

Quality Control Plan

Quality is important to any company that wants to do business. I mean no one would love to use a mobile phone that breaks within the year, right? Or how about a newly constructed building that’s already showing signs of being torn down? You wouldn’t like it at all. That’s why if ever you need an exceptional Quality Control Plan , we created this collection of Quality Control Plans that can surely help you thwart any of these uncertainties in the business. However, we’re not only providing you with a set of samples that you can use quick, but also an exceptional guide that you can use to expedite your creation process. Check it out below.
10+ Quality Control Plan Examples
1. quality control plan template.

- Google Docs
Size: A4, US
2. Restaurant Quality Control Plan Template

3. Construction Quality Control Plan Template

4. Construction Quality Control Management Plan Template

5. Quality Control Plan Example

Size: 233 KB
6. Project Quality Control Plan

7. Sample Quality Control Plan Template

Size: 34 KB
8. Quality Assurance and Control Plan

9. Contractor Quality Control Plan

Size: 47 KB
10. Sample Quality Management Control Plan

Size: 83 KB
11. Quality Control Plan in PDF

Size: 216 KB
What is a Quality Control Plan?
A quality control plan is a type of document that showcases the procedures and methods in ensuring that the products and services provided by the company are well within the expectations of the market. However, in the construction industry, this inspection may happen after the construction itself and hence ensures that the quality of the work written in the contract is upheld.
What are the four main elements of quality?
Whether you like it or not, quality control is only one of the four elements of quality. These four are the main components that boost quality management in any company. Although these four have different methods and styles they still exist to ensure quality in the product or service of the company. The four elements are listed below for you.
- Quality Planning
Quality Planning goes first. This first element creates the standard for which both the Quality Assurance and Quality Control are being done. This phase of the quality workflow creates the methods and processes to determine the quality of the product or the service provided.
- Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance focuses on making sure that nothing can ever disrupt the manufacturing, construction, production, or fulfillment of the product or service. Usually, companies determine quality assurance by providing training, resources, and other support to the workforce. In this way, the workforce can do their job properly and lessen any mistakes that can destroy quality.
- Quality Control
If Quality Assurance creates the path and ensures it is safe for passage, Quality Control is particular with the release of the product or the finishing of a construction. They can do this by creating inspections and testings on the product or service is done.
- Quality Improvement
The last element in the list is Quality Improvement that creates a new standard for the product or service. They create better standards that Quality Planning can check to enforce in both Quality Assurance and Quality Control. In this way, the company’s quality performance goes up and will never become stagnant.
How to Create a Quality Control Plan
Quality Control is one of the many important aspects of the current world’s corporate standards. ISO 9001 or any ISO Certification, for example, could dictate the prestige of your company and could even open better opportunities since people are used to quality-work and sought to desire better, always. That’s why, if you’re a startup company, it pays to start creating and implementing a quality standard so that your team will be used to providing the best quality to the people. For your information, we provided the steps below so you can create a Quality Control Plan yourself.
Step 1: Create an Organizational Chart
Having an organizational chart with a specific job description can help you gauge the quality of your products already. Remember to put the right person on the job. Without the right person for the job, you might end up losing too much. Imagine putting an electrical engineer in a janitorial job. Not only does this hinder better productivity in your workforce but it also makes the engineer feeling neglected and unappreciated.
Step 2: Work With Quality Assurance
Depending on the methods of those individuals doing Quality Assurance, your team could have the same reflection. So make sure that you work with everyone that concerns about the quality before creating your plan. In this way, you can be sure that your plan will follow the right method.
Step 3: Create an Executive Summary
Since this is a plan an executive summary is always important. People love executives for a reason and that reason is that they won’t spend so much time working, so make sure that you allow that to them. You can also include your plans within the executive summary if you feel like it.
Step 4: Push for Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance and Quality Control should work together, so they can surely improve the whole quality standard of the office or company. Even though you are only holding a project, it will count as your experience, so make sure to do it well.
What are the methods of quality control?
Quality Control is important to a company. However, it only has two methods. These two are listed below: 1. Inspection 2. Statistical Quality Control
What is the QC Process?
The QC process or a quality control process is the method in which companies ensure that not a single defective product can get out from their factories. They do these by using the two methods of quality control namely Inspection and Statistical Quality Control.
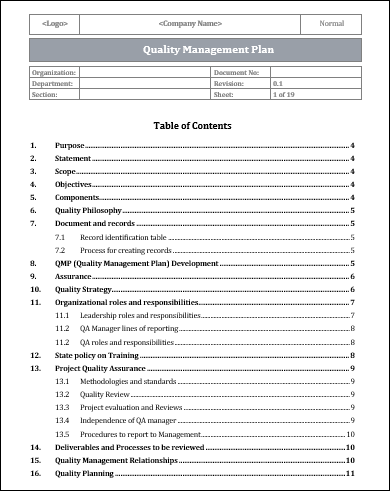
ISO 9001 Quality Management Plan Template
An ISO 9001 Quality Management Plan is a crucial document that outlines the quality management processes and procedures to be followed in an organization. This plan serves as a guide for implementing and maintaining a quality management system that meets the requirements of the ISO 9001 international standard.
By using this template, organizations can ensure that they have a comprehensive and systematic approach to managing quality in their operations. The plan includes essential sections such as quality objectives, quality policy, organizational structure, responsibilities, and resources needed for implementing the quality management system. This template is designed to help organizations develop and document their unique quality management plan, tailored to their specific requirements and processes.
Understanding the importance ISO 9001 Quality Management Plan Template
- Consistency: The ISO 9001 Quality Management Plan Template provides a consistent framework for managing quality across different projects and processes within an organization. It ensures that all quality-related activities are systematically planned, implemented, and controlled in a uniform manner.
- Compliance: ISO 9001 is an internationally recognized standard for quality management. By using the ISO 9001 Quality Management Plan Template, organizations can ensure that their quality management system meets all the requirements of the standard. This helps in achieving compliance with the ISO 9001 standard and enhancing the organization's credibility and reputation.
- Improved efficiency: The template outlines the key activities and processes that need to be followed for effective quality management. By using the template, organizations can streamline their quality-related activities and eliminate any unnecessary or redundant processes. This leads to improved efficiency and better resource utilization within the organization.
- Risk reduction: The ISO 9001 Quality Management Plan Template emphasizes the identification and mitigation of risks that could impact the quality of products or services. By following the template, organizations can proactively identify potential quality issues and take appropriate measures to prevent them. This helps in reducing the chances of quality-related problems and their associated costs.
- Customer satisfaction: The quality of products or services is a crucial factor in ensuring customer satisfaction. The ISO 9001 Quality Management Plan Template helps organizations in establishing processes for understanding customer requirements, monitoring customer feedback, and continuously improving their products or services. This results in higher customer satisfaction levels and increased customer loyalty.
- Continuous improvement: The ISO 9001 Quality Management Plan Template promotes a culture of continuous improvement within the organization. It encourages organizations to regularly review their quality management processes, identify areas for improvement, and take appropriate corrective actions. This leads to an ongoing cycle of improvement and ensures that the organization remains competitive in the market.

Key elements of an ISO 9001 quality management plan Template
Creating a Quality Management Plan (QMP) based on ISO 9001 standards is essential for organizations aiming to establish and maintain a robust quality management system. Here are key elements that you may include in an ISO 9001 Quality Management Plan template:
- Document Control: Define procedures for document creation, review, approval, distribution, and version control.Specify how changes to documents are managed and communicated.
- Quality Policy: Outline the organization's commitment to quality and adherence to ISO 9001 standards.Communicate the quality policy to all relevant stakeholders.
- Risk Management: Identify potential risks to quality and establish a risk management process.Develop mitigation strategies for identified risks.
- Responsibility and Authority: Clearly define roles and responsibilities for individuals involved in the quality management system.Specify the authority levels for each role.
- Training and Competence: Detail the procedures for identifying training needs.Describe how competence is determined and maintained.
- Communication: Establish a system for internal and external communication related to quality.Specify methods and frequency of communication.
- Monitoring and Measurement: Define processes for monitoring and measuring key performance indicators (KPIs).Specify how data is collected, analyzed, and reported.
- Process Control: Identify key processes within the organization.Define controls and parameters for each process to ensure consistency and quality.
- Product and Service Realization: Outline the steps involved in the design, development, and delivery of products or services.Specify controls to ensure conformity during realization.
- Supplier Management: Outline procedures for selecting, evaluating, and managing suppliers.Ensure that suppliers conform to relevant quality standards.
- Nonconformity and Corrective Action: Define the process for identifying and addressing nonconformities.Establish procedures for corrective and preventive actions.
- Continuous Improvement: Encourage a culture of continuous improvement.Document processes for reviewing and improving the effectiveness of the quality management system.
- Record Keeping: Specify requirements for record creation, maintenance, and retention.Ensure that records are easily retrievable for audits.
- Internal Audit: Outline the process for conducting internal audits.Ensure that audits are systematic and thorough.
- Management Review: Schedule regular reviews with top management to assess the performance of the quality management system.Use reviews to make informed decisions for improvement.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Identify applicable legal and regulatory requirements.Establish processes to monitor and ensure compliance.
- Emergency Preparedness and Response: Develop procedures for handling emergencies that may impact quality.Ensure that employees are trained on emergency response protocols.
- Documentation of the Quality Management System: Provide a comprehensive guide on how to document the quality management system.Specify formats, templates, and conventions for documentation.
The benefits of an effective quality management plan
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: An effective quality management plan ensures that products or services meet or exceed customer expectations. This leads to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty, resulting in repeat business and positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
- Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency: By implementing quality control measures, businesses can reduce operational errors and waste. This improves productivity and efficiency, allowing organizations to allocate resources effectively and meet production goals more efficiently.
- Cost Reduction: A quality management plan helps identify and address areas of waste, defects, and inefficiencies, which can result in cost savings. By minimizing defects and waste, businesses can prevent unnecessary expenditure on rework or replacement of products and materials.
- Compliance with Regulations and Standards: An effective quality management plan ensures compliance with industry regulations and standards. This helps businesses avoid penalties, fines, and legal issues resulting from non-compliance, ensuring the organization stays on the right side of the law.
- Continuous Improvement: A quality management plan promotes a culture of continuous improvement within the organization. By constantly monitoring and evaluating processes, businesses can identify opportunities for improvement, implement corrective actions, and monitor the results1. Improved customer satisfaction: A quality management plan ensures that products or services meet or exceed customer expectations. This leads to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty, resulting in repeat business and positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
- Increased efficiency and productivity: A well-designed quality management plan identifies potential areas of improvement in processes and workflows. By implementing efficient and effective quality control measures, organizations can streamline operations , reduce waste, and enhance productivity.
- Cost savings: Effective quality management helps to identify and rectify defects and errors early on, reducing the cost associated with rework, scrap, and customer complaints. It also minimizes the risk of costly product recalls, lawsuits, or regulatory penalties.
- Enhanced reputation and credibility: A robust quality management plan ensures a consistent level of quality in products or services. This builds trust and confidence in the organization among customers, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies, leading to a favorable reputation and increased credibility in the marketplace.
- Continuous improvement: A quality management plan includes provisions for ongoing monitoring, measurement, and analysis of processes and outcomes. This enables organizations to identify areas for improvement, implement corrective actions, and continuously enhance their products, services, and operations.
- Regulatory compliance: A quality management plan helps organizations meet the requirements of applicable industry standards, regulations, and certifications. By having proper quality control measures in place, organizations can ensure compliance and avoid legal or regulatory issues.
- Increased employee engagement and satisfaction: When a quality management plan is implemented effectively, it involves employees at all levels of the organization. This empowers employees, encourages accountability, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Engaged and satisfied employees contribute to better quality outcomes.
- Competitive advantage: Organizations with a strong quality management plan differentiate themselves from competitors by delivering consistent and high-quality products or services. This creates a competitive advantage in the market, attracting more customers and opportunities for business growth.
In conclusion, the ISO 9001 Quality Management Plan template is a valuable tool for organizations seeking to implement and adhere to the ISO 9001 standard. This template provides a structured framework for developing a comprehensive quality management plan that aligns with the requirements of ISO 9001.By utilizing this template, organizations can effectively document their quality objectives, processes, and procedures, as well as establish a system for monitoring and measuring performance.
The template also emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement and provides guidance on how to identify and address areas for improvement. Overall, the ISO 9001 Quality Management Plan template is a valuable resource for organizations striving to achieve and maintain compliance with the ISO 9001 standard.

Get instant access to all the ready-to-use and fully editable ISO 9001 templates to kick start your implementation.

Our specialized ISO 27001 toolkit delivers outstanding value by providing the solution for your specific needs.

Comprehensive set of templates, designed to support in implementing an effective IT Service Management System (ITSMS).
- ASQ® CQA Exam
- ASQ® CQE Exam
- ASQ® CSQP Exam
- ASQ® CSSYB Exam
- ASQ® CSSGB Exam
- ASQ® CSSBB Exam
- ASQ® CMQ/OE Exam
- ASQ® CQT Exam
- ASQ® CQPA Exam
- ASQ® CQIA Exam
- 7 Quality Tools
- Quality Gurus
- ISO 9001:2015
- Quality Cost
- Six Sigma Basics
- Risk Management
- Lean Manufacturing
- Design of Experiments
- Quality Acronyms
- Quality Awareness
- Quality Circles
- Acceptance Sampling
- Measurement System
- APQP + PPAP
- GD&T Symbols
- Project Quality (PMP)
- Full List of Quizzes >>
- Reliability Engineering
- Statistics with Excel
- Statistics with Minitab
- Multiple Regression
- Quality Function Deployment
- Benchmarking
- Statistical Process Control
- Quality Talks >> New
- Six Sigma White Belt
- Six Sigma Yellow Belt
- Six Sigma Green Belt
- Six Sigma Black Belt
- Minitab 17 for Six Sigma
- Casio fx-991MS Calculator
- CSSYB/LSSYB Mock Exam
- CSSGB/LSSGB Mock Exam
- CSSBB/LSSBB Mock Exam
- ASQ® CQA Preparation
- ASQ® CQE Preparation
- ASQ® CQPA Preparation
- ASQ® CQIA Preparation
- CQE Mock Exams
- CMQ/OE Mock Exams
- CQA Mock Exams
- CQIA Mock Exams
- CQPA Mock Exam
- CQT Mock Exam
- CQI Mock Exam
- CSQP Mock Exam
- Design of Experiments (DoE)
- Measurement System Analysis
- Statistics Using R
- Data Visualization with R
- Statistics Using Python
- Data Visualization with Python
- Regression with Minitab
- Logistic Regression
- Data Analysis Using Excel
- The Git Mindset
- Statistics Quiz
- Root Cause Analysis
- Kano Analysis
- Lean Management
- QMS Lead Auditor
- Quality Management
- ISO 9001:2015 Transition
- Project Quality Manager
- Practice Tests
- Summary Sheets
- गुणवत्ता.org
Blogs , ISO 9001
- Quality Control: Understanding Its Importance, Benefits, Approaches and Key Strategies
** Unlock Your Full Potential **

Maintaining high-quality products and services is crucial for success in today's competitive business environment. Quality control (QC) plays a critical role in ensuring that your company consistently meets customer expectations and regulatory requirements. This comprehensive guide will explore the importance of quality control, its benefits, and key strategies, with industry examples to illustrate its practical applications.
What is Quality Control?
Quality control refers to the systematic process of identifying, monitoring and correcting potential defects or deviations in products or services. This process ensures that the final output meets the established quality standards and customer requirements. QC is an essential part of the overall quality management system ( QMS ) and involves regular inspections, testing, and monitoring of various production stages.
ISO 9001:2015 defines Quality Control as “a part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements.” It includes activities such as the inspection and testing of incoming raw materials, in-process products, and finished goods.
History of Quality Control
Quality control has evolved over time to keep pace with the increasing complexity and scale of production processes. Let's take a brief look at the key milestones in the history of quality control:
Craftsmanship Era (Pre-Industrial Revolution): Before the Industrial Revolution, craftsmen were responsible for producing goods and often had a personal relationship with their customers. Quality was maintained by the craftsman's reputation, skill, and pride in their work.
Industrial Revolution (Late 18th Century to Mid-19th Century): With the advent of mass production, the responsibility for quality control shifted from individual craftsmen to factory managers. Inspectors were employed to identify and segregate defective products, but the focus was on finding and fixing defects rather than preventing them.
Scientific Management (Early 20th Century): The introduction of scientific management principles by Frederick Winslow Taylor marked a significant shift in quality control. Taylor's ideas laid the groundwork for more systematic and data-driven approaches to managing production processes, paving the way for modern quality control methods.
Statistical Quality Control (Mid-20th Century): Walter A. Shewhart introduced the concept of statistical process control ( SPC ) in the 1920s. SPC allowed manufacturers to monitor and control production processes using statistical methods, enabling them to detect and correct defects more efficiently. During World War II, the U.S. military adopted statistical quality control techniques to improve the production of munitions and other equipment.
Total Quality Management (Post-WWII): After World War II, quality management pioneers such as W. Edwards Deming and Joseph M. Juran helped spread the concept of Total Quality Management ( TQM ). TQM emphasized continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and employee involvement, transforming how companies approached quality control.
ISO 9001 and Modern Quality Control (Late 20th Century to Present): In 1987, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) introduced the ISO 9000 quality management standards, including ISO 9001 . These standards provided a global framework for implementing effective quality management systems. Today, quality has evolved to encompass a wide range of methodologies and tools, such as Six Sigma and Lean Manufacturing, helping businesses achieve higher levels of quality and efficiency.
The history of quality control shows how the concept has evolved and adapted to the changing needs of production processes and market demands. Understanding this history can help businesses appreciate the value of quality control and implement more effective systems to ensure long-term success.
Benefits and Importance of Quality Control
- Customer Satisfaction: Consistently delivering high-quality products and services helps build customer trust and loyalty, increasing the likelihood of repeat business and positive word-of-mouth marketing.
- Regulatory Compliance: QC processes help companies adhere to industry-specific regulations and standards, preventing costly fines or sanctions.
- Brand Reputation: A strong commitment to quality control enhances a company's reputation for producing reliable, high-quality products or services.
- Cost Savings: Identifying and correcting defects early in production minimizes waste and reduces the need for expensive rework or recalls.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies with robust QC systems are better positioned to differentiate themselves from competitors and capture market share.
Key Strategies for Effective Quality Control
- Establish Clear Quality Standards: Define and communicate the specific quality criteria for each product or service, ensuring all team members understand the expectations.
- Implement Regular Inspections and Testing: Conduct routine checks at various stages of production to identify defects and deviations from quality standards.
- Invest in Employee Training: Provide ongoing training to equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to maintain high-quality standards.
- Utilize Statistical Process Control ( SPC ): SPC techniques can help identify trends and patterns in production data, enabling companies to predict and prevent quality issues.
- Embrace Continuous Improvement: Encourage a culture that values ongoing learning and improvement and proactively empowers employees to identify and address quality concerns.
Quality Control Approaches
Different industries and organizations may adopt various approaches to quality, depending on their specific needs and goals. Some popular QC methodologies include:
- Total Quality Management ( TQM ): A holistic approach to quality management focuses on continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and employee involvement. It aims to integrate quality principles into all aspects of a company's operations.
- Six Sigma: Six Sigma is a data-driven quality management methodology seeking to reduce defects and process variation. The goal is to achieve a defect rate of 3.4 per million opportunities, ensuring near-perfect quality.
- Lean Manufacturing: Lean focuses on eliminating waste and optimizing processes to deliver maximum value to customers. Although not explicitly a quality control approach, Lean principles can significantly contribute to improving product quality by enhancing efficiency and reducing defects.
- ISO 9001 : This international standard sets out the criteria for a quality management system . Achieving ISO 9001 certification demonstrates a company's commitment to maintaining consistent quality standards and continuously improving its processes.
Conclusion:
Quality control plays a crucial role in ensuring that businesses deliver high-quality products and services, meeting customer expectations and regulatory requirements. Companies can develop and implement effective QC systems that contribute to long-term success by understanding its importance, benefits, and key strategies.
Similar Posts:
January 20, 2018
International Register of Certified Auditors (IRCA) – CPD
March 29, 2018
Benefits of Six Sigma and Lean
March 31, 2018
4 Types of Team Roles

32 Courses on SALE!

Project Quality Plan: The Easiest Guide (With Template)
This blog is reader-supported. When you purchase something through an affiliate link on this site, I may earn some coffee money. Thanks! Learn more .
The big risk as a project manager is that you hit all the project management success criteria: being on time and on budget, but what you deliver doesn’t meet the customer’s requirements.
That can happen for a lot of reasons, but one of the main causes is that you didn’t know what good looked like before you started. A project quality management plan can help with that. In this article, we’ll talk about how to write one and why you should. Plus I have a template to share with you.
The basics: What is a quality management plan?
A quality management plan is a document that sets out how the expectations for the project will be achieved. It is part of the project management plan.
In my experience, I’ve never written a bumper project management plan. I’ve always written several different plans and then (sometimes) had a document that references them all. Sometimes it is worth doing a project management plan and then calling out references to one or two specific other documents.
For example, I rarely write a specific risk management plan because I can just reference the PMO’s standard risk management approach which is published on the intranet. But if my project included a lot of procurement, I might write a separate procurement management plan.
The quality plan talks about how you are going to make sure that the project delivers a quality result. So what does a quality result look like?
What quality looks like
It’s hard to define quality in project management. There are so many different types of projects, each with specific goals. There is no definitive answer for how to measure quality in project management. Unfortunately.
‘Quality’ means different things to different people, so you will have to ask stakeholders what they are expecting from the project and then help them translate those into quality criteria.
Sometimes it’s easy: the website search button must a result within 0.2 seconds. Each toy brick must be 1.5cm by 3cm. The new product must be ready by 25 June.
Sometimes it’s hard, especially when the output supports organizational transformation, culture change, or something else that is difficult to quantify. Give it a go anyway; you might be surprised at what you can come up with.
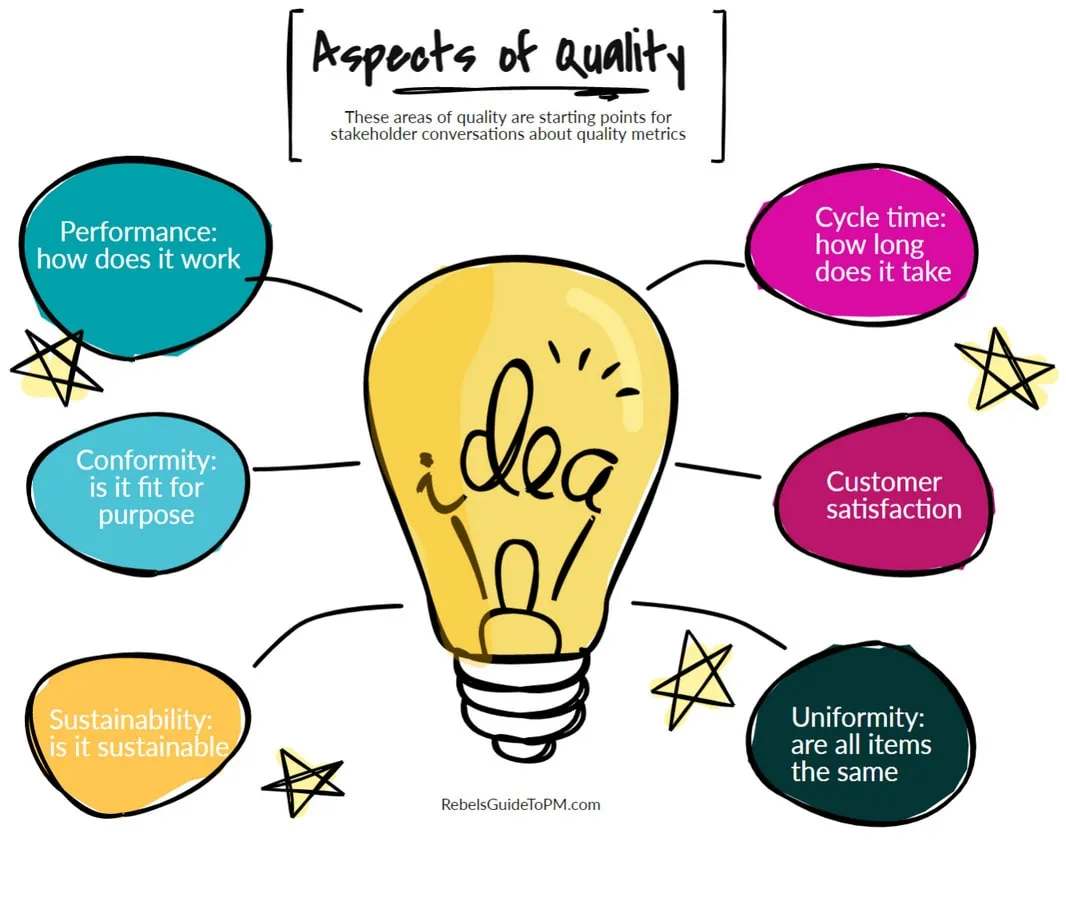
Here are some suggestions of what you could suggest to stakeholders as the basis for quality metrics. The two biggest ones are:
- Performance: How is the thing supposed to work and does it do what it is supposed to do?
- Conformity: Is the thing fit for purpose? Can we use it? Does it meet the specifications as set out in the requirements?
And here are some others:
- Sustainability: Does the thing support sustainability goals? Has it been created with sustainability in mind?
- Uniformity: If you are making lots of things, are they all the same?
- Reliability: Does the thing work on a reliable basis? Are the results you get from it consistent?
- Customer satisfaction : Do people like the thing? Is the user experience good? Are they recommending it to their friends and colleagues?
Where are quality requirements documented?
So where do you get an idea of what stakeholders want?
The expectations for performance levels i.e. the quality expected from the project are probably documented in the exit or completion criteria, the business case, requirements documents, use cases or a statement of work. Any of these might include quality targets.
Failing that, use the list above to talk to team members and the wider stakeholder community and get some ideas.
The contents of a quality management plan
You have your quality requirements. You know what good looks like and what your quality goals should be. Now it’s time to create a quality management plan.
The plan can include:
- Roles and responsibilities : Who will do the quality management tasks (e.g. external quality inspectors, quality manager)
- The quality assurance plan and approach
- The quality control approach and what activities are going to be scheduled for quality management
- The plan for how ‘continuous improvement’ is going to happen
- Any quality management system, tools, or processes that are going to be involved, for example, the process for dealing with corrective actions
- The quality standards and acceptance criteria that the project must stick to.
This is what I would include in my project quality document. There is no definitive list, so if you want to add in a section or delete one, just do it. Make the document relevant to your project.
As you can see, the plan mentions quality assurance and quality control. There are 3 processes in project quality management, and they are the other two (along with quality planning).
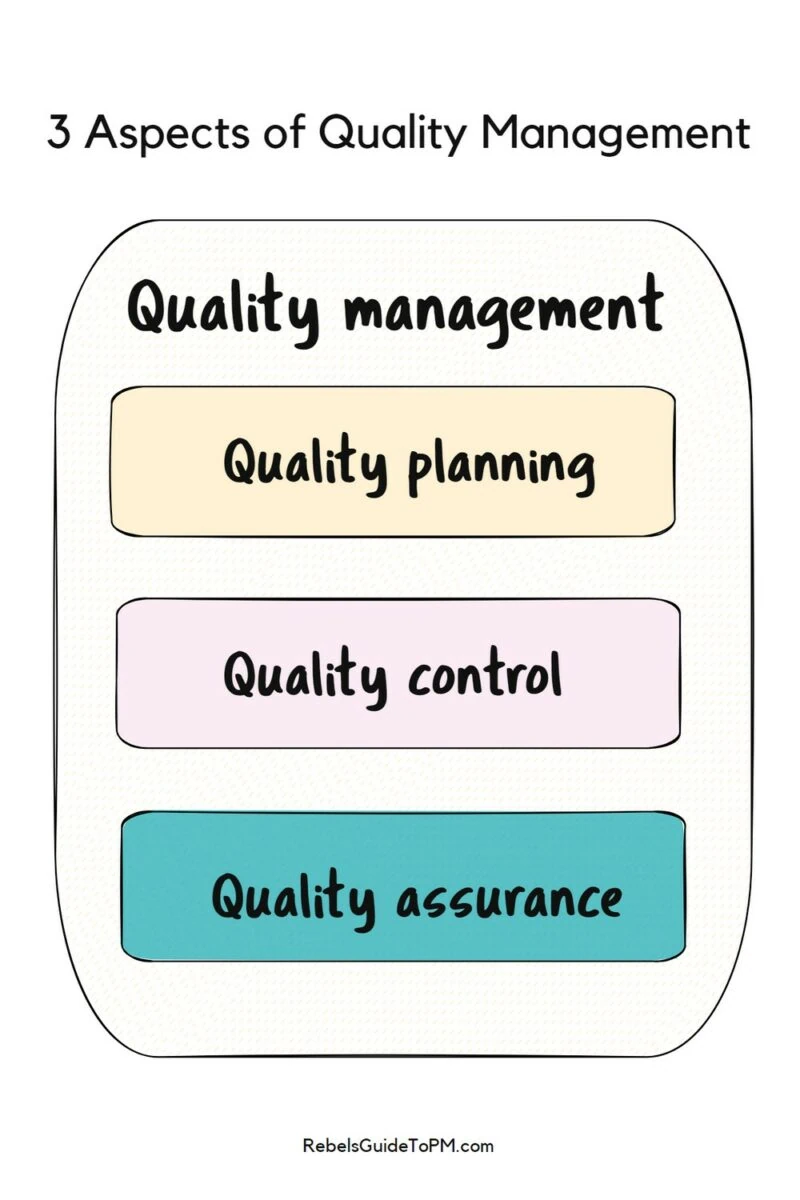
Quality assurance (QA)
Quality assurance activities are all about making sure there is a culture of quality. It sums up different ways of work to give stakeholders and the project sponsor confidence that you are doing the right things: it’s part of your overall approach to project assurance .
For example, quality assurance tasks could include:
- Writing new processes and following them
- Scheduling quality reviews and documenting the output
- Having a process for lessons learned to support ongoing organizational knowledge sharing.
The role of quality assurance in project management is proactive and process-led. It is all about planning to deliver something that meets the quality objectives.
I have never worked on a project where there is a specific quality assurance team. It has always been considered something that I would lead on, as part of the project management responsibilities.
Quality control (QC)
Quality control, on the other hand, is all about checking your work. Control tasks include:
- Testing the deliverables
- Carrying out peer reviews, internal project reviews, or quality audits
- Root cause analysis
- Failure mode and effects analysis (which is something I learned when I was doing Six Sigma training)
- Documenting the output of tests, reviews, and audits along with recommended corrective actions and a plan for how to implement these to get the deliverables up to scratch.
Quality control in project management is reactive because it happens after the deliverable is created. However, you would still have a quality control plan that sets out the schedule for audits and so on.
Some organizations will have a quality control team, so tap into them if you do have experts available to you.
Both QA and QC processes are required for certain industries, for example in healthcare and life sciences, and to ensure compliance with ISO 9000. Talk to your quality management team if you are worried about your project not being able to evidence that it has met contractual guidelines.
How to write a project quality plan
You need some inputs before you can put fingers to keyboard! Here are 3 simple steps for writing a quality plan.
1. Establish what quality looks like for this project
What does a good result look like? What metrics are you going to use? How will you track and measure what is produced?
Look at what standards exist in the organization already and then think about how that applies to your work.
Then, go a level deeper and work out the acceptance criteria (or exit criteria, depending on what you want to call them) for each aspect of the work. This gives you a complete overview of how to assess quality for each deliverable.
On an agile project , this is something you’ll do for each sprint, as the contents of each sprint are known.
2. Clarify roles and responsibilities
Will you have a dedicated quality manager for this project? If not, who is going to do all the relevant tasks? How will they fit that in? Have they been allocated those tasks on the Gantt chart or project schedule yet?
Document roles and responsibilities and make sure everyone is happy with what they are going to be doing.
3. Write it down
Use the outline template below to write your quality plan. Reference other project documents where they exist to save duplicating the effort.
Then get your plan signed off by the project sponsor or client.
We’re all for integrated project management, so once the document is complete, make sure to update any other files that reference it (or should reference it). Add any new risks to your risk log, update the stakeholder register and so on.
Quality management plan template
Here is a template you can use to create your own quality plan. Put the headings into your own organization’s document template in Word, or turn it into a set of slides in PowerPoint. I would not suggest creating this plan as an Excel file as it’s too wordy.
This outline is deliberately vague as you need to make it project-specific. There is no single checklist that I can give you because the definition of quality differs from project to project.
- Project title
- Roles and responsibilities: List the roles and what part they have to play in the quality management process.
- Tools: If you are using specific software, templates, analysis techniques (like Ishikawa or control charts) then put all that in here.
- Quality assurance approach: Outline how you will ensure high quality for the final deliverable and any process quality standards applicable to the project.
- Quality control approach: Outline how QC will work for this project
- Quality improvements: Outline how you will identify improvements and how these will be acted on.
- Quality metrics: Document the specific requirements. These might already exist in the product descriptions as part of the work breakdown structure, so don’t reinvent the wheel if you already have this information.
Finally, make sure you have all the normal version control information on there, like your name, the version number, and a history of how the document has been updated, so people can make sure they have the latest version.
Why bother with project quality?
So far, all this quality planning sounds like quite a lot of work, so what’s the purpose behind project quality management procedures and processes?
It’s obvious really: you get a better result. If you make an effort to embed quality practices in whatever you do, you are more likely to:
- Get project deliverables that are fit for purpose
- Spend less money
- Deliver results that don’t have bugs or other defects
- Meet your business objectives
- Make stakeholders happy because you have met customer requirements
- Save time because you don’t have to do rework.
What the Standard for Project Management says
The Standard for Project Management covers quality by saying we should build quality into processes and deliverables.
If you ask any customer what they want, one of the responses is going to be that they want the deliverables to be good enough. They get to define what ‘good enough’ means and then you have to make sure the project team meets those standards.
The Standard talks about maintaining:
“a focus on quality that produces deliverables that meet project objectives and align to the needs, uses and acceptance requirements set forth by relevant stakeholders.”
The Quality domain
You might not subscribe to the PMBOK® Guide 7 th Edition way of doing things, but even if you don’t, there are still a few useful takeaways in the PMI manual.
Quality falls into the Delivery Performance Domain. There isn’t much in the way of specifics in the book but what I took from it is:
- Your quality plan should link in with any organizational quality policy .
- Work procedures are part of quality management as they document the way tasks are expected to be carried out, so if you are writing new Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) they had better be good.
- Most of the cost of quality falls to the supplier doing the work, whether that is internal or external.
Cost of quality, you say? What’s that? Let’s look at that next.
What is the cost of quality?
Quality costs. As you can imagine, putting those checks and balances in place takes time and costs money.
When we talk about the cost of quality (COQ), we mean how much do we spend on getting a quality result, and how much does it cost to have to do work again because we messed up the first time. In other words, what would it cost us to not deliver a quality solution.
The cost of quality includes:
- Preventing nonconformance: the effort involved in making sure the requirements meet the right quality standard
- Checking: appraising what you deliver to check it does meet requirements
- Rework: the effort involved in having to do something again and get it right the second (or third…) time
Internal failure costs are when the project team recognizes there is a mistake before it gets to the customer. External failure costs are found by the client – that’s a big no no, plus it’s embarrassing to hand something over only to be told your customer has found an error or it isn’t up to scratch.
Quality management in agile projects
Agile projects integrate quality into everything they do. I think this is the way it should be for all projects. Why make it different, when delivering a good result should be what we turn up to work to do anyway?
The waterfall approach is often to do a quality audit and assurance work periodically or when deliverables are finished. That’s not the agile way, because agile teams have a much more holistic view of building quality into every step of the journey.
Quality assessments happen as part of sprints. Defects are detected early and fixed at the next possible opportunity.
Spotting errors early means it costs less to put them right: try backing out a line of code when there are hundreds of other processes that might be dependent on it. That’s a whole lot of regression testing that could have been avoided if only the bug was resolved earlier on.
In an agile environment, quality management is the responsibility of the product owner, but really it’s everyone’s job.
FAQ about project quality management
Who is responsible for quality management on the project.
The project manager or product owner is ultimately responsible. However, the project team might include a quality manager. Everyone is responsible for following the processes and doing a good job.
Why quality is important in project management
Quality matters because people want to get the right thing at the end of the project. They want a decent result because they’ve spent time and money on the process and they have certain expectations.
What is the purpose of project quality management?
The purpose of project quality management is to ensure the project delivers the right outputs that meet customer expectations in a controlled way while minimizing the cost of quality by building a culture where quality is baked into everything the project team does.

Project manager, author, mentor
Elizabeth Harrin is a Fellow of the Association for Project Management in the UK. She holds degrees from the University of York and Roehampton University, and several project management certifications including APM PMQ. She first took her PRINCE2 Practitioner exam in 2004 and has worked extensively in project delivery for over 20 years. Elizabeth is also the founder of the Project Management Rebels community, a mentoring group for professionals. She's written several books for project managers including Managing Multiple Projects .
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Quality Control (QC)?
- Understanding QC
- Difference With Quality Assurance
The Bottom Line
- Business Essentials
Quality Control: What It Is, How It Works, and QC Careers
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Quality control (QC) is a process through which a business seeks to ensure that product quality is maintained or improved. Quality control requires the company to create an environment where management and employees strive for perfection. This is done by training personnel, creating benchmarks for product quality, and testing products to check for statistically significant variations.
A significant aspect of quality control is the establishment of well-defined controls . These controls help standardize both production and reactions to quality issues. Limiting room for error by specifying which production activities are to be completed by which personnel reduces the chance that employees will be involved in tasks for which they do not have adequate training.
Key Takeaways
- Quality control (QC) is a process through which a business seeks to ensure that product quality is maintained or improved.
- Quality control involves testing units and determining if they are within the specifications for the final product.
- The quality control used in a business is highly dependent on the product or industry, and several techniques exist for measuring quality.
- The food industry uses quality control methods to ensure customers do not get sick from their products.
- Quality control creates safe measures that can be implemented to make sure deficient or damaged products do not end up with customers.
Ryan Oakley / Investopedia
Understanding Quality Control (QC)
Quality control involves testing units and determining if they are within the specifications for the final product. The purpose of the testing is to determine any need for corrective actions in the manufacturing process. Good quality control helps companies meet consumer demands for better products.
Why Is QC Needed?
Creating a product is costly, time-consuming, and can be unsafe without controls in place. Additionally, if a company sends defective products out for purchase, it could be held liable for injuries or issues that arise from using its products. Quality control inspectors ensure that defective or unsafe products are identified , and the causes are corrected.
How Is It Done?
Quality testing is generally completed in each step of a manufacturing or business process. Employees often begin by testing raw materials , pulling samples from the manufacturing line, and testing the finished product. Testing at the various stages of manufacturing helps identify where a production problem is occurring and the remedial steps it requires to prevent it in the future.
In a non-manufacturing business, quality testing can involve customer service evaluations, questionnaires, surveys, inspections, or audits. A business can use any process or method to verify that its end product or service meets the customer's needs and is safe and legal.
QC Is Different by Industry
The quality control used in a business is highly dependent on the product or industry. For example, in food and drug manufacturing, quality control includes ensuring the product does not make a consumer sick, so the company performs chemical and microbiological testing of samples from the production line.
In aircraft manufacturing, quality control and assurance is of the utmost importance. Manufacturers are required to document, track, inspect, and reinspect all items and phases of a build to build evidence that everything is completed to very strict standards.
In automobile manufacturing, quality control focuses on parts meeting specifications and tolerances. QC ensures engines, drive trains, and other mechanical parts operate smoothly, efficiently, safely, and as designed.
In electronics, quality testing might involve using meters that measure the flow of electricity and stress testing.
Quality Control vs. Quality Assurance
Quality control and quality assurance are terms often used to define the same thing, but there are distinct differences. Quality control focuses on quality requirements, such as ensuring a part meets specifications. Quality assurance refers to the sum of all actions and processes needed to demonstrate that quality requirements are fulfilled.
What this difference means for quality professionals is that as you move through a quality control career, you might transition from quality control to quality assurance. Quality control is part of quality assurance, which consists of programs and departments that assure upper-level management, customers, and government inspectors that products meet all quality requirements and safety standards .
Quality Control Methods
There are several methods quality control uses to communicate and track inspections and issues. For instance, a quality control chart is a graphic that depicts whether sampled products or processes are meeting their intended specifications—and, if not, the degree by which they vary from those specifications.
When one chart analyzes a specific product attribute, it is called a univariate chart. A chart that measures variances in several product attributes is called a multivariate chart. Tracking variances allows businesses to see how many defects per production unit they produce and what types of defects are occurring. Here are a few examples of some methods used.
X-Bar Chart
Randomly selected products are tested for the given attributes the chart is tracking. A common form of a quality control chart is the X-bar chart, where the y-axis on the graph tracks the degree to which the variance of the tested attribute is acceptable. The x-axis tracks the samples tested. Analyzing the variance pattern on this chart helps you determine if defects are occurring randomly or systematically.
Taguchi Method
The Taguchi Method of quality control is another approach that emphasizes the roles of research and development, product design, and product development in reducing the occurrence of defects and failures in products. The Taguchi Method considers design more important than the manufacturing process in quality control and tries to eliminate variances in production before they can occur.
100% Inspection Method
This 100% inspection method is a quality control process involving looking at and assessing all product parts. This type of quality control is done to rule out flaws in products. This method is often used to evaluate valuable metals. The 100% inspection method calls for data about the manufacturing process and software to analyze inventory.
The challenge of using this method is that looking at every single item used to build a product is expensive and could destabilize or render the product unusable. For example, if you use this method to examine organic strawberries, you risk damaging the berries, rendering them unsellable.
Quality control methods help standardize production and reactions to quality issues in various industries, from food production to automobile manufacturing.
Quality Control Careers
Quality control can be a rewarding career if you enjoy working with people, communicating, presenting results, and working to make products better and safer. To become a quality control inspector, you'll need (depending on the industry):
- A high school diploma for entry-level positions
- A bachelor's degree, depending on the industry
- Experience in an industry
- Licenses and certifications for some industries and businesses
Other qualities that are necessary for quality control professionals are:
- Attention to detail
- Mechanical and math skills
- Physical abilities and strength
- Technical skills
- Performance under pressure
Career Path
The route to a career in quality control and assurance varies by industry, so there may be differences. However, you'll generally need several years of experience in your industry. Typically, you begin by being hired as a quality assurance or control associate after meeting educational and work experience requirements.
Once you gain work experience as a quality specialist or associate, you may move into a senior specialist position and begin managing teams of quality control specialists. You may attend professional development courses sponsored by your employer or be required to gain certifications such as Six Sigma. You might also need to earn a professional designation such as Certified Quality Inspector.
Moving up the career path, you have more options. You may be able to choose from or be selected to be a:
- QA Systems Manager
- QA Operations Manager
- QA Compliance Manager
These positions can lead up to upper-level management or executive levels within quality control:
- Director of Quality
- Head of Compliance
- Vice President of Quality
Quality Control Salaries
The average pay for quality control professionals differs by industry, experience, and position. Pay increases as you gain more experience and move into management positions. As of May 2022, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reports average salaries as:
- Professional, scientific and technical services: $47,480
- Manufacturing: $44,900
- Wholesale trade: $40,560
- Administrative and support services: $34,190
What Does Quality Control Mean?
Quality control means how a company measures product quality and improves it if need be. Quality control can be done in many ways, from testing products, reviewing manufacturing processes, and creating benchmarks. This is all done to monitor significant variations in a product.
What Are the 4 Types of Quality Control?
There are several methods of quality control. These include an x-bar chart, Six Sigma, 100% inspection mode, and the Taguchi Method.
Why Is Quality Control Important?
Quality control ensures that defective goods do not go out to the public. Companies that have quality control methods in place often have employees who pay close attention to their work.
In food and drug manufacturing, quality control prevents products that make customers sick, and in manufacturing, quality control can ensure that accidents don't happen when people use a product.
What Are 3 Examples of Quality Control?
Three examples of quality control could be in the food industry; overseeing the ingredient specifications, reviewing supplier lists, and ensuring the facility where the food product is made is sanitary.
Having quality control in place within a business helps ensure product quality and the overall success of a business. The quality control environment influences employees' attitudes about the workplace and creates a sense of ownership of the products and company.
Quality control can be done in various ways, from training personnel to creating data-driven tools to test products and set standards. Quality control methods help create a safe work environment and products that are safe to use and meet customers' needs. Additionally, it is a rewarding career for someone who enjoys investigating issues and improving outcomes.
American Society for Quality. " Quality ASSURANCE & Quality control ."
Bureau of Labor Statistics. " How to Become a Quality Control Inspector ."
Proclinical. " Quality Assurance Career Path ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Quality Control Inspectors | Pay ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/business-people-using-pen-tablet-notebook-are-planning-a-marketing-plan-to-improve-the-quality-of-their-sales-in-the-future--881542122-6767a39f655b4a018019715734dcfbe0.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
24+ SAMPLE Quality Control Plans in PDF | MS Word
Quality control plans | ms word, 24+ sample quality control plans, what is a quality control plan, why should you prepare a quality control plan, the elements of a quality control plan, the two main types of quality control plans, how to build an excellent quality control plan, what are activities worth adding to a quality audit checklist, what are highly recommended quality control tools, what are the other types of quality control.
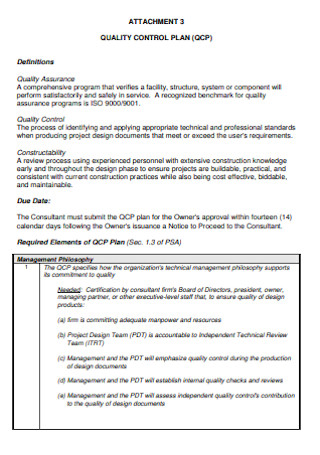
Sample Quality Control Plan

Project Quality Control Plan

Quality Assurance and Control Plan

Contractor Quality Control Plan

Production Quality Control Plan
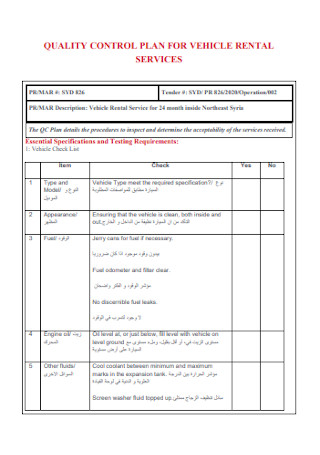
Quality Control Plan for Vehicle Rental

Quality Control Plans for Highway Bridges
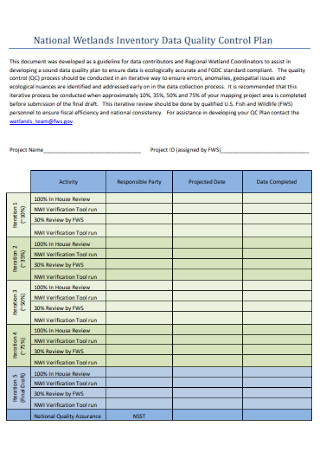
Inventory Data Quality Control Plan

Highway Safety and Quality Control Plan
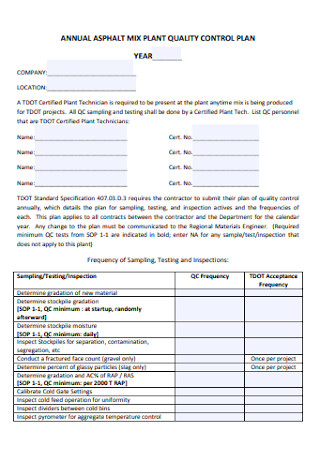
Plant Quality Control Plan

Construction Quality Control Plan Template

Simple Quality Control Plan
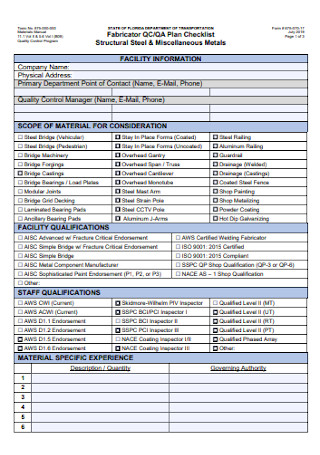
Quality Control Plan Checklist
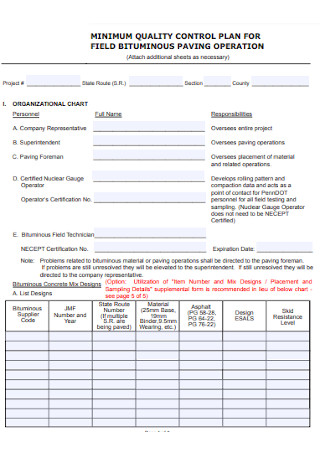
Minimum Quality Control Plan

Final Quality Control Plan

Individual Quality Control Plan

Individualized Quality Control Plan

Technology Quality Control Plan
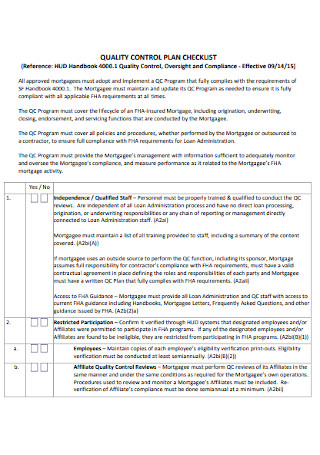
Quality Control Plan Checklist Format
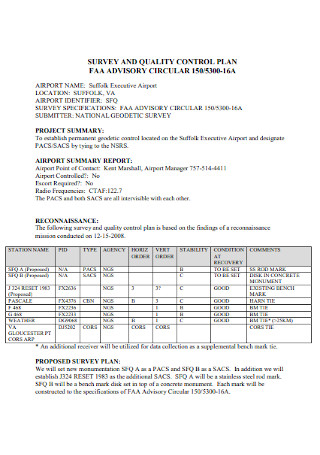
Survey and Quality Control Plan
Design Quality Control Plan

Individualzed Quality Control Plan
Poor quality identification, prevention tips and improvement plans, a detailed list of criteria and tools, a must-have for any type of industry, a plan for a better future, product quality control plan, process control plan, step 1: get to know your industry and its system, step 2: use a premade quality control plan sample, step 3: complete the elements of a qcp, step 4: produce a straightforward and easy-to-read plan, step 5: set a regular quality inspection formally, share this post on your network, file formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 5+ sample investment company business plan in pdf.

What do you do when you have tons of spare cash lying around your home or burning a hole in your wallet or expensive jeans pocket? For some people, the…
41+ SAMPLE Unit Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
As a teacher, you might know about every school policy, the steps to keep classrooms safe for intellectual development, how to set up an organized classroom, and the proposed…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Contact sales
Start free trial
The Quality Management Plan in Project Management

Project managers know all about the triple constraint: time, scope and cost. But truthfully, there should be a fourth restraint: quality. The quality of your work can make or break a project, which is why a quality management plan is so important.
If you deliver on time and under budget, but the quality doesn’t meet your stakeholders’ expectations, the project is not a success. Let’s explore the impact a quality management plan can have on a project, how to make one and look at some templates to get you started.
What Is a Quality Management Plan?
A quality management plan is a document that helps the project manager and the project team execute quality management and quality assurance actions. Quality, in the context of project management, is fulfilling the project requirements and meeting the customer’s needs.
An overall project plan will include a quality management plan, which describes the activities you will apply throughout the project’s life cycle to meet its quality objectives. You also describe these activities (and the resources you need to put them into action) in the quality management plan.
It’s foolish to expect quality without planning for it. Quality is intentional and requires skillful execution. A quality management plan is the first step to defining and codifying the steps necessary to achieve the quality expectations of the project. This is best done with project management software that can organize and share the plan with the project team.
ProjectManager is cloud-based work and project management software that has multiple project views that let you create and execute your quality management plan. Project managers can build the quality plan on Gantt charts, which link dependencies, add milestones and even filter for the critical path. Then, teams can execute the plan on kanban boards and task lists. Every work view is updated in real time for a single source of truth. Get started today for free.
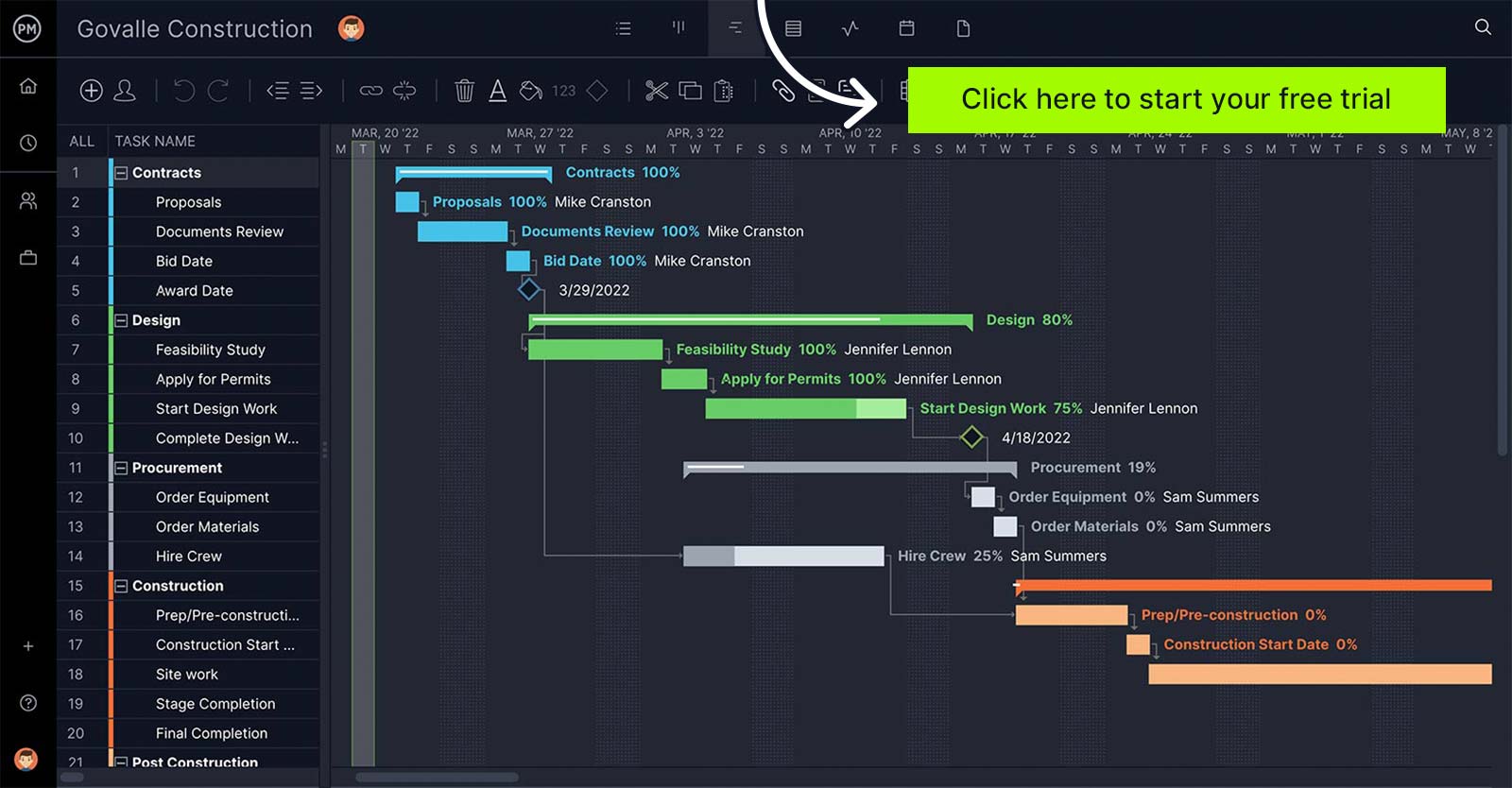
Why Is a Quality Management Plan on a Project Important?
A quality management plan is an essential component to delivering a successful project for your stakeholders. But it’s not just one project that benefits from a quality management plan. Customers expect consistency, and by having a plan in place to maintain a quality production for whatever product or service you’re manufacturing, you can consistently meet their quality expectations.
Quality management is also not limited to the project team. When everyone in the organization understands the plan, efficiency increases. While it’s of paramount importance that everyone involved in the manufacturing process uses the quality management plan for guidance, having all departments familiar with the plan boosts efficiency and creates a shared goal understood by all.
When you create a quality product or service, customers are going to take notice. The market is competitive, and quality is something that makes your brand stand out. A quality management plan helps you deliver consistent quality. That, in turn, makes customers loyal to your product or service. Loyal customers lead to brand value; and that means profitability.
Of course, nobody’s perfect, which is another reason why a project needs a quality management plan. Having guidelines and principles for your business processes means that everyone knows what to do. This creates a roadmap that reduces human error. The fewer mistakes, the less time and money you have to spend on the project.
Who’s Involved in Planning, Executing and Maintaining a Quality Management Plan?
A quality management plan is created by the project manager, who can seek guidance from some team members, stakeholders and customers. There are some projects and organizations that might have specific roles for a quality assurance professional or quality expert, but most quality management plans are planned, executed and maintained by the project manager.
Regardless of who owns the quality management plan, everyone on the project team has some role to play in order to make sure that deliverables meet quality expectations:
- The Project Manager: The PM develops the quality management process in order to make sure all deliverables meet quality expectations.
- Team Members: The team is responsible for meeting the quality expectations of the plan as they execute their tasks by following the standards designed by the project manager.
- The Organization: The org standardizes quality controls across all projects and makes sure that its staff is trained with the skills needed to deliver quality products or services.
- Stakeholders: Stakeholders need to explain clearly what their quality expectations are and they are responsible for approving the delivery of that product or service.
- Customers: Customers and users should be consulted like stakeholders if the project is designed to create a product or service for customers.
How to Create a Quality Management Plan for a Project
When making a quality management plan, you first need to identify the key components. These include the project deliverables and project process. You also need to determine the quality standards you’ll measure your deliverables by, as well as the criteria you use to measure customer satisfaction.
You’ll also need to list the quality control activities, process quality standards, stakeholder expectations, quality assurance activities and create quality deliverables. Once that is done, the quality management plan follows these four steps:
1. Plan Development of Quality Management Plan
This is where you identify the quality objectives of your customers by researching and interviewing them. You’ll want to get them to express their needs clearly and objectively. Then, you’ll look at the professional standards around your product or service, such as legal, environmental, economic, code, life safety and health.
The quality management plan will have to find a balance between what the customers want and your cost, schedule and professional standards. From there, you can start to develop a plan and processes to achieve your quality goals within the constraints of your project.
Next, you’ll want to develop performance measure thresholds in order to make sure everyone is in agreement that the quality objectives have been met. Customers will have to agree with all the quality objectives and measurements of quality.
2. Execute the Quality Management Plan
Now that you have a plan, it’s time to set it into action. Execute tasks in accordance with the approved quality management plan and standards. Communication is essential during this phase, in order to respond quickly to changing dynamics in the project. Document everything and explore them in a lessons-learned meeting after the completion of the project.
3. Perform Quality Checks
In order to make sure you’re meeting quality objectives, it’s imperative to perform quality checks, such as technical reviews, management oversight and verification that quality standards are being met. Check them against your customer quality objectives. Project managers will report these findings to stakeholders in regular meetings. Continuous improvement is the goal of this process.
4. Take Corrective Action
If, during monitoring for quality in your project, you capture anomalies, you must respond in order to bring the project back to its quality baseline. Document these changes, as such quality improvements could alter the quality management plan, procedures and resources allocation.
Quality Control Template
This free quality control template is a simple yet effective quality management tool that allows you to log any quality issues with your products or project deliverables, along with information such as who found the issue, what is its status, who’s responsible for fixing it and when is it expected to be solved.

More Free Quality Management Templates
Quality management plans are complicated. You need to plan, monitor and report on progress, all while being flexible enough to make changes fast when they’re necessary. ProjectManager has dozens of free project management templates you can use for free. Here are a few related to quality management:
RACI Chart Template
The free RACI chart template for Excel is a tool that helps make sure all your stakeholders are updated and working towards the project’s common goals. This free template lets you identify the roles and responsibilities of everyone involved with the project.
Project Management Plan Template
The quality management plan is part of your larger project plan. ProjectManager’s free management plan template for Word helps you scope out the entire project, including the quality management part. Then, you can schedule and assign tasks to your team.
Risk Register Template
There are risks inherent in every project, and if those issues arise, they can impact the quality of your work. That’s why you need a mechanism to identify and track them. ProjectManager’s free risk register template for Excel has everything you need to define the risk, determine its priority and what the potential impact on the project could be. By having your response to risk set in advance, you’re more likely to resolve it before it impacts your project.
How ProjectManager Helps with Quality Management Planning
While templates are a fine tool, they pale in comparison to project management software. The biggest problem is that templates are static documents that require a lot of work to update. ProjectManager is cloud-based software that delivers real-time data for more insightful decision-making and swifter action to keep your project on track.
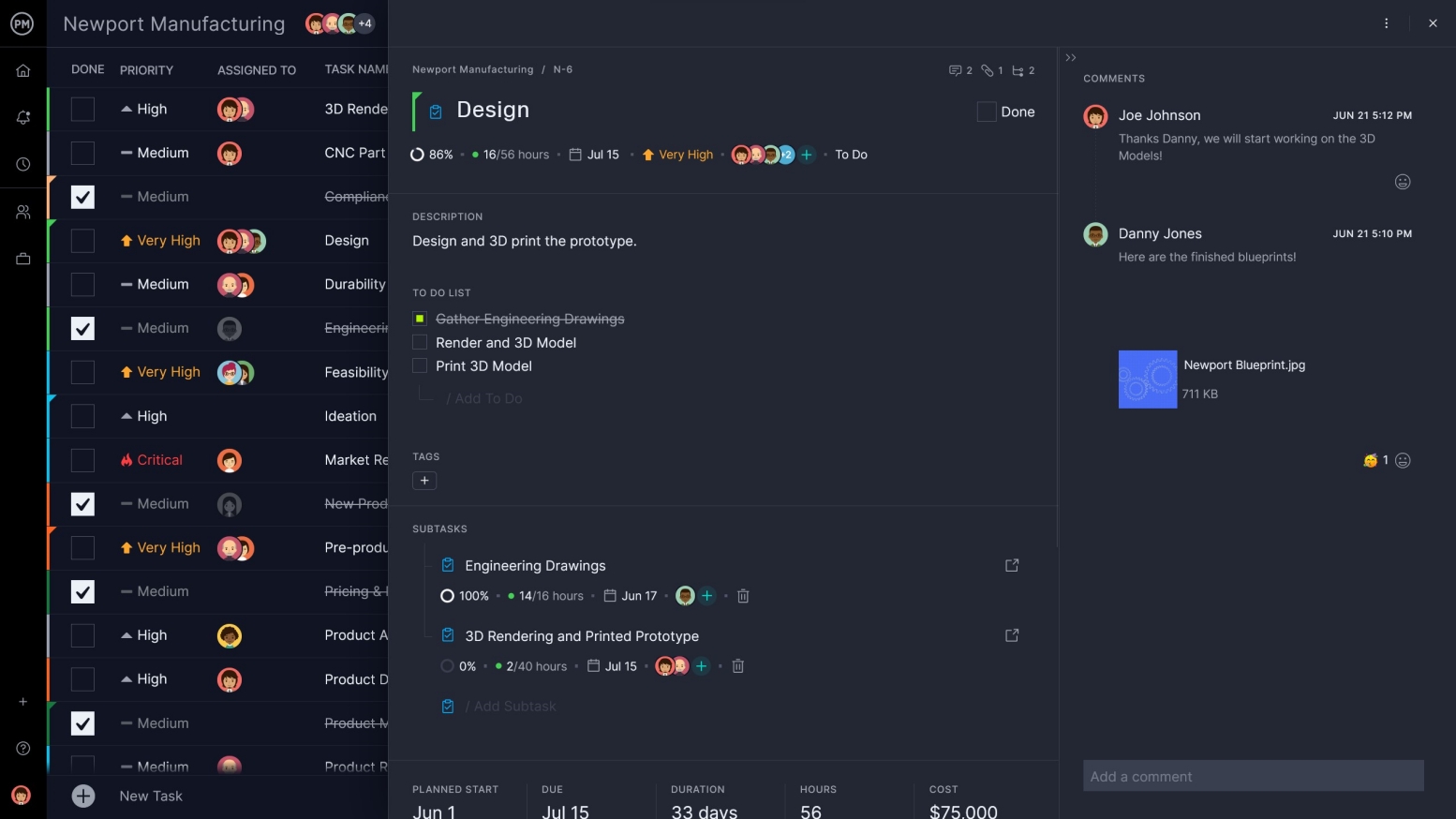
Get Multiple Project Views
Managers love Gantt charts, but they’re not ideal for teams. ProjectManager comes with multiple project tools that let teams work how they want. We have Gantt charts, sheet views, kanban boards, calendar views and kanban boards that visualize the workflow. All project views are updated in real time, so no matter which you’re working on, you’re seeing the most current view.
Use Automation to Control Quality
Managers can customize workflows and set triggers to automate routine busy work. This frees up team members so they can concentrate on delivering quality. You can also control task status with task approvals to make sure only quality moves forward in production. You authorize who will make sure the task meets quality expectations.
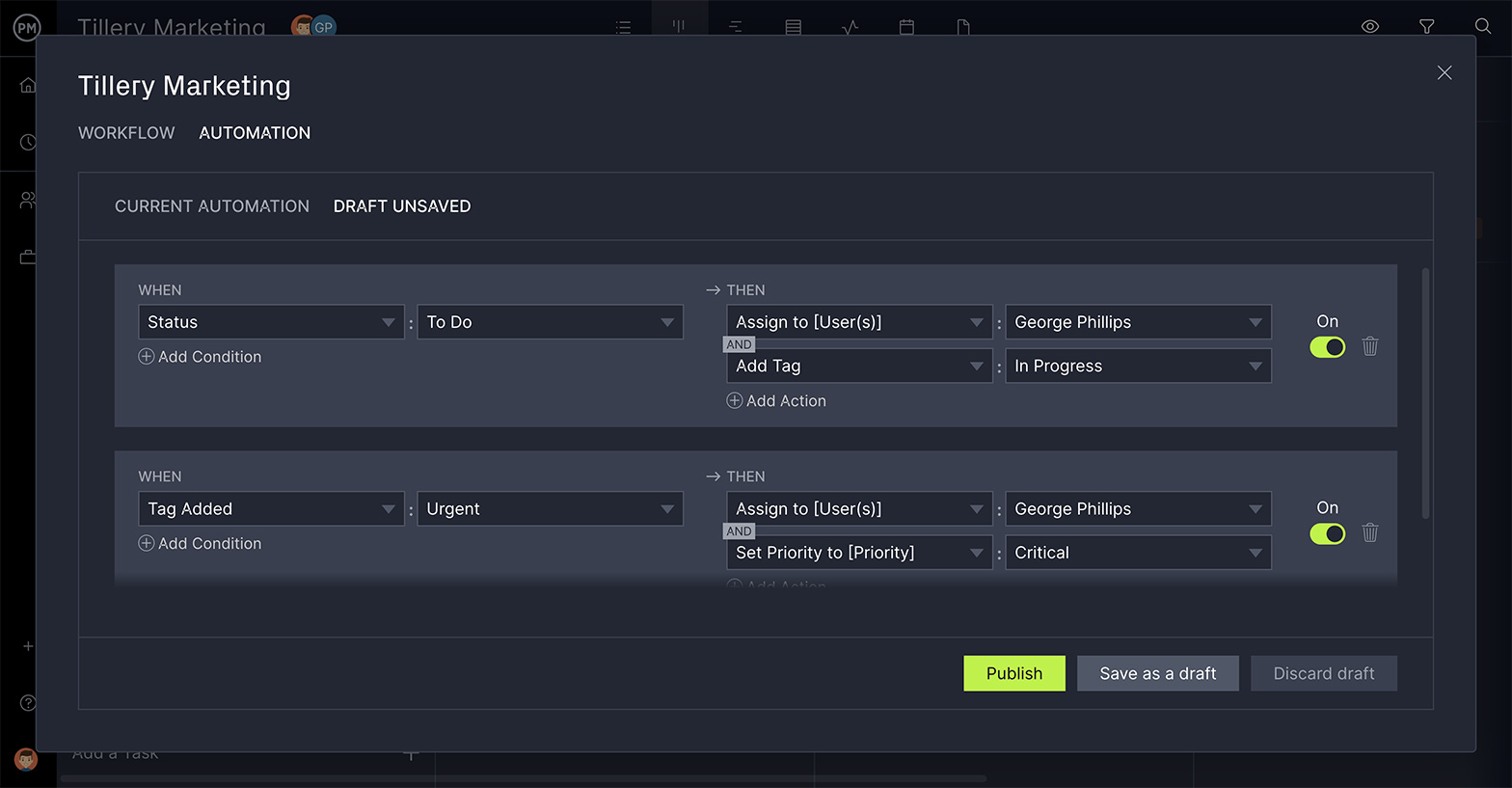
Monitor Quality in Real Time
To keep track of quality and catch any issues fast, you need real-time data. ProjectManager’s live dashboard collects real-time data and calculates the numbers for you, which display in easy-to-read graphs and charts. For more details, use the one-click reporting feature. Filter all our reports to show what you want to see, then easily share with stakeholders to keep them updated.

ProjectManager is award-winning work and project management software that helps you plan, monitor and report on every aspect of your project. Create quality management plans, assign teams, monitor their progress and report to stakeholders to manage their expectations. You also get resource and task management features. Join the teams at NASA, Seimen’s and Nestle who are delivering quality with our tool and get started today for free.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
- Business Templates
- Sample Plans
FREE 8+ Quality Control Business Plan Samples in PDF | DOC

In writing for a business plan, it is essential to undergo into a process that helps you in ensuring that the quality of a particular product is maintained. This process is called quality control . It requires most business and companies to create a type of environment through which the management and the employees will strive harder in order to achieve their goals or objectives . It can be done by having a training, creating a benchmark intended for your products, and testing your products for other related and significant variations. There has been an important aspect that contains within having a quality control. It is the establishment of controls that helps in contributing to the standardization of production and reactions. This article will lead you to more information with regards to quality control in business plans, so keep reading!

Quality Control Business Plan
8+ quality control business plan samples, 1. business licensing quality control plan, 2. quality control assurance business plan, 3. quality control compliance business partner plan, 4. quality control business review plan, 5. quality control infrastructure business plan, 6. company quality control business plan, 7. quality control program business plan, 8. quality control startup business plan, 9. quality control monitoring business plan, steps in writing a quality control plan for businesses, what are the benefits of having quality control, what are some known quality control methods.
Taking quality controls among business plans are usually considered as the final step to take. This stage is essential and will remain crucial due to the fact that it helps you determine each related processes. Depending on the type of industry you are in, you need to have an implementation of the internal and external quality controls. When we say internal control, it is the one that has been typically found in businesses that observes in-house protocols. This may even differ from having maintenance to evaluating personnel for performance analysis . The external control is used when you have to send products to third parties.

Size: 359 KB

Size: 355 KB

Size: 19 KB

Size: 263 KB

Size: 170 KB

Size: 44 KB

Size: 150 KB

Size: 32 KB
- Create an organization chart – you should have an outline of your organizational chart that enables you to provide description of the job, business qualifications, and required training to make sure that the quality assurance procedure will be performed well. Such requirements has to be documented for the purpose of showing to the employees how to conduct the exact method of inspecting. The documents need to be kept in a file in case there will be concerns of errors.
- Define responsibilities – this phase is where you will be going to outline all the essential duties for the employees or affiliates. Each one of the personnel should be able to understand the processes.
- Purchase and receive materials – the management must be able to understand all the specifications to check if it met the quality standards. It is essential to define the key characteristics of materials before you are going to start the process. Once the needed materials are already available, you should task your employees to check the shipment to make sure that the products delivered have met the standards.
- Verify the qualifications of your supplier – you have to properly perform quality assurance with regards to the more complex components. That is why companies are preferred to provide a specification to their requirements.
- Evaluate quality feedback – getting a feedback could be a great idea to help you improve the quality and item performance. You can easily determine your strengths and weaknesses by looking at the online reviews, suggestions, and complaints. Each of the business organizations must create a customer service team to cater and examine the reviews.
- Develop a process intended for corrective actions – all companies need to create a corrective plan that allows them to solve quality issues. Once you have already identified the cause of your problem, then every business must be able to implement a proper solution that would prevent things from happening again.
Practicing quality control gives you a positive impact when it comes to employee conduct. It also inspires employees to create more high quality goods that may lead to customer satisfaction.
It includes X-bar chart, Taguchi method, six sigma, and 100% inspection mode.
With a quality control business plan at hand, businesses can make sure that everything meets the standards including the corrective procedures to address a specific problem or concern. If you want to see more samples and format, check out some quality control business plan samples and templates provided in the article for your reference.
Related Posts
Free 50+ strategic planning samples in google docs | pages | pdf | ms word, free 10+ construction project plan samples in ms word | google docs | apple pages | pdf, free 10+ construction marketing business plan samples in ms word | google docs | pdf, free 17+ construction business continuity plan samples in ms word | google docs | pdf, free 11+ construction business development plan samples in ms word | google docs | pdf, free 20+ budget planning samples in pdf, free 20+ workout plan samples in ms word | google docs | pages | pdf, free 20+ lesson planning samples in pdf, free 14+ employee work plan templates in pdf | ms word, free 8+ sample weekly meal plan templates in pdf, free 17+ sample classroom management plan templates in pdf | ms word, free 13+ homework planner samples and templates in pdf | ms word, free 14+ leadership development plan samples in ms word | pages | google docs | pdf, free 15+ sample math lesson plan templates in pdf | ms word, free 11+ gym business plan templates in pdf | ms word, free 13+ sample quality manuals, free 11+ mortgage broker business plan samples, free 10+ quality assurance statement samples, free 10+ quality audit report samples.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Quality Control in a Service Business
- G.M. Hostage
As earlier HBR articles have emphasized, quality control is a crucial function in an organization that markets services. But is quality control the same thing in a service company as in a manufacturing concern? And what does management have to do to establish it in operations? Little has been written on these questions, though valuable […]
Since this article is about people, I shall begin with a story about a person I know. The purpose of this story is to provide a reference point for the discussion and analysis that follow, for in every case the programs to be described must be evaluated in terms of how well they meet the needs of particular individuals who, like the subject of my story, possess conflicting motives and desires.
- GH Mr. Hostage is president of restaurant operations for the Marriott Corporation. The largest of Marriott’s three operating groups, this organization has 20 functional divisions, nearly 1,200 company-operated and franchised units, and close to 20,000 employees. Before Mr. Hostage joined Marriott in 1963, he served with the Procter & Gamble Company.
Partner Center
All Formats
Plan Templates
15+ quality control plan templates in word | google docs | apple pages | pdf.
The best inputs give the best outputs. A quality control plan helps in keeping in check the rate of quality of the products and services, and also the quantity you provide that makes you different and unique from the others. It covers four main elements- the employees, the suppliers, assets and mainly, the clients. If you are looking for templates that can help you create an effective control plan , then you may check out and download our wide range of plan templates .

Plan Template Bundle

- Google Docs
Quality Control Plan Template

Restaurant Quality Control Plan Template

Simple Quality Action Plan Template

Design Quality Control Plan Template

- Apple Pages
Landscaping Quality Control Plan Template

Quality Assurance Plan Template

How to Create a Quality Control Plan in 6 Steps
Step 1: business plan and objectives, step 2: management review, step 3: responsibilities and authority, step 4: policies, step 5: resources and needs, step 6: internal audit and review, broker quality control plan sample template free.

Welding Quality Control Plan Word Format Free

Software Quality Control Plan PDF Format Free

Concrete Quality Control Plan Sample PDF Template

Individualized Quality Control Plan Example PDF Free
Free Mortgage Quality Control Plan Free PDF Format

General Designer Quality Control Plan Template

Free Site-Specific Quality Control Plan Template
Free Construction Quality Control Plan Template

Free Contractor Quality Control Plan Template

Conclusion:
General faqs, 1. what is a quality control plan, 2. what is the purpose of a quality control plan, 3. give an example of activities of quality control..
- Process checklists and standards
- Business documentation
- Project audit
- Inspection of products and services
- Deliverable peer reviews
- Software testing process, etc.
4. Where is the Quality Control Plan used?
5. what are the tools used for quality control.
- Checklists: used to check off items that are complete
- Flow charts : used for evaluating a sequence of events
- Stratification: used to divide the data and capture useful information for problem-solving
- Scatter diagrams: used to present the relationship between variables
- Fishbone diagrams, etc.
More in Plan Templates
Quality control chart template, spreadsheet with a chart template, assessment implementation plan template, simple quality control plan template, subcontractor quality control plan template, sample quality control plan template, project quality control plan template.
- 7+ Financial Plan Templates
- 10+ Operational Plan Templates
- 9+ Training Plan Templates
- 5+ Shooting Schedule Template
- 11+ School Counselor Lesson Plan Templates in PDF | Word
- 9+ Interdisciplinary Lesson Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Business Continuity Plan Templates in Google Docs | Ms Word | Pages | PDF
- 18+ Compensation Plan Templates in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Executive Bonus Plan Templates in PDF
- 8+ Facility Management Plan Templates in PDF
- 10+ Diversity Recruitment Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 11+ Audit Corrective Action Plan Templates in MS Word | Excel | PDF
- 9+ Recruitment Agency Marketing Plan Templates in PDF
- 10+ Recruitment Marketing Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Student Recruitment Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.

Project Management Templates | FREE Downloads Word, Excel, PDF, Visio
- #1 Mind Mapping Tool
- Collaborate Anywhere
- Stunning Presentations
- Simple Project Management
- Innovative Project Planning
- Creative Problem Solving

Quality Management Plan Template | FREE Download
This PMBOK template sets out how quality will be managed on the project. It includes the objectives, standards, roles, responsibilities and control procedures. It forms part of the Project Management plan. stakeholdermap.com
- Contents of the Quality Management Plan Template
- DOWNLOAD Quality Management Plan Template
- Other Project templates to download
The contents of the Quality Management Plan Template
Field description and tips to complete, project details and document control.
- Project Name and Reference
- Document information: ID, owner, issue date, last saved date, file name or path
- Document history: version, issue date, changes.
- Document approvals: role, name, signature, date
Quality Standards
Quality objectives.

Quality Roles and Responsibilities

Deliverables and processes subject to Quality Review

Quality Control Approach

Quality Management Plan Template
Word download - quality management plan template (word .doc), word download - quality management plan template (word .docx), opendocument download - quality management plan template (.odt), pdf download - quality management plan template (pdf), quality audit template, quality assurance checklist, quality metrics template, more project templates to download.
- Microsoft Project Plans – real world project plans in Microsoft Project.
- Project Management Templates – All of our FREE project management templates in Word and Excel
- 20 Common Project Risks
PMBOK Management Plans
- Change Management Plan
- Communications Management Plan
- Cost Management Plan
- Project Management Plan
- Schedule Management Plan
- Scope Management Plan
- Risk Management Plan
Share this Image


- Legal Templates
- Finance Templates
- Log Templates
- Planner Templates
- Agreement Templates
- Agenda Templates
- Certificates
- Analysis Templates
- Report Templates
- Letter Templates
- Medical Templates
- Remote Working Policy Template
- Work From Home Templates

30+ Free Simple Quality Control Plan Templates (PDF, Word)
A quality control plan (QCP), also known as a quality assurance plan (QAP), is a structured document or set of procedures and guidelines that outline the specific quality control measures and processes to be implemented during a project, manufacturing process, or any other type of operation. The primary purpose of a QCP is to ensure that products or services meet predefined quality standards, customer requirements, and regulatory compliance. In this article, you’ll find a collection of free Simple Quality Control Plan Templates and samples in PDF, Word, and Excel format to help you make your plan effective.
Table of Contents
Download Free Simple Quality Control Plan Templates
Main three types of quality control plan.
Quality control plans can vary depending on the industry and the specific project or product being produced. However, there are three main types of quality control plans that are commonly used across different sectors:
- Product-Based Quality Control Plan: This type of QCP focuses on ensuring the quality of the final product. It outlines the specific quality standards and criteria that the product must meet. It typically includes details about product specifications, inspection and testing methods, and acceptance criteria. Product-based QCPs are common in manufacturing and production industries where the end product’s quality is critical.
- Process-Based Quality Control Plan: In a process-based QCP, the emphasis is on monitoring and controlling the production process itself to ensure that it consistently produces products that meet quality standards. This type of plan often includes process flow charts, standard operating procedures(SOPs), and control charts to track key process parameters. It is particularly important in industries like chemical manufacturing, where variations in the production process can impact product quality.
- Supplier-Based Quality Control Plan: Supplier-based quality control plans are employed to manage the quality of components or materials supplied by external vendors or suppliers.
These plans outline the criteria and procedures for evaluating and accepting materials from suppliers. They may include supplier audits, quality checks at the receiving stage, and protocols for addressing non-conformities. Supplier-based QCPs are essential in industries such as automotive manufacturing, where various components are sourced from different suppliers.
Why Is A Quality Control Plan Important
A quality control plan is important for several reasons, especially in industries where the quality of products or services is critical. Here are some important quality control plans:
- A QCP outlines the specific standards and criteria that need to be met to ensure consistency in the quality of products or services. This consistency is essential for building trust with customers and clients.
- By defining quality standards and inspection procedures, a QCP helps identify defects and errors early in the production or service delivery process. This proactive approach reduces the likelihood of defects reaching customers.
- When products or services consistently meet or exceed quality standards, customers are more likely to be satisfied. In many industries, there are legal and regulatory requirements related to product quality and safety. A QCP helps ensure that your organization complies with these requirements, reducing the risk of legal issues.
- A QCP often includes a feedback loop for continuous improvement. By regularly reviewing and updating the plan, you can identify areas where processes can be optimized to enhance quality and efficiency.
- Quality control processes can help identify and mitigate risks associated with product or service quality. By proactively addressing potential issues, you can reduce the likelihood of costly problems arising later.
- A QCP often involves collecting and analyzing data related to quality metrics. This data can be used to make informed decisions about process improvements, resource allocation, and other aspects of quality management.
Key Element Quality Control Plan Templates
Here are some Key Element Quality Control Plans:
Quality Objective
The plan should start by clearly defining the quality objective or goals that need to be achieved. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
Quality Standards
Specify the quality standards or specifications that the products or services must meet. These standards may be industry-specific, customer-specific, or based on regulatory requirements.
Quality Control Activities
Outline the specific quality control activities and tests performed at various stages of the project or production process. This can include inspections, testing, data collection, and documentation.
Responsibilities
Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of individuals or terms involved in quality control. This ensures that everyone understands their duties and accountabilities in maintaining quality.
Acceptance Criteria
Describe the requirements that will be used to determine whether a product or service meets the required quality standards. This could include tolerance limits and sampling plans.
Documentation
Detail the documentation procedures, including record keeping, data management, and reporting. Accurate and organized documentation is essential for traceability and quality improvement.
Quality Audits
Outline plans for conducting regular quality audits or inspections to verify compliance with the QCP.
Address the training requirements for personnel involved in quality control activities. Ensure that employees have the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their roles effectively.
Benefits Of Using Quality Control Plan Templates
Using quality control plan templates can offer several benefits for organizations involved in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, healthcare, and more. Here are some advantages of using a quality control plan template:
- Quality control plan templates provide a standardized framework for documenting and implementing quality control processes. This consistency helps ensure that all relevant aspects of quality management are considered and addressed consistently across projects or processes.
- Templates can save time by eliminating the need to create a quality control plan from scratch. Organizations can adapt and customize pre-designed templates to their specific needs, reducing the time and effort required to create a new plan.
- Templates often include pre-defined sections and guidelines for documenting quality control procedures and responsibilities. This can help streamline the planning process and make it easier for teams to develop and execute quality control activities efficiently.
- These templates can be designed to align with industry-specific standards and regulations. Using a compliant template can ensure that the organization’s quality control processes meet the necessary requirements and reduce the risk of non-compliance.
- Templates provide a clear structure for documenting quality control procedures, responsibilities, and key performance indicators. This enhances communication within the organization by ensuring that all stakeholders have a shared understanding of quality control processes.
- Templates can serve as valuable training tools for new employees or team members. They provide a documented reference point for understanding quality control procedures, making it easier to onboard new personnel and maintain consistency in training.
- These templates can include sections for recording and analyzing quality data and performance metrics. This data can help organizations identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance their quality control processes over time.
- By documenting quality control processes in a structured manner, organizations can identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies. This proactive approach can help prevent quality issues and minimize their impact on projects or operations.
How To Use A Quality Control Plan Templates
A quality control plan template is a valuable tool for ensuring that products are services meet established quality standards and specifications. It provides a structured approach to quality management, outlining the processes, procedures, and responsibilities needed to maintain consistent quality. Here are some points that describe how to use templates effectively:
- Select a template that completes your needs and fill out the basic information in the template. This should include the project or process name, location, start and end dates, and the names of key stakeholders and team members.
- Clearly state the quality objectives and Goals for your project or process. This might include specific quality standards, performance criteria, and customer expectations.
- Identify the specific quality control activities that need to be performed. These can include inspections, tests, audits, or other methods for checking quality. Each activity should be described in detail, including who is responsible, when it will be conducted, and what criteria will be used for evaluation.
- Define the criteria that must be met for each quality control activity to be considered successful. This should be based on Industry standards, project requirements, or customer expectations.
- Clearly assign responsibilities for each quality control activity. Identify who will be responsible for conducting inspections, tests, and audits, as well as who will be responsible for reviewing and approving the results.
- Develop a timeline that outlines when each quality control activity will occur. ensure that this schedule aligns with the overall project or process timeline.
- Specify how quality-related information will be reported and communicated within the project team and to relevant stakeholders, including templates for quality reports and forms if necessary.
- Before implementing the QCP, ensure that all key stakeholders review and approve the plan. This ensures everyone is on the same page regarding quality expectations and responsibilities.
- Begin executing the quality control activities as outlined in the QCP. Make sure that all team members are aware of their roles and responsibilities.
- Maintain thorough documentation of all quality control activities and their results. This documentation is essential for future reference and auditing purposes.
- As the project or process progresses, update the QCP as needed to reflect any changes or improvements in quality control procedures.
How to Download Free Quality Control Plan Templates as a PDF or Word File
Downloading free Quality Control Plan Templates in PDF or Word file format is relatively easy. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to do it:
- Once you find a template, click on it to open and view it. Make sure to replace the sample content with your own details, including your name, contact information, work experience, skills, and education.
- After customizing your resume, look for options to download it. That Website offers the choice to download your resume as a PDF or Word file. Select your preferred format, and the resume will be downloaded to your computer.
- Save the downloaded file to a location on your computer where you can easily access it. Open the file to review it and make sure all your information is accurately represented.
- If you need to make further edits or updates to your resume, you can do so by opening the download file in a PDF reader or Microsoft Word.
- Please note that when you use a website for free resume templates, you may be required to create an account or provide your email address to access them.
Ultimately the goal of a Quality Control Plan is to ensure customer satisfaction. The conclusion may reiterate that meeting or exceeding customer expectations is a primary driver of success. It may end by expressing a commitment to excellence and a dedication to upholding the highest quality standards in all aspects of the project or process.
In summary, this work is a reminder of the fundamental principles and objectives of quality control and encourages stakeholders to prioritize and maintain these principles throughout the project or process. It reinforces the idea that quality control is an ongoing process that requires dedication, vigilance, and a commitment to delivering high-quality outcomes.
Reference Link
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
Related Posts:

- 10+ Free Delivery Slip Templates – Excel, DOC, PDF
- 15+ Impact Assessment (IA) Templates Free
- 20+ Blank Slip Templates – Free Printable Sample
- 25+ Free Remote Working Policy Template & Sample (PDF)
- 50+ Free Work From Home Form Templates
Everyone loves free Templates

American Templates provides you printable and downloadable templates and resources. All these templates are free to download and use for anyone.
© 2022 AmericanTemplates
- Privacy Policy

Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
This is the ultimate guide to creating a comprehensive and effective plan to start a business . In today’s dynamic business landscape, having a well-crafted business plan is an important first step to securing funding, attracting partners, and navigating the challenges of entrepreneurship.
This guide has been designed to help you create a winning plan that stands out in the ever-evolving marketplace. U sing real-world examples and a free downloadable template, it will walk you through each step of the process.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your very first startup, the guide will give you the insights, tools, and confidence you need to create a solid foundation for your business.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Embarking on the journey of creating a successful business requires a solid foundation, and a well-crafted business plan is the cornerstone. Here is the process of writing a comprehensive business plan and the main parts of a winning business plan . From setting objectives to conducting market research, this guide will have everything you need.
Executive Summary

The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your business plan, offering a snapshot of your venture’s core aspects. This section should captivate and inform, succinctly summarizing the essence of your plan.
It’s crucial to include a clear mission statement, a brief description of your primary products or services, an overview of your target market, and key financial projections or achievements.
Think of it as an elevator pitch in written form: it should be compelling enough to engage potential investors or stakeholders and provide them with a clear understanding of what your business is about, its goals, and why it’s a promising investment.
Example: EcoTech is a technology company specializing in eco-friendly and sustainable products designed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Our mission is to create innovative solutions that contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Our target market includes environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. We project a 200% increase in revenue within the first three years of operation.
Overview and Business Objectives

In the Overview and Business Objectives section, outline your business’s core goals and the strategic approaches you plan to use to achieve them. This section should set forth clear, specific objectives that are attainable and time-bound, providing a roadmap for your business’s growth and success.
It’s important to detail how these objectives align with your company’s overall mission and vision. Discuss the milestones you aim to achieve and the timeframe you’ve set for these accomplishments.
This part of the plan demonstrates to investors and stakeholders your vision for growth and the practical steps you’ll take to get there.
Example: EcoTech’s primary objective is to become a market leader in sustainable technology products within the next five years. Our key objectives include:
- Introducing three new products within the first two years of operation.
- Achieving annual revenue growth of 30%.
- Expanding our customer base to over 10,000 clients by the end of the third year.
Company Description

The Company Description section is your opportunity to delve into the details of your business. Provide a comprehensive overview that includes your company’s history, its mission statement, and its vision for the future.
Highlight your unique selling proposition (USP) – what makes your business stand out in the market. Explain the problems your company solves and how it benefits your customers.
Include information about the company’s founders, their expertise, and why they are suited to lead the business to success. This section should paint a vivid picture of your business, its values, and its place in the industry.
Example: EcoTech is committed to developing cutting-edge sustainable technology products that benefit both the environment and our customers. Our unique combination of innovative solutions and eco-friendly design sets us apart from the competition. We envision a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand, leading to a greener planet.
Define Your Target Market

Defining Your Target Market is critical for tailoring your business strategy effectively. This section should describe your ideal customer base in detail, including demographic information (such as age, gender, income level, and location) and psychographic data (like interests, values, and lifestyle).
Elucidate on the specific needs or pain points of your target audience and how your product or service addresses these. This information will help you know your target market and develop targeted marketing strategies.
Example: Our target market comprises environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking for innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Our ideal customers are those who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly products.
Market Analysis

The Market Analysis section requires thorough research and a keen understanding of the industry. It involves examining the current trends within your industry, understanding the needs and preferences of your customers, and analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
This analysis will enable you to spot market opportunities and anticipate potential challenges. Include data and statistics to back up your claims, and use graphs or charts to illustrate market trends.
This section should demonstrate that you have a deep understanding of the market in which you operate and that your business is well-positioned to capitalize on its opportunities.
Example: The market for eco-friendly technology products has experienced significant growth in recent years, with an estimated annual growth rate of 10%. As consumers become increasingly aware of environmental issues, the demand for sustainable solutions continues to rise.
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis

A SWOT analysis in your business plan offers a comprehensive examination of your company’s internal and external factors. By assessing Strengths, you showcase what your business does best and where your capabilities lie.
Weaknesses involve an honest introspection of areas where your business may be lacking or could improve. Opportunities can be external factors that your business could capitalize on, such as market gaps or emerging trends.
Threats include external challenges your business may face, like competition or market changes. This analysis is crucial for strategic planning, as it helps in recognizing and leveraging your strengths, addressing weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and preparing for potential threats.
Including a SWOT analysis demonstrates to stakeholders that you have a balanced and realistic understanding of your business in its operational context.
- Innovative and eco-friendly product offerings.
- Strong commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Skilled and experienced team with expertise in technology and sustainability.
Weaknesses:
- Limited brand recognition compared to established competitors.
- Reliance on third-party manufacturers for product development.
Opportunities:
- Growing consumer interest in sustainable products.
- Partnerships with environmentally-focused organizations and influencers.
- Expansion into international markets.
- Intense competition from established technology companies.
- Regulatory changes could impact the sustainable technology market.
Competitive Analysis

In this section, you’ll analyze your competitors in-depth, examining their products, services, market positioning, and pricing strategies. Understanding your competition allows you to identify gaps in the market and tailor your offerings to outperform them.
By conducting a thorough competitive analysis, you can gain insights into your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, enabling you to develop strategies to differentiate your business and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Example: Key competitors include:
GreenTech: A well-known brand offering eco-friendly technology products, but with a narrower focus on energy-saving devices.
EarthSolutions: A direct competitor specializing in sustainable technology, but with a limited product range and higher prices.
By offering a diverse product portfolio, competitive pricing, and continuous innovation, we believe we can capture a significant share of the growing sustainable technology market.
Organization and Management Team

Provide an overview of your company’s organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. Introduce your management team, highlighting their expertise and experience to demonstrate that your team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
Showcasing your team’s background, skills, and accomplishments instills confidence in investors and other stakeholders, proving that your business has the leadership and talent necessary to achieve its objectives and manage growth effectively.
Example: EcoTech’s organizational structure comprises the following key roles: CEO, CTO, CFO, Sales Director, Marketing Director, and R&D Manager. Our management team has extensive experience in technology, sustainability, and business development, ensuring that we are well-equipped to execute our business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered

Describe the products or services your business offers, focusing on their unique features and benefits. Explain how your offerings solve customer pain points and why they will choose your products or services over the competition.
This section should emphasize the value you provide to customers, demonstrating that your business has a deep understanding of customer needs and is well-positioned to deliver innovative solutions that address those needs and set your company apart from competitors.
Example: EcoTech offers a range of eco-friendly technology products, including energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers, and smart home devices that optimize energy usage. Our products are designed to help customers reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Marketing and Sales Strategy

In this section, articulate your comprehensive strategy for reaching your target market and driving sales. Detail the specific marketing channels you plan to use, such as social media, email marketing, SEO, or traditional advertising.
Describe the nature of your advertising campaigns and promotional activities, explaining how they will capture the attention of your target audience and convey the value of your products or services. Outline your sales strategy, including your sales process, team structure, and sales targets.
Discuss how these marketing and sales efforts will work together to attract and retain customers, generate leads, and ultimately contribute to achieving your business’s revenue goals.
This section is critical to convey to investors and stakeholders that you have a well-thought-out approach to market your business effectively and drive sales growth.
Example: Our marketing strategy includes digital advertising, content marketing, social media promotion, and influencer partnerships. We will also attend trade shows and conferences to showcase our products and connect with potential clients. Our sales strategy involves both direct sales and partnerships with retail stores, as well as online sales through our website and e-commerce platforms.
Logistics and Operations Plan

The Logistics and Operations Plan is a critical component that outlines the inner workings of your business. It encompasses the management of your supply chain, detailing how you acquire raw materials and manage vendor relationships.
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
Quality control measures are essential to maintain product standards and customer satisfaction. This plan assures investors and stakeholders of your operational competency and readiness to meet business demands.
Highlighting your commitment to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction underlines your business’s capability to maintain smooth, effective operations even as it scales.
Example: EcoTech partners with reliable third-party manufacturers to produce our eco-friendly technology products. Our operations involve maintaining strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring quality control, and managing inventory.
We also prioritize efficient distribution through various channels, including online platforms and retail partners, to deliver products to our customers in a timely manner.
Financial Projections Plan

In the Financial Projections Plan, lay out a clear and realistic financial future for your business. This should include detailed projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the next three to five years.
Ground these projections in solid assumptions based on your market analysis, industry benchmarks, and realistic growth scenarios. Break down revenue streams and include an analysis of the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and potential investments.
This section should also discuss your break-even analysis, cash flow projections, and any assumptions about external funding requirements.
By presenting a thorough and data-backed financial forecast, you instill confidence in potential investors and lenders, showcasing your business’s potential for profitability and financial stability.
This forward-looking financial plan is crucial for demonstrating that you have a firm grasp of the financial nuances of your business and are prepared to manage its financial health effectively.
Example: Over the next three years, we expect to see significant growth in revenue, driven by new product launches and market expansion. Our financial projections include:
- Year 1: $1.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $200,000.
- Year 2: $3 million in revenue, with a net profit of $500,000.
- Year 3: $4.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $1 million.
These projections are based on realistic market analysis, growth rates, and product pricing.
Income Statement

The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of your company’s revenues and expenses over a specified period. It helps you track your business’s financial performance and identify trends, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your financial goals.
Regularly reviewing and analyzing your income statement allows you to monitor the health of your business, evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies, and make data-driven decisions to optimize profitability and growth.
Example: The income statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
- Revenue: $1,500,000
- Cost of Goods Sold: $800,000
- Gross Profit: $700,000
- Operating Expenses: $450,000
- Net Income: $250,000
This statement highlights our company’s profitability and overall financial health during the first year of operation.
Cash Flow Statement

A cash flow statement is a crucial part of a financial business plan that shows the inflows and outflows of cash within your business. It helps you monitor your company’s liquidity, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to cover operating expenses, pay debts, and invest in growth opportunities.
By including a cash flow statement in your business plan, you demonstrate your ability to manage your company’s finances effectively.
Example: The cash flow statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
Operating Activities:
- Depreciation: $10,000
- Changes in Working Capital: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Operating Activities: $210,000
Investing Activities:
- Capital Expenditures: -$100,000
- Net Cash from Investing Activities: -$100,000
Financing Activities:
- Proceeds from Loans: $150,000
- Loan Repayments: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Financing Activities: $100,000
- Net Increase in Cash: $210,000
This statement demonstrates EcoTech’s ability to generate positive cash flow from operations, maintain sufficient liquidity, and invest in growth opportunities.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan

1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively.
2. Conduct thorough research: Before writing your business plan, gather as much information as possible about your industry, competitors, and target market. Use reliable sources and industry reports to inform your analysis and make data-driven decisions.
3. Set realistic goals: Your business plan should outline achievable objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting realistic goals demonstrates your understanding of the market and increases the likelihood of success.
4. Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what sets your business apart from the competition. Emphasize your USP throughout your business plan to showcase your company’s value and potential for success.
5. Be flexible and adaptable: A business plan is a living document that should evolve as your business grows and changes. Be prepared to update and revise your plan as you gather new information and learn from your experiences.
6. Use visuals to enhance understanding: Include charts, graphs, and other visuals to help convey complex data and ideas. Visuals can make your business plan more engaging and easier to digest, especially for those who prefer visual learning.
7. Seek feedback from trusted sources: Share your business plan with mentors, industry experts, or colleagues and ask for their feedback. Their insights can help you identify areas for improvement and strengthen your plan before presenting it to potential investors or partners.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
The template is divided into the following sections:
- Mission statement
- Business Overview
- Key products or services
- Target market
- Financial highlights
- Company goals
- Strategies to achieve goals
- Measurable, time-bound objectives
- Company History
- Mission and vision
- Unique selling proposition
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Pain points
- Industry trends
- Customer needs
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Competitor products and services
- Market positioning
- Pricing strategies
- Organizational structure
- Key roles and responsibilities
- Management team backgrounds
- Product or service features
- Competitive advantages
- Marketing channels
- Advertising campaigns
- Promotional activities
- Sales strategies
- Supply chain management
- Inventory control
- Production processes
- Quality control measures
- Projected revenue
- Assumptions
- Cash inflows
- Cash outflows
- Net cash flow
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines an organization’s goals, objectives, and the steps required to achieve them. It serves as a roadmap as you start a business , guiding the company’s direction and growth while identifying potential obstacles and opportunities.
Typically, a business plan covers areas such as market analysis, financial projections, marketing strategies, and organizational structure. It not only helps in securing funding from investors and lenders but also provides clarity and focus to the management team.
A well-crafted business plan is a very important part of your business startup checklist because it fosters informed decision-making and long-term success.

Why You Should Write a Business Plan
Understanding the importance of a business plan in today’s competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five compelling reasons to write a business plan:
- Attract Investors and Secure Funding : A well-written business plan demonstrates your venture’s potential and profitability, making it easier to attract investors and secure the necessary funding for growth and development. It provides a detailed overview of your business model, target market, financial projections, and growth strategies, instilling confidence in potential investors and lenders that your company is a worthy investment.
- Clarify Business Objectives and Strategies : Crafting a business plan forces you to think critically about your goals and the strategies you’ll employ to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for success. This process helps you refine your vision and prioritize the most critical objectives, ensuring that your efforts are focused on achieving the desired results.
- Identify Potential Risks and Opportunities : Analyzing the market, competition, and industry trends within your business plan helps identify potential risks and uncover untapped opportunities for growth and expansion. This insight enables you to develop proactive strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities, positioning your business for long-term success.
- Improve Decision-Making : A business plan serves as a reference point so you can make informed decisions that align with your company’s overall objectives and long-term vision. By consistently referring to your plan and adjusting it as needed, you can ensure that your business remains on track and adapts to changes in the market, industry, or internal operations.
- Foster Team Alignment and Communication : A shared business plan helps ensure that all team members are on the same page, promoting clear communication, collaboration, and a unified approach to achieving the company’s goals. By involving your team in the planning process and regularly reviewing the plan together, you can foster a sense of ownership, commitment, and accountability that drives success.
What are the Different Types of Business Plans?
In today’s fast-paced business world, having a well-structured roadmap is more important than ever. A traditional business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s goals and strategies, helping you make informed decisions and achieve long-term success. There are various types of business plans, each designed to suit different needs and purposes. Let’s explore the main types:
- Startup Business Plan: Tailored for new ventures, a startup business plan outlines the company’s mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. It helps entrepreneurs clarify their vision, secure funding from investors, and create a roadmap for their business’s future. Additionally, this plan identifies potential challenges and opportunities, which are crucial for making informed decisions and adapting to changing market conditions.
- Internal Business Plan: This type of plan is intended for internal use, focusing on strategies, milestones, deadlines, and resource allocation. It serves as a management tool for guiding the company’s growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. The internal business plan also helps identify areas of improvement, fosters collaboration among team members, and provides a reference point for measuring performance.
- Strategic Business Plan: A strategic business plan outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for the company’s direction. It typically includes a SWOT analysis, market research, and competitive analysis. This plan allows businesses to align their resources with their objectives, anticipate changes in the market, and develop contingency plans. By focusing on the big picture, a strategic business plan fosters long-term success and stability.
- Feasibility Business Plan: This plan is designed to assess the viability of a business idea, examining factors such as market demand, competition, and financial projections. It is often used to decide whether or not to pursue a particular venture. By conducting a thorough feasibility analysis, entrepreneurs can avoid investing time and resources into an unviable business concept. This plan also helps refine the business idea, identify potential obstacles, and determine the necessary resources for success.
- Growth Business Plan: Also known as an expansion plan, a growth business plan focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. It includes market analysis, new product or service offerings, and financial projections to support expansion plans. This type of plan is essential for businesses looking to enter new markets, increase their customer base, or launch new products or services. By outlining clear growth strategies, the plan helps ensure that expansion efforts are well-coordinated and sustainable.
- Operational Business Plan: This type of plan outlines the company’s day-to-day operations, detailing the processes, procedures, and organizational structure. It is an essential tool for managing resources, streamlining workflows, and ensuring smooth operations. The operational business plan also helps identify inefficiencies, implement best practices, and establish a strong foundation for future growth. By providing a clear understanding of daily operations, this plan enables businesses to optimize their resources and enhance productivity.
- Lean Business Plan: A lean business plan is a simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements such as value proposition, customer segments, revenue streams, and cost structure. It is perfect for startups looking for a flexible, adaptable planning approach. The lean business plan allows for rapid iteration and continuous improvement, enabling businesses to pivot and adapt to changing market conditions. This streamlined approach is particularly beneficial for businesses in fast-paced or uncertain industries.
- One-Page Business Plan: As the name suggests, a one-page business plan is a concise summary of your company’s key objectives, strategies, and milestones. It serves as a quick reference guide and is ideal for pitching to potential investors or partners. This plan helps keep teams focused on essential goals and priorities, fosters clear communication, and provides a snapshot of the company’s progress. While not as comprehensive as other plans, a one-page business plan is an effective tool for maintaining clarity and direction.
- Nonprofit Business Plan: Specifically designed for nonprofit organizations, this plan outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation. It helps secure grants and donations while ensuring the organization stays on track with its objectives. The nonprofit business plan also helps attract volunteers, board members, and community support. By demonstrating the organization’s impact and plans for the future, this plan is essential for maintaining transparency, accountability, and long-term sustainability within the nonprofit sector.
- Franchise Business Plan: For entrepreneurs seeking to open a franchise, this type of plan focuses on the franchisor’s requirements, as well as the franchisee’s goals, strategies, and financial projections. It is crucial for securing a franchise agreement and ensuring the business’s success within the franchise system. This plan outlines the franchisee’s commitment to brand standards, marketing efforts, and operational procedures, while also addressing local market conditions and opportunities. By creating a solid franchise business plan, entrepreneurs can demonstrate their ability to effectively manage and grow their franchise, increasing the likelihood of a successful partnership with the franchisor.
Using Business Plan Software

Creating a comprehensive business plan can be intimidating, but business plan software can streamline the process and help you produce a professional document. These tools offer a number of benefits, including guided step-by-step instructions, financial projections, and industry-specific templates. Here are the top 5 business plan software options available to help you craft a great business plan.
1. LivePlan
LivePlan is a popular choice for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features. It offers over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, and the ability to track your progress against key performance indicators. With LivePlan, you can create visually appealing, professional business plans that will impress investors and stakeholders.
2. Upmetrics
Upmetrics provides a simple and intuitive platform for creating a well-structured business plan. It features customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, and collaboration capabilities, allowing you to work with team members and advisors. Upmetrics also offers a library of resources to guide you through the business planning process.
Bizplan is designed to simplify the business planning process with a drag-and-drop builder and modular sections. It offers financial forecasting tools, progress tracking, and a visually appealing interface. With Bizplan, you can create a business plan that is both easy to understand and visually engaging.
Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on your inputs. It provides industry-specific templates, financial forecasting, and a unique performance score that updates as you make changes to your plan. Enloop also offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget.
5. Tarkenton GoSmallBiz
Developed by NFL Hall of Famer Fran Tarkenton, GoSmallBiz is tailored for small businesses and startups. It features a guided business plan builder, customizable templates, and financial projection tools. GoSmallBiz also offers additional resources, such as CRM tools and legal document templates, to support your business beyond the planning stage.
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan.
A good business plan is a well-researched, clear, and concise document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. It should be adaptable to change and provide a roadmap for achieving success.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
The three main purposes of a business plan are to guide the company’s strategy, attract investment, and evaluate performance against objectives. Here’s a closer look at each of these:
- It outlines the company’s purpose and core values to ensure that all activities align with its mission and vision.
- It provides an in-depth analysis of the market, including trends, customer needs, and competition, helping the company tailor its products and services to meet market demands.
- It defines the company’s marketing and sales strategies, guiding how the company will attract and retain customers.
- It describes the company’s organizational structure and management team, outlining roles and responsibilities to ensure effective operation and leadership.
- It sets measurable, time-bound objectives, allowing the company to plan its activities effectively and make strategic decisions to achieve these goals.
- It provides a comprehensive overview of the company and its business model, demonstrating its uniqueness and potential for success.
- It presents the company’s financial projections, showing its potential for profitability and return on investment.
- It demonstrates the company’s understanding of the market, including its target customers and competition, convincing investors that the company is capable of gaining a significant market share.
- It showcases the management team’s expertise and experience, instilling confidence in investors that the team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
- It establishes clear, measurable objectives that serve as performance benchmarks.
- It provides a basis for regular performance reviews, allowing the company to monitor its progress and identify areas for improvement.
- It enables the company to assess the effectiveness of its strategies and make adjustments as needed to achieve its objectives.
- It helps the company identify potential risks and challenges, enabling it to develop contingency plans and manage risks effectively.
- It provides a mechanism for evaluating the company’s financial performance, including revenue, expenses, profitability, and cash flow.
Can I write a business plan by myself?
Yes, you can write a business plan by yourself, but it can be helpful to consult with mentors, colleagues, or industry experts to gather feedback and insights. There are also many creative business plan templates and business plan examples available online, including those above.
We also have examples for specific industries, including a using food truck business plan , salon business plan , farm business plan , daycare business plan , and restaurant business plan .
Is it possible to create a one-page business plan?
Yes, a one-page business plan is a condensed version that highlights the most essential elements, including the company’s mission, target market, unique selling proposition, and financial goals.
How long should a business plan be?
A typical business plan ranges from 20 to 50 pages, but the length may vary depending on the complexity and needs of the business.
What is a business plan outline?
A business plan outline is a structured framework that organizes the content of a business plan into sections, such as the executive summary, company description, market analysis, and financial projections.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
The five most common business plan mistakes include inadequate research, unrealistic financial projections, lack of focus on the unique selling proposition, poor organization and structure, and failure to update the plan as circumstances change.
What questions should be asked in a business plan?
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan focuses on the overall vision, goals, and tactics of a company, while a strategic plan outlines the specific strategies, action steps, and performance measures necessary to achieve the company’s objectives.
How is business planning for a nonprofit different?
Nonprofit business planning focuses on the organization’s mission, social impact, and resource management, rather than profit generation. The financial section typically includes funding sources, expenses, and projected budgets for programs and operations.
Image: Envato Elements

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.
- Guide: Control Plan
Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is an experienced continuous improvement manager with a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt and a Bachelor's degree in Business Management. With more than ten years of experience applying his skills across various industries, Daniel specializes in optimizing processes and improving efficiency. His approach combines practical experience with a deep understanding of business fundamentals to drive meaningful change.
- Last Updated: June 11, 2023
- Learn Lean Sigma
In business it is not uncommon for processes and outputs from processes to be out of control and need action to be taken to address them. This is where Control Plans become extremely useful. Control plans have been developed to support lean Six Sigma process and quality management systems in measuring critical-to-quality (CTQ) measures of processes and their outputs to ensure they remain in control with regular data collection and clear actions to be taken to address issues if they arise.
Control plans are mostly popularized and used within the manufacturing sector. However, they can be useful for a range of processes that output variables that can be measured and controlled.
Table of Contents
What is a control plan.
A Control Plan in its basic form is a document that outlines the process, steps and actions needed to manage, control, and ensure the quality of a process or product. Developed from the principles of Lean Six Sigma, the tool is used to many industries, such as manufacturing, logistics, automotive, and aerospace.
Control plans may vary slightly from business to business as teams and management tweak them to suit local business needs. However, the Control Plan typically consists of elements such as process input variables, output variables, control points (limits), what measurements are to be taken, and actions to be taken if a deviation occurs.
Below you can see a good example of how a control plan may look. You can also download this control plan from our template section.
A control plan is usually a tool you will use towards the end of an improvement project, such as in the Control phase of the DMAIC methodology, and continues to serve as a “living document,” which means it is continually reviewed and updated as the process evolves or new data becomes available.
How to Create a Control Plan
Creating a Control Plan is an important process that involves several steps. The guide below will clearly explain each step to guide you through creating a robust and effective Control Plan.
Step 1: Identify the Process
The first step in creating a control plan is to identify a process that you are looking to control. This should be a process that is critical to the quality of your product or service and would have a significant impact on customer satisfaction or operational efficiency if it were to go wrong. Therefore, lend them to a key candidate of a process to control
It is important to have a clear understanding of the flow of the process, including the inputs and outputs and all the steps involved. It can be useful to use a tool such as a flowchart to map out the process to ensure you fully understand all the elements and variables of the process.
Step 2: List CTQs (Critical to Quality Characteristics)
Once the process has been identified, the next step in the process is to identify the CTQ characteristics. These are the key attributes or features of the product or service that need to be controlled to ensure quality. The best way to identify what the CTQs are is to understand the customer requirements, such as product specifications.
For example, let’s say a business manufactures brake pads, and the CTQ is the thickness tolerance of the brake pads; this might be ±0.5mm.
Step 3: Select Measurement Methods
Once you have listed all the CTQs that you want to control, decide how you will measure these characteristics. The method that you decide on should be accurate, reliable, and repeatable and follow the principles of Attribute Agreement Analysis (AAA). The measurement method should consider what tools, instruments, or techniques will be used. Additionally, it is important to define the frequency with which the measurement is taken and what the acceptable limits or tolerances are for each CTQ.
Step 4: Determine Control Methods
Now that you know what CTQs you want to control and the methods used to measure them you need to determine the methods of control. Control methods are the strategies, tools or techniques used to ensure that the process stays within the defined limits or customer spec limits. Popular tools and techniques used to control processes and variables include Statistical Process Control (SPC) charts, Mistake Proofing (Poka Yoke) or Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) / Standard Work Instructions (SWI), which control method you use will depend on the type of process and CTQ identified.
Step 5: Develop Action Plans
If in the event a process or variable goes out of control it is important to take action to address and correct the process and bring it back under control. To do this action plans should be developed as part of the control plan. These action plans define what steps need to be taken to bring the process back within its acceptable limits.
Like any good action plan it needs make it clear what action needs to be taken and who is responsible for taking that action.
Step 6: Train the Team
Now that you have developed a control plan its important to ensure that in the event it is needed, it is used. Therefore, you should clearly communicate what the CTQs are, what the operators need to do to measure the process and clarify what actions need to be taken by whom if a process goes out of control.
Training is key to the success of the control plan being followed.
Step 7: Implement and Monitor
Now that you have developed and trained out the plan, the next step is to officially implement it. This involves putting all the required measures and controls into place. If special tools like calipers or software’s are needed to take measurements, ensure they have what they need. The process then needs to be continuously monitored to ensure the process remains within the stated control limits. Data should then be analyzed at regular intervals to detect and trends or deviations in the process outputs.
Step 8: Review and Update
Finally Step 8, it is important to remember that the control plan is a living document that should be reviewed and updated regularly as the process or CTQs change. Regular reviews will ensure the Control Plan remains effective and relevant.
By following this process you should be able to develop a robust Control Plan that will help you control your process and ensure quality and drive continuous improvement of the process.
Implementing a Control Plan is beneficial for controlling the quality and performance of processes and preventing defects or quality issues. From identifying the process to training your team, each step is geared towards ensuring that your business operations are as seamless as possible. The goal is not just to maintain current performance levels but to set the stage for continuous improvement.
As we’ve outlined in this guide, creating and implementing a Control Plan is a detailed process involving multiple steps, each is important and builds on the previous step. You should also remember, a Control Plan is a living document must be regularly monitored and updated to its sustain success.
- Westgard, J.O., 2003. Internal quality control: planning and implementation strategies. Annals of clinical biochemistry , 40 (6), pp.593-611.
- Mehrasa, M., Pouresmaeil, E., Jørgensen, B.N. and Catalão, J.P., 2015. A control plan for the stable operation of microgrids during grid-connected and islanded modes. Electric Power Systems Research , 129 , pp.10-22.
Q: What is a control plan?
A: A control plan is a documented framework that outlines the methods, procedures, and actions necessary to maintain process control and ensure consistent and acceptable outcomes. It helps identify critical control points, measurement methods, control limits, and corrective actions to monitor and manage process performance effectively.
Q: Why is a control plan important?
A: A control plan is important because it helps organizations maintain process stability, minimize process variations, and ensure consistent product or service quality. It provides a systematic approach to monitor, control, and improve processes, leading to reduced defects, improved customer satisfaction, and increased operational efficiency.
Q: How does a control plan fit into the DMAIC methodology?
A: A control plan is a key component of the Control phase in the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology. In this phase, the control plan is developed to sustain the improvements made during the earlier phases. It helps ensure that the process remains in control, deviations are promptly addressed, and continuous improvement efforts are sustained.
Q: What are critical control points?
A: Critical control points are specific stages or activities within a process where variations can significantly impact the quality or outcome. These points need to be closely monitored and controlled to prevent defects or deviations from the desired target. Examples include temperature control, pressure control, or specific steps in a manufacturing process.
Q: How are control limits determined?
A: Control limits are determined based on historical data, customer specifications, or statistical analysis. Historical data provides insights into the process performance, while customer specifications define the acceptable range for product quality. Statistical techniques, such as process capability analysis, can help determine control limits based on the process’s inherent variation and the desired level of performance.
Q: What is the role of corrective actions in a control plan?
A: Corrective actions are specified in a control plan to address deviations from control limits or target values. These actions provide a systematic approach to identify and resolve the root causes of variations, ensuring that the process is brought back into control. Corrective actions may involve adjusting process parameters, modifying procedures, retraining employees, or conducting equipment maintenance, among other steps.
Q: Who is responsible for implementing a control plan?
A: Responsibility for implementing a control plan typically falls on the process owner or a designated team responsible for process management and improvement. These individuals or teams are accountable for monitoring the process, collecting data, analyzing it for deviations, and implementing corrective actions when necessary.
Q: How often should a control plan be reviewed and updated?
A: A control plan should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure its effectiveness and alignment with changing process requirements. It is recommended to review the control plan during regular process performance reviews or when significant changes occur in the process or customer requirements. This helps to adapt the control plan to evolving conditions and continuously improve its efficacy.
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.
Download Template
Free lean six sigma templates.
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.
Other Guides
8 Business Plan Templates You Can Get for Free
8 min. read
Updated April 10, 2024
A business plan template can be an excellent tool to simplify the creation of your business plan.
The pre-set structure helps you organize ideas, covers all critical business information, and saves you time and effort on formatting.
The only issue? There are SO many free business plan templates out there.
So, which ones are actually worth using?
To help remove the guesswork, I’ve rounded up some of the best business plan templates you can access right now.
These are listed in no particular order, and each has its benefits and drawbacks.
What to look for in a business plan template
Not all business plan templates are created equal. As you weigh your options and decide which template(s) you’ll use, be sure to review them with the following criteria in mind:
- Easy to edit: A template should save you time. That won’t be the case if you have to fuss around figuring out how to edit the document, or even worse, it doesn’t allow you to edit at all.
- Contains the right sections: A good template should cover all essential sections of a business plan , including the executive summary, product/service description, market/competitive analysis, marketing and sales plan, operations, milestones, and financial projections.
- Provides guidance: You should be able to trust that the information in a template is accurate. That means the organization or person who created the template is highly credible, known for producing useful resources, and ideally has some entrepreneurial experience.
- Software compatibility: Lastly, you want any template to be compatible with the software platforms you use. More than likely, this means it’s available in Microsoft Word, Google Docs, or PDF format at a minimum.
1. Bplans — A plan with expert guidance

Since you’re already on Bplans, I have to first mention the templates that we have available.
Our traditional and one-page templates were created by entrepreneurs and business owners with over 80 years of collective planning experience. We revisit and update them annually to ensure they are approachable, thorough, and aligned with our team’s evolving best practices.
The templates, available in Word, PDF, or Google Doc formats, include in-depth guidance on what to include in each section, expert tips, and links to additional resources.
Plus, we have over 550 real-world sample business plans you can use for guidance when filling out your template.
Download: Traditional lender-ready business plan template or a simple one-page plan template .
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
2. SBA — Introduction to business plans

The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two different business plan templates along with a short planning guide.
While not incredibly in-depth, it’s enough to help you understand how traditional and lean plans are structured and what information needs to be covered. The templates themselves are more like examples, providing you with a finished product to reference as you write your plan.
The key benefit of using these templates is that they were created by the SBA. While they may provide less guidance, you can be assured that the information and structure meet their expectations.
Explore: The SBA’s planning guide and free templates
3. SCORE — Planning workbook

SCORE’s template is more like a workbook. It includes exercises after each section to help you get your ideas down and turn them into a structured plan.
The market research worksheets are especially useful. They provide a clear framework for identifying your target market and analyzing competitors from multiple angles. Plus, they give you an easy way to document all the information you’re collecting.
You will likely have to remove the exercises in this template to make it investor-ready. But it can be worth it if you’re struggling to get past a blank page and want a more interactive planning method.
Download: SCORE’s business plan template
4. PandaDoc — A template with fillable forms

PandaDoc’s library offers a variety of industry-specific business plan templates that feature a modern design flair and concise instructions.
These templates are designed for sharing. They include fillable fields and sections for non-disclosure agreements, which may be necessary when sending a plan to investors.
But the real benefit is their compatibility with PandaDoc’s platform. Yes, they are free, but if you’re a PandaDoc subscriber, you’ll have far more customization options.
Out of all their templates, the standard business plan template is the most in-depth. The rest, while still useful, go a bit lighter on guidance in favor of tailoring the plan to a specific industry.
Explore: PandaDoc’s business plan template library
5. Canva — Pitch with your plan

Canva is a great option for building a visually stunning business plan that can be used as a pitch tool. It offers a diverse array of templates built by their in-house team and the larger creative community, meaning the number of options constantly grows.
You will need to verify that the information in the template you choose matches the standard structure of a traditional business plan.
You should do this with any template, but it’s especially important with any tool that accepts community submissions. While they are likely reviewed and approved, there may still be errors.
Remember, you can only edit these templates within Canva. Luckily, you only need a free subscription, and you may just miss out on some of the visual assets being used.
To get the most value, it may be best to create a more traditional planning document and transfer that information into Canva.
Explore: Canva’s business plan gallery
6. ClickUp — The collaborative template

Out of all the project management tools that offer free business plan templates, ClickUp’s is the most approachable.
Rather than throwing you into all the features and expecting you to figure it out—ClickUp provides a thorough startup guide with resource links, images, and videos explaining how to write a plan using the tool.
There’s also a completed sample plan (structured like an expanded one-page plan) for you to reference and see how the more traditional document can connect to the product management features. You can set goals, target dates, leave comments, and even assign tasks to someone else on your team.
These features are limited to the ClickUp platform and will not be useful for everyone. They will likely get in the way of writing a plan you can easily share with lenders or investors.
But this is a great option if you’re looking for a template that makes internal collaboration more fluid and keeps all your information in one place.
Sign Up: Get a free trial of ClickUp and explore their template library
7. Smartsheet — A wide variety of templates

I’m including Smartsheet’s library of templates on this list because of the sheer number of options they provide.
They have a simple business plan template, a one-page plan, a fill-in-the-blank template, a plan outline, a plan grading rubric, and even an Excel-built project plan. All are perfectly usable and vary in visual style, depth of instructions, and the available format.
Honestly, the only drawback (which is also the core benefit) is that the amount of templates can be overwhelming. If you’re already uncertain which plan option is right for you, the lengthy list they provide may not provide much clarity.
At the same time, it can be a great resource if you want a one-stop shop to view multiple plan types.
Explore: Smartsheet’s business plan template library
8. ReferralRock affiliate marketing business plan

I’m adding ReferralRock’s template to this list due to its specificity.
It’s not your standard business plan template. The plan is tailored with specific sections and guidance around launching an affiliate marketing business.
Most of the template is dedicated to defining how to choose affiliates, set commissions, create legal agreements, and track performance.
So, if you plan on starting an affiliate marketing business or program, this template will provide more specific guidance. Just know that you will likely need to reference additional resources when writing the non-industry sections of your plan.
Download: ReferralRock affiliate marketing business plan template
Does it matter what business plan template you use?
The short answer is no. As long as the structure is correct, it saves you time, and it helps you write your business plan , then any template will work.
What it ultimately comes down to, is what sort of value you hope to get from the template.
- Do you need more guidance?
- A simple way to structure your plan?
- An option that works with a specific tool?
- A way to make your plan more visually interesting?
Hopefully, this list has helped you hone in on an option that meets one (or several) of these needs. Still, it may be worth downloading a few of these templates to determine the right fit.
And really, what matters most is that you spend time writing a business plan . It will help you avoid early mistakes, determine if you have a viable business, and fully consider what it will take to get up and running.
If you need additional guidance, check out our library of planning resources . We cover everything from plan formats , to how to write a business plan, and even how to use it as a management tool .
If you don’t want to waste time researching other templates, you can download our one-page or traditional business plan template and jump right into the planning process.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Kody Wirth is a content writer and SEO specialist for Palo Alto Software—the creator's of Bplans and LivePlan. He has 3+ years experience covering small business topics and runs a part-time content writing service in his spare time.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
- Qualities of a good template
- ReferralRock
- Does the template matter?
Related Articles

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes

10 Min. Read
14 Reasons Why You Need a Business Plan

6 Min. Read
Business Plan vs Business Model Canvas Explained

Use This Simple Business Plan Outline to Organize Your Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This quality control action plan sample template guides you through the sections of a quality control action plan. You may add, remove, or edit sections to suit your needs. This template includes sample tables that contain content suggestions for your plan. You can customize any
Quality Control Plan: How to Write a Quality Control Plan. Even when all of an organization's stakeholders give a full-scale effort, they'll have a hard time aligning their standards and practices without a company-wide quality control plan. Learn how quality control plans lead to standardization and process improvements. Even when all of ...
QualTech is a cloud-based quality management system, which bridges compliance to ISO frameworks. As such, the product offers an alternative to traditional on-premise solutions, meanwhile offering the flexibility to scale with business growth. This is a customizable system for virtually any business, however the primary focus is on SMBs.
This being said, quality control is a small part of the overall quality assurance process that includes processes to improve designs and address the root cause of quality issues. The following are the basic stages in the quality control process followed by examples of each stage.Specifications → Planning → Production → Inspection → ...
How to Create a Quality Control Plan. Quality Control is one of the many important aspects of the current world's corporate standards. ISO 9001 or any ISO Certification, for example, could dictate the prestige of your company and could even open better opportunities since people are used to quality-work and sought to desire better, always.
8. Configure a tool of choice to tie together the quality management process. It is important to make sure everything in this process runs smoothly to benefit the project and the team. Configure your existing project management tools to support quality management. Automation is valuable here.
An ISO 9001 Quality Management Plan is a crucial document that outlines the quality management processes and procedures to be followed in an organization. This plan serves as a guide for implementing and maintaining a quality management system that meets the requirements of the ISO 9001 international standard. By using this template, organizations can ensure that they have a comprehensive and ...
A Quality Control Plan is normally used to monitor processes, assuring that improvements and standards are solid and clear over a company's lifecycle. It must detect non-conformances and launch corrective actions or process improvements to resolve unwanted outcomes. The quality plan is built to describe the practices, resources or parameters ...
Quality Plan Example. An example of a quality plan is a manufacturing company that machines metal parts. Its quality plan consists of applicable procedures (describing the production process and responsibilities), applicable workmanship standards, the measurement tolerances acceptable, the description of the material standards, and so forth.
Benefits and Importance of Quality Control. Customer Satisfaction: Consistently delivering high-quality products and services helps build customer trust and loyalty, increasing the likelihood of repeat business and positive word-of-mouth marketing. Regulatory Compliance: QC processes help companies adhere to industry-specific regulations and ...
The documents include quality control procedures, compliance requirements, corrective action plans, safety plan design, innovations, risk-based thinking, gradual improvement plans, and audit assessments. Quality instruments: The control and calibration of instruments that measure quality are essential to company success.
A quality management plan is a document that sets out how the expectations for the project will be achieved. It is part of the project management plan. ... the business case, requirements documents, use cases or a statement of work. ... Quality management plan template. Here is a template you can use to create your own quality plan. Put the ...
Quality control is a process through which a business seeks to ensure that product quality is maintained or improved and manufacturing errors are reduced or eliminated. Quality control requires ...
Step 3: Complete the Elements of a QCP. Denote the essential elements of the quality control plan in your template such as the project overview's introductory statement, background, scope, etc. Then, complete the rest of the elements such as organizational structure, work verification, and down to the quality development plan.
A quality management plan is the first step to defining and codifying the steps necessary to achieve the quality expectations of the project. This is best done with project management software that can organize and share the plan with the project team. ProjectManager is cloud-based work and project management software that has multiple project ...
Steps in Writing a Quality Control Plan for Businesses. Create an organization chart - you should have an outline of your organizational chart that enables you to provide description of the job, business qualifications, and required training to make sure that the quality assurance procedure will be performed well. Such requirements has to be documented for the purpose of showing to the ...
Quality Control in a Service Business. Since this article is about people, I shall begin with a story about a person I know. The purpose of this story is to provide a reference point for the ...
Individualized Quality Control Plan Example PDF Free. clsi.org An individualized quality control plan has all the elements necessary for a well-developed individualized quality control plan. The main areas that it covers are the employees, suppliers contract, assets, and clients which in turn help to give the best possible output. Since all of ...
In the PMBOK sixth edition the Quality Management Plan is created in the process 8.1 Plan Quality Management. This is a FREE Quality Management Plan Template in Word and PDF. The template is fully editable with Microsoft Word and can be converted or changed to suit your project requirements. See what is in the Template!
A quality control plan (QCP), also known as a quality assurance plan (QAP), is a structured document or set of procedures and guidelines that outline the specific quality control measures and processes to be implemented during a project, manufacturing process, or any other type of operation. The primary purpose of a QCP is to ensure that ...
Tips on Writing a Business Plan. 1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively. 2.
A construction quality control plan (CQCPs) outlines a construction team's plans to meet and exceed the quality standards expected by clients and regulators. This document helps keep three crucial components in check: time, quality, and cost. You can think of a CQCP as a map that guides construction teams on how to achieve the best quality ...
Quality control is the process of detecting mistakes in operational outputs such as products and services. This can involve testing every single output such as the products off an assembly line. Alternatively, it can involve taking statistically significant test samples that provide confidence that results are to specifications.The following are illustrative examples of quality control.
Step 1: Identify the Process. The first step in creating a control plan is to identify a process that you are looking to control. This should be a process that is critical to the quality of your product or service and would have a significant impact on customer satisfaction or operational efficiency if it were to go wrong.
The rest, while still useful, go a bit lighter on guidance in favor of tailoring the plan to a specific industry. Explore: PandaDoc's business plan template library. 5. Canva — Pitch with your plan. Canva is a great option for building a visually stunning business plan that can be used as a pitch tool.