Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

How I harnessed media engagement to supercharge my research career
Career Column 09 APR 24

How we landed job interviews for professorships straight out of our PhD programmes
Career Column 08 APR 24

Three ways ChatGPT helps me in my academic writing

How two PhD students overcame the odds to snag tenure-track jobs
Adopt universal standards for study adaptation to boost health, education and social-science research
Correspondence 02 APR 24

Is ChatGPT corrupting peer review? Telltale words hint at AI use
News 10 APR 24

Rwanda 30 years on: understanding the horror of genocide
Editorial 09 APR 24
Junior Group Leader Position at IMBA - Institute of Molecular Biotechnology
The Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) is one of Europe’s leading institutes for basic research in the life sciences. IMBA is located on t...
Austria (AT)
IMBA - Institute of Molecular Biotechnology
Open Rank Faculty, Center for Public Health Genomics
Center for Public Health Genomics & UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center seek 2 tenure-track faculty members in Cancer Precision Medicine/Precision Health.
Charlottesville, Virginia
Center for Public Health Genomics at the University of Virginia
Husbandry Technician I
Memphis, Tennessee
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (St. Jude)
Lead Researcher – Department of Bone Marrow Transplantation & Cellular Therapy
Researcher in the center for in vivo imaging and therapy.
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 1:27 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews


Literature Reviews
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain what literature reviews are and offer insights into the form and construction of literature reviews in the humanities, social sciences, and sciences.
Introduction
OK. You’ve got to write a literature review. You dust off a novel and a book of poetry, settle down in your chair, and get ready to issue a “thumbs up” or “thumbs down” as you leaf through the pages. “Literature review” done. Right?
Wrong! The “literature” of a literature review refers to any collection of materials on a topic, not necessarily the great literary texts of the world. “Literature” could be anything from a set of government pamphlets on British colonial methods in Africa to scholarly articles on the treatment of a torn ACL. And a review does not necessarily mean that your reader wants you to give your personal opinion on whether or not you liked these sources.
What is a literature review, then?
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period.
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. And depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant.
But how is a literature review different from an academic research paper?
The main focus of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument, and a research paper is likely to contain a literature review as one of its parts. In a research paper, you use the literature as a foundation and as support for a new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
Why do we write literature reviews?
Literature reviews provide you with a handy guide to a particular topic. If you have limited time to conduct research, literature reviews can give you an overview or act as a stepping stone. For professionals, they are useful reports that keep them up to date with what is current in the field. For scholars, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the writer in his or her field. Literature reviews also provide a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. Comprehensive knowledge of the literature of the field is essential to most research papers.
Who writes these things, anyway?
Literature reviews are written occasionally in the humanities, but mostly in the sciences and social sciences; in experiment and lab reports, they constitute a section of the paper. Sometimes a literature review is written as a paper in itself.
Let’s get to it! What should I do before writing the literature review?
If your assignment is not very specific, seek clarification from your instructor:
- Roughly how many sources should you include?
- What types of sources (books, journal articles, websites)?
- Should you summarize, synthesize, or critique your sources by discussing a common theme or issue?
- Should you evaluate your sources?
- Should you provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history?
Find models
Look for other literature reviews in your area of interest or in the discipline and read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or ways to organize your final review. You can simply put the word “review” in your search engine along with your other topic terms to find articles of this type on the Internet or in an electronic database. The bibliography or reference section of sources you’ve already read are also excellent entry points into your own research.
Narrow your topic
There are hundreds or even thousands of articles and books on most areas of study. The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to get a good survey of the material. Your instructor will probably not expect you to read everything that’s out there on the topic, but you’ll make your job easier if you first limit your scope.
Keep in mind that UNC Libraries have research guides and to databases relevant to many fields of study. You can reach out to the subject librarian for a consultation: https://library.unc.edu/support/consultations/ .
And don’t forget to tap into your professor’s (or other professors’) knowledge in the field. Ask your professor questions such as: “If you had to read only one book from the 90’s on topic X, what would it be?” Questions such as this help you to find and determine quickly the most seminal pieces in the field.
Consider whether your sources are current
Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. In the sciences, for instance, treatments for medical problems are constantly changing according to the latest studies. Information even two years old could be obsolete. However, if you are writing a review in the humanities, history, or social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be what is needed, because what is important is how perspectives have changed through the years or within a certain time period. Try sorting through some other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to consider what is currently of interest to scholars in this field and what is not.
Strategies for writing the literature review
Find a focus.
A literature review, like a term paper, is usually organized around ideas, not the sources themselves as an annotated bibliography would be organized. This means that you will not just simply list your sources and go into detail about each one of them, one at a time. No. As you read widely but selectively in your topic area, consider instead what themes or issues connect your sources together. Do they present one or different solutions? Is there an aspect of the field that is missing? How well do they present the material and do they portray it according to an appropriate theory? Do they reveal a trend in the field? A raging debate? Pick one of these themes to focus the organization of your review.
Convey it to your reader
A literature review may not have a traditional thesis statement (one that makes an argument), but you do need to tell readers what to expect. Try writing a simple statement that lets the reader know what is your main organizing principle. Here are a couple of examples:
The current trend in treatment for congestive heart failure combines surgery and medicine. More and more cultural studies scholars are accepting popular media as a subject worthy of academic consideration.
Consider organization
You’ve got a focus, and you’ve stated it clearly and directly. Now what is the most effective way of presenting the information? What are the most important topics, subtopics, etc., that your review needs to include? And in what order should you present them? Develop an organization for your review at both a global and local level:
First, cover the basic categories
Just like most academic papers, literature reviews also must contain at least three basic elements: an introduction or background information section; the body of the review containing the discussion of sources; and, finally, a conclusion and/or recommendations section to end the paper. The following provides a brief description of the content of each:
- Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
- Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
- Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Organizing the body
Once you have the basic categories in place, then you must consider how you will present the sources themselves within the body of your paper. Create an organizational method to focus this section even further.
To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario:
You’ve decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales. This is because you’ve just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale’s portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980’s. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. So you check those out. Then you look up a book written in 1968 with information on how sperm whales have been portrayed in other forms of art, such as in Alaskan poetry, in French painting, or on whale bone, as the whale hunters in the late 19th century used to do. This makes you wonder about American whaling methods during the time portrayed in Moby Dick, so you find some academic articles published in the last five years on how accurately Herman Melville portrayed the whaling scene in his novel.
Now consider some typical ways of organizing the sources into a review:
- Chronological: If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials above according to when they were published. For instance, first you would talk about the British biological studies of the 18th century, then about Moby Dick, published in 1851, then the book on sperm whales in other art (1968), and finally the biology articles (1980s) and the recent articles on American whaling of the 19th century. But there is relatively no continuity among subjects here. And notice that even though the sources on sperm whales in other art and on American whaling are written recently, they are about other subjects/objects that were created much earlier. Thus, the review loses its chronological focus.
- By publication: Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on biological studies of sperm whales if the progression revealed a change in dissection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies.
- By trend: A better way to organize the above sources chronologically is to examine the sources under another trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period. For instance, the review might examine whaling from pre-1600-1699, 1700-1799, and 1800-1899. Under this method, you would combine the recent studies on American whaling in the 19th century with Moby Dick itself in the 1800-1899 category, even though the authors wrote a century apart.
- Thematic: Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, the sperm whale review could focus on the development of the harpoon for whale hunting. While the study focuses on one topic, harpoon technology, it will still be organized chronologically. The only difference here between a “chronological” and a “thematic” approach is what is emphasized the most: the development of the harpoon or the harpoon technology.But more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as “evil” in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
- Methodological: A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the “methods” of the researcher or writer. For the sperm whale project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of whales in American, British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed. Once you’ve decided on the organizational method for the body of the review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out. They should arise out of your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period. A thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue.
Sometimes, though, you might need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. Put in only what is necessary. Here are a few other sections you might want to consider:
- Current Situation: Information necessary to understand the topic or focus of the literature review.
- History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed articles and journals.
Questions for Further Research: What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
Begin composing
Once you’ve settled on a general pattern of organization, you’re ready to write each section. There are a few guidelines you should follow during the writing stage as well. Here is a sample paragraph from a literature review about sexism and language to illuminate the following discussion:
However, other studies have shown that even gender-neutral antecedents are more likely to produce masculine images than feminine ones (Gastil, 1990). Hamilton (1988) asked students to complete sentences that required them to fill in pronouns that agreed with gender-neutral antecedents such as “writer,” “pedestrian,” and “persons.” The students were asked to describe any image they had when writing the sentence. Hamilton found that people imagined 3.3 men to each woman in the masculine “generic” condition and 1.5 men per woman in the unbiased condition. Thus, while ambient sexism accounted for some of the masculine bias, sexist language amplified the effect. (Source: Erika Falk and Jordan Mills, “Why Sexist Language Affects Persuasion: The Role of Homophily, Intended Audience, and Offense,” Women and Language19:2).
Use evidence
In the example above, the writers refer to several other sources when making their point. A literature review in this sense is just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence to show that what you are saying is valid.
Be selective
Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the review’s focus, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological.
Use quotes sparingly
Falk and Mills do not use any direct quotes. That is because the survey nature of the literature review does not allow for in-depth discussion or detailed quotes from the text. Some short quotes here and there are okay, though, if you want to emphasize a point, or if what the author said just cannot be rewritten in your own words. Notice that Falk and Mills do quote certain terms that were coined by the author, not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. But if you find yourself wanting to put in more quotes, check with your instructor.
Summarize and synthesize
Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each paragraph as well as throughout the review. The authors here recapitulate important features of Hamilton’s study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study’s significance and relating it to their own work.
Keep your own voice
While the literature review presents others’ ideas, your voice (the writer’s) should remain front and center. Notice that Falk and Mills weave references to other sources into their own text, but they still maintain their own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with their own ideas and their own words. The sources support what Falk and Mills are saying.
Use caution when paraphrasing
When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author’s information or opinions accurately and in your own words. In the preceding example, Falk and Mills either directly refer in the text to the author of their source, such as Hamilton, or they provide ample notation in the text when the ideas they are mentioning are not their own, for example, Gastil’s. For more information, please see our handout on plagiarism .
Revise, revise, revise
Draft in hand? Now you’re ready to revise. Spending a lot of time revising is a wise idea, because your main objective is to present the material, not the argument. So check over your review again to make sure it follows the assignment and/or your outline. Then, just as you would for most other academic forms of writing, rewrite or rework the language of your review so that you’ve presented your information in the most concise manner possible. Be sure to use terminology familiar to your audience; get rid of unnecessary jargon or slang. Finally, double check that you’ve documented your sources and formatted the review appropriately for your discipline. For tips on the revising and editing process, see our handout on revising drafts .
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Jones, Robert, Patrick Bizzaro, and Cynthia Selfe. 1997. The Harcourt Brace Guide to Writing in the Disciplines . New York: Harcourt Brace.
Lamb, Sandra E. 1998. How to Write It: A Complete Guide to Everything You’ll Ever Write . Berkeley: Ten Speed Press.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
Troyka, Lynn Quittman, and Doug Hesse. 2016. Simon and Schuster Handbook for Writers , 11th ed. London: Pearson.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Want to publish a literature review? Think of it as an empirical paper
What to consider if you want to publish a literature review paper
Tatiana Andreeva - Fri 23 Apr 2021 07:50 (updated Fri 27 Oct 2023 17:26)

[Guest post by CYGNA member Tatiana Andreeva ]
When you’ve been reading a lot on a particular topic – for example, reviewing the literature for your research project or for your PhD – at some point it looks like you have enough material and reflections to publish this piece of work as a separate paper. Recognize this? If you ever tried it, you might know that publishing a literature review paper in an academic journal is a tricky task. The literature review publications come in so many forms, and there is no single cheat-sheet or established format like for empirical papers that you could follow to ensure success in publication.
Through my own journey of trial-and-error on this path, as well as through reviewing for journals and for PhD students in my course, I came up with an idea that will help you to increase the chances of publishing a literature review: think of a literature review as simply another empirical research project. Think of it as an empirical study, in which your data comes not from your usual fieldwork but from the articles that you review.
Many literature reviews can be thought of as a qualitative empirical study, in which the papers included in the review substitute interviews or field observations that you would usually collect and code. Some literature reviews, e.g., meta-analyses, are more like a quantitative empirical paper, in which various numbers you extract from the papers in your dataset substitute your survey data.
Seeing literature review in this way has three important implications for how we think about our literature review, and how we can design it to increase its chances of being interesting to others - that is, of being published.
Start with a relevant research problem and an interesting research question
We learn early in our academic career that any empirical paper should have a clear research problem and a clear research question. We frequently hear from journal editors and reviewers that just having a gap in the literature, or the fact that something has not been researched before, are not good enough to justify doing yet another empirical study. They say: you need to have a problem that your study can address, and you need to have a question that we currently don’t have an answer to. Only then your empirical study can add value to existing research.
When we think of a literature review as of an empirical study, just with the different type of data at hand, we realize that the very same rationale applies. From this perspective the arguments that I often see in literature reviews – that there is no literature review in this particular area or that the existing literature reviews are quite dated – are not sufficient in the journal’s eyes to justify the publication of a literature review on a topic. If you aim to publish your literature review, start by thinking – what is the problem I would like to address? What would be my research question about this problem, that other readers would find interesting?
Design a methodologically-sound data collection and analysis protocol
When we think of any empirical study, we know that if we want to have reliable findings that will be accepted by our peers as trustworthy, we need to follow a transparent and well-thought data collection protocol. We also need to carefully choose and correctly apply relevant data analysis method. This goes without saying, right?
The same applies to the literature review! If we want our readers to trust our conclusions from the literature review, we need to make sure that the data we collect speaks to our research question, is of good quality, representative of the field, etc. The growing attention in business and management field to the systematic approach to literature reviews (Denyer & Tranfield, 2009; Rojon et al., 2021) reflects the rising expectations of the quality of the data used in literature review papers. Indeed, this approach offers exactly that: a clear data collection protocol, transparently communicated, so that someone else could replicate your study. For example, do the very same thing in 10 years and see how thinking on the topic has changed.

In the literature on doing literature reviews you will read that systematic literature review is only one of the types of literature reviews. Yet all recommendations on doing different types of the literature reviews share the idea that the data that you base your conclusions on has to be collected in a rigorous and transparent way (e.g., Callahan, 2014). In this post you can find more references on how to ensure that your literature review “data collection” protocol meets the quality expectations.
So now you have all the papers you have carefully selected, how do you go about analysing them, so that peer academics would recognize your conclusions as reliable and robust? This is the trickiest part, and we have limited methodological advice published on this. In this post I’ve mentioned some papers that discuss specific methods of literature analysis. For example, I found that a sophisticated coding rubric leveraged our literature analysis to a different level (Sergeeva & Andreeva, 2016), but must acknowledge that developing this rubric was one of the most challenging tasks of this review paper. In O’Higgins et al. (forthcoming) we used a combination of qualitative content analysis with Pearson’s chi-squared (χ²) goodness of fit test in order to validate some of our conclusions. The trick is - as with any empirical study - your choice of the analytical method needs to fit with your research question. In sum, the message is: choose your method for analysis of the selected literature carefully, apply it rigorously, and explain it transparently.
Think of the theoretical contribution beyond description of the findings
When we think of our usual empirical work, be it qualitative or quantitative, we are well-aware that just the description of our data wouldn’t do. We know that we need to leverage what our data shows to explain how it informs the broader theory, how it compares to previous studies, what is new that we see from this data?
Again, the same logic applies to the literature reviews. In practice though, we often find it difficult to apply this advice to our literature review papers, because the description of the field in itself seems to be novel, especially if nobody did such a review before. In my experience, this argument does not persuade editors and reviewers of the journals, and often rightfully so.

For example, think of a typical quantitative empirical paper: a descriptive statistics table must be provided, but no one would claim a contribution based on it, right? Cropanzano (2009:1306-1307) offers a good exercise that explains why reviewers often don’t buy the description of the field as a novel contribution. He suggests: imagine somebody who read all the primary articles in your dataset, would they still learn anything from your literature review? And if the answer is “no”, then it’s likely that your review paper doesn’t have yet the level of contribution that is needed to turn it into a publication.
I think this exercise can also help to stimulate your thinking of what a theoretical contribution of your literature review could be. For example, think – what it is that I see in this literature that others are not likely to see? In this blogpost you can find some papers that offer insights on how to leverage your literature review to have a theoretical contribution.
Callahan, J.L. (2014). Writing literature reviews: A reprise and update. Human Resource Development Review , 13(3), 271–275. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534484314536705
Cropanzano, R. (2009). Writing nonempirical articles for Journal of Management: General thoughts and suggestions. Journal of Management , 35(6), 1304–1311. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206309344118
Denyer, D., Tranfield, D. (2009). Producing a systematic review. In Buchanan, D., Bryman, A. (Eds.), The Sage handbook of organizational research methods (pp. 671–689). London, UK: Sage.
O’Higgins, C., Andreeva, T., Aramburu, N. (forthcoming). International management challenges of professional service firms: a synthesis of the literature. Review of International Business and Strategy.
Rojon, C., Okupe, A., McDowall, A. (2021). Utilization and development of systematic reviews in management research: What do we know and where do we go from here? International Journal of Management Reviews, 1– 33. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijmr.12245
Sergeeva, A., Andreeva, T. (2016). Knowledge sharing: bringing the context back in, Journal of Management Inquiry , 25, 240-261. https://doi.org/10.1177/1056492615618271
Related blogposts
- Resources on doing a literature review
- Do you really want to publish your literature review? Advice for PhD students
- How to keep up-to-date with the literature, but avoid information overload?
- Is a literature review publication a low-cost project?
- Using Publish or Perish to do a literature review
- How to conduct a longitudinal literature review?
- New: Publish or Perish now also exports abstracts
Find the resources on my website useful?
I cover all the expenses of operating my website privately. If you enjoyed this post and want to support me in maintaining my website, consider buying a copy of one of my books (see below) or supporting the Publish or Perish software .
A story about perseverance and publication failures
Copyright © 2023 Tatiana Andreeva . All rights reserved. Page last modified on Fri 27 Oct 2023 17:26

Tatiana Andreeva's profile and contact details >>

Literature Review: Examples of Published Literature Reviews
- Sample Searches
- Examples of Published Literature Reviews
- Researching Your Topic
- Subject Searching
- Google Scholar
- Track Your Work
- Citation Managers This link opens in a new window
- Citation Guides This link opens in a new window
- Tips on Writing Your Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Research Help
Ask a Librarian
Chat with a Librarian
Lisle: (630) 829-6057 Mesa: (480) 878-7514 Toll Free: (877) 575-6050 Email: [email protected]
Book a Research Consultation Library Hours

- Example of a Literature Review in History
- Comparing the Annotated Bibliography to the Literature Review
- Literature Review Guidelines Literature Review (Historiographic Essay): Making sense of what has been written on your topic.
To find examples of published literature reviews in your field or niche, try searching ProQuest Dissertations and Theses by keyword, advisor, or subject.
- Dissertations & Theses Theses and dissertations from around the world covering all areas of study.
- << Previous: Sample Searches
- Next: Researching Your Topic >>
- Last Updated: Feb 27, 2023 2:09 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.ben.edu/lit-review
Kindlon Hall 5700 College Rd. Lisle, IL 60532 (630) 829-6050
Gillett Hall 225 E. Main St. Mesa, AZ 85201 (480) 878-7514
How to write a good scientific review article
Affiliation.
- 1 The FEBS Journal Editorial Office, Cambridge, UK.
- PMID: 35792782
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.16565
Literature reviews are valuable resources for the scientific community. With research accelerating at an unprecedented speed in recent years and more and more original papers being published, review articles have become increasingly important as a means to keep up to date with developments in a particular area of research. A good review article provides readers with an in-depth understanding of a field and highlights key gaps and challenges to address with future research. Writing a review article also helps to expand the writer's knowledge of their specialist area and to develop their analytical and communication skills, amongst other benefits. Thus, the importance of building review-writing into a scientific career cannot be overstated. In this instalment of The FEBS Journal's Words of Advice series, I provide detailed guidance on planning and writing an informative and engaging literature review.
© 2022 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Publication types
- Review Literature as Topic*
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., ai + human expertise – a paradigm shift..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai....
Loading metrics
Open Access
Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliations Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France, Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
- Marco Pautasso

Published: July 18, 2013
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
- Reader Comments
Citation: Pautasso M (2013) Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review. PLoS Comput Biol 9(7): e1003149. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
Editor: Philip E. Bourne, University of California San Diego, United States of America
Copyright: © 2013 Marco Pautasso. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Funding: This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
Competing interests: The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149.g001
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
- 1. Rapple C (2011) The role of the critical review article in alleviating information overload. Annual Reviews White Paper. Available: http://www.annualreviews.org/userimages/ContentEditor/1300384004941/Annual_Reviews_WhitePaper_Web_2011.pdf . Accessed May 2013.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- 7. Budgen D, Brereton P (2006) Performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering. Proc 28th Int Conf Software Engineering, ACM New York, NY, USA, pp. 1051–1052. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/1134285.1134500 .
- 16. Eco U (1977) Come si fa una tesi di laurea. Milan: Bompiani.
- 17. Hart C (1998) Doing a literature review: releasing the social science research imagination. London: SAGE.
- 21. Ridley D (2008) The literature review: a step-by-step guide for students. London: SAGE.

CPS Online Library Research Guide (UNH Manchester Library): Create a Literature Review
- Home & Table of Contents
- Different Types of Information
- The Savvy Information Consumer
- Primary & Secondary Sources
- Periodical Literature
- Peer Review
- Research Glossary
- Business Research Databases
- Understanding the Assignment
- Preliminary Considerations
- 7 Steps to Completing a Research Assignment
- Define the Topic
- Find & Evaluate Your Sources
- Research Integrity & Citing Your Sources
- Searching for Information
- Evaluating Information
- How to Read an Academic Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- Evaluating Social Media Sources
- Writing Your Research Paper
- Create a Literature Review
- Summarize an Article
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write a Book Review
- How to Do an Annotated Bibliography
- Finding Professional Organizations
- Find Key Journals in Your Field of Study
- Find Peer-Reviewed Articles
- Write a Research Paper Proposal
- Research a Company This link opens in a new window
- Citing Your Sources
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- NHCUC Libraries
- Other Types of Research
- Academic Libraries in NH
- Government Documents
- Using Google for Academic Research
- Information Literacy
- Developing Effective Library Research Assignments
- Using Permalinks
- Primary Source Websites
What is a literature review?
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period.
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. And depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant.
But how is a literature review different from an academic research paper?
The main focus of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument, and a research paper is likely to contain a literature review as one of its parts. In a research paper, you use the literature as a foundation and as support for a new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
Why do we write literature reviews?
Literature reviews provide you with a handy guide to a particular topic. If you have limited time to conduct research, literature reviews can give you an overview or act as a stepping stone. For professionals, they are useful reports that keep them up to date with what is current in the field. For scholars, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the writer in his or her field. Literature reviews also provide a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. Comprehensive knowledge of the literature of the field is essential to most research papers.

Strategies for writing the literature review
Find a focus.
A literature review, like a term paper, is usually organized around ideas, not the sources themselves as an annotated bibliography would be organized. This means that you will not just simply list your sources and go into detail about each one of them, one at a time. No. As you read widely but selectively in your topic area, consider instead what themes or issues connect your sources together. Do they present one or different solutions? Is there an aspect of the field that is missing? How well do they present the material and do they portray it according to an appropriate theory? Do they reveal a trend in the field? A raging debate? Pick one of these themes to focus the organization of your review.
Convey it to your reader
A literature review may not have a traditional thesis statement (one that makes an argument), but you do need to tell readers what to expect. Try writing a simple statement that lets the reader know what is your main organizing principle. Here are a couple of examples:
The current trend in treatment for congestive heart failure combines surgery and medicine.
More and more cultural studies scholars are accepting popular media as a subject worthy of academic consideration.
Consider organization
You’ve got a focus, and you’ve stated it clearly and directly. Now what is the most effective way of presenting the information? What are the most important topics, subtopics, etc ., that your review needs to include? And in what order should you present them? Develop an organization for your review at both a global and local level:
First, cover the basic categories
Just like most academic papers, literature reviews are likely to contain at least three basic elements: an introduction or background information section; the body of the review containing the discussion of sources; and, finally, a conclusion and/or recommendations section to end the paper. The following provides a brief description of the content of each:
- Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
- Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
- Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Organizing the body
Once you have the basic categories in place, then you must consider how you will present the sources themselves within the body of your paper. Create an organizational method to focus this section even further.
To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario:
You’ve decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales. This is because you’ve just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale’s portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980’s. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. So you check those out. Then you look up a book written in 1968 with information on how sperm whales have been portrayed in other forms of art, such as in Alaskan poetry, in French painting, or on whale bone, as the whale hunters in the late 19th century used to do. This makes you wonder about American whaling methods during the time portrayed in Moby Dick, so you find some academic articles published in the last five years on how accurately Herman Melville portrayed the whaling scene in his novel.
Now consider some typical ways of organizing the sources into a review:
- Chronological: If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials above according to when they were published. For instance, first you would talk about the British biological studies of the 18th century, then about Moby Dick, published in 1851, then the book on sperm whales in other art (1968), and finally the biology articles (1980s) and the recent articles on American whaling of the 19th century. But there is relatively no continuity among subjects here. And notice that even though the sources on sperm whales in other art and on American whaling are written recently, they are about other subjects/objects that were created much earlier. Thus, the review loses its chronological focus.
- By publication: Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on biological studies of sperm whales if the progression revealed a change in dissection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies.
- By trend: A better way to organize the above sources chronologically is to examine the sources under another trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period. For instance, the review might examine whaling from pre-1600-1699, 1700-1799, and 1800-1899. Under this method, you would combine the recent studies on American whaling in the 19th century with Moby Dick itself in the 1800-1899 category, even though the authors wrote a century apart.
- Thematic: Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, the sperm whale review could focus on the development of the harpoon for whale hunting. While the study focuses on one topic, harpoon technology, it will still be organized chronologically. The only difference here between a “chronological” and a “thematic” approach is what is emphasized the most: the development of the harpoon or the harpoon technology.But more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as “evil” in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
- Methodological: A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the “methods” of the researcher or writer. For the sperm whale project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of whales in American, British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed. Once you’ve decided on the organizational method for the body of the review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out. They should arise out of your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period. A thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue.
Sometimes, though, you might need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. Put in only what is necessary. Here are a few other sections you might want to consider:
- Current Situation: Information necessary to understand the topic or focus of the literature review.
- History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed articles and journals.
Questions for Further Research: What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
Attribution
"Create a Literature Review" is derivative of Literature Reviews by The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill licensed Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 License .
- << Previous: Other Types of Research Assignments
- Next: Summarize an Article >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 2:30 PM
- URL: https://libraryguides.unh.edu/CPSonlineLibraryResearch
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 24, Issue 2
- Five tips for developing useful literature summary tables for writing review articles
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0157-5319 Ahtisham Younas 1 , 2 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7839-8130 Parveen Ali 3 , 4
- 1 Memorial University of Newfoundland , St John's , Newfoundland , Canada
- 2 Swat College of Nursing , Pakistan
- 3 School of Nursing and Midwifery , University of Sheffield , Sheffield , South Yorkshire , UK
- 4 Sheffield University Interpersonal Violence Research Group , Sheffield University , Sheffield , UK
- Correspondence to Ahtisham Younas, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St John's, NL A1C 5C4, Canada; ay6133{at}mun.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2021-103417
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research. 1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis in reviews, the use of literature summary tables is of utmost importance. A literature summary table provides a synopsis of an included article. It succinctly presents its purpose, methods, findings and other relevant information pertinent to the review. The aim of developing these literature summary tables is to provide the reader with the information at one glance. Since there are multiple types of reviews (eg, systematic, integrative, scoping, critical and mixed methods) with distinct purposes and techniques, 2 there could be various approaches for developing literature summary tables making it a complex task specialty for the novice researchers or reviewers. Here, we offer five tips for authors of the review articles, relevant to all types of reviews, for creating useful and relevant literature summary tables. We also provide examples from our published reviews to illustrate how useful literature summary tables can be developed and what sort of information should be provided.
Tip 1: provide detailed information about frameworks and methods
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Tabular literature summaries from a scoping review. Source: Rasheed et al . 3
The provision of information about conceptual and theoretical frameworks and methods is useful for several reasons. First, in quantitative (reviews synthesising the results of quantitative studies) and mixed reviews (reviews synthesising the results of both qualitative and quantitative studies to address a mixed review question), it allows the readers to assess the congruence of the core findings and methods with the adapted framework and tested assumptions. In qualitative reviews (reviews synthesising results of qualitative studies), this information is beneficial for readers to recognise the underlying philosophical and paradigmatic stance of the authors of the included articles. For example, imagine the authors of an article, included in a review, used phenomenological inquiry for their research. In that case, the review authors and the readers of the review need to know what kind of (transcendental or hermeneutic) philosophical stance guided the inquiry. Review authors should, therefore, include the philosophical stance in their literature summary for the particular article. Second, information about frameworks and methods enables review authors and readers to judge the quality of the research, which allows for discerning the strengths and limitations of the article. For example, if authors of an included article intended to develop a new scale and test its psychometric properties. To achieve this aim, they used a convenience sample of 150 participants and performed exploratory (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) on the same sample. Such an approach would indicate a flawed methodology because EFA and CFA should not be conducted on the same sample. The review authors must include this information in their summary table. Omitting this information from a summary could lead to the inclusion of a flawed article in the review, thereby jeopardising the review’s rigour.
Tip 2: include strengths and limitations for each article
Critical appraisal of individual articles included in a review is crucial for increasing the rigour of the review. Despite using various templates for critical appraisal, authors often do not provide detailed information about each reviewed article’s strengths and limitations. Merely noting the quality score based on standardised critical appraisal templates is not adequate because the readers should be able to identify the reasons for assigning a weak or moderate rating. Many recent critical appraisal checklists (eg, Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool) discourage review authors from assigning a quality score and recommend noting the main strengths and limitations of included studies. It is also vital that methodological and conceptual limitations and strengths of the articles included in the review are provided because not all review articles include empirical research papers. Rather some review synthesises the theoretical aspects of articles. Providing information about conceptual limitations is also important for readers to judge the quality of foundations of the research. For example, if you included a mixed-methods study in the review, reporting the methodological and conceptual limitations about ‘integration’ is critical for evaluating the study’s strength. Suppose the authors only collected qualitative and quantitative data and did not state the intent and timing of integration. In that case, the strength of the study is weak. Integration only occurred at the levels of data collection. However, integration may not have occurred at the analysis, interpretation and reporting levels.
Tip 3: write conceptual contribution of each reviewed article
While reading and evaluating review papers, we have observed that many review authors only provide core results of the article included in a review and do not explain the conceptual contribution offered by the included article. We refer to conceptual contribution as a description of how the article’s key results contribute towards the development of potential codes, themes or subthemes, or emerging patterns that are reported as the review findings. For example, the authors of a review article noted that one of the research articles included in their review demonstrated the usefulness of case studies and reflective logs as strategies for fostering compassion in nursing students. The conceptual contribution of this research article could be that experiential learning is one way to teach compassion to nursing students, as supported by case studies and reflective logs. This conceptual contribution of the article should be mentioned in the literature summary table. Delineating each reviewed article’s conceptual contribution is particularly beneficial in qualitative reviews, mixed-methods reviews, and critical reviews that often focus on developing models and describing or explaining various phenomena. Figure 2 offers an example of a literature summary table. 4
Tabular literature summaries from a critical review. Source: Younas and Maddigan. 4
Tip 4: compose potential themes from each article during summary writing
While developing literature summary tables, many authors use themes or subthemes reported in the given articles as the key results of their own review. Such an approach prevents the review authors from understanding the article’s conceptual contribution, developing rigorous synthesis and drawing reasonable interpretations of results from an individual article. Ultimately, it affects the generation of novel review findings. For example, one of the articles about women’s healthcare-seeking behaviours in developing countries reported a theme ‘social-cultural determinants of health as precursors of delays’. Instead of using this theme as one of the review findings, the reviewers should read and interpret beyond the given description in an article, compare and contrast themes, findings from one article with findings and themes from another article to find similarities and differences and to understand and explain bigger picture for their readers. Therefore, while developing literature summary tables, think twice before using the predeveloped themes. Including your themes in the summary tables (see figure 1 ) demonstrates to the readers that a robust method of data extraction and synthesis has been followed.
Tip 5: create your personalised template for literature summaries
Often templates are available for data extraction and development of literature summary tables. The available templates may be in the form of a table, chart or a structured framework that extracts some essential information about every article. The commonly used information may include authors, purpose, methods, key results and quality scores. While extracting all relevant information is important, such templates should be tailored to meet the needs of the individuals’ review. For example, for a review about the effectiveness of healthcare interventions, a literature summary table must include information about the intervention, its type, content timing, duration, setting, effectiveness, negative consequences, and receivers and implementers’ experiences of its usage. Similarly, literature summary tables for articles included in a meta-synthesis must include information about the participants’ characteristics, research context and conceptual contribution of each reviewed article so as to help the reader make an informed decision about the usefulness or lack of usefulness of the individual article in the review and the whole review.
In conclusion, narrative or systematic reviews are almost always conducted as a part of any educational project (thesis or dissertation) or academic or clinical research. Literature reviews are the foundation of research on a given topic. Robust and high-quality reviews play an instrumental role in guiding research, practice and policymaking. However, the quality of reviews is also contingent on rigorous data extraction and synthesis, which require developing literature summaries. We have outlined five tips that could enhance the quality of the data extraction and synthesis process by developing useful literature summaries.
- Aromataris E ,
- Rasheed SP ,
Twitter @Ahtisham04, @parveenazamali
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Patient consent for publication Not required.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
- Open access
- Published: 23 August 2022
Prognostic risk factors for moderate-to-severe exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic literature review
- John R. Hurst 1 ,
- MeiLan K. Han 2 ,
- Barinder Singh 3 ,
- Sakshi Sharma 4 ,
- Gagandeep Kaur 3 ,
- Enrico de Nigris 5 ,
- Ulf Holmgren 6 &
- Mohd Kashif Siddiqui 3
Respiratory Research volume 23 , Article number: 213 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
6396 Accesses
20 Citations
42 Altmetric
Metrics details
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. COPD exacerbations are associated with a worsening of lung function, increased disease burden, and mortality, and, therefore, preventing their occurrence is an important goal of COPD management. This review was conducted to identify the evidence base regarding risk factors and predictors of moderate-to-severe exacerbations in patients with COPD.
A literature review was performed in Embase, MEDLINE, MEDLINE In-Process, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL). Searches were conducted from January 2015 to July 2019. Eligible publications were peer-reviewed journal articles, published in English, that reported risk factors or predictors for the occurrence of moderate-to-severe exacerbations in adults age ≥ 40 years with a diagnosis of COPD.
The literature review identified 5112 references, of which 113 publications (reporting results for 76 studies) met the eligibility criteria and were included in the review. Among the 76 studies included, 61 were observational and 15 were randomized controlled clinical trials. Exacerbation history was the strongest predictor of future exacerbations, with 34 studies reporting a significant association between history of exacerbations and risk of future moderate or severe exacerbations. Other significant risk factors identified in multiple studies included disease severity or bronchodilator reversibility (39 studies), comorbidities (34 studies), higher symptom burden (17 studies), and higher blood eosinophil count (16 studies).
Conclusions
This systematic literature review identified several demographic and clinical characteristics that predict the future risk of COPD exacerbations. Prior exacerbation history was confirmed as the most important predictor of future exacerbations. These prognostic factors may help clinicians identify patients at high risk of exacerbations, which are a major driver of the global burden of COPD, including morbidity and mortality.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death worldwide [ 1 ]. Based upon disability-adjusted life-years, COPD ranked sixth out of 369 causes of global disease burden in 2019 [ 2 ]. COPD exacerbations are associated with a worsening of lung function, and increased disease burden and mortality (of those patients hospitalized for the first time with an exacerbation, > 20% die within 1 year of being discharged) [ 3 ]. Furthermore, patients with COPD consider exacerbations or hospitalization due to exacerbations to be the most important disease outcome, having a large impact on their lives [ 4 ]. Therefore, reducing the future risk of COPD exacerbations is a key goal of COPD management [ 5 ].
Being able to predict the level of risk for each patient allows clinicians to adapt treatment and patients to adjust their lifestyle (e.g., through a smoking cessation program) to prevent exacerbations [ 3 ]. As such, identifying high-risk patients using measurable risk factors and predictors that correlate with exacerbations is critical to reduce the burden of disease and prevent a cycle of decline encompassing irreversible lung damage, worsening quality of life (QoL), increasing disease burden, high healthcare costs, and early death.
Prior history of exacerbations is generally thought to be the best predictor of future exacerbations; however, there is a growing body of evidence suggesting other demographic and clinical characteristics, including symptom burden, airflow obstruction, comorbidities, and inflammatory biomarkers, also influence risk [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]. For example, in the prospective ECLIPSE observational study, the likelihood of patients experiencing an exacerbation within 1 year of follow-up increased significantly depending upon several factors, including prior exacerbation history, forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV 1 ), St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) score, gastroesophageal reflux, and white blood cell count [ 9 ].
Many studies have assessed predictors of COPD exacerbations across a variety of countries and patient populations. This systematic literature review (SLR) was conducted to identify and compile the evidence base regarding risk factors and predictors of moderate-to-severe exacerbations in patients with COPD.
- Systematic literature review
A comprehensive search strategy was designed to identify English-language studies published in peer-reviewed journals providing data on risk factors or predictors of moderate or severe exacerbations in adults aged ≥ 40 years with a diagnosis of COPD (sample size ≥ 100). The protocol is summarized in Table 1 and the search strategy is listed in Additional file 1 : Table S1. Key biomedical electronic literature databases were searched from January 2015 until July 2019. Other sources were identified via bibliographic searching of relevant systematic reviews.
Study selection process
Implementation and reporting followed the recommendations and standards of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) statement [ 10 ]. An independent reviewer conducted the first screening based on titles and abstracts, and a second reviewer performed a quality check of the excluded evidence. A single independent reviewer also conducted the second screening based on full-text articles, with a quality check of excluded evidence performed by a second reviewer. Likewise, data tables of the included studies were generated by one reviewer, and another reviewer performed a quality check of extracted data. Where more than one publication was identified describing a single study or trial, data were compiled into a single entry in the data-extraction table to avoid double counting of patients and studies. One publication was designated as the ‘primary publication’ for the purposes of the SLR, based on the following criteria: most recently published evidence and/or the article that presented the majority of data (e.g., journal articles were preferred over conference abstracts; articles that reported results for the full population were preferred over later articles providing results of subpopulations). Other publications reporting results from the same study were designated as ‘linked publications’; any additional data in the linked publications that were not included in the primary publication were captured in the SLR. Conference abstracts were excluded from the SLR unless they were a ‘linked publication.’
Included studies
A total of 5112 references (Fig. 1 ) were identified from the database searches. In total, 76 studies from 113 publications were included in the review. Primary publications and ‘linked publications’ for each study are detailed in Additional file 1 : Table S2, and study characteristics are shown in Additional file 1 : Table S3. The studies included clinical trials, registry studies, cross-sectional studies, cohort studies, database studies, and case–control studies. All 76 included studies were published in peer-reviewed journals. Regarding study design, 61 of the studies were observational (34 retrospective observational studies, 19 prospective observational studies, four cross-sectional studies, two studies with both retrospective and prospective cohort data, one case–control study, and one with cross-sectional and longitudinal data) and 15 were randomized controlled clinical trials.
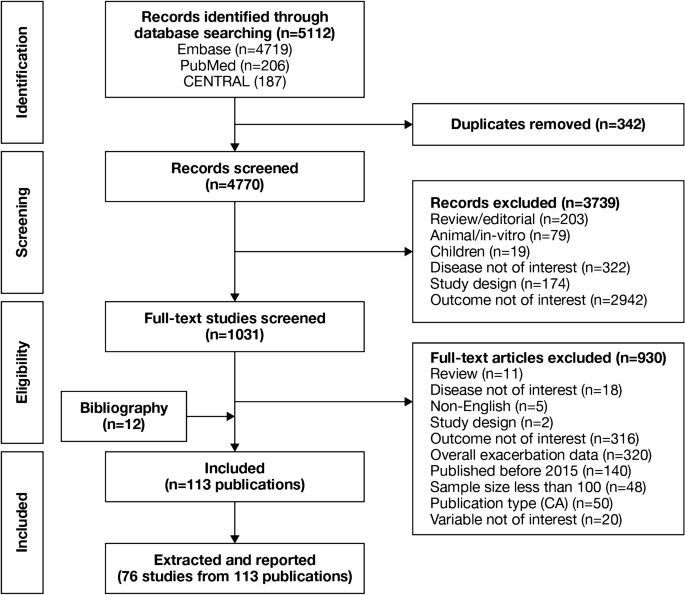
PRISMA flow diagram of studies through the systematic review process. CA conference abstract, CENTRAL Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, PRISMA Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Of the 76 studies, 16 were conducted in North America (13 studies in the USA, two in Canada, and one in Mexico); 26 were conducted in Europe (seven studies in Spain, four in the UK, three in Denmark, two studies each in Bulgaria, the Netherlands, and Switzerland, and one study each in Sweden, Serbia, Portugal, Greece, Germany, and France) and 17 were conducted in Asia (six studies in South Korea, four in China, three in Taiwan, two in Japan, and one study each in Singapore and Israel). One study each was conducted in Turkey and Australia. Fifteen studies were conducted across multiple countries.
The majority of the studies (n = 54) were conducted in a multicenter setting, while 22 studies were conducted in a single-center setting. The sample size among the included studies varied from 118 to 339,389 patients.
Patient characteristics
A total of 75 studies reported patient characteristics (Additional file 1 : Table S4). The mean age was reported in 65 studies and ranged from 58.0 to 75.2 years. The proportion of male patients ranged from 39.7 to 97.6%. The majority of included studies (85.3%) had a higher proportion of males than females.
Exacerbation history (as defined per each study) was reported in 18 of 76 included studies. The proportion of patients with no prior exacerbation was reported in ten studies (range, 0.1–79.5% of patients), one or fewer prior exacerbation in ten studies (range, 46–100%), one or more prior exacerbation in eight studies (range, 18.4–100%), and two or more prior exacerbations in 12 studies (range, 6.1–55.0%).
Prognostic factors of exacerbations
A summary of the risk factors and predictors reported across the included studies is provided in Tables 2 and 3 . The overall findings of the SLR are summarized in Figs. 2 and 3 .
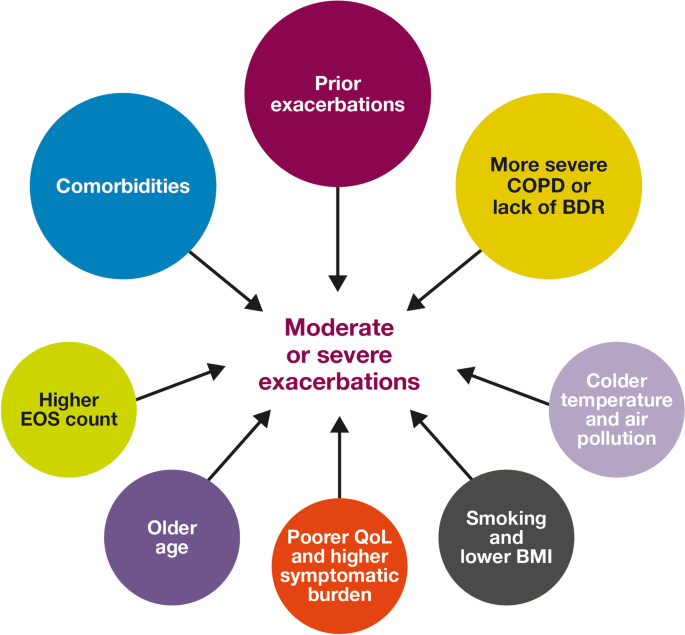
Risk factors for moderate-to-severe exacerbations in patients with COPD. Factors with > 30 supporting studies shown as large circles; factors with ≤ 30 supporting studies shown as small circles and should be interpreted cautiously. BDR bronchodilator reversibility, BMI body mass index, COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, EOS eosinophil, QoL quality of life
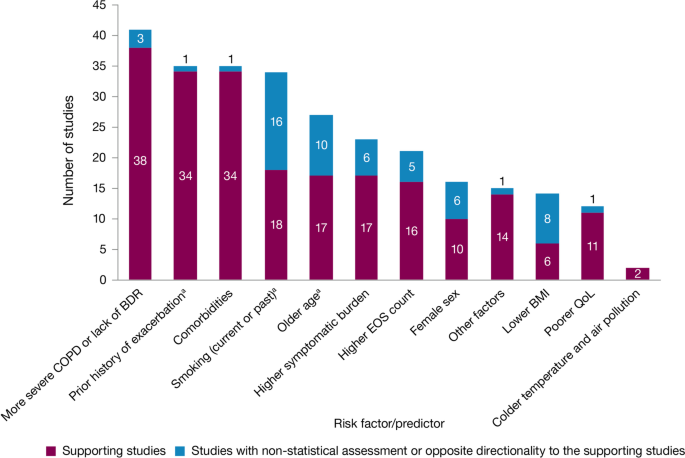
Summary of risk factors for exacerbation events. a Treatment impact studies removed. BDR bronchodilator reversibility, BMI body mass index, COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, EOS eosinophil, QoL quality of life
Exacerbation history within the past 12 months was the strongest predictor of future exacerbations. Across the studies assessing this predictor, 34 out of 35 studies (97.1%) reported a significant association between history of exacerbations and risk of future moderate-to-severe exacerbations (Table 3 ). Specifically, two or more exacerbations in the previous year or at least one hospitalization for COPD in the previous year were identified as reliable predictors of future moderate or severe exacerbations. Even one moderate exacerbation increased the risk of a future exacerbation, with the risk increasing further with each subsequent exacerbation (Fig. 4 ). A severe exacerbation was also found to increase the risk of subsequent exacerbation and hospitalization (Fig. 5 ). Patients experiencing one or more severe exacerbations were more likely to experience further severe exacerbations than moderate exacerbations [ 11 , 12 ]. In contrast, patients with a history of one or more moderate exacerbations were more likely to experience further moderate exacerbations than severe exacerbations [ 11 , 12 ].
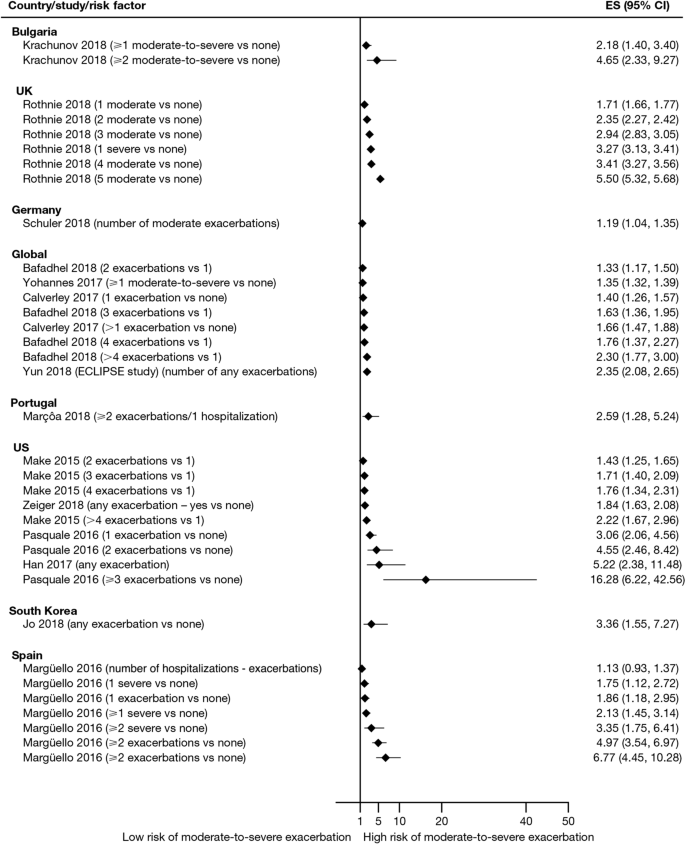
Exacerbation history as a risk factor for moderate-to-severe exacerbations. Yun 2018 included two studies; the study from which data were extracted (COPDGene or ECLIPSE) is listed in parentheses. CI confidence interval, ES effect size
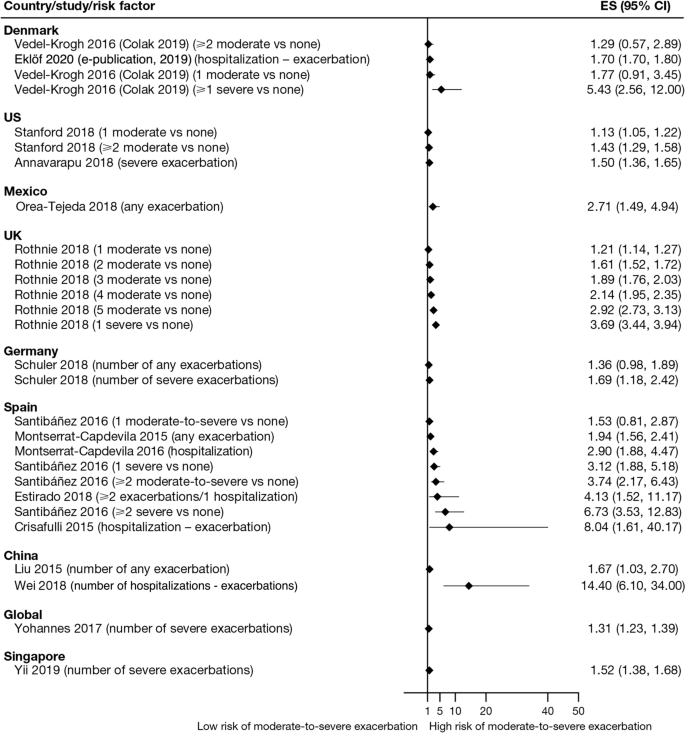
Exacerbation history as a risk factor for severe exacerbations. Where data have been extracted from a linked publication rather than the primary publication, the linked publication is listed in parentheses. CI confidence interval, ES , effect size
Overall, 35 studies assessed the association of comorbidities with the risk of exacerbation. All studies except one (97.1%) reported a positive association between comorbidities and the occurrence of moderate-to-severe exacerbations (Table 3 ). In addition to the presence of any comorbidity, specific comorbidities that were found to significantly increase the risk of moderate-to-severe exacerbations included anxiety and depression, cardiovascular comorbidities, gastroesophageal reflux disease/dyspepsia, and respiratory comorbidities (Fig. 6 ). Comorbidities that were significant risk factors for severe exacerbations included cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, and respiratory comorbidities, diabetes, and malignancy (Fig. 7 ). Overall, the strongest association between comorbidities and COPD readmissions in the emergency department was with cardiovascular disease. The degree of risk for both moderate-to-severe and severe exacerbations also increased with the number of comorbidities. A Dutch cohort study found that 88% of patients with COPD had at least one comorbidity, with hypertension (35%) and coronary heart disease (19%) being the most prevalent. In this cohort, the comorbidities with the greatest risk of frequent exacerbations were pulmonary cancer (odds ratio [OR] 1.85) and heart failure (OR 1.72) [ 7 ].
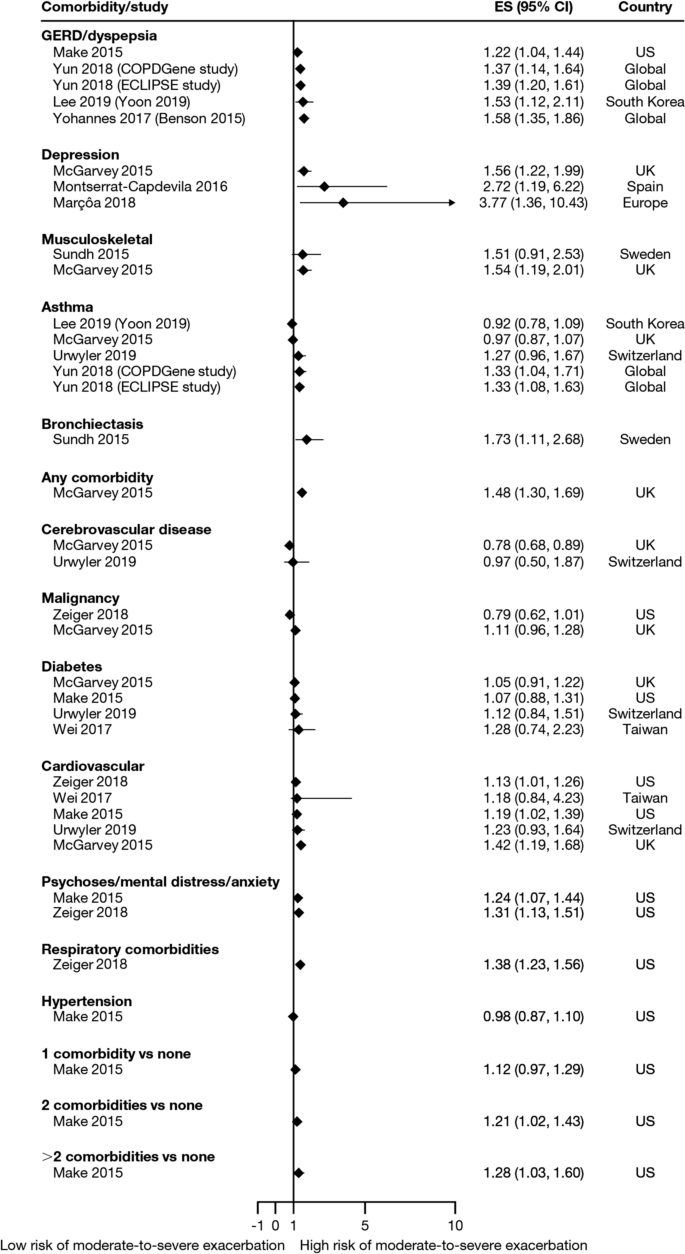
Comorbidities as risk factors for moderate-to-severe exacerbations. Yun 2018 included two studies; the study from which data were extracted (COPDGene or ECLIPSE) is listed in parentheses. Where data have been extracted from a linked publication rather than the primary publication, the linked publication is listed in parentheses. CI confidence interval, ES effect size, GERD gastroesophageal disease
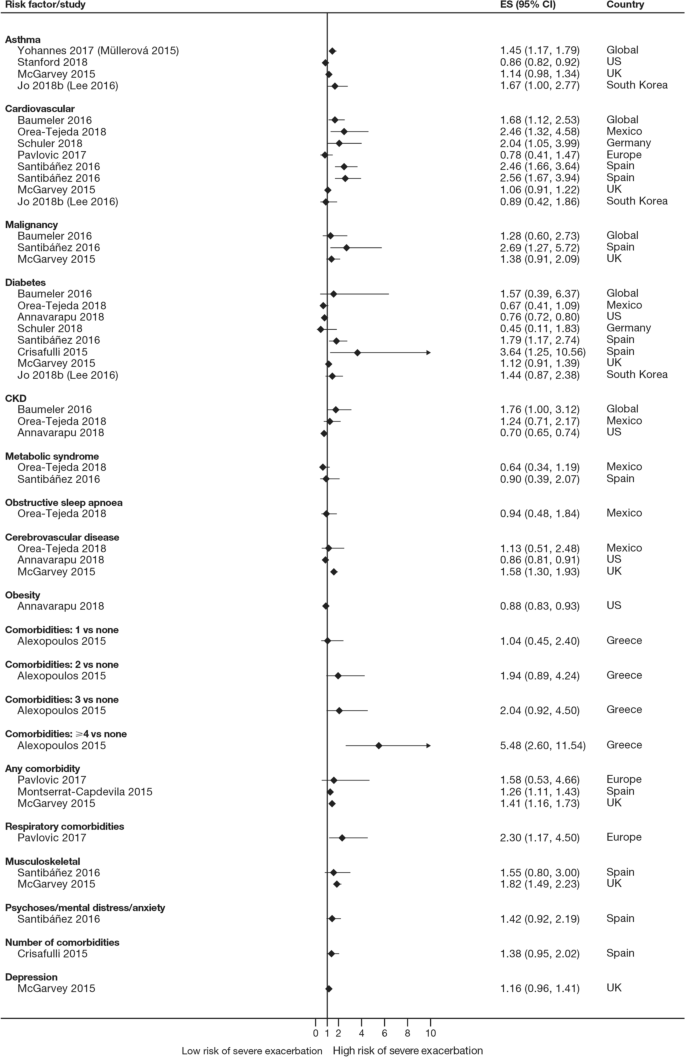
Comorbidities as risk factors for severe exacerbations. Where data have been extracted from a linked publication rather than the primary publication, the linked publication is listed in parentheses. CI confidence interval, CKD , chronic kidney disease, ES effect size
The majority of studies assessing disease severity or bronchodilator reversibility (39/41; 95.1%) indicated a significant positive relation between risk of future exacerbations and greater disease severity, as assessed by greater lung function impairment (in terms of lower FEV 1 , FEV 1 /forced vital capacity ratio, or forced expiratory flow [25–75]/forced vital capacity ratio) or more severe Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) class A − D, and a positive relationship between risk of future exacerbations and lack of bronchodilator reversibility (Table 3 , Figs. 8 and 9 ).
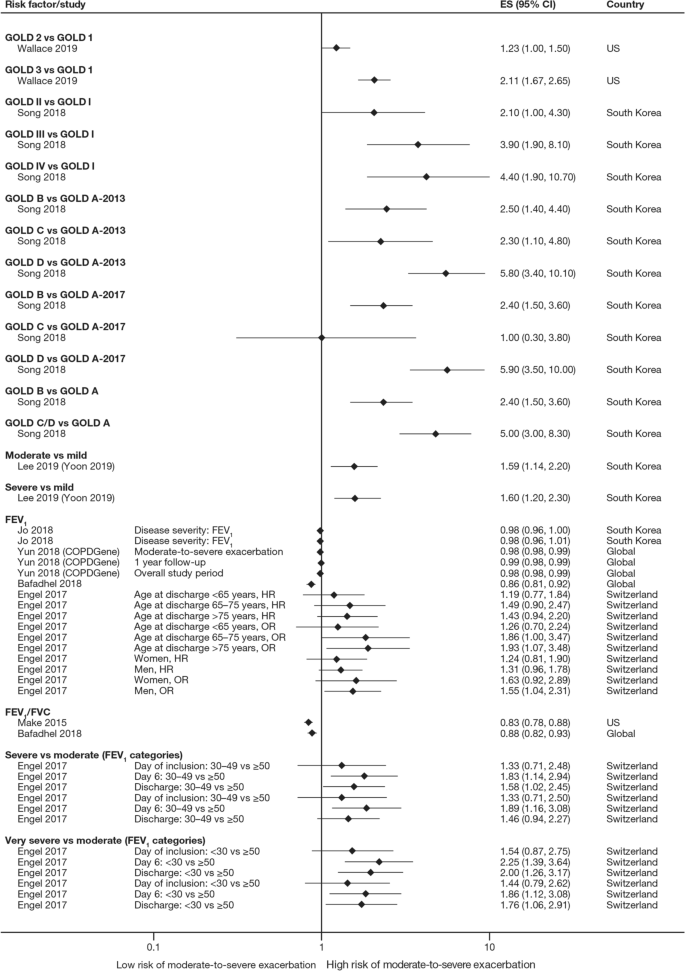
Disease severity as a risk factor for moderate-to-severe exacerbations. Yun 2018 included two studies; the study from which data were extracted (COPDGene or ECLIPSE) is listed in parentheses. Where data have been extracted from a linked publication rather than the primary publication, the linked publication is listed in parentheses. CI confidence interval, ES effect size, FEV 1 f orced expiratory volume in 1 s, FVC , forced vital capacity, GOLD Global Initiative for Obstructive Lung Disease, HR hazard ratio, OR odds ratio
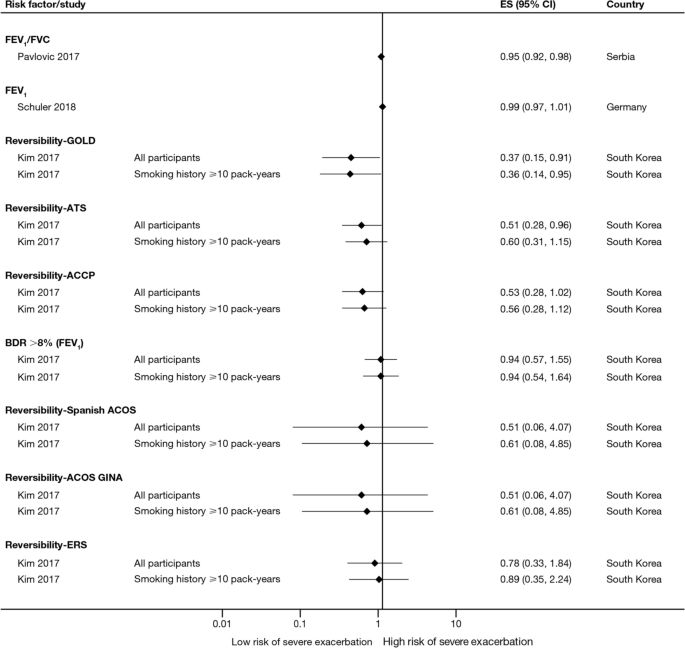
Disease severity and BDR as risk factors for severe exacerbations. ACCP American College of Chest Physicians, ACOS Asthma-COPD overlap syndrome, ATS American Thoracic Society, BDR bronchodilator reversibility, CI confidence interval, ERS European Respiratory Society, ES effect size, FEV 1 forced expiratory volume in 1 s, FVC forced vital capacity, GINA Global Initiative for Asthma, GOLD Global Initiative for Obstructive Lung Disease
Of 21 studies assessing the relationship between blood eosinophil count and exacerbations (Table 3 ), 16 reported estimates for the risk of moderate or severe exacerbations by eosinophil count. A positive association was observed between higher eosinophil count and a higher risk of moderate or severe exacerbations, particularly in patients not treated with an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS); however, five studies reported a significant positive association irrespective of intervention effects. The risk of moderate-to-severe exacerbations was observed to be positively associated with various definitions of higher eosinophil levels (absolute counts: ≥ 200, ≥ 300, ≥ 340, ≥ 400, and ≥ 500 cells/mm 3 ; % of blood eosinophil count: ≥ 2%, ≥ 3%, ≥ 4%, and ≥ 5%). Of note, one study found reduced efficacy of ICS in lowering moderate-to-severe exacerbation rates for current smokers versus former smokers at all eosinophil levels [ 13 ].
Of 12 studies assessing QoL scales, 11 (91.7%) studies reported a significant association between the worsening of QoL scores and the risk of future exacerbations (Table 3 ). Baseline SGRQ [ 14 , 15 ], Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (for which increased scores may indicate impaired QoL) [ 16 ], and Clinical COPD Questionnaire [ 17 , 18 ] scores were found to be associated with future risk of moderate and/or severe COPD exacerbations. For symptom scores, six out of eight studies assessing the association between moderate-to-severe or severe exacerbations with COPD Assessment Test (CAT) scores reported a significant and positive relationship. Furthermore, the risk of moderate-to-severe exacerbations was found to be significantly higher in patients with higher CAT scores (≥ 10) [ 15 , 19 , 20 , 21 ], with one study demonstrating that a CAT score of 15 increased predictive ability for exacerbations compared with a score of 10 or more [ 18 ]. Among 15 studies that assessed the association of modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) scores with the risk of moderate-to-severe or severe exacerbation, 11 found that the risk of moderate-to-severe or severe exacerbations was significantly associated with higher mMRC scores (≥ 2) versus lower scores. Furthermore, morning and night symptoms (measured by Clinical COPD Questionnaire) were associated with poor health status and predicted future exacerbations [ 17 ].
Of 36 studies reporting the relationship between smoking status and moderate-to-severe or severe exacerbations, 22 studies (61.1%) reported a significant positive association (Table 3 ). Passive smoking was also significantly associated with an increased risk of severe exacerbations (OR 1.49) [ 20 ]. Of note, three studies reported a significantly lower rate of moderate-to-severe exacerbations in current smokers compared with former smokers [ 22 , 23 , 24 ].
A total of 14 studies assessed the association of body mass index (BMI) with the occurrence of frequent moderate-to-severe exacerbations in patients with COPD. Six out of 14 studies (42.9%) reported a significant negative association between exacerbations and BMI (Table 3 ). The risk of moderate and/or severe COPD exacerbations was highest among underweight patients compared with normal and overweight patients [ 23 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ].
In the 29 studies reporting an association between age and moderate or severe exacerbations, more than half found an association of older age with an increased risk of moderate-to-severe exacerbations (58.6%; Table 3 ). Four of these studies noted a significant increase in the risk of moderate-to-severe or severe exacerbations for every 10-year increase in age [ 25 , 26 , 29 , 30 ]. However, 12 studies reported no significant association between age and moderate-to-severe or severe exacerbation risk.
Sixteen out of 33 studies investigating the impact of sex on exacerbation risk found a significant association (48.5%; Table 3 ). Among these, ten studies reported that female sex was associated with an increased risk of moderate-to-severe exacerbations, while six studies showed a higher exacerbation risk in males compared with females. There was some variation in findings by geographic location and exacerbation severity (Additional file 2 : Figs. S1 and S2). Notably, when assessing the risk of severe exacerbations, more studies found an association with male sex compared with female sex (6/13 studies vs 1/13 studies, respectively).
Both studies evaluating associations between exacerbations and environmental factors reported that colder temperature and exposure to major air pollution (NO 2 , O 3 , CO, and/or particulate matter ≤ 10 μm in diameter) increased hospital admissions due to severe exacerbations and moderate-to-severe exacerbation rates [ 31 , 32 ].
Four studies assessed the association of 6-min walk distance with the occurrence of frequent moderate-to-severe exacerbations (Table 3 ). One study (25.0%) found that shorter 6-min walk distance (representing low physical activity) was significantly associated with a shortened time to severe exacerbation, but the effect size was small (hazard ratio 0.99) [ 33 ].
Five out of six studies assessing the relationship between race or ethnicity and exacerbation risk reported significant associations (Table 3 ). Additionally, one study reported an association between geographic location in the US and exacerbations, with living in the Northeast region being the strongest predictor of severe COPD exacerbations versus living in the Midwest and South regions [ 34 ].
Overall, seven studies assessed the association of biomarkers with risk of future exacerbations (Table 3 ), with the majority identifying significant associations between inflammatory biomarkers and increased exacerbation risk, including higher C-reactive protein levels [ 8 , 35 ], fibrinogen levels [ 8 , 30 ], and white blood cell count [ 8 , 15 , 16 ].
This SLR has identified several demographic and clinical characteristics that predict the future risk of COPD exacerbations. Key factors associated with an increased risk of future moderate-to-severe exacerbations included a history of prior exacerbations, worse disease severity and bronchodilator reversibility, the presence of comorbidities, a higher eosinophil count, and older age (Fig. 2 ). These prognostic factors may help clinicians identify patients at high risk of exacerbations, which are a major driver of the burden of COPD, including morbidity and mortality [ 36 ].
Findings from this review summarize the existing evidence, validating the previously published literature [ 6 , 9 , 23 ] and suggesting that the best predictor of future exacerbations is a history of exacerbations in the prior year [ 8 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 26 , 29 , 34 , 35 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 ]. In addition, the effect size generally increased with the number of prior exacerbations, with a stronger effect observed with prior severe versus moderate exacerbations. This effect was observed across regions, including in Europe and North America, and in several global studies. This relationship represents a vicious circle, whereby one exacerbation predisposes a patient to experience future exacerbations and leading to an ever-increasing disease burden, and emphasizes the importance of preventing the first exacerbation event through early, proactive exacerbation prevention. The finding that prior exacerbations tended to be associated with future exacerbations of the same severity suggests that the severity of the underlying disease may influence exacerbation severity. However, the validity of the traditional classification of exacerbation severity has recently been challenged [ 61 ], and further work is required to understand relationships with objective assessments of exacerbation severity.
In addition to exacerbation history, disease severity and bronchodilator reversibility were also strong predictors for future exacerbations [ 8 , 14 , 16 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 26 , 28 , 29 , 33 , 37 , 40 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 48 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 56 , 59 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 ]. The association with disease severity was noted in studies that used GOLD disease stages 1–4 and those that used FEV 1 percent predicted and other lung function assessments as continuous variables. Again, this risk factor is self-perpetuating, as evidence shows that even a single moderate or severe exacerbation may almost double the rate of lung function decline [ 79 ]. Accordingly, disease severity and exacerbation history may be correlated. Margüello et al. concluded that the severity of COPD could be associated with a higher risk of exacerbations, but this effect was partly determined by the exacerbations suffered in the previous year [ 23 ]. It should be noted that FEV 1 is not recommended by GOLD for use as a predictor of exacerbation risk or mortality alone due to insufficient precision when used at the individual patient level [ 5 ].
Another factor that should be considered when assessing individual exacerbation risk is the presence of comorbidities [ 7 , 14 , 16 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 30 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 40 , 41 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 56 , 58 , 59 , 63 , 64 , 73 , 74 , 76 , 77 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 ]. Comorbidities are common in COPD, in part due to common risk factors (e.g., age, smoking, lifestyle factors) that also increase the risk of other chronic diseases [ 7 ]. Significant associations were observed between exacerbation risk and comorbidities, such as anxiety and depression, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory comorbidities. As with prior exacerbations, the strength of the association increased with the number of comorbidities. Some comorbidities that were found to be associated with COPD exacerbations share a common biological mechanism of systemic inflammation, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and depression [ 86 ]. Furthermore, other respiratory comorbidities, including asthma and bronchiectasis, involve inflammation of the airways [ 87 ]. In these patients, optimal management of comorbidities may reduce the risk of future COPD exacerbations (and improve QoL), although further research is needed to confirm the efficacy of this approach to exacerbation prevention. As cardiovascular conditions, including hypertension and coronary heart disease, are the most common comorbidities in people with COPD [ 7 ], reducing cardiovascular risk may be a key goal in reducing the occurrence of exacerbations. For other comorbidities, the mechanism for the association with exacerbation risk may be related to non-biological factors. For example, in depression, it has been suggested that the mechanism may relate to greater sensitivity to symptom changes or more frequent physician visits [ 88 ].
There is now a growing body of evidence reporting the relationship between blood eosinophil count and exacerbation risk [ 8 , 13 , 14 , 20 , 37 , 48 , 52 , 56 , 59 , 60 , 62 , 89 , 90 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 94 , 95 , 96 , 97 , 98 , 99 ]. Data from many large clinical trials (SUNSET [ 89 ], FLAME [ 96 ], WISDOM [ 98 ], IMPACT [ 13 ], TRISTAN [ 99 ], INSPIRE [ 99 ], KRONOS [ 91 ], TRIBUTE [ 48 ], TRILOGY [ 52 ], TRINITY [ 56 ]) have also shown relationships between treatment, eosinophil count, and exacerbation rates. Evidence shows that eosinophil count, along with other effect modifiers (e.g., exacerbation history), can be used to predict reductions in exacerbations with ICS treatment. Identifying patients most likely to respond to ICS should contribute to personalized medicine approaches to treat COPD. One challenge in drawing a strong conclusion from eosinophil counts is the choice of a cut-off value, with a variety of absolute and percentage values observed to be positively associated with the risk of moderate-to-severe exacerbations. The use of absolute counts may be more practical, as these are not affected by variations in other immune cell numbers; however, there is a lack of consensus on this point [ 100 ].
Across the studies examined, associations between sex and the risk of moderate and/or severe exacerbations were variable [ 14 , 16 , 18 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 37 , 40 , 42 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 51 , 52 , 56 , 58 , 59 , 63 , 73 , 74 , 77 , 80 , 83 , 84 , 85 ]. A greater number of studies showed an increased risk of exacerbations in females compared with males. In contrast, some studies failed to detect a relationship, suggesting that country-specific or cultural factors may play a role. A majority of the included studies evaluated more male patients than female patients; to further elucidate the relationship between sex and exacerbations, more studies in female patients are warranted. Over half of the studies that assessed the relationship between age and exacerbation risk found an association between increasing age and increasing risk of moderate-to-severe COPD exacerbations [ 14 , 16 , 18 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 33 , 40 , 42 , 44 , 45 , 47 , 51 , 52 , 54 , 56 , 63 , 73 , 74 , 77 , 80 , 83 , 85 ].
Our findings also suggested that patients with low BMI have greater risk of moderate and/or severe exacerbations. The mechanism underlying this increased risk in underweight patients is poorly understood; however, loss of lean body mass in patients with COPD may be related to ongoing systemic inflammation that impacts skeletal muscle mass [ 101 , 102 , 103 ].
A limitation of this SLR, that may have resulted in some studies with valid results being missed, was the exclusion of non-English-language studies and the limitation by date; however, the search strategy was otherwise broad, resulting in the review of a large number of studies. The majority of studies captured in this SLR were from Europe, North America, and Asia. The findings may therefore be less generalizable to patients in other regions, such as Africa or South America. Given that one study reported an association between geographic location within different regions of the US and exacerbations [ 34 ], it is plausible that risk of exacerbations may be impacted by global location. As no formal meta-analysis was planned, the assessments are based on a qualitative synthesis of studies. A majority of the included studies looked at exposures of certain factors (e.g., history of exacerbations) at baseline; however, some of these factors change over time, calling into question whether a more sophisticated statistical analysis should have been conducted in some cases to consider time-varying covariates. Our results can only inform on associations, not causation, and there are likely bidirectional relationships between many factors and exacerbation risk (e.g., health status). Finally, while our review of the literature captured a large number of prognostic factors, other variables such as genetic factors, lung microbiome composition, and changes in therapy over time have not been widely studied to date, but might also influence exacerbation frequency [ 104 ]. Further research is needed to assess the contribution of these factors to exacerbation risk.
This SLR captured publications up to July 2019. However, further studies have since been published that further support the prognostic factors identified here. For example, recent studies have reported an increased risk of exacerbations in patients with a history of exacerbations [ 105 ], comorbidities [ 106 ], poorer lung function (GOLD stage) [ 105 ], higher symptomatic burden [ 107 ], female sex [ 105 ], and lower BMI [ 106 , 108 ].
In summary, the literature assessing risk factors for moderate-to-severe COPD exacerbations shows that there are associations between several demographic and disease characteristics with COPD exacerbations, potentially allowing clinicians to identify patients most at risk of future exacerbations. Exacerbation history, comorbidities, and disease severity or bronchodilator reversibility were the factors most strongly associated with exacerbation risk, and should be considered in future research efforts to develop prognostic tools to estimate the likelihood of exacerbation occurrence. Importantly, many prognostic factors for exacerbations, such as symptom burden, QoL, and comorbidities, are modifiable with optimal pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic treatments or lifestyle modifications. Overall, the evidence suggests that, taken together, predicting and reducing exacerbation risk is an achievable goal in COPD.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Body mass index
COPD Assessment Test
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Forced expiratory volume in 1 s
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
Inhaled corticosteroid
Modified Medical Research Council
Quality of life
St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire
World Health Organization. The top 10 causes of death. 2018. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death . Accessed 22 Jul 2020.
GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet. 2020;396:1204–22.
Article Google Scholar
Hurst JR, Skolnik N, Hansen GJ, Anzueto A, Donaldson GC, Dransfield MT, Varghese P. Understanding the impact of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations on patient health and quality of life. Eur J Intern Med. 2020;73:1–6.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Zhang Y, Morgan RL, Alonso-Coello P, Wiercioch W, Bała MM, Jaeschke RR, Styczeń K, Pardo-Hernandez H, Selva A, Ara Begum H, et al. A systematic review of how patients value COPD outcomes. Eur Respir J. 2018;52:1800222.
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. 2022 GOLD Report. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management and prevention of COPD. 2022. https://goldcopd.org/2022-gold-reports-2/ . Accessed 02 Feb 2022.
Müllerová H, Shukla A, Hawkins A, Quint J. Risk factors for acute exacerbations of COPD in a primary care population: a retrospective observational cohort study. BMJ Open. 2014;4: e006171.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Westerik JAM, Metting EI, van Boven JFM, Tiersma W, Kocks JWH, Schermer TR. Associations between chronic comorbidity and exacerbation risk in primary care patients with COPD. Respir Res. 2017;18:31.
Vedel-Krogh S, Nielsen SF, Lange P, Vestbo J, Nordestgaard BG. Blood eosinophils and exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The Copenhagen General Population Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193:965–74.
Hurst JR, Vestbo J, Anzueto A, Locantore N, Müllerová H, Tal-Singer R, Miller B, Lomas DA, Agusti A, Macnee W, et al. Susceptibility to exacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1128–38.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000097.
Çolak Y, Afzal S, Marott JL, Nordestgaard BG, Vestbo J, Ingebrigtsen TS, Lange P. Prognosis of COPD depends on severity of exacerbation history: a population-based analysis. Respir Med. 2019;155:141–7.
Rothnie KJ, Müllerová H, Smeeth L, Quint JK. Natural history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations in a general practice-based population with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198:464–71.
Pascoe S, Barnes N, Brusselle G, Compton C, Criner GJ, Dransfield MT, Halpin DMG, Han MK, Hartley B, Lange P, et al. Blood eosinophils and treatment response with triple and dual combination therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: analysis of the IMPACT trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2019;7:745–56.
Yun JH, Lamb A, Chase R, Singh D, Parker MM, Saferali A, Vestbo J, Tal-Singer R, Castaldi PJ, Silverman EK, et al. Blood eosinophil count thresholds and exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:2037-2047.e10.
Yoon HY, Park SY, Lee CH, Byun MK, Na JO, Lee JS, Lee WY, Yoo KH, Jung KS, Lee JH. Prediction of first acute exacerbation using COPD subtypes identified by cluster analysis. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:1389–97.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yohannes AM, Mulerova H, Lavoie K, Vestbo J, Rennard SI, Wouters E, Hanania NA. The association of depressive symptoms with rates of acute exacerbations in patients with COPD: results from a 3-year longitudinal follow-up of the ECLIPSE cohort. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017;18:955-959.e6.
Tsiligianni I, Metting E, van der Molen T, Chavannes N, Kocks J. Morning and night symptoms in primary care COPD patients: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. An UNLOCK study from the IPCRG. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2016;26:16040.
Jo YS, Yoon HI, Kim DK, Yoo CG, Lee CH. Comparison of COPD Assessment Test and Clinical COPD Questionnaire to predict the risk of exacerbation. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:101–7.
Marçôa R, Rodrigues DM, Dias M, Ladeira I, Vaz AP, Lima R, Guimarães M. Classification of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) according to the new Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) 2017: comparison with GOLD 2011. COPD. 2018;15:21–6.
Han MK, Quibrera PM, Carretta EE, Barr RG, Bleecker ER, Bowler RP, Cooper CB, Comellas A, Couper DJ, Curtis JL, et al. Frequency of exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an analysis of the SPIROMICS cohort. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5:619–26.
Yii ACA, Loh CH, Tiew PY, Xu H, Taha AAM, Koh J, Tan J, Lapperre TS, Anzueto A, Tee AKH. A clinical prediction model for hospitalized COPD exacerbations based on “treatable traits.” Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:719–28.
McGarvey L, Lee AJ, Roberts J, Gruffydd-Jones K, McKnight E, Haughney J. Characterisation of the frequent exacerbator phenotype in COPD patients in a large UK primary care population. Respir Med. 2015;109:228–37.
Margüello MS, Garrastazu R, Ruiz-Nuñez M, Helguera JM, Arenal S, Bonnardeux C, León C, Miravitlles M, García-Rivero JL. Independent effect of prior exacerbation frequency and disease severity on the risk of future exacerbations of COPD: a retrospective cohort study. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2016;26:16046.
Engel B, Schindler C, Leuppi JD, Rutishauser J. Predictors of re-exacerbation after an index exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the REDUCE randomised clinical trial. Swiss Med Wkly. 2017;147: w14439.
PubMed Google Scholar
Benson VS, Müllerová H, Vestbo J, Wedzicha JA, Patel A, Hurst JR. Evaluation of COPD longitudinally to identify predictive surrogate endpoints (ECLIPSE) investigators. Associations between gastro-oesophageal reflux, its management and exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Med. 2015;109:1147–54.
Santibáñez M, Garrastazu R, Ruiz-Nuñez M, Helguera JM, Arenal S, Bonnardeux C, León C, García-Rivero JL. Predictors of hospitalized exacerbations and mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE. 2016;11: e0158727.
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Jo YS, Kim YH, Lee JY, Kim K, Jung KS, Yoo KH, Rhee CK. Impact of BMI on exacerbation and medical care expenses in subjects with mild to moderate airflow obstruction. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:2261–9.
Alexopoulos EC, Malli F, Mitsiki E, Bania EG, Varounis C, Gourgoulianis KI. Frequency and risk factors of COPD exacerbations and hospitalizations: a nationwide study in Greece (Greek Obstructive Lung Disease Epidemiology and health ecoNomics: GOLDEN study). Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:2665–74.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Liu D, Peng SH, Zhang J, Bai SH, Liu HX, Qu JM. Prediction of short term re-exacerbation in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:1265–73.
Müllerová H, Maselli DJ, Locantore N, Vestbo J, Hurst JR, Wedzicha JA, Bakke P, Agusti A, Anzueto A. Hospitalized exacerbations of COPD: risk factors and outcomes in the ECLIPSE cohort. Chest. 2015;147:999–1007.
de Miguel-Díez J, Hernández-Vázquez J, López-de-Andrés A, Álvaro-Meca A, Hernández-Barrera V, Jiménez-García R. Analysis of environmental risk factors for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation: a case-crossover study (2004–2013). PLoS ONE. 2019;14: e0217143.
Krachunov II, Kyuchukov NH, Ivanova ZI, Yanev NA, Hristova PA, Borisova ED, Popova TP, Pavlov PS, Nikolova PT, Ivanov YY. Impact of air pollution and outdoor temperature on the rate of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2017;59:423–9.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Baumeler L, Papakonstantinou E, Milenkovic B, Lacoma A, Louis R, Aerts JG, Welte T, Kostikas K, Blasi F, Boersma W, et al. Therapy with proton-pump inhibitors for gastroesophageal reflux disease does not reduce the risk for severe exacerbations in COPD. Respirology. 2016;21:883–90.
Annavarapu S, Goldfarb S, Gelb M, Moretz C, Renda A, Kaila S. Development and validation of a predictive model to identify patients at risk of severe COPD exacerbations using administrative claims data. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:2121–30.
Crisafulli E, Torres A, Huerta A, Méndez R, Guerrero M, Martinez R, Liapikou A, Soler N, Sethi S, Menéndez R. C-reactive protein at discharge, diabetes mellitus and ≥1 hospitalization during previous year predict early readmission in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD. 2015;12:311–20.
Bollmeier SG, Hartmann AP. Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a review focusing on exacerbations. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2020;77:259–68.
Bafadhel M, Peterson S, De Blas MA, Calverley PM, Rennard SI, Richter K, Fagerås M. Predictors of exacerbation risk and response to budesonide in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a post-hoc analysis of three randomised trials. Lancet Respir Med. 2018;6:117–26.
Calverley PM, Anzueto AR, Dusser D, Mueller A, Metzdorf N, Wise RA. Treatment of exacerbations as a predictor of subsequent outcomes in patients with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:1297–308.
Calverley PM, Tetzlaff K, Dusser D, Wise RA, Mueller A, Metzdorf N, Anzueto A. Determinants of exacerbation risk in patients with COPD in the TIOSPIR study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:3391–405.
Eklöf J, Sørensen R, Ingebrigtsen TS, Sivapalan P, Achir I, Boel JB, Bangsborg J, Ostergaard C, Dessau RB, Jensen US, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and risk of death and exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an observational cohort study of 22 053 patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26:227–34.
Estirado C, Ceccato A, Guerrero M, Huerta A, Cilloniz C, Vilaró O, Gabarrús A, Gea J, Crisafulli E, Soler N, Torres A. Microorganisms resistant to conventional antimicrobials in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Res. 2018;19:119.
Fuhrman C, Moutengou E, Roche N, Delmas MC. Prognostic factors after hospitalization for COPD exacerbation. Rev Mal Respir. 2017;34:1–18.
Krachunov I, Kyuchukov N, Ivanova Z, Yanev NA, Hristova PA, Pavlov P, Glogovska P, Popova T, Ivanov YY. Stability of frequent exacerbator phenotype in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2018;60:536–45.
Make BJ, Eriksson G, Calverley PM, Jenkins CR, Postma DS, Peterson S, Östlund O, Anzueto A. A score to predict short-term risk of COPD exacerbations (SCOPEX). Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:201–9.
Montserrat-Capdevila J, Godoy P, Marsal JR, Barbé F. Predictive model of hospital admission for COPD exacerbation. Respir Care. 2015;60:1288–94.
Montserrat-Capdevila J, Godoy P, Marsal JR, Barbé F, Galván L. Risk factors for exacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a prospective study. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2016;20:389–95.
Orea-Tejeda A, Navarrete-Peñaloza AG, Verdeja-Vendrell L, Jiménez-Cepeda A, González-Islas DG, Hernández-Zenteno R, Keirns-Davis C, Sánchez-Santillán R, Velazquez-Montero A, Puentes RG. Right heart failure as a risk factor for severe exacerbation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: prospective cohort study. Clin Respir J. 2018;12:2635–41.
Papi A, Vestbo J, Fabbri L, Corradi M, Prunier H, Cohuet G, Guasconi A, Montagna I, Vezzoli S, Petruzzelli S, et al. Extrafine inhaled triple therapy versus dual bronchodilator therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (TRIBUTE): a double-blind, parallel group, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391:1076–84.
Lipson DA, Barnhart F, Brealey N, Brooks J, Criner GJ, Day NC, Dransfield MT, Halpin DMG, Han MK, Jones CE, et al. Once-daily single-inhaler triple versus dual therapy in patients with COPD. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1671–80.
Pasquale MK, Xu Y, Baker CL, Zou KH, Teeter JG, Renda AM, Davis CC, Lee TC, Bobula J. COPD exacerbations associated with the modified Medical Research Council scale and COPD assessment test among Humana Medicare members. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016;11:111–21.
Schuler M, Wittmann M, Faller H, Schultz K. Including changes in dyspnea after inpatient rehabilitation improves prediction models of exacerbations in COPD. Respir Med. 2018;141:87–93.
Singh D, Papi A, Corradi M, Pavlišová I, Montagna I, Francisco C, Cohuet G, Vezzoli S, Scuri M, Vestbo J. Single inhaler triple therapy versus inhaled corticosteroid plus long-acting β 2 -agonist therapy for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (TRILOGY): a double-blind, parallel group, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388:963–73.
Søgaard M, Madsen M, Løkke A, Hilberg O, Sørensen HT, Thomsen RW. Incidence and outcomes of patients hospitalized with COPD exacerbation with and without pneumonia. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016;11:455–65.
Stanford RH, Nag A, Mapel DW, Lee TA, Rosiello R, Schatz M, Vekeman F, Gauthier-Loiselle M, Merrigan JFP, Duh MS. Claims-based risk model for first severe COPD exacerbation. Am J Manag Care. 2018;24:e45–53.
Stanford RH, Lau MS, Li Y, Stemkowski S. External validation of a COPD risk measure in a commercial and medicare population: the COPD treatment ratio. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2019;25:58–69.
Vestbo J, Papi A, Corradi M, Blazhko V, Montagna I, Francisco C, Cohuet G, Vezzoli S, Scuri M, Singh D. Single inhaler extrafine triple therapy versus long-acting muscarinic antagonist therapy for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (TRINITY): a double-blind, parallel group, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389:1919–29.
Wei X, Ma Z, Yu N, Ren J, Jin C, Mi J, Shi M, Tian L, Gao Y, Guo Y. Risk factors predict frequent hospitalization in patients with acute exacerbation of COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:121–9.
Whalley D, Svedsater H, Doward L, Crawford R, Leather D, Lay-Flurrie J, Bosanquet N. Follow-up interviews from The Salford Lung Study (COPD) and analyses per treatment and exacerbations. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. 2019;29:20.
Zeiger RS, Tran TN, Butler RK, Schatz M, Li Q, Khatry DB, Martin U, Kawatkar AA, Chen W. Relationship of blood eosinophil count to exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018;6:944-954.e945.
Vogelmeier CF, Kostikas K, Fang J, Tian H, Jones B, Morgan CL, Fogel R, Gutzwiller FS, Cao H. Evaluation of exacerbations and blood eosinophils in UK and US COPD populations. Respir Res. 2019;20:178.
Celli BR, Fabbri LM, Aaron SD, Agusti A, Brook R, Criner GJ, Franssen FME, Humbert M, Hurst JR, O’Donnell D, et al. An updated definition and severity classification of COPD exacerbations: the Rome proposal. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;204:1251–8.
Adir Y, Hakrush O, Shteinberg M, Schneer S, Agusti A. Circulating eosinophil levels do not predict severe exacerbations in COPD: a retrospective study. ERJ Open Research. 2018;4:00022–2018.
Bartels W, Adamson S, Leung L, Sin DD, van Eeden SF. Emergency department management of acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: factors predicting readmission. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:1647–54.
Kim V, Zhao H, Regan E, Han MK, Make BJ, Crapo JD, Jones PW, Curtis JL, Silverman EK, Criner GJ, COPDGene Investigators. The St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire definition of chronic bronchitis may be a better predictor of COPD exacerbations compared with the classic definition. Chest. 2019;156:685–95.
Abston E, Comellas A, Reed RM, Kim V, Wise RA, Brower R, Fortis S, Beichel R, Bhatt S, Zabner J, et al. Higher BMI is associated with higher expiratory airflow normalised for lung volume (FEF25-75/FVC) in COPD. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2017;4: e000231.
Emura I, Usuda H, Satou K. Appearance of large scavenger receptor A-positive cells in peripheral blood: a potential risk factor for severe exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pathol Int. 2019;69:187–92.
Erol S, Sen E, Gizem Kilic Y, Yousif A, Akkoca Yildiz O, Acican T, Saryal S. Does the 2017 revision improve the ability of GOLD to predict risk of future moderate and severe exacerbation? Clin Respir J. 2018;12:2354–60.
Han MZ, Hsiue TR, Tsai SH, Huang TH, Liao XM, Chen CZ. Validation of the GOLD 2017 and new 16 subgroups (1A–4D) classifications in predicting exacerbation and mortality in COPD patients. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:3425–33.
Huang TH, Hsiue TR, Lin SH, Liao XM, Su PL, Chen CZ. Comparison of different staging methods for COPD in predicting outcomes. Eur Resp J. 2018;51:1700577.
Jung YH, Lee DY, Kim DW, Park SS, Heo EY, Chung HS, Kim DK. Clinical significance of laryngopharyngeal reflux in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:1343–51.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kim J, Kim WJ, Lee CH, Lee SH, Lee MG, Shin KC, Yoo KH, Lee JH, Lim SY, Na JO, et al. Which bronchodilator reversibility criteria can predict severe acute exacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients? Respir Res. 2017;18:107.
Kobayashi S, Hanagama M, Ishida M, Sato H, Ono M, Yamanda S, Yamada M, Aizawa H, Yanai M. Clinical characteristics and outcomes in Japanese patients with COPD according to the 2017 GOLD classification: the Ishinomaki COPD Network Registry. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:3947–55.
Lee SH, Lee JH, Yoon HI, Park HY, Kim TH, Yoo KH, Oh YM, Jung KS, Lee SD, Lee SW. Change in inhaled corticosteroid treatment and COPD exacerbations: an analysis of real-world data from the KOLD/KOCOSS cohorts. Respir Res. 2019;20:62.
Pavlovic R, Stefanovic S, Lazic Z, Jankovic S. Factors associated with the rate of COPD exacerbations that require hospitalization. Turk J Med Sci. 2017;47:134–41.
Song JH, Lee CH, Um SJ, Park YB, Yoo KH, Jung KS, Lee SD, Oh YM, Lee JH, Kim EK, Kim DK. Clinical impacts of the classification by 2017 GOLD guideline comparing previous ones on outcomes of COPD in real-world cohorts. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2018;13:3473–84.
Sundh J, Johansson G, Larsson K, Lindén A, Löfdahl CG, Sandström T, Janson C. The phenotype of concurrent chronic bronchitis and frequent exacerbations in patients with severe COPD attending Swedish secondary care units. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:2327–34.
Urwyler P, Hussein NA, Bridevaux PO, Chhajed PN, Geiser T, Grendelmeier P, Zellweger LJ, Kohler M, Maier S, Miedinger D, et al. Predictive factors for exacerbation and reexacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an extension of the Cox model to analyze data from the Swiss COPD cohort. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2019;14:7.
Wallace AE, Kaila S, Bayer V, Shaikh A, Shinde MU, Willey VJ, Napier MB, Singer JR. Health care resource utilization and exacerbation rates in patients with COPD stratified by disease severity in a commercially insured population. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2019;25:205–17.
Halpin DMG, Decramer M, Celli BR, Mueller A, Metzdorf N, Tashkin DP. Effect of a single exacerbation on decline in lung function in COPD. Respir Med. 2017;128:85–91.
Bade BC, DeRycke EC, Ramsey C, Skanderson M, Crothers K, Haskell S, Bean-Mayberry B, Brandt C, Bastian LA, Akgün KM. Sex differences in veterans admitted to the hospital for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019;16:707–14.
Iyer AS, Bhatt SP, Dransfield M, Kinney G, Holm K, Wamboldt FS, Hanania N, Martinez C, Regan E, Foreman MG, et al. Psychological distress prospectively predicts severe exacerbations in smokers with and without airflow limitation—a longitudinal follow-up study of the COPDGene cohort [abstract]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm-conference.2017.195.1_MeetingAbstracts.A4709 .
Diamond M, Zhao H, Armstrong HF, Morrison M, Bailey KL, Carretta EE, Criner GJ, Han MK, Bleeker E, Cooper CB, et al. Anxiety and depression, either alone or in combination, are associated with respiratory exacerbations in smokers with and without COPD [abstract]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:1615–31.
Google Scholar
Lau CS, Siracuse BL, Chamberlain RS. Readmission After COPD Exacerbation Scale: determining 30-day readmission risk for COPD patients. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:1891–902.
Pikoula M, Quint JK, Nissen F, Hemingway H, Smeeth L, Denaxas S. Identifying clinically important COPD sub-types using data-driven approaches in primary care population based electronic health records. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019;19:86.
Wei YF, Tsai YH, Wang CC, Kuo PH. Impact of overweight and obesity on acute exacerbations of COPD—subgroup analysis of the Taiwan Obstructive Lung Disease cohort. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017;12:2723–9.
Barnes PJ, Celli BR. Systemic manifestations and comorbidities of COPD. Eur Resp J. 2009;33:1165–85.
Polverino E, Dimakou K, Hurst J, Martinez-Garcia MA, Miravitlles M, Paggiaro P, Shteinberg M, Aliberti S, Chalmers JD. The overlap between bronchiectasis and chronic airway diseases: state of the art and future directions. Eur Respir J. 2018;52:1800328.
Xu W, Collet JP, Shapiro S, Lin Y, Yang T, Platt RW, Wang C, Bourbeau J. Independent effect of depression and anxiety on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations and hospitalizations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;178:913–20.
Chapman KR, Hurst JR, Frent SM, Larbig M, Fogel R, Guerin T, Banerji D, Patalano F, Goyal P, Pfister P, et al. Long-term triple therapy de-escalation to indacaterol/glycopyrronium in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (SUNSET): a randomized, double-blind, triple-dummy clinical trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;198:329–39.
Couillard S, Larivée P, Courteau J, Vanasse A. Eosinophils in COPD exacerbations are associated with increased readmissions. Chest. 2017;151:366–73.
Ferguson GT, Rabe KF, Martinez FJ, Fabbri LM, Wang C, Ichinose M, Bourne E, Ballal S, Darken P, DeAngelis K, et al. Triple therapy with budesonide/glycopyrrolate/formoterol fumarate with co-suspension delivery technology versus dual therapies in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (KRONOS): a double-blind, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2018;6:747–58.
Ko FWS, Chan KP, Ngai J, Ng SS, Yip WH, Ip A, Chan TO, Hui DSC. Blood eosinophil count as a predictor of hospital length of stay in COPD exacerbations. Respirology. 2019;25:259–66.
MacDonald MI, Osadnik CR, Bulfin L, Hamza K, Leong P, Wong A, King PT, Bardin PG. Low and high blood eosinophil counts as biomarkers in hospitalized acute exacerbations of COPD. Chest. 2019;156:92–100.
Müllerová H, Hahn B, Simard EP, Mu G, Hatipoğlu U. Exacerbations and health care resource use among patients with COPD in relation to blood eosinophil counts. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:683–92.
Bafadhel M, Greening NJ, Harvey-Dunstan TC, Williams JEA, Morgan MD, Brightling CE, Hussain SF, Pavord ID, Singh SJ, Steiner MC. Blood eosinophils and outcomes in severe hospitalised exacerbations of COPD. Chest. 2016;150:320–8.
Roche N, Chapman KR, Vogelmeier CF, Herth FJF, Thach C, Fogel R, Olsson P, Patalano F, Banerji D, Wedzicha JA. Blood eosinophils and response to maintenance chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treatment. Data from the FLAME trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:1189–97.
Vestbo J, Vogelmeier CF, Small M, Siddall J, Fogel R, Kostikas K. Inhaled corticosteroid use by exacerbations and eosinophils: a real-world COPD population. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019;14:853–61.
Watz H, Tetzlaff K, Wouters EFM, Kirsten A, Magnussen H, Rodriguez-Roisin R, Vogelmeier C, Fabbri LM, Chanez P, Dahl R, et al. Blood eosinophil count and exacerbations in severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease after withdrawal of inhaled corticosteroids: a post-hoc analysis of the WISDOM trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2016;4:390–8.
Pavord ID, Lettis S, Locantore N, Pascoe S, Jones PW, Wedzicha JA, Barnes NC. Blood eosinophils and inhaled corticosteroid/long-acting beta-2 agonist efficacy in COPD. Thorax. 2016;71:118–25.
Singh D. Predicting corticosteroid response in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Blood eosinophils gain momentum. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196:1098–100.
Vestbo J, Prescott E, Almdal T, Dahl M, Nordestgaard BG, Andersen T, Sørensen TIA, Lange P. Body mass, fat-free body mass, and prognosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease from a random population sample: findings from the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173:79–83.
Agustí AGN, Noguera A, Sauleda J, Sala E, Pons J, Busquets X. Systemic effects of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 2003;21:347–60.
Agustí AGN, Sauleda J, Miralles C, Gomez C, Togores B, Sala E, Batle S, Busquets X. Skeletal muscle apoptosis and weight loss in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166:485–9.
Labaki WW, Martinez FJ. Time to understand the infrequency of the frequent exacerbator phenotype in COPD. Chest. 2018;153:1087–8.
Hartley BF, Barnes NC, Lettis S, Compton CH, Papi A, Jones P. Risk factors for exacerbations and pneumonia in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a pooled analysis. Respir Res. 2020;21:5.
Kim Y, Kim YJ, Kang YM, Cho WK. Exploring the impact of number and type of comorbidities on the risk of severe COPD exacerbations in Korean Population: a Nationwide Cohort Study. BMC Pulm Med. 2021;21:151.
Mackay AJ, Kostikas K, Roche N, Frent SM, Olsson P, Pfister P, Gupta P, Patalano F, Banerji D, Wedzicha JA. Impact of baseline symptoms and health status on COPD exacerbations in the FLAME study. Respir Res. 2020;21:93.
Smulders L, van der Aalst A, Neuhaus EDET, Polman S, Franssen FME, van Vliet M, de Kruif MD. Decreased risk of COPD exacerbations in obese patients. COPD. 2020;17:485–91.
Battisti WP, Wager E, Baltzer L, Bridges D, Cairns A, Carswell CI, Citrome L, Gurr JA, Mooney LA, Moore BJ, et al. Good publication practice for communicating company-sponsored medical research: GPP3. Ann Intern Med. 2015;163:461–4.
Putcha N, Barr RG, Han M, Woodruff PG, Bleecker ER, Kanner RE, Martinez FJ, Tashkin DP, Rennard SI, Breysse P, et al. Understanding the impact of passive smoke exposure on outcomes in COPD [abstract]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;191:411–20.
Wu Z, Yang D, Ge Z, Yan M, Wu N, Liu Y. Body mass index of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is associated with pulmonary function and exacerbations: a retrospective real world research. J Thorac Dis. 2018;10:5086–99.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Medical writing support, under the direction of the authors, was provided by Julia King, PhD, and Sarah Piggott, MChem, CMC Connect, McCann Health Medical Communications, funded by AstraZeneca in accordance with Good Publication Practice (GPP3) guidelines [ 109 ].
This study was supported by AstraZeneca.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
UCL Respiratory, University College London, London, WC1E 6BT, UK
John R. Hurst
Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
MeiLan K. Han
Formerly of Parexel International, Mohali, India
Barinder Singh, Gagandeep Kaur & Mohd Kashif Siddiqui
Parexel International, Mohali, India
Sakshi Sharma
Formerly of AstraZeneca, Cambridge, UK
Enrico de Nigris
AstraZeneca, Gothenburg, Sweden
Ulf Holmgren
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The authors have made the following declaration about their contributions. JRH and MKH made substantial contributions to the interpretation of data; BS, SS, GK, and MKS made substantial contributions to the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data; EdN and UH made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the work and the interpretation of data. All authors contributed to drafting or critically revising the article, have approved the submitted version, and agree to be personally accountable for their own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to John R. Hurst .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
JRH reports consulting fees from AstraZeneca; speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Chiesi, Pfizer, and Takeda; and travel support from GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca. MKH reports assistance with conduction of this research and publication from AstraZeneca; personal fees from Aerogen, Altesa Biopharma, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Cipla, DevPro, GlaxoSmithKline, Integrity, Medscape, Merck, Mylan, NACE, Novartis, Polarean, Pulmonx, Regeneron, Sanofi, Teva, Verona, United Therapeutics, and UpToDate; either in kind research support or funds paid to the institution from the American Lung Association, AstraZeneca, Biodesix, Boehringer Ingelheim, the COPD Foundation, Gala Therapeutics, the NIH, Novartis, Nuvaira, Sanofi, and Sunovion; participation in Data Safety Monitoring Boards for Novartis and Medtronic with funds paid to the institution; and stock options from Altesa Biopharma and Meissa Vaccines. BS, GK, and MKS are former employees of Parexel International. SS is an employee of Parexel International, which was funded by AstraZeneca to conduct this analysis. EdN is a former employee of AstraZeneca and previously held stock and/or stock options in the company. UH is an employee of AstraZeneca and holds stock and/or stock options in the company.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file1: table s1..
Search strategies. Table S2. List of included studies with linked publications. Table S3. Study characteristics across the 76 included studies. Table S4. Clinical characteristics of the patients assessed across the included studies.
Additional file 2: Fig. S1.
Sex (male vs female) as a risk factor for moderate-to-severe exacerbations. Fig. S2. Sex (male vs female) as a risk factor for severe exacerbations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Hurst, J.R., Han, M.K., Singh, B. et al. Prognostic risk factors for moderate-to-severe exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic literature review. Respir Res 23 , 213 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-022-02123-5
Download citation
Received : 02 March 2022
Accepted : 20 July 2022
Published : 23 August 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-022-02123-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Exacerbations
- Comorbidities
- Hospitalization
Respiratory Research
ISSN: 1465-993X
- General enquiries: [email protected]
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Clinics (Sao Paulo)
Approaching literature review for academic purposes: The Literature Review Checklist
Debora f.b. leite.
I Departamento de Ginecologia e Obstetricia, Faculdade de Ciencias Medicas, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, SP, BR
II Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Pernambuco, PE, BR
III Hospital das Clinicas, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Pernambuco, PE, BR
Maria Auxiliadora Soares Padilha
Jose g. cecatti.
A sophisticated literature review (LR) can result in a robust dissertation/thesis by scrutinizing the main problem examined by the academic study; anticipating research hypotheses, methods and results; and maintaining the interest of the audience in how the dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field. Unfortunately, little guidance is available on elaborating LRs, and writing an LR chapter is not a linear process. An LR translates students’ abilities in information literacy, the language domain, and critical writing. Students in postgraduate programs should be systematically trained in these skills. Therefore, this paper discusses the purposes of LRs in dissertations and theses. Second, the paper considers five steps for developing a review: defining the main topic, searching the literature, analyzing the results, writing the review and reflecting on the writing. Ultimately, this study proposes a twelve-item LR checklist. By clearly stating the desired achievements, this checklist allows Masters and Ph.D. students to continuously assess their own progress in elaborating an LR. Institutions aiming to strengthen students’ necessary skills in critical academic writing should also use this tool.
INTRODUCTION
Writing the literature review (LR) is often viewed as a difficult task that can be a point of writer’s block and procrastination ( 1 ) in postgraduate life. Disagreements on the definitions or classifications of LRs ( 2 ) may confuse students about their purpose and scope, as well as how to perform an LR. Interestingly, at many universities, the LR is still an important element in any academic work, despite the more recent trend of producing scientific articles rather than classical theses.
The LR is not an isolated section of the thesis/dissertation or a copy of the background section of a research proposal. It identifies the state-of-the-art knowledge in a particular field, clarifies information that is already known, elucidates implications of the problem being analyzed, links theory and practice ( 3 - 5 ), highlights gaps in the current literature, and places the dissertation/thesis within the research agenda of that field. Additionally, by writing the LR, postgraduate students will comprehend the structure of the subject and elaborate on their cognitive connections ( 3 ) while analyzing and synthesizing data with increasing maturity.
At the same time, the LR transforms the student and hints at the contents of other chapters for the reader. First, the LR explains the research question; second, it supports the hypothesis, objectives, and methods of the research project; and finally, it facilitates a description of the student’s interpretation of the results and his/her conclusions. For scholars, the LR is an introductory chapter ( 6 ). If it is well written, it demonstrates the student’s understanding of and maturity in a particular topic. A sound and sophisticated LR can indicate a robust dissertation/thesis.
A consensus on the best method to elaborate a dissertation/thesis has not been achieved. The LR can be a distinct chapter or included in different sections; it can be part of the introduction chapter, part of each research topic, or part of each published paper ( 7 ). However, scholars view the LR as an integral part of the main body of an academic work because it is intrinsically connected to other sections ( Figure 1 ) and is frequently present. The structure of the LR depends on the conventions of a particular discipline, the rules of the department, and the student’s and supervisor’s areas of expertise, needs and interests.

Interestingly, many postgraduate students choose to submit their LR to peer-reviewed journals. As LRs are critical evaluations of current knowledge, they are indeed publishable material, even in the form of narrative or systematic reviews. However, systematic reviews have specific patterns 1 ( 8 ) that may not entirely fit with the questions posed in the dissertation/thesis. Additionally, the scope of a systematic review may be too narrow, and the strict criteria for study inclusion may omit important information from the dissertation/thesis. Therefore, this essay discusses the definition of an LR is and methods to develop an LR in the context of an academic dissertation/thesis. Finally, we suggest a checklist to evaluate an LR.
WHAT IS A LITERATURE REVIEW IN A THESIS?
Conducting research and writing a dissertation/thesis translates rational thinking and enthusiasm ( 9 ). While a strong body of literature that instructs students on research methodology, data analysis and writing scientific papers exists, little guidance on performing LRs is available. The LR is a unique opportunity to assess and contrast various arguments and theories, not just summarize them. The research results should not be discussed within the LR, but the postgraduate student tends to write a comprehensive LR while reflecting on his or her own findings ( 10 ).
Many people believe that writing an LR is a lonely and linear process. Supervisors or the institutions assume that the Ph.D. student has mastered the relevant techniques and vocabulary associated with his/her subject and conducts a self-reflection about previously published findings. Indeed, while elaborating the LR, the student should aggregate diverse skills, which mainly rely on his/her own commitment to mastering them. Thus, less supervision should be required ( 11 ). However, the parameters described above might not currently be the case for many students ( 11 , 12 ), and the lack of formal and systematic training on writing LRs is an important concern ( 11 ).
An institutional environment devoted to active learning will provide students the opportunity to continuously reflect on LRs, which will form a dialogue between the postgraduate student and the current literature in a particular field ( 13 ). Postgraduate students will be interpreting studies by other researchers, and, according to Hart (1998) ( 3 ), the outcomes of the LR in a dissertation/thesis include the following:
- To identify what research has been performed and what topics require further investigation in a particular field of knowledge;
- To determine the context of the problem;
- To recognize the main methodologies and techniques that have been used in the past;
- To place the current research project within the historical, methodological and theoretical context of a particular field;
- To identify significant aspects of the topic;
- To elucidate the implications of the topic;
- To offer an alternative perspective;
- To discern how the studied subject is structured;
- To improve the student’s subject vocabulary in a particular field; and
- To characterize the links between theory and practice.
A sound LR translates the postgraduate student’s expertise in academic and scientific writing: it expresses his/her level of comfort with synthesizing ideas ( 11 ). The LR reveals how well the postgraduate student has proceeded in three domains: an effective literature search, the language domain, and critical writing.
Effective literature search
All students should be trained in gathering appropriate data for specific purposes, and information literacy skills are a cornerstone. These skills are defined as “an individual’s ability to know when they need information, to identify information that can help them address the issue or problem at hand, and to locate, evaluate, and use that information effectively” ( 14 ). Librarian support is of vital importance in coaching the appropriate use of Boolean logic (AND, OR, NOT) and other tools for highly efficient literature searches (e.g., quotation marks and truncation), as is the appropriate management of electronic databases.
Language domain
Academic writing must be concise and precise: unnecessary words distract the reader from the essential content ( 15 ). In this context, reading about issues distant from the research topic ( 16 ) may increase students’ general vocabulary and familiarity with grammar. Ultimately, reading diverse materials facilitates and encourages the writing process itself.
Critical writing
Critical judgment includes critical reading, thinking and writing. It supposes a student’s analytical reflection about what he/she has read. The student should delineate the basic elements of the topic, characterize the most relevant claims, identify relationships, and finally contrast those relationships ( 17 ). Each scientific document highlights the perspective of the author, and students will become more confident in judging the supporting evidence and underlying premises of a study and constructing their own counterargument as they read more articles. A paucity of integration or contradictory perspectives indicates lower levels of cognitive complexity ( 12 ).
Thus, while elaborating an LR, the postgraduate student should achieve the highest category of Bloom’s cognitive skills: evaluation ( 12 ). The writer should not only summarize data and understand each topic but also be able to make judgments based on objective criteria, compare resources and findings, identify discrepancies due to methodology, and construct his/her own argument ( 12 ). As a result, the student will be sufficiently confident to show his/her own voice .
Writing a consistent LR is an intense and complex activity that reveals the training and long-lasting academic skills of a writer. It is not a lonely or linear process. However, students are unlikely to be prepared to write an LR if they have not mastered the aforementioned domains ( 10 ). An institutional environment that supports student learning is crucial.
Different institutions employ distinct methods to promote students’ learning processes. First, many universities propose modules to develop behind the scenes activities that enhance self-reflection about general skills (e.g., the skills we have mastered and the skills we need to develop further), behaviors that should be incorporated (e.g., self-criticism about one’s own thoughts), and each student’s role in the advancement of his/her field. Lectures or workshops about LRs themselves are useful because they describe the purposes of the LR and how it fits into the whole picture of a student’s work. These activities may explain what type of discussion an LR must involve, the importance of defining the correct scope, the reasons to include a particular resource, and the main role of critical reading.
Some pedagogic services that promote a continuous improvement in study and academic skills are equally important. Examples include workshops about time management, the accomplishment of personal objectives, active learning, and foreign languages for nonnative speakers. Additionally, opportunities to converse with other students promotes an awareness of others’ experiences and difficulties. Ultimately, the supervisor’s role in providing feedback and setting deadlines is crucial in developing students’ abilities and in strengthening students’ writing quality ( 12 ).
HOW SHOULD A LITERATURE REVIEW BE DEVELOPED?
A consensus on the appropriate method for elaborating an LR is not available, but four main steps are generally accepted: defining the main topic, searching the literature, analyzing the results, and writing ( 6 ). We suggest a fifth step: reflecting on the information that has been written in previous publications ( Figure 2 ).

First step: Defining the main topic
Planning an LR is directly linked to the research main question of the thesis and occurs in parallel to students’ training in the three domains discussed above. The planning stage helps organize ideas, delimit the scope of the LR ( 11 ), and avoid the wasting of time in the process. Planning includes the following steps:
- Reflecting on the scope of the LR: postgraduate students will have assumptions about what material must be addressed and what information is not essential to an LR ( 13 , 18 ). Cooper’s Taxonomy of Literature Reviews 2 systematizes the writing process through six characteristics and nonmutually exclusive categories. The focus refers to the reviewer’s most important points of interest, while the goals concern what students want to achieve with the LR. The perspective assumes answers to the student’s own view of the LR and how he/she presents a particular issue. The coverage defines how comprehensive the student is in presenting the literature, and the organization determines the sequence of arguments. The audience is defined as the group for whom the LR is written.
- Designating sections and subsections: Headings and subheadings should be specific, explanatory and have a coherent sequence throughout the text ( 4 ). They simulate an inverted pyramid, with an increasing level of reflection and depth of argument.
- Identifying keywords: The relevant keywords for each LR section should be listed to guide the literature search. This list should mirror what Hart (1998) ( 3 ) advocates as subject vocabulary . The keywords will also be useful when the student is writing the LR since they guide the reader through the text.
- Delineating the time interval and language of documents to be retrieved in the second step. The most recently published documents should be considered, but relevant texts published before a predefined cutoff year can be included if they are classic documents in that field. Extra care should be employed when translating documents.
Second step: Searching the literature
The ability to gather adequate information from the literature must be addressed in postgraduate programs. Librarian support is important, particularly for accessing difficult texts. This step comprises the following components:
- Searching the literature itself: This process consists of defining which databases (electronic or dissertation/thesis repositories), official documents, and books will be searched and then actively conducting the search. Information literacy skills have a central role in this stage. While searching electronic databases, controlled vocabulary (e.g., Medical Subject Headings, or MeSH, for the PubMed database) or specific standardized syntax rules may need to be applied.
In addition, two other approaches are suggested. First, a review of the reference list of each document might be useful for identifying relevant publications to be included and important opinions to be assessed. This step is also relevant for referencing the original studies and leading authors in that field. Moreover, students can directly contact the experts on a particular topic to consult with them regarding their experience or use them as a source of additional unpublished documents.
Before submitting a dissertation/thesis, the electronic search strategy should be repeated. This process will ensure that the most recently published papers will be considered in the LR.
- Selecting documents for inclusion: Generally, the most recent literature will be included in the form of published peer-reviewed papers. Assess books and unpublished material, such as conference abstracts, academic texts and government reports, are also important to assess since the gray literature also offers valuable information. However, since these materials are not peer-reviewed, we recommend that they are carefully added to the LR.
This task is an important exercise in time management. First, students should read the title and abstract to understand whether that document suits their purposes, addresses the research question, and helps develop the topic of interest. Then, they should scan the full text, determine how it is structured, group it with similar documents, and verify whether other arguments might be considered ( 5 ).
Third step: Analyzing the results
Critical reading and thinking skills are important in this step. This step consists of the following components:
- Reading documents: The student may read various texts in depth according to LR sections and subsections ( defining the main topic ), which is not a passive activity ( 1 ). Some questions should be asked to practice critical analysis skills, as listed below. Is the research question evident and articulated with previous knowledge? What are the authors’ research goals and theoretical orientations, and how do they interact? Are the authors’ claims related to other scholars’ research? Do the authors consider different perspectives? Was the research project designed and conducted properly? Are the results and discussion plausible, and are they consistent with the research objectives and methodology? What are the strengths and limitations of this work? How do the authors support their findings? How does this work contribute to the current research topic? ( 1 , 19 )
- Taking notes: Students who systematically take notes on each document are more readily able to establish similarities or differences with other documents and to highlight personal observations. This approach reinforces the student’s ideas about the next step and helps develop his/her own academic voice ( 1 , 13 ). Voice recognition software ( 16 ), mind maps ( 5 ), flowcharts, tables, spreadsheets, personal comments on the referenced texts, and note-taking apps are all available tools for managing these observations, and the student him/herself should use the tool that best improves his/her learning. Additionally, when a student is considering submitting an LR to a peer-reviewed journal, notes should be taken on the activities performed in all five steps to ensure that they are able to be replicated.
Fourth step: Writing
The recognition of when a student is able and ready to write after a sufficient period of reading and thinking is likely a difficult task. Some students can produce a review in a single long work session. However, as discussed above, writing is not a linear process, and students do not need to write LRs according to a specific sequence of sections. Writing an LR is a time-consuming task, and some scholars believe that a period of at least six months is sufficient ( 6 ). An LR, and academic writing in general, expresses the writer’s proper thoughts, conclusions about others’ work ( 6 , 10 , 13 , 16 ), and decisions about methods to progress in the chosen field of knowledge. Thus, each student is expected to present a different learning and writing trajectory.
In this step, writing methods should be considered; then, editing, citing and correct referencing should complete this stage, at least temporarily. Freewriting techniques may be a good starting point for brainstorming ideas and improving the understanding of the information that has been read ( 1 ). Students should consider the following parameters when creating an agenda for writing the LR: two-hour writing blocks (at minimum), with prespecified tasks that are possible to complete in one section; short (minutes) and long breaks (days or weeks) to allow sufficient time for mental rest and reflection; and short- and long-term goals to motivate the writing itself ( 20 ). With increasing experience, this scheme can vary widely, and it is not a straightforward rule. Importantly, each discipline has a different way of writing ( 1 ), and each department has its own preferred styles for citations and references.
Fifth step: Reflecting on the writing
In this step, the postgraduate student should ask him/herself the same questions as in the analyzing the results step, which can take more time than anticipated. Ambiguities, repeated ideas, and a lack of coherence may not be noted when the student is immersed in the writing task for long periods. The whole effort will likely be a work in progress, and continuous refinements in the written material will occur once the writing process has begun.
LITERATURE REVIEW CHECKLIST
In contrast to review papers, the LR of a dissertation/thesis should not be a standalone piece or work. Instead, it should present the student as a scholar and should maintain the interest of the audience in how that dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field.
A checklist for evaluating an LR is convenient for students’ continuous academic development and research transparency: it clearly states the desired achievements for the LR of a dissertation/thesis. Here, we present an LR checklist developed from an LR scoring rubric ( 11 ). For a critical analysis of an LR, we maintain the five categories but offer twelve criteria that are not scaled ( Figure 3 ). The criteria all have the same importance and are not mutually exclusive.

First category: Coverage
1. justified criteria exist for the inclusion and exclusion of literature in the review.
This criterion builds on the main topic and areas covered by the LR ( 18 ). While experts may be confident in retrieving and selecting literature, postgraduate students must convince their audience about the adequacy of their search strategy and their reasons for intentionally selecting what material to cover ( 11 ). References from different fields of knowledge provide distinct perspective, but narrowing the scope of coverage may be important in areas with a large body of existing knowledge.
Second category: Synthesis
2. a critical examination of the state of the field exists.
A critical examination is an assessment of distinct aspects in the field ( 1 ) along with a constructive argument. It is not a negative critique but an expression of the student’s understanding of how other scholars have added to the topic ( 1 ), and the student should analyze and contextualize contradictory statements. A writer’s personal bias (beliefs or political involvement) have been shown to influence the structure and writing of a document; therefore, the cultural and paradigmatic background guide how the theories are revised and presented ( 13 ). However, an honest judgment is important when considering different perspectives.
3. The topic or problem is clearly placed in the context of the broader scholarly literature
The broader scholarly literature should be related to the chosen main topic for the LR ( how to develop the literature review section). The LR can cover the literature from one or more disciplines, depending on its scope, but it should always offer a new perspective. In addition, students should be careful in citing and referencing previous publications. As a rule, original studies and primary references should generally be included. Systematic and narrative reviews present summarized data, and it may be important to cite them, particularly for issues that should be understood but do not require a detailed description. Similarly, quotations highlight the exact statement from another publication. However, excessive referencing may disclose lower levels of analysis and synthesis by the student.
4. The LR is critically placed in the historical context of the field
Situating the LR in its historical context shows the level of comfort of the student in addressing a particular topic. Instead of only presenting statements and theories in a temporal approach, which occasionally follows a linear timeline, the LR should authentically characterize the student’s academic work in the state-of-art techniques in their particular field of knowledge. Thus, the LR should reinforce why the dissertation/thesis represents original work in the chosen research field.
5. Ambiguities in definitions are considered and resolved
Distinct theories on the same topic may exist in different disciplines, and one discipline may consider multiple concepts to explain one topic. These misunderstandings should be addressed and contemplated. The LR should not synthesize all theories or concepts at the same time. Although this approach might demonstrate in-depth reading on a particular topic, it can reveal a student’s inability to comprehend and synthesize his/her research problem.
6. Important variables and phenomena relevant to the topic are articulated
The LR is a unique opportunity to articulate ideas and arguments and to purpose new relationships between them ( 10 , 11 ). More importantly, a sound LR will outline to the audience how these important variables and phenomena will be addressed in the current academic work. Indeed, the LR should build a bidirectional link with the remaining sections and ground the connections between all of the sections ( Figure 1 ).
7. A synthesized new perspective on the literature has been established
The LR is a ‘creative inquiry’ ( 13 ) in which the student elaborates his/her own discourse, builds on previous knowledge in the field, and describes his/her own perspective while interpreting others’ work ( 13 , 17 ). Thus, students should articulate the current knowledge, not accept the results at face value ( 11 , 13 , 17 ), and improve their own cognitive abilities ( 12 ).
Third category: Methodology
8. the main methodologies and research techniques that have been used in the field are identified and their advantages and disadvantages are discussed.
The LR is expected to distinguish the research that has been completed from investigations that remain to be performed, address the benefits and limitations of the main methods applied to date, and consider the strategies for addressing the expected limitations described above. While placing his/her research within the methodological context of a particular topic, the LR will justify the methodology of the study and substantiate the student’s interpretations.
9. Ideas and theories in the field are related to research methodologies
The audience expects the writer to analyze and synthesize methodological approaches in the field. The findings should be explained according to the strengths and limitations of previous research methods, and students must avoid interpretations that are not supported by the analyzed literature. This criterion translates to the student’s comprehension of the applicability and types of answers provided by different research methodologies, even those using a quantitative or qualitative research approach.
Fourth category: Significance
10. the scholarly significance of the research problem is rationalized.
The LR is an introductory section of a dissertation/thesis and will present the postgraduate student as a scholar in a particular field ( 11 ). Therefore, the LR should discuss how the research problem is currently addressed in the discipline being investigated or in different disciplines, depending on the scope of the LR. The LR explains the academic paradigms in the topic of interest ( 13 ) and methods to advance the field from these starting points. However, an excess number of personal citations—whether referencing the student’s research or studies by his/her research team—may reflect a narrow literature search and a lack of comprehensive synthesis of ideas and arguments.
11. The practical significance of the research problem is rationalized
The practical significance indicates a student’s comprehensive understanding of research terminology (e.g., risk versus associated factor), methodology (e.g., efficacy versus effectiveness) and plausible interpretations in the context of the field. Notably, the academic argument about a topic may not always reflect the debate in real life terms. For example, using a quantitative approach in epidemiology, statistically significant differences between groups do not explain all of the factors involved in a particular problem ( 21 ). Therefore, excessive faith in p -values may reflect lower levels of critical evaluation of the context and implications of a research problem by the student.
Fifth category: Rhetoric
12. the lr was written with a coherent, clear structure that supported the review.
This category strictly relates to the language domain: the text should be coherent and presented in a logical sequence, regardless of which organizational ( 18 ) approach is chosen. The beginning of each section/subsection should state what themes will be addressed, paragraphs should be carefully linked to each other ( 10 ), and the first sentence of each paragraph should generally summarize the content. Additionally, the student’s statements are clear, sound, and linked to other scholars’ works, and precise and concise language that follows standardized writing conventions (e.g., in terms of active/passive voice and verb tenses) is used. Attention to grammar, such as orthography and punctuation, indicates prudence and supports a robust dissertation/thesis. Ultimately, all of these strategies provide fluency and consistency for the text.
Although the scoring rubric was initially proposed for postgraduate programs in education research, we are convinced that this checklist is a valuable tool for all academic areas. It enables the monitoring of students’ learning curves and a concentrated effort on any criteria that are not yet achieved. For institutions, the checklist is a guide to support supervisors’ feedback, improve students’ writing skills, and highlight the learning goals of each program. These criteria do not form a linear sequence, but ideally, all twelve achievements should be perceived in the LR.
CONCLUSIONS
A single correct method to classify, evaluate and guide the elaboration of an LR has not been established. In this essay, we have suggested directions for planning, structuring and critically evaluating an LR. The planning of the scope of an LR and approaches to complete it is a valuable effort, and the five steps represent a rational starting point. An institutional environment devoted to active learning will support students in continuously reflecting on LRs, which will form a dialogue between the writer and the current literature in a particular field ( 13 ).
The completion of an LR is a challenging and necessary process for understanding one’s own field of expertise. Knowledge is always transitory, but our responsibility as scholars is to provide a critical contribution to our field, allowing others to think through our work. Good researchers are grounded in sophisticated LRs, which reveal a writer’s training and long-lasting academic skills. We recommend using the LR checklist as a tool for strengthening the skills necessary for critical academic writing.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Leite DFB has initially conceived the idea and has written the first draft of this review. Padilha MAS and Cecatti JG have supervised data interpretation and critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read the draft and agreed with this submission. Authors are responsible for all aspects of this academic piece.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to all of the professors of the ‘Getting Started with Graduate Research and Generic Skills’ module at University College Cork, Cork, Ireland, for suggesting and supporting this article. Funding: DFBL has granted scholarship from Brazilian Federal Agency for Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education (CAPES) to take part of her Ph.D. studies in Ireland (process number 88881.134512/2016-01). There is no participation from sponsors on authors’ decision to write or to submit this manuscript.
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
1 The questions posed in systematic reviews usually follow the ‘PICOS’ acronym: Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes, Study design.
2 In 1988, Cooper proposed a taxonomy that aims to facilitate students’ and institutions’ understanding of literature reviews. Six characteristics with specific categories are briefly described: Focus: research outcomes, research methodologies, theories, or practices and applications; Goals: integration (generalization, conflict resolution, and linguistic bridge-building), criticism, or identification of central issues; Perspective: neutral representation or espousal of a position; Coverage: exhaustive, exhaustive with selective citations, representative, central or pivotal; Organization: historical, conceptual, or methodological; and Audience: specialized scholars, general scholars, practitioners or policymakers, or the general public.
Forensic neuropathology in the past decade: a scoping literature review
- Open access
- Published: 13 July 2023
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Petteri Oura 1 , 2 ,
- Antti Hakkarainen 1 , 2 &
- Antti Sajantila 1 , 2
1120 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
While there has been notable research activity in the field of clinical neuropathology over the recent years, forensic approaches have been less frequent. This scoping literature review explored original research on forensic neuropathology over the past decade (January 1, 2010, until February 12, 2022) using the MEDLINE database. The aims were to (1) analyze the volume of research on the topic, (2) describe meta-level attributes and sample characteristics, and (3) summarize key research themes and methods. Of 5053 initial hits, 2864 fell within the target timeframe, and 122 were included in the review. Only 3–17 articles were published per year globally. Most articles originated from the Europe (39.3%) and Asia (36.1%) and were published in forensic journals (57.4%). A median sample included 57 subjects aged between 16 and 80 years. The most common research theme was traumatic intracranial injury (24.6%), followed by anatomy (12.3%) and substance abuse (11.5%). Key methods included immunotechniques (31.1%) and macroscopic observation (21.3%). Although a number of novel findings were reported, most were of preliminary nature and will require further validation. In order to reach breakthroughs and validate novel tools for routine use, more research input is urged from researchers across the world. It would be necessary to ensure appropriate sample sizes and make use of control groups.
Similar content being viewed by others

Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach
Zachary Munn, Micah D. J. Peters, … Edoardo Aromataris
A 24-step guide on how to design, conduct, and successfully publish a systematic review and meta-analysis in medical research
Taulant Muka, Marija Glisic, … Oscar H. Franco

Bilateral lesions of the basal ganglia and thalami (central grey matter)—pictorial review
Sofie Van Cauter, Mariasavina Severino, … Zoran Rumboldt
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Neurological diseases [ 1 ] and trauma to the central nervous system (CNS) [ 2 ] are common causes of death globally. A comprehensive postmortem examination of the CNS often requires particular expertise and sophisticated tissue processing techniques [ 3 , 4 ]. Neuropathological expertise is therefore of high value in both clinical [ 5 ] and forensic pathology [ 3 ]. While there has been notable research activity in the field of clinical neuropathology over the recent years [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ], forensic approaches appear less frequent [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 ]. However, the role of CNS remains important in the medico-legal practice [ 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 ], as CNS-related findings may have pivotal significance in cause-of-death investigation [ 3 ] and legal proceedings [ 25 , 26 ].
Literature reviews aid in the efficient utilization of current knowledge. Systematic approaches are needed to summarize and disseminate research findings and identify gaps in the existing literature [ 27 ]. However, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, there are no broad-scoped overviews summarizing literature on forensic neuropathology, at least from the past decade. This scoping literature review explored literature on forensic neuropathology from January 1, 2010, until February 12, 2022. The aims were to (1) analyze the volume of research on the topic, (2) describe meta-level attributes and sample characteristics, and (3) summarize key research themes and methods.
Materials and methods
Research questions.
Scoping reviews are exploited to determine the scope and volume of literature on a given topic and to identify key concepts [ 28 , 29 ]. In contrast to systematic reviews, scoping reviews are particularly useful when the research question is broad and the body of literature has not been comprehensively reviewed before. We conducted a MEDLINE-based scoping review to explore scientific literature on forensic neuropathology published over the past decade.
The following research questions were formulated in accordance with the general aims of the study:
Volume of research
What is the volume of original research on forensic neuropathology per year?
Meta-level attributes and sample characteristics
Which journals publish studies on forensic neuropathology in terms of subspecialty and impact?
What is the geographical distribution of publications?
What kind of samples are used in terms of size and age distribution?
Research themes and methods
What are the key concepts, i.e., main research themes and methodological approaches in forensic neuropathology?
Are there knowledge gaps?
This review did not aim to summarize or classify particular findings of the studies; however, these are addressed in the supplementary material .
Search strategy, inclusion, and exclusion criteria
The search strategy was developed by the first author (P.O.) and reviewed by the last author of the paper (A.S.). Table 1 presents the specific search terms used in MEDLINE. Figure 1 is a flowchart demonstrating the article selection process with exclusions.
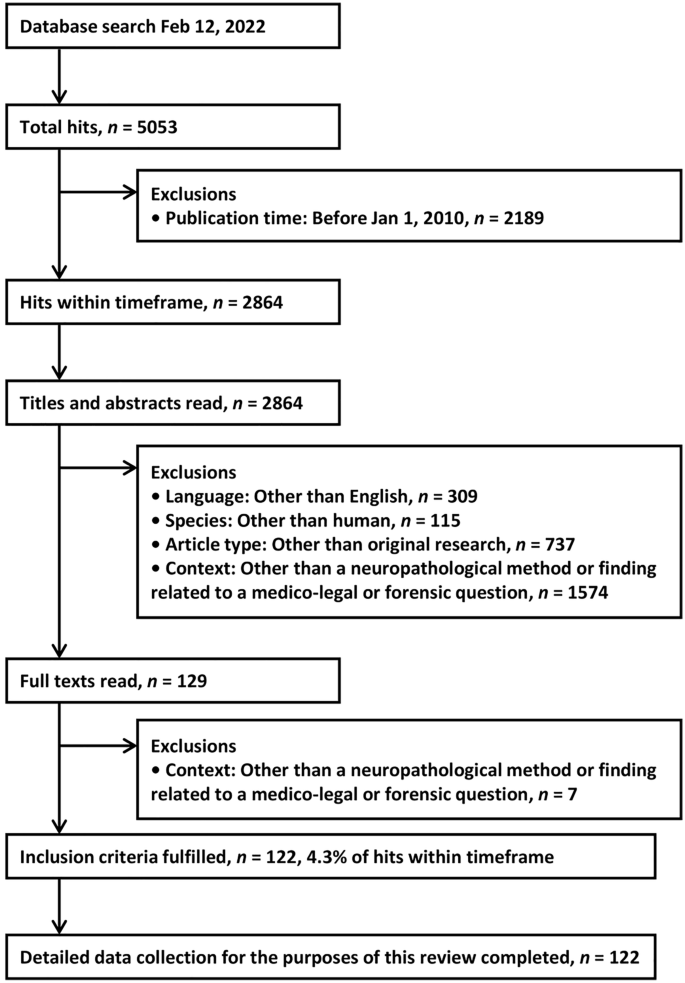
Flowchart demonstrating the article selection process with exclusions
We aimed to find peer-reviewed, original articles that addressed a neuropathological method or finding related to a medico-legal or forensic question in a human sample. A neuropathological method was defined as a macroscopic, microscopic, or other laboratory technique used to examine a tissue sample obtained from the CNS or intracranial structures including vasculature. We focused on English-language articles that were published and indexed in MEDLINE between January 1, 2010, and the database search date. Short communications, retrospective summaries of autopsy findings, and other similar publication types were included if they were original articles based on authentic human samples. Studies that solely focused on postmortem imaging, analysis of body fluids, human identification, or skull fractures without the use of neuropathological methods were excluded.
The search was conducted in the MEDLINE database February 12, 2022. First, P.O. screened all hits on the basis of titles, abstracts, and full texts, if necessary. Each hit was assigned with a rationale for inclusion or exclusion to be later validated by A.S.
Data extraction and synthesis
Data extraction was performed with the help of an Excel spreadsheet. Table 2 presents the variables collected in the data extraction process. The spreadsheet was a priori planned by P.O. and reviewed by A.S.; an internal pilot was carried out in the beginning of data collection (20 hits from the year 2010). Data extraction was performed on the basis of full texts and potential supplementary material of the articles. While P.O. was primarily responsible for extracting the data, the spreadsheet was reviewed and commented by A.S. A formal risk of bias assessment was not performed, as it is not customary in scoping reviews [ 28 ], and was not considered necessary in relation to the present research questions.
Data synthesis was conducted in accordance with the predefined research questions. The distributions of publication year, journal characteristics, geographical location, sample characteristics, primary research theme, and methodological approach were tabulated using frequencies with percentages or medians with interquartile ranges, as appropriate. In addition to these summary statistics, a supplementary table containing the extracted data of individual studies was constructed.
- Literature search
Of 5053 initial hits, 2864 fell within the target timeframe, and 122 were finally included in the review [ 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 81 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 94 , 95 , 96 , 97 , 98 , 99 , 100 , 101 , 102 , 103 , 104 , 105 , 106 , 107 , 108 , 109 , 110 , 111 , 112 , 113 , 114 , 115 , 116 , 117 , 118 , 119 , 120 , 121 , 122 , 123 , 124 , 125 , 126 , 127 , 128 , 129 , 130 , 131 , 132 , 133 , 134 , 135 , 136 , 137 , 138 , 139 , 140 , 141 , 142 , 143 , 144 , 145 , 146 , 147 , 148 , 149 , 150 , 151 ], corresponding to 4.3% of hits within timeframe (Fig. 1 ). Most exclusions were due to wrong context (e.g., forensic psychiatry) or article type (i.e., not original article). Individual summaries of the 122 included articles, together with aims and main findings, are presented in Supplementary Table 1 .
Meta-level attributes
Table 3 shows the annual distribution of publications over the review period; 3 to 17 articles were published per year globally. Table 4 is a bibliographic and geographic summary of the studies. Forensic journals were the most common publication channel (57.4%), followed by clinical journals (e.g., general medicine, neurology, or pediatric journals; 23.0%), and pathology journals (8.2%). Median impact factor was 2.3, while 11.5% of studies were published in journals without an Impact Factor. As for geographical distribution, Europe (39.3%) and Asia (36.1%) were the two most common study regions.
- Sample characteristics
Table 5 is a summary of sample characteristics. A median sample included 57 subjects (interquartile range 29–101; full range 4–1222), which included both cases and controls, if applicable. Control groups were utilized in less than half of the studies (43.4%). Medians of minimum and maximum ages were 16 and 80 years, respectively. A total of 30.3% of studies were based on adult-only samples, another 30.3% had both adults and minors, and 12.3% were based on minors. Subject ages were not stated in over a quarter of the studies (27.0%).
Lists of research themes and methodological approaches are presented in Table 6 . Individual summaries of the articles, together with aims and main findings, are presented in Supplementary Table 1 .
The most common research theme was traumatic intracranial injury (24.6%), which comprised focal and diffuse traumatic brain injuries [ 30 , 31 , 39 , 43 , 54 , 55 , 64 , 83 , 85 , 86 , 94 , 106 , 107 , 115 , 116 , 120 , 123 , 130 , 132 , 139 , 150 ] and traumatic intracranial hemorrhages [ 30 , 47 , 54 , 57 , 58 , 65 , 83 , 87 , 99 , 113 , 114 , 130 , 141 , 150 ]. Studies often used immunotechniques to identify traumatic changes and estimate the age of injury [ 39 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 94 , 106 , 107 , 115 , 120 , 132 , 139 ]. While some studies described macroscopic injury patterns and combinations in accident and assault scenarios [ 30 , 47 , 65 , 99 , 114 , 116 , 130 , 141 ], others used conventional histology [ 57 , 58 , 113 ] or several methods [ 31 , 43 , 54 , 55 , 64 , 83 , 150 ] to address varying research questions.
The second most common entity was anatomy (12.3%). While most studies described the anatomical variants of vasculature [ 41 , 68 , 75 , 105 , 126 , 127 , 135 ] and other intracranial structures [ 44 , 73 , 74 , 151 ], some aimed to generate reference values for brain weight in various populations [ 69 , 98 , 102 , 125 ]. The main techniques were macroscopic observation, conventional histology, and weight measurement. Moreover, one study evaluated the biomechanical properties of the dura mater [ 151 ].
Substance abuse was the primary entity in 11.5% of the studies. Both chronic and acute abuse were represented. The selection of substances included alcohols [ 38 , 52 , 82 ], opioids [ 38 , 100 , 109 , 117 , 118 , 119 ], stimulants [ 38 , 53 , 81 , 136 , 147 ], and other or multiple substances [ 48 , 50 , 117 , 118 ]. Immunotechniques [ 38 , 48 , 50 , 117 , 118 , 147 ], genetic techniques [ 81 ], or the two together [ 119 , 136 ] were often utilized to identify brain damage and distinguish substance abuse from other causes of death. Some studies primarily reported macroscopic observations [ 52 , 53 , 82 , 109 ] or brain weight [ 100 ] among substance abusers.
Laboratory methods were the main focus in 7.4% of the studies [ 45 , 67 , 70 , 72 , 97 , 111 , 133 , 138 , 148 ]. The studies showed notable heterogeneity, addressing technical aspects of, e.g., formalin pigment deposition [ 45 ], immunohistochemistry [ 133 ], DNA extraction [ 67 ], and freezing preparation of putrefied brain tissue [ 97 ].
Sudden unexpected deaths in infancy and childhood were addressed in 6.6% of the studies [ 33 , 40 , 51 , 61 , 66 , 79 , 84 , 91 ]. Immunotechniques [ 33 , 40 , 79 ], genetic techniques [ 51 ], conventional histology [ 91 ], and brain weight measurement [ 61 ] were used to uncover underlying mechanisms and identify brain tissue markers in these cases. Moreover, one study suggested an optimal neuropathologic examination protocol for these deaths in a medico-legal setting [ 66 ].
Other research themes were rarely addressed (< 5% each). Neurodegenerative diseases in medico-legal settings were approached using immunotechniques [ 128 , 143 , 144 ], image analysis [ 129 ], or a combination of several methods [ 104 , 112 ]. As for suicide, immunotechniques [ 32 , 89 ], genetic techniques [ 62 , 88 ], and brain weight measurement [ 146 ] were applied to identify factors that differentiate suicide victims from controls. Brain tissue markers of hypothermia and hyperthermia were studied by means of immunotechniques [ 78 , 140 , 145 ] and genetic techniques [ 60 ]. Studies that aimed to improve the estimation of postmortem interval were mainly based on immunotechniques [ 42 , 92 ] and genetic techniques [ 134 ]. Asphyxia and brain hypoxia [ 35 , 77 , 108 ], brain edema [ 36 , 37 , 96 ], brain tissue identification [ 95 , 121 , 122 ], drowning [ 34 , 71 ], and sudden unexpected death in epilepsy [ 63 , 149 ] were addressed in two to three individual studies each.
One article studied the markers of traumatic brain injury and mechanical asphyxiation using genetic techniques [ 49 ], while another focused on the potential markers of hypothermia, hyperthermia, and intoxication using immunotechniques and genetic techniques [ 59 ]. Finally, the following entities had one study each: sudden unexplained nocturnal death syndrome [ 46 ], pediatric subdural hemosiderin deposits [ 56 ], iron in fetal and infant leptomeninges [ 80 ], DNA identification based on brain tissue swab [ 76 ], zinc in brain tissue [ 90 ], intracranial aneurysms and dissections [ 101 ], age estimation [ 103 ], electrocution [ 124 ], insulin homicide [ 131 ], fire fatalities [ 137 ], phosphine poisoning [ 93 ], and carbon monoxide poisoning [ 142 ].
Main findings
This scoping review identified 122 original articles on forensic neuropathology from the years 2010–2022. Only 3–17 articles were published per year globally. Most articles originated from the Europe and Asia and were published in forensic journals. A median sample included 57 subjects aged between 16 and 80 years. The most common research theme was traumatic intracranial injury, followed by anatomy and substance abuse. Main methods included immunotechniques and macroscopic observation. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this is the first scoping review to systematically explore literature on forensic neuropathology over the past decade.
Meta-level considerations
The annual volume of research output was relatively low, which may indicate rather mild research activity in the field globally. It is obvious that breakthroughs will require consistent scientific effort and active involvement of forensic pathologists in research projects. Clinical neuropathology may have outpowered the forensic branch, possibly due to stronger translational potential and active interplay with clinicians [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]. Neuropathology is an interdisciplinary field, touching upon neighboring fields such as neurology, neurosurgery, psychiatry, legal medicine, and general pathology. Forensic neuropathology is aligned in the midway between clinical and forensic pathology, often requiring particular expertise from a general forensic pathologist [ 22 ]. Interdisciplinary cooperation may thus be the key to increasing research activity in the field.
Articles were widely distributed between journals of various disciplines, which underlines the intersectoral nature of the field. In general, articles were published in international, field-specific journals with a median impact factor of 2.3. However, it is noteworthy that over a tenth of the articles were published in journals with no impact factor whatsoever; anatomic reports appeared to be overrepresented in this subgroup. As for geographical distribution, the vast majority of articles were from European and Asian researchers. Notably, articles from American groups were less common, and only two African articles were published over the entire review period. In order to expedite the development and implementation of forensic neuropathology globally, research input is needed from medico-legal units across the world. Unfortunately, achieving this objective may prove difficult due to resource- and policy-related barriers. It would be important to ensure sufficient personnel resources, methodological expertise, access to research funding, and comprehensible research permit policies for medico-legal data.
Sample-related considerations
Sample sizes were moderate, with a median of 57 subjects; this included both cases and potential controls. Two articles appeared to lack a clear indication of sample size. Despite the relatively small sample sizes, statistical power calculations were rarely presented. In quantitative studies, power calculations guide sample collection and corroborate the statistical approach [ 152 ]. Of note is also the fact that over a half of the studies did not have a control group, which implies that most articles were descriptive in nature. A comparative design is a prerequisite for many scientifically relevant conclusions [ 153 ].
Age ranges were generally wide, which increased the generalizability of findings across age groups. However, taking into account the moderate sample sizes, the level of heterogeneity within samples may significantly increase with widening age spans. Over a quarter of studies appeared to lack a clear statement of the minimum and maximum ages of the sample; some reported standard deviations and interquartile ranges instead.
Research themes, methods, and future directions
Traumatic intracranial injury was the most common research theme. Research activity around the topic is easy to comprehend as traumatic brain injury and intracranial hemorrhages are complex and deadly entities that often present themselves to a forensic pathologist [ 2 , 21 ]. As neuropathology may have a pivotal role in a cause-of-death investigation [ 3 ] or legal proceedings [ 25 , 26 ], novel tools are needed to identify traumatic changes and estimate the age of injury. However, significant breakthroughs are yet to come.
Alongside traumatic intracranial injury, the top-three research themes included anatomy and substance abuse. Somewhat surprisingly, macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of intracranial structures were among the most popular research themes. Many of these studies reported important findings for neurosurgeons, for example, but appeared to make a minor contribution to the field of forensic neuropathology. Substance abuse, which indeed is a central medico-legal entity [ 154 ], was approached from a variety of perspectives method- and substance-wise. However, more research input will be needed to identify substance-specific markers in brain tissue and differentiate substance abuse and intoxication from other causes of death.
Neurodegenerative diseases were addressed in a handful of studies. In spite of the vast research activity in clinical neuropathology, studies in medico-legal samples are also important, as neurodegenerative diseases appear to increase the risk of unnatural deaths [ 155 ]. Providing medico-legal units with diagnostic methods that have been validated in medico-legal samples will be of utmost importance. As for sudden unexplained deaths among infants and children, studies have kept chasing potential mechanisms and biomarkers, but again, significant breakthroughs are yet to come.
Although suicide is a major and diverse entity in forensic pathology [ 156 ], only a few studies addressed the topic. Considering the obscurity behind predisposing and underlying factors, there should be a lot to achieve mechanism- and prevention-wise. Medico-legal samples may have significant translational potential in this regard. Moreover, only a few studies addressed asphyxia, drowning, hypothermia, hyperthermia, sudden unexpected death in epilepsy, and estimation of postmortem interval. Higher research activity should be directed toward these themes in order to improve postmortem diagnostics.
Immunotechniques, i.e., immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting, were commonly applied to detect potential changes in brain tissue. Genetic techniques were exploited in various approaches such as brain tissue identification and gene expression analysis. A minority of studies used conventional histology as the main method. Although a number of novel findings were reported, most were of preliminary nature and will require further validation. Macroscopic observation of intracranial structures was a common method, but the studies often merely described injury patterns or anatomic variations. The crude measurement of brain weight was also used in some studies, but these often had null findings.
Limitations of the review
This scoping review had several limitations that should be considered. First, the scope of the literature search was notably broad, and conventional search terms were covered. However, articles that used specific or uncommon terminology may have been omitted. A large number of initial hits were obtained and manually evaluated, which may have reduced the risk of omitting in-scope articles. Second, as the review focused on original articles, emerging research themes may not have been fully covered. Moreover, there is a large body of research that may not be captured in this review even though it is relevant to forensic neuropathologists (e.g., CNS infections and emerging concepts in neurodegenerative diseases). Future reviews are expected to cover these aspects. Finally, as the aim was to explore and summarize original research in the field, there were no particular restrictions on scientific rigor, and no formal bias assessment was performed.
This scoping literature review explored original research on forensic neuropathology over the years 2010–2022. A total of 122 original articles were eventually included in the synthesis. Traumatic intracranial injury was the most common research theme, immunotechniques being the most commonly applied method. Only 3–17 articles were published per year globally. Although a number of novel findings were reported, most were of preliminary nature and will require further validation. In order to reach breakthroughs and validate novel tools for routine use, more research input is urged in forensic neuropathology from researchers across the world. Interdisciplinary cooperation may be the key to increasing research activity in the field. Researchers should ensure appropriate sample sizes and make use of comparative designs whenever possible.
Knowledge of diseases and trauma related to the central nervous system has high value in forensic pathology
This scoping review explored literature on forensic neuropathology from 2010 to 2022
A total of 122 original articles were included, corresponding to 3–17 publications per year globally
4.The most common research theme was traumatic intracranial injury (24.6%), followed by anatomy (12.3%) and substance abuse (11.5%). Key methods included immunotechniques (31.1%) and macroscopic observation (21.3%)
To reach breakthroughs and validate tools for routine practice, more research input is needed from researchers across the world
Availability of data and material
This is a review of published literature. The dataset generated and analysed during the study is presented in Supplementary Table 1 .
Code availability
Not applicable.
GBD 2016 Neurology Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:459–80.
Rubiano AM, Carney N, Chesnut R, Puyana JC. Global neurotrauma research challenges and opportunities. Nature. 2015;527:S193–7.
Kalimo H, Saukko P, Graham D. Neuropathological examination in forensic context. Forensic Sci Int. 2004;146:73–81.
Bruner JM, Louis DN, McLendon R, Rosenblum MK, Archambault WT, Most S, et al. The utility of expert diagnosis in surgical neuropathology: Analysis of consultations reviewed at 5 national comprehensive cancer network institutions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2017;76:189–94.
Iacono D, Geraci-Erck M, Peng H, Bouffard JP. Symmetric bihemispheric postmortem brain cutting to study healthy and pathological brain conditions in humans. J Vis Exp. 2016;118:54602.
Trejo-Lopez JA, Yachnis AT, Prokop S. Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotherapeutics. 2022;19:173–85.
Kon T, Tomiyama M, Wakabayashi K. Neuropathology of Lewy body disease: Clinicopathological crosstalk between typical and atypical cases. Neuropathology. 2020;40:30–9.
Koga S, Sekiya H, Kondru N, Ross OA, Dickson DW. Neuropathology and molecular diagnosis of synucleinopathies. Mol Neurodegener. 2021;16:83.
Lassmann H. The contribution of neuropathology to multiple sclerosis research. Eur J Neurol. 2022;29:2869–2877.
Clark HB. The neuropathology of autoimmune ataxias. Brain Sci. 2022;12:257.
Fetit R, Hillary RF, Price DJ, Lawrie SM. The neuropathology of autism: A systematic review of post-mortem studies of autism and related disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;129:35–62.
Cole BL. Neuropathology of pediatric brain tumors: A concise review. Neurosurgery. 2022;90:7–15.
von Spreckelsen N, Kesseler C, Brokinkel B, Goldbrunner R, Perry A, Mawrin C. Molecular neuropathology of brain-invasive meningiomas. Brain Pathol. 2022;32:e13048.
Seilhean D. Infections of the central nervous system: Neuropathology. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2019;175:431–5.
Maiese A, Manetti AC, Bosetti C, del Duca F, la Russa R, Frati P, et al. SARS-CoV-2 and the brain: A review of the current knowledge on neuropathology in COVID-19. Brain Pathol. 2021;31:e13013.
Mavroudis I, Kazis D, Chowdhury R, Petridis F, Costa V, Balmus I-M, et al. Post-concussion syndrome and chronic traumatic encephalopathy: Narrative review on the neuropathology, neuroimaging and fluid biomarkers. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12:740.
Zhang L, Lucassen PJ, Salta E, Verhaert PDEM, Swaab DF. Hippocampal neuropathology in suicide: Gaps in our knowledge and opportunities for a breakthrough. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022;132:542–52.
Patodia S, Somani A, Thom M. Review: Neuropathology findings in autonomic brain regions in SUDEP and future research directions. Auton Neurosci. 2021;235:102862.
McGuone D, Crandall LG, Devinsky O. Sudden unexplained death in childhood: A neuropathology review. Front Neurol. 2020;11:582051.
Zwirner J, Kulakofsky R, Fitzek A, Schröder AS, Bohnert S, Franke H, et al. Forensic biomarkers of lethal traumatic brain injury. Int J Legal Med. 2022;136:871–86.
Bertozzi G, Maglietta F, Sessa F, Scoto E, Cipolloni L, di Mizio G, et al. Traumatic brain injury: A forensic approach: A literature review. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18:538–50.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Stewart W, Black M, Kalimo H, Graham DI. Non-traumatic forensic neuropathology. Forensic Sci Int. 2004;146:125–47.
Balestrini S, Iacono D, Devinsky O, Mcguone D, Crandall LG. Sudden unexplained death in childhood: A neuropathology review. Front Neurol. 2020;11:582051.
MacKenzie JM. Examining the decomposed brain. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2014;35:265–70.
Kresak JL, Zehe S, Reichard RR. What every neuropathologist needs to know: Neuropathology and the US legal system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2019;78:291–3.
Whitwell H, Milroy C, du Plessis D. Forensic Neuropathology. 2nd Ed. London: CRC Press; 2021.
Book Google Scholar
Pham MT, Rajić A, Greig JD, Sargeant JM, Papadopoulos A, Mcewen SA. A scoping review of scoping reviews: Advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Res Synth Methods. 2014;5:371–85.
Munn Z, Peters MDJ, Stern C, Tufanaru C, McArthur A, Aromataris E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18:143.
Peters MDJ, Godfrey CM, Khalil H, McInerney P, Parker D, Soares CB. Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2015;13:141–6.
Aghakhani K, Heidari M, Ameri M, Mehrpisheh S, Memarian A. Characteristics of traumatic brain injury among accident and falling down cases. Acta Med Iran. 2015;53:652–5.
PubMed Google Scholar
Al-Sarraj S, Fegan-Earl A, Ugbade A, Bodi I, Chapman R, Poole S, et al. Focal traumatic brain stem injury is a rare type of head injury resulting from assault: A forensic neuropathological study. J Forensic Leg Med. 2012;19:144–51.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Alvarado-Esquivel C, Mendoza-Larios LA, García-Dolores F, Sánchez-Anguiano LF, Antuna-Salcido EI, Hernández-Tinoco J, et al. Association between Toxoplasma gondii infection in brain and a history of depression in suicide decedents: A cross-sectional study. Pathogens. 2021;10:1313.
Ambrose N, Waters KA, Rodriguez ML, Bailey K, Machaalani R. Neuronal apoptosis in the brainstem medulla of sudden unexpected death in infancy (SUDI), and the importance of standardized SUDI classification. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2018;14:42–56.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
An J-L, Ishida Y, Kimura A, Kondo T. Immunohistochemical examination of intracerebral aquaporin-4 expression and its application for differential diagnosis between freshwater and saltwater drowning. Int J Legal Med. 2011;125:59–65.
Bartschat S, Fieguth A, Könemann J, Schmidt A, Bode-Jänisch S. Indicators for acute hypoxia-An immunohistochemical investigation in cerebellar Purkinje-cells. Forensic Sci Int. 2012;223:165–70.
Bauer M, Deigendesch N, Wittig H, Scheurer E, Lenz C. Tissue sample analysis for post mortem determination of brain edema. Forensic Sci Int. 2021;323:110808.
Bauer M, Gerlach K, Scheurer E, Lenz C. Analysis of different post mortem assessment methods for cerebral edema. Forensic Sci Int. 2020;308:110164.
Bohnert S, Georgiades Kosmas, ·, Monoranu C-M, Bohnert · Michael, Büttner A, Ondruschka B. Quantitative evidence of suppressed TMEM119 microglial immunohistochemistry in fatal morphine intoxications. Int J Legal Med. 2021;135:2315–22.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bohnert S, Seiffert A, Trella S, Bohnert M, Distel L, Ondruschka B, et al. TMEM119 as a specific marker of microglia reaction in traumatic brain injury in postmortem examination. Int J Legal Med. 2020;134:2167–76.
Bright FM, Byard RW, Vink R, Paterson DS. Medullary serotonin neuron abnormalities in an Australian cohort of sudden infant death syndrome. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2017;76:864–73.
Bruno-Mascarenhas MA, Ramesh VG, Venkatraman S, Mahendran J v., Sundaram S. Microsurgical anatomy of the superior sagittal sinus and draining veins. Neurol India. 2017;65:794–800.
Campell ZK, Kwon I, Finley SJ, Lee Y, Javan GT. Talin: A potential protein biomarker in postmortem investigations. J Forensic Leg Med. 2016;44:188–91.
Castellani RJ, Smith M, Bailey K, Perry G, Dejong JL. Neuropathology in consecutive forensic consultation cases with a history of remote traumatic brain injury. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;72:683–91.
Cavdar S, Solmaz B, Tanis Ö, Guler O, Dalcik H, Aydogmus E, et al. Anatomic variations of the human falx cerebelli and its association with occipital venous sinuses. Br J Neurosurg. 2021;35:306–12.
Chatzopoulos K, Treeck B van, Venable E, Serla V, Wirth T, Amirahmadi F, et al. Formalin pigment artifact deposition in autopsy tissue: predisposing factors, patterns of distribution and methods for removal. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2020;16:435–41.
Chen Z, Mu J, Chen X, Dong H. Sudden unexplained nocturnal death syndrome in Central China (Hubei): A 16-year retrospective study of autopsy cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:1–6.
Cheshire EC, Biggs MJP, Hollingbury FE, Fitzpatrick-Swallow VL, Prickett TRA, Malcomson RDG. Frequency of macroscopic intradural hemorrhage with and without subdural hemorrhage in early childhood autopsies. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2019;15:184–90.
Chindemi C, Cirielli V, Cima L, Danzi O, Raniero D, Tagliaro F, et al. Autophagy pathways in drug abusers after forensic autopsy: LC3B, ph-mTOR and p70S6K analysis. Med Sci Law. 2019;59:49–56.
Chung U, Seo J-S, Kim Y-H, Hoon Son G, Hwang J-J. Quantitative analyses of postmortem heat shock protein mRNA profiles in the occipital lobes of human cerebral cortices: Implications in cause of death. Mol Cells. 2012;34:473–80.
Cirielli V, Cima L, Chindemi C, Danzi O, Ghimenton C, Eccher A, et al. Cortical expression of the polysialylated isoform of the neural cell adhesion molecule on brain tissue to recognize drug-related death. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2018;39:8–13.
Danusso R, Alfonsi G, Ferrero S, Lavezzi AM, Lattuada D. Mitochondrial DNA content: A new potential biomarker for sudden infant death syndrome. Pediatr Res. 2022;92:1282–1287.
Darke S, Duflou J, Forensic Pathologist C, Torok M, Officer R, Prolov T, et al. Toxicology, circumstances and pathology of deaths from acute alcohol toxicity. J Forensic Leg Med. 2013;20:1122–5.
Darke S, Lappin J, Kaye S, Duflou J. Clinical characteristics of fatal methamphetamine-related stroke: A national study. J Forensic Sci. 2018;63:735–9.
Davceva N, Janevska V, Ilievski B, Petrushevska G, Popeska Z. The occurrence of acute subdural haematoma and diffuse axonal injury as two typical acceleration injuries. J Forensic Leg Med. 2012;19:480–4.
Davceva N, Janevska V, Ilievski B, Spasevska J, Jovanovic R. The importance of the detail forensic-neuropathological examination in the determination of the diffuse brain injuries. Soud Lek. 2012;57:2–6.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
del Bigio MR, Phillips SM. Retroocular and subdural hemorrhage or hemosiderin deposits in pediatric autopsies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2017;76:313–22.
Delteil C, Kolopp M, Capuani C, Humez S, Boucekine M, Leonetti G, et al. Histological dating of subarachnoid hemorrhage and retinal hemorrhage in infants. Forensic Sci Int. 2019;303:109952.
Delteil C, Humez S, Boucekine M, Jouvet A, Hedouin V, Fanton L, et al. Histological dating of subdural hematoma in infants. Int J Legal Med. 2019;133:539–46.
Du SH, Tan XH, Zhao R, Zhao D, Xue Y, Wang HJ, et al. Molecular pathology of cerebral TNF-α, IL-1β, iNOS and Nrf2 in forensic autopsy cases with special regard to deaths due to environmental hazards and intoxication. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2017;13:409–16.
Du Y, Xu J-T, Jin H-N, Zhao R, Zhao D, Du S-H, et al. Increased cerebral expressions of MMPs, CLDN5, OCLN, ZO1 and AQPs are associated with brain edema following fatal heat stroke. Sci Rep. 2017;7:1691.
Elliott JA, Vink R, Jensen L, Byard RW. Brain weight-body weight ratio in sudden infant death syndrome revisited. Med Sci Law. 2012;52:207–9.
Erbay L, Karhdag R, Oruc M, Cigremis Y, Celbis O. Association of BDNF/TRKB and NGF/TRKA levels in postmortem brain with major depression and suicide. Psychiatr Danub. 2021;33:491–8.
Esen Melez İ, Arslan M, Melez D, Şanli AN, Koç S. Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy: A retrospective autopsy study of 112 epileptic patients. Arch Neuropsychiatry. 2017;54:225–33.
Florou C, Zorilă A, Zorilă M, Marinescu M, Andrei C, Păvăloiu R, et al. Clinico-statistical and morphological aspects of severe traumatic brain injuries. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2016;57:391–400.
Flugt A, Frost L, Søndergaard C, Milidou I. Lethal abusive head trauma in infancy in Denmark from 2000 to 2011. Dan Med J. 2021;68:AO8200604.
Google Scholar
Folkerth RD, Nunez J, Georgievskaya Z, McGuone D. Neuropathologic examination in sudden unexpected deaths in infancy and childhood: Recommendations for highest diagnostic yield and cost-effectiveness in forensic settings. Acad Forensic Pathol. 2017;7:182–99.
Funabashi KS, Barcelos D, Visoná I, e Silva SM, Almeida ML, e Sousa PO, et al. DNA extraction and molecular analysis of non-tumoral liver, spleen, and brain from autopsy samples: The effect of formalin fixation and paraffin embedding. Pathol Res Pract. 2012;208:584–91.
García Corredor N, Forero Porras P, Ballesteros Acuña L. Morphological evaluation of the distal medial striated artery. A study with cadaverous material. Colomb Med (Cali). 2020;51:e204440.
Gholamzadeh S, Zarenezhad M, Montazeri M, Zareikordshooli M, Sadeghi G, Malekpour A, et al. Statistical analysis of organ morphometric parameters and weights in South Iranian adult autopsies. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96:e6447.
Gielda L, Rigg S. Extraction of amplifiable DNA from embalmed human cadaver tissue. BMC Res Notes. 2017;10:737.
Girela-López E, Beltran-Aroca CM, Dye A, Gill JR. Epidemiology and autopsy findings of 500 drowning deaths. Forensic Sci Int. 2022;330:111137.
Hanson E, Ballantyne J. Human organ tissue identification by targeted RNA deep sequencing to aid the investigation of traumatic injury. Genes (Basel). 2017;8:319.
Haque MA, Khalil M, Khalil M, Sultana SZ, Mannan S, Rahman M, et al. Morphometry of Purkinje cell body of cerebellum in Bangladeshi cadaver. Mymensingh Med J Bangladesh. 2010;19:504–9.
CAS Google Scholar
Haque MA, Khalil M, Sultana SZ, Mannan S, Uddin MM, Hossain M, et al. Morphometric study of dentate nucleus of cerebellum in Bangladeshi cadaver. Mymensingh Med J Bangladesh. 2015;24:25–33.
Hashemi R, Mahmoodi R, Amirjamshidi A. Variations in the anatomy of the Willis’ circle: A 3-year cross-sectional study from Iran (2006–2009). Are the distributions of variations of circle of Willis different in different populations? Result of an anatomical study and review of literature. Surg Neurol Int. 2013;4:65.
Helm K, Matzenauer C, Neuhuber F, Monticelli F, Meyer H, Pittner S, et al. Suitability of specific soft tissue swabs for the forensic identification of highly decomposed bodies. Int J Legal Med. 2021;135:1319–27.
Hu Y, Tian L, Ma K, Han L, Li W, Hu L, et al. ER stress-related protein, CHOP, may serve as a biomarker of mechanical asphyxia: a primary study. Int J Legal Med. 2022;136:1091–104.
Ishikawa T, Yoshida C, Michiue T, Große Perdekamp M, Pollak S, Maeda H. Immunohistochemistry of catecholamines in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system with special regard to fatal hypothermia and hyperthermia. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2010;12:121–7.
Jack E, Haas E, Haddix TL. Evaluation of the presence and distribution of leptomeningeal inflammation in SIDS/SUDI cases and comparison with a hospital-based cohort. Childs Nerv Syst. 2019;35:2391–7.
Jack E, Fennelly NK, Haddix T. The inflammatory cellular constituents of foetal and infant leptomeninges: A survey of hospital-based autopsies without trauma. Childs Nerv Syst. 2014;30:911–7.
Johnson MM, David JA, Michelhaugh SK, Schmidt CJ, Bannon MJ. Increased heat shock protein 70 gene expression in the brains of cocaine-related fatalities may be reflective of postdrug survival and intervention rather than excited delirium. J Forensic Sci. 2012;57:1519–23.
Karayel F, Turan A, Sav A, Pakis I, Akyildiz E, Ersoy G. Methanol intoxication. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2010;31:34–6.
Article Google Scholar
Kibayashi K, Shimada R, Nakao KI, Ro A. Analysis of pituitary lesions in fatal closed head injury. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2012;33:206–10.
Kinney HC, Cryan JB, Haynes RL, Paterson DS, Haas EA, Othon, et al. Dentate gyrus abnormalities in sudden unexplained death in infants: Morphological marker of underlying brain vulnerability. Acta Neuropathol. 2015;129:65–80.
Kobek M, Jankowski Z, Szala J, Gąszczyk-Ozarowski Z, Pałasz A, Skowronek R. Time-related morphometric studies of neurofilaments in brain contusions. Folia Neuropathol. 2016;54:50–8.
Krohn M, Drebler J, Bauer M, Schober K, Franke H, Ondruschka B. Immunohistochemical investigation of S100 and NSE in cases of traumatic brain injury and its application for survival time determination. J Neurotrauma. 2015;32:430–40.
Krywanczyk A, Bundock EA. Quantifying macrophages and hemosiderin in pediatric dura mater. J Forensic Sci. 2018;63:902–5.
Krzyzanowska M, Steiner J, Karnecki K, Kaliszan M, Brisch R, Wiergowski M, et al. Decreased ribosomal DNA transcription in dorsal raphe nucleus neurons differentiates between suicidal and non-suicidal death. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2016;266:217–24.
Kurtulus Dereli A, Demırci GN, Dodurga Y, Özbal S, Cankurt U, Boz B, et al. Evaluation of human pineal gland acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase immunoreactivity in suicide: A preliminary study. Med Sci Law. 2018;58:233–8.
Lech T, Sadlik J. Zinc in postmortem body tissues and fluids. Biol Trance Elem Res. 2011;142:11–7.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Leitner DF, McGuone D, William C, Faustin A, Askenazi M, Snuderl M, et al. Blinded review of hippocampal neuropathology in sudden unexplained death in childhood reveals inconsistent observations and similarities to explained paediatric deaths. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2022;e12746.
Lesnikova I, Schreckenbach MN, Kristensen MP, Papanikolaou LL, Hamilton-Dutoit S. Usability of immunohistochemistry in forensic samples with varying decomposition. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2018;39:185–91.
Liang Y, Tong F, Huang F, Liu Y, Zhu L, le Grange JM, et al. Pathological changes induced by phosphine poisoning: A study on 8 children. Int J Legal Med. 2020;134:217–28.
Lier J, Ondruschka B, Bechmann I, Dreßler J. Fast microglial activation after severe traumatic brain injuries. Int J Legal Med. 2020;134:2187–93.
Lindenbergh A, van den Berge M, Oostra R-J, Cleypool C, Bruggink A, Kloosterman A, et al. Development of a mRNA profiling multiplex for the inference of organ tissues. Int J Legal Med. 2013;127:891–900.
Lundesgaard Eidahl JM, Opdal SH, Rognum TO, Stray-Pedersen A. Postmortem evaluation of brain edema: An attempt with measurements of water content and brain-weight-to-inner-skull-circumference ratio. J Forensic Leg Med. 2019;64:1–6.
Matoba K, Hyodoh H, Murakami M, Matoba T, Saito A, Feng F, et al. Freezing preparation for macroscopic forensic investigation in putrefied brain. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2017;26:6–10.
Mehrpour O, Sheikhazadi A, Hasan Ghadyani M, Hooshyar H. Brain weight of Iranian population; The first report. J Forensic Leg Med. 2010;17:426–31.
Mohd Saman SA, Jothee S, Nor FM, Shafie MS. The pattern of injuries among motorcyclists in fatal road traffic accidents: An autopsy-based study. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2021;42:141–6.
Molina D, Vance K, Coleman M, Hargrove V. Testing an age-old adage: Can autopsy findings be of assistance in differentiating opioid versus cardiac deaths? J Forensic Sci. 2020;65:112–6.
Mori S, Takahashi S, Hayakawa A, Saito K, Takada A, Fukunaga T. Fatal intracranial aneurysms and dissections causing subarachnoid hemorrhage: An epidemiological and pathological analysis of 607 legal autopsy cases. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018;27:486–93.
Mubbunu L, Bowa K, Petrenko V, Silitongo M. Correlation of internal organ weights with body weight and body height in normal adult Zambians: A case study of Ndola Teaching Hospital. Anat Res Int. 2018;2018:4687538.
Naue J, Sänger T, Hoefsloot HCJ, Lutz-Bonengel S, Kloosterman AD, Verschure PJ. Proof of concept study of age-dependent DNA methylation markers across different tissues by massive parallel sequencing. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2018;36:152–9.
Nishida N, Yoshida K, Hata Y, Arai Y, Kinoshita K. Pathological features of preclinical or early clinical stages of corticobasal degeneration: a comparison with advanced cases. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2015;41:893–905.
Nyasa C, Mwakikunga A, Tembo LH, Dzamalala C, Ihunwo AO. Anatomical variations and morphometric properties of the circulus arteriosus cerebri in a cadaveric Malawian population. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2021;80:820–6.
Oerter S, Förster C, Bohnert M. Validation of sodium/glucose cotransporter proteins in human brain as a potential marker for temporal narrowing of the trauma formation. Int J Legal Med. 2019;133:1107–14.
Olczak M, Poniatowski Ł, Kwiatkowska M, Samojłowicz D, Tarka S, Wierzba-Bobrowicz T. Immunolocalization of dynein, dynactin, and kinesin in the cerebral tissue as a possible supplemental diagnostic tool for traumatic brain injury in postmortem examination. Folia Neuropathol. 2019;57:51–62.
Olczak M, Chutorański D, Kwiatkowska M, Samojłowicz D, Tarka S, Wierzba-Bobrowicz T. Bystin (BYSL) as a possible marker of severe hypoxic-ischemic changes in neuropathological examination of forensic cases. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2018;14:26–30.
Pelletier DE, Andrew TA. Common findings and predictive measures of opioid overdoses. Acad Forensic Pathol. 2017;7:91–8.
Pelletti G, Garagnani M, Barone R, Boscolo-Berto R, Rossi F, Morotti A, et al. Validation and preliminary application of a GC–MS method for the determination of putrescine and cadaverine in the human brain: a promising technique for PMI estimation. Forensic Sci Int. 2019;297:221–7.
Preusse-Prange A, Modrow J-H, Schwark T, von Wurmb-Schwark N. Detection of constitutive and inducible HSP70 proteins in formalin fixed human brain tissue. Forensic Sci Int. 2014;235:62–7.
Priemer DS, Folkerth RD. Dementia in the forensic setting: Diagnoses obtained using a condensed protocol at the Office of Chief Medical Examiner, New York City. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2021;80:724–30.
Rao M, Singh D, Vashista R, Sharma S. Dating of acute and subacute subdural haemorrhage: A histo-pathological study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10:HC01–7.
Rebollo-Soria MC, Arregui-Dalmases C, Sánchez-Molina D, Velázquez-Ameijide J, Galtés I. Injury pattern in lethal motorbikes-pedestrian collisions, in the area of Barcelona, Spain. J Forensic Leg Med. 2016;43:80–4.
Romero Tirado M, Pampin JMB, Gómez RG. Dating of traumatic brain injury in forensic cases using immunohistochemical markers (I): Neurofilaments and β-amyloid precursor protein. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2018;39:201–7.
Rungruangsak K, Poriswanish N. Pathology of fatal diffuse brain injury in severe non-penetrating head trauma. J Forensic Leg Med. 2021;82:102226.
Sadat-Shirazi MS, Soltani H, Nikpour N, Haghshenas M, Khalifeh S, Mokri A, et al. Alteration of orexin-A and PKCα in the postmortem brain of pure-opioid and multi-drug abusers. Neuropeptides. 2020;83:102074.
Sadat-Shirazi M-S, Zarrindast M-R, Ashabi G. Oxidative stress enzymes are changed in opioid abusers and multidrug abusers. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;72:365–8.
Sadat-Shirazi MS, Zarrindast MR, Daneshparvar H, Ziaie A, Fekri M, Abbasnezhad E, et al. Alteration of dopamine receptors subtypes in the brain of opioid abusers: A postmortem study in Iran. Neurosci Lett. 2018;687:169–76.
Sakai K, Fukuda T, Iwadate K. Immunohistochemical analysis of the ubiquitin proteasome system and autophagy lysosome system induced after traumatic intracranial injury: Association with time between the injury and death. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2014;35:38–44.
Samsuwan J, Muangsub T, Yanatatsaneejit P, Mutirangura A, Kitkumthorn N. Combined bisulfite restriction analysis for brain tissue identification. Forensic Sci Int. 2018;286:42–5.
Sauer E, Extra A, Caché P, Courts C. Identification of organ tissue types and skin from forensic samples by microRNA expression analysis. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2017;28:99–110.
Schober K, Ondruschka B, Dreßler J, Abend M. Detection of hypoxia markers in the cerebellum after a traumatic frontal cortex injury: A human postmortem gene expression analysis. Int J Legal Med. 2015;129:701–7.
Shaha KK, Joe AE. Electrocution-related mortality: A retrospective review of 118 deaths in Coimbatore, India, between January 2002 and December 2006. Med Sci Law. 2010;50:72–4.
Sheikhazadi A, Shahabeddin Sadr S, Hasan Ghadyani M, Kazem Taheri S, Asghar Manouchehri A, Nazparvar B, et al. Study of the normal internal organ weights in Tehran’s population. J Forensic Leg Med. 2010;17:78–83.
Siddiqi H, Tahir M, Lone K. Variations in cerebral arterial circle of Willis in adult Pakistani population. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2013;23:615–9.
Sultana N, Khalil M, Khan MK, Kabir A, Farjan S, Ismatsara M, et al. Variation in the position and diameter of basilar artery in different ages of Bangladeshi people. Mymensingh Med J. 2018;27:504–7.
Takayama M, Kashiwagi M, Matsusue A, Waters B, Hara K, Ikematsu N, et al. Quantification of immunohistochemical findings of neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaques for a diagnosis of dementia in forensic autopsy cases. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2016;22:82–9.
Takayama M, Kashiwagi M, Matsusue A, Waters B, Hara K, Ikematsu N, et al. Quantification of neuropathological findings by image data for the diagnosis of dementia in forensic autopsy cases. J Med Invest. 2016;63:114–8.
Tolescu S, Zorila M, Serbanescu M, Kamal K, Zorila G, Dumitru I, et al. Severe traumatic brain injury (TBI)-A seven-year comparative study in a Department of Forensic Medicine. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2020;61:95–103.
Tong F, Wu R, Huang W, Yang Y, Zhang L, Zhang B, et al. Forensic aspects of homicides by insulin overdose. Forensic Sci Int. 2017;278:9–15.
Trautz F, Franke H, Bohnert S, Hammer N, Müller W, Stassart R, et al. Survival-time dependent increase in neuronal IL-6 and astroglial GFAP expression in fatally injured human brain tissue. Sci Rep. 2019;9:11771.
Trautz F, Dreßler J, Stassart R, Müller W, Ondruschka B. Proposals for best-quality immunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded brain tissue slides in forensics. Int J Legal Med. 2018;132:1103–9.
van den Berge M, Wiskerke D, Gerretsen R, Tabak J, Sijen T. DNA and RNA profiling of excavated human remains with varying postmortem intervals. Int J Legal Med. 2016;130:1471–80.
Vasović L, Trandafilović M, Jovanović I, Ugrenović S, Vlajković S. Vertebral and/or basilar dolichoectasia in human adult cadavers. Acta Neurochir. 2012;154:1477–88.
Wang Q, Ishikawa T, Michiue T, Zhu B-L, Guan D-W, Maeda H. Molecular pathology of brain matrix metalloproteases, claudin5, and aquaporins in forensic autopsy cases with special regard to methamphetamine intoxication. Int J Legal Med. 2014;128:469–74.
Wang Q, Ishikawa T, Michiue T, Zhu B-L, Guan D-W, Maeda H. Molecular pathology of brain edema after severe burns in forensic autopsy cases with special regard to the importance of reference gene selection. Int J Legal Med. 2013;127:881–9.
Wang Q, Ishikawa T, Michiue T, Zhu B-L, Guan D-W, Maeda H. Stability of endogenous reference genes in postmortem human brains for normalization of quantitative real-time PCR data: Comprehensive evaluation using geNorm, NormFinder, and BestKeeper. Int J Legal Med. 2012;126:943–52.
Wang Q, Ishikawa T, Michiue T, Zhu B-L, Guan D-W, Maeda H. Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of human brain basic fibroblast growth factor, glial fibrillary acidic protein and single-stranded DNA expressions following traumatic brain injury. Forensic Sci Int. 2012;221:142–51.
Wang Q, Ishikawa T, Michiue T, Zhu B-L, Guan D-W, Maeda H. Evaluation of human brain damage in fatalities due to extreme environmental temperature by quantification of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), S100b and single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) immunoreactivities. Forensic Sci Int. 2012;219:259–64.
Wong B, Ong BB, Milne N. The source of haemorrhage in traumatic basal subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Forensic Leg Med. 2015;29:18–23.
Yarid NA, Harruff RC. Globus pallidus necrosis unrelated to carbon monoxide poisoning: Retrospective analysis of 27 cases of basal ganglia necrosis. J Forensic Sci. 2015;60:1484–7.
Yoshida K, Hata Y, Ichimata S, Nishida N. Tau and amyloid-β pathology in Japanese forensic autopsy series under 40 years of age: Prevalence and association with APOE genotype and suicide risk. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;72:641–52.
Yoshida K, Hata Y, Kinoshita K, Takashima S, Tanaka K, Nishida N. Incipient progressive supranuclear palsy is more common than expected and may comprise clinicopathological subtypes: A forensic autopsy series. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;133:809–23.
Yoshida C, Ishikawa T, Michiue T, Quan L, Maeda H. Postmortem biochemistry and immunohistochemistry of chromogranin A as a stress marker with special regard to fatal hypothermia and hyperthermia. Int J Legal Med. 2011;125:11–20.
Zedler B, Flaig B, Ackermann H, Parzeller M, Bratzke H. Brain weight in completed suicide and other cases of death-comparison of recent and previous studies. Int J Legal Med. 2014;128:295–301.
Zhang Z, Gong Q, Feng X, Zhang D, Quan L. Astrocytic clasmatodendrosis in the cerebral cortex of methamphetamine abusers. Forensic Sci Res. 2017;2:139–44.
Zhang H, Zhang P, Ma K, Lv Y, Li W, Luo C, et al. The selection of endogenous genes in human postmortem tissues. Sci Justice. 2013;53:115–20.
Zhuo L, Zhang Y, Zielke HR, Levine B, Zhang X, Chang L, et al. Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy: Evaluation of forensic autopsy cases. Forensic Sci Int. 2012;223:171–5.
Zorilă A, Zorilă M, Marinaş M, Ţolescu R, Zorilă G, Florou C, et al. Evaluation of brain injuries in children deceased due to head trauma. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2017;58:1417–28.
Zwirner J, Scholze M, Neil Waddell J, Ondruschka B, Hammer N. Mechanical properties of human dura mater in tension-An analysis at an age range of 2 to 94 years. Sci Rep. 2019;9:16655.
Wade A. Fear or favour? Statistics in pathology. J Clin Pathol. 2000;53:16–8.
Grimes DA, Schulz KF. Compared to what? Finding controls for case-control studies. Lancet. 2005;365:1429–33.
Büttner A. Review: The neuropathology of drug abuse. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2011;37:118–34.
An JH, Lee KE, Jeon HJ, Son SJ, Kim SY, Hong JP. Risk of suicide and accidental deaths among elderly patients with cognitive impairment. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019;11:32.
Byard RW, Austin A. The role of forensic pathology in suicide. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2010;7:1–2.
Download references
Open Access funding provided by University of Helsinki including Helsinki University Central Hospital.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Forensic Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Helsinki, P.O. Box 21, Helsinki, FI-00014, Finland
Petteri Oura, Antti Hakkarainen & Antti Sajantila
Forensic Medicine Unit, Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare, P.O. Box 30, Helsinki, FI-00271, Finland
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology: PO and AS. Formal analysis and investigation: PO and AS. Writing—original draft preparation: PO, AH, and AS. Writing—review and editing: PO, AH, and AS. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Petteri Oura .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval, consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (PDF 396 KB)
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Oura, P., Hakkarainen, A. & Sajantila, A. Forensic neuropathology in the past decade: a scoping literature review. Forensic Sci Med Pathol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-023-00672-9
Download citation
Accepted : 22 June 2023
Published : 13 July 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-023-00672-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Neuropathology
- Meta-level attribute
- Research theme
- Methodology
- Medico-legal
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
MINI REVIEW article
The impact of virtual reality on student engagement in the classroom–a critical review of the literature.

- 1 Faculty of Education, Silpakorn University, Nakhon Pathom, Thailand
- 2 Melbourne Graduate School of Education, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
- 3 Graduate Department, Xi’an Physical Education University, Xi’an, China
- 4 College of Commerce and Tourism, Hunan Vocational College for Nationalities, Yueyang, China
- 5 Graduate Department, Sehan University, Yeongam County, Republic of Korea
Objective: The purpose of this review is to identify the impact of virtual reality (VR) technology on student engagement, specifically cognitive engagement, behavioral engagement, and affective engagement.
Methods: A comprehensive search of databases such as Google, Scopus, and Elsevier was conducted to identify English-language articles related to VR and classroom engagement for the period from 2014 to 2023. After systematic screening, 33 articles were finally reviewed.
Results: The use of VR in the classroom is expected to improve student engagement and learning outcomes, and is particularly effective for students with learning disabilities. However, introducing VR into middle school education poses several challenges, including difficulties in the education system to keep up with VR developments, increased demands on students’ digital literacy, and insufficient proficiency of teachers in using VR.
Conclusion: To effectively utilize VR to increase student engagement, we advocate for educational policymakers to provide training and technical support to teachers to ensure that they can fully master and integrate VR to increase student engagement and instructional effectiveness.
Introduction
In recent years, virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a transformative technology in education, providing new avenues for immersive and interactive learning experiences ( Pottle, 2019 ). At its core, VR offers a departure from the tangible, allowing users to delve into an environment transcending conventional reality ( Brooks, 1999 ; Jeong et al., 2019 ). VR’s essence is captured in three pillars: presence, interactivity, and immersion ( Lee et al., 2017 ). Presence grants users access to previously unreachable 3D landscapes, facilitating a unique, experiential insight ( Poux et al., 2020 ). Interactivity kindles user curiosity, enabling dynamic engagements within the virtual milieu ( Steuer et al. 1995 ; Huvila, 2013 ; Song et al., 2023 ). Immersion pushes the boundaries of conventional experiences, reviving or manifesting phenomena outside the realm of everyday life ( Sanchez-Vives and Slater, 2005 ; Poux et al., 2020 ).
The introduction of VR in education might increase student engagement, which is closely related to the cognitive, behavioral, and affective dimensions of the engagement model ( Wang and Degol, 2014 ). Cognitive engagement underscores the depth of students’ attention, comprehension, and retention ( Wang and Degol, 2014 ). Behavioral engagement is observable, characterized by consistent attendance and active classroom participation ( Wang and Degol, 2014 ). Affective engagement delves into the emotional realm, encompassing motivation, passion, and learning efficacy ( Wang and Degol, 2014 ).
Existing literature emphasizes the importance of virtual reality technology in promoting full student engagement in cognitive, behavioral, and affective dimensions, and states that the application of virtual reality technology in education has become a trend ( Mystakidis et al., 2021 ). Some literature shows that higher education institutions are increasingly adopting VR, with adoption rates as high as 46% at US universities and 96% at United Kingdom universities ( United Kingdom Authority, 2019 ; Agbo et al., 2021 ). In addition, the establishment of dedicated VR laboratories at leading universities such as Harvard University and Colorado State University underscores the commitment to using VR for educational innovation and advancement ( Reid, 1987 ; Leidner and Jarvenpaa, 1995 ). This literature shows that the widespread use of VR in education has attracted the attention of a growing number of researchers and educators, with a particular interest in the impact of VR in the classroom in terms of students’ cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement.
It is worth noting that although existing literature begins to discuss the impact of VR on student engagement, there are still shortcomings in determining the impact of VR on various dimensions of student engagement, which may limit our overall understanding of the topic. Therefore, further discussion is needed to more specifically identify the impact of VR on the various dimensions of student engagement to gain a more comprehensive and concrete understanding. To accomplish this, this review is guided by the following three questions: (1) What are the positive impacts of VR in education? (2) What are the challenges of VR in education? (3) What interventions can address these challenges? With this in mind, the article will first discuss the positive impact of VR on students’ cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement to help readers understand its potential in education. It will then discuss the challenges facing VR to make constructive recommendations to address the problems in education.
Searching strategy
In our methods, we used critical review. According to Grant and Booth (2009) “an effective critical review presents, analyses and synthesizes material from diverse sources”(p.93). Critical perspectives were used to assess the potential of VR in reforming educational practices and improving teaching and learning outcomes. The purpose of this article was to collect literature on the impact of VR on student engagement. Therefore, this article summarizes the previous studies as follows. First, information was obtained from Google, Scopus, and Elsevier databases: “virtual reality,” “cognitive engagement,” “affective engagement,” “behavioral engagement” and “learning outcomes.” The search was limited to articles published between January 2014 and December 2023 in English. The first search used all combinations of the above keywords and, after an initial review, produced 97 potentially relevant articles (Google: 92, Scopus: 3, Elsevier: 2).
In the second phase, secondary terms such as “affect,” “challenge,” and “education” were added, reducing the number of studies to 63 (Google:60, Scopus:1, Elsevier:2). Of these, 34 did not meet the criteria and were excluded. They were excluded because their target audience was teachers and did not discuss the impact of VR on student engagement from the student’s perspective. In the final stage, another 53 articles were excluded because they were repetitive and their purpose was to discuss either technology or engagement, or both. Finally, their full texts were reviewed to determine if their work fits the focus of this article 20 articles (Google: 17, Scopus: 1, Elsevier: 2) qualified for final review, covered a sample on the impact of VR on student engagement, and were included in the analysis.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
To ensure the quality of the literature, we selected only peer-reviewed journal articles published in English in the last decade. The main purpose of this article was to review the impact of VR on student engagement. Therefore, we selected only review articles on the impact of VR on student engagement in educational settings. Articles that were not written in English did not discuss the impact on engagement from a student perspective, and were published beyond the previously established time and language were excluded. In addition, a selection of articles was identified and assessed by manually searching the references of articles related to the topic, of which 13 met the eligibility criteria. Therefore, 13 additional articles were added to the 20 identified. In total, 33 articles that met these eligibility criteria were included and reviewed here. Full-text versions of the articles were obtained, with each article being reviewed and confirmed as appropriate by the authors. Finally, to maximize transparency and traceability, we list the rationale and relevant evidence for all articles included (see Table 1 ). The process of article selection followed the Preferred Reporting of Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Statement ( Moher et al., 2009 ; see Figure 1 ). Figure 1 illustrates the process of article selection.
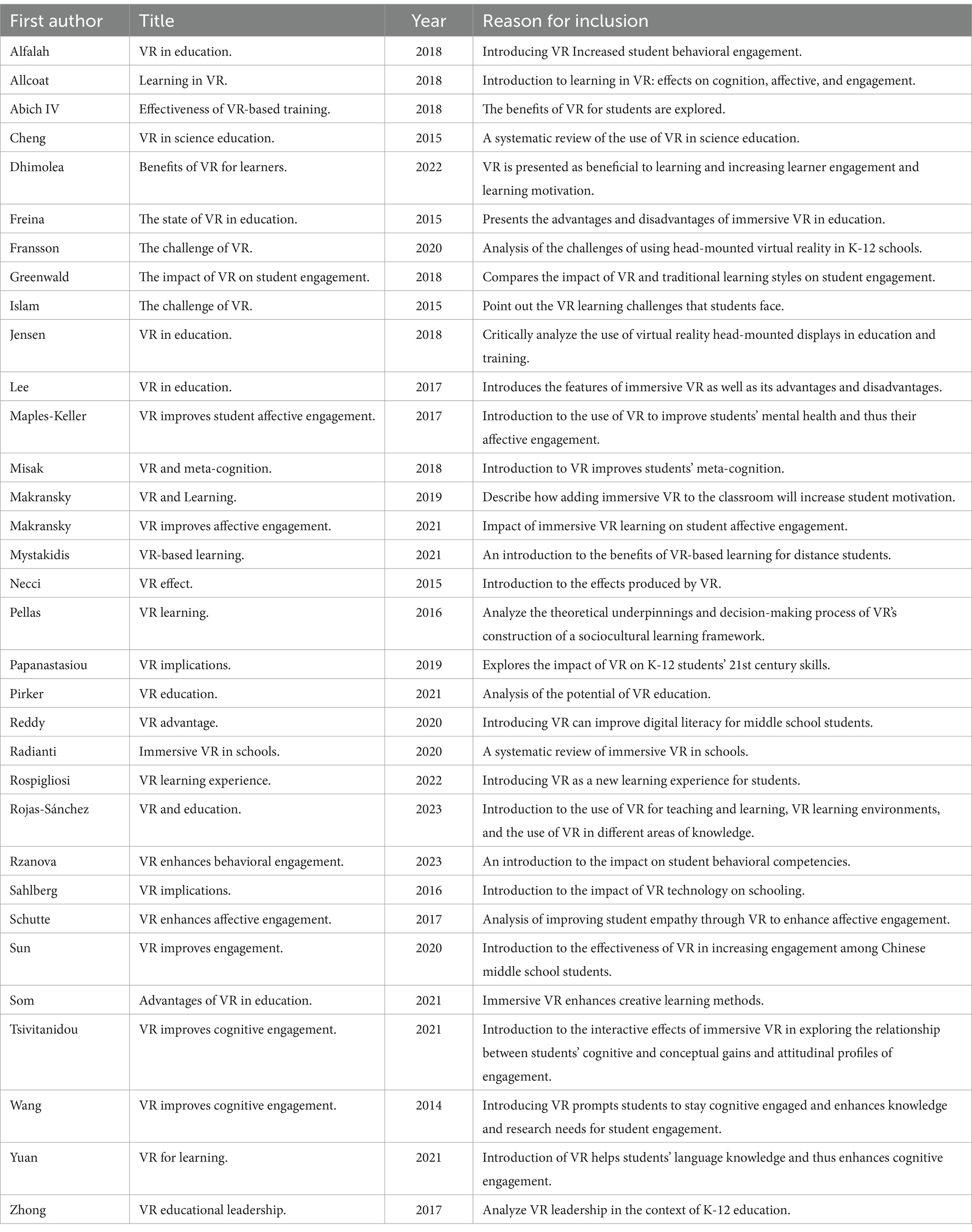
Table 1 . Publications reviewed in full text with reasons for inclusion or exclusion.
Figure 1 . PRISMA flow diagram for article selection.
The review found that the number of publications increased each year from 2014 to 2023, indicating the continued interest of researchers in exploring the impact of VR on student engagement. When reviewing the impact of VR on student engagement, Wang and Degol’s (2014) article had the most citations at 450, suggesting that the article had a strong impact in the area of student use of VR in the classroom. The majority of articles had only 10 or fewer citations, which may have indicated that these articles were relatively new or had less impact in the field. It was worth noting that more recently published articles, such as Rzanova et al. (2023) , did not have enough time to accumulate citations, so their impact on the field may not have been fully reflected in current citations.
To summarize, the differences in the number of citations for these articles highlighted their different levels of influence in the area of VR’s impact on student engagement. However, there were some limitations to the review methods. For example, some articles might not have fully reflected their impact on the field in the current citations due to their short time frames, which might have resulted in less comprehensive findings. Furthermore, the literature included was small, and in the future consideration would be given to expanding the search of literature and databases, such as PubMed and Web of Science databases, as well as expanding the search with keywords, such as “students’ attitudes toward VR.” In addition, the inclusion and exclusion criteria might have limited the generalizability of the results of the review, and therefore more caution was needed when generalizing the results of the review.
The positive impact of VR on education
This section will discuss the impact of VR on students’ cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement participation. It is important in the field of education. Radianti et al. (2020) noted that student engagement in educational settings was critical to learning outcomes and classroom climate. Yuan and Wang (2021) further noted that the combined effects of cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement could directly impact student learning outcomes and classroom contextual experiences. Therefore, a deeper understanding of the impact of VR on these three dimensions of engagement can provide valuable insights into educational practices and help educators better optimize classroom environments and teaching methods.
First, Papanastasiou et al. (2019) noted that VR immersive learning experiences promoted students’ cognitive engagement and aided in understanding complex and abstract knowledge. That is, through immersive learning, students can understand and remember what they have learned in greater depth and increase cognitive engagement. Pellas (2016) also found that VR encouraged students to learn through self-directed inquiry and move away from traditional teacher-centered instruction. Pellas (2016) further explained that, through VR scenario reenactments and simulations, students could engage in real-world unavailable learning experiences such as exploring historical sites and visiting distant planets. This means that such learning experiences enable students to explore knowledge in deeper and more varied ways, thus increasing cognitive engagement. Similarly, Maples-Keller et al. (2017) showed that VR was beneficial in engaging different types of students in learning, particularly for at-risk students, including those with learning difficulties, anxiety disorders, and other mental illnesses. VR provided personalized and adaptive learning environments that helped students improve cognitive engagement and achievement ( Maples-Keller et al., 2017 ). In summary, VR facilitates understanding of complex knowledge and promotes cognitive engagement for different types of students through immersive learning experiences and self-directed inquiry learning.
Secondly, Pirker and Dengel (2021) demonstrated that VR could promote student behavioral engagement. They discussed the potential of immersive VR in education through an in-depth analysis of 64 articles. They showed that “learning tasks in 3-D VLEs can foster intrinsic motivation for and engagement with the learning content” (p.77). Sun and Peng (2020) also suggested that by combining classical educational concepts with VR, such as Confucianism’s promotion of teaching for fun, students were better able to engage in learning activities. For example, Rzanova et al. (2023) found that the use of VR in the teaching of poetry to create the scenarios depicted in the verses enabled students to actively participate in classroom activities. Similarly, Freina and Ott (2015) also found that by simulating real school escape scenarios in VR, students could take on different roles to perform escape drills, and this sense of behavioral engagement can help students better master escape techniques and enhance safety awareness. These articles seem to echo that VR helps to enhance student behavioral engagement.
It is worth noting that there is debate about whether VR has a positive impact on student behavioral engagement. Proponents noted that students’ hands-on experience and exploration in virtual environments stimulated interest and behavioral engagement ( Wong et al., 2010 ; Allcoat and Von Mühlenen, 2018 ). This view suggests that VR provides an immersive learning experience that enhances students’ motivation and promotes deeper engagement in classroom activities. However, contrary findings exist, suggesting that the use of VR may have some negative effects. For example, students might have become addicted to the virtual world and neglected their real-life tasks and responsibilities, thus affecting their behavior in the classroom ( Cheng et al., 2015 ; Greenwald et al., 2018 ; Makransky et al., 2019 ). In addition, some other scholars noted that there might have been a gap between learning experiences in virtual environments and real-world learning experiences, which might have affected students’ ability to acquire and apply knowledge ( Makransky and Petersen, 2021 ). These conflicting results remind us that these complexities and diversities need to be taken into account when evaluating the role of VR technology in improving student engagement in the classroom.
Finally, scholars such as Wu et al. (2013) , Schutte and Stilinović (2017) , and Yuen et al. (2011) found that VR helped to promote student affective engagement. For example, Schutte and Stilinović (2017) found that contexts provided by VR for children with emotional impairments or disabilities taught them skills in communicating with people and managing their emotions, thus fostering empathy. This implies that VR may stimulate affective engagement. Wu et al. (2013) and Yuen et al. (2011) also found that VR provided opportunities for affective interaction, enabling students to interact with characters in the virtual environment. In language learning, for example, practicing through conversations with virtual characters could help students improve their oral expression ( Dhimolea et al., 2022 ). This means that affective interactions may increase students’ affective engagement with the learning content. Similarly, Misak (2018) noted that VR allowed students to role-play in virtual literature and experience the affective portrayed in the story. In other words, affective experiences may deepen students’ understanding of literary works and increase affective engagement. This literature seems to reflect that VR can promote student affective engagement.
In general, VR positively impacts students’ cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement. In terms of cognitive engagement, VR can facilitate students’ cognitive engagement with learning materials and better understanding of abstract and complex knowledge by creating immersive situations. In terms of behavioral engagement, VR stimulates active student engagement and action through interactive learning. Although there is debate about whether VR has a positive impact on student behavioral engagement, literature has demonstrated the positive impact of VR on student behavioral engagement. In terms of affective engagement, VR promotes students’ emotional engagement by triggering affective resonance through affective experience and affective interaction. This full engagement helps students improve their learning and develop empathy.
The following section discusses the challenges faced when introducing VR in education. Through understanding these challenges, we can better understand the problems in the education system and make some constructive suggestions to help address them.
The challenge of VR in education
Despite the positive impact of VR on students’ cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement, there are still two challenges to introducing VR into middle education, namely the difficulty of the educational system in keeping up with VR developments and the lack of teacher proficiency in VR use ( Islam et al., 2015 ; Zhong, 2017 ; Abich et al., 2021 ). For example, Islam et al. (2015) observed that the pace of technological advancement, including VR, outpaced the ability of the education system to adapt. This phenomenon is due to the slow reform of the education system, which takes time for the acceptance and adoption of emerging technologies ( Islam et al., 2015 ). To this end, the education sector may take longer to standardize the syllabus, resulting in students not having immediate access to VR ( Zhong, 2017 ). In other words, students may not have the opportunity to experience VR in the classroom until the education department completes the standardization process. Sahlberg (2016) further stated that while reform and standardization in the education sector took time, once VR and the education system evolved in tandem, students benefited from an education that matched the VR of the day.
Other scholars observed that VR education faced several challenges in developing digital literacy in students ( Aviram and Eshet-Alkalai, 2006 ; Sahlberg, 2016 ). According to Reddy et al. (2020) , “digital literacy is a set of skills required by 21st Century individuals to use digital tools to support the achievement of goals in their life situations” (p. 66). Digital literacy encompasses the assessment of digital technologies, critical thinking, and the ability to create and express oneself digitally ( Reddy et al., 2020 ). For example, Tsivitanidou et al. (2021) and Necci et al. (2015) emphasized the need for students to identify the differences between the results of simulation experiments and real experiments and to assess the reliability and accuracy of simulation experiments. In other words, students need to judge the plausibility of the results of simulation experiments and interpret and evaluate those results in real-world situations.
Similarly, Farmer and Farmer (2023) found that digital literacy required students to master VR painting and sculpting tools to create art. This involved learning to select appropriate colors and textures and creating three-dimensional effects with VR tools ( Skulmowski et al., 2021 ). Meanwhile, Andone et al. (2018) further noted that students also needed to learn to share and present their work to others in virtual reality. This observation seems to reflect the high demand for students’ creativity, technical skills, and expressive abilities when introducing VR into education. In sum, while the development of VR education benefits students’ learning in conjunction with VR, there are challenges to students’ digital literacy and the technological adaptability of the education system.
In addition, teachers’ lack of proficiency in the use of VR is another major challenge in introducing VR into middle education. For example, Abich et al. (2021) found that teachers might lack proficiency in the operation and application of VR, which might result in teachers not being able to fully utilize VR to supplement instruction. Jensen and Konradsen (2018) claimed that “for HMDs to become a relevant tool for instructors they must have the ability to produce and edit their content” (p.1525). This means that teachers need to spend time familiarizing themselves with HMDs and related software to create, edit, and customize content to meet their specific instructional needs. Similarly, Fransson et al. (2020) discussed the challenges of teachers operating VR equipment and software. They interviewed 28 teachers to understand teachers’ challenges with implementing helmet display VR in educational settings. Fransson et al. (2020) indicated that there might be a technological threshold and learning curve for teachers in controlling and operating VR devices, which might affect the effective use of VR for teaching and learning.
While teachers may lack familiarity with VR, there are solutions to this challenge. For example, Alfalah (2018) noted that proper training and support could help teachers make the most of VR to supplement instruction. That is, teacher training can provide teachers with the technical knowledge and operational skills they need to familiarize themselves with how VR equipment and software work. To this end, Alfalah (2018) found the impact of providing teachers with VR training in schools. They used a quantitative approach by distributing a questionnaire online to 30 IT teachers. Alfalah (2018) indicated that “technology training may be maximized for the integration of VR technology” (P.2634). This finding seems to reflect that proper teacher training and support can be effective in helping teachers overcome the operational and application of VR technology’s difficulties.
In sum, prior literature has shown that introducing VR into middle school education faces several challenges. First, the rapid development of technology makes the educational system keep up with VR, resulting in a disconnect between the educational curriculum and VR. Second, there may be a lack of proficiency in students’ digital literacy and teachers’ handling and application of VR. However, these challenges are not insurmountable. With proper training and support, teachers can make full use of VR to supplement their teaching and learning to realize the potential of VR in education. It is worth noting that through the literature we have found that in practice, due to the rapid development of technology and the limitations of the educational system, achieving a complete balance may take some time and effort. Therefore, considering how to address the gap between the speed of VR development and the education system to better integrate and apply VR in education makes sense.
This article describes the impact of VR on student cognitive, behavioral, and affective engagement and the challenges posed by VR education. The literature review finds that using VR in the classroom can positively impact student engagement and learning outcomes. An interesting finding is that VR can be a promising tool for providing education to students with learning disabilities. For example, the previous literature review section describes how for students with learning difficulties, anxiety disorders, and other mental illnesses, VR can provide personalized and adaptive learning environments that can help students improve cognitive engagement and academic performance. And, for children with emotional disorders or disabilities, VR provides contexts that can teach them skills for communicating with others and managing their emotions, thereby developing empathy and stimulating affective engagement.
However, the potential problems with incorporating VR in middle education are the difficulty of the education system in keeping up with VR developments, the higher demands of student digital literacy, and the lack of teacher proficiency in the use of VR. These challenges require educational policymakers to provide training and technical support to teachers to ensure that they can fully master and integrate VR to improve student engagement and teaching effectiveness.
Author contributions
XL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZNY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZY: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MZ: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the General Topics of China’s Hunan Province Social Science Achievement Evaluation Committee Fund [Grant no. XSP2023JYC123].
Acknowledgments
We are deeply appreciative of the editors and reviewers of this journal for their unwavering dedication and contributions that have shaped the publication of this article. Their constructive feedback and invaluable insights were instrumental in bringing this piece to fruition. We extend our heartfelt thanks to the readers with a keen interest in virtual reality technology. It is our sincere hope that this article will inspire enriched discussions within the academic community about the potential and nuances of using virtual reality in educational contexts.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abich, J., Parker, J., Murphy, J. S., and Eudy, M. (2021). A review of the evidence for training effectiveness with virtual reality technology. Virtual Reality 25, 919–933. doi: 10.1007/s10055-020-00498-8
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Agbo, F. J., Sanusi, I. T., Oyelere, S. S., and Suhonen, J. (2021). Application of virtual reality in computer science education: a systemic review based on bibliometric and content analysis methods. Educ. Sci. 11, 1–23. doi: 10.3390/educsci11030142
Alfalah, S. F. (2018). Perceptions toward adopting virtual reality as a teaching aid in information technology. Educ. Inf. Technol. 23, 2633–2653. doi: 10.1007/s10639-018-9734-2
Allcoat, D., and Von Mühlenen, A. (2018). Learning in virtual reality: effects on performance, emotion, and engagement. Res. Learn. Technol. 26, 1–13. doi: 10.25304/rlt.v26.2140
Andone, D., Vert, S., Frydenberg, M., and Vasiu, R. (2018). Open virtual reality project to improve students’ skills. In 2018 IEEE 18th International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (ICALT) , 6–10. doi: 10.1109/ICALT.2018.00008
Aviram, A., and Eshet-Alkalai, Y. (2006). Towards a theory of digital literacy: three scenarios for the next steps. Eur. J. Open Distance E Learn 9, 1–11.
Google Scholar
Brooks, F. P. (1999). What's real about virtual reality? Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE). Comput. Graph. Appl. 19, 16–27. doi: 10.1109/38.799723
Cheng, M.-T., Chen, J.-H., Chu, S.-J., and Chen, S.-Y. (2015). The use of serious games in science education: a review of selected empirical research from 2002 to 2013. J. Comput. Educ. 2, 353–375. doi: 10.1007/s40692-015-0039-9
Dhimolea, T. K., Kaplan-Rakowski, R., and Lin, L. (2022). A systematic review of research on high-immersion virtual reality for language learning. TechTrends 66, 810–824. doi: 10.1007/s11528-022-00717-w
Fransson, G., Holmberg, J., and Westelius, C. (2020). The challenges of using head mounted virtual reality in K-12 schools from a teacher perspective. Educ. Inf. Technol. 25, 3383–3404. doi: 10.1007/s10639-020-10119-1
Freina, L., and Ott, M. (2015). A literature review on immersive virtual reality in education: state of the art and perspectives. Int. Sci. Conf. E Learn. Softw. Educ. 1, 10–1007. doi: 10.12753/2066-026x-15-020
Grant, M. J., and Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inf. Libr. J. 26, 91–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Greenwald, S. W., Corning, W., Funk, M., and Maes, P. (2018). Comparing learning in virtual reality with learning on a 2D screen using electrostatics activities. J. Comput. Sci. 24, 220–245. doi: 10.3217/jucs-024-02-0220
Huvila, I. (2013). Sorting out the metaverse and how the metaverse is sorting us out . London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Islam, N., Beer, M., and Slack, F. (2015). E-learning challenges faced by academics in higher education. J. Educ. Train. Stud. 3, 102–112. doi: 10.11114/jets.v3i5.947
Jensen, L., and Konradsen, F. (2018). A review of the use of virtual reality head-mounted displays in education and training. Educ. Inf. Technol. 23, 1515–1529. doi: 10.1007/s10639-017-9676-0
Jeong, K., Kim, J., Kim, M., Lee, J., and Kim, C. (2019). Asymmetric interface: user interface of asymmetric virtual reality for new presence and experience. Symmetry 12, 1–25. doi: 10.3390/sym12010053
Lee, J., Kim, M., and Kim, J. (2017). A study on immersion and VR sickness in walking interaction for immersive virtual reality applications. Symmetry 9, 1–17. doi: 10.3390/sym9050078
Leidner, D. E., and Jarvenpaa, S. L. (1995). The use of information technology to enhance management school education: a theoretical view. Manag. Inf. Serv. Q. 19, 265–291. doi: 10.2307/249596
Makransky, G., and Petersen, G. B. (2021). The cognitive-affective model of immersive learning: a theoretical research-based model of learning in immersive virtual reality. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 33, 937–958. doi: 10.1007/s10648-020-09586-2
Makransky, G., Terkildsen, T. S., and Mayer, R. E. (2019). Adding immersive virtual reality to a science lab simulation causes more presence but less learning. Learn. Instr. 60, 225–236. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2017.12.007
Maples-Keller, J. L., Bunnell, B. E., Kim, S.-J., and Rothbaum, B. O. (2017). The use of virtual reality technology in the treatment of anxiety and other psychiatric disorders. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 25, 103–113. doi: 10.1097/HRP.0000000000000138
Misak, J. (2018). A (virtual) bridge not too far: teaching narrative sense of place with virtual reality. Comput. Compos. 50, 39–52. doi: 10.1016/j.compcom.2018.07.007
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., and Altman, D. G.PRISMA Group* (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 151, 264–269. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
Mystakidis, S., Berki, E., and Valtanen, J. P. (2021). Deep and meaningful e-learning with social virtual reality environments in higher education: a systematic literature review. Appl. Sci. 11, 1–25. doi: 10.3390/app11052412
Necci, A., Cozzani, V., Spadoni, G., and Khan, F. (2015). Assessment of domino effect: state of the art and research needs. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 143, 3–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2015.05.017
Papanastasiou, G., Drigas, A., Skianis, C., Lytras, M., and Papanastasiou, E. (2019). Virtual and augmented reality effects on K-12, higher, and tertiary education students’twenty-first-century skills. Virtual Reality 23, 425–436. doi: 10.1007/s10055-018-0363-2
Pellas, N. (2016). “Unraveling a progressive inquiry script in persistent virtual worlds: theoretical foundations and decision processes for constructing a socio-cultural learning framework” in Web design and development: Concepts, methodologies, tools, and applications (Pennsylvania, US: IGI Global), 610–647.
Pirker, J., and Dengel, A. (2021). The potential of 360 virtual reality videos and real VR for education—a literature review. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 41, 76–89. doi: 10.1109/MCG.2021.3067999
Pottle, J. (2019). Virtual reality and the transformation of medical education. Future Healthcare J. 6, 181–185. doi: 10.7861/fhj.2019-0036
Poux, F., Valembois, Q., Mattes, C., Kobbelt, L., and Billen, R. (2020). Initial user-centered design of a virtual reality heritage system: applications for digital tourism. Remote Sens. 12, 1–25. doi: 10.3390/rs12162583
Radianti, J., Majchrzak, T. A., Fromm, J., and Wohlgenannt, I. (2020). A systematic review of immersive virtual reality applications for higher education: design elements, lessons learned, and research agenda. Comput. Educ. 147, 103778–103729. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103778
Reddy, P., Sharma, B., and Chaudhary, K. (2020). Digital literacy: a review of literature. Int. J. Technoethics (IJT) 11, 65–94. doi: 10.4018/IJT.20200701.oa1
Reid, J. M. (1987). The learning style preferences of English as a second language (ESL) students. Teach. Engl. Speakers Other Lang. Q. 21, 87–111. doi: 10.2307/3586356
Rzanova, S., Yushchik, E., Markova, S., and Sergeeva, A. (2023). Impact of virtual reality technologies in the context of the case method on engineering students’ competencies. Educ. Inf. Technol. 7, 1–19. doi: 10.56028/aetr.7.1.7.2023
Sahlberg, P. (2016). The global educational reform movement and its impact on schooling. In: K. Mundy, A. Green, B. Lingard, and A. Verger The Handbook of Global Education Policy . Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons, 128–144.
Sanchez-Vives, M. V., and Slater, M. (2005). From presence to consciousness through virtual reality. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6, 332–339. doi: 10.1038/nrn1651
Schutte, N. S., and Stilinović, E. J. (2017). Facilitating empathy through virtual reality. Motiv. Emot. 41, 708–712. doi: 10.1007/s11031-017-9641-7
Skulmowski, A., Nebel, S., Remmele, M., and Rey, G. D. (2021). Is a preference for realism really naive after all? A cognitive model of learning with realistic visualizations. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 34, 1–27. doi: 10.1007/s10648-021-09638-1
Song, C., Shin, S. Y., and Shin, K. S. (2023). Optimizing foreign language learning in virtual reality: a comprehensive theoretical framework based on constructivism and cognitive load theory. Appl. Sci. 13, 1–31. doi: 10.3390/app132312557
Steuer, J., Biocca, F., and Levy, M. R. (1995). Communication in the age of virtual reality , New York: Routledge
Sun, S. Y., and Peng, L. H. (2020). Study of the virtual reality education and digitalization in China. J. Physics 1456, 012042–012047. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1456/1/012042
Tsivitanidou, O. E., Georgiou, Y., and Ioannou, A. (2021). A learning experience in inquiry-based physics with immersive virtual reality: student perceptions and an interaction effect between conceptual gains and attitudinal profiles. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 30, 841–861. doi: 10.1007/s10956-021-09924-1
United Kingdom Authority. (2019). VR and AR attract education sector interest . Available at: https://www.ukauthority.com/articles/vr-and-ar-attract-education-sector-interest/ .
Wang, M. T., and Degol, J. (2014). Staying engaged: knowledge and research need in student engagement. Child Dev. Perspect. 8, 137–143. doi: 10.1111/cdep.12073
Wong, B. M., Etchells, E. E., Kuper, A., Levinson, W., and Shojania, K. G. (2010). Teaching quality improvement and patient safety to trainees: a systematic review. Acad. Med. 85, 1425–1439. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181e2d0c6
Wu, H.-K., Lee, S. W.-Y., Chang, H.-Y., and Liang, J.-C. (2013). Current status, opportunities and challenges of augmented reality in education. Comput. Educ. 62, 41–49. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2012.10.024
Yuan, H., and Wang, Z. (2021). A review of research on technology enhancing Chinese learning . 2021 international conference on internet, education and information technology (IEIT), pp. 462–467.
Yuen, S. C.-Y., Yaoyuneyong, G., and Johnson, E. (2011). Augmented reality: an overview and five directions for augmented reality (AR) in education. J. Educ. Technol. Dev. Exchange 4, 119–140. doi: 10.18785/jetde.0401.10
Zhong, L. (2017). Indicators of digital leadership in the context of K-12 education. J. Educ. Technol. Dev. Exchange 10, 27–40. doi: 10.18785/jetde.1001.03
Keywords: virtual reality technology, cognitive engagement, affective engagement, behavioral engagement, learning outcomes
Citation: Lin XP, Li BB, Yao ZN, Yang Z and Zhang M (2024) The impact of virtual reality on student engagement in the classroom–a critical review of the literature. Front. Psychol . 15:1360574. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1360574
Received: 23 December 2023; Accepted: 22 March 2024; Published: 10 April 2024.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2024 Lin, Li, Yao, Yang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhi Yang, [email protected] ; Mingshu Zhang, [email protected]
† These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Materials Chemistry Frontiers
Lessons learned: how to report xps data incorrectly about lead-halide perovskites.

* Corresponding authors
a State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Fuzhou 350002, China E-mail: [email protected]
b Laboratory for Advanced Functional Materials, Xiamen Institute of Rare Earth Materials, Haixi Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xiamen 361021, China
c University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy is a powerful tool for identifying the interactions of additives or surface treatments with components in lead halide perovskites. However, with the increasing number of studies using XPS, inaccurate or faulty data analysis has been encountered during a literature survey. Herein, we describe the fundamental principle of chemical shifts of Pb atoms in XPS and critically review the commonly seen mistakes in the literature: (i) misinterpretation of the XPS mechanism; (ii) misinterpretations due to disturbed chemical environments; (iii) lack of awareness of the properties of the passivator; iv. misquoted references. We hope that this perspective can help the community avoid the pitfalls in applying the XPS technique and in explaining their experimental results.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2023 Materials Chemistry Frontiers Review-type Articles
Article information
Download Citation
Permissions.
C. Li, N. Zhang and P. Gao, Mater. Chem. Front. , 2023, 7 , 3797 DOI: 10.1039/D3QM00574G
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence . You can use material from this article in other publications, without requesting further permission from the RSC, provided that the correct acknowledgement is given and it is not used for commercial purposes.
To request permission to reproduce material from this article in a commercial publication , please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party commercial publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author, advertisements.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
One such way is to conduct a literature review and combine it with a meta-analysis of a relevant topic to provide some evidence of effect. This strategy has been used effectively in articles published in higher-ranked journals (e.g., Carrillat et al., 2018; Edeling & Himme, 2018; Verlegh & Steenkamp, 1999). Important to note is that simply ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say "literature review" or refer to "the literature," we are talking about the research (scholarship) in a given field. You will often see the terms "the research," "the ...
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
This article is organized as follows: The next section presents the methodology adopted by this research, followed by a section that discusses the typology of literature reviews and provides empirical examples; the subsequent section summarizes the process of literature review; and the last section concludes the paper with suggestions on how to improve the quality and rigor of literature ...
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
A literature review in its most fundamental structure provides an account of what has already been published in the peer-reviewed literature [].The purpose of a literature review is to "convey to the reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are" [].The primary purpose of a literature review is NOT to portray a list of what ...
2. Benefits of Review Articles to the Author. Analysing literature gives an overview of the "WHs": WHat has been reported in a particular field or topic, WHo the key writers are, WHat are the prevailing theories and hypotheses, WHat questions are being asked (and answered), and WHat methods and methodologies are appropriate and useful [].For new or aspiring researchers in a particular ...
The Literature Review Defined. In medical education, no organization has articulated a formal definition of a literature review for a research paper; thus, a literature review can take a number of forms. Depending on the type of article, target journal, and specific topic, these forms will vary in methodology, rigor, and depth.
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period. A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the ...
Many literature reviews can be thought of as a qualitative empirical study, in which the papers included in the review substitute interviews or field observations that you would usually collect and code. Some literature reviews, e.g., meta-analyses, are more like a quantitative empirical paper, in which various numbers you extract from the ...
Literature Review (Historiographic Essay): Making sense of what has been written on your topic. To find examples of published literature reviews in your field or niche, try searching ProQuest Dissertations and Theses by keyword, advisor, or subject.
Literature reviews are valuable resources for the scientific community. With research accelerating at an unprecedented speed in recent years and more and more original papers being published, review articles have become increasingly important as a means to keep up to date with developments in a particular area of research.
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period. A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis.
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research.1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis ...
The potential review articles have been identified by widely used electronic databases as specified in Section 3.2 by using broad terms for the search keywords in order to mitigate the risk of excluding relevant articles. It is believed that an appropriate set of relevant articles have been identified for the review that has been published on ...
This article is a practical guide to conducting data analysis in general literature reviews. The general literature review is a synthesis and analysis of published research on a relevant clinical issue, and is a common format for academic theses at the bachelor's and master's levels in nursing, physiotherapy, occupational therapy, public health and other related fields.
Systematic literature review. A comprehensive search strategy was designed to identify English-language studies published in peer-reviewed journals providing data on risk factors or predictors of moderate or severe exacerbations in adults aged ≥ 40 years with a diagnosis of COPD (sample size ≥ 100).
A sophisticated literature review (LR) can result in a robust dissertation/thesis by scrutinizing the main problem examined by the academic study; anticipating research hypotheses, methods and results; and maintaining the interest of the audience in how the dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field.
This scoping review identified 122 original articles on forensic neuropathology from the years 2010-2022. Only 3-17 articles were published per year globally. Most articles originated from the Europe and Asia and were published in forensic journals. A median sample included 57 subjects aged between 16 and 80 years.
This systematic literature review identified relevant research articles, allowing for a transparent, documented research process with inclusion and exclusion criteria. ... Table 5 shows how practices related to the dynamic capabilities view were seen in seven research articles published in 2022 and one article published in 2023. These studies ...
The search was limited to articles published between January 2014 and December 2023 in English. The first search used all combinations of the above keywords and, after an initial review, produced 97 potentially relevant articles (Google: 92, Scopus: 3, Elsevier: 2). ... The literature review finds that using VR in the classroom can positively ...
Reuber R., 2010. Strengthening your literature review. Fam. Bus. Rev. 23(2), 105-108. Crossref. Google Scholar. Snugg E., Jevons C. 2018. Reconceptualising the scholarship of marketing eduation - SoME futurescapes. ... This article was published in Australasian Marketing Journal. VIEW ALL JOURNAL METRICS. Article usage * Total views and ...
X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy is a powerful tool for identifying the interactions of additives or surface treatments with components in lead halide perovskites. However, with the increasing number of studies using XPS, inaccurate or faulty data analysis has been encountered during a literature survey. Her 2023 Materials Chemistry Frontiers Review-type Articles