desk reject
Hopefully you will have submitted your article to the perfect journal, exactly as they have requested, and your article will be sent for reviewing. However, some papers are rejected without being sent for peer review – this is commonly known as a desk reject – and of course, you want to avoid this happening to your paper.
To help you understand and minimise the risk, here are some of the most common reasons for desk rejection:
TECHNICAL SCREENING
- Language or writing issues which make it too hard for the editor to understand the paper.
- Similarity checking revealing a large amount of exact matching or plagiarised content.
- Formatting is not in the journal style
- Word count is too high
- Figures & Tables are incomplete or difficult to read
- References are incomplete
AIMS & SCOPE AND CONTENT
- Outside Aims & Scope.
- Hypothesis or purpose is not sufficiently clear.
- Methods are unclear or flawed.
- Results do not support conclusions.
- Incremental addition to knowledge.
- References miss key or recent literature.
Similarity (plagarism) checking
Many journals conduct some form of checking of article text to go alongside the reviewing of papers. Software such as iThenticate, Turnitin, PlagScan, among many others, are used either to look for similarities in text between the submitted article and published material available online.
These platforms cannot, by themselves, determine whether text has been plagiarised, only provide a score of how similar passages of text are to existing material. For this reason, these programs tend to be referred to as ‘similarity checker’, not ‘plagiarism checker’.
Papers which are processed and return high scores are likely to be investigated to determine whether the similarity does appear to be deliberate plagiarism. How a journal deals with such a paper depends on their own policies and procedures, and the extent of the plagiarism detected.
Many journals will refer to the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) Guidelines and Flowchart for dealing with “Suspected plagiarism in a submitted manuscript”. See our module on Ethics and Malpractice Statements for more detail on COPE and journal ethics.
These similarity checking programs may be used at different stages of the process, depending on journal policy and situation. Some journals may screen all papers on submission, some only when some concerns are raised by the editor on first read or by referees during review.
Receiving a decision after peer review
Once the editor has received all comments, feedback and recommendations from the reviewers, they will make a decision on the paper. These decisions may be called by different terms, but will usually fit into one of four categories:
- Accept – it is very rare than a first submission will be accepted outright, without any changes being requested.
- Revisions likely to result in acceptance – This can be a ‘minor revisions’ decision, or a more major revision, but in both cases the editor shows positivity towards a final acceptance.
- Revisions with an uncertain outcome – Often referred to as ‘major revisions’, or ‘reject, revise and resubmit’, these decisions request extensive revisions, reinterpretations of information, or deeper, more thorough explanations of details, which ultimately may not be acceptable for the journal even when responses to all reviewer comments have been provided.
- Reject – The paper is unsuitable and/or unacceptable for the journal in this form, or any alternate version. With a reject decision, a revision is not invited, and should an author resubmit the paper as a new version, it may be immediately rejected.
If you are invited to revise your paper, make sure you are methodical in your approach to tackling the revisions requested by the editor.
- Read the letter and put it aside for a day or two. However well-framed the reviewer’s comments and criticisms of your paper, there is always a chance you may feel protective over the original paper you spent so much time writing. It is not always easy to receive criticism, so don’t rush to take action immediately. Give yourself a few days to digest the reviewer comments before taking the next steps with your revision.
- In most cases, it is likely that you will be able to follow the recommendations of the reviewers.
- Organising the reviewer comments by ease of response or your ability to complete. For example, on a spectrum of requested revisions, spelling and grammar corrections would be at the easiest end, through to conducting extra experiments at the more difficult (or impossible) end.
- Numbering each of the comments from each reviewer.
- Taking a structured approach to revisions will also make it easier to respond. You will need to include a point-by-point response letter, detailing how you have addressed each reviewer point. You do not need to perform every change requested of the reviewers, but you should provide a response as to why you have not done so. It may be that reviewers request conflicting things, or the additional experiments they suggest are not possible.
- If you disagree with a comment made by one of the reviewers, try to provide an evidence-based explanation in your response.
- Try to complete your revisions by the requested deadline. If you think you will need longer, let the journal know. They will probably be happy to grant you the extension, and it is courteous to keep them updated. In addition, some online review platforms may prevent you from submitting your revision once the due date expires, so asking for an extension will avoid this problem too.
- Once your revisions are complete and you have detailed all your responses in your letter, check with any co-authors that they are all happy with the final versions before re-submitting to the journal.
- For journals with online submission forms, be sure to submit as the revision of your original article so that it is easy for the editorial office and Editor to follow. Amend any relevant fields (such as title, abstract) that have changed during your revision process, provide related cover letters, revised manuscript files and reviewer response letter in the appropriate places in the forms.
- Revisions may be sent to the previous reviewers to re-assess, or the Editor may make a decision independently. In some cases, new reviewers may be sought. As with the first submission, once all reviews have been submitted, the Editor will make a decision from the same set of categories and hopefully your paper will be accepted in just one or two rounds of resubmission. Some very strict journals will not invite a second speculative revision, but others may be more lenient and continue to invite revisions until the editor is satisfied of a decision to either Accept or Reject.
Having a submission rejected from your first-choice journal is something of an inevitability - every researcher has been rejected at some point in their careers. Even some of what we now consider ground-breaking and foundational studies were rejected from their first-choice journals. Hans Krebs' paper on citric acid cycle - the Krebs cycle – was rejected from Nature in 1937, and Kary Mullis’ first paper on polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was rejected from Science in 1993, before going on to win the Nobel Prize. Rejection happens, quite literally, to the best of us.
If this should happen to you, try not be too disappointed. It does not mean there is no future for your paper. As with our revision recommendation, set aside the letter once you have read it and give yourself some time before tackling it.
When you are ready to proceed with your paper, consider the following steps:
- From your shortlist of suitable journals for your paper, you might now consider your second-choice journal.
- Another option to consider may be ‘Cascade Journals’. Some publishers now offer a chance to publish in a ‘Cascade journal’. These are usually open access titles, published by the same organisation. Some Cascade journals will require payment of an Article Processing Charge (APC). You may or may not be offered a reduced rate as part of the transfer to the related title. It is likely that the journal will transfer the reviews received at your first-choice journal to the ‘cascade journal’. This is intended to speed up the review process, or may mean the editor does not have to conduct any reviewing at all, but it does not guarantee acceptance at this journal. The editor will still need to make a decision as to whether your paper is suitable for the journal.
- Firstly, it is likely that the comments the reviewers provided will help you improve aspects of your paper such as focusing the aims and purpose of your paper, sharpening the inferences made from your results, fine tuning the message you wish to convey, or improving the readability among many other positive edits.
- Secondly, even in reasonably large research fields, there is a chance that the same reviewers who saw your paper at the first journal will be asked to review it at the new journal. It will not reflect favourably on you if you have not acknowledged or considered any of their comments from the first round of reviews.
When submitting the new version of your paper to your second journal, there is no need to include a letter responding to the original reviewers’ comments.
- Check that the format of your paper meets the submission criteria of the new journal and make the appropriate amendments (remember, failure to comply with a journals Instructions For Authors is one of the most common causes of immediate rejection).
- If you wish, write a cover letter to the new journal, explaining the relevance of your paper to the journal, and be sure to address the correct journal editor and journal name.
- Complete your new submission to the journal.
After acceptance, you will usually be required to sign copyright or licensing documents, to give the publisher the rights to publish your article. Be sure to read these documents thoroughly to understand what you are signing.
If you would like to publish your article Open Access, Article Processing Charges are usually requested at this stage, and go hand-in-hand with the license you select, if such options are available.
Accepted papers are usually sent to a production team to format into journal style. Some have dedicated professional typesetters, copyeditors and proof-readers. For some journals, the Editors may contribute to these roles.
Some journals publish the Accepted version online within just a few days, to make it officially available before the final ‘Version of Record’ journal-styled PDF is made available.
Some journals publish articles online as soon as they are ready, into a queue of early publication manuscripts. Other journals hold all articles offline until each issue is full and publish each issue according to a defined schedule (for example, 4 times per year).
There are many different ways in which publishers and journals manage their post-acceptance stages and publication schedules. If the information about your article is not provided to you, you may contact the journal office for an update.
These are some of the more common processes and procedures that you will encounter and come to rely on throughout your research publishing career, but there may be many more variations to deal with. The submission process can be a time-consuming, frustrating experience, but with these tips, and building up your own repertoire of tools, resources and techniques, you will soon master the arts of submission and peer review.
Good luck with all your future submissions!
Further resources
Hervé Stolowy (2017) Letter from the Editor: Why Are Papers Desk Rejected at European Accounting Review? , European Accounting Review, 26:3, 411-418
- << Previous: Instructions for authors
- Last Updated: Sep 18, 2023 1:28 PM
- URL: https://ifis.libguides.com/journal-publishing-guide
Share this page:
Submission Guidelines
Submission checklist.
Carefully review each item listed below before submitting your article. Article submissions that do not follow the guidelines below will be returned to draft or immediately rejected.
- Manuscript should be prepared in a double column, single-spaced format using a required IEEE Access template. A Word or LaTex file and a PDF file are both required upon submission. Content on each file must match exactly. File sizes should not exceed 40MB. Download IEEE Access Templates for Microsoft Word and LaTex.
- The use of artificial intelligence (AI)–generated text in an article shall be disclosed in the acknowledgements section of any paper submitted to an IEEE Conference or Periodical. The sections of the paper that use AI-generated text shall have a citation to the AI system used to generate the text. For more information please click here.
- Author lists should be carefully considered before submission. For more information on what constitutes an author, please click here. Contributors who do not meet IEEE’s definition of authorship should be included in the Acknowledgment section of the article. Omitting an author who contributed to your article or including a person who did not fulfill authorship requirements is considered a breach of publishing ethics. Once the list and order of authors has been established, the list and order of authors should not be altered without permission of all living authors of that article, and the decision to allow such changes rests with the Editor.
- Corresponding authors are required to have an ORCID ID associated with their account. For more information on ORCID, click here.
- Short biographies are required for ALL authors on an article submission. As indicated in the required IEEE Access templates, biographies of all authors should be included directly within the article below the references section.
- All authors should be listed on both the source file (Word of LaTex file) and the manuscript PDF file. When submitting your files ensure the submission system successfully extracts the full author list from your files.
- The article should be thoroughly reviewed for proper grammar before being submitted. Articles with poor grammar will be immediately rejected. If needed, IEEE Access offers Paperpal Preflight to assist authors in checking their manuscript for grammar issues prior to submission. Check your manuscript on Paperpal Preflight by clicking here .
- All research works should be carefully referenced. More information to avoid plagiarism is listed below.
- The article should not be submitted elsewhere at the same time. More information about duplicate submission can be found here .
- Supplementary material for review (if any)
- Manuscript keywords (minimum of 3 and maximum of 10). Please carefully select the keywords as this is how we select a relevant Associate Editor to manage the peer review of your article.
- You will be required to select a manuscript type upon submission. A list and description of manuscript types are listed below. If you are unsure, please leave it as “Research Article”. *Please note that should your article be accepted, the manuscript type will be published on the article.
- Opposed reviewers (if any)
- Video (if any, maximum file size is 100MB)
- If the article was previously rejected after peer review with encouragement to update and resubmit, then a complete “list of updates” must be included in a separate document. The list of updates should have the following regarding each comment: 1) reviewers’ concerns, 2) authors’ response to the concerns, 3) actual changes implemented.
- IEEE Access does not have a page limit; however, we strongly recommend keeping the page count under 50 pages for ease of readability. Longer articles may result in longer peer review times. Additional content can be added as supplementary material.
- In alignment with the IEEE Code of Ethics and with respect to the wishes of the subject of the image, IEEE will no longer accept submitted papers which include the ‘Lena image’. For more information please click here .
Manuscript Types Acceptable for Peer Review
At a glance.
- Journal: IEEE Access
- Format: Open Access
- Frequency: Continuous
- Submission to Publication: 4-6 weeks (typical)
- Topics: All topics in IEEE
- Average Acceptance Rate: 27%
- Model: Binary Peer Review
- Article Processing Charge: US $1,995
Featured Articles
Accuracy Enhancement of Hand Gesture Recognition Using CNN
View in IEEE Xplore
Novel Universal Power Electronic Interface for Integration of PV Modules and Battery Energy Storages in Residential DC Microgrids
A Flexible Two-Tower Model for Item Cold-Start Recommendation
© 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this website signifies your agreement to the IEEE TERMS AND CONDITIONS.
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world’s largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity.
AWARD RULES:
NO PURCHASE NECESSARY TO ENTER OR WIN. A PURCHASE WILL NOT INCREASE YOUR CHANCES OF WINNING.
These rules apply to the “2024 IEEE Access Best Video Award Part 1″ (the “Award”).
- Sponsor: The Sponsor of the Award is The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Incorporated (“IEEE”) on behalf of IEEE Access , 445 Hoes Lane, Piscataway, NJ 08854-4141 USA (“Sponsor”).
- Eligibility: Award is open to residents of the United States of America and other countries, where permitted by local law, who are the age of eighteen (18) and older. Employees of Sponsor, its agents, affiliates and their immediate families are not eligible to enter Award. The Award is subject to all applicable state, local, federal and national laws and regulations. Entrants may be subject to rules imposed by their institution or employer relative to their participation in Awards and should check with their institution or employer for any relevant policies. Void in locations and countries where prohibited by law.
- Agreement to Official Rules : By participating in this Award, entrants agree to abide by the terms and conditions thereof as established by Sponsor. Sponsor reserves the right to alter any of these Official Rules at any time and for any reason. All decisions made by Sponsor concerning the Award including, but not limited to the cancellation of the Award, shall be final and at its sole discretion.
- How to Enter: This Award opens on January 1, 2024 at 12:00 AM ET and all entries must be received by 11:59 PM ET on June 30, 2024 (“Promotional Period”).
Entrant must submit a video with an article submission to IEEE Access . The video submission must clearly be relevant to the submitted manuscript. Only videos that accompany an article that is accepted for publication in IEEE Access will qualify. The video may be simulations, demonstrations, or interviews with other experts, for example. Your video file should not exceed 100 MB.
Entrants can enter the Award during Promotional Period through the following method:
- The IEEE Author Portal : Entrants can upload their video entries while submitting their article through the IEEE Author Portal submission site .
- Review and Complete the Terms and Conditions: After submitting your manuscript and video through the IEEE Author Portal, entrants should then review and sign the Terms and Conditions .
Entrants who have already submitted a manuscript to IEEE Access without a video can still submit a video for inclusion in this Award so long as the video is submitted within 7 days of the article submission date. The video can be submitted via email to the article administrator. All videos must undergo peer review and be accepted along with the article submission. Videos may not be submitted after an article has already been accepted for publication.
The criteria for an article to be accepted for publication in IEEE Access are:
- The article must be original writing that enhances the existing body of knowledge in the given subject area. Original review articles and surveys are acceptable even if new data/concepts are not presented.
- Results reported must not have been submitted or published elsewhere (although expanded versions of conference publications are eligible for submission).
- Experiments, statistics, and other analyses must be performed to a high technical standard and are described in sufficient detail.
- Conclusions must be presented in an appropriate fashion and are supported by the data.
- The article must be written in standard English with correct grammar.
- Appropriate references to related prior published works must be included.
- The article must fall within the scope of IEEE Access
- Must be in compliance with the IEEE PSPB Operations Manual.
- Completion of the required IEEE intellectual property documents for publication.
- At the discretion of the IEEE Access Editor-in-Chief.
- Disqualification: The following items will disqualify a video from being considered a valid submission:
- The video is not original work.
- A video that is not accompanied with an article submission.
- The article and/or video is rejected during the peer review process.
- The article and/or video topic does not fit into the scope of IEEE Access .
- The article and/or do not follow the criteria for publication in IEEE Access .
- Videos posted in a comment on IEEE Xplore .
- Content is off-topic, offensive, obscene, indecent, abusive or threatening to others.
- Infringes the copyright, trademark or other right of any third party.
- Uploads viruses or other contaminating or destructive features.
- Is in violation of any applicable laws or regulations.
- Is not in English.
- Is not provided within the designated submission time.
- Entrant does not agree and sign the Terms and Conditions document.
Entries must be original. Entries that copy other entries, or the intellectual property of anyone other than the Entrant, may be removed by Sponsor and the Entrant may be disqualified. Sponsor reserves the right to remove any entry and disqualify any Entrant if the entry is deemed, in Sponsor’s sole discretion, to be inappropriate.
- Entrant’s Warranty and Authorization to Sponsor: By entering the Award, entrants warrant and represent that the Award Entry has been created and submitted by the Entrant. Entrant certifies that they have the ability to use any image, text, video, or other intellectual property they may upload and that Entrant has obtained all necessary permissions. IEEE shall not indemnify Entrant for any infringement, violation of publicity rights, or other civil or criminal violations. Entrant agrees to hold IEEE harmless for all actions related to the submission of an Entry. Entrants further represent and warrant, if they reside outside of the United States of America, that their participation in this Award and acceptance of a prize will not violate their local laws.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Entrant grants Sponsor an irrevocable, worldwide, royalty free license to use, reproduce, distribute, and display the Entry for any lawful purpose in all media whether now known or hereinafter created. This may include, but is not limited to, the IEEE A ccess website, the IEEE Access YouTube channel, the IEEE Access IEEE TV channel, IEEE Access social media sites (LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, IEEE Access Collabratec Community), and the IEEE Access Xplore page. Facebook/Twitter/Microsite usernames will not be used in any promotional and advertising materials without the Entrants’ expressed approval.
- Number of Prizes Available, Prizes, Approximate Retail Value and Odds of winning Prizes: Two (2) promotional prizes of $350 USD Amazon gift cards. One (1) grand prize of a $500 USD Amazon gift card. Prizes will be distributed to the winners after the selection of winners is announced. Odds of winning a prize depend on the number of eligible entries received during the Promotional Period. Only the corresponding author of the submitted manuscript will receive the prize.
The grand prize winner may, at Sponsor’ discretion, have his/her article and video highlighted in media such as the IEEE Access Xplore page and the IEEE Access social media sites.
The prize(s) for the Award are being sponsored by IEEE. No cash in lieu of prize or substitution of prize permitted, except that Sponsor reserves the right to substitute a prize or prize component of equal or greater value in its sole discretion for any reason at time of award. Sponsor shall not be responsible for service obligations or warranty (if any) in relation to the prize(s). Prize may not be transferred prior to award. All other expenses associated with use of the prize, including, but not limited to local, state, or federal taxes on the Prize, are the sole responsibility of the winner. Winner(s) understand that delivery of a prize may be void where prohibited by law and agrees that Sponsor shall have no obligation to substitute an alternate prize when so prohibited. Amazon is not a sponsor or affiliated with this Award.
- Selection of Winners: Promotional prize winners will be selected based on entries received during the Promotional Period. The sponsor will utilize an Editorial Panel to vote on the best video submissions. Editorial Panel members are not eligible to participate in the Award. Entries will be ranked based on three (3) criteria:
- Presentation of Technical Content
- Quality of Video
Upon selecting a winner, the Sponsor will notify the winner via email. All potential winners will be notified via their email provided to the sponsor. Potential winners will have five (5) business days to respond after receiving initial prize notification or the prize may be forfeited and awarded to an alternate winner. Potential winners may be required to sign an affidavit of eligibility, a liability release, and a publicity release. If requested, these documents must be completed, signed, and returned within ten (10) business days from the date of issuance or the prize will be forfeited and may be awarded to an alternate winner. If prize or prize notification is returned as undeliverable or in the event of noncompliance with these Official Rules, prize will be forfeited and may be awarded to an alternate winner.
- General Prize Restrictions: No prize substitutions or transfer of prize permitted, except by the Sponsor. Import/Export taxes, VAT and country taxes on prizes are the sole responsibility of winners. Acceptance of a prize constitutes permission for the Sponsor and its designees to use winner’s name and likeness for advertising, promotional and other purposes in any and all media now and hereafter known without additional compensation unless prohibited by law. Winner acknowledges that neither Sponsor, Award Entities nor their directors, employees, or agents, have made nor are in any manner responsible or liable for any warranty, representation, or guarantee, express or implied, in fact or in law, relative to any prize, including but not limited to its quality, mechanical condition or fitness for a particular purpose. Any and all warranties and/or guarantees on a prize (if any) are subject to the respective manufacturers’ terms therefor, and winners agree to look solely to such manufacturers for any such warranty and/or guarantee.
11.Release, Publicity, and Privacy : By receipt of the Prize and/or, if requested, by signing an affidavit of eligibility and liability/publicity release, the Prize Winner consents to the use of his or her name, likeness, business name and address by Sponsor for advertising and promotional purposes, including but not limited to on Sponsor’s social media pages, without any additional compensation, except where prohibited. No entries will be returned. All entries become the property of Sponsor. The Prize Winner agrees to release and hold harmless Sponsor and its officers, directors, employees, affiliated companies, agents, successors and assigns from and against any claim or cause of action arising out of participation in the Award.
Sponsor assumes no responsibility for computer system, hardware, software or program malfunctions or other errors, failures, delayed computer transactions or network connections that are human or technical in nature, or for damaged, lost, late, illegible or misdirected entries; technical, hardware, software, electronic or telephone failures of any kind; lost or unavailable network connections; fraudulent, incomplete, garbled or delayed computer transmissions whether caused by Sponsor, the users, or by any of the equipment or programming associated with or utilized in this Award; or by any technical or human error that may occur in the processing of submissions or downloading, that may limit, delay or prevent an entrant’s ability to participate in the Award.
Sponsor reserves the right, in its sole discretion, to cancel or suspend this Award and award a prize from entries received up to the time of termination or suspension should virus, bugs or other causes beyond Sponsor’s control, unauthorized human intervention, malfunction, computer problems, phone line or network hardware or software malfunction, which, in the sole opinion of Sponsor, corrupt, compromise or materially affect the administration, fairness, security or proper play of the Award or proper submission of entries. Sponsor is not liable for any loss, injury or damage caused, whether directly or indirectly, in whole or in part, from downloading data or otherwise participating in this Award.
Representations and Warranties Regarding Entries: By submitting an Entry, you represent and warrant that your Entry does not and shall not comprise, contain, or describe, as determined in Sponsor’s sole discretion: (A) false statements or any misrepresentations of your affiliation with a person or entity; (B) personally identifying information about you or any other person; (C) statements or other content that is false, deceptive, misleading, scandalous, indecent, obscene, unlawful, defamatory, libelous, fraudulent, tortious, threatening, harassing, hateful, degrading, intimidating, or racially or ethnically offensive; (D) conduct that could be considered a criminal offense, could give rise to criminal or civil liability, or could violate any law; (E) any advertising, promotion or other solicitation, or any third party brand name or trademark; or (F) any virus, worm, Trojan horse, or other harmful code or component. By submitting an Entry, you represent and warrant that you own the full rights to the Entry and have obtained any and all necessary consents, permissions, approvals and licenses to submit the Entry and comply with all of these Official Rules, and that the submitted Entry is your sole original work, has not been previously published, released or distributed, and does not infringe any third-party rights or violate any laws or regulations.
12.Disputes: EACH ENTRANT AGREES THAT: (1) ANY AND ALL DISPUTES, CLAIMS, AND CAUSES OF ACTION ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THIS AWARD, OR ANY PRIZES AWARDED, SHALL BE RESOLVED INDIVIDUALLY, WITHOUT RESORTING TO ANY FORM OF CLASS ACTION, PURSUANT TO ARBITRATION CONDUCTED UNDER THE COMMERCIAL ARBITRATION RULES OF THE AMERICAN ARBITRATION ASSOCIATION THEN IN EFFECT, (2) ANY AND ALL CLAIMS, JUDGMENTS AND AWARDS SHALL BE LIMITED TO ACTUAL OUT-OF-POCKET COSTS INCURRED, INCLUDING COSTS ASSOCIATED WITH ENTERING THIS AWARD, BUT IN NO EVENT ATTORNEYS’ FEES; AND (3) UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES WILL ANY ENTRANT BE PERMITTED TO OBTAIN AWARDS FOR, AND ENTRANT HEREBY WAIVES ALL RIGHTS TO CLAIM, PUNITIVE, INCIDENTAL, AND CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, AND ANY OTHER DAMAGES, OTHER THAN FOR ACTUAL OUT-OF-POCKET EXPENSES, AND ANY AND ALL RIGHTS TO HAVE DAMAGES MULTIPLIED OR OTHERWISE INCREASED. ALL ISSUES AND QUESTIONS CONCERNING THE CONSTRUCTION, VALIDITY, INTERPRETATION AND ENFORCEABILITY OF THESE OFFICIAL RULES, OR THE RIGHTS AND OBLIGATIONS OF ENTRANT AND SPONSOR IN CONNECTION WITH THE AWARD, SHALL BE GOVERNED BY, AND CONSTRUED IN ACCORDANCE WITH, THE LAWS OF THE STATE OF NEW JERSEY, WITHOUT GIVING EFFECT TO ANY CHOICE OF LAW OR CONFLICT OF LAW, RULES OR PROVISIONS (WHETHER OF THE STATE OF NEW JERSEY OR ANY OTHER JURISDICTION) THAT WOULD CAUSE THE APPLICATION OF THE LAWS OF ANY JURISDICTION OTHER THAN THE STATE OF NEW JERSEY. SPONSOR IS NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY TYPOGRAPHICAL OR OTHER ERROR IN THE PRINTING OF THE OFFER OR ADMINISTRATION OF THE AWARD OR IN THE ANNOUNCEMENT OF THE PRIZES.
- Limitation of Liability: The Sponsor, Award Entities and their respective parents, affiliates, divisions, licensees, subsidiaries, and advertising and promotion agencies, and each of the foregoing entities’ respective employees, officers, directors, shareholders and agents (the “Released Parties”) are not responsible for incorrect or inaccurate transfer of entry information, human error, technical malfunction, lost/delayed data transmissions, omission, interruption, deletion, defect, line failures of any telephone network, computer equipment, software or any combination thereof, inability to access web sites, damage to a user’s computer system (hardware and/or software) due to participation in this Award or any other problem or error that may occur. By entering, participants agree to release and hold harmless the Released Parties from and against any and all claims, actions and/or liability for injuries, loss or damage of any kind arising from or in connection with participation in and/or liability for injuries, loss or damage of any kind, to person or property, arising from or in connection with participation in and/or entry into this Award, participation is any Award-related activity or use of any prize won. Entry materials that have been tampered with or altered are void. If for any reason this Award is not capable of running as planned, or if this Award or any website associated therewith (or any portion thereof) becomes corrupted or does not allow the proper playing of this Award and processing of entries per these rules, or if infection by computer virus, bugs, tampering, unauthorized intervention, affect the administration, security, fairness, integrity, or proper conduct of this Award, Sponsor reserves the right, at its sole discretion, to disqualify any individual implicated in such action, and/or to cancel, terminate, modify or suspend this Award or any portion thereof, or to amend these rules without notice. In the event of a dispute as to who submitted an online entry, the entry will be deemed submitted by the authorized account holder the email address submitted at the time of entry. “Authorized Account Holder” is defined as the person assigned to an email address by an Internet access provider, online service provider or other organization responsible for assigning email addresses for the domain associated with the email address in question. Any attempt by an entrant or any other individual to deliberately damage any web site or undermine the legitimate operation of the Award is a violation of criminal and civil laws and should such an attempt be made, the Sponsor reserves the right to seek damages and other remedies from any such person to the fullest extent permitted by law. This Award is governed by the laws of the State of New Jersey and all entrants hereby submit to the exclusive jurisdiction of federal or state courts located in the State of New Jersey for the resolution of all claims and disputes. Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, G+, YouTube, IEEE Xplore , and IEEE TV are not sponsors nor affiliated with this Award.
- Award Results and Official Rules: To obtain the identity of the prize winner and/or a copy of these Official Rules, send a self-addressed stamped envelope to Kimberly Rybczynski, IEEE, 445 Hoes Lane, Piscataway, NJ 08854-4141 USA.

We gratefully acknowledge support from the Simons Foundation, member institutions, and all contributors.
- Accessibility
- Status Information
- Ancillary Files (data, code, images)
Availability of submissions
- Category cross listing
- Endorsement
- Adding Journal Reference and DOI
- Text Overlap
- Metadata for Required and Optional Fields
- Submit a new version of a work
- Oversized Submissions
- Submit a Paper List for Conference Proceedings
- Creating tar and zip Files for Upload
- What is TeX
- Proxy / Third Party Submission
- Translations
- Version Availability
- Why Submit TeX?
- Withdraw / Retract a Submission
- Institutional Repository Interoperability
- Automated DOI and journal reference updates from publishers
- Submission schedule and cutoff time
- Content Moderation
- License and copyright
- Withdrawals
- Cross listing
- Non-English submissions
- Requiring TeX when possible
- Third party submission
- arXiv Usage Stats
Submission Guidelines
While submission to arXiv is free for authors, we do ask authors to carefully prepare their work according to these guidelines. This will improve discoverability of the work and reduce the likelihood of delays before announcement.
Submissions to arXiv should be topical and refereeable scientific contributions that follow accepted standards of scholarly communication.
- We only accept submissions from registered authors . If you are a new user or are submitting to a new category, you may be required to find endorsements .
- All submissions are subject to a moderation process that verifies material is appropriate and topical. Material that contains offensive language, non-scientific content, or is plagiarized may be removed.
- Authors must grant arXiv.org an irrevocable license to distribute the work.
- Authors must agree to the Submission Terms and Agreement .
- Authors are expected to self-submit. Submissions by a third party are only accepted under limited conditions. See instructions for third-party submissions and index submissions for conference proceedings.
- New submissions received by 14:00 (Eastern Daylight/Standard Time Zone) are generally made available at 20:00 (Eastern) based on the schedule for availability . Also see versions help pages .
Submission Preparation
- Formats for text submission
Formats for figures
- Policies for format requirements
File names and case sensitivity
- Inclusion of data sets and ancillary files (data, programs, etc.)
Title and abstract preparation
Verify and correct your submission, edit or replace your submission.
To submit an article, use the submit form or select "START NEW SUBMISSION" from your user page .
Formats for text of submission
Accepted submission formats (in order of preference):
- (La)TeX Markup Best Practices for Successful HTML Papers
- HTML with JPEG/PNG/GIF images
Our goal is to store articles in formats that are highly portable and stable over time. Currently, the best choice is TeX/LaTeX.
We do not accept dvi, PS, or PDF created from TeX/LaTeX source , and we do not accept scanned documents, regardless of format.
Accepted figure formats:
- PostScript (PS, EPS) — requires LaTeX processing
- JPEG, GIF, PNG or PDF figures — requires PDFLaTeX processing
We do not accept submissions with omitted figures, even if you provide links to view figures externally.
If you submit figures with your (La)TeX source, use standard macro packages (e.g., the graphics and graphicx packages) to have figures appear in the document. arXiv administration cannot provide help with TeX-related issues.
arXiv will accept only the following characters in file names:
a-z A-Z 0-9 _ + - . , =
File names that contain other characters (e.g., spaces, question marks, asterisks) will be rejected. These restrictions ensure maximum portability of the stored files and minimize archival risk.
File names and extensions are also case sensitive on our system. The file names Figure1.PDF and figure1.pdf are not the same. Whether your local system is case sensitive (e.g., Unix) or not (e.g., Windows) you must ensure that internal file references, such as LaTeX figure inclusion commands, match case exactly.
Inclusion of ancillary files
There are limited facilities for including data sets and ancillary files (data, programs, etc.) that are associated with articles submitted to arXiv. See separate instructions about including data sets and ancillary files.
See separate instructions for preparing the title and abstract for inclusion in metadata. This information is used on the abstract pages, in announcements, in RSS feeds, and to support searching.
Before you make the final "Submit Article" step in the submission process, be sure to carefully check the title and abstract (metadata) and the processed files, and correct any errors. Contact arXiv administrators for help.

Unsubmitting an article takes the article out of the processing queue, and announcement will be scheduled based on the later resubmission time. See the schedule of availability .
No additional versions are generated when edits are done before the submission is publicly announced.
The date stamp associated with the submission will be the time that the final "Submit Article" step is completed. Edits and final submission before 14:00 US Eastern Time (EDT/EST) Monday through Friday will not delay announcement. You may wish to check current local time .
We encourage authors to update and to make corrections to their articles. DO NOT make a new submission for a corrected article or for an erratum. Instead, replace the original submission.
For more information see our public submission availability page .
- Privacy Policy
- contact arXiv Click here to contact arXiv Contact
- subscribe to arXiv mailings Click here to subscribe Subscribe
- Report an issue Click here to report an issue with arXiv's documentation in github Report a documentation issue
- Web Accessibility Assistance
arXiv Operational Status Get status notifications via email or slack

Publish with IEEE Conferences
IEEE sponsors over 2,000 conferences and events that give technology professionals the opportunity to share innovations and interact one-on-one with the community. Publish with IEEE and join us in inspiring engineering solutions that make the world a better place.
Get Started
Learn about ieee conferences, author benefits, author tools, ieee policies.
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
9 Steps To Publish A Research Paper

Researchers and scholars undertake academic studies to advance knowledge in their respective fields of study. To this end, they also focus on getting their work published in high-impact and widely read journals. This helps them to highlight and disseminate their work, be known in their respective fields, and grow professionally in their careers.
However, the process of publishing a research paper can be challenging and time-consuming. It requires careful planning, attention to detail, and the ability to receive feedback constructively. In this blog, we outline nine steps to publish research papers successfully in high-impact journals and help researchers contribute to their fields of study.
9 Steps to Publish Research Papers Successfully
Publishing a well-written research paper can be confusing. To achieve a successful publication within a reasonable timeframe, researchers must grasp the intricacies of the publication process outlined below:
- Finalize your research topic: A contemporary research topic, reflecting current challenges and trends in your respective field of study, is an aspect that you can seriously consider while finalizing your topic.
- Choose the right journal and article type: It is crucial to identify early on the most appropriate journal for your research paper. This will save considerable time and effort and increase the likelihood of its acceptance. Discussing with peers and colleagues in the field who have authored and reviewed articles will undoubtedly be helpful. Review the aims, objectives, and scope of the journal and its area of specialization to assess if your research conforms to the necessary guidelines. Consider also the peer review process, the impact factor of the journal and the time taken to publish an article. Depending on the nature of your work, also decide on the type of article relevant to your work, which may be a completely original research paper, review paper or letter, rapid or short communication.
- Write, format, and refine your paper for submission: Even before starting to write the paper , go through the author guidelines and formatting style followed by the journal. This will make the writing process easier. Structure the article according to the type of article you are writing. Going through the published articles in the target journal will also help you in the process. A standard structure for a research paper needs to have the title, abstract, keywords, introduction, methods, results, discussion, conclusion, acknowledgements, and references.
- Prepare required documents like a cover letter and declaration of conflicts of interest: When you submit your manuscript, a cover letter is a must. It should highlight the central theme of your paper and the significance of your study. Further, clearly state that you comply with all basic requirements and declare any or no potential conflict of interest that could arise.
- Check that your work is complete and submission-ready. Read your work several times to identify any gaps and ambiguities. Review your work for innovativeness, rigour, and contribution to topical issues in the field. Seek feedback from supervisors and peers.
- Submit your manuscript to your chosen journal : Re-check the paper to ensure that there are no errors in grammar, wording, sentence construction, or formatting and that there is consistency in formatting. Professional proofreading is important in this regard. Check if there is a logical flow of arguments and that any images or graphs used are easy to understand and clear. Ensure that all co-authors have reviewed and approved the paper for submission.
- Tackle post-submission revisions (including peer review comments): Nearly all papers submitted to journals undergo a peer review process, which ensures the quality of the papers published in the journal. The reviewers may provide comments and suggestions to strengthen your paper. Review the reviewer’s comments carefully and make sure to respond to each one. Aim to send your responses using the timeline given by the journal editors.
- Revise and resubmit the manuscript (responding to peer review comments): It is essential to approach the comments as constructive criticism. Remember to be polite and respectful in your response. Make sure to provide a detailed response on how you have addressed each comment by the reviewers. If you do not agree with any comment, always respond professionally with care; avoid getting into a personal attack. Give a detailed explanation of your arguments. Resubmit the revised manuscript highlighting all the modifications carried out based on the comments by the reviewers. Along with the manuscript, provide a letter stating the author’s responses and that they have addressed the comments by the editor and the reviewers.
- Get accepted for journal publication: Once the revisions are made to the satisfaction of the editor and reviewers, the paper is accepted for publication. If your paper is rejected, make the necessary revisions and send it to the journal of your second choice.
Are you preparing to publish a research paper in a high-impact journal? Get your draft vetted by the most-trusted AI academic writing assistant. Start writing with Paperpal today !
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 10-Point Manuscript Checklist to Ensure High-Quality Journal Submissions
- Research Paper Writing: A 15-Point Academic Writing Checklist
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)
- How to Write a Conclusion for Research Papers (with Examples)
Grammarly Review: Features, Pricing, and Free Alternatives
What are the benefits of generative ai for academic writing, you may also like, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how....
Loading metrics
Open Access
Decolonising global health research: Shifting power for transformative change
Roles Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliations United Nations University-International Institute for Global Health, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, Department of Community and Family Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Jaffna, Jaffna, Sri Lanka
Roles Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation United Nations University-International Institute for Global Health, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Roles Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
- Ramya Kumar,
- Rajat Khosla,
- David McCoy

Published: April 24, 2024
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgph.0003141
- Reader Comments
Recent debates on decolonizing global health have spurred interest in addressing the power asymmetries and knowledge hierarchies that sustain colonial ideas and relationships in global health research. This paper applies three intersecting dimensions of colonialism (colonialism within global health; colonisation of global health; and colonialism through global health) to develop a broader and more structural understanding of the policies and actions needed to decolonise global health research. It argues that existing guidelines and checklists designed to make global health research more equitable do not adequately address the underlying power asymmetries and biases that prevail across the global health research ecosystem. Beyond encouraging fairer partnerships within individual research projects, this paper calls for more emphasis on shifting the balance of decision-making power, redistributing resources, and holding research funders and other power-holders accountable to the places and peoples involved in and impacted by global health research.
Citation: Kumar R, Khosla R, McCoy D (2024) Decolonising global health research: Shifting power for transformative change. PLOS Glob Public Health 4(4): e0003141. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgph.0003141
Editor: Ananya Banerjee, McGill University, CANADA
Copyright: © 2024 Kumar et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
1. Introduction
Inequity within international research partnerships has troubled the field of global health for decades. In particular, power asymmetries between actors from wealthier and historically-privileged countries and their counterparts in the Global South (GS) have led to paternalistic ways of working, unequal sharing of resources, skewed distribution of benefits, and limited commitments to capacity strengthening [ 1 ]. Recent debates on decolonizing global health have brought renewed attention to addressing these problems in global health research. In addition to highlighting equity concerns, these discussions draw attention to the epistemic injustice and “white saviour” mentalities that underpin research collaborations [ 2 – 8 ].
Recognising that power asymmetries in global health are produced by both historical and current exploitation and resource extraction, our approach to decolonizing global health involves three intersecting dimensions: 1) colonialism within global health; 2) colonisation of global health; and 3) colonialism through global health [ 9 ]. The first dimension speaks to power differentials and resource disparities between different actors within the field of global health. The second deals with the dominance of certain powerful actors and vested interests over the overall complex of global health structures, systems, policies and practices. The third dimension refers to exploitative and extractive practices that occur through the health sector [ 9 ].
This paper uses this framework of three dimensions to arrive at a broader understanding of the scope of policies and actions needed to decolonise global health research. We begin by briefly outlining persisting inequities within research partnerships- already addressed by a large body of literature. Next, we draw attention to issues that are underexplored, specifically who controls the agenda of global health research (i.e., colonisation of global health research), and who benefits from such research (i.e., colonialism through global health research) ( Fig 1 ). We then present a brief review of recent guidelines and checklists that seek to decolonize global health research and/or centre the needs and aspirations of the GS in research, revealing an emphasis on addressing inequity within research partnerships. We end by recommending policies and actions that would decolonize the field of global health research in an effective and comprehensive manner.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgph.0003141.g001
This paper employs the terminology “Global North” (GN) and “Global South” (GS) to reflect asymmetries in power and access to resources between not just countries but also population groups. This terminology only partly corresponds to the classification of countries according to per capita gross national income, i.e., low-income, middle-income, and high-income countries (LIC, MIC, and HIC) [ 10 ]. However, where we quote from sources that explicitly refer to LICs, MICs or HICs, these terms are retained. We borrow from Garcia-Basteiro and Abimbola [ 11 ] to define global health research as research that seeks to address health inequity within and across countries, aiming to improve health in what they call “low-resource settings” described as regions weighed down by financial constraints, suboptimal service delivery, underdeveloped physical and knowledge infrastructure, historical, political and sociocultural contexts/specificities, and geographical, environmental and human resource limitations.
2. Colonialism within global health research: Who leads?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2020, of the USD 37 billion spent worldwide on ‘biomedical research’, 98.7% went to HICs [ 12 ]. Perhaps more reflective of the global health research landscape, in 2021, 82% of the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation’s (BMGF) grant funding went to HIC recipients [ 13 ]. This unequal distribution of funding is striking when one considers that much global health research is carried out in GS settings.
The inequitable global health research funding patterns reflect not only the wider socio-economic disparity between GN and GS, but also the biases within the global health research system. For example, grant calls, either explicitly or through eligibility criteria or capacity requirements, favour GN-based institutions [ 14 ] with research funding agencies of key donor countries often requiring principal investigators (PI) to be based in their country or compel PIs from the GS to partner with a researcher based in the donor country [ 15 , 16 ]. Eligibility criteria based on geographic location and experience may further restrict applications from GS-based researchers [ 17 ]. GN-based researchers are also better able to navigate the funding terrain with their training, networks and resources [ 18 , 19 ].
Although most global health funding agencies require GN-based researchers to “collaborate” with local “partners,” the terms of collaboration are usually set by the former who typically conceptualise the research before inviting others onboard [ 20 ]. This gives GS-based researchers limited influence over the research, despite their expertise and familiarity with the context [ 7 , 21 , 22 ], thus supporting what has been called “parachute” research, where GN-based collaborators fly in for weeks at a time for onsite “supervision” [ 23 , 24 ]. As grant cycles are usually short, the urgency to meet deadlines results in lopsided decision-making, hasty administrative approvals and, at times, the undermining of local administrative and ethics procedures [ 8 ].
Much grant funding goes towards the salaries of GN-based researchers with substantially less dedicated to research systems and capacity strengthening in GS settings [ 2 , 14 ]. This lack of long-term commitment to the development of GS-based institutions sustains the status quo [ 25 ]. Meanwhile, extant capacity strengthening initiatives are often uni-directional and paternalistic, involving assumptions about what competencies GS collaborators may lack [ 26 ].
Inequity is further reinforced by authorship patterns that are biased towards GN-based researchers [ 27 , 28 ]. Authorship guidelines of prominent journals systematically exclude non-native English writers [ 29 ] by giving weight to written contributions over field work [ 30 ]. Representation at conferences and symposia is similarly unequal, although research collaborations do enable participation for some GS-based researchers. Even so, visa and other barriers challenge researchers from travelling to meeting destinations [ 31 ].
3. Colonisation of global health research: Who controls?
Global health funding agencies wield significant power in defining global health problems and the approaches taken to addressing them [ 7 , 32 ]. Under the current system, researchers based at universities and other research institutions respond to grant calls, crafting their research to fit with the agendas and ideologies of global health funders rather than vice versa [ 33 ].
Extreme wealth concentration under neoliberal globalization and the rise of ‘philanthrocapitalism’ by which global health problems are framed as market opportunities, has seen a shift from public to private financing in global health [ 34 , 35 ]. However, private actors have interests and priorities that may be at odds with the public interest or with achieving equity in health. For instance, the shift from publicly-funded to industry-funded research has distorted scientific evidence on infant formula with detrimental effects on infant and child health [ 36 ]. Moreover, the funding decisions of corporations and foundations are ultimately approved by a handful of largely GN-based board members, who are not subjected to any independent mechanisms of accountability for their funding decisions or their impact on people affected by these decisions [ 32 , 37 ]. Although some funders have recently instituted measures to address diversity within their leadership [ 13 , 38 ], such change will not be transformative without redistributing power and resources, and genuine efforts to improve accountability [ 39 ].
Research funders favour specific thematic areas, not always based on the health problems prevailing in specific GS settings [ 19 , 40 ]. They tend to promote technology-based solutions and favour innovation and entrepreneurship in projects that yield quick and quantifiable results [ 41 ]. The preference for short-term impact over longer-term improvements in health results in grant proposals that centre “magic bullets” (e.g., vaccines, medicines, bed nets, mobile apps) rather than systems building, local capacity strengthening and unblocking the social and political barriers to the scale up of proven and more sustainable alternatives [ 42 , 43 ].
Academic programmes in global health continue to be characterised by what has been called a “white saviour complex” or a depoliticized, patronizing and charity-based approach shaped, in part, by a wider aid industry [ 44 , 45 ]. Global health curricula remain largely disconnected from the many realities and locales of the GS, both in geography and lived experience. Dominant Eurocentric epistemologies, which are embraced and propagated by powerful global health institutions, are usually given primacy in research training, even as heterodox methodologies that interrogate power and inequality are marginalized [ 45 , 46 ].
The inability of countries of the GS to weigh in on the global health research agenda and define their own priorities is perpetuated by their minimal contributions to research funding [ 25 , 47 , 48 ]. While domestic investment is critical to shift the balance of power, debt-ridden governments of lower-income countries may have limited leeway with their health and R&D budgets owing to fiscal constraints [ 19 ]. For these countries, HIC-driven global health research collaborations may present a welcome source of foreign currency. Too often however, external funding for health research takes place with little coordination among granting agencies [ 49 , 50 ], facilitating duplication, and making impact assessment difficult.
4. Colonialism through global health research: Who benefits?
The asymmetric global health research funding structure also gives powerful states and private actors opportunities to craft research in the GS in ways that they benefit from financially or economically. These benefits are primarily driven by the commercialization of research and publishing, supported by imperatives to expand markets, unfair intellectual property rights (IPR) regimes, and predatory academic journals.
Arguably, the biggest profits are made by commercial entities that hold patents for global health technologies often tested through research carried out in GS settings. Such research aids market expansion for medicines, vaccines, diagnostic tests, mobile devices, etc. benefitting big pharma, biotechnology, and big tech companies, while doing little to strengthen public health infrastructure and services or reduce dependency [ 19 , 41 ]. Indeed, some private foundations are routing a growing proportion of their tax-subsidised grants to private for-profit organisations, in both GN and GS settings [ 37 , 51 ].
Current IPR regimes which provide private companies with extensive monopoly rights over new and modified technologies despite much basic research being funded publicly is one aspect of an R&D ecosystem biased in favour of private financial interests at the expense of public health. This was seen with the billions of dollars of private profits generated from COVID-19 vaccines despite vast amounts of public and charitable funds that went into their development [ 52 ].
The unequal benefits accrued through authorship in global health journals have been widely studied [ 27 , 28 ] but less is known about their commercial dimensions. The revenue of academic publishers is estimated to be about USD 19 billion annually, where about half the market share is controlled by five transnational companies, with Elsevier alone accounting for 16% of the market share, with profit margins in the order of 40 per cent [ 53 ]. These corporations are all headquartered in the GN and maximise profits through article processing charges (APCs), subscriptions, and the uncompensated labour of authors and peer-reviewers. Ever-increasing APCs are required to publish ‘open access’ in prestigious journals, implemented in the name of equity, but barring most GS-based researchers through stringent waiver criteria [ 54 ]. Global spending on APCs alone is estimated to exceed USD 2 billion annually [ 55 ]. Academic journals are, in turn, linked to bibliometric platforms that track the ‘impact’ of research communications, which feed into commercialised university ranking systems [ 56 ]. With research funding and citations in ‘high-impact’ journals being key elements of performance indices, the top-twenty universities, as ranked by Academic Ranking of World Universities and Time Higher Education, are all located in the GN [ 57 ].
The current system of global health education supports extraction of wealth and other resources from GS to GN. A recent analysis of masters in global health degrees revealed that 95% of them are based in HICs, costing on average USD 37,732 in tuition [ 58 ]. Given the location and cost of global health postgraduate programmes, their graduates, including those from GS settings, are likely to be drawn to work with global or GN-based institutions both to repay the debt incurred and because of the lack of well-remunerated positions back home [ 58 ]. Ultimately, career trajectories in global health are skewed towards the GN and not “low-resource settings” where global health work and resources are much needed [ 23 ].
In sum, whether in terms of leadership, control or benefits, GN-based actors and institutions are privileged within the broader global health research ecosystem, often to the detriment of researchers, institutions and ‘beneficiaries’ in GS settings. It appears that global health research supports a renewed form of extractivism, where resources in the GS, including funding, knowledge and researchers, are drawn to the GN. In the next section, we examine whether and to what extent recent guidelines on decolonising global health research address the three intersecting dimensions of colonialism in global health research.
5. Recent guidelines that aim to decolonise global health research
We searched the literature for tools that either explicitly or in their framing seek to decolonise global health research and/or centre the needs and aspirations of the GS in research. As searches on PubMed and Scopus [(“decol*” OR “colonial*”) AND “global health” AND “research” AND (manual OR guideline OR checklist)] yielded less than 10 publications, we also searched Google Scholar, Google, and pursued reference lists of identified publications. Criteria for inclusion were: addressing equity in global health research with reference to colonialism or explicit attention to making research fairer for peoples and institutions in the GS; including a set of standards or guidelines; targeting researchers, research institutions or funders; published within the five-year period of 2019 to 2023. We identified eight tools that fit our criteria as described below.
Hodson et al. [ 40 ] offer a set of “practical measures” for global health researchers, underpinned by four principles: “1) seek locally derived and relevant solutions to global health issues, 2) create paired collaborations between HIC and LMIC institutions at all levels of training, 3) provide funding for both HIC and LMIC team members, [and] 4) assign clear roles and responsibilities to value, leverage, and share the strengths of all team members.” This guideline addresses specific challenges experienced in GS settings by advocating for: educating all team members on global health history; early engagement of GN-based researchers with local administrations; capacity strengthening to support independent research in GS settings; protected research time for all team members; preventing GS-based researchers being drawn away from regular work; and ensuring knowledge translation to local communities, among other measures. Despite the commitment to long-term capacity strengthening, the guideline focuses primarily on research processes within partnerships.
Kumar et al. [ 26 ] propose a set of individual and institutional level actions to advance equity in global health research. Those at the individual level include questioning “notions of absolute scientific objectivity” (p.146), adopting a decolonial approach towards global health concepts and implicit hierarchies, cultivating respect and humility, promoting fairness at all levels (including at the level of global health leadership), and going beyond ‘equality’ to recognize ‘equity’ within collaborations. At the institutional level, they support decentring the GN in global health efforts (including the location of centres of knowledge), promoting solidarity, investing in researchers from LMICs, bi-directional capacity strengthening, evaluating partnerships by “measures of fairness” and “ethical and culturally responsive engagement,” and correcting “colonising and unethical practices” (p.146). While some of these actions aim to rectify power asymmetries well beyond research partnerships, they do not include specific guidance on implementation.
Embracing a feminist decolonial approach, Singh et al. [ 59 ] offer a guideline for researchers working in situations of forced displacement that centres participant agency, voice, and experience; it aims to address power hierarchies through a set of recommendations targeting various stages of research. The guideline demands: consideration to “political, social, economic, and historical contexts and power hierarchies of the research setting” (p.561); involving marginalised groups in the research design; reflecting on how coloniality and gendered power relations may be reinforced during data collection; an intersectional analysis of gendered power relations; collaboration in analysis and knowledge dissemination; and using research to “challenge unjust systems and policies and deliver gender transformative and equitable programmes” (p.561). Although the guideline aims to reconfigure power within individual research projects, it offers no direction on how to redistribute power.
Rashid [ 8 ] offers guidance for researchers in LICs to “[navigate] the violent process of decolonisation in global health research.” The guideline includes a list of dos and don’ts to help researchers in LICs contend with power asymmetries in international research collaborations. They recommend carefully reviewing agreements, clarifying systems of reporting and accountability, insisting on inclusion in communications with funders, meticulous documentation, boosting one’s profile, expanding networks, and building solidarity. However, this guideline focuses on change at the individual level on the part of researchers in GS settings rather than systemic change.
The TRUST Code–“A Global Code of Conduct for Equitable Research Partnerships” is based on the core values of fairness, respect, care, and honesty [ 60 ]. Compiled by a team with wide representation from the GS, the TRUST Code consists of 23 articles. Apart from conventional ethical standards, the tool emphasises: bona fide involvement of local communities in research, fairness in the transfer and ownership of data and biological materials, and fair compensation of local collaborators. It emphasises cultural acceptability, community assent, respect for local ethics review and giving consideration to the impact of research on local human resources, animal welfare, and the environment. It calls for clarity on roles, responsibilities, capacity strengthening, transparency, and integrity of the research process. Although broadly framed around justice for communities and researchers in the GS, the tool primarily concentrates on making individual research partnerships more equitable.
The Research for Health Justice Framework proposed by Pratt and colleagues [ 61 ] offers two sets of guidelines, one for health researchers and another for granting agencies. Developed through an iterative process and fine-tuned through case studies in GS settings, the guidelines emphasize equity, justice, and inclusion, with accompanying explanations on implementation. The guideline for researchers addresses: selection of the research population and research problem, research capacity development, delivery of ancillary care, and knowledge translation practices. With respect to granting agencies, it asks that they prioritise the health concerns of the worst-off, promote ownership of the research agenda by LMIC researchers and support projects that seek to advance equity within healthcare systems, atop measures to support equitable research practices. While this framework is comprehensive in scope, the guidelines are still largely limited to the research process and do not explicitly seek to transform the global health granting system and the power asymmetries within it.
Focusing specifically on global health research funding, Charani et al. [ 19 ] outline eight areas of action for funders: 1) developing situational awareness, including an understanding of institutional dynamics and who benefits from grants; 2) formulating a mission statement that pledges equity in research; 3) equitable allocation of funds to cover differential needs of HIC- and LMIC-based researchers; 4) funding structures that encourage local ownership and leadership; 5) bi-directional capacity strengthening that enables all partners to engage with funders; 6) diversity and inclusion across the grant cycle, including in design, knowledge dissemination, access to training etc.; 7) knowledge generation, including methodologies, frameworks, tools and clarity on data ownership; and 8) reflection and feedback involving HIC and LMIC researchers on equal terms. Encouraging funders to include specific requirements for grant recipients to comply with participatory approaches and fair sharing of resources and benefits, the guideline also speaks to what should be funded, who should be funded and how. Moreover, among its recommendations—albeit with no details provided—are “a transparent process for tracking the progress of funding” and “a code of ethics for global health funders”.
The Global Health Decolonisation Movement Africa [ 17 ], self-described as a collective of African citizens, has published a guideline called, Pragmatic Approaches to Decolonising Global Health in Africa . What is unique about this guideline is that it addresses multiple “stakeholders” in HICs, including individual practitioners, funding agencies, academic and training institutions, scientific publishers, and event conveners and organisers, among others. The guideline broadly seeks to address racism against Africans within global health, and promotes African leadership and self-determination. The section for funders calls for diversifying grant review panels, rejecting “parachute” proposals, and removing requirements for researchers based in Africa to collaborate with HIC-based institutions. For academic and training institutions, the guideline recommends diversifying leadership and recruitment practices, and addressing coloniality in global health curricula. And for scientific journals, it demands diversifying authorship and peer-review panels. While this guideline emphasises diversity, equity, and inclusion, it remains constrained by the limitations of the current system of global health research funding.
In sum, there is considerable variation in guidance on improving equity in research partnerships and decolonising global health research. All reviewed sources strive to make the research process fairer and rectify power asymmetries through diversity, equity and inclusion measures, but only some engage with historical imbalances in power, interrogate dominant knowledge paradigms, centre the concerns of marginalized groups, and create space for self-determination. The guidelines for funders go beyond research partnerships to address who and what is funded. However, for the most part, these guidelines neglect the wider contextual factors that shape agenda-setting in global health research, as well as the actors and institutions that control and benefit from them.
6. Shifting the balance of power in global health research: Going forward
In this section, we draw on the three intersecting dimensions of colonialism in global health research to present seven action areas that we call for to mitigate inequitable, exploitative and extractive arrangements in global health research ( Fig 2 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgph.0003141.g002
First, and most fundamentally, we call for a critical examination of the epistemological and ideological underpinnings of global health research. While current debates engage to some extent with the marginalization of indigenous perspectives, few question the dominance of positivist approaches and the biomedical paradigm. Guided by a biased hierarchy of evidence that favours quantitative assessments, global health research remains over-occupied with testing the efficacy of discrete, downstream and often clinical technologies and interventions, taking attention away from the social and structural determinants of health, which are more challenging to measure [ 41 , 43 , 62 ]. Shaped by neoliberal ideology, understandings of health and healthcare have evolved from collectivist to individualist interpretations, giving way to economistic evaluations based on assumptions that resource constraints in low-income settings are inevitable [ 63 ]. Global health education could challenge dominant paradigms and mainstream approaches that advance social justice and equity in health [ 64 ].
Second, we need a better and more detailed analysis of the overall pattern and performance of research funding: where it comes from, where it goes, how it is spent, and its impact. A few of the guidelines reviewed earlier do address the global health research funding system. For instance, Charani et al. [ 19 ] recommend that funding agencies self-monitor whom they fund and also call for a code of ethics for funders, while the Global Health Decolonisation Movement Africa [ 17 ] asks funders to remove requirements for researchers based in Africa to collaborate with GN-based institutions. Even so, these measures remain couched within the current structure and system of grant funding that lacks transparency and leaves power concentrated in the hands of largely GN-based donors. The problematic norm of donors funding favoured research areas over those that are identified locally remains largely unchallenged. At the very least, information should be available by funder, recipient, research area, and research setting, possibly through a centralized system that requires funders to provide information on their funding practices. Auditing such data should enable analysis of not only where research funding comes from and who receives it but also its impact.
Third, efforts to address power asymmetries in global health research must compel reform at the highest levels of global governance. By virtue of their funding contributions, powerful states, their bilateral agencies, private foundations, and corporate actors, among others, shape the global health research agenda. Bilateral agencies tend to push foreign policy and other domestic interests [ 65 , 66 ], while corporate actors are driven by profit, and many private foundations by the creed that the private sector can more effectively tackle intractable global health problems [ 67 ]. Bilateral and multilateral agencies should be held accountable for what they fund with taxpayer contributions, while private funders—who are primarily accountable to their boards—must be appropriately regulated and prevented from having undue influence on the shaping of research priorities [ 68 , 69 ].
A comprehensive guideline for research funders that promotes fairer distribution of resources and improved accountability is needed. Such a guideline could incorporate the measures proposed by Charani et al. [ 19 ], Pratt et al. [ 61 ] and the Global Health Decolonisation Movement Africa [ 17 ]. An international agreement, akin to the Declaration of Helsinki [ 70 ]—the World Medical Association’s ethical principles for medical research—could encourage and eventually normalise funding of equity-oriented research and local ownership. Decision-making on funding priorities must be shared with the GS, not just with governments but also with researchers, institutions, and the beneficiaries of research [ 26 ].
Fourth, national research systems should be supported and strengthened with in-built mechanisms of accountability. While there are calls for LMIC governments to invest more in R&D [ 25 ], the onus for change cannot be placed on these countries alone. Rather donors must also commit to investing in local research infrastructure, human resources, and higher education systems, all key to building research capacities. Meanwhile, government allocations for health research in GS settings should be guided by appropriate needs assessments and strategic plans to strengthen national research capacity [ 71 ] as once encouraged by the Commission on Health Research for Development (COHRED), an independent global initiative that supported research for heath and development in LMICs [ 72 ]. Systemic investments in research capacity strengthening with long-term budget commitments and harmonised mechanisms should be established [ 73 ] to replace the current piecemeal manner in which health research is conducted, often subject to the whims of external funders. Bi-directional scholarships for postgraduate training in research, with service requirements in GS settings, could target specific human resource gaps. Fifth, a global fund for research [ 74 ], guided by a multilateral framework that pools donor funds and channels them based on national health priorities may help to harmonise external funding, avoid duplication, and enable greater transparency and accountability.
Sixth, given acute human resource constraints in many GS countries, brain drain must be stemmed. The WHO Global Code of Practice on the International Recruitment of Health Personnel [ 75 ] provides a multilateral framework but fails to hold the GN to account for their unethical recruitment practices. Instead, the Code focuses on the rights of migrating health workers and places the onus on ‘developing countries’ to retain them. It does not recognize the vast amounts of (often public) resources invested in health worker training in GS settings, nor does it recommend compensation to source countries for this training. Academic global health programmes should re-orient their curricula [ 76 ] so that the primary career pathways for global health practitioners are viewed to be in GS settings.
Lastly, interventions to promote fairer distribution of benefits should look beyond authorship and academic credit, to address extractivist practices within the research industry that impede access to knowledge and technologies in the GS. The current IPR regime upholds patent protection, allowing big pharma to control product pricing and restrict market entry of generic manufacturers who could drive down the cost of medicines and other health products [ 77 , 78 ]. IPR regimes need to be revised to enhance fairness in the distribution of the benefits of science rather than support industry benefits and profit over public health.
In this paper, we applied three intersecting dimensions (colonialism within global health; colonisation of global health; and colonialism through global health) to develop a broader and more structural understanding of the policies and actions needed to decolonise global health research. We highlighted the tendency of existing guidelines that seek to make research partnerships more equitable and less colonial, to target the behaviour of researchers and research institutions within the boundaries of individual research projects. Following such guidance should result in better and more appropriate global health research. However, efforts to decolonise global health research should go beyond addressing equity within research partnerships to reconfiguring power arrangements within the global health research ecosystem. This means re-orienting research along social justice and equity lines, building research capacities in GS settings, and moving away from the existing donor-driven model.
Of critical concern is the prevailing system of research funding that functions with little transparency or downward accountability. Data should be made available to scrutinize and evaluate the funding processes of research funders and the appropriateness and impact of funding patterns and practices. It would be important to examine not just the specific outputs and outcomes of individual grant programmes and research projects, but also the impact of the entire global health research portfolio on the overall functioning of health research systems at global and national levels and, in particular, how research outputs contribute towards advancing health equity. Quick fixes and half-hearted measures would simply not work. Time is now for the global health community to come together and demand a complete overhaul of the competitive global health research funding system, and its replacement or accompaniment with a more strategic and publicly-driven pooling and harmonised allocation of resources aimed at correcting the many deep and structural inequalities across the global health research ecosystem. This would also require fostering equity-oriented research approaches, grounded in local ownership, with systems of accountability built in.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Emer Breen, Tiffany Nassiri-Ansari, and Emma Rhule, for helpful feedback on earlier versions of the paper.
- View Article
- PubMed/NCBI
- Google Scholar
- 10. World Bank Group [Internet]. World Bank country and lending groups; n.d. [cited 2023 Sept 27]. https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups
- 12. World Health Organization [Internet]. Investments on grants for biomedical research by funder, type of grant, health category and recipient; 2023 [cited 2023 Sept 27]. https://www.who.int/observatories/global-observatory-on-health-research-and-development/monitoring/investments-on-grants-for-biomedical-research-by-funder-type-of-grant-health-category-and-recipient
- 13. Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation [Internet]. DEI progress report 2021; n.d. [cited 2023 Sept 27]. https://docs.gatesfoundation.org/documents/bill_and_melinda_gates_foundation_2021_dei_progress_report.pdf
- 15. National Institutes of Health [Internet]. NIH global health funding; 2023 [cited 2023 Sept 27]. https://www.fic.nih.gov/Funding/Pages/NIH-funding-opportunities.aspx
- 16. National Institute for Health and Care Research [Internet]. Eligibility; 2023 [cited 2023 Sept 27]. https://www.nihr.ac.uk/researchers/i-need-help-funding-my-research/eligibility/
- 17. Global Health Decolonisation Movement Africa [Internet]. Pragmatic approaches to decolonizing global health in Africa; 2021 [cited 2023 Sept 27]. https://ghdmafrica.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/GHDM_brochure_web.pdf
- 30. International Committee of Medical Journal Editors ICJME. Defining the Role of Authors and Contributors; 2023 [cited 2023 Sept 27]. https://www.icmje.org/recommendations/browse/roles-and-responsibilities/defining-the-role-of-authors-and-contributors.html
- 32. Rushton S, Williams OD. Private actors in global health governance. In: Rushton S, Williams OD, editors. Partnerships and foundations in global health governance. Hampshire: Palgrave MacMillan; 2011. pp.1–25.
- 34. McCoy D, McGoey L. Global health and the Gates Foundation—in perspective. In: Rushton S, Williams OD, editors. Partnerships and foundations in global health governance. Hampshire: Palgrave MacMillan; 2011. pp.143–163.
- 35. Wilson J. Philanthrocapitalism and global health. In: Benatar S, Brock G, editors. Global health: ethical challenges. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2021. pp.416–428.
- 38. Wellcome Trust [Internet]. Diversity and inclusion: helping more ideas thrive; n.d. [cited 2023 Sept 28]. https://wellcome.org/what-we-do/diversity-and-inclusion
- 51. Breen E, Kumar, R [Internet]. Private foundations and their global health grant-making patterns: a rapid analysis of the Rockefeller Foundation, Wellcome Trust, and Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation; 2023 [cited 2024 March 29]. https://www.globalpolicy.org/en/publication/private-foundations-and-their-global-health-grant-making-patterns
- 56. Chen G, Chan L. University rankings and governance by metrics and algorithms. In: Hazelkorn E, editor. Research handbook on university rankings: theory, methodology, influence and impact. Cheltenham: Edward Elgar; 2021. pp. 424–441.
- 57. Nassir-Ansari T, McCoy D. World-class universities? Interrogating the biases and coloniality of global university rankings [Internet]. Kuala Lumpur: United Nations University-International Institute for Global Health; 2023 [cited 2023 Sept 27]. https://collections.unu.edu/eserv/UNU:9082/UNI-Ranking-paper_February-2023.pdf
- 60. TRUST (2018). The TRUST Code–A global code of conduct for equitable research partnerships. https://www.globalcodeofconduct.org/the-code/
- 63. Adams V. Metrics: what counts in global health. Durham: Duke University Press; 2016.
- 65. Oxfam. Sick development: how rich-country government and World Bank funding to for-profit private hospitals causes harm, and why it should be stopped; 2023 [cited 2023 Sept 28]. https://oxfamilibrary.openrepository.com/bitstream/handle/10546/621529/bp-sick-development-funding-for-profit-private-hospitals-260623-en.pdf?sequence=14
- 72. Commission on Health Research for Development. Health research: essential link to equity in development; 1990 [cited 2023 Sept 28]. http://www.cohred.org/downloads/open_archive/ComReports_0.pdf
- 73. WHO Council on the Economics of Health for All [Internet]. Health for all: transforming economies to deliver what matters: Final report; 2023 [cited 2023 Sept 28]. https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/council-on-the-economics-of-health-for-all/council-eh4a_finalreport_web.pdf?sfvrsn=a6505c22_5&download=true
- 75. WHO. WHO Global Code of Practice on the International Recruitment of Health Personnel; 2010 [cited 2023 Sept 28]. https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/health-workforce/migration-code/code_en.pdf?sfvrsn=367f7d35_7&download=true

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
2. Prepare your paper for submission. Download our get published quick guide (opens in new tab/window), which outlines the essential steps in preparing a paper.(This is also available in Chinese (opens in new tab/window)).It is very important that you stick to the specific "guide for authors" of the journal to which you are submitting.
When creating and submitting digital files, please follow the guidelines below. Failure to do so, or to adhere to the following guidelines, can significantly delay publication of your work ...
A systematic review paper, as defined by The Cochrane Collaboration, is a review of a clearly formulated question that uses explicit, systematic methods to identify, select, and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. These reviews differ substantially from ...
You can also choose to submit a brief, peer-reviewed data article. Your data article will be published in the dedicated, open access journal Data in Brief and will be indexed, as well as linked, with your original research article. Be sure to cite your research data in your article. This ensures you receive credit for your work, while making ...
Research Article: reports the results of original primary research, including quantitative and qualitative studies, ... Recommend 2-5 Academic Editors from the Editorial Board who you think are qualified to handle the submission. New species. If the paper describes a new taxon, provide its name.
This guide outlines key points for preparing primary research manuscripts for submission to Nature. ... Note that editors do not ensure that the paper is properly anonymized; that is the authors ...
Submitting your paper. The Instructions for Contributors document for each journal will explain the process for submitting your paper to that particular title, including guidance on additional information you should include alongside your manuscript. A growing proportion of our journals now use an online submission system - in most cases ...
Once you think your manuscript is ready for submission, the next important step is to read the aims and scope of the journals in your target research area. Doing so will improve the chances of having your manuscript accepted for publishing. Submit a cover letter with the manuscript. Never underestimate the importance of a cover letter addressed ...
The sections below provide essential information for authors and we recommend that you take the time to read them before submitting a contribution to Nature. These instructions refer to Articles ...
You can submit to most Elsevier journals using our online systems. The system you use will depend on the journal to which you submit. You can access the relevant submission system via the "submit your paper" link on the Elsevier.com journal homepage of your chosen journal. Alternatively, if you have been invited to submit to a journal, follow ...
It will give your article additional visibility. Our submission systems will offer the option to include your funding source in a standardized way. In most cases you will be able to choose your funder from the given list. Otherwise, please add it manually. The funding information will be published as searchable meta-data for the accepted article.
When submitting your article or your article revisions to an Elsevier journal, you'll find solutions to share your research data with your article directly within the submission system. For example, you can upload your research data to Mendeley Data ( opens in new tab/window ) , link to research data hosted in repositories, or co-submit a data ...
Research Reports describe the results of original research of exceptional importance. The preferred length of these articles is 6 pages, but PNAS allows articles up to a maximum of 12 pages. A standard 6-page article is approximately 4,000 words, 50 references, and 4 medium-size graphical elements (i.e., figures and tables).
Submit unassembled reads of SARS-CoV-2 with BioProject, BioSample, metadata and NGS files. GEO accepts raw data, processed data and metadata for gene expression and epigenomics datasets generated by high-throughput sequencing and microarray technologies. Submit assembled complete or incomplete/draft prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes.
Submit Your Article. After checking that your article complies with the target journal's submission guidelines, you are ready to submit. Click the Submit Your Manuscript button on the journal's home page on IEEE Xplore. You will be taken to the journal's online submission system, which will walk you through the submission process ...
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common ...
Submitting a paper. Make sure you have prepared your paper according to the instructions for authors. Double-check the journal's requirements with your article to be certain. If you need to include a cover letter with your submission, you should address the editor by formal name (e.g. Dear Professor Name---) and include the name of the ...
Submit paper. Please read the guidelines below before visiting the submission site! Submission site opens in a new tab. ... 4.6 Research ethics and patient consent. Research involving human subjects must be conducted according to the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki.
Submit your work. Once you are ready to submit your manuscript to The Lancet Group, please click on the submit button under the relevant journal title. This will take you through to the manuscript submission system where you will be able to upload your manuscript. Not quite ready yet?
A debate paper will be a scholarly technical research paper that makes the case for a particular position. The EIC may invite an opposing debate paper to create balance. A perspective article looks at the big picture, whereas a debate paper is highly technical. ... The video submission must clearly be relevant to the submitted manuscript.
To submit an article, use the submit form or select "START NEW SUBMISSION" from your user page. ... The AutoTeX system would look for any references in a paper that looked like an arXiv paper ID (such as arXiv:2402.08954, or 2402.08954), and turn the into a hyperlink to the paper on arXiv. We won't do that anymore.
Submission types. There are 4 types of submissions: Focused Technical, Context and Challenge, Regular Manuscripts, and Lengthy Manuscripts. The final published manuscript does not designate the submission category in the title. a. A focused technical paper is a short paper that has results on a technical problem of broad interest to the OR ...
Publish with IEEE Conferences. IEEE sponsors over 2,000 conferences and events that give technology professionals the opportunity to share innovations and interact one-on-one with the community. Publish with IEEE and join us in inspiring engineering solutions that make the world a better place.
9 Steps to Publish Research Papers Successfully. ... Write, format, and refine your paper for submission: Even before starting to write the paper, go through the author guidelines and formatting style followed by the journal. This will make the writing process easier. Structure the article according to the type of article you are writing.
Recent debates on decolonizing global health have spurred interest in addressing the power asymmetries and knowledge hierarchies that sustain colonial ideas and relationships in global health research. This paper applies three intersecting dimensions of colonialism (colonialism within global health; colonisation of global health; and colonialism through global health) to develop a broader and ...
We introduce phi-3-mini, a 3.8 billion parameter language model trained on 3.3 trillion tokens, whose overall performance, as measured by both academic benchmarks and internal testing, rivals that of models such as Mixtral 8x7B and GPT-3.5 (e.g., phi-3-mini achieves 69% on MMLU and 8.38 on MT-bench), despite being small enough to be deployed on a phone. The innovation lies entirely in our ...