How to Write a Persuasive Essay (This Convinced My Professor!)
.png)

Table of contents

Meredith Sell
You can make your essay more persuasive by getting straight to the point.
In fact, that's exactly what we did here, and that's just the first tip of this guide. Throughout this guide, we share the steps needed to prove an argument and create a persuasive essay.
This AI tool helps you improve your essay > This AI tool helps you improve your essay >

Key takeaways: - Proven process to make any argument persuasive - 5-step process to structure arguments - How to use AI to formulate and optimize your essay
Why is being persuasive so difficult?
"Write an essay that persuades the reader of your opinion on a topic of your choice."
You might be staring at an assignment description just like this 👆from your professor. Your computer is open to a blank document, the cursor blinking impatiently. Do I even have opinions?
The persuasive essay can be one of the most intimidating academic papers to write: not only do you need to identify a narrow topic and research it, but you also have to come up with a position on that topic that you can back up with research while simultaneously addressing different viewpoints.
That’s a big ask. And let’s be real: most opinion pieces in major news publications don’t fulfill these requirements.
The upside? By researching and writing your own opinion, you can learn how to better formulate not only an argument but the actual positions you decide to hold.
Here, we break down exactly how to write a persuasive essay. We’ll start by taking a step that’s key for every piece of writing—defining the terms.
What Is a Persuasive Essay?
A persuasive essay is exactly what it sounds like: an essay that persuades . Over the course of several paragraphs or pages, you’ll use researched facts and logic to convince the reader of your opinion on a particular topic and discredit opposing opinions.
While you’ll spend some time explaining the topic or issue in question, most of your essay will flesh out your viewpoint and the evidence that supports it.
The 5 Must-Have Steps of a Persuasive Essay
If you’re intimidated by the idea of writing an argument, use this list to break your process into manageable chunks. Tackle researching and writing one element at a time, and then revise your essay so that it flows smoothly and coherently with every component in the optimal place.
1. A topic or issue to argue
This is probably the hardest step. You need to identify a topic or issue that is narrow enough to cover in the length of your piece—and is also arguable from more than one position. Your topic must call for an opinion , and not be a simple fact .
It might be helpful to walk through this process:
- Identify a random topic
- Ask a question about the topic that involves a value claim or analysis to answer
- Answer the question
That answer is your opinion.
Let’s consider some examples, from silly to serious:
Topic: Dolphins and mermaids
Question: In a mythical match, who would win: a dolphin or a mermaid?
Answer/Opinion: The mermaid would win in a match against a dolphin.
Topic: Autumn
Question: Which has a better fall: New England or Colorado?
Answer/Opinion: Fall is better in New England than Colorado.
Topic: Electric transportation options
Question: Would it be better for an urban dweller to buy an electric bike or an electric car?
Answer/Opinion: An electric bike is a better investment than an electric car.
Your turn: Walk through the three-step process described above to identify your topic and your tentative opinion. You may want to start by brainstorming a list of topics you find interesting and then going use the three-step process to find the opinion that would make the best essay topic.
2. An unequivocal thesis statement
If you walked through our three-step process above, you already have some semblance of a thesis—but don’t get attached too soon!
A solid essay thesis is best developed through the research process. You shouldn’t land on an opinion before you know the facts. So press pause. Take a step back. And dive into your research.
You’ll want to learn:
- The basic facts of your topic. How long does fall last in New England vs. Colorado? What trees do they have? What colors do those trees turn?
- The facts specifically relevant to your question. Is there any science on how the varying colors of fall influence human brains and moods?
- What experts or other noteworthy and valid sources say about the question you’re considering. Has a well-known arborist waxed eloquent on the beauty of New England falls?
As you learn the different viewpoints people have on your topic, pay attention to the strengths and weaknesses of existing arguments. Is anyone arguing the perspective you’re leaning toward? Do you find their arguments convincing? What do you find unsatisfying about the various arguments?
Allow the research process to change your mind and/or refine your thinking on the topic. Your opinion may change entirely or become more specific based on what you learn.
Once you’ve done enough research to feel confident in your understanding of the topic and your opinion on it, craft your thesis.
Your thesis statement should be clear and concise. It should directly state your viewpoint on the topic, as well as the basic case for your thesis.
Thesis 1: In a mythical match, the mermaid would overcome the dolphin due to one distinct advantage: her ability to breathe underwater.
Thesis 2: The full spectrum of color displayed on New England hillsides is just one reason why fall in the northeast is better than in Colorado.
Thesis 3: In addition to not adding to vehicle traffic, electric bikes are a better investment than electric cars because they’re cheaper and require less energy to accomplish the same function of getting the rider from point A to point B.
Your turn: Dive into the research process with a radar up for the arguments your sources are making about your topic. What are the most convincing cases? Should you stick with your initial opinion or change it up? Write your fleshed-out thesis statement.
3. Evidence to back up your thesis
This is a typical place for everyone from undergrads to politicians to get stuck, but the good news is, if you developed your thesis from research, you already have a good bit of evidence to make your case.
Go back through your research notes and compile a list of every …
… or other piece of information that supports your thesis.
This info can come from research studies you found in scholarly journals, government publications, news sources, encyclopedias, or other credible sources (as long as they fit your professor’s standards).
As you put this list together, watch for any gaps or weak points. Are you missing information on how electric cars versus electric bicycles charge or how long their batteries last? Did you verify that dolphins are, in fact, mammals and can’t breathe underwater like totally-real-and-not-at-all-fake 😉mermaids can? Track down that information.
Next, organize your list. Group the entries so that similar or closely related information is together, and as you do that, start thinking through how to articulate the individual arguments to support your case.
Depending on the length of your essay, each argument may get only a paragraph or two of space. As you think through those specific arguments, consider what order to put them in. You’ll probably want to start with the simplest argument and work up to more complicated ones so that the arguments can build on each other.
Your turn: Organize your evidence and write a rough draft of your arguments. Play around with the order to find the most compelling way to argue your case.
4. Rebuttals to disprove opposing theses
You can’t just present the evidence to support your case and totally ignore other viewpoints. To persuade your readers, you’ll need to address any opposing ideas they may hold about your topic.
You probably found some holes in the opposing views during your research process. Now’s your chance to expose those holes.
Take some time (and space) to: describe the opposing views and show why those views don’t hold up. You can accomplish this using both logic and facts.
Is a perspective based on a faulty assumption or misconception of the truth? Shoot it down by providing the facts that disprove the opinion.
Is another opinion drawn from bad or unsound reasoning? Show how that argument falls apart.
Some cases may truly be only a matter of opinion, but you still need to articulate why you don’t find the opposing perspective convincing.
Yes, a dolphin might be stronger than a mermaid, but as a mammal, the dolphin must continually return to the surface for air. A mermaid can breathe both underwater and above water, which gives her a distinct advantage in this mythical battle.
While the Rocky Mountain views are stunning, their limited colors—yellow from aspen trees and green from various evergreens—leaves the autumn-lover less than thrilled. The rich reds and oranges and yellows of the New England fall are more satisfying and awe-inspiring.
But what about longer trips that go beyond the city center into the suburbs and beyond? An electric bike wouldn’t be great for those excursions. Wouldn’t an electric car be the better choice then?
Certainly, an electric car would be better in these cases than a gas-powered car, but if most of a person’s trips are in their hyper-local area, the electric bicycle is a more environmentally friendly option for those day-to-day outings. That person could then participate in a carshare or use public transit, a ride-sharing app, or even a gas-powered car for longer trips—and still use less energy overall than if they drove an electric car for hyper-local and longer area trips.
Your turn: Organize your rebuttal research and write a draft of each one.
5. A convincing conclusion
You have your arguments and rebuttals. You’ve proven your thesis is rock-solid. Now all you have to do is sum up your overall case and give your final word on the subject.
Don’t repeat everything you’ve already said. Instead, your conclusion should logically draw from the arguments you’ve made to show how they coherently prove your thesis. You’re pulling everything together and zooming back out with a better understanding of the what and why of your thesis.
A dolphin may never encounter a mermaid in the wild, but if it were to happen, we know how we’d place our bets. Long hair and fish tail, for the win.
For those of us who relish 50-degree days, sharp air, and the vibrant colors of fall, New England offers a season that’s cozier, longer-lasting, and more aesthetically pleasing than “colorful” Colorado. A leaf-peeper’s paradise.
When most of your trips from day to day are within five miles, the more energy-efficient—and yes, cost-efficient—choice is undoubtedly the electric bike. So strap on your helmet, fire up your pedals, and two-wheel away to your next destination with full confidence that you made the right decision for your wallet and the environment.
3 Quick Tips for Writing a Strong Argument
Once you have a draft to work with, use these tips to refine your argument and make sure you’re not losing readers for avoidable reasons.
1. Choose your words thoughtfully.
If you want to win people over to your side, don’t write in a way that shuts your opponents down. Avoid making abrasive or offensive statements. Instead, use a measured, reasonable tone. Appeal to shared values, and let your facts and logic do the hard work of changing people’s minds.
Choose words with AI

You can use AI to turn your general point into a readable argument. Then, you can paraphrase each sentence and choose between competing arguments generated by the AI, until your argument is well-articulated and concise.
2. Prioritize accuracy (and avoid fallacies).
Make sure the facts you use are actually factual. You don’t want to build your argument on false or disproven information. Use the most recent, respected research. Make sure you don’t misconstrue study findings. And when you’re building your case, avoid logical fallacies that undercut your argument.
A few common fallacies to watch out for:
- Strawman: Misrepresenting or oversimplifying an opposing argument to make it easier to refute.
- Appeal to ignorance: Arguing that a certain claim must be true because it hasn’t been proven false.
- Bandwagon: Assumes that if a group of people, experts, etc., agree with a claim, it must be true.
- Hasty generalization: Using a few examples, rather than substantial evidence, to make a sweeping claim.
- Appeal to authority: Overly relying on opinions of people who have authority of some kind.
The strongest arguments rely on trustworthy information and sound logic.
Research and add citations with AI

We recently wrote a three part piece on researching using AI, so be sure to check it out . Going through an organized process of researching and noting your sources correctly will make sure your written text is more accurate.
3. Persuasive essay structure

If you’re building a house, you start with the foundation and go from there. It’s the same with an argument. You want to build from the ground up: provide necessary background information, then your thesis. Then, start with the simplest part of your argument and build up in terms of complexity and the aspect of your thesis that the argument is tackling.
A consistent, internal logic will make it easier for the reader to follow your argument. Plus, you’ll avoid confusing your reader and you won’t be unnecessarily redundant.
The essay structure usually includes the following parts:
- Intro - Hook, Background information, Thesis statement
- Topic sentence #1 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence
- Topic sentence #2 , with supporting facts or stats
- Concluding sentence Topic sentence #3 , with supporting facts or stats
- Conclusion - Thesis and main points restated, call to action, thought provoking ending
Are You Ready to Write?
Persuasive essays are a great way to hone your research, writing, and critical thinking skills. Approach this assignment well, and you’ll learn how to form opinions based on information (not just ideas) and make arguments that—if they don’t change minds—at least win readers’ respect.
Share This Article:

Title Case vs. Sentence Case: How to Capitalize Your Titles

How to Properly Conduct Research with AI: Tools, Process, and Approach

What’s a Double Negative? + How To Fix It
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
Get 25% OFF new yearly plans in our Spring Sale
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Write a Persuasive Essay: Tips and Tricks

Allison Bressmer

Most composition classes you’ll take will teach the art of persuasive writing. That’s a good thing.
Knowing where you stand on issues and knowing how to argue for or against something is a skill that will serve you well both inside and outside of the classroom.
Persuasion is the art of using logic to prompt audiences to change their mind or take action , and is generally seen as accomplishing that goal by appealing to emotions and feelings.
A persuasive essay is one that attempts to get a reader to agree with your perspective.

Ready for some tips on how to produce a well-written, well-rounded, well-structured persuasive essay? Just say yes. I don’t want to have to write another essay to convince you!
How Do I Write a Persuasive Essay?
What are some good topics for a persuasive essay, how do i identify an audience for my persuasive essay, how do you create an effective persuasive essay, how should i edit my persuasive essay.
Your persuasive essay needs to have the three components required of any essay: the introduction , body , and conclusion .
That is essay structure. However, there is flexibility in that structure.
There is no rule (unless the assignment has specific rules) for how many paragraphs any of those sections need.
Although the components should be proportional; the body paragraphs will comprise most of your persuasive essay.

How Do I Start a Persuasive Essay?
As with any essay introduction, this paragraph is where you grab your audience’s attention, provide context for the topic of discussion, and present your thesis statement.
TIP 1: Some writers find it easier to write their introductions last. As long as you have your working thesis, this is a perfectly acceptable approach. From that thesis, you can plan your body paragraphs and then go back and write your introduction.
TIP 2: Avoid “announcing” your thesis. Don’t include statements like this:
- “In my essay I will show why extinct animals should (not) be regenerated.”
- “The purpose of my essay is to argue that extinct animals should (not) be regenerated.”
Announcements take away from the originality, authority, and sophistication of your writing.
Instead, write a convincing thesis statement that answers the question "so what?" Why is the topic important, what do you think about it, and why do you think that? Be specific.
How Many Paragraphs Should a Persuasive Essay Have?
This body of your persuasive essay is the section in which you develop the arguments that support your thesis. Consider these questions as you plan this section of your essay:
- What arguments support your thesis?
- What is the best order for your arguments?
- What evidence do you have?
- Will you address the opposing argument to your own?
- How can you conclude convincingly?

TIP: Brainstorm and do your research before you decide which arguments you’ll focus on in your discussion. Make a list of possibilities and go with the ones that are strongest, that you can discuss with the most confidence, and that help you balance your rhetorical triangle .
What Should I Put in the Conclusion of a Persuasive Essay?
The conclusion is your “mic-drop” moment. Think about how you can leave your audience with a strong final comment.
And while a conclusion often re-emphasizes the main points of a discussion, it shouldn’t simply repeat them.
TIP 1: Be careful not to introduce a new argument in the conclusion—there’s no time to develop it now that you’ve reached the end of your discussion!
TIP 2 : As with your thesis, avoid announcing your conclusion. Don’t start your conclusion with “in conclusion” or “to conclude” or “to end my essay” type statements. Your audience should be able to see that you are bringing the discussion to a close without those overused, less sophisticated signals.

If your instructor has assigned you a topic, then you’ve already got your issue; you’ll just have to determine where you stand on the issue. Where you stand on your topic is your position on that topic.
Your position will ultimately become the thesis of your persuasive essay: the statement the rest of the essay argues for and supports, intending to convince your audience to consider your point of view.
If you have to choose your own topic, use these guidelines to help you make your selection:
- Choose an issue you truly care about
- Choose an issue that is actually debatable
Simple “tastes” (likes and dislikes) can’t really be argued. No matter how many ways someone tries to convince me that milk chocolate rules, I just won’t agree.
It’s dark chocolate or nothing as far as my tastes are concerned.
Similarly, you can’t convince a person to “like” one film more than another in an essay.
You could argue that one movie has superior qualities than another: cinematography, acting, directing, etc. but you can’t convince a person that the film really appeals to them.

Once you’ve selected your issue, determine your position just as you would for an assigned topic. That position will ultimately become your thesis.
Until you’ve finalized your work, consider your thesis a “working thesis.”
This means that your statement represents your position, but you might change its phrasing or structure for that final version.
When you’re writing an essay for a class, it can seem strange to identify an audience—isn’t the audience the instructor?
Your instructor will read and evaluate your essay, and may be part of your greater audience, but you shouldn’t just write for your teacher.
Think about who your intended audience is.
For an argument essay, think of your audience as the people who disagree with you—the people who need convincing.
That population could be quite broad, for example, if you’re arguing a political issue, or narrow, if you’re trying to convince your parents to extend your curfew.
Once you’ve got a sense of your audience, it’s time to consult with Aristotle. Aristotle’s teaching on persuasion has shaped communication since about 330 BC. Apparently, it works.

Aristotle taught that in order to convince an audience of something, the communicator needs to balance the three elements of the rhetorical triangle to achieve the best results.
Those three elements are ethos , logos , and pathos .
Ethos relates to credibility and trustworthiness. How can you, as the writer, demonstrate your credibility as a source of information to your audience?
How will you show them you are worthy of their trust?

- You show you’ve done your research: you understand the issue, both sides
- You show respect for the opposing side: if you disrespect your audience, they won’t respect you or your ideas
Logos relates to logic. How will you convince your audience that your arguments and ideas are reasonable?

You provide facts or other supporting evidence to support your claims.
That evidence may take the form of studies or expert input or reasonable examples or a combination of all of those things, depending on the specific requirements of your assignment.
Remember: if you use someone else’s ideas or words in your essay, you need to give them credit.
ProWritingAid's Plagiarism Checker checks your work against over a billion web-pages, published works, and academic papers so you can be sure of its originality.
Find out more about ProWritingAid’s Plagiarism checks.
Pathos relates to emotion. Audiences are people and people are emotional beings. We respond to emotional prompts. How will you engage your audience with your arguments on an emotional level?

- You make strategic word choices : words have denotations (dictionary meanings) and also connotations, or emotional values. Use words whose connotations will help prompt the feelings you want your audience to experience.
- You use emotionally engaging examples to support your claims or make a point, prompting your audience to be moved by your discussion.
Be mindful as you lean into elements of the triangle. Too much pathos and your audience might end up feeling manipulated, roll their eyes and move on.
An “all logos” approach will leave your essay dry and without a sense of voice; it will probably bore your audience rather than make them care.
Once you’ve got your essay planned, start writing! Don’t worry about perfection, just get your ideas out of your head and off your list and into a rough essay format.
After you’ve written your draft, evaluate your work. What works and what doesn’t? For help with evaluating and revising your work, check out this ProWritingAid post on manuscript revision .
After you’ve evaluated your draft, revise it. Repeat that process as many times as you need to make your work the best it can be.
When you’re satisfied with the content and structure of the essay, take it through the editing process .
Grammatical or sentence-level errors can distract your audience or even detract from the ethos—the authority—of your work.
You don’t have to edit alone! ProWritingAid’s Realtime Report will find errors and make suggestions for improvements.
You can even use it on emails to your professors:
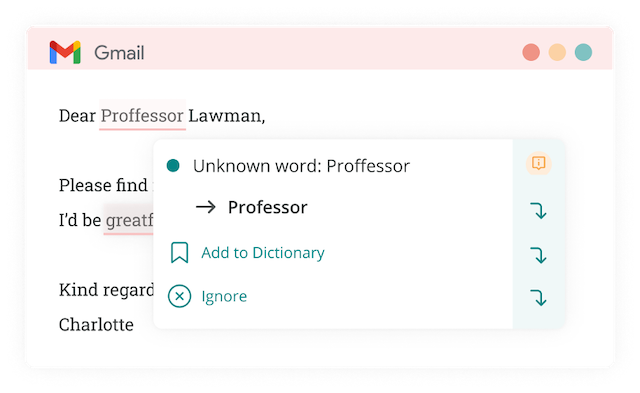
Try ProWritingAid with a free account.
How Can I Improve My Persuasion Skills?
You can develop your powers of persuasion every day just by observing what’s around you.
- How is that advertisement working to convince you to buy a product?
- How is a political candidate arguing for you to vote for them?
- How do you “argue” with friends about what to do over the weekend, or convince your boss to give you a raise?
- How are your parents working to convince you to follow a certain academic or career path?
As you observe these arguments in action, evaluate them. Why are they effective or why do they fail?
How could an argument be strengthened with more (or less) emphasis on ethos, logos, and pathos?
Every argument is an opportunity to learn! Observe them, evaluate them, and use them to perfect your own powers of persuasion.
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Allison Bressmer is a professor of freshman composition and critical reading at a community college and a freelance writer. If she isn’t writing or teaching, you’ll likely find her reading a book or listening to a podcast while happily sipping a semi-sweet iced tea or happy-houring with friends. She lives in New York with her family. Connect at linkedin.com/in/allisonbressmer.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Writing a Persuasive Essay
View in pdf format, the introduction.
Simply enough, the introductory paragraph introduces the argument of your paper. A well-constructed introductory paragraph immediately captures a reader’s interest and gives appropriate background information about the paper’s topic. Such a paragraph might include a brief summary of the ideas to be discussed in body of the paper as well as other information relevant to your paper’s argument. The most important function of the introductory paragraph, however, is to present a clear statement of the paper’s argument. This sentence is your paper’s thesis. Without a thesis, it is impossible for you to present an effective argument. The thesis sentence should reflect both the position that you will argue and the organizational pattern with which you will present and support your argument. A useful way to think about the construction of a thesis sentence is to view it in terms of stating both the “what” and the “how” of the paper’s argument. The “what” is simply the basic argument in your paper: what exactly are you arguing? The “how” is the strategy you will use to present this argument. The following are helpful questions for you to consider when formulating a thesis sentence:
- What is the argument that I am trying to convince the reader to accept?
- How exactly do I expect to convince the reader that this argument is sound?
Once you have answered these questions, the next step is to synthesize these answers into a single thesis sentence, or, if necessary, two thesis sentences.
For example: You want to convince your reader that the forces of industry did not shape American foreign policy from the late 19th century through 1914, and you plan to do this by showing that there were other factors which were much more influential in shaping American foreign policy. Both of these elements can be synthesized into a thesis sentence:
Fear of foreign influence in the Western hemisphere, national pride, and contemporary popular ideas concerning both expansion and foreign peoples had significantly more influence on American foreign policy than did the voices of industrialists.
This sentence shows the position you will argue and also sets up the organizational pattern of your paper's body.
The body of your paper contains the actual development of your paper’s argument. Each body paragraph presents a single idea or set of related ideas that provides support for your paper’s argument. Each body paragraph addresses one key aspect of your paper’s thesis and brings the reader closer to accepting the validity of your paper’s argument. Because each body paragraph should be a step in your argument, you should be mindful of the overall organization of your body paragraphs. The first step in writing an effective body paragraph is the construction of the first sentence of this paragraph, the topic sentence. Just as the thesis sentence holds together your essay, the topic sentence is the glue binding each individual body paragraph. A body paragraph’s topic sentence serves two main purposes: introducing the content of the paragraph and introducing the next step of your argument. It is important to keep in mind that the goal of the topic sentence is to advance your paper's argument, not just to describe the content of the paragraph. For example: The first part in your thesis on page two states that fear of foreign influence in the Western Hemisphere had more influence on American foreign policy than did industry. Thus, you need to elaborate on this point in your body paragraphs. An effective topic sentence for one of these paragraphs could be:
American fear of foreign influence was a key factor in the United States’ actions in the Spanish-American War. Subsequent body paragraphs might offer further evidence for the idea presented in this body paragraph.
A good way to test the strength of both your topic sentences and your argument as a whole is to construct an outline of your paper using only your paper's thesis statement and topic sentences. This outline should be a logical overview of your paper's argument; all of your paper’s topic sentences should work together to support your thesis statement.
The Conclusion
A basic purpose of your paper’s concluding paragraph is both to restate the paper’s argument and to restate how you have supported this argument in the body of the paper. However, your conclusion should not simply be a copy of your introduction. The conclusion draws together the threads of the paper’s argument and shows where the argument of your paper has gone. An effective conclusion gives the reader reasons for bothering to read your paper. One of the most important functions of this paragraph is to bring in fresh insight. Some possible questions to consider when writing your conclusion are:
- What are some real world applications of this paper’s argument?
- Why is what I am writing about important?
- What are some of the questions that this paper’s argument raises?
- What are the implications of this paper’s argument?
While the organization and structure described in this handout are necessary components of an effective persuasive essay, keep in mind that writing itself is a fluid process. There are no steadfast rules that you need to adhere to as you write. Simply because the introduction is the first paragraph in your essay does not mean that you must write this paragraph before any other. Think of the act of writing as an exploration of ideas, and let this sense of exploration guide you as you write your essay.
by Adam Polak ’98 and Jen Collins ’96
Popular resources.
- Writing a Good APA Research Paper
- Writing a Good History Paper
- Understanding Passive Voice
Office / Department Name
Nesbitt-Johnston Writing Center
Contact Name
Jennifer Ambrose
Writing Center Director

Help us provide an accessible education, offer innovative resources and programs, and foster intellectual exploration.
Site Search
Persuasive Essay Writing

How to Write a Persuasive Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide
13 min read
Published on: Jan 3, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 29, 2024

People also read
Easy and Unique Persuasive Essay Topics with Tips
The Basics of Crafting an Outstanding Persuasive Essay Outline
Ace Your Next Essay With These Persuasive Essay Examples!
Persuasive Essay About Gun Control - Best Examples for Students
Top Examples of Persuasive Essay about Covid-19
Learn How To Write An Impressive Persuasive Essay About Business
Learn How to Craft a Compelling Persuasive Essay About Abortion With Examples!
Make Your Point: Tips and Examples for Writing a Persuasive Essay About Online Education
Learn How To Craft a Powerful Persuasive Essay About Bullying
Craft an Engaging Persuasive Essay About Smoking: Examples & Tips
Learn How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Social Media With Examples
Craft an Effective Argument: Examples of Persuasive Essay About Death Penalty
Share this article
It's the night before the essay is due, and you haven't even started. Your mind is blank, and you have no idea what words will persuade your teacher.
The good news is that some tips and tricks can make the process of writing a persuasive essay much easier.
In this blog, we'll break down the components of a persuasive essay and provide helpful tips and examples along the way. By the end, you should have all the guidelines to create a winning essay that will persuade your readers to see things your way.
Let's take a closer look at all these steps.
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Persuasive Essay?
A persuasive essay presents logical arguments with emotional appeal.
Typically, persuasive essays begin with a question that the writer spends the essay arguing in favor of or opposition to.
For example: should kids be allowed to play video games on weekdays?
The writer would then spend the rest of the essay backing up their claim with reasons and evidence.
Persuasive essays often include counterarguments. These arguments oppose the writer's position.
By including counterarguments, persuasive essays become more interesting. They also force the writer to think critically about their position.
For example, an opponent of the previous argument might say that playing video games leads to poor grades.
The original writer could deny this claim by pointing to studies that show no correlation between bad grades and playing video games.
The best persuasive essays are well-researched and use data to support their claims.
However, persuasive essays are not just about logic. They also need to include emotional appeal.
After all, people are more likely to be persuaded by an argument that speaks to their feelings.
Elements of a Persuasive Essay
When a persuasive essay is a task, you must keep these three greek terms in mind. They are:
- Ethos (appeal to ethics)
- Pathos (appeal to emotion)
- Logos (appeal to logic)
A good essay will use all of these elements to convince the reader that the argument presented is valid.
Let's take a closer look at each one.
Ethos - the Credibility Element
The persuasive power of ethos lies in the character or credibility of the person making the argument.
For an argument to be persuasive, the person presenting it must be someone that the audience trusts.
This could be because they are an expert on the subject or because they have first-hand experience with it. Either way, ethos establishes the speaker's credibility and makes the audience more likely to trust what they have to say.
Pathos -the Emotional Element
While ethos deals with the character of the person making the argument, pathos has to do with the audience's emotions. A persuasive argument will tap into the audience's emotions and use them to sway their opinion.
This could be done through stories or anecdotes that evoke an emotional response or by using language that stirs certain feelings.
Logos - the Logical Element
The final element of persuasion is logos, which appeals to logic. A persuasive argument will use sound reasoning and evidence to convince the audience that it is valid. This could be done through data or using persuasive techniques like cause and effect.
Using all these elements of a persuasive essay can make your argument much more effective.
How To Write a Persuasive Essay
Writing persuasive essays can be challenging, but they don't have to be.
With the following simple steps, you can quickly turn an ordinary essay into one that will make a lasting impression.
Tough Essay Due? Hire a Writer!

How To Start a Persuasive Essay
Here is a complete guide on how to start a persuasive essay. Follow them to compose a perfect essay every time.
Brainstorm All Possible Angles
The first step in writing a persuasive essay is brainstorming. You need to develop an angle for your essay that will make it unique and interesting.
For example, let's say you're writing about the death penalty. A lot has been said on this topic, so it might be hard to find an angle that hasn't been covered already.
But if you think about it, there are many different ways to approach the issue.
Maybe you could write about the personal experiences of someone affected by the death penalty. Or maybe you could write about the economic costs of the death penalty.
There are many possibilities here - it's all about thinking creatively.
Select Your Topic
Once you've brainstormed a few ideas, it's time to choose your topic. Pick the angle you think will most effectively persuade your reader.
Once you've chosen your topic, it's time to research. Use statistics, expert opinions, and real-life examples to support your position.
Choose Your Side
Now that you've researched, it's time to take a side in the debate. Remember, you must take a strong stance on one side of the issue.
After deciding your stance, research and support it with evidence.
Appeal to Human Emotions
One of the most effective ways to persuade someone is by appealing to their emotions.
After all, we're not robots - we're human beings and always make decisions based on our feelings.
Make your reader feel something, whether it's anger, sadness, empathy, or even amusement. You'll be well on convincing them of your point of view.
Anticipate Possible Objections.
Of course, not everyone will agree, and that's okay!
The important thing is that you anticipate some of those objections and address them head-on in your essay.
This shows that you take your reader's objections seriously and are confident in your position.
Organize Your Evidence
Once you have all of your evidence collected, it's time to start organizing it into an outline for your essay.
Organizing your essay is a key step in the writing process. It helps you keep track of all the evidence you've gathered and structure your argument in an organized way.
What Are The Steps To Write Your Persuasive Essay?
Now that you have your topic essay outline, it's time to move on to the actual writing.
Here are the steps you need to take:
Step 1: Create a Compelling Introduction
You want to hook your readers with a great opening for your persuasive essay, so they'll want to keep reading.
Here are 3 tips for writing an attention-grabbing introduction for your next essay.
- Use a strong hook statement
Your hook statement should immediately draw the reader in and make them want to learn more.
A good hook statement will vary depending on whether you're writing for an academic or more casual audience.
Still, some good options include a quote, an interesting statistic, or a rhetorical question.
- Make sure your thesis statement is clear and concise
Your thesis statement is the main argument of your essay, so it needs to be stated clearly and concisely in your introduction.
A good thesis statement will be specific and limit the scope of your argument so that it can be fully addressed in the body of your paper.
- Use a transition
Transitions are important in writing for academic and non-academic audiences because they help guide the reader through your argument.
A good transition will introduce the main point of your next paragraph while still maintaining the connection to the previous one.
Step 2: Write The Body Paragraphs
Here is a formula for structuring your body paragraphs in a persuasive essay.
This formula will ensure that each body paragraph is packed with evidence and examples while still being concise and easy to read.
- The Topic Sentence
Every body paragraph should start with a topic sentence. A topic sentence is a key sentence that sums up the paragraph's main point.
It should be clear, concise, and direct.
For example, if you were writing a paragraph about the importance of exercise, your topic sentence might be this:
"Regular exercise is essential for good physical and mental health."
See how that sentence gives a clear overview of what the rest of the paragraph will be about.
- Relevant Supporting Sentences
Once your topic sentence is down, it's time to fill the rest of the paragraph with relevant supporting sentences.
These sentences should provide evidence to support the claims made in the topic sentence.
For the exercise example, we might use sentences like this:
"Exercise has been shown to improve heart health, reduce stress levels, and boost brain power."
"A sedentary lifestyle has been linked to an increased risk of obesity, heart disease, and type II diabetes."
See how each sentence ties back to the paragraph's main point. That's what you want your supporting sentences to do.
- Closing Sentence
Last but not least, every body paragraph should end with a closing (or transition) sentence. This sentence should briefly summarize the main points of the paragraph and introduce the next point that will be discussed in the following paragraph.
For the exercise example, the closing sentence might look like this:
"So, as you can see, there are many compelling reasons to make exercise a regular part of your routine."
How to End a Persuasive Essay
The end of your essay is just as important as the introduction. You must leave your readers with a lasting impression and ensure your argument convinces them.
To do this, you'll want to craft a persuasive conclusion that ties together all the points you have made in the essay.
Here is a video explaining the body paragraphs in a persuasive essay. Check it out for more information.
Step 1: Write a Persuasive Conclusion
Here are a few tips to help make sure your persuasive essay conclusion is as effective and persuasive as possible.
- Restate Your Thesis
Begin your essay conclusion by restating the thesis statement you began within your introduction. Doing so will remind readers of what you set out to prove and provide a sense of closure.
- Summarize Your Arguments
You can also use your conclusion to summarize the main points of your argument. This will help readers recall the evidence you presented and reinforce why it supports your thesis.
- Offer a Call to Action
Lastly, don't forget to include a call to action in your essay conclusion. This can be anything from a persuasive plea to a persuasive suggestion.
Step 2: Polish Up Your Essay
After youâre done with the essay, take a few minutes to read through it. Ensure that your persuasive points and evidence are clear, concise, and persuasive.
Also, double-check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation mistakes. Ensure that all of your persuasive points are properly explained and make sense to the reader.
If youâre not confident in your persuasive writing skills, you can enlist a friend or family member to read through it and provide feedback.
You can follow a proofreading checklist after completing your essay to ensure you are on track.
By following these steps, youâll end up with a persuasive essay that will impress anyone who reads it!
Format Of A Persuasive Essay
Once you have your persuasive essay topic, it's time to craft an essay structure. Crafting the perfect persuasive essay format is essential for ensuring your paper has maximum persuasive power.
Here are some tips for formatting an effective persuasive essay.
- Increase the Readability of Your Text
Ensure that you have adhered to all the paragraphing requirements of your instructor.
Double-check that your margins are set properly. A margin of 1 inch (2.5 cm) on all sides is the standard for most written documents.
This makes it easier for readers to focus and extract important information quickly.
- Use Easy-to-Read Font
Choose a font that is easy to read and professional. Stay away from script fonts or anything too fancy or difficult to read. Stick with basic fonts like Times New Roman, Arial, and Calibri.
- Keep a Defined Alignment
Align your persuasive essay to the left margin. This makes it easier for readers to follow along with your argument without having to do too much extra scrolling.
By following these simple tips, you'll be able to craft the perfect persuasive essay format.
Persuasive Essay Examples
Here are some examples of persuasive essays that can help you get the gist of essay writing.
Persuasive essay on the preservation of nature
Persuasive essay examples pdf
Example of a persuasive essay about covid-19
Check out some more persuasive essay examples here for more inspiration.
Good Persuasive Essay Topics
The right persuasive essay topics can make or break your essay. Here are a few examples of persuasive essay topics that can help you.
- Should the government increase taxes on sugary foods to reduce obesity?
- Do standardized tests accurately measure student intelligence and aptitude?
- Should studying a foreign language be mandatory in schools?
- Should all high school students complete community service hours before graduating?
- Are video games affecting the concentration and cognitive development of children?
- Should genetically modified foods be labeled as such in stores?
- Are the current copyright laws protecting artists and content creators enough?
- Should college tuition be reduced for all students?
- Is the use of animals in medical research ethical?
- Should the use of drones be regulated by the government?
- Should college athletes receive payment for their performance?
- Should students be allowed to have cell phones in school?
- Is drug testing in schools an effective way to prevent substance abuse?
- Does social media promote a healthy lifestyle or contribute to cyber bullying?
- Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
If youâre stuck with choosing topics, these are great persuasive essay topics to get you started!
Pick one of these and craft an essay that will leave your readers thinking.
Tips to Write a Compelling Persuasive Essay
Here are a few tips and tricks to help you make a lasting impression on your reader:
Pick A Topic You're Passionate About
First, you need to choose a topic you're passionate about. It will be easier to write about the topic if you care about the essay.
This will make it easier to develop persuasive arguments, and you'll be more motivated to do research.
Research Your Topic Thoroughly
After picking a persuasive essay topic, you need thorough research. This will help you gain a better understanding of the issue, which in turn will make your essay stronger. This will also ensure that you fully grasp all counterarguments on your topic.
Know Your Audience
Knowing your audience before writing is important. Are you writing to your classmates? Your teacher? The general public? Once you know your audience, you can tailor your argument to them.
Knowing your audience will help determine the tone and approach of your essay.
Hook The Reader's Attention
The first few sentences of your essay are crucial - they must grab the reader's attention and make them want to keep reading.
One way to do this is by starting with a shocking statistic or an interesting story. The reader will be instantly hooked and will be enticed to read more.
Research Both Sides
A good persuasive essay will consider both sides of an issue and present a well-rounded view. This means researching both sides of the argument before taking a stance.
Make sure to consider all the evidence before making up your mind - otherwise, your argument won't be as strong as it could be.
Ask Rhetorical Questions
Rhetorical questions are not meant to be answered but rather to make the reader think about the issue.
For example, "How can we expect our children to succeed in school if they don't have enough resources?"
Questions like this can help engage readers and get them thinking about solutions rather than just complaining about problems.
Emphasize Your Point
It's important to reiterate your main points throughout the essay so that readers don't forget what they are supposed to argue for or against by the time they reach the end of the paper.
Persuasive essays can be difficult to write, but following simple tips can help make the process easier.
In this blog, we've outlined the components of a persuasive essay and provided some tips on how to write one. We also shared examples of persuasive essays that scored high marks on standardized tests.
If you are looking for an essay writing service , look no further than CollegeEssay.org! Our experienced essay writer can provide the assistance you need to produce an essay that meets the highest standards.
Let our persuasive essay writer handle the hard work and get you started on your path to success.
Try our AI essay writer and elevate your writing to new heights today!
Frequently Asked Questions About Persuasive Essays
How long should a persuasive essay be.
Generally speaking, persuasive essays should be between 500-750 words. However, the length of your essay will depend on the instructions given by your teacher or professor.
What Techniques Are Used In Persuasive Essays?
Persuasive techniques include facts and statistics, emotion and logic, personal stories, analogies and metaphors, pathos, ethos, and logos.
How Do I Make My Persuasive Essay More Convincing?
To make your essay more convincing, cite reliable sources, use persuasive language, and provide strong evidence and arguments.
How Is Persuasive Writing Different From Argumentative Writing?
The main difference between persuasive and argumentative writing is that persuasive writing seeks to convince or persuade the reader. On the other hand, argumentative writing seeks to debate an issue.
Cathy A. (Literature, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
PRDV002: Professional Writing
Approaching Persuasion
Read this article for a comprehensive look at how to approach persuasion as a writer. It identifies common aspects of persuasive writing and how to construct or develop a project.
The Structure of a Persuasive Essay
Writing a persuasive essay.
You first need to choose a topic that you feel passionate about. If your instructor requires you to write about a specific topic, approach the subject from an angle that interests you. Begin your essay with an engaging introduction. Your thesis should typically appear somewhere in your introduction.
Next, need to acknowledge and explain points of view that may conflict with your own to build credibility and trust with your audience. You also should state the limits of your argument. This helps you sound more reasonable and honest to those who may naturally be inclined to disagree with your view. By respectfully acknowledging opposing arguments and conceding limitations to your own view, you set a measured and responsible tone for the essay.
Be sure to make your appeals in support of your thesis by using sound, credible evidence. Use a balance of facts and opinions from a wide range of sources, such as scientific studies, expert testimony, statistics, and personal anecdotes. Each piece of evidence should be fully explained and clearly stated. Also, write in a style and tone that is appropriate for your subject and audience. Tailor your language and word choice to these two factors while still being true to your own voice. Finally, write a conclusion that effectively summarizes the main argument and reinforces your thesis.
Structuring a Persuasive Essay
The formula below for organizing a persuasive essay may be one with which you are familiar. It will present a convincing argument to your reader because your discussion is well-rounded and thorough, and yo u leave your audience with your point of view at the end. Remember to consider each of these components in this formula as sections instead of paragraphs because you will probably want to discuss multiple ideas backing up your point of view to make it more convincing.
When writing a persuasive essay, it is best to begin with the most important point because it immediately captivates your readers and compels them to continue reading. For example, if you were supporting your thesis that homework is detrimental to the education of high school students, you would want to present your most convincing argument first and then move on to the less important points for your case.
Some key transitional words you should use with this method of organization are: most importantly, almost as importantly, just as importantly, and finally.
The Formula: You need to come up with objection points, but you also need to think of direct rebuttals to each of those ideas. Remember to consult your outline as you are writing because you may need to double-check that you have countered each of the possible opposing ideas you presented.
Section 1: Introduction
- Attention getter.
- Thesis (showing main and controlling ideas).
- Background.
- Signposts (make sure you outline the structure your argument will follow: Pros Cons/Pros).
Section 2: (Multiple) Ideas in Support of Claim
- Give a topic sentence introducing the point (showing main and controlling ideas).
- Give explanations + evidence on the first point.
- Make a concluding statement summarizing the point discussion (possibly transitioning to the next supporting idea).
- Repeat with multiple ideas in separate paragraphs.

Section 3: Summary of ( Some) Opposing Views
- Give a topic sentence explaining how the paragraph will include opposing points of view to provide a thorough, convincing argument.
- Present a general summary of some opposing ideas.
- Present some generalized evidence.
- Provide a brief concluding sentence for the paragraph – transitioning into the next rebuttal paragraph.
Section 4: Response to Opposing Views
- Give a topic sentence explaining how this paragraph or section connects to or expands on the previous paragraph .
- You [may recognize the validity of some of the points] then resent how your ideas are stronger.
- Present evidence directly countering or refuting ideas mentioned in the previous section.
- Give a concluding statement summarizing the countering arguments.
Section 5: Conclusion
- Restate your thesis.
- Summarize your discussion points.
- Leave the reader with a strong impression; do not waiver here.
- May provide a "call for action."
In a persuasive essay, the writer's point of view should be clearly expressed at the beginning of each paragraph in the topic sentence, which should contain the main idea of the paragraph and the writer's controlling idea.
Persuasive Essay
Definition of persuasive essay.
The term “persuasive” is an adjective derived from verb “persuade,” which means “to convince somebody.” A persuasive essay is full of all the convincing techniques a writer can employ. It presents a situation, and takes a stand – either in its favor, or against it – to prove to readers whether it is beneficial or harmful for them.
Why Persuasion?
The question arises why persuasion if the people are already aware of everything. Its answer is that each person’s ability of seeing and understanding things depend on his vision. He believes only what he sees or is told about. If another side of the coin is shown, the people do not believe so easily. That is why they are presented with arguments supported with evidences , statistics and facts. Persuasion is done for these reasons:
- A Better World : To ask the people that if they accept your argument , it will be good for them to take action and make the world a better place.
- A Worse World : It means that if readers do not do what they are asked to do, the world will become a worse place.
- Call to Action : It means to persuade or tempt readers to do what the writer wants them to do.
Difference Between a Persuasive Essay and an Argumentative Essay
A persuasive essay is intended to persuade readers to do certain things, or not to do certain things. It is the sole aim of the writer to coax or tempt readers, and force them to do certain things or take actions. However, an argumentative essay intends to make readers see both sides of the coin. It is up to them to select any of the two. In other words, an argumentative essay presents both arguments; both for and against a thing, and leaves the readers to decide. On the other hand, a persuasive essay intends to make readers do certain things. Therefore, it presents arguments only about one aspect of the issue.
Examples of Persuasive Essay in Literature
Example #1: our unhealthy obsession and sickness (by frank furedi).
“Governments today do two things that I object to in particular. First they encourage introspection, telling us that unless men examine their testicles, unless we keep a check on our cholesterol level, then we are not being responsible citizens. You are letting down yourself, your wife, your kids, everybody. We are encouraged continually to worry about our health. As a consequence, public health initiatives have become, as far as I can tell, a threat to public health. Secondly, governments promote the value of health seeking. We are meant always to be seeking health for this or that condition. The primary effect of this, I believe, is to make us all feel more ill.”
This is an excerpt from a persuasive essay of Frank Furedi. It encourages people to think about how the government is helping public health. Both the arguments of persuasion start with “First” in the first line and with “Secondly” in the second last line.
Example #2: We Are Training Our Kids to Kill (by Dave Grossman)
“Our society needs to be informed about these crimes, but when the images of the young killers are broadcast on television, they become role models. The average preschooler in America watches 27 hours of television a week. The average child gets more one-on-one communication from TV than from all her parents and teachers combined. The ultimate achievement for our children is to get their picture on TV. The solution is simple, and it comes straight out of the sociology literature: The media have every right and responsibility to tell the story , but they must be persuaded not to glorify the killers by presenting their images on TV.”
This is an excerpt from Grossman’s essay. He is clearly convincing the public about the violent television programs and their impacts on the kids. See how strong his arguments are in favor of his topic.
Example #3: The Real Skinny (by Belinda Luscombe)
“And what do we the people say? Do we rise up and say, ‘I categorically refuse to buy any article of clothing unless the person promoting it weighs more than she did when she wore knee socks?’ Or at least, ‘Where do I send the check for the chicken nuggets?’ Actually, not so much. Mostly, our responses range from ‘I wonder if that would look good on me?’ to ‘I don’t know who that skinny-ass cow is, but I hate her already.’
Just check the strength of the argument of Belinda Luscombe about purchasing things. The beauty of her writing is that she has made her readers think by asking rhetorical questions and answering them.
Function of a Persuasive Essay
The major function of a persuasive essay is to convince readers that, if they take a certain action, the world will be a better place for them. It could be otherwise or it could be a call to an action. The arguments given are either in the favor of the topic or against it. It cannot combine both at once. That is why readers feel it easy to be convinced.
Related posts:
- Elements of an Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Definition Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Types of Essay
- Analytical Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Cause and Effect Essay
- Critical Essay
- Expository Essay
- Process Essay
- Explicatory Essay
- An Essay on Man: Epistle I
- Comparison and Contrast Essay
Post navigation

What Are the Parts of a Persuasive Essay?
Every chess master was once a beginner. – Irving Chernev
For every argument, there will always be a counter-argument.
It sort of depends. Are you writing a short response (250-450 words)? Or are you writing a longer, multiple-paragraph paper (500 words or more)? Your answer to this question matters, and your your approach to each type of writing will be different.
However, for the sake of getting you some actionable advice that you can use right away, let’s go through the elements of a short persuasive response . I always preach a frame-writing approach to any essay which means that you should attack your writing in manageable frames or chunks.
In the example that follows, we’re taking a pretty typical persuasive essay topic and breaking it into a hook and a thesis statement (which, more or less, compose the essay’s introduction), a research detail , and interpretation followed a counterargument and some rebuttals (this is the body ) and a closer (conclusion) . If you wanted to break this approach into a formula, it would look like this:
Persuasive Essay = [ H + TS + RD + INT + CA + REB1 + REB2 + C ]
And if you include these parts in your persuasive essay, you’ll do well every time.
So now, let’s take a look at an actual example:
The prompt: .
In a concise, short-response essay (no more than 400 words), take a stand on whether or not you believe public schools should be allowed to require students to wear school uniforms.
The response
Part one: hook + thesis statement.
Hook: Recently, principal McGuire announced her intention to institute a school wide uniform policy at our school. Needless to say, the news has created quite a stir; much of it quite negative. I am with those who oppose this policy.
Thesis Statement: A mandatory dress code at school is quite simply a flagrant violation of young people’s’ civil rights.
- Background is provided in a short hook about principal McGuire. The thesis statement clearly states the essayist’s intentions.
Part Two: Research (proof) + Interpretation (analysis)
Research: Afterall, The First Amendment of our United States Constitution states that “Congress cannot pass laws abridging the freedom of speech.”
- The first research detail flows smoothly from the initial bridge and is short and sweet. It cites the first amendment of the Constitution beginning with the sentence starter* “states that”. The source is not cited because the existence of this document is considered common knowledge.
Interpretation: Our forefathers did not intend to have any American citizen’s right to reasonably express him or herself taken away by anybody at any time, no matter their age. This constitutional protection allows us to speak out against politicians who we disagree with. It allows us to write articles that might be controversial or even offensive to some. And it certainly extends to students who might want to wear some loose-fitting jeans or a punk-rock tee shirt. Expressing one’s style, politics or ideas with one’s choice of clothing is no different than doing so with words spoken aloud or written down on paper.
- At six sentences long, this interpretation is a healthy length. It focuses on other areas where freedom of expression is protected by the 1st amendment, then reasons that choice of clothing at school should be similarly protected. The somewhat animated tone befits a persuasive essay.
Part Three: Counterargument and Rebuttal / Your opposition gets his chance to fight back, and you, of course, return the favor.
Counterargument: Of course, there are those such as more conservative parents and school administrators who think that a school dress code is the key to maintaining law and order and a sense of discipline on campus. These critics of free dress may even cite studies demonstrating that schools that instill dress codes have fewer incidents of crime and graffiti.
- In a persuasive essay, always give some air time to the opposition. Like a tennis match, you sometimes have to let the other guy serve. In this case the opposition happens to be conservative parents and school administrators whose chief concern, of course, is law and order.
Rebuttal 1 and 2 (yes, you get two; it’s your essay): However, these small improvements do not make up for the great damaged caused by violating students’ basic civil rights. Hey, young man, give up a few of your rights and we’ll promise you a peaceful environment. It’s the wrong message to send young people. Besides, it isn’t the students’ responsibility to create law and order on campus. This is the responsibility of the teachers, administrators and, to some degree, parents. If a school can’t keep the peace when students are wearing their own choice of fashion, then perhaps the school itself should look more closely at its own policies and practices, and not at some kid’s sagging blue jeans or Yeezy tee shirt with holes in it.
- Rebuttal 1: The first part of the rebuttal strikes back by first mentioning that any gains caused by a dress code would be very modest, and even insignificant when compared to the damage done. In even suggests that such tactics might be a way of tricking kids.
- Rebuttal 2: Part 2 deflects the responsibility away from kids and back towards adults and schools themselves. Together these two rebuttals effectively take the argument back from the opposition and bring it back to the advantage of the essayist. It is done with respect and confidence.
Part 4: Closer / Let’s conclude
Closer: Undoubtedly, despite the opinions of some misguided critics, forcing students to wear school uniforms if they do not wish to is a crass violation of their basic constitutional rights.
- This closer gives mention to the counterargument with the phrase, “despite the opinions of some misguided critics”. The word “misguided” may be a bit strong, but it does make a point. Overall, this closer helps the response feel finished.
Now it’s your turn. Write using frames, and feel free to use this template to create your own persuasive essay.
Related Posts

Sharing Lessons With Colleagues

How To Write Perfect Paragraphs Every Time

Essaypop: The Perfect Solution for Elementary School Writing Instruction
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
How to Write a Persuasive Essay That Captivates Your Reader

After students progress from simple sentences to their first structured story, it’s time to enter the wonderful world of essay writing.
Though there are many types of essays , today’s post focuses on how to write a persuasive essay .
This is your (or your student’s) chance to make your voice heard and champion your cause.
If you are nervous about writing your first persuasive essay, don’t be. Perhaps you’ll find it as exciting a form of writing as I do.
Let’s walk through the writing process step-by-step.
What Is a Persuasive Essay?
The point of a persuasive essay is to—you guessed it—persuade. Also referred to as an argumentative essay, your goal is to convince your reader of your point-of-view through a presentation of sound arguments.
Ultimately, you want to move your reader to respond positively to points that you prove to be true.
The proof you provide can be in the form of facts, data, experiments, anecdotal evidence, and more.
Components of a Persuasive Essay
How do you master the art of persuasion?
What makes a great persuasive essay?
A persuasive essay that convinces its reader requires a few fundamental building blocks that include the following:
- A topic that’s debatable
- A thorough understanding of arguments from both sides
- A straightforward thesis statement
- Closely examined arguments
- A sturdy structure
- A harmonious balance of logic and emotion
- A sound and compelling conclusion

Teach Your Students to Write Skillfully
As they explore the history of ideas!
About The Author
Jordan Mitchell
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays.
You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question.
The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make.
Argumentative writing at college level
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts.
In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise.
Examples of argumentative essay prompts
At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response.
Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
- Don’t just list all the effects you can think of.
- Do develop a focused argument about the overall effect and why it matters, backed up by evidence from sources.
- Don’t just provide a selection of data on the measures’ effectiveness.
- Do build up your own argument about which kinds of measures have been most or least effective, and why.
- Don’t just analyze a random selection of doppelgänger characters.
- Do form an argument about specific texts, comparing and contrasting how they express their thematic concerns through doppelgänger characters.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion.
There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
Toulmin arguments
The Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
- Make a claim
- Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim
- Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim)
- Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay.
Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
- Claim that unconscious bias training does not have the desired results, and resources would be better spent on other approaches
- Cite data to support your claim
- Explain how the data indicates that the method is ineffective
- Anticipate objections to your claim based on other data, indicating whether these objections are valid, and if not, why not.
Rogerian arguments
The Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
- Discuss what the opposing position gets right and why people might hold this position
- Highlight the problems with this position
- Present your own position , showing how it addresses these problems
- Suggest a possible compromise —what elements of your position would proponents of the opposing position benefit from adopting?
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith.
Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
- Acknowledge that students rely too much on websites like Wikipedia
- Argue that teachers view Wikipedia as more unreliable than it really is
- Suggest that Wikipedia’s system of citations can actually teach students about referencing
- Suggest critical engagement with Wikipedia as a possible assignment for teachers who are skeptical of its usefulness.
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments.
Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion .
Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true.
In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings.
Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information.
This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position.
Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body.
No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument.
Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved April 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
Easy Steps to Writing a Persuasive Essay
Table of contents
If you’ve ever found yourself in a heated debate, passionately arguing a point, you already understand the essence of a persuasive essay. But let's clarify - what exactly is a persuasive essay? In simple terms, it's a piece of writing that takes a stand on a particular issue, and then uses facts, logic, and persuasion to convince the reader to agree with the author's viewpoint. Sounds challenging? It can be, especially if you're just starting out in the world of essay writing.
But why is learning to write persuasive essays so important? Well, these essays are not just assignments you complete for a grade. They're exercises in critical thinking, research, and communication. They help you refine your ability to argue a point convincingly, a skill that's invaluable in many career fields and everyday life situations.
As with any new skill, beginners might stumble over a few hurdles. It's completely normal. Crafting a persuasive essay that truly resonates requires a good understanding of your topic, strong arguments, a knack for counter-arguments, and of course, a dash of writing flair. Some common challenges beginners face include finding a compelling topic, structuring the essay properly, presenting strong arguments, and effectively addressing counter-arguments. It may feel like a lot, but don't worry. This guide is here to break it down step-by-step and make the process more manageable.
[VIEW] Quality Persuasive Essay Sample Written by Our Writer
Up next, we'll delve into the key elements of a persuasive essay and how you can master them. Whether you're writing for a class assignment, a debate team, or just want to convince your friends why your favorite show is the best, these tips will come in handy. And for those who might still struggle, remember: there's always help available - like the expert essay writing services at Writers Per Hour that can guide you through every step of the process.
Intrigued? Keep reading. It’s time to dive into the nuts and bolts of persuasive essay writing.
Understanding Persuasive Essays
KEY POINTS : " A persuasive essay comprises a thesis statement that declares your stance, supporting arguments that back up your viewpoint, counterarguments that tackle potential objections, and a firm conclusion that restates your thesis and arguments. The key to effective persuasion lies not only in a solid argument but also in understanding and appealing to your audience's interests and viewpoints. "
Persuasive essays might seem like an uphill battle, especially if you're new to the game. Don't fret, though! Understanding what makes a persuasive essay tick is the first significant stride you'll take on this journey. So let's break it down.
At the heart of every persuasive essay are a few key components. First up, we have the thesis statement . This is where you clearly state your viewpoint on the topic at hand. It's the flag you plant in the ground, the stand you're taking. For example, if you're writing about the merits of adopting a plant-based diet, your thesis statement might be, "Adopting a plant-based diet is beneficial for health, the environment, and animal welfare."
Then come your supporting arguments. These are the pillars that hold up your thesis statement. If the thesis statement is your claim, the supporting arguments are your evidence. Sticking with our plant-based diet example, you might argue that this diet is healthier because it's lower in saturated fats, helps the environment by reducing the demand for animal agriculture, and promotes animal welfare by reducing reliance on factory farming.
However, any good persuasive essay also addresses counterarguments . This is where you anticipate objections to your viewpoint and refute them. You might address counterarguments like the belief that plant-based diets lack sufficient protein or the notion that they are more expensive, offering evidence and arguments to the contrary.
Finally, your persuasive essay will conclude with a strong conclusion that reinforces your thesis statement and supporting arguments, refutes key counterarguments, and leaves your reader convinced of your viewpoint.
Another key element to consider when writing a persuasive essay is the audience . Knowing who your readers are, what they care about, and how they might react to your arguments is crucial to persuading them effectively. It’s not enough to have strong arguments—you also need to present them in a way that resonates with your audience.
As we venture into the steps of writing a persuasive essay, keep these elements in mind. They'll be your compass guiding you through the process. And if you're feeling lost, remember, the expert services at Writers Per Hour can offer guidance every step of the way.
5 Steps to Writing a Persuasive Essay
So, you've got a grasp on what a persuasive essay is and the key components it needs. Great! Now it's time to dive into the nitty-gritty - the step-by-step process of crafting your persuasive masterpiece.
Step 1: Topic Selection
This is where it all starts. Select a topic for your persuasive essay that's both debatable and interesting to you. If you're invested in the topic, your passion will shine through in your writing, making your arguments more convincing.
Step 2: Research
Once you've chosen your topic, it's time to hit the books (or the internet). Look for reliable sources that provide strong evidence to support your arguments. Remember, quality over quantity. It's better to have a few strong, well-sourced arguments than a pile of weak, unsupported ones.
Step 3: Outline Creation
Now, let's get organized. An outline helps you structure your essay and ensures that every argument has its place. Start with your thesis statement , list out your main arguments, anticipate potential counterarguments, and plan your conclusion. An outline doesn't just keep your writing on track; it can also help you spot weak points in your argument before you begin writing.
Step 4: Drafting the Essay
With your outline in hand, it's time to start writing. Begin with a compelling introduction that hooks your reader and presents your thesis statement. Then, move onto the body of your essay, where you'll lay out your arguments and address counterarguments. Finally, wrap everything up with a strong conclusion that reinforces your thesis and arguments.
Step 5: Revising and Editing
Once you've got your draft, it's time for the hard (but necessary) work of revising and editing. Check for clarity, coherence, and persuasiveness. Make sure your arguments are solid and your evidence is strong. And of course, proofread for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors.
Each of these steps plays a vital role in crafting a persuasive essay that hits the mark. It's a process that requires time, effort, and patience, but the end result is worth it: a persuasive essay that can sway even the most stubborn of minds.
And remember, if you ever feel stuck or overwhelmed, don't hesitate to seek help. Services like Writers Per Hour are available to assist you through every step of this process, from topic selection to final revisions.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Persuasive Essay Writing
As with any skill, mastering persuasive essay writing comes with its own set of challenges, especially when you're a beginner. Here, we'll address some of the most common hurdles and how to overcome them.
Selecting a Compelling Topic : One of the first obstacles beginners often face is choosing a topic that's both interesting and debatable. If you're struggling with this, consider what issues you feel passionate about. Then, think about whether these issues have multiple perspectives that can be argued.
Structuring the Essay : Crafting a persuasive essay isn't just about making compelling arguments; it's also about presenting them in an organized, logical way. If structuring your essay feels daunting, creating a detailed outline before you start writing can be a game-changer. This helps ensure your arguments flow logically and makes the writing process smoother.
Crafting Strong Arguments : Persuasive writing hinges on the strength of your arguments. Beginners often struggle with making their arguments compelling and credible. Overcome this by conducting thorough research, using reliable sources, and making sure each argument directly supports your thesis.
Addressing Counterarguments : It can be intimidating to think about someone disagreeing with your viewpoint, but addressing counterarguments is a crucial part of persuasive writing. Practice empathy and try to understand the other perspective. This can help you refute counterarguments effectively and make your essay more persuasive.
Remember, every writer faces challenges, especially when they're just starting out. It's part of the learning process. But with patience, practice, and a little help when needed (like from the professional persuasive writing services at Writers Per Hour), you can overcome these hurdles and become a persuasive essay pro.
Learning to craft a compelling persuasive essay is an invaluable skill that extends beyond just academic writing. It equips you with the ability to argue your viewpoint convincingly, a skill that's useful in various career fields and everyday life situations.
In this guide, we've broken down the key components of a persuasive essay and provided a step-by-step approach to crafting your own. We've also touched upon the common challenges beginners face and how to overcome them. But remember, as with any skill, mastering persuasive essay writing requires practice and patience. Don't be discouraged if your first few attempts don't turn out as you hoped. Every essay is a learning opportunity.
And of course, if you ever find yourself stuck or overwhelmed, remember that you're not alone. Professional services like Writers Per Hour are here to provide guidance and assistance at every step of the way.
From selecting a compelling topic and researching reliable sources, to drafting your arguments and refining your final draft, writing a persuasive essay is a journey. We hope this guide has illuminated the path and made the journey a little less daunting.
Additional Resources
As you embark on your persuasive essay writing journey, it's helpful to have a toolbox of resources at your disposal. Here are a few online resources that can further enhance your understanding and improve your persuasive writing skills:
1. Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL) : Purdue OWL is a fantastic resource for all things related to writing. Their section on Argumentative Essays offers in-depth guidance on writing persuasive essays.
2. The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill : The Writing Center provides a detailed guide on Argument Essays that includes strategies, examples, and tips for effective persuasive writing.
3. Khan Academy : Known for its extensive range of free online courses, Khan Academy offers a comprehensive course on Grammar that can help refine your writing skills.
4. TED-Ed : TED-Ed's YouTube channel features a useful video on "How to Make Your Writing More Persuasive" that offers a quick overview of persuasive writing techniques.
Remember, writing is a skill that improves over time and with practice. Utilize these resources, alongside the tips and strategies we've discussed in this guide, to hone your persuasive writing skills. And as always, if you need additional help, the professional writing services at Writers Per Hour are just a click away.
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.5: Persuasion
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 20304

- Ann Inoshita, Karyl Garland, Kate Sims, Jeanne K. Tsutsui Keuma, and Tasha Williams
- University of Hawaii via University of Hawaiʻi OER
Writers of persuasive essays take a stand on a controversial issue and give well-researched arguments to support this position. This section will help students define the persuasive essay as well as understand its purpose and structure.
What is an Argument?
In today’s society, arguments are all around us, in our every waking moment throughout the day, whether in online ads or in the messages one reads on one’s favorite box of cereal. The ability to think critically in terms of deciding what to believe is highly important due to the fact that individuals are bombarded by arguments, on the internet and elsewhere, on a daily basis. Deciding what arguments to accept or reject not only makes for a good essay, but has implications for success in life and for one’s future career.
Understanding the nature of argument is essential to writing a good persuasive essay. So, what is argument? It is not the act of proving who is right or wrong. Television and social media convey argument as a means of proving one’s point for the sake of arguing. This is not argument. Ancient rhetoricians such as Aristotle, Plato, and Socrates understood argument in terms of truth-seeking, and conceptualized it as a means of preventing war. In this vein, good writers engage in truth-seeking to find out what is valid so that they may communicate truths to others. Sometimes in this process of truth-seeking, the writers themselves may change their minds on a given topic. Leaders such as Queen Lili‘uokalani and Dr Martin Luther King, Jr. demonstrate argument as a means of engaging in truth-seeking. See A Letter of Protest (Queen Lili‘uokalani of Hawai‘i, 1898) and Letter from a Birmingham Jail (Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr., AU, University of Alabama, April 16, 1963).
Structure of a Persuasive Essay
Before students begin creating persuasive essays, they should engage in preliminary research. Persuasive essays often include quotes or paraphrases from experts or statistics from academic studies. These essays must also demonstrate the writer’s ability to think critically and to avoid logical errors.
Note: Persuasive essays often require research, so students should see the Research and Plagiarism chapter of this text before drafting the essay.
After writers have conducted some preliminary research to enter the conversation, they will be ready to begin writing. Drafting should include at least four aspects:
- Introduction and thesis
- Strong arguments and evidence in support of thesis
- Opposing and qualifying ideas
- A compelling and satisfying conclusion
Creating an Introduction and Thesis
The persuasive essay begins with an engaging introduction that presents the general issue. The role of this paragraph is to do the following:
- Create interest.
- Introduce a controversial topic.
- Include a thesis statement that clearly presents the writer’s position on the chosen issue, and the major points to be discussed. Instructors will give students further guidelines on where the thesis should appear, but it is usually located at the very end of the introduction.
Strong Arguments and Evidence in Support of the Thesis
The body of the persuasive essay presents the reasons for the writer’s position on the issue. Writers should provide at least three solid reasons for their position.
When developing arguments and evidence, a writer would be wise to do the following:
- Provide at least one paragraph for each reason that is presented (though some reasons may require more than one paragraph). Clearly state each reason in a topic sentence.
- Provide sufficient evidence for each reason. Much of the evidence will come from research, though writers can effectively integrate their own knowledge as evidence.
- Explain ideas thoroughly and carefully, connecting one’s sources together smoothly and logically.
- Provide follow-up discussion or explanation for the researched information one has provided.
- Remember that arguments are usually “won” or “lost” on the quantity and quality of the evidence.
Ways to Persuade
There are three primary ways to appeal to the emotion and response of readers: ethos, logos, and pathos.
Ethos is the appeal to what is right, fair and trustworthy. For example, if Aaron is arguing for more access to parks in Hawai‘i for individuals who are disabled, he could do so by pointing out that many citizens who happen to have some sort of disability pay taxes that support these parks and yet are denied access simply due to design. The unfairness of this situation would appeal to the readers’ sense of what is right or fair.
Logos appeals to the reader’s logic and reason. If Aaron is arguing for the need to make college tuition more affordable or even free, such as is the case in Norway, Sweden, and Germany, among other countries, and he uses statistics about the number of students who would not be able to obtain a college degree without some country-wide assistance, he is appealing to his reader’s logic.
An argument with pathos appeals to the reader’s emotions. In his essay in favor of students joining a sports team in high school, he could highlight his own experience of overcoming fears and physical challenges while running in high school. Such an approach would pull the heartstrings of his readers who are touched by his success due to the self-discipline, social connections, and physical strength he developed through running on a team.
Addressing Opposing Ideas and the Author’s Position
Any good argument anticipates the opposing arguments and attempts to answer or refute its main points. In refuting the opposing point, writers do the following:
- Address at least one major opposing point. Writers briefly summarize viewpoints on the other side of the argument.
- Provide reasons and evidence showing the weaknesses in this opposing idea. They may address more than one opposing viewpoint.
Conclusion: Call to Action
The conclusion should provide insight into the significance of the issue. Most important is the fact that such a conclusion would do well not to use the word “should” as in the following. “In order for the United States to increase college attendance, encourage young people to seek out higher education and advanced knowledge to be used within the professional world, and truly support the process of learning, making college tuition more affordable or even free is key.”
If writers have proven their stance within the body paragraphs using examples and quoted, paraphrased, or summarized information from professionals within the given community, a “should” isn’t needed because the reader has already been convinced.
- What facts (logos) does the advertiser provide?
- What emotions do you feel after viewing the advertisement?
- What occurred in the advertisement to cause these emotions (pathos)?
- What occurred in the advertisement that appealed to your sense of morals and ethics (ethos)?
- Overall, was the advertisement effective to persuade you to purchase their product? Why or why not?
Further Resources
- Read more about writing a thesis statement in the handout by University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill: Thesis Statements , The Writing Center.
- Watch the following video to learn more about persuasive appeals: Ethos, Pathos, Logos
- Read more about counterarguments and the language used to signal the counterargument and refutation in this handout by Harvard College Writing Center: Counterargument , Writing Resources.
- See sample persuasive essays in “Chapter 15: Introduction to Sample Essays,” Writing for Success.
- Other sample persuasive essays are “Online Monitoring: A Threat to Employee Privacy in the Wired Workplace“; (Hacker), and “ Performance Enhancement through Biotechnology Has No Place in Sports “; (Hacker). These essays are excellent references because they contain notes in the margins that explain the components of the essays and MLA format.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL). “ Transitional Devices ,” The Purdue OWL.
Works Cited
Hacker, Diana. Writer’s Reference . Bedford/St. Martins, 2007.
King, Jr., Martin Luther. “ Letter from a Birmingham Jail ,” AU, University of Alabama , April 16, 1963.
Lili`uokalani (Queen of Hawai`i). Letter to the U.S. House of Representatives (protesting U.S. assertion of ownership of Hawai`i), U.S. National Archives, Records of the U.S. House of Representatives, Record Group 233, Record HR 55A-H28.3, 19 December 1898.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The 5 Must-Have Steps of a Persuasive Essay. If you're intimidated by the idea of writing an argument, use this list to break your process into manageable chunks. Tackle researching and writing one element at a time, and then revise your essay so that it flows smoothly and coherently with every component in the optimal place. 1. A topic or ...
TIP 1: Some writers find it easier to write their introductions last. As long as you have your working thesis, this is a perfectly acceptable approach. From that thesis, you can plan your body paragraphs and then go back and write your introduction. TIP 2: Avoid "announcing" your thesis.
There are several components of a persuasive essay that are not often seen in other types of essays. The first major component of a persuasive essay is the position, which is the belief of the ...
The Purpose of Persuasive Writing. The purpose of persuasion in writing is to convince, motivate, or move readers toward a certain point of view, or opinion. The act of trying to persuade automatically implies that more than one opinion on the subject can be argued. The idea of an argument often conjures up images of two people yelling and ...
A persuasive essay is an essay in which the writer takes a side on an issue and tries to convince the reader to see the situation from the writer's point(s) of view, change the reader' s ... o The basic components of a persuasive essay are those of the five-paragraph essay. This is, however, by no means the only formula for writing such essays ...
Outline your argument. Outlining your entire essay before you get to writing it can help you organize your thoughts, research, and lay out your essay structure. Detail all your main points and pair them with all of the relevant, supporting evidence from your sources cited. 5. Write your introduction.
Writing a Persuasive Essay. View in PDF Format. Structure and organization are integral components of an effective persuasive essay. No matter how intelligent the ideas, a paper lacking a strong introduction, well-organized body paragraphs and an insightful conclusion is not an effective paper.
The purpose of persuasion in writing is to convince or move readers toward a certain point of view, or opinion. An argument is a reasoned opinion supported and explained by evidence. To argue, in writing, is to advance knowledge and ideas in a positive way. A thesis that expresses the opinion of the writer in more specific terms is better than ...
Here are the steps you need to take: Step 1: Create a Compelling Introduction. You want to hook your readers with a great opening for your persuasive essay, so they'll want to keep reading. Here are 3 tips for writing an attention-grabbing introduction for your next essay. Use a strong hook statement.
In this student paper, the student makes a persuasive case for the value of technical high schools in Georgia. As you read, pay attention to the different persuasive devices the writer uses to convince us of her position. Also note how the outline gives a structure to the paper that helps lead the reader step-by-step through the components of ...
How to Write a Persuasive Essay: The Main Components. 1. Introduction: Capturing Attention and Stating the Thesis. The introduction serves as the gateway to your persuasive essay. Begin by grabbing the reader's attention with a compelling hook—an anecdote, a surprising fact, or a thought-provoking question.
A persuasive essay is a writing piece focused on persuading the readers to believe that the author's argument is correct. Learn more about the persuasive essay, its goals, components, ways to put ...
Remember to consider each of these components in this formula as sections instead of paragraphs because you will probably want to discuss multiple ideas backing up your point of view to make it more convincing. When writing a persuasive essay, it is best to begin with the most important point because it immediately captivates your readers and ...
The term "persuasive" is an adjective derived from verb "persuade," which means "to convince somebody.". A persuasive essay is full of all the convincing techniques a writer can employ. It presents a situation, and takes a stand - either in its favor, or against it - to prove to readers whether it is beneficial or harmful for them.
In a persuasive essay, the writer's point of view should be clearly expressed at the beginning of each paragraph in the topic sentence, which should contain the main idea of the paragraph and the writer's controlling idea. 10.2: The Structure of a Persuasive Essay is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or ...
Rebuttal 1: The first part of the rebuttal strikes back by first mentioning that any gains caused by a dress code would be very modest, and even insignificant when compared to the damage done. In even suggests that such tactics might be a way of tricking kids. Rebuttal 2: Part 2 deflects the responsibility away from kids and back towards adults ...
Persuasive Tips and Techniques. The components detailed above are crucial to writing a great persuasive essay. However, you can take it to the next level by using proven persuasive techniques for essays. Consider the following list a set of "do's and don'ts" for persuasive writing: Keep balance in mind.
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
The persuasive essay begins with an engaging introduction that presents the general topic. The thesis typically appears somewhere in the introduction and states the writer's point of view. ... The ideal in persuasive writing is to let your reader know your bias, but do not let that bias blind you to the primary components of good ...
Persuasive essays might seem like an uphill battle, especially if you're new to the game. Don't fret, though! Understanding what makes a persuasive essay tick is the first significant stride you'll take on this journey. So let's break it down. At the heart of every persuasive essay are a few key components. First up, we have the thesis ...
The persuasive essay begins with an engaging introduction that presents the general issue. The role of this paragraph is to do the following: Create interest. Introduce a controversial topic. Include a thesis statement that clearly presents the writer's position on the chosen issue, and the major points to be discussed.