- Insert a picture in PowerPoint Article
- Edit pictures Article
- Add SmartArt to a slide Article
- Put a background picture on your slides Article
- Add a background picture to slides Article
- Use charts and graphs in your presentation Article
- Insert icons in PowerPoint Article


Use charts and graphs in your presentation
You can make a chart in PowerPoint or Excel. If you have lots of data to chart, create your chart in Excel , and then copy it into your presentation . This is also the best way if your data changes regularly and you want your chart to always reflect the latest numbers. In that case, when you copy and paste the chart, keep it linked to the original Excel file .
To create a simple chart from scratch in PowerPoint, click Insert > Chart and pick the chart you want.

Click Insert > Chart .
Click the chart type and then double-click the chart you want.
Tip: For help deciding which chart is best for your data, see Available chart types .
In the worksheet that appears, replace the placeholder data with your own information.

When you’ve finished, close the worksheet.
Create an org chart in PowerPoint
Create charts in Excel

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
Jazz Up Your Presentation: 6 Ways to Put an End to Ugly Charts and Graphs
Updated on: 22 December 2020

People often add charts and graphs to their presentation trying to make it more interesting. Unfortunately, most efforts to make it unique usually end up having the exact opposite effect.
Often, the enormous collection of slides with colorful presentation charts and graphs blows up your brain by the end of the presentation rather than arousing your interest in the data. You don’t want to be the person who puts his audience through this agonizing experience every time you fire up your laptop.
So, is there a way to jazz up your presentation with beautiful charts and graphs?
The short answer to this question is ‘Yes.’ Here are 6 ways to improve your presentation charts and graphs to effortlessly strengthen your message.
Refrain from Using Backgrounds
When it comes to decorating the graph background, you should avoid using gradients of color or varying the background color in any other way.
It not only undermines your ability to present the data unambiguously but also adds distraction. The context surrounding an object often influences our perception of it.

See the two graphs above, the grey background in the left graph doesn’t provide any information. On the contrary, it doesn’t contrast sufficiently with the object. As a result, it undermines the visibility of the objects in the graph. So, make sure the background is consistent with the slide background.
If you always use the default slide background, you should use ‘No Fill’ ‘or White’ background color as it matches the slide background.
Eliminate Redundant Labels
Why do you want to waste the space on redundant labels? Most graphs charts are quite self-explanatory. Repeated axis labels and legend are the two things that occupy the space for no reason.
In fact, they are taking up space that would be better spent on the graph. So, make sure to remove duplicate labels. The graph on the right looks better than the original graph to the left, as it is much easier to understand.

Alternatively, you can also label the bars directly. However, if you do, remove the Y-axis completely. As the exact value of each element is displayed, you don’t need to use the grid lines either.

Mind the Border Formatting
When it comes to graphs and charts, less is more. You should format the graph background to reduce the lines as far as possible while retaining the meaning of the data presented in it.
Though the default gridlines and borders are a sensible choice, they are a distraction as your audience is most likely not interested in knowing the exact figures for each data point.
If you want to display exact values, label the bars directly as discussed in the previous point. Removing the lines highlights the data and the pattern dramatically. So, remove all of the outer borders as well as grid lines as shown below.

Use Colors Meaningfully
Contrary to the popular belief, you should avoid using bright colors for presentation charts and graphs as far as possible. In fact, you should use natural colors to display general information and use the bright color only to highlight information that demands attention.
Using same colored bars on a graph makes it easier to compare the data. Use different colors only if they correspond to different elements in the data.
Sometimes, however, you can use different colors to highlight particular data or assemble different parts. In other words, you need to use colors meaningfully and with caution. The following examples will help explain the points mentioned above.
A) Using Natural Colors for Easier Comparison

B) Using Bright Colors to Pop Important Data

C) Using Different Colors to Point out Differences in Data Elements

Avoid Using Special Effects (Shadowing and Shading)
Avoid using special effects such as shadowing, shading, and 3D effects when creating presentation charts and graphs, especially for professional purposes. They just make it hard to compare the elements and confuse the reader.
You should, however, stick to presenting only essential information. So, keep it simple and avoid flashy special effects.

Text and Font
Using bold font isn’t going to make much difference in your graph. As far as possible, avoid using bold, underline or italic fonts. Keep the font size and type consistent throughout the presentation.
Avoid effects such as shading, outline, and 3D letters. Always lighten secondary data labels. The less you format the better.

Have More Tips for Creating Better Presentation Charts and Graphs?
When it comes to creating an attention-grabbing presentation , the rule of thumb is to display the data in a simple and clear way.
With the help of these 6 tried and tested tips, your presentation charts and graphs will look phenomenal without compromising your data. What about you? What tricks have you used to make your graphs look unique? Feel free to share your ideas and suggestions in the comments box below.
About the Author
Swati Kapoor is a qualified dietitian at Practo . She has a Masters degree in Dietetics and Food Service Management. She is a strong believer in spreading the goodness of ‘nutrition through healthy eating’. As a responsible dietitian, Swati examines her patients’ health history carefully before recommending any diet or workout regimen, because everybody has different requirements.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.

More Related Articles

Leave a comment Cancel reply
Please enter an answer in digits: 5 × three =
Download our all-new eBook for tips on 50 powerful Business Diagrams for Strategic Planning.
Home Blog Design How to Make a Presentation Graph
How to Make a Presentation Graph

Visuals are a core element of effective communication, and regardless of the niche, graphs facilitate understanding data and trends. Data visualization techniques aim to make data engaging, easy to recall and contextualize while posing as a medium to simplify complex concepts .
In this article, we’ll guide you through the process of creating a presentation graph, briefly covering the types of graphs you can use in presentations, and how to customize them for maximum effectiveness. Additionally, you can find references on how to narrate your graphs while delivering a presentation.
Table of Contents
What is a Presentation Graph?
Types of graphs commonly used in presentations, how to select a presentation graph type, design principles for effective presentation graphs, working with presentation graph templates, integrating the graph into your presentation, common mistakes to avoid when making a presentation graph, final words.
A presentation graph is a visual representation of data, crafted in either 2D or 3D format, designed to illustrate relationships among two or more variables. Its primary purpose is to facilitate understanding of complex information, trends, and patterns, making it easier for an audience to grasp insights during a presentation.
By visually encoding data, presentation graphs help highlight correlations, distributions, and anomalies within the dataset, thereby supporting more informed decision-making and discussion.
Various types of graphs are commonly used in presentations. Each type serves specific purposes, allowing presenters to choose the most suitable format for conveying their data accurately. Here, we’ll discuss some common examples of presentation graphs.
Check our guide for more information about the differences between charts vs. graphs .
A bar chart is a visual tool that represents data using horizontal bars, where the length of each bar correlates with the data value it represents. This type of chart is used to compare discrete categories or groups, highlighting differences in quantities or frequencies across these categories.
For more information check our collection of bar chart PowerPoint templates .

Column Graphs
Column graphs are a variation of bar charts. They display data through vertical columns, allowing for comparing values across different categories or over time. Each column’s height indicates the data value, making it straightforward to observe differences and trends.

Line Graphs
Line graphs depict information as a series of data points connected by straight lines. They are primarily used to show trends over time or continuous data, with the x-axis typically representing time intervals and the y-axis representing the measured values. Line graphs highlight the rate of change between the data points, indicating trends and fluctuations.
For more information check our collection of line chart PowerPoint templates .

Circle Graphs
Circle graphs, commonly known as pie charts or donut charts, present the data distribution as fractions of an entity. They provide a quick understanding of the relative sizes of each component within a dataset. Pie charts are particularly effective when the goal is to highlight the contribution of each part to the whole data.
For more information check our collection of circle diagram templates .

Area Graphs
Area graphs are similar to line graphs, but the space below the line is filled in, emphasizing the volume beneath the curve. They represent cumulative totals over time through the use of sequential data points, making it easier to see total values and the relative significance of different parts of the data.
For more information check our collection of area chart PowerPoint templates .

Cone, Cylinder, and Pyramid Graphs
Three-dimensional graphs, such as cones, cylinders, and pyramids, create a dynamic visual impact on presentations. While not as common as the other types, they are used for their ability to add depth and dimension to data representation. These graphs create a visually engaging experience for the audience, although sometimes they sacrifice accuracy for the sake of visuals.
For more information check our collection of pyramid diagram PowerPoint templates .
As a presenter, you must be aware of both the topic’s requirements to discuss and your audience’s needs. Different graphs fulfill distinct purposes, and selecting the right one is critical for effective communication.
Line Graphs for Trends Over Time
A line graph is effective when you want to present trends or changes over a continuous period, like sales performance over months. Each point on the line represents a specific time, offering a clear visual representation of the data’s progression.
Bar Graphs for Comparing Quantities
If your goal is to compare quantities or values across different categories, such as sales figures for various products, a bar graph is suitable. The varying lengths of bars make it easy to compare the magnitudes of different categories.
Pie Charts for Showing Proportions
Use pie charts when you want to illustrate parts of a whole. For example, to represent the percentage distribution of expenses in a budget, a pie chart divides the total into segments, each corresponding to a category.
Follow these guidelines to create your presentation graph for the data you intend to represent.
How to Make a Presentation Graph in PowerPoint
Start by opening your presentation slide deck. For this tutorial’s purpose, we’ll work with a blank slide.

Switch to the Insert tab and click on Chart .

A new dialogue window will open, where you have to select the chart type and the specific representation type—i.e., for area charts, you can choose from 2D or 3D area charts and their distribution method.

If you hover over the selected chart, it will zoom in to check the details. Double-click to insert the chosen graph into the slide.

As we can see, a spreadsheet to edit the data is now available. If you accidentally close it, go to Chart Design > Edit Data.

Replace the data in the numbers to reflect the data you need to showcase. The columns’ titles indicate the text the legend shows for each series. Then, we can close the spreadsheet and continue customizing it.

By clicking on the paintbrush, we access the Style options for the graph. We can change the background color, layout style, and more.

If we switch to the Color tab inside of Style , we can modify the color scheme for the presentation graph. And as simple as that is how to make a graph in PowerPoint.

How to Make a Presentation Graph in Google Slides
Now, let’s see how to create a graph in Google Slides. We start once again from a blank slide.

Go to Insert > Chart . Select your desired presentation graph option. In our case, we will work with a Pie Chart.

To change the placeholder data, click on Edit Data .

If you missed the emergent tab, you can go to the three points in the graph, click on them, and select Open Source .

The graph will most likely cover the data spreadsheet, so move it to one side to see the entire data range. In this case, the auto-generated graph is wrong as the sum gives 110%. We’ll correct that now.

And this is how it looks with the corrected data.

Next, we click on the three dots on the chart and select Edit the Chart . This shall open all customization options.

At the Setup tab, we can change the chart style and select from various options.

The data will refresh in that case and adapt its representation to the new style.

If we switch to the Customize tab (it says Customise, as the selected language is UK English), we can fine-tune our presentation graph starting from the background color.

Activate the 3D checkbox to change to a 3D pie chart (applicable to any graph).

We can find tailored settings for the Pie Chart to convert it to a donut chart, with settings like the donut hole size.

The Pie Slice section helps us change the color scheme for each one of the slices.

We can change the title and axis titles in the Chart and axis titles section.

Finally, the Legend section offers many customization options to alter the legend’s format.

Once the customization process is completed, close the Google Spreadsheets tab, go to your presentation chart, and click Update .

Google Slides will refresh the data for your created presentation graph with the last synced data.

Adhering to certain design principles is imperative for creating graphs and communicating information effectively.
Simplicity and Clarity
A graph should be clean and free from unnecessary details. Clear graphs have visible data points and helpful short texts for better understanding. Even if it looks simple, it can still show important information. To make it easy to understand, avoid adding distortions, shading, weird perspectives, too many colors, unnecessary decorations, or 3D effects [2]. It is also essential to ensure the plotted data points are clear, not hidden or covered.
Use of Color and Contrast
Thoughtful use of color and contrast enhances visual appeal and distinguishes different elements within the graph. Colors can effectively improve the chart presentation in three ways: highlighting specific data, grouping items, and encoding quantitative values. However, do not use fancy or varying colors in the background. We suggest resisting decorating graphs excessively, as it can hinder clear data presentation [4]. Only use different colors when they highlight important differences in the data.
Labeling and Legends
Accurate labeling is crucial to provide context and understanding. While designing graphs, we don’t expect the viewer to guess. Instead, we clearly label titles and axes. Clear labeling means displaying both axes on your graph, including measurement units if needed. Identify symbols and patterns in a legend or caption [3]. Legends explain symbols and patterns in a graph.
Scale and Proportion
For more clarity, we keep the measurement scales consistent and avoid distortions for accuracy. This ensures the exact difference between all the values. It will present data relationships and prevent misinterpretation due to skewed visual perceptions.
Tips for Customizing Graphs
PowerPoint provides various customization options—Right-click on elements like axes, data points, or legends to format them. You can also change colors, fonts, and styles to match your presentation’s look.
Coloring Your Data
When you want to make different parts of your chart stand out, click on a bar or line. Then, right-click and choose “Format Data Series.” Here, you can pick a color that helps each set of data pop. Do this for each part of your chart to make it visually appealing.
Changing the Chart Background
If you want to change the background color around your chart, right-click on the white space. Choose “Format Chart Area” and change the background color to something that complements your data.
Customizing Line Styles
Change the appearance of your lines for a unique look. Click on a line in your chart, right-click, and select “Format Data Series.” Experiment with different line styles, such as solid, dashed, or dotted.
Fine-tuning Axis Appearance
To make your chart axes look polished, right-click on the X or Y axis and choose “Format Axis.” Adjust properties like line color, tick marks, and label font to suit your design.
Perfecting Legends
Legends can be tweaked for a more integrated look. Right-click on the legend, select “Format Legend,” and adjust options like placement, font size, and background color to enhance the overall appearance.
Creating graphs in PowerPoint or Google Slides from scratch can be time-consuming, and ultimately, it won’t yield the same results as professional-made designs. We invite you to discover some cool designs for presentation graphs PPT templates made by SlideModel.
1. Dashboard Presentation Graph for PowerPoint & Google Slides

Don’t worry about how to make a graph in PowerPoint – let’s us bring the resources in the shape of a cool dashboard layout. Ideal for any kind of e-commerce business, you can track expenses or income, evaluate metrics, and much more.
Use This Template
2. Infographic Donut Chart Presentation Template

Explain concepts in different hierarchy levels, or processes that require a set of sequential steps by implementing this donut chart PPT template. Each segment has a bubble callout to expand further information for the areas required.
3. Presentation Graph Slide Deck PPT Template

All that’s required to create a data-driven presentation is here. Customize donut charts, funnels, histograms, point & figure charts, and more to create professionally-designed presentation slides.
4. PowerPoint Charts Slide Deck

If you’re looking for clean layouts for column graphs, area charts, line graphs and donut charts, this is the template you need in your toolbox. Perfect for marketing, financial and academic reports.
Consider its relevance to the content when incorporating your graph into the presentation. Insert the graph in a slide where it logically fits within the flow of information.
Positioning the Graph Appropriately in the Presentation
Deciding where to put your graph in the presentation is essential. You want it to be where everyone can see it easily and where it makes sense. Usually, you place the graph on a slide that talks about the data or topic related to the graph. This way, people can look at the graph simultaneously when you talk about it. Make sure it is not too small. If needed, you can make it bigger or smaller to fit nicely on the slide. The goal is to position the graph so that it helps your audience understand your information better.
Ensuring Consistency with the Overall Design of the Presentation
Align the graph with the overall design of your presentation to maintain a cohesive visual appeal. You can use consistent colors, fonts, and styles to integrate the graph seamlessly. The graph must complement the theme and tone of your slides. Therefore, you should avoid flashy or distracting elements that may deviate from the established design. The goal is to create a harmonious and professional presentation where the graph blends naturally without causing visual disruptions. However, we recommend you use bar chart templates already available for presentation.
Narrating Your Graph
When explaining your graph during the presentation, start by providing context. Clearly state what the graph illustrates and its significance to the audience. Use simple and direct language, avoiding unnecessary jargon. It is important to walk through the axes, data points, and any trends you want to highlight. Speaking moderately allows the audience to absorb the information without feeling rushed. You can take pause when needed to emphasize crucial points or transitions.
You can learn more about creative techniques to narrate your graph in our data storytelling guide.
Overloading with Information
One common mistake is presenting too much information on a single graph. Avoid filling the graph with excessive data points or unnecessary details.
Misleading Scales or Axes
Scale mistakes, such as uneven intervals or a bar chart with zero baselines, are common graphical mistakes [5]. Misleading scales can distort the interpretation of the graph and lead to incorrect conclusions. Scales should accurately present the data without exaggerating certain aspects.
Inappropriate Graph Types for the Data
Selecting an inappropriate graph type for your data is a mistake to avoid. Choose a graph type that effectively communicates the nature of your data. For instance, a pie chart for time-based trends might not be the most suitable choice. Match the graph type to the data characteristics to convey information accurately.
Working with presentation graphs may feel challenging for a beginner in presentation design software. Still, practice makes the master. Start by clearly stating your objectives in terms of data representation—this will make the presentation graph-type selection process much easier. Customize the graph by working with appropriate color combinations (you can learn more about this in our color theory guide), as this can also help highlight relevant data sections that may influence an informed decision.
Everything depends on your creative skills and how you want to showcase information. As a final piece of advice, we highly recommend working with one graph per slide, unless you opted for a dashboard layout. Ideally, graphs should be seen from a distance, and working with reduced sizes may hinder accurate data representation.
[1] https://uogqueensmcf.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/BA Modules/Medical Laboratory/Medical Laboratory Courses PPT/Year III Sem II/Biostatistics/lecture 1.pdf (Accessed: 06 March 2024).
[2] Five Principles of Good Graphs. https://scc.ms.unimelb.edu.au/resources/data-visualisation-and-exploration/data-visualisation
[3} Guide to fairly good graphs. Statistics LibreTexts. https://stats.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Applied_Statistics/Biological_Statistics_(McDonald)/07%3A_Miscellany/7.02%3A_Guide_to_Fairly_Good_Graphs
[4] Practical rules for using color in charts. https://nbisweden.github.io/Rcourse/files/rules_for_using_color.pdf
[5] https://iase-web.org/islp/documents/Media/How%20To%20Avoid.pdf [6] Duquia, R.P. et al. (2014) Presenting data in tables and charts , Anais brasileiros de dermatologia . 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20143388

Like this article? Please share
Data Analysis, Data Science, Data Visualization, Presentation Approaches Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Design • March 20th, 2024
Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)
Elevate the quality of your message by learning how to work in data presentations effectively. Insights, examples, and PPT templates here.

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 29th, 2024
How to Make a Fundraising Presentation (with Thermometer Templates & Slides)
Meet a new framework to design fundraising presentations by harnessing the power of fundraising thermometer templates. Detailed guide with examples.

Filed under Presentation Ideas • February 15th, 2024
How to Create a 5 Minutes Presentation
Master the art of short-format speeches like the 5 minutes presentation with this article. Insights on content structure, audience engagement and more.
Leave a Reply

Are looking for custom service?
- Presentation Design
- Report Design
- Brochure Design
- Infographic Design
- Illustration Design
- Package Design
- Exhibition Design
- Print Design
- Logo Design
- Video Animation
- Motion Graphics
Presentation ideas • Tips and Tricks
15 Creative Ways to Use Charts and Graphs in Presentations
Emily Bryce
12 December 2022

In today’s data-driven world, presentations are no longer just about presenting ideas and concepts, but also about presenting data in an engaging and easy-to-understand manner. This is where charts and graphs come in. They help to visualize data, making it easier for the audience to grasp and retain information. In this blog post, we will explore creative ways to use charts and graphs in presentations.
1. Use charts and graphs to compare data
One of the most common uses of charts and graphs is to compare data. Whether you are comparing sales figures, market trends or customer feedback, charts and graphs can help you present the information in a visually compelling way. Use bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, and scatter plots to showcase the data in a way that makes it easy to understand and compare.
2. Use charts and graphs to show trends
Another way to use charts and graphs in presentations is to show trends over time. For example, if you are presenting the growth of your business over the last five years, use a line graph to show the upward trend. If you want to show the fluctuations in your business over a period of time, use a scatter plot to highlight the highs and lows.
3. Use charts and graphs to show relationships
Charts and graphs can also be used to show the relationship between different sets of data. For example, if you are presenting the correlation between customer satisfaction and sales, use a scatter plot to show the relationship between the two variables. You can also use bubble charts to show the relationship between three different variables.
4. Use charts and graphs to show distribution
If you are presenting data that is distributed across a range, such as the ages of your customers, use a histogram to show the distribution. Histograms are great for showing the frequency distribution of data, and they can help you identify patterns and trends in the data.
5. Use charts and graphs to show proportions
Pie charts are a great way to show proportions. Use pie charts to show the proportion of sales for different products or the proportion of the budget allocated to different departments. Make sure to keep the number of categories to a minimum to ensure that the chart is easy to read.
6. Use creative chart and graph designs
Charts and graphs don’t have to be boring. Use creative designs and colors to make your charts and graphs stand out. For example, you can use a bar chart with a gradient background to make it more visually appealing. You can also use icons and images to make your charts and graphs more engaging.
7. Use charts and graphs to tell a story
Finally, use charts and graphs to tell a story. Don’t just present the data, but use it to support your message. Use a combination of charts and graphs to create a narrative that engages your audience and leaves them with a clear understanding of your message.
In conclusion, charts and graphs are a powerful tool for presenting data in an engaging and easy-to-understand manner. Use them creatively to showcase data, tell a story, and leave a lasting impression on your audience. With the right use of charts and graphs, you can take your presentations to the next level.
Stay Updated
Join our exclusive subscribers list to receive the latest design trends, industry updates and digital world insights in your inbox.
You can read our privacy policy here .
Related Posts

The Psychology of Color in Presentation Design

10 Tips for Creating Effective Presentations

How to Choose the Right Font for Your Presentation

Top 5 Mistakes to Avoid in Your Next Presentation

My Presentation Designer is a brand of Out of Box Ltd. which is a registered company in England and Wales under company no. 06937876 and VAT ID GB381889149 .
Copyright © 2015-2023 • My Presentation Designer • All rights reserved.
Top Tips for Using Graphs and Charts in your Presentations

Graphs and charts are a great way to convey complex information. But it is also easy to deliver information overload. We asked a range of expert presenters for their hints and tips on using graphs and charts in presentations.
Types of Graphs
Although texts carry ideas among individuals, there is no replacement for the pictorial representations that exist right from the days men lived in caves. In order to standardise the communication, many types of graphs evolved in the man’s quest for quick, easy and precise representation of data. Graphs range from simple lines to complex cosmograms that even animate.
The below infographic will share some interesting information about different graph types:
1. Less is more
I think one of the big things is to make sure you are using the right kind of chart to display the story you want your data to tell. Also, less is more. Charts are busy enough and any extra axis numbers, tick marks and such should be removed and the gridlines should be subtle colours that don’t overwhelm the image.
2. Highlight key data points
I am asked to do a lot of creative tinkering with charts, and one of the most requested items is to highlight particular data points on a line chart. An easy and effective way to do this is by assigning a unique graphic to selected data points.
To do this you simply have to insert the graphic (could also be a text box with a relevant symbol character or wingding) somewhere on the slide. Then cut the graphic item to the clipboard. Go into your chart and select the single data point you want to affect (make sure you have the single data point and not the data series selected) and paste the graphic.

Valary Oleinik
Now that data point will carry the unique appearance even as the chart figures change.
I use this in instances such as a stock price timeline where you want to highlight the price at a certain date or you want to highlight where a change occurred in a business and you want a visual marker to make a comparison of the effects prior to and after the change. I could work up a chart sample if you would like.
3. Simplify your slides
Many graphs can be simplified to make them easier to read.
Take this example.
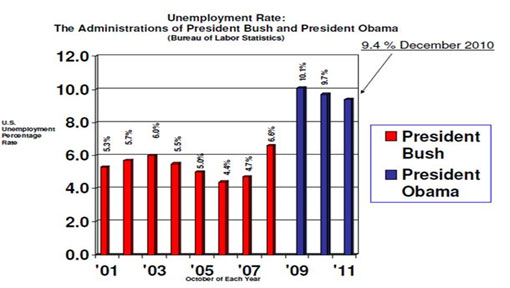
- Too much clutter, what I call mumblers and what Edward Tufte calls chartjunk. These mumblers are like the dense foliage in a jungle; you need to hack away at them with effort to work your way further into the jungle. Mumblers in this chart include horizontal lines, unnecessarily large numbers on the x- and y-axes, unnecessary detailed text.
- Large gaps between the columns. The rule of thumb is the bars should be TWICE as large as the gap.
- Sideways numbers above the bars, which are unnecessarily hard to read. In fact, you don’t need the y-axis at all if the bar values are included.
- No pictures. Whenever possible, try to convert your graphs into concrete pictures. Adding a pictures of Bush and Obama can replace the legend.
Here is an example of how this slide can be improved.
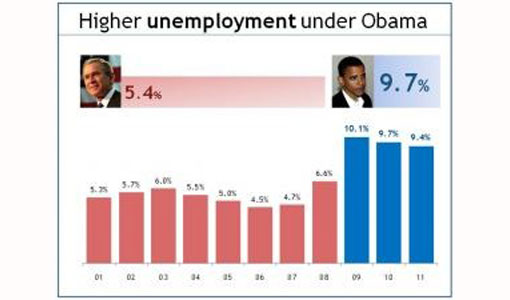
Bruce Gabrielle
4. Pie charts are not always easy to understand
Use the correct graph to display data. Pie charts are generally poor because viewers cannot quickly understand relative sizes of pie slices. Horizontal bar charts, sorted from high to low, communicate more clearly and are easier for the reader to scan quickly.
Both have their place, depending on what the audience needs.
Bruce Gabrielle – author, Speaking PowerPoint – www.speakingppt.com
5. Create better-looking graphs in PowerPoint 2010
PowerPoint 2010 creates much better graphs than the standard graphs that you get with PowerPoint 2003. Something we often do here if we are creating a PowerPoint 2003 presentation and the client does NOT need to edit the graphs themselves: we would create much better-looking graphs in PowerPoint 2010 and then copy them into the 2003 presentation as images. We know we are in the very fortunate position of having easy access to all versions of PowerPoint and this might not be possible for everyone.
6. Be careful of embedding sensitive data

But there are more reasons for doing this than just more visually aesthetic graphs. Whatever version of PowerPoint you are using, it’s still a good idea to keep the editable graph separate from your main presentation.
We know of a horror story where a presentation was left behind after an event and the Excel files that linked to the graphs contained some very commercially sensitive information.
7. Convey data in other ways than PowerPoint
Very few people remember the numbers. Convey them in some other meaningful way.
I had a participant on a course recently who was talking about a number of people that had been taken out of poverty in recent years. The number is meaningless, because I wouldn’t remember and cannot comprehend the number of people.
When he paused for a moment and said “That’s the same as the population of America”, it was easily understandable and extremely memorable.
8. Use props to convey data
Use props – check out Hans Rosling at TED on population statistics. He uses boxes and models of cars, planes and flip flops.

Paul Hayden
I once used steel buckets and coins – for the effect of the noise. If you show your market share by tipping in a (proportional number of ) few coins and then show the size of the available market left by tipping in another proportional number, people will not remember the number, but they will remember how long that noise lasted and how much share is up for grabs.
9. Only present key information
Think of what it means to the audience, perhaps just some of the data is enough (e.g. top 3 or 5 instead of the whole chart)
10. Concentrate on trends and changes
Concentrate on trends and changes rather than numbers and data.
11. 3D graphs are hard to read
Avoid 3-d graphs as much as possible, they are hard to read.
12. Animate your graphs
Try to animate the data instead of showing everything at once (overwhelming). By animating I don’t mean the custom animation on the software, but show the data gradually, one bar at a time for comparisons, one year at a time on a line chart, one piece of the pie on pie charts.
It will be like storytelling your data and the audience will be able to keep up.
Dr.Ahmad Al-Ani
13. Take a look at data visualisation

Yolanthe Smit
I find graphs and charts usually rather boring unless they are on paper or a webpage so I can study them at my leisure.
We recently devoted an entire TEDxTheHague Salon to data visualisation and watched these great presentations:
Recommended Pages

- All Templates
- Persuasive Speech Topics
- Informative
- Architecture
- Celebration
- Educational
- Engineering
- Food and Drink
- Subtle Waves Template
- Business world map
- Filmstrip with Countdown
- Blue Bubbles
- Corporate 2
- Vector flowers template
- Editable PowerPoint newspapers
- Hands Template
- Red blood cells slide
- Circles Template on white
- Maps of America
- Light Streaks Business Template
- Zen stones template
- Heartbeat Template
- Web icons template
- Google Slides Presentation Design
- Pitch Deck Design
- Powerpoint Redesign
- Other Design Services

- Design Tips
Powerpoint charts and tables
Charts and tables are an inevitable part of almost any presentation for business or for studying. Actually, they usually act as a backbone of your presentation, making the information you present more understandable and coherent. The problem is, however, that it’s really easy to get lost in the chart making, especially if there’s a lot of information to include. Tables can also become quite incoherent, especially when there’s a lot of text to put into it (and a wall of text on a slide is one of the worst crimes in presentation-making). So, how to not mess up when you’re making the flow chart or pie chart in PowerPoint . And more importantly, how to make a chart in powerpoint that would look really nice? Let’s find out together!
The Interface: Charts and Tables
Let’s first look at the tools you have for charting in powerpoint . You can insert tables up to 10×8 in size by default. However, if you need more, you can always specify the number of columns and rows in the Insert Table section. Among other table features are also the cell color, the text placement, and the layout. So, basically, you can create pretty much any chart you want in terms of size and looks. The real question is, however, whether the chart would look good on the slide?
Usually, it is the simple tables with no more than four rows and four or five columns that work the most effectively. Keep in mind that to fit a complex table, you should really reduce its size, up to the point where it would be hard to even recognize the text. To avoid such cases, it’s best to split your table into several smaller ones, which you can then display on two or three slides. However, a split table may also appear to be quite confusing, so maybe it would be worth considering another method to display your data.
With charts, however, things can get more complex. PowerPoint, being a Microsoft product, enjoys integration with Excel, where any kind of chart can be created within minutes. You can then insert Excel chart into PowerPoint as a picture asset. But how to make a chart in PowerPoint directly? Actually, there is a great tool for it in PowerPoint as well, although it may be somewhat less sophisticated, compared to Excel.
To start charting in PowerPoint, simply select Insert Chart in the Insert menu. In the pop-up Chart menu, you’ll be able to make a choice: bar chart, flow chart, or timeline chart . As with the tables, you can customize the color schemes, the size, and the layout. However, for the pie charts, you’ll still have to resort to Excel. As with tables, it’s all about simplicity here. So, try not to make your graphs overly complex.
You can see how professional presentation services use tables and graphs in their work.
The Layout: Organize your Charts and Templates
As you can see, creating the charts and tables is pretty simple. But how to place them properly in your presentation, and combine them with your other content? Actually, there are several simple rules for you to follow here, and several ways of placing your chart or table. Let’s look a little more into them.
One of the simplest answers to where to place your flow chart or pie chart in PowerPoint is to simply make it the only object on your slide. In case that all of the variables on the chart are properly marked, you’ll only need a little oral explanation to go with it. This same principle works with tables as well. What is more, it’s actually preferable to place your tables that way.
Another good way to place your charts is to put several key takeaways from it, organized into bullet points, on the right side of the slide, and the chart itself — on the left. This way you’ll make your audience grasp all the main information in a matter of seconds. In your speech, you can simply elaborate on the main bullet points in order to give the audience a more detailed view.
You can also use templates that would give you access to the more sophisticated charts and tables, such as powerpoint bubble charts or waterfall charts . Templates allow you to create charts that are borderline infographics: several pie charts merged together, cockpit charts for making waterfall charts or bar charts, tables with customizable symbols — everything you need for presenting large amounts of data in an appealing way.
While keeping your charts and tables simple in terms of data, it’s also important to make them simple visually. In essence, that means not to use all the visual effects just because you can. Things like 3D or Bevel effect are looking rather outdated, while stuff like multicolored bars in a bar chart or a funnel chart , unless necessary, may be rather confusing. The most beautiful graphs are the ones that are clear and understandable, so these are the main qualities that you should aim at.
Finally, let’s look at the data presented in your charts in PowerPoint. Here, the best way to go is to be specific. So, think of descriptive titles and precise naming of your chart variables. Another important thing is the numbers. While it’s common to have data with not that convenient numbers (with decimals and lots of zeros) it’s best not to leave the numbers as they are. Instead, try to round them, unless it’s absolutely necessary to display a precise quantity or percentage.
In conclusion
Using charts and tables in PowerPoint is not that hard, and there are only several things that you have to keep in mind while doing it. Go for simple, yet informative solutions — not only will they take up less time, but they’ll also make your presentation look clean and stylish. You’ve got lots of options to choose from: from a simple pie chart to complex gantt char t and org chart templates, depending on what kind of data you want to show. There is no 100% right way to work with charts in PowerPoint so try some of the approaches we discussed above, and maybe one of them would work for you!
- Presenting techniques
50 tips on how to improve PowerPoint presentations in 2022-2023 [Updated]
- Keynote VS PowerPoint
- Types of presentations
- Present financial information visually in PowerPoint to drive results
![presentation using charts and graphs 50 tips on how to improve PowerPoint presentations in 2022-2023 [Updated]](https://slidepeak.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/2-1170x372.png)
- Guide & How to's

How to select and use fonts in PPT
Line, bar and pie charts

How to Create Charts and Graphs to Visualize Data in PowerPoint
The use of data visualization has become increasingly important in today’s digital age, as more and more people have access to large quantities of data. Whether working with data for business, education, research, or personal use, it’s essential to present it in a clear and meaningful way, so it can be easily understood and analyzed. One of the most popular tools for creating visually appealing charts and graphs is Microsoft PowerPoint.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Importance of Data Visualization
Data visualization is the process of representing information in a visual format, such as charts, graphs, and diagrams. When done effectively, it provides a way to quickly understand complex data and identify patterns and trends that may be missed when viewing it in a static table or spreadsheet. Visualizations also allow you to tell a story with the data, making it engaging and memorable for your audience.
Moreover, data visualization can also help in identifying outliers and anomalies in the data, which can be crucial in decision-making processes. It can also aid in identifying correlations and relationships between different variables, which can lead to new insights and discoveries. Additionally, data visualization can be used to communicate data-driven insights to stakeholders and decision-makers, making it an essential tool in various industries such as business, healthcare, and education.
Choosing the Right Chart or Graph for Your Data
There are many different types of charts and graphs to choose from, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. When selecting the right chart or graph for your data, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- The type of data you have (categorical or numerical)
- The relationships between the data points
- The purpose of your presentation
Some of the most common chart types include bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, and scatter plots. Each chart type can display your data in a different way, highlighting specific features depending on the nature of your data.
Another important factor to consider when choosing a chart or graph is the audience you will be presenting to. Different types of charts and graphs may be more effective for different audiences. For example, a pie chart may be more easily understood by a general audience, while a scatter plot may be more appropriate for a technical audience.
It’s also important to consider the context in which your data will be presented. If you are presenting data in a business setting, for example, you may want to choose a chart or graph that emphasizes the financial implications of your data. On the other hand, if you are presenting data in an academic setting, you may want to choose a chart or graph that emphasizes the statistical significance of your data.
Creating a Bar Chart in PowerPoint
Bar charts are one of the most common chart types used in data visualization. They are useful for comparing values across different categories. To create a bar chart in PowerPoint:
- Select the data you want to include in the chart
- Click the ‘Insert’ tab and select the ‘Bar’ chart type
- Choose the specific bar chart subtype you want to use (such as stacked, clustered, or 100% stacked)
- Format the chart by adding labels, titles, and modifying the color scheme
With just a few clicks, you can create a visually appealing bar chart that highlights the differences and similarities between your data categories.
It is important to note that when creating a bar chart, you should carefully consider the data you are presenting and choose the appropriate chart subtype. For example, a stacked bar chart may be useful for showing the total value of each category, while a clustered bar chart may be better for comparing values within each category.
Additionally, you can customize your bar chart further by adding data labels, changing the axis titles, and adjusting the chart layout. Experiment with different options to find the best way to present your data in a clear and visually appealing way.
Making a Line Graph with PowerPoint
Line graphs are another common type of chart used to display numerical data. They are useful for showing trends over time. To create a line graph in PowerPoint:
- Click the ‘Insert’ tab and select the ‘Line’ chart type
- Choose the specific line graph subtype you want to use (such as 2D or 3D)
- Add labels, titles, and customize the color scheme
Line graphs are useful because they allow you to see how your data changes over time. They can make it easier to identify trends or patterns that may be hidden in other types of charts.
One important thing to keep in mind when creating a line graph is to ensure that your data is properly formatted. This means that your data should be organized in a way that makes sense for the type of graph you are creating. For example, if you are creating a line graph to show the sales of a particular product over time, you should organize your data by date and sales figures.
Another useful feature of line graphs in PowerPoint is the ability to add trendlines. Trendlines are lines that are added to a graph to help you see the overall trend of your data. They can be useful for identifying patterns or predicting future trends. To add a trendline in PowerPoint, simply right-click on the data series you want to add the trendline to, and select ‘Add Trendline’ from the menu.
Pie Charts: When and How to Use Them
Pie charts are a popular choice for showing proportions of a whole. They are useful for displaying categorical data and can quickly give an idea of the main contributors for something. However, they can be difficult to interpret when many sections are used. Some tips for making a great pie chart:
- Limit pie charts to 5-7 sections at most
- Make sure percentages add up to 100
- Make labels visible and clear
- Highlight important sections to draw attention
Keep in mind that while pie charts can be visually impactful, they should only be used when they effectively convey the data being presented.
Another important consideration when using pie charts is to ensure that the sections are proportional to the data they represent. If one section is significantly larger than the others, it can skew the overall perception of the data. Additionally, it’s important to choose colors that are easily distinguishable from each other, especially for those who may have color blindness.
While pie charts are a great option for displaying categorical data, they may not be the best choice for showing changes over time or comparing multiple sets of data. In these cases, a line graph or bar chart may be more appropriate. It’s important to consider the type of data being presented and choose the appropriate visualization method to effectively communicate the information.
Creating a Stacked Column Chart in PowerPoint
Stacked column charts are useful for showing how different parts of a whole contribute to the total, while also comparing values for different categories. To create a stacked column chart in PowerPoint:
- Click the ‘Insert’ tab and select the ‘Column’ chart type
- Select the ‘Stacked Column’ subtype
- Format the chart by adding labels, titles, and modifying the colors of the columns
With stacked column charts, you can communicate a lot of information clearly and efficiently.
Using Bubble Charts for Comparative Analysis
Bubble charts are a useful way to show three dimensions of data in a single graph. They are great for comparing two numerical data sets paired with a categorial one. To create a bubble chart in PowerPoint:
- Click the ‘Insert’ tab and select the ‘Bubble’ chart type
- Format the chart by adding labels, titles, and modifying the size, color, and alignment of the bubbles
Bubble charts are perfect for comparing three-dimensional data sets, highlighting the relationships between the various elements being compared.
Adding Labels and Titles to Your Charts and Graphs
Labels and titles are key to effective data visualization. They provide context for the chart or graph you’re presenting and help your audience understand your data. To add labels and titles to your charts and graphs in PowerPoint:
- Select the chart or graph you want to add labels and titles to
- Click on the ‘Chart Elements’ button in the upper-right corner of the chart
- Select the elements you want to add, and choose from the available options for formatting and positioning
By adding labels and titles, you can make your charts and graphs much more informative and easier to understand.
Customizing Colors and Styles for Better Visual Appeal
Colors, styles, and formatting can make a big difference when it comes to the visual appeal of your charts and graphs. Customizing options in PowerPoint allows you to personalize the look of your visualizations. Some tips:
- Use consistent branding colors to help maintain visual consistency
- Choose high-contrast color combinations to help text and graphics stand out
- Avoid too many colors, keeping the chart or graph simple and clear
Customizing colors and styles helps bring cohesion to your presentation while making it more engaging to your audience.
Animating Your Charts and Graphs for Presentations
Animated charts and graphs can be eye-catching and effective for presentations, as they create a sense of dynamism and show how data changes over time. To animate your charts and graphs in PowerPoint:
- Select the chart or graph you want to animate
- Click on the ‘Animations’ tab, and select the type of animation you want to use
- Customize the animation settings to suit your needs, including duration, direction and order of animations
Animations bring data to life, making them more memorable for your audience.
Tips and Tricks for Effective Data Visualization in PowerPoint
Effective data visualization isn’t just about picking the right chart or graph type. There are additional tips and tricks that you can use to make sure your data is presented in the most meaningful way. Here are some things to keep in mind:
- Keep it simple, using plain and unambiguous language
- Choose the right chart or graph type, fitting your data needs as well as your presentation goals
- Make it easy to read, using appropriate font sizes, colors, and layout
- Use engaging visuals, adding icons and images where appropriate
- Tell a story, organizing the chart or graph in a logical and meaningful manner
By paying attention to these tips, you’ll be able to create visually appealing and effective data visualizations that effectively communicate your message to your audience.
By humans, for humans - Best rated articles:
Excel report templates: build better reports faster, top 9 power bi dashboard examples, excel waterfall charts: how to create one that doesn't suck, beyond ai - discover our handpicked bi resources.
Explore Zebra BI's expert-selected resources combining technology and insight for practical, in-depth BI strategies.

We’ve been experimenting with AI-generated content, and sometimes it gets carried away. Give us a feedback and help us learn and improve! 🤍
Note: This is an experimental AI-generated article. Your help is welcome. Share your feedback with us and help us improve.
Presentation Design and PowerPoint Formatting Services
Consultants need overnight PowerPoint formatting -- We do it! Companies need presentation design inline with corporate style guide - We do that too!
33 Things you should know when designing charts in PowerPoint

When was the last time you presented a document or gave a presentation without having to show some numbers?
I bet most of your presentations have some numbers and you probably used charts for presenting them.
Charts can be easily created in PowerPoint, but to give your presentation an edge you need to work on your charts a little.
So, what you should do when designing charts in PowerPoint?
15 Ways of Visualizing Corporate PowerPoint Slides for Presentations .
Charts are commonly used for data visualization. But are you formatting them the right way?
Here are some simple yet effective pointers to design charts in PowerPoint. You can apply these rights away to make your data presentable.
1. Round off decimal numbers in your graph

When calculating figures and plotting graphs, use decimal places for accuracy.
However, while labeling your chart, round off the numbers to one or two digits. This will help your reader comprehend your chart easily.
For example, 2.854 may be more precise than 2.9 , but it distracts the reader and takes away from the visual impact of the chart.
2. Keep your chart titles specific
The chart tiles don’t necessarily have to tell the story of the chart. Just be specific. To the point. You will be explaining the rest anyway.

3. Narrow bars
Vertical bars measure discrete quantities. When the bars are too narrow, your eyes focus on the negative space, the space between the bars which carries no data.

Ensure your bars are well spaced, creating a balance.
4. Do not use shades or patterns in simple bar charts
Since all the bars measure the same variable, different shades or patterns have no relevance, they only distract readers from comparing the bars.

It is best to use one simple shade and color to present the chart and avoid distraction.
5. Avoid 3D effects in bar charts

Where is the top of the bar?
Three- dimensional vertical bars are flat out wrong. The reader is left to guess where the top of the bar meets the grid. Rendering the bars in 3D adds no information, but may bring in confusion.
Keep it simple; don’t use any chart effects like the 3D effect or patterns, etc., when you are creating bar charts.
6. Avoid special effects unless they help comprehension

Why would you want to add effects like the one you see above?
Using effects just to add variety to the visuals can be distracting. It can make your data difficult to read. Keep it simple and easy to read.
7. Keep the typography simple
Don’t permit typography with extra effects to oppress the underlying data.

Keep the typography simple. The headline can be either bold or in larger font size than the font size used in the graph.
8. Use colors to help to understand your chart/graph
Do not apply the same color to both positive and negative bars. It will lead to misinterpretation of the concept of the graph.

Red is mainly used to denote negative values. So, the color itself conveys a message. That is the right way to use color.
9. Avoid multiple colors

10. Include clear information on the graph
Do not leave the graph on a slide without labeling the data. This will lead to confusion.

Add essential information on the graph. Use the information that will help the audience understand the graph better, but do not go overboard with the information.
11. Use suitable highlights in a bar chart
Do not highlight the bars with a pattern fill, shape fill, image fill, or anything that comes as a default.
It might come out looking bizarre, just like the example here.

Highlight the bars with a contrast color (red is a common color). This will make the data easy to understand.
12. Avoid Bevel effect in bar charts
Do not use unnecessary effects, such as the Bevel effect, in the chart. Keep the chart as simple as possible so that it will give the audience a clear idea of what the bars are depicting.

13. Align graph direction with data values
Never plot horizontal bars with negative values on the right side of the size zero line, even if there are no positive numbers in the data set.

Negative numbers in a graph should always be on the left side of Y-axis. Negative bars can be red in color for added emphasis.
How to Visualize Charts for Corporate Presentations the Right Way: A Step-by-Step Guide .
14. Keep Axis labels at a readable angle
Do not rotate the axis as shown in the image below.

For easy visibility, if there is a lot of text in the axis label, make sure you always rotate the labels to 270o or 90o.
15. Start Y axis with zero
For bar charts, the numerical Y-axis must start at zero. Our eyes are very sensitive to the area of bars, and we draw inaccurate conclusions when those bars are truncated.

16. Keep your charts free of clutter
Keep charts simple. One way to simplify charts is by removing extra elements, like borders, gridlines, decimal numbers, etc.

17. Try horizontal bar charts to fit long labels
To increase readability for bar graphs that have multiple categories with long names, horizontal bar graphs can be used.

18. Format Y-axis values to include the largest data point
Make sure that your data does not overflow but falls under the x-axis.
Look at the last bar (highlighted in red) in the image below. The bar is out of the chart area because the data is more than the Y-axis. Always make sure you reset the Y-axis from the format axis option.

19. Keep bar heights optimal
In the figure, the UK bar is too high and hard to compare with the rest of the countries.

Adjust the bar height manually and add a breaking symbol on top of the bar.
20. Label data in pie charts according to the size of the chart
Do not place the data labels outside a pie graph. If the pie chart is big, the chart will look empty.

21. Keep special effects to a minimum in complex pie charts
Do not add too many effects to complex pie charts.

22. Opt for solid fill to highlight sections in pie charts
Do not highlight a section of a chart with an outline. This does not make the section stand out well.

23. Use legends if you have too many data labels
Don’t overload the chart with information.

You can add just the data labels and add a legend for the categories, to make the chart look clean.
24. Place data logically
Segments chart clockwise from smallest to largest.

25. Maintain the bar graph height according to the numbers.
Always use actual graphs instead of graph-like shapes.
26. Use suitable background images
Unsuitable background images can be distracting.


27. Use color schemes that enhance visibility
Your focus should always be on the message you want to share. Dark background for a dark-colored graph will dilute the intensity of the data or message and will affect the visibility and/or clarity.

28. Use highlights based on information be conveyed
Highlights in a line chart will depend upon the information that is to be conveyed. In the example here, Portland is highlighted since it has the highest value. To ensure that your highlight stands out, have lighter shades for the other data. If you do not have to highlight, then make them all grey but use different shades. However, it all depends on the type of information that you want to show.

29. Make comparison apparent

Notice that the chart above is a comparison between 2015 and 2016 and that even though the data points in 2016 are higher than in 2015, still 2015 looks greater than in 2016. That gives the wrong message to the reader/audience.
To ensure that such mistakes do not happen, make sure that you always set the Y-axis to the same value so that the difference is apparent at first glance.
30. Use colors judiciously
A multitude of colors can confuse readers.

The effect would be easy on the eye and also make comparison easy.
31. Use appropriate shapes in a flow chart
In a flow chart, do not use the same type of shapes for each section.

32. Use the right fit to represent percentages
In the figure, the shapes have been given heights at random. The height of the shapes does not align with the data points (percentages, in this case) that they represent.

33. Don’t let pictures overpower data
The picture superiority effect refers to the phenomenon in which pictures and images are more likely to be remembered than words.

Designing charts can be difficult when a lot of data is involved. But by using the minimalist design concept, in a presentation, you strike a balance between your charts and content.
Here is how to Use Think-Cell for Visualizing Charts Effectively .
Are you looking for better ways to design your charts? Leave a comment below.
Maybe you do not need a lead-in sentence here? If so just remove it. Maybe this will just appear as a link in the middle of the post.

Related posts:
- Quick Guide to Using New Chart Types in Office 2016
- Visualization Ideas Using PowerPoint Design Elements
- How to Use Think-Cell for Visualizing Charts Effectively
- How to Create Amazing Charts using Think-Cell?
Chillibreeze Presentation Design Experts To Your Rescue
Our customers have deadlines and need our help. Our PowerPoint design experts take their rough content - format it - apply style guidelines and deliver a polished PowerPoint deck. They appreciate the way we learn their needs, keep their information safe and rapidly deliver on-time.
Get Rescued
About Chillibreeze
Chillibreeze is fast & reliable. Our PowerPoint design experts come to the rescue of corporates & consultants in 12 - 24 hours. Try our Presentation service.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
How We Work Getting Started Examples Pricing FAQs Happy Customers Contact Us Onboarding Process Creative Services
Chillibreeze wall Timeline History Chillibreeze Stories Privacy Policy Customer Experience Holiday List Presentation Challenges and Solutions
Leadership Team Chillibreeze wall Timeline History Chillibreeze Stories Privacy Policy Production Stories Holiday List
Purpose Values and Behaviours Opportunity in Northeast India Rethink Social Responsibility The Big Picture Chillibreeze CSR Initiative
Work in Chillibreeze FAQs Career Advice
We use cookies to improve your experience on our website. You can disable them from your browser. Read more about our privacy policy.
Copyright © 2004 - 2024 Chillibreeze Solutions Pvt. Ltd.

- Certifications

5 Tips for Using Charts Effectively in PowerPoint Presentations
- December 27, 2022
PowerPoint was originally designed for business presentations; therefore, it has evolved as an integral part of different types of presentations. As a business presentation software, it has become a favourite medium to teach or assist in the development process of a particular project. However, the potential of the software lies on a hands-on role and it needs to be properly used to ensure its success in the process.
PowerPoint is widely used for presenting data. The most popular chart types that can be created in PowerPoint are the arrow and bar chart. Most commonly used types of PowerPoint charts are radial, shape, area and line charts. In addition to providing a project management solution, the best management solution must also support a robust project governance solution and a proven project support system.
For example, you need to have a structured processes and tools to manage, measure, and report on all your project’s tasks, assets, and the technical resources needed to implement it. You need to know exactly what has been accomplished, how much was wasted, and what can be improved, in order to minimize future costs and minimize the project risk. A best management solution provides all of the above. There are many software providers that provide best project management tools.
With each project having varying requirements, selecting the best charts/diagrams can be confusing at times. Therefore, we have put together popular charts used in PowerPoint with their significant features to help you make an informed choice.
Gantt Charts
In a Gantt chart , the grid layout represents the timeline, or the sequence of activities that need to be completed and that are interdependent. The lines represent the activities that need to be completed, the tasks can be as simple as addition of one or two lines to describe a single stage. The Gantt chart is numbered in units of 1 and 5. For example, Gantt charts are numbered 0-2.
If your work is in units of 1 and 5, as shown in the Gantt chart, you could use a Gantt chart to monitor the execution of each stage of the activities and make adjustments if any occurs. With Gantt charts you can highlight and emphasize the activities that are the most important in your project. Gantt charts provide insights into activities that matter most. A Gantt chart is a small representation of your plan of action for the coming days. A Gantt chart lets you visualize how tasks are going to be done and progress from one cycle to the next. A gantt chart is useful for a lot of planning tasks.
Agile Methodology
Scrum Project management project scenarios using this methodology are characterized by a “constantly evolving, spontaneous, self-organizing, and re-adjusting” environment. It provides you with a very clear line of sight into both the vision and the concrete deliverables. With a pre-scrum meeting, you make an investment in the critical time window before an actual project commences. Generally, you have two perspectives on each work item. The first one is your team’s perspective and the second is the customer’s perspective. By working in parallel, both perspectives together will drive your team towards a successful completion of the project.
Waterfall Charts
In these waterfall charts you can easily visualise how one or several processes will result in a certain result. For example, you can easily create a growth chart that illustrates the required number of sales in a specific quarter. When you run a scenario (which usually requires a forecast) you can easily visualise that there is a “if” or “when” in which your sales targets are met. With this diagram you can also easily see how two or more scenarios will intersect.
Waterfall Methodology
This methodology is almost like an extremely organised project management method which has the following elements:
- High planning and control
- Produces smooth working and maintenance schedule
- Manages multiple activities efficiently
In short, waterfall methodologies for project management aim to deliver quality outputs in a short time by closely following a set of rules and procedures. A comprehensive project management roadmap is developed and defined based on project needs and related goals. To deliver the best results, deliverables are separated into the different stages of a project.
Mekko Charts
Based on your business needs, you can create a model of your data by choosing your preferred charts. Now it’s time to move to the next step to give the data an identity. Model-based Design- We are just going to lay down our data (filtered for looking good) and our first and most important step in data modeling is creating a model of the data. First, let’s define a database schema of our dataset and then use the data we’ve created to create a model. Simple schema is used here for simplicity. Now, we can start creating a model of the data by adding columns to our data model and defining their type.
Radar Chart
Not to confuse with bubble chart, which is supposed to visualize a relationship in which the relative sizes of individual elements do not change in time. Also, while most of the charts use Cartesian coordinates , radar charts use what is known as polar coordinates: the center of the chart is given by x (direction) and y (height), and the horizontal and vertical axes are given by z (zonal) and w (area). The chart also includes a sign and bar to determine the strength of the relationship between the two axes.
Scatter Charts
A simple scatter chart that is frequently used when you want to see how various areas of your data evolve over time.
1. The 2-axis chart helps visualize the trajectory of the real-time values. This is very useful when analyzing streaming data or when you want to show the direction of an event.
2. A cross section plot is used when you want to look at the vertical axis in terms of the cross-section and the horizontal axis in terms of the locations.
3. A small scatter plotting chart is used when you want to compare an industry with another. It works especially well in comparing two or more industries or comparing two industries at the same time.
Combined chart
When you insert a chart, specify the chart type you want. Column and line graphs are built-in to PowerPoint, and a variety of different forms of charts can be embedded as well. 2. axes and axes labels Links can be added to axes to increase their specificity in your graphs. You can have axes be point, line or bar-shaped. They can have labels applied to them as well. Labels can be applied to both axes and the chart itself. 3. filter – make a difference Filter can be used to amplify the presentation of data. Filters make different graphs fit together better. For example, you can use a filter to group various types of data into two different graphs. You can group verticals or horizontal lines together. Or with combined charts you can combine multiple vertical and horizontal charts to show changes over time.
Without watermark- line chart visualizes values based on line levels. This allows the user to easily compare different types of data to see whether some of the values are constant or fluctuate. importing a chart from Excel. 2. graph that combine two different types- When you link two different line charts, you can easily show two different levels of the same data. This type of graph is great for showing data from two different data series with different scales.
1. Image without watermark- The .PNG file format stores your original image as a PNG file, without watermark. A new file, (.pptx) is produced with every exported PDF file.
Animating your charts
A key way of illustrating statistics or other data visually is through an animated chart. Animated charts provide a fun way to help your audience understand and analyse data. However, a lot of people become intimidated by chart animations, so it’s important to understand the basics. This article aims to explain and show how to use the basic animations in PowerPoint and then show you some examples of how to use the different animation options. By default, animated charts are grey, this is because they do not contain a “data object” or visualisation. You can change this by clicking on the little cross symbol and selecting a colour.
Animation is a great way to show trends that are plotted over time. As you talk about a graph in your presentation, you can show it moving or fading in and out to help the viewer visualize that data . This is much more effective than using a moving bar chart to show a trend over time. Animation makes a very effective use of charts and graphs. If you have an image to work with, you can use motion to add interest to a chart and graph. You can start with a single picture, and add motion to it to create something that really pops. It can also be great to add sound effects to a graph, or maybe even the sound of thunder or a bell. Animation is a great way to add interest to charts and graphs.
PowerPoint and Excel
Before we can animate any graph, the chart must have a row format which makes it possible to visualize a value in many different ways. This is usually a flat layout with vertical and horizontal axis and two sub-sections for data values. The axes are horizontal and vertical axis because there are some cases that graph labels cannot be shown. All the data in a flat graph has the same height. To animate any graph, it requires that all the data on the axes are visible in a table format which gives all rows the same height and only the labels and values are changed.
Links to PowerPoint charts with Excel
You can link your PowerPoint charts with Excel that you have created.
- Drag and drop navigation – This tab allows you to drag a selected section of a chart and then to drop it into another area on the screen.
- Transitions- This tab provides navigation for manipulating interactive charts. A small icon represents each transition, which you can select to navigate to another chart.
- Best chart and graph icons- First of all, choose your favorite icon for your interactive chart. This can be a geometric shape, a mark or an indicator such as a red bar or a green bar. Use this icon as a reference and fill the entire area to your chart.
Modifying an Excel chart in PowerPoint
You can create a colored line overlay and change the colors of the axis labels in Excel. In PowerPoint, you can easily use the Paint Bucket Tool to modify and add annotations to the data.
A web panel- To create a web panel in PowerPoint, simply copy and paste the link of a web panel, and it will appear in your PowerPoint. The main difference between a web panel and a web chart is that a web panel is a web application which your audience can use from their own computers, so you don’t have to worry about transferring it. You can use a web panel to present data in a new format, whether you are presenting it in a web form or a graphic map.
PowerPoint is an essential tool for learning. It’s easy to learn, and it makes it easy for people to understand what you want them to know. The ease of learn and the familiarity of PowerPoint are a major factor in its success. That said, you should look at other tools too. The best tools are used by the people who know how to use them. Learn these tools well and you will see a huge improvement in your productivity and in your communications with clients, colleagues, and other stakeholders. That’s the power of learning and using the right tools. Start with these powerful tips to get the most out of PowerPoint, then explore how to make PowerPoint work for you. P.S. With this tip, you can customize your fonts in PowerPoint even when you’re offline.
Share This Post:
3 thoughts on “5 tips for using charts effectively in powerpoint presentations”.
[…] are a number of data related PowerPoint charts that is in-built to represent numerical information. Use them extensively to illustrate numbers and […]
Wow, fantastic weblog layout! How lengthy have you ever been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The entire glance of your site is excellent, as neatly as the content material! You can see similar here sklep internetowy
I want to to thank you for this great read!! I certainly loved every little bit of it. I have you bookmarked to check out new things you postÖ
Add a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Get A 5X Raise In Salary
Reset Password
Insert/edit link.
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content
- The Complete Guide to Mastering Business Presentations
- Visual Aids in Your Business Presentation
Data Visualization in Business Presentations: Graphs and Charts Best Practices

Aayush Jain
Navigating the graphs and charts galaxy: a guide for data storytellers.

Introduction to Graphs and Charts Selection
When it comes to data visualization in business presentations , the choice of graphs and charts is pivotal. These visual aids are the storytellers of numerical tales, translating complex datasets into comprehensible narratives. The art lies in matching the story you wish to tell with the appropriate visual vehicle. Whether it’s a bar graph illustrating quarterly sales or a line chart tracking website traffic trends, the right selection can illuminate insights and guide decision-making processes. A well-chosen chart or graph not only enhances the business case presentation but also reinforces the message with clarity and impact.
Historically, visual representations of data have been instrumental in facilitating understanding. From Florence Nightingale's Coxcomb plots to John Snow's cholera outbreak maps, the ability to see patterns and relationships in data has shaped decision-making in business and beyond. Today, with the surge in big data and analytics, the role of presentation design services has grown exponentially. They specialize in harnessing the power of PowerPoint presentation design and other tools to distill and display data. The choice of graph or chart hinges on the nature of the data – categorical, time-series, comparative, or relational – and the story it is intended to convey.
Real-world Application and Current Trends
In the realm of real-world application, companies often turn to presentation design agencies to help them craft a compelling business case slide. For instance, a product launch with right presentation design agency might leverage a combination of pie charts and histograms to depict market segmentation and consumer preferences. Meanwhile, presentation design companies are increasingly adopting interactive dashboards, allowing for a dynamic and engaging data experience. These tools not only display static figures but also enable viewers to interact with the data, drilling down into specifics and exploring different scenarios on the fly.
Credibility in data representation is paramount, and referencing high-quality external sources is key to achieving this. For a presentation redesign for example, the use of business case templates with proven effectiveness can be backed by statistics from reputable agencies. According to a recent survey by a leading PowerPoint design agency, presentations that utilized tailored, data-specific graphs saw a 30% increase in audience engagement. Furthermore, a study in the Journal of Business Communication found that incorporating clear and relevant graphs in sales presentations increased the persuasiveness of the argument by 43%.
Simplifying the Complex: The Art of Streamlining Data Visualization
Introduction to Simplifying Complex Data
Data, by its nature, can be intricate and overwhelming, especially when large volumes are involved. This is where the second rule of data visualization in business presentations comes into play: simplification. The goal is to strip down complexity without losing the essence of the information. Simplifying complex data visualization involves choosing the right powerpoint presentation design services that can distill vast amounts of data into easily digestible visuals. By doing so, presentation design agencies ensure that the audience can quickly grasp the underlying patterns and messages without getting lost in a sea of numbers.
Delving into Simplification Techniques
The process of simplification is not about dumbing down data; it's about smart consolidation and prioritization. Techniques vary from employing data aggregation—whereby data is categorized into larger groups for a broader view—to highlighting significant data points to draw attention to critical trends or outliers. Google slides and other presentation software offer tools that can enhance simplicity, such as clean lines and comparative scales. These techniques by skilled presentation designers help to avoid cognitive overload and make the data more approachable and memorable.
Real-world examples abound where complex data visualization has been successfully simplified. Presentation design companies often showcase before-and-after scenarios to demonstrate their skill in transforming convoluted spreadsheets into intuitive charts. For instance, a recent corporate presentation by a tech giant exhibited a remarkable use of a minimalist interactive data dashboard that allowed the audience to explore various market scenarios with ease. Additionally, many presentation design agencies have created visual case studies that display their expertise in simplifying complex projects, making a strong case for their presentation services here.
Statistics show that presentations with simplified visuals have a higher retention rate. A survey by a top presentation design company revealed that their clients reported a 50% better understanding of data when it was presented in a simplified manner. The Harvard Business Review also emphasizes the effectiveness of simple visual aids, citing that investors and executives often prefer straightforward graphs over complex ones because they can quickly comprehend and act on the information. Thus, the importance of simplification in data visualization cannot be overstated, as evidenced by the expertise and recommendations of industry leaders.
Precision in Presentation: Ensuring Accuracy and Clarity in Data Visualization
Introduction to Accuracy and Clarity in Data
The integrity of a business case presentation hinges on the accuracy and clarity of its data visualization. This concept is a cornerstone in communicating information effectively, as even the most visually appealing business case presentation template can be rendered useless if the data it conveys is not accurate and clear. The challenge for presentation design services is to maintain the delicate balance between aesthetic appeal and the precise portrayal of data. It is a balance that requires a deep understanding of data nuances and a keen eye for design.
Background on the Importance of Accurate Data Representation
The history of data visualization is littered with examples where inaccuracies in data representation have led to misinformed decisions with significant consequences. Thus, presentation designers place a high emphasis on data integrity. Accuracy involves double-checking data sources, using appropriate scales, and avoiding misleading graph elements such as truncated axes or inappropriate intervals. Clarity is about making the data accessible, using the right type of graph to match the message, and avoiding clutter that can obscure the data's meaning.
Illustrating with Real-World Examples
Consider a PowerPoint presentation for a major product launch presentation. Here, precise market data visualization could be the difference between securing stakeholder buy-in or not. A presentation design agency might use clear, accurate bar charts to depict market share, while a sales presentation may require precise line graphs to forecast sales trends. Google Slides and other tools now offer advanced features that help ensure accuracy, such as live data integration, which can update charts in real-time to reflect the most current data.
The best presentation design companies not only focus on the aesthetics of graphs but also on the verifiability of the data presented. They often cite and link to data from credible sources, such as industry reports or academic studies, which adds a layer of trust to the presentation. For instance, a business case analysis might be supported by data from financial institutions or market research firms, complete with citations. According to a survey by a leading business school, presentations that referenced authoritative data sources were rated as more than persuasive presentations by 65% of executives surveyed.
Unveiling Success Stories: Real-world Examples of Effective Data Visualization

Introduction to Effective Data Visualization
Effective data visualization acts as a bridge between complex data sets and decision-making processes. It is a potent tool in a business case presentation, with the power to influence and inform. But what makes a data visualization effective? The answer lies in its ability to tell a story that is both compelling and understandable. It’s not just about presenting data; it’s about crafting a narrative that resonates with the audience. Presentation design services strive to achieve this by focusing on design elements that highlight the key messages within the data.
Background on Data Visualization Success
The success stories of data visualization are as varied as the fields that use them. For example, the use of infographics in business case slides has transformed dry statistics into engaging stories. Historical examples, like the work of Edward Tufte, who emphasized the importance of displaying data with integrity and simplicity, continue to influence modern presentation design. Moreover, both powerpoint presentations and presentation design services have evolved to incorporate storytelling elements, making data not just informative but also memorable.
Real-world Examples of Visualization
Among the notable instances of effective data visualization are the interactive dashboards used by major consulting firms. These dashboards have revolutionized the way data is presented, allowing users to interact with the information dynamically. For example, a business case analysis presented through an interactive dashboard can help the audience visualize the impact of different business scenarios. Another example is the annual reports of leading tech companies, which often employ a mix of charts, graphs, and animations to present financial data, user statistics, and performance metrics.
The real-world effectiveness of data visualization is often supported by research and expert opinion. A study published in the 'International Journal of Business Communication' found that incorporating well-designed charts and graphs could increase comprehension by up to 70%. Presentation design agencies often highlight these findings to validate their approaches. Additionally, companies like Google have published white papers on the effectiveness of visualization in Google Slides, demonstrating how visual storytelling aids information retention and decision-making.
The Art of Data Storytelling: Leveraging Infographics

Introduction to Data Storytelling Through Infographics
Infographics have revolutionized the way we understand and interact with data in a business case presentation. They blend visual appeal with information-rich content to create a compelling narrative. The essence of data storytelling lies in its ability to make complex information easily digestible, and infographics are the perfect vessel for this. Presentation design services use infographics to transform rows of data into a visual story that engages and informs the audience, making them a staple in the arsenal of best presentation design company.
Exploring the Evolution of Infographics
Infographics are not a modern invention; they have been used for centuries, from ancient cave paintings to the elaborate diagrams of the Renaissance. In the context of business, they have taken center stage as a means to convey business cases, market analyses, and statistical data. The evolution of presentation design tools, including PowerPoint presentation design services and Google Slides, has given rise to innovative infographic formats that combine images, charts, and text to depict information more dynamically and interactively.
Real-world Applications of Infographics
Business presentations , especially those related to marketing presentations and sales presentations, have benefited greatly from the use of infographics. For example, an infographic detailing customer demographics and purchasing behaviors can provide a clear picture of market segments in a business presentation. Presentation design agencies often showcase their expertise by creating infographics that distill complex data, such as financial reports or consumer surveys, into concise visuals that highlight key trends and insights.
Infographics must be rooted in reliable data to maintain credibility. Top presentation design companies ensure that the data they visualize comes from authoritative sources, often referencing industry reports, academic research, or proprietary data. For instance, a business case slide that includes an infographic might cite data from a well-known market research firm to back up the market trends it presents. The use of verifiable sources not only strengthens the message but also enhances the reputation of the business or individual presenting the data.
Enhancing Engagement: Animations and Transitions in Data Visualization
Introduction to Dynamic Visualizations in Presentations
In the landscape of business presentations , animations, and transitions are not mere embellishments; they serve as critical tools for enhancing the understanding and retention of data. When used judiciously, these dynamic elements can guide the audience through a narrative, revealing insights step-by-step and keeping them engaged. The judicious use of animations in PowerPoint presentation design services, for instance, can turn a static business case slide into an interactive storytelling experience.
The Role of Animations in Simplifying Information
Animations can break down complex information into manageable sequences, making it easier for the audience to follow and absorb. By progressively disclosing information, animations help to maintain focus and can effectively highlight changes over time or the relationship between data points. Presentation design agencies understand the cognitive load of their audience and use transitions to direct attention, reduce overwhelm, and facilitate the digestion of complex data.
Real-world Examples of Effective Use of Animations
Consider the impact of a well-animated product launch presentation. It can reveal market trends, product features, and user statistics in a manner that builds anticipation and keeps the audience engaged. Real-world examples include sales presentations that use motion to track the journey of a product from conception to market leader. Presentation designers may use animated charts to depict the growth trajectory, with each phase of growth revealed through a transition, creating a more memorable presentation and persuasive narrative.
While animations can add a layer of sophistication to presentations, their accuracy and relevance should be grounded in solid data. Top presentation design service companies often quote statistics on the effectiveness of animated visuals. For instance, research has shown that animated visuals in a PowerPoint presentation can increase audience engagement by up to 40%. Presentation design services ensure that the animated elements are not only visually appealing but also represent the data faithfully, often referencing and displaying source data on-screen during the presentation for transparency and trustworthiness.
Interactive Insights: The Power of Data Dashboards in Presentations
Introduction to Interactive Data Dashboards
Data dashboards are at the forefront of modern business presentations, offering a dynamic and interactive way to display complex data. They serve as a control panel, providing a comprehensive view of metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) at a glance. In a business case presentation, an interactive dashboard can empower the audience to engage directly with the data, fostering a deeper understanding and a more personalized experience.
The Evolution and Importance of Dashboards
Historically, data was presented in static tables and charts, which could be difficult to interpret and act upon. The advent of interactive dashboards has changed the game, allowing users to filter, drill down, and manipulate data in real time. This evolution has been driven by advances in presentation design services and software, with PowerPoint presentation design services now integrating dashboard functionality into their offerings. Dashboards have become an essential tool for project managers and business analysts to convey complex data succinctly and effectively.
Dashboards in Action: Case Studies
Real-world examples of dashboard implementation include multinational corporations that use them for tracking sales and operations across different regions. Presentation design agencies have crafted bespoke dashboards for these companies, which are used in executive summaries and monthly reports. These dashboards often include interactive elements like sliders and dropdown menus, allowing viewers to select different data segments and receive immediate, visual feedback.
The inclusion of interactive dashboards is supported by research indicating their effectiveness. For instance, a study from a presentation design company found that presentations featuring interactive dashboards saw a 50% increase in audience participation. Furthermore, industry experts from presentation design agencies have noted that interactive dashboards can lead to more informed decision-making, as they allow users to explore and interrogate the data themselves, leading to a more engaging and insightful presentation.
Future-Proofing Presentations: Trends in Data Visualization for Business
Introduction to Data Visualization Trends
As the business landscape evolves, so do the trends in data visualization. Keeping abreast of these trends is crucial for any business case presentation, as it reflects a company's ability to adapt and innovate. From AI-powered analytics to real-time data feeds, the latest trends in data visualization are shaping the way businesses present and interpret data. Presentation design services that stay ahead of these trends not only offer cutting-edge solutions but also provide their clients with a competitive edge.
Understanding the Impact of New Visualization Techniques
Emerging technologies are continuously influencing the techniques used in presentation design. For instance, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are beginning to find their way into powerpoint presentation design services, offering immersive ways to explore data. Big data and machine learning are also impacting the field, with algorithms now capable of identifying patterns and insights that might be missed by the human eye, and presenting them in novel and compelling ways.
Case Studies: Innovation in Data Visualization
Innovative companies are already harnessing these new trends to powerful effect. A business case slide that uses AR can allow stakeholders to visualize product placement in a real-world setting, while VR can create an immersive environment for exploring complex datasets. Presentation design agencies are also leveraging these technologies to offer more impactful and engaging presentation experiences. For example, a financial firm used an interactive, real-time data visualization to illustrate market fluctuations during a high-stakes investment meeting, enabling investors to make more informed decisions on the spot.
The future of data visualization is a hot topic among industry experts and thought leaders. Research papers and tech conferences often highlight the potential for AI and interactive elements to transform business presentations. A recent article in a tech journal by a leading presentation design company projected that the use of dynamic and interactive data visualization will increase by 70% in the next five years. This suggests a future where data visualization not only informs but also interacts with the audience in real-time, making presentations more engaging and informative.
Mastering the Numbers: Strategies for Presenting Statistical Data

Introduction to Statistical Data Presentation Strategies
Presenting statistical data effectively is a cornerstone of a persuasive business case for best presentation design agency. The challenge is to present statistics in a way that is accurate, accessible, and engaging. This requires a blend of clear communication, appropriate visualization, and a narrative that connects the data to the audience's needs and interests. Successful presentation design services understand that the right strategies can transform raw numbers into powerful insights.
Deep Dive into Effective Data Strategy
The key to presenting statistics effectively lies in understanding the audience and the context. For a product launch presentation, this might involve focusing on consumer statistics and market potential. Presentation design agencies have developed a range of strategies to handle such data, such as segmenting information, using relative comparisons, and emphasizing change over time. These techniques help to contextualize data, making it more meaningful and impactful for the audience.
Real-World Examples of Statistical Presentation
Real-world examples of statistical data presentation abound in annual business reports and market analysis presentations. For instance, sales presentations often use comparative bar graphs to show performance against competitors, while business case analyses might employ scatter plots to identify correlation between variables. In these cases, presentation designers aim to highlight the most important statistics to support the narrative of the presentation.
Credibility in statistical presentation is reinforced by sourcing data from reputable institutions. Presentation design companies often cite market research firms, government databases, and academic studies to back up the data they present. For example, a business case slide might include statistics from an industry report, adding authority to the presentation. According to a study by a leading university, presentations that include cited statistics are considered more trustworthy by 80% of business executives.
The Persuasive Power of Data: Visualization for Impact
Introduction to Persuasive Data Visualization
In the world of business presentations , data visualization is not just about displaying information; it's about persuasion. It's about using data effectively to influence and drive decision-making. A business case presentation, for instance, needs to do more than just inform—it must convince. To achieve this, presentation design services must leverage data visualization techniques that not only present data but also tell a compelling story, creating an emotional connection with the audience and emphasizing the key takeaways.
Background on the Art of Persuasion through Data
The art of persuasion in data visualization is rooted in an understanding of human psychology and the principles of design. It involves the strategic use of colors, shapes, and layouts to emphasize important data points and guide the audience's perception. For instance, a PowerPoint presentation design that wants to underscore growth will use ascending bar charts with bold, upward-pointing arrows. Presentation designers are adept at using visual hierarchies to direct attention to key factors and employ contrast to create focal points for persuasive storytelling.
Case Studies of Impactful Data Visualization
Looking at case studies, we find numerous instances where data visualization has been used to great persuasive effect. Sales presentations, for instance, often use infographics to highlight customer satisfaction rates or to compare feature benefits. A presentation design company might produce a business case slide that uses a combination of pie charts and pictograms to represent market share and demographic segments, making the data more relatable and impactful.
The persuasive power of visualizations is often backed by data and research from credible sources. Presentation design agencies typically reference statistical evidence to support the choices made in data representation. For instance, a study might show that presentations with data visualizations are 43% more persuasive than those without. Furthermore, experts from presentation design services can cite cases where their visual strategies have directly contributed to successful business outcomes, such as increased investment or improved stakeholder buy-in.
What should be included in a business case presentation?
A business case presentation should include an executive summary, problem statement, proposed solution, benefits and drawbacks, cost-benefit analysis, risk assessment, and implementation plan. Visual aids like graphs and charts should be used to support the data presented.
What are the 4 key elements that a business case should contain?
The four key elements include the executive summary, business idea, analysis of the problem or opportunity, discussion of possible solutions, and a recommendation with justification.
How do you present a business use case?
Present a business use case by starting with a clear problem statement, a simple business case template followed by the proposed solution, the benefits, and how it aligns with business objectives. Use data visualization to make your case compelling.
How do you present an effective business case?
An effective business case is presented by clearly defining the problem, showcasing the benefits of your solution, providing a detailed analysis and evidence, and concluding final presentation with a strong call to action. Incorporate visual data representation for clarity and impact.
What is a business case slide?
A business case slide is a part of a presentation deck that succinctly presents the rationale for a project or initiative, highlighting the benefits, costs, and impact on the organization. It uses graphs, charts, and bullet points for easy comprehension.
How do you structure a business case presentation?
Structure a business case presentation by including an introduction, background information, presentation of the business case, analysis of alternatives, recommended solution, implementation plan, and conclusion. Use charts and graphs to visualize data.
What should a business case include?
A business case should include an introduction, problem statement, analysis of options, technical details, recommended solution, implementation plan, financial analysis, risk assessment, and conclusion. Visual aids can enhance understanding and retention.
How do you write a case study slide?
Write a case study slide by summarizing the background, challenge, solution, and results. Use visuals like graphs, charts, and images to illustrate key points and outcomes effectively.
How much does it cost to design a PowerPoint presentation?
The cost to design a PowerPoint presentation can vary widely, from $100 to over $1,000, depending on complexity, length, and the expertise of the designer or agency involved.
How do I get a PowerPoint designer?
PowerPoint Designer is a feature within Microsoft PowerPoint that offers design ideas for slides. To use it, simply start creating a slide, and the Designer panel will offer suggestions. Ensure you have an active internet connection and a valid Microsoft 365 subscription.
How much does the presentation design cost per page?
Presentation design costs per page can range from $10 to $50 or more, based on the the design style, complexity, amount of content, and the designer's expertise.
How much does Slide Genius cost?
Slide Genius offers custom quotes based on the specific needs of a project. Pricing can vary based on the complexity of the presentation, the number of slides, and additional services required.
How do you start a product launch presentation?
Start a product launch presentation with a compelling story or statistic that highlights the need or opportunity for the product. Follow with an overview of the product, its features, benefits, and market potential, using engaging visuals to captivate the audience.
How do you introduce a product in a presentation?
Introduce a product by clearly defining the problem it solves, its unique value proposition, key features, and benefits. Use visuals and data to support your points and make the presentation partner introduction memorable.
How do you introduce a new product launch?
Introduce a new product launch by setting the stage with market insights, the inspiration behind the product, its differentiation points, and expected impact. Engage the audience with dynamic visuals and compelling data.
What are the five steps to launching a product?
The five steps to launching a product include market research, product development, creating a marketing plan, preparing the launch, and executing the launch strategy. Incorporating visual data presentations can enhance each step.
How much do presentation designers charge?
Presentation designers charge based on the project scope, with rates ranging from $50 to $200 per hour. Fixed project rates are also common, varying based on complexity and requirements.
What is a presentation design agency?
A presentation design agency specializes in creating visually appealing and effective presentation slides keynote presentations. They offer services like custom design, storytelling, and data visualization to enhance the impact of presentations.
Are presentation designers in demand?
Yes, presentation designers are in high demand, especially in fields requiring complex data visualization, persuasive storytelling, and professional branding in presentations.
Which company is best for presentation design?
The best company for presentation design depends on specific needs, but firms like Slide Genius, Presentation Design Co., and Buffalo 7 are highly regarded for their expertise and creativity in creating impactful corporate presentations.
Discover how we can create magic in your communication
%20(1).jpg)
Crafting Compelling Stories Around Your Products
Identifying the Core Message Introduction to Identifying the Core Message Every compelling product story begins with a core message, the essence of what you're trying to communicate to your audience. This isn't just about what your product does, but why it matters. Identifying this core message
Diagramming the Process: Recruitment and Selection Explained
Visualizing the Recruitment Funnel Engaging the Eye for Insight: The Power of Recruitment Funnel Visualization In the realm of talent acquisition, the recruitment funnel serves as a foundational framework, guiding HR professionals through the nuanced stages of attracting, engaging, and ultimately hiring the right candidates. By visualizing this process, organizations
Visual Storytelling: Showcasing Your Recruitment Strategy
The Art of Narrative in Recruitment Engaging the Audience: The Power of Storytelling in Recruitment In the realm of recruitment, the art of narrative isn't just a tool; it's a strategic powerhouse capable of shaping perceptions, engaging potential candidates, and setting the foundation for a strong
Influencing Trends and Lifestyle
Lifestyle Themes: Travel, Cuisine, and More Engaging the Wanderlust: The Essence of Travel and Cuisine Travel and cuisine are more than mere interests or hobbies; they are a lifestyle. The amalgamation of these elements represents a quest for exploration, not just of the world but of the flavors and traditions
Charts & Diagrams
Transform complex data into clear visuals with our extensive collection of 1,257 Charts & Diagrams templates for PowerPoint and Google Slides. Choose from flowcharts, mind maps, data-driven graphs, organizational charts, and more to engage your audience and enhance your presentations.
12-Point Diverging Process
Google Slides , PPTX
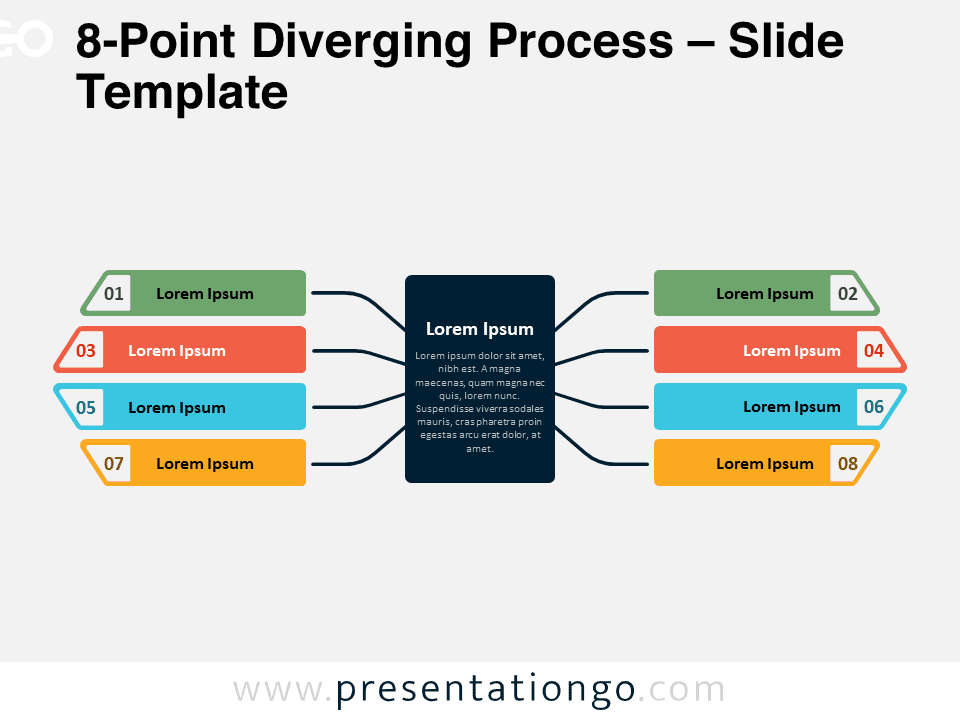
8-Point Diverging Process
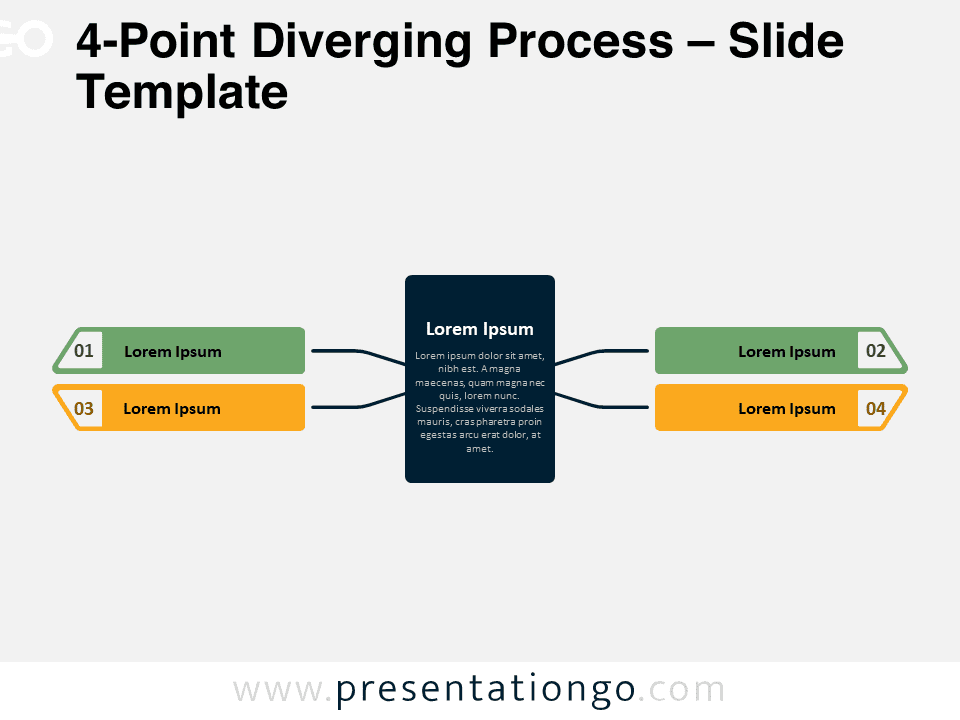
4-Point Diverging Process
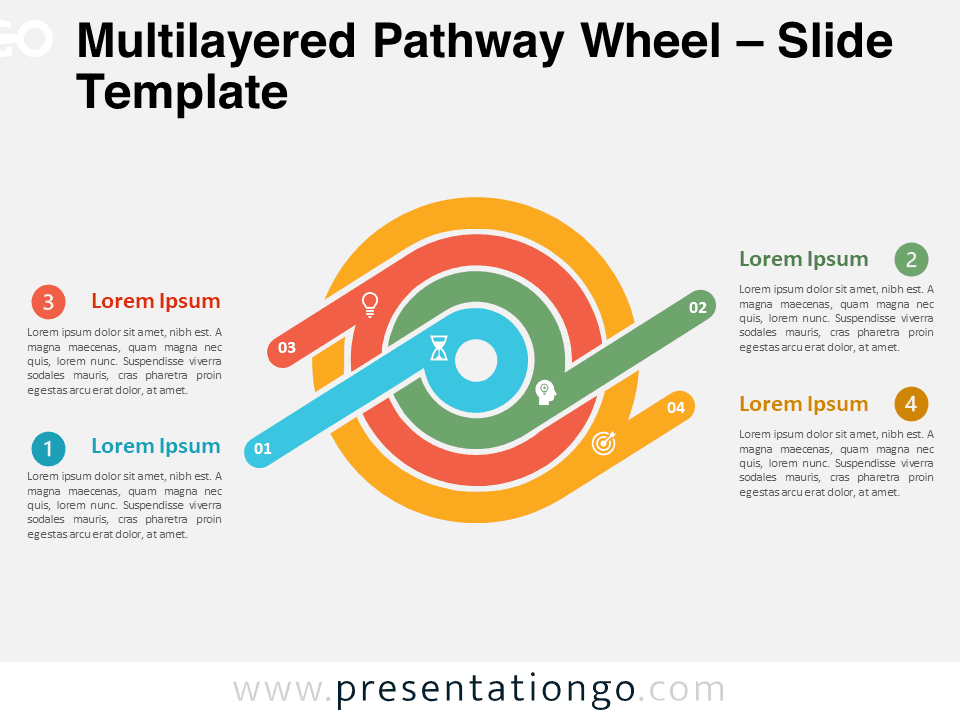
Multilayered Pathway Wheel
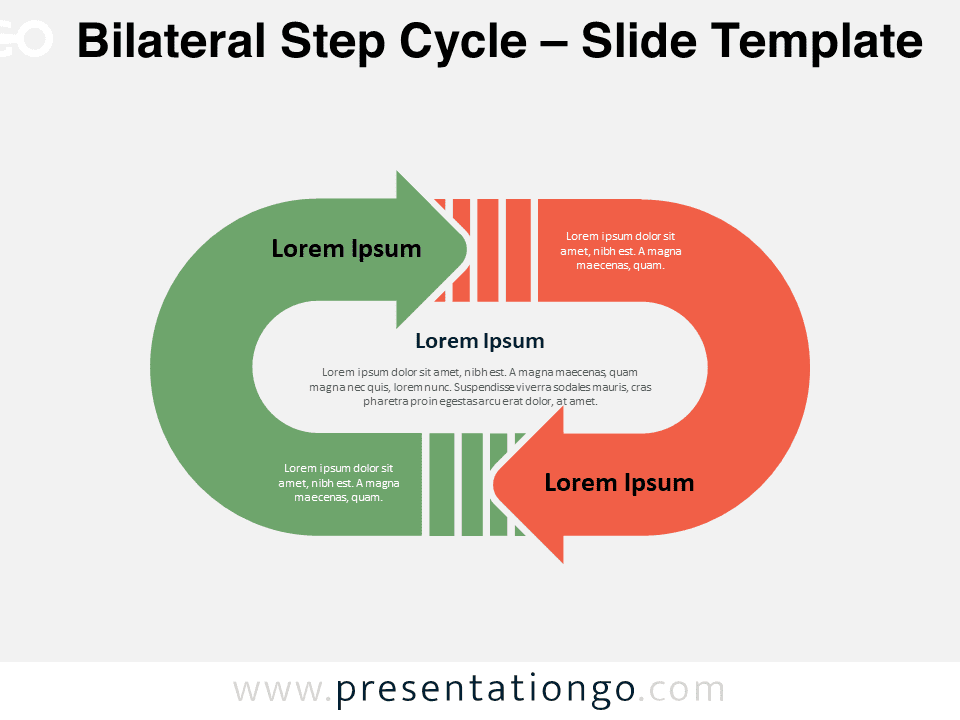
Bilateral Step Cycle
Alternating Hexagon Pair Process
5-Step Decision Funnel
4-Step Decision Funnel
3-Step Decision Funnel
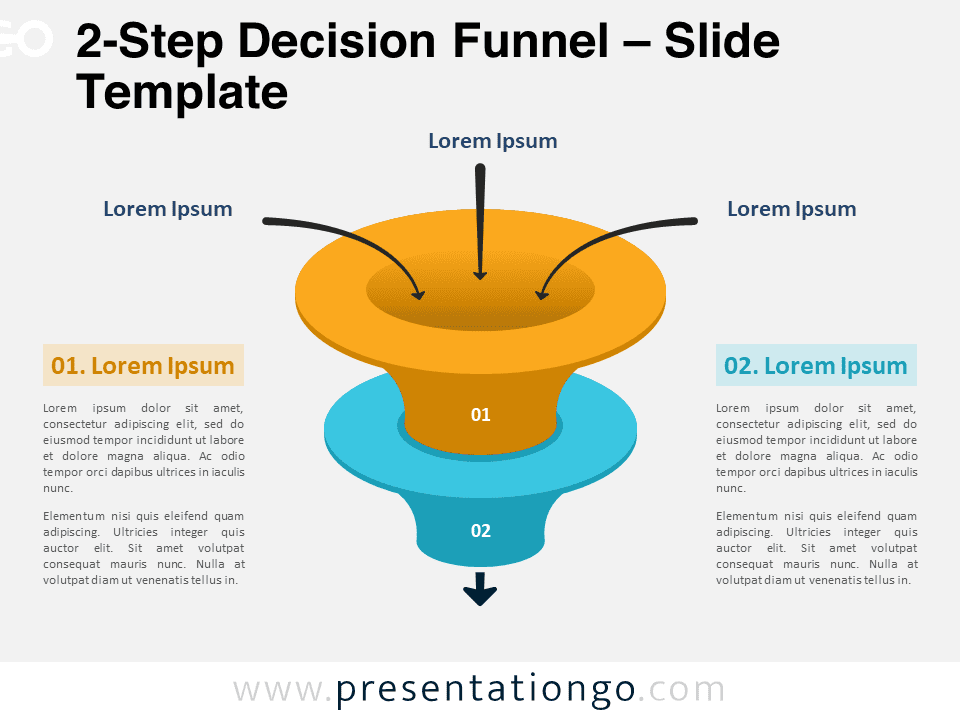
2-Step Decision Funnel
5-Position Org Chart
Neumorphic 5-Node Hierarchical
Search templates by categories, search templates by colors.
Love our templates? Show your support with a coffee!
Thank you for fueling our creativity.
Text & Tables
Graphics & Metaphors
Timelines & Planning
Best-Ofs & Tips
Terms and Conditions
Privacy Statement
Cookie Policy
Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) Policy
© Copyright 2024 Ofeex | PRESENTATIONGO® is a registered trademark | All rights reserved.

To provide the best experiences, we and our partners use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us and our partners to process personal data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site and show (non-) personalized ads. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.
Click below to consent to the above or make granular choices. Your choices will be applied to this site only. You can change your settings at any time, including withdrawing your consent, by using the toggles on the Cookie Policy, or by clicking on the manage consent button at the bottom of the screen.
Thank you for downloading this template!
Remember, you can use it for free but you have to attribute PresentationGO . For example, you can use the following text:
If you really like our free templates and want to thank/help us, you can:
Thank you for your support
- United States
- United Kingdom
By Simon Bisson , Contributor, InfoWorld |
Using Neo4j’s graph database for AI in Azure
New techniques make graph databases a powerful tool for grounding large language models in private data..

Once you get past the chatbot hype, it’s clear that generative AI is a useful tool, providing a way of navigating applications and services using natural language. By tying our large language models (LLMs) to specific data sources, we can avoid the risks that come with using nothing but training data.
While it is possible to fine-tune an LLM on specific data, that can be expensive and time-consuming, and it can also lock you into a specific time frame. If you want accurate, timely responses, you need to use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to work with your data.
RAG: the heart of Microsoft’s Copilots
The neural networks that power LLMs are, at heart, sophisticated vector search engines that extrapolate the paths of semantic vectors in an n-dimensional space, where the higher the dimensionality, the more complex the model. So, if you’re going to use RAG, you need to have a vector representation of your data that can both build prompts and seed the vectors used to generate output from an LLM. That’s why it’s one of the techniques that powers Microsoft’s various Copilots.
I’ve talked about these approaches before, looking at Azure AI Studio’s Prompt Flow, Microsoft’s intelligent agent framework Semantic Kernel , the Power Platform’s Open AI-powered boost in its re-engineered Q and A Maker Copilot Studio , and more. In all those approaches, there’s one key tool you need to bring to your applications: a vector database. This allows you to use the embedding tools used by an LLM to generate text vectors for your content, speeding up search and providing the necessary seeds to drive a RAG workflow. At the same time, RAG and similar approaches ensure that your enterprise data stays in your servers and isn’t exposed to the wider world beyond queries that are protected using role-based access controls.
While Microsoft has been adding vector search and vector index capabilities to its own databases, as well as supporting third-party vector stores in Azure, one key database technology has been missing from the RAG story. These missing databases are graph databases , a NoSQL approach that provides an easy route to a vector representation of your data with the added bonus of encoding relationships in the vertices that link the graph nodes that store your data.
Adding graphs to Azure AI with Neo4j
Graph databases like this shouldn’t be confused with the Microsoft Graph. It uses a node model for queries, but it doesn’t use it to infer relationships between nodes. Graph databases are a more complex tool, and although they can be queried using GraphQL, they have a much more complex query process, using tools such as the Gremlin query engine.
One of the best-known graph databases is Neo4j, which recently announced support for the enterprise version of its cloud-hosted service, Aura, on Azure . Available in the Azure Marketplace , it’s a SaaS version of the familiar on-premises tool, allowing you to get started with data without having to spend time configuring your install. Two versions are available, with different memory options built on reserved capacity so you don’t need to worry about instances not being available when you need them. It’s not cheap, but it does simplify working with large amounts of data, saving a lot of time when working with large-scale data lakes in Fabric.
Building knowledge graphs from your data
One key feature of Neo4j is the concept of the knowledge graph, linking unstructured information in nodes into a structured graph. This way you can quickly see relationships between, say, a product manual and the whole bill of materials that goes into the product. Instead of pointing out a single part that needs to be replaced for a fix, you have a complete dependency graph that shows what it affects and what’s necessary to make the fix.
A tool like Neo4j that can sit on top of a large-scale data lake like Microsoft’s Fabric gives you another useful way to build out the information sources for a RAG application. Here, you can use the graph visualization tool that comes as part of Neo4j to explore the complexities of your lakehouses , generating the underlying links between your data and giving you a more flexible and understandable view of your data.
One important aspect of a knowledge graph is that you don’t need to use it all. You can use the graph relationships to quickly filter out information you don’t need for your application. This reduces complexity and speeds up searches. By ensuring that the resulting vectors and prompts are confined to a strict set of relationships, it reduces the risks of erroneous outputs from your LLM.
There’s even the prospect of using LLMs to help generate those knowledge graphs. The summarization tools identify specific entities within the graph database and then provide the links needed to define relationships. This approach lets you quickly extend existing data models into graphs, making them more useful as part of an AI-powered application. At the same time, you can use the Azure Open AI APIs to add a set of embeddings to your data in order to use vector search to explore your data as part of an agent-style workflow using LangChain or Semantic Kernel.
Using graphs in AI: GraphRAG
The real benefit of using a graph database with a large language model comes with a variation on the familiar RAG approach, GraphRAG. Developed by Microsoft Research, GraphRAG uses knowledge graphs to improve grounding in private data , going beyond the capabilities of a standard RAG approach to use the knowledge graph to link related pieces of information and generate complex answers.
One point to understand when working with large amounts of private data using an LLM is the size of the context window. In practice, it’s too computationally expensive to use the number of tokens needed to deliver a lot of data as part of a prompt. You need a RAG approach to get around this limitation, and GraphRAG goes further, letting you deliver a lot more context around your query.
The original GraphRAG research uses a database of news stories, which a traditional RAG fails to parse effectively. However, with a knowledge graph, entities and relationships are relatively simple to extract from the sources, allowing the application to select and summarize news stories that contain the search terms, by providing the LLM with much more context. This is because the graph database structure naturally clusters similar semantic entities, while providing deeper context in the relationships encoded in the vertices between those nodes.
Instead of searching for like terms, much like a traditional search engine, GraphRAG allows you to extract information from the entire dataset you’re using, whether transcripts of support calls or all the documents associated with a specific project.
Although the initial research uses automation to build and cluster the knowledge graph, there is the opportunity to use Neo4j to work with massive data lakes in the Microsoft Fabric, providing a way to visualize that data so that data scientists and business analysts can create their own clusters, which can help produce GraphRAG applications that are driven by what matters to your business as much as by the underlying patterns in the data.
Having a graph database like Neo4j in the Azure Marketplace gives you a tool that helps you understand and visualize the relationships in your data in a way that supports both humans and machines. Integrating it with Fabric should help build large-scale, context-aware, LLM-powered applications, letting you get grounded results from your data in a way that standard RAG approaches can miss. It’ll be interesting to see if Microsoft starts implementing GraphRAG in its own Prompt Flow LLM tool.
Next read this:
- Why companies are leaving the cloud
- 5 easy ways to run an LLM locally
- Coding with AI: Tips and best practices from developers
- Meet Zig: The modern alternative to C
- What is generative AI? Artificial intelligence that creates
- The best open source software of 2023
- Generative AI
- Artificial Intelligence
- Graph Databases
- Microsoft Azure
- Cloud Computing
Author of InfoWorld's Enterprise Microsoft blog, Simon Bisson has worked in academic and telecoms research, been the CTO of a startup, run the technical side of UK Online, and done consultancy and technology strategy.
Copyright © 2024 IDG Communications, Inc.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

UPDATED 08:00 EDT / APRIL 10 2024
Gathid launches new identity governance solution using directed graph model

by Duncan Riley
Australian identity and access architecture company Gathid Ltd . today announced a new novel identity and access governance solution that uses a directed graph model for efficient anomaly detection and seamless integration across complex information technology infrastructures.
Designed for rapid deployment, immediate applicability and integration across varied IT infrastructures, the solution was created to tackle the need for scalable and cost-effective identity management.
Gathid argues that existing identity and access management solutions require centralized approaches, resulting in a reliance on a single or a small handful of vendors to facilitate large-scale contiguous deployments that maintain real-time identity concurrency between all systems. The large-scale deployments come at a high cost to purchase, migrate and enable, which is where Gathid aims to make an impact with its new solution.
The offering integrates with existing infrastructure to help organizations tackle increasingly complex identity security challenges. Gathid uses a novel application of a directed graph model for identity and access improvements, with a resource-efficient approach that can function across disconnected systems in hybrid and multicloud environments.
The identity model is reconstructed daily from the ground up, freeing organizations from the constraints of system syncs and incomplete delta reports. If automation misses a beat, Gathid highlights anything that has been missed and directs focus to critical compliance clean-up areas. The ongoing daily refresh cycle is claimed to be crucial in maintaining an accurate, always compliant access ecosystem.
The technology facilitates rapid deployment by efficiently integrating data from various sources, including digital platforms, operational technology and physical access control systems, without needing administrative rights or complex integrations. The platform is designed to make identity governance accessible and affordable for organizations of all sizes, analyzing role-based access and role mining even for legacy, air-gapped or specialized systems.
“We realized organizations that are not as mature as… industry giants didn’t have the resources to effectively identify who has access to what and – more importantly – whether they should have access at all,” said founder and Chief Executive Peter Hill. “This inspired us to invent a solution that helps organizations strengthen access management without completely overhauling their people, processes, physical infrastructure and technology.”
Based on the Gold Coast, Australia, with a satellite office in Seattle,Washington, Gathid is a publicly traded company, having been listed on the Australian Stock Exchange since 2017. The company was previously known as RightCrowd Ltd.
Image: Gathid
A message from john furrier, co-founder of siliconangle:, your vote of support is important to us and it helps us keep the content free., one click below supports our mission to provide free, deep, and relevant content. , join our community on youtube, join the community that includes more than 15,000 #cubealumni experts, including amazon.com ceo andy jassy, dell technologies founder and ceo michael dell, intel ceo pat gelsinger, and many more luminaries and experts..
Like Free Content? Subscribe to follow.
LATEST STORIES

Starburst to release its Iceberg-based lakehouse as a managed service

Onum raises $28M to help organizations extract their most valuable data in real time
Databricks delivers enhanced data analytics and intelligence for the energy sector
Automattic expands messaging portfolio with $125M acquisition of Beeper

Data security startup Cyera reels in $300M more at $1.4B valuation
BIG DATA - BY PAUL GILLIN . 1 MIN AGO
BIG DATA - BY MIKE WHEATLEY . 1 MIN AGO
SECURITY - BY DUNCAN RILEY . 1 MIN AGO
BIG DATA - BY MIKE WHEATLEY . 12 HOURS AGO
APPS - BY DUNCAN RILEY . 13 HOURS AGO
SECURITY - BY MARIA DEUTSCHER . 14 HOURS AGO

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To create a simple chart from scratch in PowerPoint, click Insert > Chart and pick the chart you want. Click Insert > Chart. Click the chart type and then double-click the chart you want. Tip: For help deciding which chart is best for your data, see Available chart types. In the worksheet that appears, replace the placeholder data with your own ...
Most Popular PPT Charts And Graphs You Can Use In Your Presentation. There are many different types of presentation charts and graphs you can use in PowerPoint. Depending on the data you want to analyze and present in an easy-to-understand format, you may need to do some digging around to find the best chart for your specific needs. ...
There are many other types of graphs and charts. But even those aside, anything that can help you showcase data in a visual manner will be a plus in your presentation. Your creativity is the limit! 5 tips for using data visualization in PowerPoint. Using data visualization in PowerPoint presentations is not hard, but it takes time to master it.
Click on the Chart icon to launch the Insert Chart menu. The Insert Chart menu will open with a variety of chart templates. On the left side, you'll see a variety of PowerPoint chart types, such as Column, Line, Pie, Bar and more. Start by clicking on a chart type on the left side.
Text and Font. Using bold font isn't going to make much difference in your graph. As far as possible, avoid using bold, underline or italic fonts. Keep the font size and type consistent throughout the presentation. Avoid effects such as shading, outline, and 3D letters. Always lighten secondary data labels.
Switch to the Insert tab and click on Chart . Insert > Chart to add a presentation graph in PowerPoint. A new dialogue window will open, where you have to select the chart type and the specific representation type—i.e., for area charts, you can choose from 2D or 3D area charts and their distribution method.
1. Use charts and graphs to compare data. One of the most common uses of charts and graphs is to compare data. Whether you are comparing sales figures, market trends or customer feedback, charts and graphs can help you present the information in a visually compelling way. Use bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, and scatter plots to showcase ...
Paul Hayden. 9. Only present key information. Think of what it means to the audience, perhaps just some of the data is enough (e.g. top 3 or 5 instead of the whole chart) 10. Concentrate on trends and changes. Concentrate on trends and changes rather than numbers and data. 11. 3D graphs are hard to read.
Title - The title of the graph should focus on the interpretation of the data, not the data itself. Remember that we are using a graph to help make a point, and the title will be a key factor in the audience interpreting the graph properly. For example, instead of a title like "Sales 1996-2001", you could say "Sales Up 42% '96-'01".
Add a chart or graph to your presentation in PowerPoint by using data from Microsoft Excel.
Presenting Tables, Graphs And Charts In a PowerPoint presentation doesn't have to be complicated.The tables and charts on PowerPoint have been used countless...
Now, let's start adding charts and graphs to your PowerPoint presentation. Open the PPT and create a blank slide. Then, under the Insert tab and click on Chart to get to the chart selection menu. You will get a variety of charts, including graphs, to choose from. The chart types will be given in the left panel.
To start charting in PowerPoint, simply select Insert Chart in the Insert menu. In the pop-up Chart menu, you'll be able to make a choice: bar chart, flow chart, or timeline chart. As with the tables, you can customize the color schemes, the size, and the layout. However, for the pie charts, you'll still have to resort to Excel.
To create a line graph in PowerPoint: Select the data you want to include in the chart. Click the 'Insert' tab and select the 'Line' chart type. Choose the specific line graph subtype you want to use (such as 2D or 3D) Add labels, titles, and customize the color scheme.
Add essential information on the graph. Use the information that will help the audience understand the graph better, but do not go overboard with the information. 11. Use suitable highlights in a bar chart. Do not highlight the bars with a pattern fill, shape fill, image fill, or anything that comes as a default.
5. Data Charts PowerPoint Presentation. PowerPoint graph templates like the 198 options in this are flexible. Re-use them for any number of presentations without repeating yourself. Use the flow charts, bar charts, and stacked bar charts to present your data visually. It's a great PowerPoint chart template!
Column and line graphs are built-in to PowerPoint, and a variety of different forms of charts can be embedded as well. 2. axes and axes labels Links can be added to axes to increase their specificity in your graphs. You can have axes be point, line or bar-shaped. They can have labels applied to them as well.
Introduction to Graphs and Charts Selection. When it comes to data visualization in business presentations, the choice of graphs and charts is pivotal. These visual aids are the storytellers of numerical tales, translating complex datasets into comprehensible narratives. The art lies in matching the story you wish to tell with the appropriate ...
Fortunately, there are 2 simple rules that bring clarity to your charts and graphs and make your message effective. Let's explore them…. Rule 1: Let your message decide your chart. Here is an interesting Murphy's Law when it comes to graphs and charts in presentations. 'The more proficient you are with spreadsheet software like 'Excel ...
6 tools for creating graphs and charts. Here are some of the best tools you can use to create graphs and charts, depending on your needs. Microsoft Excel Online. Cost: Free for basic features; full features available starting at $6.99/month for personal use; Best use cases: Financial modeling and analysis, budgeting and financial planning
These charts PowerPoint templates can enhance your presentations by providing visually appealing and professional-looking charts that effectively communicate data and statistics. With various chart styles and designs, you can easily present complex information in a clear and engaging manner, making your presentations more impactful and memorable.
Discover an extensive range of ready-to-use charts and diagrams for PowerPoint and Google. Our vast library features over 1,207 free, editable, and easy-to-customize designs to elevate your visual data representation and engage your audience. Charts and diagrams can be used to enhance any presentation, whether it's for a business meeting, a ...
Line Charts: Best for displaying trends over time or continuous data. Use when you have a series of data points connected by straight line segments. Pie Charts: Suitable for showing parts of a ...
Mapper is an algorithm to construct a graph that is similar to a Reeb graph, allowing for the abstraction of shape from data. Persistent homology is way to measure features in a dataset, and returns a set of points (a persistence diagram) that represents the structure of the dataset.
Here, you can use the graph visualization tool that comes as part of Neo4j to explore the complexities of your lakehouses, ... Using graphs in AI: GraphRAG.
Gathid uses a novel application of a directed graph model for identity and access improvements, with a resource-efficient approach that can function across disconnected systems in hybrid and ...
Use Microsoft Graph API to access Windows product information. Building applications and reports is becoming easier. We're starting to centralize Windows update data from across public documentation sites in the ... You can use its cohesive model to tap into the vast data reservoir across Microsoft 365, Windows, and Enterprise Mobility ...