

01 Career Opportunities
- Top 50 Java Interview Questions and Answers
- Java Developer Salary Guide in India – For Freshers & Experienced
02 Beginner
- Hierarchical Inheritance in Java
- Arithmetic operators in Java
- Unary operator in Java
- Relational operators in Java
Assignment operator in Java
- Logical operators in Java
- Primitive Data Types in Java
- Multiple Inheritance in Java
- Parameterized Constructor in Java
- Constructor Chaining in Java
- What is a Bitwise Operator in Java? Type, Example and More
- Constructor Overloading in Java
- Ternary Operator in Java
- For Loop in Java: Its Types and Examples
- Best Java Developer Roadmap 2024
- While Loop in Java
- What are Copy Constructors In Java? Explore Types,Examples & Use
- Do-While Loop in Java
- Hybrid Inheritance in Java
- Single Inheritance in Java
- Top 10 Reasons to know why Java is Important?
- What is Java? A Beginners Guide to Java
- Differences between JDK, JRE, and JVM: Java Toolkit
- Variables in Java: Local, Instance and Static Variables
- Data Types in Java - Primitive and Non-Primitive Data Types
- Conditional Statements in Java: If, If-Else and Switch Statement
- What are Operators in Java - Types of Operators in Java ( With Examples )
- Java VS Python
- Looping Statements in Java - For, While, Do-While Loop in Java
- Jump Statements in JAVA - Types of Statements in JAVA (With Examples)
- Java Arrays: Single Dimensional and Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- What is String in Java - Java String Types and Methods (With Examples)
03 Intermediate
- OOPs Concepts in Java: Encapsulation, Abstraction, Inheritance, Polymorphism
- What is Class in Java? - Objects and Classes in Java {Explained}
- Access Modifiers in Java: Default, Private, Public, Protected
- Constructors in Java: Types of Constructors with Examples
- Polymorphism in Java: Compile time and Runtime Polymorphism
- Abstract Class in Java: Concepts, Examples, and Usage
- What is Inheritance in Java: Types of Inheritance in Java
- Exception handling in Java: Try, Catch, Finally, Throw and Throws
04 Training Programs
- Java Programming Course
- C++ Programming Course
- MERN: Full-Stack Web Developer Certification Training
- Data Structures and Algorithms Training
- Assignment Operator In Ja..

Java Programming For Beginners Free Course
Assignment operators in java: an overview.
We already discussed the Types of Operators in the previous tutorial Java. In this Java tutorial , we will delve into the different types of assignment operators in Java, and their syntax, and provide examples for better understanding. Because Java is a flexible and widely used programming language. Assignment operators play a crucial role in manipulating and assigning values to variables. To further enhance your understanding and application of Java assignment operator's concepts, consider enrolling in the best Java Certification Course .
What are the Assignment Operators in Java?
Assignment operators in Java are used to assign values to variables . They are classified into two main types: simple assignment operator and compound assignment operator.
The general syntax for a simple assignment statement is:
And for a compound assignment statement:
Read More - Advanced Java Interview Questions
Types of Assignment Operators in Java
- Simple Assignment Operator: The Simple Assignment Operator is used with the "=" sign, where the operand is on the left side and the value is on the right. The right-side value must be of the same data type as that defined on the left side.
- Compound Assignment Operator: Compound assignment operators combine arithmetic operations with assignments. They provide a concise way to perform an operation and assign the result to the variable in one step. The Compound Operator is utilized when +,-,*, and / are used in conjunction with the = operator.
1. Simple Assignment Operator (=):
The equal sign (=) is the basic assignment operator in Java. It is used to assign the value on the right-hand side to the variable on the left-hand side.
Explanation
2. addition assignment operator (+=) :, 3. subtraction operator (-=):, 4. multiplication operator (*=):.
Read More - Java Developer Salary
5. Division Operator (/=):
6. modulus assignment operator (%=):, example of assignment operator in java.
Let's look at a few examples in our Java Playground to illustrate the usage of assignment operators in Java:
- Unary Operator in Java
- Arithmetic Operators in Java
- Relational Operators in Java
- Logical Operators in Java
Q1. Can I use multiple assignment operators in a single statement?
Q2. are there any other compound assignment operators in java, q3. how many types of assignment operators.
- 1. (=) operator
- 1. (+=) operator
- 2. (-=) operator
- 3. (*=) operator
- 4. (/=) operator
- 5. (%=) operator
About Author

- 22+ Video Courses
- 750+ Hands-On Labs
- 300+ Quick Notes
- 55+ Skill Tests
- 45+ Interview Q&A Courses
- 10+ Real-world Projects
- Career Coaching Sessions
- Email Support
Upcoming Master Classes
We use cookies to make interactions with our websites and services easy and meaningful. Please read our Privacy Policy for more details.
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8. Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available. See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases. See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.
Summary of Operators
The following quick reference summarizes the operators supported by the Java programming language.
Simple Assignment Operator
Arithmetic operators, unary operators, equality and relational operators, conditional operators, type comparison operator, bitwise and bit shift operators.
About Oracle | Contact Us | Legal Notices | Terms of Use | Your Privacy Rights
Copyright © 1995, 2022 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
- Enterprise Java
- Web-based Java
- Data & Java
- Project Management
- Visual Basic
- Ruby / Rails
- Java Mobile
- Architecture & Design
- Open Source
- Web Services

Developer.com content and product recommendations are editorially independent. We may make money when you click on links to our partners. Learn More .

Java provides many types of operators to perform a variety of calculations and functions, such as logical , arithmetic , relational , and others. With so many operators to choose from, it helps to group them based on the type of functionality they provide. This programming tutorial will focus on Java’s numerous a ssignment operators.
Before we begin, however, you may want to bookmark our other tutorials on Java operators, which include:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Conditional Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise and Shift Operators
Assignment Operators in Java
As the name conveys, assignment operators are used to assign values to a variable using the following syntax:
The left side operand of the assignment operator must be a variable, whereas the right side operand of the assignment operator may be a literal value or another variable. Moreover, the value or variable on the right side must be of the same data type of the operand on the left side. Otherwise, the compiler will raise an error. Assignment operators have a right to left associativity in that the value given on the right-hand side of the operator is assigned to the variable on the left. Therefore, the right-hand side variable must be declared before assignment.
You can learn more about variables in our programming tutorial: Working with Java Variables .
Types of Assignment Operators in Java
Java assignment operators are classified into two types: simple and compound .
The Simple assignment operator is the equals ( = ) sign, which is the most straightforward of the bunch. It simply assigns the value or variable on the right to the variable on the left.
Compound operators are comprised of both an arithmetic, bitwise, or shift operator in addition to the equals ( = ) sign.
Equals Operator (=) Java Example
First, let’s learn to use the one-and-only simple assignment operator – the Equals ( = ) operator – with the help of a Java program. It includes two assignments: a literal value to num1 and the num1 variable to num2 , after which both are printed to the console to show that the values have been assigned to the numbers:
The += Operator Java Example
A compound of the + and = operators, the += adds the current value of the variable on the left to the value on the right before assigning the result to the operand on the left. Here is some sample code to demonstrate how to use the += operator in Java:
The -= Operator Java Example
Made up of the – and = operators, the -= first subtracts the variable’s value on the right from the current value of the variable on the left before assigning the result to the operand on the left. We can see it at work below in the following code example showing how to decrement in Java using the -= operator:
The *= Operator Java Example
This Java operator is comprised of the * and = operators. It operates by multiplying the current value of the variable on the left to the value on the right and then assigning the result to the operand on the left. Here’s a program that shows the *= operator in action:
The /= Operator Java Example
A combination of the / and = operators, the /= Operator divides the current value of the variable on the left by the value on the right and then assigns the quotient to the operand on the left. Here is some example code showing how to use the /= operator in Java:
%= Operator Java Example
The %= operator includes both the % and = operators. As seen in the program below, it divides the current value of the variable on the left by the value on the right and then assigns the remainder to the operand on the left:
Compound Bitwise and Shift Operators in Java
The Bitwise and Shift Operators that we just recently covered can also be utilized in compound form as seen in the list below:
- &= – Compound bitwise Assignment operator.
- ^= – Compound bitwise ^ assignment operator.
- >>= – Compound right shift assignment operator.
- >>>= – Compound right shift filled 0 assignment operator.
- <<= – Compound left shift assignment operator.
The following program demonstrates the working of all the Compound Bitwise and Shift Operators :
Final Thoughts on Java Assignment Operators
This programming tutorial presented an overview of Java’s simple and compound assignment Operators. An essential building block to any programming language, developers would be unable to store any data in their programs without them. Though not quite as indispensable as the equals operator, compound operators are great time savers, allowing you to perform arithmetic and bitwise operations and assignment in a single line of code.
Read more Java programming tutorials and guides to software development .
Get the Free Newsletter!
Subscribe to Developer Insider for top news, trends & analysis
Latest Posts
What is the role of a project manager in software development, how to use optional in java, overview of the jad methodology, microsoft project tips and tricks, how to become a project manager in 2023, related stories, understanding types of thread synchronization errors in java, understanding memory consistency in java threads.

Java Tutorial
Control statements, java object class, java inheritance, java polymorphism, java abstraction, java encapsulation, java oops misc.
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share

Learn Latest Tutorials
Transact-SQL
Reinforcement Learning
R Programming
React Native
Python Design Patterns
Python Pillow
Python Turtle
Preparation

Verbal Ability

Interview Questions

Company Questions
Trending Technologies
Artificial Intelligence
Cloud Computing
Data Science
Machine Learning
B.Tech / MCA
Data Structures
Operating System
Computer Network
Compiler Design
Computer Organization
Discrete Mathematics
Ethical Hacking
Computer Graphics
Software Engineering
Web Technology
Cyber Security
C Programming
Control System
Data Mining
Data Warehouse


- Basics of Java
- ➤ Java Introduction
- ➤ History of Java
- ➤ Getting started with Java
- ➤ What is Path and Classpath
- ➤ Checking Java installation and Version
- ➤ Syntax in Java
- ➤ My First Java Program
- ➤ Basic terms in Java Program
- ➤ Runtime and Compile time
- ➤ What is Bytecode
- ➤ Features of Java
- ➤ What is JDK JRE and JVM
- ➤ Basic Program Examples
- Variables and Data Types
- ➤ What is Variable
- ➤ Types of Java Variables
- ➤ Naming conventions for Identifiers
- ➤ Data Type in Java
- ➤ Mathematical operators in Java
- ➤ Assignment operator in Java
- ➤ Arithmetic operators in Java
- ➤ Unary operators in Java
- ➤ Conditional and Relational Operators
- ➤ Bitwise and Bit Shift Operators
- ➤ Operator Precedence
- ➤ Overflow Underflow Widening Narrowing
- ➤ Variable and Data Type Programs
- Control flow Statements
- ➤ Java if and if else Statement
- ➤ else if and nested if else Statement
- ➤ Java for Loop
- ➤ Java while and do-while Loop
- ➤ Nested loops
- ➤ Java break Statement
- ➤ Java continue and return Statement
- ➤ Java switch Statement
- ➤ Control Flow Program Examples
- Array and String in Java
- ➤ Array in Java
- ➤ Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- ➤ for-each loop in java
- ➤ Java String
- ➤ Useful Methods of String Class
- ➤ StringBuffer and StringBuilder
- ➤ Array and String Program Examples
- Classes and Objects
- ➤ Classes in Java
- ➤ Objects in Java
- ➤ Methods in Java
- ➤ Constructors in Java
- ➤ static keyword in Java
- ➤ Call By Value
- ➤ Inner/nested classes in Java
- ➤ Wrapper Classes
- ➤ Enum in Java
- ➤ Initializer blocks
- ➤ Method Chaining and Recursion
- Packages and Interfaces
- ➤ What is package
- ➤ Sub packages in java
- ➤ built-in packages in java
- ➤ Import packages
- ➤ Access modifiers
- ➤ Interfaces in Java
- ➤ Key points about Interfaces
- ➤ New features in Interfaces
- ➤ Nested Interfaces
- ➤ Structure of Java Program
- OOPS Concepts
- ➤ What is OOPS
- ➤ Inheritance in Java
- ➤ Inheritance types in Java
- ➤ Abstraction in Java
- ➤ Encapsulation in Java
- ➤ Polymorphism in Java
- ➤ Runtime and Compile-time Polymorphism
- ➤ Method Overloading
- ➤ Method Overriding
- ➤ Overloading and Overriding Differences
- ➤ Overriding using Covariant Return Type
- ➤ this keyword in Java
- ➤ super keyword in Java
- ➤ final keyword in Java
Assignment Operator in Java with Example
Assignment operator is one of the simplest and most used operator in java programming language. As the name itself suggests, the assignment operator is used to assign value inside a variable. In java we can divide assignment operator in two types :
- Assignment operator or simple assignment operator
- Compound assignment operators
What is assignment operator in java
The = operator in java is known as assignment or simple assignment operator. It assigns the value on its right side to the operand(variable) on its left side. For example :
The left-hand side of an assignment operator must be a variable while the right side of it should be a value which can be in the form of a constant value, a variable name, an expression, a method call returning a compatible value or a combination of these.
The value at right side of assignment operator must be compatible with the data type of left side variable, otherwise compiler will throw compilation error. Following are incorrect assignment :
Another important thing about assignment operator is that, it is evaluated from right to left . If there is an expression at right side of assignment operator, it is evaluated first then the resulted value is assigned in left side variable.
Here in statement int x = a + b + c; the expression a + b + c is evaluated first, then the resulted value( 60 ) is assigned into x . Similarly in statement a = b = c , first the value of c which is 30 is assigned into b and then the value of b which is now 30 is assigned into a .
The variable at left side of an assignment operator can also be a non-primitive variable. For example if we have a class MyFirstProgram , we can assign object of MyFirstProgram class using = operator in MyFirstProgram type variable.
Is == an assignment operator ?
No , it's not an assignment operator, it's a relational operator used to compare two values.
Is assignment operator a binary operator
Yes , as it requires two operands.
Assignment operator program in Java
a = 2 b = 2 c = 4 d = 4 e = false
Java compound assignment operators
The assignment operator can be mixed or compound with other operators like addition, subtraction, multiplication etc. We call such assignment operators as compound assignment operator. For example :
Here the statement a += 10; is the short version of a = a + 10; the operator += is basically addition compound assignment operator. Similarly b *= 5; is short version of b = b * 5; the operator *= is multiplication compound assignment operator. The compound assignment can be in more complex form as well, like below :
List of all assignment operators in Java
The table below shows the list of all possible assignment(simple and compound) operators in java. Consider a is an integer variable for this table.

How many assignment operators are there in Java ?
Including simple and compound assignment we have total 12 assignment operators in java as given in above table.
What is shorthand operator in Java ?
Shorthand operators are nothing new they are just a shorter way to write something that is already available in java language. For example the code a += 5 is shorter way to write a = a + 5 , so += is a shorthand operator. In java all the compound assignment operator(given above) and the increment/decrement operators are basically shorthand operators.
Compound assignment operator program in Java
a = 20 b = 80 c = 30 s = 64 s2 = 110 b2 = 15
What is the difference between += and =+ in Java?
An expression a += 1 will result as a = a + 1 while the expression a =+ 1 will result as a = +1 . The correct compound statement is += , not =+ , so do not use the later one.

Java Tutorial
Java methods, java classes, java file handling, java how to, java reference, java examples, java strings.
Strings are used for storing text.
A String variable contains a collection of characters surrounded by double quotes:
Create a variable of type String and assign it a value:
Try it Yourself »
String Length
A String in Java is actually an object, which contain methods that can perform certain operations on strings. For example, the length of a string can be found with the length() method:
More String Methods
There are many string methods available, for example toUpperCase() and toLowerCase() :
Finding a Character in a String
The indexOf() method returns the index (the position) of the first occurrence of a specified text in a string (including whitespace):
Java counts positions from zero. 0 is the first position in a string, 1 is the second, 2 is the third ...
Complete String Reference
For a complete reference of String methods, go to our Java String Methods Reference .
The reference contains descriptions and examples of all string methods.
Test Yourself With Exercises
Fill in the missing part to create a greeting variable of type String and assign it the value Hello .
Start the Exercise
Using the Java Keyword new
You can also create a String and assign values to it with the new keyword:
Strings in Java are objects, and an object in Java is declared with the new keyword. However, instead of using the new keyword, you can easily just write the string text inside double quotes. This is called a "String literal". It is up to you which method you would like to use. You will learn more about objects in a later chapter.

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.
- Java Arrays
- Java Strings
- Java Collection
- Java 8 Tutorial
- Java Multithreading
- Java Exception Handling
- Java Programs
- Java Project
- Java Collections Interview
- Java Interview Questions
- Spring Boot
- Java Tutorial
Overview of Java
- Introduction to Java
- The Complete History of Java Programming Language
- C++ vs Java vs Python
- How to Download and Install Java for 64 bit machine?
- Setting up the environment in Java
- How to Download and Install Eclipse on Windows?
- JDK in Java
- How JVM Works - JVM Architecture?
- Differences between JDK, JRE and JVM
- Just In Time Compiler
- Difference between JIT and JVM in Java
- Difference between Byte Code and Machine Code
- How is Java platform independent?
Basics of Java
- Java Basic Syntax
- Java Hello World Program
- Java Data Types
- Primitive data type vs. Object data type in Java with Examples
- Java Identifiers
Operators in Java
- Java Variables
- Scope of Variables In Java
Wrapper Classes in Java
Input/output in java.
- How to Take Input From User in Java?
- Scanner Class in Java
- Java.io.BufferedReader Class in Java
- Difference Between Scanner and BufferedReader Class in Java
- Ways to read input from console in Java
- System.out.println in Java
- Difference between print() and println() in Java
- Formatted Output in Java using printf()
- Fast I/O in Java in Competitive Programming
Flow Control in Java
- Decision Making in Java (if, if-else, switch, break, continue, jump)
- Java if statement with Examples
- Java if-else
- Java if-else-if ladder with Examples
- Loops in Java
- For Loop in Java
- Java while loop with Examples
- Java do-while loop with Examples
- For-each loop in Java
- Continue Statement in Java
- Break statement in Java
- Usage of Break keyword in Java
- return keyword in Java
- Java Arithmetic Operators with Examples
- Java Unary Operator with Examples
- Java Assignment Operators with Examples
- Java Relational Operators with Examples
- Java Logical Operators with Examples
Java Ternary Operator with Examples
- Bitwise Operators in Java
- Strings in Java
- String class in Java
- Java.lang.String class in Java | Set 2
- Why Java Strings are Immutable?
- StringBuffer class in Java
- StringBuilder Class in Java with Examples
- String vs StringBuilder vs StringBuffer in Java
- StringTokenizer Class in Java
- StringTokenizer Methods in Java with Examples | Set 2
- StringJoiner Class in Java
- Arrays in Java
- Arrays class in Java
- Multidimensional Arrays in Java
- Different Ways To Declare And Initialize 2-D Array in Java
- Jagged Array in Java
- Final Arrays in Java
- Reflection Array Class in Java
- util.Arrays vs reflect.Array in Java with Examples
OOPS in Java
- Object Oriented Programming (OOPs) Concept in Java
- Why Java is not a purely Object-Oriented Language?
- Classes and Objects in Java
- Naming Conventions in Java
- Java Methods
Access Modifiers in Java
- Java Constructors
- Four Main Object Oriented Programming Concepts of Java
Inheritance in Java
Abstraction in java, encapsulation in java, polymorphism in java, interfaces in java.
- 'this' reference in Java
- Inheritance and Constructors in Java
- Java and Multiple Inheritance
- Interfaces and Inheritance in Java
- Association, Composition and Aggregation in Java
- Comparison of Inheritance in C++ and Java
- abstract keyword in java
- Abstract Class in Java
- Difference between Abstract Class and Interface in Java
- Control Abstraction in Java with Examples
- Difference Between Data Hiding and Abstraction in Java
- Difference between Abstraction and Encapsulation in Java with Examples
- Difference between Inheritance and Polymorphism
- Dynamic Method Dispatch or Runtime Polymorphism in Java
- Difference between Compile-time and Run-time Polymorphism in Java
Constructors in Java
- Copy Constructor in Java
- Constructor Overloading in Java
- Constructor Chaining In Java with Examples
- Private Constructors and Singleton Classes in Java
Methods in Java
- Static methods vs Instance methods in Java
- Abstract Method in Java with Examples
- Overriding in Java
- Method Overloading in Java
- Difference Between Method Overloading and Method Overriding in Java
- Differences between Interface and Class in Java
- Functional Interfaces in Java
- Nested Interface in Java
- Marker interface in Java
- Comparator Interface in Java with Examples
- Need of Wrapper Classes in Java
- Different Ways to Create the Instances of Wrapper Classes in Java
- Character Class in Java
- Java.Lang.Byte class in Java
- Java.Lang.Short class in Java
- Java.lang.Integer class in Java
- Java.Lang.Long class in Java
- Java.Lang.Float class in Java
- Java.Lang.Double Class in Java
- Java.lang.Boolean Class in Java
- Autoboxing and Unboxing in Java
- Type conversion in Java with Examples
Keywords in Java
- Java Keywords
- Important Keywords in Java
- Super Keyword in Java
- final Keyword in Java
- static Keyword in Java
- enum in Java
- transient keyword in Java
- volatile Keyword in Java
- final, finally and finalize in Java
- Public vs Protected vs Package vs Private Access Modifier in Java
- Access and Non Access Modifiers in Java
Memory Allocation in Java
- Java Memory Management
- How are Java objects stored in memory?
- Stack vs Heap Memory Allocation
- How many types of memory areas are allocated by JVM?
- Garbage Collection in Java
- Types of JVM Garbage Collectors in Java with implementation details
- Memory leaks in Java
- Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Stack Area
Classes of Java
- Understanding Classes and Objects in Java
- Singleton Method Design Pattern in Java
- Object Class in Java
- Inner Class in Java
- Throwable Class in Java with Examples
Packages in Java
- Packages In Java
- How to Create a Package in Java?
- Java.util Package in Java
- Java.lang package in Java
- Java.io Package in Java
- Java Collection Tutorial
Exception Handling in Java
- Exceptions in Java
- Types of Exception in Java with Examples
- Checked vs Unchecked Exceptions in Java
- Java Try Catch Block
- Flow control in try catch finally in Java
- throw and throws in Java
- User-defined Custom Exception in Java
- Chained Exceptions in Java
- Null Pointer Exception In Java
- Exception Handling with Method Overriding in Java
- Multithreading in Java
- Lifecycle and States of a Thread in Java
- Java Thread Priority in Multithreading
- Main thread in Java
- Java.lang.Thread Class in Java
- Runnable interface in Java
- Naming a thread and fetching name of current thread in Java
- What does start() function do in multithreading in Java?
- Difference between Thread.start() and Thread.run() in Java
- Thread.sleep() Method in Java With Examples
- Synchronization in Java
- Importance of Thread Synchronization in Java
- Method and Block Synchronization in Java
- Lock framework vs Thread synchronization in Java
- Difference Between Atomic, Volatile and Synchronized in Java
- Deadlock in Java Multithreading
- Deadlock Prevention And Avoidance
- Difference Between Lock and Monitor in Java Concurrency
- Reentrant Lock in Java
File Handling in Java
- Java.io.File Class in Java
- Java Program to Create a New File
- Different ways of Reading a text file in Java
- Java Program to Write into a File
- Delete a File Using Java
- File Permissions in Java
- FileWriter Class in Java
- Java.io.FileDescriptor in Java
- Java.io.RandomAccessFile Class Method | Set 1
- Regular Expressions in Java
- Regex Tutorial - How to write Regular Expressions?
- Matcher pattern() method in Java with Examples
- Pattern pattern() method in Java with Examples
- Quantifiers in Java
- java.lang.Character class methods | Set 1
- Java IO : Input-output in Java with Examples
- Java.io.Reader class in Java
- Java.io.Writer Class in Java
- Java.io.FileInputStream Class in Java
- FileOutputStream in Java
- Java.io.BufferedOutputStream class in Java
- Java Networking
- TCP/IP Model
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
- Differences between IPv4 and IPv6
- Difference between Connection-oriented and Connection-less Services
- Socket Programming in Java
- java.net.ServerSocket Class in Java
- URL Class in Java with Examples
JDBC - Java Database Connectivity
- Introduction to JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
- JDBC Drivers
- Establishing JDBC Connection in Java
- Types of Statements in JDBC
- JDBC Tutorial
- Java 8 Features - Complete Tutorial
Operators constitute the basic building block of any programming language. Java provides many types of operators that can be used according to the need to perform various calculations and functions, be it logical, arithmetic, relational, etc. They are classified based on the functionality they provide. Here are a few types:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Unary Operators
- Assignment Operator
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Ternary Operator
- Bitwise Operators
- Shift Operators
This article explains all that one needs to know regarding Ternary Operators.
Ternary Operator in Java
Java ternary operator is the only conditional operator that takes three operands. It’s a one-liner replacement for the if-then-else statement and is used a lot in Java programming. We can use the ternary operator in place of if-else conditions or even switch conditions using nested ternary operators. Although it follows the same algorithm as of if-else statement, the conditional operator takes less space and helps to write the if-else statements in the shortest way possible.
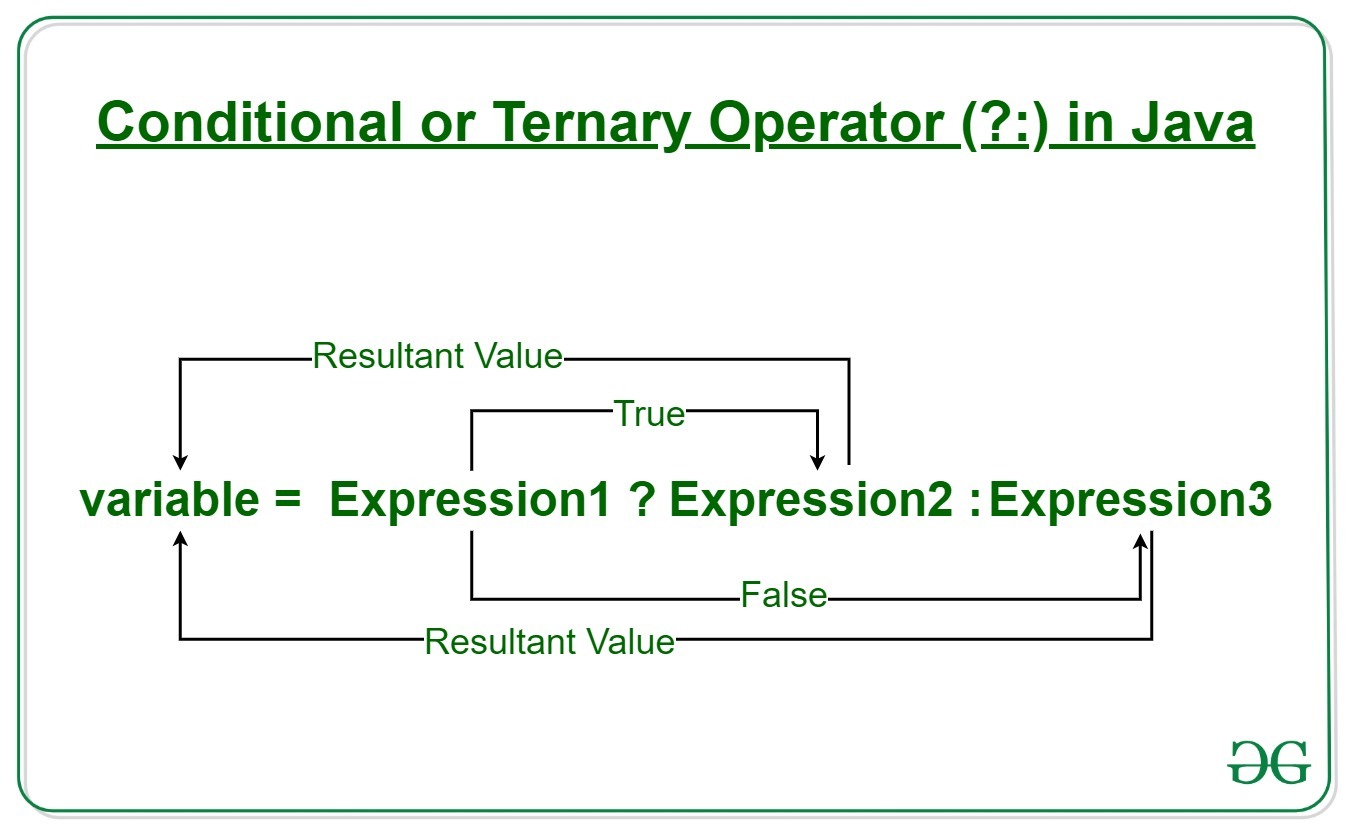
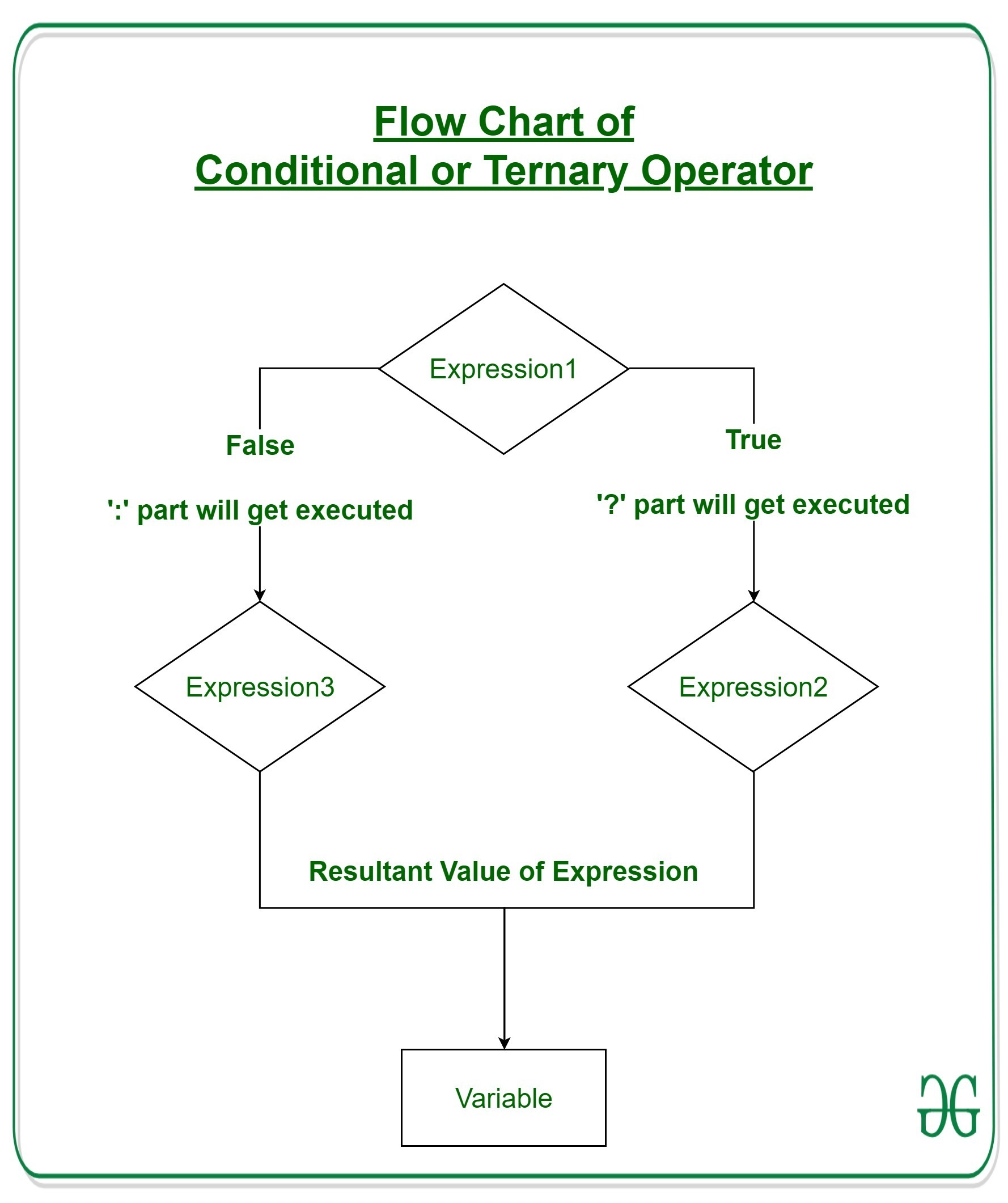
If operates similarly to that of the if-else statement as in Exression2 is executed if Expression1 is true else Expression3 is executed.
Example:
Flowchart of Ternary Operation
Examples of Ternary Operators in Java
Example 1: .
Below is the implementation of the Ternary Operator:
Complexity of the above method:
Time Complexity: O(1) Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Example 2:
Below is the implementation of the above method:
Implementing ternary operator on Boolean values:
Explanation of the above method:
In this program, a Boolean variable condition is declared and assigned the value true. Then, the ternary operator is used to determine the value of the result string. If the condition is true, the value of result will be “True”, otherwise it will be “False”. Finally, the value of result is printed to the console.
Advantages of Java Ternary Operator
- Compactness : The ternary operator allows you to write simple if-else statements in a much more concise way, making the code easier to read and maintain.
- Improved readability : When used correctly, the ternary operator can make the code more readable by making it easier to understand the intent behind the code.
- Increased performance: Since the ternary operator evaluates a single expression instead of executing an entire block of code, it can be faster than an equivalent if-else statement.
- Simplification of nested if-else statements: The ternary operator can simplify complex logic by providing a clean and concise way to perform conditional assignments.
- Easy to debug : If a problem occurs with the code, the ternary operator can make it easier to identify the cause of the problem because it reduces the amount of code that needs to be examined.
It’s worth noting that the ternary operator is not a replacement for all if-else statements. For complex conditions or logic, it’s usually better to use an if-else statement to avoid making the code more difficult to understand.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Java-Operators

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
variable operator value; Types of Assignment Operators in Java. The Assignment Operator is generally of two types. They are: 1. Simple Assignment Operator: The Simple Assignment Operator is used with the "=" sign where the left side consists of the operand and the right side consists of a value. The value of the right side must be of the same data type that has been defined on the left side.
You can also combine the arithmetic operators with the simple assignment operator to create compound assignments. For example, x+=1; and x=x+1; both increment the value of x by 1. The + operator can also be used for concatenating (joining) two strings together, as shown in the following ConcatDemo program:
I am new to JAVA programming. I have read it in my book. String a="Hello"; String b="Hello"; System.out.println(a==b); This should return false as a & b refer to different instances of String objects.. Bcoz the assignments operator compares the instances of objects but Still I am getting a true. I am using Eclipse IDE.
Java Comparison Operators. Comparison operators are used to compare two values (or variables). This is important in programming, because it helps us to find answers and make decisions. The return value of a comparison is either true or false. These values are known as Boolean values, and you will learn more about them in the Booleans and If ...
Java allows you to combine assignment and addition operators using a shorthand operator. For example, the preceding statement can be written as: i +=8; //This is same as i = i+8; The += is called the addition assignment operator. Other shorthand operators are shown below table. Operator. Name.
Assignment Operators in Java: An Overview. We already discussed the Types of Operators in the previous tutorial Java. In this Java tutorial, we will delve into the different types of assignment operators in Java, and their syntax, and provide examples for better understanding.Because Java is a flexible and widely used programming language. Assignment operators play a crucial role in ...
The following quick reference summarizes the operators supported by the Java programming language. Simple Assignment Operator = Simple assignment operator Arithmetic Operators + Additive operator (also used for String concatenation) - Subtraction operator * Multiplication operator / Division operator % Remainder operator ...
Java assignment operators are classified into two types: simple and compound. The Simple assignment operator is the equals ( =) sign, which is the most straightforward of the bunch. It simply assigns the value or variable on the right to the variable on the left. Compound operators are comprised of both an arithmetic, bitwise, or shift operator ...
The assignment operator is used to assign values to string objects. The size of the resulting string object will be the number of characters in the string value being assigned. The size of the resulting string object will be the number of characters in the string value being assigned.
The Java Assignment operators are used to assign the values to the declared variables. The equals ( = ) operator is the most commonly used Java assignment operator. For example: int i = 25; The table below displays all the assignment operators in the Java programming language. Operators.
Assignment operators are used in programming to assign values to variables. We use an assignment operator to store and update data within a program. They enable programmers to store data in variables and manipulate that data. The most common assignment operator is the equals sign (=), which assigns the value on the right side of the operator to ...
Ways of Creating a String. There are two ways to create a string in Java: String Literal. Using new Keyword. Syntax: <String_Type> <string_variable> = "<sequence_of_string>"; . 1. String literal. To make Java more memory efficient (because no new objects are created if it exists already in the string constant pool).
To assign a value to a variable, use the basic assignment operator (=). It is the most fundamental assignment operator in Java. It assigns the value on the right side of the operator to the variable on the left side. Example: int x = 10; int x = 10; In the above example, the variable x is assigned the value 10.
The = operator in java is known as assignment or simple assignment operator. It assigns the value on its right side to the operand (variable) on its left side. For example : int a = 10; // value 10 is assigned in variable a double d = 20.25; // value 20.25 is assigned in variable d char c = 'A'; // Character A is assigned in variable c. a = 20 ...
Learn how to work with Java strings, one of the most important data types in Java. This tutorial covers the basics of strings, such as creating, concatenating, comparing, and modifying them. You will also see examples of using string methods and operators, and learn how to format and manipulate strings with the String class.
This is Java doing typecasting to add the two numbers. String Concatenation. The += operator also works for string mutation. String a = "Hello"; a += "World"; System. out. println (a); Output. The string "Hello" has been mutated and the string "World" has been concatenated to it. Conclusion. The += is an important assignment operator ...
Java also supports a number of Boolean, string, and assignment operators. Boolean operators are used to perform logical comparisons, and always result in one of two values: true or false. Following are the most commonly used Boolean operators :
String x = "hello"; String y = "goodbye"; System.out.println(x.equals(x = y)); the occurrence of x before .equals is evaluated first, before the argument expression x = y. Therefore, a reference to the string hello is remembered as the target reference before the local variable x is changed to refer to the string goodbye.
The string literal "hi" will be handled by the JVM, by creating a String object on the heap, and having a reference to it from the String pool. The new operator merely takes the string object, whose reference is passed in the constructor, and create a new object. It just so happens that the string being passed to the constructor is a literal.
Java provides many types of operators that can be used according to the need to perform various calculations and functions, be it logical, arithmetic, relational, etc. They are classified based on the functionality they provide. Here are a few types: Arithmetic Operators; Unary Operators; Assignment Operator; Relational Operators; Logical Operators