- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction

Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core Collection This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: Jan 17, 2024 10:05 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

Breaking ice, and helicopter drops: winning photos of working scientists
Career Feature 23 APR 24

Londoners see what a scientist looks like up close in 50 photographs
Career News 18 APR 24
Deadly diseases and inflatable suits: how I found my niche in virology research
Spotlight 17 APR 24

Researchers want a ‘nutrition label’ for academic-paper facts
Nature Index 17 APR 24

How young people benefit from Swiss apprenticeships

How we landed job interviews for professorships straight out of our PhD programmes
Career Column 08 APR 24

Structure peer review to make it more robust
World View 16 APR 24
Postdoctoral Fellow
The Dubal Laboratory of Neuroscience and Aging at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) seeks postdoctoral fellows to investigate the ...
San Francisco, California
University of California, San Francsico
Postdoctoral Associate
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Postdoctoral Research Fellow
Description Applications are invited for a postdoctoral fellow position at the Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute, Sinai Health, to participate...
Toronto (City), Ontario (CA)
Sinai Health
Postdoctoral Research Associate - Surgery
Memphis, Tennessee
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (St. Jude)
Open Rank Faculty Position in Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics
The Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Genetics (www.virginia.edu/bmg) and the University of Virginia Cancer Center
Charlottesville, Virginia
Biochemistry & Molecular Genetics
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1

Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, what is academic writing: tips for students, why traditional editorial process needs an upgrade, paperpal’s new ai research finder empowers authors to..., what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., ai + human expertise – a paradigm shift..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content.
How to Do a Systematic Review: A Best Practice Guide for Conducting and Reporting Narrative Reviews, Meta-Analyses, and Meta-Syntheses
Affiliations.
- 1 Behavioural Science Centre, Stirling Management School, University of Stirling, Stirling FK9 4LA, United Kingdom; email: [email protected].
- 2 Department of Psychological and Behavioural Science, London School of Economics and Political Science, London WC2A 2AE, United Kingdom.
- 3 Department of Statistics, Northwestern University, Evanston, Illinois 60208, USA; email: [email protected].
- PMID: 30089228
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-psych-010418-102803
Systematic reviews are characterized by a methodical and replicable methodology and presentation. They involve a comprehensive search to locate all relevant published and unpublished work on a subject; a systematic integration of search results; and a critique of the extent, nature, and quality of evidence in relation to a particular research question. The best reviews synthesize studies to draw broad theoretical conclusions about what a literature means, linking theory to evidence and evidence to theory. This guide describes how to plan, conduct, organize, and present a systematic review of quantitative (meta-analysis) or qualitative (narrative review, meta-synthesis) information. We outline core standards and principles and describe commonly encountered problems. Although this guide targets psychological scientists, its high level of abstraction makes it potentially relevant to any subject area or discipline. We argue that systematic reviews are a key methodology for clarifying whether and how research findings replicate and for explaining possible inconsistencies, and we call for researchers to conduct systematic reviews to help elucidate whether there is a replication crisis.
Keywords: evidence; guide; meta-analysis; meta-synthesis; narrative; systematic review; theory.
- Guidelines as Topic
- Meta-Analysis as Topic*
- Publication Bias
- Review Literature as Topic
- Systematic Reviews as Topic*
- Policy & Compliance
- Peer Review Policies and Practices
Revisions to the NIH Fellowship Application and Review Process
NIH is revising the application and review criteria for fellowship applications, beginning with those submitted January 25, 2025 and beyond. This page describes the goals of the change, implications for those writing and reviewing fellowship applications, and provides links to training and other resources.
Fellowship applications submitted on or after January 25, 2025 will follow a revised application and review criteria. The goal of the changes is to improve the chances that the most promising fellowship candidates will be consistently identified by scientific review panels. The changes will:
- Better focus reviewer attention on three key assessments: the fellowship candidate’s preparedness and potential, research training plan, and commitment to the candidate
- Ensure a broad range of candidates and research training contexts can be recognized as meritorious by clarifying and simplifying the language in the application and review criteria
- Reduce bias in review by emphasizing the commitment to the candidate without undue consideration of sponsor and institutional reputation
Background
This page is designed to help you learn more about the peer review process and why we’re revising the application and review process for NIH fellowship applications submitted for due dates on or after January 25, 2025.
Changes to Fellowship Applications
Learn more about the changes being made to fellowship application forms and instructions for due dates on or after January 25, 2025.
Changes to the Fellowship Review Criteria
Learn more about the changes being made to the fellowship review criteria for applications submitted for due dates on or after January 25, 2025.
Candidate Guidance
This page provides guidance for candidates applying to fellowships for due dates on or after January 25, 2025
Reviewer Guidance (Coming in 2025)
Reviewers will be provided training and guidance materials in Spring 2025 in time for the first review meetings held in the summer of 2025 using the revised review criteria.
FAQs
Find answers to your questions about the revisions to fellowship application and review criteria.
Training and Resources
Training and resources, including presentations, webinars, and other resources to help you understand the revised fellowship application and peer review process are found on this site.
Notices, Statements, and Reports
This page provides links to Notices, blog posts, press releases, and other background reports on the revised fellowship application and review criteria.
This page last updated on: April 18, 2024
- Bookmark & Share
- E-mail Updates
- Help Downloading Files
- Privacy Notice
- Accessibility
- National Institutes of Health (NIH), 9000 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, Maryland 20892
- NIH... Turning Discovery Into Health
In the brain, bursts of beta rhythms implement cognitive control
Bursts of brain rhythms with "beta" frequencies control where and when neurons in the cortex process sensory information and plan responses. Studying these bursts would improve understanding of cognition and clinical disorders, researchers argue in a new review.
The brain processes information on many scales. Individual cells electrochemically transmit signals in circuits but at the large scale required to produce cognition, millions of cells act in concert, driven by rhythmic signals at varying frequencies. Studying one frequency range in particular, beta rhythms between about 14-30 Hz, holds the key to understanding how the brain controls cognitive processes -- or loses control in some disorders -- a team of neuroscientists argues in a new review article.
Drawing on experimental data, mathematical modeling and theory, the scientists make the case that bursts of beta rhythms control cognition in the brain by regulating where and when higher gamma frequency waves can coordinate neurons to incorporate new information from the senses or formulate plans of action. Beta bursts, they argue, quickly establish flexible but controlled patterns of neural activity for implementing intentional thought.
"Cognition depends on organizing goal-directed thought, so if you want to understand cognition, you have to understand that organization," said co-author Earl K. Miller, Picower Professor in The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory and the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences at MIT. "Beta is the range of frequencies that can control neurons at the right spatial scale to produce organized thought."
Miller and colleagues Mikael Lundqvist, Jonatan Nordmark and Johan Liljefors at the Karolinska Institutet and Pawel Herman at the KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Sweden, write that studying bursts of beta rhythms to understand how they emerge and what they represent would not only help explain cognition, but also aid in diagnosing and treating cognitive disorders.
"Given the relevance of beta oscillations in cognition, we foresee a major change in the practice for biomarker identification, especially given the prominence of beta bursting in inhibitory control processes … and their importance in ADHD, schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease," they write in the journal Trends in Cognitive Sciences .
Experimental studies covering several species including humans, a variety of brain regions, and numerous cognitive tasks have revealed key characteristics of beta waves in the cortex, the authors write: Beta rhythms occur in quick but powerful bursts; they inhibit the power of higher frequency gamma rhythms; and though they originate in deeper brain regions, they travel within specific locations of cortex. Considering these properties together, the authors write that they are all consistent with precise and flexible regulation, in space and time, of the gamma rhythm activity that experiments show carry signals of sensory information and motor plans.
"Beta bursts thus offer new opportunities for studying how sensory inputs are selectively processed, reshaped by inhibitory cognitive operations and ultimately result in motor actions," the authors write.
For one example, Miller and colleagues have shown in animals that in the prefrontal cortex in working memory tasks, beta bursts direct when gamma activity can store new sensory information, read out the information when it needs to be used, and then discard it when it's no longer relevant. For another example, other researchers have shown that beta rises when human volunteers are asked to suppress a previously learned association between word pairs, or to forget a cue because it will no longer be used in a task.
In a paper last year, Lundqvist, Herman, Miller and others cited several lines of experimental evidence to hypothesize that beta bursts implement cognitive control spatially in the brain, essentially constraining patches of the cortex to represent the general rules of a task even as individual neurons within those patches represent the specific contents of information. For example, if the working memory task is to remember a pad lock combination, beta rhythms will implement patches of cortex for the general steps "turn left," "turn right," "turn left again," allowing gamma to enable neurons within each patch to store and later recall the specific numbers of the combination. The two-fold value of such an organizing principle, they noted, is that the brain can rapidly apply task rules to many neurons at a time and do so without having to re-establish the overall structure of the task if the individual numbers change (i.e. you set a new combination).
Another important phenomenon of beta bursts, the authors write, is that they propagate across long distances in the brain, spanning multiple regions. Studying the direction of their spatial travels, as well as their timing, could shed further light on how cognitive control is implemented.
New ideas beget new questions
Beta rhythm bursts can differ not only in their frequency, but also their duration, amplitude, origin and other characteristics. This variety speaks to their versatility, the authors write, but also obliges neuroscientists to study and understand these many different forms of the phenomenon and what they represent to harness more information from these neural signals.
"It quickly becomes very complicated, but I think the most important aspect of beta bursts is the very simple and basic premise that they shed light on the transient nature of oscillations and neural processes associated with cognition," Lundqvist said."This changes our models of cognition and will impact everything we do. For a long time we implicitly or explicitly assumed oscillations are ongoing which has colored experiments and analyses. Now we see a first wave of studies based on this new thinking, with new hypothesis and ways to analyze data, and it should only pick up in years to come."
The authors acknowledge another major issue that must be resolved by further research -- How do beta bursts emerge in the first place to perform their apparent role in cognitive control?
"It is unknown how beta bursts arise as a mediator of an executive command that cascades to other regions of the brain," the authors write.
The authors don't claim to have all the answers. Instead, they write, because beta rhythms appear to have an integral role in controlling cognition, the as yet unanswered questions are worth asking.
"We propose that beta bursts provide both experimental and computational studies with a window through which to explore the real-time organization and execution of cognitive functions," they conclude. "To fully leverage this potential there is a need to address the outstanding questions with new experimental paradigms, analytical methods and modeling approaches."
- Nervous System
- Multiple Sclerosis Research
- Psychology Research
- Neuroscience
- Intelligence
- Brain-Computer Interfaces
- Social cognition
- Sensory system
- Sensory neuron
- Psychopathology
- Neurobiology
Story Source:
Materials provided by Picower Institute at MIT . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Mikael Lundqvist, Earl K. Miller, Jonatan Nordmark, Johan Liljefors, Pawel Herman. Beta: bursts of cognition . Trends in Cognitive Sciences , 2024; DOI: 10.1016/j.tics.2024.03.010
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Fossil Frogs Share Their Skincare Secrets
- Fussy Eater? Most Parents Play Short Order Cook
- Precise Time Measurement: Superradiant Atoms
- Artificial Cells That Act Like Living Cells
- Affordable and Targeted Anticancer Agent
- This Alloy Is Kinky
- Giant Galactic Explosion: Galaxy Pollution
- Flare Erupting Around a Black Hole
- Two Species Interbreeding Created New Butterfly
- Warming Antarctic Deep-Sea and Sea Level Rise
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research: More People Use Mental Health Benefits When They Hear That Colleagues Use Them Too
- Laura M. Giurge,
- Lauren C. Howe,
- Zsofia Belovai,
- Guusje Lindemann,
- Sharon O’Connor

A study of 2,400 Novartis employees around the world found that simply hearing about others’ struggles can normalize accessing support at work.
Novartis has trained more than 1,000 employees as Mental Health First Aiders to offer peer-to-peer support for their colleagues. While employees were eager for the training, uptake of the program remains low. To understand why, a team of researchers conducted a randomized controlled trial with 2,400 Novartis employees who worked in the UK, Ireland, India, and Malaysia. Employees were shown one of six framings that were designed to overcome two key barriers: privacy concerns and usage concerns. They found that employees who read a story about their colleague using the service were more likely to sign up to learn more about the program, and that emphasizing the anonymity of the program did not seem to have an impact. Their findings suggest that one way to encourage employees to make use of existing mental health resources is by creating a supportive culture that embraces sharing about mental health challenges at work.
“I almost scheduled an appointment about a dozen times. But no, in the end I never went. I just wasn’t sure if my problems were big enough to warrant help and I didn’t want to take up someone else’s time unnecessarily.”
- Laura M. Giurge is an assistant professor at the London School of Economics, and a faculty affiliate at London Business School. Her research focuses on time and boundaries in organizations, workplace well-being, and the future of work. She is also passionate about translating research to the broader public through interactive and creative keynote talks, workshops, and coaching. Follow her on LinkedIn here .
- Lauren C. Howe is an assistant professor in management at the University of Zurich. As head of research at the Center for Leadership in the Future of Work , she focuses on how human aspects, such as mindsets, socioemotional skills, and leadership, play a role in the changing world of work.
- Zsofia Belovai is a behavioral science lead for the organizational performance research practice at MoreThanNow, focusing on exploring how employee welfare can drive KPIs.
- Guusje Lindemann is a senior behavioral scientist at MoreThanNow, in the social impact and organizational performance practices, working on making the workplace better for all.
- Sharon O’Connor is the global employee wellbeing lead at Novartis. She is a founding member of the Wellbeing Executives Council of The Conference Board, and a guest lecturer on the Workplace Wellness postgraduate certificate at Trinity College Dublin.
Partner Center
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Reumatologia
- v.59(1); 2021

Peer review guidance: a primer for researchers
Olena zimba.
1 Department of Internal Medicine No. 2, Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical University, Lviv, Ukraine
Armen Yuri Gasparyan
2 Departments of Rheumatology and Research and Development, Dudley Group NHS Foundation Trust (Teaching Trust of the University of Birmingham, UK), Russells Hall Hospital, Dudley, West Midlands, UK
The peer review process is essential for quality checks and validation of journal submissions. Although it has some limitations, including manipulations and biased and unfair evaluations, there is no other alternative to the system. Several peer review models are now practised, with public review being the most appropriate in view of the open science movement. Constructive reviewer comments are increasingly recognised as scholarly contributions which should meet certain ethics and reporting standards. The Publons platform, which is now part of the Web of Science Group (Clarivate Analytics), credits validated reviewer accomplishments and serves as an instrument for selecting and promoting the best reviewers. All authors with relevant profiles may act as reviewers. Adherence to research reporting standards and access to bibliographic databases are recommended to help reviewers draft evidence-based and detailed comments.
Introduction
The peer review process is essential for evaluating the quality of scholarly works, suggesting corrections, and learning from other authors’ mistakes. The principles of peer review are largely based on professionalism, eloquence, and collegiate attitude. As such, reviewing journal submissions is a privilege and responsibility for ‘elite’ research fellows who contribute to their professional societies and add value by voluntarily sharing their knowledge and experience.
Since the launch of the first academic periodicals back in 1665, the peer review has been mandatory for validating scientific facts, selecting influential works, and minimizing chances of publishing erroneous research reports [ 1 ]. Over the past centuries, peer review models have evolved from single-handed editorial evaluations to collegial discussions, with numerous strengths and inevitable limitations of each practised model [ 2 , 3 ]. With multiplication of periodicals and editorial management platforms, the reviewer pool has expanded and internationalized. Various sets of rules have been proposed to select skilled reviewers and employ globally acceptable tools and language styles [ 4 , 5 ].
In the era of digitization, the ethical dimension of the peer review has emerged, necessitating involvement of peers with full understanding of research and publication ethics to exclude unethical articles from the pool of evidence-based research and reviews [ 6 ]. In the time of the COVID-19 pandemic, some, if not most, journals face the unavailability of skilled reviewers, resulting in an unprecedented increase of articles without a history of peer review or those with surprisingly short evaluation timelines [ 7 ].
Editorial recommendations and the best reviewers
Guidance on peer review and selection of reviewers is currently available in the recommendations of global editorial associations which can be consulted by journal editors for updating their ethics statements and by research managers for crediting the evaluators. The International Committee on Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) qualifies peer review as a continuation of the scientific process that should involve experts who are able to timely respond to reviewer invitations, submitting unbiased and constructive comments, and keeping confidentiality [ 8 ].
The reviewer roles and responsibilities are listed in the updated recommendations of the Council of Science Editors (CSE) [ 9 ] where ethical conduct is viewed as a premise of the quality evaluations. The Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) further emphasizes editorial strategies that ensure transparent and unbiased reviewer evaluations by trained professionals [ 10 ]. Finally, the World Association of Medical Editors (WAME) prioritizes selecting the best reviewers with validated profiles to avoid substandard or fraudulent reviewer comments [ 11 ]. Accordingly, the Sarajevo Declaration on Integrity and Visibility of Scholarly Publications encourages reviewers to register with the Open Researcher and Contributor ID (ORCID) platform to validate and publicize their scholarly activities [ 12 ].
Although the best reviewer criteria are not listed in the editorial recommendations, it is apparent that the manuscript evaluators should be active researchers with extensive experience in the subject matter and an impressive list of relevant and recent publications [ 13 ]. All authors embarking on an academic career and publishing articles with active contact details can be involved in the evaluation of others’ scholarly works [ 14 ]. Ideally, the reviewers should be peers of the manuscript authors with equal scholarly ranks and credentials.
However, journal editors may employ schemes that engage junior research fellows as co-reviewers along with their mentors and senior fellows [ 15 ]. Such a scheme is successfully practised within the framework of the Emerging EULAR (European League Against Rheumatism) Network (EMEUNET) where seasoned authors (mentors) train ongoing researchers (mentees) how to evaluate submissions to the top rheumatology journals and select the best evaluators for regular contributors to these journals [ 16 ].
The awareness of the EQUATOR Network reporting standards may help the reviewers to evaluate methodology and suggest related revisions. Statistical skills help the reviewers to detect basic mistakes and suggest additional analyses. For example, scanning data presentation and revealing mistakes in the presentation of means and standard deviations often prompt re-analyses of distributions and replacement of parametric tests with non-parametric ones [ 17 , 18 ].
Constructive reviewer comments
The main goal of the peer review is to support authors in their attempt to publish ethically sound and professionally validated works that may attract readers’ attention and positively influence healthcare research and practice. As such, an optimal reviewer comment has to comprehensively examine all parts of the research and review work ( Table I ). The best reviewers are viewed as contributors who guide authors on how to correct mistakes, discuss study limitations, and highlight its strengths [ 19 ].
Structure of a reviewer comment to be forwarded to authors
Some of the currently practised review models are well positioned to help authors reveal and correct their mistakes at pre- or post-publication stages ( Table II ). The global move toward open science is particularly instrumental for increasing the quality and transparency of reviewer contributions.
Advantages and disadvantages of common manuscript evaluation models
Since there are no universally acceptable criteria for selecting reviewers and structuring their comments, instructions of all peer-reviewed journal should specify priorities, models, and expected review outcomes [ 20 ]. Monitoring and reporting average peer review timelines is also required to encourage timely evaluations and avoid delays. Depending on journal policies and article types, the first round of peer review may last from a few days to a few weeks. The fast-track review (up to 3 days) is practised by some top journals which process clinical trial reports and other priority items.
In exceptional cases, reviewer contributions may result in substantive changes, appreciated by authors in the official acknowledgments. In most cases, however, reviewers should avoid engaging in the authors’ research and writing. They should refrain from instructing the authors on additional tests and data collection as these may delay publication of original submissions with conclusive results.
Established publishers often employ advanced editorial management systems that support reviewers by providing instantaneous access to the review instructions, online structured forms, and some bibliographic databases. Such support enables drafting of evidence-based comments that examine the novelty, ethical soundness, and implications of the reviewed manuscripts [ 21 ].
Encouraging reviewers to submit their recommendations on manuscript acceptance/rejection and related editorial tasks is now a common practice. Skilled reviewers may prompt the editors to reject or transfer manuscripts which fall outside the journal scope, perform additional ethics checks, and minimize chances of publishing erroneous and unethical articles. They may also raise concerns over the editorial strategies in their comments to the editors.
Since reviewer and editor roles are distinct, reviewer recommendations are aimed at helping editors, but not at replacing their decision-making functions. The final decisions rest with handling editors. Handling editors weigh not only reviewer comments, but also priorities related to article types and geographic origins, space limitations in certain periods, and envisaged influence in terms of social media attention and citations. This is why rejections of even flawless manuscripts are likely at early rounds of internal and external evaluations across most peer-reviewed journals.
Reviewers are often requested to comment on language correctness and overall readability of the evaluated manuscripts. Given the wide availability of in-house and external editing services, reviewer comments on language mistakes and typos are categorized as minor. At the same time, non-Anglophone experts’ poor language skills often exclude them from contributing to the peer review in most influential journals [ 22 ]. Comments should be properly edited to convey messages in positive or neutral tones, express ideas of varying degrees of certainty, and present logical order of words, sentences, and paragraphs [ 23 , 24 ]. Consulting linguists on communication culture, passing advanced language courses, and honing commenting skills may increase the overall quality and appeal of the reviewer accomplishments [ 5 , 25 ].
Peer reviewer credits
Various crediting mechanisms have been proposed to motivate reviewers and maintain the integrity of science communication [ 26 ]. Annual reviewer acknowledgments are widely practised for naming manuscript evaluators and appreciating their scholarly contributions. Given the need to weigh reviewer contributions, some journal editors distinguish ‘elite’ reviewers with numerous evaluations and award those with timely and outstanding accomplishments [ 27 ]. Such targeted recognition ensures ethical soundness of the peer review and facilitates promotion of the best candidates for grant funding and academic job appointments [ 28 ].
Also, large publishers and learned societies issue certificates of excellence in reviewing which may include Continuing Professional Development (CPD) points [ 29 ]. Finally, an entirely new crediting mechanism is proposed to award bonus points to active reviewers who may collect, transfer, and use these points to discount gold open-access charges within the publisher consortia [ 30 ].
With the launch of Publons ( http://publons.com/ ) and its integration with Web of Science Group (Clarivate Analytics), reviewer recognition has become a matter of scientific prestige. Reviewers can now freely open their Publons accounts and record their contributions to online journals with Digital Object Identifiers (DOI). Journal editors, in turn, may generate official reviewer acknowledgments and encourage reviewers to forward them to Publons for building up individual reviewer and journal profiles. All published articles maintain e-links to their review records and post-publication promotion on social media, allowing the reviewers to continuously track expert evaluations and comments. A paid-up partnership is also available to journals and publishers for automatically transferring peer-review records to Publons upon mutually acceptable arrangements.
Listing reviewer accomplishments on an individual Publons profile showcases scholarly contributions of the account holder. The reviewer accomplishments placed next to the account holders’ own articles and editorial accomplishments point to the diversity of scholarly contributions. Researchers may establish links between their Publons and ORCID accounts to further benefit from complementary services of both platforms. Publons Academy ( https://publons.com/community/academy/ ) additionally offers an online training course to novice researchers who may improve their reviewing skills under the guidance of experienced mentors and journal editors. Finally, journal editors may conduct searches through the Publons platform to select the best reviewers across academic disciplines.
Peer review ethics
Prior to accepting reviewer invitations, scholars need to weigh a number of factors which may compromise their evaluations. First of all, they are required to accept the reviewer invitations if they are capable of timely submitting their comments. Peer review timelines depend on article type and vary widely across journals. The rules of transparent publishing necessitate recording manuscript submission and acceptance dates in article footnotes to inform readers of the evaluation speed and to help investigators in the event of multiple unethical submissions. Timely reviewer accomplishments often enable fast publication of valuable works with positive implications for healthcare. Unjustifiably long peer review, on the contrary, delays dissemination of influential reports and results in ethical misconduct, such as plagiarism of a manuscript under evaluation [ 31 ].
In the times of proliferation of open-access journals relying on article processing charges, unjustifiably short review may point to the absence of quality evaluation and apparently ‘predatory’ publishing practice [ 32 , 33 ]. Authors when choosing their target journals should take into account the peer review strategy and associated timelines to avoid substandard periodicals.
Reviewer primary interests (unbiased evaluation of manuscripts) may come into conflict with secondary interests (promotion of their own scholarly works), necessitating disclosures by filling in related parts in the online reviewer window or uploading the ICMJE conflict of interest forms. Biomedical reviewers, who are directly or indirectly supported by the pharmaceutical industry, may encounter conflicts while evaluating drug research. Such instances require explicit disclosures of conflicts and/or rejections of reviewer invitations.
Journal editors are obliged to employ mechanisms for disclosing reviewer financial and non-financial conflicts of interest to avoid processing of biased comments [ 34 ]. They should also cautiously process negative comments that oppose dissenting, but still valid, scientific ideas [ 35 ]. Reviewer conflicts that stem from academic activities in a competitive environment may introduce biases, resulting in unfair rejections of manuscripts with opposing concepts, results, and interpretations. The same academic conflicts may lead to coercive reviewer self-citations, forcing authors to incorporate suggested reviewer references or face negative feedback and an unjustified rejection [ 36 ]. Notably, several publisher investigations have demonstrated a global scale of such misconduct, involving some highly cited researchers and top scientific journals [ 37 ].
Fake peer review, an extreme example of conflict of interest, is another form of misconduct that has surfaced in the time of mass proliferation of gold open-access journals and publication of articles without quality checks [ 38 ]. Fake reviews are generated by manipulating authors and commercial editing agencies with full access to their own manuscripts and peer review evaluations in the journal editorial management systems. The sole aim of these reviews is to break the manuscript evaluation process and to pave the way for publication of pseudoscientific articles. Authors of these articles are often supported by funds intended for the growth of science in non-Anglophone countries [ 39 ]. Iranian and Chinese authors are often caught submitting fake reviews, resulting in mass retractions by large publishers [ 38 ]. Several suggestions have been made to overcome this issue, with assigning independent reviewers and requesting their ORCID IDs viewed as the most practical options [ 40 ].
Conclusions
The peer review process is regulated by publishers and editors, enforcing updated global editorial recommendations. Selecting the best reviewers and providing authors with constructive comments may improve the quality of published articles. Reviewers are selected in view of their professional backgrounds and skills in research reporting, statistics, ethics, and language. Quality reviewer comments attract superior submissions and add to the journal’s scientific prestige [ 41 ].
In the era of digitization and open science, various online tools and platforms are available to upgrade the peer review and credit experts for their scholarly contributions. With its links to the ORCID platform and social media channels, Publons now offers the optimal model for crediting and keeping track of the best and most active reviewers. Publons Academy additionally offers online training for novice researchers who may benefit from the experience of their mentoring editors. Overall, reviewer training in how to evaluate journal submissions and avoid related misconduct is an important process, which some indexed journals are experimenting with [ 42 ].
The timelines and rigour of the peer review may change during the current pandemic. However, journal editors should mobilize their resources to avoid publication of unchecked and misleading reports. Additional efforts are required to monitor published contents and encourage readers to post their comments on publishers’ online platforms (blogs) and other social media channels [ 43 , 44 ].
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
The Federal Register
The daily journal of the united states government, request access.
Due to aggressive automated scraping of FederalRegister.gov and eCFR.gov, programmatic access to these sites is limited to access to our extensive developer APIs.
If you are human user receiving this message, we can add your IP address to a set of IPs that can access FederalRegister.gov & eCFR.gov; complete the CAPTCHA (bot test) below and click "Request Access". This process will be necessary for each IP address you wish to access the site from, requests are valid for approximately one quarter (three months) after which the process may need to be repeated.
An official website of the United States government.
If you want to request a wider IP range, first request access for your current IP, and then use the "Site Feedback" button found in the lower left-hand side to make the request.
Hyper kids? Research shows sugar isn’t the culprit
Parents long have blamed their children’s “bouncing off the wall” behavior on eating too much sugar, but experts say there’s no truth to it. “It’s a myth that sugar causes hyperactivity,” says Mark Wolraich, professor emeritus in developmental and behavioral pediatrics at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center. Yet, he acknowledges, “it’s still a strong belief. … Sometimes it’s very hard to change embedded impressions of what affects behavior.”
Wolraich conducted studies in the 1990s that disproved the notion that sugar causes attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children. These included a double-blind randomized controlled trial that found that neither sugar nor the artificial sweetener aspartame affected behavior or cognitive function among children whose parents perceived them as high energy “sugar sensitive,” compared with those with “normal” behavior, even when sugar intake exceeded typical dietary levels.
“It was pretty definitive,” Wolraich says.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention also states that sugar doesn’t make kids hyper, saying “research doesn’t support the popularly held views that ADHD is caused by eating too much sugar, watching too much television, parenting, or social and environmental factors such as poverty or family chaos.”
Parents probably continue to make this association because children tend to become overly excited during specific events – birthday parties, for example – when the menu contains high-sugar items, such as ice cream, birthday cake and goody bags.
Also, “kids tend to get a lot of sugar around the holidays, when there are other things that rev them up,” Wolraich says. “So it looks like they are getting overactive when they are eating a lot of sugary foods.”
How did this belief start?
Some experts trace its origins to 1973, when allergist Benjamin Feingold linked children’s hyperactivity to ingesting artificial food colors; additives; preservatives; and salicylates, substances found in plants and foods and also used in many medicines, such as aspirin. He also wrote a popular book on the topic.
Although sugar was not among the dietary culprits Feingold criticized, many parents mistakenly made the connection, since high amounts of sugar go hand in hand with foods containing dyes and other additives.
In recent years, studies have connected several artificial dyes, including red dye No. 3, to hyperactivity and other behavioral problems in children. A 2021 report by the California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment concluded that some children who consume food dyes exhibit these health effects, although sensitivity to them varies among children.
What else you should know
Even though sugar is absolved in this one case, it doesn’t mean kids can eat it with abandon, experts warn.
“Sugar is not vindicated from other adverse health effects,” says Donald Hensrud, associate professor of nutrition and preventive medicine at the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine. “It provides extra calories and increases weight, contributing to obesity and possibly later heart disease. It can cause cavities. It has no nutrients and displaces other foods that do.”
So, what’s the bottom-line message to parents? “I don’t promote giving children a lot of sugar,” Wolraich says. “Sugar can be a negative factor in a balanced diet because its taste is so attractive. But sugar does not have a high nutritive value. So eating a lot of sugary foods that are low in other important dietary nutrients is not a good idea – but not because of hyperactivity.”
Robotic heart surgery gives Donny Jones a rapid recovery, more energy
Donny Jones was born with a heart that was a little bit different.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Changing Partisan Coalitions in a Politically Divided Nation
1. the partisanship and ideology of american voters, table of contents.
- What this report tells us – and what it doesn’t
- Partisans and partisan leaners in the U.S. electorate
- Party identification and ideology
- Education and partisanship
- Education, race and partisanship
- Partisanship by race and gender
- Partisanship across educational and gender groups by race and ethnicity
- Gender and partisanship
- Parents are more Republican than voters without children
- Partisanship among men and women within age groups
- Race, age and partisanship
- The partisanship of generational cohorts
- Religion, race and ethnicity, and partisanship
- Party identification among atheists, agnostics and ‘nothing in particular’
- Partisanship and religious service attendance
- Partisanship by income groups
- The relationship between income and partisanship differs by education
- Union members remain more Democratic than Republican
- Homeowners are more Republican than renters
- Partisanship of military veterans
- Demographic differences in partisanship by community type
- Race and ethnicity
- Age and the U.S. electorate
- Education by race and ethnicity
- Religious affiliation
- Ideological composition of voters
- Acknowledgments
- Overview of survey methodologies
- The 2023 American Trends Panel profile survey methodology
- Measuring party identification across survey modes
- Adjusting telephone survey trends
- Appendix B: Religious category definitions
- Appendix C: Age cohort definitions
The partisan identification of registered voters is now evenly split between the two major parties: 49% of registered voters are Democrats or lean to the Democratic Party, and a nearly identical share – 48% – are Republicans or lean to the Republican Party.
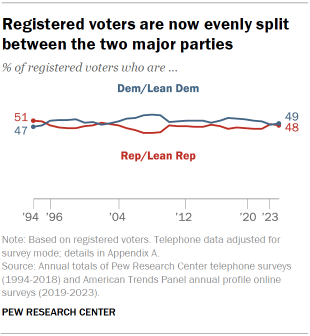
The partisan balance has tightened in recent years following a clear edge in Democratic Party affiliation during the last administration.
- Four years ago, in the run-up to the 2020 election, Democrats had a 5 percentage point advantage over the GOP (51% vs. 46%).
The share of voters who are in the Democratic coalition reached 55% in 2008. For much of the last three decades of Pew Research Center surveys, the partisan composition of registered voters has been more closely divided.
About two-thirds of registered voters identify as a partisan, and they are roughly evenly split between those who say they are Republicans (32% of voters) and those who say they are Democrats (33%). Roughly a third instead say they are independents or something else (35%), with most of these voters leaning toward one of the parties. Partisan leaners often share the same political views and behaviors as those who directly identify with the party they favor.
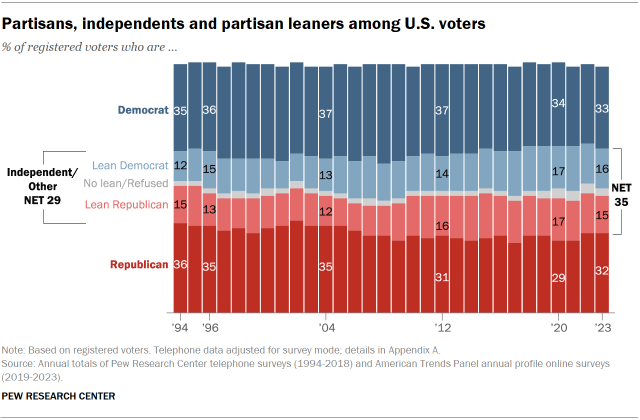
The share of voters who identify as independent or something else is somewhat higher than in the late 1990s and early 2000s. As a result, there are more “leaners” today than in the past. Currently, 15% of voters lean toward the Republican Party and 16% lean toward the Democratic Party. By comparison, in 1994, 27% of voters leaned toward either the GOP (15%) or the Democratic Party (12%).
While the electorate overall is nearly equally divided between those who align with the Republican and Democratic parties, a greater share of registered voters say they are both ideologically conservative and associate with the Republican Party (33%) than say they are liberal and align with the Democratic Party (23%).
A quarter of voters associate with the Democratic Party and describe their views as either conservative or moderate, and 14% identify as moderates or liberals and are Republicans or Republican leaners.
The partisan and ideological composition of voters is relatively unchanged over the last five years.
(As a result of significant mode differences in measures of ideology between telephone and online surveys, there is not directly comparable data on ideology prior to 2019.)
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Education & Politics
- Election 2024
- Gender & Politics
- Political Parties
- Race, Ethnicity & Politics
- Religion & Politics
- Rural, Urban and Suburban Communities
- Voter Demographics
What’s It Like To Be a Teacher in America Today?
Republican gains in 2022 midterms driven mostly by turnout advantage, more americans disapprove than approve of colleges considering race, ethnicity in admissions decisions, partisan divides over k-12 education in 8 charts, school district mission statements highlight a partisan divide over diversity, equity and inclusion in k-12 education, most popular, report materials.
- Party Identification Detailed Tables, 1994-2023
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
More From Forbes
Ntt research brings innovation to networking and security.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
NTT Research CEO Kazu Gomi speaks at NTT Upgrade 2024.
Nippon Telegraph and Telephone is a company not widely known in the United States, but I believe that will change soon. Based in Japan, NTT employs more than 300,000 people globally, including 2,000 in its research arm in Silicon Valley. That subsidiary, NTT Research, is leaning into a budget of $3 billion annually to conduct scientific investigations related to optical networking, cybersecurity, AI, sustainability, logistics and manufacturing, healthcare and more.
I recently spent time with executives at NTT Research’s Upgrade event in San Francisco, and I came away with a better understanding of the potential impacts of the company’s efforts as they relate to networking and security. I will dive deeper into each of these areas to highlight what I find most noteworthy.
All-Photonics Network
NTT Research’s All-Photonics Network investigation represents a strategic research focus area for the company. It is decidedly a different approach to optical networking, given that it integrates optics-based technology into every network element, including terminals. Typically, silicon photonics research is directed exclusively at the interconnect level within the transport networks that serve as the backbone for connectivity services. By contrast, NTT’s vision is to bring optical efficiency to the entire network infrastructure layer.
Creating an APN is a big effort that will require a significantly rearchitected approach to how networks are constructed, but the benefits could be tremendous. First, latency could theoretically be eliminated through a vertical integration of optical technology. That would support a host of use cases for the application of real-time analytics and automation. Second, the power efficiency that could be realized is a potential game changer. Optical components are highly efficient, generate less heat than alternatives and are less prone to failure as a result. This will be even more important in years to come because the applications for next-generation AI functionality, including generative AI, are power-hungry, and NTT’s vision for an APN could address concerns related to energy consumption. This is a significant point to highlight, given that nearly every enterprise today is focused on promoting sustainable operations and carbon footprint offset initiatives.
NTT’s Innovative Optical and Wireless Network APN investigation is roughly halfway towards its goal of commercialization by 2030. From my perspective, if it comes even close to its goals of a 100x improvement in energy efficiency and transmission capacity, it could revolutionize networking.
Huawei s Pura 70 Ultra Beats iPhone With Pioneering New Feature
Sh gun episode 10 review a powerful finale but not what i was expecting, the trump media stock price djt is about to adjust down by 22 7, a different approach to security.
NTT Research is also focused on efforts to reimagine security and data protection. The company uses its Security, Privacy and Integrity Protection Platform to capture its investigations and then productize the results. SPIP aims to incorporate advanced privacy technologies with the goal of simplifying data protection. From my perspective, NTT’s timing is spot-on, given the widespread concerns related to protecting the underlying data used to train large language models that power generative AI applications.
SPIP supports two important elements—attribute-based encryption and multi-party computation. ABE facilitates the ability to segregate data so that users can access only what is needed. NTT Research has made numerous contributions to the ABE standard, including publishing software libraries to allow developers to create commercially available solutions.
Meanwhile, MPC is not a new cryptography concept; its foundation can be traced back to the 1970s. It is designed to allow joint functional computation while maintaining the privacy of inputs through encryption. This is an important consideration, given the challenge of data leakage that results from encryption and decryption schemes. NTT calls its secure computational system San-Shi, and it consists of multiple servers and a client that registers data through a secret sharing process. That might sound ambiguous on the surface, but in dividing the data among multiple servers, no single server can obtain a complete view of the information. The other benefit to NTT’s approach is that there is apparently no tax to performance, as is often associated with encryption; the company says its research indicates that San-Shi’s efficiency is equal to the efficiency of non-encrypted data processing.
Wrapping Up
As I spend more time with NTT, I continue to be impressed by the company’s capabilities and research efforts. The need for more robust forms of networking and security will continue as next-generation applications place pressure on the limits of existing technology infrastructure. NTT’s APN represents the company’s “moonshot,” with SPIP having more immediate impacts today. However, the technology industry needs audacious goals, because these are what often lead to innovation breakthroughs. NTT may be one of the best kept secrets outside of Japan today, but given the company’s deep investments in groundbreaking research, that will likely change soon.
Moor Insights & Strategy provides or has provided paid services to technology companies, like all tech industry research and analyst firms. These services include research, analysis, advising, consulting, benchmarking, acquisition matchmaking and video and speaking sponsorships. Moor Insights & Strategy does not have paid business relationships with any company mentioned in this article.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Review of the Theoretical Literature" (Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.) Example literature review #2: "Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines" (Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and ...
A systematic review can be explained as a research method and process for identifying and critically appraising relevant research, as well as for collecting and analyzing data from said research (Liberati et al., 2009). The aim of a systematic review is to identify all empirical evidence that fits the pre-specified inclusion criteria to answer ...
Review of Research in Education (RRE), published annually, provides a forum for analytic research reviews on selected education topics of significance to the field.Each volume addresses a topic of broad relevance to education and learning, and publishes articles that critically examine diverse literatures and bodies of knowledge across relevant disciplines and fields.
The Review of Educational Research (RER) publishes critical, integrative reviews of research literature bearing on education, including conceptualizations, interpretations, and syntheses of literature and scholarly work in a field broadly relevant to education and educational research. View full journal description
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified.
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the ...
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
Literature search. Fink has defined research literature review as a "systematic, explicit and reproducible method for identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing the existing body of completed and recorded work produced by researchers, scholars and practitioners."[]Review of research literature can be summarized into a seven step process: (i) Selecting research questions/purpose of the ...
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
the knowledge gaps and research needs brought to light by a critical review of the relevant literature and then ensuring that their research design, methods, results, and conclusions follow logically from these objectives (Maier, 2013). There exist a number of papers devoted to instruction on how to write a good review paper. Among the most
The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say "literature review" or refer to "the literature," we are talking about the research (scholarship) in a given field. You will often see the terms "the research," "the ...
Review of Research in Education (RRE) is a periodical volume that provides an overview and analysis of selected areas of relevant research through critical and synthesizing essays. The editor of RRE, in close consultation with its editorial board, plays a critical role in reviewing and defining the current state of knowledge in the field.Each volume is designed around a particular subject.
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
Background. A systematic review, as its name suggests, is a systematic way of collecting, evaluating, integrating, and presenting findings from several studies on a specific question or topic.[] A systematic review is a research that, by identifying and combining evidence, is tailored to and answers the research question, based on an assessment of all relevant studies.[2,3] To identify assess ...
Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies ("sleeping beauties" )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
Literature review is an essential feature of academic research. Fundamentally, knowledge advancement must be built on prior existing work. To push the knowledge frontier, we must know where the frontier is. By reviewing relevant literature, we understand the breadth and depth of the existing body of work and identify gaps to explore.
Systematic reviews are characterized by a methodical and replicable methodology and presentation. They involve a comprehensive search to locate all relevant published and unpublished work on a subject; a systematic integration of search results; and a critique of the extent, nature, and quality of evidence in relation to a particular research question.
The Review of Policy Research (RPR) invites original articles that apply and/or develop theoretical approaches to public policy.This includes established as well as emerging perspectives that originate from diverse political and national contexts and/or are located at the intersection of similar disciplines such as political science, public administration, political psychology, and political ...
Fellowship applications submitted on or after January 25, 2025 will follow a revised application and review criteria. The goal of the changes is to improve the chances that the most promising fellowship candidates will be consistently identified by scientific review panels. The changes will: Better focus reviewer attention on three key ...
Apr. 25, 2023 — New research shows that rhythmic brain activity is key to temporarily maintaining important information in memory. Researchers found brain rhythms -- or patterns of neuronal ...
Yaroslav Danylchenko/Stocksy. Summary. Novartis has trained more than 1,000 employees as Mental Health First Aiders to offer peer-to-peer support for their colleagues. While employees were eager ...
The principles of peer review are largely based on professionalism, eloquence, and collegiate attitude. As such, reviewing journal submissions is a privilege and responsibility for 'elite' research fellows who contribute to their professional societies and add value by voluntarily sharing their knowledge and experience.
These opportunities will also be announced in the Federal Register . As part of this review of the ozone NAAQS, EPA intends to sponsor a four-day workshop from May 13 through May 16, 2024, to provide the opportunity for internal and external experts to highlight significant new and emerging research on ozone and related photochemical oxidants.
Research shows sugar isn't the culprit. By Marlene Cimons Special to The Washington Post. Parents long have blamed their children's "bouncing off the wall" behavior on eating too much ...
The partisanship and ideology of American voters. 2. Partisanship by race, ethnicity and education. 3. Partisanship by gender, sexual orientation, marital and parental status. 4. Age, generational cohorts and party identification. 5. Party identification among religious groups and religiously unaffiliated voters.
The Review of Religious Research (RRR) journal aims to publish manuscripts meeting these six scope criteria: (1) reports empirical research; (2) attends to religiosity and spirituality topics; (3) identifies religious groups and their adherents; … | View full journal description. This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics ...
Based in Japan, NTT employs more than 300,000 people globally, including 2,000 in its research arm in Silicon Valley. That subsidiary, NTT Research, is leaning into a budget of $3 billion annually ...