261 Macroeconomics Topics for Any Paper [+Tips]
Take a look at our macroeconomics research topics and select the most suitable one. And don’t forget to check out our tips on how to compose a paper.
- ⚖️ Macro & Micro
- 📑 Topics in Macro

🏆 Best Macroeconomics Topic Ideas & Essay Examples
📑 good research topics about macroeconomics, ⭐ simple & easy macroeconomics essay titles, 👍 good essay topics on macroeconomics.
- 📄 For Essay
- 🖥️ For Presentation
- 📊 For Project
- 👩💻 For Research
- ✍️ For Term Paper
- 🔥 20 More Hot Topics
❓ Macroeconomics Essay Questions
- 🔨 Tricks for a Paper
All finance students are required to take the macroeconomics course throughout their studies. Although the subject is crucial and useful, it is pretty challenging. In particular, it can become a problem if you want to nail an original macroeconomics project. Topics to write about can be tricky to find for students regardless of their school level.
But you won’t face any difficulties.
Our team of experts has prepared a comprehensive list of macroeconomic topics. Here you can find fascinating ideas for any type of assignment.
🤔 What Is Macroeconomics?
Of course, you could go straight away to the essay ideas search. But are you familiar with essential economic terms? If not, then the topic selection process can turn into huge trouble.
We have good news for you!
For your convenience, we developed a brief study guide on the basics of economics. So, don’t hesitate to use our prompts to make your studying process more pleasurable.
⚖️ Macroeconomics & Microeconomics
In essence, macroeconomics and microeconomics are two fundamental parts of economic science. They perfectly complement each other and provide a wide range of opportunities for economists. Nevertheless, the microeconomic and macroeconomic objectives differ to a great extent.

So, what are they?
Macroeconomics is a field of economics that studies the economic performance of countries. By employing it, governments can analyze the financial situation within a country. Macroeconomic theory’s concepts help to predict and prevent possible economic obstacles. Generally, the field presents the big picture. That is to say, it shows the economic development on a national and international level.
In contrast, microeconomics focuses on specific firms or companies. It analyzes the business owners’ decision-making process. Microeconomics does not interact with national or even international economic problems. It mainly investigates enterprises and their internal issues.
📑 Topics in Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is a broad field that covers a wide range of issues. The two topics of primary concern in macroeconomics are:
- the behavioral tendencies;
- the decision-making processes of an economy as a whole.
In other words:
Macroeconomics explores human actions and interactions from an economic perspective.
Have you ever noticed any macroeconomic topics in the news? Or maybe in the headings of magazine articles, in the posts on social media? Or have you heard the discussion of high inflation and unemployment rate on the radio or television? These are all examples of the application of macroeconomics in real life.

The spectrum of issues examined by macroeconomics impresses with its diversity. To make your studying more pleasant, our team gathered ideas in one place.
The topics studied in macroeconomics include:
- Price levels
- Inflation rates
- Political economy
- Unemployment rates
- Finance development
- Fiscal and monetary policies
- National and international trade
- Government savings and investments
- Macroeconomic and Microeconomic Analysis of Nestle Nutrition Due to high competition in the market, an increase in the prices of Nestle’s products is likely to decrease their demand, thereby reducing the firm’s sales.
- Greece and Ireland: Macroeconomic and Financial Comparison However, the growth in Ireland was more than that in Greece. For Greece, it was engaged in fighting a runaway debt since the 1990s.
- How Macroeconomics Affects on Remote Industry & Operating Environments The fourth and last macroeconomics variable is the interest rate prevailing in the economy, which is the measure of the cost of capital.
- The Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Factors in a Startup Café The objectives of this poster are to illustrate the importance of the microeconomics and macroeconomics factors in my project, which is a Startup Cafe.
- New Classical Macroeconomics The New Classical Macroeconomics school of thought is built on the assumption that all agents in the economy use the information available to make rational decisions.
- Difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics Macroeconomics Macroeconomics emphasizes on the bigger picture of the economy thus acquitting on how things in the world in terms of the structure, performance, behavior and decision making process of the whole economy.
- Basics of Microeconomics and Macroeconomics GDP is equal to all expenses of all goods and services produced in a country, equal to the total of value-added during the production of the goods and services by all industries within a country […]
- Macroeconomic Determinants of Savings in the UK The neoclassical model examines whether the development between steady states, positive changes in the savings ratio may stimulate the growth rate in the economy.
- Macroeconomic Environment: Oversight and Governance In order for the business to be listed on the exchange, it must first meet all of the listing rules and then pay any expenses associated with being listed.
- Insurance in Europe Profitability and the Macroeconomic Environment The assignment analyses the cost structure of the industry, the economic landscape in Europe, and how it relates to the insurance sector, changing consumer preference, and the impact of Covid-19 on the industry.
- Articles Explaining Macroeconomic Concepts and Events The model interprets the characteristics of the financial markets and investigates the stability of a country’s economy. The LM curve indicates the GDP output levels where the money supply is equal to the demand.
- Macroeconomic Problems Faced by Sweden and Saudi Arabia Macroeconomics studies the behavior of the economy, as well as its major sectors, such as the public and private sectors, and the monetary system, as well as the relationships between the most significant general economic […]
- The Impacts of the Macroeconomic Variables on the Business Environment These are also indicators of the rank of the well-being of the population, exports and imports operations, the overall rate of economic growth, and other economic processes.
- Macroeconomics Principles: International Commerce On the other hand, the higher the productivity gap, the greater the concentration of export businesses and the fewer their links with the rest of the economy.
- Macroeconomics Principles of Demand and Supply The article suggested that the aggregate demand must be boosted to support the monetary policies and decrease the risks faced after the pandemic’s shock for the worldwide economy.
- United States National Debt and Macroeconomics The national debt of the United States is one of the most known economic phenomena in the world. This is the real danger of using the national debt as a solution to the lack of […]
- The United States Macroeconomic Policies During COVID-19 One of the main reasons is the social hardship caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and, consequently, the government’s need to ensure a steady flow of funds to support the budget.
- Macroeconomic Variables Overview According to the data, GDP growth in 2017 was 2. The inflation rate in the same years was 2.
- Economic Principles: Macroeconomics This paper intends to describe the housing industry in the United States as presented in the Census Bureau. The housing industry is one of the most vibrant in the United States and the rest of […]
- Behavioral Finance: Meaning of Macroeconomics Keen disapproves of all the economic theories that support the concept describing their flaws and mishaps. The theories they disapprove of have some flaws that are well stated and displayed.
- Macroeconomics: US Monetary Policies in 1980-1990 The chart shows the rise in inflation that reached peak levels in the late 70’s, causing the Federal Reserve to come up with new policies to solve the issue.
- Food Security and Macroeconomics Discussion This is a bad trend which severely hurts the supply of food in third world countries which are not food sufficient.
- Macroeconomic Overview and Employment Rates in India The occupational structure of India shifted since the 1990s, and the percentage of people employed in the agricultural sector decreased considerable, which also positively affects economic growth. In summary, both the internal and external environment […]
- Macroeconomics in Unemployment Frictional unemployment is described as the unemployment that takes place because of the movement of people from one occupation to another.
- Macroeconomics and Hyperinflation in 1914-1923 The officials of the Central bank of Germany thought the cause of hyperinflation was the depreciation of the mark in foreign exchange currency.
- Interpreting World Macroeconomic Conditions The production of wine is related more to the gross domestic product compared to the rates of interest. In the United States the fast food industry is said to contribute a total of $ 1.
- Business Proposal Project and Macroeconomics Policy The purpose of this paper will be to come up with a unique technological innovation that the company can invest in order to meet the needs of the clients and the suppliers.
- Gas Prices and Macroeconomic Indicators The paper will investigate the possible effects of the change of gasoline price on changes in GDP, CPI, and unemployment rate.
- Macroeconomic Study of Latin America The economic growth as in the third quarter of 2008 was at 4. 8% and with the economic stimulus plan of $ 4Billion that is intended to quash the current meltdown in the economy, economic […]
- Macroeconomics – Fiscal Policy The stability of the Fiscal Policy is of great significance to any economy because it is one of the prime determinants of the strength of the economy of the country.
- Jordan: Macroeconomic Issues In most cases, the human development index is be termed as the welfare of the people in that economy as it encompasses per capita GDP, life expectancy, education and in remote cases purchasing power.
- Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Differences The perception of macroeconomics is in terms of a worldly view of resources while microeconomics entails a more individual feature of the economy. This makes the difference from macroeconomics, which appertains to the sum total […]
- Concepts and Problems in Macroeconomics The unemployment rate in Israel is presented in the figure below. The first massive rise in the unemployment rate was during 1988 to 1992 when there was the incidence of the Gulf War.
- Science of Economics: Microeconomics and Macroeconomics This paper will examine the issue of “why is the science of economics concerned with the activity of households and individuals at one end of the scale, and that of multinational corporations and governments at […]
- Macroeconomic Development of Haiti The political condition in Haiti is in the shambles with a long history of anarchy, insurrection, dictatorship and political infighting the Haitian economy has remained one of the poorest economies of the world. Then the […]
- Evaluating Effectiveness of Supply Side Economics on Macroeconomic Objectives This paper takes the position that supply side economics has had its day and the deregulation aspect of the theory has gone too far with the result that the US economy as well as the […]
- Macroeconomics and Unemployment The author of the article is Jennifer Steinhauer and the source where the article is taken from is the newspaper “The New York Times”, issued on September 18, 2009, that is why the information under […]
- Macroeconomic Impact on UK Hotel Chain’s Marketing Mix Other harbingers of the current economic travails are tight credit and falling home prices The country has not been spared the effects of the global economic slowdown that commenced with a recession across the Atlantic […]
- Macroeconomic Changes and Its Impact on the Agricultural Sector Formerly, the growth in the agricultural sector of the United States had been quite unpredictable. The rate of economic growth has a significant impact on the demand for agricultural products in the United States.
- Mexico Country: Micro and Macroeconomic Environment This undertaking is of vital importance to the company; it provides a view of short run costs that will have to be paid for the company to gain in the long run.
- The United States’ Macroeconomic Performance The problem of the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan will be adding more financial pressures to the economy of the United States of America.
- Kenya’s Macroeconomic Activities With the expansion of tourism, transport, and recovery in Agriculture which is in the due process, the gross domestic product per capita is expected to increase with high percentage. On top of that, Kenya’s economy […]
- India’s International Macroeconomic Environment The country is a major power in the South Asia and has got the status of full dialogue partner with ASEAN and has been admitted as a member of the ASEAN Regional Forum.
- Reductionist Effect in Macroeconomics Coddington says that limiting the supply of a product or service in the market will pull down the performance of a firm since the firm will lose its market share to competitors.
- Macroeconomics: Aggregate Demand and Supply The overall effect of the drilling in Alaska on the economy is that the economy will be rejuvenated and this cannot be more welcome in the united states at this time of financial crisis.
- Australian Fashion Industries. Macroeconomic Situation. It has been investing heavily in the industry by having designer wear that are readily available in the market and shopping malls and there are many customers who are interested and exposed to the products […]
- Macroeconomics: Increasing Firm’s Income The assumption of the equilibrium state within national income will hold and that the supply in national income is equal to the demand for the same income.
- Macroeconomics, Stagflation and Government Policy If the economy already appeared in a state of stagflation at the intersection of AD and AS2, the goal of the policy is to shift the aggregate supply curve to the right to AS.
- Macroeconomics: South Africa’s Fiscal Space Reforms The purpose of this paper is to review the article and express the author’s opinion on the subject matter. The budget of South Africa should implement the government’s commitments to reduce the budget deficit and […]
- Fiscal Policy and Macroeconomics Moreover, the peculiarities and current state of the fiscal policy can be discussed by the Council of Economic Advisers, which means that this body is another aspect that might include macro.
- Macroeconomics: Unemployment Rate in North America Such indicators of economic development as the labor force rate and the unemployment rate are the significant aspects of state development and its policies regarding the labor market.
- Applying Macroeconomic Concepts in France The focus should be on analyzing such issues influencing the economic stability in the state as the problem of unemployment, changes in the unemployment rate, as well as changes in the inflation rate.
- France: Applying Macroeconomic Concepts Its continental borders are the North Sea, the English Channel, the Atlantic Ocean, the Bay of Biscay, Spain, Monaco, and Andorra, the Mediterranean Sea, and Italy, Switzerland and Germany, and Belgium and Luxemburg.
- “The Trouble with Macroeconomics” by Paul Romer In his article, Paul Romer addresses the challenges that the global economy has been experiencing due to the rise in the influence of the factors such as scientific research on the development of macroeconomics and […]
- Macroeconomics: McDonald’s Challenges in 2012 Therefore, this hurts McDonald’s reputation as a global fast-food business. The price demand elasticity strategy was a tactic to increase McDonald’s market share.
- American Macroeconomic Situation in 2011 It should be known that various insolvencies that had been experienced are falling and this is good as far as the economy is concerned. The Federal Reserve has maintained low-interest rates and this has been […]
- Australia’s Macroeconomic Policies The unemployment rate had been above 3% once since the the1940s went above 4% in the 1970s, 1980s, and 1990s recessions. The inflation rate was above 10% in the early 1990s.
- Macroeconomic Issues and Funding Adjustments When ADF and ASF are equal, the amount of group 3 funds has for lending would be equal to the total amount group 2iwould be willing to borrow.
- Macroeconomics: Origins, Development and Current State In the event that there are these changes to these variables, the graphs presented in appendix 1 are a show of what is anticipated to happen to the core macroeconomic elements of the economy.
- Macroeconomics Course: Japanese Yen and US Dollar March 1: 1 USD = 81. 8425 JPY March 12: 1 USD = 81.
- 2008 Macroeconomic Collapse and Prevention Efforts The rise in the subprime mortgage rates led to the crash of the stock prices in the US. Therefore, in a volatile market, the aim is to reduce portfolio risk and not maximize trading profits.
- Peter Coy Views on Macroeconomics Peter Coy’s article gives insight into the economic thought on the government’s involvement in the economy. In the article by Peter Coy, critics view the free market as the only thought that can counterbalance the […]
- Macroeconomic Factors of Website Content and Services Since internet usage is advancing significantly, the long-run prices offered in internet marketing would significantly decline as a result of high competition.
- “Lectures in Macroeconomics” by Arnold Kling Both increased productivity and trade are regarded as beneficial for the economy due to the potential ability to move labor resources from one sector that experiences productivity exceeding demand to those that encounters prevalence of […]
- Classical Macroeconomic Analysis and Its Principles The repercussion of the ASF line being horizontal is seen given a scenario where the APE line shifts to the right; implying an increase in expenditure with no funding to compliment it.
- Macroeconomics: Aggregate Planned Expenditures The major role of any economy is to ensure that it coordinates the changes in the level of goods produced and the changes in the demand for the goods.
- Macroeconomic Factors and Hong Kong Stock Returns This chapter covers the background of the study, problem statement, research objectives and hypotheses and the significance of the study. He argues that the inverse relationship between inflation and real stock returns is as a […]
- Macroeconomic Coordination and Demand Shocks Based on their needs, the most appropriate options are for the consumers, especially group two to borrow money in the form of loans, spend the money, and pay back the loan with interest. However, the […]
- Britain’s Economic Issues and Macroeconomic Concepts The spending power of the population has been eroded and the growth of wages is half the level of inflation. This is because there is little excess to be affected than in the first occurrence […]
- Russian Federation’s Macroeconomics in 2011 This resulted in a major decline of the economy with the GDP and the industrial output dropping by up to 50%.
- Johnson & Johnson: Macroeconomic Variables Analysis It will be used to show the effect of the variables on the sales of the product GDP stands for the gross domestic product which is used to represent the total demand for the goods […]
- Macroeconomic Concepts and International Trade Simulation When the per capita income is high, it means that the level of production per individual in the economy is also high. This is referred to as the relative advantage of a country to produce […]
- Macroeconomics in 2010 Newspaper Articles The article has its basis on the recent global financial crisis, which started in the United States and spread to other parts of the world.
- Macroeconomics Performance and Policies of Mexico That is why it is possible to claim that inflation is one of the important macroeconomic issues that are to be solved in the future.
- Brexit Macroeconomic Impact on the United Kingdom One of the most important aspects of the referendum that appealed to pro-Brexit voters was the perception of how immigration can affect the labour market.
- Macroeconomic Indicators and Financial Data Thus, to be a macro-economist in the company means to analyze these macroeconomic factors and suggest a strategy that considers the latest trends in the market or the industry.
- Macroeconomic Elements: the Reduction of Oil Prices Oil prices in the international market have been on a consistent decline since June 2014 and the impact of this decline on the economy of the country has been evident. It is expected that the […]
- Macroeconomic and Microeconomics: Ubiquity and Popularity The discipline focuses on the analysis of global economic issues and the mechanisms and principles that determine the observed behaviors and trends to be able to model the future course of action and predict the […]
- US Macroeconomic Indicators in 2005-2012 The decline in economic growth reported in the first quarter of the year 2012 is a reflection of a lower growth rate in fixed investments and inventory by businesses.
- UAE Macroeconomics and Global Economy Changes The appearance of specific trends in the way countries interact, the high speed of globalization, and the emergence of new dominant agents impact the way economies evolve.
- Scarcity, Decision-Making, and Macroeconomics The inability to concentrate on a particular task due to distractive thoughts about an ill parent/child or the need to make provision for a family usually plays a huge disservice in the matters of general […]
- Azerbaijan Macroeconomic Risk Analysis When entering the gas and oil sector of Azerbaijan, the CEO of the company should determine whether the risk factors outweigh the positive aspects of the industry.
- Japan Macroeconomics: Problems and Possible Solutions Based on this, the problems that need to be addressed as a result of this crisis are threefold: the first is the need to implement some form of reconstruction, the second is to address the […]
- Macroeconomics Fundamentals and Terms The unemployment rate is also used to evaluate the purchasing power of consumers in a particular economy. It is used to estimate the value of a currency and the purchasing power of consumers in a […]
- Macroeconomic Environment: Self Correction of the Economy However, if the demand of shares in the stock market drops, it means that there will be a drop in income payments and many firms will be affected.
- Belgium Macroeconomic Data Analysis In Belgium, expenditure by the central government and the regional governments is separate. In 2012, central government expenditure was 23% of the total government expenditure.
- Macroeconomic Indicators and Their Impact on the Greek Economy To effectively identify and analyze macroeconomic indicators and their impact on the economy of Greece, the report undertook a research and collected information using a range of primary and secondary sources.
- Fundamentals of Macroeconomics Activities Influences The paper evaluates the way in which different activities taking place in the economy affects businesses, households and government dealings. The choices households make in relation to purchase of grocery affect other large-scale factors.
- Current Macroeconomics in the US Most importantly, the building and sale of residential houses have reduced and the cost of housing has also declined prompting a closure of the housing industry in the future.
- Current Macroeconomic Situation in US The economic situation is in the form of recession since the factors of production are not utilized to the maximum. This makes up a component of the federal system of reserve and is mandated to […]
- Wall Street Impacts – Macroeconomics The article is one of the latest reports on the improving international business at both the Wall Street and the European Union, owing to a number of fiscal policies expected within the next few months.
- Equilibrium Supply and Demand – Macroeconomic Demand is the quantity of goods desired by consumers while supply is the amount of goods the producers can offer to the market.
- Germany and Its Macroeconomics At the same time, the growing share of private consumer spending in the German GDP is a wonderful opportunity to expand employment prospects and use its positive results to improve the standards of living in […]
- Larry Elliott: Piketty’s Capital in the Twenty-First Century It is possible, to contradict the rationality of the major theme in Piketty’s book because a simple reduction in inequality may not be the solution.
- Macroeconomic Factors within the EU Recession in the EU has pushed some of the international companies out of the market because of the increased production costs in the region and low profits.
- 2008 Global Recession: UK’s Macroeconomic Policies It is on the basis of these negative effects of the global recession that the group of twenty countries met in the United Kingdom to come up with new macroeconomic policy mechanisms in response to […]
- Public Debt in Managing Macroeconomics The rates compound, and finally the government’s ability to repay the debt is doubted. The solution to the US’ debt crisis is to reduce government spending.
- Macroeconomic Concepts and Models Application Some of the impacts that have brought about more use of the biofuel in the current world have led to the replacement of the liquid oil from 1-2% recently1.
- Current macroeconomic situation in the USA In order to deal with the problem of inflation, the federal government could sell treasuries of the United States such as bonds in the international market.
- Economic Data Comparison of Australia, China, and Greece The budgetary position for Australia and Greece has been increasing from 1999 up to 2009 when the GFC occurred making the governments of these countries to reduce national expenditure and increase taxation to curb the […]
- Setting Macroeconomic Policies Initially, the government sets the inflation target and the Monetary Policy Committee forecasts the expected future inflation through economic statistics and imposes measures to curb it so as to meet the target.
- Project Macroeconomics Forecast Component Compare and contrast differences for the respective statistics prepared by the forecasters From the projection carried out by the CBO forecasters, the economic indicators seem to be at the highest between 2007 and 2010.
- European Macroeconomic Policies and Risks New entrepreneurs need to consider key macroeconomic factors such as aggregate demand polices, aggregate supply policies, fiscal policies, and the policies for the integration of the macroeconomic factors with the European social model.
- United States of America’s Macroeconomic Analysis The political system in the U.S.has been relatively stable over the years, making it the leading democracy in the world. Since the fall of the Soviet Union, the United States of America had experienced a […]
- Macroeconomic Situation of the US The United States boasts of being a leading economic power in the world, and as a result, the recent economic recession in the country led to the repercussions being felt in almost all the parts […]
- The Impact and Link of Macroeconomic Variables on the Share Prices in UK The reason of the difference of stock market behavior in the two countries is explained to be the result of slump of Japan after 1990 and liquidity trap of the late 1990 and start of […]
- Interpreting Macroeconomic Conditions: interest rate Low income levels means that the industry will spend a lot in an effort to increase sales and this will be reflected in high operating costs.
- The Impact of Macroeconomic Variables A case study of the UK and US will be used to illustrate how these variables have an impact on the real exchange markets According to Consumer Price Index can be used as a direct […]
- Nominal and Real GDP Growth Rates When the real GDP is constant, the inflation rate follows the same trend and the natural rate of unemployment is not necessarily constant. When the Real GDP is high, the unemployment rate is low and […]
- France’s Economy: Five Key Macroeconomic Variables However, the economic crisis in Europe and the global economic downturn, which began in 2007, have led to severe reduction in the country’s growth rate.
- Introduction to Macroeconomics: Sequestration and Its Impacts on an Economy According to Choi and Devereux, an increase in the permanent spending results in an increase in the released money, thus, an increase in the circulating currency.
- Macroeconomic Issues Related to the Federal Deficit and the National Debt What is affected by the federal budget deficit, which is equivalent to government debt level, is the change in the rate of interest.
- Exchange Regimes and Their Impact on Macroeconomic Performance The terms and the conditions of the exchange rates can either have a positive or a negative impact on the economic growth of a given country. The managed floating rates are a combination of the […]
- GDP Evaluation and Comparison: China, Greece, and Australia China GDP Annual Growth Rate In the year 2000 the annual growth rate of the GDP was 6% while the highest attained was 13% in the year 2009.
- Macroeconomic Policy About Population Growth Below is a list of twenty developing countries whose population growth was high in the 1960’s and 1970’s and declined at the beginning of the 21st century; Population growth rate GDP per capita Argentina 1 […]
- Macroeconomic Policy under Floating Exchange Rate This means that the exchange rate is flexible and can change from time to time in response to the dynamics of the foreign exchange markets.
- Macroeconomics: Socialism, Totalitarism and US Economics Compare and contrast the approach to economics of the U.S.system of government to Socialism Capitalism, which is the economic system in the U.
- Macroeconomic Analysis Using an Article The prize that a commodity or service is worth in the market is accumulated is summed up to the value of government expenditure and overall consumer expenses and is measured against the income value1. The […]
- Macroeconomics and Reality This demand is affected by the price of the car, the price of other models of cars, tastes and preferences of consumers among others. Many of the models in the article are also difficult to […]
- Macroeconomic Policy Settings in Australia Monetary policies on the other hand are policies used by the reserve bank of Australia to monitor the flow of money in the economy.
- Macroeconomic Policy Settings in Australia The economic growth in Australia is aimed at reducing the unemployment rates in the future. The country has succeeded in achieving economic growth and prosperity in the face of the global recession.
- Macroeconomics: Collapse of the United States Housing Market Such was the experience that the economy of the United States faced in the year 2009 following the crisis that was realized in the housing market.
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Policies The rate of interest will lower to such an extent that the aggregate demand will start to rise until it is equalized with the addition supply of funding.
- Macroeconomics: Determination of GDP It is the market value of these final goods and services that is referred to as gross domestic product. A general rise in the average price of goods and services in an economy is referred […]
- Macroeconomics: Demand of Super Bowl Tickets Rovel argues that the prices of Super Bowl tickets are plummeting because there are very few short sellers and that the location of New Orleans is not optimal since it is not easy to make […]
- Analysis of Macroeconomic Condition of Argentina Despite acquiring the land against the will of the natives, the foreigners ensured that the proceeds from agriculture were used for the development of the country.
- Macroeconomic Study about Argentina Despite the growth in the real GDP of the country, the aforementioned statistics shows a consistent rise in the rate of inflation in the country.
- The Impact of Premature Financial Liberalisation on Macroeconomic and Financial Stability Effects on rate of savings and investment One of the roles of liberalisation is to remove rigidity in the control of rates of exchange and rates of interest, compulsory allocation of credits from banks, and […]
- Comparative Analysis of Macroeconomic Indicators of USA and Brazil The rationale is that unemployment refers to a proportion of the population that has skills and is willing to provide the skills to the labor market.
- Macroeconomic forecast of Turkey for the next 5 years (up to 2017) To determine the unemployment rate, the total population of the labor force and the employed people in a given region/country is considered.
- Macroeconomics: Interest Rates Keynesian theory of interest has been used to explain the effects of changes in the Federal Reserve rate on the general interest rates and prices in the economy.
- Conceptual Study on Macroeconomics Notions The law of demand states that the higher the costof the good or service, the less people will demand it, while the law of supply states that the higher the price of a commodity, the […]
- Macroeconomic Coordination Process The graph, which is one diagram, will show the relationship between the level of interest on the vertical axis and the degrees of GDP, APE and ASF on the horizontal axis.
- A Macroeconomic And Financial Outlook Of New Zealand Some of this factors are the level of consumption of the country’s population, the level of savings and investment and the government’s fiscal and monetary policies.
- Measuring Macroeconomic Concepts As a matter of fact, it can also be referred to as the rate at which the purchasing power of individuals’ changes as time goes by. The country is in a stable period of prices […]
- Great Britain’s Macroeconomics In Relation To The US The mammoth economy was however destabilized by the innumerable costs accrued to the first and the second world wars and the great depression in the ninety’s.
- Macroeconomics: Price Elasticity of Demand Price elasticity of demand refers to the “…responsiveness of changes in the quantity of goods and services demanded in relation to the changes in their prices”.
- Rapidly Developing Macroeconomics in Chile The history of macroeconomic reforms in Chile dates back to the beginning of the 1990s, when the military government initiated the first economic reform.
- Principles of Macroeconomics: Supply and Demand Relationship In conclusion, supply and demand relationship tries to describe macroeconomic variables like price levels and amount of quantity in the economy.
- Macroeconomic Policies in Australia The policy makers therefore always strive to keep the inflation rate at low levels to minimize the effects of a high inflation rate.
🤗 Interesting Macroeconomic Topics
Did you figure out the basic economic terms and concepts? Congratulations! Now, you are ready to go to the next step of your task completing. It is a topic search. Take this step responsibly because a compelling topic is a key to a successful paper.
The process of idea selection may become a real struggle for students. But not for you! We created a list of macroeconomics paper topics. The ideas are divided into several sections based on the type of assignment you need to complete. The macroeconomics topic choice has never been so easy!
📄 Macroeconomics Topics for Essay
- Effect of oil prices on different countries’ GDP.
- The political economy of international trade.
- Limitations of GDP as a measure of economic welfare.
- The significance of Adam Smith’s “invisible hand” concept in modern economics.
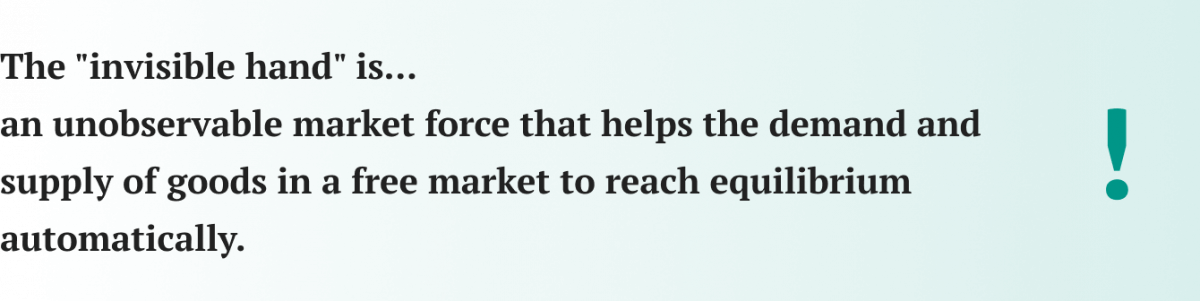
- Remittances role in spurring global economic growth.
- Economic factors of Dubai tourism demand.
- The effects of inflation targeting.
- The interactions of economic and political science.
- The nature of the catch-up growth phenomenon in developing countries.
- The benefits of medical tourism to the world economy.
- The economic recession of 2007-2009 . Conduct an economic analysis of the worldwide crisis of 2007-2009. What were the causes and effects of the recession? Analyze the role of monetary and fiscal policies. What role do they play in reducing the risks of a total financial collapse during the crisis?
- The tourism industry in the state of Oregon . Investigate traveling commerce in Oregon from an economic perspective. How thousands of tourists help to maintain the appropriate level of economic growth? Explore the impact of tourism on the economy of Oregon and the USA. Look at them separately.
- The impact of the COVID -19 outbreak on the global economy . Explore the influence of the pandemic on the different branches of the economy. Analyze the readiness of the countries to face financial difficulties. Were the governments’ reactions to the risks of recession effective enough?
- Practical problems of active economic stabilization policy . There are three key negative effects of stabilization policy: – recognition lag – decision lag – impact lagDiscuss how these lags may lead to destabilization of the economy instead of stabilization. Why can a stabilization policy be useful for one class of enterprises? Why can it be ineffective for another one?
- Neoclassical economists. Analyze the scientific impact of three the most famous neoclassical economists: -Thorstein Veblen -Eliot Roy Weintraub -George Joseph StiglerCompare and contrast their approaches to macroeconomic objectives. How did these figures contribute to the development of the modern economy?
🖥️ Macroeconomics Topics for Presentation
- Sustainable economic development. The four greens.
- European macroeconomic policies and risks.
- International environmental concerns in economics.
- Macroeconomic environment: self-correction of the economy .
- Economic systems types: free market and a mixed economy.
- Abu Dhabi commercial bank and financial regulation.
- Economic inequality as a result of globalization.
- Cultural differences and ethics of international trading.
- Economic analysis of criminal law.

- Economic fluctuations in aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
- Theory of liquidity preference . Analyze Keyne’s theory of liquidity preference. Can interest rate adjustments indeed bring money supply and demand in balance? Use visual aids (graphs, charts) to make the understanding of the topic more accessible.
- Who leads the economy: economists or politicians? Explore the influence of politics on the economic sector. Why economics and politics cannot exist independently? Investigate the positive and negative outcomes of economic and political interactions. List all the key ideas on the slides. Appropriate illustrations will help the audience comprehend your ideas more effectively.
- Money laundering as one of the most critical financial crimes . Explain the mechanisms of economic crimes that occur in modern society. What criminal procedures are applied to deal with money laundering? What are the possible ways to reduce the risks of crimes against the property?
- Short-run aggregate supply and long-run aggregate supply differences. Explore the notions. What do they mean? How are they familiar? To make your presentation more professional, use slides. Demonstrate the correlation of short-run aggregate supply and long-run aggregate supply curves on the graph.
- Keynesian economics . Briefly introduce John Maynard Keynes. What were his economic approaches? Illustrate his models (the liquidity trap, IS-LM plot, Keynes–Samuelson cross). Highlight the significance of Keynesian discoveries for modern economics.
📊 Macroeconomics Topics for Project
- The costs and benefits of incurring an annual federal budget deficit.
- Cause and effects of the mortgage crisis.
- The effects of the introduction of the national minimum wage on employment.
- GDP growth rate and economic future of the United States.
- Alternative policies towards the exchange rate.
- Economic tools: alcohol abuse problem-solving.
- Optimizing production in the food industry.
- Automatic economic stabilizers.
- Methods of sustainable economic development.
- The role of China and the USA for the international economy. Compare and contrast the impact of both countries for global economic development.
- Strategies to overcome economic recession . Develop your ways to deal with economic obstacles. How to be ready for a financial crisis? How to reduce the negative consequences of the recession? State your ideas clearly and structure them wisely.
- Ways to reduce the unemployment level . Examine the causes and effects of unemployment. What would be possible mechanisms of dealing with the issue of lack of working places in a country? Explore the concept of the natural unemployment level and consider it while developing your project.
- Business establishment. Imagine you are planning to open a company. Applying economic concepts, develop a business plan for your enterprise. Organize the funds’ distribution within a company. What macroeconomic concepts should be used for this project

- Inflation vs. deflation. Investigate the positive and negative sides of inflation and deflation. What causes more harm to the national economy? Develop a strategic plan of dealing with the obstacles of inflation and deflation.
- Overconsumption of goods: beneficial for the producers, bad for the environment. Comment on the problem of unreasonable goods’ purchases. Why don’t people consider the lack of environmental resources while buying useless stuff? Develop a mechanism to control the consumption of the products to save the environment.
👩💻 Macroeconomics Topics for Research
- Different forms of currency regimes and their impact on economic determinants.
- The implications of internet-banking on bank profitability.
- The trickle-down economics definition and aspects .
- Effects of increasing interest rates in Africa.
- The structure, history, and activities of the World Bank.
- Analysis of economic indicators for the United States and South Korea.
- The impact of demographic fluctuations within a country on its economic performance.
- The importance of the governmental support of small and medium businesses.
- The causes of economic inequality, poverty of underdeveloped countries.
- Macroeconomic implications of the healthcare sector development.
- The real exchange rate and the nominal exchange rate. Conduct research and analyze the differences between real and nominal exchange rates. What are the reasons for utilizing a real exchange rate? Support your ideas with arguments and appropriate examples.
- Theory of effective demand. Explore the significance of a balanced demand for the global economy. What place does Keynesianism take in this theory? For convenience, demonstrate your findings in the graphs.
- The bright future of the economy of ASEAN countries . Explain how the ASEAN (the Association of Southeast Asian Nations) can become a leading economic force globally. What opportunities and benefits do these countries have? Using economic thinking, suggest the right direction for the economic growth of ASEAN countries.

- How the Coronavirus outbreak affected stock prices and growth expectations? The worldwide pandemic noticeably weakened international economic performance. Discuss the adverse effects of COVID-19 on stock prices. What strategies did the governments implement to maintain a stable financial situation in a country?
- The impact of immigration on the national economy. What are the positive and negative effects of immigration? Develop an economic strategy to reduce the drawback of immigration on the national economy and maximize the benefits.
✍️ Macroeconomics Topics for Term Paper
- Unemployment rate as the most prominent national economy challenge .
- The nation’s budget deficit and how it relates to economic theory and crisis .
- Market elasticity in the banking industry.
- Minimum wages and their effects on the hospitality industry .
- New liquidity standards and implications.
- Corporate entrepreneurship and new business venturing.
- Economic factors on the stock market.
- The threat of Norwegian commercial banks for the economic stability of a country.
- Indicators of the upcoming recession and the strategies to prevent it.
- Influence of consumers’ tastes and preferences on market growth.
- The economy of France: five key macroeconomic variables . Provide a brief background of France’s economy and the overview of five variables. Analyze of the country’s economy. What would be some possible policy recommendations? Provide graphs, charts, or tables if necessary.
- Strategies for raising the country’s per capita gross domestic product. Explore the possible ways to increase the GDP per capita. How will the rise of GDP stimulate the country’s economic growth? Provide clear arguments to support your opinion.
- The benefits of investments in innovative technologies . Explain why business owners should invest in innovations. How will it help them to increase the profitability of the companies? Examine the future of economics. Will the high-quality production be possible without modern technologies?
- Profit maximization strategies. Analyze the existing ways of maximizing the firms’ profit. What are the benefits and drawbacks of these strategies? Develop your profit-maximizing method. What macroeconomic principles and theories would you use for it? State your ideas clearly and provide examples to support your position.

- Globalization: an opportunity or a threat to the international economy? Analyze the positive and negative effects of globalization. What obstacles does globalization cause to small entrepreneurial organizations? How does globalization influence huge corporations? Present bright examples to solidify your ideas.
🔥 20 More Hot Topics in Macroeconomics
Did you look through our ideas and still unsure of which one to select? Then, take a look at the following section. Here, you can find the most popular and effective macroeconomics paper topics. Use one of the ideas from this list, and don’t worry that it will be inappropriate.
- International political economy perspectives.
- An invisible network of demand and supply.
- Factors affecting marketing and production decisions.
- The impact of monetary policy on economic stabilization.
- Behavioral finance and economics.
- Elasticity and its crucial role in business development.
- Sustainability and trends of the global trade imbalance.
- Financial economics for infrastructure and fiscal policy.
- The ways to increase the stockholders’ equities after the settlement of liabilities.
- Core-Econ: what economic data offers this online platform?
- The causes and effects of inflationary and deflationary gaps.
- The most effective ways to reach market equilibrium.
- The application of the macroeconomic concepts in real-life situations.
- Price discrimination problem. Introduce the phenomenon of price discrimination in the modern economic environment. What are the causes of the problem? What are the possible solutions? After the problem is solved, suggest future directions to prevent further concerns about price discrimination.
- The impact of the governmental regulations on the national economy. This is a topic of multiple-purpose. Are you searching for an idea for a term paper, presentation, or a capstone project? Then use this topic. It is quite relatable and offers a wide variety of sources to explore.
- The impact of biology progress on economic growth . Explain how biological innovations improve the production capacities of firms. What impact do such changes have on the healthcare, food, and agricultural industries? Refer to statistical data from reliable sources to support your ideas.
- Economic ethics . Analyze the progress of economic ethics from middle ages to contemporary times. Why is the following of moral rules while developing a business essential? Provide solid arguments and clear examples to prove your position.
- The importance of GDP for investors. Explain how investors make their decisions based on the GDP of a country. What factors do the investors take into consideration while investing money?

- Unemployment and inflation rates correlation. Explore the relationship between inflation and unemployment in the short-run and the long-run. Why do the outcomes of their correlation are different in the short-run and long-run? Refer to the Philips curve line graph to demonstrate your findings.
- Securities market structures. There are four types of securities market structures: – Quote-driven markets – Order-driven markets – Hybrid markets – Brokered markets Compare and contrast them. What structure is the most transparent and effective? How to minimize the risks of the securities market collapse?
- What Is Macroeconomics in Economics?
- What Are Macroeconomics and Examples?
- What Are the Five Macroeconomics?
- What Are the Four Main Factors of Macroeconomics?
- Which Is the Main Objective of Macroeconomics?
- Why Is Macroeconomics Important?
- What Are the Primary Tools of Macroeconomics?
- How Do Macroeconomics Factors Affect SMEs?
- How Does the Study of Microeconomics Differ From That of Macroeconomics?
- How Does Macroeconomics Affect Business?
- How Does Macroeconomics Affect Managerial Decision Making?
- How Well Can the New Open Economy Macroeconomics Explain the Exchange Rate?
- What Can Civil Society Expect From Academic Macroeconomics?
- What’s Wrong With Modern Macroeconomics?
- What Does the Entrepreneurial Problem Reveal About Keynesian Macroeconomics?
- What Are the Consequences for Macroeconomics During the Past 60 Years?
- Where Did Modern Macroeconomics Go Wrong?
- Which Way Forward for Macroeconomics and Policy Analysis?
- Why Does Macroeconomics Not Supervene on Microeconomics?
- Will the New Keynesian Macroeconomics Resurrect the IS-LM Model?
- Does Akerlof and Shiller’s Animal Spirits Provide a Helpful New Approach to Macroeconomics?
- Does Macroeconomics Need Microeconomic Foundations?
- How Macroeconomics Different From Microeconomics?
- How Can Macroeconomists Use Microeconomic Theory to Guide Them in Their Work?
- Macroeconomics: Should the Minimum Wage Increase?
- Macroeconomics: What Are the Main Causes of Unemployment in an Economy?
🔨 Tricks to Nail a Macroeconomics Paper
You are likely to have a general idea of essay writing. A thesis statement, five-paragraph structure, and arguments with supporting evidence are all part of it. Your paper on macroeconomics will probably follow the same old formula as well. However, we found a few tricks that will make the writing process less complicated. They can be used for any paper on macroeconomics.
- Find out the type of assignment beforehand. The structure of the project will differ drastically from that of the research paper. If it’s an essay, determine whether its an argumentative, informative, cause and effect, etc. Follow the structure If you need to prepare a presentation. Make appropriate slides to help the audience get your ideas. But remember to make the PowerPoint presentation professional. Use a readable font and suitable design to impress your listeners.
- academic style;
- suitable writing formats;
- reliable sources;
- proper citations.
- Change the central idea. The first viewpoint that comes to your mind can be erroneous. Any piece of academic writing requires a thought-out message. If you’re not sure what to state in your thesis, search for another macroeconomic topic for a paper. And don’t be afraid of changing it if necessary. Remember, a well-developed central idea is a key to a high grade. So, take enough time to compose a strong thesis statement.
- Research before writing. Macroeconomics is a broad field, so you have to make sure you see all the angles of the issue. Look for related macroeconomic topics or overlapping areas of study. If needed, improve your research question or change the perspective of your research. Make sure to select only credible sources. And don’t forget to cite them properly. Are you unsure about formatting requirements? Double-check the rules of the writing format you use.
- Outline your paper. Any writing guide will tell you that this is a great way to ensure the logical order. A well-developed outline will help you to structure your paper correctly. Thus, the readers will get your ideas without any difficulties. Moreover, fixing it is easier than the written text. So, don’t skip this step. By spending some time on outlining, you will save a lot of time on writing.
- Set out the size of each part. Remember that the introduction and conclusion must be shorter than the body. Moreover, the central part of your paper has to be divided into several sections. Use a separate body paragraph for each key point. A long and complicated text unit will only distract the readers’ attention. So, each part should follow its purpose and deliver the idea effectively.
- Find examples . Appropriate examples always improve the quality of a paper. Firstly, the readers understand the ideas more deeply when the writer presents the illustrations. Secondly, well-selected cases establish the credibility of a document. So, you can use them for reference. But be careful. To avoid confusion, make sure you provide suitable and relatable examples.
- Use online grammar correctors. We are not robots, and we make mistakes. That’s natural! Fortunately, we have an opportunity to use online grammar correctors. Such tools will ensure you haven’t missed an error while proofreading. One of the most useful and efficient ones is Grammarly . Besides correcting your spelling or grammar mistakes, it will also suggest style and vocabulary improvements. Why not use the benefits of correcting tools if there is such an opportunity?

Thank you for visiting our page! We hope your article was helpful. Don’t forget to share your macroeconomic topics and essay writing tips with your friends!
🔗References
- Macroeconomics: Economics and Finance, Khan Academy
- Macroeconomics: Articles, Research, & Case Studies on Macroeconomics, HBS Working Knowledge
- Top 100 Economics Blogs Of 2020: Prateek Agarwal, Economics Theory & News, Intelligent Economist
- Hot Topics in the U.S. Economy: US Economy and News, The Balance
- Writing Economics: Robert Neugeboren with Mireille Jacobson, Harvard University
- Macroeconomics Essay: Bartleby
- Organizing an Essay: Writing Advice by Jerry Plotnick, University College Writing Centre, University of Toronto
- Academic Essay Writing, Some Guidelines: Department of Economics, Carleton University
- Sample Business and Economics Essay: Research & Learning Online, Monash University
- Macroeconomics: Britannica
- Studies in Macroeconomic History: Cambridge Core, Cambridge University Press
- 14 Types of Essay Hooks with Samples And How to Write Them: EduPeet
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 28). 261 Macroeconomics Topics for Any Paper [+Tips]. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/macroeconomics-essay-topics/
"261 Macroeconomics Topics for Any Paper [+Tips]." IvyPanda , 28 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/macroeconomics-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '261 Macroeconomics Topics for Any Paper [+Tips]'. 28 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "261 Macroeconomics Topics for Any Paper [+Tips]." February 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/macroeconomics-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "261 Macroeconomics Topics for Any Paper [+Tips]." February 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/macroeconomics-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "261 Macroeconomics Topics for Any Paper [+Tips]." February 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/macroeconomics-essay-topics/.
- Financial Crisis Paper Topics
- Economic Growth Research Ideas
- Acquisition Essay Ideas
- Managerial Economics Essay Topics
- Behavioral Finance Titles
- National Debt Research Topics
- Corporate Finance Essay Ideas
- Budget Ideas
- Forecasting Questions
- Marxism Essay Ideas
- Collective Bargaining Essay Titles
- Economic Inequality Questions
- Market Research Titles
- Unemployment Essay Topics
- Trade Questions

Macroeconomics – Notes and Essays
Main topics in macroeconomics
- Policies to reduce current account deficit
- Policies to reduce budget deficit
- Causes of Boom and Bust Cycles
- Policies to increase economic growth
- Theories of economic growth
- Environmental economics
- Fiscal policy
- Globalisation
- Effect of an appreciation
- Effect of devaluation
- European Union
- Monetary policy
- Policies to reduce inflation
- International trade
- Supply-side policies
- Policies to reduce unemployment
- Saving Ratio
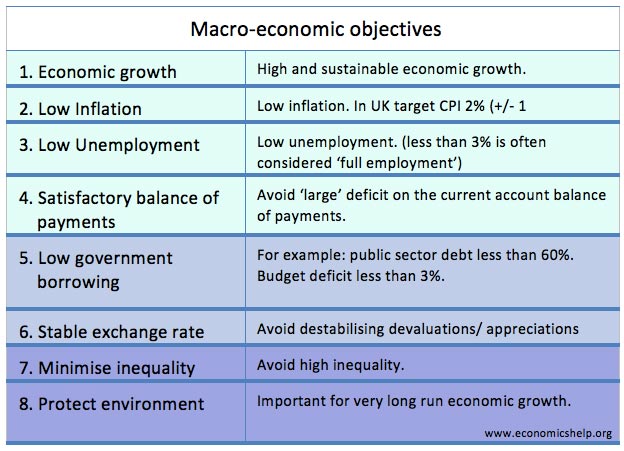
- Macroeconomic objectives and conflicts
Macroeconomic schools
- Classical vs Keynesian
- Real Business Cycle
- Austrian economics
Macro Graphs and data
- Economic growth
- Unemployment
- Current account b of p
UK economic periods
- 1940s and 1950s – Austerity, rationing, war debt, but full employment, the new welfare state and rising living standards.
- 1960s – The ‘You’ve never had it so good era’ starts to unwind .
- 1970s – The Era of Discontent . Strikes, 3 day weeks, inflation, boom and bust. The 70s had everything except stability
- 1980s – Boom and Bust economy – The UK economy in the 1980s
- Late 1980s – The Lawson Boom . Rapid growth, inflation and recession
- 1990s – Recession and great stability – Recovering from the recession and leaving ERM
- The economics of the 2000s – from stability to financial crisis
- 1992-2007 – The great moderation – a period of economic growth between 1992 and 2007
- 2010-16 – The austerity years – The economic record of Cameron and Osborne.
- Great Depression of 1929-37
- UK recession of 1981
- UK recession of 1991-92
- UK recession of 2008-2013
Devaluations
- UK devaluation of 1967
- Leaving the ERM in 1992
- Brexit devaluation 2016
- Economists toolkit – general tips on answering macroeconomic questions.
Latest Blogs
- Latest on UK economy
Macro Economic Essays
- Essays on Recessions
- Essays on Credit Crunch
- Discuss whether the primary macroeconomic target of the govt should be low inflation? “The govt has given the MPC an inflation target of CPI 2.% +/-1. Therefore Monetary policy will be designed in order to achieve this goal…”
- inflation “Inflation occurs when there is a continuous increase in the general price level as measured by the RPIX. There are various explanations for this..”
- What determines the Natural Rate of Unemployment “The natural or (equilibrium) level of unemployment is determined by calculating the level of unemployment when the labour market is in equilibrium.”
- What Changes the Natural Rate of Unemployment “The Natural rate is mainly composed of frictional and structural unemployment, therefore, factors that affect these types of unemployment will alter the natural rate.”
- Should Government Seek to Increase the Rate of Economic Growth? Arguments for and against increasing the rate of economic growth
- Government Intervention in the Macro Economy
- AS Macro Economic Essays
Essays on Inequality / Poverty
- Minimum Wage in the UK
- Distribution of Income in the UK
- Policies to Reduce Inequality
- Causes of Poverty
- Tax System in the UK
- Definitions of Investment
- View: A-level Model essays (macro and micro)
- View: AS Model essays
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Macroeconomics?
Understanding macroeconomics.
- Macro vs. Microeconomics
- Limitations
- Schools of Thought
How to Influence Macroeconomics
The bottom line.
- Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics Definition, History, and Schools of Thought
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Group1805-3b9f749674f0434184ef75020339bd35.jpg)
Thomas J Catalano is a CFP and Registered Investment Adviser with the state of South Carolina, where he launched his own financial advisory firm in 2018. Thomas' experience gives him expertise in a variety of areas including investments, retirement, insurance, and financial planning.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/P2-ThomasCatalano-d5607267f385443798ae950ece178afd.jpg)
Pete Rathburn is a copy editor and fact-checker with expertise in economics and personal finance and over twenty years of experience in the classroom.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/E7F37E3D-4C78-4BDA-9393-6F3C581602EB-2c2c94499d514e079e915307db536454.jpeg)
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of an overall economy, which encompasses markets, businesses, consumers, and governments. Macroeconomics examines economy-wide phenomena such as inflation, price levels, rate of economic growth, national income, gross domestic product (GDP), and changes in unemployment.
Some of the key questions addressed by macroeconomics include: What causes unemployment? What causes inflation? What creates or stimulates economic growth? Macroeconomics attempts to measure how well an economy is performing, understand what forces drive it, and project how performance can improve.
Key Takeaways
- Macroeconomics is the branch of economics that deals with the structure, performance, behavior, and decision-making of the whole, or aggregate, economy.
- The two main areas of macroeconomic research are long-term economic growth and shorter-term business cycles.
- Macroeconomics in its modern form is often defined as starting with John Maynard Keynes and his theories about market behavior and governmental policies in the 1930s; several schools of thought have developed since.
- In contrast to macroeconomics, microeconomics is more focused on the influences on and choices made by individual actors—such as people, companies, and industries—in the economy.
Investopedia / Julie Bang
As the term implies, macroeconomics is a field of study that analyzes an economy through a wide lens. This includes looking at variables like unemployment, GDP , and inflation . In addition, macroeconomists develop models explaining the relationships between these factors.
These models, and the forecasts they produce, are used by government entities to aid in constructing and evaluating economic, monetary, and fiscal policy. Businesses use the models to set strategies in domestic and global markets, and investors use them to predict and plan for movements in various asset classes.
Properly applied, economic theories can illuminate how economies function and the long-term consequences of particular policies and decisions. Macroeconomic theory can also help individual businesses and investors make better decisions through a more thorough understanding of the effects of broad economic trends and policies on their own industries.
History of Macroeconomics
While the term "macroeconomics" dates back to the 1940s, many of the field's core concepts have been subjects of study for much longer. Topics like unemployment, prices, growth, and trade have concerned economists since the beginning of the discipline in the 1700s. Elements of earlier work from Adam Smith and John Stuart Mill addressed issues that would now be recognized as the domain of macroeconomics.
In its modern form, macroeconomics is often defined as starting with John Maynard Keynes and his book The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money in 1936. In it, Keynes explained the fallout from the Great Depression , when goods went unsold and workers were unemployed.
Throughout the 20th century, Keynesian economics, as Keynes' theories became known, diverged into several other schools of thought.
Before the popularization of Keynes' theories, economists generally did not differentiate between microeconomics and macroeconomics. The same microeconomic laws of supply and demand that operate in individual goods markets were understood to interact between individual markets to bring the economy into a general equilibrium , as described by Leon Walras .
The link between goods markets and large-scale financial variables such as price levels and interest rates was explained through the unique role that money plays in the economy as a medium of exchange by economists such as Knut Wicksell, Irving Fisher, and Ludwig von Mises.
Macroeconomics vs. Microeconomics
Macroeconomics differs from microeconomics , which focuses on smaller factors that affect choices made by individuals. Individuals are typically classified into subgroups, such as buyers, sellers , and business owners. These actors interact with each other according to the laws of supply and demand for resources, using money and interest rates as pricing mechanisms for coordination. Factors studied in both microeconomics and macroeconomics typically influence one another.
A key distinction between microeconomics and macroeconomics is that macroeconomic aggregates can sometimes behave in very different ways or even the opposite of similar microeconomic variables. For example, Keynes referenced the so-called Paradox of Thrift, which argues that individuals save money to build wealth on a microeconomic level. However, when everyone tries to increase their savings at once, it can contribute to a slowdown in the economy and less wealth in the aggregate, macroeconomic level. This is because there would be a reduction in spending, affecting business revenues, and lowering worker pay.
Limits of Macroeconomics
It is also important to understand the limitations of economic theory. Theories are often created in a vacuum and lack specific real-world details like taxation, regulation, and transaction costs. The real world is also decidedly complicated and includes matters of social preference and conscience that do not lend themselves to mathematical analysis.
It is common to find the phrase ceterus paribus , loosely translated as "all else being equal," in economic theories and discussions. Economists use this phrase to focus on specific relationships between variables being discussed, while assuming all other variables remain fixed.
Even with the limits of economic theory, it is important and worthwhile to follow significant macroeconomic indicators like GDP, inflation, and unemployment. This is because the performance of companies, and by extension their stocks, is significantly influenced by the economic conditions in which the companies operate.
Likewise, it can be invaluable to understand which theories are currently in favor, and how they may be influencing a particular government administration. Such economic theories can say much about how a government will approach taxation, regulation, government spending, and similar policies. By better understanding economics and the ramifications of economic decisions, investors can get at least a glimpse of the probable future and act accordingly with confidence.
Macroeconomic Schools of Thought
The field of macroeconomics is organized into many different schools of thought, with differing views on how the markets and their participants operate.
Classical economists held that prices, wages, and rates are flexible and markets tend to clear unless prevented from doing so by government policy; these ideas build on Adam Smith's original theories. The term “classical economists” is not actually a school of macroeconomic thought but a label applied first by Karl Marx and later by Keynes to denote previous economic thinkers with whom they disagreed.
Keynesian economics was founded mainly based on the works of John Maynard Keynes and was the beginning of macroeconomics as a separate area of study from microeconomics. Keynesians focus on aggregate demand as the principal factor in issues like unemployment and the business cycle.
Keynesian economists believe that the business cycle can be managed by active government intervention through fiscal policy, where governments spend more in recessions to stimulate demand or spend less in expansions to decrease it. They also believe in monetary policy, where a central bank stimulates lending with lower rates or restricts it with higher ones.
Keynesian economists also believe that certain rigidities in the system, particularly sticky prices , prevent the proper clearing of supply and demand.
The Monetarist school is a branch of Keynesian economics credited mainly to the works of Milton Friedman. Working within and extending Keynesian models, Monetarists argue that monetary policy is generally a more effective and desirable policy tool to manage aggregate demand than fiscal policy. However, monetarists also acknowledge limits to monetary policy that make fine-tuning the economy ill-advised and instead tend to prefer adherence to policy rules that promote stable inflation rates.
New Classical
The New Classical school, along with the New Keynesians, is mainly built on integrating microeconomic foundations into macroeconomics to resolve the glaring theoretical contradictions between the two subjects.
The New Classical school emphasizes the importance of microeconomics and models based on that behavior. New Classical economists assume that all agents try to maximize their utility and have rational expectations , which they incorporate into macroeconomic models. New Classical economists believe that unemployment is largely voluntary and that discretionary fiscal policy destabilizes, while inflation can be controlled with monetary policy.
New Keynesian
The New Keynesian school also attempts to add microeconomic foundations to traditional Keynesian economic theories. While New Keynesians accept that households and firms operate based on rational expectations, they still maintain that there are a variety of market failures, including sticky prices and wages. Because of this "stickiness," the government can improve macroeconomic conditions through fiscal and monetary policy.
The Austrian Schoo l is an older school of economics that is seeing some resurgence in popularity. Austrian economic theories mainly apply to microeconomic phenomena. However, like the so-called classical economists, they never strictly separated microeconomics and macroeconomics.
Austrian theories also have important implications for what are otherwise considered macroeconomic subjects. In particular, the Austrian business cycle theory explains broadly synchronized (macroeconomic) swings in economic activity across markets due to monetary policy and the role that money and banking play in linking (microeconomic) markets to each other and across time.
Macroeconomic Indicators
Macroeconomics is a rather broad field, but two specific research areas dominate the discipline. The first area looks at the factors that determine long-term economic growth . The other looks at the causes and consequences of short-term fluctuations in national income and employment, also known as the business cycle .
Economic Growth
Economic growth refers to an increase in aggregate production in an economy. Macroeconomists try to understand the factors that either promote or retard economic growth to support economic policies that will support development, progress, and rising living standards.
Economists can use many indicators to measure economic performance. These indicators fall into 10 categories:
- Gross Domestic Product indicators : Measure how much the economy produces
- Consumer Spending indicators : Measure how much capital consumers feed back into the economy
- Income and Savings indicators : Measure how much consumers make and save
- Industry Performance indicators : Measure GDP by industry
- International Trade and Investment indicators : Indicate the balance of payments between trade partners, how much is traded, and how much is invested internationally
- Prices and Inflation indicators : Indicate fluctuations in prices paid for goods and services and changes in currency purchasing power
- Investment in Fixed Assets indicators : Indicate how much capital is tied up in fixed assets
- Employment indicators : Show employment by industry, state, county, and other areas
- Government indicators : Show how much the government spends and receives
- Special indicators : Include all other economic indicators, such as distribution of personal income, global value chains, healthcare spending, small business well-being, and more
The Business Cycle
Superimposed over long-term macroeconomic growth trends, the levels and rates of change of significant macroeconomic variables such as employment and national output go through fluctuations. These fluctuations are called expansions, peaks, recessions, and troughs—they also occur in that order. When charted on a graph, these fluctuations show that businesses perform in cycles; thus, it is called the business cycle.
The National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) measures the business cycle, which uses GDP and Gross National Income to date the cycle. The NBER is also the agency that declares the beginning and end of recessions and expansions.
Because macroeconomics is such a broad area, positively influencing the economy is challenging and takes much longer than changing the individual behaviors within microeconomics. Therefore, economies need to have an entity dedicated to researching and identifying techniques that can influence large-scale changes.
In the U.S., the Federal Reserve is the central bank with a mandate of promoting maximum employment and price stability. These two factors have been identified as essential to positively influencing change at the macroeconomic level.
To influence change, the Fed implements monetary policy through tools it has developed over the years, which work to affect its dual mandates. It has the following tools it can use:
- Federal Funds Rate Range : A target range set by the Fed that guides interest rates on overnight lending between depository institutions to boost short-term borrowing
- Open Market Operations : Purchase and sell securities on the open market to change the supply of reserves
- Discount Window and Rate : Lending to depository institutions to help banks manage liquidity
- Reserve Requirements : Maintaining a reserve to help banks maintain liquidity
- Interest on Reserve Balances : Encourages banks to hold reserves for liquidity and pays them interest for doing so
- Overnight Repurchase Agreement Facility : A supplementary tool used to help control the federal funds rate by selling securities and repurchasing them the next day at a more favorable rate
- Term Deposit Facility : Reserve deposits with a term, used to drain reserves from the banking system
- Central Bank Liquidity Swaps : Established swap lines for central banks from select countries to improve liquidity conditions in the U.S. and participating countries' central banks
- Foreign and International Monetary Authorities Repo Facility : A facility for institutions to enter repurchase agreements with the Fed to act as a backstop for liquidity
- Standing Overnight Repurchase Agreement Facility : A facility to encourage or discourage borrowing above a set rate, which helps to control the effective federal funds rate
The Fed continuously updates the tools it uses to influence the economy, so it has a list of many other previously used tools it can implement again if needed.
What is the most important concept in all of macroeconomics?
The most important concept in all of macroeconomics is said to be output, which refers to the total amount of good and services a country produces. Output is often considered a snapshot of an economy at a given moment.
What are the 3 Major Concerns of Macroeconomics?
Three major macroeconomic concerns are the unemployment level, inflation, and economic growth.
Why Is Macroeconics Important?
Macroeconomics helps a government evaluate how an economy is performing and decide on actions it can take to increase or slow growth.
Macroeconomics is a field of study used to evaluate overall economic performance and develop actions that can positively affect an economy. Economists work to understand how specific factors and actions affect output, input, spending, consumption, inflation, and employment.
The study of economics began long ago, but the field didn't start evolving into its current form until the 1700s. Macroeconomics now plays a large part in government and business decision-making.
Bureau of Economic Analysis. " Data by Topic ."
National Bureau of Economic Research. " US Business Cycle Expansions and Contractions ."
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve. " Policy Tools ."
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. " Policy Tools | Expired Tools ."
- Economics Defined with Types, Indicators, and Systems 1 of 33
- Economy: What It Is, Types of Economies, Economic Indicators 2 of 33
- A Brief History of Economics 3 of 33
- Is Economics a Science? 4 of 33
- Finance vs. Economics: What's the Difference? 5 of 33
- Macroeconomics Definition, History, and Schools of Thought 6 of 33
- Microeconomics Definition, Uses, and Concepts 7 of 33
- 4 Economic Concepts Consumers Need To Know 8 of 33
- Law of Supply and Demand in Economics: How It Works 9 of 33
- Demand-Side Economics Definition, Examples of Policies 10 of 33
- Supply-Side Theory: Definition and Comparison to Demand-Side 11 of 33
- What Is a Market Economy and How Does It Work? 12 of 33
- Command Economy: Definition, How It Works, and Characteristics 13 of 33
- Economic Value: Definition, Examples, Ways To Estimate 14 of 33
- Keynesian Economics Theory: Definition and How It's Used 15 of 33
- What Is Social Economics, and How Does It Impact Society? 16 of 33
- Economic Indicator: Definition and How to Interpret 17 of 33
- Top 10 U.S. Economic Indicators 18 of 33
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Formula and How to Use It 19 of 33
- What Is GDP and Why Is It So Important to Economists and Investors? 20 of 33
- Consumer Spending: Definition, Measurement, and Importance 21 of 33
- Retail Sales: Definition, Measurement, and Use As an Economic Indicator 22 of 33
- Job Market: Definition, Measurement, Example 23 of 33
- The Top 25 Economies in the World 24 of 33
- What Are Some Examples of Free Market Economies? 25 of 33
- Is the United States a Market Economy or a Mixed Economy? 26 of 33
- Primary Drivers of the Chinese Economy 27 of 33
- Japan Inc.: What It is, How It Works, History 28 of 33
- The Fundamentals of How India Makes Its Money 29 of 33
- European Union (EU): What It Is, Countries, History, Purpose 30 of 33
- The German Economic Miracle Post WWII 31 of 33
- The Economy of the United Kingdom 32 of 33
- How the North Korean Economy Works 33 of 33
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Economies-of-Scale-56a093c45f9b58eba4b1b0b2.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Macroeconomics - Free Essay Samples And Topic Ideas
Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole, including topics such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. Essays could delve into the basic principles of macroeconomics, explore different macroeconomic models and theories, and discuss the implications of macroeconomic policy on individuals and businesses. We’ve gathered an extensive assortment of free essay samples on the topic of Macroeconomics you can find at Papersowl. You can use our samples for inspiration to write your own essay, research paper, or just to explore a new topic for yourself.
Great Depression Vs. Great Recession
Both the Great Depression and the Great Recession were major events that have occurred in the United States economy that have had lasting effects on the country and other countries around the world. But these events were necessarily good ones. They were two of the greatest crises in American economic history. The Great Depression was first, occurring from 1929 to1939. The Great Recession happened many decades in the future, starting in late 2007 and ending in early 2010. Comparison of […]
Why was Herbert Hoover Blamed for the Great Depression?
President Herbert Hoover is often blamed for the great depression for many reasons, he had ideas put into place that were meant to aid the problems in the economy but hurt it instead. Pro-labour policies made by President Hoover after the stock market crash of 1929 caused the majority of the nation's gross domestic product to decline over the next two years. This made what could have been a bad recession turn into the Great Depression. There were many reasons […]
What was the Great Depression and why did it Start in the USA
There are many significant events that have shaped America’s history. Some were infamous, some scandalous and some we choose to overlook..According to the PBS film “The Great Depression”, The Great Depression was one of the most traumatic and gut wrenching event throughout history. This film outline the events leading up to the great depression and highlights some of the significant events during this time period. The Great Depression was an economic downturn that began in 1929 while president Herbert Hoover […]
We will write an essay sample crafted to your needs.
Great Depression: what Happened, Causes, how it Ended
During the 1930s. America went through one of the worst economic declines in world history, The Great Depression. Many believe it was sole because of the stock market crash, however other factors played a huge role in causing the Great Depression to occur. Bank failures, the Smoot-Hawley Tariff in the 1930s, and weather conditions from the Dust Bowl all played a critical factor in influencing this economic depression within America. Throughout America's history, much examination has been placed in the […]
The Social Theories Behind Illegal Immigration
Overview In the U.S., there approximately eleven million undocumented immigrants and more are to come. Illegal immigration has become a serious problem in the cause of many social, economic, security, and legal issues within the country. Although illegal immigrants have helped the economy, humbled, and developed the overall image of America, members of the House find that the U.S. should not allow anyone to enter the country illegally to be a “citizen” in the country. With this thought going around, […]
How does the Unemployment Rate Effect the Economy?
The rate of unemployment is more than a percentage of unemployed people, it is used as key a macroeconomic indicator when determining the health of an economy. The unemployment rate is found by taking the labor force and dividing it by the number of people who are currently searching for a job, also know as the number of unemployed people. The unemployment rate is composed from three types of unemployment: frictional, cyclical, and structural. This could create a potentially serious […]
Examining GDP and Unemployment
Research over the years has shown that unemployment rates and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) figures go hand in hand. This paper aims to define and discuss GDP, and its relation to economic growth. Additionally, the paper will discuss how the use of fiscal or monetary policies can effectively battle recession and aid in the growth of the economy, and how losing a battle to a recession can severely impact unemployment and the unemployment rate, along with other factors leading to […]
GDP and Unemployment
The gross domestic product (GDP) is the measure of goods and services produced in a country during a year (Boone 2016). When GDP is increasing, the economy is in expansion mode. When GDP is decreasing, the economy is in a recession. Economic growth occurs when the GDP increases over time. When economists use the term "economic growth," they are normally referring to sustained increases that occur over a substantial time period, rather than the quarterly changes often discussed in the […]
Impact of Foreign Direct Investment on Economic Growth in Afghanistan
Our study includes four variables GDP which is the dependant variable, whilst the independent variables are FDI, export (EX) and official development assistance (ODA). The following table (4.1) unfolds the descriptive statistics for all those variables; it shows the Mean, Median, Maximum, Minimum and Standard Deviation. We can note that the mean of the GDP is equal 8.7512 USD with the standard deviation equal 1.1753 USD therefore the mean of FDI is equal 18.8318 USD with standard deviation 1.6227 USD […]
How could the Great Depression been Pre Tive
The Great Depression started in 1929 and lasted through 1939, where over a short period of time drastic changes occurred not just to the United States but also other countries that were involved in the United Nations. Even though the economy suffered, unemployment increased and the stock market fell this could have been prevented looking back at it now. The start of the Depression was caused by the engagement of the government decision over the nation's economy and also the […]
Wal-Mart: the High Cost of Low Price in China
Walmart's EDLP Strategy: Chinese Consumer Preferences and the One-Child Policy Challenge Walmart has been struggling to increase its performance in China. There are a few struggles for Walmart in China. Walmart's struggle with the Global Policy of Everyday Low Prices backfired. Everyday Low Price is Wal-Mart's main strategy and trademark. Within this strategy, Wal-Mart will always sell its products at low prices. This strategy was also used in China to attract Chinese customers. However, this strategy did not work because […]
Additional Example Essays
- Discrimination in Workplace
- Homelessness Problem In LA
- Gender Inequality in the Workplace
- Bill Gates entrepreneur
- Examples of Manipulation in Animal Farm
- Religious Discrimination Throughout Cultures and the Workplace
- Compare And Contrast In WW1 And WW2
- Logical Fallacies in Letter From Birmingham Jail
- Research Paper #1 – The Trail of Tears
- History of Mummification
- Followership and Servant Leadership
- The Mental Health Stigma
How to Write Essay About Macroeconomics
Crafting an essay on macroeconomics involves understanding complex economic concepts and theories and effectively communicating them in a structured and insightful manner. Here's a guide to help you write a compelling macroeconomics essay:
Understanding the Essay Topic
Firstly, it's crucial to thoroughly understand the specific macroeconomic topic or question you are addressing. Macroeconomics covers broad areas such as inflation, unemployment, GDP growth, fiscal policy, monetary policy, and international trade. Clarify if your essay should analyze a particular economic theory, policy, historical economic event, or current economic issue.
Conducting Thorough Research
Research is key in a macroeconomics essay. Utilize credible sources like economic journals, textbooks, government publications, and reputable online resources. Focus on gathering data, statistics, historical examples, and expert opinions relevant to your topic. Keeping abreast of current economic conditions and trends can also provide valuable real-time examples for your essay.
Developing a Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement should clearly express the main argument or perspective of your essay. In macroeconomics, this could be a stance on a particular policy, an interpretation of an economic trend, or an argument about the implications of a certain economic theory. Ensure your thesis is concise and directly relates to the essay question.
Structuring the Essay
Organize your essay in a clear, logical manner. Start with an introduction that sets the context and presents your thesis statement. In the body, divide your main points into paragraphs, each focusing on a specific aspect of your argument. Use economic data, theories, and real-world examples to support your points. Conclude by summarizing your arguments and restating your thesis, considering the evidence you’ve presented.
Writing the Essay
Use clear and precise language in your writing. Explain economic concepts and jargon so they are accessible to your audience, without oversimplifying. Present your arguments logically, backing them with data and examples. Be critical and analytical, especially when discussing economic models and policies. It’s important to show the complexity and nuances of macroeconomic issues.
Including Data and Analysis
Macroeconomics heavily relies on data and statistics. When incorporating these, ensure they are relevant and up to date. Present your data clearly, using graphs or tables if necessary. Analyze the data to explain how it supports your argument or sheds light on the economic issue you are discussing.
Citing Your Sources
Proper citation is essential in academic writing. Use an appropriate citation style (such as APA, MLA, or Chicago) and ensure you consistently cite all your sources, including data, theories, and quotations.
Editing and Proofreading
Review your essay for clarity, coherence, and logical flow. Check for accuracy in your economic arguments and ensure that your analysis is thorough. Proofread for grammar, spelling, and formatting. It can be beneficial to have someone else read your essay for feedback, especially if they have knowledge of economics.
Writing an essay on macroeconomics requires a blend of in-depth understanding of economic theories and current events, critical analysis, and effective communication. By methodically approaching your research, structuring your essay logically, and presenting your arguments with clarity and precision, you can create a compelling macroeconomic essay that demonstrates your grasp of this complex and dynamic field.
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

On the site
- business & economics
Critical Essay on Modern Macroeconomic Theory

by Frank Hahn and Robert M. Solow
ISBN: 9780262581547
Pub date: August 21, 1997
- Publisher: The MIT Press
208 pp. , 6 x 9 in ,
ISBN: 9780262082419
Pub date: December 8, 1995
- 9780262581547
- Published: August 1997
- Rights: not for sale in Europe or the UK Commonwealth, except Canada
- 9780262082419
- Published: December 1995
- MIT Press Bookstore
- Penguin Random House
- Barnes and Noble
- Bookshop.org
- Books a Million
Other Retailers:
- Amazon.co.uk
- Waterstones
- Description
Macroeconomics began as the study of large-scale economic pathologies such as prolonged depression, mass unemployment, and persistent inflation. In the early 1980s, rational expectations and new classical economics dominated macroeconomic theory, with the result that such pathologies can hardly be discussed within the vocabulary of the theory. This essay evolved from the authors' profound disagreement with that trend. It demonstrates not only how the new classical view got macroeconomics wrong, but alsohow to go about doing macroeconomics the right way. Hahn and Solow argue that what was originally offered as a normative model based on perfect foresight and universal perfect competition—useful for predicting what an ideal, omniscient planner should do—has been almost casually transformed into a model for interpreting real macroeconomic behavior, leading to Panglossian economics that does not reflect actual experience. Following an explanation of microeconomic foundations, chapters introduce the basic elements for a better macro model. The model is simple, but combined with the appropriate model of the labor market it can say useful things about the fluctuation of employment, the correlation between wages and employment, and the role for corrective monetary policy.
Frank Hahn, one of Britain's most eminent economists, is Professor of Economics at Cambridge University and author of Equilibrium and Macroeconomics (MIT Press 1985).
Robert M. Solow is Institute Professor of Economics.
Like the great debate between Einstein and Bohr on quantum physics,the debate between Hahn-Solow and Lucas's rational expectationismis a must for all serious students of macro. This is how scientificprogress should be done—by sober analysis rather than cleverrhetoric or frenzied ideology. Paul A. Samuelson, Professor of Economics, M.I.T.
Professors Hahn and Solow pick up the simple general equilibrium models of new classical macroeconomics and run with them. Of course, they head off in directions that are theirs alone. Critics of these models, and enthusiasts, will want to read this book and see how far they get. Paul M. Romer, Professor of Economics, University of Californiaat Berkeley
Related Books

Key Concepts and Summary
1.1 what is economics, and why is it important.
Economics seeks to solve the problem of scarcity, which is when human wants for goods and services exceed the available supply. A modern economy displays a division of labor, in which people earn income by specializing in what they produce and then use that income to purchase the products they need or want. The division of labor allows individuals and firms to specialize and to produce more for several reasons: a) It allows the agents to focus on areas of advantage due to natural factors and skill levels; b) It encourages the agents to learn and invent; c) It allows agents to take advantage of economies of scale. Division and specialization of labor only work when individuals can purchase what they do not produce in markets. Learning about economics helps you understand the major problems facing the world today, prepares you to be a good citizen, and helps you become a well-rounded thinker.
1.2 Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Microeconomics and macroeconomics are two different perspectives on the economy. The microeconomic perspective focuses on parts of the economy: individuals, firms, and industries. The macroeconomic perspective looks at the economy as a whole, focusing on goals like growth in the standard of living, unemployment, and inflation. Macroeconomics has two types of policies for pursuing these goals: monetary policy and fiscal policy.
1.3 How Economists Use Theories and Models to Understand Economic Issues
Economists analyze problems differently than do other disciplinary experts. The main tools economists use are economic theories or models. A theory is not an illustration of the answer to a problem. Rather, a theory is a tool for determining the answer.
1.4 How To Organize Economies: An Overview of Economic Systems
We can organize societies as traditional, command, or market-oriented economies. Most societies are a mix. The last few decades have seen globalization evolve as a result of growth in commercial and financial networks that cross national borders, making businesses and workers from different economies increasingly interdependent.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-macroeconomics-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Steven A. Greenlaw, David Shapiro
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Macroeconomics 2e
- Publication date: Oct 11, 2017
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-macroeconomics-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-macroeconomics-2e/pages/1-key-concepts-and-summary
© Jun 15, 2022 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Essay on Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
In this essay we will discuss about Microeconomics and Macroeconomics. After reading this essay you will learn about: 1. Meaning of Microeconomics 2. Scope of Microeconomics 3. Limitations of Microeconomics 4. Importance of Microeconomics 5. Problems of Interrelation and Integration of Micro and Macroeconomics 6. Meaning of Macroeconomics 7. Scope and Importance of Macroeconomics 8. Limitations of Macroeconomics.
- Essay on the Limitations of Macroeconomics
Essay # 1. Meaning of Microeconomics:
Microeconomics is the study of the economic actions of individuals and small groups of individuals. This includes “the study of particular firms, particular households, individual prices, wages, income, individual industries, and particular commodities.”
It concerns itself with the analysis of price determination and the allocation of resources to specific uses. The determination of equilibrium output of the firm or industry, the wage of a particular type of labour, the price of a particular commodity like rice, tea, or car are some of the fields of microeconomic theory.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In the words of Ackley:
“Microeconomics deals with the division of total output among industries, products and firms and the allocations of resources among competing groups. It considers problems of income distribution. Its interest is in relative prices of particular goods and services.”
Microeconomics is, in fact, a microscopic study of the economy, according to Maurice Dobb. It is like looking at the economy through a microscope to find out the working of markets for individual commodities and the behaviour of individual consumers and producers.
In other words, in microeconomics we study the interrelationships of individual households and individual firms, and individual firms and individual industries to each other. In this sense, microeconomics involves the study of aggregates.
Essay # 2. Scope of Microeconomics :
“Price and value theory, the theory of the household, the firm and the industry, most production and welfare theory are of the microeconomic variety,”
Thus, microeconomics studies:
(i) How resources are allocated to the production of particular goods and services,
(ii) How the goods and services are distributed among the people, and
(iii) How efficiently they are distributed.
While studying the conditions in which the price of a particular good is determined, microeconomics assumes the total quantity of resources as given and seeks to explain their allocation to the production of that commodity.
The allocation of resources to a particular good depends upon the prices of other goods and the prices of factors producing them. It is, therefore, the relative prices of goods and services that determine the allocation of resources.
In other words, other things being equal, it is the allocation of resources that determines what to produce, how to produce, and how much to produce. This decision, in turn, depends upon the relative prices of goods and services. Thus, microeconomics is the study of price theory: how the price of a particular commodity like rice, tea, milk, fans, scooters, etc. is determined; how the wages of a particular type of labour, interest on a particular type of capital asset, rent on a particular land and profits of a particular entrepreneur are determined; and how efficiently the various resources are allocated to individual consumers and producers.
We briefly study these problems below.
In microeconomics the analysis of price determination and allocation of resources is studied in three different stages:
(i) The equilibrium of individual consumers and producers,
(ii) The equilibrium of a single market, and
(iii) The simultaneous equilibrium of all markets. Individual consumers and producers are unable to influence the prices of goods they buy and sell. A consumer is faced with given prices and he buys that much of the commodity which maximises his utility.
For an individual producer, input and output prices are given and he produces that much of the product which maximises his profits. In the market, the price and quantity bought and sold are determined by the actions of buyers and sellers. The aggregate demand and supply curves are derived from individual demand and supply curves.
The equality of aggregate demand and supply curves determines the price and the quantity bought and sold in the market. It applies both to product and factor markets. By relaxing some of the assumptions of the perfectly competitive market, this analysis is extended to monopoly, oligopoly and monopolistic, competition markets.
Finally, in microeconomics, the interrelations between the different markets are taken so as to determine all prices simultaneously.
Though, it is generally said that microeconomics is related to partial equilibrium analysis which is the study of the equilibrium position of an individual, a firm, an industry or group of industries, yet it is also a study of their interrelationships and interdependences within the economy which falls under the general equilibrium analysis.
First, there is the consumers market in which the quantity of each commodity demanded depends not only on its own price but also on the price of every other commodity available in the market. In this market, consumers meet producers to buy commodities which the former demand and the latter sell.
The demand of consumers for the various commodities depends upon their prices and the prices of the services which they offer. In other words, a consumer earns by selling the productive services he owns and creates demands for commodities.
The price at which a commodity sells depends upon its costs of production. The costs of production, in turn, depend on the quantities of the various productive services employed and the prices paid for them. Thus the supply of commodities in the market depends on the costs of the firms, and the prices and quantities of the various productive services used by them.
Secondly, there is the producers market or factor market. In this market, the demand for productive services (factors of production) comes from the producers, and supply from the consumers. The quantity of a service (factor) used in producing a commodity depends on the relationship between the prices of that service and other services, and on the prices of commodities.
Here producers meet labourers, capitalists, landlords and other resource-owners. In this market, money incomes are earned by resource-owners who own and sell their resources, the majority of whom are consumers. Thus microeconomics is a study of interacting units of consumers, producers, and resource-owners.
In this system, all prices are relative to one another. A change in any one price establishes a ripple which touches both product and factor markets. The interrelation between product and factor markets through prices is shown in Figure 1.
In this system, consumers and firms are linked through the product market where goods and services are bought and sold. They are also linked through the factor market where the factors of production are bought and sold. In the inner circle that consumers who are resource-owners sell productive resources in the factor market which are used by firms.
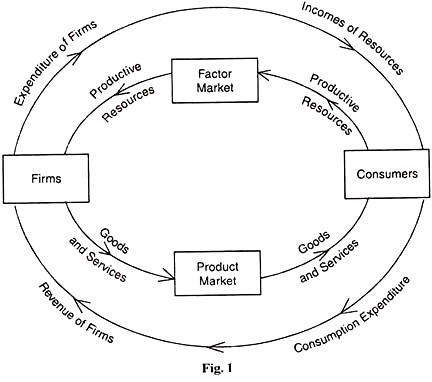

4. Help to Business Executive:
Microeconomics helps the business executive in the attainment of maximum productivity with existing resources. It is with its help that he is able to know the consumer demand and calculate the costs of his product.
5. Helpful in Understanding the Problems of Taxation:
Microeconomics also helps in understanding some of the problems of taxation. It is used to explain the welfare implications of a tax. A tax leads to the reallocation of resources from their optimal level. Microeconomics helps in explaining as to whether an income tax leads to a diminution of social welfare or an excise duty or sales tax.
It is the imposition of an excise duty or sales tax that leads to the diminution of social welfare rather than an income tax. Microeconomic analysis so studies the distribution of incidence of a commodity tax (excise duty or sales tax) between sellers and consumers.
6. Helpful in International Trade:
In the field of international trade, it is used to explain the gains from international trade, balance of payments disequilibrium and the determination of the foreign exchange rate It is the relative elasticity’s of demand for each other’s products that determine the gains from international trade.
The disequilibrium in the balance of payments is the inequality between the demand and supply of foreign currency. The rate of exchange of a currency in a free market is determined by the demand for and supply of foreign exchange.
7. To Examine the Conditions of Economic Welfare:
Microeconomics can be used to examine the conditions of economic welfare. “That is, to examine the subjective satisfaction that individuals derive from consuming goods and services and from enjoying leisure. It involves the study of welfare economics which is one of defining an ideal economy.”
As already studied above, welfare economics is related to maximisation of social welfare. This is possible only under perfect competition. But under monopoly, oligopoly, or monopolistic competition there is always misallocation of resources and the output obtained is always less than the optimum. Thus there is considerable wastage of resources.
Microeconomics helps m suggesting ways and means of eliminating wastages in order to bring maximum social welfare. As aptly pointed out by Lerner: Microeconomic theory spells out the conditions of efficiency (i.e., for the elimination of all kinds of inefficiency) and suggests how they might be achieved.
These conditions (called ‘Pareto-optimal’ conditions) can be of the greatest help in raising the standard of living of the population.
8. The Basis for Prediction:
“Microeconomic theory can be used as the basis for prediction. This does not mean that it will enable us to predict the future. Rather, it will enable the possessor to make condition^ predictions. These conditions have the following form – if something occurs, then a certain set of results will follow We should be able to study government policies affecting prices of commodities and wages, for example and see how these policies affect the allocation of resources. Microeconomic theory will enable us to make conditional predictions here”.
9. Construction and Use of Models:
Microeconomics constructs and uses simple methods for the understanding of the actual economic phenomena.
As pointed out by Bilas:
“The theoretical approach to microeconomics utilizes abstract models in an attempt to see how prices are established and how resources are allocated to various uses. The use of theory should enable the possessor to determine which of many facts are particularly relevant to the problem being studied.”
Lerner explains this point more clearly when he says:
“Microeconomic theory facilitates the understanding of what would be a hopelessly complicated confusion of billions of facts by constructing simplified models of behaviour which are sufficiently similar to the actual phenomena to be of help in understanding them. These models at the same time enable the economists to explain the degree to which the actual phenomena depart from certain ideal constructions that would most completely achieve individual and social objectives. They, thus, help not only to describe the actual economic situation but to suggest policies that would most successfully and most efficiently bring about desired results and to predict the outcomes of such policies and other events.” Thus it is an elegant method of problem solving, according to Ackley.
Essay # 5. Problems of Interrelation and Integration of Micro and Macroeconomics:
This rough division between micro- and macroeconomics is not rigid, for the parts affect the whole and the whole affects the parts:
Dependence of Microeconomic Theory on Macroeconomics:
Take for instance when aggregate demand rises during a period of prosperity, the demand for individual products also rises. If this increase in demand is due to a reduction in the rate of interest, the demand for different types of capital goods will go up. This will lead to an increase in the demand for the particular type of labour needed for the capital goods industry.
If the supply of such labour is less elastic, its wage rate will rise. The rise in wage rate is made possible by increase in profits as a consequence of increased demand for capital goods. Thus, a macroeconomic change brings about changes in the values of microeconomic variables—in the demand for particular goods, in the wage rates of particular industries, in the profits of particular firms and industries, and in the employment position of different groups of workers.
Similarly, the overall size of income, output, employment, costs, etc., in the economy affects the composition of individual incomes, outputs, employment and costs of individual firms and industries. To take another instance, when total output falls in a period of depression, the output of capital goods falls more than that of consumer goods. Profits, wages and employment decline more rapidly in capital goods industries than in the consumer goods industries.
Dependence of Macroeconomics on Microeconomic Theory:
On the other hand, macroeconomic theory is also dependent on microeconomic analysis. The total is made up of the parts. National income is the sum of the incomes of individuals, households, firms and industries. Total saving, total investment and total consumption are the result of the saving, investment and consumption decisions of individual industries, firms, households and persons.
The general price level is the average of all prices of individual goods and services. Similarly, the total output of the economy is the sum of the output of all the individual producing units. Thus, “the aggregates and averages that are studied in macroeconomics are nothing but aggregates and averages of the individual quantities which are studied in microeconomics”.
Let us take a few concrete examples of this macro dependence on microeconomics. If the economy concentrates all its resources in producing only agricultural commodities, the total output of the economy will decline because the other sectors of the economy will be neglected. The total level of output, income and employment in the economy also depends upon income distribution.
If there is unequal distribution of income so that income is concentrated in the hands of a few rich, it will tend to reduce the demand for consumer goods. Profits, investment and output will decline, unemployment will spread and ultimately the economy will be faced with depression. Thus, both macro and micro approaches to economic problems are interrelated and interdependent.
Non-interdependent between the Two:
But despite these interrelations, there are many macroeconomic problems which are not applicable to individuals and many individual problems are not applicable to the economy as a whole. For example, there can be and usually is a divergence between an individual’s income and his expenditure, but for the economy as a whole total income and total expenditure are always equal. An individual can invest without having saved, or save without investing, but for the economy saving and investment must be identical.
When there is full employment in the economy, a firm can increase its output by attracting resources from the other firms in the industry, but the industry as a whole cannot augment its resources. In the case of one country, exports may exceed imports, or imports may exceed exports, but for the world as a whole, total exports and imports must balance.
Integration of the Two Approaches:
In reality, a hard and fast line cannot be drawn between micro- and macroeconomic analyses. A general theory of the economy should cover both. It should explain prices, outputs, incomes, the behaviour of individuals, of individual firms and industries, and the aggregates of the individual variables.
“Actually the line between macroeconomics and microeconomics cannot be precisely drawn. A truly “general” theory of the economy would clearly embrace both: it would explain individual behaviour, individual outputs, incomes and prices, and the sums or averages of the individual results would constitute the aggregates with which macroeconomics is concerned.
Such a general theory exists, but its very generality leaves it with little substantive content. Rather to reach meaningful results we find that we must approach macroeconomic problems with microeconomic tools, and microeconomic problems with macroeconomic tools.”
Thus the need is for a proper integration of the two approaches. Prof. Ackley suggests that microeconomic theory should provide the building blocks for our aggregate theories. But macroeconomics may also contribute to microeconomic understanding.
If we discover, for example, empirically stable macroeconomic generalisations which appear inconsistent with microeconomic theories, or which relate to aspects of behaviour which microeconomics has neglected, macroeconomics may permit us to improve our understanding of individual behaviour.
But in order to proceed in either direction we need to be aware of some rather technical problems of aggregation which point out that “progress in macroeconomics depends on further progress in the microeconomic theory of prices and distribution of income.”
Essay # 6. Meaning of Macroeconomics:
Macroeconomics is the study of aggregates or averages covering the entire economy, such as total employment, unemployment, national income, national output, total investment, total consumption, total savings, aggregate supply, aggregate demand, and general price level, wage level, interest rates and cost structure.
In other words, it is aggregative economics which examines the interrelations among the various aggregates, their determination and causes of fluctuations in them.
Thus in the words of Ackley:
“Macroeconomics deals with economic affairs ‘in the large’, it concerns the overall dimensions of economic life. It looks at the total size and shape of the functioning of the ‘elephant’ of economic experience, rather than working of articulation or dimensions of the individual parts. It studies the character of the forest, independently of the trees which compose it.”
Macroeconomics is also known as the theory of income and employment, or, simply income analysis. It is concerned with the problems of unemployment, economic fluctuations, inflation, deflation, instability, stagnation, international trade and economic growth. It is the study of the causes of unemployment, and the various determinants of employment.
In the field of business cycles, it concerns itself with the effect of investment on total output, total income, and aggregate employment. In the monetary sphere, it studies the effect of the total quantity of money on the general price level. In international trade, the problems of balance of payments and foreign aid fall within the purview of macro-economic analysis.
Above all, macroeconomic theory discusses the problems of determination of the total income of a country and causes of its fluctuations. Finally, it studies the factors that retard growth and those which bring the economy on the path of economic development.
Essay # 7. Scope and Importance of Macroeconomics:
As a method of economic analysis macroeconomics is of much theoretical and practical importance.
The study of macroeconomic variables is indispensable for understanding the working of the economy. Our main economic problems are related to the behaviour of total income, output, employment and the general price level in the economy.
These variables are statistically measurable, thereby facilitating the possibilities of analysing the effects on the functioning of the economy. As Tinbergen observes, macroeconomic concepts help in “making the elimination process understandable and transparent”. For instance, one may not agree on the best method of measuring different prices, but the general price level is helpful in understanding the nature of the economy.
2. In Economic Policies:
Macroeconomics is extremely useful from the point of view of economic policy. Modern governments, especially of the underdeveloped economies, are confronted with innumerable national problems. They are the problems of overpopulation, inflation, balance of payments, general underproduction, etc.
The main responsibility of these governments rests in the regulation and control of overpopulation, general prices, general volume of trade, general outputs, etc. Tinbergen says: “Working with macroeconomic concepts is a bare necessity in order to contribute to the solutions of the great problems of our times.” No government can solve these problems in terms of individual behaviour. Let us analyse the use of macroeconomic study in the solution of certain complex economic problems.
(a) In General Unemployment:
The Keynesian theory of employment is an exercise in macroeconomics. The general level of employment in an economy depends upon effective demand which, in turn, depends on aggregate demand and aggregate supply functions.
Unemployment is thus caused by deficiency of effective demand. In order to eliminate it, effective demand should be raised by increasing total investment, total output, total income and total consumption. Thus, macroeconomics has special significance in studying the causes, effects and remedies of general unemployment.
(b) In National Income:
The study of macroeconomics is very important for evaluating the overall performance of the economy in terms of national income. With the advent of the Great Depression of the 1930s, it became necessary to analyse the causes of general overproduction and general unemployment.
This led to the construction of the data on national income. National income data help in forecasting the level of economic activity and to understand the distribution of income among different groups of people in the economy.
(c) In Economic Growth:
The economics of growth is also a study in macroeconomics. It is on the basis of macroeconomics that the resources and capabilities of an economy are evaluated. Plans for the overall increase in national income, output and employment are framed and implemented so as to raise the level of economic development of the economy as a whole.
(d) In Monetary Problems:
It is in terms of macroeconomics that monetary problems can be analysed and understood properly. Frequent changes in the value of money—inflation or deflation—affect the economy adversely. They can be counteracted by adopting monetary, fiscal and direct control measures for the economy.
(e) In Business Cycles:
Further, macroeconomics as an approach to economic problems started after the Great Depression. Thus its importance lies in analysing the causes of economic fluctuations and in providing remedies.
3. For Understanding the Behaviour of Individual Units:
Last but not the least, for understanding the behaviour of individual units the study of macroeconomics is imperative. Demand for individual products depends upon aggregate demand in the economy. Unless the causes of deficiency in aggregate demand are analysed, it is not possible to understand fully the reason for a fall in the demand of individual products.
The reasons for increase in costs of a particular firm or industry cannot be analysed without knowing the average cost conditions of the whole economy. Thus, the study of individual units is not possible without macroeconomics.
We may conclude that macroeconomics enriches our knowledge of the functioning of an economy by studying the behaviour of national income, output, investment, saving and consumption. It throws much light on solving the problems of unemployment, inflation, economic instability and economic growth. Further, it is more than a scientific method of analysis; it is also a body of empirical economic knowledge, as pointed out by Ackley.
Essay # 8. Limitations of Macroeconomics:
There are, however, certain limitations of macroeconomic analysis. Mostly, these stem from attempts to yield macroeconomic generalisations from individual experiences.
1. Fallacy of Composition:
In macroeconomic analysis the “fallacy of composition” is involved, i.e., aggregate economic behaviour is the sum total of individual activities. But what is true of individuals is not necessarily true of the economy as a whole. For instance, savings are a private virtue but a public vice.
If total savings in the economy increase, they may initiate a depression unless they are invested. Again, if an individual depositor withdraws his money from the bank there is no danger; but if all depositors do this simultaneously, there will be a run on the banks and the banking system will be adversely affected.
2. To Regard Aggregates as Homogeneous:
The main defect in macro analysis is that it regards the aggregates as homogeneous without caring about their internal composition and structure. The average wage in a country is the sum total of wages in all occupations, i.e., wages of clerks, typists, teachers, nurses, etc. But the volume of aggregate employment depends on the relative structure of wages rather than on the average wage. If, for instance, wages of nurses’ increase but of typists fall, the average may remain unchanged. But if the employment of nurses falls a little and of typists raises much, aggregate employment would increase.
3. Aggregate Variables may not be Important Necessarily:
The aggregate variables which form the economic system may not be of much significance. For instance, the national income of a country is the total of all individual incomes. A rise in national income does not mean that individual incomes have risen.
The increase in national income might be the result of the increase in the incomes of a few rich people in the country. Thus a rise in national income of this type has little significance from the point of view of the community. Boulding calls these three difficulties as “macroeconomic paradoxes” which are true when applied to a single individual but which are untrue when applied to the economic system as a whole.
4. Indiscriminate Use of Macroeconomics Misleading:
An indiscriminate and uncritical use of macroeconomics in analysing the problems of the real world can often be misleading. For instance, if the policy measures needed to achieve and maintain full employment in the economy are applied to structural unemployment in individual firms and industries, they become irrelevant. Similarly, measures aimed at controlling general prices cannot be applied with much advantage for controlling prices of individual products.
5. Statistical and Conceptual Difficulties:
The measurement of macroeconomic concepts involves a number of statistical and conceptual difficulties. These problems relate to the aggregation of microeconomic variables. If individual units are almost similar, aggregation does not present much difficulty. But if microeconomic variables relate to similar individual units, their aggregation into one macroeconomic variable may be wrong and dangerous.
Related Articles:
- Difference between Macroeconomics and Microeconomics
- Distinction between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
- Difference between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Home — Essay Samples — Economics — Macroeconomics
Essays on Macroeconomics
Brief description of macroeconomics.
Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole, focusing on factors such as inflation, unemployment, economic growth, and the effects of government economic policies. It is an essential field of study for understanding the functioning of national and global economies, and it provides valuable insights into how economic decisions impact individuals and societies.
Importance of Writing Essays on This Topic
Essays on macroeconomics are significant for both academic and personal exploration. They allow students to delve deeper into complex economic concepts, develop critical thinking skills, and gain a better understanding of real-world economic issues. Additionally, writing essays on macroeconomics enables individuals to engage with current economic debates and contribute to the discourse on economic policy and societal well-being.
Tips on Choosing a Good Topic
- Consider current events and their impact on the economy, such as the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on economic stability.
- Explore the intersection of macroeconomics with other disciplines, such as environmental economics or labor economics, to find unique and thought-provoking topics.
- Focus on areas of economic policy and its implications for society, such as the debate over austerity measures or the relationship between economic inequality and social welfare.
Essay Topics
- The impact of government stimulus packages on economic recovery
- The relationship between inflation and unemployment
- Analyzing the effectiveness of monetary policy in controlling inflation
- The role of international trade in economic growth
- Investigating the causes and consequences of economic recessions
- The impact of automation on employment and wages
- Exploring the concept of sustainable economic growth
- The implications of national debt on future generations
- The role of central banks in stabilizing the economy
- Analyzing the economic effects of immigration policies
Concluding Thought
Engaging with macroeconomics through essay writing provides an opportunity to deepen your understanding of economic principles and their real-world applications. By exploring diverse topics within the field of macroeconomics, you can develop critical thinking skills and contribute to the ongoing discourse on economic policy and societal well-being. Embrace the opportunity to explore and critically engage with macroeconomics through essay writing.
Inflation Reduction Act in The Frame of Macroeconomic Challenges
Analyzing the inflation reduction act, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Exploring The Implications of The Inflation Reduction Act
The theory and policy of macroeconomics on inflation rate, the government tools and means to alleviate pressure from consumers and businesses alike, the issue of fiscal and monetary policy in usa, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Pakistan is at a Verge of Collapsing Its Macroeconomics
Africa's macroeconomic performance and prospects, impact of the macroeconomic policies imposed in correa's government on the ecuadorian industry, the issue of income inequality in europe, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Supporting The Developing Countries to Use Renewable Resources
The pakistan china economic corridor, nobel prize in economics: a report on nordhaus and romer, review of various economic reasoning, the impact of macroeconomic variables on stock prices in pakistan, trade war statistics & products affected in the usa, role of mircroeconomics in politics, the impact of inflation reduction act on the international economic stage, relevant topics.
- American Dream
- Industrialization
- Supply and Demand
- Minimum Wage
- Unemployment
- Real Estate
- Materialism
- Income Inequality
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Macroeconomics →

- 07 Jan 2019
- Research & Ideas
The Better Way to Forecast the Future
We can forecast hurricane paths with great certainty, yet many businesses can't predict a supply chain snafu just around the corner. Yael Grushka-Cockayne says crowdsourcing can help. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 04 Mar 2016
- Working Paper Summaries
Credit-Market Sentiment and the Business Cycle
Using United States data from 1929 to 2013, Jeremy C. Stein and colleagues emphasize the role of credit-market sentiment as an important driver of the business cycle.
- 10 Feb 2016
Land Institutions and Chinese Political Economy: Institutional Complementarities and Macroeconomic Management
This paper shows the ways in which the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) has used land as a policy tool. CCP leaders intentionally reorganized fiscal, financial, and land institutions to put land at the center of local government finances in the mid-1990s. Since the late 1990s, the CCP has used the land supply as a key tool of macroeconomic expansion and contraction. Local officials act as agents of the center: pursuing land development when pushed to so do by central authorities concerned about managing economic growth.
- 10 Dec 2015
The Probability of Rare Disasters: Estimation and Implications
Emil Siriwardane analyzes the probability for risk of large-scale financial disasters.
- 24 May 2010
Stimulus Surprise: Companies Retrench When Government Spends
Research from Harvard Business School suggests that federal spending in states appears to cause local businesses to cut back rather than grow. A conversation with Joshua Coval. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 25 Jan 2010
A Macroeconomic View of the Current Economy
Concerned or confused by the economic environment? Take some lessons from history and concepts from macroeconomics to get a better understanding of how the economy works. A Q&A with HBS professor David A. Moss, author of A Concise Guide to Macroeconomics: What Managers, Executives, and Students Need to Know. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 05 Jun 2009
- What Do You Think?
What Does Slower Economic Growth Really Mean?
Respondents to this month's column by HBS professor Jim Heskett came close to general agreement on the proposition that economic growth is not measured properly by GDP, calling for new indicators. Jim sums up. (Online forum now closed. Next forum begins July 6.) Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 22 Aug 2005
Restoring a Global Economy, 1950–1980
In his recent book Multinationals and Global Capitalism, professor Geoffrey Jones dissects the influence of multinationals on the world economy. This excerpt recalls the rebuilding of the global economy following World War II. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- Search Menu
- Browse content in A - General Economics and Teaching
- Browse content in A1 - General Economics
- A10 - General
- A12 - Relation of Economics to Other Disciplines
- A13 - Relation of Economics to Social Values
- A14 - Sociology of Economics
- Browse content in A2 - Economic Education and Teaching of Economics
- A29 - Other
- Browse content in B - History of Economic Thought, Methodology, and Heterodox Approaches
- B0 - General
- Browse content in B1 - History of Economic Thought through 1925
- B11 - Preclassical (Ancient, Medieval, Mercantilist, Physiocratic)
- B12 - Classical (includes Adam Smith)
- Browse content in B2 - History of Economic Thought since 1925
- B20 - General
- B21 - Microeconomics
- B22 - Macroeconomics
- B25 - Historical; Institutional; Evolutionary; Austrian
- B26 - Financial Economics
- Browse content in B3 - History of Economic Thought: Individuals
- B31 - Individuals
- Browse content in B4 - Economic Methodology
- B41 - Economic Methodology
- Browse content in B5 - Current Heterodox Approaches
- B55 - Social Economics
- Browse content in C - Mathematical and Quantitative Methods
- Browse content in C0 - General
- C00 - General
- C02 - Mathematical Methods
- Browse content in C1 - Econometric and Statistical Methods and Methodology: General
- C10 - General
- C11 - Bayesian Analysis: General
- C12 - Hypothesis Testing: General
- C13 - Estimation: General
- C14 - Semiparametric and Nonparametric Methods: General
- C15 - Statistical Simulation Methods: General
- C19 - Other
- Browse content in C2 - Single Equation Models; Single Variables
- C21 - Cross-Sectional Models; Spatial Models; Treatment Effect Models; Quantile Regressions
- C22 - Time-Series Models; Dynamic Quantile Regressions; Dynamic Treatment Effect Models; Diffusion Processes
- C23 - Panel Data Models; Spatio-temporal Models
- C24 - Truncated and Censored Models; Switching Regression Models; Threshold Regression Models
- C25 - Discrete Regression and Qualitative Choice Models; Discrete Regressors; Proportions; Probabilities
- C26 - Instrumental Variables (IV) Estimation
- Browse content in C3 - Multiple or Simultaneous Equation Models; Multiple Variables
- C31 - Cross-Sectional Models; Spatial Models; Treatment Effect Models; Quantile Regressions; Social Interaction Models
- C32 - Time-Series Models; Dynamic Quantile Regressions; Dynamic Treatment Effect Models; Diffusion Processes; State Space Models
- C33 - Panel Data Models; Spatio-temporal Models
- C34 - Truncated and Censored Models; Switching Regression Models
- C35 - Discrete Regression and Qualitative Choice Models; Discrete Regressors; Proportions
- C36 - Instrumental Variables (IV) Estimation
- Browse content in C4 - Econometric and Statistical Methods: Special Topics
- C41 - Duration Analysis; Optimal Timing Strategies
- C43 - Index Numbers and Aggregation
- Browse content in C5 - Econometric Modeling
- C51 - Model Construction and Estimation
- C52 - Model Evaluation, Validation, and Selection
- C53 - Forecasting and Prediction Methods; Simulation Methods
- C54 - Quantitative Policy Modeling
- Browse content in C6 - Mathematical Methods; Programming Models; Mathematical and Simulation Modeling
- C60 - General
- C61 - Optimization Techniques; Programming Models; Dynamic Analysis
- C62 - Existence and Stability Conditions of Equilibrium
- C63 - Computational Techniques; Simulation Modeling
- Browse content in C7 - Game Theory and Bargaining Theory
- C71 - Cooperative Games
- C72 - Noncooperative Games
- C73 - Stochastic and Dynamic Games; Evolutionary Games; Repeated Games
- C78 - Bargaining Theory; Matching Theory
- Browse content in C8 - Data Collection and Data Estimation Methodology; Computer Programs
- C81 - Methodology for Collecting, Estimating, and Organizing Microeconomic Data; Data Access
- C82 - Methodology for Collecting, Estimating, and Organizing Macroeconomic Data; Data Access
- C83 - Survey Methods; Sampling Methods
- Browse content in C9 - Design of Experiments
- C90 - General
- C91 - Laboratory, Individual Behavior
- C92 - Laboratory, Group Behavior
- C93 - Field Experiments
- Browse content in D - Microeconomics
- Browse content in D0 - General
- D00 - General
- D01 - Microeconomic Behavior: Underlying Principles
- D02 - Institutions: Design, Formation, Operations, and Impact
- D03 - Behavioral Microeconomics: Underlying Principles
- D04 - Microeconomic Policy: Formulation; Implementation, and Evaluation
- Browse content in D1 - Household Behavior and Family Economics
- D10 - General
- D11 - Consumer Economics: Theory
- D12 - Consumer Economics: Empirical Analysis
- D13 - Household Production and Intrahousehold Allocation
- D14 - Household Saving; Personal Finance
- D15 - Intertemporal Household Choice: Life Cycle Models and Saving
- D16 - Collaborative Consumption
- D18 - Consumer Protection
- D19 - Other
- Browse content in D2 - Production and Organizations
- D21 - Firm Behavior: Theory
- D22 - Firm Behavior: Empirical Analysis
- D23 - Organizational Behavior; Transaction Costs; Property Rights
- D24 - Production; Cost; Capital; Capital, Total Factor, and Multifactor Productivity; Capacity
- D29 - Other
- Browse content in D3 - Distribution
- D30 - General
- D31 - Personal Income, Wealth, and Their Distributions
- D33 - Factor Income Distribution
- D39 - Other
- Browse content in D4 - Market Structure, Pricing, and Design
- D40 - General
- D41 - Perfect Competition
- D43 - Oligopoly and Other Forms of Market Imperfection
- D44 - Auctions
- Browse content in D5 - General Equilibrium and Disequilibrium
- D50 - General
- D53 - Financial Markets
- D58 - Computable and Other Applied General Equilibrium Models
- Browse content in D6 - Welfare Economics
- D60 - General
- D61 - Allocative Efficiency; Cost-Benefit Analysis
- D62 - Externalities
- D63 - Equity, Justice, Inequality, and Other Normative Criteria and Measurement
- D64 - Altruism; Philanthropy
- D69 - Other
- Browse content in D7 - Analysis of Collective Decision-Making
- D70 - General
- D71 - Social Choice; Clubs; Committees; Associations
- D72 - Political Processes: Rent-seeking, Lobbying, Elections, Legislatures, and Voting Behavior
- D73 - Bureaucracy; Administrative Processes in Public Organizations; Corruption
- D74 - Conflict; Conflict Resolution; Alliances; Revolutions
- D78 - Positive Analysis of Policy Formulation and Implementation
- Browse content in D8 - Information, Knowledge, and Uncertainty
- D80 - General
- D81 - Criteria for Decision-Making under Risk and Uncertainty
- D82 - Asymmetric and Private Information; Mechanism Design
- D83 - Search; Learning; Information and Knowledge; Communication; Belief; Unawareness
- D84 - Expectations; Speculations
- D85 - Network Formation and Analysis: Theory
- D86 - Economics of Contract: Theory
- Browse content in D9 - Micro-Based Behavioral Economics
- D90 - General
- D91 - Role and Effects of Psychological, Emotional, Social, and Cognitive Factors on Decision Making
- D92 - Intertemporal Firm Choice, Investment, Capacity, and Financing
- Browse content in E - Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Browse content in E0 - General
- E00 - General
- E01 - Measurement and Data on National Income and Product Accounts and Wealth; Environmental Accounts
- E02 - Institutions and the Macroeconomy
- Browse content in E1 - General Aggregative Models
- E10 - General
- E11 - Marxian; Sraffian; Kaleckian
- E12 - Keynes; Keynesian; Post-Keynesian
- E13 - Neoclassical
- E19 - Other
- Browse content in E2 - Consumption, Saving, Production, Investment, Labor Markets, and Informal Economy
- E20 - General
- E21 - Consumption; Saving; Wealth
- E22 - Investment; Capital; Intangible Capital; Capacity
- E23 - Production
- E24 - Employment; Unemployment; Wages; Intergenerational Income Distribution; Aggregate Human Capital; Aggregate Labor Productivity
- E25 - Aggregate Factor Income Distribution
- E26 - Informal Economy; Underground Economy
- E27 - Forecasting and Simulation: Models and Applications
- Browse content in E3 - Prices, Business Fluctuations, and Cycles
- E30 - General
- E31 - Price Level; Inflation; Deflation
- E32 - Business Fluctuations; Cycles
- E37 - Forecasting and Simulation: Models and Applications
- Browse content in E4 - Money and Interest Rates
- E40 - General
- E41 - Demand for Money
- E42 - Monetary Systems; Standards; Regimes; Government and the Monetary System; Payment Systems
- E43 - Interest Rates: Determination, Term Structure, and Effects
- E44 - Financial Markets and the Macroeconomy
- E47 - Forecasting and Simulation: Models and Applications
- Browse content in E5 - Monetary Policy, Central Banking, and the Supply of Money and Credit
- E50 - General
- E51 - Money Supply; Credit; Money Multipliers
- E52 - Monetary Policy
- E58 - Central Banks and Their Policies
- Browse content in E6 - Macroeconomic Policy, Macroeconomic Aspects of Public Finance, and General Outlook
- E60 - General
- E61 - Policy Objectives; Policy Designs and Consistency; Policy Coordination
- E62 - Fiscal Policy
- E63 - Comparative or Joint Analysis of Fiscal and Monetary Policy; Stabilization; Treasury Policy
- E65 - Studies of Particular Policy Episodes
- E69 - Other
- Browse content in E7 - Macro-Based Behavioral Economics
- E70 - General
- E71 - Role and Effects of Psychological, Emotional, Social, and Cognitive Factors on the Macro Economy
- Browse content in F - International Economics
- Browse content in F0 - General
- F02 - International Economic Order and Integration
- Browse content in F1 - Trade
- F10 - General
- F11 - Neoclassical Models of Trade
- F12 - Models of Trade with Imperfect Competition and Scale Economies; Fragmentation
- F13 - Trade Policy; International Trade Organizations
- F14 - Empirical Studies of Trade
- F15 - Economic Integration
- F16 - Trade and Labor Market Interactions
- F17 - Trade Forecasting and Simulation
- F18 - Trade and Environment
- Browse content in F2 - International Factor Movements and International Business
- F21 - International Investment; Long-Term Capital Movements
- F22 - International Migration
- F23 - Multinational Firms; International Business
- F24 - Remittances
- Browse content in F3 - International Finance
- F30 - General
- F31 - Foreign Exchange
- F32 - Current Account Adjustment; Short-Term Capital Movements
- F33 - International Monetary Arrangements and Institutions
- F34 - International Lending and Debt Problems
- F35 - Foreign Aid
- F36 - Financial Aspects of Economic Integration
- F37 - International Finance Forecasting and Simulation: Models and Applications
- Browse content in F4 - Macroeconomic Aspects of International Trade and Finance
- F40 - General
- F41 - Open Economy Macroeconomics
- F42 - International Policy Coordination and Transmission
- F43 - Economic Growth of Open Economies
- F44 - International Business Cycles
- F45 - Macroeconomic Issues of Monetary Unions
- Browse content in F5 - International Relations, National Security, and International Political Economy
- F50 - General
- F51 - International Conflicts; Negotiations; Sanctions
- F52 - National Security; Economic Nationalism
- F53 - International Agreements and Observance; International Organizations
- F55 - International Institutional Arrangements
- F59 - Other
- Browse content in F6 - Economic Impacts of Globalization
- F62 - Macroeconomic Impacts
- F63 - Economic Development
- F64 - Environment
- Browse content in G - Financial Economics
- Browse content in G0 - General
- G01 - Financial Crises
- G02 - Behavioral Finance: Underlying Principles
- Browse content in G1 - General Financial Markets
- G10 - General
- G11 - Portfolio Choice; Investment Decisions
- G12 - Asset Pricing; Trading volume; Bond Interest Rates
- G14 - Information and Market Efficiency; Event Studies; Insider Trading
- G15 - International Financial Markets
- G18 - Government Policy and Regulation
- Browse content in G2 - Financial Institutions and Services
- G20 - General
- G21 - Banks; Depository Institutions; Micro Finance Institutions; Mortgages
- G22 - Insurance; Insurance Companies; Actuarial Studies
- G24 - Investment Banking; Venture Capital; Brokerage; Ratings and Ratings Agencies
- G28 - Government Policy and Regulation
- Browse content in G3 - Corporate Finance and Governance
- G32 - Financing Policy; Financial Risk and Risk Management; Capital and Ownership Structure; Value of Firms; Goodwill
- G33 - Bankruptcy; Liquidation
- G34 - Mergers; Acquisitions; Restructuring; Corporate Governance
- G35 - Payout Policy
- G38 - Government Policy and Regulation
- Browse content in H - Public Economics
- Browse content in H0 - General
- H00 - General
- Browse content in H1 - Structure and Scope of Government
- H10 - General
- H11 - Structure, Scope, and Performance of Government
- H12 - Crisis Management
- Browse content in H2 - Taxation, Subsidies, and Revenue
- H20 - General
- H21 - Efficiency; Optimal Taxation
- H22 - Incidence
- H23 - Externalities; Redistributive Effects; Environmental Taxes and Subsidies
- H24 - Personal Income and Other Nonbusiness Taxes and Subsidies; includes inheritance and gift taxes
- H25 - Business Taxes and Subsidies
- H26 - Tax Evasion and Avoidance
- Browse content in H3 - Fiscal Policies and Behavior of Economic Agents
- H30 - General
- H31 - Household
- Browse content in H4 - Publicly Provided Goods
- H40 - General
- H41 - Public Goods
- H42 - Publicly Provided Private Goods
- Browse content in H5 - National Government Expenditures and Related Policies
- H50 - General
- H51 - Government Expenditures and Health
- H52 - Government Expenditures and Education
- H53 - Government Expenditures and Welfare Programs
- H54 - Infrastructures; Other Public Investment and Capital Stock
- H55 - Social Security and Public Pensions
- H56 - National Security and War
- Browse content in H6 - National Budget, Deficit, and Debt
- H60 - General
- H61 - Budget; Budget Systems
- H62 - Deficit; Surplus
- H63 - Debt; Debt Management; Sovereign Debt
- Browse content in H7 - State and Local Government; Intergovernmental Relations
- H70 - General
- H71 - State and Local Taxation, Subsidies, and Revenue
- H72 - State and Local Budget and Expenditures
- H75 - State and Local Government: Health; Education; Welfare; Public Pensions
- H76 - State and Local Government: Other Expenditure Categories
- H77 - Intergovernmental Relations; Federalism; Secession
- Browse content in H8 - Miscellaneous Issues
- H83 - Public Administration; Public Sector Accounting and Audits
- H84 - Disaster Aid
- H87 - International Fiscal Issues; International Public Goods
- Browse content in I - Health, Education, and Welfare
- Browse content in I0 - General
- I00 - General
- Browse content in I1 - Health
- I10 - General
- I12 - Health Behavior
- I14 - Health and Inequality
- I15 - Health and Economic Development
- I18 - Government Policy; Regulation; Public Health
- I19 - Other
- Browse content in I2 - Education and Research Institutions
- I20 - General
- I21 - Analysis of Education
- I22 - Educational Finance; Financial Aid
- I23 - Higher Education; Research Institutions
- I24 - Education and Inequality
- I25 - Education and Economic Development
- I26 - Returns to Education
- I28 - Government Policy
- I29 - Other
- Browse content in I3 - Welfare, Well-Being, and Poverty
- I30 - General
- I31 - General Welfare
- I32 - Measurement and Analysis of Poverty
- I38 - Government Policy; Provision and Effects of Welfare Programs
- Browse content in J - Labor and Demographic Economics
- Browse content in J0 - General
- J00 - General
- J01 - Labor Economics: General
- J08 - Labor Economics Policies
- Browse content in J1 - Demographic Economics
- J10 - General
- J11 - Demographic Trends, Macroeconomic Effects, and Forecasts
- J12 - Marriage; Marital Dissolution; Family Structure; Domestic Abuse
- J13 - Fertility; Family Planning; Child Care; Children; Youth
- J14 - Economics of the Elderly; Economics of the Handicapped; Non-Labor Market Discrimination
- J15 - Economics of Minorities, Races, Indigenous Peoples, and Immigrants; Non-labor Discrimination
- J16 - Economics of Gender; Non-labor Discrimination
- J17 - Value of Life; Forgone Income
- J18 - Public Policy
- Browse content in J2 - Demand and Supply of Labor
- J20 - General
- J21 - Labor Force and Employment, Size, and Structure
- J22 - Time Allocation and Labor Supply
- J23 - Labor Demand
- J24 - Human Capital; Skills; Occupational Choice; Labor Productivity
- J26 - Retirement; Retirement Policies
- J28 - Safety; Job Satisfaction; Related Public Policy
- Browse content in J3 - Wages, Compensation, and Labor Costs
- J30 - General
- J31 - Wage Level and Structure; Wage Differentials
- J32 - Nonwage Labor Costs and Benefits; Retirement Plans; Private Pensions
- J33 - Compensation Packages; Payment Methods
- J38 - Public Policy
- Browse content in J4 - Particular Labor Markets
- J41 - Labor Contracts
- J42 - Monopsony; Segmented Labor Markets
- J45 - Public Sector Labor Markets
- J46 - Informal Labor Markets
- J48 - Public Policy
- Browse content in J5 - Labor-Management Relations, Trade Unions, and Collective Bargaining
- J50 - General
- J51 - Trade Unions: Objectives, Structure, and Effects
- J52 - Dispute Resolution: Strikes, Arbitration, and Mediation; Collective Bargaining
- J53 - Labor-Management Relations; Industrial Jurisprudence
- J54 - Producer Cooperatives; Labor Managed Firms; Employee Ownership
- J58 - Public Policy
- Browse content in J6 - Mobility, Unemployment, Vacancies, and Immigrant Workers
- J60 - General
- J61 - Geographic Labor Mobility; Immigrant Workers
- J62 - Job, Occupational, and Intergenerational Mobility
- J63 - Turnover; Vacancies; Layoffs
- J64 - Unemployment: Models, Duration, Incidence, and Job Search
- J65 - Unemployment Insurance; Severance Pay; Plant Closings
- J68 - Public Policy
- Browse content in J7 - Labor Discrimination
- J71 - Discrimination
- Browse content in J8 - Labor Standards: National and International
- J81 - Working Conditions
- J88 - Public Policy
- Browse content in K - Law and Economics
- Browse content in K0 - General
- K00 - General
- Browse content in K1 - Basic Areas of Law
- K11 - Property Law
- K12 - Contract Law
- K13 - Tort Law and Product Liability; Forensic Economics
- K14 - Criminal Law
- K16 - Election Law
- Browse content in K3 - Other Substantive Areas of Law
- K31 - Labor Law
- K32 - Environmental, Health, and Safety Law
- K34 - Tax Law
- K37 - Immigration Law
- Browse content in K4 - Legal Procedure, the Legal System, and Illegal Behavior
- K41 - Litigation Process
- K42 - Illegal Behavior and the Enforcement of Law
- K49 - Other
- Browse content in L - Industrial Organization
- Browse content in L0 - General
- L00 - General
- Browse content in L1 - Market Structure, Firm Strategy, and Market Performance
- L10 - General
- L11 - Production, Pricing, and Market Structure; Size Distribution of Firms
- L12 - Monopoly; Monopolization Strategies
- L13 - Oligopoly and Other Imperfect Markets
- L14 - Transactional Relationships; Contracts and Reputation; Networks
- L16 - Industrial Organization and Macroeconomics: Industrial Structure and Structural Change; Industrial Price Indices
- Browse content in L2 - Firm Objectives, Organization, and Behavior
- L20 - General
- L21 - Business Objectives of the Firm
- L22 - Firm Organization and Market Structure
- L23 - Organization of Production
- L24 - Contracting Out; Joint Ventures; Technology Licensing
- L25 - Firm Performance: Size, Diversification, and Scope
- L26 - Entrepreneurship
- L29 - Other
- Browse content in L3 - Nonprofit Organizations and Public Enterprise
- L30 - General
- L31 - Nonprofit Institutions; NGOs; Social Entrepreneurship
- L32 - Public Enterprises; Public-Private Enterprises
- L33 - Comparison of Public and Private Enterprises and Nonprofit Institutions; Privatization; Contracting Out
- Browse content in L4 - Antitrust Issues and Policies
- L40 - General
- L41 - Monopolization; Horizontal Anticompetitive Practices
- L43 - Legal Monopolies and Regulation or Deregulation
- Browse content in L5 - Regulation and Industrial Policy
- L50 - General
- L51 - Economics of Regulation
- L52 - Industrial Policy; Sectoral Planning Methods
- L53 - Enterprise Policy
- Browse content in L6 - Industry Studies: Manufacturing
- L60 - General
- L66 - Food; Beverages; Cosmetics; Tobacco; Wine and Spirits
- Browse content in L7 - Industry Studies: Primary Products and Construction
- L71 - Mining, Extraction, and Refining: Hydrocarbon Fuels
- L78 - Government Policy
- Browse content in L8 - Industry Studies: Services
- L81 - Retail and Wholesale Trade; e-Commerce
- L83 - Sports; Gambling; Recreation; Tourism
- L86 - Information and Internet Services; Computer Software
- Browse content in L9 - Industry Studies: Transportation and Utilities
- L94 - Electric Utilities
- L98 - Government Policy
- Browse content in M - Business Administration and Business Economics; Marketing; Accounting; Personnel Economics
- Browse content in M1 - Business Administration
- M12 - Personnel Management; Executives; Executive Compensation
- M14 - Corporate Culture; Social Responsibility
- M16 - International Business Administration
- Browse content in M3 - Marketing and Advertising
- M31 - Marketing
- Browse content in M5 - Personnel Economics
- M50 - General
- M51 - Firm Employment Decisions; Promotions
- M52 - Compensation and Compensation Methods and Their Effects
- M53 - Training
- M54 - Labor Management
- M55 - Labor Contracting Devices
- Browse content in N - Economic History
- Browse content in N1 - Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics; Industrial Structure; Growth; Fluctuations
- N10 - General, International, or Comparative
- N11 - U.S.; Canada: Pre-1913
- N12 - U.S.; Canada: 1913-
- N13 - Europe: Pre-1913
- N15 - Asia including Middle East
- Browse content in N2 - Financial Markets and Institutions
- N20 - General, International, or Comparative
- N24 - Europe: 1913-
- N25 - Asia including Middle East
- Browse content in N3 - Labor and Consumers, Demography, Education, Health, Welfare, Income, Wealth, Religion, and Philanthropy
- N31 - U.S.; Canada: Pre-1913
- N33 - Europe: Pre-1913
- N34 - Europe: 1913-
- Browse content in N4 - Government, War, Law, International Relations, and Regulation
- N40 - General, International, or Comparative
- N45 - Asia including Middle East
- N47 - Africa; Oceania
- Browse content in N5 - Agriculture, Natural Resources, Environment, and Extractive Industries
- N50 - General, International, or Comparative
- N53 - Europe: Pre-1913
- N57 - Africa; Oceania
- Browse content in N7 - Transport, Trade, Energy, Technology, and Other Services
- N70 - General, International, or Comparative
- N72 - U.S.; Canada: 1913-
- Browse content in N9 - Regional and Urban History
- N97 - Africa; Oceania
- Browse content in O - Economic Development, Innovation, Technological Change, and Growth
- Browse content in O1 - Economic Development
- O10 - General
- O11 - Macroeconomic Analyses of Economic Development
- O12 - Microeconomic Analyses of Economic Development
- O13 - Agriculture; Natural Resources; Energy; Environment; Other Primary Products
- O14 - Industrialization; Manufacturing and Service Industries; Choice of Technology
- O15 - Human Resources; Human Development; Income Distribution; Migration
- O16 - Financial Markets; Saving and Capital Investment; Corporate Finance and Governance
- O17 - Formal and Informal Sectors; Shadow Economy; Institutional Arrangements
- O18 - Urban, Rural, Regional, and Transportation Analysis; Housing; Infrastructure
- O19 - International Linkages to Development; Role of International Organizations
- Browse content in O2 - Development Planning and Policy
- O22 - Project Analysis
- O23 - Fiscal and Monetary Policy in Development
- O24 - Trade Policy; Factor Movement Policy; Foreign Exchange Policy
- O25 - Industrial Policy
- Browse content in O3 - Innovation; Research and Development; Technological Change; Intellectual Property Rights
- O30 - General
- O31 - Innovation and Invention: Processes and Incentives
- O32 - Management of Technological Innovation and R&D
- O33 - Technological Change: Choices and Consequences; Diffusion Processes
- O34 - Intellectual Property and Intellectual Capital
- O38 - Government Policy
- O39 - Other
- Browse content in O4 - Economic Growth and Aggregate Productivity
- O40 - General
- O41 - One, Two, and Multisector Growth Models
- O42 - Monetary Growth Models
- O43 - Institutions and Growth
- O47 - Empirical Studies of Economic Growth; Aggregate Productivity; Cross-Country Output Convergence
- O49 - Other
- Browse content in O5 - Economywide Country Studies
- O50 - General
- O52 - Europe
- O53 - Asia including Middle East
- O55 - Africa
- O57 - Comparative Studies of Countries
- Browse content in P - Economic Systems
- Browse content in P1 - Capitalist Systems
- P10 - General
- P13 - Cooperative Enterprises
- P16 - Political Economy
- P17 - Performance and Prospects
- Browse content in P2 - Socialist Systems and Transitional Economies
- P20 - General
- P26 - Political Economy; Property Rights
- Browse content in P3 - Socialist Institutions and Their Transitions
- P31 - Socialist Enterprises and Their Transitions
- Browse content in P4 - Other Economic Systems
- P48 - Political Economy; Legal Institutions; Property Rights; Natural Resources; Energy; Environment; Regional Studies
- Browse content in P5 - Comparative Economic Systems
- P50 - General
- Browse content in Q - Agricultural and Natural Resource Economics; Environmental and Ecological Economics
- Browse content in Q0 - General
- Q02 - Commodity Markets
- Browse content in Q1 - Agriculture
- Q11 - Aggregate Supply and Demand Analysis; Prices
- Q13 - Agricultural Markets and Marketing; Cooperatives; Agribusiness
- Q15 - Land Ownership and Tenure; Land Reform; Land Use; Irrigation; Agriculture and Environment
- Q16 - R&D; Agricultural Technology; Biofuels; Agricultural Extension Services
- Q17 - Agriculture in International Trade
- Q18 - Agricultural Policy; Food Policy
- Browse content in Q2 - Renewable Resources and Conservation
- Q20 - General
- Q22 - Fishery; Aquaculture
- Q23 - Forestry
- Q25 - Water
- Q26 - Recreational Aspects of Natural Resources
- Q29 - Other
- Browse content in Q3 - Nonrenewable Resources and Conservation
- Q30 - General
- Q32 - Exhaustible Resources and Economic Development
- Q33 - Resource Booms
- Q34 - Natural Resources and Domestic and International Conflicts
- Q38 - Government Policy
- Browse content in Q4 - Energy
- Q40 - General
- Q41 - Demand and Supply; Prices
- Q42 - Alternative Energy Sources
- Q43 - Energy and the Macroeconomy
- Q48 - Government Policy
- Browse content in Q5 - Environmental Economics
- Q50 - General
- Q51 - Valuation of Environmental Effects
- Q52 - Pollution Control Adoption Costs; Distributional Effects; Employment Effects
- Q53 - Air Pollution; Water Pollution; Noise; Hazardous Waste; Solid Waste; Recycling
- Q54 - Climate; Natural Disasters; Global Warming
- Q56 - Environment and Development; Environment and Trade; Sustainability; Environmental Accounts and Accounting; Environmental Equity; Population Growth
- Q58 - Government Policy
- Browse content in R - Urban, Rural, Regional, Real Estate, and Transportation Economics
- Browse content in R1 - General Regional Economics
- R10 - General
- R11 - Regional Economic Activity: Growth, Development, Environmental Issues, and Changes
- R15 - Econometric and Input-Output Models; Other Models
- Browse content in R2 - Household Analysis
- R23 - Regional Migration; Regional Labor Markets; Population; Neighborhood Characteristics
- R29 - Other
- Browse content in R4 - Transportation Economics
- R40 - General
- R41 - Transportation: Demand, Supply, and Congestion; Travel Time; Safety and Accidents; Transportation Noise
- Browse content in R5 - Regional Government Analysis
- R58 - Regional Development Planning and Policy
- Browse content in Z - Other Special Topics
- Browse content in Z1 - Cultural Economics; Economic Sociology; Economic Anthropology
- Z10 - General
- Z11 - Economics of the Arts and Literature
- Z12 - Religion
- Z13 - Economic Sociology; Economic Anthropology; Social and Economic Stratification
- Z19 - Other
- Browse content in Z2 - Sports Economics
- Z21 - Industry Studies
- Z22 - Labor Issues
- Z29 - Other
- Browse content in Z3 - Tourism Economics
- Z30 - General
- Advance articles
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- About Oxford Economic Papers
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Terms and Conditions
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Managing Editors
James Forder
Francis J. Teal
About the journal
Oxford Economic Papers is a general economics journal, publishing refereed papers in economic theory, applied economics, econometrics, economic development, economic history, and the history of economic thought.
Symposium on Inequality
Browse research from the latest Oxford Economic Papers Symposium on Inequality. Articles discuss selective schooling systems, increased income inequality in advanced economies since the 1980s, and the impact of wealth on children’s exposure to environmental pollutants.
Browse papers
Special Issue: Sovereign Debt Restructuring
Read the latest Special Issue from Oxford Economic Papers , which investigates the mechanisms that help ensure the orderly functioning of sovereign debt markets, as well as conditions under which these same mechanisms lead to default, crisis, and costly debt restructuring.
Explore the issue
Hicks Lectures
Since 1984, Oxford Economic Papers has annually sponsored the Hicks lectures, a crucial element in fostering economic education. These lectures feature renowned researchers, including Nobel laureates, who impart valuable insights to both Oxford economic students and faculty.
Explore now
In the News
Developed countries benefit economically from counterterrorism efforts
A new study in Oxford Economic Papers suggests that developed counties may see significant economic gains from their efforts to combat terrorist threats. Developing counties, in contrast, appear to suffer economically from counterterrorism threats.
Read the press release | Read the article
Latest articles

Who are the super-rich and why they are paid so much?
One of the most common arguments against contemporary capitalism is that it generates extreme inequalities. Few individuals – it is often said – earn huge earnings, while the rest of society has to struggle to make ends meet...
Read the blog post | Read the article

Prostitution: The world's oldest public policy issue
Ever since the first arrangements were made for the exchange of some form of money for some form of sex, buying (or selling) sex has raised thorny issues for society's rulers and governments...

What are the hidden effects of tax credits?
UK tax credits are benefits first introduced in 1999 to help low-paid families through topping up their wages with the aims of 'making work pay' and reducing poverty, although they also cover non-working families with children...

The economics behind detecting terror plots
How many good guys are needed to catch the bad guys? This is the staffing question faced by counterterrorism agencies the world over...

Recommend to your library
Fill out our simple online form to recommend Oxford Economic Papers to your library.
Recommend now

JEL Codes Explained
Articles from Oxford Journals economics titles are classified according to the system used by the Journal of Economic Literature (commonly known as 'JEL codes').

Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE)
This journal is a member of and subscribes to the principles of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE)
publicationethics.org
Related Titles
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1464-3812
- Print ISSN 0030-7653
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Mark your calendar!
The fall 2024 bpea conference will be held september 26-27..
The Brookings Papers on Economic Activity (BPEA) is a semi-annual academic conference and journal that pairs rigorous research with real-time policy analysis to address the most urgent economic challenges of the day. Working drafts of the papers are presented and discussed at conferences typically held twice each year, and the final versions of the papers and comments along with summaries of the general discussions are published in the journal several months later. The views expressed by the authors, discussants and conference participants in BPEA are strictly those of the authors, discussants and conference participants, and not of the Brookings Institution. As an independent think tank, the Brookings Institution does not take institutional positions on any issue. Please contact Haowen Chen ( [email protected] ) if you have any questions.

Spring 2024

For authors
Search all bpea papers, subscribe to the journal.
Interested in writing a BPEA paper?

Subscribe to the Brookings Podcast on Economic Activity

New and Noteworthy
The evolution of banking in the 21st century
Samuel G. Hanson, Victoria Ivashina, Laura Nicolae, Jeremy C. Stein, Adi Sunderam, and Daniel K. Tarullo

Why do we dislike inflation?
Stefanie Stantcheva
Accounting for the widening mortality gap between American adults with and without a BA
Anne Case and Angus Deaton

The power of substitution: The Great German Gas debate in retrospect
Benjamin Moll, Moritz Schularick, and Georg Zachmann

Where are the missing workers?
Katharine Abraham and Lea Rendell

Economic implications of the climate provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act
John Bistline, Neil R. Mehrotra, and Catherine Wolfram

Understanding US inflation during the COVID era
Laurence Ball, Daniel Leigh, and Prachi Mishra

Working from home around the world
Cevat Giray Aksoy, Jose Maria Barrero, Nicholas Bloom, Steven J. Davis, Mathias Dolls, and Pablo Zarate

Losing the inflation anchor
Ricardo Reis

The economic gains from equity
Shelby R. Buckman, Laura Y. Choi, Mary C. Daly, and Lily M. Seitelman

Understanding the economic impact of COVID-19 on women
Claudia Goldin

Monetary policy and racial inequality
Alina Kristin Bartscher, Moritz Kuhn, Moritz Schularick, and Paul Wachtel

The sustainability of state and local government pensions: A public finance approach
Jamie Lenney, Byron Lutz, Finn Schüle, and Louise Sheiner

The economic costs of pretrial detention
Will Dobbie and Crystal S. Yang

Has the Paycheck Protection Program succeeded?
Glenn Hubbard and Michael R. Strain

Fiscal effects of COVID-19
Alan J. Auerbach, William G. Gale, Byron Lutz, and Louise Sheiner

Policies for a second wave
David Baqaee, Emmanuel Farhi, Michael J. Mina, and James Stock
Corporate debt overhang and credit policy
Markus Brunnermeier and Arvind Krishnamurthy

What's up with the Phillips Curve?
Marco Del Negro, Michele Lenza, Giorgio E. Primiceri, and Andrea Tambalotti

Declining worker power and American economic performance
Anna Stansbury and Lawrence H. Summers

Progressive wealth taxation
Emmanuel Saez and Gabriel Zucman

The real effects of the financial crisis
Ben S. Bernanke

Saving the heartland: Place-based policies in 21st Century America
Benjamin Austin, Edward Glaeser, and Lawrence Summers
Mortality and Morbidity in the 21st Century
Anne Case and Sir Angus Deaton
BPEA in the News

Nothing Defines America’s Social Divide Like a College Education
The Atlantic - October 4, 2023

U.S. labor force gap mostly due to pre-pandemic trends, study finds
Reuters - March 30, 2023

Reducing inequality, hiking minimum wage could boost U.S. economy -White House
Reuters - April 14, 2022

Fed's inclusive recovery put to the test
Axios - March 30, 2022

The Most Important Number You’ve Never Heard Of
The New York Times - September 17, 2021

The Cost of American Inequality
Bloomberg - September 9, 2021

A roller coaster six months leaves U.S. recovery still uncertain
Reuters - September 24, 2020

Biden Faces Challenge as Congress Drops State Aid to Secure Stimulus
The New York Times - December 17, 2020
Covid-19 Is Dividing the American Worker
The Wall Street Journal - August 22, 2020

Pandemic wage cuts are roughly double what they were in the Great Recession, study shows
Business Insider - June 26, 2020

How ECB purchases of corporate bonds helped reduce firms’ borrowing costs
European Central Bank - January 28, 2020

The College Wealth Divide Continues to Grow
Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis - January 17, 2020

There are consequences to making college free
The Washington Post - October 26, 2019

The French Economist Who Helped Invent Elizabeth Warren’s Wealth Tax
The New Yorker - October 19, 2019
BPEA Editors

Janice C. Eberly Nonresident Senior Fellow - Economic Studies

Jón Steinsson Nonresident Senior Fellow - Economic Studies
BPEA Leadership
This website uses cookies.
By clicking the "Accept" button or continuing to browse our site, you agree to first-party and session-only cookies being stored on your device to enhance site navigation and analyze site performance and traffic. For more information on our use of cookies, please see our Privacy Policy .
American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics
Current issue, find articles in this journal.
The 2024 AEJ Best Paper Awards Have Been Announced
Learn more about the papers chosen as the 2024 AEJ Best Papers.
Forthcoming Articles
View articles accepted for publication in AEJ: Macroeconomics .
Current editors and editorial staff of the AEJ: Macroeconomics .
AEJ Best Paper Awards
View articles selected for the annual AEJ Best Paper Awards.
Contact AEJ: Macroeconomics
Need to contact staff at the AEJ: Macroeconomics ?
2014 Theses Doctoral
Essays on Macroeconomics
Miyamoto, Wataru
This dissertation is a collection of three essays on macroeconomics, examining the sources of business cycles. In particular, we are interested in understanding how shocks propagate over the business cycle in both closed economy and open economy settings. The common approach we take in these chapters is to use both theory and data in a structural estimation based on a dynamic stochastic general equilibrium model. In the first chapter, motivated by the correlation of business cycles across countries, we provide a new empirical evidence about the role of common shocks in business cycles for small open economies. Specifically, we conduct a structural estimation of a small open economy real business cycle model featuring a realistic debt adjustment cost and common shocks. Using a novel dataset for 17 small developed and developing countries between 1900 and 2006, we find that common shocks are a primary source of business cycles, explaining nearly 50% of the output fluctuations over the last 100 years in small open economies. The estimated common shocks capture important historical episodes such as the Great depression, the two World Wars and the two oil price shocks. Moreover, these common shocks are important for not only small developed countries but also developing countries. We point out the importance of our structural approach in identifying the sizable role of both productivity and other common shocks such as interest rate premium shocks. The reduced form dynamic factor model approach in the previous literature, which often assumes one type of common component, would predict only a third of the contribution estimated in the structural model. In the second chapter, we focus on the transmission from one country to another through international trade. First, we argue that while we observe substantial business cycle correlation across countries, especially among developed economies, most existing models are not able to generate strong transmission of shocks endogenously through international trade. In the framework of structural model, we show that the nature of such transmission depends fundamentally on the features determining the responsiveness of labor supply and labor demand to international relative prices. We augment a standard international macroeconomic model to incorporate three key features: a weak short run wealth effect on labor supply, variable capital utilization, and imported intermediate inputs for production. This model can generate large and significant endogenous transmission of technology shocks through international trade. We demonstrate this by estimating the model using data for Canada and the United States with quasi-Bayesian methods. We find that this model can account for the substantial transmission of permanent U.S. technology shocks to Canadian aggregate variables such as output and hours documented in a structural vector autoregression. Transmission through international trade is found to explain the majority of the business cycle comovement between the United States and Canada while exogenous correlation of technology shocks is not important. In the third chapter, we turn to the sources of business cycles in a closed economy setting and analyzes the effects of news shocks, which are found to be an important driver of business cycles in the U.S. in the recent literature. The innovation of this chapter is that we use data on expectations to inform us about the role of news shocks. This approach exploits the fact that news shocks cause agents to adjust their expectations about the future even when current fundamentals are not affected, therefore, data on expectations are particularly informative about the role of news shocks. Using data on expectations, we estimate a dynamic, stochastic, general equilibrium model that incorporates news shocks for the U.S. between 1955Q1 and 2006Q4. We find that the contribution of news shocks to output is about half of that estimated without data on expectations. The precision of the estimated role of news shocks also greatly improves when data on expectations are used. Moreover, the contribution of news shocks to explaining short run fluctuations is negligible. These results arise because data on expectations show that changes in expectations are not large and do not resemble actual movements of output. Therefore, news shocks cannot be the main driver of business cycles.

More About This Work
- DOI Copy DOI to clipboard
- Faculty of Arts and Sciences
- FAS Theses and Dissertations
- Communities & Collections
- By Issue Date
- FAS Department
- Quick submit
- Waiver Generator
- DASH Stories
- Accessibility
- COVID-related Research
Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- By Collections
- By Departments
Essays on Macroeconomics, Finance, and Energy
Access Status
Citable link to this page, collections.
- FAS Theses and Dissertations [6136]
Contact administrator regarding this item (to report mistakes or request changes)
Macroeconomics of Mental Health
We develop an economic theory of mental health. The theory is grounded in classic and modern psychiatric literature, is disciplined with micro data, and is formalized in a life-cycle heterogeneous agent framework. In our model, individuals experiencing mental illness have pessimistic expectations and lose time due to rumination. As a result, they work less, consume less, invest less in risky assets, and forego treatment which in turn reinforces mental illness. We quantify the societal burden of mental illness and evaluate the efficacy of prominent policy proposals. We show that expanding the availability of treatment services and improving treatment of mental illness in late adolescence substantially improve mental health and welfare.
We thank Adam Blandin, Quentin Huys, Ellen McGrattan, Kim Peijnenburg, and Martin Schneider for useful discussions. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
Working Groups
Mentioned in the news, more from nber.
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .


COMMENTS
Humorous. Top 10 Reasons For Studying Economics. Inflation explained by Victor Borge. Funny Exam Answers. Humorous look at Subprime crisis. A collection of macro-economic essays on topics Inflation, Economic growth, government borrowing, balance of payments. Evaluation and critical analysis of all latest issues of the current day.
Macroeconomics is a field of economics that studies the economic performance of countries. By employing it, governments can analyze the financial situation within a country. Macroeconomic theory's concepts help to predict and prevent possible economic obstacles. Generally, the field presents the big picture.
WRITING ASSIGNMENTS IN ECONOMICS 970 In Sophomore Tutorial (Economics 970), you will receive several writing assignments including a term paper, an empirical exercise, short essays, response papers, and possibly a rewrite. Below is a description of these types: • Term Paper (10-15pp.). In all tutorials, you will be required to write a
1980s - Boom and Bust economy - The UK economy in the 1980s. Late 1980s - The Lawson Boom. Rapid growth, inflation and recession. 1990s - Recession and great stability - Recovering from the recession and leaving ERM. The economics of the 2000s - from stability to financial crisis. 1992-2007 - The great moderation - a period of ...
Macroeconomics is a branch of the economics field that studies how the aggregate economy behaves. In macroeconomics, a variety of economy-wide phenomena is thoroughly examined such as, inflation ...
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix makro- meaning "large" and economics) is a branch of economics dealing with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole, rather than individual markets. This includes national, regional, and global economies. [1] [2] With microeconomics, macroeconomics is one of the ...
Essays on Political Economy and Macroeconomics Abstract This dissertation consists of four essays on a range of topics in political economy and macroeconomics which are united by having current policy relevance. The first essay studies the effects of social policy laws on beliefs and attitudes held by the public.
11 essay samples found. Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole, including topics such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. Essays could delve into the basic principles of macroeconomics, explore different macroeconomic models and theories, and discuss the implications of macroeconomic policy on individuals and ...
Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone. OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit. Give today and help us reach more students. Help. OpenStax. This free textbook is an OpenStax resource written to increase student access to high-quality, peer-reviewed learning materials.
by Frank Hahn and Robert M. Solow. Paperback. $25.00. Paperback. ISBN: 9780262581547. Pub date: August 21, 1997. Publisher: The MIT Press. 208 pp., 6 x 9 in, MIT Press Bookstore Penguin Random House Amazon Barnes and Noble Bookshop.org Indiebound Indigo Books a Million.
Learning about economics helps you understand the major problems facing the world today, prepares you to be a good citizen, and helps you become a well-rounded thinker. 1.2 Microeconomics and Macroeconomics. Microeconomics and macroeconomics are two different perspectives on the economy. The microeconomic perspective focuses on parts of the ...
Essays on Macroeconomic Stabilization Abstract Motivated by policy debates emerging from the U.S. Great Recession and Eurozone crisis, I study the stabilization role of monetary, fiscal, and macroprudential policies in response to short-run fluctuations. In the first essay on "Unemployment Insurance in Macroeconomic
Essays on Macroeconomics, Finance, and Energy. Doctoral dissertation, Harvard University Graduate School of Arts and Sciences. Macroeconomic stability, access to finance, and access to reliable energy are three critical pillars of economic growth and development. This dissertation is composed of three independent essays that examine the impacts ...
Essay # 1. Meaning of Microeconomics: Microeconomics is the study of the economic actions of individuals and small groups of individuals. This includes "the study of particular firms, particular households, individual prices, wages, income, individual industries, and particular commodities.". It concerns itself with the analysis of price determination and the allocation of resources to ...
Essays on Macroeconomics and Labor Economics A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY John Carter Braxton IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF Doctor of Philosophy Ellen McGrattan, Advisor Kyle Herkenho , Co-Advisor May, 2020
Additionally, writing essays on macroeconomics enables individuals to engage with current economic debates and contribute to the discourse on economic policy and societal well-being. Tips on Choosing a Good Topic. Consider current events and their impact on the economy, such as the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on economic stability. ...
Yu She joined the doctoral program in the Department of Economics at Cornell University in the fall of 2014. His broad research interests are in applied macroeconomics, monetary and fiscal policy, and his doctoral research focuses on the heterogeneous impacts of monetary/fiscal policies over the distribution of heterogeneous firms/households.
Macroeconomics. New research on macroeconomics from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including how the Chinese Communist Party used land supply as a key tool of macroeconomic expansion and contraction, why federal spending in states appears to cause local businesses to cut back rather than grow, and why the GDP is not an accurate ...
Oxford Economic Papers is a general economics journal, publishing refereed papers in economic theory, applied economics, econometrics, economic development, economic history, and the history of economic thought. Find out more about the journal. Advertisement. Symposium on Inequality.
The Brookings Papers on Economic Activity (BPEA) is a semi-annual academic conference and journal that pairs rigorous research with real-time policy analysis to address the most urgent economic ...
American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics focuses on studies of aggregate fluctuations and growth and the role of policy in that context. ... Learn more about the papers chosen as the 2024 AEJ Best Papers. Forthcoming Articles View articles accepted for publication in AEJ: Macroeconomics. Editors. Current editors and editorial ...
Essays on Macroeconomics. Miyamoto, Wataru. This dissertation is a collection of three essays on macroeconomics, examining the sources of business cycles. In particular, we are interested in understanding how shocks propagate over the business cycle in both closed economy and open economy settings. The common approach we take in these chapters ...
Essays on Macroeconomics, Finance, and Energy. Doctoral dissertation, Harvard University Graduate School of Arts and Sciences. Abstract Macroeconomic stability, access to finance, and access to reliable energy are three critical pillars of economic growth and development. This dissertation is composed of three independent essays that examine ...
This article explores the development of Law and Macroeconomics (LawMacro) and its ideological divergence from the Law and Economics (LawEcon) tradition. It emphasizes that LawMacro's innovation lies in its adoption of Keynesian economics rather than merely in the incorporation of macroeconomic perspectives.
these papers for further details and re nements. The economy is static and involves the production of a unique nal good, and all markets are competitive.7 The production of a unique nal good takes place by combining a set of tasks, with measure N, using the following production function Y = B(N) Z N 0 y(z)˙ 1 ˙ dz ˙ ˙ 1; (1)
Working Papers; Macroeconomics of Mental Health Macroeconomics of Mental Health. Boaz Abramson, Job Boerma & Aleh Tsyvinski. Share. X LinkedIn Email. Working Paper 32354 DOI 10.3386/w32354 Issue Date April 2024. We develop an economic theory of mental health. The theory is grounded in classic and modern psychiatric literature, is disciplined ...