- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions

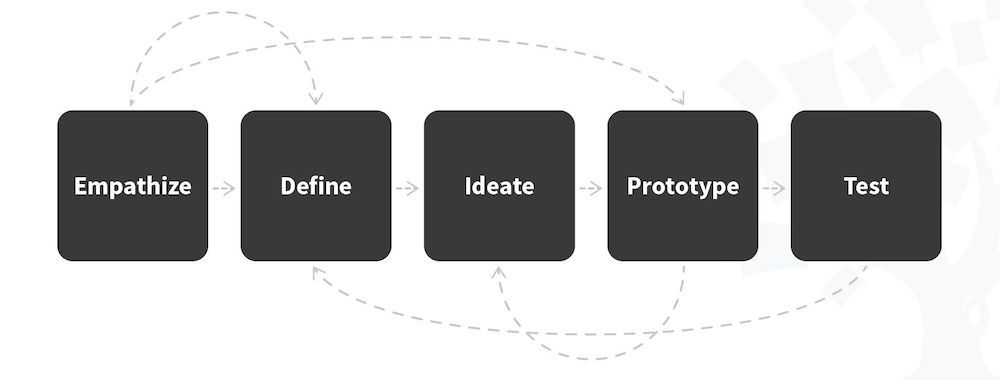
The 5 Stages in the Design Thinking Process
Design thinking is a methodology which provides a solution-based approach to solving problems. It’s extremely useful when used to tackle complex problems that are ill-defined or unknown—because it serves to understand the human needs involved, reframe the problem in human-centric ways, create numerous ideas in brainstorming sessions and adopt a hands-on approach to prototyping and testing. When you know how to apply the five stages of design thinking you will be impowered because you can apply the methodology to solve complex problems that occur in our companies, our countries, and across the world.
Design thinking is a non-linear, iterative process that can have anywhere from three to seven phases, depending on whom you talk to. We focus on the five-stage design thinking model proposed by the Hasso Plattner Institute of Design at Stanford (the d.school) because they are world-renowned for the way they teach and apply design thinking.
What are the 5 Stages of the Design Thinking Process
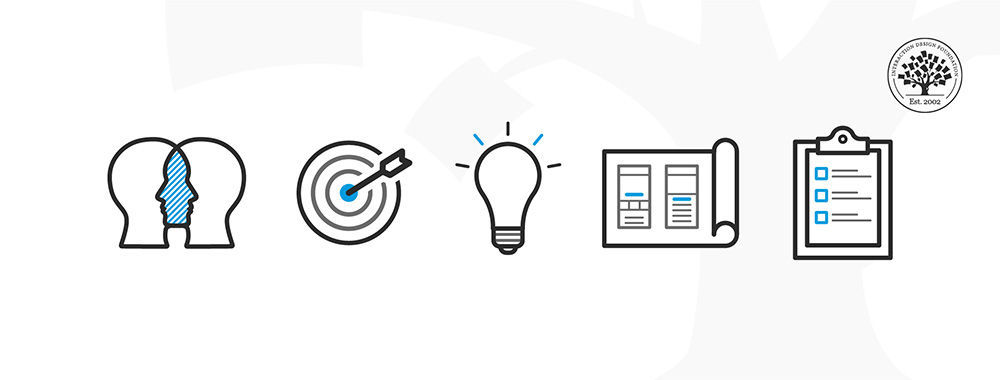
The five stages of design thinking, according to the d.school, are:
Empathize : research your users' needs .
Define : state your users' needs and problems.
Ideate : challenge assumptions and create ideas.
Prototype : start to create solutions.
Test : try your solutions out.
Let’s dive into each stage of the design thinking process.
Hasso-Platner Institute Panorama
Ludwig Wilhelm Wall, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
- Transcript loading…
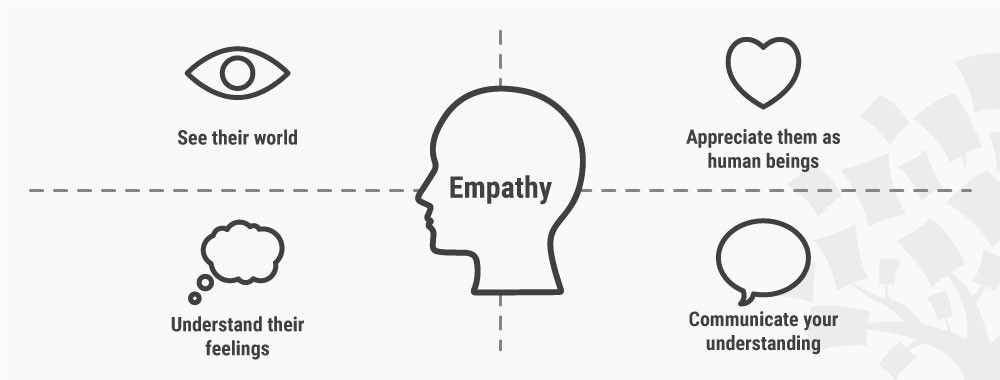
Stage 1: Empathize—Research Your Users' Needs

Empathize: the first phase of design thinking, where you gain real insight into users and their needs.
© Teo Yu Siang and the Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-NC-SA 3.0.
The first stage of the design thinking process focuses on user-centric research . You want to gain an empathic understanding of the problem you are trying to solve. Consult experts to find out more about the area of concern and conduct observations to engage and empathize with your users. You may also want to immerse yourself in your users’ physical environment to gain a deeper, personal understanding of the issues involved—as well as their experiences and motivations . Empathy is crucial to problem solving and a human-centered design process as it allows design thinkers to set aside their own assumptions about the world and gain real insight into users and their needs.
Depending on time constraints, you will gather a substantial amount of information to use during the next stage. The main aim of the Empathize stage is to develop the best possible understanding of your users, their needs and the problems that underlie the development of the product or service you want to create.
Stage 2: Define—State Your Users' Needs and Problems

Define: the second phase of design thinking, where you define the problem statement in a human-centered manner.
In the Define stage, you will organize the information you have gathered during the Empathize stage. You’ll analyze your observations to define the core problems you and your team have identified up to this point. Defining the problem and problem statement must be done in a human-centered manner .
For example, you should not define the problem as your own wish or need of the company: “We need to increase our food-product market share among young teenage girls by 5%.”
You should pitch the problem statement from your perception of the users’ needs: “Teenage girls need to eat nutritious food in order to thrive, be healthy and grow.”
The Define stage will help the design team collect great ideas to establish features, functions and other elements to solve the problem at hand—or, at the very least, allow real users to resolve issues themselves with minimal difficulty. In this stage, you will start to progress to the third stage, the ideation phase, where you ask questions to help you look for solutions: “How might we encourage teenage girls to perform an action that benefits them and also involves your company’s food-related product or service?” for instance.
Stage 3: Ideate—Challenge Assumptions and Create Ideas

Ideate: the third phase of design thinking, where you identify innovative solutions to the problem statement you’ve created.
During the third stage of the design thinking process, designers are ready to generate ideas. You’ve grown to understand your users and their needs in the Empathize stage, and you’ve analyzed your observations in the Define stage to create a user centric problem statement. With this solid background, you and your team members can start to look at the problem from different perspectives and ideate innovative solutions to your problem statement .
There are hundreds of ideation techniques you can use—such as Brainstorm, Brainwrite , Worst Possible Idea and SCAMPER . Brainstorm and Worst Possible Idea techniques are typically used at the start of the ideation stage to stimulate free thinking and expand the problem space. This allows you to generate as many ideas as possible at the start of ideation. You should pick other ideation techniques towards the end of this stage to help you investigate and test your ideas, and choose the best ones to move forward with—either because they seem to solve the problem or provide the elements required to circumvent it.
Stage 4: Prototype—Start to Create Solutions

Prototype: the fourth phase of design thinking, where you identify the best possible solution.
The design team will now produce a number of inexpensive, scaled down versions of the product (or specific features found within the product) to investigate the key solutions generated in the ideation phase. These prototypes can be shared and tested within the team itself, in other departments or on a small group of people outside the design team.
This is an experimental phase, and the aim is to identify the best possible solution for each of the problems identified during the first three stages . The solutions are implemented within the prototypes and, one by one, they are investigated and then accepted, improved or rejected based on the users’ experiences.
By the end of the Prototype stage, the design team will have a better idea of the product’s limitations and the problems it faces. They’ll also have a clearer view of how real users would behave, think and feel when they interact with the end product.
Stage 5: Test—Try Your Solutions Out

Test: the fifth and final phase of the design thinking process, where you test solutions to derive a deep understanding of the product and its users.
Designers or evaluators rigorously test the complete product using the best solutions identified in the Prototype stage. This is the final stage of the five-stage model; however, in an iterative process such as design thinking, the results generated are often used to redefine one or more further problems. This increased level of understanding may help you investigate the conditions of use and how people think, behave and feel towards the product, and even lead you to loop back to a previous stage in the design thinking process. You can then proceed with further iterations and make alterations and refinements to rule out alternative solutions. The ultimate goal is to get as deep an understanding of the product and its users as possible.
Did You Know Design Thinking is a Non-Linear Process?
We’ve outlined a direct and linear design thinking process here, in which one stage seemingly leads to the next with a logical conclusion at user testing . However, in practice, the process is carried out in a more flexible and non-linear fashion . For example, different groups within the design team may conduct more than one stage concurrently, or designers may collect information and prototype throughout each stage of the project to bring their ideas to life and visualize the problem solutions as they go. What’s more, results from the Test stage may reveal new insights about users which lead to another brainstorming session (Ideate) or the development of new prototypes (Prototype).
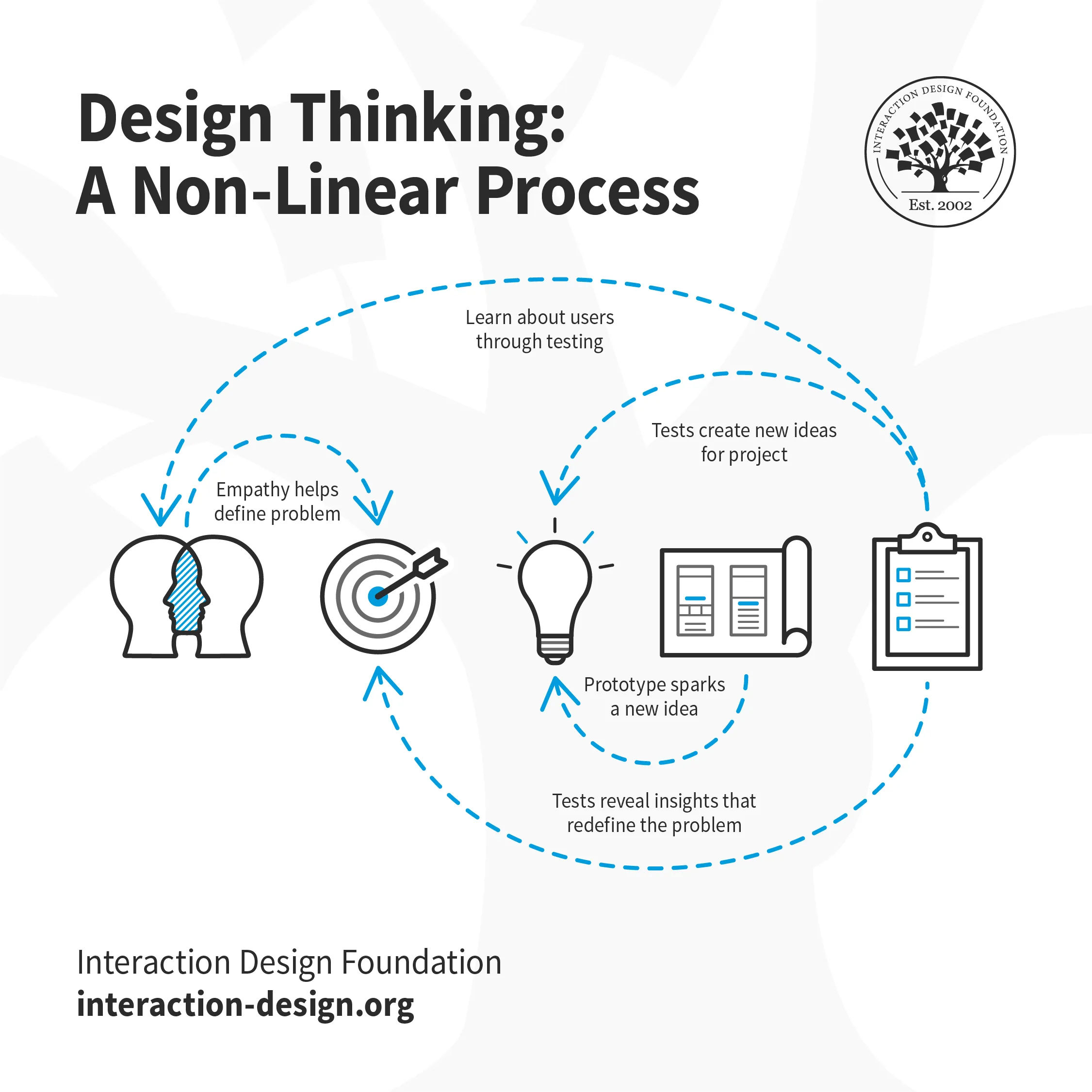
It is important to note the five stages of design thinking are not always sequential. They do not have to follow a specific order, and they can often occur in parallel or be repeated iteratively. The stages should be understood as different modes which contribute to the entire design project, rather than sequential steps.
The design thinking process should not be seen as a concrete and inflexible approach to design; the component stages identified should serve as a guide to the activities you carry out. The stages might be switched, conducted concurrently or repeated several times to gain the most informative insights about your users, expand the solution space and hone in on innovative solutions.
This is one of the main benefits of the five-stage model. Knowledge acquired in the latter stages of the process can inform repeats of earlier stages . Information is continually used to inform the understanding of the problem and solution spaces, and to redefine the problem itself. This creates a perpetual loop, in which the designers continue to gain new insights, develop new ways to view the product (or service) and its possible uses and develop a far more profound understanding of their real users and the problems they face.
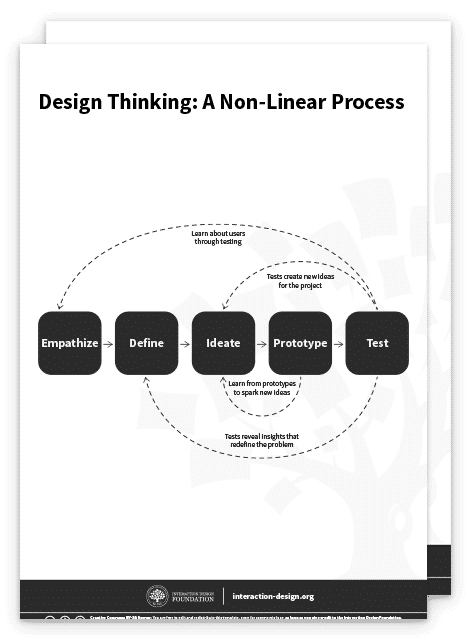
The Take Away
Design thinking is an iterative, non-linear process which focuses on a collaboration between designers and users. It brings innovative solutions to life based on how real users think, feel and behave.
This human-centered design process consists of five core stages Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test.
It’s important to note that these stages are a guide. The iterative, non-linear nature of design thinking means you and your design team can carry these stages out simultaneously, repeat them and even circle back to previous stages at any point in the design thinking process.
References & Where to Learn More
Take our Design Thinking course which is the ultimate guide when you want to learn how to you can apply design thinking methods throughout a design thinking process. Herbert Simon, The Sciences of the Artificial (3rd Edition), 1996.
d.school, An Introduction to Design Thinking PROCESS GUIDE , 2010.
Gerd Waloszek, Introduction to Design Thinking , 2012.
Hero Image: © the Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-NC-SA 3.0.
Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide

Get Weekly Design Insights
Topics in this article, what you should read next, what is design thinking and why is it so popular.
- 1.6k shares
Personas – A Simple Introduction

- 1.5k shares
Stage 2 in the Design Thinking Process: Define the Problem and Interpret the Results

- 1.3k shares
What is Ideation – and How to Prepare for Ideation Sessions
- 1.2k shares
Affinity Diagrams: How to Cluster Your Ideas and Reveal Insights

Stage 1 in the Design Thinking Process: Empathise with Your Users
- 3 years ago
Empathy Map – Why and How to Use It
What Is Empathy and Why Is It So Important in Design Thinking?
10 Insightful Design Thinking Frameworks: A Quick Overview
Define and Frame Your Design Challenge by Creating Your Point Of View and Ask “How Might We”

- 1.1k shares
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share the knowledge!
Share this content on:
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!
Smart. Open. Grounded. Inventive. Read our Ideas Made to Matter.
Which program is right for you?

Through intellectual rigor and experiential learning, this full-time, two-year MBA program develops leaders who make a difference in the world.
A rigorous, hands-on program that prepares adaptive problem solvers for premier finance careers.
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems.
Earn your MBA and SM in engineering with this transformative two-year program.
Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only.
A doctoral program that produces outstanding scholars who are leading in their fields of research.
Bring a business perspective to your technical and quantitative expertise with a bachelor’s degree in management, business analytics, or finance.
A joint program for mid-career professionals that integrates engineering and systems thinking. Earn your master’s degree in engineering and management.
An interdisciplinary program that combines engineering, management, and design, leading to a master’s degree in engineering and management.
Executive Programs
A full-time MBA program for mid-career leaders eager to dedicate one year of discovery for a lifetime of impact.
This 20-month MBA program equips experienced executives to enhance their impact on their organizations and the world.
Non-degree programs for senior executives and high-potential managers.
A non-degree, customizable program for mid-career professionals.
Disciplined entrepreneurship: 6 questions for startup success
Startup tactics: How and when to hire technical talent
Robots could give humans ‘superpowers’
Credit: Mimi Phan
Ideas Made to Matter
Design thinking, explained
Rebecca Linke
Sep 14, 2017
What is design thinking?
Design thinking is an innovative problem-solving process rooted in a set of skills.The approach has been around for decades, but it only started gaining traction outside of the design community after the 2008 Harvard Business Review article [subscription required] titled “Design Thinking” by Tim Brown, CEO and president of design company IDEO.
Since then, the design thinking process has been applied to developing new products and services, and to a whole range of problems, from creating a business model for selling solar panels in Africa to the operation of Airbnb .
At a high level, the steps involved in the design thinking process are simple: first, fully understand the problem; second, explore a wide range of possible solutions; third, iterate extensively through prototyping and testing; and finally, implement through the customary deployment mechanisms.
The skills associated with these steps help people apply creativity to effectively solve real-world problems better than they otherwise would. They can be readily learned, but take effort. For instance, when trying to understand a problem, setting aside your own preconceptions is vital, but it’s hard.
Creative brainstorming is necessary for developing possible solutions, but many people don’t do it particularly well. And throughout the process it is critical to engage in modeling, analysis, prototyping, and testing, and to really learn from these many iterations.
Once you master the skills central to the design thinking approach, they can be applied to solve problems in daily life and any industry.
Here’s what you need to know to get started.

Understand the problem
The first step in design thinking is to understand the problem you are trying to solve before searching for solutions. Sometimes, the problem you need to address is not the one you originally set out to tackle.
“Most people don’t make much of an effort to explore the problem space before exploring the solution space,” said MIT Sloan professor Steve Eppinger. The mistake they make is to try and empathize, connecting the stated problem only to their own experiences. This falsely leads to the belief that you completely understand the situation. But the actual problem is always broader, more nuanced, or different than people originally assume.
Take the example of a meal delivery service in Holstebro, Denmark. When a team first began looking at the problem of poor nutrition and malnourishment among the elderly in the city, many of whom received meals from the service, it thought that simply updating the menu options would be a sufficient solution. But after closer observation, the team realized the scope of the problem was much larger , and that they would need to redesign the entire experience, not only for those receiving the meals, but for those preparing the meals as well. While the company changed almost everything about itself, including rebranding as The Good Kitchen, the most important change the company made when rethinking its business model was shifting how employees viewed themselves and their work. That, in turn, helped them create better meals (which were also drastically changed), yielding happier, better nourished customers.
Involve users
Imagine you are designing a new walker for rehabilitation patients and the elderly, but you have never used one. Could you fully understand what customers need? Certainly not, if you haven’t extensively observed and spoken with real customers. There is a reason that design thinking is often referred to as human-centered design.
“You have to immerse yourself in the problem,” Eppinger said.
How do you start to understand how to build a better walker? When a team from MIT’s Integrated Design and Management program together with the design firm Altitude took on that task, they met with walker users to interview them, observe them, and understand their experiences.
“We center the design process on human beings by understanding their needs at the beginning, and then include them throughout the development and testing process,” Eppinger said.
Central to the design thinking process is prototyping and testing (more on that later) which allows designers to try, to fail, and to learn what works. Testing also involves customers, and that continued involvement provides essential user feedback on potential designs and use cases. If the MIT-Altitude team studying walkers had ended user involvement after its initial interviews, it would likely have ended up with a walker that didn’t work very well for customers.
It is also important to interview and understand other stakeholders, like people selling the product, or those who are supporting the users throughout the product life cycle.
The second phase of design thinking is developing solutions to the problem (which you now fully understand). This begins with what most people know as brainstorming.
Hold nothing back during brainstorming sessions — except criticism. Infeasible ideas can generate useful solutions, but you’d never get there if you shoot down every impractical idea from the start.
“One of the key principles of brainstorming is to suspend judgment,” Eppinger said. “When we're exploring the solution space, we first broaden the search and generate lots of possibilities, including the wild and crazy ideas. Of course, the only way we're going to build on the wild and crazy ideas is if we consider them in the first place.”
That doesn’t mean you never judge the ideas, Eppinger said. That part comes later, in downselection. “But if we want 100 ideas to choose from, we can’t be very critical.”
In the case of The Good Kitchen, the kitchen employees were given new uniforms. Why? Uniforms don’t directly affect the competence of the cooks or the taste of the food.
But during interviews conducted with kitchen employees, designers realized that morale was low, in part because employees were bored preparing the same dishes over and over again, in part because they felt that others had a poor perception of them. The new, chef-style uniforms gave the cooks a greater sense of pride. It was only part of the solution, but if the idea had been rejected outright, or perhaps not even suggested, the company would have missed an important aspect of the solution.
Prototype and test. Repeat.
You’ve defined the problem. You’ve spoken to customers. You’ve brainstormed, come up with all sorts of ideas, and worked with your team to boil those ideas down to the ones you think may actually solve the problem you’ve defined.
“We don’t develop a good solution just by thinking about a list of ideas, bullet points and rough sketches,” Eppinger said. “We explore potential solutions through modeling and prototyping. We design, we build, we test, and repeat — this design iteration process is absolutely critical to effective design thinking.”
Repeating this loop of prototyping, testing, and gathering user feedback is crucial for making sure the design is right — that is, it works for customers, you can build it, and you can support it.
“After several iterations, we might get something that works, we validate it with real customers, and we often find that what we thought was a great solution is actually only just OK. But then we can make it a lot better through even just a few more iterations,” Eppinger said.
Implementation
The goal of all the steps that come before this is to have the best possible solution before you move into implementing the design. Your team will spend most of its time, its money, and its energy on this stage.
“Implementation involves detailed design, training, tooling, and ramping up. It is a huge amount of effort, so get it right before you expend that effort,” said Eppinger.
Design thinking isn’t just for “things.” If you are only applying the approach to physical products, you aren’t getting the most out of it. Design thinking can be applied to any problem that needs a creative solution. When Eppinger ran into a primary school educator who told him design thinking was big in his school, Eppinger thought he meant that they were teaching students the tenets of design thinking.
“It turns out they meant they were using design thinking in running their operations and improving the school programs. It’s being applied everywhere these days,” Eppinger said.
In another example from the education field, Peruvian entrepreneur Carlos Rodriguez-Pastor hired design consulting firm IDEO to redesign every aspect of the learning experience in a network of schools in Peru. The ultimate goal? To elevate Peru’s middle class.
As you’d expect, many large corporations have also adopted design thinking. IBM has adopted it at a company-wide level, training many of its nearly 400,000 employees in design thinking principles .
What can design thinking do for your business?
The impact of all the buzz around design thinking today is that people are realizing that “anybody who has a challenge that needs creative problem solving could benefit from this approach,” Eppinger said. That means that managers can use it, not only to design a new product or service, “but anytime they’ve got a challenge, a problem to solve.”
Applying design thinking techniques to business problems can help executives across industries rethink their product offerings, grow their markets, offer greater value to customers, or innovate and stay relevant. “I don’t know industries that can’t use design thinking,” said Eppinger.
Ready to go deeper?
Read “ The Designful Company ” by Marty Neumeier, a book that focuses on how businesses can benefit from design thinking, and “ Product Design and Development ,” co-authored by Eppinger, to better understand the detailed methods.
Register for an MIT Sloan Executive Education course:
Systematic Innovation of Products, Processes, and Services , a five-day course taught by Eppinger and other MIT professors.
- Leadership by Design: Innovation Process and Culture , a two-day course taught by MIT Integrated Design and Management director Matthew Kressy.
- Managing Complex Technical Projects , a two-day course taught by Eppinger.
- Apply for M astering Design Thinking , a 3-month online certificate course taught by Eppinger and MIT Sloan senior lecturers Renée Richardson Gosline and David Robertson.
Steve Eppinger is a professor of management science and innovation at MIT Sloan. He holds the General Motors Leaders for Global Operations Chair and has a PhD from MIT in engineering. He is the faculty co-director of MIT's System Design and Management program and Integrated Design and Management program, both master’s degrees joint between the MIT Sloan and Engineering schools. His research focuses on product development and technical project management, and has been applied to improving complex engineering processes in many industries.
Read next: 10 agile ideas worth sharing
Related Articles

Skip navigation
- Log in to UX Certification

World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
Design Thinking 101

July 31, 2016 2016-07-31
- Email article
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Twitter
In This Article:
Definition of design thinking, why — the advantage, flexibility — adapt to fit your needs, scalability — think bigger, history of design thinking.
Design thinking is an ideology supported by an accompanying process . A complete definition requires an understanding of both.
Definition: The design thinking ideology asserts that a hands-on, user-centric approach to problem solving can lead to innovation, and innovation can lead to differentiation and a competitive advantage. This hands-on, user-centric approach is defined by the design thinking process and comprises 6 distinct phases, as defined and illustrated below.
The design-thinking framework follows an overall flow of 1) understand, 2) explore, and 3) materialize. Within these larger buckets fall the 6 phases: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, test, and implement.

Conduct research in order to develop knowledge about what your users do, say, think, and feel .
Imagine your goal is to improve an onboarding experience for new users. In this phase, you talk to a range of actual users. Directly observe what they do, how they think, and what they want, asking yourself things like ‘what motivates or discourages users?’ or ‘where do they experience frustration?’ The goal is to gather enough observations that you can truly begin to empathize with your users and their perspectives.
Combine all your research and observe where your users’ problems exist. While pinpointing your users’ needs , begin to highlight opportunities for innovation.
Consider the onboarding example again. In the define phase, use the data gathered in the empathize phase to glean insights. Organize all your observations and draw parallels across your users’ current experiences. Is there a common pain point across many different users? Identify unmet user needs.
Brainstorm a range of crazy, creative ideas that address the unmet user needs identified in the define phase. Give yourself and your team total freedom; no idea is too farfetched and quantity supersedes quality.
At this phase, bring your team members together and sketch out many different ideas. Then, have them share ideas with one another, mixing and remixing, building on others' ideas.
Build real, tactile representations for a subset of your ideas. The goal of this phase is to understand what components of your ideas work, and which do not. In this phase you begin to weigh the impact vs. feasibility of your ideas through feedback on your prototypes.
Make your ideas tactile. If it is a new landing page, draw out a wireframe and get feedback internally. Change it based on feedback, then prototype it again in quick and dirty code. Then, share it with another group of people.
Return to your users for feedback. Ask yourself ‘Does this solution meet users’ needs?’ and ‘Has it improved how they feel, think, or do their tasks?’
Put your prototype in front of real customers and verify that it achieves your goals. Has the users’ perspective during onboarding improved? Does the new landing page increase time or money spent on your site? As you are executing your vision, continue to test along the way.
Put the vision into effect. Ensure that your solution is materialized and touches the lives of your end users.
This is the most important part of design thinking, but it is the one most often forgotten. As Don Norman preaches, “we need more design doing.” Design thinking does not free you from the actual design doing. It’s not magic.
“There’s no such thing as a creative type. As if creativity is a verb, a very time-consuming verb. It’s about taking an idea in your head, and transforming that idea into something real. And that’s always going to be a long and difficult process. If you’re doing it right, it’s going to feel like work.” - Milton Glaser
As impactful as design thinking can be for an organization, it only leads to true innovation if the vision is executed. The success of design thinking lies in its ability to transform an aspect of the end user’s life. This sixth step — implement — is crucial.
Why should we introduce a new way to think about product development? There are numerous reasons to engage in design thinking, enough to merit a standalone article, but in summary, design thinking achieves all these advantages at the same time.
Design thinking:
- Is a user-centered process that starts with user data, creates design artifacts that address real and not imaginary user needs, and then tests those artifacts with real users
- Leverages collective expertise and establishes a shared language, as well as buy-in amongst your team
- Encourages innovation by exploring multiple avenues for the same problem
Jakob Nielsen says “ a wonderful interface solving the wrong problem will fail ." Design thinking unfetters creative energies and focuses them on the right problem.
The above process will feel abstruse at first. Don’t think of it as if it were a prescribed step-by-step recipe for success. Instead, use it as scaffolding to support you when and where you need it. Be a master chef, not a line cook: take the recipe as a framework, then tweak as needed.
Each phase is meant to be iterative and cyclical as opposed to a strictly linear process, as depicted below. It is common to return to the two understanding phases, empathize and define, after an initial prototype is built and tested. This is because it is not until wireframes are prototyped and your ideas come to life that you are able to get a true representation of your design. For the first time, you can accurately assess if your solution really works. At this point, looping back to your user research is immensely helpful. What else do you need to know about the user in order to make decisions or to prioritize development order? What new use cases have arisen from the prototype that you didn’t previously research?
You can also repeat phases. It’s often necessary to do an exercise within a phase multiple times in order to arrive at the outcome needed to move forward. For example, in the define phase, different team members will have different backgrounds and expertise, and thus different approaches to problem identification. It’s common to spend an extended amount of time in the define phase, aligning a team to the same focus. Repetition is necessary if there are obstacles in establishing buy-in. The outcome of each phase should be sound enough to serve as a guiding principle throughout the rest of the process and to ensure that you never stray too far from your focus.

The packaged and accessible nature of design thinking makes it scalable. Organizations previously unable to shift their way of thinking now have a guide that can be comprehended regardless of expertise, mitigating the range of design talent while increasing the probability of success. This doesn’t just apply to traditional “designery” topics such as product design, but to a variety of societal, environmental, and economical issues. Design thinking is simple enough to be practiced at a range of scopes; even tough, undefined problems that might otherwise be overwhelming. While it can be applied over time to improve small functions like search, it can also be applied to design disruptive and transformative solutions, such as restructuring the career ladder for teachers in order to retain more talent.
It is a common misconception that design thinking is new. Design has been practiced for ages : monuments, bridges, automobiles, subway systems are all end-products of design processes. Throughout history, good designers have applied a human-centric creative process to build meaningful and effective solutions.
In the early 1900's husband and wife designers Charles and Ray Eames practiced “learning by doing,” exploring a range of needs and constraints before designing their Eames chairs, which continue to be in production even now, seventy years later. 1960's dressmaker Jean Muir was well known for her “common sense” approach to clothing design, placing as much emphasis on how her clothes felt to wear as they looked to others. These designers were innovators of their time. Their approaches can be viewed as early examples of design thinking — as they each developed a deep understanding of their users’ lives and unmet needs. Milton Glaser, the designer behind the famous I ♥ NY logo, describes this notion well: “We’re always looking, but we never really see…it’s the act of attention that allows you to really grasp something, to become fully conscious of it.”
Despite these (and other) early examples of human-centric products, design has historically been an afterthought in the business world, applied only to touch up a product’s aesthetics. This topical design application has resulted in corporations creating solutions which fail to meet their customers’ real needs. Consequently, some of these companies moved their designers from the end of the product-development process, where their contribution is limited, to the beginning. Their human-centric design approach proved to be a differentiator: those companies that used it have reaped the financial benefits of creating products shaped by human needs.
In order for this approach to be adopted across large organizations, it needed to be standardized. Cue design thinking, a formalized framework of applying the creative design process to traditional business problems.
The specific term "design thinking" was coined in the 1990's by David Kelley and Tim Brown of IDEO, with Roger Martin, and encapsulated methods and ideas that have been brewing for years into a single unified concept.
We live in an era of experiences , be they services or products, and we’ve come to have high expectations for these experiences. They are becoming more complex in nature as information and technology continues to evolve. With each evolution comes a new set of unmet needs. While design thinking is simply an approach to problem solving, it increases the probability of success and breakthrough innovation.
Learn more about design thinking in the full-day course Generating Big Ideas with Design Thinking .
Download the illustrations from this article from the link below in a high-resolution version that you can print as a poster or any desired size.
Free Downloads
Related courses, generating big ideas with design thinking.
Unearthing user pain points to drive breakthrough design concepts
Interaction
Service Blueprinting
Use service design to create processes that are core to your digital experience and everything that supports it
Assessing UX Designs Using Proven Principles
Analyze user experiences using heuristics and assessments
Related Topics
- Design Process Design Process
- Managing UX Teams
Learn More:
Please accept marketing cookies to view the embedded video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6lmvCqvmjfE

The Role of Design
Don Norman · 5 min

Design Thinking Activities
Sarah Gibbons · 5 min

Design Thinking: Top 3 Challenges and Solutions
Related Articles:
Design Thinking: Study Guide
Kate Moran and Megan Brown · 4 min
Service Blueprinting in Practice: Who, When, What
Alita Joyce and Sarah Gibbons · 7 min
Design Thinking Builds Strong Teams
User-Centered Intranet Redesign: Set Up for Success in 11 Steps
Kara Pernice · 10 min
UX Responsibilities in Scrum Events
Anna Kaley · 13 min
Journey Mapping: 9 Frequently Asked Questions
Alita Joyce and Kate Kaplan · 7 min
A complete guide to the design thinking process

Learn the five stages of the design thinking process, get practical tips to apply them, and get templates to seamlessly run design thinking exercises.
How many projects have you worked on that stalled because your team couldn’t align on the best path forward? How many more got shelved because they didn’t meet user needs or expectations? And how many got delayed in rounds and rounds of never-ending feedback?
Thankfully, you don’t have to keep repeating those experiences month after month. The (not so) secret weapon: design thinking .
Design thinking gives teams a new way to approach their projects and overcome some of those well-known challenges. It can help teams understand their users' needs and challenges, then apply those learnings to solve problems in a creative, innovative way. Understanding design thinking can transform your team’s problem-solving approach — and how you work together.
What is design thinking?
Design thinking is an iterative process where teams seek to understand user needs, challenge assumptions, define complex problems to solve, and develop innovative solutions to prototype and test. The goal of design thinking is to come up with user-focused solutions tailored to the particular problem at hand.
While often used in product design, service design, and customer experience, you can use design thinking in virtually any situation, industry, or organization to create user-centric solutions to specific problems.
Design thinking process 101: Definitions and approaches
The design thinking process puts customers’ and users’ needs at the center and aims to solve challenges from their perspective.
Design thinking typically follows five distinct stages:
Empathize stage
The first stage of design thinking lays the foundation for the rest of the process because it focuses on the needs of the real people using your product. At this stage, you want to get familiar with the people experiencing the problems you’re trying to solve, understanding their point of view, and learning about their user experience. You want to understand their challenges and what they need from your product or company to address them.
The goal of this stage is for your team to develop a user-centered vision of the core problem you need to solve. The idea is to challenge any assumptions or biases teams have, instead using their customer perspective as a guiding source. This is important because it aligns the team on what needs to be considered during the rest of the design thinking process.
To help you get a solid understanding of the problems you’re solving, you can ask a lot of questions to build empathy with your users. These will invite people to share their experiences and observations to help your team better understand the problem. Then, you can move on to some specific exercises for the empathy stage of the process.
As you build up your understanding of your users, it's helpful to visualize their experience. A common way to do this is to assemble a customer journey map . This helps identify areas of friction and understand customer preferences.
Learn more: 7 types of questions to build empathy for design thinking
Ideate stage
Your priority here is to think outside the box and source as many ideas as possible from all areas of the business. Bring in people from different departments so you benefit from a wider range of experiences and perspectives during ideation sessions. Don’t worry about coming up with concrete solutions or how to implement each one — you’ll build on that later. The goal is to explore new and creative ideas rather than come up with an actual plan.
Key steps in the ideation phase:
- Define your problem : Creating a problem statement ensures that your team can focus on solving the right problem and staying aligned with your end-user or customer’s problem
- Start ideating : Choose a brainstorming technique to help organize team participation that fits your goal (More on that in the next section.)
- Prioritize your ideas : Once you have several ideas, prioritize them based on how well they take into account the customer’s needs
- Choose the best solution : Choose the best ideas to move forward to either the define stage or the prototype stage
Learn more: The ideation stage of design thinking: What you need to know
Your priority here is to generate as many ideas as possible, without judging or evaluating them. This step encourages designers to think creatively and push the boundaries of what's possible. We’ve put together a list of different brainstorming techniques to help your teams come up with creative new ideas.
Put it into practice: How to facilitate a brainstorming session
Prototyping stage
At this stage, your team’s goal is to remove uncertainty around your proposed solutions. This is where you start thinking about them in more detail, including how you’ll bring them to life. Your prototypes should help the team understand if the design or solution will work as it’s intended to.
Here, the focus is on speed and efficiency — you don’t want to invest a ton of time or resources into these solutions yet because you’re not sure they’re the best ones for the problem you’re trying to solve. You just need a functional, interactive prototype that can prove your concept. These are learning opportunities to help you spot any issues or opportunities before you take it any further.
Learn more: A guide to prototyping: the 4th stage of design thinking
Testing stage
The testing stage is normally one of the last stages of the design thinking process. After you’ve developed a concept or prototype, you need to test it in the real-world to understand its viability and usability. It’s where your product, design, or development teams evaluate the creative solutions they’ve come up with, to see how real users interact with them.
Testing your concepts and observing how people interact with them helps you understand whether or not the prototype solves real problems and meets their needs, before you invest in it fully.
However, design thinking is an iterative process: You may go through the ideation, prototyping, and testing phases multiple times to improve and refine your solutions as you learn more from your users.
Read the guide: Testing: A guide to the 5th stage of design thinking
The relationship between human-centered design and design thinking
These two terms are often used together, because they complement one another. However, they’re two different things, so understanding their differences is important.
Simply put, design thinking is a working process, while human-centered design is a mindset or approach.
The first step in finding success with design thinking is to foster a culture of human-centered design within your team. This is because design thinking focuses so heavily on the users and customers — the people using your product or service.
To inspire your team, we’ve put together four human-centered design examples — and explain why they work so well.
Benefits of design thinking
For organizations who’ve never run a design thinking workshop before, it can feel like a big change in how you approach the design process. But it can offer many benefits for your business.
Foster a true design culture within your organization
Design thinking is an iterative process — it’s not something you do once and call it done. The more you do it, the more you’ll see a design-focused culture emerge within your organization, which is much more effective than going to one-off creative retreats or setting up expensive innovation centers that no one ever uses.
This mindset and cultural shift can help scale design thinking within the business. But it’s important to know how to avoid some of the pitfalls companies can face when trying to create a design culture internally.
Learn more: How to use the LUMA System of Innovation for everyday design thinking
Encourage collaboration across departments
Design thinking isn’t just for the designers on the team. The earlier stages of the process — Empathize, Define, and Ideate — are perfect for bringing in people from across the business. In fact, bringing in varied viewpoints and perspectives can help you come up with more creative or effective solutions.
You can use the design thinking process to get more people involved, and help everyone contribute ideas.
Improve understanding of user needs
So many companies say they’re “customer focused,” but lack a clear understanding of what really matters most to their customers in the context of their product or service. Design thinking puts the user front and center, with the Empathize stage dedicated to understanding and discovering user needs.
Learn more: How to identify user needs and pain points
Skills and behaviors needed for successful design thinking
To get the most out of a design thinking exercise, you’ll need a collaborative and creative mindset within your team. The team needs to be willing to explore new ideas, and laser-focused on customer or user needs.
Here are some specific skills to help your design thinking process run smoothly.
Divergent and convergent thinking
Divergence and convergence is a human-centered design approach to problem-solving. It switches between expansive and focused thinking, giving you a process that balances understanding people’s problems and developing solutions.
It focuses on understanding a user's needs, behaviors, and motivations, to help you develop empathy for their problems. Then, it encourages experimentation and iteration to help you effectively design solutions to meet those needs.
Collaborative working
Design thinking isn’t a solo activity. You’ll bring in people from different teams or business areas. To get the most out of the process, everyone needs to collaborate and communicate effectively. Teams that are good at collaborating drive the best outcomes, while also making it an enjoyable experience working together.
There are several core collaboration skills your team needs to succeed:
- Open-mindedness
- Communication
- Adaptability
- Organization
- Time management
Learn more about why these skills are so important and how you can improve them individually or as a team: 7 collaboration skills your team needs to succeed
Participatory or collaborative design
For many design teams and creative folks, the idea of designing something with other people can be enough to make them shudder. “Design by committee” is their idea of a nightmare. But the design thinking process isn’t about “making the logo 10% bigger” or “using a different shade of blue.” It’s user- and solution-focused.
You’ll get the best outcomes if you bring insights, perspectives, and expertise from multiple stakeholders. That includes at the Prototype and Test stages, as everyone will have ideas to contribute to help you bring solutions to life.
Learn more: What is co-design? A primer on participatory design
Common challenges in design thinking
If your team hasn’t mastered or fully committed to each one of the design thinking steps, you may encounter problems that make it harder to reap the benefits of design thinking.
Here are 4 common challenges that teams face when implementing design thinking practices.
- A company culture that doesn't foster collaboration
- An inability to adjust to non-linear processes
- A lack of in-depth user research
- Getting too invested in a single idea
Learn how to address these in Mural's guide on design thinking challenges .
Design thinking tools and templates to help you get started
Using mural for design thinking.
There are lots of tools you can use to run design thinking workshops — including Mural. We help designers work as effectively as possible, so they can get to better solutions quicker. We’ve incorporated some design thinking shortcuts and “hidden” features into our application, making it perfect for in-person or remote (or even asynchronous) collaborative sessions. These include:
- Use the C-key shortcut to quickly connect ideas with arrows
- Seamlessly import existing information from spreadsheets
- Duplicate elements you already created for faster visualization
- Fit your canvas to your screen and zoom in
- Get even more options using the right-click menu
And to help you get started, we’ve hand-picked some Mural templates relevant to each stage of the design process below.
Templates for the Empathy stage
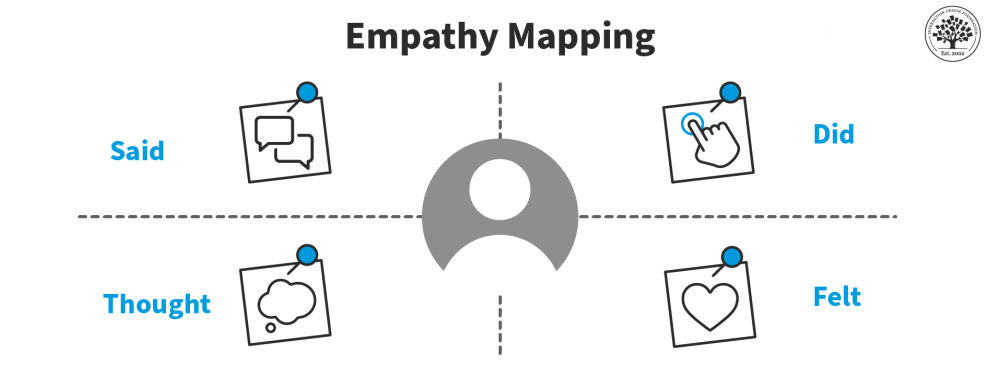
The empathy map template helps you visualize the thoughts, feelings, and actions of your customersto help you develop a better understanding of the their experiences. The map is divided into four quadrants, where you record the following:
- Thoughts: the customer’s internal dialogue and beliefs
- Feelings: the customer’s emotional responses
- Actions: the customer’s actions and behaviors
- Observations: what the customer is seeing and hearing.
Try Mural’s empathy map template
Templates for the Define stage
This exercise helps you understand a situation or problem by identifying what’s working, what’s not, and areas for improvement. You start by listing out the problem, then identifying the positive aspects (the rose), negatives (thorn), and possible solutions for improvement (the buds).
You can use this template to run the exercise individually or in groups. It gives you a way to gather new ideas and perspectives on the problem you’re solving in real-time.
Try Mural’s Rose, thorn, bud template
Templates for the Ideate stage
The round robin brainstorming exercise is a collaborative session where every person contributes multiple ideas. This is a great way to come up with lots of different ideas and solutions in the ideation stage of design thinking, where you’re focusing on quantity and creativity.
Bringing in ideas from every team member encourages people to share their unique perspectives, and can also help you avoid groupthink.
Try Mural’s Round robin template
Templates for the Prototype stage
This template helps you map out how an idea will work in practice, as a functional system. Schematic diagramming is very flexible, so it can be used in many types of projects to make sure your idea is structurally sound. It can help you map out workflows and identify any decisions you need to make to bring your idea to life.
Try Mural’s Schematic diagramming template
Templates for the Test stage
In think aloud testing, users test out a product or prototype and talk through the relevant tasks as they complete them. You can use this template to record the feedback, insights, and experiences of your testers, and identify the success and failure points in your proposed solution.
Try Mural’s Think aloud testing template
Design thinking examples: What it looks like in practice
Design thinking is a very flexible approach that works for companies of any size, from large enterprises to small startups.
Here are some examples of how companies use design thinking, for many types of creative projects.
IBM uses design thinking to design at scale
IBM was traditionally an engineering-led organization, but now it's shifting its focus onto design, working to spread a design culture throughout the business. One of the main ways of doing that is by launching IBM Design Camps.
These camps are comprehensive educational programs that help people understand the concept of design thinking and how it specifically works at IBM.
Learn more about how IBM runs design thinking workshops with remote or distributed teams .
Somersault Innovation uses design thinking to transform its sales process
Somersault Innovation has used design thinking methods to help their sales team co-create solutions with their customers. It’s helped sellers become more customer-centric.
Now, their sellers can create mutual success plans with their prospects, making it easier for them to find a path forward together.
Mural uses design thinking to drive growth
At Mural, our marketing team is constantly following new trends, evaluating metrics, and working to deliver the best experiences for our customers. Design thinking helps us adopt a customer-centric approach by ensuring that we're focused on the right problems. This helps us have the biggest impact on the company’s long-term growth while creating the most value for our users.
David J. Bland planned a book using the design thinking methodology
It’s not just visual creative projects that can benefit from the design thinking process. Founder, speaker, and author David J. Bland used the methodology to plan out his book and collaborate with other team members in the process. In addition to helping him refine and adjust the structure, Bland also used it to gather feedback from early readers and target audiences, which helped get the final product just right.
Support design thinking with tools that facilitate creative collaboration
While we’ve covered some of the skills and behaviors you need to successfully run design thinking exercises, having the right tools can help a lot, too. A collaborative platform helps teams communicate, share ideas, and turn those ideas into solutions together.
Mural helps teams visualize their ideas in a collaboration platform that unlocks teamwork . This helps everyone stay on the same page, while giving them the ability to add their own ideas freely and easily. Mural facilitates effective collaboration both in person and remotely, making it ideal for design thinking workshops for co-located and distributed teams. Plus, it has tons of ready-to-use templates (like the ones we listed above) to help you get started.
Ready to give it a try? Start your Free Forever account today, and run your next design thinking workshop in Mural.
About the authors

Bryan Kitch
Tagged Topics
Related blog posts

4 common challenges and pitfalls in design thinking
.jpg)
How to encourage thinking outside the box

What Is hybrid work? A primer on the new way of working
Related blog posts.
%20(3).jpg)
20 top strategic planning tools and frameworks [templates & examples]
%20(1).jpg)
How to make a digital vision board: A complete guide
%20(1).jpg)
5 ways visual task management benefits your team
Get the free 2023 collaboration trends report.
Extraordinary teamwork isn't an accident
InVisionApp, Inc.
Inside Design
What is design thinking, and how do we apply it?
Emily stevens, • jan 30, 2020.
T he famous inventor, engineer, businessman, and holder of no fewer than 186 patents Charles Kettering once said, “If you have always done it that way, it is probably wrong.”
If you’re a designer, an entrepreneur, or any kind of employee, you are no stranger to the constant pressure to innovate. It’s the secret sauce, after all; the key to progress and success. Our capacity for innovation—the ability to conceive ideas which are at once actionable and effective—is what gives us the upper hand in competitive industries.
The Apples, Airbnbs, and Ubers of this world were all borne of innovation. Now, the challenge that all of these companies—and your company too, no doubt—face is to continue that innovation in order to maintain or further advance their position in their respective markets. Innovation can’t be a one-time affair; it needs to be part of the company’s DNA.
You also know that innovation doesn’t always come that easily.
That’s where design thinking comes in.
Design thinking has long been considered the holy grail of innovation—and the remedy to stagnation. It has been credited with remarkable feats, like transforming Airbnb from a failing startup to a billion-dollar business . It’s a concept that’s becoming increasingly hard to ignore, and yet, despite such high-profile success stories, it’s a concept that continues to be shrouded in mystery.
Enough of the vague definitions and abstract descriptions. In this post, we’ll show you exactly what design thinking is and what it looks like in action. Let’s get into:
What is design thinking?
- What are the key principles of design thinking?
- What is the design thinking methodology and how can I use it?
- How can I apply the design thinking framework?
Ready to leverage the power of design thinking? Let’s go.
Design thinking originally came about as a way of teaching engineers how to approach problems creatively, like designers do. One of the first people to write about design thinking was John E. Arnold, professor of mechanical engineering at Stanford University. In 1959, he wrote “ Creative Engineering ,” the text that established the four areas of design thinking. From there, design thinking began to evolve as a “way of thinking” in the fields of science and design engineering—as can be seen in Herbert A. Simon’s book “ The Sciences of the Artificial ” and in Robert McKim’s “ Experiences in Visual Thinking ”.
With the rise of human-centered design in the 80s and the formation of design consultancy IDEO in the 90s, design thinking became increasingly popular. By the start of the 21st century, design thinking was making its way into the world of business. In 2005, Stanford University’s d.school began teaching design thinking as an approach to technical and social innovation.
Indeed, many of the methods and techniques used in design thinking have been borrowed from the designer’s toolkit.
So what exactly is design thinking?
Design thinking is both an ideology and a process that seeks to solve complex problems in a user-centric way. It focuses on achieving practical results and solutions that are:
- Technically feasible : They can be developed into functional products or processes;
- Economically viable : The business can afford to implement them;
- Desirable for the user : They meet a real human need.
The ideology behind design thinking states that, in order to come up with innovative solutions, one must adopt a designer’s mindset and approach the problem from the user’s perspective. At the same time, design thinking is all about getting hands-on; the aim is to turn your ideas into tangible, testable products or processes as quickly as possible.
The design thinking process outlines a series of steps that bring this ideology to life—starting with building empathy for the user, right through to coming up with ideas and turning them into prototypes.
At this point, you’re probably thinking that this sounds suspiciously like UX. So what makes design thinking so special?
Design thinking helps us tackle “wicked” problems
The uniqueness of design thinking lies in the kinds of problems it addresses. When it comes to the problems to be solved with design thinking, we’re not just talking about ordinary, common problems that have tried-and-tested solutions. We’re talking about highly complex, “wicked” problems: the kind that refuse to be solved using standard methods and approaches.
Not only are these problems difficult to define, but any attempt to solve them is likely to give way to even more problems. Wicked problems are everywhere, ranging from global issues such as climate change and poverty, to challenges that affect almost all businesses such as change management, achieving sustainable growth, or maintaining your competitive edge.
Design thinking is an actionable approach which can be used to tackle the world’s wickedest of problems. It fosters user-centricity, creativity, innovation, and out-of-the-box thinking.
With that in mind, let’s explore the principles and pillars of design thinking in more detail.
What are the principles of design thinking?
There are certain principles that are pivotal to design thinking. These are reflected in the design thinking methodology, which we’ll explore in detail a little later on. We’ve outlined five of design thinking’s most important principles below.
1. User-centricity and empathy
Design thinking is all about finding solutions that respond to human needs and user feedback. People, not technology, are the drivers of innovation, so an essential part of the process involves stepping into the user’s shoes and building genuine empathy for your target audience.
2. Collaboration
The aim of design thinking is to pool a diverse variety of perspectives and ideas; this is what leads to innovation! Design thinking encourages collaboration between heterogeneous, multidisciplinary teams which may not typically work together.
3. Ideation
Design thinking is a solution-based framework, so the focus is on coming up with as many ideas and potential solutions as possible. Ideation is both a core design thinking principle and a step in the design thinking process. The ideation step is a designated judgment-free zone where participants are encouraged to focus on the quantity of ideas, rather than the quality.
4. Experimentation and iteration
It’s not just about coming up with ideas; it’s about turning them into prototypes, testing them, and making changes based on user feedback. Design thinking is an iterative approach, so be prepared to repeat certain steps in the process as you uncover flaws and shortcomings in the early versions of your proposed solution.
5. A bias towards action
Design thinking is an extremely hands-on approach to problem-solving favoring action over discussion. Instead of hypothesizing about what your users want, design thinking encourages you to get out there and engage with them face-to-face. Rather than talking about potential solutions, you’ll turn them into tangible prototypes and test them in real-world contexts.
The design thinking methodology in action
So far, we’ve covered quite a bit of theory. We know what design thinking is and the key principles that shape it. Now let’s consider what the design thinking methodology looks like in action, starting with the five key steps in the design thinking process .
The design thinking framework: five key steps
The design thinking framework can be divided into three distinct phases: immersion, ideation, and implementation. This framework can be further broken down into five actionable steps which make up the design thinking process:
Although these steps appear to be sequential, it’s important to point out that design thinking doesn’t follow a strictly linear process. At each stage in the process, you’re likely to make new discoveries that require you to go back and repeat a previous step.
Step 1. Empathize
- What? During the empathize phase, you’ll engage with and observe your target audience.
- Why? The aim of this step is to paint a clear picture of who your end users are, what challenges they face, and what needs and expectations must be met.
- How? In order to build user empathy, you’ll conduct surveys, interviews, and observation sessions.
- For example: You want to address the issue of employee retention, so you ask each employee to complete an anonymous survey. You then hold user interviews with as many employees as possible to find out how they feel about retention within the company.
Step 2. Define
- What? Based on what you’ve learned in the empathize phase, the next step is to define a clear problem statement.
- Why? Your problem statement sets out the specific challenge you will address. It will guide the entire design process from here on out, giving you a fixed goal to focus on and helping to keep the user in mind at all times.
- How? When framing your problem statement, you’ll focus on the user’s needs rather than those of the business. A good problem statement is human-centered, broad enough for creativity, yet specific enough to provide guidance and direction.
- For example: “My employees need to be able to maintain a healthy lifestyle while working in the office” is much more user-centric than “I need to keep my employees healthy and happy in order to boost retention.”
Step 3. Ideate
- What? With a clear problem statement in mind, you’ll now aim to come up with as many ideas and potential solutions as possible.
- Why? The ideation phase gets you thinking outside the box and exploring new angles. By focusing on quantity of ideas rather than quality, you’re more likely to free your mind and stumble upon innovation!
- How? During dedicated ideation sessions, you’ll use a range of different ideation techniques such as bodystorming, reverse thinking, and worst possible idea.
- For example: Based on what you’ve learned in the empathize phase, you hold several ideation sessions with a variety of different stakeholders. With your problem statement to hand, you come up with as many ideas as possible for how you might make your employees happier and thus more likely to stay with the company.
Step 4. Prototype
- What? Having narrowed your ideas down to a select few, you’ll now turn them into prototypes—or “scaled-down” versions of the product or concept you want to test.
- Why? The prototyping stagegives you something tangible that can be tested on real users. This is crucial in maintaining a user-centric approach.
- How? Depending on what you’re testing, prototypes can take various forms—from basic paper models to interactive, digital prototypes. When creating your prototypes, have a clear goal in mind; know exactly what you want your prototype to represent and therefore test.
- For example: During the ideation phase, one idea that came up was to offer free yoga classes. To prototype this idea, you set up a dedicated yoga room in the office, complete with mats, water bottles, and hand towels.
Step 5. Test
What? The fifth step in the design thinking process will see you testing your prototypes on real or representative users.
- Why? The testing phase enables you to see where your prototype works well and where it needs improving. Based on user feedback, you can make changes and improvements before you spend time and money developing and/or implementing your solution.
- How? You’ll run user testing sessions where you observe your target users as they interact with your prototype. You may also gather verbal feedback. With everything you learn from the testing phase, you’ll make changes to your design or come up with a completely new idea altogether!
- For example: You decide to test the yoga idea for two months to see how employees respond. You find that people enjoy the yoga classes, but are put off by the fact that they are in the middle of the day and there is nowhere to shower. Based on this feedback, you decide to move the yoga classes to the evening.
Applying the design thinking framework to your own work
Design thinking can also start small—you don’t need to become a UX designer in order to apply design thinking to your own work! You might choose to focus on just one aspect of the design thinking process, such as getting to know your customers and making a conscious effort to be more empathy-driven on a day to day basis. If you’re struggling to gather positive customer reviews, for example, you might choose to conduct user interviews in order to find out what your customers are missing.
Perhaps you want to focus on the collaborative nature of design thinking, in which case you might hold ideation sessions with representatives from a diverse variety of teams. If you notice that marketing and design constantly struggle to see eye-to-eye, for example, a few design thinking-style brainstorming sessions might help to get everybody on the same page.
Another increasingly popular method of applying design thinking is through design thinking workshops . If you have a specific problem you want to solve, such as coming up with a new product idea or figuring out how to boost employee retention, a design thinking workshop will take you through the entire design thinking process in a short space of time. Design thinking workshops are also used to teach non-design professionals how to innovate and find creative solutions—an essential skill in any area of business.
Examples of design thinking success
Product and service design are the most obvious contexts to benefit from design thinking. However, the design thinking framework can be used to tackle all kinds of challenges beyond the realm of design!
Design thinking is increasingly being integrated into business as a way to foster innovation and teamwork. IBM developed their Enterprise Design Thinking framework in order to “help multidisciplinary teams align around the real needs of their users,” claiming that businesses who use the framework are twice as quick to get their products to market, 75% more efficient in terms of teamwork, and enjoy a 300% return on investment.
Insurance firm MassMutual used a design thinking approach to tackle the challenge of getting young adults to purchase life insurance. In partnership with IDEO , they conducted extensive user research over the course of two years. Based on what they learned, they then embarked on a further two years of prototyping and testing. The end result was Society of Grownups , a suite of digital tools that help to educate young people to make smart financial choices.
Here at CareerFoundry , we not only teach design thinking as part of our UX Design Course , but we also incorporate it in the way we work and make decisions. The majority of our users are adult learners who are juggling online study with full-time work, and so one of the biggest challenges they face is time management. Based on the design thinking framework, we conducted extensive user research, including an in-house time management workshop with real students. With these new insights, we redesigned certain aspects of our e-learning dashboard—such as how project milestones are displayed, for example. In true design thinking fashion, we’ll continue to gather user feedback in order to iterate on and improve our current solution.
Now you know what design thinking is and how it can be applied to almost any context. If you’d like to learn more about design thinking, this comprehensive beginner’s guide explains how design thinking, lean, and agile work together, and sheds some light on the relationship between design thinking and UX design. If you’re keen to start incorporating design thinking into your work right away, check out these nine design thinking tools to try with your team .
Want to learn more about design thinking?
- 9 design thinking tools to try with your team
- 4 ways to improve your design thinking process
- Why the world needs more design thinking
Keep your design and dev teams synced on accessibility work using DSM.
by Emily Stevens
Collaborate in real time on a digital whiteboard try freehand, get awesome design content in your inbox each week, give it a try—it only takes a click to unsubscribe., thanks for signing up, you should have a thank you gift in your inbox now-and you’ll hear from us again soon, get started designing better. faster. together. and free forever., give it a try. nothing’s holding you back..

What Is Design Thinking? A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide

Design thinking is both an ideology and a process, concerned with solving complex problems in a highly user-centric way.
In this guide, we’ll give you a detailed definition of design thinking, illustrate exactly what the process involves, and underline why it matters: What is the value of design thinking, and in what contexts is it particularly useful?
We’ll also analyze the relationship between user experience design and design thinking and discuss two real-world case studies that show design thinking in action.
All sound a little overwhelming? Don’t worry—we’ve broken the guide down into digestible chunks.
If you want to skip to a certain section, just click on the relevant menu heading and you’ll go straight there.
- What is Design Thinking?
- What is the Design Thinking process?
- What is the purpose of Design Thinking?
- How do Design Thinking, lean, and agile work together?
- What are the benefits of Design Thinking at work?
- Design Thinking methodology in action: Case studies
- What is the relationship between Design Thinking and UX Design?
Ready to explore the fascinating world of Design Thinking? Let’s go!
1. What is Design Thinking?
Design thinking is an approach used for practical and creative problem-solving. It is based heavily on the methods and processes that designers use (hence the name), but it has actually evolved from a range of different fields—including architecture, engineering and business. Design thinking can also be applied to any field; it doesn’t necessarily have to be design-specific.
For an audio-visual introduction, watch this video from design expert and CareerFoundry mentor, Camren Browne:
It’s important to note that design thinking is different from user-centered design . Learn more about this other approach to design here: Design Thinking vs. User-Centered Design .
Design thinking is extremely user-centric. It focuses on humans first and foremost , seeking to understand people’s needs and come up with effective solutions to meet those needs. It is what we call a solution-based approach to problem-solving.
What does this actually mean? Let’s take a look.
What’s the difference between Solution-Based and Problem-Based Thinking?
As the name suggests, solution-based thinking focuses on finding solutions; coming up with something constructive to effectively tackle a certain problem. This is the opposite of problem-based thinking, which tends to fixate on obstacles and limitations.
A good example of these two approaches in action is an empirical study carried out by Bryan Lawson, a Professor of Architecture at the University of Sheffield. Lawson wanted to investigate how a group of designers and a group of scientists would approach a particular problem.
He set each group the task of creating one-layer structures from a set of coloured blocks. The perimeter of the structure had to use either as many red bricks or as many blue bricks as possible (we can think of this is as the solution, the desired outcome), but there were unspecified rules regarding the placement and relationship of some of the blocks (the problem or limitation).
Lawson published his findings in his book How Designers Think , in which he observed that the scientists focused on identifying the problem (problem-based thinking) whilst the designers prioritized the need to find the right solution:
“The scientists adopted a technique of trying out a series of designs which used as many different blocks and combinations of blocks as possible as quickly as possible. Thus they tried to maximise the information available to them about the allowed combinations. If they could discover the rule governing which combinations of blocks were allowed, they could then search for an arrangement which would optimise the required colour around the layout.”
The designers, on the other hand:
“…selected their blocks in order to achieve the appropriately coloured perimeter. If this proved not to be an acceptable combination, then the next most favourably coloured block combination would be substituted and so on until an acceptable solution was discovered.”
Lawson’s findings go to the heart of what Design Thinking is all about: it’s an iterative process which favours ongoing experimentation until the right solution is found.
To learn more, check out this video introduction to design thinking , led by expert designer Camren Browne. For now, let’s take a look at the design thinking process and what that entails.
2. What is the Design Thinking process?
As already mentioned, the Design Thinking process is progressive and highly user-centric . Before looking at the process in more detail, let’s consider the four principles of Design Thinking as laid out by Christoph Meinel and Harry Leifer of the Hasso-Plattner-Institute of Design at Stanford University, California.

The Four Principles of Design Thinking
- The human rule: No matter what the context, all design activity is social in nature, and any social innovation will bring us back to the “human-centric point of view”.
- The ambiguity rule: Ambiguity is inevitable, and it cannot be removed or oversimplified. Experimenting at the limits of your knowledge and ability is crucial in being able to see things differently.
- The redesign rule: All design is redesign. While technology and social circumstances may change and evolve, basic human needs remain unchanged. We essentially only redesign the means of fulfilling these needs or reaching desired outcomes.
- The tangibility rule: Making ideas tangible in the form of prototypes enables designers to communicate them more effectively.
The Five Phases of Design Thinking
Based on these four principles, the Design Thinking process can be broken down into five steps or phases, as per the aforementioned Hasso-Plattner-Institute of Design at Stanford (otherwise known as d.school): Empathise, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test. Let’s explore each of these in more detail.
Phase 1: Empathise
Empathy provides the critical starting point for Design Thinking . The first stage of the process is spent getting to know the user and understanding their wants, needs and objectives.
This means observing and engaging with people in order to understand them on a psychological and emotional level. During this phase, the designer seeks to set aside their assumptions and gather real insights about the user. Learn all about key empathy-building methods in our guide .
Phase 2: Define
The second stage in the Design Thinking process is dedicated to defining the problem. You’ll gather all of your findings from the empathise phase and start to make sense of them: what difficulties and barriers are your users coming up against? What patterns do you observe? What is the big user problem that your team needs to solve?
By the end of the define phase, you will have a clear problem statement . The key here is to frame the problem in a user-centered way; rather than saying “We need to…”, frame it in terms of your user: “Retirees in the Bay area need…”
Once you’ve formulated the problem into words, you can start to come up with solutions and ideas — which brings us onto stage three.
Phase 3: Ideate
With a solid understanding of your users and a clear problem statement in mind, it’s time to start working on potential solutions. The third phase in the Design Thinking process is where the creativity happens, and it’s crucial to point out that the ideation stage is a judgement-free zone!
Designers will hold ideation sessions in order to come up with as many new angles and ideas as possible. There are many different types of ideation technique that designers might use, from brainstorming and mindmapping to bodystorming (roleplay scenarios) and provocation—an extreme lateral-thinking technique that gets the designer to challenge established beliefs and explore new options and alternatives.
Towards the end of the ideation phase, you’ll narrow it down to a few ideas with which to move forward. You can learn about all the most important ideation techniques in this guide .
Phase 4: Prototype
The fourth step in the Design Thinking process is all about experimentation and turning ideas into tangible products. A prototype is basically a scaled-down version of the product which incorporates the potential solutions identified in the previous stages. This step is key in putting each solution to the test and highlighting any constraints and flaws.
Throughout the prototype stage, the proposed solutions may be accepted, improved, redesigned or rejected depending on how they fare in prototype form. You can read all about the prototyping stage of Design Thinking in our in-depth guide .
Phase 5: Test
After prototyping comes user testing, but it’s important to note that this is rarely the end of the Design Thinking process. In reality, the results of the testing phase will often lead you back to a previous step, providing the insights you need to redefine the original problem statement or to come up with new ideas you hadn’t thought of before. Learn all about user testing in this guide .
Is Design Thinking a linear process?
No! You might look at these clearly defined steps and see a very logical sequence with a set order. However, the Design Thinking process is not linear; it is flexible and fluid, looping back and around and in on itself! With each new discovery that a certain phase brings, you’ll need to rethink and redefine what you’ve done before—you’ll never be moving in a straight line!
3. What is the purpose of Design Thinking?
Now we know more about how Design Thinking works, let’s consider why it matters. There are many benefits of using a Design Thinking approach—be it in a business, educational, personal or social context.
First and foremost, Design Thinking fosters creativity and innovation. As human beings, we rely on the knowledge and experiences we have accumulated to inform our actions. We form patterns and habits that, while useful in certain situations, can limit our view of things when it comes to problem-solving.
Rather than repeating the same tried-and-tested methods, Design Thinking encourages us to remove our blinkers and consider alternative solutions. The entire process lends itself to challenging assumptions and exploring new pathways and ideas.
Design Thinking is often cited as the healthy middle ground of problem-solving—it is not steeped wholly in emotion and intuition, nor does it rely solely on analytics, science and rationale; it uses a mixture of both.
Another great benefit of Design Thinking is that it puts humans first. By focusing so heavily on empathy, it encourages businesses and organizations to consider the real people who use their products and services—meaning they are much more likely to hit the mark when it comes to creating meaningful user experiences. For the user, this means better, more useful products that actually improve our lives. For businesses, this means happy customers and a healthier bottom line.
What’s a “wicked problem” in Design Thinking?
Design Thinking is especially useful when it comes to solving “wicked problems”. The term “wicked problem” was coined by design theorist Horst Rittel in the 1970s to describe particularly tricky problems that are highly ambiguous in nature.
With wicked problems, there are many unknown factors; unlike “tame” problems, there is no definitive solution. In fact, solving one aspect of a wicked problem is likely to reveal or give rise to further challenges. Another key characteristic of wicked problems is that they have no stopping point; as the nature of the problem changes over time, so must the solution.
Solving wicked problems is therefore an ongoing process that requires Design Thinking! Some examples of wicked problems in our society today include things like poverty, hunger, and climate change.
If you’d like to learn more about them, and how Design Thinking can help tackle them, check out our full guide to wicked problems .
4. Design Thinking in the workplace: How do Design Thinking, lean, and agile work together?
Now we know what Design Thinking is, let’s consider how it fits into the overall product design process. You may be familiar with the terms “lean” and “agile”—and, as a UX designer, it’s important to understand how these three approaches work together.
What are lean and agile?
Based on the principles of lean manufacturing, lean UX focuses on streamlining the design process as much as possible—minimizing waste and maximizing value. Some core tenets of lean UX are:
- Cross-functional collaboration between designers, engineers, and product managers.
- Gathering feedback quickly and continuously, ensuring that you’re constantly learning and adapting as you go.
- Deciding as late as possible and delivering fast, with less focus on long-term deliverables.
- A strong emphasis on how the team operates as a whole.
Lean UX is a technique that works in conjunction with agile development methods. Agile is a software development process that works in iterative, incremental cycles known as sprints. Unlike traditional development methods, agile is flexible and adaptive. Based on the Agile Development Manifesto created in 2001, agile adheres to the following principles:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools.
- Working software over comprehensive documentation.
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation.
- Responding to change over following a plan.
Combining Design Thinking with lean and agile
Design Thinking, lean, and agile are often seen as three separate approaches. Companies and teams will ask themselves whether to use lean or agile or Design Thinking—but actually, they can (and should!) be merged for optimal results.
Why? Because applying Design Thinking in a lean, agile environment helps to create a product development process that is not only user-centric, but also highly efficient from a business perspective. While it’s true that each approach has its own modus operandi, there is also significant overlap.
Combining principles from each can be crucial in keeping cross-functional teams on the same page—ensuring that designers, developers, product managers, and business stakeholders are all collaborating on one common vision.
So how do Design Thinking, lean, and agile work together?
As Jonny Schneider, Product Strategy and Design Principal at ThoughtWorks , explains: “Design Thinking is how we explore and solve problems; Lean is our framework for testing our beliefs and learning our way to the right outcomes; Agile is how we adapt to changing conditions with software.”
That’s all well and good, but what does it look like in practice?
As we’ve learned, Design Thinking is a solution-based approach to exploring and solving problems. It focuses on generating ideas with a specific problem in mind, keeping the user at the heart of the process throughout. Once you’ve established and designed a suitable solution, you’ll start to incorporate lean principles —testing your ideas, gathering quick and ongoing feedback to see what works—with particular emphasis on cross-team collaboration and overcoming departmental silos.
Agile ties all of this into short sprint cycles, allowing for adaptability in the face of change. In an agile environment, products are improved and built upon incrementally. Again, cross-team collaboration plays a crucial role; agile is all about delivering value that benefits both the end user and the business as a whole.
Together, Design Thinking, lean, and agile cut out unnecessary processes and documentation, leveraging the contributions of all key stakeholders for continuous delivery and improvement.
5. What are the benefits of Design Thinking at work?
As a designer, you have a pivotal role to play in shaping the products and experiences that your company puts to market. Integrating Design Thinking into your process can add huge business value, ultimately ensuring that the products you design are not only desirable for customers, but also viable in terms of company budget and resources.
With that in mind, let’s consider some of the main benefits of using Design Thinking at work:
- Significantly reduces time-to-market: With its emphasis on problem-solving and finding viable solutions, Design Thinking can significantly reduce the amount of time spent on design and development—especially in combination with lean and agile.
- Cost savings and a great ROI: Getting successful products to market faster ultimately saves the business money. Design Thinking has been proven to yield a significant return on investment; teams that are applying IBM’s Design Thinking practices , for example, have calculated an ROI of up to 300% as a result.
- Improves customer retention and loyalty: Design Thinking ensures a user-centric approach, which ultimately boosts user engagement and customer retention in the long term.
- Fosters innovation: Design Thinking is all about challenging assumptions and established beliefs, encouraging all stakeholders to think outside the box. This fosters a culture of innovation which extends well beyond the design team.
- Can be applied company-wide: The great thing about Design Thinking is that it’s not just for designers. It leverages group thinking and encourages cross-team collaboration. What’s more, it can be applied to virtually any team in any industry.
Whether you’re establishing a Design Thinking culture on a company-wide scale, or simply trying to improve your approach to user-centric design, Design Thinking will help you to innovate, focus on the user, and ultimately design products that solve real user problems.
6. Design Thinking methodology in action: Case studies
So we’ve looked in quite some detail at the theory behind Design Thinking and the processes involved — but what does this look like in action? Let’s explore some case studies where Design Thinking has made a huge real-world impact .
Healthcare Case Study: How Design Thinking transformed the Rotterdam Eye Hospital
Executives at the Rotterdam Eye Hospital wanted to transform the patient experience from the typically grim, anxiety-riddled affair into something much more pleasant and personal. To do this, they incorporated Design Thinking and design principles into their planning process. Here’s how they did it:

First, they set out to understand their target user — patients entering the hospital for treatment. The hospital CEO, CFO, managers, staff and doctors established that most patients came into hospital with the fear of going blind.
Based on their findings from the empathise stage, they determined that fear reduction needed to be a priority. Their problem statement may have looked something like the following: “Patients coming into our hospital need to feel comfortable and at ease.”
Armed with a deep understanding of their patients and a clear mission statement, they started to brainstorm potential solutions. As any good design thinker would, they sought inspiration from a range of both likely and unlikely sources. They looked to flagship airline KLM and supermarket chain Albert Heijn to learn about scheduling, for example, while turning to other medical organizations for inspiration on operational excellence.
In the prototyping stage, the team presented the most promising ideas they had come up with so far to those in charge of caregiving at the hospital. These teams of caregivers then used these insights to design informal, small-scale experiments that could test a potential solution and see if it was worthy of wide-scale adoption.
The testing phase consisted of running the aforementioned experiments and seeing if they took off. As Dirk Deichmann and Roel van der Heijde explain , the “transition to formal adoption of these ideas tended to be more gradual. If an idea worked, sooner or later other groups would ask if they could try it too, and the best ideas spread organically.”
The outcome
By adopting a Design Thinking approach, the Rotterdam Eye Hospital were able to get to the heart of their users’ needs and find effective solutions to fulfil them. In doing so, they have greatly improved the user experience: patient intake has risen 47%, and the hospital has since won several awards for safety, quality and design.
Business Case Study: How Design Thinking helped financial service provider MLP regain consumer trust
After the financial crisis hit, financial service provider MLP found that consumer trust was at an all-time low. They needed to re-engage with their target users and come up with new ways of building trust. In search of innovation, they decided to test out a Design Thinking approach. Here’s what they learned:
By focusing on their users and making a conscious effort to understand their needs first-hand, MLP learned that the assumptions they’d been going on were not so accurate after all. As Thomas Freese, division manager for marketing at MLP, explains :
“We always used to speak to customers about the goals they want to achieve. But they do not want to commit to a certain goal, as they often do not know themselves what that is. Rather, they want to talk about their ideas as it is more open and flexible regarding their financial planning.”
With this newfound empathy for their users, MLP were able to reframe their mission statement. They knew that they needed to rebuild consumer trust, and that the way to do this would be to speak to the customer in their own language and become a more relatable brand.
Ideate and Prototype
During the ideate and prototype phases, they decided to experiment with a completely new image. Instead of the formal business attire typically associated with the financial sector, the MLP team members went out in casual clothing. They tested Lego prototypes and homemade posters in designated hotspots — including a university campus and train stations.
By testing this new approach, they learned some extremely valuable lessons about their users and how to communicate with them. They found that even something as simple as dressing more casually had a huge impact in reducing the negative connotations associated with financial services. They also learned the value of asking open questions; rather than trying to sell their prototype, Design Thinking taught them to ask questions that focus on the user’s needs.
The Outcome
Their first foray into Design Thinking proved to be a huge learning curve for MLP. Taking the time to speak to their users gave them the insights they needed to redesign their messaging, allowing them to start marketing much more effectively.
In light of their findings, MLP opened up a new office space in a student district, putting their editorial and social media teams in close proximity to their customer base. Of course, Design Thinking is an iterative process, so this is just one way in which MLP hopes to continue learning to speak their customers’ language.
7. What is the relationship between Design Thinking and UX Design?
At this point, you’ve no doubt noticed lots of similarities between Design Thinking and user experience design , and may be wondering how they relate to one another. Both are extremely user-centric and driven by empathy, and UX designers will use many of the steps laid out in the Design Thinking process, such as user research , prototyping and testing.
Despite these similarities, there are certain distinctions that can be made between the two. For one, the impact of Design Thinking is often felt on a more strategic level; it explores a problem space—in the context of understanding users, technological feasibility, and business requirements—to discover possible solutions. As we have seen from the Rotterdam Eye Hospital and MLP case studies, Design Thinking is embraced and implemented by all different teams across the business, including C-level executives.
If Design Thinking focuses on finding solutions, UX design is concerned with actually designing these solutions and making sure they are usable, accessible and pleasant for the user.
You can think of Design Thinking as a toolset that UX designers dip into, and if you’re operating within the UX design field, it is one of many crucial methodologies you’ll rely on when it comes to creating fantastic user experiences. You can learn more about UX Design and Design Thinking in our UX Design Course , as well as earn a design thinking certification by completing a course in it.
Further reading
Want to see what design thinking looks like in practice? Here’s an article for you: 5 Game-Changing Examples of Design Thinking .
And if you’re new to the design field and wondering what all these newfangled terms mean, you may well be interested in the following guides:
- Learn How To Run Your Very Own Design Thinking Workshop!
- What Are Design Sprints?
- A Brief Guide To The Steps And Principles Of The Design Thinking Process
- How To Learn UX Design And Become A UX Designer
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Why Design Thinking Works
- Jeanne Liedtka

While we know a lot about practices that stimulate new ideas, innovation teams often struggle to apply them. Why? Because people’s biases and entrenched behaviors get in the way. In this article a Darden professor explains how design thinking helps people overcome this problem and unleash their creativity.
Though ostensibly geared to understanding and molding the experiences of customers, design thinking also profoundly reshapes the experiences of the innovators themselves. For example, immersive customer research helps them set aside their own views and recognize needs customers haven’t expressed. Carefully planned dialogues help teams build on their diverse ideas, not just negotiate compromises when differences arise. And experiments with new solutions reduce all stakeholders’ fear of change.
At every phase—customer discovery, idea generation, and testing—a clear structure makes people more comfortable trying new things, and processes increase collaboration. Because it combines practical tools and human insight, design thinking is a social technology —one that the author predicts will have an impact as large as an earlier social technology: total quality management.
It addresses the biases and behaviors that hamper innovation.
Idea in Brief
The problem.
While we know a lot about what practices stimulate new ideas and creative solutions, most innovation teams struggle to realize their benefits.
People’s intrinsic biases and behavioral habits inhibit the exercise of the imagination and protect unspoken assumptions about what will or will not work.
The Solution
Design thinking provides a structured process that helps innovators break free of counterproductive tendencies that thwart innovation. Like TQM, it is a social technology that blends practical tools with insights into human nature.
Occasionally, a new way of organizing work leads to extraordinary improvements. Total quality management did that in manufacturing in the 1980s by combining a set of tools—kanban cards, quality circles, and so on—with the insight that people on the shop floor could do much higher level work than they usually were asked to. That blend of tools and insight, applied to a work process, can be thought of as a social technology.
- JL Jeanne Liedtka is a professor of business administration at the University of Virginia’s Darden School of Business.
Partner Center
What is design thinking?

Design and conquer: in years past, the word “design” might have conjured images of expensive handbags or glossy coffee table books. Now, your mind might go straight to business. Design and design thinking are buzzing in the business community more than ever. Until now, design has focused largely on how something looks; these days, it’s a dynamic idea used to describe how organizations can adjust their problem-solving approaches to respond to rapidly changing environments—and create maximum impact and shareholder value. Design is a journey and a destination. Design thinking is a core way of starting the journey and arriving at the right destination at the right time.
Simply put, “design thinking is a methodology that we use to solve complex problems , and it’s a way of using systemic reasoning and intuition to explore ideal future states,” says McKinsey partner Jennifer Kilian. Design thinking, she continues, is “the single biggest competitive advantage that you can have, if your customers are loyal to you—because if you solve for their needs first, you’ll always win.”
Get to know and directly engage with senior McKinsey experts on design thinking
Tjark Freundt is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Hamburg office, Tomas Nauclér is a senior partner in the Stockholm office, Daniel Swan is a senior partner in the Stamford office, Warren Teichner is a senior partner in the New York office, Bill Wiseman is a senior partner in the Seattle office, and Kai Vollhardt is a senior partner in the Munich office.
And good design is good business. Kilian’s claim is backed up with data: McKinsey Design’s 2018 Business value of design report found that the best design performers increase their revenues and investor returns at nearly twice the rate of their industry competitors. What’s more, over a ten-year period, design-led companies outperformed the S&P 500 by 219 percent.
As you may have guessed by now, design thinking goes way beyond just the way something looks. And incorporating design thinking into your business is more than just creating a design studio and hiring designers. Design thinking means fundamentally changing how you develop your products, services, and, indeed, your organization itself.
Read on for a deep dive into the theory and practice of design thinking.
Learn more about McKinsey’s Design Practice , and check out McKinsey’s latest Business value of design report here .
How do companies build a design-driven company culture?
There’s more to succeeding in business than developing a great product or service that generates a financial return. Empathy and purpose are core business needs. Design thinking means putting customers, employees, and the planet at the center of problem solving.
McKinsey’s Design Practice has learned that design-led organizations start with design-driven cultures. Here are four steps to building success through the power of design:
Understand your audience. Design-driven companies go beyond asking what customers and employees want, to truly understanding why they want it. Frequently, design-driven companies will turn to cultural anthropologists and ethnographers to drill down into how their customers use and experience products, including what motivates them and what turns them away.
Makeup retailer Sephora provides an example. When marketing leaders actually watched shoppers using the Sephora website, they realized customers would frequently go to YouTube to watch videos of people using products before making a purchase. Using this information, the cosmetics retailer developed its own line of demonstration videos, keeping shoppers on the site and therefore more likely to make a purchase.
- Bring design to the executive table. This leader can be a chief design officer, a chief digital officer, or a chief marketing officer. Overall, this executive should be the best advocate for the company’s customers and employees, bringing the point of view of the people, the planet, and the company’s purpose into strategic business decisions. The design lead should also build bridges between multiple functions and stakeholders, bringing various groups into the design iteration process.
- Design in real time. To understand how and why people—both customers and employees—use processes, products, or services, organizations should develop a three-pronged design-thinking model that combines design, business strategy, and technology. This approach allows business leaders to spot trends, cocreate using feedback and data, prototype, validate, and build governance models for ongoing investment.
Act quickly. Good design depends on agility. That means getting a product to users quickly, then iterating based on customer feedback. In a design-driven culture, companies aren’t afraid to release products that aren’t quite perfect. Designers know there is no end to the design process. The power of design, instead, lies in the ability to adopt and adapt as needs change. When designers are embedded within teams, they are uniquely positioned to gather and digest feedback, which can lead to unexpected revelations. Ultimately, this approach creates more impactful and profitable results than following a prescribed path.
Consider Instagram. Having launched an initial product in 2010, Instagram’s founders paid attention to what the most popular features were: image sharing, commenting, and liking. They relaunched with a stripped-down version a few months later, resulting in 100,000 downloads in less than a week and over two million users in under two months —all without any strategic promotion.
Learn more about McKinsey’s Design Practice .
What’s the relationship between user-centered design and design thinking?
Both processes are design led. And they both emphasize listening to and deeply understanding users and continually gathering and implementing feedback to develop, refine, and improve a service.
Where they are different is scale. User-centered design focuses on improving a specific product or service . Design thinking takes a broader view as a way to creatively address complex problems—whether for a start-up, a large organization, or society as a whole.
User-centered design is great for developing a fantastic product or service. In the past, a company could coast on a superior process or product for years before competitors caught up. But now, as digitization drives more frequent and faster disruptions, users demand a dynamic mix of product and service. Emphasis has shifted firmly away from features and functions toward purpose, lifestyle, and simplicity of use.

Introducing McKinsey Explainers : Direct answers to complex questions
McKinsey analysis has found that some industries—such as telecommunications, automotive, and consumer product companies— have already made strides toward combining product and service into a unified customer experience . Read on for concrete examples of how companies have applied design thinking to offer innovative—and lucrative—customer experiences.
Learn more about our Operations Practice .
What is the design-thinking process?
McKinsey analysis has shown that the design-thinking approach creates more value than conventional approaches. The right design at the right price point spurs sustainability and resilience in a demonstrable way—a key driver of growth.
According to McKinsey’s Design Practice, there are two key steps to the design-thinking process:
- Developing an understanding of behavior and needs that goes beyond what people are doing right now to what they will need in the future and how to deliver that. The best way to develop this understanding is to spend time with people.
- “Concepting,” iterating, and testing . First start with pen and paper, sketching out concepts. Then quickly put these into rough prototypes—with an emphasis on quickly. Get feedback, refine, and test again. As American chemist Linus Pauling said : “The way to get good ideas is to get lots of ideas and throw the bad ones away.”
What is D4VG versus DTV?
For more than a decade, manufacturers have used a design-to-value (DTV) model to design and release products that have the features needed to be competitive at a low cost. During this time, DTV efforts were groundbreaking because they were based on data rather than experience. They also reached across functions, in contrast to the typical value-engineering approach.
The principles of DTV have evolved into design for value and growth (D4VG), a new way of creating products that provide exceptional customer experiences while driving both value and growth. Done right, D4VG efforts generate products with the features, form, and functionality that turn users into loyal fans .
D4VG products can cost more to build, but they can ultimately raise margins by delivering on a clear understanding of a product’s core brand attributes, insights into people’s motivations, and design thinking.
Learn more about our Consumer Packaged Goods Practice .
What is design for sustainability?
As consumers, companies, and regulators shift toward increased sustainability, design processes are coming under even more scrutiny. The challenge is that carbon-efficient production processes tend to be more complex and can require more carbon-intensive materials. The good news is that an increased focus on design for sustainability (DFS), especially at the research and development stage , can help mitigate some of these inefficiencies and ultimately create even more sustainable products.
For example, the transition from internal-combustion engines to electric-propulsion vehicles has highlighted emissions-intensive automobile production processes. One study found that around 20 percent of the carbon generated by a diesel vehicle comes from its production . If the vehicle ran on only renewable energy, production emissions would account for 85 percent of the total. With more sustainable design, electric-vehicle (EV) manufacturers stand to reduce the lifetime emissions of their products significantly.
To achieve design for sustainability at scale, companies can address three interrelated elements at the R&D stage:
- rethinking the way their products use resources, adapting them to changing regulations, adopting principles of circularity, and making use of customer insights
- understanding and tracking emissions and cost impact of design decisions in support of sustainability goals
- fostering the right mindsets and capabilities to integrate sustainability into every product and design decision
What is ‘skinny design’?
Skinny design is a less theoretical aspect of design thinking. It’s a method whereby consumer goods companies reassess the overall box size of products by reducing the total cubic volume of the package. According to McKinsey analysis , this can improve overall business performance in the following ways:
- Top-line growth of 4 to 5 percent through improvements in shelf and warehouse holding power. The ability to fit more stock into warehouses ultimately translates to growth.
- Bottom-line growth of more than 10 percent . Packing more product into containers and trucks creates the largest savings. Other cost reductions can come from designing packaging to minimize the labor required and facilitate automation.
- Sustainability improvements associated with reductions in carbon emissions through less diesel fuel burned per unit. Material choices can also confer improvements to the overall footprint.
Read more about skinny design and how it can help maximize the volume of consumer products that make it onto shelves.
Learn more about McKinsey’s Operations Practice .
How can a company become a top design performer?
The average person’s standard for design is higher than ever. Good design is no longer just a nice-to-have for a company. Customers now have extremely high expectations for design, whether it’s customer service, instant access to information, or clever products that are also aesthetically relevant in the current culture.
McKinsey tracked the design practices of 300 publicly listed companies over a five-year period in multiple countries. Advanced regression analysis of more than two million pieces of financial data and more than 100,000 design actions revealed 12 actions most correlated to improved financial performance. These were then clustered into the following four themes:
- Analytical leadership . For the best financial performers, design is a top management issue , and design performance is assessed with the same rigor these companies use to approach revenue and cost. The companies with the top financial returns have combined design and business leadership through bold, design-centric visions. These include a commitment to maintain a baseline level of customer understanding among all executives. The CEO of one of the world’s largest banks, for example, spends one day a month with the bank’s clients and encourages all members of the company’s C-suite to do the same.
- Cross-functional talent . Top-performing companies make user-centric design everyone’s responsibility, not a siloed function. Companies whose designers are embedded within cross-functional teams have better overall business performance . Further, the alignment of design metrics with functional business metrics (such as financial performance, user adoption rates, and satisfaction results) is also correlated to better business performance.
- Design with people, not for people . Design flourishes best, according to our research, in environments that encourage learning, testing, and iterating with users . These practices increase the odds of creating breakthrough products and services, while at the same time reducing the risk of costly missteps.
- User experience (UX) . Top-quartile companies embrace the full user experience by taking a broad-based view of where design can make a difference. Design approaches like mapping customer journeys can lead to more inclusive and sustainable solutions.
What are some real-world examples of how design thinking can improve efficiency and user experience?
Understanding the theory of design thinking is one thing. Seeing it work in practice is something else. Here are some examples of how elegant design created value for customers, a company, and shareholders:
- Stockholm’s international airport, Arlanda, used design thinking to address its air-traffic-control problem. The goal was to create a system that would make air traffic safer and more effective. By understanding the tasks and challenges of the air-traffic controllers, then collaboratively working on prototypes and iterating based on feedback, a working group was able to design a new departure-sequencing tool that helped air-traffic controllers do their jobs better. The new system greatly reduced the amount of time planes spent between leaving the terminal and being in the air, which in turn helped reduce fuel consumption.
- When Tesla creates its electric vehicles , the company closely considers not only aesthetics but also the overall driving experience .
- The consumer electronics industry has a long history of dramatic evolutions lead by design thinking. Since Apple debuted the iPhone in 2007, for example, each new generation has seen additional features, new customers, and lower costs—all driven by design-led value creation .
Learn more about our Consumer Packaged Goods and Sustainability Practices.
For a more in-depth exploration of these topics, see McKinsey’s Agile Organizations collection. Learn more about our Design Practice —and check out design-thinking-related job opportunities if you’re interested in working at McKinsey.
Articles referenced:
- “ Skinny design: Smaller is better ,” April 26, 2022, Dave Fedewa , Daniel Swan , Warren Teichner , and Bill Wiseman
- “ Product sustainability: Back to the drawing board ,” February 7, 2022, Stephan Fuchs, Stephan Mohr , Malin Orebäck, and Jan Rys
- “ Emerging from COVID-19: Australians embrace their values ,” May 11, 2020, Lloyd Colling, Rod Farmer , Jenny Child, Dan Feldman, and Jean-Baptiste Coumau
- “ The business value of design ,” McKinsey Quarterly , October 25, 2018, Benedict Sheppard , Hugo Sarrazin, Garen Kouyoumjian, and Fabricio Dore
- “ More than a feeling: Ten design practices to deliver business value ,” December 8, 2017, Benedict Sheppard , John Edson, and Garen Kouyoumjian
- “ Creating value through sustainable design ,” July 25, 2017, Sara Andersson, David Crafoord, and Tomas Nauclér
- “ The expanding role of design in creating an end-to-end customer experience ,” June 6, 2017, Raffaele Breschi, Tjark Freundt , Malin Orebäck, and Kai Vollhardt
- “ Design for value and growth in a new world ,” April 13, 2017, Ankur Agrawal , Mark Dziersk, Dave Subburaj, and Kieran West
- “ The power of design thinking ,” March 1, 2016, Jennifer Kilian , Hugo Sarrazin, and Barr Seitz
- “ Building a design-driven culture ,” September 1, 2015, Jennifer Kilian , Hugo Sarrazin, and Hyo Yeon

Want to know more about design thinking?
Related articles.

Skinny design: Smaller is better

The business value of design

More than a feeling: Ten design practices to deliver business value
About this site
Design thinking in context, design thinking today.
- Designer's Mindset
- Adoption and Integration
- Teaching and Learning
- New Applications
- Privacy Policy
Design Thinking Defined
—tim brown, executive chair of ideo.
Thinking like a designer can transform the way organizations develop products, services, processes, and strategy. This approach, which is known as design thinking, brings together what is desirable from a human point of view with what is technologically feasible and economically viable. It also allows people who aren't trained as designers to use creative tools to address a vast range of challenges.
IDEO did not invent design thinking, but we have become known for practicing it and applying it to solving problems small and large. It’s fair to say that we were in the right place at the right time. When we looked back over our shoulder, we discovered that there was a revolutionary movement behind us.
This design thinking site is just one small part of the IDEO network. There’s much more, including full online courses we've developed on many topics related to design thinking and its applications. We fundamentally believe in the power of design thinking as a methodology for creating positive impact in the world—and we bring that belief into our client engagements as well as into creating open resources such as this.
At IDEO, we’re often asked to share what we know about design thinking. We’ve developed this website in response to that request. Here, we introduce design thinking, how it came to be, how it is being used, and steps and tools for mastering it. You’ll find our particular take on design thinking, as well as the perspectives of others. Everything on this site is free for you to use and share with proper attribution .
(From 2008-2018, designthinking.ideo.com was the home of IDEO's design thinking blog, written by our CEO, Tim Brown . You can find that blog here .)
We live and work in a world of interlocking systems, where many of the problems we face are dynamic, multifaceted, and inherently human. Think of some of the big questions being asked by businesses, government, educational and social organizations: How will we navigate the disruptive forces of the day, including technology and globalism? How will we grow and improve in response to rapid change? How can we effectively support individuals while simultaneously changing big systems? For us, design thinking offers an approach for addressing these and other big questions.
There’s no single definition for design thinking. It’s an idea, a strategy, a method, and a way of seeing the world. It’s grown beyond the confines of any individual person, organization or website. And as it matures, its history deepens and its impact evolves. For IDEO, design thinking is a way to solve problems through creativity. Certainly, it isn’t a fail-safe approach; nor is it the only approach. But based on the impact we are seeing in our work, the relevance of design thinking has never been greater.
Design thinking is maturing. It’s moving from a nascent practice to an established one, and with that comes interest and critique. People are debating its definition, pedigree, and value. As a leading and committed practitioner of design thinking, IDEO has a stake in this conversation—and a responsibility to contextualize its value in the present moment and, importantly, in the future.
We’ve learned a lot over the years, and we’d like to share our insights. We’ve seen design thinking transform lives and organizations, and on occasion we’ve seen it fall short when approached superficially, or without a solid foundation of study. Design thinking takes practice; and as a community of designers, entrepreneurs, engineers, teachers, researchers, and more, we’ve followed the journey to mastery, and developed maps that can guide others.
Designer's mindset
At IDEO, we are a community of designers who naturally share a mindset due to our profession. Our teams include people who've trained in applied fields such as industrial design, environmental architecture, graphic design, and engineering; as well as people from law, psychology, anthropology, and many other areas. Together, we have rallied around design thinking as a way of explaining design's applications and utility so that others can practice it, too. Design thinking uses creative activities to foster collaboration and solve problems in human-centered ways. We adopt a “beginner’s mind,” with the intent to remain open and curious, to assume nothing, and to see ambiguity as an opportunity.
To think like a designer requires dreaming up wild ideas, taking time to tinker and test, and being willing to fail early and often. The designer's mindset embraces empathy, optimism, iteration, creativity, and ambiguity. And most critically, design thinking keeps people at the center of every process. A human-centered designer knows that as long as you stay focused on the people you're designing for—and listen to them directly—you can arrive at optimal solutions that meet their needs.
Anyone can approach the world like a designer. But to unlock greater potential and to learn how to work as a dynamic problem solver, creative confidence is key. For IDEO founder David Kelley, creative confidence is the belief that everyone is creative, and that creativity isn’t the ability to draw or compose or sculpt, but a way of understanding the world.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Design Thinking & Why Is It Important?

- 18 Jan 2022
In an age when innovation is key to business success and growth, you’ve likely come across the term “design thinking.” Perhaps you’ve heard it mentioned by a senior leader as something that needs to be utilized more, or maybe you’ve seen it on a prospective employee's resume.
While design thinking is an ideology based on designers’ workflows for mapping out stages of design, its purpose is to provide all professionals with a standardized innovation process to develop creative solutions to problems—design-related or not.
Why is design thinking needed? Innovation is defined as a product, process, service, or business model featuring two critical characteristics: novel and useful. Yet, there’s no use in creating something new and novel if people won’t use it. Design thinking offers innovation the upgrade it needs to inspire meaningful and impactful solutions.
But what is design thinking, and how does it benefit working professionals?
What Is Design Thinking?
Design thinking is a mindset and approach to problem-solving and innovation anchored around human-centered design . While it can be traced back centuries—and perhaps even longer—it gained traction in the modern business world after Tim Brown, CEO and president of design company IDEO, published an article about it in the Harvard Business Review .
Design thinking is different from other innovation and ideation processes in that it’s solution-based and user-centric rather than problem-based. This means it focuses on the solution to a problem instead of the problem itself.
For example, if a team is struggling with transitioning to remote work, the design thinking methodology encourages them to consider how to increase employee engagement rather than focus on the problem (decreasing productivity).

The essence of design thinking is human-centric and user-specific. It’s about the person behind the problem and solution, and requires asking questions such as “Who will be using this product?” and “How will this solution impact the user?”
The first, and arguably most important, step of design thinking is building empathy with users. By understanding the person affected by a problem, you can find a more impactful solution. On top of empathy, design thinking is centered on observing product interaction, drawing conclusions based on research, and ensuring the user remains the focus of the final implementation.
The Four Phases of Innovation
So, what does design thinking entail? There are many models of design thinking that range from three to seven steps.
In the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar leverages a four-phase innovation framework. The phases venture from concrete to abstract thinking and back again as the process loops, reverses, and repeats. This is an important balance because abstract thinking increases the likelihood that an idea will be novel. It’s essential, however, to anchor abstract ideas in concrete thinking to ensure the solution is valid and useful.
Here are the four phases for effective innovation and, by extension, design thinking.

The first phase is about narrowing down the focus of the design thinking process. It involves identifying the problem statement to come up with the best outcome. This is done through observation and taking the time to determine the problem and the roadblocks that prevented a solution in the past.
Various tools and frameworks are available—and often needed—to make concrete observations about users and facts gathered through research. Regardless of which tools are implemented, the key is to observe without assumptions or biased expectations.
Once findings from your observations are collected, the next step is to shape insights by framing those observations. This is where you can venture into the abstract by reframing the problem in the form of a statement or question.
Once the problem statement or question has been solidified—not finalized—the next step is ideation. You can use a tool such as systematic inventive thinking (SIT) in this stage, which is useful for creating an innovative process that can be replicated in the future.
The goal is to ultimately overcome cognitive fixedness and devise new and innovative ideas that solve the problems you identified. Continue to actively avoid assumptions and keep the user at the forefront of your mind during ideation sessions.
The third phase involves developing concepts by critiquing a range of possible solutions. This includes multiple rounds of prototyping, testing, and experimenting to answer critical questions about a concept’s viability.
Remember: This step isn’t about perfection, but rather, experimenting with different ideas and seeing which parts work and which don’t.
4. Implement
The fourth and final phase, implementation, is when the entire process comes together. As an extension of the develop phase, implementation starts with testing, reflecting on results, reiterating, and testing again. This may require going back to a prior phase to iterate and refine until you find a successful solution. Such an approach is recommended because design thinking is often a nonlinear, iterative process.
In this phase, don’t forget to share results with stakeholders and reflect on the innovation management strategies implemented during the design thinking process. Learning from experience is an innovation process and design thinking project all its own.
Check out the video about the design thinking process below, and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more explainer content!
Why Design Thinking Skills Matter
The main value of design thinking is that it offers a defined process for innovation. While trial and error is a good way to test and experiment what works and what doesn’t, it’s often time-consuming, expensive, and ultimately ineffective. On the other hand, following the concrete steps of design thinking is an efficient way to develop new, innovative solutions.
On top of a clear, defined process that enables strategic innovation, design thinking can have immensely positive outcomes for your career—in terms of both advancement and salary.

As of December 2021, the most common occupations requiring design thinking skills were:
- Marketing managers
- Industrial engineers
- Graphic designers
- Software developers
- General and operations managers
- Management analysts
- Personal service managers
- Architectural and engineering managers
- Computer and information systems managers
In addition, jobs that require design thinking statistically have higher salaries. Take a marketing manager position, for example. The median annual salary is $107,900. Marketing manager job postings that require design thinking skills, however, have a median annual salary of $133,900—a 24 percent increase.

Overall, businesses are looking for talent with design thinking skills. As of November 2021, there were 29,648 job postings in the United States advertising design thinking as a necessary skill—a 153 percent increase from November 2020, and a 637 percent increase from November 2017.
As businesses continue to recognize the need for design thinking and innovation, they’ll likely create more demand for employees with those skills.
Learning Design Thinking
Design thinking is an extension of innovation that allows you to design solutions for end users with a single problem statement in mind. It not only imparts valuable skills but can help advance your career.
It’s also a collaborative endeavor that can only be mastered through practice with peers. As Datar says in the introduction to Design Thinking and Innovation : “Just as with learning how to swim, the best way to practice is to jump in and try.”
If you want to learn design thinking, take an active role in your education. Start polls, problem-solving exercises, and debates with peers to get a taste of the process. It’s also important to seek out diverse viewpoints to prepare yourself for the business world.
In addition, if you’re considering adding design thinking to your skill set, think about your goals and why you want to learn about it. What else might you need to be successful?
You might consider developing your communication, innovation, leadership, research, and management skills, as those are often listed alongside design thinking in job postings and professional profiles.

You may also notice skills like agile methodology, user experience, and prototyping in job postings, along with non-design skills, such as product management, strategic planning, and new product development.


Is Design Thinking Right for You?
There are many ways to approach problem-solving and innovation. Design thinking is just one of them. While it’s beneficial to learn how others have approached problems and evaluate if you have the same tools at your disposal, it can be more important to chart your own course to deliver what users and customers truly need.
You can also pursue an online course or workshop that dives deeper into design thinking methodology. This can be a practical path if you want to improve your design thinking skills or require a more collaborative environment.
Are you ready to develop your design thinking skills? Explore our online course Design Thinking and Innovation to discover how to leverage fundamental design thinking principles and innovative problem-solving tools to address business challenges.

About the Author
Learn / Guides / Design thinking guide
Back to guides
Design thinking methodology: 5 principles to follow
When user empathy is at the core of product development, everyone wins.
Your users feel seen and heard, and your product development process is resilient and efficient. That’s the power of embracing design thinking.
Last updated
Reading time.

In this chapter, we unpack five principles of the design thinking methodology to help you build excellent products and features for your customers.
Make your users a priority
Use Hotjar to learn what your users need and how your product fits in so you can launch updates and features that make their lives better.
A quick refresher: what is design thinking?
Design thinking is an iterative process for solving problems in product development. The main thing to remember about design thinking is that the search for a solution puts the user front-and-center.
It’s a framework that empowers you to ask important questions about your product and how it affects users. If you want to throw out assumptions about your product experience and never hear “that’s how we’ve always done it” as reasoning for a product decision, design thinking is the way to go.
The 5 core principles of the design thinking methodology
The design thinking methodology is made of five principles:
User-centricity and empathy: your users, their problems, and their experience in your product are a priority, not an afterthought
Collaboration: every level and every role can contribute to, and see results from, design thinking
Ideation: the goal is to generate as many solutions as possible for a problem you’ve identified
Experimentation and iteration: the best solution ideas are turned into prototypes you can run experiments on
A bias towards action: ideas are most powerful when executed in real life, so taking action is essential
The focus on user empathy and action is the name of the game in design thinking; everything you do within design thinking ties back to the user and product experience.
Let’s dive into each principle and the role it plays in your work as a product team.
1. User-centricity and empathy
User-centricity and empathy are at the forefront of design thinking. When you explore solutions through design thinking, you do so based on human needs and user feedback.
The approach is about understanding what the user wants, needs, and struggles with when it comes to your product and its role in their life. It involves digging into how they feel about your product.
Think about it this way: if you struggle with customer churn, your business goal might be to reduce your churn rate (or increase your retention rate). But when you prioritize user-centricity and empathy, your actual goal is to improve the experience your customers have when using your product—which in turn positively impacts your business metrics.
Here are a few ways to start understanding your users and prioritizing empathy:
Surveys: ask users for direct feedback in key moments, like when they’re taking longer to complete a task or are about to abandon their session before reaching their goal
Recordings: peek over users’ virtual shoulders to understand what draws their attention, what frustrates them, and where they struggle
User interviews : unbiased, open-ended questions can reveal a mountain of insights you otherwise might not spot
It’s important to remember that the work you do to prioritize empathy never ends; you’ll never be ‘done’ understanding your users. Some of the biggest companies in the world know this: UberEats constantly interviews restaurant workers, delivery drivers, and meal recipients; Apple makes iterative customer involvement part of their design and development process.
Learn more about these (and other) examples in the design thinking examples chapter of this guide.
Hotjar helps us empathize with our users. It reminds us that there are real human beings on the other end. It also confirms that our work as a product development team has an impact, and is making our customer's lives easier. Hotjar helps us empathize with our users. It reminds us that there are real human beings on the other end. It also confirms that our work as a product development team has an impact, and is making our customer's lives easier.
2. Collaboration
Collaboration is a key dimension of design thinking. It allows product teams to step outside of your usual problem-solving and decision-making patterns and consider diverse ideas and perspectives. It sets the base for innovation and potential product solutions that would otherwise remain hidden.
In design thinking, input from teams like customer support, marketing, sales, customer success, and data or business intelligence is particularly useful in creating a problem statement—an actionable, concise sentence or question that drives your UX purpose and direction.
An effective problem statement is one that considers the entire user journey, start-to-finish—and this is where collaboration comes in: marketing and sales have a deeper insight into the earlier part of the customer journey, while support and customer success understand customer needs and struggles as they use your product.
We really love Hotjar. I share all the insights I find with the team. We get the Customer Success Manager to watch Recordings. UX person to watch recordings. Devs watch recordings. It’s a team effort. It’s democratic learning.
The wide range of skills across different teams is crucial to make your problem statement as useful as possible.
One excellent example of this in practice is Citrix. Knowing that many employees have little or no contact with users, they actively encourage design thinking and focus on the problems that matter to customers (and ultimately benefit the business, too).
See more problem statement examples in the problem statement chapter of this guide.
🔥 If you’re using Hotjar
Share product experience insights that would otherwise remain hidden to other teams. For example:
Use Recordings to show your customer support team the user behavior that led to an issue users told them about over live chat
Use Feedback to give the marketing team in-depth insights about parts of the pricing page that confuse potential customers
Use Surveys to share open-ended survey responses to user onboarding with sales reps who won them over
3. Ideation
In design thinking, designers hold ideation sessions to generate as many potential solutions to an issue as possible. Design thinking can’t happen without ideation—after all, it is a solution-focused process. Ideas are its essential building material.
The goal is to propose as many solutions as possible—no matter how 'good' or 'bad' they might be—based on what you learn through user empathy and collaboration on a problem statement.
Here are a few things to keep in mind to get the most out of your ideation sessions:
Create a judgment-free zone: every idea is welcome, and the best way to generate as many ideas as possible is to ensure no one is holding back
No HiPPOs: the Highest Paid Person’s Opinion (HiPPO) can make one person's ideas seem more important or relevant than others’, so prevent that by giving all ideas equal space
Use as many ideation techniques as you can: take advantage of brainstorming, mind mapping, brain writing, sketching, and any other method that suits the people involved
Ignore the obstacles (for now): note down and log all ideas that come up during this process, even those that don’t seem feasible given the circumstances and resources you have
With people from different teams and rich, diverse skill sets taking part in ideation, you’ll end up with ideas you can combine, reframe, and consider in different contexts of your product.
💡 Pro tip: make the most of your product experience insights —the data that reveals how your users interact with your product—in the ideation phase.
For example, heatmaps might give you an idea of UX updates that will make the user journey smoother. Or you could compare session recordings between users who completed a task and those who abandoned it to brainstorm product improvements that might help more users reach their goal with your product.
4. Experimentation and iteration
With a bank of ideas, your next step is to narrow them down to a few you can focus on and—most importantly—run experiments with.
Embracing a product experimentation culture is key to product teams that put the customer first. It’s no wonder it also fits into the design thinking methodology. Use product prioritization to choose an idea to focus on and create a prototype you can test:
First, build thorough experiments. Define your goal, build a hypothesis, and choose KPIs you’ll use to measure results. This is essential to understand the true impact of your design thinking solutions. Otherwise, you’ll end up making assumptions and educated guesses (at best) about why a solution worked or failed.
Then, measure and iterate. As you run experiments on your ideas, like A/B tests or funnel tests, monitor results daily and keep an eye on additional quantitative and qualitative insights that give you context about the user experience.
For example, if you tweak a step in your product onboarding for a portion of your users, track the KPIs that measure its success, such as the completion rate. But don’t stop there: look at session recordings to better understand user progression and behavior during onboarding, and set up a Customer Effort Score survey to track ease of use for the original and updated versions.
5. A bias towards action
Much about the first four principles is focused on ideas—relying on empathy for the user to create as many ideas as possible, then testing prototypes in the real world.
The final building block of the design thinking methodology is to consistently and cyclically take action.
Ideas that stay in a team member’s mind don’t have any impact.
Ideas you experiment with have the potential to help a small portion of your users.
And ideas you choose to learn from, tweak, and release to your user base can have a lasting impact on both your users and your company’s success and long-term viability.
Consider the approach that RazorPay, an end-to-end payment solutions provider, took when updating their user dashboard:
Instead of endlessly hypothesizing and making vague assumptions, the RazorPay team released their redesign to just 10% of their users.
Then, instead of only tracking standard web analytics to measure success, they also kept an eye on the score these users gave their experience on a scale from 1 to 10. If the score was low, users could explain their rating in an open-ended survey.
At this point, RazorPay didn’t pat themselves on the back for a job well done— they kept working on the dashboard through multiple iterations based on continuous user feedback.
Read RazorPay's full story here .
Use design thinking to keep learning about your users
As you embrace design thinking and learn how your product team can make the most of it, remember: there’s no end to the process , and you can always use what you’ve learned from taking action to refine the ideas you’ve developed.
Make product decisions based on what your users need
Use insights from Recordings, Heatmaps, Surveys, and Feedback to learn what your users need—and build a product that fits right in.
FAQs about design thinking methodology
What are the five design thinking principles.
The design thinking methodology focuses on solving issues by embodying these five principles:
User-centricity and empathy for user problems and experiences
Collaboration between teams
Ideation and generating as many solutions as possible
Experimentation and iteration of best ideas
A bias towards action and learning from experiments
Where can you find ideas for design thinking solutions?
Design thinking solution ideas can originate from anywhere in the user journey, from their experience signing up and onboarding to product usage and drop-off points.
Use design thinking software to find and develop ideas. A tool like Hotjar lets you observe user behavior in your product and ask the right questions at the right time. Other design thinking tools help you conduct live user interviews, run collaborative brainstorming sessions, and shape ideas into prototypes.
What is the key to making the design thinking methodology work?
Design thinking emphasizes taking action. Even the best ideas are wasted if you don’t implement them and learn from them for future improvements.
For example, when you brainstorm a new feature based on what you know about your customers, prototype it and test it with real users. Data like session recordings and survey responses will give you a world of learning you can build upon to improve your product.
Design thinking process
Previous chapter
Examples of design thinking
Next chapter
- Project planning |
- How to solve problems using the design ...
How to solve problems using the design thinking process

The design thinking process is a problem-solving design methodology that helps you develop solutions in a human-focused way. Initially designed at Stanford’s d.school, the five stage design thinking method can help solve ambiguous questions, or more open-ended problems. Learn how these five steps can help your team create innovative solutions to complex problems.
As humans, we’re approached with problems every single day. But how often do we come up with solutions to everyday problems that put the needs of individual humans first?
This is how the design thinking process started.
What is the design thinking process?
The design thinking process is a problem-solving design methodology that helps you tackle complex problems by framing the issue in a human-centric way. The design thinking process works especially well for problems that are not clearly defined or have a more ambiguous goal.
One of the first individuals to write about design thinking was John E. Arnold, a mechanical engineering professor at Stanford. Arnold wrote about four major areas of design thinking in his book, “Creative Engineering” in 1959. His work was later taught at Stanford’s Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design (also known as d.school), a design institute that pioneered the design thinking process.
This eventually led Nobel Prize laureate Herbert Simon to outline one of the first iterations of the design thinking process in his 1969 book, “The Sciences of the Artificial.” While there are many different variations of design thinking, “The Sciences of the Artificial” is often credited as the basis.
Anatomy of Work Special Report: How to spot—and overcome—the most crucial enterprise challenges
Learn how enterprises can improve processes and productivity, no matter how complex your organization is. With fewer redundancies, leaders and their teams can hit goals faster.
![design thinking methodology process [Resource Card] AOW Blog Image](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/fdc408f5-063d-4ea7-8d73-cb3ec61704fc/Global-AOW23-Black-Hole?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A non-linear design thinking approach
Design thinking is not a linear process. It’s important to understand that each stage of the process can (and should) inform the other steps. For example, when you’re going through user testing, you may learn about a new problem that didn’t come up during any of the previous stages. You may learn more about your target personas during the final testing phase, or discover that your initial problem statement can actually help solve even more problems, so you need to redefine the statement to include those as well.
Why use the design thinking process
The design thinking process is not the most intuitive way to solve a problem, but the results that come from it are worth the effort. Here are a few other reasons why implementing the design thinking process for your team is worth it.
Focus on problem solving
As human beings, we often don’t go out of our way to find problems. Since there’s always an abundance of problems to solve, we’re used to solving problems as they occur. The design thinking process forces you to look at problems from many different points of view.
The design thinking process requires focusing on human needs and behaviors, and how to create a solution to match those needs. This focus on problem solving can help your design team come up with creative solutions for complex problems.
Encourages collaboration and teamwork
The design thinking process cannot happen in a silo. It requires many different viewpoints from designers, future customers, and other stakeholders . Brainstorming sessions and collaboration are the backbone of the design thinking process.
Foster innovation
The design thinking process focuses on finding creative solutions that cater to human needs. This means your team is looking to find creative solutions for hyper specific and complex problems. If they’re solving unique problems, then the solutions they’re creating must be equally unique.
The iterative process of the design thinking process means that the innovation doesn’t have to end—your team can continue to update the usability of your product to ensure that your target audience’s problems are effectively solved.
The 5 stages of design thinking
Currently, one of the more popular models of design thinking is the model proposed by the Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design (or d.school) at Stanford. The main reason for its popularity is because of the success this process had in successful companies like Google, Apple, Toyota, and Nike. Here are the five steps designated by the d.school model that have helped many companies succeed.
1. Empathize stage
The first stage of the design thinking process is to look at the problem you’re trying to solve in an empathetic manner. To get an accurate representation of how the problem affects people, actively look for people who encountered this problem previously. Asking them how they would have liked to have the issue resolved is a good place to start, especially because of the human-centric nature of the design thinking process.
Empathy is an incredibly important aspect of the design thinking process. The design thinking process requires the designers to put aside any assumptions and unconscious biases they may have about the situation and put themselves in someone else’s shoes.
For example, if your team is looking to fix the employee onboarding process at your company, you may interview recent new hires to see how their onboarding experience went. Another option is to have a more tenured team member go through the onboarding process so they can experience exactly what a new hire experiences.
2. Define stage
Sometimes a designer will encounter a situation when there’s a general issue, but not a specific problem that needs to be solved. One way to help designers clearly define and outline a problem is to create human-centric problem statements.
A problem statement helps frame a problem in a way that provides relevant context in an easy to comprehend way. The main goal of a problem statement is to guide designers working on possible solutions for this problem. A problem statement frames the problem in a way that easily highlights the gap between the current state of things and the end goal.
Tip: Problem statements are best framed as a need for a specific individual. The more specific you are with your problem statement, the better designers can create a human-centric solution to the problem.
Examples of good problem statements:
We need to decrease the number of clicks a potential customer takes to go through the sign-up process.
We need to decrease the new subscriber unsubscribe rate by 10%.
We need to increase the Android app adoption rate by 20%.
3. Ideate stage
This is the stage where designers create potential solutions to solve the problem outlined in the problem statement. Use brainstorming techniques with your team to identify the human-centric solution to the problem defined in step two.
Here are a few brainstorming strategies you can use with your team to come up with a solution:
Standard brainstorm session: Your team gathers together and verbally discusses different ideas out loud.
Brainwrite: Everyone writes their ideas down on a piece of paper or a sticky note and each team member puts their ideas up on the whiteboard.
Worst possible idea: The inverse of your end goal. Your team produces the most goofy idea so nobody will look silly. This takes out the rigidity of other brainstorming techniques. This technique also helps you identify areas that you can improve upon in your actual solution by looking at the worst parts of an absurd solution.
It’s important that you don’t discount any ideas during the ideation phase of brainstorming. You want to have as many potential solutions as possible, as new ideas can help trigger even better ideas. Sometimes the most creative solution to a problem is the combination of many different ideas put together.
4. Prototype stage
During the prototype phase, you and your team design a few different variations of inexpensive or scaled down versions of the potential solution to the problem. Having different versions of the prototype gives your team opportunities to test out the solution and make any refinements.
Prototypes are often tested by other designers, team members outside of the initial design department, and trusted customers or members of the target audience. Having multiple versions of the product gives your team the opportunity to tweak and refine the design before testing with real users. During this process, it’s important to document the testers using the end product. This will give you valuable information as to what parts of the solution are good, and which require more changes.
After testing different prototypes out with teasers, your team should have different solutions for how your product can be improved. The testing and prototyping phase is an iterative process—so much so that it’s possible that some design projects never end.
After designers take the time to test, reiterate, and redesign new products, they may find new problems, different solutions, and gain an overall better understanding of the end-user. The design thinking framework is flexible and non-linear, so it’s totally normal for the process itself to influence the end design.
Tips for incorporating the design thinking process into your team
If you want your team to start using the design thinking process, but you’re unsure of how to start, here are a few tips to help you out.
Start small: Similar to how you would test a prototype on a small group of people, you want to test out the design thinking process with a smaller team to see how your team functions. Give this test team some small projects to work on so you can see how this team reacts. If it works out, you can slowly start rolling this process out to other teams.
Incorporate cross-functional team members : The design thinking process works best when your team members collaborate and brainstorm together. Identify who your designer’s key stakeholders are and ensure they’re included in the small test team.
Organize work in a collaborative project management software : Keep important design project documents such as user research, wireframes, and brainstorms in a collaborative tool like Asana . This way, team members will have one central source of truth for anything relating to the project they’re working on.
Foster collaborative design thinking with Asana
The design thinking process works best when your team works collaboratively. You don’t want something as simple as miscommunication to hinder your projects. Instead, compile all of the information your team needs about a design project in one place with Asana.
Related resources

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to drive product development

How Asana uses work management to streamline project intake processes

How Asana uses work management for smoother creative production
- Graphic Design
- USER EXPERIENCE (UX) DESIGN
- User Interface (UI) Design
- Interior Design
- Motion Graphics
- Graphic design
- USER EXPERIENCE Design
- Motion graphics
- Interior design

A Breakdown of Each Step in The Design Thinking Process
Design thinking is an important approach to problem-solving. In this article, learn all about each step of the design thinking process, including how to implement it and why it matters.
Whatever problem you’re attempting to solve next, whether it is in the field of business, design, or something else, it can benefit significantly from the application of design thinking. That is because design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that places paramount emphasis on the core principles of empathy, creativity, and iterative processes, which often result in the generation of truly innovative and effective solutions.
This article will serve as your guide to understanding the definitive, 5-step design thinking process. We'll break down each step for you, offering a comprehensive understanding of its purpose and relevance, along with a brief guide on how to execute it.
What is the Design Thinking Process and Why is it so Popular?
- Next Steps to Learn Design Thinking
Design thinking is a human-centred and creative problem-solving approach that places a strong emphasis on understanding and addressing the unmet needs of users. It prioritises the use of empathy to delve deep into users' perspectives, and uncover latent desires and insights that are often overlooked by conventional problem-solving methods.
Design thinking follows a five-step process - empathise, define, ideate, prototype, and test - in which iteration and continuous refinement play an important part. This can often make the process non-linear in its application, that is to say, these five steps are not always followed sequentially. You may frequently find yourself moving back and forth between steps, and therefore repeating one or more steps, in order to eventually reach the best possible solution.
The popularity of design thinking stems from its user-centricity, its applicability in situations where the problem itself may be ill-defined or unknown, and its capacity to fuel creative and innovative solutions. These give the process its transformative potential and wide application for problem-solving across industries.
Breakdown of Each Step of the Design Thinking Process
Let us now take a closer look at each of the five steps of the design thinking process, to better understand why they matter and how they can be implemented.

Step 1: Empathise
Empathising is the foundational step in the design thinking process. It involves putting oneself in the shoes of the end-users to gain a deep understanding of their needs, desires, and pain points. Empathy is not just about understanding what users say but also about comprehending their unspoken emotions, frustrations, and aspirations. This step establishes the critical human-centric perspective that underpins the entire design thinking approach.
Why does this step matter?
Helps understand user needs: Empathy allows one to step into the shoes of the end-users and gain a deep understanding of their needs, desires, and pain points. This enables one to formulate solutions that genuinely address user needs.
Aids human-centred design: This step ensures that solutions go beyond just functionality and recognise the emotional and psychological aspects of the user experience. This makes it possible to create products that resonate deeply with the user.
Reduces assumptions: By empathising with users and collecting real-world data through reliable methods, problem-solvers can minimise assumptions and biases that might otherwise influence the design of the solution.
Enhances innovation: By understanding the problems and experiences of users, one can uncover opportunities for groundbreaking solutions that might not be apparent through a purely analytical approach. The extensive research involved at this stage allows one to identify hitherto unknown gaps, giving one an advantage when it comes to creating solutions.
How to implement this step?
Putting oneself in the shoes of the user is a challenging task, especially when attempted on a large scale. This has given rise to various methods of data collection that can assist in making informed decisions and solving user problems. Let's briefly look at a few of these methods:

Step 2: Define
The second step in the design thinking process is to objectively define the core issue that one is trying to fix. At this stage, design thinkers delve deep into the issue at hand by studying the data collected, striving to understand it from the user's perspective and frame clear problem statements. This step serves as the bedrock upon which the rest of the journey is built.
For problem-framing: This step is essential for framing a clear and concise problem statement that is grounded in the needs and perspectives of the users. Without a well-defined and user-centric problem statement, the process to follow will lack direction, making it challenging to come up with a targeted solution that truly serves the user’s needs.
For alignment: This step aligns the entire design thinking team and stakeholders by providing a common understanding of the problem to be solved and is essential to avoid miscommunication and misunderstandings as the design thinking process moves forward.
For evaluating success: Throughout the process, the problem statement can be used to assess whether the proposed solutions are effective. It provides a clear criteria for evaluating the success of the final solution / product / service / design.
For generating ideas: The problem statement generated in this step becomes a catalyst for idea generation in the subsequent step. It guides the team in brainstorming creative solutions that directly target the defined problem.
For reducing risk: By clearly defining the problem early in the process, this step helps reduce the risk of investing time and resources in developing a solution that ultimately doesn't address the core issue. It ensures that the design efforts are focused and purposeful.
Defining a concrete problem statement is the sole objective at this stage and there is a wide consensus on how to approach this. Here are key touchpoints to keep in mind while defining the problem statement:
Empathise with users: As you have probably picked up from what you have read thus far, empathising with the user is at the core of the process. Before you can create a meaningful problem statement, you must first deeply understand your users. This is where analysing the research from 'Step 1' comes into play. By immersing yourself in the users' world, you'll be better equipped to formulate a problem statement that truly resonates with their experiences.
Use the "How might we" framework: The "How might we" framework is a powerful tool for shaping your problem statement. It begins with the phrase "How might we..." and continues with a succinct description of the challenge you want to address. This open-ended format encourages creative thinking and brainstorming of diverse solutions. For example, instead of saying, 'We need a new website,' you might frame it as, 'How might we make it easier for users to find information on our website?'
Focus on user-centric language: Your problem statement should revolve around the user. Use language that is drawn from their needs, challenges, and aspirations. Rather than a generic statement like, 'Develop a new product,' consider a user-centric approach such as, 'How might we create a product that simplifies daily tasks for busy professionals?' This approach ensures that the problem statement reflects the user's world.
Be specific: Avoid vague or overly broad statements. A well-defined problem statement should be specific and focused. The more precise it is, the easier it will be to brainstorm solutions and measure success. If your statement is too broad, it may lead to unclear, un-focused design efforts. For instance, instead of saying, 'Enhance customer experience,' consider specifying, 'How might we improve the checkout process to reduce cart abandonment rates on our e-commerce website?'
Step 3: Ideate
The ideate phase is a departure from the analytical stages that precede it. Ideation is where the magic happens in the design thinking process. It's the stage where the raw material for innovative solutions is gathered. By embracing creativity, utilising brainstorming techniques and fostering an open-minded atmosphere, one can harness the full potential of ideation.
Builds a diverse pool of ideas: Brainstorming is one of the most common ways to ideate freely and effectively and come up with a variety of innovative solutions. It is recommended to use all relevant means of collaboration at this stage to build a comprehensive and varied pool of ideas.
Helps with problem reframing, if necessary: During the ideation process, design thinkers may discover a weakness in the problem that has been defined. Since design thinking is an iterative and non-linear process, ideation can aid in closing any such gaps before one moves ahead with the rest of the process.
Produces refined ideas: Ideation is not just about generating ideas but also about refining and evolving them. Teams can combine, modify and build upon the best ideas from the ideation phase, leading to more refined and effective solutions.
Helps overcome biases: Ideation allows for the examination and mitigation of biases that might influence the problem-solving process. By actively encouraging diverse perspectives and ideas, teams can reduce the impact of cognitive biases on their decision-making.
Here are some ways in which the ideation step is implemented by design thinkers.
Classic brainstorming: This involves a group of people generating ideas through free association. The goal is to build upon each other's ideas, and generate a large and diverse pool of ideas. You can also use digital collaboration tools like Miro or MURAL for virtual brainstorming sessions, allowing team members to contribute remotely.
Mind mapping: This method uses visual diagrams that connect ideas and concepts. It helps explore relationships between ideas and solutions and identify new possibilities.
SCAMPER technique: SCAMPER stands for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate and Reverse. In this technique, all of these action verbs are used as questions to stimulate ideation.
Provocation: This method uses provocative questions like "What if we did the opposite?" or "How might we break all the rules?" to encourage out-of-the-box thinking.
Random word generation: This technique involves picking a random word and trying to relate it to your problem. This can lead to unexpected and creative associations.
Step 4: Prototype
The Prototype stage in the Design Thinking process is where your ideas take shape. It's the practical manifestation of the creative solutions you've generated during ideation. This stage involves creating tangible representations of your concepts and testing them to refine and improve your solution, product, or service. These tangible representations can range from simple sketches to high-fidelity, near-final products.
For visualising ideas: Prototypes allow you to visualise and communicate complex ideas in a concrete and tangible way.
For reducing ambiguity: By providing a tangible representation of a concept, prototypes reduce misunderstandings and misinterpretations among team members and stakeholders.
For testing concepts: Using prototypes, you can test your design concepts with real users and stakeholders to gather feedback and insights.
For validating assumptions: Prototypes enable you to verify whether the envisioned solution aligns with real-world user needs and requirements, and thereby validate assumptions that were made in earlier stages of the process.
For refining solutions: Through iteration, prototyping helps in refining and improving ideas and solutions, by addressing issues and enhancing the user experience.
How to implement this step
There are various methods and techniques for prototyping in the design thinking process, and the choice of method depends on your specific needs and goals for a project . Here's an overview of some common ones:
Wireframes: Wireframes are widely used for creating simplified, visual representations of the layout and structure of an idea or solution. They are essential for defining the basic structure and content placement for digital interfaces and websites.
Interactive prototypes: Interactive prototypes are popular for simulating user interactions with a design. Tools like InVision , Figma and Adobe XD are widely used for creating interactive prototypes that allow users to click through and experience the functionality of the intended solution.
Paper prototyping: Paper prototyping is a low-tech, low-cost method that involves sketching ideas on paper and physically simulating user interactions. It's a simple yet effective way to ideate and test concepts.
High-fidelity prototypes: High-fidelity prototypes are often created with design tools like Sketch, Adobe XD or Figma, and they closely resemble the final product's appearance and interactions. These are used in later stages of the process for more polished and realistic user testing.
3D prototypes: In the realm of product and industrial design, 3D prototypes are commonly used to create tangible, physical models of products. 3D printing, CNC machining and other manufacturing processes are employed to bring these prototypes to life.

Step 5: Test
The Test stage in the design thinking process is where you evaluate your solutions to ensure they align with user needs and expectations. This step is pivotal in validating and refining your ideas, and turning them into effective, user-centric solutions.
Reduction of risk: By testing early and continuously, you minimise the risk of investing time and resources in a solution that doesn't meet user expectations. While testing incurs some initial costs, it can ultimately save resources by avoiding expensive late-stage re-designs and re-work. Testing helps you identify and address issues before they become costly problems.
Refinement: Testing provides valuable insights and feedback, which can be used to refine and improve the design. It's a fundamental aspect of the iterative nature of design thinking.
Market fit: Testing helps gauge the market fit of a product or solution. It ensures that the designed solution aligns with market needs and trends, increasing the chances of market success and product competence.
Several types of testing can be conducted to assess the effectiveness of your solutions.
Usability testing: This type of testing focuses on how easily users can interact with the design. Gathering direct feedback from users through surveys, interviews or user testing sessions is invaluable. This feedback provides insights into their preferences, frustrations, and suggestions for improvement.
A/B testing: A/B testing involves comparing two or more versions of a design to determine which one performs better in terms of user engagement, conversion rates, and/or other relevant metrics.
Prototype testing: Testing can start with low-fidelity prototypes and progress to high-fidelity versions as the design evolves. This allows for early feedback and refinement.
Next Steps To Learn Design Thinking
Through this exploration of the design thinking process, we have hopefully been able to illustrate the transformative potential of design thinking for problem-solving, and offered you a glimpse into its fascinating world. Now, it's time to take your journey further.
To truly immerse yourself in the principles and practices of design thinking, you can begin by exploring our list of the best design thinking books . This collection provides in-depth insights, expert perspectives, and practical guidance, making it indispensable for anyone on the journey of creative problem-solving.
For those eager to take an active step towards mastering design thinking, we encourage you to consider enrolling in our UX UI Design courses . Our programs are designed to provide you with the knowledge, tools, and hands-on experience necessary to use design thinking to become a proficient UX UI designer.
To dive deeper into the world of UI/UX design itself, consider taking the following steps:
- Watch this session by Shiva Viswanathan, Design Head of Ogilvy Pennywise, and Naman Singh, Product Experience Designer at RED.
- Talk to a course advisor to discuss how you can transform your career with one of our courses.
- Pursue our UX UI Design courses - all courses are taught through live, interactive classes by industry experts, and some even offer a Job Guarantee.
- Take advantage of the scholarship and funding options that come with our courses to overcome any financial hurdle on the path of your career transformation.
Note: All information and/or data from external sources is believed to be accurate as of the date of publication.

UI UX Design
A Complete Guide to UI Developer Salaries for 2024
Find out all the information you need on UI development salaries, high-paying industries, the job market, and how to land your first position. …

All You Need To Know About Interaction Design (and Why It Matters)
Welcome to your ultimate introduction to interaction design. Learn what interaction design is, why it’s so important, and the key principles that drive this fascinating field. …

What Is a UX Researcher and How Can You Become One?
A UX researcher is a specialist member of the product design team. Learn what a UX researcher does and how to become one in this guide.…

5 Examples of User Personas To Inspire the UX Designer in You
User personas are a valuable part of the UX design process. Take a behind-the-scenes look at how they are created with these 5 user persona examples.…

7 Examples of Design Thinking in Practice (And What We Can Learn From Them)
Design thinking is a problem-solving methodology that actively addresses user-centric challenges. Learn how industry leaders implement this concept through our compilation...…

How To Create an Impressive UX Designer Resume
If you want to impress UX hiring managers, you will need a well-designed resume. Learn how to create a professional UX design resume with this guide.…

8 Wireframe Examples to Guide Your Next Project
Curious to learn more about different kinds of wireframes? From hand-drawn paper sketches to interactive blueprints, find out how different types of wireframe support ideation, collaboration...…

How to Create a UI UX Designer Resume in 2024?
Learn how to create a standout UI UX designer resume with this guide. Discover key elements for industry approval, how to organize it effectively, and tips to tailor your resume to job openings.…

Step-by-Step Guide to Wireframes and Wireframe Design
Want to learn how to create your own wireframes? With our detailed guide, you’ll learn every step of the wireframing process as well as industry best practices and popular tools.…

Is Coding an Essential Skill for UX UI Designers?
Explore if the industry today necessitates coding for UX UI designers and delve into the intricate relationship between such designers and coders in creating digital products...…

21 UI Developer Interview Questions (and How To Answer Them)
Prepare to ace your UI developer job interview. In this guide, we share 21 UI developer interview questions and tips for how to answer them.…

10 Best (Free and Paid) Wireframe Tools That Designers Need To Use In 2024
There are several wireframe tools on the market, and choosing one can be overwhelming. Here’s a curated list of the 10 best wireframe tools...…

7 Awesome (and Free) User Persona Templates for UX Designers
User personas are an essential part of the UX designer’s toolkit. Get started with these free, fully customisable user persona templates.…

Considering a Career as a UX Designer? Try These 10 Free UX Design Courses to Get Started
Has the fascinating world of UX design caught your attention? Perhaps you wish to formally pursue this discipline but are not looking to invest financially? This comprehensive list of free UX design...…

11 Must-Have UI Developer Skills for a Successful Career in the Field
Are you thinking about becoming a UI developer? Discover the top skills you’ll need to get hired—and how to master them.…

The 17 Best UX Design Tools and Software (Free and Paid) for 2024
Discover the perfect tool to meet your UX design needs with this curated list of 17 options, including both free and premium choices. This selection guarantees a nuanced exploration to identify the ideal...…

What Is a User Persona and How Do You Create One?
User personas are a tried-and-tested UX design tool—but what exactly are they and how do you create one? Learn everything you need to know in this practical guide. …

The Ultimate UX Designer Salary Guide for 2024
Want to know what you can earn as a UX designer in 2024? Then keep reading for this year’s complete guide to UX designer salaries. …

How to Get a UX Design Internship as a Recent Graduate
Are you hoping to land a UX design internship? If so, check out our comprehensive guide, complete with hands-on tips to ensure you find the right role and get your career off to the very best start.…

12 Fundamental UI Design Principles You Should Know About
A great user interface simply blends into the background, leaving behind a natural and intuitive interaction. Learn the 12 most important UI design principles...…

A Guide to How Design Thinking Fosters Empathy and Improves Design Outcomes
Design thinking is a user-centric problem-solving method centered around the use of empathy. Read this guide to understand how applying design thinking can lead...…

12 Top UX Design Jobs to Consider in 2024
Thinking about launching a career in UX design? From Interaction Design Lead to Voice User Interface Designer, here are some key roles, from junior to senior, for you to consider.…

8 Good UX Design Examples to Inspire Your Next Project
Looking for some inspiration to improve the UX design of your product or service? Check out our list of UX frontrunners who have paved the way in the field of UX and user-centered design.…

What Is a UI Developer and How Can You Become One?
If you’re looking for a career that spans creative, user-centred design and technical expertise, you might consider becoming a UI developer. Not sure what that is? Keep reading. …

10 Stunning Examples of Website UI Design To Inspire Your Next Project
Make sure your next website UI design project is a success. Discover the 6 elements of a great website and take inspiration from our stunning real-world examples. …

A Complete Guide to App UI Design (With Examples)
Do you want to learn about mobile app UI design? Look no further than this guide, complete with fundamental principles, best practices, templates, and a step-by-step process. …

The 12 UX Design Books to Add to Your Reading List in 2024
Excited to learn more about UX design in 2024? Then check out these influential UX design books covering everything from UX design principles to the psychology...…

The 10 Best Design Thinking Courses and Certification To Take in 2024
Do you want to enhance your problem-solving skills and learn how to innovate? Then consider a design thinking certification. …

7 Best UI UX Design Courses in Chennai for 2024
Looking to enhance your UI UX design skills? Explore the top 7 UI UX design courses in Chennai, available both online and on-campus. Evaluate their prices, durations, advantages, and disadvantages to make..…

13 UI Design Software and Tools (Free & Paid) to Consider in 2024
Navigating the UI design tools landscape? Explore and discover the ideal fit for your needs from a curated list of 20 UI design software, encompassing both free and premium options.…

A Glossary of 50+ UI UX Design Terms You Should Know About
Want to be fluent in the language of UI UX design? Here are 50+ essential UX UI terms and their definitions. …

How to Land Your First UI Designer Job in 2024
A job in UI design can be creative, fulfilling, and highly rewarding for those with the right skills, knowledge, and experience. But how do you land your first...…

The 11 best UI design courses to do in 2024
Ready to start learning UI design but not sure where to start? If that sounds like you, we’ve simplified the decision-making process. Check out our list...…

A Guide to UI Designer Salaries for 2024
Find out what you can expect to earn as a UI designer, which industries offer the highest-paid positions, and how to land a job in this user-centric and creative role …

The 10 Best UX Design Courses and Certifications in 2024
A comprehensive course with a career-oriented curriculum and robust placement assistance can go a long way in helping you get started with a design career...…

All you need to know about UI designer skills, tools, and processes
Are you considering a career in UI design? If so, keep reading for the skills, tools, and processes that are the foundation of this rewarding profession. …

What is Design Thinking? Everything You Need To Know
Design thinking is an approach that makes a very strong case for user-centric problem-solving. But what exactly is this approach and what makes it unique?...…

Everything You Need to Know About UI and UI Design
Are you curious to find out about UI design? In this ultimate guide, you’ll learn the key processes, principles, skills, and job roles in this creative and engaging...…

18 Design Thinking Books Everyone Should Read
Want to explore design thinking and learn from the best? Our handcrafted list of 18 Design Thinking books is the perfect selection to begin your journey with. …

What is user experience (UX) design? Everything you need to know
UX design has been getting a great deal of attention in recent years. And there are good reasons for it! As a proven methodology for engaging...…

What is the UX design process? A step-by-step guide
In this guide to the UX design process, we’ll be walking you through the meaning and value of the UX design process, providing you with clear steps...…

How To Become A UX Designer In 2024: The Ultimate Guide
In this ultimate guide to becoming a UX designer, we’ll discuss everything you need to know to successfully launch a UX Design career–from best practices... …

16 UI UX Interview Questions and Answers For 2024
Prepare to pass your next job interview with flying colours. In this guide, we share 16 of the most common UI UX interview questions, and show you how to ...…

Top 10 UI UX Designer Jobs in 2024 (and Their Salaries)
There are many different career paths within the UX UI design field—but which should you pursue? In this post, we weigh up whether or not UX UI is a good career.…

How To Create a UX Designer Portfolio That Will Get You Hired
Perhaps you’re applying for your first UX design position, hoping for a promotion at work, or looking to land some new clients as a freelancer.…

Which UX Designer Skills Do You Need in 2024? A Complete Guide
If you’re considering launching a career in UX design, having a deep knowledge of the UX designer skills you’ll need will be crucial to getting your learning off to the...…

Fundamental UX Design Principles and How To Apply Them
If you’re thinking about launching a career in UX design, you might be wondering about the skills and knowledge you need if you’re going to succeed in this...…

13 Common UX Design Job Interview Questions and Answers for 2024
If you’re a UX designer applying for a new job, a sure-fire way of preparing for interviews is to familiarize yourself with the UX designer interview questions...…

Best UI UX Design Courses in Kolkata for 2024
Are you ready to embark on an exciting journey into the world of UI UX design in the city of Kolkata? Here’s a definitive guide to the top UI UX design courses...…

How To Learn UI-UX Design: A Step-by-Step Guide for 2024
In this five-step guide, we show you how to learn UI/UX design—from the essential theory to practical application, and everything else in between.…

How To Become An Expert UI UX Designer in 7 Steps
Do you want to become a UI/UX designer? We’ll show you how to go from beginner to professional in this 7-step guide. So what else does it take?…

15 Must-Have UI UX Design Skills & How To Develop Them
What are the most important skills for a UI/UX designer to have, and how can you develop them? Find out in this post.Working in UX/UI design ...…

UI vs UX Design: What’s the Difference?
What is the difference between UX and UI design? What skills do they each require, and which pays more?Learn all about two of the most important design...…

UI/UX Designer Salary Guide for 2024
Whether you’re starting a new career in UX/UI design or searching for another job within the field, salary is an important factor to consider.…

The 10 Best UI/UX Design Courses To Do in 2024
Is learning UI/UX design one of your goals for 2023? Then you’ll want to start with a good quality course. Discover the best UI/UX design courses in this comparison guide.…

The Complete Guide to UI UX Design
What is UX/UI design and what do UX/UI designers do? Learn everything you need to know about UX and UI in this all-encompassing guide.…

Best UI UX Design Courses in Ahmedabad for 2024
Explore the best UI UX design courses in Ahmedabad through this guide and learn about course durations, prices, curriculum, pros, cons, and tips to choose a course.…

Best UI UX Design Courses in Jaipur for 2024
Looking to pursue a career in UI UX design? This comprehensive list of the best UI UX design courses in Jaipur could be a great starting point. Read on for a detailed.....…

Best UI UX Design Courses in Delhi for 2024
An industry-relevant course can go a long way in getting started with a design career. Here’s an extensive list of the leading UI UX design courses in Delhi.....…

Best UI UX Design Courses in Hyderabad For 2024
Looking for an industry-relevant course that could help build a strong foundation for your design career? Our comprehensive list of the best UI UX Design courses in Hyderabad...…

Best UI UX Design Courses in Pune for 2024
A comprehensive course serves as the foundation for a successful career. Here’s an extensive list of the top UI UX design courses available in Pune. Read ahead to learn about the duration, pros...…

Best UI UX Design Courses in Mumbai for 2024
Want to pursue a career in UI UX design but don’t know where to start? This comprehensive list of the top programmes in Mumbai is precisely what you need. …

Best UI UX Design Courses in Bangalore for 2024
Explore the best UI UX Design courses that Bangalore has to offer. This list will help you understand the bottom line of each course - duration, intensity, cost, special offerings, and pros and cons. …

How to Create a Standout UI UX Design Portfolio
Build your UI/UX design portfolio with the help of this five-step guide—then follow our top tips to make sure your portfolio stands out. The most important...…
Consult Course Advisors
Hire Our Graduate / Upskill Your Team
Become An Instructor
Course(s) you can teach
- Research + Insights
- Design Thinking
- The Complete Design Thinking Process [2024 Guide]
The Complete Design Thinking Process
Learn about the Design Thinking process powering today’s most user-friendly products, services and solutions.
About The Design Thinking Process
What is the design thinking process.
The Design Thinking process helps teams use work through “wicked” problems and turn opportunities into innovations. When teams apply the Design Thinking process, they work through a series of steps and activities toward a solution that is desirable, feasible and viable — also known as the Three Lenses of Human-Centered Design .
Given the iterative nature of design, the Design Thinking process can be considered more of a playbook than a predefined agenda. When teams need to learn more about their users, they turn to Empathy. When it’s time to test models, they pivot to Prototype. Often, Test results can reframe the opportunity, resulting in fresh rounds of Ideation and Definition.
Who participates in the Design Thinking process?
Unlike methods made for manufacturing or software development, the Design Thinking Process is designed for everybody. In fact, the Design Thinking process becomes more efficient as more skill sets are added to the team. This is because Design Thinking leans heavily on empathy and divergence, which both benefit from increased perspectives.
In practice, the most effective Design Thinking teams usually include 6 – 12 core members with diverse strategic and technical profiles. Some participants may be designers, but most will be experts and leaders in connected disciplines such as strategy, technology or marketing. Users are also common participants on the Design Thinking teams, as are other stakeholders or community members.
When building a Design Thinking team, consider the range of skills you need in order to make effective decisions during the workshop itself. This usually means having a mix of strategic and technical experts on-hand. In practice, teams with a mixture of “T-profiles” are most effective — that is, subject matter experts with a range of experiences.
Who facilitates the Design Thinking process?
While anyone can participate in Design Thinking, coaching a team through the process does take practice. Facilitating the Design Thinking process typically entails coordinating research efforts and running multi-day workshops.
According to a study published by the Hasso Plattner Institute of Design [1], the three most active facilitators of Design Thinking in organizations are:
- Research & Development Leads
- Design Thinking Consultants
- Marketing Leads
The Design Thinking Framework
The Design Thinking framework provides a convenient mental model of the decision making process. It breaks the innovation process into simple steps, and helps teams know where to focus and when.
The framework was pioneered by John Arnold, an MIT professor who described an early version as: Question, Observe, Associate and Predict. [2]
Arnold encouraged the iteration of his approach, and the Design Thinking framework has since been widely adapted to suit diverse organizations, technologies and needs.
The Double Diamond Model
The Double Diamond model is one of the most influential models of the Design Thinking framework. It was published by the British Design Council in the early 2000s, and helped crystallize underlying concepts for the working world. Specifically, the Double Diamond model depicts how the two phases of divergent and convergent thinking work together to develop ideas. Other common cyclical Design Thinking models include those published by Nielsen Norman Group and IDEO.
Basically, there’s a problem statement at the beginning and a solution at the end, and the solution is reached in an iterative procedure.
The Integrated Model
Staged frameworks are designed to help organizations integrate the iterative design process. The Integrated Design Thinking framework at Konrad is divided into three major stages containing a total of seven steps.
The following sections describe the Stages and Steps of the Design Thinking process, including what their objectives and key activities.
Design Thinking Stages
What are the stages of design thinking.
There are three primary stages of the Design Thinking process: Discover, Design, Deliver. Referred to as the 3 “Ds”, stages help organizations adopt Design Thinking into their existing processes. Together, the three stages provide a convenient way to coordinate complex projects containing iterative steps.
Design Thinking Stage 1: Discover
“We’ve sensed an opportunity and are exploring the space”
Every Design Thinking project kicks off in Discover. The goal of Discover is to move from a sense of the opportunity to a clear picture of the current landscape. This stage is often completed by a core project team who share their results with the broader team during Design Thinking workshops.
Key Output: A comprehensive landscape of the opportunity
Design Thinking Stage 2: Design
“We’ve aligned on objectives and are building experiences”
The Design stage is where rapid iteration occurs as teams shape insights into innovation. During the Design stage, teams work through five core steps of every Design Thinking process: Empathy, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test. These steps are completed through a series of design workshops and sprints that are tailored to each team.
Key Output: A working prototype ready to scale
Design Thinking Stage 3: Deliver
“We’ve found our solution and are ready to grow”
The Deliver stage is where lead prototypes are integrated with new and existing technologies. Whereas earlier stages are focused on working through ambiguity, the Deliver stage focuses on efficient execution and streamlined integration through training and technology.
Key Output: A real-world solution
The Design Thinking Process in Practice
How gillette designed india’s favorite shave.
Read how Gillette used Design Thinking to develop the Gillette Guard: A made-for-India experience for 400-million people.
Gillette’s Opportunity

Shortly after Gillette was acquired by P&G in 2005, they set out to redesign the shaving experience for 400 million men in India. At the time, Gillette’s Western-style offerings were only catering to a sliver of the market, and the vast majority relied on (very) low-cost double-edged razors. After mapping the value chain from the steel to the sink, a cross functional team leveraged Design Thinking to re-learn the art of shaving in India — and bring an innovative product to market.
The Insights

The team met with men from across the country and saw first-hand how different the shaving experience was compared to in the United States. They saw how many men sat on the ground to shave using a mirror in their free hand. Often, only a small bowl of water was used to clean the blade. They saw the care it took to avoid cuts, and how long it could take (up to 30 minutes). While men had become experts in the craft, the desire for a less strenuous experience was clear — as long as it fit their current needs:
- a faster, more relaxing experience
- can still handle beards without running water
- doesn’t clog easily from hair/shaving lather
- priced competitively
The Innovation
With these criteria, the team worked through a series of design iterations before arriving at the Gillette Guard: A made-for-India experience that delivered a relaxing shave for an affordable price. What makes the Guard unique is how it uses small plastic “teeth” to flatten the skin ahead of the blade, along with a custom pivoting head that works well in still water.

Thanks to a cost-saving design and distributed manufacturing model, the Gillette Guard sells profitably for 25 cents — or just 2% of the Mach 3 price. Launched in 2010, today 2 out of every 3 razors sold in India are Gillette Guards. [4]
Read more about how P&G tripled its innovation success by engineering reverse innovations at Harvard Business Review.
Design Thinking Steps
What are the steps of design thinking.
Instead of trying to jump from mountains of research data straight to ideas, the Design Thinking steps help unpack the black box of creativity, and provide clear objectives for collaboration. Each step of the Design Thinking process works through a handful of core activities, completed with an array of tools.
Design Thinking steps begin with Research, end with Implement, and traverse an iterative 5-step core of Empathy, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test. This core set of 5 steps has been adopted by diverse industries and is championed by leading UX design communities including the Interaction Design Foundation.
Step 1 Design Thinking Research
Build the Foundation . Research helps move from sensing an opportunity, to seeing it in the context. It requires carefully studying the opportunity from every direction, and provides the foundation cross-functional teams need to work together effectively. Without a holistic view of the opportunity, teams will struggle to find feasible solutions that satisfy their innovation goals.
Core Design Thinking Research Activities
Create a current landscape.
The current landscape describes all the systems and structures expected to underpin the solution. While the elements of the landscape are tailored to every project, the goal is always the same: Create a holistic view of the opportunity so disciplines can make decisions in real-time. The landscape is often created by a core team of project owners and design thinking consultants, and then shared with the complete team during design thinking workshops. Research Tools like AEIOU can help organize your landscape and identify any gaps.
Consider Key Performance Indicators
The most successful design thinking projects begin with a shared understanding of what success looks like. Discussing the quantitative and qualitative KPIs early in the process helps teams have better conversations about the feasibility and viability of their ideas. If you aren’t sure where to start, you can use the Three Lenses of Human Centered Design as a guide (desirability, feasibility, viability).
Draft a Statement of Opportunity
After the current landscape has been created and shared among the team, and the KPIs have been discussed and drafted, teams are ready to “align on 1 line” with a statement of opportunity. Also called a problem statement, this activity helps complex teams speak the same language by articulating the high-level opportunity in simple terms. The most important part of the statement of opportunity is ensuring all disciplines are involved in drafting it.
Step 2 Design Thinking Empathy
Become your Users . The first step of the Design stage, Empathy is where teams immerse themselves in the user experience and challenge their own assumptions. Often referred to as ethnography , the Empathy step studies people in the context of their culture and environment. Depending on the scale and complexity of the opportunity, the Empathy step can take just a few days or up to several months, as was the case in the Gillette Guard example above.
Before drafting jumping into Empathy activities, teams must be clear who their primary users are. For a company like AirBnB, that means considering both people who rent apartments, and the people with apartments to rent. These two groups have very different needs, and should be considered separately to avoid compromising designs. When drafting user personas, these groups would be further divided based on shared travel interests, demographics, or other criteria.
Core Design Thinking Empathy Activities
Connect with user experiences.
Design Thinking Empathy is about immersing yourself in the user experience. That means interviewing real users, observing them in their daily life, and walking a mile in their shoes. Direct observation is a powerful creative tool, and small details can be very inspiring during ideation. Teams should look to connect both directly and indirectly with users, creating a holistic view of their experience through interviews, analytics and heuristic approaches.
Draft user personas
User personas help design teams put a face to a name. They are the center of human-centered design, and a critical activity of the Empathy step. If you have worked with personas before, you’ll appreciate the level of realism and clarity of purpose Design Thinking personas provide. Personas are commonly drafted in advance of workshops by a core team and finalized together.
Generate user stories
User stories allow teams to clearly articulate what users want and why. Without user stories (or closely related job stories / jobs to be done) teams would be overwhelmed trying to compare all the competing insights and user goals. It’s best to generate as many specific user stories as possible before converging on the top opportunities in a later activity.

Step 3 Design Thinking Define
Make choices . The Define step helps teams frame insights from Research and Empathy steps into a compass for their collaboration. During Define, teams validate, prioritize and align on next moves using guided activities in Design Thinking workshops. Without the Design Thinking process, aligning a cross functional team on human-centered opportunities would be very difficult, if not impossible. By the end of the Define step, ideas for solutions will begin to appear everywhere.
Core Design Thinking Define Activities
Validate statement of opportunity.
It’s important for teams to challenge their Statement of Opportunity several times throughout the Design Thinking process. Does it still stand? Or should it be updated to reflect new insights about users or feasibility? Validating the statement during Define keeps everyone on the same page.
Validate user personas
A user persona should be as realistic as possible to inspire desirable ideas. Given how critical strong user personas are, design thinking teams should take care to make sure they reflect reality. Workshop tools like the Gallery Walk can be a refreshing way to review and revise draft personas, especially when combined with Dot Voting or other consensus-generating methods.
Rank user stories
User stories provide UX teams with a single source of truth to design solutions with. Design Thinking provides transparent prioritization tools to help teams identify and apply the most effective criteria.
Map user journeys
User journeys are a powerful visualization technique that combine user personas and user stories into a complete experience roadmap. Defining the journey helps uncover new moments and opportunities to delight users and improve the user experience.
Define solution requirements
Defining the requirements of the solution is a major milestone in the Design Thinking process. While the statement of opportunity outlines what the team is hoping to achieve, the requirements (sometimes called the Minimum Viable Product) give shape to the solution. For example, a team may begin with the opportunity to improve their online shopping experience, and after Research and Empathy they align on what specific user goals they need to support.
A design team working in the normal way might never appreciate that the problem had so many ramifications.”
Step 4 Design Thinking Ideate
Create choices . Ideate is where the magic of Design Thinking happens. Following weeks of research and immersion in the user experience, teams will begin seeing human-centered solutions everywhere they look. Core activities in the Ideate step help structure brainstorms and inspire new perspectives with creative tools like Brainwriting and SCAMPER. The Ideate step is usually revisited several times during the design thinking process as teams reframe opportunities and refine their solutions.
Core Design Thinking Ideate Activities
Share inspiration.
Sharing inspiring or innovative solutions among the team helps spark new ideas and creates a frame of reference for members with widely different professional disciplines or experiences. When planning a Design Thinking workshop, save time to have participants discuss a design or service that has personally surprised or delighted them. And be sure to look for inspiration outside your sector — hospitals can learn a lot from hospitality and vice versa.
Brainstorm solutions
Brainstorming is where human insights become innovative ideas. It is a highly divergent activity, dedicated to creating as many interesting avenues as possible. In practice, brainstorms are most effective when they’re focused on supporting a specific user goal. For example, “how can we help people get from X to Y”. For this reason, Design Thinking teams often split into small groups when brainstorming, each tackling one user story or moment. While not every brainstorm idea will be feasible or financially viable, each will reveal some truth about what users really want, which may inspire new ideas or be further expanded.
Expand on ideas
Step 5 design thinking prototype.
Create context . The Prototype step puts ideas in context, allowing teams to make performance-based design decisions before any big commitments are made. Prototyping begins with low-resolution sketches that can be quickly created and compared, adding resolution as more is learned. In practice, the best prototypes provide just enough context to keep users focused on the aspects you want to learn about.
Core Design Thinking Prototype Activities
Prototype the concept.
Making abstract ideas more tangible is an important first step in prototyping. It allows teams to compare strategic alternatives before committing resources, and provides valuable context for technical teams during production. Sketches, storyboards, or other ways to capture the concept will work well.
Prototype the experience
Modern prototyping tools are a design thinking superpower. From cloud-based tools to 3D printing, today’s designers can quickly simulate and iterate realistic experiences unlike ever before. This removes a lot of guesswork from the traditional design process, and creates more connected experiences at launch.
Step 6 Design Thinking Test
Measure outcomes . The Test step in Design Thinking Test helps teams gather valuable feedback from users and other stakeholders. This step works hand-in-hand with Prototyping to inspire fresh ideas and refine working solutions. And just like with prototyping, the fidelity of the test should fit the situation — while “launch and learn” may be the best test for some projects, others have far lower risk tolerance.
Core Design Thinking Test Activities
Test for impressions.
You only get one chance to make a first impression, so it’s important to know what users say, think and feel when they first encounter your solution. Tools like the Feedback Capture Grid help organize user impressions to inform the design of higher-fidelity prototypes.
Test for risks
While not mandatory, evaluating solutions using tools like crowdsourced QA or live A/B testing can dramatically de-risk production.
Step 7 Design Thinking Implement
Make reality . Implement is the final step of the Design Thinking process, and the first step of full-scale development. Here, teams map out how to integrate their proven prototype with the current landscape they explored during Research, optimizing as needed along the way. If you’re interested in learning more about what end-to-end design thinking consultants can offer, contact us .

Core Design Thinking Tools
Design Thinking tools help teams combine perspectives and shape ideas. Each tool supports specific steps of the design thinking process, and comes in several flavors. The following section introduces the most popular Design Thinking tools, with additional links to more detailed resources.
Empathy Map
Develop a holistic understanding of your current or potential users and capture it in a simple cognitive canvas.
Empathy maps help organize and compare emotional insights about your users. They are typically divided into six parts to create a holistic view of a person’s experience and needs: Think + Feel, Say + Do, See, Hear, Pain and Gain While not a requirement of all Design Thinking projects, empathy maps are an excellent source of insight most often used to build user personas, brainstorm user stories and map user journeys.
How to create an Empathy Map
- Divide a whiteboard or sheet of paper into the six sections above — preferably right after a user interview ends
- Arrange your notes and verbatims around the canvas
- Review interview recordings to fill in any gaps and dig deeper
- Compare notes with other interviewers and look to build on one another’s observations
- Share your empathy map with the broader team and align on the major Pains and Gains
Note: If you are working alone or in small groups, waiting to complete the pains and gains sections as a team can help create better ideas and alignment.
User Persona
Create a rich, realistic profile of your users that brings their experience to life for the entire team.
A user persona is a fictitious character profile that embodies one segment of your potential audience. They contain detailed descriptions on their background (age, career, education), behaviors (patterns, interests), and goals.
User personas are created based on observations from a variety of user surveys, interviews and analytics. As a critical piece of the Design Thinking process, user personas help teams focus all their downstream problem-solving efforts.
How to create a User Persona
- Think about a specific user role or goal you want to support
- Name your persona
- Fill out their personal details based on your observations of similar users
- Write a brief description about their current role and responsibilities as they pertain to your project
- List 4-5 relevant behaviors or patterns they have using the insights gathered in an empathy map, interview for empathy or other Design Thinking research tool
- Add a photo or mood board that captures their personality
Note: Avoid making more user personas than your team can remember in detail at once. Working with 3-6 user personas is usually best. Also consider scheduling quarterly team reviews of all your active user personas. This has the dual-benefit of keeping your users top of mind and your personas up to date.
User Journey Map
Develop a bird’s eye view of one user persona that encompasses all the important touch points relevant to your solution over time.
User journey maps are a powerful visualization technique. They are built in small teams using inputs from ethnographic research, empathy and ideation activities.
Common elements of user journey maps include basic details about the user persona, a timeline from start to finish, the user’s thoughts and emotions at each key moment, and significant opportunities to improve the experience.
How to create a User Journey Map
- Select one of your user personas
- Fill in basic details about the scenario
- Divide the journey into overarching phases
- Subdivide each phase into key moments
- Overlay emotions and quotes from interviews and empathy maps
- Identify user needs and opportunities to exceed expectations
- Discuss your journey map with the full team and iterate until complete
Note: Mapping your user’s entire journey – not just when they interact with you – is a great source for inspiration. You can upgrade a user journey to a service blueprint by connecting KPIs and organizational processes.
User Stories
Describe what your users want and why in a format that can be easily captured and compared among the team.
User stories help teams align on high-priority opportunities to improve the user experience. They are formatted as a single sentence that answers 3 W-H questions: WHO is the user, WHAT do they want, and WHY.
User stories are often created during brainstorming activities and discussed as a team using tools like a cluster matrix. User stories are common in Agile methodologies, and can be grouped together to form epics and themes .
How to create a User Story
- Grab post its or open your user stories template
- As a [person in a specific role]
- I want [to perform a specific action]
- So that [I can achieve a specific goal]
- Write as many stories about your different users as you can
- Review user stories as a team
Note: Defining what needs to happen to “complete” the story can add more clarity for designers downstream. This is called the “acceptance criteria”.
Build upon an existing idea or solution with a simple, structured brainstorming technique.
SCAMPER is a brainstorming activity for breaking through to unexpected ideas. The word is an acronym for seven words that serve as cognitive prompts to help push thinking “outside the box”. SCAMPER stands for: Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate and Revers
How to brainstorm with SCAMPER
- Start with a solution you want to improve
- Answer probing questions labelled under each letter
- Generate as many ideas as possible
- Move to the next letter if you get stuck
Note: Assigning one letter per person and rotating every 2-3 minutes can push ideas even farther.
Statement of Opportunity
Align on a singular statement that encompasses the spirit and scope of the current opportunity.
The statement of opportunity, also called a problem statement, is a simple tool for aligning teams. They answer the WHO, WHAT and WHY of your project in a single line, and are similar to user stories but with a different focus.
Statement of opportunity is usually developed early in a Design Thinking workshop and revisited throughout the process.
How to create a Statement of Opportunity
- Grab post its or open your statement of opportunity template
- Write down what you believe the project’s strategic opportunity to be
- Share your statements with the team
- Align on a single statement of opportunity
Note: It is more helpful to focus on writing exactly what you feel the statement should be, instead of generating a pile of half-thought ideas
Gallery Walk
Share immersive user research with a broader team to mine for insights and opportunities.

Gallery walks are an engaging way to share detailed results discovered during the Research or Empathy steps. They are intended to replicate the thoughtful experience of browsing in an art gallery, and participants are given worksheets or encouraged to record what stood out or surprised them.
Gallery walks are most often used to pressure test working user personas, with one large poster dedicated to visualizing each user type.
How to conduct a Gallery Walk
- Create a “canvas” for each user persona
- Hang your canvases around the room
- Invite the full team come and browse
- Provide a worksheet to focus discussion
- Discuss the show and validate findings
Note: Gallery walks are best when stakeholders can actually walk. Use large posters, big pictures and fat markers. In addition, rules like no talking and changing stations at set intervals makes it easier to organize your thoughts.
So what is the Design Thinking process?
Simply put, the Design Thinking process is a playbook that helps teams shape a field of opportunities into specific innovations. It breaks down the human-centered design process into a series of stages and steps, and guides complex collaborations with tools and activities.
Given the collaborative nature, most Design Thinking activities are completed during design workshops with the help of experienced facilitators. To learn more about putting the process into practice, see our guide How to Run a Design Thinking Workshop .
- Schmiedgen J, Rhinow H, Köppen E. Parts without a whole?: The current state of Design Thinking practice in organizations. Universitätsverlag Potsdam; 2016.
- Smith P. Creativity: An Examination of the Creative Process; a Report on the Third Communications Conference of the Art Directors Club of New York. Paul Smith, Editor. 1959.
- Lewrick M, Link P, Leifer L. The Design Thinking Playbook: Mindful Digital Transformation of Teams, Products, Services, Businesses and Ecosystems. John Wiley & Sons; 2018.
- Harvard Business Review, Brown T, Christensen CM, Nooyi I, Govindarajan V. HBR’s 10 Must Reads on Design Thinking (with featured article “Design Thinking” By Tim Brown). Harvard Business Press; 2020.
- Jones JC. Design Methods. John Wiley & Sons; 1992.

Designorate
Design thinking, innovation, user experience and healthcare design
Design Thinking Tools and Methods Complete Guide
There are several design thinking tools and methods out there. At the beginning of my learning about these tools, How can we formulate these methods in a clear design thinking methodology to solve different design challenges? Understanding the nature of design thinking helps us identify where and when to use the design thinking tools and methods. For example, in the Double Diamond Process, we can determine which design thinking methods are suitable for each stage of the four-stage process. Additionally, we can find design thinking tools that can be used in more than one stage while considering the aim of the tool deployment, which will dictate how the tools are used.
This article will explore the different design thinking tools and methods and how they are used in each Double Diamond process stage. Basically, design thinking methods refer to the practice we use, such as brainstorming the Six Thinking Hats, while the design thinking tools refer to tools we use while applying these methods. In this article, I will discuss both based on the flow of the four stages of the Double Diamond process.
- 13 Online Design Thinking Tools for Mind Mapping
- Design Thinking Tools for Ideation
- The Double Diamond Design Thinking Process and How to Use it
The Design Thinking Process
It is crucial to understand the different tools and methods and when they are applied during the design thinking stages. So, it is vital to determine the design thinking process we need to follow. As highlighted earlier, the main principle behind design thinking is the ability to think as a design, including a creative mindset, focusing on human needs, adopting a reflective practice approach and problem-solving attitude. Several design thinking process models have been introduced based on these principles over the last few decades.
The design thinking process is more like multiple intersected arenas of thinking than systematic linear stages. However, understanding it in the form of stages helps us explore each stage’s nature separately. In this guide for the design thinking tools and methods, The Double Diamond Design Thinking Process and How to Use it , I would like to follow the Double Diamond Design Process’s four main stages: Discover, Define, Develop and Deliver.
Design Thinking Tools and Methods
They’re two types of resources for the practice during the Double Diamond Design Thinking Process: methods and tools. The Design Thinking Methods refer to individual or group practice to research problems, explore solutions, and test proposed solutions. Both methods and tools discussed below will be based on the Double Diamond Design Thinking process. However, some tools can be used in different stages with changing the aim of each method or tool.
Wait, Join my Newsletters!
As always, I try to come to you with design ideas, tips, and tools for design and creative thinking. Subscribe to my newsletters to receive new updated design tools and tips!
The Discover stage, also known in other Design Thinking Processes as explore or inspire, aims to explore the problem or situation. This aim gives this stage a divergent nature where inspirational and research methods are used to discover all the available information related to the problem. So, the methods below will be divided into design research and idea generation methods.
Design Research Methods
The research methods here are similar to both desk (secondary) and field (primary) research methods that aim to understand situations where people are involved in the research.
Secondary Research:
This is where the designer looks into previous information such as previous projects, competitive clients and different types of data already there. This type of research is helpful early as it helps designers build a vision of the situation and determine the type of research needed. The disadvantage of using secondary research alone is that every design challenge has its unique situation. So, the secondary data won’t sufficiently provide you with the accurate information needed to solve the design challenge. As the secondary data are essential to understand the problem at hand, we need to decide if the issue needs to have primary data or not.
Primary Research:
In this type of research, the design team collect the data themselves. IN the majority of the design thinking practise, the primary data collection refers to field research where designers meet with the client sample and observe how they communicate with the problem at hand in real-life situations. However, using available research tools such as surveys can be helpful in different cases. We must define the appropriate method to understand the problem and provide the proper solution.
Qualitative Methods:
The qualitative methods refer to the research tools that collect nominal descriptive rather than numerical data. These types of data are crucial as it helps us to understand ulna needs and feelings, which can’t be described in numbers.
Interviews:
Interviews are very common when trying to understand the client or the user. It allows you to see their impressions, listens to their experience directly and be able to ask more questions if needed. There is the type of interviews based on how we prepare for them:
- Structured : We start the interview questions with no intention to change, modify or add to the interview questions. It can be useful if there is a limited time for the interview, but it is not good from the perspective that the answers can ignite more ideas and questions during the discussion.
- Semi-structured : This type solves the fixed nature of structured interviews. It allows us to modify our questions and add questions to elaborate the discussion as more ideas and data are shared. It is the most convenient tool as it allows us to learn more and be flexible for the project’s benefits.
- Non-structured : In this one, the conversation evolves the questions. It is not a recommended method, but sometimes, it can be a method, especially when the interview happens without prior planning.
Focus Groups:
The difference between interviews and focus groups is that focus groups include more than one person, and they answer the questions and discuss it together. This helps to see more ideas during the discussions. However, it has its weakness as many people feel shy to express their thoughts in groups or get influenced by others’ answers.
Observation:
Observation is the most commonly used method in most design projects. We observe the users’ context of use. The observation could be through taking notes or participating with the users to practice their experience. Usually, this method is underestimated, especially when we use it all the time. Understanding the importance of observation allows us to open our eyes and see the user practice as valuable data to use in the next stages of the design thinking process.
Interviews and Focus Group Tools:
While it is helpful to have physical meetings to build a broader understanding of the context of the use of the product or the service, it can be hard sometimes due to several reasons, including the travel cost, time difficulties and the Covid-19 pandemic. Online tools can provide virtual meetings with users, and there are several meeting tools such as the following:
- Zoom
Quantitative Methods:
While the qualitative methods are commonly used, we can’t underestimate the quantitative methods, and the top is the surveys. While surveys tend to get numerical, ordinal or categorical data, they can work very well as an early step before the interviews; it helps users know helpful information that can be used to build discussions or face group questions.
For the survey tools, there are seven online tools such as:
- SurveyMonky.com
Social media such as Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn allow a one-question poll which can be helpful to get quick answers to general questions as a starting point.
The Consumer Journey Mapping
The consumer journey maps aim to observe the consumer interacting with the system and record their different experience. For example, consumer journey mapping can map the consumer experience when visiting a physical or online store to make a purchase or file a complaint. Following each step as the consumers progress in the process helps us gather information about the pain points facing them while using a product or service.

My article, Customer Journey Mapping: A Complete Guide for Designers , includes how to use consumer journey maps in the Develop step. We will use consumer journey mapping to test different prototypes and ensure that the developed prototype achieves the aimed target when used by consumers.
Starbursting
The Startbursting technique explores the problem or situation by asking specific questions. These questions allow us to see the problem based on the different parts of the problem, such as:
- Who will use this product?
- Who are the stakeholders?
- What is the problem?
- What are its dimensions?
- How does the problem happen?
- How does it affect the consumer?
- Where in the process does this problem occur?
- Where does the consumer face the situation?
- When does the problem happen?
- When is the consumer’s pain point?
- Why does this problem happen?
- Why do we think this is a problem?
In the article, Starbursting Technique: Evaluating New Ideas , you can find more details about the Starbursting and how to apply it in practice.
The Define stage of the Double Diamond Process is concurrent, meaning that the ideas collected from the previous step are analysed to define the problem that needs to be solved clearly. The practice in this stage’s tools is based on the findings of the previous stage’s collected data. The nature of this stage is to reflect on the collected data rather than rigour analysis of the data.
Mind maps and brainstorming
The mind maps allow us to explore ideas and the connection between these ideas. Each idea or a bit of information is added in an oval or circle shape; then, we build the connection between ideas in a tree branch form. Identifying the connection and the ideas that have a significant impact by being connected with the majority of the ideas can help us define the challenge and its characteristics.
Reversed Brainstorming
When the ideas are stuck and we face a dead end in defining the problem (or the possible solutions), the reverse brainstorming method aims to solve problems rather than solve them. Through this radical change in directions, ideas can evolve and subsequently reverse the direction of the thing to define the problem (or solve it) based on the new findings. Reversed brainstorming is one of the tools that can be used in box defining the issues and solutions. Check ( Design Thinking Tools: Reverse Brainstorming ).
Defining the root cause of problems is crucial to finding a sustainable solution that provides a solution for the core problem in the given situation. The 5 WHYs is one of the root-cause problem-solving tools based on a simple principle: asking the question (Why?) around five times. By repeating the questions multiple times, we can reach the core cause of the problem. The number of questions depends on the depth of the problem until reaching the saturation point. How to Apply Root Cause Analysis Using 5 Whys includes details on applying the 5WHYs in practice.

Cause Effect Diagram (Fish-Bone Diagram)
The Cause Effect Diagram (also known as the fishbone diagram) explores the root cause of problems by investigating the possible causes related to three main categories:
- Manufacturing industry (5 Ms): Machine, Method, Material, Man Power, and Measurement
- Marketing industry (7 Ps): Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence
- Service industry (5 Ss): Surrounding, Suppliers, Systems, Skills, and Safety
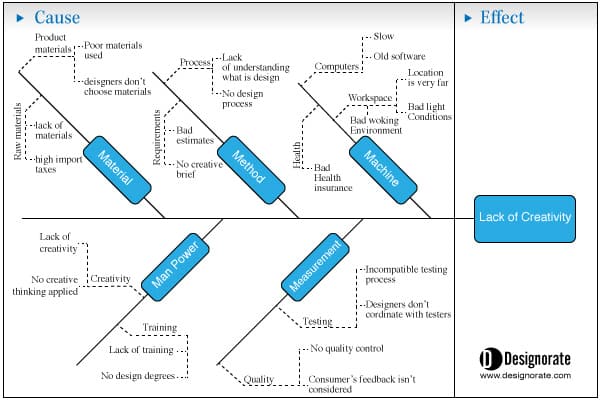
By exploring the problem through the highlighted areas, the team can clearly define the core problem that needs to be solved, as demonstrated in the Problem-Solving Using Cause and Effect Diagram article.
Affinity Diagram
Unlike the tree nature of the mind maps, the affinity diagrams organise data in categories and then rate the organised sat based on its importance. The data are represented with keywords arranged in groups based on similarity. Then, these keywords are measured based on their relation to each other. There are three methods to measure the importance of each element in the Affinity Diagram, as discussed in detail in the article Using the Affinity Diagram to Organise Ideas .
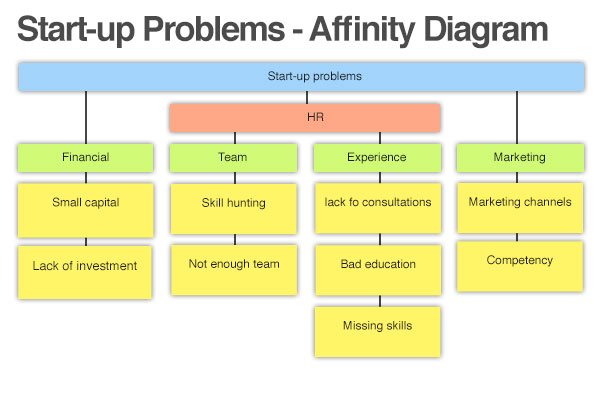
Similar to the Cause-Effect Diagram, the SCAMPER explores problems from seven main opportunities that can be used to solve the problem:
- Substitute: Change part of the problem and replace it with another that may solve or improve the system.
- Combine: Merging two ideas that may produce an improved system.
- Adapt : Adjust or tweak a product or service to solve the problem.
- Modify, minify or magnify : Chang the process in a way that solves the problem or inspires new ideas.
- Put to another use: Put the current product in another service aiming to solve problems.
- Eliminate or elaborate : Identify the parts of the process that can be eliminated to solve the problem.
- Reverse: Reverse or rearrange technique aims to explore the innovative potential when changing the order of the process.
Find more about how to use the SCAMPER technique in A Guide to the SCAMPER Technique for Creative Thinking .
Develop: Design Thinking Tools
Once the main state of the problem or the challenge to address is clearly defined, we move to the second part of the Double Diamond Process, where the solution is formed. The first stage in this part is the Develop, where we start to develop solutions’ prototypes and evaluate them. To achieve this goal, several tools can be used in this stage.
Rapid prototyping
Rapid prototyping or 3D printing is one of the evolving technologies that help us develop prototypes with different levels of the qualities, which depend on the type of the 3D printer used and its accuracy. Mainly, there are three types of 3D printers:
- The Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM),
- Stereolithography (SLA) 3D Printing and
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
The first type (FDM) is the most common and affordable. There are drawbacks to the 3D printing prototypes, such as the long time required to complete the model and the cost required to create several prototypes. Guide for 3D Printing Technologies includes more details about these types.
Drawing, Clay and Cardboard Prototypes
Several materials could be used in prototyping. While their quality is lower than that of 3D printing, it could be used in quick, low-fidelity prototypes before 3D printing. This practice reduces the cost because the early prototypes are tested using the low fidelity prototypes before moving to the high fidelity ones. The advantage of these materials is that they are easy to form and change, making them affordable for the team members to use regardless of their creative skills.
Lego Serious Play
Lego Serious Play is a commonly used tool by managers and executive boards to encourage creative thinking when it comes to addressing challenges. Lego Serious Play is an effective tool as it drives the team to think in a modular type and try to visualise their ideas through metaphoric characters. Compared with the Lego Serious Play, it is more effective than the materials prototyping because it doesn’t require experience in sculpturing or drawing. It is a simple tool that many of us use grown playing them. Another advantage of the Lego Serious Play is that it can be used for visual services and products. Check Using Lego Serious Play as a Design Thinking Tool for detailed steps on how to use the tool.

Delivery: Design Thinking Methods
The final stage is where the product is tested and delivered to the consumer. After the prototyping stage, the team tries the product to reach the final delivered solution to the consumer. Several methods are used in testing and evaluating based on the product and how it is doing the testing. The evaluation is a professional practice (mainly the development and testing team). The consumers or users themselves conduct the testing. Evaluation and testing determine if the product can be delivered to the consumer or iterated and modified. Several tools could be used for evaluation and testing.
Six Thinking Hats
The Six Thinking Hats is a simple tool that allows professionals to evaluate the product from five perspectives based on six metaphoric hats. It will enable the team to focus on one direction of thinking at a time. These hats address the problem as follows (Check What Are The Six Thinking Hats? And How to Use Them? ):
- Blue hat: This hat is usually owned by the facilitator who manages the feedback or meeting session where the Six Thinking Hats method is implemented.
- White hat: The team discusses the information and facts related to the problem or situation.
- Yellow hat: This hat reflects positive ideas about the situation. The stakeholders think from an optimistic point of view about the problem.
- Green hat : the green hat aims to discuss the positive and creative ideas that can be used to solve the problem.
- Red hat: This hat refers to the feelings related to the problem.
- Black hat: This hat represents caution and negative thoughts about the problem.

By discussing each of these perspectives separately, the team can have the opportunity to address the situation rationally and in a more organised way. Check this article for a step-by-step example to apply the Six Thinking Hats: What Are The Six Thinking Hats? And How to Use Them?
Using the appropriate design thinking process tools and methods in the related stage helps reach an effective outcome of the design process. However, there is confusion in determining which is the most effective tool to use. The above design thinking tools and methods guide the different stages and examples of the appropriate tools and methods to use in each stage.
Bibiliography
Dorst, K. (2010). The nature of design thinking . In Design thinking research symposium . DAB Documents.
Kimbell, L. (2011). Rethinking design thinking: Part I . Design and culture , 3 (3), 285-306.
Kimbell, L. (2012). Rethinking design thinking: Part II . Design and Culture , 4 (2), 129-148.
Lewrick, M., Link, P., & Leifer, L. (2020). The design thinking toolbox: A guide to mastering the most popular and valuable innovation methods . John Wiley & Sons.
Liedtka, J., & Ogilvie, T. (2011). Designing for growth: A design thinking tool kit for managers . Columbia University Press.
Meinel, C., & Leifer, L. (2012). Design thinking research . In Design thinking research (pp. 1-11). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Stickdorn, M., Hormess, M. E., Lawrence, A., & Schneider, J. (2018). This is service design doing: applying service design thinking in the real world . ” O’Reilly Media, Inc.”.
The Double Diamond Design Thinking process consists of four stages: Discover: The design team explores the problem or the challenge at hand. This practice may involve doing field research. Define: In this stage, the team develops a clear understanding of the problem. Develop: The team develops several prototypes and ideas to solve the problem. Deliver: The team tests the different prototypes and reaches the final product that must be delivered to the client.
Design thinking tools and methods are the different practices conducted in each stage of the design thinking process to solve problems or address challenges. The tools and methods differ based on the stages: Discover: Field research and desk research methods (interviews, focus groups, observation, and surveys) Define: mind mapping, reversed brainstorming, affinity diagram, 5 Whys, Cause-effect diagram. Develop: 3D printing, online prototyping, clay and cardboard models. Deliver: Testing, validation, A/B testing, and six thinking hats
Post main image copyrights: Collaboration vector created by vectorjuice – www.freepik.com
Designorate team is a group of authors and editors who write for Designorate and share their insight and passion with you, our amazing reader!
You May Also Like

Starbursting Technique: Evaluating New Ideas

Why Design Thinking Doesn’t Work

Problem Solving Using Hurson’s Production Thinking Model

How to Use Decision Trees in the Decision-Making Process

What are Design Research Types and Applications?

What is the 8D Problem Solving? And How to use the 8D Report?
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Sign me up for the newsletter!
- Open access
- Published: 09 April 2024
Flipped online teaching of histology and embryology with design thinking: design, practice and reflection
- Yan Guo 1 ,
- Xiaomei Wang 1 ,
- Yang Gao 1 ,
- Haiyan Yin 1 ,
- Qun Ma 1 &
- Ting Chen 2
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 388 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
153 Accesses
Metrics details
Flexible hybrid teaching has become the new normal of basic medical education in the postepidemic era. Identifying ways to improve the quality of curriculum teaching and achieve high-level talent training is a complex problem that urgently needs to be solved. Over the course of the past several semesters, the research team has integrated design thinking (DT) into undergraduate teaching to identify, redesign and solve complex problems in achieving curriculum teaching and professional talent training objectives.
This study is an observational research. A total of 156 undergraduate stomatology students from Jining Medical University in 2021 were selected to participate in two rounds of online flipped teaching using the design thinking EDIPT (empathy, definition, idea, prototype, and test) method. This approach was applied specifically to the chapters on the respiratory system and female reproductive system. Data collection included student questionnaires, teacher-student interviews, and exam scores. GraphPad Prism software was used for data analysis, and the statistical method was conducted by multiple or unpaired t test.
According to the questionnaire results, the flipped classroom teaching design developed using design thinking methods received strong support from the majority of students, with nearly 80% of students providing feedback that they developed multiple abilities during the study process. The interview results indicated that teachers generally believed that using design thinking methods to understand students' real needs, define teaching problems, and devise instructional design solutions, along with testing and promptly adjusting the effectiveness through teaching practices, played a highly positive role in improving teaching and student learning outcomes. A comparison of exam scores showed a significant improvement in the exam scores of the class of 2021 stomatology students in the flipped teaching chapters compared to the class of 2020 stomatology students, and this difference was statistically significant. However, due to the limitation of the experimental chapter scope, there was no significant difference in the overall course grades.
The study explores the application of design thinking in histology and embryology teaching, revealing its positive impact on innovative teaching strategies and students' learning experience in medical education. Online flipped teaching, developed through design thinking, proves to be an effective and flexible method that enhances student engagement and fosters autonomous learning abilities.
Peer Review reports
Research background and motivation
Histology is the study of the microstructure and related functions of the human body [ 1 ], while embryology studies the laws and mechanisms of ontogenesis and development; these two sciences are interrelated and self-contained [ 2 ]. As one of the important professional core programs of most medical specialties, Histology and Embryology (HE) has been an indispensable curriculum bridge between normal microstructure and pathological changes in tissue and organs.
The teaching targets of HE are mainly first-year undergraduate students in clinical medicine, psychiatry, stomatology, nursing, etc. The importance of fostering the development of empathy in undergraduate students is continuously emphasized in international recommendations for medical education [ 3 ]. Freshmen have a certain ability to think logically and analyse problems, but this ability is limited, and they have a yet to develop familiarity with scientific research hotspots. Moreover, they are often unaware of their creative potential, and this phenomenon often causes them to passively accept knowledge, and their autonomous learning ability and student participation in class are less than that of upperclassmen. These first year students face the need to develop scientific literacy and the ability to integrate theory with practice [ 4 ]. However, traditional teaching methods may have failed to fully meet students' need for a profound understanding of these abstract concepts, leading to challenges such as low interest in learning and inadequate knowledge absorption. Consequently, educators urgently need to seek innovative teaching strategies to enhance students' learning experience and academic performance.
In the information age, teacher teaching is no longer a simple superposition of knowledge and teaching methods but a fusion innovation of technology and teaching oriented to a more complex learning environment. The Teacher Standards issued by the American Educational Technology International Association note that the important role of future teachers is that of a "designer" [ 5 ]. DT combines a creative and innovative approach to dealing with complex problems, which serves as a valuable tool for those seeking to improve the challenging issues in medical education [ 6 ]. DT is a process of analysis that relies on the deconstruction of ideas and a creative process that relies on the construction of ideas. There are no judgements in DT. This eliminates the fear of failure and encourages maximum input and participation. Wild ideas are welcome since they often lead to the most creative solutions. Everyone is a designer, and DT is a way to apply design methodologies to any situation [ 5 ].
In the field of education, DT has been advocated as a means to promote the cultivation of innovative talent through innovative teaching methods. With the help of DT, and adhering learning as the concept in teaching, the transformation of teaching allows learners to explore real needs in real life scenes, to propose innovative solutions to meet those needs through teamwork, and to test the effectiveness of those solutions through prototype production. This process facilitates the further application of constructivism [ 7 ].
In the process of both conventional teaching and teaching innovation, the research team utilizes the “EDIPT” (Empathy, Define, Ideate, Prototype and TEST) DT theory [ 8 ] which originating in the Stanford University Design School to design teacher activities and student activities and select technical tools [ 9 ]. The basic process is shown in Fig. 1 . The team is very accustomed to consciously applying DT methodology when facing difficulties and challenges to consistently obtain the desired results [ 10 ]. This study sets the teaching objectives and plans of a large cycle (one semester) to guide the teaching implementation of a small cycle (one section or one chapter); Then, small-cycle teaching feedback and achievement accumulation promote the progress of large-cycle teaching to ensure the coherence, effectiveness and improvement of teaching reform. For example, the difficult problem in the process of cardiovascular system embryogenesis is atrial separation; the team uses cardboard and plastic film to construct room partition "products" [ 11 ] to provide vivid explanations and body movements for clearer explication. In another example, they integrate scattered knowledge points including cleavage, blastocyst formation and implantation into a unified narrative called "the initial journey." It solves the pain point that the dynamic abstraction of embryology knowledge is difficult to intuitively understand. The above are two examples of using EDIPT steps of design thinking to solve teaching pain points.
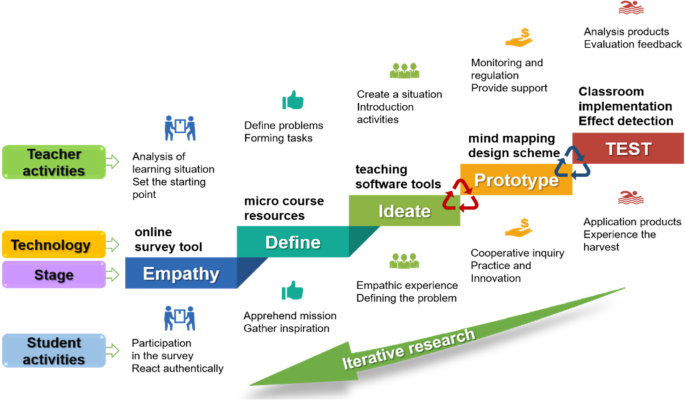
Problem solving steps incorporating DT
Research objectives and significance
In the 2021 Horizon Report: Teaching and Learning Edition, blended learning was once again selected as the key technology affecting the future development and practice of higher education [ 12 ], demonstrating great application potential. In this format, the teaching team adheres to the following practical principles to promote more blended learning courses to ensure high-quality outcomes [ 13 ]. In the recent period of epidemic prevention and control, effective online teaching combines asynchronous and synchronous delivery modes, addresses knowledge learning and ability development, and highlights interaction in teaching activities to improve the online teaching experience for both teachers and students and enhance the overall quality of online teaching. Online teaching is not simply an emergency measure taken during the epidemic but rather represents the future trend of education.
The aim of this study is to explore the application of design thinking in the teaching of histology and embryology courses. By investigating the impact of design thinking in the teaching process, we aim to gain a deeper understanding of the effects of this innovative teaching strategy on students' learning experience and academic performance, as well as its potential applications in medical education.
The significance of this research lies in its contribution to medical education with novel teaching methods and strategies. By incorporating design thinking, educators can better cater to students' learning needs and enhance their comprehension and mastery of the subject matter. Furthermore, this study contributes to the expansion of teaching research in the field of medical education, providing valuable insights for educational reform and improvements in teaching quality.
The analysis of the correlation between design thinking and this study
Design thinking plays a crucial role in formulating the educational reform. During the empathize phase, an in-depth understanding of teachers' and students' needs and challenges is achieved. This includes considering teachers' expectations and pedagogical beliefs, as well as students' learning styles and feedback, leading to a clear definition of the problem and setting specific objectives for the educational reform. In the define phase, the importance of improving teachers' pedagogical approaches and methods, and cultivating students' creative learning and competencies is underscored. This serves as the foundation for selecting appropriate teaching strategies and establishes the specific direction for incorporating design thinking in the flipped classroom model. During the ideate phase, innovative thinking is employed to explore diverse teaching strategies. For enhancing teachers' pedagogical approaches, approaches such as case-based teaching and collaborative learning are recommended to stimulate students' intrinsic motivation for active learning. For promoting students' creative learning and overall competencies, methods like project-based learning and critical thinking cultivation are considered to facilitate holistic student development. In the prototype phase, the devised teaching strategies are implemented in the flipped classroom setting. Continuous prototyping and rapid experimentation facilitate the collection of valuable feedback and data from students and teachers, enabling further optimization of the teaching strategies to align with the original intent of design thinking. Finally, in the test phase, a comprehensive evaluation of the teaching implementation is conducted. By collecting and analyzing data, the study delves deep into the impact of the educational reform on teachers' pedagogical beliefs and students' creative learning and overall competencies. This process provides crucial feedback and evidence for the ongoing improvement of the educational reform.
In conclusion, the selection of flipped classroom as a pedagogical strategy is closely guided by design thinking principles. Through the application of design thinking, this observational study aims to enhance teachers' pedagogical approaches and methods while fostering students' creative learning and overall competencies, thus promoting the successful implementation of the educational reform.”
Flipped classroom sessions can also allow learners to gain competence through their educational endeavours [ 14 ]. As Bransford writes, “To develop competence in an area, students must: a) have a deep foundation of factual knowledge, b) understand facts and ideas in the context of a conceptual framework, and c) organize knowledge in ways that facilitate retrieval and application” [ 15 ]. Flipped classrooms can lead to competence in factual knowledge by fostering mastery of content through content understanding and application, as in traditional classrooms [ 16 ].
“O-PIRAS” Flipped classroom
The flipped classroom teaching model used in this study was formed and adjusted on the basis of Professor Jianpeng Guo's “O-PIRTAS” model. The flipped teaching mode can enable both teachers and students to acquire further abilities through teaching activities [ 17 ].
The first step(O: Objective) in flipped classroom teaching design is to formulate two types of teaching objectives: low level and high level. The lower level teaching objectives include two cognitive objectives from Bloom's classification of teaching objectives: the memory and understanding of knowledge, while the higher level teaching objectives include four cognitive objectives from Bloom's classification: application, analysis, evaluation and creation, as well as objectives pertaining to movement skills and emotion [ 18 ]. The second step is to design a preparation activity (P: Preparation) for students to complete before class, which helps students form necessary prior knowledge and stimulates their learning motivation by exploring relevant issues prior to the class [ 19 ]. The third step is for teachers to send teaching materials (I: Instructional video) to their students for pre-class learning to facilitate their early acquisition of knowledge [ 19 ]. Fourth, teaching is transferred from online classes to offline classes. The teacher briefly reviews (R: Review) the video content before class to help students quickly focus on and prepare for the next stage of learning both cognitively and psychologically. Fifth, teachers should design classroom activities (A: Activity) appropriate to high-level teaching objectives to promote in-depth learning and successfully achieve high-level objectives. Sixth, teachers should conduct classroom summaries (S: Summary), reflection and improvement to help students form integrated structured knowledge. The six steps of flipping the classroom link form a closed loop, which can be summarized as in Fig. 2 .
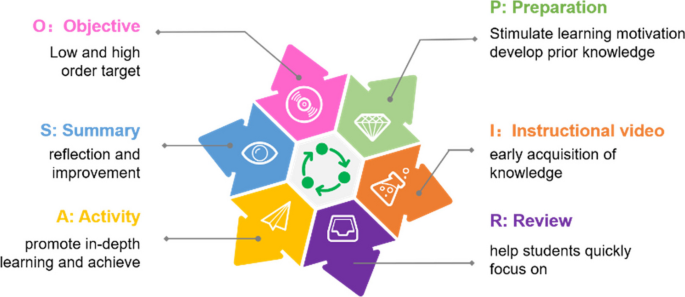
Process of “O-PIRAS” flipped teaching
Research method and data collection
Conveniently selecting 156 undergraduate students majoring in Dentistry from the 2021 cohort of Jining Medical University, we designated classes 1 to 3 as the class of 2021 stomatology students. As the class of 2020 stomatology students, we chose 155 undergraduate students majoring in Dentistry from the 2020 cohort, also from classes 1 to 3. Prior to the start of the study, we conducted communication sessions with both teachers and students, ensuring that all students were well-informed about the study and provided their consent. The two groups of students had the same course hours, faculty resources, learning materials, and learning spaces. The only difference was the application of design thinking methods in course and teaching design, including the implementation of flipped classroom teaching, specifically tailored for the 2021 cohort of students.
Data collection was conducted through various methods, including distributing questionnaires, conducting pre-, mid-, and post-research interviews, and recording course and corresponding chapter test scores. The implementation chapter selected the respiratory system, which plays a bridging role within histology, and the female reproductive system, which plays a transitional role between histology and embryology.
Before studying "Respiratory System", students have already mastered the basic methods of using design thinking to learn histology, and have a deep understanding of the four basic tissues and two types of organs (hollow and substantial organs). The main organs of the respiratory system—the trachea and lungs—belong to two types, respectively. The female reproductive system, as the concluding chapter of histology, is separated from the flipped classroom of the respiratory system by two weeks, leaving appropriate time for teachers to iteratively design and students to adapt to new methods. Four surveys were administered during the research process: Pre-flipped classroom survey for Chapter 16 "Respiratory System", Post-flipped classroom survey for Chapter 16 "Respiratory System", Pre-flipped classroom survey for Chapter 19 "Female Reproductive System", and Post-flipped classroom survey for Chapter 19 "Female Reproductive System", to gather student feedback and opinions on the teaching methods. The questionnaires were designed based on the research objectives and questions, and were refined through pre-testing to ensure clarity, accuracy, and appropriateness of the questions and options. The questionnaire mainly includes the following dimensions: ⑴Basic information of students, Q 1–3; ⑵ Learning and satisfaction: Q 4, What is the division of labor in your group in this cooperation? Q 7, About flipping class, how long will you spend studying before class? Q 6 Compared with the last flip class, are you satisfied with the teacher's teaching time in this flip class? Q 12, What are you most satisfied with this flip class? (3) Learning experience and ability improvement: Q 5, What kind of class learning form do you like best in flip class? Q 8, What are your learning pain points or difficulties after this flip class? Q 9, What abilities have you improved in this flip class? ⑷ Classroom Improvement and Feedback: Q 11, What are the advantages of this flip class compared with the last flip class? Q 10, In the course of embryo formation, do you like to use flip class for multiple course contents? Q13, What suggestions do you have for improving the embryo flipping class? Interviews were conducted at various stages, including before the study to understand teaching pain points, during the research process to gauge teachers' and students' attitudes and perspectives on the teaching activities, and after the study to obtain overall feedback. Additionally, we conducted both stage-specific and overall tests, and promptly collected relevant data for comparative analysis with the class of 2020 stomatology students. These data provided comprehensive insights into the performance and experiences of students in both the experimental and class of 2020 stomatology studentss.
Application of design thinking in course design
In course design, we employed design thinking methods to redesign the histology and embryology curriculum. Firstly, we gained a deep understanding of students' learning needs and interests to define course objectives and content. Secondly, we innovatively designed online materials and videos to enhance the appeal and practicality of the learning experience. We encouraged students to actively participate in discussions and problem-solving during class to unleash their creative potential. Additionally, we continuously optimized the teaching content and methods through iteration and feedback to ensure a sustained improvement in teaching effectiveness. Through the application of design thinking in course design, we expected to optimize the teaching process, enhance students' learning experiences, and improve their academic performance.
Design and implementation of flipped teaching
The HE course covers 22 chapters, totaling 60 h, including 44 h of theoretical classes and 16 h of practical classes. The theoretical teaching is roughly divided into three stages: the first stage consists of 12 h, focusing on introducing the four basic human tissues; the second stage comprises 18 h, covering the structure of human organs and systems; and the third stage spans 14 h, elucidating the process of human embryonic development. To facilitate a deep understanding and mastery of human tissue structures, four practical classes, each lasting 4 h, are incorporated to complement the theoretical content.
The entire course relies on a blended teaching approach, combining online and offline instruction, leveraging the resources of Shandong's top undergraduate course in HE, and utilizing the "Zhidao" flipped classroom tool. At the beginning of the course, the teachers introduce the purpose, teaching process, weekly plan, grading components, and assessment methods of incorporating design thinking into the blended HE teaching. The flipped classroom teaching for the class of 2021 stomatology students is set between two stage tests to investigate whether this innovative teaching method has an impact on students' test scores.
The teaching team consists of 4 associate professors and 3 lecturers, with an average teaching experience of 11.4 years in teaching nursing major foundation courses and possessing rich teaching experience. In addition, the project leader and team teachers have undergone multiple training sessions in design thinking innovation and systematic training in domestic and on-campus blended teaching theories.
At the beginning of the semester, the curriculum teaching plan should be formulated, and chapters suitable for flipped teaching should be selected according to the teaching plan” and content characteristics [ 20 ]. Teaching and research team members should jointly analyse the teaching content and formulate the flipped classroom syllabus [ 21 ], clarify teaching objectives (knowledge objectives, ability objectives and emotional objectives, i.e., low-order objectives and high-order objectives), develop chapter teaching plans and teaching courseware (traditional classrooms are obviously different from flipped classrooms) [ 22 ], record pre-class video (design the course content in a fragmented way and systematically present it in accordance with the teaching plan) [ 23 ], divide students into groups and engage with all students through “zhidao” teaching software and the QQ class committee. The specific design and implementation plan for the preparation of the above teaching materials for a flipped classroom course on the respiratory system. The teaching team seminar is held three weeks before the class.
While completing the preparation of teaching materials in accordance with the teaching plan, the team clarified what methods and tasks teachers and students should complete before and during the implementation of the flipped classroom so that everyone can understand the design intent of these teaching activities to facilitate more satisfactory teaching results.
Practice processes and instructional evaluation
The teaching design was discussed and approved by all members of the research team and used in the classroom teaching of respiratory system conversion with slightly modified specific content. One week before class, it was distributed through the zhizhuishu teaching platform to all the students [ 24 ] participating in flipped classroom teaching. The resources provided to students include preview materials, textbook chapters, courseware, videos, etc.; Preview questions, some questions related to preview materials, guide students to think and explore, stimulate learning interest and initiative; Learning objectives, clarify the knowledge objectives, ability objectives, and literacy objectives for pre class learning. In addition, there are also learning platforms (Wisdom Tree Online Course- https://coursehome.zhihuishu.com/courseHome/1000007885/199185/20#onlineCourse ),WeChat class group chat, learning community. In flipping the method of respiratory system class delivery, the team first tried to perform a complete flip of the class. At the beginning of the class, the teacher clarified six themes, and then the group spokespersons demonstrated their understanding of all the knowledge points, including key points and difficulties, in class by drawing lots. The teams provided feedback for each other. The teacher only played a guiding role in the activities involving the entirety of the class. After summarizing the classroom content, the teacher assigned homework, such as creating mind maps and engaging in thematic discussions on the learning platform, and distributed the questionnaire regarding the group pre-class preparations, classroom activities and learning experiences for the respiratory system flipped classroom. The questionnaire mainly consists of the following questions. How was the work divided among your team for this activity? What kind of in-class learning style do you like best in the flipped classroom? Compared with the last flipped classroom, are you satisfied with the length of teaching in this flipped classroom? How long do you spend on pre-class learning for a flipped class? What are your learning pain points or difficulties after this flipped lesson? What abilities have you improved in this flipped classroom? Are you satisfied with the length of lectures in this class compared with that in the last flipped class? What percentage of the course content do you prefer to be delivered by the flipped classroom model? Compared with the last flipped classroom, what are the advantages of this flipped classroom? What you are most satisfied with in this flipped lesson? Please offer suggestions for the improvement of your flipped class on embryos.
According to the steps and links involved in DT, when the “product” (teaching plan) is tested and problems are found, the design team should complete the iteration as soon as possible to better meet the needs of “customers” (students)[ 25 , 26 ]. Three days after the questionnaires, the teaching team adjusted the flipped classroom teaching design scheme for the Female Reproductive System course according to the questionnaire results, and arranged the pre-class tasks one week prior to the class, which differed from the previous class. Explanations of key points and difficult points were appropriately added to the teaching design, which did not depend on students as thoroughly as it had the last time, reducing the difficulty of the flipped classroom to a certain extent, improving students' level in participation, and improving the learning effect and teaching quality of the class.
A total of four questionnaires were distributed before and after the two flipped classes, and video recordings were made of the flipped classroom teaching process for a nursing and a stomatology class. Tencent conference recording instructions were issued by teachers. HE course scores consisted of three parts, including the usual score (30%), experimental score (10%) and final score (60%). The course scores of the 2021 nursing class and stomatology class were derived from the education management system of Jining Medical College, and the course scores of the nursing and stomatology majors who did not classes that had implemented online flipped classroom teaching in 2020 were derived as a control. Comparing the proportion of students in each of two grades, the total correct response rate of test questions, and the correct response rate of respiratory system and female reproductive system course test questions delivered through flipped classroom teaching were analysed using GraphPad Prism software through the statistical method of multiple or unpaired t tests.
Teaching strategies developed using design thinking methods improves multiple student abilities
According to the results of the questionnaire distributed before the beginning of the first flipped class, 51.2% of the students reported not understanding the new learning method and that they could not check the data, 21.6% of the students were not interested in flipped lessons and preferred traditional passive learning methods, 25.6% of the students said that they did not have strong self-control and were unwilling to take the initiative to learn, 56.8% of the students said that they had a great fear of speaking in front of their classmates and that their public speaking skills were not strong, and 46.4% of the students did not know how make suitable PowerPoint Presentation (PPT). After two sessions of flipped classroom learning, the majority of students felt that their pain points had been effectively solved and various abilities had been developed. The results of the question after the flipped classroom teaching of the female reproductive system are shown in Table 1 .
Positive feedback and growth experience of students in teaching strategies developed using design thinking methods
The informal discussion following the flipped lesson on the female reproductive system shows that compared with the "Teacher almost let go" response in the previous respiratory system flipping class, the students are more inclined to respond with "The teacher will solve the problems left in our preview," "Feedback is provided between groups, and the groups are complementary," "The teacher emphasizes the key points, explains the process in detail, and plays videos to consolidate knowledge," and " the teacher commented on the performance of the group speaker". The students thought that after two sessions of participation in a flipped classroom, "We are more active in learning and the classroom design is more live," and "The students are more involved and confident." "By applying design thinking to study the course of organizational design, I have found new learning methods and approaches, and successfully applied these learning methods to other courses, which has benefited me greatly."
The comparison results of grades
Under the premise that there is no significant difference in the difficulty of test questions and other criteria between the flipped and traditional classrooms, the class of 2021 stomatology students' course scores showed a slight improvement. However, there was no significant difference in the distribution of the number of students in each score segment compared to the class of 2020 stomatology students. In contrast, for the chapters that implemented flipped classroom teaching, specifically the respiratory system and female reproductive system chapters, the class of 2021 stomatology students' test scores showed a significant increase. The difference between the two groups was statistically significant. The details are depicted in Fig. 3 .
Distribution of final exam scores for the two graduating classes. A The proportion of students in different grades, no significant difference Statistical method: Multiple t tests. B Total accuracy, no significant difference. Statistical method: Unpaired test. C The accuracy of flipped classroom chapters, unpaired test, P < 0.05. Mean ± SEM of column A 0.7075 ± 0.009587 N = 3, Mean ± SEM of column B 0.7913 ± 0.02872 N = 3
Firstly, significant achievements have been made in enhancing students' overall abilities through the application of design thinking methods in formulating flipped classroom teaching strategies. Preliminary surveys revealed various challenges faced by students before the commencement of the flipped classes, including difficulties in understanding new learning methods, lack of interest in flipped classes, low self-discipline, and fear of public speaking. However, after two sessions of flipped classroom learning, the majority of students believe that their pain points have been effectively addressed, and various skills have been developed. This aligns with the findings of previous research by Awan OA [ 15 ], indicating that the application of design thinking methods in teaching strategies can significantly enhance students' subject engagement and skill development.
Secondly, regarding the positive feedback and students' growth experiences in applying design thinking methods to formulate teaching strategies, there is a positive trend observed in informal discussions following the flipped classroom on the female reproductive system. Students tend to perceive a more proactive role played by teachers in the flipped classroom, addressing the issues they encountered during previewing. Students also highlighted the complementary feedback provided among groups, emphasizing the importance of teamwork. Additionally, students positively acknowledged the efforts of teachers in emphasizing key points, providing detailed explanations of processes, and reinforcing knowledge through video presentations. They believe that this teaching approach stimulates their interest in learning and enhances their motivation. This aligns with the findings of research by Scheer A [ 7 ] and Deitte LA [ 11 ], supporting the positive impact of design thinking methods in education.
Finally, the results of the performance comparison indicate that there is no significant difference between flipped classroom and traditional classroom based on criteria such as question difficulty. However, the overall grades of the 2021 cohort of dental medicine students have shown a slight improvement. Specifically, in the chapters on the respiratory and female reproductive systems within the flipped courses, the exam scores of the 2021 cohort students have significantly increased, and this difference is statistically significant. This suggests that the flipped classroom teaching formulated through design thinking methods has a significant positive impact on the development of subject-specific skills in specific chapters. This aligns with the relevant findings of Cheng X [ 1 ], further emphasizing the instructional advantages of design thinking methods in specific topics.
Main finding
The team used DT to reveal the pain point that flexible mixed teaching can not guarantee students' participation and the realization of teaching objectives, and the application of online flip classroom teaching solved this problem well Students play a leading role in this kind of teaching, so they need to devote more time and energy to preview textbooks and consult relevant materials before class to improve their autonomous learning ability It is helpful to cultivate team spirit in flip teaching in the form of group, which is helpful to cultivate team leadership and management ability. The main requirements of mixed teaching are to integrate pre-recorded videos into the course as a whole and provide online learning resources to supplement face-to-face teaching in an organized and selective way [ 27 ] As assessment expert Mag says, if you are teaching something that cannot be assessed, you are already in an awkward position-that is, you can't explain the teaching content clearly [ 28 ] Therefore, reasonable teaching objectives in mixed teaching can make teachers and students reach a common understanding and consensus on learning results, enhance emotional communication and resonance between teachers and students, and jointly promote the implementation of curriculum teaching. The successful implementation of online flip class needs certain network and students' enthusiasm and cooperation At the same time, teachers need to be particularly familiar with the curriculum to design lectures and targeted comments [ 29 ].
Limitations and future research
In this study, the respiratory system and female reproductive system in HE were selected as subjects for conducting flipped classroom teaching. The examination results shoe that although the overall course performance has not significantly improved, the accuracy of the chapter test questions in flipped classrooms significantly improved, which demonstrates that this teaching method can improve students' learning performance while cultivating their various abilities. It is worth expanding the scope of implementation to more chapters. However, not all chapters are suitable for flipped classroom teaching. Because the two chapters involved in this paper belong to the "organs and systems" module, it does not fully reflect the applicability of this research in this course. Some chapters of the basic tissue module and embryogenesis module are also the scope of our future teaching research In addition, what is the highest proportion of total course hours converted to flip teaching? All these problems need further study in the future. What is the most appropriate ratio of total course hours to convert into flipped teaching? These issues need to be further studied in the future.
When DT is introduced into education, evaluating students' learning and development becomes more important than evaluating students' design products or knowledge and ability. Changes in consciousness and attitude include whether they can fully participate in current cognitive activities, learn independently, communicate and cooperate, and continuously monitor and adjust themselves. By clarifying this guidance, we can formulate or select appropriate evaluation criteria through a literature review during the implementation of the project and adjust the subsequent research conditions in a timely manner according to the evaluation results.
Online flipped teaching is an effective way to integrate DT into the flexible and mixed teaching of HE, which can effectively enhance students' learning input and cultivate students' autonomous learning ability. This research aims to reshape the method of classroom teaching through the deep integration of modern information technology into pedagogical design. Future work should appropriately expand the scope of flipped teaching content and explore the appropriate proportion of course content. In the course design, various forms of cross-professional cooperation with clinical doctors should be increased as much as possible, and the contents of flipped classroom should be expanded from basic knowledge to clinical skills.
Through the application of design thinking in the teaching of histology and embryology courses, we have gained a deeper understanding of its positive impact on innovative teaching strategies, improvement of students' learning experience and academic performance, and the potential value it holds in medical education. We have discovered that the "product" developed through design thinking, namely online flipped teaching, serves as an effective and flexible blended teaching method. It not only enhances students' engagement in learning and fosters their autonomous learning abilities but also encourages both teachers and students to cultivate their innovative capabilities and reshape classroom teaching approaches. Moving forward, further exploration should be undertaken to determine the optimal balance for expanding the content of flipped teaching, to continually uncover its potential in medical education.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
Histology and Embryology
Design Thinking
Cheng X, Ka Ho Lee K, Chang EY, Yang X. The “flipped classroom” approach: Stimulating positive learning attitudes and improving mastery of histology among medical students. Anat Sci Educ. 2017;10(4):317–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.1664 .
Article Google Scholar
Cheng X, Chan LK, Li H, Yang X. Histology and Embryology Education in China: The Current Situation and Changes Over the Past 20 Years. Anat Sci Educ. 2020;13(6):759–68. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.1956 .
Magalhaes E, Salgueira AP, Costa P, Costa MJ. Empathy in senior year and first year medical students: a cross-sectional study. BMC Med Educ. 2011;11:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-11-52 .
Boyd VA, Whitehead CR, Thille P, Ginsburg S, Brydges R, Kuper A. Competency-based medical education: the discourse of infallibility. Med Educ. 2018;52(1):45–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.13467 .
Roberts JP, Fisher TR, Trowbridge MJ, Bent C. A design thinking framework for healthcare management and innovation. Healthc (Amst). 2016;4(1):11–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hjdsi.2015.12.002 .
Madson MJ. Making sense of design thinking: A primer for medical teachers. Med Teach. 2021;43(10):1115–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/0142159X.2021.1874327 .
Scheer A, Noweski C, Meinel C: Transforming Constructivist Learning into Action: Design Thinking in education. Design and Technology Education 2012, 17 3; https://www.researchgate.net/publication/332343908 Transforming Constructivist Learning into Action Design Thinking in education
Gottlieb M, Wagner E, Wagner A, Chan T. Applying Design Thinking Principles to Curricular Development in Medical Education. AEM Educ Train. 2017;1(1):21–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/aet2.10003 .
IDEO: Design Thinking for Educators Toolkit. https://www.ideo.com/work/toolkit-for-educators .
Badwan B, Bothara R, Latijnhouwers M, Smithies A, Sandars J. The importance of design thinking in medical education. Med Teach. 2018;40(4):425–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/0142159X.2017.1399203 .
Deitte LA, Omary RA. The Power of Design Thinking in Medical Education. Acad Radiol. 2019;26(10):1417–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2019.02.012 .
2021 EDUCAUSE Horizon Report® _ Teaching and Learning Edition
Chen M, Ye L, Weng Y. Blended teaching of medical ethics during COVID-19: practice and reflection. BMC Med Educ. 2022;22(1):361. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-022-03431-6 .
Ge L, Chen Y, Yan C, Chen Z, Liu J. Effectiveness of flipped classroom vs traditional lectures in radiology education: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(40):e22430. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000022430 .
Awan OA. The Flipped Classroom: How to Do it in Radiology Education. Acad Radiol. 2021;28(12):1820–1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2021.02.015 .
Sertic M, Alshafai L, Guimaraes L, Probyn L, Jaffer N. Flipping the Classroom: An Alternative Approach to Radiology Resident Education. Acad Radiol. 2020;27(6):882–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2019.08.013 .
Guo J. The use of an extended flipped classroom model in improving students’ learning in an undergraduate course. J Comput High Educ. 2019;31(2):362–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12528-019-09224-z .
Adams NE. Bloom’s taxonomy of cognitive learning objectives. J Med Libr Assoc. 2015;103(3):152–3. https://doi.org/10.3163/1536-5050.103.3.010 .
Wagner KC, Byrd GD. Evaluating the effectiveness of clinical medical librarian programs: a systematic review of the literature. J Med Libr Assoc. 2004;92(1):14–33.
Google Scholar
Vanka A, Vanka S, Wali O. Flipped classroom in dental education: A scoping review. Eur J Dent Educ. 2020;24(2):213–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/eje.12487 .
Eaton M. The flipped classroom. Clin Teach. 2017;14(4):301–2. https://doi.org/10.1111/tct.12685 .
Tang F, Chen C, Zhu Y, Zuo C, Zhong Y, Wang N, Zhou L, Zou Y, Liang D. Comparison between flipped classroom and lecture-based classroom in ophthalmology clerkship. Med Educ Online. 2017;22(1):1395679. https://doi.org/10.1080/10872981.2017.1395679 .
Erbil DG. A Review of Flipped Classroom and Cooperative Learning Method Within the Context of Vygotsky Theory. Front Psychol. 2020;11:1157. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01157 .
Singh K, Mahajan R, Gupta P, Singh T. Flipped Classroom: A Concept for Engaging Medical Students in Learning. Indian Pediatr. 2018;55(6):507–12.
Gomez FC Jr, Trespalacios J, Hsu YC, Yang D. Exploring Teachers’ Technology Integration Self-Efficacy through the 2017 ISTE Standards. TechTrends. 2022;66(2):159–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-021-00639-z .
Wolcott MD, McLaughlin JE, Hubbard DK, Rider TR, Umstead K. Twelve tips to stimulate creative problem-solving with design thinking. Med Teach. 2021;43(5):501–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/0142159X.2020.1807483 .
Bliuc A-M, Goodyear P, Ellis RA. Research focus and methodological choices in studies into students’ experiences of blended learning in higher education. The Internet and Higher Education. 2007;10(4):231–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2007.08.001 .
de Jong N, van Rosmalen P, Brancaccio MT, Bleijlevens MHC, Verbeek H, Peeters IGP. Flipped Classroom Formats in a Problem-Based Learning Course: Experiences of First-Year Bachelor European Public Health Students. Public Health Rev. 2022;43:1604795. https://doi.org/10.3389/phrs.2022.1604795 .
Qureshi SS, Larson AH, Vishnumolakala VR. Factors influencing medical students’ approaches to learning in Qatar. BMC Med Educ. 2022;22(1):446. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-022-03501-9 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Jining Medical College and Shandong Provincial Education Department for support.
Undergraduate Teaching Reform Research Project of Shandong Provincial Education Department No. M2021364, M2022159. Research on classroom teaching reform key program in Jining Medical College [2022] No. 2022KT001.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Basic Medicine, Jining Medical University, 133 Hehua Road, Jining, 272067, China
Yan Guo, Xiaomei Wang, Yang Gao, Haiyan Yin & Qun Ma
Academic Affair Office, Jining Medical University, 133 Hehua Road, Jining, 272067, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Yan G, Ting C: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing-original draft preparation. Xiaomei W, Yang G: Interview, Data curation, Formal Analysis. Haiyan Y, Qun M: Formal analysis, Writing-reviewing and editing. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ting Chen .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Research involving human participants, human material, or human data was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. All experimental protocols were approved by the Ethics Review Committee of Jining Medical University (No. JNMC-2020-JC-013). Informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardians. The consent was obtained in written form.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Guo, Y., Wang, X., Gao, Y. et al. Flipped online teaching of histology and embryology with design thinking: design, practice and reflection. BMC Med Educ 24 , 388 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05373-7
Download citation
Received : 23 February 2023
Accepted : 29 March 2024
Published : 09 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05373-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Flexible hybrid teaching
- Design thinking
- Flipped teaching
- Histology and embryology
- Basic Medical Education
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. What are the 5 Stages of the Design Thinking Process. Stage 1: Empathize—Research Your Users' Needs. Stage 2: Define—State Your Users' Needs and Problems. Stage 3: Ideate—Challenge Assumptions and Create Ideas. Stage 4: Prototype—Start to Create Solutions. Stage 5: Test—Try Your Solutions Out.
Design thinking is an innovative problem-solving process rooted in a set of skills.The approach has been around for decades, but it only started gaining traction outside of the design community after the 2008 Harvard Business Review article [subscription required] titled "Design Thinking" by Tim Brown, CEO and president of design company IDEO.
Stage 1: Empathy. The first stage of the design thinking process is empathy. During this stage, design teams set aside their own biases and work to gain a deeper understanding of real users and their needs—often through direct observation and engagement. Empathy is one of the most crucial phases of design thinking.
The design thinking process is a problem-solving methodology used by designers to approach complex problems and find innovative solutions. It typically involves five stages: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test.
Cue design thinking, a formalized framework of applying the creative design process to traditional business problems. The specific term "design thinking" was coined in the 1990's by David Kelley and Tim Brown of IDEO, with Roger Martin, and encapsulated methods and ideas that have been brewing for years into a single unified concept. Conclusion
Design thinking process 101: Definitions and approaches. The design thinking process puts customers' and users' needs at the center and aims to solve challenges from their perspective. Design thinking typically follows five distinct stages: Empathize.
The design thinking methodology in action. So far, we've covered quite a bit of theory. We know what design thinking is and the key principles that shape it. Now let's consider what the design thinking methodology looks like in action, starting with the five key steps in the design thinking process. The design thinking framework: five key steps
rather they emerge from a process of synthesizing information to discover connections and patterns. In a word, the DeÞne mode is sensemaking. WHY deÞne The DeÞne mode is critical to the design process because it results in your point-of-view (POV): the explicit expression of the problem you are striving to address. More importantly,
Design thinking is an approach used for practical and creative problem-solving. It is based heavily on the methods and processes that designers use (hence the name), but it has actually evolved from a range of different fields—including architecture, engineering and business.
Design thinking provides a structured process that helps innovators break free of counterproductive tendencies that thwart innovation. Like TQM, it is a social technology that blends practical ...
Design thinking is a core way of starting the journey and arriving at the right destination at the right time. Simply put, "design thinking is a methodology that we use to solve complex problems, and it's a way of using systemic reasoning and intuition to explore ideal future states," says McKinsey partner Jennifer Kilian.
This design thinking site is just one small part of the IDEO network. There's much more, including full online courses we've developed on many topics related to design thinking and its applications. We fundamentally believe in the power of design thinking as a methodology for creating positive impact in the world—and we bring that belief ...
The first, and arguably most important, step of design thinking is building empathy with users. By understanding the person affected by a problem, you can find a more impactful solution. On top of empathy, design thinking is centered on observing product interaction, drawing conclusions based on research, and ensuring the user remains the focus ...
The 5 core principles of the design thinking methodology. The design thinking methodology is made of five principles: User-centricity and empathy: your users, their problems, and their experience in your product are a priority, not an afterthought. Collaboration: every level and every role can contribute to, and see results from, design thinking.
The design thinking process is a problem-solving design methodology that helps you develop solutions in a human-focused way. Initially designed at Stanford's d.school, the five stage design thinking method can help solve ambiguous questions, or more open-ended problems. Learn how these five steps can help your team create innovative solutions ...
There are various methods and techniques for prototyping in the design thinking process, and the choice of method depends on your specific needs and goals for a project. Here's an overview of some common ones: Wireframes: Wireframes are widely used for creating simplified, visual representations of the layout and structure of an idea or ...
Unlike methods made for manufacturing or software development, the Design Thinking Process is designed for everybody. In fact, the Design Thinking process becomes more efficient as more skill sets are added to the team. This is because Design Thinking leans heavily on empathy and divergence, which both benefit from increased perspectives.
Design Thinking is a problem-solving framework. Unlike other brainstorming methods, design thinking uses empathetic observation to focus on human-centered needs first before diving into ideation. The process of design thinking is derived from the methods that designers, architects, and engineers all use to do their work.
Design thinking tools and methods are the different practices conducted in each stage of the design thinking process to solve problems or address challenges. The tools and methods differ based on the stages: Define: mind mapping, reversed brainstorming, affinity diagram, 5 Whys, Cause-effect diagram.
Design thinking refers to the set of cognitive, strategic and practical procedures used by designers in the process of designing, and to the body of knowledge that has been developed about how people reason when engaging with design problems.. Design thinking is also associated with prescriptions for the innovation of products and services within business and social contexts.
Abstract. Design thinking is generally defined as an analytic and creative process that engages a person in opportunities to experiment, create and prototype models, gather feedback, and redesign. Several characteristics (e.g., visualization, creativity) that a good design thinker should possess have been identified from the literature.
Flexible hybrid teaching has become the new normal of basic medical education in the postepidemic era. Identifying ways to improve the quality of curriculum teaching and achieve high-level talent training is a complex problem that urgently needs to be solved. Over the course of the past several semesters, the research team has integrated design thinking (DT) into undergraduate teaching to ...