
Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.

What is Database Search?
Harvard Library licenses hundreds of online databases, giving you access to academic and news articles, books, journals, primary sources, streaming media, and much more.
The contents of these databases are only partially included in HOLLIS. To make sure you're really seeing everything, you need to search in multiple places. Use Database Search to identify and connect to the best databases for your topic.
In addition to digital content, you will find specialized search engines used in specific scholarly domains.
Related Services & Tools
- All Solutions

Expertly curated abstract & citation database
About Scopus
Scopus is the largest abstract and citation database of peer-reviewed literature: scientific journals, books and conference proceedings. Delivering a comprehensive overview of the world's research output in the fields of science, technology, medicine, social sciences, and arts and humanities, Scopus features smart tools to track, analyse and visualise research.
As research becomes increasingly global, interdisciplinary and collaborative, you can make sure that critical research from around the world is not missed when you choose Scopus.
“Speed is very important … I can easily identify what I need to know, read it, digest it and move on to the next one.” James, Research Pathologist, Medical Device R&D, Scopus user
“Scopus is very customer-friendly… You get more information from all different fields. It saves a lot of time.” Chris, Head of R&D, Diagnostic Testing, Scopus user
“Scopus informs every phase of the editorial process. I would not want to do this job without it, and I intend to continue using it throughout my career.” William, Professor of Economics, University of Tennessee
More information (in English)
- Why I would not want to be without Scopus; an editor’s story
- NASI Scopus Young Scientists Awards 2019
Elsevier.com visitor survey
We are always looking for ways to improve customer experience on Elsevier.com. We would like to ask you for a moment of your time to fill in a short questionnaire, at the end of your visit . If you decide to participate, a new browser tab will open so you can complete the survey after you have completed your visit to this website. Thanks in advance for your time.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
PubMed® comprises more than 37 million citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books. Citations may include links to full text content from PubMed Central and publisher web sites.
Featured Bookshelf titles

Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Araki T, editor.

Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®)
Literature databases
Books and reports
Ontology used for PubMed indexing
Books, journals and more in the NLM Collections
Scientific and medical abstracts/citations
Full-text journal articles
Gene sequences and annotations used as references for the study of orthologs structure, expression, and evolution
Collected information about gene loci
Functional genomics studies
Gene expression and molecular abundance profiles
Homologous genes sets for selected organisms
Sequence sets from phylogenetic and population studies
Protein sequences, 3-D structures, and tools for the study of functional protein domains and active sites
Conserved protein domains
Protein sequences grouped by identity
Protein sequences
Models representing homologous proteins with a common function
Experimentally-determined biomolecular structures
A tool to find regions of similarity between biological sequences
Search nucleotide sequence databases
Search protein sequence databases
Search protein databases using a translated nucleotide query
Search translated nucleotide databases using a protein query
Find primers specific to your PCR template
Genome sequence assemblies, large-scale functional genomics data, and source biological samples
Genome assembly information
Museum, herbaria, and other biorepository collections
Biological projects providing data to NCBI
Descriptions of biological source materials
Genome sequencing projects by organism
DNA and RNA sequences
High-throughput sequence reads
Taxonomic classification and nomenclature
Heritable DNA variations, associations with human pathologies, and clinical diagnostics and treatments
Privately and publicly funded clinical studies conducted around the world
Human variations of clinical significance
Genotype/phenotype interaction studies
Short genetic variations
Genome structural variation studies
Genetic testing registry
Medical genetics literature and links
Online mendelian inheritance in man
Repository of chemical information, molecular pathways, and tools for bioactivity screening
Bioactivity screening studies
Chemical information with structures, information and links
Molecular pathways with links to genes, proteins and chemicals
Deposited substance and chemical information
Research news
Talk therapy cuts risk of postpartum depression.
An intervention given to pregnant women by non-specialist providers greatly reduced the chances of developing postpartum depression or anxiety.
How excess niacin may promote cardiovascular disease
Findings about a metabolite of niacin, or vitamin B3, raise concerns about the health effects of too much niacin and suggest new measures to help prevent or treat cardiovascular disease
Birds, bees and even plants might act weird during the solar eclipse
A total eclipse isn’t just a spectacle in the sky. Birds, insects and even plants will take notice, and might start acting strange.
Recent blog posts
Medgen users, we want your feedback.
Do you use NCBI’s MedGen? If so, then you probably know it’s NCBI’s one-stop-shop for genetic phenotype information. If you are a healthcare provider, genetic professional, researcher, or anyone who uses MedGen, we want to hear from you to help us make this resource better meet your needs! We want to know: How you currently … Continue reading MedGen Users, We Want Your Feedback! →
Immune Checkpoint Discovery Has Implications for Treating Cancer and Autoimmune Diseases
Your immune system should ideally recognize and attack infectious invaders and cancerous cells. But the system requires safety mechanisms, or brakes, to keep it from damaging healthy cells. To do this, T cells—the immune system’s most powerful attackers—rely on immune “checkpoints” to turn immune activation down when they receive the right signal. While these interactions have been well studied, a research team supported in part by NIH has made an unexpected discovery into how a key immune checkpoint works, with potentially important implications for therapies designed to boost or dampen immune activity to treat cancer and autoimmune diseases.
“Computers don’t diagnose the same way that doctors do” - NLM Lecture Explored How a Cancer Diagnosis Can Help Illustra…
How can cancer help us understand algorithmic bias? At this year’s NLM Science, Technology, and Society Lecture, journalist and AI ethics expert Meredith Broussard shared how her personal experience with breast cancer can help illuminate the potential impact that racial and gender bias can have on the use of AI in medical contexts.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Trending Articles
- Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators. Lancet. 2024. PMID: 38582094
- How effective is digitalis in the treatment of congestive heart failure? Kimmelstiel C, et al. Am Heart J. 1988. PMID: 3051982 Review.
- A pan-cancer analysis of the microbiome in metastatic cancer. Battaglia TW, et al. Cell. 2024. PMID: 38599211
- Identifying and Characterizing a Novel Peritrophic Matrix Protein (MdPM-17) Associated With Antibacterial Response From the Housefly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae). Wang Y, et al. J Insect Sci. 2020. PMID: 33347588 Free PMC article.
- Alectinib in Resected ALK -Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Wu YL, et al. N Engl J Med. 2024. PMID: 38598794 Clinical Trial.
Latest Literature
- Cancer Res (1)
- J Biol Chem (1)
- J Immunol (2)
- PLoS One (2)
- Pediatrics (1)
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (5)
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
The top list of academic search engines
1. Google Scholar
4. science.gov, 5. semantic scholar, 6. baidu scholar, get the most out of academic search engines, frequently asked questions about academic search engines, related articles.
Academic search engines have become the number one resource to turn to in order to find research papers and other scholarly sources. While classic academic databases like Web of Science and Scopus are locked behind paywalls, Google Scholar and others can be accessed free of charge. In order to help you get your research done fast, we have compiled the top list of free academic search engines.
Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles
- Abstracts: only a snippet of the abstract is available
- Related articles: ✔
- References: ✔
- Cited by: ✔
- Links to full text: ✔
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, Vancouver, RIS, BibTeX
BASE is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany. That is also where its name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles (contains duplicates)
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✘
- References: ✘
- Cited by: ✘
- Export formats: RIS, BibTeX

CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open-access research papers. For each search result, a link to the full-text PDF or full-text web page is provided.
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles
- Links to full text: ✔ (all articles in CORE are open access)
- Export formats: BibTeX
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need anymore to query all those resources separately!
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles and reports
- Links to full text: ✔ (available for some databases)
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX (available for some databases)
Semantic Scholar is the new kid on the block. Its mission is to provide more relevant and impactful search results using AI-powered algorithms that find hidden connections and links between research topics.
- Coverage: approx. 40 million articles
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, BibTeX

Although Baidu Scholar's interface is in Chinese, its index contains research papers in English as well as Chinese.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 100 million articles
- Abstracts: only snippets of the abstract are available
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX

RefSeek searches more than one billion documents from academic and organizational websites. Its clean interface makes it especially easy to use for students and new researchers.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 1 billion documents
- Abstracts: only snippets of the article are available
- Export formats: not available
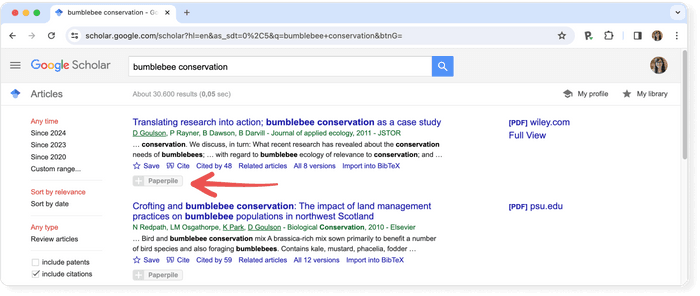
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to save, organize, and cite your references. Paperpile integrates with Google Scholar and many popular databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons:
Google Scholar is an academic search engine, and it is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only let's you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free, but also often provides links to full text PDF file.
Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature developed at the Allen Institute for AI. Sematic Scholar was publicly released in 2015 and uses advances in natural language processing to provide summaries for scholarly papers.
BASE , as its name suggest is an academic search engine. It is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany and that's where it name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open access research papers. For each search result a link to the full text PDF or full text web page is provided.
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need any more to query all those resources separately!
🇺🇦 make metadata, not war
A comprehensive bibliographic database of the world’s scholarly literature
The world’s largest collection of open access research papers, machine access to our vast unique full text corpus, core features, indexing the world’s repositories.
We serve the global network of repositories and journals
Comprehensive data coverage
We provide both metadata and full text access to our comprehensive collection through our APIs and Datasets
Powerful services
We create powerful services for researchers, universities, and industry
Cutting-edge solutions
We research and develop innovative data-driven and AI solutions
Committed to the POSI
Cost-free PIDs for your repository
OAI identifiers are unique identifiers minted cost-free by repositories. Ensure that your repository is correctly configured, enabling the CORE OAI Resolver to redirect your identifiers to your repository landing pages.
OAI IDs provide a cost-free option for assigning Persistent Identifiers (PIDs) to your repository records. Learn more.
Who we serve?
Enabling others to create new tools and innovate using a global comprehensive collection of research papers.

“ Our partnership with CORE will provide Turnitin with vast amounts of metadata and full texts that we can ... ” Show more
Gareth Malcolm, Content Partner Manager at Turnitin
Academic institutions.
Making research more discoverable, improving metadata quality, helping to meet and monitor open access compliance.

“ CORE’s role in providing a unified search of repository content is a great tool for the researcher and ex... ” Show more
Nicola Dowson, Library Services Manager at Open University
Researchers & general public.
Tools to find, discover and explore the wealth of open access research. Free for everyone, forever.

“ With millions of research papers available across thousands of different systems, CORE provides an invalu... ” Show more
Jon Tennant, Rogue Paleontologist and Founder of the Open Science MOOC
Helping funders to analyse, audit and monitor open research and accelerate towards open science.

“ Aggregation plays an increasingly essential role in maximising the long-term benefits of open access, hel... ” Show more
Ben Johnson, Research Policy Adviser at Research England
Our services, access to raw data.
Create new and innovative solutions.
Content discovery
Find relevant research and make your research more visible.
Managing content
Manage how your research content is exposed to the world.
Companies using CORE

Gareth Malcolm
Content Partner Manager at Turnitin
Our partnership with CORE will provide Turnitin with vast amounts of metadata and full texts that we can utilise in our plagiarism detection software.
Academic institution using CORE
Kathleen Shearer
Executive Director of the Confederation of Open Access Repositories (COAR)
CORE has significantly assisted the academic institutions participating in our global network with their key mission, which is their scientific content exposure. In addition, CORE has helped our content administrators to showcase the real benefits of repositories via its added value services.
Partner projects

Ben Johnson
Research Policy Adviser
Aggregation plays an increasingly essential role in maximising the long-term benefits of open access, helping to turn the promise of a 'research commons' into a reality. The aggregation services that CORE provides therefore make a very valuable contribution to the evolving open access environment in the UK.

A free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature
- Stephen D. Evans
- Social Security Tax
- Nanotechnology
New & Improved API for Developers
Introducing semantic reader in beta.
Stay Connected With Semantic Scholar Sign Up What Is Semantic Scholar? Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature, based at the Allen Institute for AI.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Download 55 million PDFs for free
Explore our top research interests.

Engineering

Anthropology

- Earth Sciences

- Computer Science

- Mathematics

- Health Sciences

Join 257 million academics and researchers
Track your impact.
Share your work with other academics, grow your audience and track your impact on your field with our robust analytics
Discover new research
Get access to millions of research papers and stay informed with the important topics around the world
Publish your work
Publish your research with fast and rigorous service through Academia.edu Publishing. Get instant worldwide dissemination of your work
Unlock the most powerful tools with Academia Premium

Work faster and smarter with advanced research discovery tools
Search the full text and citations of our millions of papers. Download groups of related papers to jumpstart your research. Save time with detailed summaries and search alerts.
- Advanced Search
- PDF Packages of 37 papers
- Summaries and Search Alerts

Share your work, track your impact, and grow your audience
Get notified when other academics mention you or cite your papers. Track your impact with in-depth analytics and network with members of your field.
- Mentions and Citations Tracking
- Advanced Analytics
- Publishing Tools
Real stories from real people

Used by academics at over 16,000 universities

Get started and find the best quality research
- Academia.edu Publishing
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Cognitive Science
- Academia ©2024
21 Legit Research Databases for Free Journal Articles in 2022
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
Has this ever happened to you? While looking for websites for research, you come across a research paper site that claims to connect academics to a peer-reviewed article database for free.
Intrigued, you search for keywords related to your topic, only to discover that you must pay a hefty subscription fee to access the service. After the umpteenth time being duped, you begin to wonder if there's even such a thing as free journal articles .
Subscription fees and paywalls are often the bane of students and academics, especially those at small institutions who don't provide access to many free article directories and repositories.
Whether you're working on an undergraduate paper, a PhD dissertation, or a medical research study, we want to help you find tools to locate and access the information you need to produce well-researched, compelling, and innovative work.
Below, we discuss why peer-reviewed articles are superior and list out the best free article databases to use in 2022.
Download Our Free Research Database Roundup PDF
Why peer-reviewed scholarly journal articles are more authoritative.

Determining what sources are reliable can be challenging. Peer-reviewed scholarly journal articles are the gold standard in academic research. Reputable academic journals have a rigorous peer-review process.
The peer review process provides accountability to the academic community, as well as to the content of the article. The peer review process involves qualified experts in a specific (often very specific) field performing a review of an article's methods and findings to determine things like quality and credibility.
Peer-reviewed articles can be found in peer-reviewed article databases and research databases, and if you know that a database of journals is reliable, that can offer reassurances about the reliability of a free article. Peer review is often double blind, meaning that the author removes all identifying information and, likewise, does not know the identity of the reviewers. This helps reviewers maintain objectivity and impartiality so as to judge an article based on its merit.
Where to Find Peer-Reviewed Articles
Peer-reviewed articles can be found in a variety of research databases. Below is a list of some of the major databases you can use to find peer-reviewed articles and other sources in disciplines spanning the humanities, sciences, and social sciences.
What Are Open Access Journals?
An open access (OA) journal is a journal whose content can be accessed without payment. This provides scholars, students, and researchers with free journal articles . OA journals use alternate methods of funding to cover publication costs so that articles can be published without having to pass those publication costs on to the reader.

Some of these funding models include standard funding methods like advertising, public funding, and author payment models, where the author pays a fee in order to publish in the journal. There are OA journals that have non-peer-reviewed academic content, as well as journals that focus on dissertations, theses, and papers from conferences, but the main focus of OA is peer-reviewed scholarly journal articles.
The internet has certainly made it easier to access research articles and other scholarly publications without needing access to a university library, and OA takes another step in that direction by removing financial barriers to academic content.
Choosing Wisely
Features of legitimate oa journals.
There are things to look out for when trying to decide if a free publication journal is legitimate:
Mission statement —The mission statement for an OA journal should be available on their website.
Publication history —Is the journal well established? How long has it been available?
Editorial board —Who are the members of the editorial board, and what are their credentials?
Indexing —Can the journal be found in a reliable database?
Peer review —What is the peer review process? Does the journal allow enough time in the process for a reliable assessment of quality?
Impact factor —What is the average number of times the journal is cited over a two-year period?
Features of Illegitimate OA Journals
There are predatory publications that take advantage of the OA format, and they are something to be wary of. Here are some things to look out for:
Contact information —Is contact information provided? Can it be verified?
Turnaround —If the journal makes dubious claims about the amount of time from submission to publication, it is likely unreliable.
Editorial board —Much like determining legitimacy, looking at the editorial board and their credentials can help determine illegitimacy.
Indexing —Can the journal be found in any scholarly databases?
Peer review —Is there a statement about the peer review process? Does it fit what you know about peer review?
How to Find Scholarly Articles
Identify keywords.
Keywords are included in an article by the author. Keywords are an excellent way to find content relevant to your research topic or area of interest. In academic searches, much like you would on a search engine, you can use keywords to navigate through what is available to find exactly what you're looking for.
Authors provide keywords that will help you easily find their article when researching a related topic, often including general terms to accommodate broader searches, as well as some more specific terms for those with a narrower scope. Keywords can be used individually or in combination to refine your scholarly article search.
Narrow Down Results
Sometimes, search results can be overwhelming, and searching for free articles on a journal database is no exception, but there are multiple ways to narrow down your results. A good place to start is discipline.
What category does your topic fall into (psychology, architecture, machine learning, etc.)? You can also narrow down your search with a year range if you're looking for articles that are more recent.
A Boolean search can be incredibly helpful. This entails including terms like AND between two keywords in your search if you need both keywords to be in your results (or, if you are looking to exclude certain keywords, to exclude these words from the results).
Consider Different Avenues
If you're not having luck using keywords in your search for free articles, you may still be able to find what you're looking for by changing your tactics. Casting a wider net sometimes yields positive results, so it may be helpful to try searching by subject if keywords aren't getting you anywhere.
You can search for a specific publisher to see if they have OA publications in the academic journal database. And, if you know more precisely what you're looking for, you can search for the title of the article or the author's name.
The Top 21 Free Online Journal and Research Databases
Navigating OA journals, research article databases, and academic websites trying to find high-quality sources for your research can really make your head spin. What constitutes a reliable database? What is a useful resource for your discipline and research topic? How can you find and access full-text, peer-reviewed articles?
Fortunately, we're here to help. Having covered some of the ins and outs of peer review, OA journals, and how to search for articles, we have compiled a list of the top 21 free online journals and the best research databases. This list of databases is a great resource to help you navigate the wide world of academic research.
These databases provide a variety of free sources, from abstracts and citations to full-text, peer-reviewed OA journals. With databases covering specific areas of research and interdisciplinary databases that provide a variety of material, these are some of our favorite free databases, and they're totally legit!
CORE is a multidisciplinary aggregator of OA research. CORE has the largest collection of OA articles available. It allows users to search more than 219 million OA articles. While most of these link to the full-text article on the original publisher's site, or to a PDF available for download, five million records are hosted directly on CORE.
CORE's mission statement is a simple and straightforward commitment to offering OA articles to anyone, anywhere in the world. They also host communities that are available for researchers to join and an ambassador community to enhance their services globally. In addition to a straightforward keyword search, CORE offers advanced search options to filter results by publication type, year, language, journal, repository, and author.
CORE's user interface is easy to use and navigate. Search results can be sorted based on relevance or recency, and you can search for relevant content directly from the results screen.
Collection: 219,537,133 OA articles
Other Services: Additional services are available from CORE, with extras that are geared toward researchers, repositories, and businesses. There are tools for accessing raw data, including an API that provides direct access to data, datasets that are available for download, and FastSync for syncing data content from the CORE database.
CORE has a recommender plug-in that suggests relevant OA content in the database while conducting a search and a discovery feature that helps you discover OA versions of paywalled articles. Other features include tools for managing content, such as a dashboard for managing repository output and the Repository Edition service to enhance discoverability.
Good Source of Peer-Reviewed Articles: Yes
Advanced Search Options: Language, author, journal, publisher, repository, DOI, year
2. ScienceOpen
Functioning as a research and publishing network, ScienceOpen offers OA to more than 74 million articles in all areas of science. Although you do need to register to view the full text of articles, registration is free. The advanced search function is highly detailed, allowing you to find exactly the research you're looking for.
The Berlin- and Boston-based company was founded in 2013 to "facilitate open and public communications between academics and to allow ideas to be judged on their merit, regardless of where they come from." Search results can be exported for easy integration with reference management systems.
You can also bookmark articles for later research. There are extensive networking options, including your Science Open profile, a forum for interacting with other researchers, the ability to track your usage and citations, and an interactive bibliography. Users have the ability to review articles and provide their knowledge and insight within the community.
Collection: 74,560,631
Other Services: None
Advanced Search Options: Content type, source, author, journal, discipline
3. Directory of Open Access Journals
A multidisciplinary, community-curated directory, the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ) gives researchers access to high-quality peer-reviewed journals. It has archived more than two million articles from 17,193 journals, allowing you to either browse by subject or search by keyword.
The site was launched in 2003 with the aim of increasing the visibility of OA scholarly journals online. Content on the site covers subjects from science, to law, to fine arts, and everything in between. DOAJ has a commitment to "increase the visibility, accessibility, reputation, usage and impact of quality, peer-reviewed, OA scholarly research journals globally, regardless of discipline, geography or language."
Information about the journal is available with each search result. Abstracts are also available in a collapsible format directly from the search screen. The scholarly article website is somewhat simple, but it is easy to navigate. There are 16 principles of transparency and best practices in scholarly publishing that clearly outline DOAJ policies and standards.
Collection: 6,817,242
Advanced Search Options: Subject, journal, year
4. Education Resources Information Center
The Education Resources Information Center (ERIC) of the Institution of Education Sciences allows you to search by topic for material related to the field of education. Links lead to other sites, where you may have to purchase the information, but you can search for full-text articles only. You can also search only peer-reviewed sources.
The service primarily indexes journals, gray literature (such as technical reports, white papers, and government documents), and books. All sources of material on ERIC go through a formal review process prior to being indexed. ERIC's selection policy is available as a PDF on their website.
The ERIC website has an extensive FAQ section to address user questions. This includes categories like general questions, peer review, and ERIC content. There are also tips for advanced searches, as well as general guidance on the best way to search the database. ERIC is an excellent database for content specific to education.
Collection: 1,292,897
Advanced Search Options: Boolean
5. arXiv e-Print Archive
The arXiv e-Print Archive is run by Cornell University Library and curated by volunteer moderators, and it now offers OA to more than one million e-prints.
There are advisory committees for all eight subjects available on the database. With a stated commitment to an "emphasis on openness, collaboration, and scholarship," the arXiv e-Print Archive is an excellent STEM resource.
The interface is not as user-friendly as some of the other databases available, and the website hosts a blog to provide news and updates, but it is otherwise a straightforward math and science resource. There are simple and advanced search options, and, in addition to conducting searches for specific topics and articles, users can browse content by subject. The arXiv e-Print Archive clearly states that they do not peer review the e-prints in the database.
Collection: 1,983,891
Good Source of Peer-Reviewed Articles: No
Advanced Search Options: Subject, date, title, author, abstract, DOI
6. Social Science Research Network
The Social Science Research Network (SSRN) is a collection of papers from the social sciences community. It is a highly interdisciplinary platform used to search for scholarly articles related to 67 social science topics. SSRN has a variety of research networks for the various topics available through the free scholarly database.
The site offers more than 700,000 abstracts and more than 600,000 full-text papers. There is not yet a specific option to search for only full-text articles, but, because most of the papers on the site are free access, it's not often that you encounter a paywall. There is currently no option to search for only peer-reviewed articles.
You must become a member to use the services, but registration is free and enables you to interact with other scholars around the world. SSRN is "passionately committed to increasing inclusion, diversity and equity in scholarly research," and they encourage and discuss the use of inclusive language in scholarship whenever possible.
Collection: 1,058,739 abstracts; 915,452 articles
Advanced Search Options: Term, author, date, network
7. Public Library of Science
Public Library of Science (PLOS) is a big player in the world of OA science. Publishing 12 OA journals, the nonprofit organization is committed to facilitating openness in academic research. According to the site, "all PLOS content is at the highest possible level of OA, meaning that scientific articles are immediately and freely available to anyone, anywhere."
PLOS outlines four fundamental goals that guide the organization: break boundaries, empower researchers, redefine quality, and open science. All PLOS journals are peer-reviewed, and all 12 journals uphold rigorous ethical standards for research, publication, and scientific reporting.
PLOS does not offer advanced search options. Content is organized by topic into research communities that users can browse through, in addition to options to search for both articles and journals. The PLOS website also has resources for peer reviewers, including guidance on becoming a reviewer and on how to best participate in the peer review process.
Collection: 12 journals
Advanced Search Options: None
8. OpenDOAR
OpenDOAR, or the Directory of Open Access Repositories, is a comprehensive resource for finding free OA journals and articles. Using Google Custom Search, OpenDOAR combs through OA repositories around the world and returns relevant research in all disciplines.
The repositories it searches through are assessed and categorized by OpenDOAR staff to ensure they meet quality standards. Inclusion criteria for the database include requirements for OA content, global access, and categorically appropriate content, in addition to various other quality assurance measures. OpenDOAR has metadata, data, content, preservation, and submission policies for repositories, in addition to two OA policy statements regarding minimum and optimum recommendations.
This database allows users to browse and search repositories, which can then be selected, and articles and data can be accessed from the repository directly. As a repository database, much of the content on the site is geared toward the support of repositories and OA standards.
Collection: 5,768 repositories
Other Services: OpenDOAR offers a variety of additional services. Given the nature of the platform, services are primarily aimed at repositories and institutions, and there is a marked focus on OA in general. Sherpa services are OA archiving tools for authors and institutions.
They also offer various resources for OA support and compliance regarding standards and policies. The publication router matches publications and publishers with appropriate repositories.
There are also services and resources from JISC for repositories for cost management, discoverability, research impact, and interoperability, including ORCID consortium membership information. Additionally, a repository self-assessment tool is available for members.
Advanced Search Options: Name, organization name, repository type, software name, content type, subject, country, region
9. Bielefeld Academic Search Engine
The Bielefeld Academic Search Engine (BASE) is operated by the Bielefeld University Library in Germany, and it offers more than 240 million documents from more than 8,000 sources. Sixty percent of its content is OA, and you can filter your search accordingly.
BASE has rigorous inclusion requirements for content providers regarding quality and relevance, and they maintain a list of content providers for the sake of transparency, which can be easily found on their website. BASE has a fairly elegant interface. Search results can be organized by author, title, or date.
From the search results, items can be selected and exported, added to favorites, emailed, and searched in Google Scholar. There are basic and advanced search features, with the advanced search offering numerous options for refining search criteria. There is also a feature on the website that saves recent searches without additional steps from the user.
Collection: 276,019,066 documents; 9,286 content providers
Advanced Search Options: Author, subject, year, content provider, language, document type, access, terms of reuse

10. Digital Library of the Commons Repository
Run by Indiana University, the Digital Library of the Commons (DLC) Repository is a multidisciplinary journal repository that allows users to access thousands of free and OA articles from around the world. You can browse by document type, date, author, title, and more or search for keywords relevant to your topic.
DCL also offers the Comprehensive Bibliography of the Commons, an image database, and a keyword thesaurus for enhanced search parameters. The repository includes books, book chapters, conference papers, journal articles, surveys, theses and dissertations, and working papers. DCL advanced search features drop-down menus of search types with built-in Boolean search options.
Searches can be sorted by relevance, title, date, or submission date in ascending or descending order. Abstracts are included in selected search results, with access to full texts available, and citations can be exported from the same page. Additionally, the image database search includes tips for better search results.
Collection: 10,784
Advanced Search Options: Author, date, title, subject, sector, region, conference
11. CIA World Factbook
The CIA World Factbook is a little different from the other resources on this list in that it is not an online journal directory or repository. It is, however, a useful free online research database for academics in a variety of disciplines.
All the information is free to access, and it provides facts about every country in the world, which are organized by category and include information about history, geography, transportation, and much more. The World Factbook can be searched by country or region, and there is also information about the world’s oceans.
This site contains resources related to the CIA as an organization rather than being a scientific journal database specifically. The site has a user interface that is easy to navigate. The site also provides a section for updates regarding changes to what information is available and how it is organized, making it easier to interact with the information you are searching for.
Collection: 266 countries
12. Paperity
Paperity boasts its status as the "first multidisciplinary aggregator of OA journals and papers." Their focus is on helping you avoid paywalls while connecting you to authoritative research. In addition to providing readers with easy access to thousands of journals, Paperity seeks to help authors reach their audiences and help journals increase their exposure to boost readership.
Paperity has journal articles for every discipline, and the database offers more than a dozen advanced search options, including the length of the paper and the number of authors. There is even an option to include, exclude, or exclusively search gray papers.
Paperity is available for mobile, with both a mobile site and the Paperity Reader, an app that is available for both Android and Apple users. The database is also available on social media. You can interact with Paperity via Twitter and Facebook, and links to their social media are available on their homepage, including their Twitter feed.
Collection: 8,837,396
Advanced Search Options: Title, abstract, journal title, journal ISSN, publisher, year of publication, number of characters, number of authors, DOI, author, affiliation, language, country, region, continent, gray papers
13. dblp Computer Science Bibliography
The dblp Computer Science Bibliography is an online index of major computer science publications. dblp was founded in 1993, though until 2010 it was a university-specific database at the University of Trier in Germany. It is currently maintained by the Schloss Dagstuhl – Leibniz Center for Informatics.
Although it provides access to both OA articles and those behind a paywall, you can limit your search to only OA articles. The site indexes more than three million publications, making it an invaluable resource in the world of computer science. dblp entries are color-coded based on the type of item.
dblp has an extensive FAQ section, so questions that might arise about topics like the database itself, navigating the website, or the data on dblp, in addition to several other topics, are likely to be answered. The website also hosts a blog and has a section devoted to website statistics.
Collection: 5,884,702
14. EconBiz
EconBiz is a great resource for economic and business studies. A service of the Leibniz Information Centre for Economics, it offers access to full texts online, with the option of searching for OA material only. Their literature search is performed across multiple international databases.
EconBiz has an incredibly useful research skills section, with resources such as Guided Walk, a service to help students and researchers navigate searches, evaluate sources, and correctly cite references; the Research Guide EconDesk, a help desk to answer specific questions and provide advice to aid in literature searches; and the Academic Career Kit for what they refer to as Early Career Researchers.
Other helpful resources include personal literature lists, a calendar of events for relevant calls for papers, conferences, and workshops, and an economics terminology thesaurus to help in finding keywords for searches. To stay up-to-date with EconBiz, you can sign up for their newsletter.
Collection: 1,075,219
Advanced Search Options: Title, subject, author, institution, ISBN/ISSN, journal, publisher, language, OA only

15. BioMed Central
BioMed Central provides OA research from more than 300 peer-reviewed journals. While originally focused on resources related to the physical sciences, math, and engineering, BioMed Central has branched out to include journals that cover a broader range of disciplines, with the aim of providing a single platform that provides OA articles for a variety of research needs. You can browse these journals by subject or title, or you can search all articles for your required keyword.
BioMed Central has a commitment to peer-reviewed sources and to the peer review process itself, continually seeking to help and improve the peer review process. They're "committed to maintaining high standards through full and stringent peer review." They publish the journal Research Integrity and Peer Review , which publishes research on the subject.
Additionally, the website includes resources to assist and support editors as part of their commitment to providing high-quality, peer-reviewed OA articles.
Collection: 507,212
Other Services: BMC administers the International Standard Randomised Controlled Trial Number (ISRCTN) registry. While initially designed for registering clinical trials, since its creation in 2000, the registry has broadened its scope to include other health studies as well.
The registry is recognized by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors, as well as the World Health Organization (WHO), and it meets the requirements established by the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform.
The study records included in the registry are all searchable and free to access. The ISRCTN registry "supports transparency in clinical research, helps reduce selective reporting of results and ensures an unbiased and complete evidence base."
Advanced Search Options: Author, title, journal, list
A multidisciplinary search engine, JURN provides links to various scholarly websites, articles, and journals that are free to access or OA. Covering the fields of the arts, humanities, business, law, nature, science, and medicine, JURN has indexed almost 5,000 repositories to help you find exactly what you're looking for.
Search features are enhanced by Google, but searches are filtered through their index of repositories. JURN seeks to reach a wide audience, with their search engine tailored to researchers from "university lecturers and students seeking a strong search tool for OA content" and "advanced and ambitious students, age 14-18" to "amateur historians and biographers" and "unemployed and retired lecturers."
That being said, JURN is very upfront about its limitations. They admit to not being a good resource for educational studies, social studies, or psychology, and conference archives are generally not included due to frequently unstable URLs.
Collection: 5,064 indexed journals
Other Services: JURN has a browser add-on called UserScript. This add-on allows users to integrate the JURN database directly into Google Search. When performing a search through Google, the add-on creates a link that sends the search directly to JURN CSE. JURN CSE is a search service that is hosted by Google.
Clicking the link from the Google Search bar will run your search through the JURN database from the Google homepage. There is also an interface for a DuckDuckGo search box; while this search engine has an emphasis on user privacy, for smaller sites that may be indexed by JURN, DuckDuckGo may not provide the same depth of results.
Advanced Search Options: Google search modifiers
Dryad is a digital repository of curated, OA scientific research data. Launched in 2009, it is run by a not-for-profit membership organization, with a community of institutional and publisher members for whom their services have been designed. Members include institutions such as Stanford, UCLA, and Yale, as well as publishers like Oxford University Press and Wiley.
Dryad aims to "promote a world where research data is openly available, integrated with the scholarly literature, and routinely reused to create knowledge." It is free to access for the search and discovery of data. Their user experience is geared toward easy self-depositing, supports Creative Commons licensing, and provides DOIs for all their content.
Note that there is a publishing charge associated if you wish to publish your data in Dryad. When searching datasets, they are accompanied by author information and abstracts for the associated studies, and citation information is provided for easy attribution.
Collection: 44,458
Advanced Search Options: No
Run by the British Library, the E-Theses Online Service (EThOS) allows you to search over 500,000 doctoral theses in a variety of disciplines. All of the doctoral theses available on EThOS have been awarded by higher education institutions in the United Kingdom.
Although some full texts are behind paywalls, you can limit your search to items available for immediate download, either directly through EThOS or through an institution's website. More than half of the records in the database provide access to full-text theses.
EThOS notes that they do not hold all records for all institutions, but they strive to index as many doctoral theses as possible, and the database is constantly expanding, with approximately 3,000 new records added and 2,000 new full-text theses available every month. The availability of full-text theses is dependent on multiple factors, including their availability in the institutional repository and the level of repository development.
Collection: 500,000+
Advanced Search Options: Abstract, author's first name, author's last name, awarding body, current institution, EThOS ID, year, language, qualifications, research supervisor, sponsor/funder, keyword, title
PubMed is a research platform well-known in the fields of science and medicine. It was created and developed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) at the National Library of Medicine (NLM). It has been available since 1996 and offers access to "more than 33 million citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books."
While PubMed does not provide full-text articles directly, and many full-text articles may be behind paywalls or require subscriptions to access them, when articles are available from free sources, such as through PubMed Central (PMC), those links are provided with the citations and abstracts that PubMed does provide.
PMC, which was established in 2000 by the NLM, is a free full-text archive that includes more than 6,000,000 records. PubMed records link directly to corresponding PMC results. PMC content is provided by publishers and other content owners, digitization projects, and authors directly.
Collection: 33,000,000+
Advanced Search Options: Author's first name, author's last name, identifier, corporation, date completed, date created, date entered, date modified, date published, MeSH, book, conflict of interest statement, EC/RN number, editor, filter, grant number, page number, pharmacological action, volume, publication type, publisher, secondary source ID, text, title, abstract, transliterated title
20. Semantic Scholar
A unique and easy-to-use resource, Semantic Scholar defines itself not just as a research database but also as a "search and discovery tool." Semantic Scholar harnesses the power of artificial intelligence to efficiently sort through millions of science-related papers based on your search terms.
Through this singular application of machine learning, Semantic Scholar expands search results to include topic overviews based on your search terms, with the option to create an alert for or further explore the topic. It also provides links to related topics.
In addition, search results produce "TLDR" summaries in order to provide concise overviews of articles and enhance your research by helping you to navigate quickly and easily through the available literature to find the most relevant information. According to the site, although some articles are behind paywalls, "the data [they] have for those articles is limited," so you can expect to receive mostly full-text results.
Collection: 203,379,033
Other Services: Semantic Scholar supports multiple popular browsers. Content can be accessed through both mobile and desktop versions of Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, Apple Safari, and Opera.
Additionally, Semantic Scholar provides browser extensions for both Chrome and Firefox, so AI-powered scholarly search results are never more than a click away. The mobile interface includes an option for Semantic Swipe, a new way of interacting with your research results.
There are also beta features that can be accessed as part of the Beta Program, which will provide you with features that are being actively developed and require user feedback for further improvement.
Advanced Search Options: Field of study, date range, publication type, author, journal, conference, PDF
Zenodo, powered by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), was launched in 2013. Taking its name from Zenodotus, the first librarian of the ancient library of Alexandria, Zenodo is a tool "built and developed by researchers, to ensure that everyone can join in open science." Zenodo accepts all research from every discipline in any file format.
However, Zenodo also curates uploads and promotes peer-reviewed material that is available through OA. A DOI is assigned to everything that is uploaded to Zenodo, making research easily findable and citable. You can sort by keyword, title, journal, and more and download OA documents directly from the site.
While there are closed access and restricted access items in the database, the vast majority of research is OA material. Search results can be filtered by access type, making it easy to view the free articles available in the database.
Collection: 2,220,000+
Advanced Search Options: Access, file type, keywords
Check out our roundup of free research databases as a handy one-page PDF.
How to find peer-reviewed articles.
There are a lot of free scholarly articles available from various sources. The internet is a big place. So how do you go about finding peer-reviewed articles when conducting your research? It's important to make sure you are using reputable sources.
The first source of the article is the person or people who wrote it. Checking out the author can give you some initial insight into how much you can trust what you’re reading. Looking into the publication information of your sources can also indicate whether the article is reliable.
Aspects of the article, such as subject and audience, tone, and format, are other things you can look at when evaluating whether the article you're using is valid, reputable, peer-reviewed material. So, let's break that down into various components so you can assess your research to ensure that you're using quality articles and conducting solid research.
Check the Author
Peer-reviewed articles are written by experts or scholars with experience in the field or discipline they're writing about. The research in a peer-reviewed article has to pass a rigorous evaluation process, so it’s a foregone conclusion that the author(s) of a peer-reviewed article should have experience or training related to that research.
When evaluating an article, take a look at the author’s information. What credentials does the author have to indicate that their research has scholarly weight behind it? Finding out what type of degree the author has—and what that degree is in—can provide insight into what kind of authority the author is on the subject.
Something else that might lend credence to the author’s scholarly role is their professional affiliation. A look at what organization or institution they are affiliated with can tell you a lot about their experience or expertise. Where were they trained, and who is verifying their research?
Identify Subject and Audience
The ultimate goal of a study is to answer a question. Scholarly articles are also written for scholarly audiences, especially articles that have gone through the peer review process. This means that the author is trying to reach experts, researchers, academics, and students in the field or topic the research is based on.
Think about the question the author is trying to answer by conducting this research, why, and for whom. What is the subject of the article? What question has it set out to answer? What is the purpose of finding the information? Is the purpose of the article of importance to other scholars? Is it original content?
Research should also be approached analytically. Is the methodology sound? Is the author using an analytical approach to evaluate the data that they have obtained? Are the conclusions they've reached substantiated by their data and analysis? Answering these questions can reveal a lot about the article’s validity.
Format Matters
Reliable articles from peer-reviewed sources have certain format elements to be aware of. The first is an abstract. An abstract is a short summary or overview of the article. Does the article have an abstract? It's unlikely that you're reading a peer-reviewed article if it doesn’t. Peer-reviewed journals will also have a word count range. If an article seems far too short or incredibly long, that may be reason to doubt it.
Another feature of reliable articles is the sections the information is divided into. Peer-reviewed research articles will have clear, concise sections that appropriately organize the information. This might include a literature review, methodology, and results in the case of research articles and a conclusion.
One of the most important sections is the references or bibliography. This is where the researcher lists all the sources of their information. A peer-reviewed source will have a comprehensive reference section.
An article that has been written to reach an academic community will have an academic tone. The language that is used, and the way this language is used, is important to consider. If the article is riddled with grammatical errors, confusing syntax, and casual language, it almost definitely didn't make it through the peer review process.
Also consider the use of terminology. Every discipline is going to have standard terminology or jargon that can be used and understood by other academics in the discipline. The language in a peer-reviewed article is going to reflect that.
If the author is going out of their way to explain simple terms, or terms that are standard to the field or discipline, it's unlikely that the article has been peer reviewed, as this is something that the author would be asked to address during the review process.
Publication
The source of the article will be a very good indicator of the likelihood that it was peer reviewed. Where was the article published? Was it published alongside other academic articles in the same discipline? Is it a legitimate and reputable scholarly publication?
A trade publication or newspaper might be legitimate or reputable, but it is not a scholarly source, and it will not have been subject to the peer review process. Scholarly journals are the best resource for peer-reviewed articles, but it's important to remember that not all scholarly journals are peer reviewed.
It’s helpful to look at a scholarly source’s website, as peer-reviewed journals will have a clear indication of the peer review process. University libraries, institutional repositories, and reliable databases (and you now might have a list of some legit ones) can also help provide insight into whether an article comes from a peer-reviewed journal.

Common Research Mistakes to Avoid
Research is a lot of work. Even with high standards and good intentions, it’s easy to make mistakes. Perhaps you searched for access to scientific journals for free and found the perfect peer-reviewed sources, but you forgot to document everything, and your references are a mess. Or, you only searched for free online articles and missed out on a ground-breaking study that was behind a paywall.
Whether your research is for a degree or to get published or to satisfy your own inquisitive nature, or all of the above, you want all that work to produce quality results. You want your research to be thorough and accurate.
To have any hope of contributing to the literature on your research topic, your results need to be high quality. You might not be able to avoid every potential mistake, but here are some that are both common and easy to avoid.
Sticking to One Source
One of the hallmarks of good research is a healthy reference section. Using a variety of sources gives you a better answer to your question. Even if all of the literature is in agreement, looking at various aspects of the topic may provide you with an entirely different picture than you would have if you looked at your research question from only one angle.
Not Documenting Every Fact
As you conduct your research, do yourself a favor and write everything down. Everything you include in your paper or article that you got from another source is going to need to be added to your references and cited.
It's important, especially if your aim is to conduct ethical, high-quality research, that all of your research has proper attribution. If you don't document as you go, you could end up making a lot of work for yourself if the information you don’t write down is something that later, as you write your paper, you really need.
Using Outdated Materials
Academia is an ever-changing landscape. What was true in your academic discipline or area of research ten years ago may have since been disproven. If fifteen studies have come out since the article that you're using was published, it's more than a little likely that you're going to be basing your research on flawed or dated information.
If the information you're basing your research on isn’t as up-to-date as possible, your research won't be of quality or able to stand up to any amount of scrutiny. You don’t want all of your hard work to be for naught.
Relying Solely on Open Access Journals
OA is a great resource for conducting academic research. There are high-quality journal articles available through OA, and that can be very helpful for your research. But, just because you have access to free articles, that doesn't mean that there's nothing to be found behind a paywall.
Just as dismissing high-quality peer-reviewed articles because they are OA would be limiting, not exploring any paid content at all is equally short-sighted. If you're seeking to conduct thorough and comprehensive research, exploring all of your options for quality sources is going to be to your benefit.
Digging Too Deep or Not Deep Enough
Research is an art form, and it involves a delicate balance of information. If you conduct your research using only broad search terms, you won't be able to answer your research question well, or you'll find that your research provides information that is closely related to your topic but, ultimately, your findings are vague and unsubstantiated.
On the other hand, if you delve deeply into your research topic with specific searches and turn up too many sources, you might have a lot of information that is adjacent to your topic but without focus and perhaps not entirely relevant. It's important to answer your research question concisely but thoroughly.
Different Types of Scholarly Articles
Different types of scholarly articles have different purposes. An original research article, also called an empirical article, is the product of a study or an experiment. This type of article seeks to answer a question or fill a gap in the existing literature.
Research articles will have a methodology, results, and a discussion of the findings of the experiment or research and typically a conclusion.
Review articles overview the current literature and research and provide a summary of what the existing research indicates or has concluded. This type of study will have a section for the literature review, as well as a discussion of the findings of that review. Review articles will have a particularly extensive reference or bibliography section.
Theoretical articles draw on existing literature to create new theories or conclusions, or look at current theories from a different perspective, to contribute to the foundational knowledge of the field of study.
10 Tips for Navigating Journal Databases
Use the right academic journal database for your search, be that interdisciplinary or specific to your field. Or both!
If it’s an option, set the search results to return only peer-reviewed sources.
Start by using search terms that are relevant to your topic without being overly specific.
Try synonyms, especially if your keywords aren’t returning the desired results.

Even if you’ve found some good articles, try searching using different terms.
Explore the advanced search features of the database(s).
Learn to use Booleans (AND, OR, NOT) to expand or narrow your results.
Once you’ve gotten some good results from a more general search, try narrowing your search.
Read through abstracts when trying to find articles relevant to your research.
Keep track of your research and use citation tools. It’ll make life easier when it comes time to compile your references.
7 Frequently Asked Questions
1. how do i get articles for free.
Free articles can be found through free online academic journals, OA databases, or other databases that include OA journals and articles. These resources allow you to access free papers online so you can conduct your research without getting stuck behind a paywall.
Academics don’t receive payment for the articles they contribute to journals. There are often, in fact, publication fees that scholars pay in order to publish. This is one of the funding structures that allows OA journals to provide free content so that you don’t have to pay fees or subscription costs to access journal articles.
2. How Do I Find Journal Articles?
Journal articles can be found in databases and institutional repositories that can be accessed at university libraries. However, online research databases that contain OA articles are the best resource for getting free access to journal articles that are available online.
Peer-reviewed journal articles are the best to use for academic research, and there are a number of databases where you can find peer-reviewed OA journal articles. Once you've found a useful article, you can look through the references for the articles the author used to conduct their research, and you can then search online databases for those articles, too.
3. How Do I Find Peer-Reviewed Articles?
Peer-reviewed articles can be found in reputable scholarly peer-reviewed journals. High-quality journals and journal articles can be found online using academic search engines and free research databases. These resources are excellent for finding OA articles, including peer-reviewed articles.
OA articles are articles that can be accessed for free. While some scholarly search engines and databases include articles that aren't peer reviewed, there are also some that provide only peer-reviewed articles, and databases that include non-peer-reviewed articles often have advanced search features that enable you to select “peer review only.” The database will return results that are exclusively peer-reviewed content.
4. What Are Research Databases?
A research database is a list of journals, articles, datasets, and/or abstracts that allows you to easily search for scholarly and academic resources and conduct research online. There are databases that are interdisciplinary and cover a variety of topics.
For example, Paperity might be a great resource for a chemist as well as a linguist, and there are databases that are more specific to a certain field. So, while ERIC might be one of the best educational databases available for OA content, it's not going to be one of the best databases for finding research in the field of microbiology.
5. How Do I Find Scholarly Articles for Specific Fields?
There are interdisciplinary research databases that provide articles in a variety of fields, as well as research databases that provide articles that cater to specific disciplines. Additionally, a journal repository or index can be a helpful resource for finding articles in a specific field.
When searching an interdisciplinary database, there are frequently advanced search features that allow you to narrow the search results down so that they are specific to your field. Selecting “psychology” in the advanced search features will return psychology journal articles in your search results. You can also try databases that are specific to your field.
If you're searching for law journal articles, many law reviews are OA. If you don’t know of any databases specific to history, visiting a journal repository or index and searching “history academic journals” can return a list of journals specific to history and provide you with a place to begin your research.
6. Are Peer-Reviewed Articles Really More Legitimate?
The short answer is yes, peer-reviewed articles are more legitimate resources for academic research. The peer review process provides legitimacy, as it is a rigorous review of the content of an article that is performed by scholars and academics who are experts in their field of study. The review provides an evaluation of the quality and credibility of the article.
Non-peer-reviewed articles are not subject to a review process and do not undergo the same level of scrutiny. This means that non-peer-reviewed articles are unlikely, or at least not as likely, to meet the same standards that peer-reviewed articles do.
7. Are Free Article Directories Legitimate?
Yes! As with anything, some databases are going to be better for certain requirements than others. But, a scholarly article database being free is not a reason in itself to question its legitimacy.
Free scholarly article databases can provide access to abstracts, scholarly article websites, journal repositories, and high-quality peer-reviewed journal articles. The internet has a lot of information, and it's often challenging to figure out what information is reliable.
Research databases and article directories are great resources to help you conduct your research. Our list of the best research paper websites is sure to provide you with sources that are totally legit.
Get Professional Academic Editing
Hire an expert academic editor , or get a free sample, about the author.

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained numerous degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

How to Write a Research Proposal

How to Write a Scientific Paper

How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).



- Ask a Librarian
Citation Databases
- Searching Scopus
- Researcher Profiles
- Researcher IDs
- Searching Web of Science
- Google Scholar
- Research Impact and Metrics

Bibliometrics Overview
Welcome to Purdue University's Citation Databases Research Guide
Here you will find...
- Information on citation databases
- Descriptions of these databases
- Helpful examples on how to use them
- Use cases for each of the major citation databases
- Useful tips and tricks on how to best make use of them
Here are some definitions of common terms made use of by citation databases
- Bibliometrics is the statistical analysis of scholarly output like articles, book chapters, and reviews.
- Altmetrics: is the statistical analysis of alternative forms of capture such as twitter impressions of a piece of scholarly output.
Some common metrics are the H-index, Journal Impact Factor, and the FWCI (called CNCI in Web of Science).
- H-Index is a measure of how many times a journals published articles are cited, an index of fifteen means an article has been cited 15 times.
- Journal Impact Factor (IF) – A measurement of how many times a journal’s published articles are cited by different researchers.
- FWCI – Publication Field weighted citation indices indicate how the number of citations received by researcher’s publications compared to the average number for similar publications.
- Category Normalized Citation Impact (CNCI) – Calculated using Web of Science, CNCI is “an indicator of impact normalized for subject focus, age and document type. A CNCI of 1 is at par with the world average, anything above 2 is twice the global average
- SJR - Scimago Journal Rank is a measure of the "prestige" of journals which makes use of both the number of citations a journal accrues and the perception of those journals in the wider academic community
- SNIP - Source Normalized Impact per Paper is a metric which accounts for the field specific differences between journals. The need for this is that some fields have different publishing practices, time frames, and constraints. This results in the need for a metric like SNIP which is calculated by comparing the citations per journal with the citation potential of the field as a whole, in other words it would measure of history journal against other history journals and vice versa for other academic disciplines
Here are the five most common Citation Databases' Key Strengths and Use Cases
- Web of Science: Core Collection Access the world’s leading scholarly literature in the sciences, social sciences, arts, and humanities and examine proceedings of international conferences, symposia, seminars, colloquia, workshops, and conventions. -Science Citation Index Expanded (1900-present) -Social Sciences Citation Index (1900-present) -Arts & Humanities Citation Index (1975-present) -Conference Proceedings Citation Index- Science (1990-present) -Conference Proceedings Citation Index- Social Science & Humanities (1990-present) -Book Citation Index– Science (2005-present) -Book Citation Index– Social Sciences & Humanities (2005-present) -Current Chemical Reactions (1985-present) (Includes Institut National de la Propriete Industrielle structure data back to 1840) -Index Chemicus (1993-present) -Emerging Sources Citation Index (2005 – present)
- Google Scholar Searches for scholarly materials such as peer-reviewed papers, theses, books, preprints, abstracts and technical reports from broad areas of research. It includes a variety of academic publishers, professional societies, preprint repositories and universities, as well as scholarly articles available across the web.
- Dimensions Dimensions is a citations database which specializes in providing abstracts, citations, and patents to users. While the Library does not currently subscribe, you can access the free version of the database from this link
- Next: Scopus >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 9:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.purdue.edu/citationdatabases
AI Index Report
The AI Index Report tracks, collates, distills, and visualizes data related to artificial intelligence. Our mission is to provide unbiased, rigorously vetted, broadly sourced data in order for policymakers, researchers, executives, journalists, and the general public to develop a more thorough and nuanced understanding of the complex field of AI. The report aims to be the world’s most credible and authoritative source for data and insights about AI.
Subscribe to receive the 2024 report in your inbox!
Coming Soon: 2024 AI Index Report!
The 2024 AI Index Report will be out April 15! Sign up for our mailing list to receive it in your inbox.
Steering Committee Co-Directors

Ray Perrault
Steering committee members.

Erik Brynjolfsson

John Etchemendy

Katrina Ligett

Terah Lyons

James Manyika

Juan Carlos Niebles

Vanessa Parli

Yoav Shoham

Russell Wald
Staff members.

Loredana Fattorini

Nestor Maslej
Letter from the co-directors.
AI has moved into its era of deployment; throughout 2022 and the beginning of 2023, new large-scale AI models have been released every month. These models, such as ChatGPT, Stable Diffusion, Whisper, and DALL-E 2, are capable of an increasingly broad range of tasks, from text manipulation and analysis, to image generation, to unprecedentedly good speech recognition. These systems demonstrate capabilities in question answering, and the generation of text, image, and code unimagined a decade ago, and they outperform the state of the art on many benchmarks, old and new. However, they are prone to hallucination, routinely biased, and can be tricked into serving nefarious aims, highlighting the complicated ethical challenges associated with their deployment.
Although 2022 was the first year in a decade where private AI investment decreased, AI is still a topic of great interest to policymakers, industry leaders, researchers, and the public. Policymakers are talking about AI more than ever before. Industry leaders that have integrated AI into their businesses are seeing tangible cost and revenue benefits. The number of AI publications and collaborations continues to increase. And the public is forming sharper opinions about AI and which elements they like or dislike.
AI will continue to improve and, as such, become a greater part of all our lives. Given the increased presence of this technology and its potential for massive disruption, we should all begin thinking more critically about how exactly we want AI to be developed and deployed. We should also ask questions about who is deploying it—as our analysis shows, AI is increasingly defined by the actions of a small set of private sector actors, rather than a broader range of societal actors. This year’s AI Index paints a picture of where we are so far with AI, in order to highlight what might await us in the future.
- Jack Clark and Ray Perrault
Our Supporting Partners

Analytics & Research Partners

Stay up to date on the AI Index by subscribing to the Stanford HAI newsletter.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Year in Review
- Published: 04 April 2024
Climate chronicles
Ocean heat content in 2023
- Lijing Cheng ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9854-0392 1 , 2 ,
- Karina von Schuckmann ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9922-8528 3 ,
- Audrey Minière 3 ,
- Maria Z. Hakuba 4 ,
- Sarah Purkey ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1893-6224 5 ,
- Gavin A. Schmidt ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2258-0486 6 &
- Yuying Pan 1 , 2
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment volume 5 , pages 232–234 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
2615 Accesses
258 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Climate change
- Physical oceanography
In 2023, global full-depth ocean heat content (OHC) reached a record increase of 464 ± 55 ZJ since 1960, with strong heat gain observed in the Southern and Atlantic Oceans. OHC was 16 ± 10 ZJ higher than in 2022, continuing the long-term increasing trend that started in 1960.
Full-depth OHC peaked in 2023, with 40%, 24%, 28%, and 8% of heat accumulated within the 0–300 m, 300–700 m, 700–2000 m and below-2000 m layers, respectively, since 1960.
In situ and satellite approaches indicate an increasing — and accelerating — global heating rate, with a trend of 0.16 ± 0.02 W m –2 dec –1 estimated from 1960–2023.
Observed global ocean warming in 2023 is consistent with the projection of the CMIP6 multi-model-median.
You have full access to this article via your institution.
Improved integrated ocean observation systems since the 1960s have made estimates of ocean heat content (OHC) possible 1 . These observations indicate that approximately 90% of extra heat stored in the climate system is taken up by the ocean 2 , resulting in marked OHC increases 3 . Indeed, from 1958 to 2019, it is estimated that the top 2,000 m of the global ocean gained 351 ± 59.8 ZJ (1 ZJ = 10 21 J) heat, with most heat stored in the Atlantic and Southern Oceans (ocean area south of 35 o S) 1 .
On longer timescales, this ocean warming is largely attributed to human-induced greenhouse gas emissions and aerosols 4 . However, OHC variability is also evident at other timescales, including year-to-year variability linked to the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) 5 . Although these interannual fluctuations are small (particularly compared to other climate indicators, such as global mean surface temperature), the combined effect with long-term trends determines total annual OHC 6 . Given that 2023 was the warmest year on record for global surface temperature, it is to be expected that OHC also exhibited a record value 3 .
Here, we document the status of OHC for 2023, focusing on gridded observations (the IAP/CAS-OHC dataset 3 , which compiles all available measurements from the surface down to the abyss) supplemented by deep ocean observations below 2000 m (ref. 7 ), satellite observations 8 , 9 and state-of-the-art climate model results 6 ( Supplementary Information ).
Changes in 2023 ocean heat content
According to IAP gridded in situ observational data, total global OHC accumulation since 1960 reached 464 ± 55 ZJ (1 ZJ = 10 21 Joules; throughout, uncertainty represents 90% confidence intervals) in 2023 — the highest levels since reliable records started (Fig. 1a ). In fact, OHC records have been broken every year since 2017, highlighting continued ocean warming. For instance, year-on-year increases of 10 ± 6 ZJ were observed from 2019 to 2020, 19 ± 6 ZJ from 2020 to 2021, and 18 ± 8 ZJ from 2021 to 2022, culminating to an increase of 16 ± 10 ZJ from 2022 to 2023. The slightly smaller increment in 2022–2023 compared to the previous two years is likely associated with increased ocean heat release associated with anomalously high sea surface temperature in the tropical Pacific Ocean during the El Niño event in 2023. This slightly reduced heat gain does not affect the long-term continuous increases.
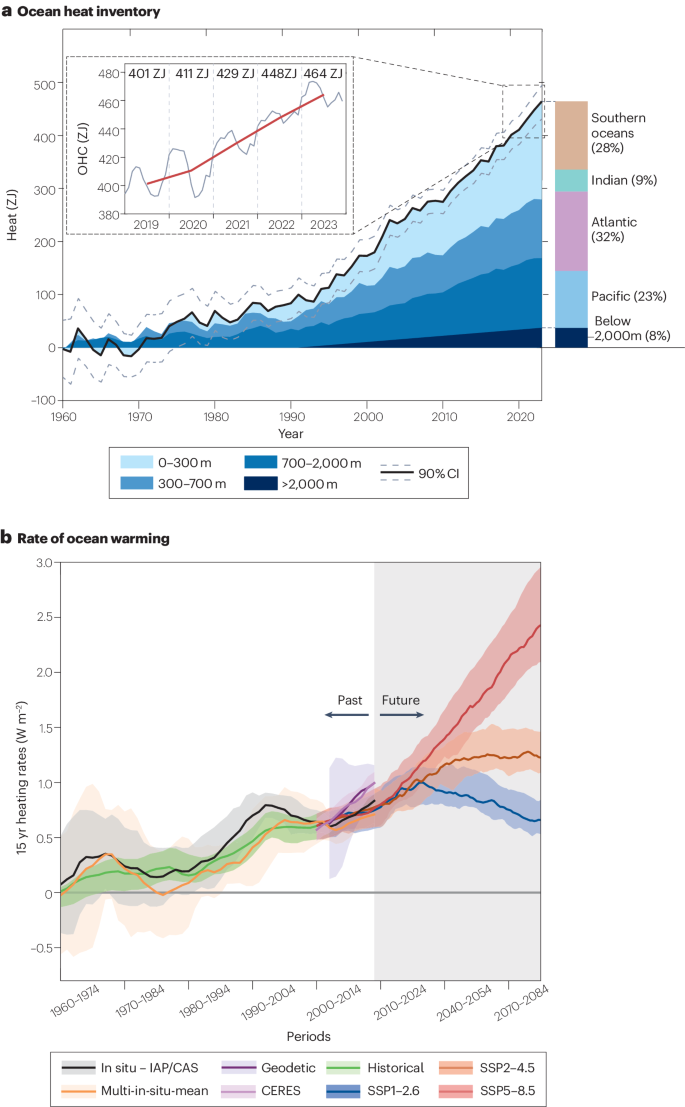
a , Full-depth ocean heat content time series from observations 3 relative to a 1958–1962 baseline. Blue shadings indicate OHC changes by depth layer; OHC for the upper 2000 m is from ref. 3 and OHC below 2000 m is adapted from ref. 7 (using a linear increase of 1.17 ± 0.51 ZJ yr –1 after 1992 and assuming a zero heating rate before 1991). Grey dashed lines represent the 90% confidence interval (CI) of the OHC estimate, calculated by summing the uncertainty estimates of upper 3 and lower 7 depth layers. The bar on the right depicts the 1960–2023 total heat accumulation by the ocean basin and the below-2000 m layer. The inset displays monthly OHC since January 2019, with the red line depicting the annual means. b , Running 15-year OHC heating rates (solid lines) and uncertainties (shading) for the full-depth in situ data 3 , 7 , the full-depth multi-in situ-data 7 , 10 , the geodetic estimate 9 , satellite observations at the top of the atmosphere (Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System, CERES) 8 , and various CMIP6 multi-model-medians 6 . For observational datasets, uncertainty is represented by 1.65 standard deviations of the linear weighted least squares regression in each 15-year sliding window 10 . For CMIP6, a 17–83% model spread is shown to quantify model uncertainty based on 24 models listed in ref. 1 . The x -axis is scaled after 2023. Various lines of evidence outline that ocean warming reached the highest observed levels in 2023, continuing the ongoing and accelerating trend that models suggest will continue into the future in the absence of drastic emissions reductions.
Ocean heat accumulates at different magnitudes depending on the depth level (Fig. 1a ) owing to various oceanographic mechanisms 4 . Of the 464 ± 55 ZJ heat accumulated since 1960, 40%, 24%, 28% and 8% are stored within the 0–300 m, 300–700 m, 700–2000 m and >2000 m layers, respectively (consistent with estimates from ten available datasets 2 ). In 2023, these values reflect OHC of 185.0 ± 2.9 ZJ (increasing by 17.3 from 2022) for 0–300 m; 110.6 ± 39.7 ZJ (a reduction of 1.3 ZJ from 2022) for 300–700 m; 131.2 ± 32.8 ZJ (a reduction of 0.8 ZJ from 2022) for 700–2000 m; and 37.4 ± 0.5 ZJ (an increase of 1.2 ZJ from 2022) for >2000 m. In general, 2023 reflects greater heat accumulation in the upper layers compared to the deeper layers, consistent with the slower response of the deep ocean to anthropogenic forcings. Some specific differences from 2022 to 2023 also reflect heat redistribution associated with El Niño, namely the redistribution of heat from the 100–700 m layer (–12.8 ZJ from 2022) to the 0–100 m layer (+ 29.0 ZJ from 2022) associated with more tropical thermocline flatting in the Indo-Pacific basin compared to La Niña years and neutral conditions 5 .
Changes in OHC also exhibit spatial differences linked to greenhouse gases, aerosol effects and natural variability 3 . All major basins exhibit warming, albeit at different rates. The upper 2000 m Atlantic and Southern Oceans (south of 35 o S) have warmed at a rate of 2.25 ± 0.11 ZJ yr –1 and 2.04 ± 0.12 ZJ yr –1 , respectively, from 1960 to 2023; that is to say, faster than the Pacific (1.77 ± 0.13 ZJ yr –1 ) and Indian (0.65 ± 0.08 ZJ yr –1 ) Oceans (Fig. 1a ). In particular, the deep (700–2000 m) warming of the Atlantic Ocean (0.85 ± 0.06 ZJ yr –1 ) and Southern Oceans (0.67 ± 0.08 ZJ yr –1 ) is much stronger than that observed in the Pacific (0.36 ± 0.05 ZJ yr –1 ) and Indian Oceans (0.20 ± 0.04 ZJ yr –1 ). This basin-wide difference is mainly due to changes in the deep-reaching ocean circulations and stronger mixing in the Atlantic and Southern Oceans that takes heat more efficiently into the deep layers. From 2022 to 2023, the Atlantic, Southern, and Indian Oceans continued the long-term increase of 0–2000 m OHC of 4.3 ZJ, 7.8 ZJ, and 3.2 ZJ, respectively. By contrast, the upper 2000 m of the Pacific Ocean lost –0.1 ZJ heat.
As alluded to, OHC changes in 2023 provide evidence of ongoing and accelerated heat gain. The acceleration is mainly associated with the elevated ocean warming rate since the 1990s, with a two- to four-fold increase in the rate of OHC since this time 2 , 10 (Fig. 1b ; Supplementary Tables 1 , 2 ). For instance, the full-depth OHC rate increased from 0.16 ± 0.02 W m –2 dec –1 over 1960–2023, 0.19 ± 0.03 W m –2 dec –1 over 1975–2023, 0.06 ± 0.04 W m –2 dec –1 over 1990–2023, to 0.35 ± 0.06 W m –2 dec –1 over 2005–2023 (Supplementary Tables 3 – 6 ; Supplementary Fig. 1 , the acceleration is calculated by taking two times the quadratic term of a quadratic regression).
Supporting evidence for ocean warming
In addition to direct evidence from in situ observations, estimates of 2023 OHC changes can also come from other sources, including sea level budgets, model simulations and the Earth’s energy imbalance (EEI) (Fig. 1b ). As ocean warming, together with ice melt on land, is a major driver of sea level rise 4 , the sea level budget can be used to quantify OHC. Geodetic data 9 updated through November 2023 independently confirm that 2023 experienced the highest OHC on record, yielding a total heat increase of 37 ± 21 ZJ from 2022. Although larger than direct in situ measurements, these values are within their range of uncertainty (Fig. 1a ). The CMIP6 multi-model-median forced with SSP2-4.5 (an intermediate emission scenario that approximately reflects current emissions) is even more consistent with observations: total heat gains of 14 [10, 20] ZJ (17–83% CI for model results) are apparent from 2022 and 368 [283, 445] since 1960. The choice of the emission scenario has only a small effect on the current OHC increase.
Beyond 2023, these different data products and approaches also provide supporting evidence for OHC acceleration. However, specific numbers differ owing to dataset differences, time periods and methodological choices (Supplementary Tables 3 – 6 ). As above, in situ observations suggest an acceleration of OHC gain of 0.16 ± 0.02 W m –2 dec –1 for IAP/CAS and 0.15 ± 0.03 W m –2 dec –1 for multi-in situ-data ensemble mean over 1960–2023 (Fig. 1b ). For 2005–2023, geodetic data suggest an acceleration of 0.54 ± 0.39 W m –2 dec –1 . The CMIP6-MMM (with SSP2-4.5 after 2014) reveals an almost identical long-term acceleration as compared to the observations: from 0.15 [0.13, 0.21] W m –2 dec –1 over 1960–2023 to 0.19 [-0.00, 0.36] W m –2 dec –1 over 2005–2023 (Fig. 1b ). CMIP6 models project that this warming acceleration will only cease between about 2030 and 2040 under a low-emission scenario (SSP1-2.6) 1 , by which time full-depth ocean warming rate peaks at ~1 W m –2 . For the simulated higher emission paths, ocean warming acceleration will continue throughout the twenty-first century.
Given that ocean warming provides direct evidence that the climate system is out of thermal equilibrium and, hence, accumulating heat, the Earth’s Energy Imbalance (EEI) 8 can also be used as a supporting metric. Radiometric data estimates based on satellite observations at the top of the atmosphere (Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System, CERES) indicate an annual mean EEI of 1.8 ± 0.7 W m –2 from 2022 to 2023. EEI using geodetic OHC amounts to 2.5 ± 1.4 W m –2 from 2022 to 2023. These EEI estimates are broadly similar and within uncertainties with the OHC-based estimates (assuming 90% of the heat goes into the ocean), which is 1.1 ± 0.8 W m –2 . As for other OHC metrics, the EEI is increasing. For instance, radiometric data suggest an increasing EEI of 0.57 ± 0.18 W m –2 dec –1 over 2005–2023, consistent with the geodetic OHC acceleration of 0.54 ± 0.39 W m –2 dec –1 over the same period (Fig. 1b ; Supplementary Table S6 ). The increase of EEI calculated using in situ OHC data over the same periods are 0.35 ± 0.06 W m –2 dec –1 for IAP/CAS data and 0.21 ± 0.17 W m –2 dec –1 for the ensemble mean of other in situ observational data (Supplementary Table S6 ).
Collectively, these various lines of evidence confirm a robust long-term ocean warming acceleration, with the warming trend progressively increasing since the 1960s. These long-term warming trends set the stage for the record-high OHC in 2023.
OHC reached a record high in 2023, continuing its long-term increasing trend. Ocean warming has already led to pervasive impacts and consequences, for example, altering ocean circulation, rising sea level and vertical stratification, intensifying tropical cyclones, reducing ocean oxygen levels, melting sea ice and ice sheets from below, busting marine heat waves, and other extremes 1 . With the ocean’s large thermal inertia, deep ocean warming is expected to continue for at least hundreds of years. Thus, the consequences of ocean warming are expected to become even more severe. Indeed, the level and the rate of warming depend critically on socioeconomic scenarios, which makes OHC a policy-relevant metric 1 . Detecting changes in ocean warming is crucial for informed decision-making in international climate negotiations to limit anthropogenic warming to specific levels. As a result, it requires sustained and extended monitoring of OHC (and EEI), improved understanding and reduction of uncertainty, and reconciliation of the various heating rate estimates and approaches.
Data availability
Argo data were collected and made freely available by the International Argo Program and the national programmes contributing to it ( https://argo.ucsd.edu , https://www.ocean-ops.org ). The IAP/CAS (Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences) observation and model data used are available at www.ocean.iap.ac.cn .
Cheng, L. et al. Past and future ocean warming. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 3 , 776–794 (2022).
Article Google Scholar
von Schuckmann, K. et al. Heat stored in the Earth system 1960–2020: where does the energy go? Earth Syst. Sci. Data 15 , 1675–1709 (2023).
Cheng, L. et al. New Record Ocean temperatures and related climate impact drivers in 2023. Adv. Atmos. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-024-3378-5 (2024).
Gulev, S. et al. Changing state of the climate system. In Climate Change 2021: The physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the sixth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change (eds. Masson-Delmotte, V. et al.) 287–422 (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2021).
Cheng, L. et al. Evolution of Ocean Heat Content Related to ENSO. J. Clim. 32 , 3529–3556 (2019).
Eyring, V. et al. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 9 , 1937–1958 (2016).
Purkey, S. G. & Johnson, G. C. Warming of Global Abyssal and Deep Southern Ocean Waters between the 1990s and 2000s: Contributions to Global Heat and Sea Level Rise Budgets. J. Clim. 23 , 6336–6351 (2010).
Loeb, N. G. et al. Satellite and Ocean Data Reveal Marked Increase in Earth’s Heating Rate. Geophys. Res. Lett. 48 , e2021GL093047 (2021).
Hakuba, M. Z., Frederikse, T. & Landerer, F. W. Earth’s Energy Imbalance From the Ocean Perspective (2005–2019). Geophys. Res. Lett. 48 , e2021GL093624 (2021).
Minière, A., von Schuckmann, K. Sallée, J.-B. & Vogt, L. Robust acceleration of Earth system heating observed over the past six decades. Sci. Rep. 13 , 22975 (2023).
Download references
Acknowledgements
L. C. acknowledges financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 42076202), the new Cornerstone Science Foundation through the XPLORER PRIZE; Youth Innovation Promotion Association, Chinese Academy of Sciences; National Key Scientific and Technological Infrastructure project “Earth System Science Numerical Simulator Facility” (EarthLab). Research by M. H. was carried out at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under a contract with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (80NM0018D0004). Research by K. v. S. was carried out at Mercator Ocean International, France. We thank B. Beckley for providing updated GMSL data utilized in the geodetic analysis. We acknowledge the World Climate Research Programme’s Working Group on Coupled Modelling, which is responsible for CMIP, and we thank the climate modelling groups for producing and making available their model output through the Earth System Grid Federation. The Argo Program is part of the Global Ocean Observing System.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
Lijing Cheng & Yuying Pan
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
Mercator Ocean International, Toulouse, France
Karina von Schuckmann & Audrey Minière
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA
Maria Z. Hakuba
Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, CA, USA
Sarah Purkey
Goddard Institute for Space Studies, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, New York City, NY, USA
Gavin A. Schmidt
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Lijing Cheng .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Cheng, L., von Schuckmann, K., Minière, A. et al. Ocean heat content in 2023. Nat Rev Earth Environ 5 , 232–234 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-024-00539-9
Download citation
Published : 04 April 2024
Issue Date : April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-024-00539-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computation and Language
Title: realm: reference resolution as language modeling.
Abstract: Reference resolution is an important problem, one that is essential to understand and successfully handle context of different kinds. This context includes both previous turns and context that pertains to non-conversational entities, such as entities on the user's screen or those running in the background. While LLMs have been shown to be extremely powerful for a variety of tasks, their use in reference resolution, particularly for non-conversational entities, remains underutilized. This paper demonstrates how LLMs can be used to create an extremely effective system to resolve references of various types, by showing how reference resolution can be converted into a language modeling problem, despite involving forms of entities like those on screen that are not traditionally conducive to being reduced to a text-only modality. We demonstrate large improvements over an existing system with similar functionality across different types of references, with our smallest model obtaining absolute gains of over 5% for on-screen references. We also benchmark against GPT-3.5 and GPT-4, with our smallest model achieving performance comparable to that of GPT-4, and our larger models substantially outperforming it.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
RESEARCH PAPERS: How To Find Sources & Make Citations
Monday, april 15, 2024.

In-Person Option: Library | HLRC - Rm 218
On Zoom Option: Meeting ID: 847 8072 5347 Password: 487592
For more information: (310) 287-4269 | Library
Database Searching
How to search for credible sources using databases such as ProQuest, JSTOR, EBSCO & more.
- Mon, Apr 15 - 2:00 PM
- Wed, May 8 - 12:30 PM
Cite Right Series
Avoid plagiarism, learn to cite sources for academic papers in MLA or APA style.
- MLA Style - Apr 17 Wed, 1:00 PM
- APA Style - May 14 Tue, 5:30 PM (online only)
- MLA Style - May 21 Tue, 12:30 PM
- APA Style - May 23 Thurs, 2:00 PM
Intro to Research: Mon, Apr 22 - 11:30AM
Get started on research! Learn the steps of brainstorming ideas, researching, writing a thesis statement & more.
Using AI in Research: Tues, May 7 @ 12:30
Learn how to integrate the use of AI tools into your research.
Link copied to clipboard

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world's leading museums, archives, and scholars. JSTOR is a digital library of academic journals ...
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile. 1. Scopus. Scopus is one of the two big commercial, bibliographic databases that cover scholarly literature from almost any discipline. Besides searching for research articles, Scopus also provides academic journal rankings, author profiles, and an h-index calculator. 2.
Bibliographic database for planning and building related publications, chronological coverage since 1975. Focus: German-language publications, journal articles, book chapters, conference papers, research reports. Subscription Fraunhofer IRB: Russian Science Citation Index: Multidisciplinary: 35,409,829
What is Database Search? Harvard Library licenses hundreds of online databases, giving you access to academic and news articles, books, journals, primary sources, streaming media, and much more. The contents of these databases are only partially included in HOLLIS. To make sure you're really seeing everything, you need to search in multiple places.
Advanced. Journal List. PubMed Central ® (PMC) is a free full-text archive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature at the U.S. National Institutes of Health's National Library of Medicine (NIH/NLM)
3.3 million articles on ScienceDirect are open access. Articles published open access are peer-reviewed and made freely available for everyone to read, download and reuse in line with the user license displayed on the article. ScienceDirect is the world's leading source for scientific, technical, and medical research.
Access 160+ million publications and connect with 25+ million researchers. Join for free and gain visibility by uploading your research.
Find the research you need | With 160+ million publications, 1+ million questions, and 25+ million researchers, this is where everyone can access science
Scopus is the largest abstract and citation database of peer-reviewed literature: scientific journals, books and conference proceedings. Delivering a comprehensive overview of the world's research output in the fields of science, technology, medicine, social sciences, and arts and humanities, Scopus features smart tools to track, analyse and visualise research.
arXiv is a free distribution service and an open-access archive for nearly 2.4 million scholarly articles in the fields of physics, mathematics, computer science, quantitative biology, quantitative finance, statistics, electrical engineering and systems science, and economics.
Search all biomedical databases provided by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), an agency of the U.S. National Library of Medicine at the NIH ... While these interactions have been well studied, a research team supported in part by NIH has made an unexpected discovery into how a key immune checkpoint works, with ...
How to search academic databases. 1. Use the campus network to access research databases. 2. Find databases that are specifically related to your topic. 3. Set up the search parameters within a database to be as narrow as possible. 4. Ask a librarian for help.
Moved Permanently. The document has moved here.
Academic search engines have become the number one resource to turn to in order to find research papers and other scholarly sources. While classic academic databases like Web of Science and Scopus are locked behind paywalls, Google Scholar and others can be accessed free of charge. In order to help you get your research done fast, we have compiled the top list of free academic search engines.
A comprehensive bibliographic database of the world's scholarly literature. Explore CORE data. The world's largest collection of open access research papers. ... Enabling others to create new tools and innovate using a global comprehensive collection of research papers.
Semantic Reader is an augmented reader with the potential to revolutionize scientific reading by making it more accessible and richly contextual. Try it for select papers. Semantic Scholar uses groundbreaking AI and engineering to understand the semantics of scientific literature to help Scholars discover relevant research.
Work faster and smarter with advanced research discovery tools. Search the full text and citations of our millions of papers. Download groups of related papers to jumpstart your research. Save time with detailed summaries and search alerts. Advanced Search. PDF Packages of 37 papers.
These databases provide a variety of free sources, from abstracts and citations to full-text, peer-reviewed OA journals. With databases covering specific areas of research and interdisciplinary databases that provide a variety of material, these are some of our favorite free databases, and they're totally legit! 1.
Search Millions of Research Papers. This fulltext search index includes over 35 million research articles and other scholarly documents preserved in the Internet Archive. The collection spans from digitized copies of eighteenth century journals through the latest Open Access conference proceedings and preprints crawled from the World Wide Web.
Find support. Find answers to questions about products, access, setup, and administration. Visit the support center. ProQuest powers research in academic, corporate, government, public and school libraries around the world with unique content. Explore millions of resources from scholarly journals, books, newspapers, videos and more.
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature ...
A database management system (DBMS) is an integral part of effectively all software systems, and therefore it is logical that different studies have compared the performance of different DBMSs in hopes of finding the most efficient one. This study systematically synthesizes the results and approaches of studies that compare DBMS performance and ...
Scopus is the largest abstract and citation database of peer-reviewed research literature. With over 19,000 titles from more than 5,000 international publishers, Scopus supports research needs in the scientific, technical, medical, social sciences, and the arts and humanities. ... Searches for scholarly materials such as peer-reviewed papers ...
The AI Index Report tracks, collates, distills, and visualizes data related to artificial intelligence. Our mission is to provide unbiased, rigorously vetted, broadly sourced data in order for policymakers, researchers, executives, journalists, and the general public to develop a more thorough and nuanced understanding of the complex field of AI.
In 2023, global full-depth ocean heat content (OHC) reached a record increase of 464 ± 55 ZJ since 1960, with strong heat gain observed in the Southern and Atlantic Oceans. OHC was 16 ± 10 ZJ ...
Reference resolution is an important problem, one that is essential to understand and successfully handle context of different kinds. This context includes both previous turns and context that pertains to non-conversational entities, such as entities on the user's screen or those running in the background. While LLMs have been shown to be extremely powerful for a variety of tasks, their use in ...
Database Searching. How to search for credible sources using databases such as ProQuest, JSTOR, EBSCO & more. Mon, Apr 15 - 2:00 PM; Wed, May 8 - 12:30 PM Cite Right Series. Avoid plagiarism, learn to cite sources for academic papers in MLA or APA style. MLA Style - Apr 17 Wed, 1:00 PM; APA Style - May 14 Tue, 5:30 PM (online only)