- Contact sales
Start free trial

Top 10 Project Management Methodologies: An Overview

Table of Contents
- Waterfall Methodology
- Agile Methodology
- Scrum Methodology
- PMI / PMBOK
- Critical Path Method (CPM)
- Kanban Methodology
- Extreme Programming (XP)
- Lean Methodology
What Is a Project Management Methodology?
A project management methodology is a set of principles, tools and techniques that are used to plan, execute and manage projects. Project management methodologies help project managers lead team members and manage work while facilitating team collaboration.
There are many different project management methodologies, and they all have pros and cons. Some of them work better in particular industries or projects , so you’ll need to learn about project management methodologies to decide which one works best for you.
We’ll go through some of the most popular project management methodologies, which are applied in many sectors such as software development, R&D and product development.
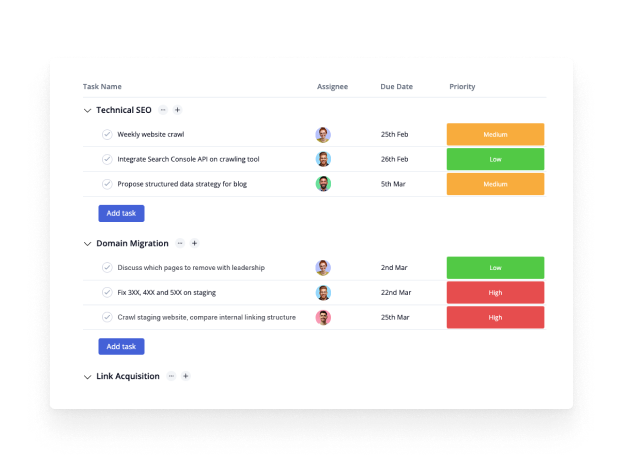
Top 10 Project Management Methodologies
If you manage projects, you need to learn about project management methodologies. Here’s a quick overview of the most commonly used project management methods that you can use.
1. Waterfall Methodology
This may be the most straightforward and linear of all the project management methods in this list, as well as the most traditional approach. The name is apt, as the waterfall methodology is a process in which the phases of the project flow downward. The waterfall model requires that you move from one project phase to another only once that phase has been successfully completed.
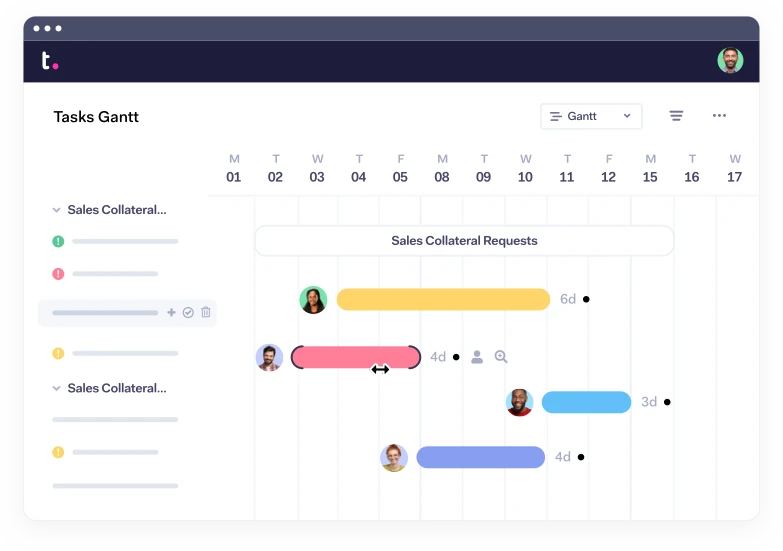
When to use it: The waterfall approach is great for manufacturing and construction projects , which are highly structured, and when it’s too expensive to pivot or change anything after the fact. The waterfall method makes use of Gantt charts for planning and scheduling.
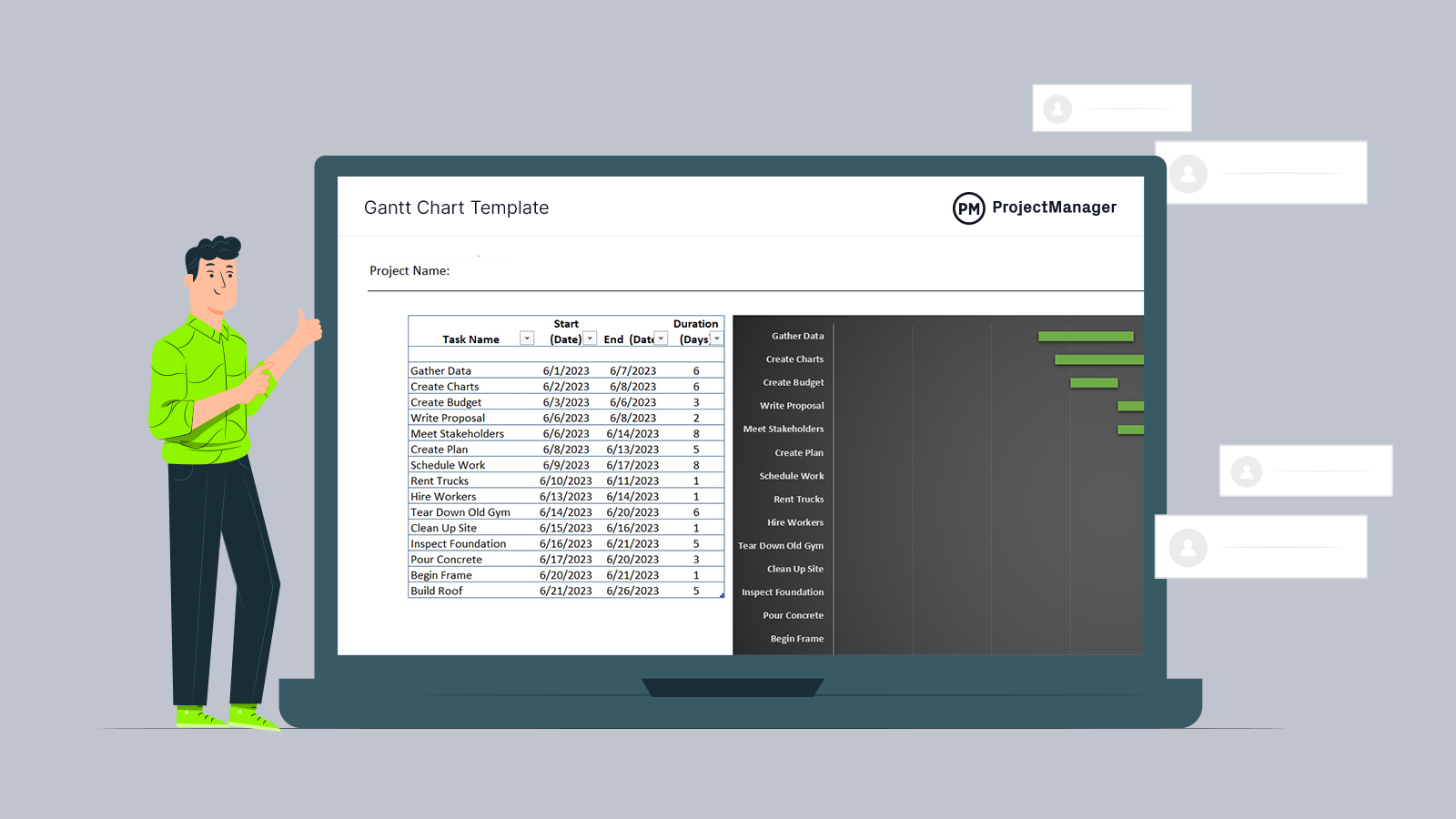
Get your free
Gantt Chart Template
Use this free Gantt Chart Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
2. Agile Methodology
What it is: In a nutshell, Agile project management is an evolving and collaborative way to self-organize across teams. When implementing the agile methodology , project planning and work management are adaptive, evolutionary in development, seeking early delivery and are always open to change if that leads to process improvement. It’s fast and flexible, unlike waterfall project management.
The agile methodology offers project teams a very dynamic way to work and collaborate and that’s why it is a very popular project management methodology for product and software development. That’s because what we think of as agile really appeared in 2001 with the publication of the “Manifesto for Agile Software Development,” authored by 17 software developers.
When to use it: The practice originated in software development and works well in that culture. How do you know if agile is for you? It has been applied to non-software products that seek to drive forward with innovation and have a level of uncertainty, such as computers, motor vehicles, medical devices, food, clothing, music and more. It’s also being used in other types of projects that need a more responsive and fast-paced production schedule , such as marketing.
3. Scrum Methodology
What it is: Scrum is a short “sprint” approach to managing projects. The scrum methodology is It’s ideal for teams of no more than 10 people and often is wedded to two-week cycles with short daily meetings, known as daily scrum meetings . It’s led by what is called a scrum master . Scrum works within an agile project management framework, though there have been attempts to scale Scrum to fit larger organizations.
The term scrum was introduced in a “Harvard Business Review” article from 1986 by Hirotaka Takeuchi and Ikujiro Nonaka. It became a part of agile when Ken Schwaber and Mike Beedle wrote the book “Agile Software Development with Scrum” in 2001. Schwaber formed the Scrum Alliance in 2002, a certified scrum accreditation series. Schwaber left the Scrum Alliance in 2009 to start a parallel accreditation organization called Scrum.org.
When to use it: Like agile, the scrum methodology has been used predominantly in software development, but proponents note it is applicable across any industry or business, including retail logistics, event planning or any project that requires some flexibility. It does require strict scrum roles , however.
4. Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK)
What it is: This is the granddaddy of methodologies if it’s a methodology at all. The Project Management Institute (PMI) is a not-for-profit membership association, project management certification and standards organization.
This organization produces a book called the “Project Management Body of Knowledge” or PMBOK. The PMBOK provides definitions and guidelines for project planning, scheduling, executing and controlling. For example, the project management process groups describe the project life cycle, while the 10 project management knowledge areas explain how to manage a project.

When to use it: Almost any project can benefit from PMBOK, as all projects big and small are going to go through the various stages of the project life cycle outlined in the book. It’s a great way to keep everyone on the same page, so to speak, and offers a clear definition of how a project is managed.
The Project Management Institute it’s also the organization that grants various project management certifications such as the project management professional (PMP) certification, which is the gold standard among project managers and is recognized all over the world. PMBOK is a great traditional framework to run a project.
5. Critical Path Method (CPM)
What it is: In the critical path method (CPM), you build a model of the project, including all the activities listed in a work breakdown structure , the duration of those tasks, what if any task dependencies there are and marking off milestones to indicated larger phases of the project or points in which your project deliverables are due.
With this information, you can identify the longest sequence of tasks to finish the project, which is called the critical path. You’ll need to keep an eye on those tasks because if one of them is delayed, the whole project will be delayed.
The critical path method was developed in the late 1950s by Morgan R. Walker of DuPont and James E. Kelley, Jr., of Remington Rand. DuPont was already using a precursor of CPM as early as the 1940s, and it was applied to the Manhattan Project.
When to use it: CPM works better with smaller or mid-sized projects. The larger the project, the more difficult it can be to take all the data you need to diagram and make sense of it without project management software .
6. Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM)
What it is: In , you’re focusing on resources that you’ll be using to complete the project, such as teams, equipment, office space, etc. It’s a less technical method of project management that doesn’t put as much emphasis on task order or schedule , but rather on balancing resources and keeping them flexible.
First introduced in 1997, in the book “Critical Path” by Eliyahu M. Goldratt, it has been credited with making projects anywhere from 10-50% faster and/or cheaper.
When to use it: CCPM can be applied to both large and small companies, and for projects that include industries such as construction, software development and tech research and development.
7. Kanban Methodology
What it is: The kanban methodology is a visual approach to project management. The name is literally billboard in Japanese. It helps manage workflow by placing tasks on a kanban board where workflow and progress are clear to all team members. The kanban methodology helps reduce inefficiencies and is a great project management tool for many purposes such as lean manufacturing or agile projects.
Kanban project management has been around since the late 1940s when it was studied by Toyota used the rate of demand to control the rate of production of its vehicles. The car company applied it to its lean manufacturing model, known as the Toyota production system.

With the dawn of visual planning boards in software in our era, like Trello, there are now new uses for kanban tools and kanban methods. Agile teams use kanban boards for story-boarding user stories and for backlog planning in software development.
When to use it: Another process developed initially for manufacturing and for software teams, the kanban method has since expanded and has been used in human resources, marketing, organizational strategy, executive process and accounts receivable and payable. Almost anyone can plan with Kanban boards, adding cards to represent project phases, task deadlines, people, ideas and more. Kanban software makes this methodology especially accessible.
8. Extreme Programming (XP)
What it is: It sounds like some dangerous sport the kids are into, but in fact, XP is a type of agile software development with short development cycles and multiple releases to improve productivity. Customer requirements are sought and can adapt to the course of the project.
Created by Kent Beck while working on the Chrysler Comprehensive Compensation System payroll project, he literally wrote the book (“Extreme Programming Explained”) in 1999. But many of its practices have been around for a while.
When to use it: When requirements change frequently, then you’ll want to use a methodology such as XP. It’s good when your customer doesn’t have a clear idea of what they want.
9. Lean Methodology
What it is: Lean project management is what you’d think it is from its name: a way to cut waste and in so doing increase value in projects and manufacturing processes. So, lean focuses on eliminating waste from key processes to continuously be impacting positively on the value stream. It does this by optimizing separate technologies, assets and verticals.
Lean project management goes back to Henry Ford and his flow production for automating the process of building cars. Toyota picked up on the idea, as well, extending their idea beyond manufacturing to the continuous improvement of the product development process.
Today, software development teams run lean processes to focus on end-user feedback and increased value, which means Lean methodology has taken on a new meaning, particularly with the publishing of Lean Startup, by Eric Ries, who advocates for rapid prototyping, end-user feedback and early and rapid product delivery.
When to use it: Lean project management was first developed by Toyota and is obviously a great methodology for manufacturing. In fact, it’s also referred to as lean manufacturing , but it has been adopted by construction and education industries, among others in the manufacturing space and countless startups and software development firms looking to drive products focused on the end-user.
10. Six Sigma
What it is: Introduced by engineers working at Motorola in the mid-1980s, Six Sigma works to improve quality by identifying what is not working in the project. It applies quality management, including empirical statistics, and employs personnel who are experts in these disciplines. There is also a Lean Six Sigma that adds lean methodology to eliminate waste.
As a doctrine, it says that continued efforts to achieve results that are stable and expected are most important to success. Processes can be refined and improved. It takes the whole organization, from the top down, to sustain quality in a project.
When to use it: This methodology works best in larger organizations. Even companies with a few hundred employees are likely too small to take advantage of its benefits. It requires a certification to practice. Learn about six sigma certification here.
11. PRINCE2
What it is: PRINCE2 stands for Projects IN Controlled Environments and is a structured certified methodology. It was initially created by the UK government for IT projects. PRINCE2 is not like other traditional methods like waterfall, in that it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, but follows seven principles, themes and procedures.
When the UK government adopted standards for IT systems in 1989, they called in PRINCE. PRINCE2 came about in 1996 as a more general project management method. It is now a popular project management methodology throughout all UK governmental agencies and the United Nations.
When to use it: Adopted by many other countries’ governments, PRINCE2, so, as you can imagine, it’s not always suitable for smaller projects.
ProjectManager Works with Any Project Management Methodology
There are almost as many methods to manage as there are projects. But they all share one thing in common: getting deliverables done on time and within budget. No matter which project management methodology you choose ProjectManager is the one software you’ll need to do it.
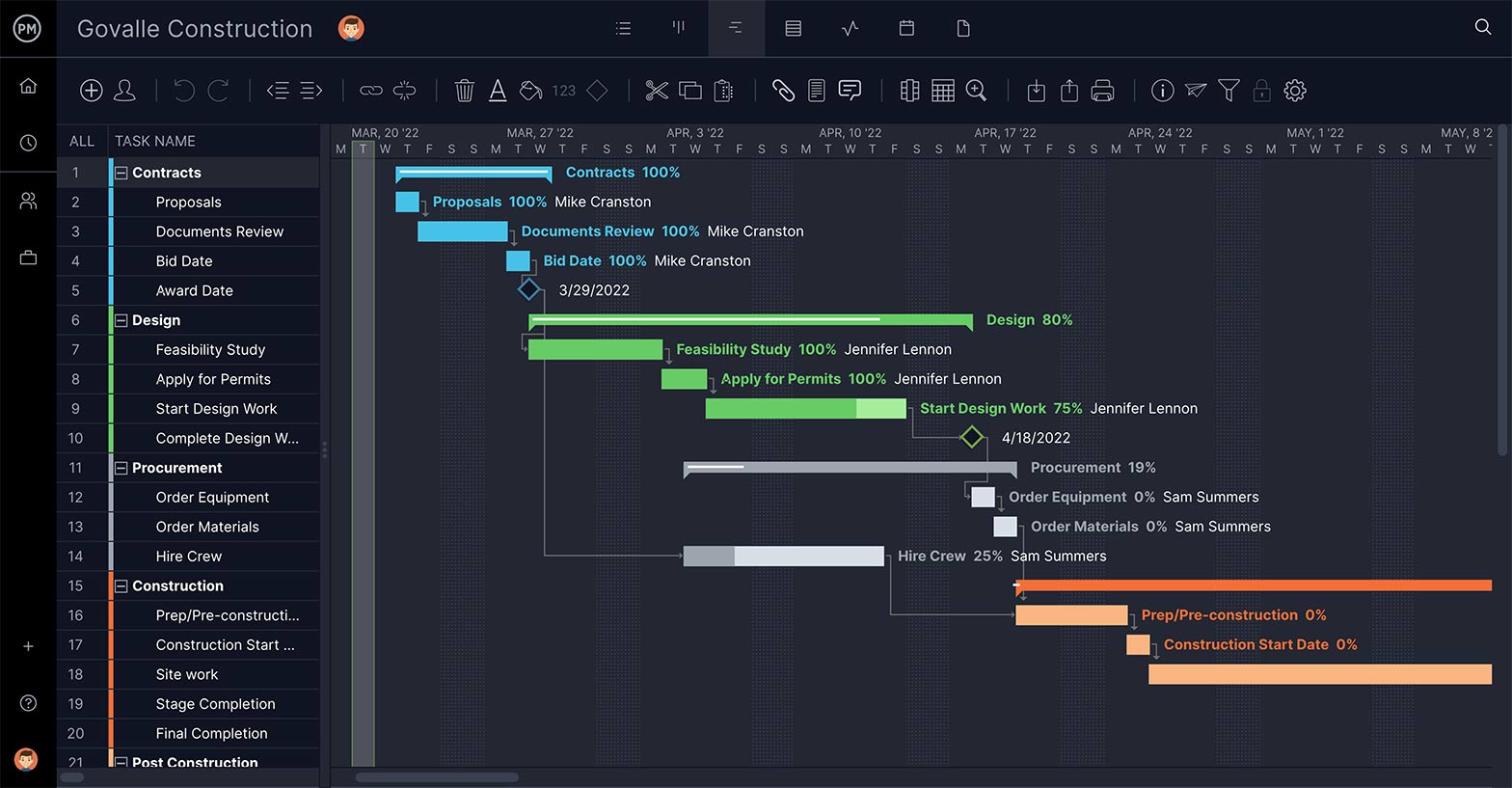
Tools for Waterfall Project Management
Waterfall is structured. One thing follows the next and it’s all planned out. No problem. ProjectManager has an online Gantt chart . Import your task list to start a new project. Add due dates and the tasks populate a timeline. Link-dependent tasks to avoid bottlenecks. Set milestones to separate the project into phases. You control the project step by step.
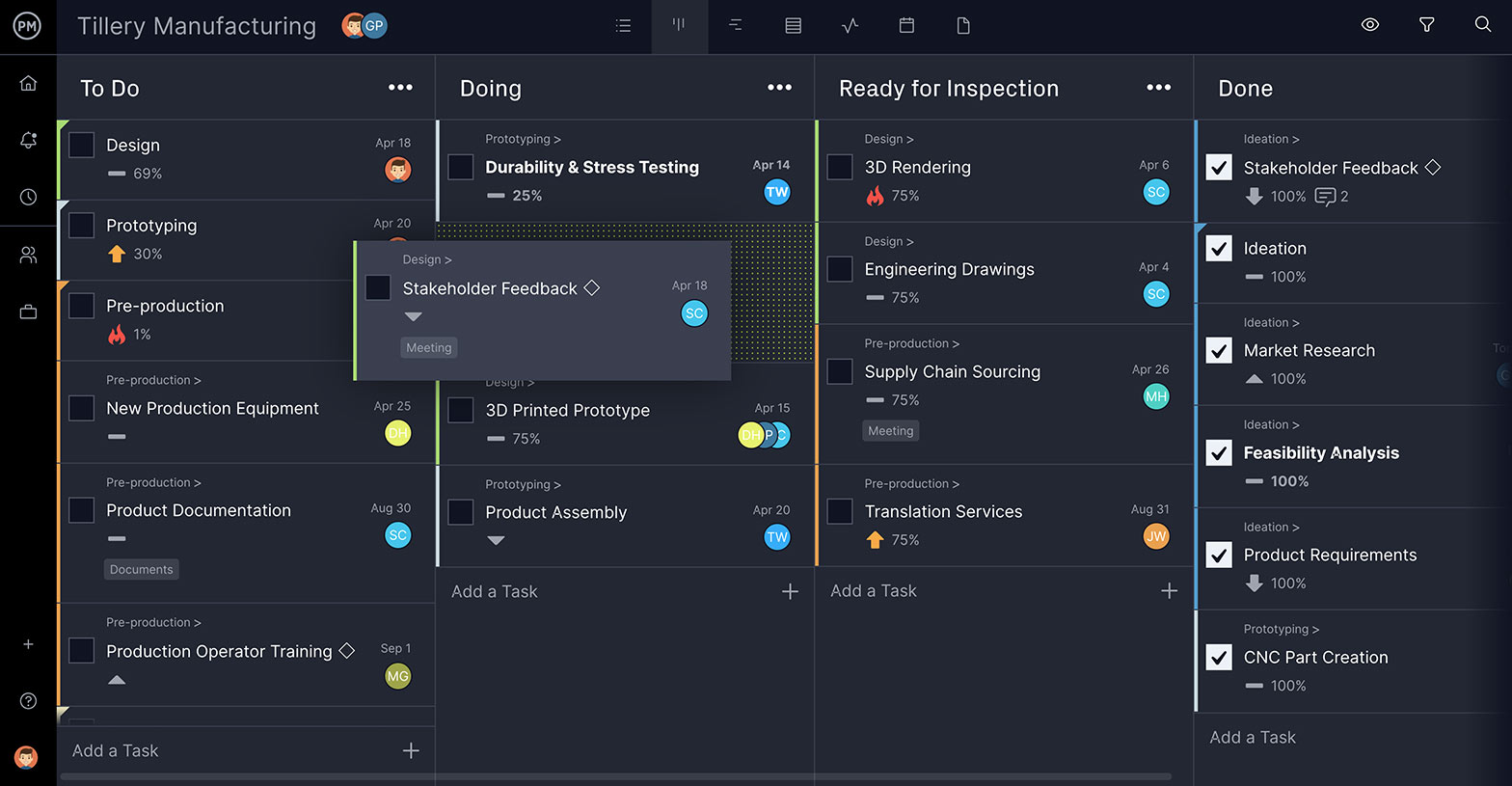
Tools for Agile Project Management
Gantt charts aren’t going to help as much as other project tools if you’re working in an agile framework. That’s true, but ProjectManager is flexible enough to serve scrum teams with multiple project views.
Use the kanban view to map out your sprint. Product backlogs are collected on cards, which can be prioritized for scrum teams to know which user story to work on first. Then the sprint can be archived, so when doing a sprint retrospective, teams can learn from their mistakes and improve the process.
Multiple Views for Diverse Teams
What if your organization is larger, with different divisions, some that work with an agile project management framework and others with a more traditional waterfall methodology? What’s great about ProjectManager is that it can switch from one view to the other, giving IT teams a kanban board view for their scrum sprints and managers a Gantt chart for a bigger project planning overview.
The real-time dashboard and reporting features gather the same data and crunch the same numbers, so whatever project management method you use is tracking the same results.
Yes, ProjectManager is an award-winning project management software for a reason. It’s flexible enough to work in an agile environment, traditional waterfall methodology or a hybrid of the two. You decide, not the software, which means ProjectManager is the one tool to bring in your project, however, you manage it, successfully.
Related Content
- Project Integration Management
- Waterfall Project Management Software
- Agile Project Management Software
- Critical Path Software
There are more project management methodologies, but these are some of the most popular. Regardless of which you use, you need a project management tool to best manage all your processes and projects. ProjectManager is an online PM tool, so whatever methodology is right for you our software will help you apply it to a successful end. Try it free for 30 days and see for yourself.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
Chapter 3: Project management methodologies
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
There are many project management methodologies and frameworks out there, designed to assist with different types of projects. But how do you know which one is best for your efforts?
In this section, we’ll walk through the most popular PM methodologies, and share advice for how to choose the best method to fit your needs.
Waterfall or traditional project management
Waterfall or traditional project management is based on a defined set of tasks that are completed sequentially to produce a final deliverable. This method of PM is simple and predictable, but not very flexible.
Waterfall project management is ideal for projects with a single, large deliverable, like a building. While it’s less useful for projects that require a lot of flexibility, are subject to change, or require multiple, dependent tasks to be completed in tandem, like software development.
The main benefits of Waterfall are tight planning and organization, and a high degree of control over each project task and the greater project schedule. That said, using Waterfall can make it difficult to adapt to unexpected events or changes to project scope, which can result in added time, resources, and cost.
Teams often use a Gantt chart , a visual timeline tool that maps out project tasks in succession, in Waterfall-managed projects. Learn more about Gantt charts in Chapter 9 .
To learn more about the phases and pros and cons of Waterfall, visit our in-depth guide to creating and using a Waterfall chart .
The Agile family
The Agile family is a category of project management methodologies that prioritizes flexibility and continuous improvement over rigid, sequential processes. There are many popular methodologies within Agile, and we’ve dug into each below.
Agile project management
In Agile project management , teams complete smaller, incremental tasks, and then continually review, refine, and iterate based on feedback and demands of the end users.
Agile project management was formalized in 2001 by a group of software developers intent on finding a more collaborative, flexible method to complete projects. The group documented their ideas in the Manifesto for Agile Development , which lays out the following four values:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
Agile PM prioritizes a collaborative relationship between the end user and the project team. The customer sets the project objectives, but the deliverables are subject to change as the team incrementally executes each project task. In Agile, each development feature is called a user story , which reflects how the end user will interact with it.
Agile project management was initially intended for software development, but is now commonly used across a variety of industries and types of projects. Learn more about the Agile process and how to implement it by reading our comprehensive guide to Agile PM .
Pros and cons of Agile project management
Agile is a good fit for projects that require a high degree of flexibility and are likely to shift as the project progresses. The top benefits of Agile include the following:
- Less upfront planning
- Increased open communication
- Continual feedback
- Flexible objectives
When used effectively, Agile also often leads to speedier delivery.
However, there are some tradeoffs to this flexible approach:
- Lack of concrete delivery date, which can lead to scope creep
- A high degree of dedication and flexibility from the project team
Is Agile right for you?
Remember, Agile isn’t for everyone. The methodology is likely not right for your team if any of the following apply to you:
- Your project is not very urgent.
- Your client’s expectations don’t support Agile (e.g., they want to give final approval at every stage of the project, or incremental delivery isn’t appropriate for the project specs).
- You or your client’s organization requires detailed documentation at every stage.
- Your current processes are not set up for a more flexible approach.
- Your team or organization doesn’t currently use Agile, and implementing it would be too costly or time consuming.
In the following sections, we’ll go over other methodologies that fall within the Agile family.
Additional Resources
The ultimate agile dictionary, free agile project management templates, best practices for agile project planning.
Scrum , the most popular Agile methodology, involves smaller teams that complete tasks in short, time-bound periods, called sprints , in order to incrementally work through pieces of a larger project or release.
Scrum typically leads to greater responsiveness in customer relationships, lower costs of development, increased job satisfaction, and more immediate returns. Scrum is a fluid practice that takes many moving parts, teams, and goals into consideration as the project progresses.
Scrum teams also engage in four regular meetings, or ceremonies , which provide structure to each sprint:
- Sprint planning: At this meeting, the product is presented and everyone on the Scrum team voices any concerns and feedback. The team designates priorities and estimates the timeline.
- Daily stand-up: The Scrum team meets daily during the sprint to debrief with the team, establish a daily plan, and voice any concerns so the team can address them together.
- Sprint review: Held at the end of each sprint, this meeting is a review of the working product and gives stakeholders transparency into what the team accomplished during the sprint.
- Sprint retrospective: The sprint retrospective is a meeting that occurs after each sprint to discuss team performance and establish ways to improve future efforts.
Each Scrum team has designated members who own specific pieces of the process. These roles include the following:
- Product owner: Possesses a thorough understanding of the product’s business value and serves as the middleman who communicates the stakeholder needs to the development team and writes and prioritizes user stories.
- Development team: Performs the technical development of the product and is responsible for the analysis, design, code writing, testing, and technical communication based on the user stories provided by the product owner.
- Scrum Master: Assists in the progress of the Scrum team by working hand-in-hand with the product owner and the development team to streamline work and eliminate distractions.
As with Agile, Scrum is popular in software development, but it can also be deployed successfully across marketing, design, and other creative projects. Learn more by reading our guide to implementing Scrum with the right tools .
Kanban is an Agile framework that prioritizes continuous improvement , an ongoing effort to improve a product or service incrementally. Kanban teams complete work items based on team capacity and manage resources using a visual kanban board that shows task status.
Kanban originated in Japan in the 1940s. Based on what he had seen in supermarkets, Toyota engineer Taiichi Ohno implemented a supply-and-demand method on the factory floor, which greatly improved the company’s inventory management.
Teams at Toyota created a visual cue (a kanban, which translates to “visual sign” or “card”) to communicate that they were ready to “pull,” or take on, more tasks or materials to complete their work. This approach enabled workers to only take on new tasks when they had capacity for them, which reduced excess work in progress (WIP) . This style of work is now known as the just-in-time (JIT) approach.
How to use a kanban board
The Kanban methodology centers on the kanban board, which is either a physical or digital “board” that includes three columns (or lanes ): to-do, doing, and done. Team members move cards, representing individual tasks, to different columns as a way to track task status. This provides a quick view of how items are progressing and ensures teams have adequate capacity to take on new work.
In recent years, teams have moved to online, digital kanban boards, which helps distributed teams collaborate on projects and gain real-time visibility into the work getting done. You can learn more about setting up a Kanban board with our guide .
Pros and cons of Kanban
Overall, Kanban is great for teams that have many incoming requests, short work cycles, and flexibility with resources and scheduling. However, Kanban can be difficult for teams that work on many interconnected, dependent tasks, or have tight deadlines to adhere to.
To learn more about implementing kanban from the ground up, read our complete guide for newbies .
Critical path method
Critical path method (CPM) is a technique for estimating the total duration of a project by identifying the order in which you must complete all project tasks, and then mapping out your sequenced tasks, called dependencies .
CPM follows the basic steps below:
- Identify all project tasks.
- Identify dependencies among tasks.
- Estimate the duration of each task.
- Add up the durations to calculate the total duration of your project.
- Update the critical path as the project progresses to compare estimated vs. actual timelines.
CPM helps teams reduce project timelines by identifying and scheduling the most important tasks and then scheduling other tasks to happen in parallel. CPM also helps with project planning, as you can easily reference estimated vs. actual project schedules and more accurately estimate how long each task will take on future projects.
Learn more about the steps and advantages of the method with our beginner’s guide to the CPM .
The change management methodologies
Change management is an umbrella term for techniques that help individuals, teams, and organizations implement new processes or achieve organizational change. In this section, we’ll cover event chain and extreme project management.
To learn more, visit our essential guide to change management , or find free change management templates .
Event Chain methodology
In event chain methodology , you identify tasks (events) and their relationships (event chains) in order to properly allocate resources and assess and reduce project risk.
The goal of event chain is to estimate the amount of time and resources you need to complete a project. This method follows some of the same steps as the critical path method — you also break down activities into smaller tasks and outline their dependencies and durations. But, in event chain, you do so to create a realistic timeline and budget, rather than to simply better manage the tasks (and task order).
Event chain can also serve as a modeling technique to create more conservative scheduling estimates, which ultimately improves performance by building in time to address unforeseen risks.
This methodology is often used in change management efforts to eliminate the need to overhaul projects, which can be extremely time consuming and resource-heavy.
Extreme project management
Extreme project management (XP or XPM) is used to manage a massive amount of change in a short period of time. XPM is ideal for fast-paced, complex projects that can handle a trial-and-error approach to successfully pull off the effort.
Think of XPM as the opposite of Waterfall methodology. As opposed to valuing a linear, planned project development process, XPM allows you to change your project plan, budget, and the final deliverable as requirements shift. In XPM, the onus is on the project team to self-correct and shift as necessary.
Extreme project management works well for projects with a high-degree of uncertainty, but is less useful for projects with a clear-cut timeline, budget, and scope.
The process-based methodologies
Process-based methodologies approach work as a collection of processes, rather than a strict methodology that you apply to a single project. These approaches are sometimes used as part of a larger business process management (BPM) strategy.
Lean is an approach aimed at maximizing value while minimizing waste. When deployed properly, Lean helps to identify and eliminate bottlenecks, delays, and other inefficiencies in order to deliver value faster.
Lean originated in manufacturing in the 1950s, but it has evolved over time and is used today across industries. As laid out in the book Lean Thinking , Lean involves the following five core principles and activities:
- Define value: Identify the value of each product or service in the eyes of the customer.
- Map the value stream: Map out the process (aka value stream ) and identify areas of waste, in terms of resources, time, or redundancy.
- Create flow: Create a flow plan that eliminates the waste you identified.
- Employ a pull system: Progress through the plan only as the customer has new needs. Doing so will prevent you from taking on too much at once, or creating a bottleneck at any stage of the process.
- Pursue perfection: Using the idea of continuous improvement, aim to eliminate as much waste as possible from your process.
Visit our comprehensive guide to Lean project management to learn more about different types of Lean methodologies and the best tools for implementing Lean.
Six Sigma is a process improvement methodology that aims to improve quality across projects. Six Sigma takes a statistical approach to measuring and eliminating bugs or defects in project deliverables and raising quality standards.
The basic steps in Six Sigma include finding defects, identifying and eliminating their cause(s), and optimizing processes to increase reliability and accuracy going forward.
Building off the Lean principle of pursuing perfection, Six Sigma aims to eliminate all opportunities for defects by using data-driven improvement cycles to achieve its goal.
There are two main Six Sigma methodologies:
- DMAIC: This stands for define , measure, analyze, improve, control , and is intended to help you improve existing processes.
- DMADV: This stands for define, measure, analyze, improve, verify, and is best for when creating new processes or products.
There is no single, formal certification body for Six Sigma, but many organizations offer training so teams can learn to implement the practice in their organization. Read our article on Six Sigma belts and certifications to learn more.
Six Sigma works well for teams who are interested in implementing data-driven ways to reduce defects and optimize business processes, but is less ideal for those looking for a strict set of steps to follow.
Read our in-depth guide to all things Six Sigma to learn more.
Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma is a hybrid approach to process improvement that combines the Lean principle of no waste and the Six Sigma principle of no defects to improve quality across processes, projects, and products.
Lean Six Sigma offers the following benefits:
- Increased cost savings due to fewer bugs or defects
- Improved quality
- Time savings due to fewer process issues
- Improved data-driven decision making
- Continuous process improvement throughout the organization
While Lean Six Sigma originated in manufacturing, a variety of industries can deploy it to reap benefits. The most common use cases include healthcare, construction, design, and government.
All About Lean Six Sigma
Free lean six sigma templates, other project management methodologies.
Below, you’ll find details on a few more project management methodologies that are gaining traction in the modern PM world.
PRINCE2 , or Projects in Controlled Environments , is a project management methodology that focuses on defining and delivering work against precise requirements. As opposed to Agile PM, PRINCE2 emphasizes intense planning and documentation of work items.
PRINCE2 is a hybrid methodology initially used for information technology (IT) projects to help reduce cost and time overruns. Now, it’s deployed across many different industries.
This approach works well for projects with a clearly defined goal. However, if you need more flexibility, or don’t have time to properly plan and document work, Agile methods might be a better option.
PRiSM , or Projects Integrating Sustainable Methods , is a modern project management methodology that values sustainability over all else. The goal of PRiSM projects is to reduce the environmental impact of a project and drive meaningful social impact.
The PRiSM model is based on the following six principles:
- Commitment and accountability
- Ethical decision making
- Integration and transparency
- Principal and values-based deployments
- Social and ecological equity
- Economic prosperity
Implementing PRiSM is a long term mindset shift that puts sustainability and equity at the center of all processes and projects and aims to maximize value for all involved.
Why you should choose a PM methodology for your organization
Choosing an organization-wide project management method ensures teams have a consistent guideline for how to manage each aspect of their projects, like resources, budget, communication, timeline, and more.
Of course, some teams and projects require different levels of planning, flexibility, and documentation. And, it can be overwhelming to choose one “perfect” approach when there are so many options out there.
But, by assessing the types of projects that you typically take on — as well as your existing processes — you can identify the most effective methodology for you.
In some cases, organizations may select multiple project management types to meet the requirements of different projects and teams.
How to choose the best PM methodology for you
To identify the right project management methodology, first consider the details of your project. Then, assess your existing systems and processes. Look at both what you need as well as what you already have in place to select the best method.
Ask yourself the following questions to evaluate your project needs:
Project basics
- What is the project’s focus?
- What industry are you in?
- How complex is the project?
- Is the project scalable?
Flexibility
- How flexible are your timeline, budget, and deliverables?
- How much planning do you need to do beforehand?
- What is your allotted budget, and how flexible is it?
- What resources do you have, and what additional resources do you need to obtain?
- How flexible is your timeline?
- Are there set start and end dates?
- Does your project have key milestones or a critical path?
Roles and responsibilities
- How many people or teams are working together on this project?
- How specialized is the work?
- What is the level of customer and stakeholder involvement?
After you’ve worked through the project-related questions, follow these steps to identify which methodology aligns best:
- Outline the main variables, like timeline, resources, and budget, that will drive the project.
- Consider how the methodology you choose will impact these variables, such as how a more flexible approach might affect a hard-and-fast deadline.
- Weigh the pros and cons of each methodology against the needs of your project. Think both about which will be the best fit and which will be least disruptive to your current processes.
- Collaborate with other team members to get input.
- Roll out the methodology to the team. This includes educating everyone on the new processes and setting up the necessary tools and documentation systems.
- Apply the methodology to the project and monitor it for success.

Here’s a simplified cheat sheet you can use to identify which methodology will work for your next project:
Discover a better way to streamline workflows and eliminate silos for good.
- Jira Software
- Jira Work Management
- Jira Service Management
- Atlassian Access
- Company News
- Continuous Delivery
- Inside Atlassian
- IT Service Management
- Work Management
- Project Management

6 popular project management methodologies and what they’re best suited for
You’re a project manager who has just been tasked with managing two very different, yet intertwined projects. It’s up to you to choose the best project management methodology for each project.
One project is with your development team. They need to overhaul your organization’s website to improve the clunky and somewhat confusing user experience—from the moment that a customer lands on the site to after they make a purchase. The development team is super flexible and open to breaking up into smaller teams in order to tackle specific aspects of the website overhaul faster.
The catch with this project? It’s on a time crunch.
The website has to be overhauled before the launch of your second and longer-term project: a large-scale marketing campaign around a new line of products that are launching next quarter.
First of all, you can do this! Breath in, breath out, read on, choose the best project management methodology for each task, and get to work doing what you do best!
How To Choose The Best Project Management Methodology
No two projects are alike.
Some may remind you of a past project (that you absolutely nailed, by the way!) but there’s always a catch, isn’t there? One project may have unlimited budgets, endless resources, and flexible timelines—a walk in the park for you—, while another may have high stakeholder expectations, limited budget, tight timelines, multiple teams, and dozens of dependencies.
Since every project is so different, there are many project management methodologies to choose from that support the various project and team needs. There are so many methodologies, in fact, that new ones may have emerged while you’re reading this!
What Is A Project Management Methodology?
Glad you asked. Methodologies are the systems (or simply, methods) used to do something.
The Project Management Institute defined it as “a system of practices, techniques, procedures, and rules used by those who work in a discipline.”
Choosing the right methodology , as well as project management tools and teams, will set you up for success before your project kicks off. For example, you wouldn’t pick a fast-paced, quick iteration project management methodology for a long-term, large-scale, inflexible, and stakeholder-heavy project. Pair like projects with like systems.
To do that, let’s look at your project factors or considerations, such as constraints and dependents.
What Project Factors Are You Working With?
As mentioned earlier, there are many considerations at play that make each project unique. Some factors to consider what you’re evaluating your project management methodologies include:
- Project budget: How much money is going to be spent on this project? How is it divided up?
- Timeline: When is your project due by?
- Goals: What are the project’s end goals and deliverables? Start there and work backward.
- Values: How do your organizational goals and values apply to this project? Knowing this will help set expectations (and help you hold team members accountable for their commitments ).
- Complexity and Scale: How complex or simple is this project?
- Flexibility: How flexible or rigid is this project and its end goals, timelines, deliverables, and team or stakeholder expectations?
- Project type and industry: Some methodologies work best for certain industries and project types, such as highly creative projects or product development sprints.
- Team: Consider the team size, diversity, flexibility, experience, and individual expertise or strengths and weaknesses, as well as their ability to collaborate and communicate when choosing a methodology.
6 Popular Project Management Methodologies And What They’re Best Suited For
It’s important to learn the similarities and differences of various methodologies available to you. For example, some project management methodologies work best if the end goal is fixed and clear, such as the Waterfall method, whereas others better suit those projects that aren’t, such as Agile and Scrum. Keep your project factors in mind while you read on—and then choose the best method for your team.
Let’s get to the methodologies.
1. Agile: Flexible, Fast, And Short Collaborative Sprint Projects
More than a methodology, agile is a set of principles that would be ideal to follow for your first (hypothetical) project.
Agile is made up of fundamental values that are ideal for small teams to work in short and fast project cycles or sprints without blockers. Blockers include too much documentation, work in progress, meetings, or processes to slow them down. The working team would need to be protected from these blockers so that they can stay focused on the tasks at hand.
Teams who work well together can collaborate on small tasks and adapt and respond to an ever-changing task list. Because agile is an iterative design and build process, teams must be flexible with the outcomes and the path they take to get there.
2. Scrum: Quick And Continuous Development Projects
If agile is a set of principles that teams follow to work quickly and respond adaptively to changes as they arise, then Scrum is a project management methodology and the most popular and simple framework that puts agile principles to use.
Scrum is an ideal methodology for your project with the development team to overhaul the website. It’s ideal for continuous improvement and rolling task lists. Something like improving the customer journey on a website may have a timeline, but will always have room for improvement—especially as customer expectations and the digital space change so quickly.
The goal of Scrum is to develop, build, deliver, and sustain complex products using small collaborative and highly accountable teams and iterative task lists. There are roles, events, and artifacts. Roles include a product owner, development team, and scrum master, while events include sprints, daily scrums, or standup meetings, and artifacts include product and sprint backlogs.
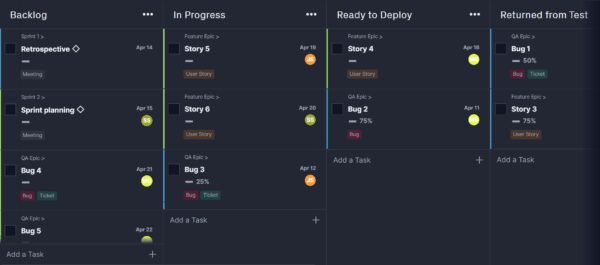
3. Kanban: Visualize Task Progress For Agile Teams
Like Scrum, Kanban is another product management methodology that follows agile principles. Kanban is ideal for projects that are done by small, flexible, and collaborative teams, like Scrum, but there is a highly visual aspect as well.
Tasks are visually displayed in-person on sticky notes or in software such as Trello using columns as they progress. This is called a Kanban board. Tasks move from a backlog through the board’s columns that represent various stages of the process from the backlog, start to finish.

Having a visual representation of backlogged work, work in progress, and completed tasks is a great project management tool for most projects.
This would also be helpful for your second project, in particular, to keep track of tasks’ status as they move throughout the creative process. For example, designing a webpage for the new line of products will have various steps and creative team members involved. Visually seeing how the project is progressing will help you and the team to see how it’s coming along and where blockers are.
4. Lean: Projects That Do More With Less
For those organizations that are looking to transform how they do business, the lean methodology may be one to consider. Lean aims to maximize customer value and minimize waste. This is a great way to put out quality work while increasing efficiencies that minimize unnecessary spending, resources, teams output, or time.
Lean was created in the Japanese manufacturing industry to improve quality control and remove redundancies that may increase the price or value for customers down the line.
Known as the three M’s, Lean methodology defines three types of project waste: muda, mura, and muri.
- Muda is about getting rid of the waste or anything that doesn’t add value.
- Mura streamlines processes, so if one aspect of the project takes too long, for instance, then something further down the task list will have to be completed faster.
- Muri is about removing blockers, such as too many stakeholder meetings.
5. Waterfall: Large-Scale, End-Goal Focused, And Fixed Projects
Tried, tested, and true, the Waterfall methodology has been around since the 1970s. Like a waterfall that cascades downhill, this method is sequential with ordered tasks following one after another as they are completed.
The Waterfall method requires a very solid understanding of the end goal and the necessary steps to get there. As such, it doesn’t leave much room for errors or flexibility. This is great for projects that you’ve done in the past where there is minimal need to adapt on the fly.
This could be something to consider for your large-scale marketing project if you’ve launched new product lines many times in the past and don’t expect any surprises.
With this method, collect and analyze any and all project requirements and deadlines. This requires a lot of up-front work and planning. Then design your approach to meet every stage and their deadline in sequence before reviewing it and putting it into action.
6. Hybrid: Flexible And Fast-Paced Projects With Structured Plans
If agile aims to move fast, adapt quickly, and be flexible, Waterfall is its polar opposite, with fixed deadlines, clear deliverables, and mapped-out categorized project plans.
Hybrid is a methodology that blends the two. Think of it as the best of both worlds. You get the structure and organization of planning milestones out and the flexibility and speed of agile workflows.
It takes the flexible and fast pace of agile principles and blends them with the structured goals and mapped out plans of Waterfall. Take a look at your project requirements, task list, deadlines, and goals. The hybrid methodology uses those as your guidelines, but when it comes to getting the work done, teams should work with some flexibility on rapid iterations.
May The Best Methodology Help You Deliver On Your Projects
There are many more methodologies to name and discuss—and picking the right one for your project can be tricky! In the end, however, it’s all about picking a system that works for you, your project, and your team.
Project management methodologies were created to help you deliver the best possible outcomes based on your project’s circumstances. Take your time to find what works best, try them out, and do a debrief with your team on what worked and what didn’t. If it wasn’t the right methodology for one project, it may be ideal for another—and now you’re armed with that much more knowledge and expertise.
Happy project planning!
Advice, stories, and expertise about work life today.
Project Management Methodologies
Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, Kanban and more. If you’re wondering which methodology you should choose, then you need to read this guide to project management methodologies.
Table of Contents
What is a project management methodology, why are there so many different types of project management methodologies, the project management process: how to choose the right project management methodology, 17 project management methodology examples and frameworks, choosing the right project management methodology.
Once you’ve decided you want to become a project manager , the next step is to figure out which project management methodologies are right for you and your team.
The landscape of project management methodologies can seem a bit overwhelming.
Whether you have a formal project management certification or you’re learning to become a project manager from experience, there’s an absolute smorgasbord of project methodologies to choose from. And they often come with their own rules, lists, principles, and endless acronyms.
We believe that finding the right project management methodology to manage your work shouldn’t be rocket science. So we’ve compiled this list of different project management methodologies to help you figure out which methods, principles and approaches you can use for each team and project.
The only all-in-one platform for client work
Trusted by 20,000 businesses and 6,000 agencies, Teamwork.com lets you easily manage, track, and customize multiple complex projects. Get started with a free 30-day trial.
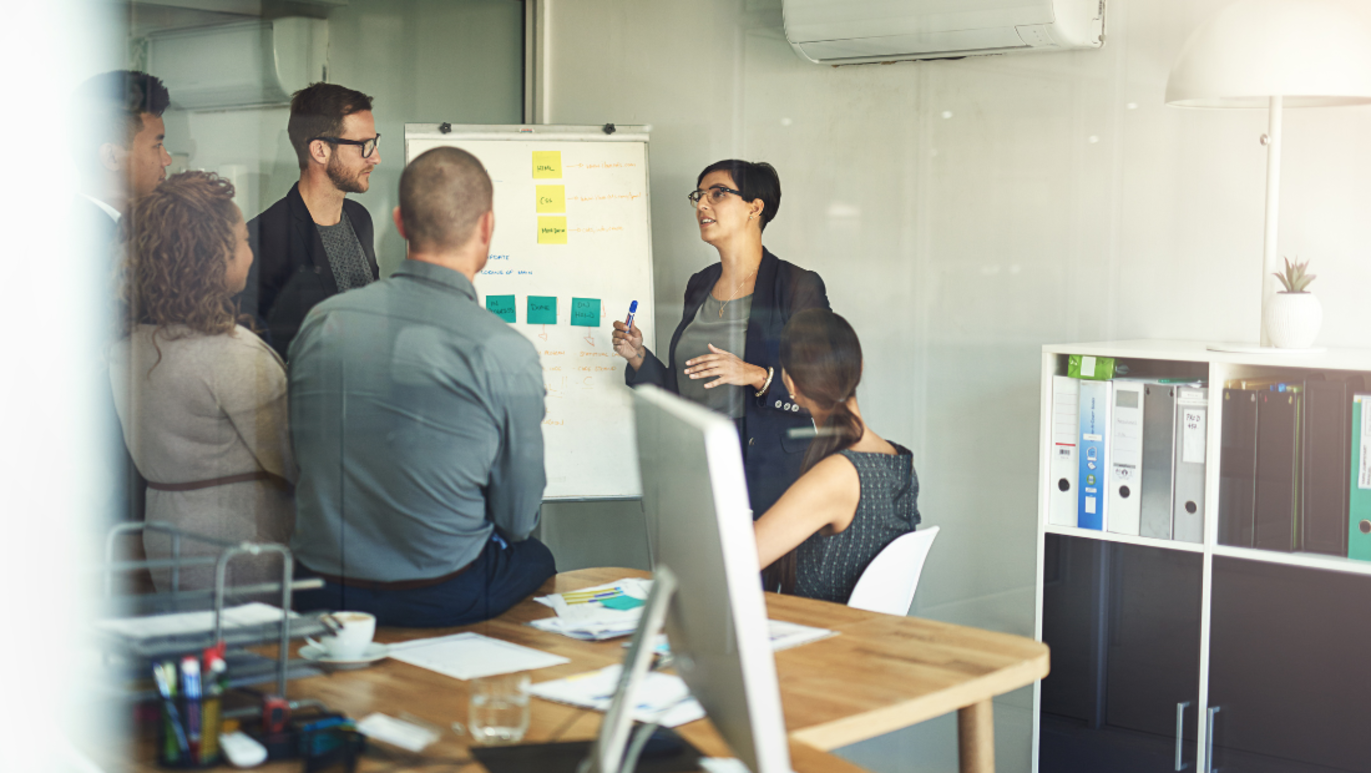

A project management methodology is a set of principles and practices that guide you in organizing your projects to ensure their optimum performance.
Basically, it’s a framework that helps you to manage your project in the best way possible.
Project management is so important to organizations and teams, but in order for it to be really effective, you need to make sure you’re correctly mapping your project management methodology to your team type, project, organization, and goals.
No two projects are exactly the same (even when you’re using handy features like project templates to replicate your past successes).
And when you factor in the different goals, KPIs and production methods of not only different types of teams but also different types of industries , it makes sense that there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to managing a project.
What works best for one type of team could be an absolute nightmare for another.
For example, many software developers started to find that traditional project management methods were hindering — rather than helping — their workflows and negatively affecting their performance and results.
As a result, software teams began to develop a new type of project management methodology, which was designed to address their particular concerns.
Before long, other teams and industries started to adapt those new project management methods to fit their unique needs and concerns. And on and on, with different project management methodologies being repurposed and adapted for different industries and tweaked to fit specific use cases.
What we’re left with is a ton of different project management methodologies to choose from. So how do you know which project management method (or methods, plural) is right for you and your team?
There are lots of factors that will impact which project management methodology is right for your project, team, and organization. Here’s a quick breakdown of some of the key considerations that can help you decide:
Cost and budget: On a scale of $ to $$$, what sort of budget are you working with? Is there room for that to change if necessary, or is it essential that it stays within these predetermined limits?
Team size: How many people are involved? How many stakeholders? Is your team relatively compact and self-organizing, or more sprawling, with a need for more rigorous delegation?
Ability to take risks: Is this a huge project with a big impact that needs to be carefully managed in order to deliver Very Serious Results? Or is it a smaller-scale project with a bit more room to play around?
Flexibility: Is there room for the scope of the project to change during the process? What about the finished product?
Timeline: How much time is allotted to deliver on the brief? Do you need a quick turnaround, or is it more important that you have a beautifully finished result, no matter how long it takes?
Client/stakeholder collaboration: How involved does the client/stakeholder need — or want — to be in the process? How involved do you need — or want — them to be?
Waterfall methodology
Agile methodology
Scrum methodology
Kanban methodology
Scrumban methodology
eXtreme programming (XP) methodology
Adaptive project framework (APF) methodology
Lean methodology
Critical path method
Critical chain project management
New product introduction (NPI)
Package enabled reengineering (PER)
Outcome mapping
PMI’s PMBOK
PRINCE2 methodology
Rapid application development (RAD) methodology
We’ve compiled a list of 17 effective project management methodologies to help you get to grips with the basics. Let’s dive right in.
1. Waterfall methodology
The Waterfall method is a traditional approach to project management. In it, tasks and phases are completed in a linear, sequential manner, and each stage of the project must be completed before the next begins.
The stages of Waterfall project management generally follow this sequence:
Requirements
Construction
Deployment & maintenance
Progress flows in one direction, like a real waterfall.
Also like a real waterfall, though, this can quickly get dangerous. Since everything is mapped out at the beginning, there’s a lot of room for error if expectations don’t match up with reality. And there’s no going back to a previous stage once it’s completed (just imagine trying to swim against a waterfall — not fun).
Try this project management methodology if:
The end goal of your project is clearly defined — and isn’t going to change.
The stakeholders know exactly what they want (and it isn’t going to change).
Your project is consistent and predictable (i.e. isn’t going to change).
You’re working in a regulated industry that needs extensive project tracking or documentation.
You might need to bring new people into the project midway through and get them up to speed quickly.
This project management methodology might not be for you if:
Your project is liable to change.
You don’t have a full picture of all the requirements before you start.
You need to do continuous testing or adapt to feedback during the process.
2. Agile methodology
Agile project leaders help their team balance at the edge of chaos - some structure, but not too much; adequate documentation, but not too much; some up-front architecture work, but not too much. Finding these balance points is the art of agile leadership." ~ Jim Highsmith, author and software engineer
The agile project management methodology came from a growing dissatisfaction with the linear approach of traditional project management methodologies.
Frustrated with the limitations of project management methods that couldn’t adapt with a project as it progressed, the focus began to shift to more iterative models that allowed teams to revise their project as needed during the process instead of having to wait until the end to review and amend.
The concept of agile project management has gone on to spark several specific sub-frameworks and methodologies, such as scrum, kanban, and lean. But what do they all have in common? The key principles of agile project management methodologies are:
It’s collaborative.
It’s quick.
It’s open to data-driven change.
As such, agile project management methodologies usually involve short phases of work with frequent testing, reassessment, and adaptation throughout.
In many agile methods, all of the work to be done is added to a backlog that teams can work through in each phase or cycle, with project managers or product owners prioritizing the backlog so teams know what to focus on first.
You’re not sure at the outset what the solution will look like.
You need to work quickly, and it’s more important that you see speedy progress than perfect results.
Your stakeholders or client needs (or wants) to be involved at every stage.
This project management methodology isn’t for you if:
You need a lot of documentation (for example, if you’ll be bringing new people on-board during the project).
You need a predictable deliverable, and you need to be crystal clear about what that looks like from the outset.
Your project can’t afford to change during its course.
You don’t have self-motivated people.
You have strict deadlines or deliverables that you need to stay on top of.

The Best Agile Project Management Tools To Use In 2023 & Beyond
It does little good to adopt the Agile method while still using a software that bogs down or complicates your projects. The best agile project management software should go hand-in-hand with the Agile method and make these adaptations smooth, fast, and easy.
3. Scrum methodology
Scrum is a form of agile project management. You can think of it more like a framework than as a project management methodology in itself.
With Scrum, work is split into short cycles known as “sprints”, which usually last about 1-2 weeks. Work is taken from the backlog (see: Agile project management, above) for each sprint iteration,
Small teams are led by a Scrum Master (who is not the same as the project manager ) for the duration of the sprint, after which they review their performance in a “sprint retrospective” and make any necessary changes before starting the next sprint.
You’re striving for continuous improvement.
You don’t have the full commitment from the team needed to make it work.
4. Kanban methodology
"Kanban is not a software development lifecycle methodology or an approach to project management. It requires that some process is already in place so that Kanban can be applied to incrementally change the underlying process." ~ David J. Anderson, Author and pioneer of the Kanban method
Kanban is another method within agile project management.
Originating from the manufacturing industry, the term “kanban” has evolved to denote a framework in which tasks are visually represented as they progress through columns on a kanban board . Work is pulled from the predefined backlog on a continuous basis as the team has capacity and moved through the columns on the board, with each column representing a stage of the process.
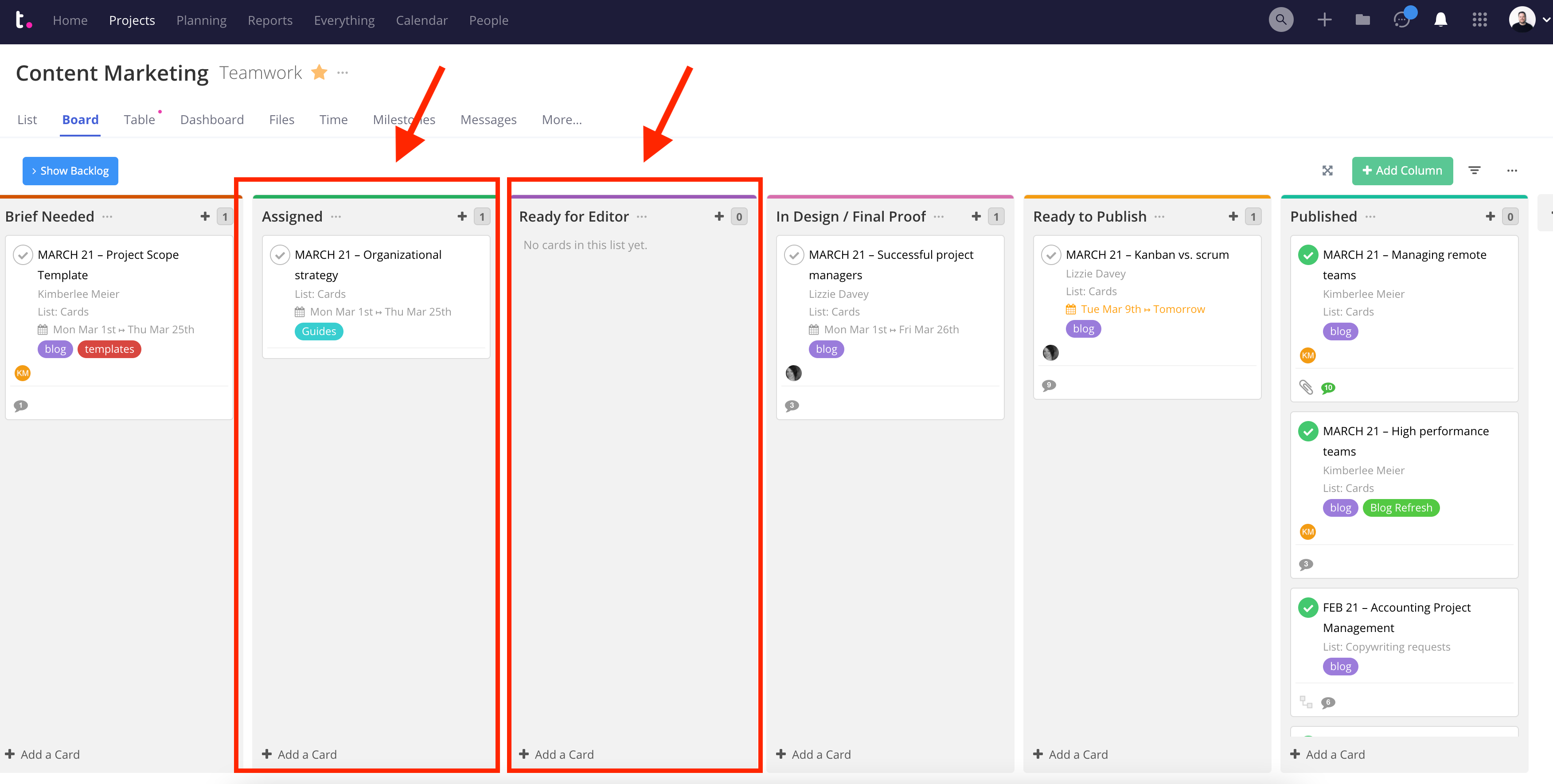
Kanban is great for giving everyone an immediate visual overview of where each piece of work stands at any given time. (You can use kanban boards for everything from your content marketing process to hiring and recruitment .)
It also helps you to see where bottlenecks are at risk of forming — if you notice one of your columns getting clogged, for example, you’ll know that that’s a stage of your process that needs to be examined.
When used as part of an agile project management methodology, it’s also common to implement work in progress (WIP) limits. Work in progress limits restrict the amount of tasks in play at any given time, meaning that you can only have a certain number of tasks in each column (or on the board overall).
This prevents your team from spreading their energy across too many tasks, and instead ensures that they can work more productively by focusing on each task individually.
You’re looking for a visual representation of your project’s progress.
You want at-a-glance status updates.
You want to encourage using WIP limits so your team can stay focused.
You prefer to work on a continuous “pull” basis.
Your process is super complex or has tons of stages.
You want a push system instead of a pull system.
Kanban board view
Use kanban boards in Teamwork.com to map out your workflow, quickly see the status of tasks, and automate your processes.
5. Scrumban methodology
It’s the answer to the age-old question: what if scrum and kanban had a baby?
Scrumban is a hybrid agile project management methodology that has scrum’s nose and kanban’s eyes.
The main benefit of scrumban as a method is that instead of deciding which task from the backlog to work on in each sprint at the outset (like you would in a “traditional” scrum framework), scrumban allows teams to continuously “pull” from the backlog based on their capacity (like they would in a kanban framework).
And using work in progress limits (from kanban) during your sprint cycle (from scrum), you can keep a continuous flow while still incorporating project planning , reviews and retrospectives as needed.
You’ve ever looked at scrum and kanban and thought “I wish those two crazy kids would get together”.
You’ve ever looked wistfully out the window and thought, “Oh, scrum is scrum, and kanban is kanban, and never the twain shall meet”.
6. eXtreme programming (XP) methodology
The eXtreme Programming (XP) methodology is another form of agile project management that was designed for software developmen t.
It emphasizes teamwork and collaboration across managers, customers, and developers, with teams self-organizing. It has a defined set of rules that teams should follow, which are based on its five values: simplicity, communication (face to face is preferred), feedback, respect, and courage.
You want to foster teamwork and collaboration.
You have a small, co-located team.
You’re a rulebreaker.
Your team is spread across different places and time zones.
7. Adaptive project framework (APF) methodology
The adaptive project framework (APF) methodology, also known as adaptive project management (APM), is a type of agile project management methodology that was designed with the inevitability of change in mind.
The adaptive project framework knows that, as John Steinbeck might say, even the best-laid projects of mice and men often go awry. So the fundamental attribute of APF is that teams need to be able to adaptively respond to change.
That means that using adaptive project framework methods, teams must try to anticipate the risks and prepare for the unexpected in their project. They need to understand that key components are constantly in flux, and be able to constantly re-evaluate results and decisions with these moving parts in mind.
This requires lots of communication with all stakeholders and — like other agile project management methodologies — be able to work collaboratively.
You know your ultimate goals (in project management terms, you’ve outlined your Conditions of Satisfaction; or, in Beastie Boys terms, you’re clear about you’re clear about whatcha whatcha whatcha want).
You need predictability.
You don’t have the resources to handle the potential negatives of adaptability (e.g. scope creep, rework, misuse of time).
8. Lean methodology
Lean is another project management methodology that has its origins in manufacturing (and specifically the Toyota Production System). It’s all about applying lean principles to your project management methods to maximize value and minimize waste.
While this originally referred to reducing physical waste in the manufacturing process, it now refers to other wasteful practices in the project management process. These are known as the 3Ms: muda, mura, and muri.
Muda (wastefulness) consumes resources without adding value for the customer.
Mura (unevenness) occurs when you have overproduction in one area that throws all of your other areas out of whack, leaving you with too much inventory (wasteful!) or inefficient processes (also wasteful!).
Muri (overburden) occurs when there is too much strain on resources such as equipment and people, which can often lead to breakdowns — in both machines and humans.
Using the key principles of lean, a project manager can reduce these types of waste to create more efficient workflows.
You’re looking for a set of principles that will help you cut the fat and optimize your flow.
You’re always trying to improve and add value for the customer.
You want to ultimately decrease costs.
You can’t afford to run into supply problems (e.g. you don’t have enough inventory in stock) or lose room for error (e.g. in the case of essential equipment failure).
You don’t have the budget to invest in it (while lean project management aims to reduce costs overall, it can be costly to implement).
You’re a raccoon and you love waste, actually.
9. Critical path method
A project without a critical path is like a ship without a rudder." ~ D. Meyer, Illinois Construction Law
The critical path method (also known as critical path analysis) is a way of identifying and scheduling all of the critical tasks that comprise your project, as well as their dependencies.
That means that you need to:
Identify all of the essential tasks you need to do to achieve your project goal
Estimate how much time each of those tasks will take (bearing in mind that certain tasks will need to be completed before others can be started)
Use all of that information to schedule the “critical path” you’ll need to take in order to get the project done as quickly as possible without missing any crucial steps.
The longest sequence of critical tasks becomes your critical path, and will define the timeframe for your project.
Along the path, you’ll have milestones to meet that will signal when one set of tasks (or phase) is over and you can move on to the next one.
There are lots of ways to visualize the critical path, depending on the complexity of your project, from flow graphs to Gantt charts .
Your project is large-scale and complex.
Your project has a lot of dependencies.
You’re looking for a visual way to map out the sequence of tasks.
You need to identify which tasks are the most important so you can better allocate your resources.
You have a strict plan and deadlines, with no room for silly business.
You love algorithms. Love ‘em!
You don’t need something with a lot of complexity.
You’re unsure about deadlines, timings, or durations.
Your project needs wiggle room to change.
10. Critical chain project management
Critical chain project management (or CCPM) takes the critical path method (CPM) one step further.
While the critical path method defines the length of time needed to get each critical activity done from the beginning of the project to the end, it can often be, well, unrealistic when the time comes to actually put it into practice.
Critical chain project management addresses those issues by allowing a bit more time for the human elements of your project — like delays and resourcing issues.
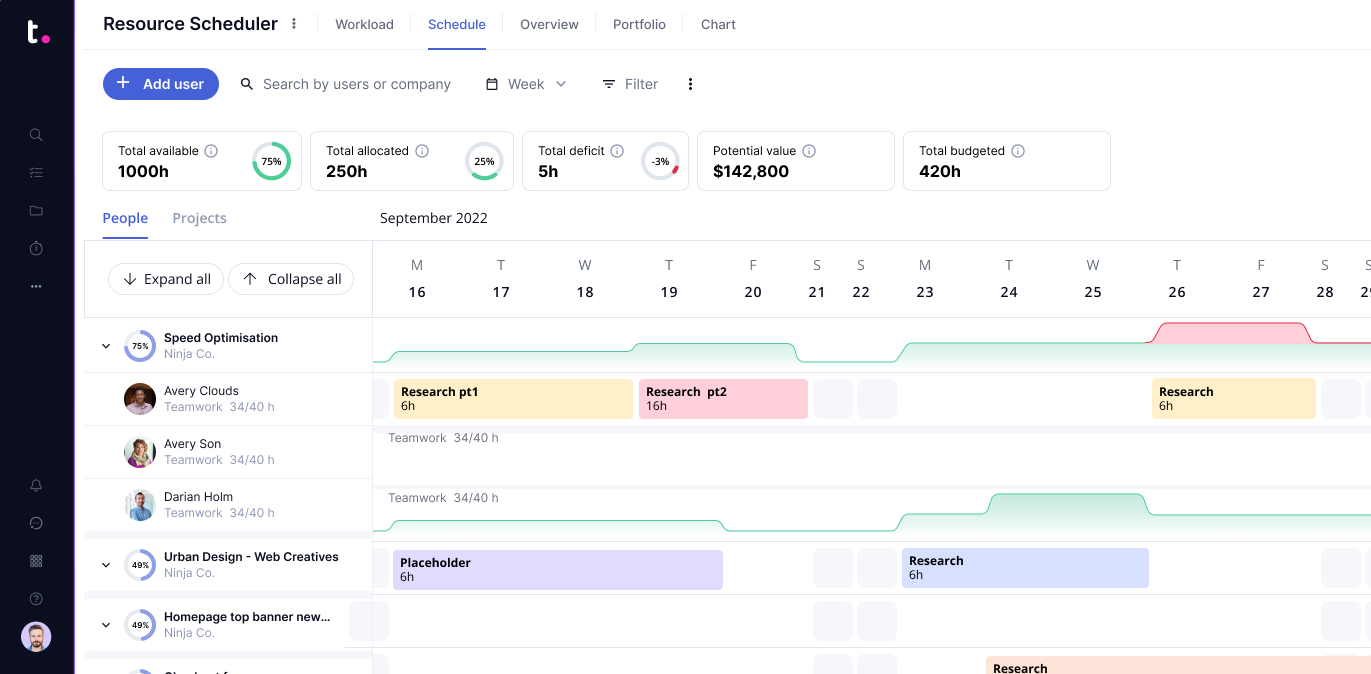
In critical chain project management, you have a few buffers built in that your critical chain can use without derailing everything else, so that your entire project doesn’t have to go off track just because life happens.
You like the sound of the critical path method, but you want something a little more realistic.
You were already overestimating task durations in CPM to allow for a buffer and you want more accurate data on how long the work is actually taking compared to your projections.
You think buffers are just a safety net for people who didn’t plan it right the first time.
Nothing could possibly go wrong.
11. New product introduction (NPI)
New product introduction is a great project management methodology for when you want to, well, introduce a new product.
Also known as new product development (NPD), the new product introduction process covers everything you need to define, develop and launch a new (or improved) product.
The project follows a single product through the entire development process. This process involves multiple phases or a stage-gate process, which can vary from organization to organization, but usually include things like:
Defining the product spec and project scope
Evaluating the feasibility
Developing the prototype
Validating the prototype via testing and analysis
Manufacturing the product on a larger scale
Evaluating the product’s success in the market after launch
As the requirements for a successful new product introduction span a number of departments across an organization, from leadership to product managers to marketing and more, it requires a lot of cross-functional collaboration and communication.
Project management template
Nail your next project with our project management template. Manage the bigger picture, and turn plans into actionable tasks - without missing a single detail.
You’re bringing a new or improved product to market.
You’re focusing on a single product.
You want to foster key stakeholder and cross-functional alignment right from the beginning.
You’re not bringing a new or improved product to market.
You’re looking for a more agile approach to product development (as NPI is usually sequential rather than iterative).
12. Package enabled reengineering (PER)
Package enabled reengineering (PER) is a project management methodology that aims to help organizations redesign products or processes with fresh eyes. It focuses on facilitating business transformations quickly and strategically, whether through redesign of processes or realignment of people.
Your organization needs an overhaul.
You need a fresh perspective on your products or processes.
You’re not trying to improve an existing system.
13. Outcome mapping
Outcome mapping is a project progress measurement system that was designed by the International Development Research Centre (IDRC). It differs from the other project management methodologies on this list in that it doesn’t focus on measurable deliverables; instead, it focuses on creating lasting behavioural change.
It’s a common project management methodology used in charitable projects in developing countries. As a project management methodology, it’s less about the project itself than the long-term impact of the project and its ability to effect change in the community. As a result, it measures influence rather than other (perhaps more “typical”) measures of project progress.
Outcome mapping consists of a lengthy design phase followed by a record-keeping phase to track the results.
Your project is aimed at changing behaviour rather than producing deliverables.
Your project is related to change and social transformation (e.g. in the fields of international development, charity, communications, research).
Your project is all about finished products rather than behavioural outcomes.
14. Six Sigma
"Measurement is the first step that leads to control and eventually to improvement. If you can't measure something, you can't understand it. If you can't understand it, you can't control it. If you can't control it, you can't improve it." ~ H. James Harrington, author and management mentor
Six Sigma is a method for improving processes with an emphasis on ensuring consistency in output and impeccable quality. (And if it’s good enough for Jack Donaghy… )
There are a few different flavors available, such as Lean Six Sigma and Agile Sigma, but ultimately Six Sigma is a business methodology that aims to eliminate defects and reduce variation by using its defined methodologies.
Six Sigma methods can be used to optimize and improve existing processes or create new ones.
To improve business processes, you can use the Six Sigma DMAIC process, which stands for the phases in the project methodology: D efine, M easure, A nalyze, I mprove, C ontrol.
To create new processes or products, you can use the Six Sigma DMADV process: D efine, M easure, A nalyze, D esign, V erify.
As a set of principles and techniques (sometimes it’s even described as a “philosophy”) rather than a project management methodology in itself, Six Sigma methods can be applied alongside many other project management methodologies, like Lean and Agile.
You’re looking for a set of principles and philosophies you can bring with you to almost every project and organization.
You don’t have a lot of budget to invest in training — it can be expensive to get trained and certified.
You’re looking for a defined process for a particular project rather than a set of guiding rules.
15. PMI’s PMBOK
The Project Management Institute’s Project Management Book of Knowledge (AKA the PMI’s PMBOK) isn’t a project management methodology in and of itself. However, it is a best practices guide — and it forms the basis of the PMI’s Project Management Professional (PMP) certification, one of the leading project management qualifications.
As such, the PMBOK is an industry-standard set of guiding principles that you can use to ensure that your projects across multiple types of teams and organizations meet the PMI’s high standards and comply with best practices.
You have (or want to get) a PMP.
You want to stay up-to-date with industry standards and best practices.
You live and work in a place where the PMP is the standard project management qualification (such as the US).
You need a solid project management methodology to map your project, rather than general (albeit helpful) project management knowledge.
16. PRINCE2 methodology
PRINCE2 ( PR ojects IN C ontrolled E nvironments) is a project management methodology and certification that aims to equip project managers with knowledge of best practices and processes.
Unlike the PMP certification, it doesn’t require a number of prerequisites, making it a good choice for project managers looking to get both a methodological grounding and a qualification.
Also unlike the PMP, PRINCE2 is a methodology in itself. It’s guided by seven principles, which in turn dictate the seven processes a project manager needs to use in each project when using PRINCE2.
You’re looking for a certification to give you an edge.
You live and work in a place where PRINCE2 is the standard project management qualification (such as the UK).
You don’t want to commit to full certification.
The seven-step process doesn’t map to your projects.
You find yourself tailoring (or outright ignoring) the process stages so much that it becomes PINO — “PRINCE in name only”.
17. Rapid application development (RAD) methodology
Rapid application development (RAD) is a type of agile project management methodology that aims to facilitate faster software development .
It uses rapid prototype releases and iterations to gather feedback in a short period of time, and values that user feedback over strict planning and requirements recording.
You want to be able to give customers/clients/stakeholders a working model much sooner (even if it’s not perfect).
You want to create multiple prototypes and work with stakeholders to choose the best one.
Speed is of the essence.
You want to encourage code reuse.
You don’t have an experienced team.
Your clients or stakeholders don’t have the time to commit to such a collaborative process or can’t give feedback within the necessary timeframes.
You have a large team.
You prefer to have a detailed spec that outlines all functional and non-functional requirements.

The right project management methodology can elevate your project and help the project manager to get the best out of each team.
Whether you prefer the agile methods favored in IT project management or the more traditional waterfall project management and critical path methodology used in construction and manufacturing, there’s a project management methodology for every team.
But no matter which methodology you go for, you need a collaborative, flexible, and easy-to-use project management tool to support you every step of the way.
Choosing a team management software that supports multiple methodologies — i.e. that doesn’t lock you into one methodology or way of using it — like Teamwork.com means that every team in your organization has the freedom to work the way that works for them without sacrificing on features or complexity.
No matter how you like to work, Teamwork.com helps your team to replicate their best practices, ensure compliance and consistency, and constantly improve their processes.
What project management methodology allows some of the phases and tasks to overlap?
The project management methodology that allows some of the phases and tasks to overlap is known as "Agile" or "Agile Project Management." Agile is a flexible and iterative approach to project management that tends to be divided into "Sprints", which are time-boxed periods of work. Within each Sprint, cross-functional teams work on various tasks and features, allowing for a degree of overlap between different project phases.
What project management methodology requires the team to complete the previous phase before the next phase starts?
The project management methodology that typically requires the team to complete the previous phase before the next phase starts is the "Waterfall" methodology. Waterfall is a traditional, linear, and sequential approach to project management. In a Waterfall project, each phase must be completed in its entirety before the next phase can begin.
Why do project managers use project management methodologies?
Project managers use project management methodologies to bring structure and organization to their projects, ensuring consistency, risk management, resource allocation, and quality assurance. These methodologies promote effective communication, change management, and scope control, leading to increased efficiency, client and stakeholder satisfaction, and overall project success. They also foster a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability, allowing project managers to navigate changing requirements and uncertainties effectively.
How many project management methodologies are there?
There are numerous project management methodologies, with dozens of well-known approaches like Waterfall, Agile, Scrum, PRINCE2, Kanban, Lean, and Six Sigma, among others. Custom methodologies are also created by organizations to meet specific needs.
What is the difference between agile and scrum?
Agile is a broader project management philosophy that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback, while Scrum is a specific Agile framework. Scrum introduces roles (Scrum Master, Product Owner, Development Team), fixed-time sprints, and defined ceremonies (Sprint Planning, Daily Standup, Sprint Review, Sprint Retrospective) to guide project teams. It also includes key artifacts like the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment.
You may also like...

Get started with Teamwork.com
Start working together beautifully. See how Teamwork.com can help your team with our 30-day free trial.

Project Management Methodology: Definition, Types, Examples

What is a project management methodology ? How can it be defined? In simple terms, it is a must-have to avoid failure and reduce risks because it is one of the critical success factors as well as the core competency of the management team. It is the straightforward way to guide the team through the development and execution of the phases, processes and tasks throughout the project management life-cycle.
What is a Methodology? The Definition in Project Management
The term “ project management methodology ” was first defined in the early 1960s when various business organizations began to look for effective ways that could simplify the realization of business benefits and organize the work into a structured and unique entity (which was called “ project ” later on). Communication and collaboration were the key criteria for establishing productive work relationships between the teams and departments within one and the same organization.
Since that time, the term has been changed and modified many times, new definitions have been created, new elements and functions have been added. Today we consider a project management methodology as a set of broad principles and rules to manage a specific project that has a definite beginning and end. Below is the current definition of methodology .
Project Management Methodology is a strictly defined combination of logically related practices, methods and processes that determine how best to plan, develop, control and deliver a project throughout the continuous implementation process until successful completion and termination. It is a scientifically-proven, systematic and disciplined approach to project design, execution and completion.
The purpose of project methodology is to allow for controlling the entire management process through effective decision making and problem solving, while ensuring the success of specific processes, approaches, techniques, methods and technologies.
Typically, a project management methodology provides a skeleton for describing every step in depth, so that the project manager or program manager will know what to do in order to deliver and implement the work according to the schedule, budget and client specification.
Referring to the above mentioned definition, an appropriately chosen project management methodology paves the way for gaining the following achievements:
- The needs of stakeholders are defined
- A common “language” is established and understood by the team, so they know what’s expected of them
- Cost estimates are complete, accurate and credible
- Every task is done using a common methodological approach
- Most conflicts are spotted and resolved early
- Expected deliverables are produced and handed over
- Lessons are learned and solutions are quickly implemented
Methodology in Project Management Framework
Project management (the acronym “PM”) provides the framework of planning, doing and delivering projects of any kind, size, nature and type. PM framework focuses on the realization of desired change in line with a chosen methodological approach. Actually, change is the core aspect that should be managed. PM framework identifies and defines how to best manage change. And methodology serves as the “way” to systematically realize change in terms of time, cost and quality.
Managing projects means describing and performing the activities required to meet the specific objectives of making change.
For example, writing a book is a kind of project in which the objective is to write a book. This objective can be fulfilled by a series of activities, including defining the topic, collecting material, creating a draft, typing, proofreading, others. So in terms of project management, the author needs to define and then complete all the necessary activities in order to write a book (which means make change).
Here’s a simplified example of how a project methodology can be presented in the management hierarchical structure:
PM Framework precedes Methodology which in turn precedes Lifecycle Stages and determines the project management Processes, Tasks and Activities
Project Management Methodology Types
In project management there are a variety of approaches and methods that can be employed in managing different kinds of project. All the types of project methodology can be conditionally divided into traditional and modern approaches.
Traditional Approach
A traditional approach involves a series of consecutive stages in the project management process. It is a step-by-step sequence to design, develop and deliver a product or service. It entails achieving the succession in the implementation process and provides the benefits of milestone-based planning and team building. In IT and software development, this methodology type is called “ Waterfall ” – one portion of work follows after another in linear sequence.
The following stages are included the traditional project management methodology:
- Initiation (requirements specification)
- Planning and design
- Execution (construction and coding)
- Control and integration
- Validation (testing and debugging)
- Closure (installation and maintenance)
Modern Approaches
Modern methodologies do not focus on linear processes but they provide an alternative look at project management. Some of the methods are best for IT and software development, while others can be implemented in production, process improvement, product engineering, and so on. Modern PM approaches use different models of the management process.
Project Management Methodology Examples
It is the matter of a project’s type, size and nature to select the right methodology. Here are the most popular PM methodologies:
PMBOK® Guide
Although A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge IS NOT a PM methodology in its “ pure state “, many people regard it as the methodological approach to planning, executing, controlling and terminating various projects. Meanwhile, the PMBOK® Guide is a broad inventory of best practices and ideas on planning and implementing projects. Please note that it is just a guide but not a project management methodology.
PRojects IN Controlled Environments 2 ( PRINCE2 ) presents a suite of process-driven methods and documentation-oriented approaches that allow driving various projects in the private sector. It was developed the UK Government, and today this great example of project management methodology is used both in the UK and internationally.
Critical path method (CPM) explores the most important or critical tasks of a project by defining possible activity sequences and estimating the longest duration of each sequence. It helps figure out how long it will take to complete the work and what tasks will compose the scope.
Lean PM methodology intends to maximize customer value and minimize resource waste. Lean project management lets organizations create higher value for their customers with fewer resources. This approach achieves perfection in customer satisfaction and value generation through implementing an optimized process flow that eliminates waste in products, services, transportation, inventories, etc.
The method of Six Sigma was originally developed by Motorola to improve its production processes by eliminating defects (defined as “non-conformity of a product or service to its specifications”). Today Six Sigma is one of the most popular and worldwide trusted examples of project management methodology for ensuring the accuracy and speed of a process’s implementation through eliminating or minimizing waste.
Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) is the way to plan, implement and review various kinds of work in single- and multi-project environments. This management methodology uses Theory of Constraints (TOC) and the concept of buffers to establish improved task durations and manage resource-dependent tasks and activities.
SCRUM is an example of Agile PM methodology that involves teams in producing a software product in 30-day “ sprints ” and monthly “ scrum sessions “. In a SCRUM-driven project, the deliverables are broken down into 30-day intervals. This methodology example is specific and applicable mainly to collaborative, 100%-dedicated teams, with no heavily constrained time and materials budget.
Project Management for Students
Project management for students is a vital part of the education and training process. Students can easily get a project management degree, but it does not mean that it comes as easy as taking the homework. Students need to take into account some important aspects if they want to manage a project properly.
For instance, choosing the best admission essay writing service is of great importance because if for some reason the student cannot deliver a high-quality essay in time, he will most likely fail the course or even worse he will be expelled from the college or university.
Students should prepare well for the project or the essay. They need to research on the topic beforehand, keep track of what is going on, write on time and work within the deadline.
This will allow them to catch up with their fellow students, focusing only on what they have to do and not worrying about what other people are doing.
Worth Reading

5 Tips for Gathering and Implementing Business Intelligence the Right Way
April 6, 2021

Project Pre-Charter as a Sub-Phase of the Initiation Phase
November 24, 2010

Project Readiness Checklist
December 15, 2010

Tax Deductions for Independent Workers: A Guide
September 16, 2023

The Concept of Feasibility Study in Project Planning
October 19, 2010
#ezw_tco-3 .ez-toc-title{ font-size: 120%; ; ; } #ezw_tco-3 .ez-toc-widget-container ul.ez-toc-list li.active{ background-color: #ededed; } Table of Contents Toggle

Project Implementation Guide
Project Deliverables Statement

5 Best Practices for Building and Nurturing Customer Trust in Retail

Project initiation stage – Project Initiation Document (PID). Duties of project owner and project team

Organizing Procurement and Purchasing Activities in a Project

Two Common Mistakes in Project Procurement Contracts

Project Sponsor – The Role and Responsibilities
5 Popular Project Management Methodologies and When To Use Them
With all the project management methodologies out there, how do you pick the right one? As a project manager, you know that selecting the correct methodology is an essential part of getting the project done correctly and on time. These processes provide you with guidance and a series of predefined steps that lead to task completion, but each one has its own set of rules, principles, and practices that enable progress and manage complications that may arise during project delivery.
So which one should you choose? It depends on your project scope, your project management tool and requirements: there is no such thing as a ‘right’ methodology for all situations. While there are different processes available (Six Sigma, Kanban, and Lean are popular examples), not all of them are a perfect fit for every project. Below is a list of 5 popular project methodologies and when they should be used for maximum efficacy.

Agile project management is well-named. It values individual interactions over impersonal processes and tools, so one of its core strengths is its ability to adapt to changing situations and ongoing feedback results. It uses iterative and incremental work sequences that are referred to as ‘sprints.’
When members of your team collaborate closely with upper management and clients, directions and solutions tend to evolve and change recognition is important. The Agile methodology is adaptable and flexible enough to allow for these face-to-face interactions and collaborative practices without sending the project off-track or even worse, stalling it completely.
Best suited for: Projects that involve a certain amount of uncertainty and complexity, such as software development. More emphasis tends to be on continuous improvement in the name of high-quality results and obtaining a competitive advantage for the client. IBM is one company that openly uses the Agile methodology to develop its software.
Although Kanban is technically an Agile framework, it is widely regarded as its own methodology. Originally developed to improve Toyota factory production lines during the 1940s, Kanban is a visual process that paints a picture of the project workflow system so that bottlenecks and similar problems can be detected during the early stages of product development.
Kanban visual cues are:
- A Kanban board that can be physical (such as a whiteboard drawing or carefully arranged sticky notes) or digital, like charts produced by web-based project management tools such as Trello . Its basic layout is three columns marked ‘ To Do’, ‘In Progress’ and ‘Done.’
- Kanban cards that each depict a task in the work process. They are used to visually convey information such as project status , upcoming deadlines, and overall progress.
- Kanban swimlanes that provide a good overview of the project workflow by categorizing tasks and deliverable and laying them out horizontally.
Best suited for: Software development and any other project that emphasizes continuous improvements in the development process. Many people also use it for personal productivity action plans.

The lean methodology aims to maximize customer value by using fewer resources, which minimized waste. Like Agile, it is a concept that evolved from the Japanese manufacturing industry, which emphasizes the elimination of waste as a method of improving quality and reducing both costs and production time.
Lean project management recognizes three types of waste, commonly known as the 3Ms:
- Muda : Eliminating a process or activity that does not add value to the project. It can refer to a physical waste, such as raw materials and inventory, or a waste of resources, such as over-processing and overproduction.
- Mura : Trimming away workflow process delays that could affect scheduling and operations. Examples include a worker spending too much time perfecting a design, giving team members at the next stage in the timeline less time to do their work.
- Muri : Getting rid of excess baggage so that the process does not slow down. It refers mainly to project managers who slow their team members down via poor organization, micromanaging, and other time-wasting practices.
Best suited for: Companies that want to change the way that they do business. As a methodology, it addresses more operational than project processes.
4. Waterfall
One of the best-known and more traditional project management methodologies, Waterfall takes a sequential and linear design approach in which progress ‘flows’ downwards, in a single fluid direction, like a waterfall. It originally appeared in the construction and manufacturing industry, where plans are rigidly structured and change and experimentation cost money. The premise of the waterfall methodology is that the team can only move to the next stage in the project timeline after the present phase has been successfully completed. The phases are:
- System and software requirements
Best suited for: Bigger projects, such as public infrastructure, that require the team to maintain strict deadlines and move from one stage only after the previous one has been completed. Before Agile appeared, the Waterfall methodology was used to develop software, but it was later found to be too non-adaptive and not conducive to customer feedback.

5. Six Sigma
Originally introduced by Motorola engineers during the mid-1980s, Six Sigma strives to improve project quality and success by identifying what is not working and removing it from the process. Its main resources are quality management tools that rely on statistical and empirical data as well as expert input, to reduce the number of errors.
Six Sigma has two primary methodologies:
- DMAIC , an acronym for defining the problem and project goals, measuring the aspects of the process currently being used, analyzing data to detect core defects, improving the process, and controlling how it is carried out in the future.
- DMADV , an acronym for defining the project goals, measuring the essential parts of the process and product, analyzing the data to develop various process designs and choose the best one, designing and testing the new process and verifying its quality via simulations and other testing
Best suited for : Bigger organizations and companies that want to use data to improve their operating efficiency and output quality.
Choosing the right methodology for your project is critical to its success. When you find one that meets the needs of the project, industry, and / or organization your team will have the blueprint it needs to deliver quality results.
Rose Keefe is an author and technical writer who has over ten years’ experience in supporting project managers in the manufacturing and construction sectors. One of her primary responsibilities was developing product manuals that supported efficient use of industrial equipment. She continues to write on the subject of time management and commercial productivity for trade websites and publications.
Join 30,000+ subscribers getting the best tips on productivity, work management, hiring and more!
We promise we won't spam you and you can unsubscribe anytime.
You might also like...
Related to Project Management

6 Tips to Be an Effective Project Manager (Without Micromanaging)
10 Best Project Tracking Software To Deliver Projects On Time (2022)
Resource Loading In Project Management: What, Why, And How
Take a peek at our most popular categories:
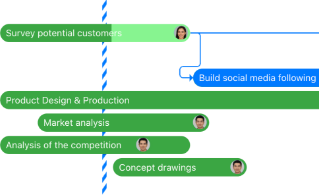
Finally see how to stop getting stuck in a project management tool
20 min. personalized consultation with a project management expert
10 Most Popular Project Management Methodologies: An Overview
Find the right approach for you and your team!

Choosing the right project management framework is the foundation of every successful project. Project managers have a broad portfolio of proven and modern project management methodologies at their disposal. In particular, agile project management methods like Scrum and Kanban have now become absolute trend strategies.
But be careful: One-for-All does not apply in project management! Each project has individual characteristics, requirements, and risks that you should definitely consider when choosing the appropriate project management method.
In this article, we present the 10 most renowned project management solutions and show you exactly what is suitable for you and your company.
The following points will be covered in this article:
✅ Important principles for selecting your project management framework
✅ The 10 most effective project management methodologies and their key characteristics
✅ Examples for choosing the most suitable approach for your team
Project Management Methodologies: More structure and less risk
Projects aim to achieve a specific, unique goal, such as the development of new software. This must be accomplished within a certain timeframe without exceeding the predefined limits of personnel, monetary, and time resources . If project managers approach this task unprepared and disorganized, it is very likely that the project will fail.
The more complex the project, the higher the external risk factors, and the more employees involved, the more important it is to approach the project in a structured and systematic manner.
Finding “The One”
A project management methodology that represents an universal solution for all project types seems desirable. However, we must quickly abandon this thought. Projects are defined by their unique nature. They differ significantly in the following factors:
- Strategic goal alignment and company values
- Key business factors (e.g., pricing strategies)
- Stakeholder requirements
- Project risks
- Project size
- Resource availability
- Project complexity
What works for one project can be completely unsuitable for another. These individual differences require tailored approaches in project management. A one-size-fits-all solution is not capable of meeting the specific requirements and challenges of each project.
Project Management Methodologies in comparison
Agile? Lean? Waterfall? Project managers are spoilt for choice. The following project management methodologies have already established themselves in practice. Now it’s time to decide which method fits your principles and processes.
1. Waterfall Methodology
The Waterfall methodology is a traditional project management method. It proceeds step by step – like a waterfall – in these phases:
- Planning and Analysis
- Setting up the Resource Plan
- Completion of the Project
All tasks of the project are processed according to the fixed sequence of the Waterfall project management methodology. New tasks are only started when the previous ones are completed.
In the framework of the Waterfall method, the project manager plans in advance exactly the required resource deployment and aligns the entire planning of the project management process accordingly. Unlike agile project management methodologies , no feedback processes are provided within the individual project steps. The Waterfall methodology allows only minimal deviation from the pre-established resource planning.
What is this Project Management Methodology suitable for?
The Waterfall methodology is particularly suitable for projects whose tasks are dependent on each other. Projects that follow this method shouldn’t be very extensive and of short duration. Or they should include tasks that are repetitive and already known to the participants. The Waterfall methodology is well suited, for example, for projects in production that primarily involve sequential processes. These sequential phases and processes are often visualized in Waterfall project management using Gantt charts .
In the implementation of step-by-step project management frameworks, errors often become apparent only at the end of a project. Therefore, the Waterfall methodology is not well suited for projects with many unpredictable factors.
Opportunities & Risks
Unknown Fact : Although the Waterfall methodology is often seen as traditional and sequential, it did not originate in computer science or engineering. In fact, the Waterfall methodology was first introduced in an article by Dr. Winston W. Royce in 1970, where he described the project management method as problematic and prone to errors. Ironically, the Waterfall methodology still became popular. Today it’s one of the most well-known project management methodologies, even though its original creator viewed its application with reservations.
2. Agile Methodology
Originally, the Agile project management methodology was designed in 2001 by 13 industry leaders as part of the Agile Manifesto for software development. Since then, agile methodology has also proven itself as a project management framework. Agile project management questions the processes, tasks, and role distributions of traditional approaches and replaces them with a more flexible, future-oriented principle. The optimization of customer benefit is foregrounded.
The core principle of the agile methodology is based on 12 guidelines and includes the following pillars:
- Direct and Open Communication
Agile project management methodologies are based on short, direct communication channels. When all team members are on the same level of knowledge, requests for changes can be responded to immediately and comprehensively.
- Implementation Cycles that Allow for Short-Term Changes
To optimize customer benefit, it must be possible to respond to short-term requests for changes. Instead of delivering a complete final package to the customer, which they may not be satisfied with, agile project management allows for regular feedback processes and constant improvement of the product – even during the project process!
- Implementation of Flat Hierarchies
Agile work can only be carried out in a familiar team atmosphere. Strict hierarchy prevents quick and flexible responses to requests for changes. In agile teams, each member acts on their own responsibility. Agile leaders must therefore be able to delegate tasks and responsibility and have trust in their employees.

Agile project management methodologies are flexible in their application. Therefore, they are excellently suited for large, complex projects whose requirements are unpredictable and which can entail high risks. Aligned with the principles of the Agile Manifesto, various agile implementation methods, such as Scrum and Kanban, have been developed. However, since these have also developed their own structures, roles, and terminologies, they are treated as distinct project management methods in the following. Another project management tool that is especially popular in agile project management are Mind Maps . They help organize complex information and promote creativity and collaboration within the team.
Unknown Fact: According to a survey by the PMI (Project Management Institute) , agile projects have a higher success rate compared to traditional projects. The study found that 71% of agile projects were rated as successful compared to 55% of non-agile projects.
3. Scrum Methodology
Scrum is also considered an Agile method but distinguishes itself through its own set of firm rules, roles, and processes. This project management methodology is based on the notion that extensive projects are too complex to plan precisely in advance. Thus, most of the potential risks and requirements are unclear at the start of the project. To counter this fact, Scrum involves setting up and discussing interim results.
At the beginning of the project, Scrum establishes a long-term plan (Product Backlog) . Unlike the traditional Waterfall methodology, this plan is regularly adjusted and optimized during the execution of the project. Tasks and actions associated with the project are implemented in repeating cycles (Sprints) . Each Sprint aims to present a functioning interim product.
To enable Scrum teams to achieve this, all project participants gather at the start of each day in Daily Scrums to discuss tasks, problems, and progress. The Scrum project management methodology defines the following roles within a team:
- Product Owner: A product expert who represents the project’s stakeholders and advocates the views and wishes of the customer
- Development Team: A project team (e.g., developers and designers) that is involved in the execution of the project and takes on tasks
- Scrum Master: Facilitates and supports the development team and is responsible for ensuring that Scrum is correctly implemented. He also mediates between the development team and the Product Owner. However, it’s important to note that the Scrum Master does not play a traditional boss role. He does not dictate who should complete which task

Scrum supports extensive, complex projects whose character is difficult to define in advance and therefore require a flexible project management methodology. Especially teams consisting of fewer than seven people benefit from Scrum.
Unknown Fact: Although Scrum originally emerged as a framework for software development, it was later successfully expanded to other industries, including marketing, HR, and even in the field of education.
4. Kanban Methodology
Kanban is based on regular feedback loops and teams that work independently. This Agile project management methodology was originally developed in the 1950s by Toyota in Japan . Kanban aims to optimally control each stage of a project to achieve faster throughput times.
The core principle of Kanban is effective teamwork . Short, daily stand-up meetings are practical, where all team members can discuss progress, successes, problems, and the next steps in the project.
The Kanban method visualizes project workflows using Kanban boards . Kanban boards can be created both physically and digitally.
In the classic model, tasks that are not yet being processed are listed as To-Dos in the left column of the board.
When you start working on a task, move it to the middle column of the board and mark it as Doing . The Kanban method allows all team members to decide in which order to process tasks.
Once a task is considered complete, it is moved to the right column of the Kanban board and marked as Done .
It’s important to work on only a limited number of tasks simultaneously. A key aspect of implementing Kanban in project management is that tasks are consistently prioritized to keep processes clear and organized.
If a so-called bottleneck, or task backlog, forms, your Kanban board will show a large number of Kanban cards in the To-Do or Doing column. Here you must intervene and analyze the problem.
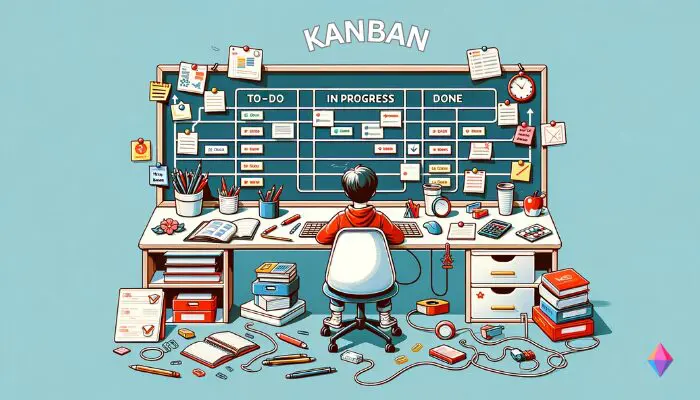
Originally, Kanban was developed by Toyota for production and later adapted for software development by David Anderson in 2007. Nowadays, due to its transparent structures and high flexibility, Kanban can be used for any project that benefits from continuous improvements and feedback processes during its execution.
By the way: The Kanban project management methodology is perfect for personal and creative endeavours .
Unknown Fact: According to an internal analysis of companies that have implemented Kanban, the average cycle time for tasks has been reduced by up to 50%.
5. Lean Methodology
Lean aims to create value without waste. Customer benefit and process efficiency are optimized without wasting resources. The Lean project management methodology distinguishes between three different types of resource waste :
Muda refers to activities or processes that do not create value. Lean identifies potential resource wastage in seven original processes :
- Movement (of employees)
- Waiting times
- Overproduction
- Incorrect use of technology or poor manufacturing processes
- Waste and possibly rework
Mura refers to losses that occur due to unbalanced processes. If the individual process steps are not aligned, deviations, irregularities, and disruptions arise.
Muri refers to an unbalanced workload on employees and machines. According to Lean principles, processes should neither be too fast nor too slow. Ideally, Lean reduces monotonous activities without overburdening employees and overloading machines.

Since Lean (Project) Management is much more a project management philosophy than just a tool, this project management methodology is suitable for any company interested in transforming the values of their project management to save costs and other resources in the long term.
Key prerequisites for a comprehensive implementation of Lean project management are:
- Breaking up traditional thought structures and work processes
- The ability to design projects and processes flexibly
- A strong team culture
- Support from the entire leadership level
- A firm commitment to the company value of “customer proximity”
Unknown Fact: Lean project management is based on the principles of Kaizen , which means “continuous improvement” in Japanese. The constant pursuit of improvement at all levels of the company, from processes to work culture, contributes to strengthening the agility and adaptability of the organization.
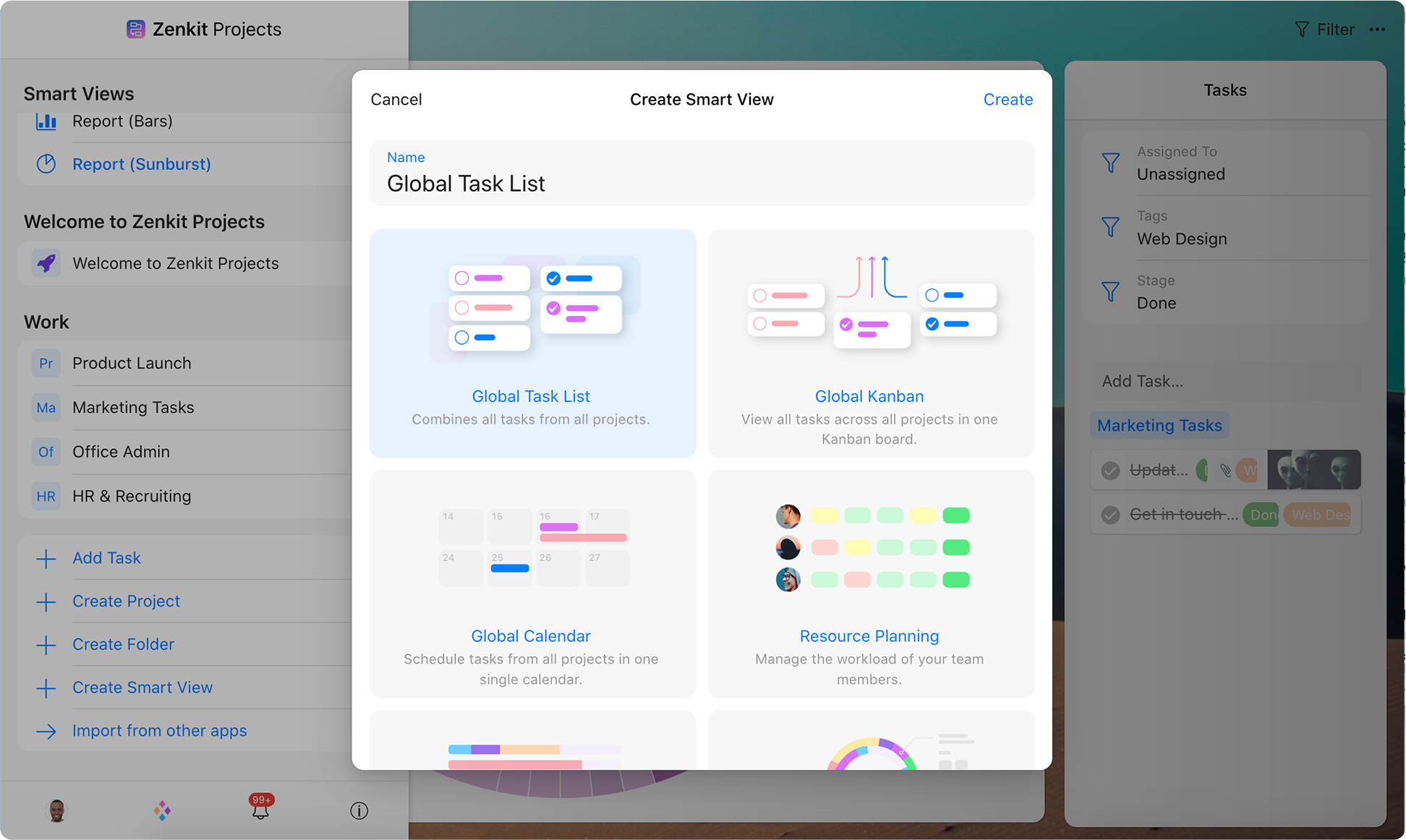
10 popular project management methodologies, but only one home needed for all of them. Get the most out of your project
6. Six Sigma Methodology
The Six Sigma methodology was developed in 1987 in the USA by Motorola . Six Sigma is based on the assumption that every business process can be represented as a mathematical function. The description, measurement, analysis, control, and optimization of these processes are carried out using statistical means.
The main tool of this project management methodology is the DMAIC cycle . DMAIC aims to make business processes measurable and optimize them. The following actions determine the DMAIC cycle:
- D efine: Identification and documentation of the problem in the process to be improved. What should the target state look like?
- M easure: To what extent does the process meet the requirements?
- A nalyze: Identification of the causes of the problem
- I mprove: Resolution of the problem
- C ontrol: Ensuring the sustainability of the solution by monitoring the new process with statistical methods
The leadership of Six Sigma projects is undertaken by specially trained employees. The role designations in Six Sigma teams are based on the belt colors in Japanese martial arts, which serve as a ranking system. For example, there is the Master Black Belt (coach and trainer) or the Black Belt (project manager). A comprehensive explanation of all team roles in this project management methodology can be found here .

Six Sigma is especially popular in large companies. This project management methodology is favored in the manufacturing industry and the service sector. Variants of the Six Sigma method have also become established in software development and the financial industry. Six Sigma is ideally suited for projects with clearly measurable results and a duration of between three and six months.
Unknown Fact: The term “Six Sigma” refers to the statistical expression for a process’s ability to produce only 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
7. Critical Chain Project Management Methodology
Critical Chain project management (CCPM) is an effective project management methodology for managing projects based on the principles of the Theory of Constraints .
Unlike traditional project management approaches, CCPM focuses on the identification and management of bottlenecks in the project. The method concentrates on utilizing critical resources as effectively as possible to shorten throughput times.
The central idea behind CCPM is the creation of a critical chain of tasks, where buffer times are strategically used to account for uncertainties and fluctuations in the project’s progression.

CCPM is particularly suitable for projects with uncertain resource capacities and dynamic requirements. This includes companies from various sectors such as manufacturing, IT, construction, research, and development. The method emphasizes the prioritization of tasks and maximizing efficiency, leading to accelerated project execution. Companies that value lean and targeted project management will find CCPM a valuable method for optimal project results.
Unknown Fact: Critical Chain project management (CCPM) aims not only to identify bottlenecks but also to overcome psychological barriers. CCPM acknowledges that human uncertainty and behavior patterns can impact project performance. Therefore, the project management methodology integrates strategies to cope with uncertainty and promote a positive team environment.
8. PRINCE2 Methodology
Prince2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is a proven project management methodology for structured project management that is recognized worldwide.
The method is characterized by clear processes, roles, and responsibilities. Prince2 defines detailed phases in the project cycle, starting with initiation, followed by planning, execution, control, and completion. It places great importance on the involvement of stakeholders and emphasizes the regular review and adjustment of the project status.

Prince2 is particularly suitable for projects with clear definitions, fixed structures, and comprehensive documentation requirements. The method offers flexibility to adapt to various project sizes and types. Large companies with complex projects that seek a methodical approach with clear governance structures will find Prince2 to be a robust method for ensuring project success.
Unknown Fact: Prince2, with its roots in IT projects, was originally developed in the United Kingdom and introduced by the British government.
9. Extreme Programming Methodology
Extreme Programming (XP) is an Agile methodology that focuses on software development and is based on principles such as flexibility and continuous improvement.
Originally developed in 1996, XP has evolved into a versatile project management methodology. XP emphasizes direct communication, collaboration, and customer orientation. With a focus on short development cycles (iterations), Extreme Programming enables rapid adaptation to changing requirements. Pair programming, Test Driven Development (TDD), and continuous integration are key elements of XP. These methods promote high code quality and early detection of errors.

XP is particularly suitable for projects where the requirements are not clearly defined from the beginning and high flexibility is required. Companies looking for an Agile method to quickly respond to customer feedback and deliver high-quality software will find an effective solution in Extreme Programming (XP).
Unknown Fact: Extreme Programming popularized the practice of “User Stories”. User Stories are short, understandable descriptions of features or requirements from the perspective of the end-user. This method helps to improve usability and ensures that the developed features provide clear added value for the users.
10. PMI/PMBOK
PMI stands for the project management Institute which is a not-for-profit membership association, project management certification, and standards organization. Through the PMI, comes the PMBOK which is not quite a methodology but a guide detailing a set of standards that characterize project management.
PMBOK stands for the project management Body of Knowledge and is a set of standard terminology and guidelines for project management. It states that there are five process groups that are prevalent in almost every project. They are:
- Initiating : Defining the start of a new project or new phase of an existing project.
- Planning : Where the scope of the project, objectives, and how the objectives will be achieved.
- Executing : Actually doing the work defined in the project management plan.
- Monitoring and Controlling : When you need to track, review, and regulate the progress and performance.
- Closing : Concluding all activities across all Process Groups to formally close the project or phrase.
Along with this, it includes best practices, conventions, and techniques that are considered the industry standard. Regularly updating their guide to ensure that they echo the most up-to-date project management practices, the PMBOK is currently up to its seventh edition which was published in print and online in 2021.
Because it’s more of a reference guide than an actual project management methodology, you can’t implement PMI/PMBOK to a project. However, it can be used when you want to weigh in on the best practices for your project.
Unknown Fact: The PMBOK originated from an effort to standardize the information and practices in the field of project management and was first published as a white paper in 1987.
Have you found your Favorite?
Whether it’s a start-up, a corporation, a family business, or even for private projects – the presented selection of various project management methodologies includes solutions for (almost) every team size and project character.
If you have set your sights on one of the project management frameworks, you should familiarize yourself with it thoroughly once again. Especially complex project management methodologies like Scrum or Six Sigma fill entire books and must therefore be understood in the smallest detail.
Are you missing a specific methodology in our overview or would you like to learn more about one of the methods presented? Then leave us a comment. Have you successfully implemented one of the methods? Tell us and other readers about your experiences.
As always, we look forward to hearing from you.
See you soon!
FREE 20 MIN. CONSULTATION WITH A PROJECT MANAGEMENT EXPERT
Wanna see how to simplify your workflow with Zenkit in less than a day?
- Critical Chain
- Extreme Programming
- Project Management
More from Asmo
How to Manage a Team: 10 Tips for Success
What is Agile Methodology? (An Overview)
More from Benjamin Argyle-Ross
The 6 Most Frequently Asked Project Management Questions
58 thoughts on “ 10 Most Popular Project Management Methodologies: An Overview ”
Projects that require flexibility and have a level of complexity or uncertainty. For instance, a product or service that hasn’t been built by the team.
Agile is a methodology that has methodologies within itself, such as Scrum and Kanban. While some may argue that they should be considered more as frameworks, they are used to develop and deliver a product or service and carry their own set of characteristics and terminology which I think makes them worthy enough to be included on this list.
Hello, What applications are best and worst suited for the use of Agile principles? What are the challenges in using this approach that Systems Analysts and Project Managers need to be aware of?
What about research projects in Information technologies? What is the typical approach or does it very much depend on the type of domain of research?
Hi Fernando, The approach really depends on the type of domain of research. But I’ve found that agile approaches are common.
Thank you for sharing.
Brilliant overview or Synopsis. There is so much changing in project management world that it does get confusing. This article does align all ducks in a row.
Thanks, Yogesh. Appreciate your support!
Hope this message finds you doing well!
I’m an aircraft engineer and currently interested I’m learning and being certified in QM systems. Now there is a lot of information available online on different methodologies being used hence too much information is not helping. I am currently working in the manufacturing industry where all sorts of vehicles are made.
So far I understand that the methodologies that will suit my industry would be six sigma, Kaizen and LEAN; please do correct me if I am wrong or if there are others available which I have not mentioned. Now with that said. I have 2 questions.
1. Which certification recommendations do you have for engineers in the manufacturing industry.
2. What methodology do you recommend for a startup manufacturing business and which methodologies should they evolve to.
Thank you so much for your time.
Regards, Danish
Hi Danish, Regarding certification, I would recommend enquiring with someone within the manufacturing industry as they’d have more knowledge about this kind of stuff. As for methodology recommendations, as you mentioned, LEAN and Six Sigma could work, but once again, I would advise doing further research.
what methodology is best suited for hospital management?
Hi Kiran, Like most projects, it all depends. There are instances where Waterfall would be ideal, but then there are other instances where agile methodologies would best suit. I would recommend doing research beyond this article as we’re not too acquainted with hospital management. 🙂
Could you please upload all of these as well ? ITIL, PYMBOK, PMI, Prince2. Lean, Waterfall, Six Sigma (I know some of them are mentioned and some of them are not)
PLEASE KINDLY UPLOAD THEM SOON !!!!
ESPECIALLY PRINCE 2 !!!!!!!
Hi Mitz, thanks for your suggestion. I’ll be sure to add it to our list. If you have further feedback, I’d recommend sending them to our customer service team at [email protected] 🙂
Is there a number I can reach you at. I am a general contractor submitting a bid on a large project and I need to provide an awful lot of information on project methodology. I would really appreciate if I could reach out to you for a quick call.
Hi Paul, The best thing to do would be to send a quick email to [email protected] – our team will be able to get back to you and set up a time to call.
Hello Dinnie, I am from finance field. But for my project book i need information of agile methodology. As i’m Non – IT background your article helps me to undestand it in a simple way & info which is in your article helps me to write it on my project book. Thank You..!!
Glad you’ve found the article helpful. Appreciate your support, Aditi.
What methodology would you recommend for a corporate email implementation? The current system needs updating to accommodate over 2,500 staff members.
Thank you for the concise explanation. I am currently in R&D and moving towards software development. I was not familiar with any software development methodologies before. Your article was very concise to get to know some of the well-known methodologies.
Thanks, Ali. Glad you found the article helpful 🙂
ITIL, PYMBOK, PMI, Prince2. Lean, Waterfall, Six Sigma are solid methods, structures or libraries used in conjunction.
Most of the other methodologies were invented due to the high cost of software development. Agile is really done in non regulated areas due to the high cost of documentation vs development so you find a great deal of in fighting in IT environments and then there are high rates of sacking until you find a team that works well in agile, scrum, kanban together. These methods are more a process requirements to me having studied most of the methods.
I am an IT specialist and I can tell you that any construction industry laughs at agile, scrum and kanban. Only suitable for IT and it creates bullying and discrimination. If you enforce ITIL then much of agile, kanban and scrum can be heaped into one name and that would be ‘continuous objectives’ which is not a project as the definition is one of a kind. The same type of software can be built numerous different ways and therefore fails the once off unique definition.
Great insight, Daffy. Thanks for sharing.
Pmi pmbok is not a methodology. P.2, 6 edt.
Hi, I did point out that they’re not methodologies but more guides that detail a set of standards that characterize project management. Appreciate your comment. 🙂
Thanks for the article. It is easy to understand!
Glad you enjoyed it, Christelle 🙂
methodologies outlined clearly. Helpful. thanks
Appreciate your comment, Nancy. 🙂
first of all; I would like to thank you for the amazing article. secondly; If I have a design project (architectural) do you think that the best methodology for that is the Aigle?
Hi Samar, Glad you enjoyed the article 🙂 Agile isn’t the most popular method to use for design projects, however, if you feel that it could work for yours, it wouldn’t hurt to give it a go.
Hii good afternoon……Nice Info……Which company use agile method for quality assurance in software development?
Hi Nithya, I’m sure many companies use agile methods for quality assurance in software development. Unfortunately, I couldn’t tell you which exactly. Thanks for reading 🙂
Hi Good afternoon. could you suggest the best methodology for a project in putting up IT infrastructure (Hardware setup).
Hi Jay 🙂 Considering a hardware setup is a pretty standard procedure, I would recommend something along the lines of the Waterfall method. There’s a lot of planning and documentation involved, so it could be fitting. Hope that helps!
Nice Info! Let me ask: and what about “CRISP-DM” methodology for Data Mining Projects? You think is a good option for? Regards from Perú!
Hi Juanalfieri, I can’t say I’m overly experienced with CRISP-DM, so I would recommend further reading elsewhere. Thanks for the note though, I will look this up and perhaps include it in a revised version of this article 🙂
Thanks for the article. It amazing how it articulates so much knowledge, on a succinct way and gives to the user a quick and sufficient overview of the PM methods as well as the initial boost for a further research deepening down, if needed. What do you would be the best mix methods or mix of them in an ERP implementation such as SAP? Thanks in advance for your reply!
Thanks, Yannis! I haven’t had any experience with ERP implementation myself, however, as they’re usually complex projects, perhaps something agile would be ideal. This is the part where I would suggest to do further research 🙂
Good overview in a prescise manner, easily understood…
Thanks Nazima 🙂
Thanks for the article, it was very helpful.
hye, what is the best methdology for gym management system? thank u
While I’m not all too familiar with gym management systems, I can recommend Kanban. It provides great flow management and the board and cards used offer a visual structure to track various tasks/items in the one place.
Hi Dinnie, great article and very informative. I currently work in a company and we execute contract both government and private contract. I was hired in February and there were 41 contract job being worked on. Ranging from road construction to procurement/supplies etc. I am having a hard time determining which methodology to use and how to track these projects. Most of them have been completed.
Hi Chris, Construction and procurement are traditionally associated with Waterfall, however, I would advise to do further research on whether or not this would apply to your situation. Thanks for the support 🙂
What about Dev Ops methodology? Can you check explain it .
Thanks for the tip, Abdulrahman. Sounds like something that could be included in a revised version of this article.
What methodologies best suit in establishing a retail shop?
Hi Aruni, Establishing a retail shop seems to me something that may involve a few uncertainties and surprises, so I would probably recommend something Agile as they provide leeway and flexibility.
excellent article. found it very useful. Thanks a lot
Cheers Abdul. Glad it could help 🙂
Good article, very informative and helpful. Good job @Dinnie.
Thanks, Prativa 🙂
What about PRINCE2? It seems to me that PMI and PRINCE2 are quite comperable, but PMI is more common in US, while PRINCE2 in in EMEA region. Very good overview btw, great work. 🙂
Thanks, Ivan 🙂 Ah yes, PRINCE2, perhaps I’ll have to include it in a revised version of this article. Cheers for the tip!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Zenkit Comment Policy
At Zenkit, we strive to post helpful, informative, and timely content. We want you to feel welcome to comment with your own thoughts, feedback, and critiques, however we do not welcome inappropriate or rude comments. We reserve the right to delete comments or ban users from commenting as needed to keep our comments section relevant and respectful.
What we encourage:
- Smart, informed, and helpful comments that contribute to the topic. Funny commentary is also thoroughly encouraged.
- Constructive criticism, either of the article itself or the ideas contained in it.
- Found technical issues with the site? Send an email to [email protected] and specify the issue and what kind of device, operating system, and OS version you are using.
- Noticed spam or inappropriate behaviour that we haven’t yet sorted out? Flag the comment or report the offending post to [email protected] .
What we’d rather you avoid:
Rude or inappropriate comments.
We welcome heated discourse, and we’re aware that some topics cover things people feel passionately about. We encourage you to voice your opinions, however in order for discussions to remain constructive, we ask that you remember to criticize ideas, not people.
Please avoid:
- name-calling
- ad hominem attacks
- responding to a post’s tone instead of its actual content
- knee-jerk contradiction
Comments that we find to be hateful, inflammatory, threatening, or harassing may be removed. This includes racist, gendered, ableist, ageist, homophobic, and transphobic slurs and language of any sort. If you don’t have something nice to say about another user, don't say it. Treat others the way you’d like to be treated.
Trolling or generally unkind behaviour
If you’re just here to wreak havoc and have some fun, and you’re not contributing meaningfully to the discussions, we will take actions to remove you from the conversation. Please also avoid flagging or downvoting other users’ comments just because you disagree with them.
Every interpretation of spamming is prohibited. This means no unauthorized promotion of your own brand, product, or blog, unauthorized advertisements, links to any kind of online gambling, malicious sites, or otherwise inappropriate material.
Comments that are irrelevant or that show you haven’t read the article
We know that some comments can veer into different topics at times, but remain related to the original topic. Be polite, and please avoid promoting off-topic commentary. Ditto avoid complaining we failed to mention certain topics when they were clearly covered in the piece. Make sure you read through the whole piece before saying your piece!
Breaches of privacy
This should really go without saying, but please do not post personal information that may be used by others for malicious purposes. Please also do not impersonate authors of this blog, or other commenters (that’s just weird).

Project Management Methodologies
Project Management Guide
- 1. Project Management Basics
A. The traditional, sequential methodologies
B. the agile family, c. the change management methodologies, d. the process-based methodologies, e. other methodologies, f. the pmbok “method”.
- 3. Project Management Life Cycle
- 4. Best Project Management Software
- 5. Team Collaboration Tips
- 6. Agile Methodology Basics
- 7. Agile Project Management Tools & Techniques
- 8. Project Management Frameworks
- 9. Resources
- 10. Glossary
- 11. FAQ
The top project management methodologies
“You mean there’s more than one project management methodology?” There are quite a lot of them, actually, and some even combine to form new hybrid approaches. But what are they exactly? How do they help project teams work better? And what makes one methodology better than another?
Project management methodologies are essentially different ways to approach a project. Each one has a unique process and workflow.
Here, we look at some of the top project management methodologies, grouped by similarity and popularity.
Before we begin, you can unlock a free trial with Wrike right now to try out our powerful features, collaborate with colleagues in real time, and streamline all your projects in one platform.

Waterfall project management methodology
The most common way to plan out a project is to sequence the tasks that lead to a final deliverable and work on them in order. This process is also known as the waterfall methodology — the traditional method for managing projects and the one that is simplest to understand. You have to complete one task before the next one begins in a connected sequence of items that add up to the overall deliverable. It’s an ideal method for projects that result in physical objects (buildings, computers), and you can easily replicate project plans for future use.
The power of this methodology is that every step is preplanned and laid out in the proper sequence. While this may be the simplest method to implement initially, any changes in stakeholders’ needs or priorities will disrupt the series of tasks, making it very difficult to manage. This methodology excels in predictability but lacks in flexibility.
Critical path method (CPM)
The critical path method was developed in the 1950s, based on the idea that there are some tasks you can’t start until you finish the previous one. When you string these dependent tasks together from start to finish, you plot out your critical path.
Identifying and focusing on this critical path allows project managers to prioritize and allocate resources to get the most important work done and reschedule any lower priority tasks that may be clogging up your team’s bandwidth. This way, if you need to make changes to the project schedule, you can optimize your team’s work process without delaying the results.
This way, if you need to make changes to the project schedule, you can optimize your team’s work process without delaying the results. A Gantt chart is one of the most common ways to visualize the critical path in project management.
Further Reading:
Critical Path Is as Easy as 1-2-3
How to Calculate Critical Path in Project Management
Critical chain project management (CCPM)
Critical chain project management takes the critical path method one step further. CCPM is a methodology that focuses on the resources needed to complete the project’s tasks by adding resource availability to the critical path. It also builds buffers of time around these tasks in the project’s schedule, ensuring the project meets its deadlines.
Agile project management methodologies are growing in popularity, thanks to a highly competitive business environment and increased innovation. In general, Agile methodologies prioritize shorter, iterative cycles and flexibility.
Let’s take a look at some of the most popular Agile frameworks.
Agile project management methodology
The core of the Agile methodology was developed in 2001 with four central values:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
The Agile Manifesto of Software Development put forth a groundbreaking mindset on delivering value and collaborating with customers. Today, Agile can refer to these values as well as the frameworks for implementing them, including Scrum, Kanban, extreme programming, and adaptive project framework.
What do these various Agile frameworks have in common?
Project objectives are made clear by the customer (internal or external), while the final deliverable can change as the project progresses. The project team works in iterative cycles, always evaluating results at the end. Depending on the results of these evaluations, the final deliverable may be modified to better answer the customer’s needs. Continuous collaboration is key, both within the project team and with project stakeholders .
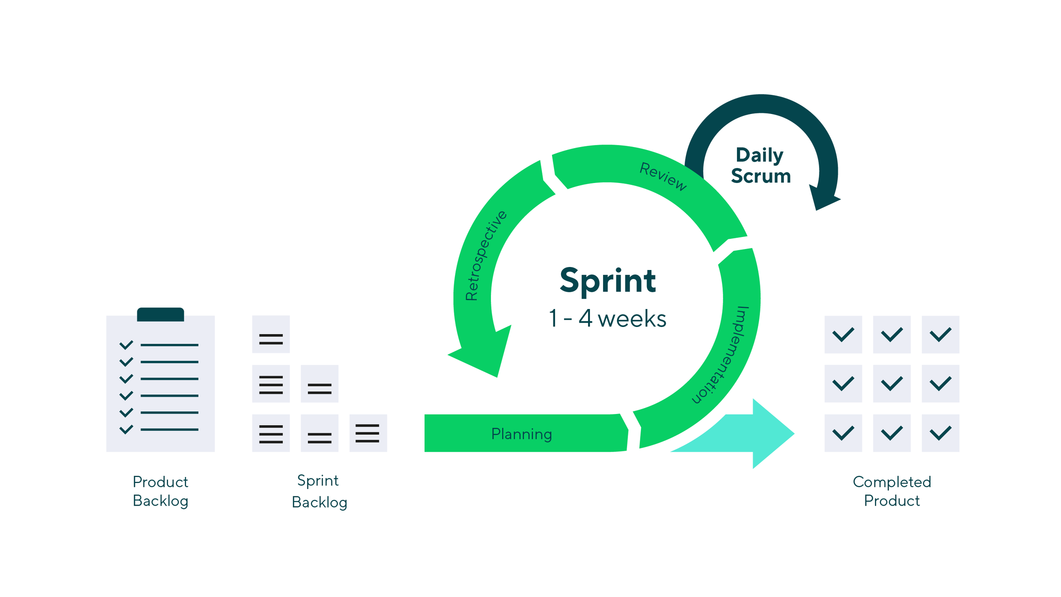
7 Steps to Developing an Agile Marketing Team
Should Your Business Go Agile?
Scrum is the most popular Agile development framework because it is relatively simple to implement. It also solves many problems that software developers struggled with in the past, such as convoluted development cycles, inflexible project plans, and shifting production schedules.
In Scrum, a small team is led by a Scrum master whose main job is to clear away all obstacles to working efficiently. The team works in short cycles of two weeks called “sprints,” though the team members meet daily to discuss their work and any roadblocks that need clearing. This methodology allows for rapid development and testing, especially within small teams.
Fundamentals of the Scrum Methodology
Scrum in Wrike: Making Software Development More Agile
Kanban is another framework for implementing Agile based on a team’s capacity. It originated in Toyota’s factories during the 1940s. The departments used a visual system of cards (“Kanban”) to signal that their team was ready for more raw materials and had more capacity to produce.
Today, this visual approach to managing a project is well-suited to work that requires steady output. Project teams create visual representations of their tasks, often using sticky notes and whiteboards (or online Kanban boards ), moving the notes or tasks through predetermined stages to see progress as it happens and identify where roadblocks could occur.
Extreme Programming (XP)
Extreme programming (XP) is another offshoot of Agile. XP is a methodology designed to enhance software quality (and simplicity) and a development team’s ability to adapt to customers’ needs. Much like the original Agile formula, XP features short work sprints, frequent iterations, and constant collaboration with stakeholders. Change can happen within a sprint. If work hasn’t started on a specific feature, it can be swapped out and replaced by a similar task.
Adaptive Project Framework (APF)
Adaptive project framework grew from the difficulty in managing most IT projects using traditional project management methods due to uncertain and changing requirements.
APF begins with a requirements breakdown structure (RBS) to define strategic project goals based on product requirements, functions, sub-functions, and features. The project proceeds in iterative stages, and at the end of each step, teams evaluate previous results to improve performance and practices. Stakeholders can also change the project’s scope at the start of each stage so the team can produce the most business value.
Some methodologies deal with managing projects, but with an extra focus on change management — especially planning for risks and taking control of change when it happens. Notable methods include:
Event chain methodology (ECM)
The underlying idea behind event chain methodology is that potential risks often lie outside the project’s scope. It’s essential to prepare for these risks and plan your response since unexpected events will impact your project’s schedule, deliverables, and potentially its success.
Extreme Project Management (XPM)
Extreme project management (XPM) is the opposite of waterfall. It offers you a way to manage massive change and still move forward to project completion. In XPM, you can alter the project plan, budget, and even the final deliverable to fit changing needs, no matter how far along the project is. It’s a good option when managing projects with a short timeline of anywhere from a few weeks to mere days.
What Is Extreme Project Management and Is It Right for Your Team?
Next, we have the project management methods that practically veer into business process management (BPM), where each approach focuses on work as a collection of processes. While project management purists may argue that these methods belong on a different list, we think these are still good ways to plan and execute a project.
Lean is a methodology focused on streamlining and cutting out waste. The first step is to create a work process breakdown to identify and eliminate bottlenecks and delays. The goal is to do more with less — to deliver value to the customer using less manpower, less money, and less time.
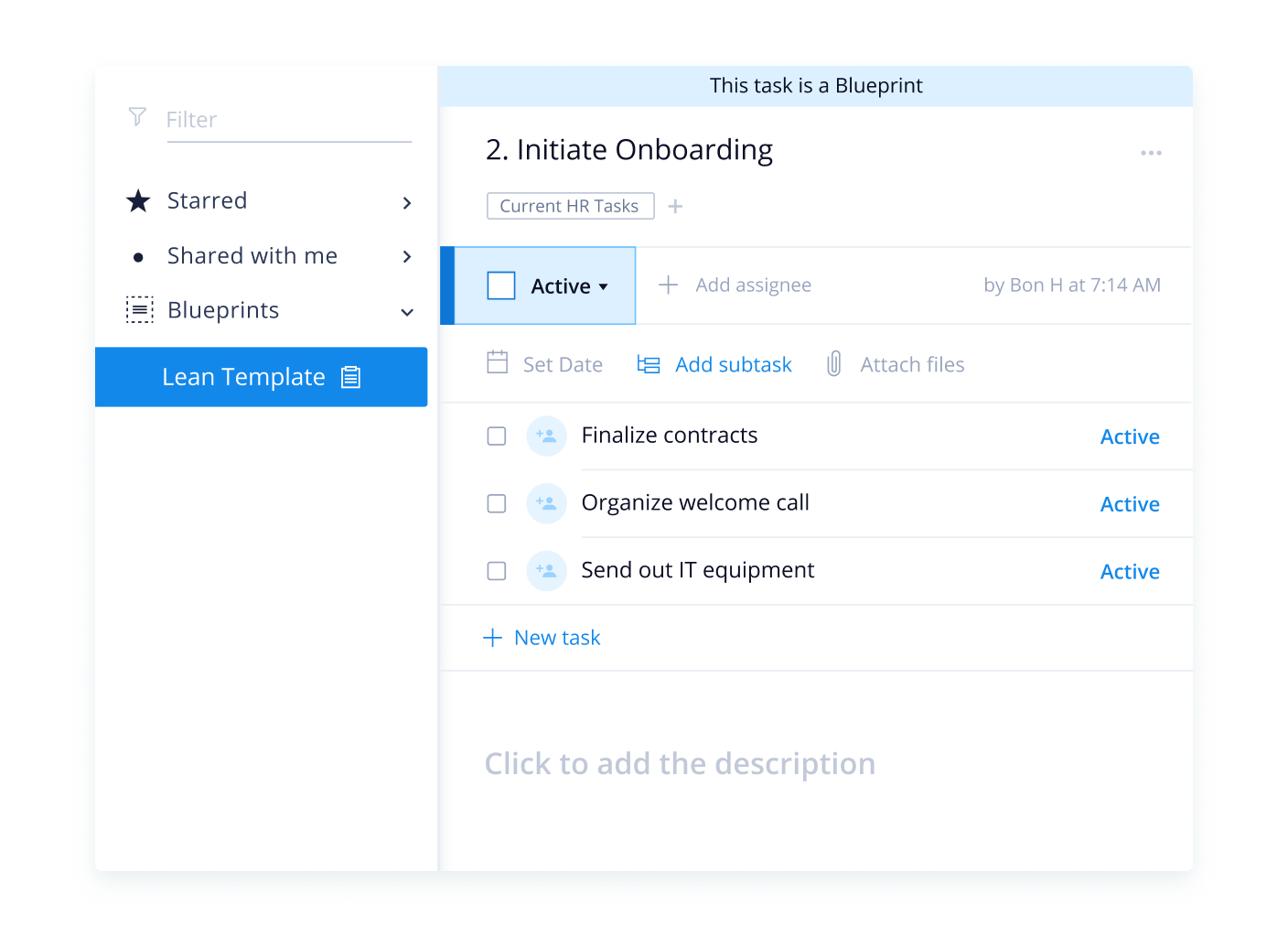
Product Development Tips From the Wright Brothers
Startups Should Lean on Lean Project Management
Six sigma is a statistics-based methodology seeking to improve the quality of a process by measuring the defects or bugs present and eliminating as many as possible. A process can attain a six sigma rating if 99.99966% of the final product — your project deliverable — is defect-free.
Lean six sigma
Combining the minimalist approach of lean (“no waste!”) and the quality improvement of six sigma (“zero defects!”), lean six sigma focuses on eliminating waste so that projects are more efficient, cost-effective, and truly answer customers’ needs.
Process-based project management
Process-based project management is a methodology aligning all project objectives with a company’s larger mission and corporate values. All project goals and tasks remain strategic and must roll up to the larger corporate objectives. The steps involved include defining the process, establishing metrics, measuring methods, adjusting goals when these prove unstable, planning improvements, and implementing them.
PRINCE2 stands for Projects In Controlled Environments. It’s a method for managing projects used by the UK government and characterized by a product-based planning approach. In PRINCE2, a structured project board is in charge of high-level activities such as setting the business justification and resource allocation. A project manager takes care of the lower level, day-to-day activities like scheduling. This methodology gives teams greater control of resources and the ability to mitigate risk effectively.
PRINCE2 Explained
PRiSM stands for Projects Integrating Sustainable Methods and aims at managing change while incorporating environmental sustainability into its processes. The goal with PRiSM is to complete tasks while reducing a company’s negative environmental and social impact. It is, quite literally, green project management.
Benefits realization
From conception to execution to delivery and beyond, the benefits realization methodology focuses on whether your deliverables satisfy the benefits the customer expects, and not just whether you delivered it on time or within budget. This methodology ensures that you provide real value to customers and stakeholders.
From Surviving to Thriving: 3 Challenges PMOs Need to Conquer Now
While it may be debatable whether this is a true project management methodology, you will find organizations that say they use the project management body of knowledge (PMBOK) method for managing projects.
While not an official methodology, this system involves breaking down projects into the five process groups agreed upon by the Project Management Institute (PMI) and documented in the Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK). The five stages include:
- Controlling
What’s inside the PMBOK guide
WThe PMBOK collects set processes, best practices, terminologies, and guidelines that the project management industry accepts as standards. You’ll find it documented in the book, A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) , compiled and overseen by the Project Management Institute (PMI).
The PMBOK Guide provides project managers with guidelines and best practices, defining everything from the project life cycle to project management strategies and concepts. The PMBOK Guide details the various project management processes that interact and overlap throughout a project’s life cycle.
The 10 project management knowledge areas of PMBOK
PMBOK officially recognizes 47 typical project management processes, organized into 10 knowledge areas:
- Project communication management: Processes that disseminate information among team members and external stakeholders, ensuring that data is exchanged continuously, and more importantly, understood by all concerned.
- Project cost management: Processes regarding budgets, funding, spending allocation, and timing. Cost management is dependent on activity estimates from time management.
- Project human resources management: Processes involving managing your project team, like sourcing, hiring, assigning roles, professional development, and fostering team spirit.
- Project integration management: Processes necessary to define, consolidate, and coordinate all the other processes and project management activities. These processes are vital in setting expectations and keeping communication lines open.
- Project procurement management: Processes for planning, budgeting, and purchasing resources — whether physical or informational — to complete work.
- Project quality management: Processes that define a project’s success or criteria for considering the task complete. The team manages quality at every stage of the project, from planning to continuous performance improvement.
- Project risk management: Processes involved with preparing for and managing unexpected risks.
- Project scope management : Processes managing the scope or parameters of a project. These processes ensure the range is well-defined and that all requirements remain within the limit.
- Project stakeholder management : Processes that identify who will be impacted by the project and manage relationships with them, including strategies for collaborating with stakeholders on project direction and execution.
- Project time management: Processes needed to ensure the project is completed before the specified deadline.
PMP Certification? Use this List of Helpful PMBOK Guide Resources
20 Online Training Resources for Project Managers
What Project Management Books Should You Read?
Top Project Management Methodologies & Frameworks for Successful Teams
Empower your project management methodology with Wrike
In conclusion, choosing the right project management methodology can make a significant difference in the success of your project. Each methodology has its unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, and selecting the appropriate one depends on various factors such as project size, complexity, and team expertise.
Wrike offers an extensive range of features that cater to different project methodology needs and objectives, from Agile to Waterfall. With customizable workflows, pre-built templates, time-saving automation, and a user-friendly interface, Wrike makes it easy to implement new methodologies from scratch.
Whether you run a small business or a large enterprise, Wrike can help you manage your tasks more efficiently and tick off your to-do list. Use Wrike to increase your team’s productivity and deliver projects on time, every time.
Choose the Right Project Management Methodology
How to choose the right project management methodology.
How do you choose the right methodology for your project with so many different options available? You should pick based on the needs of your project and your team. Two tips are relevant here:
A. Start with the end in mind
Take a look at your requirements, project goals, and objectives. What does your final deliverable need to look like? What benefits should it provide? Here are some examples:
- If it’s a physical object, such as a building or a household product with very definite materials and stakeholder expectations, it may benefit from a sequential methodology such as waterfall or critical path.
- If it’s a software product or app that is not set in stone, a flexible Agile methodology may be just what the project needs.
- If environmental sustainability is a core value of your organization and essential to the delivery of your product, try PRiSM.
- Process-based methodologies such as lean or lean six sigma support the rapid development of a minimum viable product.
B. Assess what’s already working
Don’t forget to look at the processes you already have in place that have proven successful for your team. In what kind of work environment does your team excel?
- If they thrive on collaboration, incorporating new ideas as they work, and even last-minute pivots due to changing needs, consider methodologies such as Scrum, Kanban, XP, or APF.
- Or do they prefer an orderly, structured plan that accomplishes tasks sequentially? Then look at methodologies such as waterfall, critical path, and critical chain project management.
Now that you’ve been introduced to the various methodologies, the next step is to understand each phase of the project life cycle, so you can start planning your project from start to finish.
In the next section, we outline everything you need to know about the project life cycle.
Basic Project Management
- Project Charter
- Project Management Stakeholders
- What is a Project?
- Work Breakdown Structure
- Project Objectives
- Project Baseline
- Project Management Scheduling
- Project Management Work Packages
- Project Management Scope
- Scope Creep
Advanced Project Management
- What is PERT?
- Network Diagram
- Risk Management
- Cost Estimation
- Feasibility Study
- Monte Carlo Analysis
- Project Integration
- Cost Management
- PMI Project Management
- What To Do With Certification
- Certification
- Become Certified
- PMP Certification
- Best Certification
Software Features
- Critical Success Factors
- Capacity Planning
- User Role Access Permissions
- Time Tracking
- Budget Tracking
- Request Forms
- Work Assignments
- Version Control
- Dependency Managements
- Project management Milestones
- Project Management Software
- Project Management Tools
- Project Management System
- Gantt Charts
Shawwal offers - up to 30%
Total with VAT: {{CartWithDetails.cartMaster.total_after_vat}} {{currency}}
Your cart is empty.
12 Project Management Methodologies: Types, Tools, Techniques, And How to Choose
Written By : Bakkah
27 Feb 2024
Table of Content
Definition of Project Management Methodologies:
Types of project management methodologies, project management methodologies tools , project management methodologies techniques, how to choose a project management methodology, explore bakkah's leading courses to boost your skills in project management and business analysis:, popular articles.
PRINCE2 Methodology - 2024 Full Guide About Advantages and Disadvantages
Prosci Methodology - Change Management Methodology
Application of PMO in government entities in Saudi Arabia
Project management methodologies are systematic frameworks and guidelines utilized by organizations to efficiently plan, execute, and complete projects. They offer structured approaches to project management, ensuring adherence to timelines, budgets, and objectives. These methodologies encompass diverse principles, practices, and tools designed to facilitate effective communication and coordination among project-implementing teams.
Project management methodologies vary in their approach, with some emphasizing flexibility and adaptability (e.g., Agile) while others focus on sequential and structured processes (e.g., Waterfall). The appropriate methodology must be selected according to the type of project and its unique circumstances. The goal is to enhance project efficiency, minimize risks, and deliver high-quality results, ultimately contributing to achieving the specified goals and objectives of the project.
Project management methodologies refer to the systematic frameworks, processes, and guidelines organizations follow to plan, execute, monitor, and complete projects. These methodologies provide a structured approach to managing projects, ensuring they are completed on time, within budget, and meet the specified goals and objectives.
Project management methodologies encompass diverse principles, practices, and tools designed to facilitate effective communication and coordination among project-implementing teams.
They can vary in their approach, with some methodologies emphasizing flexibility and adaptability (e.g., Agile), while others focus on sequential and structured processes (e.g., Waterfall). The appropriate methodology must be selected according to the type of project and its unique circumstances.
The goal of Project Management Methodologies is to enhance project efficiency, minimize risks, and deliver high-quality results, ultimately contributing to achieving the specified goals and objectives of the project.
Various tools support their implementation, enhancing collaboration and communication, while diverse techniques facilitate effective project planning, execution, and control.
There are diverse project management methodologies, each with different principles, processes, and approaches. Here are some common types:
1. Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall project management is a traditional approach to project management where tasks are completed sequentially and linearly.
The methodology is called "waterfall" because progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards through phases, like a waterfall. Each phase must be completed before moving on to the next one, and changes to the project are generally not allowed once a phase is closed.
Here are the main phases in the waterfall project management methodology:
- Requirements: Define project scope, objectives, and deliverables.
- Design: Create a detailed plan for how the solution meets requirements.
- Implementation (or Construction): Include coding or construction of the project.
- Testing: Ensure the project meets specified requirements through various testing phases.
- Deployment (or Implementation): Implement the project in the production environment after the success of testing.
- Maintenance and Support: Address issues and user concerns and make updates as needed.
The waterfall methodology is best suited for projects where the requirements are well-understood and unlikely to change significantly during the development process.
It is often used in industries like construction and manufacturing. However, one of its main drawbacks is its inflexibility to adapt to changes once the project has started, as it does not easily accommodate changes in requirements.
2. Agile Methodology
Agile methodology is an iterative and flexible approach to project management that focuses on collaboration, adaptability, and customer satisfaction.
Unlike the linear nature of the waterfall model, agile divides a project into small increments with minimal planning and delivers functional pieces of the project in short time frames, known as iterations or sprints.
Primary principles and practices of agile include:
- Projects are divided into small manageable iterations, delivering potentially shippable product increments.
- Collaboration and communication between team members, stakeholders, and customers are crucial for quick adaptation to changes and alignment with goals.
- Continuous customer feedback allows for adjustments based on changing requirements.
- Agile is flexible and adaptable to changes in requirements or priorities at any stage.
- Continuous delivery aims for a potentially shippable product at the end of each iteration, allowing for early and regular value delivery to the customer.
- Prioritization and timeboxing based on value and importance ensure focus and urgency in delivering value.
- Agile encourages self-organizing, cross-functional team formation that collectively possess the necessary skills to deliver a complete product.
Popular agile frameworks include Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming (XP), each with specific practices and roles.
Agile is widely used in software development and various industries for its adaptability and customer-centric approach.
3. Scrum Framework
Scrum is one of the most widely used agile frameworks for managing complex software development projects. It provides a structured yet flexible approach to product development.
Key elements of the Scrum framework include:
- Roles: Include Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team.
- Artifacts: Comprise the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment.
- Events: Include Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-up, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective.
Scrum's iterative and incremental approach, along with its emphasis on collaboration and adaptability, makes it particularly effective for projects where requirements may change or evolve during development.
4. Kanban Methodology
Kanban is a project management methodology that visualizes workflow using boards, cards, and columns. It also limits tasks that are in progress simultaneously to prevent overloading the team and ensure a steady flow of work.
Emphasizing continuous improvement, Kanban employs feedback loops and a pull system, adapting work based on demand. Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are often used in Kanban to define the expected time frames.
Known for flexibility and adaptability, Kanban suits various industries like architecture, construction, marketing, education, software development, design, and law. Kanban fosters collaboration and shared responsibility and allows incremental process improvements based on specific needs and context.
5. Lean Project Management
Lean Project Management (LPM) is an approach to project management that draws inspiration from Lean principles. The Lean philosophy focuses on minimizing waste, optimizing efficiency, and continuously improving processes.
Lean principles are applied to enhance project delivery, reduce unnecessary activities, and deliver value more effectively.
Principal aspects of Lean Project Management methodology include eliminating waste, using value stream mapping, continuous improvement (Kaizen), customer focus, pull scheduling, visual management, batch size reduction, flexible planning, and cross-functional team use. LPM is suitable for industries like manufacturing, construction, and software development.
Its focus on efficiency and customer value makes it a valuable approach for organizations seeking to optimize their project delivery processes.
6. PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments)
PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments) is a widely adopted project management methodology developed by the UK government. It provides a structured and process-driven approach to project management, emphasizing flexibility and adaptability.
PRINCE2 divides projects into manageable stages, with defined roles and responsibilities, ensuring organized and controlled project execution.
The methodology consists of seven processes:
- Starting Up a Project (SU): Ensures project prerequisites are in place.
- Initiating a Project (IP): Defines project scope, objectives, and plans.
- Directing a Project (DP): Provides senior management with chief controls.
- Controlling a Stage (CS): Manages day-to-day project activities.
- Managing Product Delivery (MP): Ensures efficient product work.
- Managing a Stage Boundary (SB): Focuses on transitioning between stages.
- Closing a Project (CP): Formally closes the project and ties up loose ends.
PRINCE2 is known for its focus on continuous improvement and adaptability, making it a valuable tool for delivering successful projects within time, cost, and quality constraints.
Boost your career with Bakkah’s PRINCE2 courses:
- PRINCE2® Training Course Online
- PRINCE2® Agile Foundation & Practitioner Online Course and Certification
7. Critical Path Method (CPM)
Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique that identifies the critical path of activities, potential risks, team roles, and the sequence of tasks determining the shortest project duration. Key steps:
- Task Breakdown: Identify and sequence project tasks.
- Duration Estimation: Assign time estimates to tasks.
- Network Diagram: Create a visual representation of task dependencies.
- Critical Path Identification: Find the path critical for project completion.
- Float/Slack Calculation: Determine non-critical task flexibility.
- Resource Allocation: Efficiently allocate resources.
- Monitoring and Control: Monitor progress continuously, update schedules, and take corrective actions., update schedules, and take corrective actions.
CPM is an essential tool for effective project planning and control. It aids in prioritizing critical tasks, managing time constraints, and optimizing project schedules. CMP can be used in several projects, such as engineering, manufacturing, construction, and science.
8. Six Sigma ( Continuous Improvement Methodology)
Six Sigma is a data-driven project management methodology focused on improving process efficiency continuously and reducing defects or errors. Developed by Motorola in the 1980s, Six Sigma seeks to minimize variations and achieve higher levels of quality in processes. It is often applied in manufacturing and process improvement projects. Here is a concise overview of the Six Sigma project management methodology:
- Define (D): Clearly articulate the problem, project goals, scope, and customer requirements.
- Measure (M): Establish metrics, collect data, and measure baseline performance.
- Analyze (A): Use statistical tools to identify root causes of defects or inefficiencies.
- Improve (I): Develop and implement solutions, testing and refining as needed.
- Control (C): Establish measures to sustain improvements and prevent recurrence of defects or issues.
The Six Sigma methodology is often represented by the acronym DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control). Additionally, for more complex or considerable process changes, there is another phase known as DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify).
Bakkah provides certification levels such as Six Sigma Green Belt and Six Sigma Black Belt are available for individuals to demonstrate proficiency in applying Six Sigma principles and methodologies. Organizations implementing Six Sigma often experience enhanced efficiency, reduced defects, and improved customer satisfaction.
9. RAD (Rapid Application Development)
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is a project development methodology that prioritizes quick iterations and prototypes over extensive planning.
It involves user participation throughout the process, parallel development of system components, and a flexible, adaptive approach. Prototyping is a key feature, allowing for continuous refinement based on user feedback. RAD aims to deliver a functional product rapidly, focusing on time and cost efficiency.
Popular RAD tools include Microsoft Visual Basic, PowerBuilder, and OutSystems. The methodology suits projects with changing requirements but may not be ideal for highly structured endeavors.
10. Incremental and Iterative Methodologies
Incremental development involves dividing the project into small increments, each delivering a part of the final product's functionality linearly. User feedback is integrated after each increment, providing ongoing adaptability and the ability to identify and correct issues early. This approach enables early delivery and reduced project risk.
On the other hand, iterative development goes through cycles or iterations, refining the entire system with each iteration. It is highly flexible and accommodates changing requirements throughout the development process.
11. Hybrid Methodologies
Hybrid methodologies in project development involve blending elements from different traditional and agile approaches to create a flexible and tailored solution. That allows teams to adapt practices based on the project's unique requirements, leveraging both structured planning and iterative development.
In a hybrid methodology, the most appropriate elements from each methodology are identified and combined harmoniously. Examples include combining Waterfall and Scrum or integrating lean principles with agile practices.
The goal is to manage risks effectively, enhance flexibility, and address the project-specific needs. Effective communication is crucial to mitigate potential challenges introduced by diverse practices integration.
12. Extreme Programming (XP)
XP is an Agile methodology that emphasizes collaboration, adaptability, and delivering high-quality software through practices such as continuous testing and frequent releases.
Extreme Programming methodology is one of the famous methodologies for managing and developing software and other technical projects. It is based on diverse principles and practices, focusing on increasing software quality and improving team productivity.
A team needs to follow this method if the project is fast-paced or subject to regular change and thus has a dynamic rather than static nature.
The Extreme methodology also aims to achieve productive cooperation between team members and increase the quality of the final product and its flexibility in the face of changes.
Here are the main principles and practices of Extreme Programming:
- XP is built on a set of core values, including communication, simplicity, feedback, and courage.
- Developers work in pairs, one writing code and the other reviewing it in real time. That promotes collaboration, knowledge sharing, and code quality.
- Developers write tests before writing the actual code. That ensures that the code meets specifications and facilitates maintenance and updates.
- Code is integrated frequently to identify and address integration issues early in the development process.
- XP improves code design regularly without changing its functionality.
- XP keeps the design as simple as possible, making it easier to understand, modify, and maintain.
- Frequent and direct interaction with the customer allows for quick adjustments to changing requirements and priorities.
- XP emphasizes continuous improvement through regular reflection on the development process and changes in implementation to enhance efficiency and quality.
Bakkah provides a variety of accredited project management Courses for all professional certificates in project management, risk management, and others.
In brief, choosing the most suitable project management methodology depends on factors such as project size, complexity, industry, and organizational culture. Project managers often customize or combine methodologies to best fit the unique requirements of their projects.
Project management methodologies are often supported and implemented using various tools to enhance efficiency, collaboration, and communication throughout the project lifecycle. Here are some commonly used tools associated with project management methodologies:
1. Project Management Software
Tools like Microsoft Project, Asana, Jira, Trello, and Monday.com provide features for project planning, scheduling, task assignment, and progress tracking.
2. Version Control Systems
Git, SVN (Subversion), and Mercurial help manage changes to source code and documentation, ensuring version control and collaboration in software development projects.
3. Communication and Collaboration Tools
Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Discord facilitate real-time communication, file sharing, and collaboration among team members, supporting Agile and remote work environments.

4. Gantt Charts
Tools like GanttPRO and SmartDraw help create visual representations of project timelines, tasks, and dependencies, commonly used in Waterfall and traditional project management methodologies.
5. Kanban Boards
Trello, KanbanFlow, and LeanKit enable teams to visualize work and optimize workflow, particularly in Agile and Lean methodologies.
6. Scrum Tools
Jira, VersionOne, and Targetprocess support the Scrum framework with features for sprint planning, backlog management, and burndown charts.
7. Resource Management Tools
Workfront, Mavenlink, and TeamGantt assist in resource allocation, workload tracking, and managing team capacity in project management.
8. Risk Management Tools
RiskWatch, RiskyProject, and ProjectManager.com help identify, assess, and manage risks throughout the project lifecycle.
9. Collaborative Document Management
Tools like SharePoint, Google Workspace, and Dropbox Business enable teams to collaborate on documents, share project-related files, and ensure version control.
10. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD) Tools
Jenkins, Travis CI, and GitLab CI/CD automate integration code changes process and deploying software, commonly used in Agile and DevOps methodologies.
11. Time Tracking and Timesheet Tools
Harvest, Toggl, and Clockify assist in tracking project-related activities, allowing for accurate time management and resource allocation.
12. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Tools
Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM support customer-centric projects. That helps teams manage client interactions, feedback, and requirements.
Project managers and teams should carefully select tools that align with their chosen methodologies and project requirements. Integrating these tools can significantly improve project management efficiency and contribute to successful project outcomes.
Project management methodologies involve various techniques to plan, execute, and control projects effectively. Here are some commonly used techniques associated with project management methodologies:
1. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Break a project into smaller, manageable tasks and create a hierarchical structure to define clearly the scope and deliverables.
2. PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) and CPM (Critical Path Method)
Techniques for scheduling and managing tasks by identifying critical paths and dependencies and estimating project duration.
2. SWOT Analysis
Evaluate the project's Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
3. Risk Management
Identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor risks throughout the project lifecycle to minimize potential negative impacts.
4. Stakeholder Analysis
Identify and analyze stakeholders to understand their interests, influence, and expectations and ensure effective communication and engagement.
5. PERT Charts (Program Evaluation and Review Technique)
Graphical representations of project tasks and their dependencies, helping visualize the project schedule and critical path.
6. Scrum Meetings
Daily Standups, Sprint Planning, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective are regular Scrum meetings that facilitate communication and collaboration in Agile projects.
7. Earned Value Management (EVM)
Analyze project performance by measuring the planned value, earned value, and actual cost to assess progress and forecast future performance.
8. Quality Management
Implement techniques such as quality audits, inspections, and control charts to ensure project deliverables meet predefined quality standards.
9. Mind Mapping
Visualize project ideas, requirements, and tasks using mind maps to stimulate creative thinking and organize information in a structured way.
10. Critical Chain Method
Identify and manage resource dependencies to optimize project schedules and improve overall performance.
11. Prototyping
Creating a working model or prototype of a product or system to gather feedback early in the development process is common in Agile and iterative methodologies.
12. Benchmarking
Compare project performance metrics and processes against industry standards or best practices to identify areas for improvement.
13. Dependency Mapping
Identify and visualize dependencies between different tasks or project activities to understand their interrelationships and potential impacts.
14. Agile Estimation Techniques
Use techniques like Planning Poker, Relative Sizing, and Story Points to estimate the effort required for Agile project tasks.
15. Change Management
Implement strategies and techniques to manage and communicate changes effectively, ensuring minimal disruptions to project progress.
16. Communication Plans
Developing plans outlines how project information will be communicated to stakeholders, ensuring clear and consistent communication.
These techniques are often applied based on the specific requirements, characteristics, and principles of the chosen project management methodology. Project managers may tailor and combine these techniques to suit the needs of their projects.
Choosing a suitable project management methodology is crucial for the success of a project. The decision should be based on the project's characteristics, team dynamics, organizational culture, and the nature of the work to be performed. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to choose a project management methodology:
1. Understand Project Requirements
Clearly define the project scope, objectives, and deliverables. Consider the size, complexity, and nature of the project work.
2. Assess Team Skills and Experience
Evaluate the skills and experience of the project team. Consider their familiarity with different methodologies and their adaptability to new approaches.
3. Consider Project Flexibility
Assess the level of flexibility required throughout the project. Some projects may benefit from a more adaptive and iterative approach, while others may require a more structured and sequential process.
4. Examine Project Constraints
Identify any constraints such as budget limitations, time constraints, regulatory requirements, or client preferences that may influence the choice of methodology.
5. Evaluate Organizational Culture
Consider the existing organizational culture and whether it aligns with the principles of certain project management methodologies. Some organizations may prefer traditional, plan-driven approaches, while others may be more receptive to Agile or iterative methods.
6. Define Stakeholder Involvement
Determine the level of involvement and collaboration required from project stakeholders. Some methodologies, like Agile, emphasize continuous stakeholder engagement and feedback.
7. Analyze Project Risks
Evaluate the potential risks associated with the project. Some methodologies, such as Agile, are well-suited for projects with high uncertainty and evolving requirements.
8. Review Industry Standards
Consider industry standards and best practices. Certain industries or project types may have specific guidelines or regulations that align with particular methodologies.
9. Explore Hybrid Approaches
Assess the possibility of combining elements from different methodologies to create a hybrid approach tailored to the project's specific needs.
10. Pilot or Prototype
If feasible, consider running a pilot or prototype using a small-scale version of the project to test how well a methodology fits the team and project requirements.
11. Consult with Stakeholders
Seek input from key stakeholders, including team members, clients, and sponsors. Understand their preferences, expectations, and concerns regarding project management approaches.
12. Training and Transition Plan
Evaluate the readiness of the team to adopt a new methodology. Plan for necessary training and establish a transition plan to smoothly implement the chosen methodology.
13. Continuous Improvement
Be open to evaluating and adjusting the chosen methodology throughout the project. Continuous improvement is essential to address evolving project needs and improve overall project management processes.
Elevate your project management skills with Bakkah Learning's expert-led courses. From PMP to Prince2, Six Sigma to Agile, we offer tailored programs to suit your career goals. With interactive learning, flexible access, and certification preparation, we're your partner for professional growth. Start your journey to mastery today with Bakkah Learning!
Here are some Project Management Courses :
- Certified Associate in Project Management CAPM Course
- PMI-ACP® certification
- PgMP certification
- PMI Scheduling Professional - PMI-SP certification
Risk Management Courses And Certifications:
- Risk Management Professional - PMI-RMP Course
- MoR Certification and course
PRINCE2 Courses
- PRINCE2 Certification
- PRINCE2 Agile.
Project Management Tools:
- Primavera P6 Course
- MSP Course - Managing Successful Programmes
- Microsoft Project training course
Portfolio Management
- P3O Foundation certification
- Management of Portfolios MoP
- The Portfolio Management Professional – PfMP certificate
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Course
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Course
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Course
Ultimately, the choice of a project management methodology should be a thoughtful and informed decision that aligns with the unique characteristics of the project and the organization. Regularly reassess the chosen methodology to ensure its continued effectiveness and make adjustments as needed.
Related Courses
Our learning programs are delivered through a tested and professionally designed methodology.

Exam is included

2,102.5 SAR
Live Online

1,270.75 SAR

2,600.15 SAR

2,712.56 SAR

3,677.7 SAR

Your experience on this site will be improved by allowing cookies.
Added to Cart
{{ convertjson(lastcartitem.course.title) }}, features with this course, total with vat, {{ parsefloat(totalfeatures(lastcartitem)) }} {{currency}}.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1 Project management methodologies: overview and definitions
Learning Outcomes
- Assess what constitutes project management methodologies.
- Determine the importance of methodologies in project management.
- Contextualise the various types of methodologies.
What exactly are methodologies in project management?
Methodologies for project management are a series of distinct processes that have been developed to offer assistance to project managers and team members. There are various definitions of a project management methodology but they all have the same grounding: it is a set of procedures, concepts, and regulations for managing a project to a successful end.
We would like to define it as: a collection of guiding principles and procedures for managing a project .
Project management methodologies describe the way we operate and communicate while managing projects. Methodologies are collections of guiding ideas and procedures that can be used to plan, manage, and execute projects. These methods of managing work are focused entirely on determining the most effective way to begin, plan, and carry out tasks. However, as a project manager, remember that your choice of approach for managing projects will impact how work is prioritised and how it is carried out.
When it comes to project management, using these methodologies serves 2 purposes: first, it expedites the completion of the duties associated with the project, and second, it provides solutions for dealing with problems as they appear. In addressing these two main purposes, the methodologies also guide the team through the entire project and provide them with steps to take and goals to work towards, while aiming to achieve the successful completion of the project.
Why use a project management methodology?
One of the most important objectives of a methodology is to standardise, structure, and organise the many methods within which the work is performed. This helps us to integrate all initiatives in the same way while offering us the capacity to reproduce successful components of the project. Well-adopted methodologies will also help us to learn from our previous errors, and ultimately lead us into a process of continuous improvement. Therefore, using a methodology can be a very helpful tool for developing project efficiency.
- Using a methodology in project management offers the opportunity for project managers to:
- better organise project life cycles
- adopt specific tools that allow for a precise time and cost estimation
- oversee and mitigate risks associated with the project
- improve the cost-benefit analysis of the project resources in a pragmatic way
- develop the team capabilities and competencies
In terms of resources, a methodology may help to speed up the learning curve of the project team, as it provides a well-established framework and structure for executing the project. When it is used in complex projects, methodologies can be adjusted and updated to be more in line with the individual working style of the team members as well as the strategic direction of the organisation. If a project manager selects a methodology that is acceptable and standardised, it is quite possible to improve the work performance while simultaneously lowering the need for extra resources to accommodate any changes triggered by the complexities of the project.
There is no doubt that the project team benefits from having access to a set of standards – a methodology that assists them to initiate and manage specific projects to a successful closure. Consequently, an effective methodology should have clear and transparent definitions, guidelines, and sample processes for the numerous project management activities that must be accomplished to execute successful projects. A project management methodology establishes a common basis for all the organisation’s activities. But most importantly, it establishes the grounds for success.
Project management methodologies offer the perfect planning framework to support the project throughout its life cycle. However, before attempting to implement a certain methodology style, it is necessary to have a thorough understanding of its benefits. Different project types require different management approaches. As a project manager, if you do not have a complete understanding of the benefits, you will be unable to maximise these effectively. Every methodology can be thought of as a reference framework, some of which are better suited to specific circumstances than others. Having the right methodology is critical. The right methodology adoption and implementation will assist project managers to lower or mitigate potential risks, prevent unnecessary duplication of tasks and activities, and eventually boost the overall outcome of the project. A methodology is a form of control mechanism that will enable and potentially ensure that the project closure is reached in the most efficient and effective way. Organisations that use a methodology in a disciplined, well-managed, and consistent manner will gain a competitive advantage and achieve consistent project success.
Figure 1. Project management methodologies support areas, by Carmen Reaiche and Samantha Papavasiliou, licensed under CC BY (Attribution) 4.0
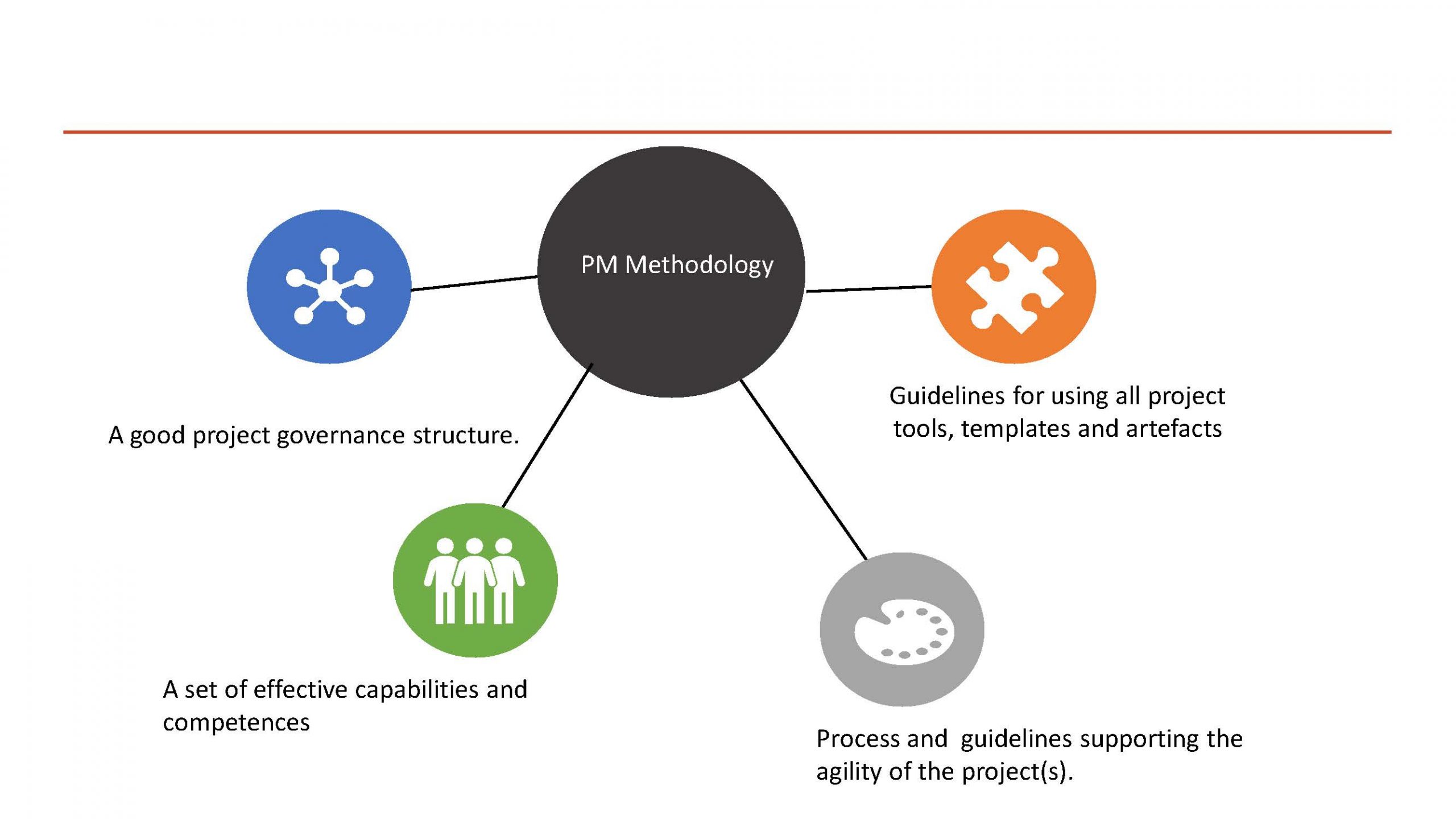
Some of the benefits of having a project management methodology are shown above in Figure 1. But there are five significant advantages to using a project management methodology that we would like to focus on.
Advantage 1: Communication flow
When the project team members adhere to the same method, the communication channels and inclusive language become standardised. Because organisations often have many projects going at once, communication might become quite challenging. Having clear communication channels enables interaction and integration between various projects managers, allows team members and stakeholders to integrate their views, and helps sponsors to make decisions that are consistently sound and based on accessible information. Organisations should prioritise communication as an important goal and having a good methodology can support this goal.
Advantage 2: Control management
When project managers implement and run the right methodology, they are better equipped to monitor how the project and their management initiatives are progressing. A methodology provides a control system that enables project managers to monitor what is working well and what isn’t and determine whether objectives are meeting their maximum potential.
Methodologies are control management systems. When applied correctly, these systems act as governance tools that can guarantee that everything that is going on in the project life cycle can be easily identified, and that governance decisions are transparent and on time. In fact, project governance and monitoring make up a considerable portion of the components that comprise a project management methodology. They pave the way for project activities to progress in a manner that is not only organised but also easy to comprehend and communicate.
Advantage 3: Global competence
Tendering can be a complex process and in the globalised arena in which we live today it can be especially challenging for businesses to win contractual projects. The tendering process asks an organisation to respond to a formal request for the supply of goods, services and/or projects. Adhering to a consistent process can help an organisation win external contracts. In project management, there are a lot of bids that demand the use of specific methodologies. For example, in the engineering field there are many bids that list PRINCE2 as a prerequisite. In the public sector, tendering will require the application of Agile tools. Even if your role as project manager doesn’t require you to be involved in tendering or to participate in the bidding process of a contractual project, adopting a methodology (of any kind) is an essential component of good project management. It serves as a safeguard against everything that could possibly go wrong with projects and helps us to get back on track.
Advantage 4: Providing support during uncertain times
Methodologies can also assist project managers with overcoming the unknowns and uncertainties that are an inherent part of project management. With the support of procedures such as end-of-phase and gate reviews, it is possible for projects to transition from one stage to the next in a controlled and effective way. Without the proper control tools and methodology, many project managers would find it difficult to manage a project and access the information they need.
According to the literature (see, for example, Betts and Landsley 1995; Charvat 2003; Bondarenko 2017), the methodology capability of assisting with organising and structuring information is one of the main reasons why methodologies are important, particularly to project managers new to the trade. They provide supportive mechanisms that ensure that a project manager sticks to all the set protocols, follows the relevant processes, and obtains the required authorisations when required. These mechanisms are particularly useful and relevant in the face of uncertain events, ensuring that project managers do all the required tasks at the appropriate times. If project managers don’t have access to a set structure or guide, or lack instructions that might assist them, then they may be forced to access more management support to avoid managing their projects to failure.
Advantage 5: Mapping processes to success
Project managers with any level of expertise may benefit from methodologies that display a degree of flexibility as they provide the required level of support to aid efficiency and facilitate the project manager’s work. Methodologies can be very regimented, which means that they do not provide a great deal of room for deviations. To some project managers, this could be a disadvantage as it can restrict creativity. However, a well-structured methodology is more likely to guarantee successful project completion. Distinctions between the steps of the process can enable users to divide tasks more quickly and minimise errors that would otherwise be impossible to manage. Because of a methodology’s rigidity, project managers are required to pay meticulous attention to each stage, which in turn results in an automatically improved, controlled approach to the final outcome of the project.
Disadvantages
From a practitioner’s perspective we could extend the list of advantages presented above; however, it is also important to highlight some of the disadvantages that are prevalent when a project management methodology is adopted. The advantages of having a methodology are very encouraging, but there is some research that suggests that methodologies provide no value to projects (see, for example, Bondarenko et al. 2018; Perrin 2018). The lack of value is seen in scenarios where project managers are experts in the field of the project, have extensive expertise in managing complex large projects, and have a clear understanding of the organisation’s strategy. Methodologies have been proven to be effective in situations where they replace and/or complement project managers who lack the necessary expertise and skills, and this has generated a misconception that it is the only value they bring to projects. However, we should acknowledge that, when it comes to mid-level, experienced project managers who have an average amount of experience and accountability, there is also a point in the middle of managing a project, where the benefits of using a methodology begin to diminish.
Another disadvantage that we have seen is the disconnection that sometimes exists between what project managers believe to be of value for the project and what the organisation believes to be beneficial on a strategic level. Therefore, it is critical to establish a good communication system between all stakeholders and have everyone on the same level of understanding when implementing a methodology.
Methods aren’t flawless, but they do offer a lot of benefits to the individual project manager as well as the organisation. There are many different routes that can be taken to successfully implement a methodology and complete a project. The best and most popular approaches, strategies, and frameworks are always evolving so we cannot suggest a single example for you to adopt. Behind any successfully completed project is a plethora of different strategies, methodologies, and procedures. In fact, you will most likely have the opportunity to make use of more than one of them during your project management career.
In this book, we will discuss some of the key methodologies, as well as specific components of these methodologies, that you may apply in practice in order to successfully deliver projects to completion. Table 1 lists some of these key project management methodologies and provides a brief explanation of the techniques that will be covered in the next modules.
Table 1. Project management methodologies groups, by Carmen Reaiche and Samantha Papavasiliou, licensed under CC BY (Attribution) 4.0
In sum, the various methodologies, strategies, and frameworks available to project managers are also useful to others. Figure 2 below shows a few guidelines for adopting a new methodology, but keep in mind that there is no one-size-fits-all framework. As discussed earlier, the whole team working on the project will benefit from these as they will need a tool to help them gain a solid grasp of the project objectives and maximise the project’s and organisation’s resources. The right methodology will help the team achieve these. Irrespective of the methodology option you select, the processes embedded under each methodology will ensure that the rest of the project requirements and procedures are carried out without a glitch. Keep in mind that there is no such thing as a standard organisation strategy, typical project or team members – each of these are unique to the environment in which they and the project operates and resides. Therefore, each methodology must be understood and applied accordingly. Keep in mind that it is also possible that you will not find success using a methodology or an approach that has been successful for someone else. Because of this, we highly recommend that you try multiple methodologies and forecast in which way you might use these effectively for each of your unique projects.
Figure 2. A project management methodology roadmap adoption, by Carmen Reaiche and Samantha Papavasiliou, licensed under CC BY (Attribution) 4.0
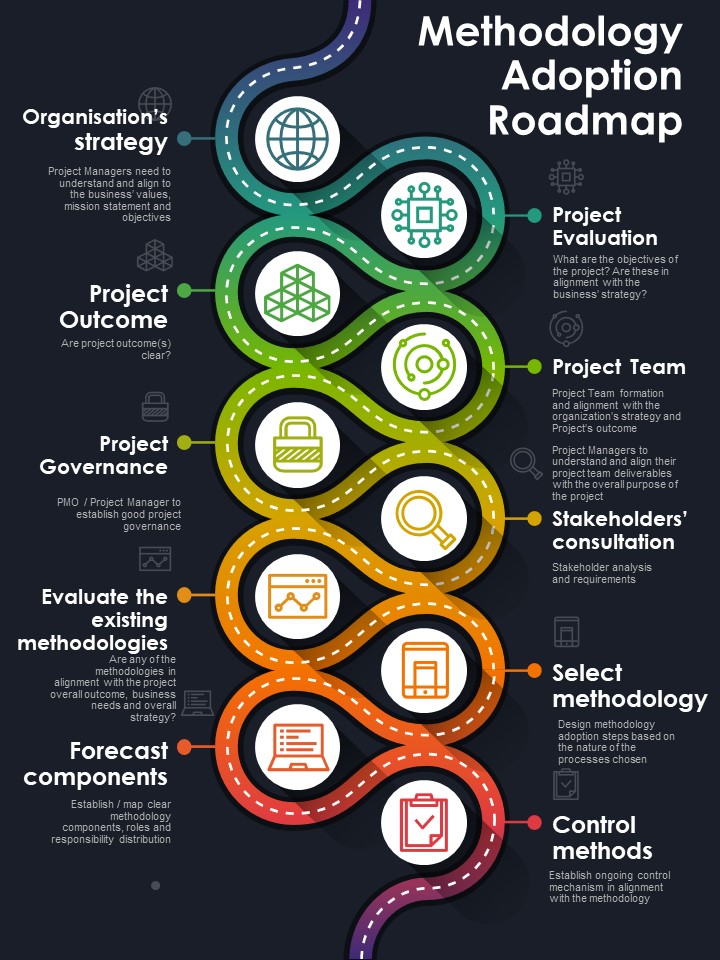
Test your knowledge
Key Takeaways
- As a project manager, aim to establish a productive culture for project management which will enable you and your team to employ a project management methodology in an efficient manner.
- Enhance the abilities of your project team members and provide them with a comprehensive understanding as well as a stable basis so that they may effectively manage their projects.
- A methodology should facilitate the clarification of goals and the scope of the project by integrating the organisation’s strategy and best practices of all project management group processes.
Betts M and Lansley P (1995) ‘ International Journal of Project Management : a review of the first ten years’, International Journal of Project Management , 13(4):207–217.
Bondarenko S (2017) ‘Synergetic management as a management technology of enterprise innovative development’, Journal of Applied Management and Investments , 6(4): 223–230.
Bondarenko S, Lagodienko V, Sedikova I and Kalaman O (2018) ‘Application of project analysis software in project management in the pre-investment phase’, Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology , 9(13):676–684.
Charvat J (2003) Project management methodologies: selecting, implementing and supporting methodologies and processes for projects , John Wiley & Sons.
Perrin JM (2018) ‘The best-laid plans of mice and men often go awry: the disadvantages of project management’, Project Management in the Library Workplace ( Advances in Library Administration and Organization, Vol. 38 ), Emerald Publishing Limited, Bingley, 71–88.
Management Methods for Complex Projects Copyright © 2022 by Carmen Reaiche and Samantha Papavasiliou is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Popular project management methodologies

From information technology to marketing, teams operating across a diverse range of industries and disciplines rely on project management methodologies to deliver for their organizations.
While project management methods are widely used, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Rather, there are dozens of different ways to manage projects. If you want to set the stage for the success of your project while also ensuring that your time and resources are used efficiently, it’s vital that you choose the right management framework.
With that in mind, here’s an overview of 23 of the best project management methodologies. Armed with this information, you’ll be able to identify the approach that best serves your business.
This post will also touch on the following topics:
- What a project management methodology is
23 popular project management methodologies
How to choose a project management methodology, what is a project management methodology.
A project management methodology is a set of tools and guidelines that help you organize projects in a way that optimizes efficiency and performance. More specifically, a given project management method helps you more easily manage a project by providing a repeatable series of steps and principles. The goal of any framework is to promote collaboration, increase operational efficiency, keep the project on budget, and enhance the quality of the final deliverable.
While there are many methodologies within project management , the following are some of the most well-known.
1. Waterfall methodology
Alternatively referred to as the software development life cycle (SDLC), the Waterfall method is a linear approach to project management. In this methodology, each phase of work “cascades” into the next.
When using this approach, project managers connect each task to the previous one with a dependency, meaning teams can’t move on to the next piece of work unless they’ve addressed outstanding tasks. This approach promotes collaboration and ensures that the team stays focused on the task at hand.
Who should use it? Because of the Waterfall method’s thorough, detail-oriented nature, this technique is best suited for large teams working on big projects involving multiple clients and stakeholders.
2. Agile methodology
The Agile methodology is one of the most commonly used project management frameworks, surpassing even Waterfall in popularity. However, it isn’t actually a formal methodology but a principle that focuses on speed, agility, collaboration, and iterative processes. Typically, teams will apply the Agile concept to a specific project management methodology, such as Kanban, Scrum, Crystal, or Extreme Programming.
You may find that using a hybrid approach that combines Agile and another framework is the best project management strategy for your team. As such, it’s important to use flexible project management software that can handle a variety of methods, including a singular Agile framework or multiple techniques.
Who should use it? Marketing teams find Agile appealing, as it provides more flexibility and promotes better creativity than more rigid frameworks like Waterfall.
3. Kanban methodology
The Kanban methodology uses a “Kanban board” to visualize project backlogs. Agile teams frequently use the Kanban framework to track project progress and avoid bottlenecks.
Traditionally, project managers built Kanban boards using physical items, such as bulletin boards or whiteboards. Today, Kanban boards are created using digital tools that allow users to drag assignments from column to column as the team completes assignments.
Kanban is a very loosely defined methodology, meaning teams can adapt it to their needs. This attribute also makes it a great pairing with Agile.
Who should use it? Kanban is a good fit for teams of any size, especially if the group is composed of hybrid or remote workers.

4. Scrum methodology
Short bouts of work known as “sprints” are a foundational component of the Scrum methodology. Each sprint lasts one to two weeks and involves a team of no more than 10 people.
Scrums are run by a Scrum master, who is tasked with leading daily meetings, overseeing sprints and sprint retrospectives (work recaps), and presenting demos to stakeholders. Like Kanban, the Scrum methodology is often used with Agile principles.
Who should use it? Any team that’s using or has considered adopting Agile principles should try the Scrum methodology.
5. Critical Path Method
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a framework for identifying and scheduling key tasks within a long-term project. Project managers use CPM to create task dependencies, identify project goals, and track progress toward those objectives.
The core function of this framework is to help managers map out milestones and deliverables so they can meet important deadlines.
Who should use it? The CPM framework is best suited for small-to-midsize teams. Its simplistic approach may not be a good match for complex projects.
6. Lean project management methodology
The Lean project management methodology prioritizes eliminating waste via its simple framework.
Under the traditional Lean methodology popularized by Motorola and Toyota, “waste” referred to physical materials. Today, waste refers to any practice that consumes resources but doesn’t add value, any task that over-taxes existing resources (including team members), or overproduction in general.
Who should use it? Lean is an excellent methodology for teams that frequently encounter efficiency challenges. Using Lean to reduce waste will have a major impact on big companies, but it can also benefit smaller organizations.
7. Six Sigma methodology
Six Sigma is primarily used for quality-management purposes. It isn’t a methodology in the traditional sense but rather a philosophy designed to support continual procedural improvement and remove product defects.
Six Sigma is often combined with the Agile framework or the Lean methodology. These hybrids are known as Agile Six Sigma and Lean Six Sigma, respectively.
Who should use it? Six Sigma aligns well with organizations that have at least several hundred employees and want to remove waste from projects to increase profitability.
8. Critical Chain Project Management methodology
The Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) methodology is a more detailed variation of CPM. In addition to providing a breakdown of each piece of work, CCPM also sets specific time constraints for each task.
CCPM makes it apparent when a piece of work is exceeding the amount of time allotted to it. This framework also incorporates resource-leveling principles, which quickly resolve large workloads by distributing tasks across the team.
Who should use it? CCPM can be a good option for large and small teams alike and is most effective for resolving project efficiency issues.
9. Event Chain Methodology
Event Chain Methodology (ECM) acknowledges that any number of outside events or factors can impact a project’s progress.
ECM strives to account for and manage these factors so project leaders can meet important deadlines and stay on budget. As inevitable hurdles arise during the project lifecycle, managers can update their ECM strategy as needed to stay on track.
Who should use it? Teams that have struggled to meet deadlines or have had projects derailed by external factors may want to consider the ECM framework.
10. Extreme Programming methodology
The Extreme Programming (XP) methodology is designed for fast-paced projects facing stringent deadlines. XP features short development cycles and a large number of releases. This approach optimizes productivity and yields quick turnarounds on deliverables.
XP’s core values include feedback, respect, communication, simplicity, and courage. The framework encourages team members to take calculated risks and pursue project objectives.
Who should use it? The Extreme Programming framework can be applied with results to small or midsize teams facing tight deadlines. It should be used sparingly, however, as the rigorous nature of the method can lead to burnout.
11. Crystal methodology
Like the Agile framework, the Crystal methodology focuses on team members, not processes and tools. By prioritizing interactions between individuals, Crystal promotes collaboration and team chemistry to optimize productivity.
The Crystal methodology assigns defined time spans to each bout of work. After each round, the project manager gathers feedback from the team and makes adjustments to avoid bottlenecks.
Who should use it? The Crystal methodology is good for small teams that want a lightweight, customizable framework.
12.Feature Driven Development methodology
Feature Driven Development (FDD) also borrows heavily from the Agile framework. FDD works in repetitive rotations while prioritizing features that the client is looking for in the final deliverable.
The FDD methodology includes five steps:
- Develop a model.
- Build a feature list.
- Plan by feature.
- Design by feature.
- Build by feature.
After each rotation, the team repeats the above steps to optimize the final product and add on must-have features.
Who should use it? The FDD methodology is a good fit for teams that tend to work with highly involved clients.
13. Dynamic Systems Development Method
Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM) also incorporates many Agile principles. However, it distinguishes itself by calling for time, quality, and cost requirements to be defined before work gets underway.
Once work begins, the DSDM framework prioritizes tasks into four categories — musts, shoulds, coulds, and won’t-haves. Tasks can be recategorized to meet project deadlines.
Who should use it? DSDM is a good match for teams that want the flexibility of Agile but are also required to define cost, quality, and time constraints in the project brief.
14. Adaptive Software Development methodology
As the name implies, the Adaptive Software Development methodology is designed for technology developers. It recognizes that processes must be continuously adapted and modified to align with the work that needs to be completed.
The Adaptive Software Development method is based on three cyclical steps — speculate (plan), collaborate (balance changing external factors and work), and learn (gather feedback and implement changes).
Who should use it? This framework should be employed by software development teams that need a relatively simple yet adaptable set of processes to facilitate project completion.
15. Rational Unified Process methodology
Rational Unified Process (RUP) consists of three foundational elements — roles (who’s involved in a project), work products (what’s being created), and tasks (units of work assigned to a role).
RUP also features four phases — inception (developing a raw project idea and evaluating its viability), elaboration (defining clear project objectives and identifying what resources you will need), construction (completing the software development project), and transition (beta testing, gathering feedback, and optimizing the user experience).
Who should use it? The Rational Unified Process methodology is well-suited for managing smaller projects and organizing compact teams. Due to its simplistic nature, it can be difficult to adapt to larger, enterprise-level projects that involve bigger teams and multiple stakeholders.
16. PRINCE2 — PRojects IN Controlled Environments methodology
PRojects IN Controlled Environments (PRINCE2) was developed by the UK government. Based on the Waterfall methodology, PRINCE2 is comprised of seven core principles:
- Starting the project
- Directing the project
- Initiating the project
- Controlling the project
- Managing delivery of the project
- Managing the stage boundary
- Closing the project
Due to its rigidness, it’s best suited for large, big-budget undertakings as opposed to more fast-paced projects.
Who should use it? PRINCE2 is a great approach for large-scale IT projects that involve multiple stakeholders.
17. Scrumban methodology
Due to Kanban’s loosely defined framework, it can be — and often is — combined with Agile. But recently, project managers have begun combining Kanban with Scrum, creating the hybrid Scrumban methodology.
Scrumban uses sprints to quickly achieve tasks and frequent meetings to promote collaboration. However, it also includes a project board to visualize work and help keep team members apprised of upcoming deadlines.
Who should use it? Scrumban may be a good fit for teams that need a way to visualize work but like the concept of dividing a project into short bouts of work.
18. Adaptive Project Framework methodology
Alternatively referred to as “Adaptive Project Management” (APM), the Adaptive Project Framework (APF) accounts for unknown factors that can emerge during a project. It’s designed to help teams prepare for the unexpected and respond in a way that keeps the project on task and under budget.
The APF methodology features five phases:
- Project scope
- Cycle build
- Client checkpoint
- Final review
Who should use it? The APF methodology supports collaboration with stakeholders and ensures that they’re satisfied with the final results. It’s a good fit if your stakeholders are highly involved.
19. New Product Introduction methodology
The New Product Introduction (NPI) methodology is a multistep strategy for taking a product from concept to market-ready deliverable.
The NPI framework involves frequent assessments throughout the project lifecycle to verify that it’s progressing as planned. Representatives from each department will participate in these reviews, as will the stakeholders.
Who should use it? The New Product Introduction methodology is effective for managing large teams that may have conflicting interests, goals, and ideas. The frequent reviews help achieve synergy across departments and teams to yield a higher quality deliverable.
20. Package-Enabled Reengineering methodology
The Package-Enabled Reengineering (PER) framework helps businesses revamp existing processes or products.
PER facilitates business transformation by giving a different set of team members the opportunity to redesign processes and past project deliverables.
Who should use it? Businesses should use the PER approach if they need to completely overhaul core products, services, or processes. It isn’t a good fit for incrementally optimizing existing systems.
21. Outcome Mapping methodology
Outcome Mapping (OM) shifts the focus away from deliverables and instead prioritizes measuring the impacts or outcomes of a project.
The Outcome Mapping framework was created by the International Development Research Center (IDRC) as a means of gauging the efficacy of social projects. It’s primarily used to modify behavior to achieve desired outcomes.
Who should use it? If your project’s top priority involves modifying behavior rather than producing deliverables, you should consider using the MP methodology.
22. Rapid Application Development methodology
Designed to facilitate faster software development, the Rapid Application Development (RAD) methodology is based on the Agile framework. Under this framework, developers rapidly release software iterations, gather feedback, and apply that information to improve the deliverable.
The RAD methodology allows developers to present clients with a functional model (albeit an imperfect one) much sooner. By doing so, they can gather vital feedback from the stakeholder and ensure that the final product aligns with their expectations.
Who should use it? Your team should consider the RAD methodology if you have an experienced team of software developers, prioritize speed, and want to keep the client directly involved in the project.
23. Project Management Body of Knowledge methodology
The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) methodology was created by the Project Management Institute . This set of principles and best practices outline core development processes that are a staple of any project. The framework outlines five project management phases, which are:
- Performance
One caveat of the PMBOK is that it isn’t as detailed as many other project management methods, meaning you’ll need to prioritize tasks on your own. However, the freedom to prioritize tasks on your own can be advantageous, such as if your team is working on nontraditional or nonlinear projects.
Who should use it? The PMBOK methodology can serve as a standalone project management tool for small teams working on relatively straightforward tasks. However, it should be paired with a more comprehensive framework if you’re working on a complex project.
Now that you know what options you have regarding project management methodologies, it’s time to find the right framework for your organization.
Numerous factors combine and interact to determine which project management method is the best fit for a particular team and organization. Here are some variables you should be mindful of when exploring different methodologies:
- Client or stakeholder collaboration. If a client or stakeholder is going to be closely involved, you’ll need a more flexible framework, as they’ll likely suggest last-minute changes to the project. Conversely, if your client will be involved minimally, a rigid framework can provide the guidance your team needs to expedite operational efficiency and streamline tasks.
- Flexibility. Ensure that your methodology provides the necessary flexibility for the project’s scope to change after work has begun. Some methods are rigid enough to prevent anyone, including the stakeholder, from changing the scope or goals once work has started. If you want to keep the scope or objectives from evolving mid-project, choose a stringent methodology. Conversely, more flexible methods allow your team to alter course, which is beneficial if you work with dynamic goals.
- Timeline. If you are working under tight time constraints, you need a fast-paced methodology that will keep everyone on task and apprised of upcoming deadlines. However, if you are prioritizing product quality above all else and have the room to stretch deadlines, you can leverage a looser project methodology.
- Risk tolerance. Taking on any project involves incurring some degree of risk. However, large, big-budget endeavors involve significantly more risk to your team and the organization. Smaller projects often have more leeway to explore out-of-the-box solutions. Choosing the right methodology will help your team mitigate risks and protect stakeholders’ interests.
- Budget. Some methodologies require you to set and closely monitor your budget for the entire project lifecycle, whereas others offer some degree of flexibility. If you might need additional resources mid-project, make sure your methodology leaves room to pull in more funding or team members.
- Team size. Consider whether your team is small and compact or large and scattered across multiple departments. Some methodologies are especially effective at managing small teams, whereas others are better suited for organizing large, multidisciplinary groups.

By considering these factors, you can quickly rule out project management methodologies that are a poor fit for your team and shift your attention to frameworks that are aligned with your goals. In doing so, you stand to acquire a better defined and more well-organized view of your project, boost team morale, and enhance efficiency exponentially. Streamline project management with Adobe Workfront Learning about project management methods can help you find the right one for your projects. After familiarizing yourself with the various frameworks available, choose a project management methodology that aligns with your business goals and industry-specific needs. Once you’ve selected a methodology, the next step is to optimize its efficiency by pairing it with intuitive project management software, such as Adobe Workfront . Workfront unifies your teams and empowers your brand to deliver personalized customer experiences at scale. From IT initiatives to marketing campaigns, you can run any business project with Workfront. As a customizable solution, you can customize your Workfront experience to align with your chosen project management methodology. Schedule a Workfront product tour or watch our overview video to learn more.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-project-management
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/kanban-board-examples
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/agile-frameworks

.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5th, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project planning |
- What is project planning? (Plus, 7 ste ...
What is project planning? (Plus, 7 steps to write a successful project plan)

Organize your projects with project plans to keep things on track—before you even start. A project plan houses all the necessary details of your project, such as goals, tasks, scope, deadlines, and deliverables. This shows stakeholders a clear roadmap of your project, ensures you have the resources for it, and holds everyone accountable from the start. In this article, we teach you the seven steps to create your own project plan.
Project plans are essential to keeping your project organized and on track. A great project plan will help you kick off your work with all the necessary pieces—from goals and budgets to milestones and communication plans—in one place. Save yourself time (and a few headaches) by creating a work plan that will make your project a success.
What is a project planning?
Project planning is the second stage in the project management process, following project initiation and preceding project execution. During the project planning stage, the project manager creates a project plan, which maps out project requirements. The project planning phase typically includes setting project goals, designating project resources, and mapping out the project schedule.
What is a project plan?
If you're still unsure about what a project plan is, here's how it differs from other project elements:
Project plan vs. work plan: A project plan and a work plan are the same thing. Different teams or departments might prefer one term or another—but they both ultimately describe the same thing: a list of big-picture action steps you need to take to hit your project objectives .
Project plan vs. project charter: A project charter is an outline of your project. Mostly, you use project charters to get signoff from key stakeholders before you start. Which means your project charter comes before your project plan. A project charter is an outline of a simple project plan—it should only include your project objectives, scope, and responsibilities. Then, once your charter has been approved, you can create a project plan to provide a more in-depth blueprint of the key elements of your project.
Project plan vs. project scope: Your project scope defines the size and boundaries of your project. As part of your project plan, you should outline and share the scope of your project with all project stakeholders. If you’re ever worried about scope creep , you can refer back to your pre-defined scope within your project plan to get back on track.
Project plan vs. agile project: Agile project management is a framework to help teams break work into iterative, collaborative components . Agile frameworks are often run in conjunction with scrum and sprint methodologies. Like any project, an Agile project team can benefit from having a project plan in place before getting started with their work.
Project plan vs. work breakdown structure: Similar to a project plan, your work breakdown structure (WBS) helps you with project execution. While the project plan focuses on every aspect of your project, the WBS is focused on deliverables—breaking them down into sub-deliverables and project tasks. This helps you visualize the whole project in simple steps. Because it’s a visual format, your WBS is best viewed as a Gantt chart (or timeline), Kanban board , or calendar—especially if you’re using project management software .
Why are project plans important?
Project plans set the stage for the entire project. Without one, you’re missing a critical step in the overall project management process . When you launch into a project without defined goals or objectives, it can lead to disorganized work, frustration, and even scope creep. A clear, written project management plan provides a baseline direction to all stakeholders, while also keeping everyone accountable. It confirms that you have the resources you need for the project before it actually begins.
A project plan also allows you, as the person in charge of leading execution, to forecast any potential challenges you could run into while the project is still in the planning stages. That way, you can ensure the project will be achievable—or course-correct if necessary. According to a study conducted by the Project Management Institute , there is a strong correlation between project planning and project success—the better your plan, the better your outcome. So, conquering the planning phase also makes for better project efficiency and results.
![project work methodology [Product UI] Brand campaign project plan in Asana, spreadsheet-style list (Lists)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/f8cc1f69-97b6-4806-9471-b27453e459a9/inline-generic-list-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
7 steps to write a project plan to keep you on track
To create a clear project management plan, you need a way to track all of your moving parts . No matter what type of project you’re planning, every work plan should have:
Goals and project objectives
Success metrics
Stakeholders and roles
Scope and budget
Milestones , deliverables , and project dependencies
Timeline and schedule
Communication plan.
Not sure what each of these mean or should look like? Let’s dive into the details:
Step 1: Define your goals and objectives
You’re working on this project plan for a reason—likely to get you, your team, or your company to an end goal. But how will you know if you’ve reached that goal if you have no way of measuring success?
Every successful project plan should have a clear, desired outcome. Identifying your goals provides a rationale for your project plan. It also keeps everyone on the same page and focused on the results they want to achieve. Moreover, research shows that employees who know how their work is contributing to company objectives are 2X as motivated . Yet only 26% of employees have that clarity. That’s because most goal-setting happens separate from the actual work. By defining your goals within your work plan, you can connect the work your team is doing directly to the project objectives in real-time.
What's the difference between project goals and project objectives?
In general, your project goals should be higher-level than your project objectives. Your project goals should be SMART goals that help you measure project success and show how your project aligns with business objectives . The purpose of drafting project objectives, on the other hand, is to focus on the actual, specific deliverables you're going to achieve at the end of your project. Your project plan provides the direction your team needs to hit your goals, so you can create a workflow that hits project objectives.
Your project plan provides the direction your team needs to hit your goals, by way of your project objectives. By incorporating your goals directly into your planning documentation, you can keep your project’s North Star on hand. When you’re defining your project scope, or outlining your project schedule, check back on your goals to make sure that work is in favor of your main objectives.
Step 2: Set success metrics
Once you’ve defined your goals, make sure they’re measurable by setting key success metrics. While your goal serves as the intended result, you need success metrics to let you know whether or not you’re performing on track to achieve that result. The best way to do that is to set SMART goals . With SMART goals, you can make sure your success metrics are clear and measurable, so you can look back at the end of your project and easily tell if you hit them or not.
For example, a goal for an event might be to host an annual 3-day conference for SEO professionals on June 22nd. A success metric for that goal might be having at least 1,000 people attend your conference. It’s both clear and measurable.
Step 3: Clarify stakeholders and roles
Running a project usually means getting collaborators involved in the execution of it. In your project management plan, outline which team members will be a part of the project and what each person’s role will be. This will help you decide who is responsible for each task (something we’ll get to shortly) and let stakeholders know how you expect them to be involved.
During this process, make sure to define the various roles and responsibilities your stakeholders might have. For example, who is directly responsible for the project’s success? How is your project team structured (i.e. do you have a project manager, a project sponsor , etc.)? Are there any approvers that should be involved before anything is finalized? What cross-functional stakeholders should be included in the project plan? Are there any risk management factors you need to include?
Consider using a system, such as a RACI chart , to help determine who is driving the project forward, who will approve decisions, who will contribute to the project, and who needs to remain informed as the project progresses.
Then, once you’ve outlined all of your roles and stakeholders, make sure to include that documentation in your project plan. Once you finalize your plan, your work plan will become your cross-functional source of truth.
Step 4: Set your budget
Running a project usually costs money. Whether it’s hiring freelancers for content writing or a catering company for an event, you’ll probably be spending some cash.
Since you’ve already defined your goals and stakeholders as part of your project plan, use that information to establish your budget. For example, if this is a cross-functional project involving multiple departments, will the departments be splitting the project cost? If you have a specific goal metric like event attendees or new users, does your proposed budget support that endeavor?
By establishing your project budget during the project planning phase (and before the spending begins), you can get approval, more easily track progress, and make smart, economical decisions during the implementation phase of your project. Knowing your budget beforehand helps you with resource management , ensuring that you stay within the initial financial scope of the project. Planning helps you determine what parts of your project will cost what—leaving no room for surprises later on.
Step 5: Align on milestones, deliverables, and project dependencies
An important part of planning your project is setting milestones, or specific objectives that represent an achievement. Milestones don’t require a start and end date, but hitting one marks a significant accomplishment during your project. They are used to measure progress. For example, let’s say you’re working to develop a new product for your company . Setting a milestone on your project timeline for when the prototype is finalized will help you measure the progress you’ve made so far.
A project deliverable , on the other hand, is what is actually produced once you meet a milestone. In our product development example, we hit a milestone when we produced the deliverable, which was the prototype. You can also use project dependencies —tasks that you can’t start until others are finished. Dependencies ensure that work only starts once it’s ready. Continuing the example, you can create a project dependency to require approval from the project lead before prototype testing begins.
If you’re using our free project plan template , you can easily organize your project around deliverables, dependencies, and milestones. That way, everyone on the team has clear visibility into the work within your project scope, and the milestones your team will be working towards.
Step 6: Outline your timeline and schedule
In order to achieve your project goals, you and your stakeholders need clarity on your overall project timeline and schedule. Aligning on the time frame you have can help you better prioritize during strategic planning sessions.
Not all projects will have clear-cut timelines. If you're working on a large project with a few unknown dates, consider creating a project roadmap instead of a full-blown project timeline. That way, you can clarify the order of operations of various tasks without necessarily establishing exact dates.
Once you’ve covered the high-level responsibilities, it’s time to focus some energy on the details. In your work plan template , start by breaking your project into tasks, ensuring no part of the process is skipped. Bigger tasks can even be broken down into smaller subtasks, making them more manageable.
Then, take each task and subtask, and assign it a start date and end date. You’ll begin to visually see everything come together in a cohesive project timeline . Be sure to add stakeholders, mapping out who is doing what by when.
![project work methodology [Product UI] Brand campaign project in Asana, Gantt chart-style view (Timeline)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/10e77bb8-a116-4169-83d5-d4d644824c54/inline-gantt-chart-basics-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Step 7: Share your communication plan
We’ve established that most projects include multiple stakeholders. That means communication styles will vary among them. You have an opportunity to set your expectations up front for this particular project in your project plan. Having a communication plan is essential for making sure everyone understands what’s happening, how the project is progressing, and what’s going on next. And in case a roadblock comes up, you’ll already have a clear communication system in place.
As you’re developing your communication plan, consider the following questions:
How many project-related meetings do you need to have? What are their goals?
How will you manage project status updates ? Where will you share them?
What tool will you use to manage the project and communicate progress and updates?
![project work methodology [inline illustration] Communication plan for brand campaign in Asana (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/3cf9f2d5-69b4-454e-b7e6-9452122a07d7/inline-project-planning-communication-plan-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Like the other elements of your project plan, make sure your communication plan is easily accessible within your project plan. Stakeholders and cross-functional collaborators should be able to easily find these guidelines during the planning and execution phases of your project. Using project planning tools or task management software that integrates with apps like Slack and Gmail can ensure all your communication happens in one easily accessible place.
Example project plan
Next, to help you understand what your project management plan should look like, here are two example plans for marketing and design projects that will guide you during your own project planning.
Project plan example: annual content calendar
Let’s say you’re the Content Lead for your company, and it’s your responsibility to create and deliver on a content marketing calendar for all the content that will be published next year. You know your first step is to build your work plan. Here’s what it might look like:
Goals and success metrics
You establish that your goal for creating and executing against your content calendar is to increase engagement by 10%. Your success metrics are the open rate and click through rate on emails, your company’s social media followers, and how your pieces of content rank on search engines.
Stakeholders and each person’s role
There will be five people involved in this project.
You, Content Lead: Develop and maintain the calendar
Brandon and Jamie, Writers: Provide outlines and copy for each piece of content
Nate, Editor: Edit and give feedback on content
Paula, Producer: Publish the content once it’s written and edited
Your budget for the project plan and a year’s worth of content is $50,000.
Milestones and deliverables
Your first milestone is to finish the content calendar, which shows all topics for the year. The deliverable is a sharable version of the calendar. Both the milestone and the deliverables should be clearly marked on your project schedule.
You’ve determined that your schedule for your content calendar project plan will go as follows:
October 15 - November 1: The research phase to find ideas for topics for content
November 2 - November 30: Establish the topics you’ll write about
December 1 - January 1: Build the calendar
January 1 - December 31: Content will be written by Brandon and Jamie, and edited by Nate, throughout the year
January 16 - December 31: Paula will begin publishing and continue to do so on a rolling basis throughout the year.
You’ll have a kick-off meeting and then monthly update meetings as part of your communication plan. Weekly status updates will be sent on Friday afternoons. All project-related communication will occur within a project management tool .
How ClassPass manages project plans from start to finish
Kerry Hoffman, Senior Project Manager of Marketing Operations at ClassPass , oversees all marketing projects undertaken by the creative, growth, and content teams. Here are her top three strategies for managing project plans:
Identify stakeholders up front: No matter the size of the project, it’s critical to know who the stakeholders are and their role in the project so you ensure you involve the right people at each stage. This will also make the review and approval process clear before the team gets to work.
Agree on how you want to communicate about your project: Establish where and when communication should take place for your project to ensure that key information is captured in the right place so everyone stays aligned.
Be adaptable and learn other people’s working styles: Projects don’t always go according to plan, but by implementing proper integration management you can keep projects running smoothly. Also, find out how project members like to work so you take that into account as you create your plan. It will help things run smoother once you begin executing.
Write your next project plan like a pro
Congratulations—you’re officially a work planning pro. With a few steps, a little bit of time, and a whole lot of organization, you’ve successfully written a project plan.
Keep yourself and your team on track, and address challenges early by using project planning software like Asana . Work through each of the steps of your project plan with confidence, and streamline your communications with the team.
Related resources
Smooth product launches are simpler than you think

What is stakeholder analysis and why is it important?

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning
Understanding dependencies in project management

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Project Methodology Templates with Samples and Examples

Vaishali Rai
Project management is confusing. Have you ever been in a situation like this, sitting at your project meeting, perhaps feeling out of your depth, and finding it hard to follow the conversation around you? It may be due to unstructured and unorganized execution of the project's principles. You also might need to apply a suitable project management methodology.
What is project management methodology?
A project management methodology is a set of principles, techniques, and procedures Project Managers use to execute and manage projects. There are several methodologies and all require different workflows, deliverables, and project management software development. The project management methodologies facilitate team collaboration by directing team members to work for a common objective.
Are your projects complex or straightforward? Whatever the case may be, these Top 10 Project Management Cycle Templates will help you organize and track every bit of it!
When a project is carried out systematically, chances of success are better. Project managers are responsible for planning tasks, tracking progress, and delivering results. Here’s when a project methodology comes in. It includes certain procedures that help you structure your team’s workflow.
There are many project methodologies available for the systematic execution of a project. Choosing the best one among a landscape of methodologies can be overwhelming. Some of these work well in specific projects or industries. However, Product managers select the methodology that best suits the way their teams work.
Here, in this blog, we'll talk about project methodologies and templates you can use in your projects.
Let’s explore!
Template 1: Project Management Methodologies PowerPoint Presentation Slides
This PPT displays an elaborative project agenda, including the project brief essential to operate efficiently. The layout also consists of details about the company's products. Showcase the progress summary, and the milestones achieved and reflect on the potential goals. Download now!

Download now!
Template 2: Three Principles of Waterfall Project Methodology
This PPT is designed while keeping in mind the linear approach, meaning that the tasks are organized in a sequence. This template allows you to map the tasks from beginning to end and work accordingly. It includes three essential waterfall project methodology principles: low customer involvement, robust project documentation, and sequential stages that smoothen up the project management process. Download now!
Template 3: 5D Consulting Project Methodology with Implementation
This PPT Template portrays a five-dimensional visualization process for consulting projects. It includes major steps like discovering, designing, developing, designing, and determining while considering budgetary and cost requirements. It also comprises activities like process assessment, tools management, collaboration, etc., that aid in accurate project deployment and maintenance. Download now!
Template 4: Enterprise Resource Planning Consulting Project Methodology
This template displays an execution method for designing ERP software for both parties; the consulting firm and the buyer. It includes the implementation team, administrative project management, project management team, etc. Ace your resource planning game by organizing, identifying, and listing the resources required to complete a project. Get it now!
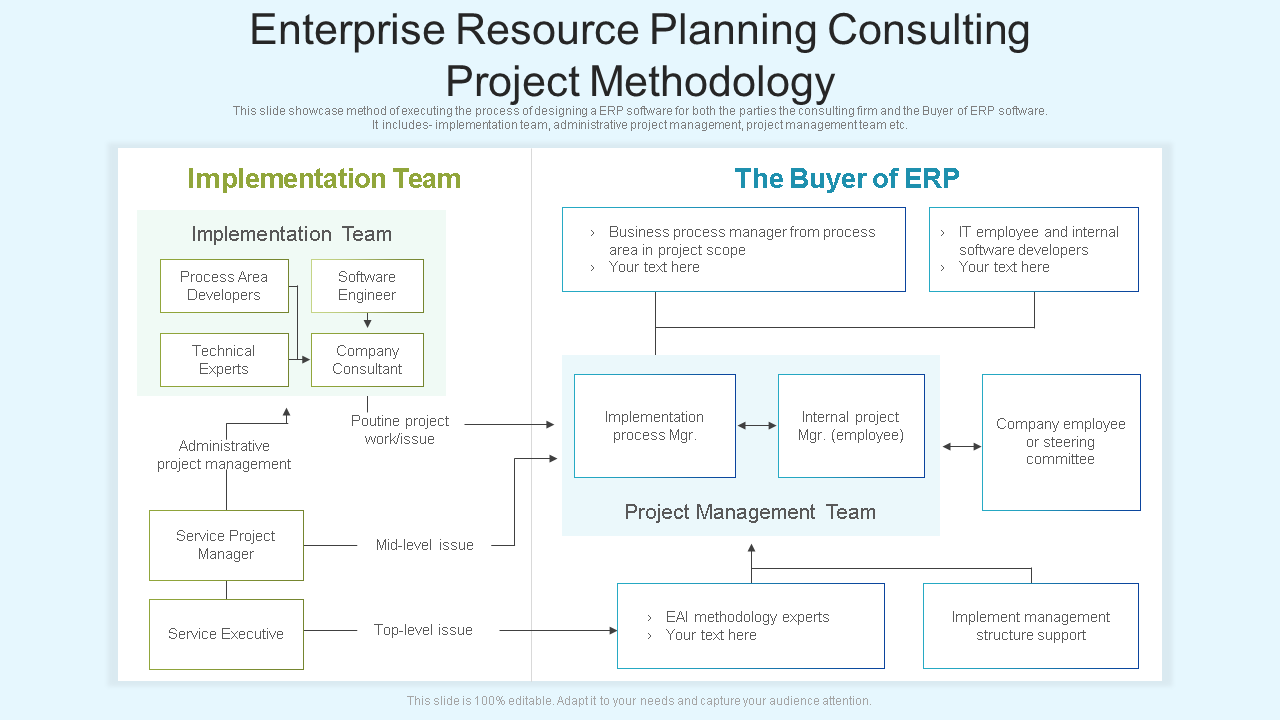
Template 5: Rotation Process Illustrating Agile Project Methodology
Agile is more of an approach than a methodology. It is collaborative, fast and effective, data-backed, and values individuals over processes. This template lets you analyze processes, provide suggestions, plan & design projects, project construction, and evaluate & monitor processes. Download now!
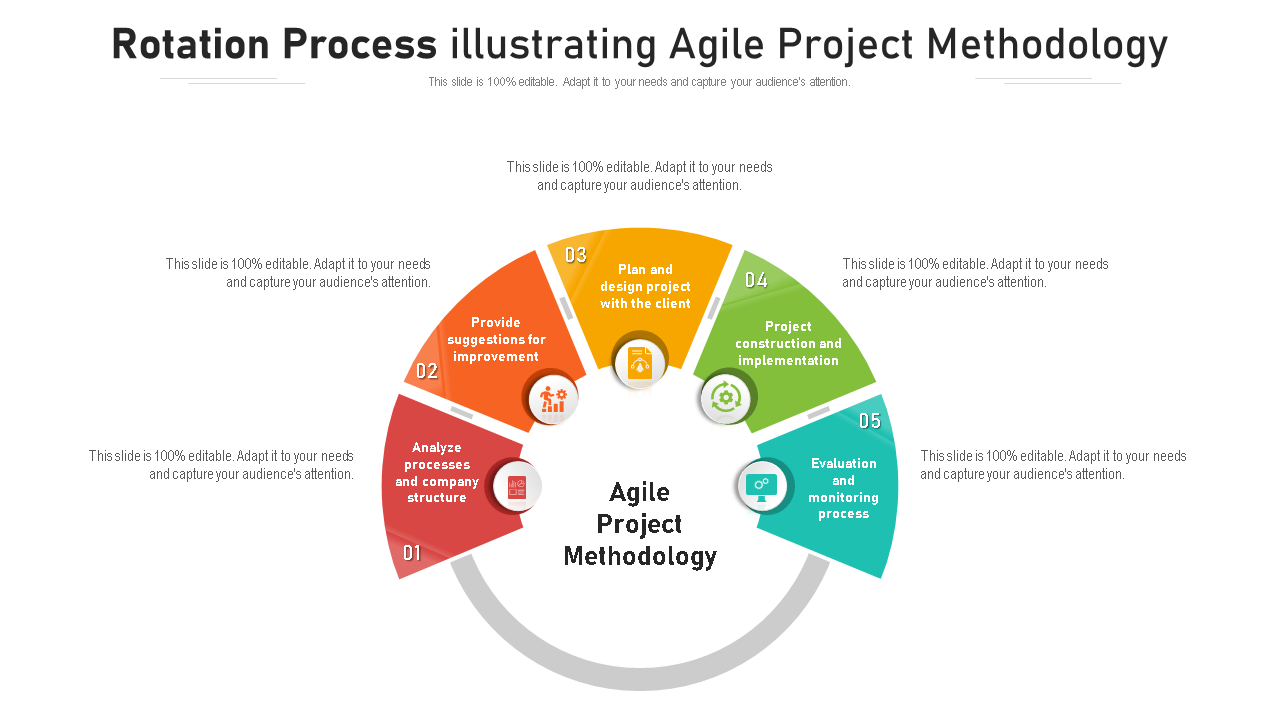
Template 6: Consulting Project Methodology for Supply Chain and Logistics
This template exhibits consulting project methodology for supply chain and logistics. It includes the five-step process of mapping, internal audit, gap assessment, solution design, and implementation. The topics discussed in this slide are gap analysis, solution design, implementation, internal audit, and mapping. Download this versatile template now!
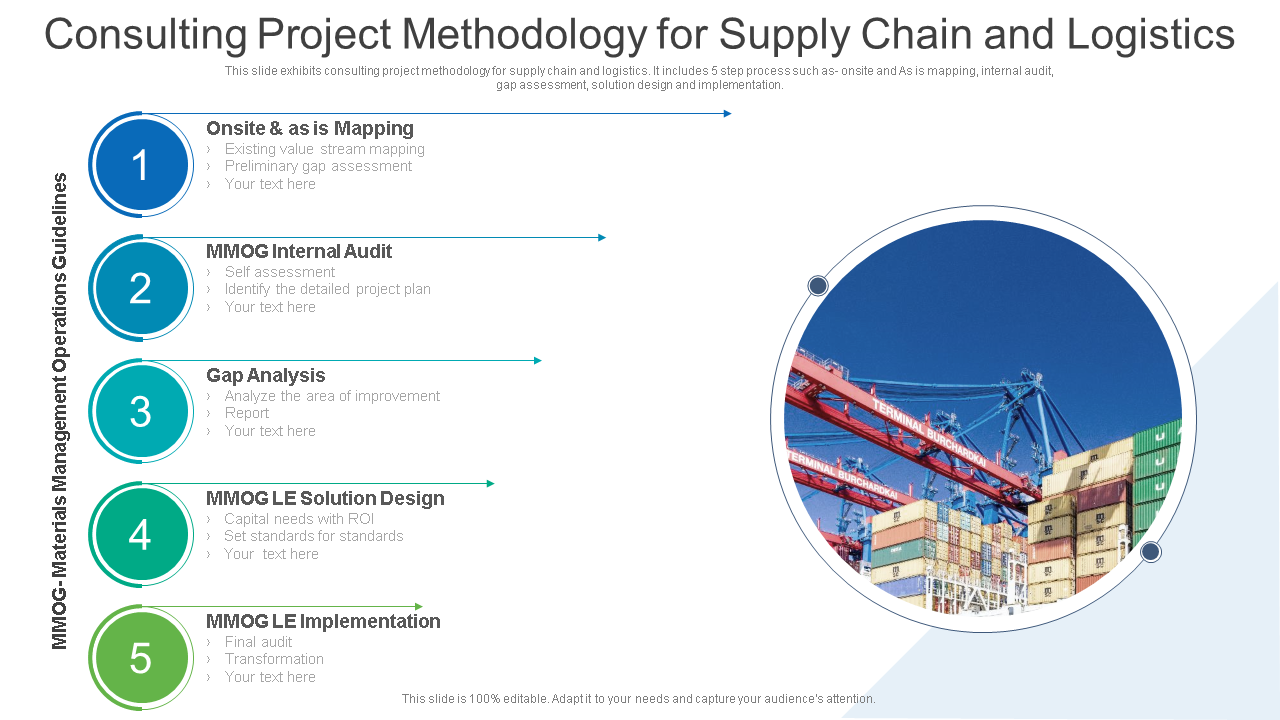
Template 7: Project Management Methodology Including Planning
This methodology is the one most used by project managers. It portrays the tasks in a chronological manner involving designing, developing, testing, and deploying a project. If you're looking for a comprehensive guide to your next project, look no further than this. Download it now!
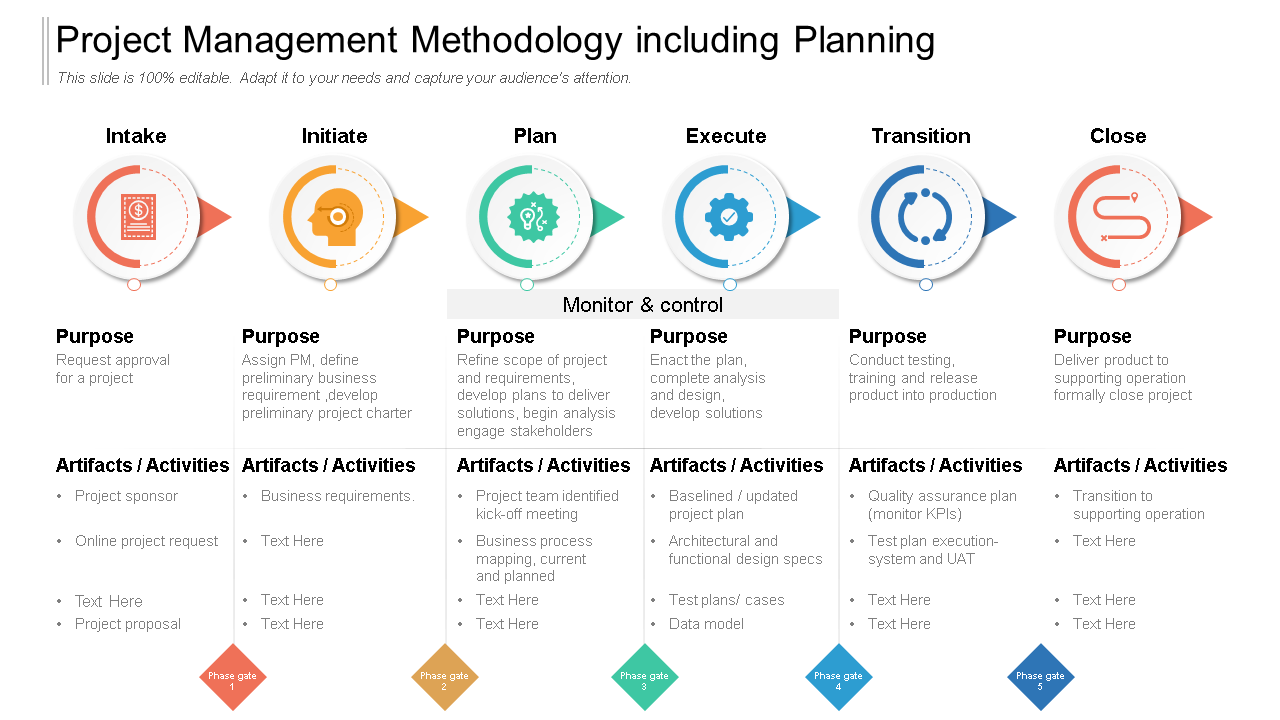
Template 8: Project Management and Implementation Methodology Overview
Project management and implementation methodology plays a significant role in ensuring successful delivery of projects. This template explains how these methods can be used to ensure the successful delivery of projects, along with some tips for implementing them. They also include a variety of practical examples to help you understand how the methodology can be applied in a real-world scenario. Get it now!
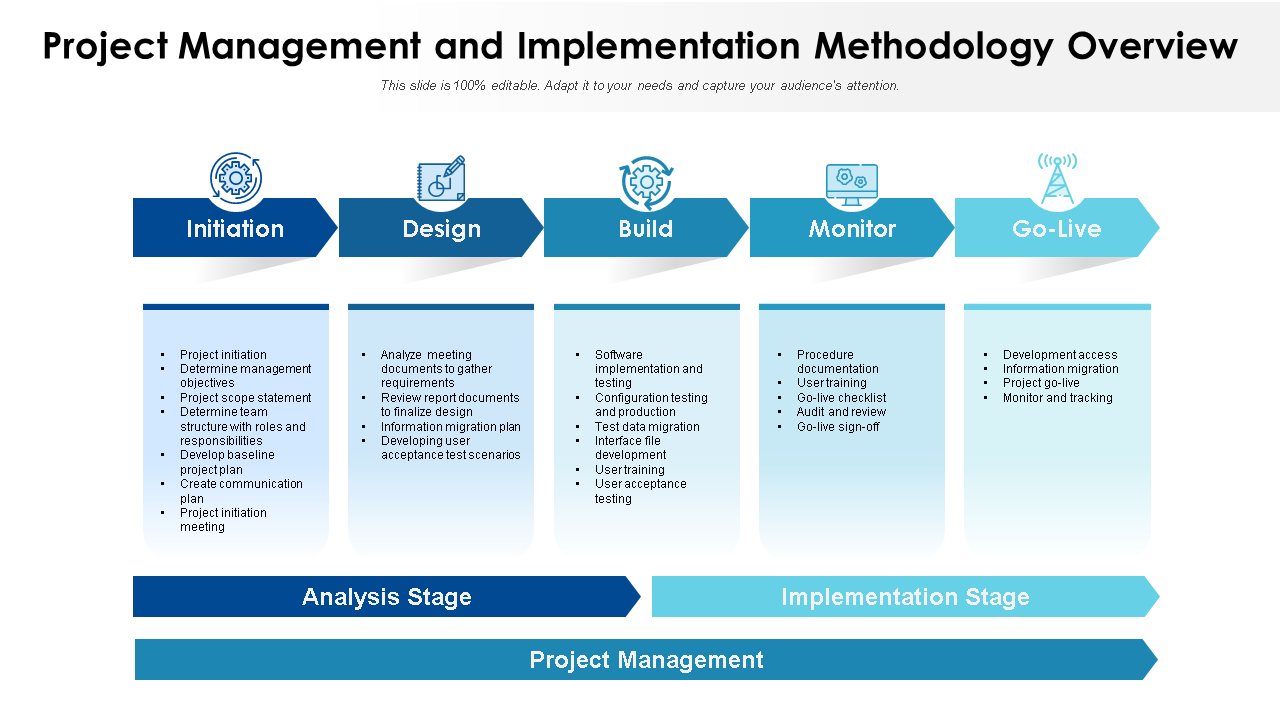
Template 9: Waterfall vs Agile Development Methodology for Project
This two-stage process template for projects is explicit and effective. It combines clarity and concise expression to achieve holistic project development by enabling client/stakeholder collaboration. It encourages frequent interaction of team members, making them resolve any complexities and meet requirements before deadlines. Download this now!
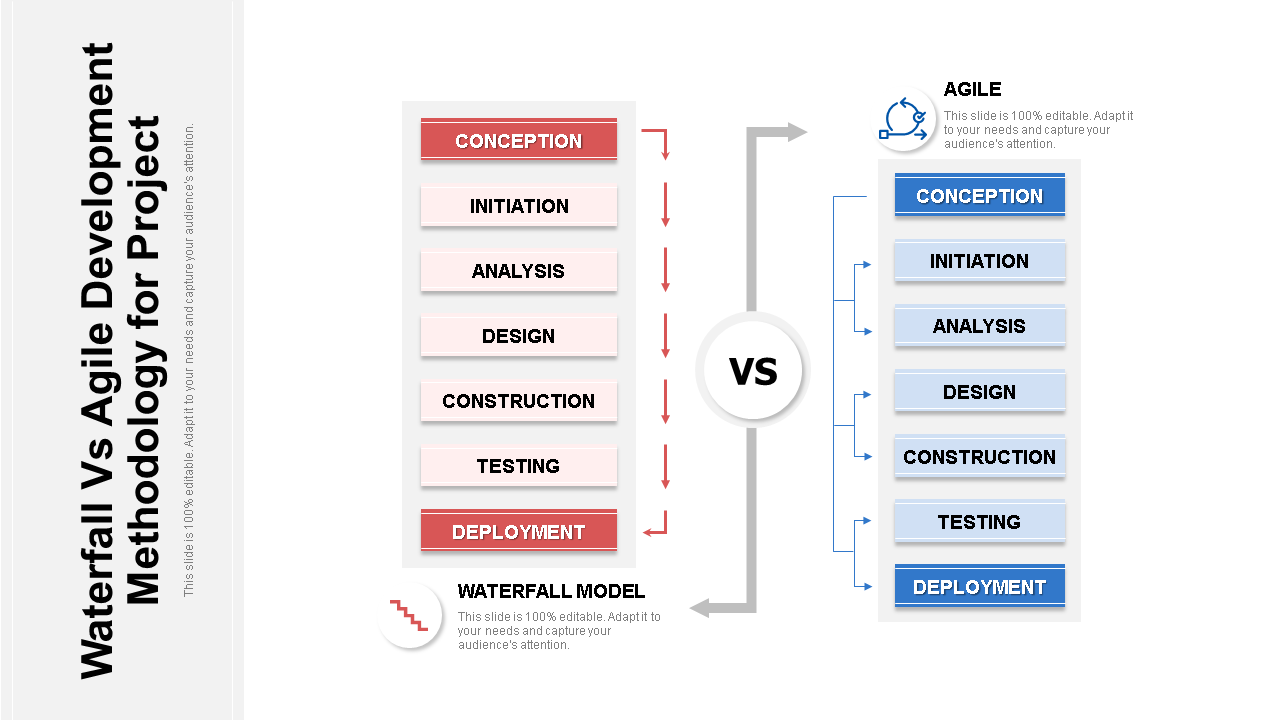
Template 10: Methodology Five Steps Indicating Project Lifecycle
Strategically important complex projects that are long-term, resource-heavy, and extensive, require flexible project management methodology. This template includes five steps of a project lifecycle that helps bring more cohesion to your project. Keep every team member on the same page with this helpful and 100% customizable template. Download now!
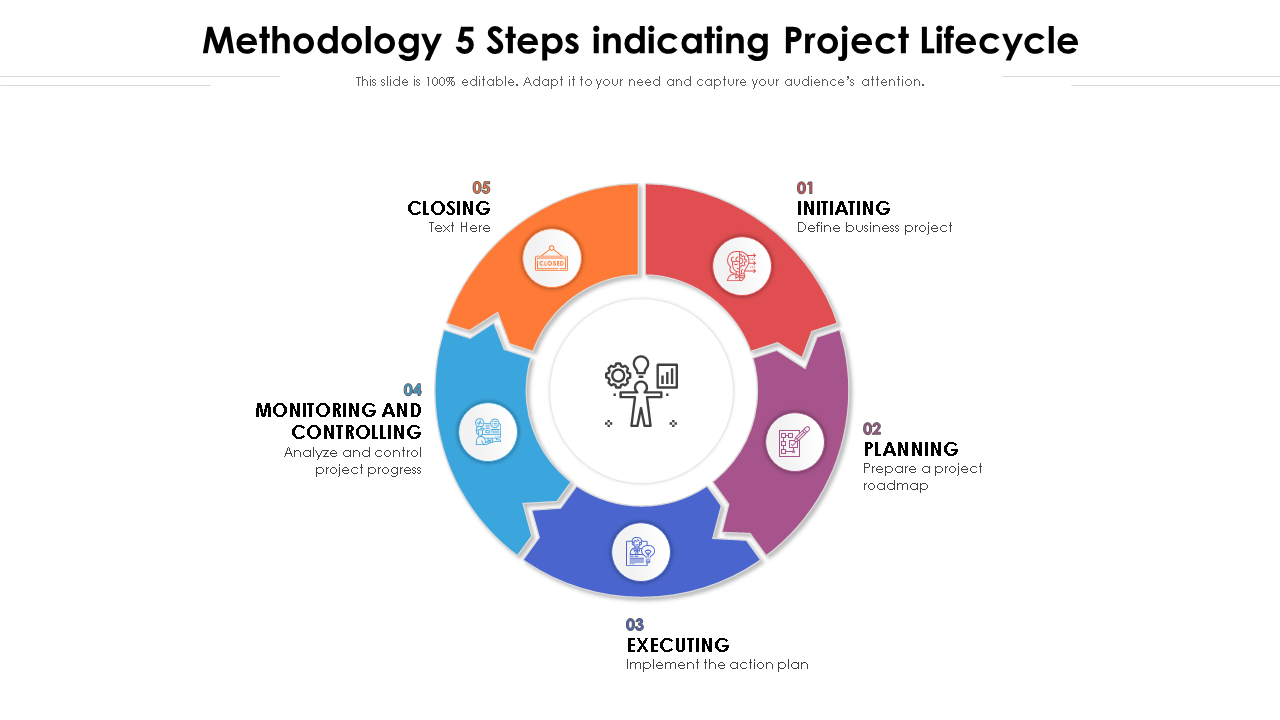
Manage Your Projects Well
By choosing the right project management methodology at the right time and the right place, you’ll be able to make your projects more efficient. Finding the perfect project methodology also helps implement processes right for you, your team, and your organization.
We hope that the above set of templates serves as the ultimate tool in your belt!
FAQs on Project Methodology
What is a project methodology.
A project management methodology is a detailed manual to supervise project completion. A project team uses this set of defined processes to initiate, plan, and execute the project. The type of project methodology you choose establishes the way of work organization, prioritization, and completion.
The project management methodology aims to standardize, structure, and organize work requirements and methods. This helps focus on what works best and enables the repetition of successful aspects and learning from mistakes, resulting in a continuous improvement process.
What are the five project methodologies?
Here are five common project methodologies used by Project Managers to manage workflow:
- Agile : This method is best suited for projects which require extreme flexibility and speed. It focuses less on documentation and more on customer satisfaction. Agile methodology is good for products with a faster release cycle.
- Scrum : Scrum methodology has an iterative project management style. It follows the principles followed in Agile methodology. In this method, the work is done in sessions known as ‘Sprints’. Here, the Scrum Master facilitates the process instead of a Project Manager.
- Waterfall : It is based on traditional methods and mainly focuses on following the processes. Here, much emphasis is given to project documentation.
- Critical Path Method : This methodology is a step-by-step method and works best for projects with independent tasks. Its key role is to measure and prioritize tasks.
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique : This method is commonly used along with CPM (Critical Path Method). It is mostly used by businesses that are looking for expansion. It measures progress to create timelines and budgets.
- Critical Chain Method : A separate classification, this methodology is more advanced than the CPM methodology. Here, goals are created based on constraints while focusing on cost-saving benefits.
What are the three major types of project methodologies?
Here are three major types of methodologies commonly used:
- Scrum method : Scrum is the most widely used agile methodology for project management. It allows you to do more by scheduling tasks in short cycles named sprints. It enables you to work as a dedicated team to analyze processes, meet requirements, and meet deadlines. It also helps you receive continuous feedback rather than using final evaluations. The scrum methodology is mostly used to develop new projects, compile budgets, and organize annual reports.
- Waterfall method : This method is linear and phase-based. It arranges and organizes tasks chronologically, which helps identify major areas of errors. Documentation is a huge part of waterfall methodology. It entails precise details about what you’re doing and how you’re doing it. This methodology doesn’t provide any room for flexibility.
- Lean and Six Sigma method : Lean and Six Sigma method is famous for its ability to manage the resource and time wastage that occurs in other methodologies. It is an approach to continuous improvement that is divided into two types of initiatives- Ongoing improvement initiatives and project-based initiatives. Each of these is associated with a set of methods and tools for you to employ. Ultimately, this methodology is based on the Kaizen principle that aims at making small changes on a daily basis for continuous improvement in small, easy steps.
How do you prepare a project methodology?
A good project method will represent the convergence of many factors, such as your scope, professional experience, and the research done. Here’s how you can prepare a project methodology in five steps:
- Communicate deliverables : A solid plan requires proper research and pre-planning. So, the first step is to set clear objectives, cost & budget, project requirements, and deliverables to work upon.
- Define the process : Choose the project methodology that best suits your team’s workflow and organizational structure. Sit with your team and draft a process that matches your work style and project requirements.
- Communicate risks and deadlines : Analyzing the ability to manage risks while meeting project deadlines is the next step in preparing a methodology. You need to observe the level of risk you can handle based on the size of the project.
- Determine task dependencies : Next, it is important to understand if you can perform tasks while keeping room for flexibility to alter the processes.
Define client/ stakeholder collaboration : Finally, you need to oversee the level of involvement you need from your stakeholders and clients in a project. It also defines team roles and assignments to help break down bigger projects into small and easy tasks.
Related posts:
- [Updated 2023] An All-Encompassing Guide to Project Planning (With 30+ PowerPoint Templates to Help You Get Started)
- [Updated 2023] Top 20 One Page Project Plans, Project Proposals, and Executive Summaries for Project Management
- Top 10 Research Paper Proposal Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 10 Project Report Templates With Samples And Examples
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Project Management Checklist Templates With Samples and Examples (Free PDF Attached)

Top 10 Project Management Cycle Templates with Samples and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

- Learn center
- Project management
A step-by-step guide through the project execution phase
Georgina Guthrie
April 19, 2024
Project kick-off is an exciting time, and the execution phase offers peak thrills: It’s where everyone springs into action and turns plans into something tangible. But it’s also the most dangerous part, where said plans could turn into an expensive mistake, with resources, teams, and time being wasted or underused.
Luckily, the project execution plan is here to help. Here’s everything you need to know about mastering this phase like a pro.
What is project execution?
Project execution is a core phase in the project management life cycle, which itself comprises 5 distinct stages:
- Monitoring
This stage breathes life into theoretical frameworks, translating plans into physical or digital outputs. Success hinges on good resource deployment, smart planning, savvy task execution, and plenty of stakeholder engagement.
In simpler terms, think of it as the ‘doing’ phase.
What happens during the execution phase?
Here’s a quick summary of the key moments. It’s not necessarily a linear process, but you will move through each of these at least once.
1. Resource allocation : The project manager allocates and organizes resources . This includes humans, equipment, and materials.
2. Team assignments: The manager assigns specific tasks to team members based on the project plan.
3. Task execution: Actual work on the project begins. It involves following the methods and processes set out during the planning stage, ticking off tasks as you go.
4. Quality assurance: Tasks need to be reviewed for quality as they’re completed.
5. Performance reporting: This includes updating schedules, budgets, and resources. Effective communication during this phase helps keep everyone informed and involved (stakeholders included).
6. Problem-solving and adjustments : Invariably, issues will crop up, calling for adjustments to the original plan.
7. Stakeholder engagement: This might involve regular meetings, reports, or demonstrations of work in progress. Stakeholder feedback is incredibly useful and might lead to adjustments to the original plan.
What’s produced during the execution phase?
From documents to products, there’s a lot that comes out of this crucial stage. Here’s what teams can generally expect to produce.
- Deliverables: These are the tangible products or services that the project was initiated to create. These can range from cakes to software products and constructed buildings to training sessions and events. They are the primary output and your project’s reason for existing.
- Documentation : Projects create documentation. This includes technical docs, project status reports, and revised project plans. Love it or loathe it, it’s essential for transparency, tracking progress, and ensuring consistency and quality throughout the project lifecycle.
- Status updates: Regular updates on the progress of the project are a must. These updates keep stakeholders in the loop. They also might lead to timely feedback that can affect the course of the project.
- Issue logs and change requests: Issues are as certain as night following day. When they do, issue logs record these challenges and the strategies used to address them. Similarly, change requests document any needs for alterations to the project scope or deliverables, which must be approved by relevant stakeholders to keep the project aligned with its goals.
- Performance data : Data helps you analyze efficiency and make adjustments accordingly. It could include time tracking, cost management, and resource utilization to name but a few metrics . This data is vital for analyzing efficiency, making adjustments, and planning future projects.
- Quality records: Inspections, tests, and reviews all produce records that are part of maintaining quality. Records help you maintain a certain level from project start to finish.
- Approval and acceptance forms: Every deliverable needs to go through a sign-off process. Usually, it’s the client or stakeholder doing the final checks. Sign-off documents are the standard way to formalize the process.
What is a project execution plan?
A project execution plan is a key document used by project managers to direct the execution phase, describing how the project will be carried out, who will do what, and how it will be monitored. Essentially, it acts as a template for project implementation and a road map for project teams.
It outlines all the vital elements needed to ensure the project’s success. Think of it as a living document that you update as the project goes on and new information comes to light. Regular reviews and updates are necessary to keep it on track.
What should your project execution plan include?
All the essential components needed to guide the project team over the finish line. This typically includes the following.
- Objectives : Clear, measurable targets aligning with the broader business or organizational goals.
- Scope : Detailed description of deliverables and the boundaries of the project.
- Tasks and activities: A breakdown of all the tasks, including who is responsible for what and how they interrelate.
- Resources : Specification of the human, financial, and material resources required for the project.
- Timeline : A schedule outlining when each task begins and ends, plus important deadlines and milestones .
- Budget : Detailed financial plan that outlines the costs associated with each aspect of the project, including labor, materials, and other expenses.
- Risk management plan: Identification of potential risks , the likelihood of these risks occurring, their potential impact, and strategies for mitigating them.
- Quality management: Standards and metrics to ensure that the project’s deliverables meet the required quality, plus procedures for quality control and assurance.
- Communication plan: For stakeholders, including the methods, frequency, and channels .
- Change management process: Procedures for handling changes to the project scope or plan, including how you’ll approve and document those changes.
Why is monitoring an important part of project execution?
With regular monitoring, managers can swiftly spot and fix deviations from the intended scope, budget, or timeframe.
Here’s why keeping a close eye on this phase is so important.
- Resource management: Monitoring helps ensure resources are used efficiently.
- Risk mitigation: Early risk identification helps you spot issues before they snowball into bigger ones.
- Quality control: Ongoing monitoring helps you spot quality issues in the deliverables, ensuring the project meets the required standards and satisfies the clients/stakeholders.
- Keeping stakeholders happy: Continuous monitoring also boosts stakeholder confidence by keeping them engaged.
- Staying on track: Projects can start well, but without regular check-ins, even the best-planned events can stall, and the dreaded ‘project gap’ opens up.
The project execution gap explained
A project execution gap is the discrepancy between where a project should be according to the plan, and where it actually stands at any given point.
Delays, unforeseen obstacles, resource shortages, or changes in project scope can all lead to this problem. And it is a real issue: this gap between expectation and reality can delay deadlines, lead to budget overruns, and compromise project quality. You’ll find some of the most common culprits in the next section.
Common project execution challenges
Even the best-made plans get waylaid. Problems arise when you don’t have a contingency plan , aka a ‘plan B’, which is often the difference between taking problems in your stride, and letting them derail you. Here are some common challenges you’ll need to keep an eye out for.
- Resource constraints
- Scope creep
- Miscommunication
- Stakeholder conflict
- Technical challenges
- Scheduling issues
- Compliance and regulatory changes
11 project execution strategies
The key to mastering the execution phase is to head in with a plan. Here are 11 failsafe strategies to get your project across the line.
1. Get everyone aligned
Strategic alignment from the get-go is critical to the project’s success. This means that the aims and objectives should be in line with overall corporate plans and stakeholder expectations.
To do this, invite key stakeholders to participate in the planning phase to discuss and agree on the project’s scope, objectives, and expected outcomes.
This early involvement helps you identify and resolve any differences in expectations sooner rather than later. Review on a regular basis to account for changes in company strategy or external factors that may influence the project’s trajectory.
2. Plan for effective handoffs
Effective handoffs guarantee the project flows smoothly and that no information is lost between stages. This is especially important when transferring tasks from one team to another or when certain phases of the project are complex.
- Document all processes and important information.
- Create handoff checklists that contain accomplished tasks, outstanding issues, and future steps.
- Make sure everyone participating in the project has access to these materials.
- Organize transition meetings where outgoing and incoming teams can chat about the status of the project.
3. Be aware of the domino effect
This refers to the interconnectivity of activities and how the delay or acceleration of one might affect others later on. Project delays, resource misallocation, and budget overruns tend to follow.
To successfully manage it, prepare a precise project plan that includes all jobs and their dependencies. Then use project management tools that display these dependencies, such as Gantt charts or critical path analysis , to help you identify the tasks that are most likely to trigger a domino effect.
Regularly update your schedules to reflect the actual progress and adjust dependencies as needed.
4. Delegate generously but with care
Delegation involves assigning the right tasks to the right team members based on their skills, experience, and current workload. It’s obviously key when it comes to resource optimization — but giving employees extra responsibility is also great for morale .
- Define each task, including its scope, deadline, and expected outcomes
- Provide the necessary resources and authority for team members to complete their tasks
- Match tasks with team members’ strengths and career aspirations, which can boost motivation and engagement.
Following task delegation, do regular follow-ups and feedback sessions. These help you monitor progress, provide support where needed, and ensure tasks are on track to meet their deadlines.
5. Keep a firm grip on project scope
Scope creep can spell disaster for a project. This happens when new elements are added to the project without equivalent increases in resources, time, or adjustments to project objectives.
- Start with a well-defined project scope document that clearly outlines what’s included and what isn’t
- Get a written agreement from all stakeholders
- Implement a formal change control process to handle any requests for changes in the scope.
- For every change request, assess how the proposed change will impact the project’s budget, timeline, and resources
- Ensure no changes go ahead without stakeholder authorization
- Document all changes and communicate them to the wider team and stakeholders
- Revisit the project scope during status meetings to ensure the project remains aligned with the original objectives
- Train team members to recognize and report potential scope changes — they are often the first to notice when project boundaries are being stretched.
6. Empower the team
When team members are empowered to make decisions, it can lead to faster problem resolution, increased engagement, and increased innovation. This empowerment also reduces bottlenecks , as not every decision needs to go through management.
- Establish clear guidelines that outline which types of decisions team members can make on their own and which should be escalated
- Provide training and resources to help team members make informed decisions
- Encourage a culture of open communication and trust
- Let your team know that it’s okay to take calculated risks and that they have support even if outcomes don’t always meet expectations. By trusting your team’s expertise and judgment, you boost their confidence.
7. Master your team’s communication
Good communication helps everyone collaborate better, from stakeholders to interns and beyond. It also helps prevent communication breakdowns , which can spell disaster for a project.
- Develop a communication plan that outlines who needs to receive information, when they need it, and through what channels. This plan should cover all forms, including meetings, emails, reports, informal updates, and so on.
- Use tools that facilitate good communication, not limiting yourself to email: Project management software, collaborative platforms, and regular status meetings all count.
- Make sure these tools are accessible and used consistently.
- Encourage an open communication culture where team members feel comfortable sharing their thoughts.
- Regular feedback loops between project managers, team members, and other stakeholders are also crucial. This keeps everyone aligned and feeling like one big happy team.
8. Keep an open mind
Being open to new ideas can result in better procedures, solutions, and overall project results. This openness generates a creative environment in which team members feel valued and encouraged to give their very best.
- Create a supportive atmosphere where all suggestions are welcomed and considered
- Run regular brainstorming sessions, which can be a great way to gather insights and solutions from a wider range of people
- Implement a process for evaluating and implementing feasible ideas. This could involve setting up a small committee or using project management tools to track and manage suggestions
- Recognize and reward team members whose ideas lead to positive changes, reinforcing the value of creative thinking within the team.
9. Measure progress
Just like an athlete working towards a competition, measuring progress is essential for keeping the project on track. It also helps you spot any issues and take remedial action if necessary.
- Establish clear metrics and milestones at the outset of the project. These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART ).
- Use project management tools that enable real-time tracking, especially task completion rates, budget expenditures, and milestone achievements.
- Schedule regular progress review meetings with the project team and stakeholders. During these meetings, discuss the project status, review the metrics, and examine any areas where the project may be falling behind.
10. Keep the quality high
Stakeholders have the power to declare a project a success or a failure, so it pays to keep them smiling. Quality management impacts not only the final outcome but also the project’s credibility, not to mention the satisfaction of these VIPs.
Establish a quality management plan at the start. This should outline the quality standards, criteria for acceptance, and the methods for hitting these standards. Key components might include:
- Quality metrics: Define metrics for measuring the quality of deliverables at various stages of the project.
- Quality control processes : Implement regular checks and audits to ensure the work meets the established standards. Peer reviews, testing processes, and quality audits are all good options.
- Quality assurance activities: Think about building in processes that prevent quality issues from happening in the first place. This could include training, feedback loops, encouraging accountability, selecting high-quality materials, using Andon , refining processes, or all of the above.
11. Use project management tools
Using project management tools properly is critical for project success. These technologies speed up processes, improve communication, and give insights into project health, helping teams stay on track.
- Choose tools that best fit the needs of your project. Consider factors like the size of your team, the complexity of the project, and specific functionalities like task management, scheduling, resource allocation, and communication.
- Train your team to use the tools. This training should cover advanced feature usage along with the basics.
- Integrate tools so they’re an integral part of daily operations.
- Take advantage of real-time capabilities to keep track of progress and address issues promptly.
- Use collaboration features like shared workspaces, discussion boards, and document sharing to keep communication clear and centralized.
- Use the reporting and analytics functions to help you identify trends, foresee potential problems, and make smart decisions about future projects.
Project management software helps ensure every phase of your project — from initiation to closure — is conducted with precision and efficiency. Ready to take Backlog for a spin? Try it for free today!

What is a project brief, and why does it matter?

Simplifying project planning with Gantt chart software
Subscribe to our newsletter.
Learn with Nulab to bring your best ideas to life
- Online Degree Explore Bachelor’s & Master’s degrees
- MasterTrack™ Earn credit towards a Master’s degree
- University Certificates Advance your career with graduate-level learning
- Top Courses
- Join for Free
4 Phases of the Project Management Lifecycle Explained
Discover the four steps of the project management lifecycle—initiating, planning, executing, and closing—and how to get started in this field.
![project work methodology [Featured Image] A project team in the planning phase of the project management lifecycle going over data in an office.](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/6jWnvI2Vnw2GbGUP7unZg/8362d2380cf820bec335f783b635abe8/Business-professionals-discussing-over-a-graph-1127726411_8477x5651.jpeg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
What is the project management lifecycle?
The project management lifecycle is a step-by-step framework of best practices used to shepherd a project from its beginning to its end. This project management process generally includes four phases: initiating, planning, executing, and closing. Some may also include a fifth “monitoring and controlling” phase between the executing and closing stages.
The purpose of the project management lifecycle is to provide project managers with:
A structured way to create, execute, and finish a project.
Clear phases, milestones, and deliverables
Better communication among stakeholders
Risk management
Quality control
By following each step of the lifecycle, a project team increases the chance of achieving its goals. As a project manager , you'll need to know this process well.
Read more: What Does a Project Manager Do? A Career Guide
Transitioning into a project management role? You can gain job-ready skills with an industry leader through Google's Project Management Professional Certificate program. In just 6 months , you'll gain an understanding of key concepts like change and risk management, organizational culture, strategic thinking, stakeholder management, Scrum, and Agile:
The Project Management Lifecycle: 4 Steps
1. initiating.
In the initiation phase, you’ll define the project, including:
Project goals, scope, and resources
Project purpose
What roles are needed on the team
What stakeholders expect out of the project
This is a crucial phase to the project’s success, as it gives the team direction. Without clarity around what needs to be achieved and why, the project runs the risk of not accomplishing the end goals and meeting stakeholders' expectations.
Some steps in the initiation phase include:
Communicating with stakeholders to understand the purpose and desired outcomes of the project
Identifying project scope
Determining SMART goals (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound)
Clarifying resources like budget and time constraints
Confirming team size and roles required
Determining how often and which stakeholders will be involved throughout the project
Compiling a project proposal and project charter
Tools and documents used in the initiation phase can include:
Project proposal: The project proposal defines a project and outlines key dates, requirements, and goals.
Project charter: This is a definitive document that describes the project and main details necessary to reach its goals. This can include potential risks, benefits, constraints, and key stakeholders.
RACI chart: A RACI chart plots the roles and responsibilities of members on a project team.
2. Planning
In the planning phase, you’ll determine the steps to actually achieve the project goals—the “how” of completing a project.
You’ll establish budgets, timelines, and milestones, and source materials and necessary documents. This step also involves calculating and predicting risk, putting change processes into place, and outlining communication protocols. If the initiation phase is assembling your troops, the planning phase is deciding what to do with them.
The planning phase can include the following steps:
Deciding on milestones that lead up to goal completion
Developing a schedule for tasks and milestones, including time estimates and potential time buffers
Establishing change processes
Determining how and how often to communicate with team members and stakeholders
Creating and signing documents such as non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or requests for proposal (RFPs)
Assessing and managing risk by creating a risk register
Holding a kick-off meeting to start project
Tools you might use in a this phase include:
Gantt chart: A horizontal bar chart in which members can see what tasks must be completed in what order, and how long each is expected to take
Risk register: A chart that lists risks associated with the project, along with their probability, potential impact, risk level, and mitigation plans
Read more: What Is Change Management? + How to Use It Effectively
3. Execute and complete tasks
Executing a project means putting your plan into action and keeping the team on track. Generally this means tracking and measuring progress, managing quality, mitigating risk, managing the budget, and using data to inform your decisions.
Specific steps might include:
Using tools like GANTT or burndown charts to track progress on tasks
Responding to risks when they manifest
Recording costs
Keeping team members motivated and on task
Keeping stakeholders informed of progress
Incorporating changes via change requests
Some tools you might use include:
Change requests: These are documents used to propose changes to a project’s scope or goals
Burndown chart: This chart breaks down tasks on a granular level and visualizes the amount of time remaining
4. Close projects
In the closing phase of the project management lifecycle, you’ll conclude project activities, turn the finished product or service over to its new owners, and assess the things that went well and didn’t go so well. It’ll also be a time to celebrate your hard work.
Steps in the closing phase can include:
Conducting retrospectives and take notes of changes you can implement in the future
Communicating to stakeholders of the end of the project and providing an impact report
Communicating with the new owners of a project
Creating a project closeout report
Celebrating the end of the project and your successes
Tools used in the closing phase include:
Impact report: This report compiles a series of metrics that showcase how your project made a difference and is presented to your stakeholders.
Project closeout report: A project closeout report provides a summary of your project’s accomplishments, and provides key learnings for future project managers to reference.
The following video provides an overview of the project management lifecycle. This is a preview of the Google Project Management Professional Certification .
How to explore the project management lifecycle
Exploring the project management lifecycle more extensively can be a great way to familiarize yourself with this process, discover how it works in real-life situations, and build a foundation for using the lifecycle in the future. Here are three ways you can learn more:
Read project management books.
Reading books is a low-cost way to gain insight into the project management lifecycle and project management in general in your spare time.
Read more: 12 Project Management Books for Beginners
Take online courses or watch tutorials.
Online courses and tutorials offer a visual way to grasp key project management concepts, including the four lifecycle phases.
Network with project managers.
Engaging in discussions with other project managers allows you to gain first-hand accounts of how the project lifecycle works. By building relationships and creating community with other project managers, you can ask questions, get practical tips, and potentially observe projects in action.
Not ready to take classes or jump into a project yet? Consider subscribing to our weekly newsletter, Career Chat . It's a low-commitment way to stay current with industry trends and skills you can use to guide your career path.
Sharpen your project management skills with Coursera
Mastering all steps of the project management lifecycle is an ongoing process that will continue throughout your career. Learning the formal aspects—the tools, steps, and vocabulary used in the process—can set you up for success in your beginning days as a project manager.
If you’re interested in deepening your knowledge of project management, consider the Google Project Management: Profe ssional Certificate to learn job-ready project management skills at your own pace.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
Advancing social justice, promoting decent work ILO is a specialized agency of the United Nations
Migrated Content
Date of publication
2 November 2021
Files for download

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Stages of the waterfall model. 1. Requirements: In this first phase, you'll work with stakeholders to clearly define the project scope and requirements. 2. Design: The critical design phase is when you'll plan what the final product will look like and what steps your team needs to take to get there. 3.
Project management is an ever-evolving field that requires a number of approaches to be successful. Learning the most popular project management methodologies can help you become an industry expert. A project management methodology is a system of principles, techniques, and procedures used by those who work in a discipline.
Learn about the most popular project management methodologies, such as waterfall, agile, scrum, PMI, CPM, Kanban and more. Find out their pros and cons, applicability and examples for different industries and projects.
A project management methodology is a set of principles that project managers and team leaders use to plan, execute and manage a successful project. One of the most common is the Agile project ...
Scrum, the most popular Agile methodology, involves smaller teams that complete tasks in short, time-bound periods, called sprints, in order to incrementally work through pieces of a larger project or release.. Scrum typically leads to greater responsiveness in customer relationships, lower costs of development, increased job satisfaction, and more immediate returns.
Project type and industry: Some methodologies work best for certain industries and project types, such as highly creative projects or product development sprints. Team: Consider the team size, diversity, flexibility, experience, and individual expertise or strengths and weaknesses, as well as their ability to collaborate and communicate when ...
Try this project management methodology if: You're striving for continuous improvement. This project management methodology might not be for you if: You don't have the full commitment from the team needed to make it work. 4. Kanban methodology "Kanban is not a software development lifecycle methodology or an approach to project management.
Project management methodologies are frameworks that outline the way work is completed throughout a project by providing procedures, rules, and practices. A methodology does not have to be a complete full-stack implementation "system" to be considered a methodology. Some project management methodologies simply define principles, like agile.
February 2nd, 2024 7 min read. Summary. Agile methodology is a project management framework that breaks projects down into several dynamic phases, commonly known as sprints. In this article, get a high-level overview of Agile project management, plus a few common frameworks to choose the right one for your team. Scrum, Kanban, waterfall, Agile.
The purpose of project methodology is to allow for controlling the entire management process through effective decision making and problem solving, ... Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) is the way to plan, implement and review various kinds of work in single- and multi-project environments. This management methodology uses Theory of ...
For example, if a project is behind schedule, switching to a more agile methodology such as Kanban or Scrum may help to get things back on track. On the other hand, if budget constraints are an issue, switching to a more 'slender' methodology such as the lean methodology may be the best course of action.
1. Agile. Agile project management is well-named. It values individual interactions over impersonal processes and tools, so one of its core strengths is its ability to adapt to changing situations and ongoing feedback results. It uses iterative and incremental work sequences that are referred to as 'sprints.'.
Now it's time to decide which method fits your principles and processes. 1. Waterfall Methodology. The Waterfall methodology is a traditional project management method. It proceeds step by step - like a waterfall - in these phases: Initiation. Planning and Analysis. Setting up the Resource Plan. Execution.
XP is a methodology designed to enhance software quality (and simplicity) and a development team's ability to adapt to customers' needs. Much like the original Agile formula, XP features short work sprints, frequent iterations, and constant collaboration with stakeholders. Change can happen within a sprint.
Here are some commonly used techniques associated with project management methodologies: 1. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Break a project into smaller, manageable tasks and create a hierarchical structure to define clearly the scope and deliverables. 2. PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) and CPM (Critical Path Method)
2. Design: The critical design phase is when you'll plan what the final product will look like and what steps your team needs to take to get there. 3. Implementation: This is where all your planning gets put into action. For software projects, this is when programmers will write the actual code. 4.
Project management methodologies describe the way we operate and communicate while managing projects. Methodologies are collections of guiding ideas and procedures that can be used to plan, manage, and execute projects. These methods of managing work are focused entirely on determining the most effective way to begin, plan, and carry out tasks.
23 popular project management methodologies. While there are many methodologies within project management, the following are some of the most well-known. 1. Waterfall methodology. Alternatively referred to as the software development life cycle (SDLC), the Waterfall method is a linear approach to project management.
Agile frameworks are often run in conjunction with scrum and sprint methodologies. Like any project, an Agile project team can benefit from having a project plan in place before getting started with their work. Project plan vs. work breakdown structure: Similar to a project plan, your work breakdown structure (WBS) helps you with project ...
Adaptive Project Management. Ideal for projects where requirements are subject to high level of uncertainty and volatility and are likely to change throughout a project. Uses an iterative and incremental approach, allowing more flexibility and adaptation. Encourages continuous collaboration and embraces change as a natural part of the process.
Waterfall: It is based on traditional methods and mainly focuses on following the processes. Here, much emphasis is given to project documentation. Critical Path Method: This methodology is a step-by-step method and works best for projects with independent tasks. Its key role is to measure and prioritize tasks.
A project management methodology standardizes how teams work on projects. It functions like a roadmap, and if used properly, organizations stand to achieve greater project productivity. Each ...
Here are the steps to follow when writing a methodology: 1. Restate your thesis or research problem. The first part of your methodology is a restatement of the problem your research investigates. This allows your reader to follow your methodology step by step, from beginning to end. Restating your thesis also provides you an opportunity to ...
2. Design: The critical design phase is when you will plan what the final product will look like and what steps your team needs to take to get there. 3. Implementation: This is where you can picture all your planning into action. For software projects, this is when programmers will write the actual code. 4.
1. Resource allocation: The project manager allocates and organizes resources. This includes humans, equipment, and materials. 2. Team assignments: The manager assigns specific tasks to team members based on the project plan. 3. Task execution: Actual work on the project begins. It involves following the methods and processes set out during the ...
The project management lifecycle is a step-by-step framework of best practices used to shepherd a project from its beginning to its end. This project management process generally includes four phases: initiating, planning, executing, and closing. Some may also include a fifth "monitoring and controlling" phase between the executing and ...
Jeff Weide. As an academic director and professor at the University of Denver, Jeff oversees health informatics programs and teaches courses on topics such as leadership, strategy, lean, project ...
We have recently updated the ILO website and are in the process of rebuilding a number of pages. You might encounter layout issues on pages as we work on them. Thank you for your understanding while we improve your experience. A methodology to estimate the needs of workers and their families.
Project 10Million is an initiative aimed at delivering internet connectivity to millions of underserved student households at no cost. Partnering with school districts across the country, the program offers free high-speed data and free mobile hotspots—and access to at-cost laptops and tablets.