- Preferences


THE URINARY SYSTEM - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
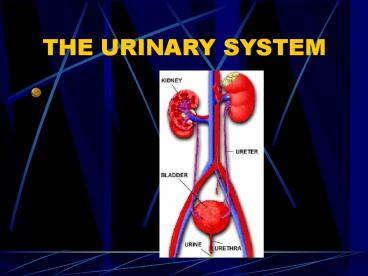
THE URINARY SYSTEM
The urinary system functions of the urinary system 1. excretion removing nitrogenous wastes, certain salts, and excess water from blood 2. – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- 1. Excretion removing nitrogenous wastes, certain salts, and excess water from blood
- 2. Maintain acid-base balance
- 3. Secrete waste products in the form of urine
- Eliminate urine from blodder
- 2 bean shaped organs that are about 4 inches long by 2-3 inches wide by 1 inch thick.
- Left is slightly larger and higher
- Located between peritoneum and the back muscles are protected by the lower ribs (RETROPERITONEAL)
- HILUM indentation along concave medial border is where the lymph vessels, nerves, blood vessels, and ureter enter the kidney
- Blood brought to kidney the renal artery branch off the aorta
- Renal artery subdivides into smaller branches which make contact with nephrons
- Blood leaves via the renal vein which connects to inferior vena cava
- Kidney is divided into 2 regions
- Renal cortex is the outer portion of the kidney
- Renal Medulla contains the tubes in which urine is formed and collected
- Tubes in the medulla form a number of cone-shaped structures call renal pyramids
- Tips of pyramids point toward the renal pelvis a funnel shaped basin that forms the upper end of the ureter
- The base of each renal pyramid faces cortex, while apex empties into cuplike cavities which collect urine called calyces
- Urine that collects in the pelvis, then passes down the ureters to the bladder.
- Functional unit of kidney - urine making units.
- 1 million microscopic units per kidney
- They purify blood by removing waste substances and also control the amount of water and salt in blood
- One tube from each kidney (15 to 18 inches long)
- Carry urine from renal pelvis of kidney to bladder
- One inch of the ureter enters the bladder at an angle
- A full bladder compresses the ureter and prevents the backflow of urine
- Smooth muscle tube with mucus membrane lining
- Urine enters the ureters every 10 to 30 seconds in spurts due to peristaltic movement and gravity
- Muscular sac that receives and stores urine
- Made of elastic fibers and involuntary muscle
- Lines with rugae
- Stores urine usually about 500 cc
- Emptying urine (voiding) is involuntary but controlled through nervous system (voluntary)
- Micturate empty bladder (void, urinate.)
- Canal for the excretion of urine from the body.
- Urine leaves through URETHRA to outside opening URINARY MEATUS
- Female 1 to 1½ inches long urinary meatus located between the clitoris and the vagina
- Male 8 inches long, passes from the bladder through the prostate gland and the penis ot the meatus located at the end of the penis carries both urine and semen
- Renal corpuscle is subdivided into Bowmans capsule and the glomerulus
- Bowmans capsule cup-shaped top of the nephron that surrounds the glomerulus
- Blood flows into the glomerulus through the afferent arterioles and leaves the glomerulus through the efferent arterioles
- In the Glomerulus the high-pressure, leaky capillaries ooze a fluid (glomerular filtrate) similar to blood plasma minus most proteins
- Next 4 segments are known as the renal tubule
- Proximal convoluted tubule filtrate flows here next where the majority of reabsorption takes place via active transport
- Next is the Loop of Henle -note it consists of a straight descending limb, a hairpin loop, and a straight ascending limb
- The Distal Convoluted tubule is a major site of secretion of ions (potassium)
- Collecting tubule straight part of the renal tubule Urine from the collecting tubules exits from the pyramids and enter the calyces and renal pelvic.
- The renal corpuscles and both proximal and distal convoluted tubules are in the cortex of the kidney
- The medulla contains the loop of Henle and collecting tubules.
- 1 Filtration
- 2 Reabsorption
- 3 - Secretion
- First step in urine formation
- Blood from renal artery enters glomerulus
- High blood pressure in glomerulus forces fluid (FILTRATE) to filter into Bowmans capsule
- Filtrate does not contain plasma proteins or RBCs theyre too big
- Bowmans capsule filters out 125cc of fluid/min 7500 cc/hr - 180 liters/day
- As filtrate continues through nephron, 90 of water is reabsorped.
- H20 and useful substances
- are reabsorbed (moves substances out of the urine into the blood)
- Begins in the proximal convoluted tubules and continues in the loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubules, and collecting tubules
- If blood levels of certain substances are high (glucose, amino acids, vitamins, sodium) then those substances will not be reabsorbed (THRESHOLD)
- Opposite of reabsorption (moves substances out of the blood into the urine)
- Secretion transports substances from blood into collecting tubules
- Substances include creatinine, hydrogen ions, potassium ions, and some drugs
- Electrolytes are selectively secreted to maintain acid-base balance
- Average urine output 1500 ml/day
- Anuria absence of urine
- Oliguria scanty amounts of urine
- Polyuria an unusually large amount of urine
- Nocturia frequent urination at night
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.


- Upload Ppt Presentation
- Upload Pdf Presentation
- Upload Infographics
- User Presentation
- Related Presentations

Urinary System
By: Zuriel Views: 1910

Atherosclerosis Is The Liver Disease
By: KhushbuSG Views: 419

Everything You Need to Know About Anxiety- The Depth of Mental Well-being
By: rainbowstart Views: 120

Ophthalmic Anatomy and Physiology
By: yourdoctors Views: 531

What is a Mental Health Disorder
By: rainbowstart Views: 419

Krebs Cycle
By: vvvvvvvvv Views: 3797

- Occupation :
- Specialty :
HEALTH A TO Z
- Eye Disease
- Heart Attack
- Medications
urinary system ppt
All Formats
Resource types, all resource types.
- Rating Count
- Price (Ascending)
- Price (Descending)
- Most Recent
Urinary system ppt
Urinary System PowerPoint and Notes

- Google Apps™

Urinary System - Human Body PowerPoint , Notes and Lab

Urinary or Excretory System Advanced Presentation PPT With Student Summary Notes

Anatomy and Physiology Unit 10: Urinary System Notes & Slides BUNDLE

Digestive and Urinary / Excretory System - Slides & Pear Deck Presentation

- Google Slides™
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 10: Urinary System Editable Slides

URINARY SYSTEM ~Digital Resource for Google Slides ~ ANATOMY

- Internet Activities

Urinary System - drag-and-drop, labeling activity in Slides

Urinary System Slides and Guided Notes

- Google Drive™ folder

Urinary System Google Slide Lecture

Digestive & Urinary Systems Bundle - PowerPoint , Guided Notes, CLOZE, Quiz

Excretory / Urinary System Doodle Notes--- POWER POINT


Urinary System PowerPoint

Test Review | Urinary System NO-PREP Google Slides ™

Urinary System Slide presentation, Study Guide & Test

URINARY SYSTEM - PPT

Disease Presentation - Urinary System Google Slides ™

Urinary System multiple choice Review Game on Google Slides
The Urinary System - Google Slides & Distance Learning Ready

Urinary System - Interactive Google Slide Activities | Distance Learning

Excretion/ Urinary System The Complete Lesson Bundle ( PowerPoint & Assessments)

Urinary and Reproductive Systems PowerPoint and notes for Special Education

Digestive and Urinary / Excretory System - Google Slides Presentation
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

46 templates

suicide prevention
8 templates

49 templates

18 templates

41 templates

29 templates
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
This medical theme has all a health professional can possibly need: visual infographics, charts, tables, icons, graphs… and, of course, the most important: a modern, attractive and unique design in yellow tones! We have dedicated some texts to urinary incontinence, a problem that affects lots of people worldwide, but you can edit the texts and resources if you want to speak about any other illness.
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 26 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Urinary System
Mar 31, 2019
710 likes | 1.14k Views
Urinary System. Consists of: . Kidney(s) Ureters Urinary Bladder Urethra. Functions:. Filter gallons of fluid from bloodstream Filter plasma 60 times/day Responsible for removing: Toxins Metabolic Wastes Excess ions. Regulates volume and chemical make up of blood
Share Presentation
- filtration pressure
- naci h2o water
- h2o naci h2o h2o
- active form
- renal cortex
- naci h2o naci h2o

Presentation Transcript
Consists of: • Kidney(s) • Ureters • Urinary Bladder • Urethra
Functions: • Filter gallons of fluid from bloodstream • Filter plasma 60 times/day • Responsible for removing: • Toxins • Metabolic Wastes • Excess ions • Regulates volume and chemical make up of blood • Maintains the proper pH between water, salts, acids and bases • Maintains blood pH between 7.35 – 7.45
Functions • Regulatory functions include: • Produce hormones Renin and erthropoietin • Renin helps regulate BP and kidney function • Erthropoietin stimulates RBC production in bone marrow • Assists in metabolizing Vitamin D to its active form.
Kidney Anatomy Medulla • Kidneys are covered by fatty tissue; anchors kidneys to posterior wall • Internal Anatomy – 3 distinct regions • Pelvis – where kidneys join ureters; responsible for collecting urine • Renal Cortex – outer region; most of nephrons are found here • Medulla – Middle region; Renal pyramids
Nephron – Working Unit of Kidney; Carry out processes that form urine Cortex Medulla
Nephron • Glomerulus – tuft of capillaries • Parts of Nephron • Bowman’s capsule • Renal Tubule - 3 cm in length • Proximal Convoluted tubule (PCT) • Loop of Henle • Distal Convoluted tubule (DCT) • Collecting Duct
Urine Formation Involves 3 processes Filtration glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule Renal Reabsorption Carried out by renal tubules Secretion Carried out by renal tubules
Glomerular Filtration • Blood enters via afferent arteriole (larger diameter) and leaves via the efferent arteriole • Difference in vessel diameter increases BP in glomerulus and assists with filtration
Podocytes (Bowman’s capsule) – surround capillaries • Passive, nonselective process where fluids and solutes are passed through a membrane • Force is cause by hydrostatic pressure • What caused pressure increase?
GFR (Glomerular filtration rate) is the amount of filtrate produced in the kidneys in one minute. • Renin regulates GFR by causing an increase in blood volume and blood pressure (Constricts blood vessels)
Filtration Pressure – Increase in BP at glomerulus forces water and solutes out of blood and into capsule. • What passes through? What remains in the blood? Filtrate is not Urine
Filtrate contains both wastes and needed water and solutes • Reabsorbion begins as soon as nutrients enters the PCT • All water can’t be excreted, so tubules claim what it needs • Why is it called reabsorption and not absorption?
What is reabsorbed? • 100 % of organic nutrients • Most electrolytes by facilitated diffusion • Water is passively reabsorbed • 60 – 70 % of fluid is reaborbed by PCT Rate and degree of reabsorption is regulated by hormones Problems: Hyperglycemia
Where does Reabsorption occur in the nephron? • PCT are most active reabsorbers • The descending loop of Henleis permeable to water but not solutes • The ascending loop of Henleis impermeable to water and most solutes • Na and Cl are actively reabsorbed into the blood stream • DCT is impermeable to solutes • Reabsorption of Na, K, and water is controlled by hormones
Milliosmols Na+ (65%) Glucose Amino acids H2O (65%) and many ions (e.g. Cl– and K+) Cortex (d) (a) 300 (e) Outer medulla (b) (c) 600 Some drugs HCO3– H+, NH4+ Inner medulla Blood pH regulation (a) Proximal convoluted tubule: • 65% of filtrate volume reabsorbed • Na+, glucose, amino acids, and other nutrients actively transported; H2O and many ions follow passively • H+ and NH4+ secretion and HCO3–reabsorption to maintain blood pH • Some drugs are secreted 1200 Active transport (primary or secondary) Passive transport Figure 25.18a
Reabsorption (b) The descending loop of Henle • Freely permeable to H2O • Not permeable to NaCl or other solutes • Filtrate becomes increasingly concentrated as H20 leaves by ____________? Active transport (primary or secondary) Passive transport
Milliosmols Cortex Na+ (d) Cl– (a) K+ 300 (e) Outer medulla (b) Urea Na+ (c) Cl– 600 Inner medulla (c) Ascending limb of loop of Henle • Impermeable to H2O • Permeable to NaCl • Filtrate becomes increasingly dilute as salt is reabsorbed 1200 Active transport (primary or secondary) Passive transport Figure 25.18c
Osmolality of interstitial fluid (mOsm) Filtrate entering the loop of Henle is contains many substances that are needed in the body H2O NaCI Cortex Active transport Passive transport NaCI H2O Water impermeable NaCI H2O NaCI H2O The descending limb: • Permeable to H2O • Impermeable to NaCl As filtrate flows, it becomes increasingly concentrated as H2O leaves the tubule by osmosis. The filtrate osmolalityincreases. Outer medulla H2O NaCI H2O H2O Inner medulla Loop of Henle The ascending limb: • Impermeable to H2O • Permeable to NaCl Filtrate becomes increasingly dilute as NaCl leaves, eventually becoming hypo-osmotic to blood . NaCl leaving the ascending limb increases the osmolality of blood. Figure 25.16a
What’s left in the nephron? • Non-reabsorbed substances are: • Urea – 50 % is reclaimed; the rest is waste • Creatinine – a large lipid; insoluble molecule that is not reabsorbed at all • Uric Acid – 50 % is reclaimed; waste product of RNA synthesis
Tubular Secretion – “Reabsorption in Reverse” • Urine is formed from filtered and secreted substances • Secretion occurs in the DCT tubules and collecting ducts • Hormones assist with this process • ADH (antidiuretic hormone) • Aldosterone • ANP
Na+; aldosterone-regulated Ca2+; PTH-regulated Cl–; follows Na+ Milliosmols Cortex (d) (a) 300 (e) Outer medulla (b) (c) 600 Inner medulla (d) Distal convoluted tubule • Na+reabsorption regulated by aldosterone • Ca2+reabsortion regulated by parathyroid hormone (PTH) • Cl–cotransported with Na+ 1200 Active transport (primary or secondary) Passive transport Figure 25.18d
Milliosmols Cortex H2O regulated by ADH (d) (a) 300 Regulated by aldosterone: Urea; increased by ADH (e) Na+ Outer medulla (b) K+ Blood pH regulation (c) 600 H+ HCO3– Inner medulla NH4+ 1200 (e) Collecting duct • H2O reabsorptionregulated by ADH • Na+reabsorption and K+ secretion regulated by aldosterone • H+ and HCO3–reabsorption or secretion to maintain blood pH • Urea reabsorption increased by ADH Why? Active transport (primary or secondary) Passive transport Figure 25.18e
Substances that are not reabsorbed • Substances that lack carry proteins along membrane • Urea • Uric acid • Substances that are not lipid soluble • Substances that are too large to pass • Creatinine
1 Label the parts of the nephron Describe what is occurring at sections 1-6. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 5 2 6 4 3
Hormonal Control of Secretion • Osmolarity – number of solute particles dissolved in one liter of water Affects osmosis • Kidneys are responsible for regulating solute concentrations in the body; the concentration of urine is regulated by hormones • Four Hormones Control Kidney Function • Renin • Aldosterone • AtrialNatiuretic Peptide (ANP) • Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Renin • Released when glomerular pressure is low • Causes blood vessels to constrict; raising blood pressure in arteries • The efferent arteriole constricts which increases glomerular pressure • Stimulates secretion of ADH and aldosterone
Aldosterone • Released by adrenal glands • When secreted causes Na+to be reabsorbed from DCT • H20 follow Na+, so both Na+ and H2O are reabsorbed • Eliminates K+ into urine • Stimuli that cause the release of aldosterone • Decreased blood volume • Decreased sodium in blood • Increased potassium in blood (heart block)
If too much aldosterone is secreted:- Excessive Na+ and H20 retention (edema, hypertension- Accelerated secretion of K ions (muscle responsiveness)
Lasix – (Diuretic) inhibits Na from being reabsorbed; thus water is not reabsorbed.
AtrialNatiuretic Peptide (ANP) • Works against aldosterone • Released by atrial cardiac cells when blood volume and BP are too high. • Why would the atrial cells detect a change in blood volume? • When ANP is secreted: • CausesNa+ to be dumped into tubules (urine) • H2Ofollows sodium into urine • Capillaries in glomerulus dilate; increasing blood flow to Bowman’s capsule; increasing UO • Inhibits the secretion of renin, aldosterone and ADH • Urine contains more Na+H2O; blood pressure and blood volume decrease
ADH (Antiduretic hormone) • When ADH is secreted, water is reabsorbed from DCT and collecting tubules • Person feels thirsty • When ADH is not secreted, DCT and collecting tubules are impermeable to water, no reabsorption occurs here.
Concentration of Urine is controlled by ADH • Dilute Urine • Na and other ions are removed from filtrate • Urine appears clear in color • Concentrated Urine • ADH is secreted; distal and collecting tubules reabsorb water • When water leaves filtrate; urine concentration increases Without use of hormones, DCT and collecting duct are relatively impermeable to water and sodium
Work of the Nephron with Hormone Secretion
Diuretics – chemicals which increase UO • Any substance that is not reabsorbed and carrries water out of body • Alcohol – inhibits ADH • Caffeine – Increases filtration rate (GFR) • Diuretic drugs are taken for CHF, edema and to increase UO
Active transport Passive transport Collecting duct Descending limb of loop of Henle DCT Cortex NaCI H2O NaCI Outer medulla NaCI Urea H2O Inner medulla Large volume of dilute urine (a) Absence of ADH Figure 25.17a
Maintaining a Balance • Other Systems assist in excretion and affect kidney function • Integumentary • Respiratory • Digestive • Fluid and Electrolyte Balance • Water into body = Water out of the body • Neither a net gain or loss of electrolytes should occur in body • Acid-Base Balance • Blood pH ranges between 7.35 – 7.45 • Kidneys will secrete H+ ions when blood pH drops
Imbalances • Acidosis – Blood pH drops below 7.35 • Respiratory Acidosis • Due to an increase of CO2 levels in body • Metabolic Acidosis • Due to cell metabolism in the body • Lactic acid in muscle metabolism • Ketone bodies by the breakdown of fat • Diabetics don’t use glucose due to lack of insulin; so cells will break down fat instead Blood ph < 7.05 disrupts the stability of cell membrane, alters protein function (enzyme), causes heart arrhythmias and leads to coma
Kidney Stones • Hardened mineral deposits that form in kidney • Symptoms • Blood in urine • Increased need to go • Nausea and vomiting • Pain during urination • Tenderness in abdomen and kidney region • Treatment • Lithotripsy • Medication
Renal Failure – Kidney Failure • Nephrons in kidney stop functioning • Unable to filter or excrete waste • Can’t regulate composition of body fluids • Can’t control erythrocyte function or blood pressure • Can’t control salt balance
- More by User

Urinary System. Functions of Urinary System. Filter Blood Regulation of Blood Volume/Pressure [renin] Regulation of the solute concentration of the Blood: Na + , Cl - , K + , Ca +2 , HPO 4 -2 pH regulation of extracellular fluid Regulation of RBC synthesis [erythropoietin]
865 views • 28 slides

Urinary System . Mrs. Atchison HS I. 4.01 Remember the structures of the urinary system Essential Question. What are the structures of the urinary system?. Urinary System. Functions of Urinary System: Excretion- removing nitrogenous wastes, certain salts and excess water from blood.
1.63k views • 81 slides
Urinary System. Chapter 25. urinary bladder. Urinary System. Two kidneys. Two ureters. Urethra. Functions of the Kidneys. Filters blood plasma, eliminates waste, returns useful chemicals to blood Regulates blood volume and pressure Secretes aldosterone controls BP, electrolyte balance
732 views • 28 slides

Urinary System. FUNCTIONS. MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS OF pH, COMPOSITION AND VOLUME OF BODY FLUIDS REMOVES: METABOLIC WASTE, EXCESS MATERIAL, FOREIGN SUBSTANCES (DRUGS). PARTS. KIDNEYS URETER S URINARY BLADDER URETHRA FUNCTIONS?. http://miyessence.files.wordpress.com/2006/12/urinary.jpg.
649 views • 51 slides

Urinary System . Introduction • The urinary system rids the body of waste materials and controls the volume and composition of body fluids. . Endocrine and Synthetic functions. EPO Controls RBC production from stem cells in marrow
422 views • 27 slides

Urinary System. Yes. We ARE serious. Please stop laughing. By: Kirk Risher Matt Phillips Sikandar Raza Ian Smith. Function of the Urinary System. You Urinary system is made up of four organs that produce, store, and obliterate wastes. It cleans blood & maintains the body’s water levels.
240 views • 10 slides

Urinary System. Josh Whiteside, Tori Stanley, Kristian DeVito. Bladder. Bladder - Organ that stores urine after its formation by the kidneys. It consists of three layers: a lining of mucous membrane. Kidney. Kidneys.
245 views • 7 slides

Urinary System. Sanjaya Adikari Department of Anatomy. Urinary system comprises of Two kidneys Two ureters Bladder Urethra . 12. 6. Position and size of the kidneys. Retro-peritoneal Size 12 x 6 x 3 cm Weighs about 130 g Hilum is 5 cm from midline. Position and size …. Back.
820 views • 54 slides
Urinary System. As the Urine Flows. Functions of the Urinary System. Excretion- removing nitrogenous wastes, certain salts and excess water from blood. Maintain acid-base balance Secrete waste products in the form of urine Eliminate urine from bladder. Kidneys. Bean shaped organs
326 views • 14 slides
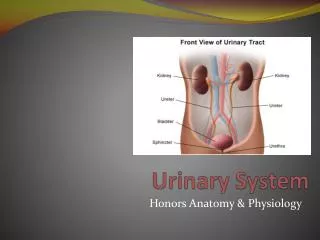
Urinary System. Honors Anatomy & Physiology. Kidneys. Filter 200L of fluid from blood excreting waste as urine Regulate blood volume, balance water & salts, pH Secretes renin (BP) & erythropoeitin (EPO) Renal Cortex – superficial (light)
262 views • 8 slides
Urinary System. Ch 25. Function. Remove nitrogenous wastes Maintain electrolyte, acid-base, and fluid balance of blood Homeostatic organ Acts as blood filter Release hormones: calcitriol & erythropoietin. Kidneys as Filters. Diuretic- lose water; coffee, alcohol
809 views • 54 slides

Urinary system
Urinary system. Tutorial. Antibody mediated glomerular disease. B - linear pattern C - granular pattern. Causes of the nephrotic syndrome. Proteinuria> 3.5 g of urinary protein:hypoalbuminaemia <3g/dl: oedema, hyperlipidaemia and lipiduria. A – minimal change B – membranous GN.
418 views • 27 slides

Urinary system. What is the urinary system?.
233 views • 15 slides

1) The average person pees about 3000 times a year. 2) Most people, on average, would breath about 6,286,920 times a year. 3) The human intestine is usually 27 feet long and 10 inches. (8.5 meters long) .
353 views • 34 slides

Urinary System. The Urinary System. Function. Remove nitrogenous wastes Maintain electrolyte, acid-base, and fluid balance of blood Homeostatic organ Acts as blood filter Release hormones: calcitriol & erythropoietin. Kidneys as Filters. Diuretic- loose water; coffee, alcohol
580 views • 54 slides

Urinary System. Introduction. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
257 views • 21 slides

Urinary System. Major Parts of the Machine. food, water intake. oxygen intake. Based on: Starr, C., Biology: Concepts and Applications , Brooks/Cole. elimination of carbon dioxide. Digestive System. Respiratory System. nutrients, water, salts. oxygen. carbon dioxide.
297 views • 25 slides

Urinary System. Dr. Manodeep Chakraborty. Urinary system is the main excretory system and consists of following structures Kidneys (2) : Secretes urine Ureters (2) : Convey the urine from the kidneys to urinary bladder Urinary bladder : Where the urine collects and is temporarily stored
196 views • 16 slides
Urinary system. Anatomical structure. The kidney present in the lower back of t the abdominal wall. Adrenal gland. kidney. ureter. Urinary bladder. urethra. The nephrone. Bowman’s capsule. and glomerulus. The nephrone. Nepherone. Its small functional unit, which is equal
197 views • 13 slides

Urinary System. Four major structures Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra. Kidneys Organ that produces urine Performs other functions Contains nephrons microscopic structure that produces urine. Left kidney lies in the upper ABD behind the spleen
365 views • 31 slides

Urinary System. Urinary System Functions. Remove salts and nitrogenous waste Maintain water and electrolyte concentration Regulate pH and volume of fluids Help control RBC production by secreting erythropoieten Made of Kidneys-filtering units
451 views • 13 slides

Urinary System . SPECIAL THANKS: Dr. Ali Mohammed PhD 427 histology team. HISTICS: Bilal M. K. Marwa AbdulWahhab Idrees Sarah Al-Morit نبع الوفاء. Urinary System. Consists of :- Two kidneys Two ureters Urinary Bladder Urethra. The kidney. The kidney consists of:- Outer cortex
767 views • 25 slides

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Anatomy of Urinary system simplified for Nursing students. Health & Medicine. 1 of 42. Download Now. Download to read offline. Urinary System Anatomy - ppt - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
The ureters are tubes that carry urine from the pelvis of the kidneys to the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder temporarily stores urine until it is released from the body. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body. • 1) urea (a nitrogenous waste produced in the liver from the breakdown ...
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to form urine. The urine travels from the kidneys down the ureters to the urinary bladder, where it is stored until urination. During urination, the bladder contracts and the urethra carries the urine out of the body.
Presentation Transcript. The Urinary System • Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra • Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra • Filter the blood and return most of water and solutes to the bloodstream. Overview of Kidney Functions • Regulation of blood ionic composition ...
PK !ÌÑ•/ " [Content_Types].xml ¢ ( Ę]o›0 †ï'í? ßNÁ¡Ûºv éÅ>®öQ©Ý ðà@¼ Û² ¬ù÷;@šQD—¦Žå›HÆœó>Ç ûå,®î 'lÀX®dN²tN …*¹¬sòãöóì‚$Ö1Y2¡$äd -\-_¾XÜn5Ø £¥ÍÉÊ9ýžR[¬ a6U $ÎTÊ4ÌáÐÔT³â7« žÍçç´PÒ t3×æ ËÅG¨ØZ¸äÓ ^îI~i¨Iò¡¿±ÕÊ oÚ Ý Œ1 ì(†i-xÁ VG7² 'ÍvT)Fv÷Ø ×ö ¢"i…væ!ÔPàñ ...
It begins at the neck of the urinary bladder by the internal urethral orifice (or internal urinary meatus). It opens into the vestibule of vagina by the external urethral orifice (or external urinary meatus). It has two parts: 1. intramural part (corresponds with the neck of bladder); 2. perineal part (which pierces the perineum).
Slide 5-. The urinary system is the main excretory system and consists of the following structures: 2 kidneys, which secrete urine. 2ureters that convey the urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. the urinary bladder, which collects and stores urine. the urethra through which urine leaves the body.
Title: Anatomy of the Urinary System. 1. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Organ System Cluster. Prepared by Maria Michaela Valenzuela, PTRP. 2. LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Enumerate the organs of the urinary system. Describe the essential gross features of each.
Presentation Transcript. Physiology of the Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Major Nitrogenous Wastes Formation of Urine Filtration Reabsorption Secretion. Functions of the Urinary System • Remove waste products from blood • Maintain water balance • Maintain salt balance • Regulate blood pressure. Major Nitrogen-containing ...
The urinary system, also known as the excretory system , is responsible for removing certain wastes and excess water from the body It also maintains the body's acid-base balance. 383 views • 14 slides. Urinary System. Urinary System. Chapter 13 A&P1 Tutor: Eleshia Howell. The urinary system is the main excretory system, removing the ...
THE URINARY SYSTEM. Description: THE URINARY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM 1. Excretion removing nitrogenous wastes, certain salts, and excess water from blood 2. - PowerPoint PPT presentation. Number of Views: 2380. Avg rating:3.0/5.0. Slides: 21.
Slide 1-. Eurydice Cardona THE URINARY SYSTEM. Slide 2-. The urinary system: its functions and its organs The urinary system, also referred to as the genitourinary system (abbreviation GU), is responsible for filtering waste products out of the blood and removing them from the body. It is also responsible for adjusting water and electrolyte ...
What we'll talk about... Components of the urinary system. The kidney performs several critical functions. Nephrons filter blood and reabsorb solutes and water. The kidney contains two types of nephrons to filter blood and regulate electrolyte concentration and pH. Arcuate arteries define the border between cortex and medulla in the kidney.
THE URINARY SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS OF NEPHRON. THE URINARY SYSTEM STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS OF NEPHRON . LECTURE - 1 Dr. Zahoor. Urinary System. Consists of Urine forming organs kidneys Structures that carry urine from the kidneys to the outside for elimination from the body Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra . Urinary System. 655 views ...
11. $3.00. PPTX. This is a 35 slide PowerPoint that covers the Urinary System. It discusses the purpose of the urinary and describes the four main parts of the urinary system: the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It also lists some common problems people may have with their urinary system.
Histology of the Urinary System. Lecture Objectives. Describe the normal microscopic appearance of the different parts of the kidney including cortex, medulla, juxtaglomerular apparatus and the distribution of the vasculature within the kidney. Slideshow 8912761 by rsanford.
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. This medical theme has all a health professional can possibly need: visual infographics, charts, tables, icons, graphs… and, of course, the most important: a modern, attractive and unique design in yellow tones! We have dedicated some texts to urinary incontinence, a problem that affects lots ...
Urinary System. Health & Medicine. 1 of 52. Download Now. Download to read offline. Urinary system - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Presentation Transcript. Urinary System. Consists of: • Kidney (s) • Ureters • Urinary Bladder • Urethra. Functions: • Filter gallons of fluid from bloodstream • Filter plasma 60 times/day • Responsible for removing: • Toxins • Metabolic Wastes • Excess ions • Regulates volume and chemical make up of blood • Maintains ...