Unit 2: Linear Functions
Answer keys, lf1: i can write a linear equation from a situation or pattern.

LF1 Writing Linear Equations
Independent and Dependent Variables
Linear Intro
Writing equations, extra resources.
LF1 Skill Sheets
LF2: I use a linear equation to answer a question about a situation.
LF2 Using Linear Equations
Using equations.
LF2 Skill Sheets
LF3: I can write a linear equation from a table.
LF3 Equations from Tables
LF3 Skill Sheets
LF4: I can solve for "b."
LF4 Solving for "b"
Solving for "b".
LF4 Skill Sheets
LF5: I can write a linear equation from a graph.
LF5 Equations from Graphs
Horizontal and Vertical Lines
Equation from graph.
LF5 Skill Sheets
LF6: I can write a linear equation from two points.
LF6 Slope Formula
LF6 Skill Sheets
LF7: I can graph a line written in slope-intercept form: y=mx+b.
LF7 Graphing Lines
Graphing lines.
LF7 Skill Sheets
LF8: I can write and graph a line written in point-slope form: (y - y1) = m(x - x2).
LF8 Point-Slope Form
Point-slope form.
LF8 Skill Sheets
LF9: I can graph a line written in Standard Form: Ax + By = C.
LF9 Standard Form
Standard form, word problems.
All three forms
Google Slides Graphing Practice
LF9 Skill Sheets
LF10: I can transform equations between all three forms.

LF10 Transforming Between Forms
Transforming forms.
LF10 Skill Sheets
Previous Assessments (2018/2019)

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.4: Graphing Linear Equations- Answers to the Homework Exercises
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 45036

- Darlene Diaz
- Santiago Canyon College via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
Graphing and Slope
- \(\frac{1}{3}\)
- \(\frac{4}{3}\)
- \(\frac{1}{2}\)
- \(-\frac{1}{3}\)
- \(\frac{16}{7}\)
- \(-\frac{7}{17}\)
- \(\frac{1}{16}\)
- \(\frac{24}{11}\)
- \(x=\frac{23}{6}\)
- \(y=-\frac{29}{6}\)
Equations of Lines
- \(y=-\frac{3}{4}x-1\)
- \(y = −6x + 4\)
- \(y = − \frac{1}{4} x + 3\)
- \(y = \frac{1}{3} x + 3\)
- \(y = −3x + 5\)
- \(y = − \frac{1}{10} x − \frac{37}{10}\)
- \(y = \frac{7x}{3} − 8\)
- \(y = −4x + 3\)
- \(y = \frac{1}{10} x − \frac{3}{10}\)
- \(y = − \frac{4}{7} x + 4\)
- \(y=\frac{5}{2}x\)

- \(y − (−5) = 9(x − (−1))\)
- \(y − (−2) = −3(x − 0)\)
- \(y − (−3) = \frac{1}{5} (x − (−5))\)
- \(y − 2 = 0(x − 1)\)
- \(y − (−2) = −2(x − 2)\)
- \(y − 1 = 4(x − (−1))\)
- \(y − (−4) = − \frac{2}{3} (x − (−1))\)
- \(y = − \frac{3}{5} x + 2\)
- \(y = − \frac{3}{2} x + 4\)
- \(y = x − 4\)
- \(y = − \frac{1}{2} x\)
- \(y = − \frac{2}{3} x − \frac{10}{3}\)
- \(y = − \frac{5}{2} x − 5\)
- \(y = −3\)
- \(y − 3 = −2(x + 4)\)
- \(y + 2 = \frac{3}{2} (x + 4)\)
- \(y + 3 = − \frac{8}{7} (x − 3)\)
- \(y − 5 = − \frac{1}{8} (x + 4)\)
- \(y + 4 = −(x + 1)\)
- \(y = − \frac{8}{7} x − \frac{5}{7}\)
- \(y = −x + 2\)
- \(y = − \frac{1}{10} x − \frac{3}{2}\)
- \(y=\frac{1}{3}x+1\)
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
- \(m_{||} = 2\)
- \(m_{||} = 1\)
- \(m_{||} = − \frac{2}{3}\)
- \(m_{||} = \frac{6}{5}\)
- \(m_{⊥} = 0\)
- \(m_{⊥} = −3\)
- \(m_{⊥} = 2\)
- \(m_{⊥} = − \frac{1}{3}\)
- \(y − 4 = \frac{9}{2} (x − 3)\)
- \(y − 3 = \frac{7}{5} (x − 2)\)
- \(y + 5 = −(x − 1)\)
- \(y − 2 = \frac{1}{5} (x − 5)\)
- \(y − 2 = − \frac{1}{4} (x − 4)\)
- \(y + 2 = −3(x − 2)\)
- \(y = −2x + 5\)
- \(y = − \frac{4}{3} x − 3\)
- \(y = − \frac{1}{2} x − 3\)
- \(y = − \frac{1}{2} x − 2\)
- \(y = x − 1\)
- \(y=-2x+5\)

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 3: Graphing
3.4 Graphing Linear Equations
There are two common procedures that are used to draw the line represented by a linear equation. The first one is called the slope-intercept method and involves using the slope and intercept given in the equation.
If the equation is given in the form [latex]y = mx + b[/latex], then [latex]m[/latex] gives the rise over run value and the value [latex]b[/latex] gives the point where the line crosses the [latex]y[/latex]-axis, also known as the [latex]y[/latex]-intercept.
Example 3.4.1
Given the following equations, identify the slope and the [latex]y[/latex]-intercept.
- [latex]\begin{array}{lll} y = 2x - 3\hspace{0.14in} & \text{Slope }(m)=2\hspace{0.1in}&y\text{-intercept } (b)=-3 \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{lll} y = \dfrac{1}{2}x - 1\hspace{0.08in} & \text{Slope }(m)=\dfrac{1}{2}\hspace{0.1in}&y\text{-intercept } (b)=-1 \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{lll} y = -3x + 4 & \text{Slope }(m)=-3 &y\text{-intercept } (b)=4 \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{lll} y = \dfrac{2}{3}x\hspace{0.34in} & \text{Slope }(m)=\dfrac{2}{3}\hspace{0.1in} &y\text{-intercept } (b)=0 \end{array}[/latex]
When graphing a linear equation using the slope-intercept method, start by using the value given for the [latex]y[/latex]-intercept. After this point is marked, then identify other points using the slope.
This is shown in the following example.
Example 3.4.2
Graph the equation [latex]y = 2x - 3[/latex].
First, place a dot on the [latex]y[/latex]-intercept, [latex]y = -3[/latex], which is placed on the coordinate [latex](0, -3).[/latex]
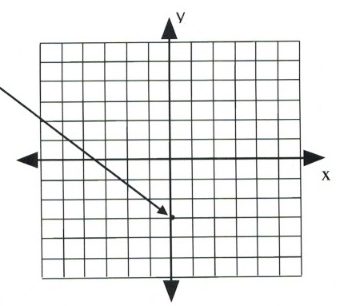
Now, place the next dot using the slope of 2.
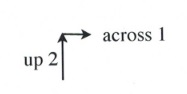
A slope of 2 means that the line rises 2 for every 1 across.
Simply, [latex]m = 2[/latex] is the same as [latex]m = \dfrac{2}{1}[/latex], where [latex]\Delta y = 2[/latex] and [latex]\Delta x = 1[/latex].
Placing these points on the graph becomes a simple counting exercise, which is done as follows:
Once several dots have been drawn, draw a line through them, like so:
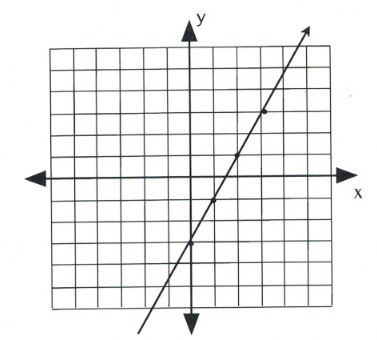
Note that dots can also be drawn in the reverse of what has been drawn here.
Slope is 2 when rise over run is [latex]\dfrac{2}{1}[/latex] or [latex]\dfrac{-2}{-1}[/latex], which would be drawn as follows:
Example 3.4.3
Graph the equation [latex]y = \dfrac{2}{3}x[/latex].
First, place a dot on the [latex]y[/latex]-intercept, [latex](0, 0)[/latex].
Now, place the dots according to the slope, [latex]\dfrac{2}{3}[/latex].
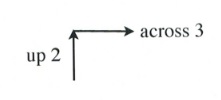
This will generate the following set of dots on the graph. All that remains is to draw a line through the dots.
The second method of drawing lines represented by linear equations and functions is to identify the two intercepts of the linear equation. Specifically, find [latex]x[/latex] when [latex]y = 0[/latex] and find [latex]y[/latex] when [latex]x = 0[/latex].
Example 3.4.4
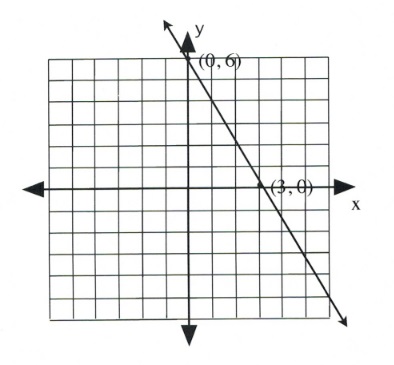
Graph the equation [latex]2x + y = 6[/latex].
To find the first coordinate, choose [latex]x = 0[/latex].
This yields:
[latex]\begin{array}{lllll} 2(0)&+&y&=&6 \\ &&y&=&6 \end{array}[/latex]
Coordinate is [latex](0, 6)[/latex].
Now choose [latex]y = 0[/latex].
[latex]\begin{array}{llrll} 2x&+&0&=&6 \\ &&2x&=&6 \\ &&x&=&\frac{6}{2} \text{ or } 3 \end{array}[/latex]
Coordinate is [latex](3, 0)[/latex].
Draw these coordinates on the graph and draw a line through them.
Example 3.4.5
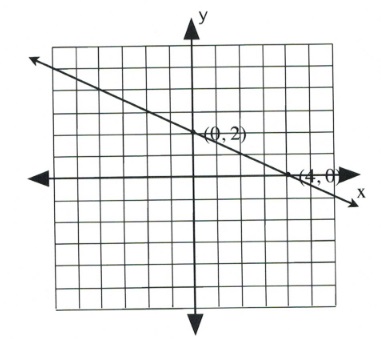
Graph the equation [latex]x + 2y = 4[/latex].
[latex]\begin{array}{llrll} (0)&+&2y&=&4 \\ &&y&=&\frac{4}{2} \text{ or } 2 \end{array}[/latex]
Coordinate is [latex](0, 2)[/latex].
[latex]\begin{array}{llrll} x&+&2(0)&=&4 \\ &&x&=&4 \end{array}[/latex]
Coordinate is [latex](4, 0)[/latex].
Example 3.4.6
Graph the equation [latex]2x + y = 0[/latex].
[latex]\begin{array}{llrll} 2(0)&+&y&=&0 \\ &&y&=&0 \end{array}[/latex]
Coordinate is [latex](0, 0)[/latex].
Since the intercept is [latex](0, 0)[/latex], finding the other intercept yields the same coordinate. In this case, choose any value of convenience.
Choose [latex]x = 2[/latex].
[latex]\begin{array}{rlrlr} 2(2)&+&y&=&0 \\ 4&+&y&=&0 \\ -4&&&&-4 \\ \hline &&y&=&-4 \end{array}[/latex]
Coordinate is [latex](2, -4)[/latex].
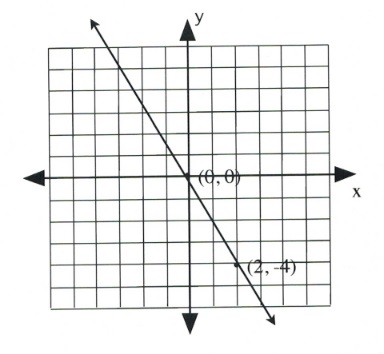
For questions 1 to 10, sketch each linear equation using the slope-intercept method.
- [latex]y = -\dfrac{1}{4}x - 3[/latex]
- [latex]y = \dfrac{3}{2}x - 1[/latex]
- [latex]y = -\dfrac{5}{4}x - 4[/latex]
- [latex]y = -\dfrac{3}{5}x + 1[/latex]
- [latex]y = -\dfrac{4}{3}x + 2[/latex]
- [latex]y = \dfrac{5}{3}x + 4[/latex]
- [latex]y = \dfrac{3}{2}x - 5[/latex]
- [latex]y = -\dfrac{2}{3}x - 2[/latex]
- [latex]y = -\dfrac{4}{5}x - 3[/latex]
- [latex]y = \dfrac{1}{2}x[/latex]
For questions 11 to 20, sketch each linear equation using the [latex]x\text{-}[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex]-intercepts.
- [latex]x + 4y = -4[/latex]
- [latex]2x - y = 2[/latex]
- [latex]2x + y = 4[/latex]
- [latex]3x + 4y = 12[/latex]
- [latex]4x + 3y = -12[/latex]
- [latex]x + y = -5[/latex]
- [latex]3x + 2y = 6[/latex]
- [latex]x - y = -2[/latex]
- [latex]4x - y = -4[/latex]
For questions 21 to 28, sketch each linear equation using any method.
- [latex]y = -\dfrac{1}{2}x + 3[/latex]
- [latex]y = 2x - 1[/latex]
- [latex]y = -\dfrac{5}{4}x[/latex]
- [latex]y = -3x + 2[/latex]
- [latex]y = -\dfrac{3}{2}x + 1[/latex]
- [latex]y = \dfrac{1}{3}x - 3[/latex]
- [latex]y = \dfrac{3}{2}x + 2[/latex]
- [latex]y = 2x - 2[/latex]
For questions 29 to 40, reduce and sketch each linear equation using any method.
- [latex]y + 3 = -\dfrac{4}{5}x + 3[/latex]
- [latex]y - 4 = \dfrac{1}{2}x[/latex]
- [latex]x + 5y = -3 + 2y[/latex]
- [latex]3x - y = 4 + x - 2y[/latex]
- [latex]4x + 3y = 5 (x + y)[/latex]
- [latex]3x + 4y = 12 - 2y[/latex]
- [latex]2x - y = 2 - y \text{ (tricky)}[/latex]
- [latex]7x + 3y = 2(2x + 2y) + 6[/latex]
- [latex]x + y = -2x + 3[/latex]
- [latex]3x + 4y = 3y + 6[/latex]
- [latex]2(x + y) = -3(x + y) + 5[/latex]
- [latex]9x - y = 4x + 5[/latex]
Answer Key 3.4
Intermediate Algebra Copyright © 2020 by Terrance Berg is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Kindergarten
- Greater Than Less Than
- Measurement
- Multiplication
- Place Value
- Subtraction
- Punctuation
- 1st Grade Reading
- 2nd Grade Reading
- 3rd Grade Reading
- Cursive Writing
Unit 2 Linear Equations Homework 3 Writing Linear Equations
Unit 2 Linear Equations Homework 3 Writing Linear Equations - Displaying top 8 worksheets found for this concept.
Some of the worksheets for this concept are Unit 4 linear equations homework 12 gina wilson, Gina wilson 2012 homework 4 linear equations word problems, Unit 2 linear equations and inequalities, Algebra 1 spencer unit 4 notes inequalities and, Solving linear equations, Georgia standards of excellence curriculum frameworks, Grade 9 working with linear equations, National 5 homework with worked solutionspupil version.
Found worksheet you are looking for? To download/print, click on pop-out icon or print icon to worksheet to print or download. Worksheet will open in a new window. You can & download or print using the browser document reader options.
1. Unit 4 Linear Equations Homework 12 Gina Wilson
2. gina wilson 2012 homework 4 linear equations word problems, 3. unit 2: linear equations and inequalities, 4. algebra 1 spencer unit 4 notes: inequalities and ..., 5. solving linear equations, 6. georgia standards of excellence curriculum frameworks ..., 7. grade 9 working with linear equations -, 8. national 5 homework with worked solutions:pupil version.
- List of Lessons
- 1.0 Marking the Text in Mathematics
- 1.1 Order of Operations
- 1.2 Translating Verbal Phrases
- 1.3 Functions as Rules and Tables
- 1.4 Functions as Graphs
- Unit 1 Review
- Unit 1 Skillz Review Help
- 2.1 Real Numbers
- 2.2 Add and Subtract Real Numbers
- 2.3 Multiply and Divide Real Numbers
- 2.4 Combine Like Terms and Distributive Property
- Unit 2 Review
- Unit 2 Skillz Review
- 3.1 One Step Equations
- 3.2 Two Step Equations
- 3.3 MultiStep Equations
- 3.4 Variables on Both Sides of the Equation
- Unit 3 Review
- 4.1 Ratios and Proportions
- 4.2 Solving Proportions using Cross Products
- 4.3 Solving Percent Problems
- 4.4 Solving for Y
- Unit 4 Shortcuts
- Unit 4 Review
- 5.1 Plot Points in a Coordinate Plane
- 5.2 Graphing Linear Equations and Using Intercepts
- 5.3 Slope and Rate of Change
- 5.4 Graph in Slope-Intercept Form
- 5.5 Graph Linear Functions
- Unit 5 Review
- 6.1 Write Equations in Slope Intercept Form
- 6.2 Use Equations in Slope Intercept Form
- 6.3 Equations in Parallel/Perpendicular Form
- 6.4 Fit Line To Data
- Unit 6 Review
- Unit 6 Skillz Review Help
- SEMESTER EXAM REVIEW
- 7.1 Inequalities
- 7.2 Solving Inequalities
- 7.3 Multi-step Inequalities
- 7.4 Absolute Value Equations
- 7.5 Linear Inequalities in Two Variables
- Unit 7 Skillz Review Help
- 8.1 Solving Systems by Graphing
- 8.2 Solving Systems using Substitution
- 8.3 Solving Systems using Elimination
- 8.4 Solving Special Case Systems
- 8.5 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities
- Unit 8 Review
- 9.1 Expand and Condense Exponents
- 9.2 Exponent Rules
- 9.3 Zero and Negative Exponents
- 9.4 Scientific Notation
- Unit 9 Review
- 10.1 Add and Subtract Polynomials
- 10.2 Multiply Polynomials
- 10.3 Polynomial Equations in Factored Form
- 10.4 Factoring Trinomials
- 10.5 Solving Quadratics by Factoring
- 10.6 Double Factoring
- Unit 10 Review
- Unit 10 Skillz Review Help
- 11.1 Simplifying Radicals
- 11.2 Operations with Square Roots
- Unit 11 Review
- 12.1 Graphing Quadratics
- 12.2 Solve Quadratics by Graphing
- 12.3 Solve Quadratics Using Square Roots
- 12.4 Solve Quadratics Using the Quadratic Formula
- Unit 12 Review
- Unit 12 Skillz Review
- SEMESTER 2 EXAM REVIEW
- Teacher Resources
- Flippedmath.com
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 4: Linear equations and linear systems
Lesson 3: balanced moves.
- Intro to equations with variables on both sides (Opens a modal)
- Equations with variables on both sides: 20-7x=6x-6 (Opens a modal)
- Equations with variables on both sides Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 4: More balanced moves
- Equations with parentheses (Opens a modal)
- Equations with parentheses Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 5: Solving any linear equation
- Multi-step equations review (Opens a modal)
Lesson 6: Strategic solving
- No videos or articles available in this lesson
- Equations with variables on both sides: decimals & fractions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Equations with parentheses: decimals & fractions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Extra practice: Linear equations
- Sums of consecutive integers (Opens a modal)
- Sum of integers challenge (Opens a modal)
- Equation practice with vertical angles (Opens a modal)
- Equation practice with complementary angles (Opens a modal)
- Equation practice with supplementary angles (Opens a modal)
- Sums of consecutive integers Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Equation practice with vertical angles Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Equation practice with angle addition Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 7: All, some, or no solutions
- Creating an equation with no solutions (Opens a modal)
- Creating an equation with infinitely many solutions (Opens a modal)
- Number of solutions to equations challenge Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 8: How many solutions?
- Number of solutions to equations (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: number of solutions to equations (Opens a modal)
- Number of solutions to equations Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 9: When are they the same?
- Age word problem: Imran (Opens a modal)
- Age word problem: Ben & William (Opens a modal)
- Age word problem: Arman & Diya (Opens a modal)
- Age word problems Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 10: On or off the line?
- Solutions of systems of equations Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 12: Systems of equations
- Systems of equations: trolls, tolls (1 of 2) (Opens a modal)
- Systems of equations: trolls, tolls (2 of 2) (Opens a modal)
- Systems of equations with graphing (Opens a modal)
- Systems of equations with graphing: y=7/5x-5 & y=3/5x-1 (Opens a modal)
- Systems of equations with graphing Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Number of solutions to a system of equations graphically Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 13: Solving systems of equations
- Systems of equations with substitution: y=-1/4x+100 & y=-1/4x+120 (Opens a modal)
- Number of solutions to a system of equations graphically (Opens a modal)
- Number of solutions to system of equations review (Opens a modal)
- Number of solutions to a system of equations algebraically Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 14: Solving more systems
- Systems of equations with substitution: 2y=x+7 & x=y-4 (Opens a modal)
- Systems of equations with substitution (Opens a modal)
- Systems of equations with substitution: y=4x-17.5 & y+2x=6.5 (Opens a modal)
- Systems of equations with substitution: y=-5x+8 & 10x+2y=-2 (Opens a modal)
- Substitution method review (systems of equations) (Opens a modal)
- Systems of equations with substitution Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Lesson 16: Solving problems with systems of equations
- System of equations word problem: no solution (Opens a modal)
- Systems of equations with substitution: coins (Opens a modal)
- Systems of equations word problems Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Question: Unit 2: Linear Functions Date: Bell: Homework 3: Writing Linear Equations, Applications, & Linear Regression **This is a 2-page documenti ** Point Slope & Two Points: Write a linear equation in slope-intercept form with the given Information 1. slope = -6; passes through (-4,1) 2. slope = passes through (-5, -6) 3. passes through (-4 ...
The equation of the lines are given by the points on the line from which. the slope and y-intercept are determined. Responses;. 1. y = -6·x - 23. 2. 3. 4. y = 9 - x. 5. a) b) 315 miles 6. a) b) Mikayla will not be ready for the marathon in 12 weeks
2-5 Writing Linear Functions Homework. 2-5 Writing and Interpreting Functions ANSWERS. 2-5 Writing and Interpreting Functions. 2-4 Homework ANSWERS. 2-4 Homework. 2-4 Writing Linear Equations ANSWERS. 2-4 Writing Linear Equations. 2-3 Function Notation Practice 2 ANSWERS. 2-3 Function Notation Practice 2.
So in the equation that I said, let's find the y-intercept first. You would plug in 0 for x. So the equation would be 8*0 -2y =24, or -2y =24. Then you can solve it like a regular equation and you would get y =-12. For the x-intercept, it's basically the same thing, except you plug in 0 for y instead of x. So you would get 8x -2*0 =24 or 8x =24 ...
Writing Equations from a Graph Example 1: Given the graph, write the equation for the line in slope intercept form. Step 1: Determine the y-intercept Step 2: Find the slope Step 3: Write the equation in slope intercept form. Example 2: Given the graph, write the equation for the line in slope intercept form. Step 1: Determine the y-intercept
Unit 2: Linear Functions. Answer Keys. LF1: I can write a linear equation from a situation or pattern. LF1 Writing Linear Equations. p. 1 . Independent and Dependent Variables. ... LF6: I can write a linear equation from two points. LF6 Slope Formula. p. 15-16. Extra Resources. LF6 Skill Sheets. LF7: I can graph a line written in slope ...
Algebra (all content) 20 units · 412 skills. Unit 1 Introduction to algebra. Unit 2 Solving basic equations & inequalities (one variable, linear) Unit 3 Linear equations, functions, & graphs. Unit 4 Sequences. Unit 5 System of equations. Unit 6 Two-variable inequalities. Unit 7 Functions. Unit 8 Absolute value equations, functions, & inequalities.
The domain is comprised of all real numbers because any number may be doubled, and then have one added to the product. Definition: Linear Function. A linear function is a function whose graph is a line. Linear functions can be written in the slope-intercept form of a line. f(x) = mx + b (3.2.2) (3.2.2) f ( x) = m x + b.
Algebra questions and answers. Unit 2, Homework 3 - Determine Linear vs. Exponential & Review Score: 30/93 7/24 answered Question 8 < > Writing Linear and Exponential Equations When a new charter school opened in 2010, there were 880 students enrolled. Using function notation, write a formula representing the number, N, of students attending ...
y = 2 y = 2. y = −x + 3 y = − x + 3. y = −2x + 5 y = − 2 x + 5. This page titled 2.4: Graphing Linear Equations- Answers to the Homework Exercises is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Darlene Diaz ( ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative) via source content that was edited to the ...
Unit 2 - Linear Expressions, Equations, and Inequalities. This unit is all about linear topics, which is a major focus of Common Core Algebra I. We develop general methods for solving linear equations using properties of equality and inverse operations. Thorough review is given to review of equation solving from Common Core 8th Grade Math.
a relationship that graphs as a straight line. point slope form. y-y₁=m (x-x₁) rise. rose, risen. slope-intercept form. y=mx+b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept of the line. standard form. Ax + By=C, where A, B, and C are not decimals or fractions, where A and B are not both zero, and where A is not a negative.
Slope is 2 when rise over run is 2 1 2 1 or −2 −1 − 2 − 1, which would be drawn as follows: Example 3.4.3. Graph the equation y = 2 3x y = 2 3 x. First, place a dot on the y y -intercept, (0,0) ( 0, 0). Now, place the dots according to the slope, 2 3 2 3. This will generate the following set of dots on the graph.
a (b + c) = ab + ac or a (b - c) = ab - ac. equation. a mathematical sentence whose verb is 'equal' (=) identity. an equation that is true for all values of the variable. interest. a payment for the use of money borrowed or invested. like terms. terms that have the same variable (s), with each variable raised to the same exponent.
EXAMPLE 5: WRITING AND GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS GIVEN A Y-INTERCEPT AND A SLOPE Write an equation of a line with the given slope and y-intercept. Then graph the equation. a) slope of 1/5 and y-intercept is (0, -3) b) slope of -2 and y-intercept is (0, 7) y= 1 5 x−3 y=−2x+7 EXAMPLE 6: GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like y = 2/3 x + 8, 5x - y = 7, a set of ordered pairs and more.
Unit 2 Linear Equations Homework 3 Writing Linear Equations - Displaying top 8 worksheets found for this concept.. Some of the worksheets for this concept are Unit 4 linear equations homework 12 gina wilson, Gina wilson 2012 homework 4 linear equations word problems, Unit 2 linear equations and inequalities, Algebra 1 spencer unit 4 notes inequalities and, Solving linear equations, Georgia ...
Be careful with equations such as (y + 3) = 2(x - 4) Because our general form has minus signs with our x's and y's, if we see a plus sign in a specific equation, that coordinate is a negative value.
Unit 4: Linear Equations Homework 8: Writing Linear Equations REVIEW Direcüons: Write the linear equation in slope-intercept form given the following: 1. slope = Z; ... Unit 4: Linear Equations Homework 10: Parallel & Perpendicular Lines (Day 2) Write an equation passing through the point and PARALLEL to the given line. + 6 5.1 =
Unit 5 - Linear Functions. 5.1 Plot Points in the Coordinate Plane. 5.2 Graph Linear Equations using Intercepts. 5.3 Rate of Change (Slope) 5.4 Graph Linear in Slope Intercept Form. 5.5 Graph Linear Functions.
Piecewise Linear Functions. LESSON/HOMEWORK. LESSON VIDEO. ANSWER KEY. EDITABLE LESSON. EDITABLE KEY. Lesson 7. Systems of Linear Equations (Primarily 3 by 3) LESSON/HOMEWORK.
8th grade (Illustrative Mathematics) 8 units · 114 skills. Unit 1 Rigid transformations and congruence. Unit 2 Dilations, similarity, and introducing slope. Unit 3 Linear relationships. Unit 4 Linear equations and linear systems. Unit 5 Functions and volume. Unit 6 Associations in data. Unit 7 Exponents and scientific notation.
8th grade (Illustrative Mathematics) 8 units · 114 skills. Unit 1 Rigid transformations and congruence. Unit 2 Dilations, similarity, and introducing slope. Unit 3 Linear relationships. Unit 4 Linear equations and linear systems. Unit 5 Functions and volume. Unit 6 Associations in data. Unit 7 Exponents and scientific notation.