Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 25 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Apr 1, 2024 9:56 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core Collection This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: Jan 17, 2024 10:05 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
How To Structure Your Literature Review
3 options to help structure your chapter.
By: Amy Rommelspacher (PhD) | Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | November 2020 (Updated May 2023)
Writing the literature review chapter can seem pretty daunting when you’re piecing together your dissertation or thesis. As we’ve discussed before , a good literature review needs to achieve a few very important objectives – it should:
- Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic
- Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these
- Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one)
- Inform your own methodology and research design
To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure . Get the structure of your literature review chapter wrong and you’ll struggle to achieve these objectives. Don’t worry though – in this post, we’ll look at how to structure your literature review for maximum impact (and marks!).

But wait – is this the right time?
Deciding on the structure of your literature review should come towards the end of the literature review process – after you have collected and digested the literature, but before you start writing the chapter.
In other words, you need to first develop a rich understanding of the literature before you even attempt to map out a structure. There’s no use trying to develop a structure before you’ve fully wrapped your head around the existing research.
Equally importantly, you need to have a structure in place before you start writing , or your literature review will most likely end up a rambling, disjointed mess.
Importantly, don’t feel that once you’ve defined a structure you can’t iterate on it. It’s perfectly natural to adjust as you engage in the writing process. As we’ve discussed before , writing is a way of developing your thinking, so it’s quite common for your thinking to change – and therefore, for your chapter structure to change – as you write.
Need a helping hand?
Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components – an introduction , a body and a conclusion .
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
1: The Introduction Section
Just like any good introduction, the introduction section of your literature review should introduce the purpose and layout (organisation) of the chapter. In other words, your introduction needs to give the reader a taste of what’s to come, and how you’re going to lay that out. Essentially, you should provide the reader with a high-level roadmap of your chapter to give them a taste of the journey that lies ahead.
Here’s an example of the layout visualised in a literature review introduction:
Your introduction should also outline your topic (including any tricky terminology or jargon) and provide an explanation of the scope of your literature review – in other words, what you will and won’t be covering (the delimitations ). This helps ringfence your review and achieve a clear focus . The clearer and narrower your focus, the deeper you can dive into the topic (which is typically where the magic lies).
Depending on the nature of your project, you could also present your stance or point of view at this stage. In other words, after grappling with the literature you’ll have an opinion about what the trends and concerns are in the field as well as what’s lacking. The introduction section can then present these ideas so that it is clear to examiners that you’re aware of how your research connects with existing knowledge .

2: The Body Section
The body of your literature review is the centre of your work. This is where you’ll present, analyse, evaluate and synthesise the existing research. In other words, this is where you’re going to earn (or lose) the most marks. Therefore, it’s important to carefully think about how you will organise your discussion to present it in a clear way.
The body of your literature review should do just as the description of this chapter suggests. It should “review” the literature – in other words, identify, analyse, and synthesise it. So, when thinking about structuring your literature review, you need to think about which structural approach will provide the best “review” for your specific type of research and objectives (we’ll get to this shortly).
There are (broadly speaking) three options for organising your literature review.

Option 1: Chronological (according to date)
Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
The benefit of this option is that it makes it easy to discuss the developments and debates in the field as they emerged over time. Organising your literature chronologically also allows you to highlight how specific articles or pieces of work might have changed the course of the field – in other words, which research has had the most impact . Therefore, this approach is very useful when your research is aimed at understanding how the topic has unfolded over time and is often used by scholars in the field of history. That said, this approach can be utilised by anyone that wants to explore change over time .

For example , if a student of politics is investigating how the understanding of democracy has evolved over time, they could use the chronological approach to provide a narrative that demonstrates how this understanding has changed through the ages.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself to help you structure your literature review chronologically.
- What is the earliest literature published relating to this topic?
- How has the field changed over time? Why?
- What are the most recent discoveries/theories?
In some ways, chronology plays a part whichever way you decide to structure your literature review, because you will always, to a certain extent, be analysing how the literature has developed. However, with the chronological approach, the emphasis is very firmly on how the discussion has evolved over time , as opposed to how all the literature links together (which we’ll discuss next ).
Option 2: Thematic (grouped by theme)
The thematic approach to structuring a literature review means organising your literature by theme or category – for example, by independent variables (i.e. factors that have an impact on a specific outcome).
As you’ve been collecting and synthesising literature , you’ll likely have started seeing some themes or patterns emerging. You can then use these themes or patterns as a structure for your body discussion. The thematic approach is the most common approach and is useful for structuring literature reviews in most fields.
For example, if you were researching which factors contributed towards people trusting an organisation, you might find themes such as consumers’ perceptions of an organisation’s competence, benevolence and integrity. Structuring your literature review thematically would mean structuring your literature review’s body section to discuss each of these themes, one section at a time.

Here are some questions to ask yourself when structuring your literature review by themes:
- Are there any patterns that have come to light in the literature?
- What are the central themes and categories used by the researchers?
- Do I have enough evidence of these themes?
PS – you can see an example of a thematically structured literature review in our literature review sample walkthrough video here.
Option 3: Methodological
The methodological option is a way of structuring your literature review by the research methodologies used . In other words, organising your discussion based on the angle from which each piece of research was approached – for example, qualitative , quantitative or mixed methodologies.
Structuring your literature review by methodology can be useful if you are drawing research from a variety of disciplines and are critiquing different methodologies. The point of this approach is to question how existing research has been conducted, as opposed to what the conclusions and/or findings the research were.

For example, a sociologist might centre their research around critiquing specific fieldwork practices. Their literature review will then be a summary of the fieldwork methodologies used by different studies.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself when structuring your literature review according to methodology:
- Which methodologies have been utilised in this field?
- Which methodology is the most popular (and why)?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the various methodologies?
- How can the existing methodologies inform my own methodology?
3: The Conclusion Section
Once you’ve completed the body section of your literature review using one of the structural approaches we discussed above, you’ll need to “wrap up” your literature review and pull all the pieces together to set the direction for the rest of your dissertation or thesis.
The conclusion is where you’ll present the key findings of your literature review. In this section, you should emphasise the research that is especially important to your research questions and highlight the gaps that exist in the literature. Based on this, you need to make it clear what you will add to the literature – in other words, justify your own research by showing how it will help fill one or more of the gaps you just identified.
Last but not least, if it’s your intention to develop a conceptual framework for your dissertation or thesis, the conclusion section is a good place to present this.

Example: Thematically Structured Review
In the video below, we unpack a literature review chapter so that you can see an example of a thematically structure review in practice.
Let’s Recap
In this article, we’ve discussed how to structure your literature review for maximum impact. Here’s a quick recap of what you need to keep in mind when deciding on your literature review structure:
- Just like other chapters, your literature review needs a clear introduction , body and conclusion .
- The introduction section should provide an overview of what you will discuss in your literature review.
- The body section of your literature review can be organised by chronology , theme or methodology . The right structural approach depends on what you’re trying to achieve with your research.
- The conclusion section should draw together the key findings of your literature review and link them to your research questions.
If you’re ready to get started, be sure to download our free literature review template to fast-track your chapter outline.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

27 Comments
Great work. This is exactly what I was looking for and helps a lot together with your previous post on literature review. One last thing is missing: a link to a great literature chapter of an journal article (maybe with comments of the different sections in this review chapter). Do you know any great literature review chapters?
I agree with you Marin… A great piece
I agree with Marin. This would be quite helpful if you annotate a nicely structured literature from previously published research articles.
Awesome article for my research.
I thank you immensely for this wonderful guide
It is indeed thought and supportive work for the futurist researcher and students
Very educative and good time to get guide. Thank you
Great work, very insightful. Thank you.
Thanks for this wonderful presentation. My question is that do I put all the variables into a single conceptual framework or each hypothesis will have it own conceptual framework?
Thank you very much, very helpful
This is very educative and precise . Thank you very much for dropping this kind of write up .
Pheeww, so damn helpful, thank you for this informative piece.
I’m doing a research project topic ; stool analysis for parasitic worm (enteric) worm, how do I structure it, thanks.
comprehensive explanation. Help us by pasting the URL of some good “literature review” for better understanding.
great piece. thanks for the awesome explanation. it is really worth sharing. I have a little question, if anyone can help me out, which of the options in the body of literature can be best fit if you are writing an architectural thesis that deals with design?
I am doing a research on nanofluids how can l structure it?
Beautifully clear.nThank you!
Lucid! Thankyou!
Brilliant work, well understood, many thanks
I like how this was so clear with simple language 😊😊 thank you so much 😊 for these information 😊
Insightful. I was struggling to come up with a sensible literature review but this has been really helpful. Thank you!
You have given thought-provoking information about the review of the literature.
Thank you. It has made my own research better and to impart your work to students I teach
I learnt a lot from this teaching. It’s a great piece.
I am doing research on EFL teacher motivation for his/her job. How Can I structure it? Is there any detailed template, additional to this?
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through something like this before. So nice to find somebody with some genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I’m asked to do conceptual, theoretical and empirical literature, and i just don’t know how to structure it
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Literature Review
Definition:
A literature review is a comprehensive and critical analysis of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It involves identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing relevant literature, including scholarly articles, books, and other sources, to provide a summary and critical assessment of what is known about the topic.
Types of Literature Review
Types of Literature Review are as follows:
- Narrative literature review : This type of review involves a comprehensive summary and critical analysis of the available literature on a particular topic or research question. It is often used as an introductory section of a research paper.
- Systematic literature review: This is a rigorous and structured review that follows a pre-defined protocol to identify, evaluate, and synthesize all relevant studies on a specific research question. It is often used in evidence-based practice and systematic reviews.
- Meta-analysis: This is a quantitative review that uses statistical methods to combine data from multiple studies to derive a summary effect size. It provides a more precise estimate of the overall effect than any individual study.
- Scoping review: This is a preliminary review that aims to map the existing literature on a broad topic area to identify research gaps and areas for further investigation.
- Critical literature review : This type of review evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It aims to provide a critical analysis of the literature and identify areas where further research is needed.
- Conceptual literature review: This review synthesizes and integrates theories and concepts from multiple sources to provide a new perspective on a particular topic. It aims to provide a theoretical framework for understanding a particular research question.
- Rapid literature review: This is a quick review that provides a snapshot of the current state of knowledge on a specific research question or topic. It is often used when time and resources are limited.
- Thematic literature review : This review identifies and analyzes common themes and patterns across a body of literature on a particular topic. It aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the literature and identify key themes and concepts.
- Realist literature review: This review is often used in social science research and aims to identify how and why certain interventions work in certain contexts. It takes into account the context and complexities of real-world situations.
- State-of-the-art literature review : This type of review provides an overview of the current state of knowledge in a particular field, highlighting the most recent and relevant research. It is often used in fields where knowledge is rapidly evolving, such as technology or medicine.
- Integrative literature review: This type of review synthesizes and integrates findings from multiple studies on a particular topic to identify patterns, themes, and gaps in the literature. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.
- Umbrella literature review : This review is used to provide a broad overview of a large and diverse body of literature on a particular topic. It aims to identify common themes and patterns across different areas of research.
- Historical literature review: This type of review examines the historical development of research on a particular topic or research question. It aims to provide a historical context for understanding the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.
- Problem-oriented literature review : This review focuses on a specific problem or issue and examines the literature to identify potential solutions or interventions. It aims to provide practical recommendations for addressing a particular problem or issue.
- Mixed-methods literature review : This type of review combines quantitative and qualitative methods to synthesize and analyze the available literature on a particular topic. It aims to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research question by combining different types of evidence.
Parts of Literature Review
Parts of a literature review are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction of a literature review typically provides background information on the research topic and why it is important. It outlines the objectives of the review, the research question or hypothesis, and the scope of the review.
Literature Search
This section outlines the search strategy and databases used to identify relevant literature. The search terms used, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and any limitations of the search are described.
Literature Analysis
The literature analysis is the main body of the literature review. This section summarizes and synthesizes the literature that is relevant to the research question or hypothesis. The review should be organized thematically, chronologically, or by methodology, depending on the research objectives.
Critical Evaluation
Critical evaluation involves assessing the quality and validity of the literature. This includes evaluating the reliability and validity of the studies reviewed, the methodology used, and the strength of the evidence.
The conclusion of the literature review should summarize the main findings, identify any gaps in the literature, and suggest areas for future research. It should also reiterate the importance of the research question or hypothesis and the contribution of the literature review to the overall research project.
The references list includes all the sources cited in the literature review, and follows a specific referencing style (e.g., APA, MLA, Harvard).
How to write Literature Review
Here are some steps to follow when writing a literature review:
- Define your research question or topic : Before starting your literature review, it is essential to define your research question or topic. This will help you identify relevant literature and determine the scope of your review.
- Conduct a comprehensive search: Use databases and search engines to find relevant literature. Look for peer-reviewed articles, books, and other academic sources that are relevant to your research question or topic.
- Evaluate the sources: Once you have found potential sources, evaluate them critically to determine their relevance, credibility, and quality. Look for recent publications, reputable authors, and reliable sources of data and evidence.
- Organize your sources: Group the sources by theme, method, or research question. This will help you identify similarities and differences among the literature, and provide a structure for your literature review.
- Analyze and synthesize the literature : Analyze each source in depth, identifying the key findings, methodologies, and conclusions. Then, synthesize the information from the sources, identifying patterns and themes in the literature.
- Write the literature review : Start with an introduction that provides an overview of the topic and the purpose of the literature review. Then, organize the literature according to your chosen structure, and analyze and synthesize the sources. Finally, provide a conclusion that summarizes the key findings of the literature review, identifies gaps in knowledge, and suggests areas for future research.
- Edit and proofread: Once you have written your literature review, edit and proofread it carefully to ensure that it is well-organized, clear, and concise.
Examples of Literature Review
Here’s an example of how a literature review can be conducted for a thesis on the topic of “ The Impact of Social Media on Teenagers’ Mental Health”:
- Start by identifying the key terms related to your research topic. In this case, the key terms are “social media,” “teenagers,” and “mental health.”
- Use academic databases like Google Scholar, JSTOR, or PubMed to search for relevant articles, books, and other publications. Use these keywords in your search to narrow down your results.
- Evaluate the sources you find to determine if they are relevant to your research question. You may want to consider the publication date, author’s credentials, and the journal or book publisher.
- Begin reading and taking notes on each source, paying attention to key findings, methodologies used, and any gaps in the research.
- Organize your findings into themes or categories. For example, you might categorize your sources into those that examine the impact of social media on self-esteem, those that explore the effects of cyberbullying, and those that investigate the relationship between social media use and depression.
- Synthesize your findings by summarizing the key themes and highlighting any gaps or inconsistencies in the research. Identify areas where further research is needed.
- Use your literature review to inform your research questions and hypotheses for your thesis.
For example, after conducting a literature review on the impact of social media on teenagers’ mental health, a thesis might look like this:
“Using a mixed-methods approach, this study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes in teenagers. Specifically, the study will examine the effects of cyberbullying, social comparison, and excessive social media use on self-esteem, anxiety, and depression. Through an analysis of survey data and qualitative interviews with teenagers, the study will provide insight into the complex relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes, and identify strategies for promoting positive mental health outcomes in young people.”
Reference: Smith, J., Jones, M., & Lee, S. (2019). The effects of social media use on adolescent mental health: A systematic review. Journal of Adolescent Health, 65(2), 154-165. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2019.03.024
Reference Example: Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page range. doi:0000000/000000000000 or URL
Applications of Literature Review
some applications of literature review in different fields:
- Social Sciences: In social sciences, literature reviews are used to identify gaps in existing research, to develop research questions, and to provide a theoretical framework for research. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as sociology, psychology, anthropology, and political science.
- Natural Sciences: In natural sciences, literature reviews are used to summarize and evaluate the current state of knowledge in a particular field or subfield. Literature reviews can help researchers identify areas where more research is needed and provide insights into the latest developments in a particular field. Fields such as biology, chemistry, and physics commonly use literature reviews.
- Health Sciences: In health sciences, literature reviews are used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments, identify best practices, and determine areas where more research is needed. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as medicine, nursing, and public health.
- Humanities: In humanities, literature reviews are used to identify gaps in existing knowledge, develop new interpretations of texts or cultural artifacts, and provide a theoretical framework for research. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as history, literary studies, and philosophy.
Role of Literature Review in Research
Here are some applications of literature review in research:
- Identifying Research Gaps : Literature review helps researchers identify gaps in existing research and literature related to their research question. This allows them to develop new research questions and hypotheses to fill those gaps.
- Developing Theoretical Framework: Literature review helps researchers develop a theoretical framework for their research. By analyzing and synthesizing existing literature, researchers can identify the key concepts, theories, and models that are relevant to their research.
- Selecting Research Methods : Literature review helps researchers select appropriate research methods and techniques based on previous research. It also helps researchers to identify potential biases or limitations of certain methods and techniques.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Literature review helps researchers in data collection and analysis by providing a foundation for the development of data collection instruments and methods. It also helps researchers to identify relevant data sources and identify potential data analysis techniques.
- Communicating Results: Literature review helps researchers to communicate their results effectively by providing a context for their research. It also helps to justify the significance of their findings in relation to existing research and literature.
Purpose of Literature Review
Some of the specific purposes of a literature review are as follows:
- To provide context: A literature review helps to provide context for your research by situating it within the broader body of literature on the topic.
- To identify gaps and inconsistencies: A literature review helps to identify areas where further research is needed or where there are inconsistencies in the existing literature.
- To synthesize information: A literature review helps to synthesize the information from multiple sources and present a coherent and comprehensive picture of the current state of knowledge on the topic.
- To identify key concepts and theories : A literature review helps to identify key concepts and theories that are relevant to your research question and provide a theoretical framework for your study.
- To inform research design: A literature review can inform the design of your research study by identifying appropriate research methods, data sources, and research questions.
Characteristics of Literature Review
Some Characteristics of Literature Review are as follows:
- Identifying gaps in knowledge: A literature review helps to identify gaps in the existing knowledge and research on a specific topic or research question. By analyzing and synthesizing the literature, you can identify areas where further research is needed and where new insights can be gained.
- Establishing the significance of your research: A literature review helps to establish the significance of your own research by placing it in the context of existing research. By demonstrating the relevance of your research to the existing literature, you can establish its importance and value.
- Informing research design and methodology : A literature review helps to inform research design and methodology by identifying the most appropriate research methods, techniques, and instruments. By reviewing the literature, you can identify the strengths and limitations of different research methods and techniques, and select the most appropriate ones for your own research.
- Supporting arguments and claims: A literature review provides evidence to support arguments and claims made in academic writing. By citing and analyzing the literature, you can provide a solid foundation for your own arguments and claims.
- I dentifying potential collaborators and mentors: A literature review can help identify potential collaborators and mentors by identifying researchers and practitioners who are working on related topics or using similar methods. By building relationships with these individuals, you can gain valuable insights and support for your own research and practice.
- Keeping up-to-date with the latest research : A literature review helps to keep you up-to-date with the latest research on a specific topic or research question. By regularly reviewing the literature, you can stay informed about the latest findings and developments in your field.
Advantages of Literature Review
There are several advantages to conducting a literature review as part of a research project, including:
- Establishing the significance of the research : A literature review helps to establish the significance of the research by demonstrating the gap or problem in the existing literature that the study aims to address.
- Identifying key concepts and theories: A literature review can help to identify key concepts and theories that are relevant to the research question, and provide a theoretical framework for the study.
- Supporting the research methodology : A literature review can inform the research methodology by identifying appropriate research methods, data sources, and research questions.
- Providing a comprehensive overview of the literature : A literature review provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge on a topic, allowing the researcher to identify key themes, debates, and areas of agreement or disagreement.
- Identifying potential research questions: A literature review can help to identify potential research questions and areas for further investigation.
- Avoiding duplication of research: A literature review can help to avoid duplication of research by identifying what has already been done on a topic, and what remains to be done.
- Enhancing the credibility of the research : A literature review helps to enhance the credibility of the research by demonstrating the researcher’s knowledge of the existing literature and their ability to situate their research within a broader context.
Limitations of Literature Review
Limitations of Literature Review are as follows:
- Limited scope : Literature reviews can only cover the existing literature on a particular topic, which may be limited in scope or depth.
- Publication bias : Literature reviews may be influenced by publication bias, which occurs when researchers are more likely to publish positive results than negative ones. This can lead to an incomplete or biased picture of the literature.
- Quality of sources : The quality of the literature reviewed can vary widely, and not all sources may be reliable or valid.
- Time-limited: Literature reviews can become quickly outdated as new research is published, making it difficult to keep up with the latest developments in a field.
- Subjective interpretation : Literature reviews can be subjective, and the interpretation of the findings can vary depending on the researcher’s perspective or bias.
- Lack of original data : Literature reviews do not generate new data, but rather rely on the analysis of existing studies.
- Risk of plagiarism: It is important to ensure that literature reviews do not inadvertently contain plagiarism, which can occur when researchers use the work of others without proper attribution.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips


Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid..., how to write an essay introduction (with examples)..., similarity checks: the author’s guide to plagiarism and..., what is a master’s thesis: a guide for..., authorship in academia: ghost, guest, and gift authorship, should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., what are the benefits of generative ai for....
15 Literature Review Examples
Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal . They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed.
Ideally, once you have completed your literature review, you will be able to identify how your research project can build upon and extend existing knowledge in your area of study.
Generally, for my undergraduate research students, I recommend a narrative review, where themes can be generated in order for the students to develop sufficient understanding of the topic so they can build upon the themes using unique methods or novel research questions.
If you’re in the process of writing a literature review, I have developed a literature review template for you to use – it’s a huge time-saver and walks you through how to write a literature review step-by-step:
Get your time-saving templates here to write your own literature review.
Literature Review Examples
For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics.
1. Narrative Review Examples
Also known as a traditional literature review, the narrative review provides a broad overview of the studies done on a particular topic.
It often includes both qualitative and quantitative studies and may cover a wide range of years.
The narrative review’s purpose is to identify commonalities, gaps, and contradictions in the literature .
I recommend to my students that they should gather their studies together, take notes on each study, then try to group them by themes that form the basis for the review (see my step-by-step instructions at the end of the article).
Example Study
Title: Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations
Citation: Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcp.12686
Overview: This narrative review analyzed themes emerging from 69 articles about communication in healthcare contexts. Five key themes were found in the literature: poor communication can lead to various negative outcomes, discontinuity of care, compromise of patient safety, patient dissatisfaction, and inefficient use of resources. After presenting the key themes, the authors recommend that practitioners need to approach healthcare communication in a more structured way, such as by ensuring there is a clear understanding of who is in charge of ensuring effective communication in clinical settings.
Other Examples
- Burnout in United States Healthcare Professionals: A Narrative Review (Reith, 2018) – read here
- Examining the Presence, Consequences, and Reduction of Implicit Bias in Health Care: A Narrative Review (Zestcott, Blair & Stone, 2016) – read here
- A Narrative Review of School-Based Physical Activity for Enhancing Cognition and Learning (Mavilidi et al., 2018) – read here
- A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents (Dyrbye & Shanafelt, 2015) – read here
2. Systematic Review Examples
This type of literature review is more structured and rigorous than a narrative review. It involves a detailed and comprehensive plan and search strategy derived from a set of specified research questions.
The key way you’d know a systematic review compared to a narrative review is in the methodology: the systematic review will likely have a very clear criteria for how the studies were collected, and clear explanations of exclusion/inclusion criteria.
The goal is to gather the maximum amount of valid literature on the topic, filter out invalid or low-quality reviews, and minimize bias. Ideally, this will provide more reliable findings, leading to higher-quality conclusions and recommendations for further research.
You may note from the examples below that the ‘method’ sections in systematic reviews tend to be much more explicit, often noting rigid inclusion/exclusion criteria and exact keywords used in searches.
Title: The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review
Citation: Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092422441730122X
Overview: This systematic review included 72 studies of food naturalness to explore trends in the literature about its importance for consumers. Keywords used in the data search included: food, naturalness, natural content, and natural ingredients. Studies were included if they examined consumers’ preference for food naturalness and contained empirical data. The authors found that the literature lacks clarity about how naturalness is defined and measured, but also found that food consumption is significantly influenced by perceived naturalness of goods.
- A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018 (Martin, Sun & Westine, 2020) – read here
- Where Is Current Research on Blockchain Technology? (Yli-Huumo et al., 2016) – read here
- Universities—industry collaboration: A systematic review (Ankrah & Al-Tabbaa, 2015) – read here
- Internet of Things Applications: A Systematic Review (Asghari, Rahmani & Javadi, 2019) – read here
3. Meta-analysis
This is a type of systematic review that uses statistical methods to combine and summarize the results of several studies.
Due to its robust methodology, a meta-analysis is often considered the ‘gold standard’ of secondary research , as it provides a more precise estimate of a treatment effect than any individual study contributing to the pooled analysis.
Furthermore, by aggregating data from a range of studies, a meta-analysis can identify patterns, disagreements, or other interesting relationships that may have been hidden in individual studies.
This helps to enhance the generalizability of findings, making the conclusions drawn from a meta-analysis particularly powerful and informative for policy and practice.
Title: Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk: A Meta-Meta-Analysis
Citation: Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Source: https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060386
O verview: This study examines the relationship between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Researchers conducted a systematic search of meta-analyses and reviewed several databases, collecting 100 primary studies and five meta-analyses to analyze the connection between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. They find that the literature compellingly demonstrates that low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels significantly influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
- The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research (Wisniewski, Zierer & Hattie, 2020) – read here
- How Much Does Education Improve Intelligence? A Meta-Analysis (Ritchie & Tucker-Drob, 2018) – read here
- A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling (Geiger et al., 2019) – read here
- Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits (Patterson, Chung & Swan, 2014) – read here
Other Types of Reviews
- Scoping Review: This type of review is used to map the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It can be undertaken as stand-alone projects in their own right, or as a precursor to a systematic review.
- Rapid Review: This type of review accelerates the systematic review process in order to produce information in a timely manner. This is achieved by simplifying or omitting stages of the systematic review process.
- Integrative Review: This review method is more inclusive than others, allowing for the simultaneous inclusion of experimental and non-experimental research. The goal is to more comprehensively understand a particular phenomenon.
- Critical Review: This is similar to a narrative review but requires a robust understanding of both the subject and the existing literature. In a critical review, the reviewer not only summarizes the existing literature, but also evaluates its strengths and weaknesses. This is common in the social sciences and humanities .
- State-of-the-Art Review: This considers the current level of advancement in a field or topic and makes recommendations for future research directions. This type of review is common in technological and scientific fields but can be applied to any discipline.
How to Write a Narrative Review (Tips for Undergrad Students)
Most undergraduate students conducting a capstone research project will be writing narrative reviews. Below is a five-step process for conducting a simple review of the literature for your project.
- Search for Relevant Literature: Use scholarly databases related to your field of study, provided by your university library, along with appropriate search terms to identify key scholarly articles that have been published on your topic.
- Evaluate and Select Sources: Filter the source list by selecting studies that are directly relevant and of sufficient quality, considering factors like credibility , objectivity, accuracy, and validity.
- Analyze and Synthesize: Review each source and summarize the main arguments in one paragraph (or more, for postgrad). Keep these summaries in a table.
- Identify Themes: With all studies summarized, group studies that share common themes, such as studies that have similar findings or methodologies.
- Write the Review: Write your review based upon the themes or subtopics you have identified. Give a thorough overview of each theme, integrating source data, and conclude with a summary of the current state of knowledge then suggestions for future research based upon your evaluation of what is lacking in the literature.
Literature reviews don’t have to be as scary as they seem. Yes, they are difficult and require a strong degree of comprehension of academic studies. But it can be feasibly done through following a structured approach to data collection and analysis. With my undergraduate research students (who tend to conduct small-scale qualitative studies ), I encourage them to conduct a narrative literature review whereby they can identify key themes in the literature. Within each theme, students can critique key studies and their strengths and limitations , in order to get a lay of the land and come to a point where they can identify ways to contribute new insights to the existing academic conversation on their topic.
Ankrah, S., & Omar, A. T. (2015). Universities–industry collaboration: A systematic review. Scandinavian Journal of Management, 31(3), 387-408.
Asghari, P., Rahmani, A. M., & Javadi, H. H. S. (2019). Internet of Things applications: A systematic review. Computer Networks , 148 , 241-261.
Dyrbye, L., & Shanafelt, T. (2016). A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents. Medical education , 50 (1), 132-149.
Geiger, J. L., Steg, L., Van Der Werff, E., & Ünal, A. B. (2019). A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling. Journal of environmental psychology , 64 , 78-97.
Martin, F., Sun, T., & Westine, C. D. (2020). A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018. Computers & education , 159 , 104009.
Mavilidi, M. F., Ruiter, M., Schmidt, M., Okely, A. D., Loyens, S., Chandler, P., & Paas, F. (2018). A narrative review of school-based physical activity for enhancing cognition and learning: The importance of relevancy and integration. Frontiers in psychology , 2079.
Patterson, G. T., Chung, I. W., & Swan, P. W. (2014). Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits: A meta-analysis. Journal of experimental criminology , 10 , 487-513.
Reith, T. P. (2018). Burnout in United States healthcare professionals: a narrative review. Cureus , 10 (12).
Ritchie, S. J., & Tucker-Drob, E. M. (2018). How much does education improve intelligence? A meta-analysis. Psychological science , 29 (8), 1358-1369.
Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Wisniewski, B., Zierer, K., & Hattie, J. (2020). The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 , 3087.
Yli-Huumo, J., Ko, D., Choi, S., Park, S., & Smolander, K. (2016). Where is current research on blockchain technology?—a systematic review. PloS one , 11 (10), e0163477.
Zestcott, C. A., Blair, I. V., & Stone, J. (2016). Examining the presence, consequences, and reduction of implicit bias in health care: a narrative review. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations , 19 (4), 528-542

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2024 9:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS
- v.35(2); Jul-Dec 2014
Reviewing literature for research: Doing it the right way
Shital amin poojary.
Department of Dermatology, K J Somaiya Medical College, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
Jimish Deepak Bagadia
In an era of information overload, it is important to know how to obtain the required information and also to ensure that it is reliable information. Hence, it is essential to understand how to perform a systematic literature search. This article focuses on reliable literature sources and how to make optimum use of these in dermatology and venereology.
INTRODUCTION
A thorough review of literature is not only essential for selecting research topics, but also enables the right applicability of a research project. Most importantly, a good literature search is the cornerstone of practice of evidence based medicine. Today, everything is available at the click of a mouse or at the tip of the fingertips (or the stylus). Google is often the Go-To search website, the supposed answer to all questions in the universe. However, the deluge of information available comes with its own set of problems; how much of it is actually reliable information? How much are the search results that the search string threw up actually relevant? Did we actually find what we were looking for? Lack of a systematic approach can lead to a literature review ending up as a time-consuming and at times frustrating process. Hence, whether it is for research projects, theses/dissertations, case studies/reports or mere wish to obtain information; knowing where to look, and more importantly, how to look, is of prime importance today.
Literature search
Fink has defined research literature review as a “systematic, explicit and reproducible method for identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing the existing body of completed and recorded work produced by researchers, scholars and practitioners.”[ 1 ]
Review of research literature can be summarized into a seven step process: (i) Selecting research questions/purpose of the literature review (ii) Selecting your sources (iii) Choosing search terms (iv) Running your search (v) Applying practical screening criteria (vi) Applying methodological screening criteria/quality appraisal (vii) Synthesizing the results.[ 1 ]
This article will primarily concentrate on refining techniques of literature search.
Sources for literature search are enumerated in Table 1 .
Sources for literature search

PubMed is currently the most widely used among these as it contains over 23 million citations for biomedical literature and has been made available free by National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), U.S. National Library of Medicine. However, the availability of free full text articles depends on the sources. Use of options such as advanced search, medical subject headings (MeSH) terms, free full text, PubMed tutorials, and single citation matcher makes the database extremely user-friendly [ Figure 1 ]. It can also be accessed on the go through mobiles using “PubMed Mobile.” One can also create own account in NCBI to save searches and to use certain PubMed tools.

PubMed home page showing location of different tools which can be used for an efficient literature search
Tips for efficient use of PubMed search:[ 2 , 3 , 4 ]
Use of field and Boolean operators
When one searches using key words, all articles containing the words show up, many of which may not be related to the topic. Hence, the use of operators while searching makes the search more specific and less cumbersome. Operators are of two types: Field operators and Boolean operators, the latter enabling us to combine more than one concept, thereby making the search highly accurate. A few key operators that can be used in PubMed are shown in Tables Tables2 2 and and3 3 and illustrated in Figures Figures2 2 and and3 3 .
Field operators used in PubMed search

Boolean operators used in PubMed search

PubMed search results page showing articles on donovanosis using the field operator [TIAB]; it shows all articles which have the keyword “donovanosis” in either title or abstract of the article

PubMed search using Boolean operators ‘AND’, ‘NOT’; To search for articles on treatment of lepra reaction other than steroids, after clicking the option ‘Advanced search’ on the home page, one can build the search using ‘AND’ option for treatment and ‘NOT’ option for steroids to omit articles on steroid treatment in lepra reaction
Use of medical subject headings terms
These are very specific and standardized terms used by indexers to describe every article in PubMed and are added to the record of every article. A search using MeSH will show all articles about the topic (or keywords), but will not show articles only containing these keywords (these articles may be about an entirely different topic, but still may contain your keywords in another context in any part of the article). This will make your search more specific. Within the topic, specific subheadings can be added to the search builder to refine your search [ Figure 4 ]. For example, MeSH terms for treatment are therapy and therapeutics.

PubMed search using medical subject headings (MeSH) terms for management of gonorrhea. Click on MeSH database ( Figure 1 ) →In the MeSH search box type gonorrhea and click search. Under the MeSH term gonorrhea, there will be a list of subheadings; therapy, prevention and control, click the relevant check boxes and add to search builder →Click on search →All articles on therapy, prevention and control of gonorrhea will be displayed. Below the subheadings, there are two options: (1) Restrict to medical subject headings (MeSH) major topic and (2) do not include MeSH terms found below this term in the MeSH hierarchy. These can be used to further refine the search results so that only articles which are majorly about treatment of gonorrhea will be displayed
Two additional options can be used to further refine MeSH searches. These are located below the subheadings for a MeSH term: (1) Restrict to MeSH major topic; checking this box will retrieve articles which are majorly about the search term and are therefore, more focused and (2) Do not include MeSH terms found below this term in the MeSH hierarchy. This option will again give you more focused articles as it excludes the lower specific terms [ Figure 4 ].
Similar feature is available with Cochrane library (also called MeSH), EMBASE (known as EMTREE) and PsycINFO (Thesaurus of Psychological Index Terms).
Saving your searches
Any search that one has performed can be saved by using the ‘Send to’ option and can be saved as a simple word file [ Figure 5 ]. Alternatively, the ‘Save Search’ button (just below the search box) can be used. However, it is essential to set up an NCBI account and log in to NCBI for this. One can even choose to have E-mail updates of new articles in the topic of interest.

Saving PubMed searches. A simple option is to click on the dropdown box next to ‘Send to’ option and then choose among the options. It can be saved as a text or word file by choosing ‘File’ option. Another option is the “Save search” option below the search box but this will require logging into your National Center for Biotechnology Information account. This however allows you to set up alerts for E-mail updates for new articles
Single citation matcher
This is another important tool that helps to find the genuine original source of a particular research work (when few details are known about the title/author/publication date/place/journal) and cite the reference in the most correct manner [ Figure 6 ].

Single citation matcher: Click on “Single citation matcher” on PubMed Home page. Type available details of the required reference in the boxes to get the required citation
Full text articles
In any search clicking on the link “free full text” (if present) gives you free access to the article. In some instances, though the published article may not be available free, the author manuscript may be available free of charge. Furthermore, PubMed Central articles are available free of charge.
Managing filters
Filters can be used to refine a search according to type of article required or subjects of research. One can specify the type of article required such as clinical trial, reviews, free full text; these options are available on a typical search results page. Further specialized filters are available under “manage filters:” e.g., articles confined to certain age groups (properties option), “Links” to other databases, article specific to particular journals, etc. However, one needs to have an NCBI account and log in to access this option [ Figure 7 ].

Managing filters. Simple filters are available on the ‘search results’ page. One can choose type of article, e.g., clinical trial, reviews etc. Further options are available in the “Manage filters” option, but this requires logging into National Center for Biotechnology Information account
The Cochrane library
Although reviews are available in PubMed, for systematic reviews and meta-analysis, Cochrane library is a much better resource. The Cochrane library is a collection of full length systematic reviews, which can be accessed for free in India, thanks to Indian Council of Medical Research renewing the license up to 2016, benefitting users all over India. It is immensely helpful in finding detailed high quality research work done in a particular field/topic [ Figure 8 ].

Cochrane library is a useful resource for reliable, systematic reviews. One can choose the type of reviews required, including trials
An important tool that must be used while searching for research work is screening. Screening helps to improve the accuracy of search results. It is of two types: (1) Practical: To identify a broad range of potentially useful studies. Examples: Date of publication (last 5 years only; gives you most recent updates), participants or subjects (humans above 18 years), publication language (English only) (2) methodological: To identify best available studies (for example, excluding studies not involving control group or studies with only randomized control trials).
Selecting the right quality of literature is the key to successful research literature review. The quality can be estimated by what is known as “The Evidence Pyramid.” The level of evidence of references obtained from the aforementioned search tools are depicted in Figure 9 . Systematic reviews obtained from Cochrane library constitute level 1 evidence.

Evidence pyramid: Depicting the level of evidence of references obtained from the aforementioned search tools
Thus, a systematic literature review can help not only in setting up the basis of a good research with optimal use of available information, but also in practice of evidence-based medicine.
Source of Support: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Advertisement
Advancing the scientific study of prehospital mass casualty response through a Translational Science process: the T1 scoping literature review stage
- Review Article
- Open access
- Published: 15 April 2023
- Volume 49 , pages 1647–1660, ( 2023 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Eric S. Weinstein ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1147-5656 1 ,
- Joseph L. Cuthbertson 1 ,
- Teri Lynn Herbert 2 ,
- George T. Voicescu 1 ,
- Michelangelo Bortolin 1 ,
- Sabina Magalini 3 ,
- Daniele Gui 3 ,
- Mariana Helou 4 ,
- Kristina Lennquist Montan 5 ,
- Carl Montan 5 ,
- Chaim Rafalowsky 6 ,
- Giuseppe Ratto 7 ,
- Stefano Damele 7 ,
- Simone Bazurro 7 ,
- Itamar Laist 8 ,
- Federica Marzi 3 ,
- Alessandro Borrello 3 ,
- Pietro Fransvea 3 ,
- Andrea Fidanzio 3 ,
- Carlos Yanez Benitez 8 ,
- Roberto Faccincani 8 ,
- Luca Ragazzoni 1 , 9 &
- Marta Caviglia 1 , 10
2298 Accesses
5 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation funding program awarded the NIGHTINGALE grant to develop a toolkit to support first responders engaged in prehospital (PH) mass casualty incident (MCI) response. To reach the projects’ objectives, the NIGHTINGALE consortium used a Translational Science (TS) process. The present work is the first TS stage (T1) aimed to extract data relevant for the subsequent modified Delphi study (T2) statements.
The authors were divided into three work groups (WGs) MCI Triage, PH Life Support and Damage Control (PHLSDC), and PH Processes (PHP). Each WG conducted simultaneous literature searches following the PRISMA extension for scoping reviews. Relevant data were extracted from the included articles and indexed using pre-identified PH MCI response themes and subthemes.
The initial search yielded 925 total references to be considered for title and abstract review (MCI Triage 311, PHLSDC 329, PHP 285), then 483 articles for full reference review (MCI Triage 111, PHLSDC 216, PHP 156), and finally 152 articles for the database extraction process (MCI Triage 27, PHLSDC 37, PHP 88). Most frequent subthemes and novel concepts have been identified as a basis for the elaboration of draft statements for the T2 modified Delphi study.
The three simultaneous scoping reviews allowed the extraction of relevant PH MCI subthemes and novel concepts that will enable the NIGHTINGALE consortium to create scientifically anchored statements in the T2 modified Delphi study.
Similar content being viewed by others
A translational triage research development tool: standardizing prehospital triage decision-making systems in mass casualty incidents
Amir Khorram-Manesh, Johan Nordling, … Frederick M. Burkle

The updated national research agenda 2021–2026 for prehospital emergency medical services in the Netherlands: a Delphi study
Lilian C. M. Vloet, Gijs Hesselink, … Remco H. A. Ebben
Prehospital clinical practice guidelines for unintentional injuries: a scoping review and prioritisation process
Desmond Kuupiel, Nasreen S. Jessani, … Michael McCaul
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Sudden onset disasters (SODs) and mass casualty incidents (MCIs) from the past have made it evident that collaborative planning activities between public safety, public health, and clinical healthcare providers are essential for successful responses from the whole spectrum of prehospital (PH) response agencies, that must work together to forge and strengthen relationships to produce efficient and effective PH MCI responses [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. As SODs and MCIs continue to increase, there is a real need to develop PH systems that are truly interoperable and integrated. Already in 2007, in response to the need for stronger connections and information exchange between response agencies, the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) created the Terrorism Injuries: Information, Dissemination, and Exchange (TIIDE) program [ 4 , 5 ], ultimately aiming to decrease morbidity and mortality from MCIs, including those related to intentional acts of violence and terrorism. One of the projects awarded in the TIIDE was to work toward a national guideline for MCI response, gathering professionals that spanned over the continuum of care: emergency medical services, emergency medical specialists, and trauma surgeons. To achieve this objective, the TIIDE grant consortium partners used consensus methodology based on the best available science to propose the Sort, Assess, Life-Saving interventions, Treatment and/or Transport (SALT) national triage guideline[ 6 ] and a model uniform core criteria for mass casualty triage (MUCC) [ 7 ]. (Fig. 1 ).
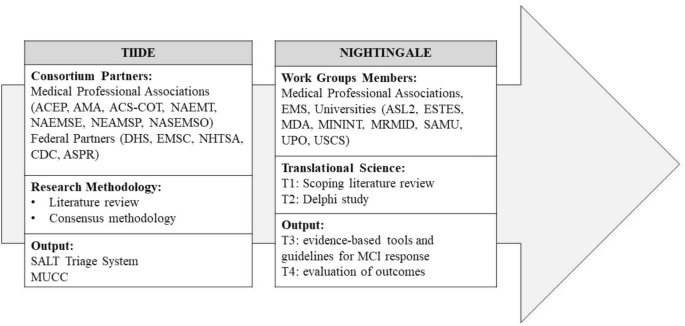
Evolution of the structure and methodology adopted between the TIIDE and NIGHTINGALE project. ACEP American College of Emergency Physicians, ACS-COT American College of Surgeons-Committee on Trauma, AMA American Medical Association, ASL2 Azienda Sociosanitaria Ligure 2 (Italy), EMS Emergency Medical Services, ESTES European Society for Trauma and Emergency Surgery, MCI Mass Casualty Incidents, MDA Magen David Adom—Israel National Emergency Pre-Hospital Medical and Blood Services, MININT Ministry of Interior Italy, MRMID Swedish International Association for Promotion of Education and Training in Major Incidents and Disasters, MUCC Model Uniform Core Criteria for Mass Casualty Triage, NAEMT National Association of Emergency Medical Technicians (US), NAEMSE National Association of Emergency Medical System Educators (US), NAEMSP National Association of Emergency Medical System Physicians (US), NASEMSO National Association of State Emergency Medical System Officials (US), SAMU Service d'Aide Médicale Urgente, Paris (France), SALT Sort, Assess, Life-Saving interventions, Treatment and/or Transport, UPO Università del Piemonte Orientale (Italy), USCS Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore (Italy)
Despite the literature emerging from the TIIDE project, that spurred further research, discussion, policy, and procedure, current emergency medical services and non-medical civil practitioners involved in PH MCI response often have to rely on complicated or even outdated procedures, multiple protocols or lack of homogeneity in response methods and guidelines, and technology of the past. [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ]
To this end, the Directorate-General for European Civil Protection and Humanitarian Aid Operations has been emphasizing the need to promote first responders’ preparedness through targeted actions that include the development and update of contingency plans, standard operating procedures, and multi-sector intervention, encouraging involvement of those affected by MCIs and disasters in the design and implementation of such preparedness actions. [ 12 ]
In 2020, the European Research Executive Agency (REA), in conjunction with the European Union (EU) Horizon 2020 research and innovation funding program, awarded the Novel InteGrated toolkit for enhanced pre-Hospital life support and Triage IN challenGing And Large Emergencies (NIGHTINGALE) grant to a consortium comprised of a similar wide distribution of PH MCI response agencies and research centers as TIIDE [ 13 ] (Fig. 1 .). The NIGHTINGALE project features 11 objectives ranging from developing and implementing advanced devices and artificial intelligence, incorporating bystanders into the PH MCI response and addressing ethical challenges, enhancing the collaborative approach across different agencies (Supplementary Table 1). Having acknowledged the evidence produced by the TIIDE project [ 14 ], the NIGHTINGALE project seeks to strengthen the existing research in the field of PH MCI and to advance the depth and breadth of PH MCI response guidelines, as advocated by the REA. Therefore, the focus is to upgrade the evaluation of the injured, optimizing life support and damage control procedures and allow a shared response across different MCI responding agencies, including emergency medical services, non-medical civil protection personnel, volunteers, and citizens. To guide the creation of such evidence-based guidelines, the NIGHTINGALE consortium adopted the Translational Science (TS) consensus process that features progressive stages aiming to translate research-informed data into new knowledge in the form of recommendations and guidelines [ 15 ] (Fig. 1 ). As described by Caviglia et al., [ 16 ] starting from the TS question (T0), “how to develop, integrate, test, deploy, demonstrate and validate a Novel Integrated Toolkit for Emergency Medical Response which ensures an upgrade to PH MCI response?”, the application of TS in the NIGHTINGALE project entails the identification of current approaches and published data (T1, scoping literature review stage), the use of a consensus methodology as a basis for the development of evidence-based tools and guidelines (T2, modified Delphi), the translation into practice (T3, development of tools and guidelines), and a final evaluation stage (T4, evaluation and outcome assessment) (Fig. 1 ). In the T1 stage, three simultaneous scoping literature reviews were designed to identify sources and references on MCI Triage, PH Life Support and Damage Control (PHLSDC) interventions, and PH processes (PHP) that could then be interrogated using a defined data extraction tool to determine concepts, theories, and knowledge gaps. [ 15 , 16 ] Hence, the aim of this work was to map, extract, and synthetize current evidence-based knowledge, gap, and challenges on MCI Triage, PHLSDC, and PHP through three different simultaneous scoping literature reviews, to inform the creation of an initial set of statements for the T2 modified Delphi study.
This study describes the structured T1 scoping literature reviews guided by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR) [ 17 , 18 ]. To specifically address each component of the PH MCI response, the authors were divided into the three work groups (WGs) of MCI Triage, PHLSDC, and PHP. Each WG included health professionals and researchers with specific expertise in MCI response and patient management. Under the direction of a medical informaticist, the search strategy included only terms relating to or describing sudden onset disaster PH MCI response. The WGs conducted simultaneous searches from November 2021 to January 2022 following the same search term methodology until the search became more specific relating to each WG (MCI Triage, PHLSDC, and PHP), as shown in Table 1 .
Eligibility criteria
The search included English-language papers published from January 1983 to October 2021 on PubMed, SCOPUS, CINAHL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, EBSCO, Elton B. Stephens Company, Ipswich, Massachusetts USA), DTIC (Defense Technical Information Center, U.S. Department of Defense), CRI (Emergency Care Research Institute, Plymouth Meeting, Pennsylvania, USA), and PsycInfo (American Psychological Association, Washington D.C., USA). The search terms were adapted for use with other bibliographic databases in combination with database-specific filters for controlled trials, where these were available. An ancestry search was also performed to identify additional references from the bibliography of references retrieved in the searches. The reference manager was EndNote™ X9 and 20 (Clarivate; Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA). References that did not meet the inclusion criteria, specifically did not study or report an MCI or MCI exercise, were excluded.
Search strategy
After each WG conducted its initial search, duplicates were removed. Reviewers in each WG independently screened reference titles and abstracts to determine if inclusion criteria were met. Any disagreement was resolved by discussion within the WG. Each WG removed any reference that did not meet inclusion criteria from further consideration. Subsequently, full texts of included articles were screened, disagreement was resolved by discussion, and references that did not meet inclusion criteria were removed. The remaining included articles for each WG underwent data extraction into an Excel database (Microsoft Corp.; Redmond, Washington, USA) that was developed using themes and subthemes from PH MCI response literature and in compliance with the NIGHTINGALE objectives. This raw data, together with other information gleaned from the full reference review process (such as relevant tables, figures, or writings) constituted the base for the development of the initial set of statements in the T2 modified Delphi stage. Specifically, the data extraction process focused on extracting data that could lead to the creation of relevant statements for the T2 stage by identifying recurrent subjects and innovative concepts that have the potential to improve current practices in PH MCI management but for which validation in clinical settings is still underway.
The initial search for all 3 WGs yielded 925 references. Following title and abstract review, 483 articles were considered for full text review. Finally, 152 articles were included in the database extraction process: MCI Triage [ 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 ], PHLSDC [ 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 , 68 , 69 , 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 , 75 , 76 , 77 , 78 , 79 , 80 , 81 ], PHP [ 30 , 43 , 82 , 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 87 , 88 , 89 , 90 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 94 , 95 , 96 , 97 , 98 , 99 , 100 , 101 , 102 , 103 , 104 , 105 , 106 , 107 , 108 , 109 , 110 , 111 , 112 , 113 , 114 , 115 , 116 , 117 , 118 , 119 , 120 , 121 , 122 , 123 , 124 , 125 , 126 , 127 , 128 , 129 , 130 , 131 , 132 , 133 , 134 , 135 , 136 , 137 , 138 , 139 , 140 , 141 , 142 , 143 , 144 , 145 , 146 , 147 , 148 , 149 , 150 , 151 , 152 , 153 , 154 , 155 , 156 , 157 , 158 , 159 , 160 , 161 , 162 , 163 , 164 , 165 , 166 , 167 ]. (Table 2 ).
Different thematic categories and related subthemes were created by each WG (Table 3 ). The data extraction process drew attention to subthemes frequently mentioned in the included references. Specifically, recurrent subthemes in the MCI Triage WG were the recording of mechanism of injury ( n = 21), the involvement of bystanders ( n = 8), the use of basic monitoring in support of PH triage procedures (including cardiac monitoring and pulse oximetry, respectively, mentioned n = 12 and n = 10 times), re-assessment of MCI casualties though continuous vital signs monitoring ( n = 14), treatment prioritization ( n = 15), and evacuation prioritization ( n = 19) as the main outcomes of the MCI Triage process. Additionally, references included in the MCI Triage data extraction drew attention to the concepts of shock index, pulse pressure, and heart rate variability to be used in the PH assessment of casualties [ 23 , 35 ].
Among the 37 references included in the PHLSDC data extraction, the subthemes more frequently identified were the collection of the mechanism of injury ( n = 13) and exposure to environment time ( n = 12), the importance of stopping the bleeding maneuvers ( n = 11) and PH fluid resuscitation ( n = 14), basic and advanced monitoring to guide PHLSDC interventions, including cardiac monitoring ( n = 9), pulse oximetry ( n = 6), and physiological monitoring ( n = 7), re-assessment of MCI casualties through continuous vital signs monitoring ( n = 8) and treatment of casualties according to triage prioritization ( n = 13). Furthermore, the authors identified the following “hot” issues worthy of further attention: PH management of crush syndrome [ 75 ], resuscitation of avalanche victims [ 53 , 54 ], and shared CBRNE treatment protocols [ 60 , 81 ].
Lastly, the subthemes commonly identified in the PHP data extraction included aspects pertaining to MCI PHP terminology, policy and planning framework, and incident activation/notification. Aspects related to decontamination ( n = 10) and hazard assessment ( n = 15) were also frequently mentioned. Furthermore, subthemes related to casualty distribution (either through coordinated/planned methodologies n = 19 or an ad hoc distribution model n = 19), communication and situational awareness (including the use of social media, radio communication and drones), resource allocation and the integration of technology to support PHP were identified.
The three simultaneous PRISMA scoping reviews were performed in the T1 stage of a TS process, ultimately seeking to advance MCI PH response guidelines in the framework of the EU-funded NIGHTINGALE project. This initial step of mapping current available evidence through the analysis of recurrent subthemes, common practices, and new concepts identified in MCI Triage, PHLSDC, and PHP literature will serve as the basis for the development of three initial sets of statements during the T2 modified Delphi stage. Indeed, results of the three scoping reviews emphasized several aspects that have been recurrently investigated in the MCI literature and for which expert consensus was deemed as needed by the authors.
Despite MCI Triage being the mainstay of initial casualty management, no global consensus or gold standard definition exists across different countries, and most PH practitioners have received training in the initial MCI Triage system favored by their specific agency and jurisdiction [ 6 ]. Since numerous attempts have been made toward developing shared guidelines for MCI Triage [ 5 ] or in the attempt to create a universal triage tool [ 168 ], the NIGHTINGALE project recognizes the necessity to study these efforts as a progression of the previous above mentioned projects. Results of the MCI Triage scoping review determined that recording the mechanism of injury from the initial assessment and as more details emerge over the continuum of care is important for the definitive treatment team [ 19 , 21 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 39 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 ]. This includes obtaining information not only from EMS staff but also non-medical bystanders who rendered first aid or assisted EMS [ 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 ], reinforcing the concept that gathering relevant observations from bystanders could support the MCI response efforts, in compliance with the NIGHTINGALE objectives. Information supporting the continuum of care involving the initial and subsequent assessments of vital signs should determine treatment and evacuation prioritization, considering the use of cardiac monitors and pulse oximetry when available. While literature suggests the use of advanced physiologic monitoring and the incorporation of point-of-care ultrasound in the continuum of care [ 21 , 31 ], it is also evident that initial assessment of MCI casualties should remain quick, practical, easy to remember by all first responders and applicable across different environments including austere settings, thus, to be performed without diagnostic equipment. Appropriate tagging and tracing of MCI casualties remains a pillar of any MCI Triage system adopted, opening the door for innovative solutions and tools possibly fulfilling the triple function of tagging, tracing, and continuous monitoring [ 27 , 42 , 44 ].
References from the PHLSDC scoping review highlighted the need to focus on assessment and treatment guidelines for crush injuries during MCIs [ 46 , 63 , 75 ], as well as for the development of awareness on chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, and explosive (CRBNE) events, advocating for education, training, and competencies to be developed across all agencies [ 48 , 57 , 71 , 76 , 79 , 81 ]. Similarly, control of major hemorrhages as an integral part of the triage process emerged as a recurrent topic in the included PHLSDC references, with a special emphasis on the role of non-medical bystanders, as specifically stressed by the Hartford Consensus after the Sandy Hook Elementary School mass shooting and by Lesaffre and colleagues after the 2015 Paris attacks [ 46 , 47 , 48 , 50 , 51 , 61 , 62 , 63 , 73 , 77 , 80 , 169 ]. Overall, attention was given to the importance of continuous real-time monitoring and re-assessment of casualties to guide prioritization of life-saving interventions and transportation, suggesting the possibility to introduce deployable technology, provided it to be quick, reliable, and easy to use [ 48 , 50 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 63 , 69 , 75 , 76 ].
Results of the PHP scoping review stressed the importance of a common terminology to be adopted across all agencies working in the same jurisdiction, along with the urgent need to include practices that support gender diversity and are contextual to vulnerable groups and special needs populations [ 30 , 111 , 140 , 147 , 159 , 160 ]. Included references addressed the role of technology in supporting the different PH MCI processes, from inter-agencies communication systems, to telemedicine and information management systems to coordinate the different resources deployed (including human resources, equipment, and vehicles) and to distribute MCI casualties in different health facilities [ 90 , 92 , 99 , 146 , 160 ]. Data supported that standard trauma transportation decisions and overall MCI coordination may have to be adapted in context to the hazard impact and health system capacity, taking into account the possibility of CBRNE threats demanding from patient decontamination and personnel self-care [ 86 , 88 , 89 , 100 , 102 , 103 , 108 , 136 ]. Additionally, from the results emerged that frequently definitive care may require alternative care sites to include field hospitals, adapted structures such as conventions centers, schools, or religious buildings like churches and mosques that have the capacity and capability to attend the injured [ 105 , 131 , 151 ]. The concept of enhancing situational awareness through available technology (such as drones) to better guide critical decision-making during MCIs emerged in some of the included references, especially in remote areas with access constraints [ 90 , 92 , 99 , 109 , 117 , 129 , 133 , 139 , 146 , 160 ]. Moreover, the role of spontaneous volunteers and bystanders both in assisting relief efforts [ 88 , 107 , 133 , 134 , 141 , 144 , 166 ] and in providing information through social media that could be used for rapid situation assessment [ 129 ] consistently emerges in the included references. Lastly, a recurrent notion highlighted in the included references was the need for a structured MCI plan able to regulate the use of technical advances, to foster education and training competences across different agencies, to allow for structured debriefing in a collaborative manner, and to promote the use of key performance indicators to evaluate and improve the response [ 83 , 84 , 85 , 86 , 91 , 98 , 100 , 101 , 102 , 103 , 104 , 107 , 109 , 110 , 111 , 112 , 116 , 119 , 120 , 122 , 124 , 131 , 135 , 137 , 142 , 145 , 148 , 153 , 158 , 160 , 164 , 166 ].
Limitations
A scoping review intends to capture all included peer-reviewed publications as well as the ancestry publications that were cited in these publications. The Grey literature presents challenges to obtain relevant references and all attempts were made to include these references, but some may not have been obtained. There is no way to know if these potential missing references would have made a difference in the available information to extract data. The raw data extracted by WG members and the work group lead are intended to undergo further analysis within each work group to create the initial T2 modified Delphi statements. This data extraction process, though intended to be encompassing and comprehensive, may not have captured relevant data due to the thematic approach of the database. There is no way to know if relevant data were not extracted but the secondary data retained by each work group member as they read each full reference article provide additional information for the statement creation process.
The progression of the science to critically examine the PH MCI response peer-reviewed medical literature and other sources has enabled the NIGHTINGALE partners to methodically obtain raw data and secure relevant tables, figures, or writings that will contribute to each WG’s creation of the initial T2 modified Delphi study statements. Once submitted to experts, statements that achieve consensus will be used to define guidelines and recommendation, in compliance with the objectives of the NIGHTINGALE project.
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
Heide E. Disaster response: principles of preparation & coordination. Publ Prod Manag Rev. 1989;1:15. https://doi.org/10.2307/3380618 .
Article Google Scholar
Kapucu N. Interorganizational coordination in complex environments of disasters: the evolution of intergovernmental disaster response systems. J Homeland Secur Emergency Manag [Internet]. 2009 Jul 10 [cited 2022 Nov 16];6(1). https://doi.org/10.2202/1547-7355.1498
Mills AF, Helm JE, Jola-Sanchez AF, Tatikonda MV, Courtney BA. Coordination of autonomous healthcare entities: emergency response to multiple casualty incidents. Prod Oper Manag. 2018;27(1):184–205. https://doi.org/10.1111/poms.12790 .
Injury Center Funding Opportunity Announcements (FOAs). United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Division of Injury Response, created the Terrorism Injuries: Information, Dissemination and Exchange (TIIDE) project. [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2022 Nov 11].
Hunt R. TIIDE Project 2009 Annual Report Terrorism Injuries: Information, Dissemination and Exchange. Supplemental Material.
Lerner EB, Schwartz RB, Coule PL, Weinstein ES, Cone DC, Hunt RC, et al. Mass casualty triage: an evaluation of the data and development of a proposed national guideline. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2008;2(Suppl 1):S25-34. https://doi.org/10.1097/DMP.0b013e318182194e .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lerner EB, Cone DC, Weinstein ES, Schwartz RB, Coule PL, Cronin M, et al. Mass casualty triage: an evaluation of the science and refinement of a national guideline. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2011;5(2):129–37. https://doi.org/10.1001/dmp.2011.39 .
Federal Interagency Committee on EMS. National Implementation of the Model Uniform Core Criteria for Mass Casualty Incident Triage [Internet]. 2014 Mar [cited 2022 Nov 15].
American Academy of Pediatrics, American College of Emergency Physicians, American College of Surgeons—Committee on Trauma, American Trauma Society, Children’s National Medical Center, Child Health Advocacy Institute, Emergency Medical Services for Children National Resource Center, International Association of Emergency Medical Services Chiefs, et al. Model uniform core criteria for mass casualty triage. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2011 Jun;5(2):125–8. https://doi.org/10.1001/dmp.2011.41
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. Model Uniform Core Criteria for Mass Casualty Incident Triage: Addendum to the Paramedic Instructional Guidelines [Internet]. 2017 Dec [cited 2022 Nov 5].
Holgersson A. Review of On-Scene Management of Mass-Casualty Attacks. Journal of Human Security. 2016 Aug 29;12. https://doi.org/10.12924/johs2016.12010091
European Commission. DG ECHO Guidance Note - Disaster Preparedness. 01012021. :84.
Novel InteGrated toolkit for enhanced pre-Hospital life support and Triage IN challenGing And Large Emergencies [Internet]. [cited 2022 Nov 14].
EMSFocus. Teaching Mass Casualty Triage: Implementing the New MUCC Instructional Guidelines. [Internet]. [cited 2022 Sep 24].
Weinstein ES, Cuthbertson JL, Ragazzoni L, Verde M. A T2 translational science modified delphi study: spinal motion restriction in a resource-scarce environment. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2020;35(5):538–45. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X20000862 .
Caviglia M, Cuthbertson J, Sdongos E, Faccincani R, Ragazzoni L, Weinstein ES. Translational Science in Disaster Medicine: from grant to deliverables. Int J Disaster Risk Reduction. 2022 Jul 1;
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA Extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73. https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850 .
Munn Z, Peters MDJ, Stern C, Tufanaru C, McArthur A, Aromataris E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18(1):143. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-018-0611-x .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cancio LC, Wade CE, West SA, Holcomb JB. Prediction of mortality and of the need for massive transfusion in casualties arriving at combat support hospitals in Iraq. J Trauma. 2008 Feb;64(2 Suppl):S51–55; discussion S55–56. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3181608c21
Coimbra R, Lee J, Bansal V, Hollingsworth-Fridlund P. Recognizing/accepting futility: prehospital, emergency center, operating room, and intensive care unit. J Trauma Nurs. 2007 Jun;14(2):73–6; quiz 77–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.JTN.0000278791.43783.df
Convertino VA, Cooke WH, Salinas J, Holcomb JB. Advanced Capabilities for Combat Medics. [cited 2022 Nov 14];
Arcos González P, Castro Delgado R, Cuartas Alvarez T, Garijo Gonzalo G, Martinez Monzon C, Pelaez Corres N, et al. The development and features of the Spanish prehospital advanced triage method (META) for mass casualty incidents. Scandinavian J Trauma Resuscitation Emergency Med. 2016;24(1):63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13049-016-0255-y .
Cooke WH, Salinas J, Convertino VA, Ludwig DA, Hinds D, Duke JH, et al. Heart rate variability and its association with mortality in prehospital trauma patients. J Trauma. 2006 Feb;60(2):363–70; discussion 370. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ta.0000196623.48952.0e
Di Carlo S, Cavallaro G, Palomeque K, Cardi M, Sica G, Rossi P, et al. Prehospital hemorrhage assessment criteria: a concise review. J Trauma Nurs. 2021;28(5):332–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTN.0000000000000608 .
Duke JH, Holcomb JB. Noninvasive Continuous Physiologic Data Acquisition and Analysis as a Predictor of Outcome Following Major Trauma: A Pilot Study [Internet]. [cited 2022 Nov 14].
Eastridge BJ, Butler F, Wade CE, Holcomb JB, Salinas J, Champion HR, et al. Field triage score (FTS) in battlefield casualties: validation of a novel triage technique in a combat environment. Am J Surg. 2010;200(6):724–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2010.08.006 .
Elmasllari E, Reiners R. Learning From Non-Acceptance: Design Dimensions for User Acceptance of E-Triage Systems. In: 14th Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Systems for Crisis Response and Management, Albi, France, May 21–24, 2017 [Internet]. ISCRAM Association; 2017 [cited 2022 Nov 14].
Jetten WD, Seesink J, Klimek M. Prehospital triage by lay person first responders: a scoping review and proposal for a new prehospital triage tool. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2021;8:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1017/dmp.2021.19 .
Lockey DJ, Mackenzie R, Redhead J, Wise D, Harris T, Weaver A, et al. London bombings July 2005: the immediate pre-hospital medical response. Resuscitation. 2005;66(2):ix–xii. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2005.07.005 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Lyle K, Thompson T, Graham J. Pediatric mass casualty: triage and planning for the prehospital provider. Clin Pediatric Emergency Med. 2009;10(3):173–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpem.2009.06.004 .
Maddry J, Savell S, Baldwin DS. Austere, Pre-Transport, Qualitative Clinical Testing. [cited 2022 Nov 14];
Martín-Rodríguez F, López-Izquierdo R, Del Pozo VC, Delgado Benito JF, Carbajosa Rodríguez V, Diego Rasilla MN, et al. Accuracy of national early warning score 2 (NEWS2) in prehospital triage on in-hospital early mortality: a multi-center observational prospective cohort study. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2019;34(6):610–8. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X19005041 .
Newgard CD, Richardson D, Holmes JF, Rea TD, Hsia RY, Mann NC, et al. Physiologic field triage criteria for identifying seriously injured older adults. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2014;18(4):461–70. https://doi.org/10.3109/10903127.2014.912707 .
Newgard CD, Rudser K, Hedges JR, Kerby JD, Stiell IG, Davis DP, et al. A critical assessment of the out-of-hospital trauma triage guidelines for physiologic abnormality. J Trauma. 2010;68(2):452–62. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3181ae20c9 .
Newgard CD, Cheney TP, Chou R, Fu R, Daya MR, O’Neil ME, et al. Out-of-hospital circulatory measures to identify patients with serious injury: a systematic review. Acad Emerg Med. 2020;27(12):1323–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/acem.14056 .
Parker B. Neural network medical decision algorithms for pre-hospital trauma care [Internet]. [cited 2022 Sep 29].
Reifman J, Chen L, Khitrov MY, Reisner AT. Automated Decision-Support Technologies for Prehospital Care of Trauma Casualties [Internet]. [cited 2022 Nov 14].
Reisner A, Chen X, Kumar K, Reifman J. Prehospital heart rate and blood pressure increase the positive predictive value of the glasgow coma scale for high-mortality traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2014;31(10):906–13. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2013.3128 .
Rickards CA, Ryan KL, Cooke WH, Romero SA, Convertino VA. Combat stress or hemorrhage? Evidence for a decision-assist algorithm for remote triage. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2008;79(7):670–6. https://doi.org/10.3357/asem.2223.2008 .
Rodriguez D, Heuer S, Guerra A, Stork W, Weber B, Eichler M. Towards automatic sensor-based triage for individual remote monitoring during mass casualty incidents. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). 2014. p. 544–51. https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBM.2014.6999217
Romero Pareja R, Castro Delgado R, Turégano Fuentes F, Jhon Thissard-Vasallo I, Sanz Rosa D, Arcos GP. Prehospital triage for mass casualty incidents using the META method for early surgical assessment: retrospective validation of a hospital trauma registry. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020;46(2):425–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-018-1040-6 .
Ryan K, George D, Liu J, Mitchell P, Nelson K, Kue R. The use of field triage in disaster and mass casualty incidents: a survey of current practices by EMS personnel. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2018;22(4):520–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/10903127.2017.1419323 .
Turner CDA, Lockey DJ, Rehn M. Pre-hospital management of mass casualty civilian shootings: a systematic literature review. Crit Care. 2016;20(1):362. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-016-1543-7 .
Zhao X, Rafiq A, Hummel R, Fei D-Y, Merrell RC. Integration of information technology, wireless networks, and personal digital assistants for triage and casualty. Telemed J E Health. 2006;12(4):466–74. https://doi.org/10.1089/tmj.2006.12.466 .
Lin C-H, Lin C-H, Tai C-Y, Lin Y-Y, Shih FF-Y. Challenges of burn mass casualty incidents in the prehospital setting: lessons from the formosa fun coast park color party. Prehospital Emergency Care. 2019 Jan 2;23(1):44–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/10903127.2018.1479473
Ashkenazi I, Isakovich B, Kluger Y, Alfici R, Kessel B, Better OS. Prehospital management of earthquake casualties buried under rubble. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2005;20(2):122–33. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049023x00002302 .
Bachman MW, Anzalone BC, Williams JG, DeLuca MB, Garner DG, Preddy JE, et al. Evaluation of an integrated rescue task force model for active threat response. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2019;23(3):309–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/10903127.2018.1521487 .
Baker DJ. Management of respiratory failure in toxic disasters. Resuscitation. 1999;42(2):125–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0300-9572(99)00098-2 .
Bartkus EA, Daya M, Hedges JR, Jui J. ExacTech blood glucose meter clinical trial. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1993;8(3):217–27. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049023x00040395 .
Blackbourne LH, Baer DG, Eastridge BJ, Kheirabadi B, Bagley S, Kragh JF, et al. Military medical revolution: prehospital combat casualty care. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;73(6 Suppl 5):S372-377. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3182755662 .
Bobko JP, Lai TT, Smith R, Shapiro G, Baldridge T, Callaway DW. Tactical emergency casualty care?pediatric appendix: novel guidelines for the care of the pediatric casualty in the high-threat, prehospital environment. J Spec Oper Med. 2013;13(4):94–107. https://doi.org/10.55460/EF77-LDYW
Ct B, Wg D. Organizing the orthopaedic trauma association mass casualty response team. Clinical orthopaedics and related research [Internet]. 2004 May [cited 2022 Nov 14];(422). https://doi.org/10.1097/01.blo.0000131200.12795.2b
Boué Y, Payen J-F, Brun J, Thomas S, Levrat A, Blancher M, et al. Survival after avalanche-induced cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2014;85(9):1192–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2014.06.015 .
Brugger H, Paal P, Boyd J. Prehospital resuscitation of the buried avalanche victim. High Alt Med Biol. 2011;12(3):199–205. https://doi.org/10.1089/ham.2011.1025 .
Cardoso MM, Banner MJ, Melker RJ, Bjoraker DG. Portable devices used to detect endotracheal intubation during emergency situations: a review. Crit Care Med. 1998;26(5):957–64. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-199805000-00036 .
Carley S, Mackway-Jones K, Randic L, Dunn K. Planning for major burns incidents by implementing an accelerated Delphi technique. Burns. 2002;28(5):413–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0305-4179(02)00107-9 .
Carli P, Telion C, Baker D. Terrorism in France. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2003;18(2):92–9. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049023x00000820 .
Corcoran F, Bystrzycki A, Masud S, Mazur SM, Wise D, Harris T. Ultrasound in pre-hospital trauma care. Trauma. 2016;18(2):101–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/1460408615606753 .
Davis BL, Martin MJ, Schreiber M. Military resuscitation: lessons from recent battlefield experience. Curr Trauma Rep. 2017;3(2):156–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40719-017-0088-9 .
de Schoutheete J-C, Hachimi Idrissi S, Watelet J-B. Pre-hospital interventions: introduction to life support systems. B-ENT. 2016;Suppl 26(1):41–54. PMID:29461733
Dudaryk R, Pretto EA. Resuscitation in a multiple casualty event. Anesthesiol Clin. 2013;31(1):85–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anclin.2012.11.002 .
Eastridge BJ, Mabry RL, Seguin P, Cantrell J, Tops T, Uribe P, et al. Death on the battlefield (2001–2011): implications for the future of combat casualty care. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;73(6 Suppl 5):S431-437. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3182755dcc .
Eilertsen KA, Winberg M, Jeppesen E, Hval G, Wisborg T. Prehospital tourniquets in civilians: a systematic review. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2021;36(1):86–94. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X20001284 .
Fattah S, Rehn M, Reierth E, Wisborg T. Systematic literature review of templates for reporting prehospital major incident medical management. BMJ Open. 2013 Aug 1;3(8):e002658. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2013-002658
Fuse A, Okumura T, Tokuno S, Saitoh D, Yokota H. Current Status of Preparedness for Blast Injuries in Japan. 2011;54(5):8
Hardwick JM, Murnan SD, Morrison-Ponce DP, Devlin JJ. Field expedient vasopressors during aeromedical evacuation: a case series from the puerto rico disaster response. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2018;33(6):668–72. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X18000973 .
Horrocks P, Hobbs L, Tippett V, Aitken P. Paramedic disaster health management competencies: a scoping review. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2019;34(3):322–9. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X19004357 .
Jacobs LM, Wade DS, McSwain NE, Butler FK, Fabbri WP, Eastman AL, et al. The hartford consensus: THREAT, a medical disaster preparedness concept. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217(5):947–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.07.002 .
Kornhall DK, Martens-Nielsen J. The prehospital management of avalanche victims. J R Army Med Corps. 2016;162(6):406–12. https://doi.org/10.1136/jramc-2015-000441 .
Lal D, Weiland S, Newton M, Flaten A, Schurr M. Prehospital hyperventilation after brain injury: a prospective analysis of prehospital and early hospital hyperventilation of the brain-injured patient. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2003;18(1):20–3. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049023x00000637 .
Laurent JF, Richter F, Michel A. Management of victims of urban chemical attack: the French approach. Resuscitation. 1999;42(2):141–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0300-9572(99)00099-4 .
Leclerc T, Potokar T, Hughes A, Norton I, Alexandru C, Haik J, et al. A simplified fluid resuscitation formula for burns in mass casualty scenarios: analysis of the consensus recommendation from the WHO emergency medical teams technical working group on burns. Burns. 2021;47(8):1730–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2021.02.022 .
Loftus A, Pynn H, Parker P. Improvised first aid techniques for terrorist attacks. Emerg Med J. 2018;35(8):516–21. https://doi.org/10.1136/emermed-2018-207480 .
Mansky R, Scher C. Thoracic trauma in military settings: a review of current practices and recommendations. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2019;32(2):227–33. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0000000000000694 .
Mardones A, Arellano P, Rojas C, Gutierrez R, Oliver N, Borgna V. Prevention of crush syndrome through aggressive early resuscitation: clinical case in a buried Worker. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2016;31(3):340–2. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X16000327 .
O’Brien DJ, Walsh DW, Terriff CM, Hall AH. Empiric management of cyanide toxicity associated with smoke inhalation. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2011;26(5):374–82. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X11006625 .
Pons PT, Jerome J, McMullen J, Manson J, Robinson J, Chapleau W. The hartford consensus on active shooters: implementing the continuum of prehospital trauma response. J Emerg Med. 2015;49(6):878–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2015.09.013 .
Randic L, Carley S, Mackway-Jones K, Dunn K. Planning for major burns incidents in the UK using an accelerated Delphi technique. Burns. 2002;28(5):405–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0305-4179(02)00108-0 .
Riccobono D, Valente M, Drouet M, Calamai F, Abriat A. French policies for victim management during mass radiological accidents/attacks. Health Phys. 2018;115(1):179–84. https://doi.org/10.1097/HP.0000000000000839 .
Soffer D, Klausner JM. Trauma system configurations in other countries: the Israeli model. Surg Clin North Am. 2012 Aug;92(4):1025–40, x. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2012.04.007
Tokuda Y, Kikuchi M, Takahashi O, Stein GH. Prehospital management of sarin nerve gas terrorism in urban settings: 10 years of progress after the Tokyo subway sarin attack. Resuscitation. 2006;68(2):193–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2005.05.023 .
CDC 2017 Hurricane Incident Management System Team. Hurricane Season Public Health Preparedness, Response, and Recovery Guidance for Health Care Providers, Response and Recovery Workers, and Affected Communities - CDC, 2017. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017 Sep 22;66(37):995–8. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6637e1
Adini B, Bodas M, Nilsson H, Peleg K. Policies for managing emergency medical services in mass casualty incidents. Injury. 2017;48(9):1878–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2017.05.034 .
Adini B, Cohen R, Glassberg E, Azaria B, Simon D, Stein M, et al. Reconsidering policy of casualty evacuation in a remote mass-casualty incident. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2014;29(1):91–5. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X13008935 .
Adini B, Peleg K. On constant alert: lessons to be learned from Israel’s emergency response to mass-casualty terrorism incidents. Health Aff (Millwood). 2013;32(12):2179–85. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2013.0956 .
Agiv-Berland A, Ashkenazi I, Aharonson-Daniel L. The Cross-National Adaptability of EMS Protocols for Mass Casualty Incidents. Journal of Homeland Security and Emergency Management [Internet]. 2012 Oct 31 [cited 2022 Nov 14];9(2). https://doi.org/10.1515/1547-7355.2036
Al Thobaity A, Plummer V, Williams B. What are the most common domains of the core competencies of disaster nursing? A scoping review Int Emerg Nurs. 2017;31:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ienj.2016.10.003 .
Amat Camacho N, Karki K, Subedi S, von Schreeb J. International Emergency Medical Teams in the Aftermath of the 2015 Nepal Earthquake. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2019;34(3):260–4. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X19004291 .
Amlôt R, Carter H, Riddle L, Larner J, Chilcott RP. Volunteer trials of a novel improvised dry decontamination protocol for use during mass casualty incidents as part of the UK’S Initial Operational Response (IOR). PLOS ONE. 2017 Jun 16;12(6):e0179309. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179309
Amlot R, Larner J, Matar H, Jones DR, Carter H, Turner EA, et al. Comparative analysis of showering protocols for mass-casualty decontamination. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2010;25(5):435–9. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049023x00008529 .
Amram O, Schuurman N, Hedley N, Hameed SM. A web-based model to support patient-to-hospital allocation in mass casualty incidents. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72(5):1323–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e318246e879 .
Anan H, Otomo Y, Homma M, Oshiro K, Kondo H, Shimamura F, et al. Proposal for reforming prehospital response to chemical terrorism disasters in Japan: going back to the basics of saving the lives of the injured by securing the safety of the rescue team. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2020;35(1):88–91. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X19005119 .
Arnold JL, Levine BN, Manmatha R, Lee F, Shenoy P, Tsai M-C, et al. Information-sharing in out-of-hospital disaster response: the future role of information technology. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2004;19(3):201–7. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049023x00001783 .
Assa A, Landau D-A, Barenboim E, Goldstein L. Role of air-medical evacuation in mass-casualty incidents–a train collision experience. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2009;24(3):271–6. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049023x00006920 .
Aylwin CJ, König TC, Brennan NW, Shirley PJ, Davies G, Walsh MS, et al. Reduction in critical mortality in urban mass casualty incidents: analysis of triage, surge, and resource use after the London bombings on July 7, 2005. Lancet. 2006;368(9554):2219–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69896-6 .
Bloch YH, Schwartz D, Pinkert M, Blumenfeld A, Avinoam S, Hevion G, et al. Distribution of casualties in a mass-casualty incident with three local hospitals in the periphery of a densely populated area: lessons learned from the medical management of a terrorist attack. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2007;22(3):186–92. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049023x00004635 .
Campion EM, Juillard C, Knudson MM, Dicker R, Cohen MJ, Mackersie R, et al. Reconsidering the resources needed for multiple casualty events: lessons learned from the crash of asiana airlines flight 214. JAMA Surg. 2016;151(6):512–7. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2015.5107 .
Carter H, Drury J, Rubin GJ, Williams R, Amlôt R. Public experiences of mass casualty decontamination. Biosecur Bioterror. 2012;10(3):280–9. https://doi.org/10.1089/bsp.2012.0013 .
Castro Delgado R, Naves Gómez C, Cuartas Álvarez T, Arcos GP. An epidemiological approach to mass casualty incidents in the Principality of Asturias (Spain). Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2016;24(24):18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13049-016-0211-x .
Chan TC, Griswold WG, Buono C, Kirsh D, Lyon J, Killeen JP, et al. Impact of wireless electronic medical record system on the quality of patient documentation by emergency field responders during a disaster mass-casualty exercise. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2011;26(4):268–75. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X11006480 .
Chilcott RP, Mitchell H, Matar H. Optimization of nonambulant mass casualty decontamination protocols as part of an initial or specialist operational response to chemical incidents. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2019;23(1):32–43. https://doi.org/10.1080/10903127.2018.1469705 .
Chokshi NK, Behar S, Nager AL, Dorey F, Upperman JS. Disaster management among pediatric surgeons: preparedness, training and involvement. Am J Disaster Med. 2008;3(1):5–14 ( PMID:18450274 ).
Collins S, James T, Carter H, Symons C, Southworth F, Foxall K, et al. Mass casualty decontamination for chemical incidents: research outcomes and future priorities. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(6):3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063079 .
Cordner S, Ellingham STD. Two halves make a whole: Both first responders and experts are needed for the management and identification of the dead in large disasters. Forensic Sci Int. 2017;279:60–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2017.07.020 .
Cotter S. Treatment area considerations for mass casualty incidents. Emerg Med Serv. 2006;35(2):48–51 ( PMID:16541952 ).
PubMed Google Scholar
Cowley RA, Gretes AJ. EMS Response to Mass Casualties. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 1984;2(3):687–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0733-8627(20)30882-8 .
Curnin S. Large civilian air medical jets: implications for Australian disaster health. Air Med J. 2012;31(6):284–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amj.2012.04.001 .
Daddoust L, Asgary A, McBey KJ, Elliott S, Normand A. Spontaneous volunteer coordination during disasters and emergencies: Opportunities, challenges, and risks. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction. 2021 Nov 1;65:102546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2021.102546
Dart R, Bevelaqua A, DeAtley C, Sidell F, Goldfrank L, Madsen J, et al. Countering Chemical Agents: Multi-specialty panel presents consensus guidelines for prehospital management of mass casualties from chemical warfare agents. Jems: Journal of Emergency Medical Services. 2006 Dec 1;31:36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0197-2510(06)70586-1
Daud L, Utaberta N, Ismail N, Yazid M, Mohd YUNOS MY, Mohd Ariffin N, et al. Mitigating flood disaster in Kelantan : Effectiveness of emergency response by volunteers. Advances in Environmental Biology. 2015 Jan 1;9:61–4.
Desmond M, Schwengel D, Chilson K, Rusy D, Ingram K, Ambardekar A, et al. Paediatric patients in mass casualty incidents: a comprehensive review and call to action. Br J Anaesth. 2022;128(2):e109–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2021.10.026 .
Doyle CJ. Mass casualty incident. Integration with prehospital care. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 1990 Feb;8(1):163–75. PMID:2403920
Egan JR, Amlôt R. Modelling mass casualty decontamination systems informed by field exercise data. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2012;9(10):3685–710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9103685 .
Epstein RH, Ekbatani A, Kaplan J, Shechter R, Grunwald Z. Development of a staff recall system for mass casualty incidents using cell phone text messaging. Anesth Analg. 2010;110(3):871–8. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181cb3f9e .
Fenn J, Rega P, Stavros M, Buderer NF. Assessment of U.S. helicopter emergency medical services’ planning and preparedness for disaster response. Air Med J. 1999 Mar;18(1):12–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1067-991x(99)90003-2
Garner A, Nocera A. Should New South Wales hospital disaster teams be sent to major incident sites? Aust N Z J Surg. 1999;69(10):702–6. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1622.1999.01672.x .
Griffiths JL, Kirby NR, Waterson JA. Three years experience with forward-site mass casualty triage-, evacuation-, operating room-, ICU-, and radiography-enabled disaster vehicles: development of usage strategies from drills and deployments. Am J Disaster Med. 2014;9(4):273–85. https://doi.org/10.5055/ajdm.2014.0179 .
Gulesan OB, Anil E, Boluk PS. Social media-based emergency management to detect earthquakes and organize civilian volunteers. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction. 2021 Nov 1;65:102543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2021.102543
Hale JF. Managing a disaster scene and multiple casualties before help arrives. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2008 Mar;20(1):91–102, vii. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2007.10.012
Hall TN, McDonald A, Peleg K. Identifying factors that may influence decision-making related to the distribution of patients during a mass casualty incident. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2018;12(1):101–8. https://doi.org/10.1017/dmp.2017.43 .
Han R, Wang W, Shi J. Motivation of sichuan earthquake volunteers and its implication for emergency management. Proceedings—4th International Joint Conference on Computational Sciences and Optimization, CSO 2011. 2011. 658 p. https://doi.org/10.1109/CSO.2011.168
Hunt P. Lessons identified from the 2017 Manchester and London terrorism incidents. Part 1: introduction and the prehospital phase. BMJ Mil Health. 2020 Apr;166(2):111–4. https://doi.org/10.1136/jramc-2018-000934
Hyder S, Manzoor AF, Iqbal MA. Policy Implementation: Teachers’ Role as First Responders in Emergencies and Disasters. Kesmas: Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Nasional (National Public Health Journal) [Internet]. 2020 Nov 1 [cited 2022 Nov 14];15(4). https://doi.org/10.21109/kesmas.v15i4.2989
Ishikawa K, Jitsuiki K, Ohsaka H, Yoshizawa T, Obinata M, Omori K, et al. Management of a mass casualty event caused by electrocution using doctor helicopters. Air Med J. 2016;35(3):180–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amj.2015.12.012 .
Kaplowitz L, Reece M, Hershey JH, Gilbert CM, Subbarao I. Regional health system response to the Virginia Tech mass casualty incident. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2007;1(1 Suppl):S9-13. https://doi.org/10.1097/DMP.0b013e318149f5a2 .
Kearns RD, Holmes JH, Skarote MB, Cairns CB, Strickland SC, Smith HG, et al. Disasters; the 2010 Haitian earthquake and the evacuation of burn victims to US burn centers. Burns. 2014;40(6):1121–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2013.12.015 .
Kearns R, Hubble M, Holmes J, Cairns B. Disaster planning: transportation resources and considerations for managing a burn disaster. J Burn Care Res. 2013;28:35. https://doi.org/10.1097/BCR.0b013e3182853cf7 .
Khajehaminian MR, Ardalan A, Hosseini Boroujeni SM, Nejati A, Keshtkar A, Foroushani AR, et al. Criteria and models for the distribution of casualties in trauma-related mass casualty incidents: a systematic literature review protocol. Syst Rev. 2017;6(1):141. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-017-0538-z .
Khajehaminian MR, Ardalan A, Keshtkar A, Hosseini Boroujeni SM, Nejati A, Ebadati EOME, et al. A systematic literature review of criteria and models for casualty distribution in trauma related mass casualty incidents. Injury. 2018;49(11):1959–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2018.09.005 .
Kryvasheyeu Y, Chen H, Obradovich N, Moro E, Van Hentenryck P, Fowler J, et al. Rapid assessment of disaster damage using social media activity. Science Advances. 2016 Mar 11;2(3):e1500779. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1500779
Lavon O, Hershko D, Barenboim E. Large-scale air-medical transport from a peripheral hospital to level-1 trauma centers after remote mass-casualty incidents in Israel. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2009;24(6):549–55. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049023x00007500 .
Lee W-H, Chiu T-F, Ng C-J, Chen J-C. Emergency medical preparedness and response to a Singapore airliner crash. Acad Emerg Med. 2002;9(3):194–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1553-2712.2002.tb00243.x .
Levy MJ. Intentional Mass Casualty Events: Implications for Prehospital Emergency Medical Services Systems. J Spec Oper Med. 2015;15(4):157–9. https://doi.org/10.55460/K4BK-WQNR
Ludwig T, Kotthaus C, Reuter C, van Dongen S, Pipek V. Situated crowdsourcing during disasters: managing the tasks of spontaneous volunteers through public displays. Int J Hum Comput Stud. 2017;1(102):103–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2016.09.008 .
Martínez P, Jaime D, Contreras D, Moreno M, Bonacic C, Marín M. Design and validation of an instrument for selecting spontaneous volunteers during emergencies in natural disasters. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction. 2021 Jun 1;59:102243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2021.102243
McCunn M, Ashburn MA, Floyd TF, Schwab CW, Harrington P, Hanson CW, et al. An organized, comprehensive, and security-enabled strategic response to the Haiti earthquake: a description of pre-deployment readiness preparation and preliminary experience from an academic anesthesiology department with no preexisting international disaster response program. Anesth Analg. 2010;111(6):1438–44. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181f42fd3 .
Monteith RG, Pearce LDR. Self-care decontamination within a chemical exposure mass-casualty incident. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2015;30(3):288–96. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X15004677 .
Morris G. Common errors in mass casualty management. Corrective actions for the prehospital provider. JEMS. 1986 Feb;11(2):34–8. PMID:10275920
Mundorff AZ, Bartelink EJ, Mar-Cash E. DNA preservation in skeletal elements from the world trade center disaster: recommendations for mass fatality management. J Forensic Sci. 2009;54(4):739–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-4029.2009.01045.x .
Nagata T, Rosborough SN, Rosborogh SN, VanRooyen MJ, Kozawa S, Ukai T, et al. Express railway disaster in Amagasaki: a review of urban disaster response capacity in Japan. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2006;21(5):345–52. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049023x0000399x .
O’Neill PA. The ABC’s of disaster response. Scand J Surg. 2005;94(4):259–66. https://doi.org/10.1177/145749690509400403 .
Ocak T, Duran A, Ozdes T, Hocagil C, Kucukbayrak A. Problems encountered by volunteers assisting the relief efforts in van, turkey and the surrounding earthquake area. J Acad Emergency Med. 2013;24(12):66–70. https://doi.org/10.5152/jaem.2013.029 .
Olchin L, Krutz A. Nurses as first responders in a mass casualty: are you prepared? J Trauma Nurs. 2012;19(2):122–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTN.0b013e3182562984 .
Orr SM, Robinson WA. The hyatt regency skywalk collapse: an EMS-based disaster response. Ann Emerg Med. 1983;12(10):601–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0196-0644(83)80203-0 .
Paciarotti C, Cesaroni A, Bevilacqua M. The management of spontaneous volunteers: a successful model from a flood emergency in Italy. Int J Disaster Risk Reduction. 2018;1(31):260–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2018.05.013 .
Pereira BMT, Morales W, Cardoso RG, Fiorelli R, Fraga GP, Briggs SM. Lessons learned from a landslide catastrophe in Rio de Janeiro. Brazil Am J Disaster Med. 2013;8(4):253–8. https://doi.org/10.5055/ajdm.2013.0131 .
Plischke M, Wolf KH, Lison T, Pretschner DP. Telemedical support of prehospital emergency care in mass casualty incidents. Eur J Med Res. 1999;4(9):394–8 ( PMID:10477508 ).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Postma ILE, Weel H, Heetveld MJ, van der Zande I, Bijlsma TS, Bloemers FW, et al. Patient distribution in a mass casualty event of an airplane crash. Injury. 2013;44(11):1574–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2013.04.027 .
Raiter Y, Farfel A, Lehavi O, Goren OB, Shamiss A, Priel Z, et al. Mass casualty incident management, triage, injury distribution of casualties and rate of arrival of casualties at the hospitals: lessons from a suicide bomber attack in downtown Tel Aviv. Emerg Med J. 2008;25(4):225–9. https://doi.org/10.1136/emj.2007.052399 .
Ran Y, Hadad E, Daher S, Ganor O, Yegorov Y, Katzenell U, et al. Triage and air evacuation strategy for mass casualty events: a model based on combat experience. Mil Med. 2011;176(6):647–51. https://doi.org/10.7205/milmed-d-10-00390 .
Rauner MS, Schaffhauser-Linzatti MM, Niessner H. Resource planning for ambulance services in mass casualty incidents: a DES-based policy model. Health Care Manag Sci. 2012;15(3):254–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10729-012-9198-7 .
Romundstad L, Sundnes Ko, Pillgram-Larsen J, Røste Gk, Gilbert M. Challenges of major incident management when excess resources are allocated: experiences from a mass casualty incident after roof collapse of a military command center. Prehospital and disaster medicine [Internet]. 2004 Jun [cited 2022 Nov 14];19(2). https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049023x00001710
Roy N. The Asian Tsunami: PAHO disaster guidelines in action in India. Prehosp Disaster Med. 2006;21(5):310–5. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1049023x00003939 .
Salazar MK, Kelman B. Planning for biological disasters: occupational health nurses as “first responders.” AAOHN J. 2002;50(4):174–81. https://doi.org/10.1177/216507990205000411 .
Service Medical du Raid null, Reuter P-G, Baker C, Loeb T. Specific stretchers enhance rapid extraction by tactical medical support teams in mass casualty incidents. Injury. 2019 Feb;50(2):358–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2018.12.012
Severance HW. Mass-casualty victim “surge” management. Preparing for bombings and blast-related injuries with possibility of hazardous materials exposure. N C Med J. 2002 Oct;63(5):242–6. PMID:12970967
Shah AA, Rehman A, Sayyed RH, Haider AH, Bawa A, Zafar SN, et al. Impact of a predefined hospital mass casualty response plan in a limited resource setting with no pre-hospital care system. Injury. 2015;46(1):156–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2014.08.029 .
Shartar SE, Moore BL, Wood LM. Developing a Mass Casualty Surge Capacity Protocol for Emergency Medical Services to Use for Patient Distribution. South Med J. 2017 Dec;110(12):792–5. https://doi.org/10.14423/SMJ.0000000000000740
Shirm S, Liggin R, Dick R, Graham J. Prehospital preparedness for pediatric mass-casualty events. Pediatrics. 2007;120(4):e756-761. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2006-2856 .
Smith SW, Braun J, Portelli I, Malik S, Asaeda G, Lancet E, et al. Prehospital indicators for disaster preparedness and response: New York City emergency medical services in hurricane sandy. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2016;10(3):333–43. https://doi.org/10.1017/dmp.2015.175 .
Stănescu A, Gordon PE, Copotoiu SM, Boeriu CM. Moving toward a universal digital era in mass casualty incidents and disasters: emergency personnel’s perspective in Romania. Telemed J E Health. 2018;24(4):283–91. https://doi.org/10.1089/tmj.2017.0037 .
Thiel CC, Schneider JE, Hiatt D, Durkin ME. 9–1-1 EMS process in the Loma Prieta earthquake. Prehosp Disaster Med. 1992;7(4):348–58. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X00039765 .
Timbie JW, Ringel JS, Fox DS, Waxman DA, Pillemer F, Carey C, et al. Allocation of scarce resources during mass casualty events. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2012;207:1–305 ( PMID:24422904 ).
Google Scholar
Turkdogan KA, Korkut S, Arslan E, Ozyavuz MK. First response of emergency health care system and logistics support in an earthquake. Disaster Emergency Med J. 2021;6(2):63–9. https://doi.org/10.5603/DEMJ.a2021.0013 .
Veenema TG, Boland F, Patton D, O’Connor T, Moore Z, Schneider-Firestone S. Analysis of emergency health care workforce and service readiness for a mass casualty event in the Republic of Ireland. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2019;13(2):243–55. https://doi.org/10.1017/dmp.2018.45 .
Vernon A. EMS response to mass violence. What should you know to keep you and your fellow responders safe? EMS Mag. 2010 Apr;39(4):33–6. PMID:20432984
Yafe E, Walker BB, Amram O, Schuurman N, Randall E, Friger M, et al. Volunteer first responders for optimizing management of mass casualty incidents. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2019;13(2):287–94. https://doi.org/10.1017/dmp.2018.56 .
Khorram-Manesh A, Nordling J, Carlström E, Goniewicz K, Faccincani R, Burkle FM. A translational triage research development tool: standardizing prehospital triage decision-making systems in mass casualty incidents. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2021;29(1):119. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13049-021-00932-z .
Lesaffre X, Tourtier J-P, Violin Y, Frattini B, Rivet C, Stibbe O, et al. Remote damage control during the attacks on Paris: Lessons learned by the Paris Fire Brigade and evolutions in the rescue system. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017 Jun;82(6S Suppl 1):S107–13. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0000000000001438
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Partners of the NIGHTINGALE Consortium and the User Advisory Board Members who provided their valuable inputs during the different steps of the TS methodology.
This paper is supported by the NIGHTINGALE project ‘Novel InteGrated toolkit for enhanced pre-Hospital life support and Triage IN challenging And Large Emergencies’. This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 101021957.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
CRIMEDIM—Center for Research and Training in Disaster Medicine, Humanitarian Aid, and Global Health, Università del Piemonte Orientale, Novara, Italy
Eric S. Weinstein, Joseph L. Cuthbertson, George T. Voicescu, Michelangelo Bortolin, Luca Ragazzoni & Marta Caviglia
Research and Education Services, Medical University of South Carolina Library, Charleston, SC, USA
Teri Lynn Herbert
Department of Surgery, Policlinico Gemelli, Catholic University of the Sacred Heart, Rome, Italy
Sabina Magalini, Daniele Gui, Federica Marzi, Alessandro Borrello, Pietro Fransvea & Andrea Fidanzio
School of Medicine, Department of Emergency Medicine, Lebanese American University, Beirut, Lebanon
Mariana Helou
MRMID—International Association for Medical Response to Major Incidents and Disasters, and Vascular Surgery, Department of Molecular Medicine and Surgery, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden
Kristina Lennquist Montan & Carl Montan
Magen David Adom, National Emergency Medical, Disaster, Ambulance and Blood Bank Service, Ashkelon, Israel
Chaim Rafalowsky
Emergency Department, Azienda Sociosanitaria Ligure 2, Liguria, Italy
Giuseppe Ratto, Stefano Damele & Simone Bazurro
ESTES—European Society for Trauma and Emergency Surgery, Disaster and Military Surgery Section, Milan, Italy
Itamar Laist, Carlos Yanez Benitez & Roberto Faccincani
Department of Sustainable Development and Ecological Transition, Università del Piemonte Orientale, Vercelli, Italy
Luca Ragazzoni
Department of Translational Medicine, Università del Piemonte Orientale, Novara, Italy
Marta Caviglia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Eric S. Weinstein .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (DOCX 15 kb)
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Weinstein, E.S., Cuthbertson, J.L., Herbert, T.L. et al. Advancing the scientific study of prehospital mass casualty response through a Translational Science process: the T1 scoping literature review stage. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 49 , 1647–1660 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-023-02266-0
Download citation
Received : 28 November 2022
Accepted : 26 March 2023
Published : 15 April 2023
Issue Date : August 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-023-02266-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Scoping review
- Translational science
- Mass casualty incident
- NIGHTINGALE project
- Damage control interventions
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Open access
- Published: 13 December 2023
Attributes of errors, facilitators, and barriers related to rate control of IV medications: a scoping review
- Jeongok Park ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4978-817X 1 ,
- Sang Bin You ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1424-4140 2 ,
- Gi Wook Ryu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4533-7788 3 &
- Youngkyung Kim ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3696-5416 4
Systematic Reviews volume 12 , Article number: 230 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
821 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Intravenous (IV) medication is commonly administered and closely associated with patient safety. Although nurses dedicate considerable time and effort to rate the control of IV medications, many medication errors have been linked to the wrong rate of IV medication. Further, there is a lack of comprehensive studies examining the literature on rate control of IV medications. This study aimed to identify the attributes of errors, facilitators, and barriers related to rate control of IV medications by summarizing and synthesizing the existing literature.
This scoping review was conducted using the framework proposed by Arksey and O’Malley and PRISMA-ScR. Overall, four databases—PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, and CINAHL—were employed to search for studies published in English before January 2023. We also manually searched reference lists, related journals, and Google Scholar.
A total of 1211 studies were retrieved from the database searches and 23 studies were identified from manual searches, after which 22 studies were selected for the analysis. Among the nine project or experiment studies, two interventions were effective in decreasing errors related to rate control of IV medications. One of them was prospective, continuous incident reporting followed by prevention strategies, and the other encompassed six interventions to mitigate interruptions in medication verification and administration. Facilitators and barriers related to rate control of IV medications were classified as human, design, and system-related contributing factors. The sub-categories of human factors were classified as knowledge deficit, performance deficit, and incorrect dosage or infusion rate. The sub-category of design factor was device. The system-related contributing factors were classified as frequent interruptions and distractions, training, assignment or placement of healthcare providers (HCPs) or inexperienced personnel, policies and procedures, and communication systems between HCPs.
Conclusions
Further research is needed to develop effective interventions to improve IV rate control. Considering the rapid growth of technology in medical settings, interventions and policy changes regarding education and the work environment are necessary. Additionally, each key group such as HCPs, healthcare administrators, and engineers specializing in IV medication infusion devices should perform its role and cooperate for appropriate IV rate control within a structured system.
Peer Review reports
Medication errors are closely associated with patient safety and the quality of care [ 1 , 2 ]. In particular, medication errors, which denote a clinical issue of global importance for patient safety, negatively affect patient morbidity and mortality and lead to delays in discharge [ 3 , 4 ]. The National Health Service in the UK estimates that 237 million medication errors occur each year, of which 66 million cause clinically significant harm [ 5 ]. The US Food and Drug Administration reported that they received more than 100,000 reports each year associated with suspected medication errors [ 6 ]. Additionally, it was estimated that 40,000–98,000 deaths per year in the USA could be attributed to errors by healthcare providers (HCPs) [ 7 ]. Previous studies have revealed that medication errors account for 6–12% of hospital admissions [ 8 ].
Intravenous (IV) medication is a common treatment in hospitalized patient care [ 9 ]. It is used in wards, intensive care units (ICUs), emergency rooms, and outpatient clinics in hospitals [ 9 , 10 ]. As direct HCPs, nurses are integral in patient safety during the IV medication process which could result in unintended errors or violations of recommendations [ 3 ]. As many drugs injected via the IV route include high-risk drugs, such as chemotherapy agents, insulin, and opioids [ 10 ], inappropriate dose administration could lead to adverse events (AEs), such as death and life-threatening events [ 11 , 12 ].
IV medication process is a complex and multistage process. There are 12 stages in the IV medication process, which can be classified as follows: (1) obtain the drug for administration, (2) obtain the diluent, (3) reconstitute the drug in the diluent, (4) take the drug at the patient’s bedside, (5) check for the patient’s allergies, (6) check the route of drug administration, (7) check the drug dose, (8) check the patency of the cannula, (9) expel the air from the syringe, (10) administer the drug, (11) flush the cannula, and (12) sign the prescription chart [ 13 ]. IV medication errors can occur at any of these stages. It is imperative to administer the drug at the correct time and rate during the IV medication process [ 13 ]. The National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention (NCC MERP) defined an error in IV medication rates as “too fast or too slow rate than that intended” [ 14 ]. Maintaining the correct rate of IV medication is essential for enhancing the effectiveness of IV therapy and reducing AEs [ 9 ].
Infusion pumps are devices designed to improve the accuracy of IV infusions, with drug flow, volume, and timing programmed by HCPs [ 15 ]. A smart pump is an infusion pump with a software package containing a drug library. During programming, the smart pump software warns users about entering drug parameters that deviate from the recommended parameters, such as the type, dose, and dosage unit of the drug [ 15 ]. In the absence of a device for administering IV medication, such as an infusion pump or smart pump, the IV rate is usually controlled by counting the number of fluid drops falling into the drip chamber [ 9 ].
According to the previous study, applying an incorrect rate was the most prevalent IV medication error, accounting for 536 of 925 (57.9%) total IV medication errors [ 16 ]. Although rate control of IV medications is critical to patient safety and quality care, few studies review and map the relevant literature on rate control of IV medications. Therefore, this study aimed to identify the attributes of errors, facilitators, and barriers related to rate control of IV medications by summarizing the existing literature.
The specific research questions of this study are as follows:
What are the general characteristics of the studies related to rate control of IV medications?
What are the attributes of errors associated with rate control of IV medications?
What are the facilitators and barriers to rate control of IV medications?
This scoping review followed the framework suggested by Arksey and O’Malley [ 17 ] and developed by Levac et al. [ 18 ] and Peters et al. [ 19 ]. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) developed in 2020 by the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) were used to ensure reliability in the reporting of methodology (Additional file 1 ) [ 19 ].
Search strategy
According to the JBI Manuals for Evidence Synthesis, a three-step search strategy was adopted [ 19 ]. First, a preliminary search in PubMed was conducted based on the title, abstract, keywords, and index terms of articles to develop our search strategy. In the preliminary search, we used keywords such as “patients,” “nurse,” “IV therapy,” “monitoring,” “rate,” and “medication error.” The search results indicated that studies on medical devices and system-related factors were excluded. Therefore, we decided to exclude the keywords “patients” and “nurse” and focus on “IV therapy,” “monitoring,” “rate,” and “medication error” to comprehensively include studies on factors associated with rate control of infusion medications. Secondly, we used all identified keywords and index terms across all included databases following consultations with a research librarian at Yonsei University Medical Library to elaborate our search strategy. Four databases—PubMed, CINAHL, EMBASE, and Web of Science—were searched using the keywords, index terms, and a comprehensive list of keyword variations to identify relevant studies published before January 2023. The details of the search strategy are described in Additional file 2 . All database search results were exported into Endnote version 20. Finally, we manually searched the reference lists of the included articles identified from the database search. Furthermore, we manually searched two journals related to medication errors and patient safety, and Google Scholar to comprehensively identify the relevant literature. When performing a search on Google Scholar, keywords such as “medication,” “rate,” “IV therapy,” “intravenous administration,” and “medication error” were appropriately combined using search modifiers.
Eligibility criteria
Inclusion criteria were established according to the participants, concept, and context (PCC) framework recommended by the JBI manuals for scoping reviews [ 19 ]. The participants include patients receiving IV therapy, HCPs involved in administering IV medications, and experts from non-healthcare fields related to rate control of IV medications. The concepts were facilitators and barriers to rate control of IV medications, and the contexts were the environments or situations in which errors in rate control of IV medications occurred. While screening the literature identified by the three-step search based on the inclusion criteria, we refined the exclusion criteria through discussion among researchers. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) not available in English, (2) not an original article, (3) studies of medication errors in general, (4) not accessible, or (5) prescription error.
Study selection
Once duplicates were automatically removed through Endnote, two independent researchers assessed the eligibility of all articles by screening the titles and abstracts based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Studies identified via database searches were screened by GWR and YK and studies identified via other methods were screened by SBY and YK. Full-text articles were obtained either when the studies met the inclusion criteria or when more information was needed to assess eligibility and the researchers independently reviewed the full-text articles. In case of any disagreement in the study selection process, a consensus was reached through discussion among three researchers (GWR, SBY, and YK) and a senior researcher (JP).
Data extraction
Through consensus among the researchers, a form for data extraction was developed to extract appropriate information following the JBI manuals for scoping reviews [ 19 ]. The following data were collected from each study: author information, publication year, country, study design, study period, aims, participants or events (defined as the occurrences related to patient care focused on in the study), contexts, methods, errors related to the control of IV medications (observed results or intervention outcomes), error severity, facilitators, and barriers according to the NCC MERP criteria. Three researchers (GWR SBY, and YK) independently conducted data charting and completed the data extraction form through discussion.
Data synthesis
The general characteristics of included studies such as publication year, country, study design, and study period were analyzed using descriptive statistics to identify trends or patterns. The aims, participants, events, contexts, and methods of the included studies were classified into several categories through a research meeting including a senior researcher (JP) to summarize and analyze the characteristics of the included studies comprehensively. Attributes of errors associated with rate control of IV medications were analyzed and organized through consensus among researchers based on extracted data. Facilitators and barriers to rate control of IV medications were independently classified according to NCC MERP criteria by three researchers (GWR, SBY, and YK) and iteratively modified. Discrepancies were resolved by discussion and re-reading the articles, with the final decision made in consultation with the senior researcher (JP).
A total of 1211 studies were selected through a database search. After reviewing the titles and abstracts of the studies, 42 studies were considered for a detailed assessment by the three researchers. In particular, 2 were not available in English, 3 were not original articles, 24 were studies of medication error in general without details on rate control of IV medications, 2 were regarding prescription errors, and 1 was not accessible. Finally, 10 studies were identified through a database search. Additionally, 23 studies were identified from a manual search. Among the 23, 5 were not original articles, and 6 were studies on medication error in general. Finally, 12 studies were identified via other methods. Hence, 22 studies were included in the data analysis (Fig. 1 , Additional file 3 ).
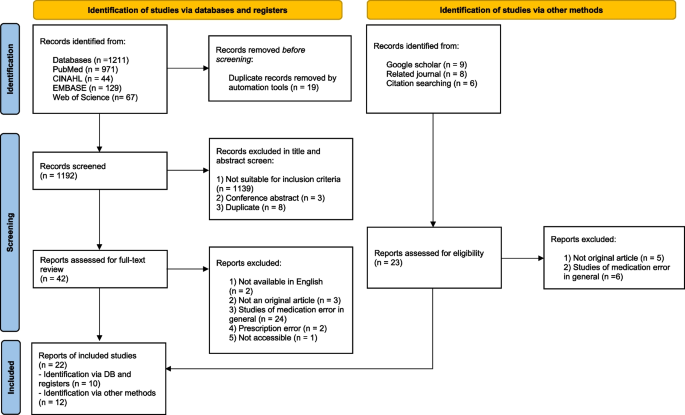
PRISMA flow chart for literature selection
Characteristics of the studies
General characteristics.
Table 1 presents the general characteristics of the included studies. Two of the included studies had a publication year before 2000 [ 20 , 21 ], and more than half of the studies ( n = 15) were published in 2010 and later. A majority of the included studies were conducted in Western countries ( n = 15) [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 ], four were conducted in Asia [ 20 , 37 , 38 , 39 ], two were conducted in Australia [ 21 , 40 ], and one was conducted in Egypt [ 2 ]. In terms of the study design, most studies were project studies ( n = 7) [ 22 , 24 , 27 , 28 , 30 , 34 , 39 ] or prospective observational studies ( n = 5) [ 2 , 20 , 29 , 32 , 40 ], followed by retrospective studies ( n = 3) [ 21 , 25 , 35 ], qualitative or mixed-methods studies ( n = 3) [ 23 , 26 , 33 ], and descriptive cross-sectional studies ( n = 2) [ 36 , 38 ]. Additionally, there was one controlled pre-posttest study [ 37 ] and one simulation laboratory experiment study [ 31 ]. The study period also varied greatly from 2 days [ 32 ] to 6 years [ 25 ].
The aims of the included studies were divided into two main categories. First, 13 studies identified the current status, causes, and factors influencing errors that could occur in healthcare settings [ 2 , 20 , 21 , 23 , 25 , 26 , 29 , 32 , 33 , 35 , 36 , 38 , 40 ]. Among these, three studies were on errors that may occur in specific healthcare procedures, such as anesthesia [ 20 ], vascular access [ 21 ], and pediatric chemotherapy [ 25 ]. Additionally, three studies explored possible errors associated with specific settings and medications, such as an obstetric emergency ward [ 2 ], cardiac critical care units [ 38 ], and high-alert medications [ 36 ], and three studies investigated the errors associated with the overall IV medication preparation or administration [ 23 , 33 , 40 ]. Moreover, three studies aimed at identifying potential problems associated with the use of IV medication infusion devices [ 26 , 32 , 35 ], and one study was about errors in medication preparation and administration that could occur in a setting using a specific system connected to electronic medical records [ 29 ]. Second, nine studies described the procedure of developing interventions or identified the effect of interventions [ 22 , 24 , 27 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 34 , 37 , 39 ].
Participants and events
Participants in the 22 studies included HCPs such as nurses, doctors, pharmacists, and patients. Notably, four of these studies were only for nurses [ 31 , 37 , 38 , 40 ] and there was also one study involving only pharmacists [ 36 ]. Furthermore, there were five studies wherein people from various departments or roles participated [ 23 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 39 ]. There were three studies wherein the patients were participants, and two studies included both patients and medical staff [ 29 , 33 ].
Among the included studies, nine studies focused on errors in IV medication preparation and administration as events [ 23 , 26 , 30 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 37 , 38 , 40 ] and five studies focused on the administration process only [ 30 , 32 , 34 , 37 , 40 ]. Four studies focused on problems in the administration of all types of drugs including errors associated with rate control of IV medications [ 2 , 22 , 28 , 29 ]. Additionally, four studies focused on events that occurred with IV medication infusion devices [ 24 , 27 , 35 , 39 ], two studies explored the events that occurred during chemotherapy [ 22 , 25 ], and some analyzed events with problems in vascular access [ 21 ], iatrogenic events among neonates [ 28 ], and critical events in anesthesia cases [ 20 ].
Contexts and methods
The contexts can be largely divided into healthcare settings, including hospitals and laboratory settings. Three hospital-based studies were conducted in the entire hospital [ 20 , 22 , 24 ], eight studies were conducted at several hospitals, and the number of hospitals involved varied from 2 to 132 [ 23 , 26 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 38 , 40 ]. Furthermore, four studies were conducted in different departments within one hospital [ 29 , 30 , 37 , 39 ], three studies were conducted in only one department [ 2 , 27 , 28 ], two studies considered other healthcare settings and were not limited to hospitals [ 21 , 25 ], and one study was conducted in a simulation laboratory setting that enabled a realistic simulation of an ambulatory chemotherapy unit [ 31 ].
Specifically, seven out of the nine studies developed or implemented interventions based on interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary collaboration [ 22 , 24 , 28 , 30 , 34 , 37 , 39 ]. Two studies developed and identified the effectiveness of interventions that created an environment for nurses to improve performance and correct errors associated with medication administration [ 31 , 39 ], and two intervention studies were on error reporting methods or observation tools and the processes of addressing reported errors [ 28 , 30 ]. There were also a study on a pharmacist-led educational program for nurses [ 37 ], a comprehensive intervention from drug prescription to administration to reduce chemotherapy-related medication errors [ 22 ], infusion safety intervention bundles [ 34 ], the implementation of a smart IV pump equipped with failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) [ 24 ], and a smart system to prevent pump programming errors [ 27 ].
Data collection methods were classified as a review of reported incidents [ 20 , 21 , 22 , 25 , 35 ], a review of medical charts [ 26 ], observations [ 23 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 37 , 40 ], follow-up on every pump alert [ 27 ], and self-reporting questionnaires or surveys [ 36 , 38 ]. Some studies utilized retrospective reviews of reported incidents and self-report questionnaires [ 39 ]. Also, in the study by Kandil et al., observation, nursing records review, and medical charts review were all used [ 2 ].
Attributes of errors associated with rate control of IV medications
Table 2 presents the attributes of errors related to rate control of IV medications in observed results or intervention outcomes, and error severity. Notably, 6 of 13 studies presenting observed results reported errors related to IV medication infusion devices among the rate control errors [ 20 , 25 , 32 , 33 , 35 , 36 ]. Additionally, four studies reported errors in bolus dose administration or IV push and flushing lines among IV rate errors [ 2 , 23 , 36 , 40 ]. Among the 13, nine studies reported error severity, and among these, three studies used NCC MERP ratings [ 25 , 32 , 33 ]. In four studies, error severity was reported by describing several cases in detail [ 2 , 21 , 23 , 25 ], and two studies reported no injuries or damages due to errors [ 26 , 29 ]. Among the nine studies that developed interventions and identified their effectiveness, four presented the frequency of incorrect rate errors as an outcome variable [ 28 , 30 , 34 , 37 ]. Moreover, two studies suggested compliance rates for intervention as outcome variables [ 24 , 31 ].
Among the nine project or experiment studies, three showed a decrease in error rate as a result of the intervention [ 28 , 31 , 34 ]. Three studies developed interventions to reduce rate errors but did not report the frequency or incidence of rate errors [ 22 , 24 , 27 ]. A study reported the frequency of rate errors only after the intervention; the effect of the intervention could not be identified [ 30 ]. Also, three studies showed the severity of errors related to rate control of IV medications [ 24 , 30 , 34 ], two used NCC MERP severity ratings [ 30 , 34 ], and one reported that all errors caused by smart IV pumps equipped with FMEA resulted in either temporary harm or no harm [ 24 ].
Facilitators and barriers to rate control of IV medications
Table 3 presents the facilitators and barriers related to rate control of IV medications according to the NCC MERP taxonomy based on the 22 included studies. Sub-categories of human factors were classified as knowledge deficit, performance deficit, miscalculation of dosage or infusion rate, and stress. The sub-category of design factor was device. System-related contributing factors were classified as frequent interruptions and distractions, inadequate training, poor assignment or placement of HCPs or inexperienced personnel, policies and procedures, and communication systems between HCPs [ 14 ].
Human factors
Among the barriers extracted from the 22 studies, 11 factors belonged to the “knowledge deficit,” “performance deficit,” “miscalculation of dosage or infusion rate,” and “stress (high-volume workload)” in this category. Half of these factors are related to the “performance deficit.” Barriers identified in two or more studies were tubing misplacement [ 24 , 35 ] and non-compliance with protocols and guidelines [ 2 , 25 ], all of which belonged to the “performance deficit.” Additionally, the high workload and environmental characteristics of the ICU, which corresponded to the “stress,” were also identified as barriers to rate control of IV medications [ 23 , 37 ].
Most factors in this category were related to IV medication infusion devices such as infusion pumps and smart pumps. In the study by Lyons et al., the use of devices, such as patient-controlled analgesia pumps and syringe drivers, was a facilitator of rate control of IV medications [ 33 ]. In addition to the use of these devices, the expansion of capabilities [ 26 ], monitoring programming [ 27 ], and standardization [ 22 ] were also facilitators. Unexpected equipment faults, a barrier, were identified in five studies [ 2 , 20 , 25 , 35 , 38 ]. Moreover, the complex design of the equipment [ 23 , 24 ] and incomplete drug libraries in smart pumps [ 33 , 35 ] were identified in two studies each. Factors such as the misassembly of an unfamiliar infusion pump [ 21 ] and smart pumps not connected to electronic systems [ 30 ] were also barriers.
Contributing factors (system related)
The factors belonging to the “frequent interruptions and distractions” in this category were all barriers. Specifically, running multiple infusions at once [ 24 , 27 ], air-in-line alarms, or cleaning air [ 24 ] were identified as barriers. Among the facilitators of the “training,” there were education and training on the use of smart IV pumps [ 24 ] and chemotherapy errors [ 22 ]. There are two factors in the “assignment or placement of a HCP or inexperienced personnel,” where ward-based pharmacists were facilitators [ 36 ], but nurses with less than 6 years of experience were barriers [ 40 ]. The sub-category with the most factors was “policies and procedures,” where the facilitators extracted in the four studies were double-checks through the process [ 22 , 24 , 28 , 36 ]. Among the barriers, two were related to keep-the-vein-open, which was identified in three studies [ 30 , 32 , 33 ]. The lack of automated infusion pumps [ 2 ], the absence of culture for use [ 32 , 33 ], and problems in the drug prescription process [ 33 ] were also identified as barriers. Communication with physicians in instances of doubt identified was the only identified facilitator in the “communication systems between HCPs” [ 28 ].
Resolutions for the barriers to rate control of IV medications
Table 4 presents the resolutions for the barriers to rate control of IV medications in the included studies. The suggested resolutions primarily belonged to the “contributing factors (system-related)” category. Resolutions in the “human factors” category were mainly related to the knowledge and performance of individual healthcare providers, and there were no studies proposing resolutions specifically addressing stress (high-volume workload), which is one of the barriers. Resolutions in the “design” category focused on the development [ 26 , 30 ], appropriate use [ 24 , 33 ], evaluation [ 26 ], improvement [ 24 , 26 , 30 ], and supply [ 23 ] of infusion pumps or smart pumps. Resolutions addressing aspects within the “contributing factors (system-related)” category can be classified into six main areas: interdisciplinary or inter-institution collaboration [ 23 , 25 , 28 , 30 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 ], training [ 24 , 37 , 40 ], implementation of policies or procedures [ 29 , 31 , 34 , 35 , 37 , 39 ], system improvement [ 25 , 30 , 32 ], creating a patient safety culture [ 25 , 37 , 38 ], and staffing [ 2 , 38 ].
This scoping review provides the most recent evidence on the attributes of errors, facilitators, and barriers related to rate control of IV medications. The major findings of this study were as follows: (1) there were a few intervention studies that were effective in decreasing the errors related to rate control of IV medications; (2) there was limited research focusing on the errors associated with IV medication infusion devices; (3) a few studies have systematically evaluated and analyzed the severity of errors associated with rate control of IV medications; and (4) the facilitators and barriers related to rate control of IV medications were identified by NCC MERP taxonomy as three categories (human factors, design, and system-related contributing factors).
Among the nine project or experiment studies, only two interventions showed statistically significant effectiveness for IV rate control [ 28 , 31 ]. Six studies did not report the specific statistical significance of the intervention [ 22 , 24 , 27 , 30 , 37 , 39 ], and one study found that the developed intervention had no statistically significant effect [ 34 ]. In another study, administration errors, including rate errors, increased in the experimental group and decreased in the control group [ 37 ]. IV rate control is a major process in medication administration that is comprehensively related to environmental and personal factors [ 3 , 41 ]. According to previous studies, interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary cooperation is associated with the improvement in patient safety and decreased medical errors [ 42 , 43 , 44 ]. Seven of the included studies were also project or experiment studies that developed interventions based on an interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary approach [ 22 , 24 , 28 , 30 , 34 , 37 , 39 ]. Additionally, an effective intervention was developed by a multidisciplinary care quality improvement team [ 28 ]. Therefore, it is crucial to develop effective interventions based on an interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary approach to establish practice guidelines with a high level of evidence related to IV rate control.
Of the 22 included studies, three identified potential problems associated with the use of IV medication infusion devices [ 26 , 32 , 35 ], and four described the application of interventions or explored the effects of the intervention developed to reduce errors that occur when using IV medication infusion devices [ 24 , 27 , 34 , 39 ]. IV medication infusion devices, such as infusion pumps and smart pumps, are widely used in healthcare environments and allow more rigorous control in the process of administering medications that are continuously infused [ 45 ]. Smart pumps are recognized as useful devices for providing safe and effective nursing care [ 15 ]. However, the use of IV medication infusion devices requires an approach different from traditional rate monitoring by counting the number of fluid drops falling into the drip chamber [ 9 ]. However, there exist many problems, such as bypassing the drug library, device maintenance, malfunction, tubing/connection, and programming in the use of IV medication infusion devices [ 32 , 35 ]. None of the four studies that described the application of interventions or explored the effects of the intervention demonstrated statistically significant effects. All four studies had no control group [ 24 , 27 , 34 , 39 ] and two studies had only post-test designs [ 24 , 27 ]. Therefore, further research needs to be conducted to analyze errors in rate control related to IV medication infusion devices and develop effective interventions.
A few studies have systematically evaluated and analyzed the severity of errors associated with rate control of IV medications. Among the 12 studies that reported the severity of errors associated with rate control of IV medications, five studies used NCC MERP, an internationally validated and reliable tool for assessing error severity, and one study used the Severity Assessment Code (SAC) developed by the New South Wales Health Department. Six studies did not use tools to assess error severity. The term “error severity” means the degree of potential or actual harm to patients [ 46 ]. Evaluating the severity of medication errors is a vital point in improving patient safety throughout the medication administration process. This evaluation allows for distinguishing errors based on their severity to establish the development of risk mitigation strategies focused on addressing errors with the great potential to harm patients [ 47 , 48 ]. Specifically, errors associated with rate control of IV medications were categorized as A to E on the NCC MERP and to groups 3 and 4 on the SAC. Additionally, errors associated with rate control of IV medications caused direct physical damage [ 2 , 21 ] and necessitated additional medication to prevent side effects or toxicity [ 23 ]. Therefore, as errors in rate control of IV medications are likely to cause actual or potential harm to the patient, research systematically evaluating and analyzing error severity should be conducted to provide the basis for developing effective risk reduction strategies in the rate control of IV medications.
Facilitators and barriers were identified as human, design, and system-related contributing factors. Among the human factors, “performance deficit” included failure to check equipment properly, tubing misplacement, inadequate monitoring, non-compliance with protocols and guidelines, and human handling errors with smart pumps. Nurses play a major role in drug administration; thus, their monitoring and practices related to IV medication infusion devices can influence patient health outcomes [ 3 , 49 ]. A major reason for the lack of monitoring was overwork, which was related to the complex working environment, work pressure, and high workload [ 3 , 11 , 49 ]. Moreover, two of the included studies identified high workload as a barrier to rate control of IV medications [ 23 , 37 ]. Therefore, to foster adequate monitoring of rate control of IV medications, a systematic approach to alleviating the complex working environment and work pressure should be considered.
Most facilitators and barriers in the devices category were related to IV medication infusion devices. In particular, expanding pump capabilities [ 26 ], monitoring pump programming [ 27 ], standardization [ 22 ], and using a pump [ 33 ] can facilitate rate control of IV medications. However, unexpected equipment faults are significant barriers, as identified in five studies among the included studies [ 2 , 20 , 25 , 35 , 38 ]. Moreover, the design [ 23 , 24 ], user-friendliness [ 21 ], connectivity to electronic systems [ 30 ], and completeness of drug libraries [ 33 , 35 ] are factors that can affect rate control of IV medications. Therefore, it is important to improve, monitor, and manage IV medication infusion devices so that they do not become barriers. Moreover, because rate errors caused by other factors can be prevented by devices, active utilization and systematic management of devices at the system level are required.
Although there are many benefits of infusion and smart pumps for reducing errors in rate control of IV medications, they cannot be used in all hospitals because of the limitation of medical resources. The standard infusion set, which is a device for controlling the rate of IV medication by a controller [ 9 ], is widely used in outpatient as well as inpatient settings [ 32 ]. Devices for monitoring the IV infusion rate, such as FIVA™ (FIVAMed Inc, Halifax, Canada) and DripAssist (Shift Labs Inc, Seattle, USA), which can continuously monitor flow rate and volume with any gravity drip set, have been commercialized [ 33 ]. However, they have not been widely used in hospitals. Therefore, developing novel IV infusion rate monitoring devices that are simple to use, can be used remotely, and are affordable for developing and underdeveloped countries can help nurses to reduce their workloads in monitoring IV infusion rates and thus maintain patient safety.
Most facilitators and barriers were system-related contributing factors, most of which belonged to the “policies and procedures.” In four studies, the absence of hospital policies or culture related to rate control of IV medications was identified as a barrier [ 2 , 30 , 32 , 33 ]. Medication errors related to incorrect rate control are problems that should be approached from macroscopic levels, such as via institutional policies and safety cultures. Therefore, large-scale research including more diverse departments and institutions needs to be conducted.
The second most common categories in system-related contributing factors were “frequent interruptions and distractions” and “training.” Although nurses experienced frequent interruptions and distributions during work, only one of the included studies was on interventions that were developed to create an environment with reduced interruptions [ 31 ]. Additionally, four studies found that education for nurses who are directly associated with medication administration is mandatory [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 36 ]. Therefore, education and a work environment for safety culture should be created to improve IV rate control.
Based on resolutions for barriers to rate control of IV medications, key groups relevant to rate control of IV medications include HCPs, healthcare administrators, and engineers specializing in IV medication infusion devices. HCPs directly involved in the preparation and administration of IV medications need to enhance their knowledge of drugs, raise awareness for the importance of rate control of IV medications, and improve performance related to IV infusion device monitoring. Engineers specializing in IV medication infusion devices should develop these devices by integrating various information technologies used in clinical settings. Additionally, they should identify issues related to these devices and continuously enhance both software and hardware. Healthcare administrators play a crucial role in establishing and leading interdisciplinary or inter-institution collaborations. They should foster leadership, build a patient safety culture within the organization, and implement training, interventions, and policies for correct rate control of IV medications. Decreasing medication errors, including errors in IV rate control, is closely linked to the various key groups [ 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 ], and multidisciplinary collaboration is emphasized for quality care [ 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 ]. Therefore, each key group should perform its role and cooperate for appropriate IV rate control within a structured system.
This review has some limitations that should be considered. As there was no randomized controlled trial in this review, the causal relationship between wrong rate errors and their facilitators or barriers could not be determined. Moreover, only limited literature may have been included in this review because we included literature published in English and excluded gray literature. Since we did not evaluate the quality of the study, there may be a risk of bias in data collection and analysis. Despite these limitations, this study provides a meaningful assessment of published studies related to rate control of IV medications. This contribution will provide an important basis for new patient safety considerations in IV medication administration when determining future policies and device development.
The findings of this review suggest that further research is needed to be conducted to develop effective interventions to improve the practice of IV rate control. Moreover, given the rapid growth of technology in medical settings, research on IV medication infusion devices should be conducted. Additionally, to establish effective risk reduction strategies, it is necessary to systematically evaluate and analyze the severity of errors related to the rate control of IV medications. Several facilitators and barriers to rate control of IV medications were identified in this review to ensure patient safety and quality care, interventions and policy changes related to education and the work environment are required. Additionally, the development of a device capable of monitoring the flow of IV medication is necessary. This review will be useful for HCPs, hospital administrators, and engineers specializing in IV medication infusion devices to minimize errors in rate control of IV medications and improve patient safety.
Availability of data and materials
The corresponding author can provide the datasets that were utilized and/or examined during the present study upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Adverse event
Healthcare provider
Intensive care unit
Intravenous
Joanna Briggs Institute
The National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention
Cousins DD, Heath WM. The National Coordinating Council for medication error reporting and prevention: promoting patient safety and quality through innovation and leadership. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2008;34(12):700–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1553-7250(08)34091-4 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Kandil M, Sayyed T, Emarh M, Ellakwa H, Masood A. Medication errors in the obstetrics emergency ward in a low resource setting. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012;25(8):1379–82. https://doi.org/10.3109/14767058.2011.636091 .
Parry AM, Barriball KL, While AE. Factors contributing to registered nurse medication administration error: a narrative review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2015;52(1):403–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2014.07.003 .
Vrbnjak D, Denieffe S, O’Gorman C, Pajnkihar M. Barriers to reporting medication errors and near misses among nurses: a systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2016;63:162–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2016.08.019 .
Elliott RA, Camacho E, Jankovic D, Sculpher MJ, Faria R. Economic analysis of the prevalence and clinical and economic burden of medication error in England. BMJ Qual Saf. 2021;30(2):96–105. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2019-010206 .
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) . Working to reduce medication errors [Internet]. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 2019. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/information-consumers-and-patients-drugs/working-reduce-medication-errors . Cited 27 Dec 2022
Institute of Medicine (US). Committee on quality of health care in America. In: Kohn LT, Corrigan JM, Donaldson MS, editors. To err is human: building a safer health system. Washington: National Academies Press (US); 2000. PMID: 25077248.
Google Scholar
EscriváGracia J, Brage Serrano R, Fernández GJ. Medication errors and drug knowledge gaps among critical-care nurses: a mixed multi-method study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019;19(1):640. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-019-4481-7 .
Article Google Scholar
Park K, Lee J, Kim SY, Kim J, Kim I, Choi SP, et al. Infusion volume control and calculation using metronome and drop counter based intravenous infusion therapy helper. Int J Nurs Pract. 2013;19(3):257–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijn.12063 .
Marwitz KK, Giuliano KK, Su WT, Degnan D, Zink RJ, DeLaurentis P. High-alert medication administration and intravenous smart pumps: a descriptive analysis of clinical practice. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2019;15(7):889–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sapharm.2019.02.007 .
Kale A, Keohane CA, Maviglia S, Gandhi TK, Poon EG. Adverse drug events caused by serious medication administration errors. BMJ Qual Saf. 2012;21(11):933–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2012-000946 .
Yoon J, Yug JS, Ki DY, Yoon JE, Kang SW, Chung EK. Characterization of medication errors in a medical intensive care unit of a university teaching hospital in South Korea. J Patient Saf. 2022;18(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/pts.0000000000000878 .
McDowell SE, Mt-Isa S, Ashby D, Ferner RE. Where errors occur in the preparation and administration of intravenous medicines: a systematic review and Bayesian analysis. Qual Saf Health Care. 2010;19(4):341–5. https://doi.org/10.1136/qshc.2008.029785 .
National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention. Taxonomy of medication errors. NCC MERP. 2001. Available from: https://www.nccmerp.org/taxonomy-medication-errors . Cited 27 Dec 2022
Moreira APA, Carvalho MF, Silva R, Marta CB, Fonseca ERD, Barbosa MTS. Handling errors in conventional and smart pump infusions: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Rev Esc Enferm USP. 2020;54:e03562. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1980-220x2018032603562 .
Sutherland A, Canobbio M, Clarke J, Randall M, Skelland T, Weston E. Incidence and prevalence of intravenous medication errors in the UK: a systematic review. Eur J Hosp Pharm. 2020;27(1):3–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/ejhpharm-2018-001624 .
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Levac D, Colquhoun H, O’Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. 2010;5:1–9.
Peters MDJ, Marnie C, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Munn Z, Alexander L, et al. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid Implement. 2021;19(1):3–10. https://doi.org/10.1097/xeb.0000000000000277 .
Short TG, O’Regan A, Lew J, Oh TE. Critical incident reporting in an anaesthetic department quality assurance programme. Anaesthesia. 1993;48(1):3–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2044.1993.tb06781.x .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Singleton RJ, Webb RK, Ludbrook GL, Fox MA. The Australian incident monitoring study. Problems associated with vascular access: an analysis of 2000 incident reports. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1993;21(5):664–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/0310057x9302100531 .
Goldspiel BR, DeChristoforo R, Daniels CE. A continuous-improvement approach for reducing the number of chemotherapy-related medication errors. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2000;15(57 Suppl 4):S4-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajhp/57.suppl_4.S4 . PMID: 11148943.
Taxis K, Barber N. Causes of intravenous medication errors: an ethnographic study. Qual Saf Health Care. 2003;12(5):343–7. https://doi.org/10.1136/qhc.12.5.343 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wetterneck TB, Skibinski KA, Roberts TL, Kleppin SM, Schroeder ME, Enloe M, et al. Using failure mode and effects analysis to plan implementation of smart i.v. pump technology. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2006;63(16):1528–38. https://doi.org/10.2146/ajhp050515 .
Rinke ML, Shore AD, Morlock L, Hicks RW, Miller MR. Characteristics of pediatric chemotherapy medication errors in a national error reporting database. Cancer. 2007;110(1):186–95. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.22742 .
Nuckols TK, Bower AG, Paddock SM, Hilborne LH, Wallace P, Rothschild JM, et al. Programmable infusion pumps in ICUs: an analysis of corresponding adverse drug events. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23:41–5.
Evans RS, Carlson R, Johnson KV, Palmer BK, Lloyd JF. Enhanced notification of infusion pump programming errors. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2010;160(Pt 1):734–8 PMID: 20841783.
PubMed Google Scholar
Ligi I, Millet V, Sartor C, Jouve E, Tardieu S, Sambuc R, Simeoni U. Iatrogenic events in neonates: beneficial effects of prevention strategies and continuous monitoring. Pediatrics. 2010;126(6):e1461–8. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-2872 .
Rodriguez-Gonzalez CG, Herranz-Alonso A, Martin-Barbero ML, Duran-Garcia E, Durango-Limarquez MI, Hernández-Sampelayo P, Sanjurjo-Saez M. Prevalence of medication administration errors in two medical units with automated prescription and dispensing. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2012;19(1):72–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/amiajnl-2011-000332 .
Ohashi K, Dykes P, McIntosh K, Buckley E, Wien M, Bates DW. Evaluation of intravenous medication errors with smart infusion pumps in an academic medical center. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2013;2013:1089–98 PMID: 24551395; PMCID: PMC3900131.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Prakash V, Koczmara C, Savage P, Trip K, Stewart J, McCurdie T, et al. Mitigating errors caused by interruptions during medication verification and administration: interventions in a simulated ambulatory chemotherapy setting. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(11):884–92. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2013-002484 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Schnock KO, Dykes PC, Albert J, Ariosto D, Call R, Cameron C, et al. The frequency of intravenous medication administration errors related to smart infusion pumps: a multihospital observational study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2017;26(2):131–40. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2015-004465 .
Lyons I, Furniss D, Blandford A, Chumbley G, Iacovides I, Wei L, et al. Errors and discrepancies in the administration of intravenous infusions: a mixed methods multihospital observational study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2018;27(11):892–901. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2017-007476 .
Schnock KO, Dykes PC, Albert J, Ariosto D, Cameron C, Carroll DL, et al. A multi-hospital before-after observational study using a point-prevalence approach with an infusion safety intervention bundle to reduce intravenous medication administration errors. Drug Saf. 2018;41(6):591–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40264-018-0637-3 .
Taylor MA, Jones R. Risk of medication errors with infusion pumps: a study of 1,004 events from 132 hospitals across Pennsylvania. Patient Safety. 2019;1(2):60–9. https://doi.org/10.33940/biomed/2019.12.7 .
Schilling S, Koeck JA, Kontny U, Orlikowsky T, Erdmann H, Eisert A. High-alert medications for hospitalised paediatric patients - a two-step survey among paediatric clinical expert pharmacists in Germany. Pharmazie. 2022;77(6):207–15. https://doi.org/10.1691/ph.2022.12025 .
Nguyen HT, Pham HT, Vo DK, Nguyen TD, van den Heuvel ER, Haaijer-Ruskamp FM, Taxis K. The effect of a clinical pharmacist-led training programme on intravenous medication errors: a controlled before and after study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(4):319–24. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2013-002357 .
Bagheri-Nesami M, Esmaeili R, Tajari M. Intravenous medication administration errors and their causes in cardiac critical care units in Iran. Mater Sociomed. 2015;27(6):442–6. https://doi.org/10.5455/msm.2015.27.442-446 .
Tsang LF, Tsang WY, Yiu KC, Tang SK, Sham SYA. Using the PDSA cycle for the evaluation of pointing and calling implementation to reduce the rate of high-alert medication administration incidents in the United Christian Hospital of Hong Kong, China. J Patient Safety Qual Improv. 2017;5(3):577–83. https://doi.org/10.22038/PSJ.2017.9043 .
Westbrook JI, Rob MI, Woods A, Parry D. Errors in the administration of intravenous medications in hospital and the role of correct procedures and nurse experience. BMJ Qual Saf. 2011;20(12):1027–34. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2011-000089 .
Daker-White G, Hays R, McSharry J, Giles S, Cheraghi-Sohi S, Rhodes P, Sanders C. Blame the patient, blame the doctor or blame the system? A meta-synthesis of qualitative studies of patient safety in primary care. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(8):e0128329. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128329 .
Kucukarslan SN, Peters M, Mlynarek M, Nafziger DA. Pharmacists on rounding teams reduce preventable adverse drug events in hospital general medicine units. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(17):2014–8. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.163.17.2014 .
Lemieux-Charles L, McGuire WL. What do we know about health care team effectiveness? A review of the literature. Med Care Res Rev. 2006;63(3):263–300. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077558706287003 .
O’Leary KJ, Buck R, Fligiel HM, Haviley C, Slade ME, Landler MP, et al. Structured interdisciplinary rounds in a medical teaching unit: improving patient safety. Arch Intern Med. 2011;171(7):678–84. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2011.128 .
Yu D, Obuseh M, DeLaurentis P. Quantifying the impact of infusion alerts and alarms on nursing workflows: a retrospective analysis. Appl Clin Inform. 2021;12(3):528–38. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1730031 . Epub 2021 Jun 30. PMID: 34192773; PMCID: PMC8245209.
Gates PJ, Baysari MT, Mumford V, Raban MZ, Westbrook JI. Standardising the classification of harm associated with medication errors: the harm associated with medication error classification (HAMEC). Drug Saf. 2019;42(8):931–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40264-019-00823-4 .
Assunção-Costa L, Ribeiro Pinto C, Ferreira Fernandes Machado J, Gomes Valli C, de PortelaFernandes Souza LE, Dean FB. Validation of a method to assess the severity of medication administration errors in Brazil: a study protocol. J Public Health Res. 2022;11(2):2022. https://doi.org/10.4081/jphr.2022.2623 .
Walsh EK, Hansen CR, Sahm LJ, Kearney PM, Doherty E, Bradley CP. Economic impact of medication error: a systematic review. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2017;26(5):481–97. https://doi.org/10.1002/pds.4188 .
Khalil H, Shahid M, Roughead L. Medication safety programs in primary care: a scoping review. JBI Database Syst Rev Implement Rep. 2017;15(10):2512–26. https://doi.org/10.11124/jbisrir-2017-003436 .
Atey TM, Peterson GM, Salahudeen MS, Bereznicki LR, Simpson T, Boland CM, et al. Impact of partnered pharmacist medication charting (PPMC) on medication discrepancies and errors: a pragmatic evaluation of an emergency department-based process redesign. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(2):1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021452 .
Atey TM, Peterson GM, Salahudeen MS, Bereznicki LR, Wimmer BC. Impact of pharmacist interventions provided in the emergency department on quality use of medicines: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Emerg Med J. 2023;40(2):120–7. https://doi.org/10.1136/emermed-2021-211660 .
Hanifin R, Zielenski C. Reducing medication error through a collaborative committee structure: an effort to implement change in a community-based health system. Qual Manag Health Care. 2020;29(1):40–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/qmh.0000000000000240 .
Kirwan G, O’Leary A, Walsh C, Grimes T. Economic evaluation of a collaborative model of pharmaceutical care in an Irish hospital: cost-utility analysis. HRB Open Res. 2023;6:19. https://doi.org/10.12688/hrbopenres.13679.1 .
Billstein-Leber M, Carrillo CJD, Cassano AT, Moline K, Robertson JJ. ASHP guidelines on preventing medication errors in hospitals. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2018;75(19):1493–517. https://doi.org/10.2146/ajhp170811 .
Lewis KA, Ricks TN, Rowin A, Ndlovu C, Goldstein L, McElvogue C. Does simulation training for acute care nurses improve patient safety outcomes: a systematic review to inform evidence-based practice. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2019;16(5):389–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/wvn.12396 .
Mardani A, Griffiths P, Vaismoradi M. The role of the nurse in the management of medicines during transitional care: a systematic review. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020;13:1347–61. https://doi.org/10.2147/jmdh.S276061 .
L Naseralallah D Stewart M Price V Paudyal 2023 Prevalence, contributing factors, and interventions to reduce medication errors in outpatient and ambulatory settings: a systematic review Int J Clin Pharm https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-023-01626-5
Download references
This research was supported by the Korea Medical Device Development Fund grant funded by the Korea government (the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, the Ministry of Health & Welfare, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety) (Project Number: RS-2020-KD000077) and Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2020R1A6A1A03041989). This work also supported by the Brain Korea 21 FOUR Project funded by National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea, Yonsei University College of Nursing.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Nursing, Mo-Im Kim Nursing Research Institute, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
Jeongok Park
University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Sang Bin You
Department of Nursing, Hansei University, 30, Hanse-Ro, Gunpo-Si, 15852, Gyeonggi-Do, Korea
Gi Wook Ryu
College of Nursing and Brain Korea 21 FOUR Project, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
Youngkyung Kim
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization: JP; study design: JP; data collection: GWR, YK, SBY; data analysis: JP, GWR, YK, SBY; administration: JP; funding acquisition: JP; writing—original draft: JP, GWR, YK; writing—review and editing: JP, YK.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Gi Wook Ryu or Youngkyung Kim .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) checklist.
Additional file 2:
Search queries and strategies by electronic databases.
Additional file 3:
Studies included in the data analysis.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Park, J., You, S.B., Ryu, G.W. et al. Attributes of errors, facilitators, and barriers related to rate control of IV medications: a scoping review. Syst Rev 12 , 230 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-023-02386-z
Download citation
Received : 15 May 2023
Accepted : 08 November 2023
Published : 13 December 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-023-02386-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Medication safety
- Patient safety
- Quality improvement
- Safety culture
Systematic Reviews
ISSN: 2046-4053
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

English Assignment Reflections: Literature Review
Paid on delivery
I am in need of keen freelancers who can produce detailed literature review reflections for my English assignments.
- The Subject: The subject matter involves different English literary works which you will review.
- Reflection Type: I require literature reviews, not personal experiences or critical analyses. This involves understanding and discussing existing research around each assignment's subject matter.
- Assignment Length: Each reflection should exceed 1000 words, indicating a deep engagement with the literturer.
Ideal experts for this task are those with a strong background in English literature and academic writing, demonstrating the ability to deliver scholarly and thorough literature reviews. Familiarity with different English literary works is strongly preferred.
Research Writing Research Article Writing Report Writing Technical Writing
About the project
Place your bid, benefits of bidding on freelancer, 88 freelancers are bidding on average $28 for this job.
I have read and understood all your project details "English Assignment Reflections: Literature Review" and I feel my self the best candidate to complete this project with 100 percent accuracy. I am Faisal Mahmood, I More
Hi there, I will complete your English assignments efficiently in your desired budget. I am an experienced academic research writer. You may visit my profile and portfolio for more satisfaction. Thanks
Hey Hope you are doing great :) I have read your project description. I am a Ph.D.-qualified writer. I will surely assist you in writing 1000 words literature review. I will cover all the points which you have ment More
Hi,with my in-depth knowledge and vast experience in research and technical writing, I am confident in my ability to deliver the precise type of work you require for your English assignment reflections. Demanding a sol More
I am damn sure that I can complete this project "English Assignment Reflections: Literature Review" beyond your expectations and within your given time and budget. I am a specialized writer who has been providing pro More
Hi, I will provide you detailed research literature writing. I am a PhD writer with 10 years of experience. I have worked on several similar projects of literature research, and can deliver professional market resear More
Hi, I have seen your your project details and I am the "BEST CANDIDATE" for this job "English Assignment Reflections: Literature Review". I am Aisha Mujahid, an experienced professional offering comprehensive writing More
I am an expert in writing research papers, English literature review papers and reports ,I have done many English literature review papers and sure can handle your project on English literature. I read your project de More
As someone who has been honing my craft for the past 6 years in the world of writing, I have developed a robust understanding of English literature and academic writing. I've successfully completed over 800 papers, whi More
Hi, I read the requirements for your literature review and confirm that I understand them. I have more than 18 year's experience in academic writing and I have written more than a thousand similar papers. With my exper More
English Assignment Reflections: Literature Review My name is Rabia Faisal, I am working in the writing industry since 2011. During this time, I have served countless clients with a full amount of satisfaction by provi More
English Assignment Reflections: Literature Review My name is "Usama Safdar" and I am a Ph.D degree holder which means I am highly-capable to tackle this project "Content Editor " with 100 percent accuracy. I am a p More
With over five years of experience in academic writing and a keen interest in English literature, I am well-equipped to tackle your project. My familiarity with various English literary works means that I can effortles More
I have 7+ years of experience in the Writing Industry and I can provide you with “SUPREME QUALITY WORK” within your “GIVEN DEADLINE” with “PERFECT GRAMMAR” and “ZERO PLAGIARISM”. I have 100+ "EXCELLENT REVIEWS" which a More
Hello dear, I am a professional writer with over 9 years of experience in the field of writing. I am a professional in providing high quality writing service. I am interested in this project. I have completed many simi More
Hi, I'm offering my services to produce detailed literature review reflections for your English assignments. With a degree in English literature, I'm well-equipped to deliver scholarly reviews exceeding 1000 words each More
Affordable, Early Delivery. ★★★★★★★★★★★★★★I hold a Masters degree which gives me the requisite background to handle writing from various subjects. I am a highly committed person towards my work. You can rely on Qualit More
Using my well-honed writing skills and comprehensive knowledge of English literature, I am confident that I can deliver the exceptional literature reviews you are seeking for your assignments. Over the past 3 years, I' More
Hello, As a versatile and experienced wordsmith, I have acquired an in-depth knowledge of the intricacies of research-based and academic writing. In my prolific career spanning over 8 years, I have catered to diverse More
Greetings, I hope you are good, I bring over a decade of extensive experience as a Lawyer, Patent Attorney, Litigation Writer, Legal Researcher, Thinker, and Writer. My expertise spans various local and international More
Welcome, ! Processing …
Link to existing freelancer account.
The email address is already associated with a Freelancer account. Enter your password below to link accounts:
Link your account to a new Freelancer account
Link to your existing Freelancer account

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others, "standing on the shoulders of giants", as Newton put it.The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.. Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure ...
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
A literature review is important because it: Explains the background of research on a topic. Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area. Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas. Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic. Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
The word "literature review" can refer to two related things that are part of the broader literature review process. The first is the task of reviewing the literature - i.e. sourcing and reading through the existing research relating to your research topic. The second is the actual chapter that you write up in your dissertation, thesis or ...
A literature review is a review or discussion of the current published material available on a particular topic. It attempts to synthesizeand evaluatethe material and information according to the research question(s), thesis, and central theme(s). In other words, instead of supporting an argument, or simply making a list of summarized research ...
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
What kinds of literature reviews are written? Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified.
A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the ...
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other ... find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is ...
Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic. Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these. Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one) Inform your own methodology and research design. To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
Types of Literature Review are as follows: Narrative literature review: This type of review involves a comprehensive summary and critical analysis of the available literature on a particular topic or research question. It is often used as an introductory section of a research paper. Systematic literature review: This is a rigorous and ...
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. Therefore, questions can be raised about the quality and trustworthiness of these types of reviews.
A literature review is a surveys scholarly articles, books and other sources relevant to a particular. issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, providing a description, summary, and ...
Experimental literature review basically refers to surveying all the information available on a particular topic and critically analyzing the gaps that need to be worked upon. In this sense, it essentially forms the first experiment of any research project. The more extensive the review, the more precise and systematic the research project will be.
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
A literature review is defined as "a critical analysis of a segment of a published body of knowledge through summary, classification, and comparison of prior research studies, reviews of literature, and theoretical articles." (The Writing Center University of Winconsin-Madison 2022) A literature review is an integrated analysis, not just a summary of scholarly work on a specific topic.
15 Literature Review Examples. Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal. They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed. Ideally, once you have completed your ...
Steps for Conducting a Lit Review; Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing; APA Style This link opens in a new window; Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window; MLA Style This link opens in a new window; Sample Literature Reviews. Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts; Have an exemplary literature review? Get Help!
2. MOTIVATE YOUR RESEARCH in addition to providing useful information about your topic, your literature review must tell a story about how your project relates to existing literature. popular literature review narratives include: ¡ plugging a gap / filling a hole within an incomplete literature ¡ building a bridge between two "siloed" literatures, putting literatures "in conversation"
Literature search. Fink has defined research literature review as a "systematic, explicit and reproducible method for identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing the existing body of completed and recorded work produced by researchers, scholars and practitioners."[]Review of research literature can be summarized into a seven step process: (i) Selecting research questions/purpose of the ...
@article{Luchang2023ProjectBasedL, title={Project-Based Learning (Pbl) In Enhancing Students' Higher-Order Thinking Skills (Hots): Systematic Literature Review}, author={Alice Laong Luchang and Nurfaradilla Mohamad Nasri}, journal={International Journal of Academic Research in Progressive Education and Development}, year={2023}, url={https ...
Despite the literature emerging from the TIIDE project, that spurred further research, discussion, policy, and procedure, current emergency medical services and non-medical civil practitioners involved in PH MCI response often have to rely on complicated or even outdated procedures, multiple protocols or lack of homogeneity in response methods and guidelines, and technology of the past.
Background Intravenous (IV) medication is commonly administered and closely associated with patient safety. Although nurses dedicate considerable time and effort to rate the control of IV medications, many medication errors have been linked to the wrong rate of IV medication. Further, there is a lack of comprehensive studies examining the literature on rate control of IV medications. This ...
Article Writing & Research Writing Projects for $10 - $30. I am in need of keen freelancers who can produce detailed literature review reflections for my English assignments. - The Subject: The subject matter involves different English literary works which ...