
Academic Manual
- 7. Classification


Section 7: Classification
Published for 2023-24
7.1 Overarching Principles
7.2 calculating classifications, 7.2.1 averages and rounding, 7.2.2 classification year mean (ug programmes only), 7.2.3 weighting of reassessment and deferral marks , 7.2.4 credit awarded via the recognition of prior learning (rpl) , 7.2.5 pass / fail degrees , 7.2.6 study abroad and placements , 7.2.7 academic partnerships, 7.3 pre-honours classification scheme , 7.4 honours degree classification scheme, 7.4.1 general principles , 7.4.2 honours classification scheme a , 7.4.3 honours classification scheme b , 7.4.4 honours classification scheme c , 7.4.5 determination of honours classifications , 7.5 graduate classification scheme , 7.6 taught postgraduate classification scheme , 7.7 research masters (mres) classification scheme , 7.8 non-modular programmes , 7.8.1 ba (hons) english , 7.8.2 ba (hons) fine art , 7.8.3 bfa (hons) fine art , 7.8.4 mbbs (bachelor of medicine, bachelor of surgery), 7.8.5 ma fine art , 7.8.6 mfa fine art in the slade school of fine art, advice for students.
Further information and advice for students about assessment is available on the Examinations & Awards webpages .
Recent Changes
A guide to changes to the regulations are available from the Recent Changes page.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

How to survive marking dissertations
About a decade ago I clearly remember a colleague and I negotiating marks for a dissertation. And he browbeat me into awarding a higher mark (and therefore degree classification) than I felt was deserved. It's stuck with me – I can even remember the student's name. I should have stuck to my guns and agreed to put it to a third marker.
The whole business of dissertation marking is a fascinating and all too human process. On the face of it, awarding marks should be a predominantly objective procedure. There are assessment and grade criteria, specific headings that students know they need to deliver against – are the aims and objectives clear and tracked through? Does the literature review provide good coverage of existing sources relevant to the dissertation topic? Are the adopted methods explained, appropriate and justified? Does it read well and look 'the biz'?
So in the next few weeks colleagues – including myself – will be hit by a tidal wave of incoming final year undergraduate dissertations. Often these are worth two module credits and can disproportionately weigh in the balance when it comes to determining a final degree award. Typically dissertations are blind double marked. So that each marker judges the work independently and only then discusses with a colleague, the definitive mark to be awarded. At this point there are three outcomes – first, markers are of one mind and agree; second, they pace around like fencers, land a few good arguments and, again, reach a settlement. Third, they disagree so dramatically about the quality of the work and its mark that it must go to a third marker.
How do such divisions arise? There are various reasons: the dissertation adviser will likely have formed a working relationship with the student, and it may be difficult to disentangle things like effort from achievement. Related to this is the fact that where a second marker criticises a submission, the adviser/first marker may not only feel (partly) responsible, but can become defensive as they blur boundaries between marking student work and being drawn in to assessing their own inputs and advice. The key point here is to stick to the evidence and, in particular, to focus on major points such as good literature coverage but very limited primary research; clear articulation and delivery of aims and objectives.
Then there is 'power play'. In my experience the vast majority of cases of mark negotiation are cordial, professional and straightforward. But occasionally you find yourself discussing with a colleague who is determined to 'have their way'. Equally – with substantial numbers of dissertations to assess - you may find yourself uncomfortably at the edge of your known world in terms of expertise. This in turn may lead to overly lenient or punitive marking.
So what to do?
Try to start marking as soon as the dissertations are distributed for marking and – just like student dissertation writers – do a little and often. Personally – whether as a marker or external examiner – I can't cope with more than about four dissertations a day. Beyond which it's hard to know which way is up.
Over about 18 years I have learned that it takes me about 1.5 hours to read a dissertation and write up a report on it. I (and colleagues) use a template with headings such as 'abstract', 'literature review', 'methodology', 'findings and discussion', 'conclusions' (and recommendations where relevant), quality of bibliography and appendices and so on. This helps to ensure that negotiations review the same aspects and sections.
Try to hone in on key points – see the wood for the trees; don't get fixated on every jot and tittle. Is it a good read? Is it professionally turned out? Does it do what it says on the tin – title matches aims and objectives, that then inform methods, that deliver persuasive findings and lead up to reasoned conclusions, that link back to starting objectives?
Remember it's the piece of work you are marking, not the student overall; nor the fact that they worked very hard at it or are delightful. What you see is what they get.
Be clear about whether or not you are allowed to give an agreed mark to the student prior to exam board consideration. At my institution we are not allowed to do this; so we email qualitative feedback that gives a clear nod as to how the wind is blowing. Here's an extract from 2011: "Overall this is an excellent piece of research. Very well done…A beautifully and meticulously presented piece of work that demonstrated an excellent level of endeavour and research. Strengths of your work aside from the clear and methodical layout include…Areas that could be improved…" So, what was the mark? You guessed - a first class 70%+ piece of work.
Double markers should try to agree a mark otherwise it creates more work for another colleague as third marker. But if it does go to a third person, be clear about the procedure – is their decision 'final'? Do the disagreeing colleagues mutually agree a third marker? Or is it the module/course leader that does this? There also needs to be a written trail so that, for example, an external examiner can see how two staff diverged, and how the third decided on the given mark.
Colleagues may like to read my article : Shall we dance? The importance of staff-student relationships to undergraduate dissertation preparation in the journal Active Learning in Higher Education Volume 12 Issue 2, July 2011.
James Derounian is a principal lecturer in community development and local governance and National Teaching Fellow, University of Gloucestershire
- Universities
- Professional development
- Higher education
Comments (…)
Most viewed.
- Formatting Your Dissertation
- Introduction
Harvard Griffin GSAS strives to provide students with timely, accurate, and clear information. If you need help understanding a specific policy, please contact the office that administers that policy.
- Application for Degree
- Credit for Completed Graduate Work
- Ad Hoc Degree Programs
- Acknowledging the Work of Others
- Advanced Planning
- Dissertation Submission Checklist
- Publishing Options
- Submitting Your Dissertation
- English Language Proficiency
- PhD Program Requirements
- Secondary Fields
- Year of Graduate Study (G-Year)
- Master's Degrees
- Grade and Examination Requirements
- Conduct and Safety
- Financial Aid
- Non-Resident Students
- Registration
On this page:
Language of the Dissertation
Page and text requirements, body of text, tables, figures, and captions, dissertation acceptance certificate, copyright statement.
- Table of Contents
Front and Back Matter
Supplemental material, dissertations comprising previously published works, top ten formatting errors, further questions.
- Related Contacts and Forms
When preparing the dissertation for submission, students must follow strict formatting requirements. Any deviation from these requirements may lead to rejection of the dissertation and delay in the conferral of the degree.
The language of the dissertation is ordinarily English, although some departments whose subject matter involves foreign languages may accept a dissertation written in a language other than English.
Most dissertations are 100 to 300 pages in length. All dissertations should be divided into appropriate sections, and long dissertations may need chapters, main divisions, and subdivisions.
- 8½ x 11 inches, unless a musical score is included
- At least 1 inch for all margins
- Body of text: double spacing
- Block quotations, footnotes, and bibliographies: single spacing within each entry but double spacing between each entry
- Table of contents, list of tables, list of figures or illustrations, and lengthy tables: single spacing may be used
Fonts and Point Size
Use 10-12 point size. Fonts must be embedded in the PDF file to ensure all characters display correctly.
Recommended Fonts
If you are unsure whether your chosen font will display correctly, use one of the following fonts:
If fonts are not embedded, non-English characters may not appear as intended. Fonts embedded improperly will be published to DASH as-is. It is the student’s responsibility to make sure that fonts are embedded properly prior to submission.
Instructions for Embedding Fonts
To embed your fonts in recent versions of Word, follow these instructions from Microsoft:
- Click the File tab and then click Options .
- In the left column, select the Save tab.
- Clear the Do not embed common system fonts check box.
For reference, below are some instructions from ProQuest UMI for embedding fonts in older file formats:
To embed your fonts in Microsoft Word 2010:
- In the File pull-down menu click on Options .
- Choose Save on the left sidebar.
- Check the box next to Embed fonts in the file.
- Click the OK button.
- Save the document.
Note that when saving as a PDF, make sure to go to “more options” and save as “PDF/A compliant”
To embed your fonts in Microsoft Word 2007:
- Click the circular Office button in the upper left corner of Microsoft Word.
- A new window will display. In the bottom right corner select Word Options .
- Choose Save from the left sidebar.
Using Microsoft Word on a Mac:
Microsoft Word 2008 on a Mac OS X computer will automatically embed your fonts while converting your document to a PDF file.
If you are converting to PDF using Acrobat Professional (instructions courtesy of the Graduate Thesis Office at Iowa State University):
- Open your document in Microsoft Word.
- Click on the Adobe PDF tab at the top. Select "Change Conversion Settings."
- Click on Advanced Settings.
- Click on the Fonts folder on the left side of the new window. In the lower box on the right, delete any fonts that appear in the "Never Embed" box. Then click "OK."
- If prompted to save these new settings, save them as "Embed all fonts."
- Now the Change Conversion Settings window should show "embed all fonts" in the Conversion Settings drop-down list and it should be selected. Click "OK" again.
- Click on the Adobe PDF link at the top again. This time select Convert to Adobe PDF. Depending on the size of your document and the speed of your computer, this process can take 1-15 minutes.
- After your document is converted, select the "File" tab at the top of the page. Then select "Document Properties."
- Click on the "Fonts" tab. Carefully check all of your fonts. They should all show "(Embedded Subset)" after the font name.
- If you see "(Embedded Subset)" after all fonts, you have succeeded.
The font used in the body of the text must also be used in headers, page numbers, and footnotes. Exceptions are made only for tables and figures created with different software and inserted into the document.
Tables and figures must be placed as close as possible to their first mention in the text. They may be placed on a page with no text above or below, or they may be placed directly into the text. If a table or a figure is alone on a page (with no narrative), it should be centered within the margins on the page. Tables may take up more than one page as long as they obey all rules about margins. Tables and figures referred to in the text may not be placed at the end of the chapter or at the end of the dissertation.
- Given the standards of the discipline, dissertations in the Department of History of Art and Architecture and the Department of Architecture, Landscape Architecture, and Urban Planning often place illustrations at the end of the dissertation.
Figure and table numbering must be continuous throughout the dissertation or by chapter (e.g., 1.1, 1.2, 2.1, 2.2, etc.). Two figures or tables cannot be designated with the same number. If you have repeating images that you need to cite more than once, label them with their number and A, B, etc.
Headings should be placed at the top of tables. While no specific rules for the format of table headings and figure captions are required, a consistent format must be used throughout the dissertation (contact your department for style manuals appropriate to the field).
Captions should appear at the bottom of any figures. If the figure takes up the entire page, the caption should be placed alone on the preceding page, centered vertically and horizontally within the margins.
Each page receives a separate page number. When a figure or table title is on a preceding page, the second and subsequent pages of the figure or table should say, for example, “Figure 5 (Continued).” In such an instance, the list of figures or tables will list the page number containing the title. The word “figure” should be written in full (not abbreviated), and the “F” should be capitalized (e.g., Figure 5). In instances where the caption continues on a second page, the “(Continued)” notation should appear on the second and any subsequent page. The figure/table and the caption are viewed as one entity and the numbering should show correlation between all pages. Each page must include a header.
Landscape orientation figures and tables must be positioned correctly and bound at the top so that the top of the figure or table will be at the left margin. Figure and table headings/captions are placed with the same orientation as the figure or table when on the same page. When on a separate page, headings/captions are always placed in portrait orientation, regardless of the orientation of the figure or table. Page numbers are always placed as if the figure were vertical on the page.
If a graphic artist does the figures, Harvard Griffin GSAS will accept lettering done by the artist only within the figure. Figures done with software are acceptable if the figures are clear and legible. Legends and titles done by the same process as the figures will be accepted if they too are clear, legible, and run at least 10 or 12 characters per inch. Otherwise, legends and captions should be printed with the same font used in the text.
Original illustrations, photographs, and fine arts prints may be scanned and included, centered between the margins on a page with no text above or below.
Use of Third-Party Content
In addition to the student's own writing, dissertations often contain third-party content or in-copyright content owned by parties other than you, the student who authored the dissertation. The Office for Scholarly Communication recommends consulting the information below about fair use, which allows individuals to use in-copyright content, on a limited basis and for specific purposes, without seeking permission from copyright holders.
Because your dissertation will be made available for online distribution through DASH , Harvard's open-access repository, it is important that any third-party content in it may be made available in this way.
Fair Use and Copyright
What is fair use?
Fair use is a provision in copyright law that allows the use of a certain amount of copyrighted material without seeking permission. Fair use is format- and media-agnostic. This means fair use may apply to images (including photographs, illustrations, and paintings), quoting at length from literature, videos, and music regardless of the format.
How do I determine whether my use of an image or other third-party content in my dissertation is fair use?
There are four factors you will need to consider when making a fair use claim.
1) For what purpose is your work going to be used?
- Nonprofit, educational, scholarly, or research use favors fair use. Commercial, non-educational uses, often do not favor fair use.
- A transformative use (repurposing or recontextualizing the in-copyright material) favors fair use. Examining, analyzing, and explicating the material in a meaningful way, so as to enhance a reader's understanding, strengthens your fair use argument. In other words, can you make the point in the thesis without using, for instance, an in-copyright image? Is that image necessary to your dissertation? If not, perhaps, for copyright reasons, you should not include the image.
2) What is the nature of the work to be used?
- Published, fact-based content favors fair use and includes scholarly analysis in published academic venues.
- Creative works, including artistic images, are afforded more protection under copyright, and depending on your use in light of the other factors, may be less likely to favor fair use; however, this does not preclude considerations of fair use for creative content altogether.
3) How much of the work is going to be used?
- Small, or less significant, amounts favor fair use. A good rule of thumb is to use only as much of the in-copyright content as necessary to serve your purpose. Can you use a thumbnail rather than a full-resolution image? Can you use a black-and-white photo instead of color? Can you quote select passages instead of including several pages of the content? These simple changes bolster your fair use of the material.
4) What potential effect on the market for that work may your use have?
- If there is a market for licensing this exact use or type of educational material, then this weighs against fair use. If however, there would likely be no effect on the potential commercial market, or if it is not possible to obtain permission to use the work, then this favors fair use.
For further assistance with fair use, consult the Office for Scholarly Communication's guide, Fair Use: Made for the Harvard Community and the Office of the General Counsel's Copyright and Fair Use: A Guide for the Harvard Community .
What are my options if I don’t have a strong fair use claim?
Consider the following options if you find you cannot reasonably make a fair use claim for the content you wish to incorporate:
- Seek permission from the copyright holder.
- Use openly licensed content as an alternative to the original third-party content you intended to use. Openly-licensed content grants permission up-front for reuse of in-copyright content, provided your use meets the terms of the open license.
- Use content in the public domain, as this content is not in-copyright and is therefore free of all copyright restrictions. Whereas third-party content is owned by parties other than you, no one owns content in the public domain; everyone, therefore, has the right to use it.
For use of images in your dissertation, please consult this guide to Finding Public Domain & Creative Commons Media , which is a great resource for finding images without copyright restrictions.
Who can help me with questions about copyright and fair use?
Contact your Copyright First Responder . Please note, Copyright First Responders assist with questions concerning copyright and fair use, but do not assist with the process of obtaining permission from copyright holders.
Pages should be assigned a number except for the Dissertation Acceptance Certificate . Preliminary pages (abstract, table of contents, list of tables, graphs, illustrations, and preface) should use small Roman numerals (i, ii, iii, iv, v, etc.). All pages must contain text or images.
Count the title page as page i and the copyright page as page ii, but do not print page numbers on either page .
For the body of text, use Arabic numbers (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, etc.) starting with page 1 on the first page of text. Page numbers must be centered throughout the manuscript at the top or bottom. Every numbered page must be consecutively ordered, including tables, graphs, illustrations, and bibliography/index (if included); letter suffixes (such as 10a, 10b, etc.) are not allowed. It is customary not to have a page number on the page containing a chapter heading.
- Check pagination carefully. Account for all pages.
A copy of the Dissertation Acceptance Certificate (DAC) should appear as the first page. This page should not be counted or numbered. The DAC will appear in the online version of the published dissertation. The author name and date on the DAC and title page should be the same.
The dissertation begins with the title page; the title should be as concise as possible and should provide an accurate description of the dissertation. The author name and date on the DAC and title page should be the same.
- Do not print a page number on the title page. It is understood to be page i for counting purposes only.
A copyright notice should appear on a separate page immediately following the title page and include the copyright symbol ©, the year of first publication of the work, and the name of the author:
© [ year ] [ Author’s Name ] All rights reserved.
Alternatively, students may choose to license their work openly under a Creative Commons license. The author remains the copyright holder while at the same time granting up-front permission to others to read, share, and (depending on the license) adapt the work, so long as proper attribution is given. (By default, under copyright law, the author reserves all rights; under a Creative Commons license, the author reserves some rights.)
- Do not print a page number on the copyright page. It is understood to be page ii for counting purposes only.
An abstract, numbered as page iii , should immediately follow the copyright page and should state the problem, describe the methods and procedures used, and give the main results or conclusions of the research. The abstract will appear in the online and bound versions of the dissertation and will be published by ProQuest. There is no maximum word count for the abstract.
- double-spaced
- left-justified
- indented on the first line of each paragraph
- The author’s name, right justified
- The words “Dissertation Advisor:” followed by the advisor’s name, left-justified (a maximum of two advisors is allowed)
- Title of the dissertation, centered, several lines below author and advisor
Dissertations divided into sections must contain a table of contents that lists, at minimum, the major headings in the following order:
- Front Matter
- Body of Text
- Back Matter
Front matter includes (if applicable):
- acknowledgements of help or encouragement from individuals or institutions
- a dedication
- a list of illustrations or tables
- a glossary of terms
- one or more epigraphs.
Back matter includes (if applicable):
- bibliography
- supplemental materials, including figures and tables
- an index (in rare instances).
Supplemental figures and tables must be placed at the end of the dissertation in an appendix, not within or at the end of a chapter. If additional digital information (including audio, video, image, or datasets) will accompany the main body of the dissertation, it should be uploaded as a supplemental file through ProQuest ETD . Supplemental material will be available in DASH and ProQuest and preserved digitally in the Harvard University Archives.
As a matter of copyright, dissertations comprising the student's previously published works must be authorized for distribution from DASH. The guidelines in this section pertain to any previously published material that requires permission from publishers or other rightsholders before it may be distributed from DASH. Please note:
- Authors whose publishing agreements grant the publisher exclusive rights to display, distribute, and create derivative works will need to seek the publisher's permission for nonexclusive use of the underlying works before the dissertation may be distributed from DASH.
- Authors whose publishing agreements indicate the authors have retained the relevant nonexclusive rights to the original materials for display, distribution, and the creation of derivative works may distribute the dissertation as a whole from DASH without need for further permissions.
It is recommended that authors consult their publishing agreements directly to determine whether and to what extent they may have transferred exclusive rights under copyright. The Office for Scholarly Communication (OSC) is available to help the author determine whether she has retained the necessary rights or requires permission. Please note, however, the Office of Scholarly Communication is not able to assist with the permissions process itself.
- Missing Dissertation Acceptance Certificate. The first page of the PDF dissertation file should be a scanned copy of the Dissertation Acceptance Certificate (DAC). This page should not be counted or numbered as a part of the dissertation pagination.
- Conflicts Between the DAC and the Title Page. The DAC and the dissertation title page must match exactly, meaning that the author name and the title on the title page must match that on the DAC. If you use your full middle name or just an initial on one document, it must be the same on the other document.
- Abstract Formatting Errors. The advisor name should be left-justified, and the author's name should be right-justified. Up to two advisor names are allowed. The Abstract should be double spaced and include the page title “Abstract,” as well as the page number “iii.” There is no maximum word count for the abstract.
- The front matter should be numbered using Roman numerals (iii, iv, v, …). The title page and the copyright page should be counted but not numbered. The first printed page number should appear on the Abstract page (iii).
- The body of the dissertation should be numbered using Arabic numbers (1, 2, 3, …). The first page of the body of the text should begin with page 1. Pagination may not continue from the front matter.
- All page numbers should be centered either at the top or the bottom of the page.
- Figures and tables Figures and tables must be placed within the text, as close to their first mention as possible. Figures and tables that span more than one page must be labeled on each page. Any second and subsequent page of the figure/table must include the “(Continued)” notation. This applies to figure captions as well as images. Each page of a figure/table must be accounted for and appropriately labeled. All figures/tables must have a unique number. They may not repeat within the dissertation.
- Any figures/tables placed in a horizontal orientation must be placed with the top of the figure/ table on the left-hand side. The top of the figure/table should be aligned with the spine of the dissertation when it is bound.
- Page numbers must be placed in the same location on all pages of the dissertation, centered, at the bottom or top of the page. Page numbers may not appear under the table/ figure.
- Supplemental Figures and Tables. Supplemental figures and tables must be placed at the back of the dissertation in an appendix. They should not be placed at the back of the chapter.
- Permission Letters Copyright. permission letters must be uploaded as a supplemental file, titled ‘do_not_publish_permission_letters,” within the dissertation submission tool.
- DAC Attachment. The signed Dissertation Acceptance Certificate must additionally be uploaded as a document in the "Administrative Documents" section when submitting in Proquest ETD . Dissertation submission is not complete until all documents have been received and accepted.
- Overall Formatting. The entire document should be checked after all revisions, and before submitting online, to spot any inconsistencies or PDF conversion glitches.
- You can view dissertations successfully published from your department in DASH . This is a great place to check for specific formatting and area-specific conventions.
- Contact the Office of Student Affairs with further questions.
CONTACT INFO
Katie riggs, explore events.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | Guide, Examples, & Template
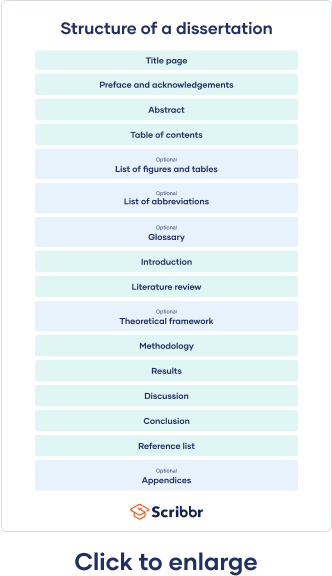
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program.
Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you’ve ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating to know where to begin.
Your department likely has guidelines related to how your dissertation should be structured. When in doubt, consult with your supervisor.
You can also download our full dissertation template in the format of your choice below. The template includes a ready-made table of contents with notes on what to include in each chapter, easily adaptable to your department’s requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
- In the US, a dissertation generally refers to the collection of research you conducted to obtain a PhD.
- In other countries (such as the UK), a dissertation often refers to the research you conduct to obtain your bachelor’s or master’s degree.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Dissertation committee and prospectus process, how to write and structure a dissertation, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your dissertation, free checklist and lecture slides.
When you’ve finished your coursework, as well as any comprehensive exams or other requirements, you advance to “ABD” (All But Dissertation) status. This means you’ve completed everything except your dissertation.
Prior to starting to write, you must form your committee and write your prospectus or proposal . Your committee comprises your adviser and a few other faculty members. They can be from your own department, or, if your work is more interdisciplinary, from other departments. Your committee will guide you through the dissertation process, and ultimately decide whether you pass your dissertation defense and receive your PhD.
Your prospectus is a formal document presented to your committee, usually orally in a defense, outlining your research aims and objectives and showing why your topic is relevant . After passing your prospectus defense, you’re ready to start your research and writing.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The structure of your dissertation depends on a variety of factors, such as your discipline, topic, and approach. Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an overall argument to support a central thesis , with chapters organized around different themes or case studies.
However, hard science and social science dissertations typically include a review of existing works, a methodology section, an analysis of your original research, and a presentation of your results , presented in different chapters.
Dissertation examples
We’ve compiled a list of dissertation examples to help you get started.
- Example dissertation #1: Heat, Wildfire and Energy Demand: An Examination of Residential Buildings and Community Equity (a dissertation by C. A. Antonopoulos about the impact of extreme heat and wildfire on residential buildings and occupant exposure risks).
- Example dissertation #2: Exploring Income Volatility and Financial Health Among Middle-Income Households (a dissertation by M. Addo about income volatility and declining economic security among middle-income households).
- Example dissertation #3: The Use of Mindfulness Meditation to Increase the Efficacy of Mirror Visual Feedback for Reducing Phantom Limb Pain in Amputees (a dissertation by N. S. Mills about the effect of mindfulness-based interventions on the relationship between mirror visual feedback and the pain level in amputees with phantom limb pain).
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you. In some cases, your acknowledgements are part of a preface.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150 to 300 words long. Though this may seem very short, it’s one of the most important parts of your dissertation, because it introduces your work to your audience.
Your abstract should:
- State your main topic and the aims of your research
- Describe your methods
- Summarize your main results
- State your conclusions
Read more about abstracts
The table of contents lists all of your chapters, along with corresponding subheadings and page numbers. This gives your reader an overview of your structure and helps them easily navigate your document.
Remember to include all main parts of your dissertation in your table of contents, even the appendices. It’s easy to generate a table automatically in Word if you used heading styles. Generally speaking, you only include level 2 and level 3 headings, not every subheading you included in your finished work.
Read more about tables of contents
While not usually mandatory, it’s nice to include a list of figures and tables to help guide your reader if you have used a lot of these in your dissertation. It’s easy to generate one of these in Word using the Insert Caption feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
Similarly, if you have used a lot of abbreviations (especially industry-specific ones) in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
In addition to the list of abbreviations, if you find yourself using a lot of highly specialized terms that you worry will not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary. Here, alphabetize the terms and include a brief description or definition.
Read more about glossaries
The introduction serves to set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance. It tells the reader what to expect in the rest of your dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving the background information needed to contextualize your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of your research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your research questions and objectives
- Outline the flow of the rest of your work
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant. By the end, the reader should understand the what, why, and how of your research.
Read more about introductions
A formative part of your research is your literature review . This helps you gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic.
Literature reviews encompass:
- Finding relevant sources (e.g., books and journal articles)
- Assessing the credibility of your sources
- Critically analyzing and evaluating each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g., themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps) to strengthen your overall point
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing sources. Your literature review should have a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear justification for your own research. It may aim to:
- Address a gap in the literature or build on existing knowledge
- Take a new theoretical or methodological approach to your topic
- Propose a solution to an unresolved problem or advance one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework. Here, you define and analyze the key theories, concepts, and models that frame your research.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to critically assess its credibility. Your methodology section should accurately report what you did, as well as convince your reader that this was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- The overall research approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative ) and research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment )
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Any tools and materials you used (e.g., computer programs, lab equipment)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses , or themes, but avoid including any subjective or speculative interpretation here.
Your results section should:
- Concisely state each relevant result together with relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Briefly state how the result relates to the question or whether the hypothesis was supported
- Report all results that are relevant to your research questions , including any that did not meet your expectations.
Additional data (including raw numbers, full questionnaires, or interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix. You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results. Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is your opportunity to explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research question. Here, interpret your results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. Refer back to relevant source material to show how your results fit within existing research in your field.
Some guiding questions include:
- What do your results mean?
- Why do your results matter?
- What limitations do the results have?
If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your dissertation’s conclusion should concisely answer your main research question, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your central argument and emphasizing what your research has contributed to the field.
In some disciplines, the conclusion is just a short section preceding the discussion section, but in other contexts, it is the final chapter of your work. Here, you wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you found, with recommendations for future research and concluding remarks.
It’s important to leave the reader with a clear impression of why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known? Why is your research necessary for the future of your field?
Read more about conclusions
It is crucial to include a reference list or list of works cited with the full details of all the sources that you used, in order to avoid plagiarism. Be sure to choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your dissertation. Each style has strict and specific formatting requirements.
Common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA , but which style you use is often set by your department or your field.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
Your dissertation should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents such as interview transcripts or survey questions can be added as appendices, rather than adding them to the main body.
Read more about appendices
Making sure that all of your sections are in the right place is only the first step to a well-written dissertation. Don’t forget to leave plenty of time for editing and proofreading, as grammar mistakes and sloppy spelling errors can really negatively impact your work.
Dissertations can take up to five years to write, so you will definitely want to make sure that everything is perfect before submitting. You may want to consider using a professional dissertation editing service , AI proofreader or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect prior to submitting.
After your written dissertation is approved, your committee will schedule a defense. Similarly to defending your prospectus, dissertation defenses are oral presentations of your work. You’ll present your dissertation, and your committee will ask you questions. Many departments allow family members, friends, and other people who are interested to join as well.
After your defense, your committee will meet, and then inform you whether you have passed. Keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality; most committees will have resolved any serious issues with your work with you far prior to your defense, giving you ample time to fix any problems.
As you write your dissertation, you can use this simple checklist to make sure you’ve included all the essentials.
Checklist: Dissertation
My title page includes all information required by my university.
I have included acknowledgements thanking those who helped me.
My abstract provides a concise summary of the dissertation, giving the reader a clear idea of my key results or arguments.
I have created a table of contents to help the reader navigate my dissertation. It includes all chapter titles, but excludes the title page, acknowledgements, and abstract.
My introduction leads into my topic in an engaging way and shows the relevance of my research.
My introduction clearly defines the focus of my research, stating my research questions and research objectives .
My introduction includes an overview of the dissertation’s structure (reading guide).
I have conducted a literature review in which I (1) critically engage with sources, evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, (2) discuss patterns, themes, and debates in the literature, and (3) address a gap or show how my research contributes to existing research.
I have clearly outlined the theoretical framework of my research, explaining the theories and models that support my approach.
I have thoroughly described my methodology , explaining how I collected data and analyzed data.
I have concisely and objectively reported all relevant results .
I have (1) evaluated and interpreted the meaning of the results and (2) acknowledged any important limitations of the results in my discussion .
I have clearly stated the answer to my main research question in the conclusion .
I have clearly explained the implications of my conclusion, emphasizing what new insight my research has contributed.
I have provided relevant recommendations for further research or practice.
If relevant, I have included appendices with supplemental information.
I have included an in-text citation every time I use words, ideas, or information from a source.
I have listed every source in a reference list at the end of my dissertation.
I have consistently followed the rules of my chosen citation style .
I have followed all formatting guidelines provided by my university.
Congratulations!
The end is in sight—your dissertation is nearly ready to submit! Make sure it's perfectly polished with the help of a Scribbr editor.
If you’re an educator, feel free to download and adapt these slides to teach your students about structuring a dissertation.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation Binding and Printing | Options, Tips, & Comparison
- Example of a dissertation abstract
- Figure and Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalization | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Purpose and structure of an advisory report
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Shorten your abstract or summary
- Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What is your plagiarism score?
Mathematics Institute
Msc awarding of degrees.
The progress review Board receives the result of all coursework assessments and examinations. Students who pass are permitted to proceed to the dissertation.
In September there is a meeting of the full Board of Examiners for the MSc (including the External Examiner) where the results from all examinations and dissertations for each candidate are available. The Board makes use of University Regulations and Departmental guidelines on the award of MSc degrees and Postgraduate Diplomas. Based on all the available information, including any special circumstances, the Board will make one of the following recommendations. Special consideration is given to borderline or special cases.
- Award of MSc degree Normally awarded if the average mark on the taught modules and the dissertation mark are both greater than or equal to 50%, and if at least 60 CATS of level 7 taught modules ( year 4 or above e.g. MA4xx, MA5yy ) have been passed at the 50% level.
- Award of Merit Grade Normally awarded if the average combined mark on the taught modules and the dissertation mark is at least 60% and, in addition, the mark on the dissertation is at least 60%.
Normally awarded if the average combined mark on the taught modules and the dissertation mark is at least 70% and, in addition, the mark on the dissertation is at least 70%.
- Award of Postgraduate Diploma Normally awarded under the following conditions: (a) average mark on taught modules in the range 40% - 49%, (b) marks of 50% or more in at least 60 CATS of level 7 taught modules, (c) a mark of at least 40% in the dissertation or postgraduate diploma project (see below). Candidates for the MSc degree who have submitted an MSc dissertation but who fail to reach the required standard for the award of an MSc are considered for the award of a Postgraduate Diploma. Candidates who do not achieve the required standard at the end of the taught stage of the MSc are normally asked to submit a postgraduate diploma project (30 CATS) rather than the dissertation (90 CATS), for the consideration of an award of a Postgraduate Diploma.
Failure to meet any of the above conditions.
The above decisions are subject to approval by the Senate.
Resits and Resubmission of dissertations
Students are permitted to resit failed taught modules in September. The maximum possible mark in any resit exam is 50%. The resit for a failed module could either be a written exam or a viva, depending on the recommendation of the Examination Board.
Resubmission of the research project is likewise possible in certain circumstances. Where minor corrections are required the Board may pass the candidate subject to the necessary changes being made. It is then the duty of the supervisor to confirm that these have been carried out.
Postgraduate Studentships - Search for funding opportunities.

- Studying a Postgraduate degree
The formula for Masters Degree Grades
Share this article.
- Facebook Sharer
- Twitter Sharer
- LinkedIn Sharer

Explore other topics
- Finding a Masters Course
- Funding a Postgraduate course
- Living as a Postgraduate student
- Popular masters degree subjects
- Student Wellbeing
Think Postgrad
Frequently asked questions.
It depends. If you’re looking for a job after completing your Master's, your grades wouldn’t matter that much. However, good grades will still give you a better reputation as a student and as a potential employee. If you are planning to pursue PhD after Masters, your grades will definitely matter as it reflects your overall academic performance.
Masters involve a lot of independent studying which is difficult to do for some students. There are also higher expectations for postgraduate students when it comes to coursework.
However, just like studying for a Bachelor's degree, students will be able to easily pass if they commit themselves to work hard and spend enough time studying.
Studying masters in the UK will be challenging but it will definitely be worth it.
Masters degree grades follow a pattern, but the grading system for degrees varies from one country to another. Here’s what you need to know about the formula for masters degree grades when it comes to studying a masters in the UK.
What are masters degree grades?
Your Master's degree grades are determined by creating a weighted average. A combination of your results from different assignments that you have completed throughout the course will affect your overall master's degree grade. However, if you’re studying Integrated Masters, your grade will be calculated differently. In Integrated Masters, more weighting will be applied to the latter period of your studies.
Every piece of work is graded differently and different factors will affect your grade depending on the requirements. For example, an essay will be graded completely differently than a presentation or an exam.
Assignments that form part of a degree assessment are marked according to standards that are required by the validating body. In the UK this is the QAA . Some of these will be ‘double-blind marked’. This means that two lecturers or tutors will be reviewing your work and then agree on a grade they would like to give you.
Assessment and weighting
Masters degrees in the UK are worth 180 credits in total. You will earn your credits through a combination of modules, projects, and dissertation - some will be compulsory and some will be optional.
Each module is usually worth 10 to 30 credits depending on the length and the amount of assessment they require. Most universities will have different ways of splitting those 180 credits. For example, you may have six modules each worth 10 credits in your first year. Then get three modules that are worth 20 credits each in your second year and 60 credits for your dissertation in your third year.
Assessments can include:
- Written assessments
- Examinations
- Presentations
- Bibliographies
- Reflective journals
All the mentioned assessments will be weighted differently for each module. The formula for achieving your masters degree grades will depend on your professor, your university, and your chosen subjects.
Masters degree grades and your dissertation
Most universities will require you to do a postgraduate dissertation or thesis during the last year of your study. A dissertation will usually be worth around 60 credits or higher. A masters dissertation is a lengthy written study or piece of coursework on a topic chosen by a student.
While creating a dissertation, all students will be guided by faculty supervisors or professors and will require an extensive amount of time for research and writing. A dissertation is usually divided into chapters and will usually have around 15,000-25,000 words depending on the chosen topic.
In some universities, students might not be required to undertake a dissertation. In that case, students will be required to score highly throughout the rest of their course in order to graduate and finish their Masters degree.
Masters degree results and classifications
Once you have finished your Master's degree, your credits will then translate into either a Distinction, Merit, Pass or Fail. Different universities may have different boundaries but as a general rule:
- Distinction - 70%+
- Merit - 60-69%
- Pass - 50-59%
- Fail - 40-49%
Students who study Integrated Masters will get different results from the one mentioned above. The grading for Integrated Masters will be similar to the grades given in a bachelor's degree:
- First-Class Honours - 70%+
- Upper Second Class Honours - 60-70%
- Lower Second-Class Honours - 50-60%
- Third-Class Honours - 45-50%
- Pass - 40-45%
- Fail - below 40%
How do I get a Distinction in my Masters?
To get a distinction in your Masters, you will need to have at least a 70% or higher grade by the end of your degree. Everyone has unique strategies on how to achieve a Distinction grade but here are a few things you can do to achieve your goal:
- Don’t leave your coursework and dissertation to the last minute. Assignments are given in advance at university to help you prepare enough and do your best on each assignment. Plan ahead and have a proper schedule on when to do your assignments.
- Make the most of the support available to you. You will have professors and supervisors who will be there to help you during your masters, reach out to them or other relevant academics for opinions, insights, and advice.
- Research your dissertation topic thoroughly, do not choose a topic mainly because of your personal interest.
- Explore different angles of various dissertation topics before you make your final choice.
Next Steps:
Search and compare masters degree courses from hundreds of UK universities on Masters Compare
- Advertisers
- Cookie Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Sorry! You need to sign up
Sign up to Postgraduate Studentships
Sign up to compare masters
Opportunity added!
Thanks for making your selection. Click below to view your list.
Course Added
Thanks for making your selection. Click below to view your comparisons.

Think Postgrad Ltd 2008-2024 Website By Parachute
Browser does not support script.
We use cookies on this site. By browsing our site you agree to our use of cookies. Close this message Find out more

- Find your course
- The Principal
- Our experts
- Our history
- Facts & figures
- Art Collections & Picture Gallery
- Exhibitions
- Online shop
- Organisation of the College
- Charitable status
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Research degrees
- Scholarships
- Accommodation
- Guide for parents
- Schools & colleges
- Lifelong learning
- Passport Award
- Discover Arts
- Discover Science
- Careers & Employability
- Departments and Schools
- Biological Sciences
- Comparative Literature & Culture
- Computer Science
- Drama,Theatre & Dance
- Earth Sciences
- Electronic Engineering
- European Studies
- Information Security
- Liberal Arts
- Mathematics
- Modern Languages, Literatures & Cultures
- Politics & International Relations
- Professional Studies
- Social Work
- Student life
- Campus & facilities
- Social life
- Royal Holloway and Me
- What our students say
- Student media
- Students' Union
- Active lifestyle & sport
- Volunteering
- Support, health & welfare
- Jobs while you study
- Sustainability
- International
- Why Royal Holloway?
- English language & university preparation
- Study abroad & exchanges
- Immigration & visas
- Your country
- Fees & scholarships
- After applying
- Support for international students
- Information for agents
- Virtual Open Day
- Current research
- Doctoral School
- Impact case studies
- Research support
- Funding opportunities
- Departments & Groups
- Pure support
- Commercialisation seed funds
- Research data management
- For business
- The Institute for Cyber Security Innovation
- Conferences & hospitality
- Consultancy
- Enterprise centre / incubation
- Licensing / commercialisation
- Research & business
- Recruiting our students
- Proof of award
- Get involved
- Benefits & services
- Events & reunions
- Higher magazine
- Why support the College?
- Our priorities
- A gift in your will
- American Foundation
- Tax efficient giving
Dissertation - Marking Criteria
The text below is an extract from the MSc handbook for students
Each dissertation is independently marked by two examiners; one of these is normally the supervisor. An external examiner moderates the assessment. The examiners may conduct an oral examination if they wish to check the depth of the student's understanding and to ensure that the dissertation is the student's own work. Students must obtain a pass grade on the dissertation to pass the MSc degree. The examiners give up to 100 points where the points translate to the following categories:
85 − 100: An exceptionally high level of understanding and outstanding research potential.
70 − 84.99: Very high competence and excellent research potential.
60 − 69.99: Evidence of some creativity and independence of thought.
50 − 59.99: Sound understanding of the literature, but lack of accuracy or originality.
0 − 49.99: Insufficient or no understanding of the topic, poor quality of work.
The points are given according to the following guidelines:
Knowledge of subject (25)
21 − 25: Deep understanding and near-comprehensive knowledge.
18 − 20: Deep understanding.
15 − 17: Very good understanding.
12 − 14: Sound knowledge of relevant information.
10 − 11: Basic understanding of the main issues.
0 − 9: Little or no understanding of the main issues.
Organisation of material (25)
21 − 25: Of publishable quality.
18 − 20: Arguments clearly constructed; material very well-organised.
15 − 17: Well-organised; aims met with no significant errors or omissions.
12 − 14: Coherent and competent organisation.
10 − 11: Lack of clarity in written presentation or aims only partially met.
6 − 9: Major flaws in arguments; aims of project not met.
0 − 5: Arguments are missing/deficient. Disorganised or fragmentary.
Originality, interpretation and analysis (20)
17 − 20: Significant originality in the interpretation and/or analysis; project aims challenging.
14 − 16: Some originality; evidence of excellent analytical and problem- solving skills.
12 − 13: Good attempt to interpret and analyse existing literature.
10 − 11: Minor flaws in interpretation/analysis of existing literature.
5 − 9: Poor interpretation/analysis or project aims too simple.
0 − 4: Little or no interpretation or analysis; project aims trivial.
Evidence of reading (10)
8 − 10: Independent reading including research papers.
6 − 7: Good use of outside reading.
4 − 5: Some evidence of outside reading.
0 − 3: Little or no evidence of outside reading.
Bibliography and referencing (10)
9 − 10: Of publishable quality.
7 − 8: Good referencing and bibliography.
5 − 6: Either poor bibliography or poor referencing.
3 − 4: Poor bibliography and little or no referencing.
0 − 2: No bibliography and little or no referencing.
Style, spelling, punctuation and grammar (10)
9 − 10: Incisive and fluent, no errors of spelling, punctuation or grammar.
7 − 8: Very minor errors of spelling, punctuation or grammar.
4 − 6: Some errors of spelling, punctuation or grammar.
0 − 3: Many errors of spelling, punctuation or grammar.
Find your Mathematics course
- Mathematical Studies BSc
- Mathematics BSc
- Mathematics MSci
- Mathematics and Management BSc
- Mathematics and Music BA
- Mathematics and Physics BSc
- Mathematics and Physics MSci
- Mathematics with French BSc
- Mathematics with German BSc
- Mathematics with Italian BSc
- Mathematics with Management BSc
- Mathematics with Philosophy BSc
- Mathematics with Spanish BSc
- Mathematics with Statistics BSc
- Computer Science and Mathematics BSc
- Economics and Mathematics BSc
- Economics and Mathematics with a Year in Business BSc
- Finance and Mathematics BSc
- Finance and Mathematics with a Year in Business BSc
- Management with Mathematics BSc
- Modern Languages with Mathematics BA
- Mathematics for Applications MSc
- Mathematics of Cryptography and Communications MSc
- settings Undergraduate Postgraduate taught Postgraduate research Search Mathematics All departments View all undergraduate courses for 2018 View all undergraduate courses for 2019 View all postgraduate courses for 2018
- Mobile site view
- Desktop site view
- Media enquiries
- Modern Slavery Act
- IT Services
- Social media
- CampusAnywhere
- Terms and conditions
Comment on this page
Did you find the information you were looking for? Is there a broken link or content that needs updating? Let us know so we can improve the page.
Note: If you need further information or have a question that cannot be satisfied by this page, please call our switchboard on +44 (0)1784 434455.
This window will close when you submit your comment.
Dissertation Structure Strategies: A Roadmap to Academic Success

Dissertations, often hailed as the pinnacle of academic achievement, represent the culmination of years of research, dedication, and intellectual prowess. They are your opportunity to make a significant contribution to your field of study, a chance to leave your mark on the academic world.
What might surprise you, however, is that the average dissertation contains roughly 80,000 to 100,000 words—equivalent to a short novel! These comprehensive research projects require not just intellectual prowess but also a clear, well-structured roadmap to guide readers through your academic exploration.
These research documents are vital as they allow scholars to delve deeply into a particular subject, fostering a deeper understanding of complex topics and offering the opportunity to make meaningful contributions to their respective disciplines. Structuring a dissertation effectively is crucial to communicating these contributions clearly and coherently.
Ever Wondered What the Missing Piece of Your Academic Puzzle Looks Like?
Let us craft your bespoke dissertation and embark on a journey to scholarly excellence!
How to Structure Your Dissertation
The structure of a dissertation is the blueprint that underpins your entire research endeavor, a scaffold upon which the intricate layers of your study will be built. Like a skilled craftsman, a well-structured piece ensures that your ideas flow logically, offering readers a clear and engaging path through your scholarly exploration. In the following sections, we will delve into the essential dissertation chapters that compose its structural framework, equipping you with the knowledge and tools necessary to create a research document that stands as a testament to your academic rigor and expertise.
Introduction
The introduction is your first opportunity to set the stage, frame the research problem, and provide a roadmap for what lies ahead. This section typically encompasses the following key elements:
.webp)
- Contextualization : Begin by introducing the broader context of your research. Why is the topic important, and how does it fit into the larger field of study? For instance, if your own research, as outlined on the title page, explores the impact of climate change on agriculture, you might highlight the growing global concern over environmental issues and their implications for food security.
- Problem Statement : Clearly state the specific problem or research question your research aims to address. Make it concise and thought-provoking. For example, 'How can sustainable agricultural practices mitigate the adverse effects of climate change on crop yields in developing countries?'
- Objectives and Hypotheses : Outline the objectives of your research and any hypotheses you intend to test. For the above problem statement, you might state that your objectives are to analyze existing agricultural practices, assess their sustainability, and test the hypothesis that sustainable methods can enhance crop resilience in the face of climate change.
- Justification : Why is your research significant? What knowledge gaps will it fill? Perhaps you'll mention the lack of comprehensive studies on sustainable agriculture in specific regions or the urgency of addressing food security in the face of climate-related challenges.
- Scope and Limitations : Define the scope of your academic writing, setting clear boundaries on what you will and won't cover. Mention any potential limitations, such as constraints on data availability or time for fieldwork.
Questions to Consider :
- What led me to choose this topic, and how does it resonate with my academic interests?
- How does my research relate to existing knowledge in the field?
- What are the specific challenges or gaps in the current literature that my actual research addresses?
- What are the broader implications of my research findings?
By addressing these components in your introduction, you'll provide readers with a solid foundation for understanding the purpose and significance of your research project. It's your opportunity to engage their interest and prepare them for the intellectual voyage that follows in the subsequent chapters.
Experimental Design
In these pivotal parts of a dissertation, you'll delve into the heart of your research process: the experimental design. Here, you will describe in detail how you conducted your study, the methods employed, and the rationale behind your choices. The chapter typically consists of the following key components:
%20(5).webp)
- Research Methodology : Begin by explaining the research methodology you've chosen. Common methodologies include qualitative, quantitative, mixed methods, case studies, surveys, or experiments. Each has its own strengths and limitations, so justify your choice based on what best suits your research question.
- Data Collection : Describe how you collected the data. What instruments or tools did you use? For instance, if your study involves surveys, specify the survey questions and distribution methods. If it's a laboratory experiment, explain the equipment and procedures.
- Sampling : Detail the process of selecting your sample. Who or what is included, and why? If your research involves human subjects, address ethical considerations and provide evidence of any necessary approvals from ethics committees.
- Variables and Measurements : Clearly define the variables under investigation and the measurements you used. Explain how each variable was operationalized. If you're measuring something like crop yield in agriculture, specify the units of measurement, tools, and techniques.
- Data Analysis : Briefly introduce the statistical or analytical methods you'll employ to analyze the data. If your research is qualitative, describe the approach you'll use for coding and thematic analysis.
- Pilot Study : Mention any pilot studies or pre-tests you conducted to refine your methodology. This demonstrates your commitment to the rigor of your research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the validity and reliability of your research methods. How did you ensure that your data collection tools measure what they are supposed to, and how consistently do they do so?
- Limitations : Acknowledge any limitations in your experimental design. No study is perfect, and recognizing limitations demonstrates transparency and thoughtful evaluation of your research.
- Why did you choose this specific methodology and data collection techniques?
- How did you mitigate potential biases or confounding variables?
- What challenges did you encounter during data collection, and how did you overcome them?
- What steps did you take to ensure the credibility and trustworthiness of your findings?
The Results chapter is where the fruits of your research labor come to light. Here, you'll present the outcomes of your study, providing a clear and objective account of the data you've collected. This section is crucial for demonstrating the empirical support for your research hypothesis or objectives. It typically includes the following components:
.webp)
- Data Presentation : Begin by presenting your data in a clear and organized manner. This can involve tables, graphs, charts, and textual descriptions. Make sure to label and title all visual representations and use clear, concise language when discussing the findings.
- Descriptive Statistics : If applicable, provide descriptive statistics, such as means, medians, and standard deviations, to summarize your data. This helps readers quickly grasp the central tendencies and variations in your results.
- Inferential Statistics : If your study involves statistical analysis, present the results of your tests or models. Explain the statistical significance of your findings and their implications for your research question.
- Relationships and Patterns : Interpret the data by discussing any observed relationships, patterns, or trends. Are there any noteworthy correlations or variations? Are the results in line with your expectations, or do they challenge your initial hypotheses?
- Validity and Reliability : Reflect on the validity and reliability of your results. Discuss any potential sources of error or bias and explain how you addressed them during the data collection and analysis phases.
- Negative or Null Results : Be candid about any findings that did not support your hypotheses or expectations. This transparency is essential for a comprehensive research account.
- Comparisons : If your study involves multiple groups, conditions, or variables, make comparisons to highlight differences or similarities. Use appropriate statistical tests to support your comparisons.
- Visual Aids : Consider using visual aids, like charts and graphs, to illustrate key findings. These can make complex data more accessible to your readers.
- How do the results align with your research objectives and hypotheses?
- What are the most important findings, and what do they mean in the context of your study?
- Are there any unexpected or anomalous results, and how can you explain them?
- How do the results contribute to the broader understanding of the topic in your field?
The Discussion chapter is the intellectual nucleus of your dissertation, where you dissect and interpret the results you've presented in the previous section. According to our essay service experts, here, you'll not only explain the significance of your findings but also relate them to existing knowledge in your field.
.webp)
- Interpretation of Results : Begin by interpreting the results of your study. Explain what the data you've presented in the Results chapter means in the context of your research objectives and hypotheses.
- Comparison with Existing Literature : Relate your findings to the existing research in your field, as explored in the literature review chapter. Discuss how your results align with or differ from previous research, and articulate the implications of these comparisons.
- Theoretical Framework : If your research is rooted in a particular theoretical framework, discuss how your results support, challenge, or expand this framework.
- Answering Research Questions : Address each of your research questions or hypotheses one by one, indicating whether they were confirmed or refuted by your data.
- Limitations Revisited : Revisit the limitations you identified in the earlier chapters and discuss how they may have influenced your results. This demonstrates your awareness of the study's constraints and their potential impact, underscoring your research skills in critically evaluating your work.
- Implications : Explore the broader implications of your findings. How do they contribute to the advancement of knowledge in your field? Are there practical applications or policy implications stemming from your research?
Questions to Consider as per our dissertation service experts:
- What do your results reveal about the topic of your dissertation?
- How do your findings compare to previous research, and what do these comparisons signify?
- What theoretical, practical, or policy implications can be drawn from your research?
- How have you addressed the research questions or hypotheses that guided your study?
Whether you buy dissertation or write yourself, remember that the discussion chapter is an opportunity to articulate the broader significance of your research. By providing a clear and insightful analysis of your findings and their implications, you create a compelling narrative that underscores the value of your work.
While learning how to structure a dissertation, the Conclusion chapter serves as the culminating segment as it brings together the key elements of your study. This is your chance to offer a succinct yet comprehensive synthesis of your work and its implications. This section typically comprises the following components:
.webp)
- Restate Research Objectives : Begin by reiterating the primary research objectives or questions that guided your research project. Concisely remind your readers of the core focus of your study.
- Summary of Key Findings : Provide a condensed summary of the most significant findings from your research. Highlight the main takeaways without delving into exhaustive detail.
- Contributions to the Field : Emphasize the contributions your research has made to the field. Discuss how your study has added to existing knowledge, addressed research gaps, or opened new avenues for exploration.
- Practical and Theoretical Implications : Elaborate on the practical and theoretical implications of your findings. Consider the real-world applications, policy recommendations, or theoretical advancements your research suggests.
- Final Thoughts on Hypotheses : Reflect on whether your research hypotheses were supported by the data. If they were not, discuss what this means in the context of your study and the broader field.
- Closing Remarks : Offer some closing remarks that encapsulate the essence of your research. This is an opportunity to leave a lasting impression on your readers by tying together the threads of your study.
- Research Journey Reflection : Share your personal reflections on the research journey. Discuss the challenges you encountered, the insights you gained, and the significance of the experience.
- Future Directions : Suggest possible avenues for future research based on the findings and questions that have emerged from your work. Highlight the ongoing conversation in your field and how your research can contribute.
- How do your findings and contributions align with your initial research objectives and the broader context of your field?
- What key messages do you want readers to take away from your research project?
- How has your research advanced the academic discourse and addressed gaps in the literature?
- What further research opportunities have emerged as a result of your study?
Final Perspective
As you learn how to write a dissertation , it's essential to keep in mind that this journey is not just about academic rigor; it's also an opportunity for personal and intellectual growth. Along the way, you'll encounter challenges, make discoveries, and contribute to the ever-evolving landscape of human knowledge.
Here are some unique and specific education dissertation topics you may find useful for your endeavor:
- Digital Privacy and Surveillance in the Age of Smart Cities : Investigate the ethical and legal implications of increased digital surveillance in urban environments.
- The Psychology of Decision-Making in Extreme Environments : Analyze the cognitive and emotional factors influencing decision-making in high-stress, life-threatening situations, such as emergency medicine or space exploration.
- The Role of Music Therapy in Pediatric Pain Management : Explore the effectiveness of music therapy in alleviating pain and anxiety in children undergoing medical procedures.
- Preserving Indigenous Languages in the Digital Age : Investigate the role of technology and social media in revitalizing and preserving endangered indigenous languages.
- Psychological Impact of Virtual Reality (VR) Therapy for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) : Evaluate the therapeutic potential of VR in treating PTSD and related mental health conditions.
These topics cover a wide range of subjects and offer unique perspectives that can make your master's dissertation or journal articles both engaging and impactful within your chosen field.
Ever Wondered What It Feels Like to Hold Your Intellect in Your Hands?
Order your dissertation, and let's make your academic mark together!
Related Articles
.webp)
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started
Published on 26 March 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 5 May 2022.
A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree.
The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the level and field of study. However, there are some key questions that can help you understand the requirements and get started on your dissertation project.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
When and why do you have to write a dissertation, who will supervise your dissertation, what type of research will you do, how should your dissertation be structured, what formatting and referencing rules do you have to follow, frequently asked questions about dissertations.
A dissertation, sometimes called a thesis, comes at the end of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree. It is a larger project than the other essays you’ve written, requiring a higher word count and a greater depth of research.
You’ll generally work on your dissertation during the final year of your degree, over a longer period than you would take for a standard essay . For example, the dissertation might be your main focus for the last six months of your degree.
Why is the dissertation important?
The dissertation is a test of your capacity for independent research. You are given a lot of autonomy in writing your dissertation: you come up with your own ideas, conduct your own research, and write and structure the text by yourself.
This means that it is an important preparation for your future, whether you continue in academia or not: it teaches you to manage your own time, generate original ideas, and work independently.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
During the planning and writing of your dissertation, you’ll work with a supervisor from your department. The supervisor’s job is to give you feedback and advice throughout the process.
The dissertation supervisor is often assigned by the department, but you might be allowed to indicate preferences or approach potential supervisors. If so, try to pick someone who is familiar with your chosen topic, whom you get along with on a personal level, and whose feedback you’ve found useful in the past.
How will your supervisor help you?
Your supervisor is there to guide you through the dissertation project, but you’re still working independently. They can give feedback on your ideas, but not come up with ideas for you.
You may need to take the initiative to request an initial meeting with your supervisor. Then you can plan out your future meetings and set reasonable deadlines for things like completion of data collection, a structure outline, a first chapter, a first draft, and so on.
Make sure to prepare in advance for your meetings. Formulate your ideas as fully as you can, and determine where exactly you’re having difficulties so you can ask your supervisor for specific advice.
Your approach to your dissertation will vary depending on your field of study. The first thing to consider is whether you will do empirical research , which involves collecting original data, or non-empirical research , which involves analysing sources.
Empirical dissertations (sciences)
An empirical dissertation focuses on collecting and analysing original data. You’ll usually write this type of dissertation if you are studying a subject in the sciences or social sciences.
- What are airline workers’ attitudes towards the challenges posed for their industry by climate change?
- How effective is cognitive behavioural therapy in treating depression in young adults?
- What are the short-term health effects of switching from smoking cigarettes to e-cigarettes?
There are many different empirical research methods you can use to answer these questions – for example, experiments , observations, surveys , and interviews.
When doing empirical research, you need to consider things like the variables you will investigate, the reliability and validity of your measurements, and your sampling method . The aim is to produce robust, reproducible scientific knowledge.
Non-empirical dissertations (arts and humanities)
A non-empirical dissertation works with existing research or other texts, presenting original analysis, critique and argumentation, but no original data. This approach is typical of arts and humanities subjects.
- What attitudes did commentators in the British press take towards the French Revolution in 1789–1792?
- How do the themes of gender and inheritance intersect in Shakespeare’s Macbeth ?
- How did Plato’s Republic and Thomas More’s Utopia influence nineteenth century utopian socialist thought?
The first steps in this type of dissertation are to decide on your topic and begin collecting your primary and secondary sources .
Primary sources are the direct objects of your research. They give you first-hand evidence about your subject. Examples of primary sources include novels, artworks and historical documents.
Secondary sources provide information that informs your analysis. They describe, interpret, or evaluate information from primary sources. For example, you might consider previous analyses of the novel or author you are working on, or theoretical texts that you plan to apply to your primary sources.
Dissertations are divided into chapters and sections. Empirical dissertations usually follow a standard structure, while non-empirical dissertations are more flexible.
Structure of an empirical dissertation
Empirical dissertations generally include these chapters:
- Introduction : An explanation of your topic and the research question(s) you want to answer.
- Literature review : A survey and evaluation of previous research on your topic.
- Methodology : An explanation of how you collected and analysed your data.
- Results : A brief description of what you found.
- Discussion : Interpretation of what these results reveal.
- Conclusion : Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your findings contribute to knowledge in your field.
Sometimes the order or naming of chapters might be slightly different, but all of the above information must be included in order to produce thorough, valid scientific research.
Other dissertation structures
If your dissertation doesn’t involve data collection, your structure is more flexible. You can think of it like an extended essay – the text should be logically organised in a way that serves your argument:
- Introduction: An explanation of your topic and the question(s) you want to answer.
- Main body: The development of your analysis, usually divided into 2–4 chapters.
- Conclusion: Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your analysis contributes to knowledge in your field.
The chapters of the main body can be organised around different themes, time periods, or texts. Below you can see some example structures for dissertations in different subjects.
- Political philosophy
This example, on the topic of the British press’s coverage of the French Revolution, shows how you might structure each chapter around a specific theme.

This example, on the topic of Plato’s and More’s influences on utopian socialist thought, shows a different approach to dividing the chapters by theme.

This example, a master’s dissertation on the topic of how writers respond to persecution, shows how you can also use section headings within each chapter. Each of the three chapters deals with a specific text, while the sections are organised thematically.

Like other academic texts, it’s important that your dissertation follows the formatting guidelines set out by your university. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
Formatting guidelines concern things like:
- line spacing
- page numbers
- punctuation
- title pages
- presentation of tables and figures
If you’re unsure about the formatting requirements, check with your supervisor or department. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
How will you reference your sources?
Referencing means properly listing the sources you cite and refer to in your dissertation, so that the reader can find them. This avoids plagiarism by acknowledging where you’ve used the work of others.
Keep track of everything you read as you prepare your dissertation. The key information to note down for a reference is:
- The publication date
- Page numbers for the parts you refer to (especially when using direct quotes)
Different referencing styles each have their own specific rules for how to reference. The most commonly used styles in UK universities are listed below.
You can use the free APA Reference Generator to automatically create and store your references.
APA Reference Generator
The words ‘ dissertation ’ and ‘thesis’ both refer to a large written research project undertaken to complete a degree, but they are used differently depending on the country:
- In the UK, you write a dissertation at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a thesis to complete a PhD.
- In the US, it’s the other way around: you may write a thesis at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a dissertation to complete a PhD.
The main difference is in terms of scale – a dissertation is usually much longer than the other essays you complete during your degree.
Another key difference is that you are given much more independence when working on a dissertation. You choose your own dissertation topic , and you have to conduct the research and write the dissertation yourself (with some assistance from your supervisor).
Dissertation word counts vary widely across different fields, institutions, and levels of education:
- An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000–15,000 words
- A master’s dissertation is typically 12,000–50,000 words
- A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000–100,000 words
However, none of these are strict guidelines – your word count may be lower or higher than the numbers stated here. Always check the guidelines provided by your university to determine how long your own dissertation should be.
At the bachelor’s and master’s levels, the dissertation is usually the main focus of your final year. You might work on it (alongside other classes) for the entirety of the final year, or for the last six months. This includes formulating an idea, doing the research, and writing up.
A PhD thesis takes a longer time, as the thesis is the main focus of the degree. A PhD thesis might be being formulated and worked on for the whole four years of the degree program. The writing process alone can take around 18 months.

Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, May 05). What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/what-is-a-dissertation/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples.
Dissertations
[ Back ] [ Home ] [ Who to Talk to ] [ Study Skills ] [ Library ] [ Things to do ] [ Regulations ] [ Welcome ]
Browse through the information below for general advice on the different aspects of a dissertation.
You can download the advice in the following sections as a complete guide here.
Getting Started
What is a dissertation.
A Dissertation is a major assessment task, sometimes labelled as an Honours Project, Independent Study Module or another module of 30 credits or more with a single assessment point. They typically involve researching a topic which has been agreed and approved by a programme tutor. Information on these will be found in your Programme and Module Handbooks. (Extract taken from The Student Regulation Framework: Major Assessment Tasks )
A number of elements distinguish a dissertation from other assignments you might have undertaken:
- Independent – A dissertation is an exercise in independent study. Previous assignments might have had a great deal of guidance on the topic beforehand. A dissertation puts you in the position of researcher and subject-expert and is used to assess your ability to apply the principles of research to an original, independent project.
- Focus – The focus of your dissertation will be much narrower than any assignment you’ve had in the past. The purpose of a dissertation is to conduct a detailed examination of a topic in your discipline. You will need to consider multiple perspectives and demonstrate your understanding through the development of a new point of view.
- Length – A dissertation is substantially longer than other assignments, and for some students, it will be the longest piece of writing they compose in their whole life. An undergraduate dissertation can range from between 5,000 to 12,00 words depending on your discipline and your other modules.
- Structure – There are some components that will be present in every dissertation, and others will vary depending on the discipline or word count. A dissertation is typically structured by major chapters and other minor elements. Specifics will be detailed in your module handbook.
- Weight – A dissertation will have more module credits and therefore, will account for a larger percentage of your mark. You should be able to find specific details about this in your module handbook.
Before you do anything else
Word count – Find out the word count for your dissertation. This will allow you to plan how many words should be dedicated to each section.
Academic writing in your discipline – Clarify if your discipline has any specific conventions to adhere to during the writing process, for example, if the use of first person is permitted or if subject-specific terminology requires an explanation or a glossary.
When and how you must submit your dissertation – Get the due date in your calendar! Find out exactly how you need to submit your dissertation. Typically, you should submit a copy via Turnitin and submit a printed and bound copy to the Student Admin Office. You can get your copy printed and bound via the University Copyshop.
Know who your supervisor is – Every undergraduate conducting research will be assigned a dissertation supervisor. You will be assigned to an academic at Marjon with expertise in your chosen topic. Therefore, your supervisor might be someone you have never met before. Don’t underestimate the value of your supervisor; make every effort to attend all meetings and take on board their feedback and advice.
Familiarise yourself with dissertations – Make use of the Dissertation PCs in the Library to view other Marjon undergraduate dissertations. Getting acquainted with the style, content and structure of a dissertation early on will get you off to a good start and allow you to implement similar techniques in your own report.
Developing your research question
What do we mean by a research question?
Put simply, a research question is a narrow focus or ‘question’ which you will plan and build your independent research around. It’s important to note that your research question is by no means set in stone from the minute it is devised, but is used to guide your reading and research, in order to maintain focus and direction. A research question needs to be:
- Clear – It provides enough specific information for the audience to be aware of the nature and purpose of the research without requiring additional information.
- Focused – It is narrow enough to allow an adequate explanation within the confines of the word count.
- Concise – It is expressed in as few words as possible.
- Complex – It isn’t answered by ‘yes’ or ‘no’ but rather through an examination of a number of influencing factors and perspectives.
- Debateable – It naturally lends itself to debate or argument and isn’t determined simply by accepted facts.
- Appropriate – It is appropriately related to your discipline or field of study.
(The George Mason University Writing Center, 2018)
Where to start?
One of the hardest parts of a dissertation is forming a research question that is narrow in focus but isn’t so narrow that it is impossible to find existing research! A dissertation should never be a demonstration of all you know about a topic. It should guide your reader through key argument. One piece of advice is to choose a topic that grabs your interest. A dissertation is a lengthy piece of work, so spend your time ‘doing what you love’, and you will have a much better outcome. Your dissertation supervisor is a great sounding board for these ideas. Here are some other things to ponder when considering your topic:
- Overly ambitious or challenging topics – You may want to change the world with your dissertation; but you probably want to graduate too! Your dissertation work will be governed by time constraints and your ability to be specific. There is no possible way you can write everything there is to know on a topic either, so be selective and realistic.
- Emotional links to topics – Sometimes, having an emotional link to a topic can make your research all the more meaningful, but in cases where it is likely to affect your well-being or stir up old memories, it is best to divert your focus. Dissertations by their very nature are meant to be objective pieces of research, so if you have an emotional connection to a topic, think how this might affect your research, your own ability and your own drive to complete the assignment.
- Contentious topics – If you feel particularly strongly or disgruntled by a topic, then it will be difficult to remain objective in your research. For instance, if your results challenge your expectations, then you might not be able to offer an impartial view or reflect on the research experience in full.
- Originality – If you are going to dedicate a great many hours to a piece of research, then you might as well make it worthy of that time and ensure that it is original. If you have an area where theorists or perspectives don’t agree, then this might be a good point to explore. If you admire a particular piece of research, try not to simply ‘replicate’ it, but rather put your own spin on it by changing some of the variables.
(Rudestam & Newton, 2001)
Narrowing it down

The Dissertation proposal
What is a dissertation proposal?
A dissertation proposal is “a careful description of what your dissertation will be about and how you intend to carry out the work involved until it’s completion” (Walliman, 2014, p. 67). You will be asked to submit a proposal for most courses, not only so your supervisor can check that your dissertation is within the realms of possibility and conforms to course requirements, but also so you can justify what you intend to do and why; how you intend to apply what you have learned over the course of your degree and how you will make a useful contribution to your discipline.
What should a dissertation proposal look like?
Each discipline will have specific guidelines on the structure of a dissertation proposal, so consult your module handbook or assessment guidelines. A proposal is typically no more than 2-3 sides of A4, to provide your reader with a snapshot of your planned dissertation. It will typically be divided into subheadings, which will vary according to word count and discipline, but typically, you will be expected to include aims and objectives, an introduction, a methods section, literature and research concepts or limitations.
The title problem
You will be expected to submit a dissertation title/ research question. Try to capture the main themes of your proposed research in the title so your reader is able to summarise what you will be doing from the title alone. If you are unsure where to start, try to identify themes by returning to your reading and picking out the key concepts that occur in the literature. Once you have these key concepts, illustrate the scope of your research with additional words that limit location or time. Remember, that this will be a working title: you are likely to tweak it as your research progresses.
Aims & objectives
You should aim to summarise the aims and objectives of your dissertation in no more than 3-4 bullet points. These should be a very focused summary of the reasons for your research and should lead your reader neatly into the subject background. You should also clearly set out the limitations of your dissertation here, so that the exact scope of the research is distinct.
Introduce the subject background
Your introduction needs to outline the current situation in terms of subject literature to your reader in a way that could be understood by anybody; not just subject specialists. Therefore, take extra care to make define any subject-specific terminology and any complex theories or concepts. Additionally, your introduction will need to convince your dissertation supervisor that you have undertaken adequate preparatory reading in the subject you intend to study. You can do this by:
- Introducing research conducted so far and what is has discovered
- Stating what has not been determined by research so far
- Introducing the need for research in this particular area in light of literature
The use of evidence from a wide range of sources will be crucial to your dissertation proposal. Don’t dismiss literature if it isn’t directly linked to your topic; look for any subtle, indirect links and pull these out to draw relationships between concepts. Your dissertation supervisor will tell you if you have missed any critical readings and might be able to direct you towards helpful resources.

The key to an excellent dissertation proposal is the ability to deliver your understanding, argument and research intentions succinctly. You will need to contextualise your research in a concise style. Be selective: you are not expected to deliver everything you know on the topic in your proposal; just enough to demonstrate that you have a clear understanding of the literature and how your research feeds into this.
You will need to detail how you intend to carry out your research and link your chosen methods to the research question. Be as clear as you possibly can, especially if you intend to use more than one method. Stipulate clearly which aim a method intends to address. This may require a bit of background reading on research methods. If you are unsure where to start, Skills You Need is an excellent introductory resource on research methods. Here are a number of things you could address in your methods proposal:
- State a research design
- Identify the research population – lay out the situation
- Select a sample – size, location, number of people
- Collecting data – through interviews, surveys, observations etc.
- Analysing data – through coding statistical tests etc.
(Walliman, 2014, p. 74)
Expected outcomes
You should include a few sentences on what you expect the outcomes of your research to be and predict who might benefit from the findings. The outcomes should be linked closely to the aims and objectives of the research and should be relative to your timeframe and resources.
What do I do with a proposal once approved?
The proposal will be an excellent foundation for your dissertation in terms of research and write up, so expect to refer to it regularly in order to plan your research. Eventually, the proposal will be superseded by the dissertation document itself, but it is helpful to keep a copy to keep your research on track.
Major Dissertation Chapters
The following sections will be an essential part of every undergraduate honours dissertation. You should refer to your module handbook for precise guidance. The following advice centres on the main components, structure and style of each chapter. This does not supersede any advice given to you by your dissertation supervisor or in module handbooks.
Click here for a Dissertation Chapter Checklist
Introduction
The purpose of the introduction
Mewburn, Firth and Lehmann (2019) liken a dissertation introduction to a map: your reader will never have encountered this exact piece of research, so the introduction needs to serve as guide to your reader on what’s to follow throughout the rest of your report. (See this guide to using signposts ). Additionally, your introduction should contextualise your research. You may find that broader background information is required to contextualise the literature referred to in your literature review, so the introduction would be the natural place for this to sit. However, don’t release all details of your research in the introduction; your reader just needs a taste of your research so they continue reading!
Introduction content checklist
Dissertation Tip #3
Don’t dismiss the value of a good introduction in a dissertation. You may find it easier to outline your introduction in the early stages of writing and then draft it thoroughly after you have completed the research and understand fully what you are introducing. This is because your ideas will develop over the writing and researching process and your introduction will need to reflect this process.
Further Resources
Skills You Need. (2019). Writing a dissertation: The introduction. Retrieved from https://www.skillsyouneed.com/learn/dissertation-introduction.html
Warwick University. (2017). Writing an introduction. Retrieved from https://warwick.ac.uk/fac/soc/al/globalpad/openhouse/academicenglishskills/writing/moreinfo/
Literature Review
Your literature review is a major chapter in your dissertation and is your chance to present the current state of play for research in your chosen subject. You will need to consult the literature in your discipline to ensure that the research you are planning to conduct hasn’t already been carried out, and to justify why your chosen subject is worth investigation. Your literature review is the section of your dissertation where you begin to narrow your focus too, so you can examine all the nitty-gritty details of the research problem.
Dissertation Tip #4
You will need to refer to several sources in your literature review; some of these might be or be located in places you are unsure of. The University’s AIM sessions offer informative sessions on using Discovery, so you can optimise your searches, locate information quickly and make the research process easier. You can view all sessions and book on Learning Space.
What should I cover in my lit review?
The clue is in the title! You should be consulting a range of sources related to your research question and collating this information to provide your reader with a current state of events in your chosen subject. Here are some of the things you can look for in your dissertation reading:
- Theory – A consideration of your topic from the perspective of multiple theories and how they explain certain phenomenon. Draw upon the strengths and weaknesses of theories and compare and contrast them.
- History – How have we arrived at the current situation in your discipline? Examine problems or phenomenon that has developed over time, examine their consequences and argue whether it has helped or hindered the situation.
- Developments – What are the current ways of thinking in your discipline? What are the current problems and how are they being tackled? What conflicts exist within the subject?
- Research methods – what techniques have been used to research the issues so far? How has data been collected and analysed? How have the outcomes been explained?
(Walliman, 2014, p. 101)
Remember that you won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has ever been written in your field. The literature review is an iterative process; it will need to be drafted, adapted, edited and redrafted, so a source that is essential at the beginning of the process might be substituted for something more relevant at a later point.
Keeping a record
Throughout the dissertation process, it is vital that you keep a record of your reading so that you can easily refer back to material that you wish to include in your report and be able to track down details for citations. It can be difficult to know which parts of a source will be useful to your dissertation. For each source you read, write a summary in no more than 3 lines, so you will know the content at a glance. Create a standard way of noting themes, or papers that are essential. Appendix C has a reading chart as an example of how to standardise your notes, engage critically and make the most of your reading.
Further Resources for Literature Reviews
- 2 Turning an annotated bibliography on steroids in a proper literature review (pp 138-144) in Mewburn, I., Firth, K. & Lehmann, S. (2019). How to fix your academic writing trouble: A practical guide.
- Skills You Need. (2019). Researching and writing a literature review. Retrieved from https://www.skillsyouneed.com/learn/literature-review.html
Methodology
Purpose of a methodology
The methodology chapter is a justification for your chosen research methods in terms of philosophy and your research question (Skills You Need, 2019a). It needs to demonstrate exactly how your research was conducted so that it can be replicated step-by-step and so that your reasons for using certain protocol or methods is clear (Rudestam & Newton, 2001).
What should I cover in my methodology?
What you cover and how you write about these elements in your methodology will be largely governed by your use of quantitative or qualitative research methods. Broadly speaking:
Quantitative research tends to involve relatively large-scale and representative sets of data, and if often, … presented or perceived as being about the gathering of ‘facts’. Qualitative research, on the other hand, is concerned with collecting and analysing information in as many forms, chiefly non-numeric, as possible … and aims to achieve ‘depth’ rather than ‘breadth’.
(Blaxter, Hughes and Tight, 2010, p. 65)
Your methodology needs to be written in the past or present tense so that you can reflect on what methods were used, what went well and what you amended. It also needs to distinguish your research methods and your data collection methods and discuss them in terms of their pros and cons for your research.
You should also remember to include details on any equipment or procedures used, details about your participants and how you ensured the validity and reliability of your research. You should consult your module handbook for more information on the specific subheadings for inclusion in your methodology or consult texts on research methods to differentiate between the methodological details of qualitative and quantitative research.
Dissertation Tip #5
Marjon TELKit has a lot of tools you can use to facilitate your research methods such as online surveys, SPSS for statistical analysis and recording software for interviews. Ensure that any software you use can store data ethically and that you include the name of the software used in your methodology chapter for potential replication.
Often, research is dependent on the involvement of other people. This means you must conduct your research in a way that adheres to ethical guidelines; whether this is guidelines within your discipline, or the guidelines set up by Plymouth Marjon University , you should design your research in a way that is ethical, safe and respectful. Your methodology should have a subheading for ethical considerations, so you can demonstrate how these ethical guidelines have been followed throughout the research process, for instance participant consent, anonymity and the right to withdraw. Please be aware that you cannot carry out any research until you have received ethical approval.
Further Resources on Methodology
- Chapter 5 – The method chapter: Describing your research plan in Rudestam, K. E. and Newton, R. R. (2001). Surviving your dissertation: A comprehensive guide to content and process. (2 nd ed). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
- Chapter 10 – What’s all this about ethics? In Walliman, N. (2014). Your undergraduate dissertation: The essential guide for success. (2 nd ). London, UK: Sage.
- Bryman, A. (2016). Social research methods. (5 th ). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Results & Discussion
Please note that this guide considers the results and discussion of your dissertation as one chapter. Some disciplines require separate chapters, so consult your module handbook for specific guidance.
Purpose of results
The results section of your dissertation is where you describe your results, or what has occurred. If you are using statistical tests, then this is the section where you would discuss statistical significance and whether it has been achieved or not. The results section should include charts, graphs and tables so that you can refer to them and ‘state what you see’. You should include snapshots of your results here including overall results, instances of high or low phenomena, and any anomalies. Your raw data will need to go into your appendices and can be referred to for specifics, such as answers in interviews. Make sure you guide your reader through what you consider to be the most important observations.
Purpose of discussion
The discussion section is where you review and link the findings from your research to the existing literature and critically evaluate your contribution against other research. Put simply, your discussion section explains why and should perform four major functions:

What should I cover in my results and discussion?
Think of your discussion section as a long, persuasive essay. It needs to refer to the readings in your literature review and any other sources you have deemed essential in light of your findings. It is important that your discussion is critical so that you can make appropriate links between your research question, the literature and your findings. This means building an argument to persuade your reader and using your results to construct an argument on multiple grounds:
- Agree with, defend or confirm a point of view you have found in the literature
- Propose a new point of view
- Concede on some facets of a theory, but use your results to warrant a re-examination of other facets
- Reformulate an existing point of view to provide a better explanation
- Dismiss another’s point of view on the grounds of inadequacy or irrelevance
- Reject or rebut the argument of another on various grounds
- Reconcile two positions that may seem at odds, but are connected
- Retract or reject your previous position in light of evidence or arguments
(Taylor, 2009, p. 112-113)
Dissertation Tip #6
Your discussion section will need to create a strong argument. The University’s AIM sessions include Advanced Critical Thinking which looks at how to create and write strong, persuasive arguments through the use of evidence, rejection of fallacies and evaluation of rhetoric.
Sources for Results and Discussion
- Chapter 6 – Presenting the results of empirical studies in Rudestam, K. E. and Newton, R. R. (2001). Surviving your dissertation: A comprehensive guide to content and process. (2 nd ed). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
- University of Leicester. (2019). Writing a dissertation. Retrieved from https://www2.le.ac.uk/offices/ld/resources/writing/writing-resources/writing-dissertation
- ‘Where’s your evidence for this?’ : using what you know to make a case In Mewburn, I., Firth, K. & Lehmann, S. (2019). How to fix your academic writing trouble: A practical guide. London, UK: Open University Press.
The purpose of the conclusion
The conclusion is a chapter that should not be underestimated. The conclusion is your time to shine; your platform to state everything you have found out through your research and what this indicates. Furthermore, your conclusion is your chance to recommend as a practitioner in your field, so don’t pass up this opportunity in your dissertation writing!
Your conclusion should include:
- A brief summary of your key findings and essential results (try to avoid repetition of your introduction)
- An explicit account of the conclusions you have drawn from your research in relation to your research question, separating the confident conclusions from the uncertain
- An indication of why your research is important (to other researchers, practitioners, policy etc.)
- Recommendations for future research or future practice (within the realms of possibility!)
- A final statement to round off your dissertation; typically, a hedged prediction of the future or any explicit conclusions
(Skills You Need, 2019c; Taylor, 2009)
Reference List
A reference list is an absolutely essential component of your dissertation. every single work you mention in any chapter of your dissertation must be included in the reference list in the appropriate apa style. whilst there is no official guidance on how many references will sufficiently aid a dissertation, you should be reading widely and consulting more than just books and webpages..
Dissertation Tip #7
Don’t leave your reference list until last! Try using a referencing tool such as Mendeley to keep track of all your readings and automate citations for your dissertation report and the reference list. The University’s AIM sessions include Mendeley training and Organising Information , which equips you with the tools to manage your sources more effectively.
Additional Dissertation Sections
The following sections might be essential for some courses, but optional for others. Please adhere to your module handbook in the first instance, or clarify with your dissertation supervisor.
An abstract provides your reader with a ‘map’ to the structure of your dissertation and allows your reader to decide whether your dissertation is relevant to them (without reading the whole document). Your abstract should be written after you have completed your major chapters and therefore needs to be written in the past tense. It needs to describe the crucial elements of your dissertation in the fewest words possible, including:
- What the research question is and the aims and objectives
- Acknowledgement of a main theorist or theory (if applied)
- A short note on the main methods used
- A brief note on the major results
- Summary of the main conclusion and recommendations
An abstract should not include :
- Lengthy background information
- Waffle – be succinct and to the point
- Citations or references to other works
- Images, figures, tables
- Acronyms, abbreviations or subject-specific terminology
(University of Southern California, 2019)
TIP: Take a look at some of the journal articles you have read and note how they construct the abstract. These can act as a good model for this section of your dissertation.
Contents & Tables
Reports as standard require contents pages. You will need to include a table of contents, a list of figures and a list of tables so that your dissertation can be easily navigated. You can learn how to create these elements in your dissertation document, and more in the AIM Dissertation Formatting session. Book on Learning Space to attend!
Statement of originality
You will need to include a statement of originality in a standard format towards the beginning of your dissertation. This statement confirms that you have cited all sources within your work and that any work outside of these citations is your own. Good research is underpinned by academic integrity, including the acknowledgment of the work of others and having the confidence to undertake your own research and writing. Don’t fall at the final hurdle! If you are concerned about something, speak to your dissertation supervisor. Here is the exact statement that needs to be included:
I confirm that I have fully acknowledged all sources of information and help received and that where such acknowledgement is not made the work is my own.
Signed: …………………..
Dated: …………………..
Acknowledgements
The acknowledgements page is the part of your dissertation where you can thank anybody who has helped you during the research process. Typically, this should include your dissertation supervisor and any participants in your study; but be mindful of anonymity with the latter. The acknowledgements can extend to anyone you’d like to include and don’t need to be written in an academic style, as they are personal to you. However, don’t be unnecessarily offensive; your work will be viewed by many Marjon students in years to come, so set a good example!
A glossary is a list of key terms used in a specific context or technical terminology that might require some description in order to aid your reader’s understanding of the terms. A glossary is used to make your dissertation more available and accessible to a wider audience through clear explanations of words. You should only include a glossary if it is going to be of genuine use to your reader. A glossary should:
- Be alphabetical for easy look-up of terms
- Be restricted to words that your reader might need to clarify
- Not include acronyms – these should be included in a List of Acronyms if they are numerous
Bibliography/Supervision Log
A bibliography is a requirement for some disciplines, but not all. The same goes for a supervision log; this is a common requirement for teaching degrees. You should check your module handbook for any specific guidance. If you are required to include these, then they should be included directly after your reference list and listed in your Table of Contents. Your bibliography should be formatted in APA, alphabetically and with a hanging indent.
Remember: if you cite something from your bibliography in your dissertation then it needs to be moved to your reference list!
Think of your appendices as filing location for any essential documents that need to be submitted in conjunction with or referred to within your dissertation. Anything that supports or extends the main body of the dissertation should be submitted as an appendix. Traditionally, appendices are labelled A, B, C… with a short description of the contents, for easy referral within the main body of your dissertation. Things that typically get included in appendices are:
- Ethical clearance forms
- Consent forms
- Examples of blank questionnaires/interview questions/datasets
- Raw data from results
- Transcriptions of interviews or focus groups
- Coded data from thematic analysis
Your appendices are not suitable for the inclusion of material that you can’t fit into the allocated word count! If something is worth saying, the ensure you include it in the appropriate chapter of your dissertation and use artful editing to get within the word count limits.
Qualifications and awards
Exceptions to regulations for individual programmes.
88. A student following a programme of study which does not lead to a qualification (a credit-only programme) may be provided with an award of completion, in addition to a transcript of credits achieved.
89. A student who has accumulated sufficient credits for the qualification, and meets the regulatory requirements will be awarded the qualification (subject to no outstanding tuition fee debt).
90. Degree programme tables define the curricula and conditions to be met in order to be eligible for an award in named subject(s), subject to satisfying all regulatory requirements.
91. A student must meet all requirements (i.e. passed all modules) at least 30 days before the appropriate graduation ceremony.
93. Programmes adhere to the Scottish Credit and Qualifications Framework for the purposes of the level of named programmes and credit accumulation. Minimum credits at each level are as follows:
94. Successful completion of all credits at level 11 (and not as qualified pass credit at level 10) is compulsory for the application of the merit/distinction algorithm.
95. Where a programme includes modules assessed on a pass/fail basis, these will be discounted for the purposes of awarding the degree with merit/distinction.
96. For awards with distinction the criteria are:
97. For awards with merit the criteria are:
98. Where a student achieves a dissertation mark of between 65 and 70 and over 70 for all other modules, then the Board of Examiners has discretion to award a Master’s with Distinction.
99. Where a student achieves a dissertation mark of between 55 and 60 and over 60 for all other modules, then the Board of Examiners has discretion to award a Master’s with Merit.
100. A board of examiners may recommend to Academic Council that an aegrotat or posthumous award be conferred in respect to an undergraduate or taught postgraduate programme.
Aegrotat awards may be considered where no degree award may be made within the regulations, and the student is close to completing the award but is prevented from doing so because of illness.
In recommending an aegrotat award, a board of examiners should be satisfied that: the student's prior performance clearly demonstrates that he/she would have satisfied the requirements for the award, but for the illness experienced; and the student is unlikely to be able to return to complete his/her studies at a later date.
A posthumous award can be considered where a student has died and has either; completed the programme of study, including the required assessments, and has satisfied the requirements of the award; or has not completed the programme of study but the board of examiners is satisfied that the student would have been able to complete or satisfy the requirements for the award.
In making a recommendation for a posthumous award in this case, the board of examiners shall consider the evidence of the student’s academic performance overall and in respect to any coursework submitted or assessments completed.
MSc/PgDip Social Work Studies
101. Progression. A student must be registered as a social work student with the Scottish Social Services Council, including clearance under the Protecting Vulnerable Groups (PVG) Scheme by the end of March in their first semester in order to progress. Registration must be maintained throughout the entire programme of study.
102. Progression. Any leave of absence of one year or more will require the student to complete a readiness to return to studies assessment prior to recommencing the programme.
103. Assessment. Some modules may contain elements of assessment that are assessed on a pass/fail basis and these assessments require to be passed in order to achieve a pass in the module. Where a module contains such an assessment the module mark will not be calculated on a weighted average basis.
104. Assessment Only. Due to the interactive nature of teaching and practice skill requirements on some modules, students are not permitted to repeat these module on an assessment only basis, they must be repeated on a teaching and assessment basis. Details of which modules this applies to are contained in the module outlines.
105. Study Duration. A student must complete the programme within 4 years of programme commencement (inclusive of periods of leave of absence.
MBA course and MSc Business and Management course – Stirling Management School
106. Assessment. Students must achieve 50% in the sum of the weighted component marks, rounded to the nearest whole number; students must also achieve at least 40% in each component. Where a student fails to meet the 40% minimum requirement in any component a fail (X) will be awarded for the module. Re-assessment of failed modules will follow the agreed Taught Postgraduate Regulations.
- Cookies & Privacy
- GETTING STARTED
- Introduction
- FUNDAMENTALS
Getting to the main article
Choosing your route
Setting research questions/ hypotheses
Assessment point
Building the theoretical case
Setting your research strategy
Data collection
Data analysis
CONSIDERATION TWO
Where to find the best marks.
Not every chapter, or every section of every chapter, is going to land you lots of nice marks, especially the particularly nice marks that are needed for a top grade. Some sections are fillers - necessary, but expected for a standard mark - whilst others give you the chance to show why your dissertation is significant, worthy of a higher mark. In Route #1: Replication-based dissertations , where these different sections are will depend on (a) the route you adopted (i.e., Route A: Duplication , Route B: Generalisation or Route C: Extension ) and (b) your specific dissertation focus. Therefore, in the sections that follow, we explain what you should consider based on whether you adopted Route A: Duplication , Route B: Generalisation or Route C: Extension :
Route A: Duplication
When following Route A: Duplication , there are three main areas to focus on to get a good mark: (a) justifying duplication; (b) the creation and execution of a strong sampling strategy; and (c) the appropriateness and accuracy of your statistical analysis and comparisons.
Justifying duplication
Presenting a strong justification to duplicate previous research is very important to getting a good mark when following Route A: Duplication because more often than not, duplication is not considered to be a sufficient contribution, whether you are a student performing a dissertation, or even a seasoned academic. Therefore, you need to stress, right from the start of Chapter One: Introduction , the importance of testing the reliability , internal validity and external validity of the original study, as well as any other reasons that are specific to your dissertation.
Creating and execution of a strong sampling strategy
As you'll know, when pursuing Route A: Duplication , you cannot always rely on applying the sample sampling strategy as the one used in the main journal article. However, the characteristics of the sample and population you study should mirror , as closely as possible, the ones used in the main journal article. This enables you to make close comparisons between the findings in the main journal article and those from your dissertation. For this reason, when writing up Chapter Three: Research Strategy , you need to pay close attention to explaining and justifying not only the strengths and weaknesses of your sampling strategy, but also the fit between your sampling strategy and the one followed in the main journal article. This will strengthen your case when discussing the generalizability of your findings (i.e., the external validity of your findings) in Chapter Five: Conclusion .
The appropriateness and accuracy of your statistical analysis and comparisons
Comparing your findings to those in the main journal article is particularly important in Route A: Duplication , so being able to make such comparisons in Chapter Four: Results is essential for a good mark. In addition, you need to remember that since you're doing a quantitative dissertation, the appropriateness and accuracy of your statistical analysis is vital to getting a good mark. You can succeed in everything you do up until this stage, and then perform the wrong analysis or interpret it incorrectly, failing to answer your research questions/hypotheses, which can seriously jeopardize the mark you're awarded for your dissertation. Now this doesn?t mean that you have to do fancy analysis. You just need to make the right choices, which means: (a) thoughtfully analysing your data, which leads to choosing the correct statistical tests (i.e., appropriateness ); and (b) accurately interpreting the results from these statistical tests in order to answer your research questions/hypotheses (i.e., accuracy ). These are things that you need to first explain and justify in the Data Analysis section of Chapter Three: Research Strategy , and then demonstrate throughout Chapter Four: Results .
Route B: Generalisation
When following Route B: Generalisation , there are three main areas to focus on to get a good mark: (a) the theoretical justification for your type of generalisation, (b) the external validity of your findings, and (c) the appropriateness and accuracy of your statistical analysis and comparisons.
The theoretical justification for your type of generalisation
As you?ll know, each approach within Route B: Generalisation is underpinned by different theoretical justifications (i.e., the reasons to carry out a treatment-based generalisation will be very different from a population-based generalisation ). This makes it particularly important to theoretically explain and justify your particular approach . More often than not, such theoretical justifications will come from a critical analysis of the main journal article or from your understanding of the literature (i.e., STAGE FIVE: Building the theoretical case ). In either case, high marks come from being able to theoretically justify the approach you have adopted, something you will do briefly in Chapter One: Introduction , but mainly in Chapter Two: Literature Review .
The external validity of your findings
Since the purpose of Route B: Generalisation is to make generalisations across populations, settings/contexts, treatments or time, demonstrating that your dissertation was externally valid is important to getting a good mark. To do this, you will need to explain in Chapter Three: Research Strategy how you reduced threats to external validity through the research strategy you set, as well as discussing how such threats could have affected your findings (i.e., something you will do in Chapter Four: Results and the Research Limitations section of Chapter Five: Discussion/Conclusion ).
You're doing a quantitative dissertation, so the appropriateness and accuracy of your statistical analysis is vital to getting a good mark. You can succeed in everything you do up until this stage, and then perform the wrong analysis or interpret it incorrectly, failing to answer your research questions/hypotheses, which can seriously jeopardize the mark you?re awarded for your dissertation. Now this doesn?t mean that you have to do fancy analysis. You just need to make the right choices, which means: (a) thoughtfully analysing your data, which leads to choosing the correct statistical tests (i.e., appropriateness ); and (b) accurately interpreting the results from these statistical tests in order to answer your research questions/hypotheses (i.e., accuracy ). These are things that you need to first explain and justify in the Data Analysis section of Chapter Three: Research Strategy , and then demonstrate throughout Chapter Four: Results . In addition, since the purpose of Route B: Generalisation is to make generalisations across populations, settings/contexts, treatments or time, comparing your findings with those in the main journal article is important for a good mark. Such comparisons will help to show the extent to which the results from your dissertation are similar to those of the main journal article (i.e., how far the results can be generalised to other populations, settings/contexts, treatments, or time; that is, how externally valid the hypotheses that were tested are).
Route C: Extension
When taking on Route C: Extension , there is a lot of potential to get high marks, especially when compared with Route A: Duplication and Route B: Generalisation , which do not have the same level of originality and independent thought . However, three areas in particular that you should focus on in order to get a good mark are: (a) the theoretical justification for your type of extension; (b) a thoughtful approach towards research quality; and (c) the appropriateness and accuracy of your statistical analysis.
The theoretical justification for your type of extension
As you'll know, Route C: Extension is more than just replication because the changes you make to components of the main journal article, such as the research design , constructs/variables , methods and measurement procedures , and/or data analysis approach adds a great deal more originality and independent thought to the traditional replication routes (i.e., compared with Route A: Duplication , and even Route B: Generalisation ). This makes it particularly important to theoretically explain and justify your particular approach within Route C: Extension (i.e., whether a population and context/setting-based extension , design-based extension or method or measurement-driven extension ). Such theoretical justifications can come a critical analysis of the main journal article or from your understanding of the literature (i.e., STAGE FIVE: Building the theoretical case ), or an understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of the research design, methods and measurement procedures used in the main journal article (i.e., STAGE SIX: Setting the research strategy ). In either case, high marks come from being able to theoretically justify the approach you have adopted, something you will do briefly in Chapter One: Introduction , but mainly in Chapter Two: Literature Review and the appropriate sections of Chapter Three: Research Strategy .
A thoughtful approach towards research quality
Whilst you will pick up more marks for carrying out a dissertation with greater originality and independent thought , this counts for little if your results cannot be trusted. Focusing on research quality is so important to a good mark in all approaches to Route C: Extension because of the changes that you make to the research strategy of the main journal article - whether some aspect of the research design , research methods and measures , or sampling strategy - any of which can significantly affect the quality of your findings. Implementing a thoughtful approach towards research quality means that you have carefully considered and incorporated all aspects of research quality into your research strategy (i.e., internal validity , external validity , reliability and construct validity ). By doing this, you demonstrate not only the ability to produce a dissertation with greater originality and independent thought, but also the ability to effectively carry out such a dissertation in the field. This makes the Research Quality section of Chapter Three: Research Strategy particularly important in your write up.
The appropriateness and accuracy of your statistical analysis
You're doing a quantitative dissertation, so the appropriateness and accuracy of your statistical analysis is vital to getting a good mark. You can succeed in everything you do up until this stage, and then perform the wrong analysis or interpret it incorrectly, failing the answer your research questions/hypotheses, which can seriously jeopardize the mark you're awarded for your dissertation. Now this doesn't mean that you have to do fancy analysis. You just need to make the right choices, which means: (a) thoughtfully analysing your data, which leads to choosing the correct statistical tests (i.e., appropriateness ); and (b) accurately interpreting the results from these statistical tests in order to answer your research questions/hypotheses (i.e., accuracy ). These are things that you need to first explain and justify in the Data Analysis section of Chapter Three: Research Strategy , and then demonstrate throughout Chapter Four: Results .
- How it works
Published by Nicolas at March 5th, 2024 , Revised On March 5, 2024
What Is The Average Dissertation Length?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to answering the question, “How long should my dissertation be?”. However, the standard is as follows.
Table of Contents
Shorter Dissertations
Some fields or programs may have shorter dissertation requirements, particularly in disciplines where the research tends to be more focused or where a shorter document suffices to convey the research findings. In such cases, dissertations might range from 50 to 100 pages or even shorter.
Average-Length Dissertations
For many doctoral programs, particularly in the humanities, social sciences, and some STEM fields, the average dissertation length falls between 150 and 300 pages . This length allows for a thorough exploration of the research top ic , a review of literature , methodology, data analysis, and a discussion of findings.
Longer Dissertations
In certain scientific or technical fields and interdisciplinary studies, dissertations can be longer, ranging from 300 to 500 pages or more. These longer dissertations often involve extensive data collection, complex analyses, multiple experiments or case studies, and detailed discussion of results and implications.
Hire an Expert Writer
- Formally drafted in academic style
- Plagiarism free
- 100% Confidential
- Never Resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements
Factors Affecting Dissertation Length
There are a number of factors that contribute to the length, including
Field of Study
Your dissertation depends on your discipline. Humanities and social sciences usually have a lower average word count compared to sciences and engineering because the latter requires extensive data analysis and experimentation.
University Requirements
Most universities have certain specific guidelines influenced by department and faculty expectations. It is important to go through them before you start writing.
Research Methodology
The complexity of the research design and methodology can impact the length. Dissertations having comprehensive data collection might need additional space for detailed justification.
Literature Review
Depending on how novel your research topic is, the length of your literature review varies. If there is a lot of research done on your variables, your dissertation will be longer.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a dissertation exceed recommended length.
Yes, but ensure all content is relevant and contributes meaningfully to the research.
How can I manage dissertation length effectively?
Plan meticulously, prioritize content, and seek feedback to ensure conciseness without sacrificing depth.
You May Also Like
The answer to the question, “Can literature review include newspaper articles?” is provided in this comprehensive guide. Read more.
Learn how to write a reference letter that seals the deal: Expert tips to make yours stand out and get that job, admission, or rental house!
How to write date in Canada – ISO 8601 format – YYYY-MM-DD – For example, January 4, 2024, will be written as 2024-01-04.
Ready to place an order?
USEFUL LINKS
Learning resources, company details.
- How It Works
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
How long is a dissertation, published by steve tippins on april 9, 2019 april 9, 2019.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 05:03 am
How long is a dissertation? This is a question that almost every doctoral student asks at some point. It is not a new question–in fact, it’s been asked every time a paper of some sort is assigned in any class.
The simple answer (for any paper) is, “long enough to answer the question.” Not a really helpful answer, but satisfying from a professor’s perspective.
The truth is, there is no one answer to how long a dissertation is. I can’t say 146 pages is what’s needed, as you may write to page 146 and stop without fully exploring your topic. 90 pages could adequately address your research question, or you could write 200 pages and still not fully answer what you set out to. Every topic is unique, as is each person’s writing style.
Some websites even give specific answers that are simply inaccurate. In my experience, dissertations vary too much to be pinned down like that.
However, there are some practical suggestions I can make about how long your dissertation should be, how to adequately address the requirements of each section, as well as how to expand or reduce the length of specific chapters according to your needs. I’ll explore these below.
But first, let’s try and at least give the beginning of an answer to the question “how long is a dissertation?”
Marcus Beck Sets Out to Answer “How Long Is A Dissertation?”
Any discussion of dissertation length must include the work done by Marcus Beck . As a way to distract himself from his own dissertation writing, Beck calculated the average length of dissertations in the University of Minnesota database.
You can see from looking at his data that average length varies by discipline. So the first answer to how long a dissertation is, is that it depends upon what area you are writing your dissertation. It appears that a dissertation in History will be much longer, on average, than one in Chemistry. He also calculated the average across all disciplines.
Don’t be intimidated by how long the average dissertation is.
Many people look at the average length of a dissertation and get intimidated by the high page count. But, as Marcus Beck says in his blog post, “The actual written portion may only account for less than 50% of the page length.”
I’ve found this to be true. References, appendixes, tables and figures, page breaks, and white space all contribute to the high page count. The actual number of words you need to write is likely considerably less than the page count initially implies.
How Long Should My Dissertation Be?
Even though there’s no single answer about how long a dissertation should be, there probably is an ideal range which your dissertation falls into. This depends on your topic of research, but also on other factors. I’ll discuss some of these below.
Institutional Guidelines
I know of schools that have policies such as “Chapter 2 must be at least 40 pages long and no more than 60 pages.” Why this type of requirement? In my mind, there are two reasons.
First, they want to give some sort of guideline for students that is helpful but does not overburden faculty (a 230-page lit review is daunting to read).
Second, credibility is important. An 8-page lit review does not reflect well upon the student or the institution.
Most schools now have a dissertation template with the headings that are needed for most sections. If you take the time to completely fill in the headings with all of the relevant information, you should come up with an adequate number of pages. Remember, in academic writing, we don’t leave much to chance, we tell the reader everything.
Committee Preferences
It is likely that you will get a committee member who will give you priceless advice such as, “more is needed here.” When you get this type of comment it can be frustrating as specific feedback can be much more helpful.
Usually, what a committee member means by comments like this is that you haven’t really convinced the reader that you have fully explored the area or demonstrated a strong understanding of the material. So, expand what you are saying. Don’t imply anything, state it directly. This lets your committee know that you really do get it.
Sometimes you will get committee members giving contradictory advice. One member may want more information and another may want less. My first piece of advice is to negotiate these types of requests through your Chairperson.
This is where your Chair’s experience and guidance can be very helpful. Second, if a member really wants material included but others do not think it is very helpful, then adding the material in an appendix may make everyone happy.
Practical Suggestions For Dissertation Length, Chapter-By-Chapter

If you adequately and succinctly address each required section, you should end up with the right length for each chapter (and therefore, a dissertation of the right length). I’ll also give some rough guidelines on average page length where appropriate.
This is the introduction to your study. It is important to lay out the agenda for your research. Be sure that your problem statement, title, and research questions are in alignment (all referring to the same idea).
Chapter 1 tends to average in the 15-25 page range. If you get beyond 25 pages, you are usually including material that is better presented elsewhere in the dissertation.
Chapter 2 should thoroughly explore the existing research on your topic. However, it shouldn’t go on and on.
- If you are looking to beef up Chapter 2, it is always helpful to add research that supports the methodology that you are planning to use.
- If the chapter is too long, try to reduce the references you cite to those that are the most relevant and recent.
Make sure that you tell the reader what you did and how you did it. What type of analysis did you use and why? How many respondents were involved and how did you find them? The idea is to make sure that readers understand what you did and could replicate it if they want to.
As this is a plan for your research, it seems to naturally fall in the 15 to 20 page range.
The results of your study are presented here. Include all material that will help the reader understand what you found. There is a tendency to inundate the reader with tables, charts, and graphs. If they don’t directly relate to what you found or are redundant they can be included in an appendix. You don’t want to lose your reader in an avalanche of tables and numbers.
In most dissertations, it is Chapter 5 where you get to explain what the results of your research mean and the implications. This is the only chapter where you have some freedom to really express your opinions. Go ahead and do so.
I am always surprised when someone has spent 15 months of their life working on a research topic and they submit a Chapter 5 that is 8 pages long. Spread your wings and really explore what your results mean.

How Long is a Dissertation? Summary
The is no doubt about it, a dissertation is a long document. It is, however, not written in one sitting. You work on it for many months, crafting paragraphs and coming to conclusions. Many people find that because the document can be written in pieces that when it’s all put together, it is longer than expected. Keep writing and adding your thoughts and you will make it.
Many students find it helps to have a supportive guide who’s both been through the dissertation writing process before and is experienced in helping students. If that would be useful to you, feel free to reach out to me about my dissertation coaching or dissertation editing services.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
What makes a good research question.
Creating a good research question is vital to successfully completing your dissertation. Here are some tips that will help you formulate a good research question. What Makes a Good Research Question? These are the three Read more…

Dissertation Structure
When it comes to writing a dissertation, one of the most fraught questions asked by graduate students is about dissertation structure. A dissertation is the lengthiest writing project that many graduate students ever undertake, and Read more…

Choosing a Dissertation Chair
Choosing your dissertation chair is one of the most important decisions that you’ll make in graduate school. Your dissertation chair will in many ways shape your experience as you undergo the most rigorous intellectual challenge Read more…
Make This Your Last Round of Dissertation Revision.
Learn How to Get Your Dissertation Accepted .
Discover the 5-Step Process in this Free Webinar .
Almost there!
Please verify your email address by clicking the link in the email message we just sent to your address.
If you don't see the message within the next five minutes, be sure to check your spam folder :).
Hack Your Dissertation
5-Day Mini Course: How to Finish Faster With Less Stress
Interested in more helpful tips about improving your dissertation experience? Join our 5-day mini course by email!
- Skip to main content
- Skip to main navigation
- Skip to search
- Skip to talk navigation
Advertisement
For free parenting resources please check out the Early Years Alliance's Family Corner .
Just got my dissertation grade back and I am gutted :-(
Icanonlytry · 28/01/2012 15:56

Can you investigate it and dispute it? If it is so out of character, it is worth looking into.

There should be separate reports from each of your markers and then an agreed feedback sheet to you. I would ask to see them (they cannot be witheld if you ask) as it might throw up discrepancies, or suggest, as Linerunner says that one of them hasnt read it properly. Normally UG dissertations are not marked externally as a matter of course but you can ask for it to go to a third internal marker as far as I know - most departments would do this. However, it would be better for you if you can put forward some reasons why you believe it deserved more than a 2:2 rather than just complaining. TBH if I marked a dissertation at 56% it would be quite poor and I would need to provide significant reasons why it was marked so low. I know its hard doing this with an infant - I've been there and you have my sympathies - but after three years you cant throw it away. Ask for an extension and then as Linerunner says, ask on here - its surprising how varied the knowledge is!

I am a lecturer (not in your field) and I agree with Mytholmroyd, it sounds like there is a big mismatch between the comments and the grade. In my field, a 56 for a dissertation would have comments that were more along the lines of 'your literature review demonstrated some familiarity with the field but the range of sources cited was too narrow and lacked engagement with theoretical perspectives' etc. I would get hold of a copy of the assessment criteria, map the comments against them, and query this. IME most students get their best mark for their dissertation, and it is very unusual for the mark to fall this far below their average. If it's not that an error has been made in marking it, then you might well have grounds for complaint about the adequacy of your supervision.
when I was choosing my title my supervisor said that certain types of dissertations cannot be marked high because the marking criteria was biased to other types so you could do a flawless lit based dissertation but never get a first in it because the criteria is aimed more at lab/field/survey based ones does that ring any bells?
I imagine that leadership doesn't need to be you leading but also being led, if that helps? The reflective account do you have notes of things you've done? As its reflective it can be based in the past and ML would be an understandable reason for it to be a fairly long time ago.

There are quite a few books on reflective writing, if that helps.
I have just received my UG dissertation result and I am devastated. The feedback has not been issued yet but I got 58% and this is 20% lower than my marks for the rest of the year. In the days leading upto the deadline I had a massive dispute with the old programme leader regarding the supervision and I feel really sabotaged... Surely I can't have got 20% less in this assignment than every other assignment this year! I was predicted a first class degree and now it's down the drain.....
To comment on this thread you need to create a Mumsnet account.
- pop Culture
- Facebook Navigation Icon
- Twitter Navigation Icon
- WhatsApp icon
- Instagram Navigation Icon
- Youtube Navigation Icon
- Snapchat Navigation Icon
- TikTok Navigation Icon
- pigeons & planes
- newsletters
- Youtube logo nav bar 0 youtube
- Twitch logo twitch
- Netflix logo netflix
- Hulu logo hulu
- Roku logo roku
- Crackle Logo Crackle
- RedBox Logo RedBox
- Tubi logo tubi
- Facebook logo facebook
- Twitter Navigation Icon x
- Instagram Navigation Icon instagram
- Snapchat Navigation Icon snapchat
- TikTok Navigation Icon tiktok
- WhatsApp icon whatsapp
- Flipboard logo nav bar 1 flipboard
- RSS feed icon rss feed
Complex Sites
- complexland
Work with us
Complex global.
- united states
- united kingdom
- netherlands
- philippines
- complex chinese
terms of use
privacy policy
cookie settings
california privacy
public notice
accessibility statement
COMPLEX participates in various affiliate marketing programs, which means COMPLEX gets paid commissions on purchases made through our links to retailer sites. Our editorial content is not influenced by any commissions we receive.
© Complex Media, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Complex.com is a part of
'The Matrix 5' in Development With Lana Wachowski Executive Producing, New Writer-Director Stepping In
The fifth installment will follow 2021's 'The Matrix Resurrections' and mark the first time that neither Lana nor Lilly Wachowski will direct.

A fifth installment in the Matrix film franchise is in the works.
According to Variety , Drew Goddard will write and direct the tentatively-titled The Matrix 5 , with Lana Wachowski serving as an executive producer. It will be the first time a new Matrix movie is not directed by Lana and/or Lilly Wachowski.
The Wachowskis directed the original trilogy which released from 1999 to 2003. Lana co-wrote, directed, and produced 2021’s The Matrix Resurrections .
Jesse Ehrman, Warner Bros. Motion Pictures president of production, said in a statement that Goddard approached the studio with an idea that will expand upon the Matrix world while also honoring what the Wachowskis started.
Goddard’s previous screenwriting credits include The Martian , Cloverfield, and World War Z . He also wrote and directed the 2018 thriller Bad Times at El Royale and 2012's The Cabin in the Woods.
"It is not hyperbole to say The Matrix films changed both cinema and my life," Goddard said. "Lana and Lilly's exquisite artistry inspires me on a daily basis, and I am beyond grateful for the chance to tell stories in their world."
It is too early to confirm if Keanu Reeves , Carrie-Anne Moss, Laurence Fishburne , or Jada Pinkett-Smith will reprise their roles. The Matrix Resurrections welcomed Yahya Abdul-Mateen II, Jessica Henwick, Jonathan Groff, Neil Patrick Harris, and Priyanka Chopra Jonas, among other notable actors.
View this photo on Instagram
SHARE THIS STORY
Sign up for the
Complex Newsletter
Your leading source for what’s now and what’s next in Music, Style, Sports, and Pop Culture.
By entering your email and clicking Sign Up, you’re agreeing to let us send you customized marketing messages about us and our advertising partners. You are also agreeing to our
Latest in Pop Culture

| BY JOSE MARTINEZ

| BY MARK ELIBERT
Drake Bell Says He Was ‘Incredibly Irresponsible’ When Recalling Past With Underaged Girl

| BY JAELANI TURNER-WILLIAMS
‘SNL’ Cast Members Laugh Off Notion Show Doesn’t Hire Attractive Women

| BY AMBER MCKYNZIE
From McDonald’s To Kentucky Police Chief: The Unlikely Career Path Of Lawrence W

Raven-Symoné Reflects on 2014 'I'm Not an African-American' Comment: 'There's a Difference Between Being Black and African'

| BY BRAD CALLAS
Steve-O Declined Bill Maher Interview When Host Refused Not to Smoke Weed Despite 'Jackass' Alum's Sobriety

Nick Cannon and Abby De La Rosa's 2-Year-Old Son Zillion Diagnosed With Autism: 'Our Beautiful Boy Experiences Life in 4D'

| BY TARA MAHADEVAN
Taylor Swift Joins Jay-Z, Rihanna, More on Celeb Billionaires List, First Artist to Get There Solely From Music and Concerts

Zooey Deschanel Rejects Notion She's a 'Nepo Baby' Despite Having Oscar-Nominated Father

Lewis Hamilton Was Almost in ‘Top Gun: Maverick,’ Says It ‘Broke My Heart’ to Turn Down Tom Cruise
A 32-year market vet warns the S&P 500 is set to fall 50%-70% in the years ahead with valuations at historic highs — and says that an imminently weakening labor market will be the catalyst for the crash
- Jon Wolfenbarger warns against long-term investment in the stock market due to high valuations.
- Wolfenbarger believes a weakening labor market and impending recession could trigger a sell-off.
- While some indicators suggest an economic slowdown, consensus views remain optimistic.
There has seldom been a worse time to invest money in the stock market for the long term, according to Jon Wolfenbarger .
That's because valuations are historically elevated today, and over the period of around a decade, they carry significant weight in determining return outcomes. According to Bank of America, valuation levels explain 80% of the market's return over a 10-year period.
There are many ways to measure valuation levels in the overall market. Wolfenbarger, the founder of investing newsletter BullAndBearProfits.com and a former investment banker at JPMorgan and Merrill Lynch, cites John Hussman's ratio of the market cap of all non-financial stocks to the gross value added of those stocks. Hussman says it's the most accurate indicator of future market returns that he's found.
Right now, the metric shows -5% returns annually over the next 12 years. In the chart below, the valuation measure is shown in blue and is inverted, and actual subsequent S&P 500 returns are shown in red.
Other valuation measures are also hovering at historically high levels. The so-called Warren Buffett indicator of total market cap-to-GDP well exceeds dot-com bubble levels and is reapproaching its 2022 highs. And, the Shiller cyclically-adjusted price-to-earnings ratio is above 1929 levels and trails levels only seen in 1999 and 2021.
Based on historical long-term returns when valuations are this high, Wolfenbarger said that the S&P 500 is likely to suffer a long and drawn-out sell-off. By the bottom of the market cycle, the index will have likely fallen 50%-70%, he said.
While it sounds like a doomsday call, it's important to remember that these kinds of scenarios have in fact played out in recent decades. Stocks took two years to bottom when they crashed almost 50% after the dot-com bubble. They took a year-and-a-half from peak-to-trough in the Great Financial Crisis. And nine years following the dot-com bubble peak in 2000, the S&P 500 was still down about 50%.
Why will stocks crash?
Valuations by themselves aren't typically a good enough catalyst for a stock-market sell-off. Another look at the Bank of America chart above shows they matter very little in the short term.
A sufficient catalyst, Woflenbarger said, is weakening in the labor market and a subsequent recession, which he believes is about to unfold.
Wolfenbarger shared with Business Insider multiple indicators he's watching that show the unemployment rate could rise in the months ahead.
Related stories
The first is the National Federation of Independent Business' hiring plans index. Its three-month moving average has surged, indicating the unemployment rate could soon follow.
Second, The Conference Board's Employment Trends Index (in blue) has declined in recent years. Historically, this has meant trouble for total non-farm employment in the US, which has not yet unfolded.
Third, the number of US states with a rising unemployment rate is spiking, meaning that the overall unemployment rate should see further upside.
And fourth, about five quarters after the US Treasury yield curve inverts (using the 10-year and 2-year durations), unemployment has historically started to tick up. April will mark the start of the sixth quarter since the yield curve officially inverted, which according to the indicator's founder, Cam Harvey, is when the curve stays inverted for a duration of three months.
The US unemployment rate is already on a slight uptrend, having climbed from 3.4% in April 2023 to 3.9% as of February. According to the Sahm Rule, named after former Fed economist Claudia Sahm, once the three-month moving average of the unemployment rate moves up by 0.5% from its low over the previous 12 months, the US economy is in a recession in real time. The indicator has a perfect track record of identifying downturns. Today, it sits at 0.27.
Wolfenbarger's views in context
Wolfenbarger's stock market call is on the more extreme end of Wall Street outlooks. Fellow market bears Jeremy Grantham, John Hussman, and David Rosenberg have all stuck to their significant downside expectations. But most top strategists at major banks see limited downside from here, if any at all. Many, including Goldman Sachs' David Kostin and Bank of America's Savita Subramanian, have had to revise upward their 2024 targets already this year.
Wolfenbarger's recession call is also out of consensus these days, with many bearish forecasters abandoning their downbeat outlooks. But many see slower growth and a softening labor market going forward, even if that doesn't mean an outright recession.
This week, Pantheon Macroeconomics Founder and Chief Economist Ian Shepherdson laid out several reasons he sees unemployment ticking up in the coming months.
For example, layoffs are rising, which is usually followed by rising unemployment claims.
"For the first time in this cycle, an array of indicators point tentatively to a meaningful slowdown in economic growth, driven by the consumer, and a clear weakening in the labor market, as soon as the second quarter," Shepherdson said in a client note.
For now, however, bad data simply hasn't shown up yet, and bulls have ridden the wave to all-time highs — a trend that could very well continue. Only time will tell how Wolfenbarger's forecasts hold up in the near- and long-terms.
Watch: How bitcoin halving affects crypto prices
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A first class dissertation should demonstrate professional standards of research design and management, and give confidence that the student could undertake professional work in a similar ... This mark is usually reserved for cases where there is no serious attempt to complete the dissertation (as defined in College Regulations). It may also be ...
A mark greater than or equal to 70.00% in the Dissertation. Qualifies for Merit: A Final Weighted Mark greater than or equal to 59.50% and A mark greater than or equal to 60% in the Dissertation. or A Final Weighted Mark greater than or equal to 58.50% and Module marks of at least 60.00% in at least 50% of the taught credits and
Typically dissertations are blind double marked. So that each marker judges the work independently and only then discusses with a colleague, the definitive mark to be awarded. At this point there ...
Most dissertations are 100 to 300 pages in length. All dissertations should be divided into appropriate sections, and long dissertations may need chapters, main divisions, and subdivisions. Page and Text Requirements Page Size. 8½ x 11 inches, unless a musical score is included; Margins. At least 1 inch for all margins; Spacing. Body of text ...
satisfactory understanding of issues and debates. reasonable, although flawed, ability to select and interpret appropriate material/authority. some flaws or gaps in the construction of an argument. a written style not entirely appropriate for study at the level of work. poor or unclear expression.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
A mark between 40 and 49 provides students with an opportunity to make amendments which would allow a pass mark to be reached. Please note that this is the only opportunity that students have to make changes to their dissertation that may result in a different mark being awarded. If successful this mark will be capped at 50.
Normally awarded under the following conditions: (a) average mark on taught modules in the range 40% - 49%, (b) marks of 50% or more in at least 60 CATS of level 7 taught modules, (c) a mark of at least 40% in the dissertation or postgraduate diploma project (see below). Candidates for the MSc degree who have submitted an MSc dissertation but ...
A dissertation will usually be worth around 60 credits or higher. A masters dissertation is a lengthy written study or piece of coursework on a topic chosen by a student. While creating a dissertation, all students will be guided by faculty supervisors or professors and will require an extensive amount of time for research and writing.
Dissertation - Marking Criteria. The text below is an extract from the MSc handbook for students. Each dissertation is independently marked by two examiners; one of these is normally the supervisor. An external examiner moderates the assessment. The examiners may conduct an oral examination if they wish to check the depth of the student's ...
Master the structure of a dissertation and pave your way to academic success. Our guide will help you craft a well-organized research masterpiece for your scholarly journey. ... a chance to leave your mark on the academic world. What might surprise you, however, is that the average dissertation contains roughly 80,000 to 100,000 words ...
Revised on 5 May 2022. A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree. The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the ...
My dissertation mark was 74, which I believe is a bit above average. The top mark in my year was around 90, which is very impressive. My overall grade was 78 and a bit, which got me a distinction. In Oxford (at least for the Maths, CS, Physics and similar subjects), the professors aim to make the exams hard enough so that the average mark is ...
under the supervision of a member of the teaching staff. Dissertation reports were double marked by the student's supervisor and a second member of staff (and later moderated by an external examiner) using a fixed spot-marking scheme. 1. on a 0-100% scale. A mark of 70% or above (74, 80, 85, 90, 95 or 100) is a first (A); a mark between
A dissertation is typically structured by major chapters and other minor elements. Specifics will be detailed in your module handbook. Weight - A dissertation will have more module credits and therefore, will account for a larger percentage of your mark. You should be able to find specific details about this in your module handbook.
Where a student achieves a dissertation mark of between 65 and 70 and over 70 for all other modules, then the Board of Examiners has discretion to award a Master's with Distinction. ... Where a module contains such an assessment the module mark will not be calculated on a weighted average basis.
You might want to check the relevant academic office regulations, because in most universities it's 58% with a preponderance of marks in the 2:1 category. In other works, 58-60%, but with the majority of your weighted average at 60% or over (which your 2:2 dissertation mark may make less likely). I usually suggest to students in this position ...
Some sections are fillers - necessary, but expected for a standard mark - whilst others give you the chance to show why your dissertation is significant, worthy of a higher mark. In Route #1: Replication-based dissertations , where these different sections are will depend on (a) the route you adopted (i.e., Route A: Duplication , Route B ...
Shorter Dissertations. Some fields or programs may have shorter dissertation requirements, particularly in disciplines where the research tends to be more focused or where a shorter document suffices to convey the research findings. In such cases, dissertations might range from 50 to 100 pages or even shorter. Average-Length Dissertations
The truth is, there is no one answer to how long a dissertation is. I can't say 146 pages is what's needed, as you may write to page 146 and stop without fully exploring your topic. 90 pages could adequately address your research question, or you could write 200 pages and still not fully answer what you set out to.
It will vary but 65 is or will be among the most common grades. Sometimes dissertation averages can be a little higher then typical averages but 65 is probably within a standard deviation of the average. See more. Yeah I guess that's probably right as a lot of people I know received between 62 and 68. 3 years ago.
I'm interested in what the average dissertation grade is. It would also be interesting to know if your dissertation grade was lower, higher, or more-or-less the same as your other marks. ... My tutor refuses to mark my dissertation; Show 10 more. Latest. Sheffield Uni 2024 prospective students; 2024 MRes Developmental Neuroscience and ...
Icanonlytry, When I marked dissertations I was required to give extensive feedback in writing and to explain the mark in some detail, including 'where you could have gained extra marks'. This was written in a constructive way. I was also aware that the marks and comments would be reviewed by the university's external examiner, and/or could be 2nd marked or appealed, so couldn't just be the ...
| by mark elibert Nick Cannon and Abby De La Rosa's 2-Year-Old Son Zillion Diagnosed With Autism: 'Our Beautiful Boy Experiences Life in 4D' The 'Midnights' singer's total net worth is $1.1 billion.
The average money market account earns 0.67% Annual Percentage Yield (APY), according to the FDIC . The actual interest rate on a money market account may depend on the account balance and bank ...
The fifth installment will follow 2021's 'The Matrix Resurrections' and mark the first time that neither Lana nor Lilly Wachowski will direct. By Jose Martinez. Apr 04, 2024 COMMENT. Image via ...
A 32-year market vet warns the S&P 500 is set to fall 50%-70% in the years ahead with valuations at historic highs — and says that an imminently weakening labor market will be the catalyst for ...