An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.


StatPearls [Internet].
Breech presentation.
Caron J. Gray ; Meaghan M. Shanahan .
Affiliations
Last Update: November 6, 2022 .
- Continuing Education Activity
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. This activity reviews the cause and pathophysiology of breech presentation and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in its management.
- Describe the pathophysiology of breech presentation.
- Review the physical exam of a patient with a breech presentation.
- Summarize the treatment options for breech presentation.
- Explain the importance of improving care coordination among interprofessional team members to improve outcomes for patients affected by breech presentation.
- Introduction
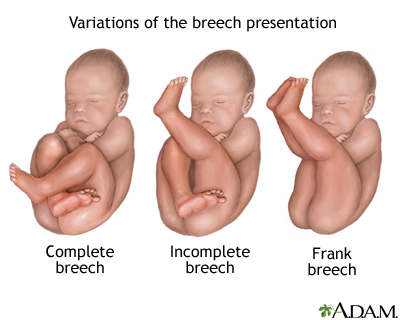
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. The complete breech has the fetus sitting with flexion of both hips and both legs in a tuck position. Finally, the incomplete breech can have any combination of one or both hips extended, also known as footling (one leg extended) breech, or double footling breech (both legs extended). [1] [2] [3]
Clinical conditions associated with breech presentation include those that may increase or decrease fetal motility, or affect the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. Prematurity, multiple gestations, aneuploidies, congenital anomalies, Mullerian anomalies, uterine leiomyoma, and placental polarity as in placenta previa are most commonly associated with a breech presentation. Also, a previous history of breech presentation at term increases the risk of repeat breech presentation at term in subsequent pregnancies. [4] [5] These are discussed in more detail in the pathophysiology section.
- Epidemiology
Breech presentation occurs in 3% to 4% of all term pregnancies. A higher percentage of breech presentations occurs with less advanced gestational age. At 32 weeks, 7% of fetuses are breech, and 28 weeks or less, 25% are breech.
Specifically, following one breech delivery, the recurrence rate for the second pregnancy was nearly 10%, and for a subsequent third pregnancy, it was 27%. Prior cesarean delivery has also been described by some to increase the incidence of breech presentation two-fold.
- Pathophysiology
As mentioned previously, the most common clinical conditions or disease processes that result in the breech presentation are those that affect fetal motility or the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity. [6] [7]
Conditions that change the vertical polarity or the uterine cavity, or affect the ease or ability of the fetus to turn into the vertex presentation in the third trimester include:
- Mullerian anomalies: Septate uterus, bicornuate uterus, and didelphys uterus
- Placentation: Placenta previa as the placenta is occupying the inferior portion of the uterine cavity. Therefore, the presenting part cannot engage
- Uterine leiomyoma: Mainly larger myomas located in the lower uterine segment, often intramural or submucosal, that prevent engagement of the presenting part.
- Prematurity
- Aneuploidies and fetal neuromuscular disorders commonly cause hypotonia of the fetus, inability to move effectively
- Congenital anomalies: Fetal sacrococcygeal teratoma, fetal thyroid goiter
- Polyhydramnios: Fetus is often in unstable lie, unable to engage
- Oligohydramnios: Fetus is unable to turn to vertex due to lack of fluid
- Laxity of the maternal abdominal wall: Uterus falls forward, the fetus is unable to engage in the pelvis.
The risk of cord prolapse varies depending on the type of breech. Incomplete or footling breech carries the highest risk of cord prolapse at 15% to 18%, while complete breech is lower at 4% to 6%, and frank breech is uncommon at 0.5%.
- History and Physical
During the physical exam, using the Leopold maneuvers, palpation of a hard, round, mobile structure at the fundus and the inability to palpate a presenting part in the lower abdomen superior to the pubic bone or the engaged breech in the same area, should raise suspicion of a breech presentation.
During a cervical exam, findings may include the lack of a palpable presenting part, palpation of a lower extremity, usually a foot, or for the engaged breech, palpation of the soft tissue of the fetal buttocks may be noted. If the patient has been laboring, caution is warranted as the soft tissue of the fetal buttocks may be interpreted as caput of the fetal vertex.
Any of these findings should raise suspicion and ultrasound should be performed.
Diagnosis of a breech presentation can be accomplished through abdominal exam using the Leopold maneuvers in combination with the cervical exam. Ultrasound should confirm the diagnosis.
On ultrasound, the fetal lie and presenting part should be visualized and documented. If breech presentation is diagnosed, specific information including the specific type of breech, the degree of flexion of the fetal head, estimated fetal weight, amniotic fluid volume, placental location, and fetal anatomy review (if not already done previously) should be documented.
- Treatment / Management
Expertise in the delivery of the vaginal breech baby is becoming less common due to fewer vaginal breech deliveries being offered throughout the United States and in most industrialized countries. The Term Breech Trial (TBT), a well-designed, multicenter, international, randomized controlled trial published in 2000 compared planned vaginal delivery to planned cesarean delivery for the term breech infant. The investigators reported that delivery by planned cesarean resulted in significantly lower perinatal mortality, neonatal mortality, and serious neonatal morbidity. Also, there was no significant difference in maternal morbidity or mortality between the two groups. Since that time, the rate of term breech infants delivered by planned cesarean has increased dramatically. Follow-up studies to the TBT have been published looking at maternal morbidity and outcomes of the children at two years. Although these reports did not show any significant difference in the risk of death and neurodevelopmental, these studies were felt to be underpowered. [8] [9] [10] [11]
Since the TBT, many authors since have argued that there are still some specific situations that vaginal breech delivery is a potential, safe alternative to planned cesarean. Many smaller retrospective studies have reported no difference in neonatal morbidity or mortality using these specific criteria.
The initial criteria used in these reports were similar: gestational age greater than 37 weeks, frank or complete breech presentation, no fetal anomalies on ultrasound examination, adequate maternal pelvis, and estimated fetal weight between 2500 g and 4000 g. In addition, the protocol presented by one report required documentation of fetal head flexion and adequate amniotic fluid volume, defined as a 3-cm vertical pocket. Oxytocin induction or augmentation was not offered, and strict criteria were established for normal labor progress. CT pelvimetry did determine an adequate maternal pelvis.
Despite debate on both sides, the current recommendation for the breech presentation at term includes offering external cephalic version (ECV) to those patients that meet criteria, and for those whom are not candidates or decline external cephalic version, a planned cesarean section for delivery sometime after 39 weeks.
Regarding the premature breech, gestational age will determine the mode of delivery. Before 26 weeks, there is a lack of quality clinical evidence to guide mode of delivery. One large retrospective cohort study recently concluded that from 28 to 31 6/7 weeks, there is a significant decrease in perinatal morbidity and mortality in a planned cesarean delivery versus intended vaginal delivery, while there is no difference in perinatal morbidity and mortality in gestational age 32 to 36 weeks. Of note, due to lack of recruitment, no prospective clinical trials are examining this issue.
- Differential Diagnosis
- Face and brow presentation
- Fetal anomalies
- Fetal death
- Grand multiparity
- Multiple pregnancies
- Oligohydramnios
- Pelvis Anatomy
- Preterm labor
- Primigravida
- Uterine anomalies
- Pearls and Other Issues
In light of the decrease in planned vaginal breech deliveries, thus the decrease in expertise in managing this clinical scenario, it is prudent that policies requiring simulation and instruction in the delivery technique for vaginal breech birth are established to care for the emergency breech vaginal delivery.
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
A breech delivery is usually managed by an obstetrician, labor and delivery nurse, anesthesiologist and a neonatologist. The ultimate decison rests on the obstetrician. To prevent complications, today cesarean sections are performed and experienced with vaginal deliveries of breech presentation is limited. For healthcare workers including the midwife who has no experience with a breech delivery, it is vital to communicate with an obstetrician, otherwise one risks litigation if complications arise during delivery. [12] [13] [14]
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Caron Gray declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Meaghan Shanahan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Gray CJ, Shanahan MM. Breech Presentation. [Updated 2022 Nov 6]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- [What effect does leg position in breech presentation have on mode of delivery and early neonatal morbidity?]. [Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 1997] [What effect does leg position in breech presentation have on mode of delivery and early neonatal morbidity?]. Krause M, Fischer T, Feige A. Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 1997 Jul-Aug; 201(4):128-35.
- The effect of intra-uterine breech position on postnatal motor functions of the lower limbs. [Early Hum Dev. 1993] The effect of intra-uterine breech position on postnatal motor functions of the lower limbs. Sival DA, Prechtl HF, Sonder GH, Touwen BC. Early Hum Dev. 1993 Mar; 32(2-3):161-76.
- The influence of the fetal leg position on the outcome in vaginally intended deliveries out of breech presentation at term - A FRABAT prospective cohort study. [PLoS One. 2019] The influence of the fetal leg position on the outcome in vaginally intended deliveries out of breech presentation at term - A FRABAT prospective cohort study. Jennewein L, Allert R, Möllmann CJ, Paul B, Kielland-Kaisen U, Raimann FJ, Brüggmann D, Louwen F. PLoS One. 2019; 14(12):e0225546. Epub 2019 Dec 2.
- Review Breech vaginal delivery at or near term. [Semin Perinatol. 2003] Review Breech vaginal delivery at or near term. Tunde-Byass MO, Hannah ME. Semin Perinatol. 2003 Feb; 27(1):34-45.
- Review [Breech Presentation: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice - Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Complications]. [Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2...] Review [Breech Presentation: CNGOF Guidelines for Clinical Practice - Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Complications]. Mattuizzi A. Gynecol Obstet Fertil Senol. 2020 Jan; 48(1):70-80. Epub 2019 Nov 1.
Recent Activity
- Breech Presentation - StatPearls Breech Presentation - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

- Pregnancy Classes

Breech Births
In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby’s buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3–4% of full-term births.
What are the different types of breech birth presentations?
- Complete breech: Here, the buttocks are pointing downward with the legs folded at the knees and feet near the buttocks.
- Frank breech: In this position, the baby’s buttocks are aimed at the birth canal with its legs sticking straight up in front of his or her body and the feet near the head.
- Footling breech: In this position, one or both of the baby’s feet point downward and will deliver before the rest of the body.
What causes a breech presentation?
The causes of breech presentations are not fully understood. However, the data show that breech birth is more common when:
- You have been pregnant before
- In pregnancies of multiples
- When there is a history of premature delivery
- When the uterus has too much or too little amniotic fluid
- When there is an abnormally shaped uterus or a uterus with abnormal growths, such as fibroids
- The placenta covers all or part of the opening of the uterus placenta previa
How is a breech presentation diagnosed?
A few weeks prior to the due date, the health care provider will place her hands on the mother’s lower abdomen to locate the baby’s head, back, and buttocks. If it appears that the baby might be in a breech position, they can use ultrasound or pelvic exam to confirm the position. Special x-rays can also be used to determine the baby’s position and the size of the pelvis to determine if a vaginal delivery of a breech baby can be safely attempted.
Can a breech presentation mean something is wrong?
Even though most breech babies are born healthy, there is a slightly elevated risk for certain problems. Birth defects are slightly more common in breech babies and the defect might be the reason that the baby failed to move into the right position prior to delivery.
Can a breech presentation be changed?
It is preferable to try to turn a breech baby between the 32nd and 37th weeks of pregnancy . The methods of turning a baby will vary and the success rate for each method can also vary. It is best to discuss the options with the health care provider to see which method she recommends.
Medical Techniques
External Cephalic Version (EVC) is a non-surgical technique to move the baby in the uterus. In this procedure, a medication is given to help relax the uterus. There might also be the use of an ultrasound to determine the position of the baby, the location of the placenta and the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus.
Gentle pushing on the lower abdomen can turn the baby into the head-down position. Throughout the external version the baby’s heartbeat will be closely monitored so that if a problem develops, the health care provider will immediately stop the procedure. ECV usually is done near a delivery room so if a problem occurs, a cesarean delivery can be performed quickly. The external version has a high success rate and can be considered if you have had a previous cesarean delivery.
ECV will not be tried if:
- You are carrying more than one fetus
- There are concerns about the health of the fetus
- You have certain abnormalities of the reproductive system
- The placenta is in the wrong place
- The placenta has come away from the wall of the uterus ( placental abruption )
Complications of EVC include:
- Prelabor rupture of membranes
- Changes in the fetus’s heart rate
- Placental abruption
- Preterm labor
Vaginal delivery versus cesarean for breech birth?
Most health care providers do not believe in attempting a vaginal delivery for a breech position. However, some will delay making a final decision until the woman is in labor. The following conditions are considered necessary in order to attempt a vaginal birth:
- The baby is full-term and in the frank breech presentation
- The baby does not show signs of distress while its heart rate is closely monitored.
- The process of labor is smooth and steady with the cervix widening as the baby descends.
- The health care provider estimates that the baby is not too big or the mother’s pelvis too narrow for the baby to pass safely through the birth canal.
- Anesthesia is available and a cesarean delivery possible on short notice
What are the risks and complications of a vaginal delivery?
In a breech birth, the baby’s head is the last part of its body to emerge making it more difficult to ease it through the birth canal. Sometimes forceps are used to guide the baby’s head out of the birth canal. Another potential problem is cord prolapse . In this situation the umbilical cord is squeezed as the baby moves toward the birth canal, thus slowing the baby’s supply of oxygen and blood. In a vaginal breech delivery, electronic fetal monitoring will be used to monitor the baby’s heartbeat throughout the course of labor. Cesarean delivery may be an option if signs develop that the baby may be in distress.
When is a cesarean delivery used with a breech presentation?
Most health care providers recommend a cesarean delivery for all babies in a breech position, especially babies that are premature. Since premature babies are small and more fragile, and because the head of a premature baby is relatively larger in proportion to its body, the baby is unlikely to stretch the cervix as much as a full-term baby. This means that there might be less room for the head to emerge.
Want to Know More?
- Creating Your Birth Plan
- Labor & Birth Terms to Know
- Cesarean Birth After Care
Compiled using information from the following sources:
- ACOG: If Your Baby is Breech
- William’s Obstetrics Twenty-Second Ed. Cunningham, F. Gary, et al, Ch. 24.
- Danforth’s Obstetrics and Gynecology Ninth Ed. Scott, James R., et al, Ch. 21.
BLOG CATEGORIES
- Can I get pregnant if… ? 3
- Child Adoption 19
- Fertility 54
- Pregnancy Loss 11
- Breastfeeding 29
- Changes In Your Body 5
- Cord Blood 4
- Genetic Disorders & Birth Defects 17
- Health & Nutrition 2
- Is it Safe While Pregnant 54
- Labor and Birth 65
- Multiple Births 10
- Planning and Preparing 24
- Pregnancy Complications 68
- Pregnancy Concerns 62
- Pregnancy Health and Wellness 149
- Pregnancy Products & Tests 8
- Pregnancy Supplements & Medications 14
- The First Year 41
- Week by Week Newsletter 40
- Your Developing Baby 16
- Options for Unplanned Pregnancy 18
- Paternity Tests 2
- Pregnancy Symptoms 5
- Prenatal Testing 16
- The Bumpy Truth Blog 7
- Uncategorized 4
- Abstinence 3
- Birth Control Pills, Patches & Devices 21
- Women's Health 34
- Thank You for Your Donation
- Unplanned Pregnancy
- Getting Pregnant
- Healthy Pregnancy
- Privacy Policy
Share this post:
Similar post.

Episiotomy: Advantages & Complications

Retained Placenta

What is Dilation in Pregnancy?
Track your baby’s development, subscribe to our week-by-week pregnancy newsletter.
- The Bumpy Truth Blog
- Fertility Products Resource Guide
Pregnancy Tools
- Ovulation Calendar
- Baby Names Directory
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Quiz
Pregnancy Journeys
- Partner With Us
- Corporate Sponsors
Babies in utero spend most of their gestation head-up. As they get heavier and prepare for delivery, they turn head-down. This usually happens around 32 weeks. When it doesn’t, and baby is still head-up at term, we call this baby breech.
When the baby’s head is up by the mother’s heart, the baby may be curled up in any number of positions—all of which are breech.
A footling breech baby is presenting feet or foot first . If we could look through the cervix, the first thing we’d see would be a foot. If labor started and the baby was pushed out this way, the first thing to emerge would be a foot.
A single footling has one knee drawn up so that only one foot is down and a double footling breech has both her feet together over the cervix.
Most breech babies come butt-first–Frank breech or complete breech. In this case, when the mother pushes her baby out, it’s a butt that is crowning, not a head (often called ‘rumping’).
Only about 20% of breech babies are footling breeches.
Footling breeches are trickier vaginal births. For one thing, there isn’t anything nice and solid and heavy pressing on the cervix to help it dilate. With a butt or a head over the cervix, it’s likely to dilate quicker and more efficiently.
Another risk of footling breech birth is cord prolapse . If the water is broken and a part of the umbilical cord falls through the cervix, it can create a dangerous situation for the baby due to cord compression and congealing.
Extremely rare in head-down birth, the incidence of cord prolapse rises considerably with breeches. Footling breeches have the highest risk (10-25%) because there is no butt or head blocking the cervix.
For many providers who are comfortable delivering a breech baby normally, footling breech position is a contraindication . For vaginal breech birth to be considered safe, a number of conditions must be met. The baby’s position is high on the list of questions.
Frank breech babies are generally seen as the safest because they can be delivered like a baby tube, neatly packaged with bum over cervix. These babies tend to do well in labor.
Part of the reason they do well is that the baby’s compacted body ‘opens the door’ for the head to pass through easily. With a footling, the baby’s feet can come down anytime and the birth canal may not be stretched as fully. Sometimes this makes birthing the head more difficult or dangerous.
Sometimes it does no such thing.
Check out some of the great footling breech birth stories and videos here.
Sometimes a footling will convert to a complete breech and come down butt-first once contractions begin. Keep this in mind when thinking about and discussing your options.
Finding a provider to attend and assist at your vaginal breech birth is already hard. Finding one who feels comfortable with a footling breech is even more difficult.
Some people do think it is easier to turn a footling . If you’re interested in ways to help a breech baby flip , it may just work. An ECV is safe and does reduce the likelihood a mother will end up with a cesarean.
Only you can make the decision, and I hope that if you feel comfortable with it you will convince your doctor to get some training or even consider traveling to avoid a cesarean.
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Key Points |
Abnormal fetal lie or presentation may occur due to fetal size, fetal anomalies, uterine structural abnormalities, multiple gestation, or other factors. Diagnosis is by examination or ultrasonography. Management is with physical maneuvers to reposition the fetus, operative vaginal delivery , or cesarean delivery .
Terms that describe the fetus in relation to the uterus, cervix, and maternal pelvis are
Fetal presentation: Fetal part that overlies the maternal pelvic inlet; vertex (cephalic), face, brow, breech, shoulder, funic (umbilical cord), or compound (more than one part, eg, shoulder and hand)
Fetal position: Relation of the presenting part to an anatomic axis; for transverse presentation, occiput anterior, occiput posterior, occiput transverse
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse
Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position.
Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with
Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
Fetal congenital anomalies
Uterine structural abnormalities (eg, fibroids, synechiae)
Multiple gestation
Several common types of abnormal lie or presentation are discussed here.

Transverse lie
Fetal position is transverse, with the fetal long axis oblique or perpendicular rather than parallel to the maternal long axis. Transverse lie is often accompanied by shoulder presentation, which requires cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation
There are several types of breech presentation.
Frank breech: The fetal hips are flexed, and the knees extended (pike position).
Complete breech: The fetus seems to be sitting with hips and knees flexed.
Single or double footling presentation: One or both legs are completely extended and present before the buttocks.
Types of breech presentations
Breech presentation makes delivery difficult ,primarily because the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge. Having a poor dilating wedge can lead to incomplete cervical dilation, because the presenting part is narrower than the head that follows. The head, which is the part with the largest diameter, can then be trapped during delivery.
Additionally, the trapped fetal head can compress the umbilical cord if the fetal umbilicus is visible at the introitus, particularly in primiparas whose pelvic tissues have not been dilated by previous deliveries. Umbilical cord compression may cause fetal hypoxemia.

Predisposing factors for breech presentation include
Preterm labor
Uterine abnormalities
Fetal anomalies
If delivery is vaginal, breech presentation may increase risk of
Umbilical cord prolapse
Birth trauma
Perinatal death

Face or brow presentation
In face presentation, the head is hyperextended, and position is designated by the position of the chin (mentum). When the chin is posterior, the head is less likely to rotate and less likely to deliver vaginally, necessitating cesarean delivery.
Brow presentation usually converts spontaneously to vertex or face presentation.
Occiput posterior position
The most common abnormal position is occiput posterior.
The fetal neck is usually somewhat deflexed; thus, a larger diameter of the head must pass through the pelvis.
Progress may arrest in the second phase of labor. Operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
Position and Presentation of the Fetus
If a fetus is in the occiput posterior position, operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
In breech presentation, the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge, which can cause the head to be trapped during delivery, often compressing the umbilical cord.
For breech presentation, usually do cesarean delivery at 39 weeks or during labor, but external cephalic version is sometimes successful before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Learn how UpToDate can help you.
Select the option that best describes you
- Medical Professional
- Resident, Fellow, or Student
- Hospital or Institution
- Group Practice
- Patient or Caregiver
- Find in topic
RELATED TOPICS
INTRODUCTION
This topic will provide an overview of major issues related to breech presentation, including choosing the best route for delivery. Techniques for breech delivery, with a focus on the technique for vaginal breech delivery, are discussed separately. (See "Delivery of the singleton fetus in breech presentation" .)
TYPES OF BREECH PRESENTATION
● Frank breech – Both hips are flexed and both knees are extended so that the feet are adjacent to the head ( figure 1 ); accounts for 50 to 70 percent of breech fetuses at term.
● Complete breech – Both hips and both knees are flexed ( figure 2 ); accounts for 5 to 10 percent of breech fetuses at term.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- COVID-19 Vaccines
- Occupational Therapy
- Healthy Aging
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
What Is Breech?
When a fetus is delivered buttocks or feet first
- Types of Presentation
Risk Factors
Complications.
Breech concerns the position of the fetus before labor . Typically, the fetus comes out headfirst, but in a breech delivery, the buttocks or feet come out first. This type of delivery is risky for both the pregnant person and the fetus.
This article discusses the different types of breech presentations, risk factors that might make a breech presentation more likely, treatment options, and complications associated with a breech delivery.
Verywell / Jessica Olah
Types of Breech Presentation
During the last few weeks of pregnancy, a fetus usually rotates so that the head is positioned downward to come out of the vagina first. This is called the vertex position.
In a breech presentation, the fetus does not turn to lie in the correct position. Instead, the fetus’s buttocks or feet are positioned to come out of the vagina first.
At 28 weeks of gestation, approximately 20% of fetuses are in a breech position. However, the majority of these rotate to the proper vertex position. At full term, around 3%–4% of births are breech.
The different types of breech presentations include:
- Complete : The fetus’s knees are bent, and the buttocks are presenting first.
- Frank : The fetus’s legs are stretched upward toward the head, and the buttocks are presenting first.
- Footling : The fetus’s foot is showing first.
Signs of Breech
There are no specific symptoms associated with a breech presentation.
Diagnosing breech before the last few weeks of pregnancy is not helpful, since the fetus is likely to turn to the proper vertex position before 35 weeks gestation.
A healthcare provider may be able to tell which direction the fetus is facing by touching a pregnant person’s abdomen. However, an ultrasound examination is the best way to determine how the fetus is lying in the uterus.
Most breech presentations are not related to any specific risk factor. However, certain circumstances can increase the risk for breech presentation.
These can include:
- Previous pregnancies
- Multiple fetuses in the uterus
- An abnormally shaped uterus
- Uterine fibroids , which are noncancerous growths of the uterus that usually appear during the childbearing years
- Placenta previa, a condition in which the placenta covers the opening to the uterus
- Preterm labor or prematurity of the fetus
- Too much or too little amniotic fluid (the liquid that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy)
- Fetal congenital abnormalities
Most fetuses that are breech are born by cesarean delivery (cesarean section or C-section), a surgical procedure in which the baby is born through an incision in the pregnant person’s abdomen.
In rare instances, a healthcare provider may plan a vaginal birth of a breech fetus. However, there are more risks associated with this type of delivery than there are with cesarean delivery.
Before cesarean delivery, a healthcare provider might utilize the external cephalic version (ECV) procedure to turn the fetus so that the head is down and in the vertex position. This procedure involves pushing on the pregnant person’s belly to turn the fetus while viewing the maneuvers on an ultrasound. This can be an uncomfortable procedure, and it is usually done around 37 weeks gestation.
ECV reduces the risks associated with having a cesarean delivery. It is successful approximately 40%–60% of the time. The procedure cannot be done once a pregnant person is in active labor.
Complications related to ECV are low and include the placenta tearing away from the uterine lining, changes in the fetus’s heart rate, and preterm labor.
ECV is usually not recommended if the:
- Pregnant person is carrying more than one fetus
- Placenta is in the wrong place
- Healthcare provider has concerns about the health of the fetus
- Pregnant person has specific abnormalities of the reproductive system
Recommendations for Previous C-Sections
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) says that ECV can be considered if a person has had a previous cesarean delivery.
During a breech delivery, the umbilical cord might come out first and be pinched by the exiting fetus. This is called cord prolapse and puts the fetus at risk for decreased oxygen and blood flow. There’s also a risk that the fetus’s head or shoulders will get stuck inside the mother’s pelvis, leading to suffocation.
Complications associated with cesarean delivery include infection, bleeding, injury to other internal organs, and problems with future pregnancies.
A healthcare provider needs to weigh the risks and benefits of ECV, delivering a breech fetus vaginally, and cesarean delivery.
In a breech delivery, the fetus comes out buttocks or feet first rather than headfirst (vertex), the preferred and usual method. This type of delivery can be more dangerous than a vertex delivery and lead to complications. If your baby is in breech, your healthcare provider will likely recommend a C-section.
A Word From Verywell
Knowing that your baby is in the wrong position and that you may be facing a breech delivery can be extremely stressful. However, most fetuses turn to have their head down before a person goes into labor. It is not a cause for concern if your fetus is breech before 36 weeks. It is common for the fetus to move around in many different positions before that time.
At the end of your pregnancy, if your fetus is in a breech position, your healthcare provider can perform maneuvers to turn the fetus around. If these maneuvers are unsuccessful or not appropriate for your situation, cesarean delivery is most often recommended. Discussing all of these options in advance can help you feel prepared should you be faced with a breech delivery.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. If your baby is breech .
TeachMeObGyn. Breech presentation .
MedlinePlus. Breech birth .
Hofmeyr GJ, Kulier R, West HM. External cephalic version for breech presentation at term . Cochrane Database Syst Rev . 2015 Apr 1;2015(4):CD000083. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000083.pub3
By Christine Zink, MD Dr. Zink is a board-certified emergency medicine physician with expertise in the wilderness and global medicine.
Explore NYSORA knowledge base for free:

Breech presentation
Learning objectives.
- Types of breech presentation
- Management of breech presentation
Definition and mechanisms
- Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first
- Frank breech: fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position
- Complete breech: fetus sits with flexion of both hips and both legs in a tuck position
- Incomplete breech: can have any combination of one or both hips extended, also known as footling (one leg extended) breech, or double footling breech (both legs extended)
- A higher percentage of breech presentations occurs with less advanced gestational age
- At 32 weeks, 7% of fetuses are breech
- At 28 weeks or less, 25% are breech
- Clinical conditions associated with a breech presentation include those that may increase or decrease fetal motility, or affect the vertical polarity of the uterine cavity
- It is unsafe for a breech baby to be born vaginally due to the risk of injury (dislocated or broken bones) or umbilical cord problems (flattening or twisting)
- Turning the baby into the head-first position and/or a planned C-section are the safest option
- Prematurity
- Multiple gestations
- Aneuploidies
- Congenital anomalies: fetal sacrococcygeal teratoma, fetal thyroid goiter
- Mullerian anomalies
- Uterine leiomyoma
- Placental polarity as in placenta previa
- Polyhydramnios
- Oligohydramnios
- Previous history of breech presentation (recurrence rate is 10% for the second pregnancy and 27% in the third pregnancy)
- Physical exam: palpation of a hard, round, mobile structure at the fundus and the inability to palpate a presenting part in the lower abdomen superior to the pubic bone or the engaged breach in the same area, should raise suspicion of a breech presentation
- Cervical exam: the lack of a palpable presenting part, palpation of a lower extremity, usually a foot, or for the engaged breech, palpation of the soft tissue of the fetal buttocks may be noted
- Note that the soft tissue of the fetal buttocks may be interpreted as caput of the fetal vertex if the patient has been laboring
- Ultrasound confirms the diagnosis

Suggested reading
- Gray CJ, Shanahan MM. 2022. Breech presentation. StatPearls.
- Hofmeyer GD. 2022. Overview of breech presentation. Up to date.
- 2017. Management of Breech Presentation. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 124, e151–e177.
- Stitely ML, Gherman RB. Labor with abnormal presentation and position. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2005;32(2):165-179.
- Pratt SD. Anesthesia for breech presentation and multiple gestation. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2003;46(3):711-729.
- Pollack KL, Chestnut DH. 1990. Anesthesia for complicated vaginal deliveries. Anesthesiology clinics of North America. 8;1:115-129.
We would love to hear from you. If you should detect any errors, email us [email protected]


Footling presentation
- Report problem with article
- View revision history
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
At the time the article was last revised Dennis Odhiambo Agolah had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
- Footling fetal presentation
- Incomplete breech presentation
A footling presentation (sometimes termed an incomplete breech presentation ) is a variation in fetal presentation and is considered a form of breech presentation . It is uncommon and thought to account for around 10-30% of births. In this presentation the fetus has a longitudinal lie but has one of both hips extended with feet presenting towards the pelvis. This therefore can be subclassified as
single footling presentation : one leg extended
double footling presentation : both legs extended
Footling presentation has the highest rate of cord prolapse(15-18%) out of the other breech presentations. 3
- 1. Curet L. Management of Footling Breech Presentation. Wis Med J. 1982;81(3):32. - Pubmed
- 2. Caron J. Gray & Meaghan M. Shanahan. Breech Presentation. StatPearls Publishing. 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448063/ - Pubmed
- 3. Gray C & Shanahan M. Breech Presentation. 2022. - Pubmed
- 4. Kaneti H, Rosen D, Markov S, Beyth Y, Fejgin M. Intrapartum External Cephalic Version of Footling-Breech Presentation. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2000;79(12):1083-5. - Pubmed

Incoming Links
- Variation in fetal presentation
Promoted articles (advertising)
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
By Section:
- Artificial Intelligence
- Classifications
- Imaging Technology
- Interventional Radiology
- Radiography
- Central Nervous System
- Gastrointestinal
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Head & Neck
- Hepatobiliary
- Interventional
- Musculoskeletal
- Paediatrics
- Not Applicable
Radiopaedia.org
- Feature Sponsor
- Expert advisers


An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Health Topics
- Drugs & Supplements
- Medical Tests
- Medical Encyclopedia
- About MedlinePlus
- Customer Support
Breech - series—Types of breech presentation
- Go to slide 1 out of 7
- Go to slide 2 out of 7
- Go to slide 3 out of 7
- Go to slide 4 out of 7
- Go to slide 5 out of 7
- Go to slide 6 out of 7
- Go to slide 7 out of 7
There are three types of breech presentation: complete, incomplete, and frank.
Complete breech is when both of the baby's knees are bent and his feet and bottom are closest to the birth canal.
Incomplete breech is when one of the baby's knees is bent and his foot and bottom are closest to the birth canal.
Frank breech is when the baby's legs are folded flat up against his head and his bottom is closest to the birth canal.
There is also footling breech where one or both feet are presenting.
Review Date 11/21/2022
Updated by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Related MedlinePlus Health Topics
- Childbirth Problems
6.1 Breech presentation
Presentation of the feet or buttocks of the foetus.
6.1.1 The different breech presentations
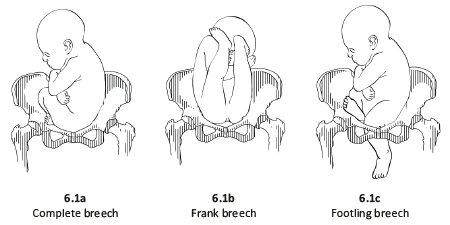
- In a complete breech presentation, the legs are tucked, and the foetus is in a crouching position (Figure 6.1a).
- In a frank breech presentation, the legs are extended, raised in front of the torso, with the feet near the head (Figure 6.1b).
- In a footling breech presentation (rare), one or both feet present first, with the buttocks higher up and the lower limbs extended or half-bent (Figure 6.1c).
6.1.2 Diagnosis
- The cephalic pole is palpable in the uterine fundus; round, hard, and mobile; the indentation of the neck can be felt.
- The inferior pole is voluminous, irregular, less hard, and less mobile than the head.
- During labour, vaginal examination reveals a “soft mass” divided by the cleft between the buttocks, with a hard projection at end of the cleft (the coccyx and sacrum).
- After rupture of the membranes: the anus can be felt in the middle of the cleft; a foot may also be felt.
- The clinical diagnosis may be difficult: a hand may be mistaken for a foot, a face for a breech.
6.1.3 Management
Route of delivery.
Before labour, external version (Chapter 7, Section 7.7 ) may be attempted to avoid breech delivery.
If external version is contra-indicated or unsuccessful, the breech position alone – in the absence of any other anomaly – is not, strictly speaking, a dystocic presentation, and does not automatically require a caesarean section. Deliver vaginally, if possible – even if the woman is primiparous.
Breech deliveries must be done in a CEmONC facility, especially for primiparous women.
Favourable factors for vaginal delivery are:
- Frank breech presentation;
- A history of vaginal delivery (whatever the presentation);
- Normally progressing dilation during labour.
The footling breech presentation is a very unfavourable position for vaginal delivery (risk of foot or cord prolapse). In this situation, the route of delivery depends on the number of previous births, the state of the membranes and how far advanced the labour is.
During labour
- Monitor dilation every 2 to 4 hours.
- If contractions are of good quality, dilation is progressing, and the foetal heart rate is regular, an expectant approach is best. Do not rupture the membranes unless dilation stops.
- If the uterine contractions are inadequate, labour can be actively managed with oxytocin.
Note : if the dilation stales, transfer the mother to a CEmONC facility unless already done, to ensure access to surgical facility for potential caesarean section.
At delivery
- Insert an IV line before expulsion starts.
- Consider episiotomy at expulsion. Episiotomy is performed when the perineum is sufficiently distended by the foetus's buttocks.
- Presence of meconium or meconium-stained amniotic fluid is common during breech delivery and is not necessarily a sign of foetal distress.
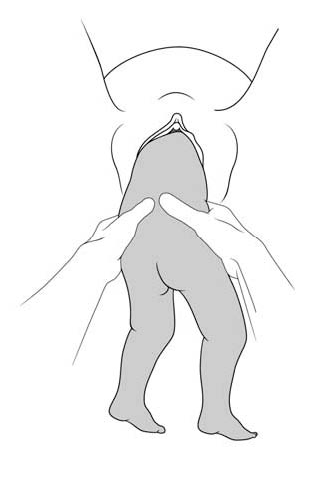
- The infant delivers unaided , as a result of the mother's pushing, simply supported by the birth attendant who gently holds the infant by the bony parts (hips and sacrum), with no traction. Do not pull on the legs.
Once the umbilicus is out, the rest of the delivery must be completed within 3 minutes, otherwise compression of the cord will deprive the infant of oxygen. Do not touch the infant until the shoulder blades appear to avoid triggering the respiratory reflex before the head is delivered.
- Monitor the position of the infant's back; impede rotation into posterior position.
Figures 6.2 - Breech delivery
6.1.4 Breech delivery problems
Posterior orientation.
If the infant’s back is posterior during expulsion, take hold of the hips and turn into an anterior position (this is a rare occurrence).
Obstructed shoulders
The shoulders can become stuck and hold back the infant's upper chest and head. This can occur when the arms are raised as the shoulders pass through the mother's pelvis. There are 2 methods for lowering the arms so that the shoulders can descend:
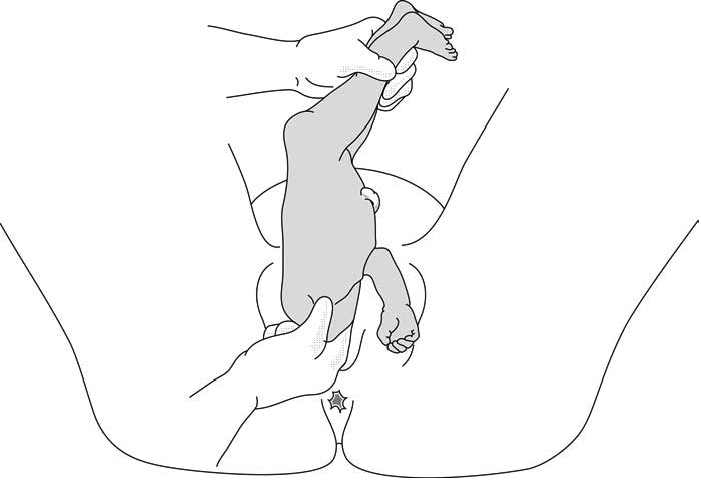
1 - Lovset's manoeuvre
- With thumbs on the infant's sacrum, take hold of the hips and pelvis with the other fingers.
- Turn the infant 90° (back to the left or to the right), to bring the anterior shoulder underneath the symphysis and engage the arm. Deliver the anterior arm.
- Then do a 180° counter-rotation (back to the right or to the left); this engages the posterior arm, which is then delivered.
Figures 6.3 - Lovset's manoeuvre
6.3c - Delivering the anterior arm and shoulder
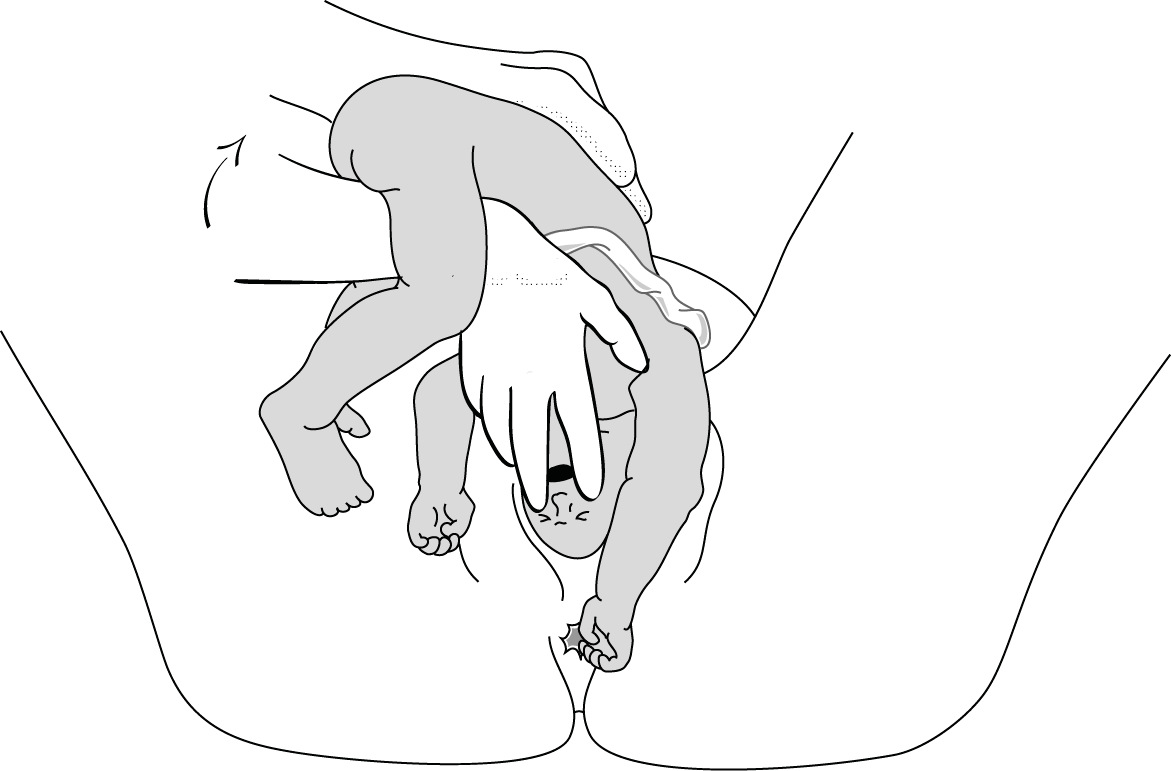
2 - Suzor’s manoeuvre
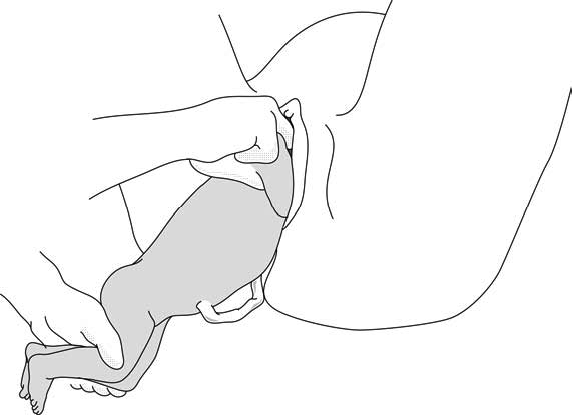
In case the previous method fails:
- Turn the infant 90° (its back to the right or to the left).
- Pull the infant downward: insert one hand along the back to look for the anterior arm. With the operator thumb in the infant armpit and middle finger along the arm, bring down the arm (Figure 6.4a).
- Lift infant upward by the feet in order to deliver the posterior shoulder (Figure 6.4b).
Figures 6.4 - Suzor's manoeuvre
6.4b - Delivering the posterior shoulder
Head entrapment
The infant's head is bulkier than the body, and can get trapped in the mother's pelvis or soft tissue.
There are various manoeuvres for delivering the head by flexing it, so that it descends properly, and then pivoting it up and around the mother's symphysis. These manoeuvres must be done without delay, since the infant must be allowed to breathe as soon as possible. All these manoeuvres must be performed smoothly, without traction on the infant.
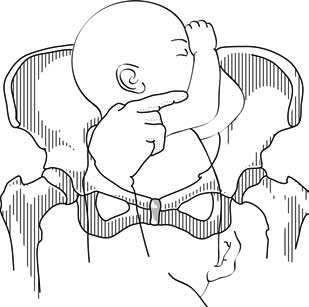
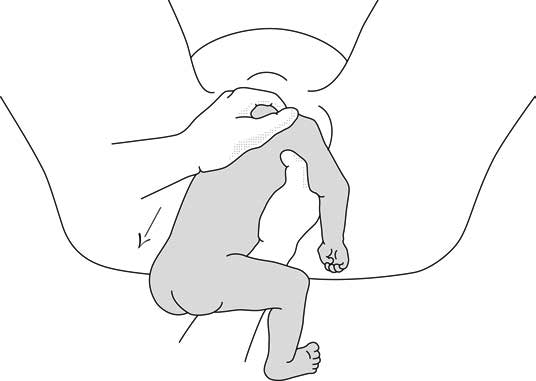
1 - Bracht's manoeuvre
- After the arms are delivered, the infant is grasped by the hips and lifted with two hands toward the mother's stomach, without any traction, the neck pivoting around the symphysis.
- Having an assistant apply suprapubic pressure facilitates delivery of the aftercoming head.
2 - Modified Mauriceau manoeuvre
- Infant's head occiput anterior.
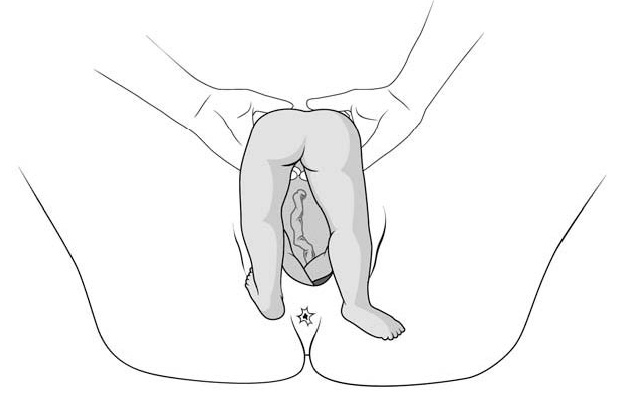
- Kneel to get a good traction angle: 45° downward.
- Support the infant on the hand and forearm, then insert the index and middle fingers, placing them on the infant’s maxilla. Placing the index and middle fingers into the infant’s mouth is not recommended, as this can fracture the mandible.
- Place the index and middle fingers of the other hand on either side of the infant's neck and lower the infant's head to bring the sub-occiput under the symphysis (Figure 6.6a).
- Tip the infant’s head and with a sweeping motion bring the back up toward the mother's abdomen, pivoting the occiput around her symphysis pubis (Figure 6.6b).
- Suprapubic pressure on the infant's head along the pelvic axis helps delivery of the head.
- As a last resort, symphysiotomy (Chapter 5, Section 5.7 ) can be combined with this manoeuvre.
Figures 6.6 - Modified Mauriceau manoeuvre
6.6a - Step 1 Infant straddles the birth attendant's forearm; the head, occiput anterior, is lowered to bring the occiput in contact with the symphysis.
6.6b - Step 2 The infant's back is tipped up toward the mother's abdomen.
3 - Forceps on aftercoming head
This procedure can only be performed by an operator experienced in using forceps.
- Getting Pregnant
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
- Birth Clubs
- See all in Community
- Ovulation Calculator
- How To Get Pregnant
- How To Get Pregnant Fast
- Ovulation Discharge
- Implantation Bleeding
- Ovulation Symptoms
- Pregnancy Symptoms
- Am I Pregnant?
- Pregnancy Tests
- See all in Getting Pregnant
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Pregnant Sex
- Weight Gain Tracker
- Signs of Labor
- Morning Sickness
- COVID Vaccine and Pregnancy
- Fetal Weight Chart
- Fetal Development
- Pregnancy Discharge
- Find Out Baby Gender
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- See all in Pregnancy
- Baby Name Generator
- Top Baby Names 2023
- Top Baby Names 2024
- How to Pick a Baby Name
- Most Popular Baby Names
- Baby Names by Letter
- Gender Neutral Names
- Unique Boy Names
- Unique Girl Names
- Top baby names by year
- See all in Baby Names
- Baby Development
- Baby Feeding Guide
- Newborn Sleep
- When Babies Roll Over
- First-Year Baby Costs Calculator
- Postpartum Health
- Baby Poop Chart
- See all in Baby
- Average Weight & Height
- Autism Signs
- Child Growth Chart
- Night Terrors
- Moving from Crib to Bed
- Toddler Feeding Guide
- Potty Training
- Bathing and Grooming
- See all in Toddler
- Height Predictor
- Potty Training: Boys
- Potty training: Girls
- How Much Sleep? (Ages 3+)
- Ready for Preschool?
- Thumb-Sucking
- Gross Motor Skills
- Napping (Ages 2 to 3)
- See all in Child
- Photos: Rashes & Skin Conditions
- Symptom Checker
- Vaccine Scheduler
- Reducing a Fever
- Acetaminophen Dosage Chart
- Constipation in Babies
- Ear Infection Symptoms
- Head Lice 101
- See all in Health
- Second Pregnancy
- Daycare Costs
- Family Finance
- Stay-At-Home Parents
- Breastfeeding Positions
- See all in Family
- Baby Sleep Training
- Preparing For Baby
- My Custom Checklist
- My Registries
- Take the Quiz
- Best Baby Products
- Best Breast Pump
- Best Convertible Car Seat
- Best Infant Car Seat
- Best Baby Bottle
- Best Baby Monitor
- Best Stroller
- Best Diapers
- Best Baby Carrier
- Best Diaper Bag
- Best Highchair
- See all in Baby Products
- Why Pregnant Belly Feels Tight
- Early Signs of Twins
- Teas During Pregnancy
- Baby Head Circumference Chart
- How Many Months Pregnant Am I
- What is a Rainbow Baby
- Braxton Hicks Contractions
- HCG Levels By Week
- When to Take a Pregnancy Test
- Am I Pregnant
- Why is Poop Green
- Can Pregnant Women Eat Shrimp
- Insemination
- UTI During Pregnancy
- Vitamin D Drops
- Best Baby Forumla
- Postpartum Depression
- Low Progesterone During Pregnancy
- Baby Shower
- Baby Shower Games
Breech, posterior, transverse lie: What position is my baby in?

Fetal presentation, or how your baby is situated in your womb at birth, is determined by the body part that's positioned to come out first, and it can affect the way you deliver. At the time of delivery, 97 percent of babies are head-down (cephalic presentation). But there are several other possibilities, including feet or bottom first (breech) as well as sideways (transverse lie) and diagonal (oblique lie).
Fetal presentation and position
During the last trimester of your pregnancy, your provider will check your baby's presentation by feeling your belly to locate the head, bottom, and back. If it's unclear, your provider may do an ultrasound or an internal exam to feel what part of the baby is in your pelvis.
Fetal position refers to whether the baby is facing your spine (anterior position) or facing your belly (posterior position). Fetal position can change often: Your baby may be face up at the beginning of labor and face down at delivery.
Here are the many possibilities for fetal presentation and position in the womb.
Medical illustrations by Jonathan Dimes
Head down, facing down (anterior position)
A baby who is head down and facing your spine is in the anterior position. This is the most common fetal presentation and the easiest position for a vaginal delivery.
This position is also known as "occiput anterior" because the back of your baby's skull (occipital bone) is in the front (anterior) of your pelvis.
Head down, facing up (posterior position)
In the posterior position , your baby is head down and facing your belly. You may also hear it called "sunny-side up" because babies who stay in this position are born facing up. But many babies who are facing up during labor rotate to the easier face down (anterior) position before birth.
Posterior position is formally known as "occiput posterior" because the back of your baby's skull (occipital bone) is in the back (posterior) of your pelvis.
Frank breech
In the frank breech presentation, both the baby's legs are extended so that the feet are up near the face. This is the most common type of breech presentation. Breech babies are difficult to deliver vaginally, so most arrive by c-section .
Some providers will attempt to turn your baby manually to the head down position by applying pressure to your belly. This is called an external cephalic version , and it has a 58 percent success rate for turning breech babies. For more information, see our article on breech birth .
Complete breech
A complete breech is when your baby is bottom down with hips and knees bent in a tuck or cross-legged position. If your baby is in a complete breech, you may feel kicking in your lower abdomen.
Incomplete breech
In an incomplete breech, one of the baby's knees is bent so that the foot is tucked next to the bottom with the other leg extended, positioning that foot closer to the face.
Single footling breech
In the single footling breech presentation, one of the baby's feet is pointed toward your cervix.
Double footling breech
In the double footling breech presentation, both of the baby's feet are pointed toward your cervix.
Transverse lie
In a transverse lie, the baby is lying horizontally in your uterus and may be facing up toward your head or down toward your feet. Babies settle this way less than 1 percent of the time, but it happens more commonly if you're carrying multiples or deliver before your due date.
If your baby stays in a transverse lie until the end of your pregnancy, it can be dangerous for delivery. Your provider will likely schedule a c-section or attempt an external cephalic version , which is highly successful for turning babies in this position.
Oblique lie
In rare cases, your baby may lie diagonally in your uterus, with his rump facing the side of your body at an angle.
Like the transverse lie, this position is more common earlier in pregnancy, and it's likely your provider will intervene if your baby is still in the oblique lie at the end of your third trimester.
Was this article helpful?
What to know if your baby is breech

What's a sunny-side up baby?

What happens to your baby right after birth

How your twins’ fetal positions affect labor and delivery

BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies .
Ahmad A et al. 2014. Association of fetal position at onset of labor and mode of delivery: A prospective cohort study. Ultrasound in obstetrics & gynecology 43(2):176-182. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23929533 Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Gray CJ and Shanahan MM. 2019. Breech presentation. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448063/ Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Hankins GD. 1990. Transverse lie. American Journal of Perinatology 7(1):66-70. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2131781 Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Medline Plus. 2020. Your baby in the birth canal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002060.htm Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]

Where to go next

Breech baby at the end of pregnancy
Published: July 2017
Please note that this information will be reviewed every 3 years after publication.
This patient information page provides advice if your baby is breech towards the end of pregnancy and the options available to you.
It may also be helpful if you are a partner, relative or friend of someone who is in this situation.
The information here aims to help you better understand your health and your options for treatment and care. Your healthcare team is there to support you in making decisions that are right for you. They can help by discussing your situation with you and answering your questions.
This information is for you if your baby remains in the breech position after 36 weeks of pregnancy. Babies lying bottom first or feet first in the uterus (womb) instead of in the usual head-first position are called breech babies.
This information includes:
- What breech is and why your baby may be breech
- The different types of breech
- The options if your baby is breech towards the end of your pregnancy
- What turning a breech baby in the uterus involves (external cephalic version or ECV)
- How safe ECV is for you and your baby
- Options for birth if your baby remains breech
- Other information and support available
Within this information, we may use the terms ‘woman’ and ‘women’. However, it is not only people who identify as women who may want to access this information. Your care should be personalised, inclusive and sensitive to your needs, whatever your gender identity.
A glossary of medical terms is available at A-Z of medical terms .
- Breech is very common in early pregnancy, and by 36–37 weeks of pregnancy most babies will turn into the head-first position. If your baby remains breech, it does not usually mean that you or your baby have any problems.
- Turning your baby into the head-first position so that you can have a vaginal delivery is a safe option.
- The alternative to turning your baby into the head-first position is to have a planned caesarean section or a planned vaginal breech birth.
Babies lying bottom first or feet first in the uterus (womb) instead of in the usual head-first position are called breech babies. Breech is very common in early pregnancy, and by 36-37 weeks of pregnancy, most babies turn naturally into the head-first position.
Towards the end of pregnancy, only 3-4 in every 100 (3-4%) babies are in the breech position.
A breech baby may be lying in one of the following positions:

It may just be a matter of chance that your baby has not turned into the head-first position. However, there are certain factors that make it more difficult for your baby to turn during pregnancy and therefore more likely to stay in the breech position. These include:
- if this is your first pregnancy
- if your placenta is in a low-lying position (also known as placenta praevia); see the RCOG patient information Placenta praevia, placenta accreta and vasa praevia
- if you have too much or too little fluid ( amniotic fluid ) around your baby
- if you are having more than one baby.
Very rarely, breech may be a sign of a problem with the baby. If this is the case, such problems may be picked up during the scan you are offered at around 20 weeks of pregnancy.
If your baby is breech at 36 weeks of pregnancy, your healthcare professional will discuss the following options with you:
- trying to turn your baby in the uterus into the head-first position by external cephalic version (ECV)
- planned caesarean section
- planned vaginal breech birth.
What does ECV involve?
ECV involves applying gentle but firm pressure on your abdomen to help your baby turn in the uterus to lie head-first.
Relaxing the muscle of your uterus with medication has been shown to improve the chances of turning your baby. This medication is given by injection before the ECV and is safe for both you and your baby. It may make you feel flushed and you may become aware of your heart beating faster than usual but this will only be for a short time.
Before the ECV you will have an ultrasound scan to confirm your baby is breech, and your pulse and blood pressure will be checked. After the ECV, the ultrasound scan will be repeated to see whether your baby has turned. Your baby’s heart rate will also be monitored before and after the procedure. You will be advised to contact the hospital if you have any bleeding, abdominal pain, contractions or reduced fetal movements after ECV.
ECV is usually performed after 36 or 37 weeks of pregnancy. However, it can be performed right up until the early stages of labour. You do not need to make any preparations for your ECV.
ECV can be uncomfortable and occasionally painful but your healthcare professional will stop if you are experiencing pain and the procedure will only last for a few minutes. If your healthcare professional is unsuccessful at their first attempt in turning your baby then, with your consent, they may try again on another day.
If your blood type is rhesus D negative, you will be advised to have an anti-D injection after the ECV and to have a blood test. See the NICE patient information Routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis for women who are rhesus D negative , which is available at: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta156/informationforpublic .
Why turn my baby head-first?
If your ECV is successful and your baby is turned into the head-first position you are more likely to have a vaginal birth. Successful ECV lowers your chances of requiring a caesarean section and its associated risks.
Is ECV safe for me and my baby?
ECV is generally safe with a very low complication rate. Overall, there does not appear to be an increased risk to your baby from having ECV. After ECV has been performed, you will normally be able to go home on the same day.
When you do go into labour, your chances of needing an emergency caesarean section, forceps or vacuum (suction cup) birth is slightly higher than if your baby had always been in a head-down position.
Immediately after ECV, there is a 1 in 200 chance of you needing an emergency caesarean section because of bleeding from the placenta and/or changes in your baby’s heartbeat.
ECV should be carried out by a doctor or a midwife trained in ECV. It should be carried out in a hospital where you can have an emergency caesarean section if needed.
ECV can be carried out on most women, even if they have had one caesarean section before.
ECV should not be carried out if:
- you need a caesarean section for other reasons, such as placenta praevia; see the RCOG patient information Placenta praevia, placenta accreta and vasa praevia
- you have had recent vaginal bleeding
- your baby’s heart rate tracing (also known as CTG) is abnormal
- your waters have broken
- you are pregnant with more than one baby; see the RCOG patient information Multiple pregnancy: having more than one baby .
Is ECV always successful?
ECV is successful for about 50% of women. It is more likely to work if you have had a vaginal birth before. Your healthcare team should give you information about the chances of your baby turning based on their assessment of your pregnancy.
If your baby does not turn then your healthcare professional will discuss your options for birth (see below). It is possible to have another attempt at ECV on a different day.
If ECV is successful, there is still a small chance that your baby will turn back to the breech position. However, this happens to less than 5 in 100 (5%) women who have had a successful ECV.
There is no scientific evidence that lying down or sitting in a particular position can help your baby to turn. There is some evidence that the use of moxibustion (burning a Chinese herb called mugwort) at 33–35 weeks of pregnancy may help your baby to turn into the head-first position, possibly by encouraging your baby’s movements. This should be performed under the direction of a registered healthcare practitioner.
Depending on your situation, your choices are:
There are benefits and risks associated with both caesarean section and vaginal breech birth, and these should be discussed with you so that you can choose what is best for you and your baby.
Caesarean section
If your baby remains breech towards the end of pregnancy, you should be given the option of a caesarean section. Research has shown that planned caesarean section is safer for your baby than a vaginal breech birth. Caesarean section carries slightly more risk for you than a vaginal birth.
Caesarean section can increase your chances of problems in future pregnancies. These may include placental problems, difficulty with repeat caesarean section surgery and a small increase in stillbirth in subsequent pregnancies. See the RCOG patient information Choosing to have a caesarean section .
If you choose to have a caesarean section but then go into labour before your planned operation, your healthcare professional will examine you to assess whether it is safe to go ahead. If the baby is close to being born, it may be safer for you to have a vaginal breech birth.
Vaginal breech birth
After discussion with your healthcare professional about you and your baby’s suitability for a breech delivery, you may choose to have a vaginal breech birth. If you choose this option, you will need to be cared for by a team trained in helping women to have breech babies vaginally. You should plan a hospital birth where you can have an emergency caesarean section if needed, as 4 in 10 (40%) women planning a vaginal breech birth do need a caesarean section. Induction of labour is not usually recommended.
While a successful vaginal birth carries the least risks for you, it carries a small increased risk of your baby dying around the time of delivery. A vaginal breech birth may also cause serious short-term complications for your baby. However, these complications do not seem to have any long-term effects on your baby. Your individual risks should be discussed with you by your healthcare team.
Before choosing a vaginal breech birth, it is advised that you and your baby are assessed by your healthcare professional. They may advise against a vaginal birth if:
- your baby is a footling breech (one or both of the baby’s feet are below its bottom)
- your baby is larger or smaller than average (your healthcare team will discuss this with you)
- your baby is in a certain position, for example, if its neck is very tilted back (hyper extended)
- you have a low-lying placenta (placenta praevia); see the RCOG patient information Placenta Praevia, placenta accreta and vasa praevia
- you have pre-eclampsia or any other pregnancy problems; see the RCOG patient information Pre-eclampsia .
With a breech baby you have the same choices for pain relief as with a baby who is in the head-first position. If you choose to have an epidural, there is an increased chance of a caesarean section. However, whatever you choose, a calm atmosphere with continuous support should be provided.
If you have a vaginal breech birth, your baby’s heart rate will usually be monitored continuously as this has been shown to improve your baby’s chance of a good outcome.
In some circumstances, for example, if there are concerns about your baby’s heart rate or if your labour is not progressing, you may need an emergency caesarean section during labour. A paediatrician (a doctor who specialises in the care of babies, children and teenagers) will attend the birth to check your baby is doing well.
If you go into labour before 37 weeks of pregnancy, the balance of the benefits and risks of having a caesarean section or vaginal birth changes and will be discussed with you.
If you are having twins and the first baby is breech, your healthcare professional will usually recommend a planned caesarean section.
If, however, the first baby is head-first, the position of the second baby is less important. This is because, after the birth of the first baby, the second baby has lots more room to move. It may turn naturally into a head-first position or a doctor may be able to help the baby to turn. See the RCOG patient information Multiple pregnancy: having more than one baby .
If you would like further information on breech babies and breech birth, you should speak with your healthcare professional.
Further information
- NHS information on breech babies
- NCT information on breech babies
If you are asked to make a choice, you may have lots of questions that you want to ask. You may also want to talk over your options with your family or friends. It can help to write a list of the questions you want answered and take it to your appointment.
Ask 3 Questions
To begin with, try to make sure you get the answers to 3 key questions , if you are asked to make a choice about your healthcare:
- What are my options?
- What are the pros and cons of each option for me?
- How do I get support to help me make a decision that is right for me?
*Ask 3 Questions is based on Shepherd et al. Three questions that patients can ask to improve the quality of information physicians give about treatment options: A cross-over trial. Patient Education and Counselling, 2011;84:379-85
- https://aqua.nhs.uk/resources/shared-decision-making-case-studies/
Sources and acknowledgements
This information has been developed by the RCOG Patient Information Committee. It is based on the RCOG Green-top Clinical Guidelines No. 20a External Cephalic Version and Reducing Incidence of Term Breech Presentation and No. 20b Management of Breech Presentation . The guidelines contain a full list of the sources of evidence we have used.
This information was reviewed before publication by women attending clinics in Nottingham, Essex, Inverness, Manchester, London, Sussex, Bristol, Basildon and Oxford, by the RCOG Women’s Network and by the RCOG Women’s Voices Involvement Panel.
Please give us feedback by completing our feedback survey:
- Members of the public – patient information feedback
- Healthcare professionals – patient information feedback
External Cephalic Version and Reducing the Incidence of Term Breech Presentation Green-top Guideline
Management of Breech Presentation Green-top Guideline

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. The three types of breech presentation include frank breech, complete breech, and incomplete breech. In a frank breech, the fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. The complete breech has the ...
Footling breech: One or both of the baby's feet point downward and will deliver before the rest of their body. Transverse lie: This is a form of breech presentation where your baby is positioned horizontally across your uterus instead of vertically. This would make their shoulder enter the vagina first.
Breech Births. In the last weeks of pregnancy, a baby usually moves so his or her head is positioned to come out of the vagina first during birth. This is called a vertex presentation. A breech presentation occurs when the baby's buttocks, feet, or both are positioned to come out first during birth. This happens in 3-4% of full-term births.
A footling breech baby is presenting feet or foot first. If we could look through the cervix, the first thing we'd see would be a foot. If labor started and the baby was pushed out this way, the first thing to emerge would be a foot. A single footling has one knee drawn up so that only one foot is down and a double footling breech has both ...
Single or double footling presentation: One or both legs are completely extended and present before the buttocks. Types of breech presentations. Breech presentation makes delivery difficult ,primarily because the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge. Having a poor dilating wedge can lead to incomplete cervical dilation, because the ...
The main types of breech presentation are: Frank breech - Both hips are flexed and both knees are extended so that the feet are adjacent to the head ( figure 1 ); accounts for 50 to 70 percent of breech fetuses at term. Complete breech - Both hips and both knees are flexed ( figure 2 ); accounts for 5 to 10 percent of breech fetuses at term.
At full term, around 3%-4% of births are breech. The different types of breech presentations include: Complete: The fetus's knees are bent, and the buttocks are presenting first. Frank: The fetus's legs are stretched upward toward the head, and the buttocks are presenting first. Footling: The fetus's foot is showing first.
Overview. Breech presentation is defined as a fetus in a longitudinal lie with the buttocks or feet closest to the cervix. This occurs in 3-4% of all deliveries. The percentage of breech deliveries decreases with advancing gestational age from 22-25% of births prior to 28 weeks' gestation to 7-15% of births at 32 weeks' gestation to 3-4% of ...
Breech delivery is the single most common abnormal presentation. The incidence is highly dependent on the gestational age. At 20 weeks, about one in four pregnancies are breech presentation. By full term, the incidence is about 4%. Other contributing factors include: Abnormal shape of the pelvis, uterus, or abdominal wall,
Breech presentation: clinical practice guideline from the French College of Gynaecologists and Obstetricians [2020] ... The lack of a standard definition of a footling breech is problematic because the term is open to interpretation and will invariably lead to a higher rate of C/S for breech in this setting, further limiting birth mode options ...
The strict criteria included 'normal' (definition unstated) radiological pelvimetry which was performed in 82.5% of planned vaginal births, continuous EFM and routine ultrasound. ... footling breech presentation, an extended neck, 'obstructing' fetal abnormalities and an existing indication for caesarean birth.
Extended Breech, Flexed Breech and Footling Breech. The position of the baby inside the uterus keeps changing during pregnancy. At the time of delivery, the best position for the baby to be in is ...
A footling breech is often listed as a contraindication to a VBB [13, 15, 17]. The SOGC guidelines defines a footling breech presentation as a fetus where "…one or both hips are extended" and provides an explanation for the recommendation of a C/S, that being a ten-fold risk of cord prolapse (10% versus 1%) compared to frank breech [15].
Breech presentation occurs in 3-4% of term deliveries and is more common in preterm deliveries and nulliparous women. Breech presentation is associated with uterine and congenital abnormalities, and has a significant recurrence risk. Term babies presenting by the breech have worse outcomes than cephalic presenting babies, irrespective of the ...
Definition and mechanisms. Breech presentation refers to the fetus in the longitudinal lie with the buttocks or lower extremity entering the pelvis first. Three types: Frank breech: fetus has flexion of both hips, and the legs are straight with the feet near the fetal face, in a pike position. Complete breech: fetus sits with flexion of both ...
A footling presentation (sometimes termed an incomplete breech presentation) is a variation in fetal presentation and is considered a form of breech presentation. It is uncommon and thought to account for around 10-30% of births. In this presentation the fetus has a longitudinal lie but has one of both hips extended with feet presenting towards ...
Overview. There are three types of breech presentation: complete, incomplete, and frank. Complete breech is when both of the baby's knees are bent and his feet and bottom are closest to the birth canal. Incomplete breech is when one of the baby's knees is bent and his foot and bottom are closest to the birth canal.
Presentation of the feet or buttocks of the foetus. 6.1.1 The different breech presentations. In a complete breech presentation, the legs are tucked, and the foetus is in a crouching position (Figure 6.1a).; In a frank breech presentation, the legs are extended, raised in front of the torso, with the feet near the head (Figure 6.1b).; In a footling breech presentation (rare), one or both feet ...
In the double footling breech presentation, both of the baby's feet are pointed toward your cervix. Transverse lie. In a transverse lie, the baby is lying horizontally in your uterus and may be facing up toward your head or down toward your feet. Babies settle this way less than 1 percent of the time, but it happens more commonly if you're ...
Definition Breech presentation is when the baby's buttocks, foot or feet present instead of its head. Breech presentation is sometimes associated with uterine, ... the type of breech presentation (i.e. to exclude a footling breech). An ultrasound and vaginal examination should be performed on admission in labour. Please refer to patient ...
Babies lying bottom first or feet first in the uterus (womb) instead of in the usual head-first position are called breech babies. Breech is very common in early pregnancy, and by 36-37 weeks of pregnancy, most babies turn naturally into the head-first position. Towards the end of pregnancy, only 3-4 in every 100 (3-4%) babies are in the breech ...
A breech presentation at delivery occurs when the fetus does not turn to a cephalic presentation. ... Footling and kneeling breeches have a higher risk of cord prolapse and head entrapment. Parity - Parity refers to the number of times a woman has given birth before. If a woman has given birth vaginally, her pelvis has "proven" it is big ...
footling breech presentation: Neonatology A breech presentation in which one leg flops out of the birth canal