Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Essay
Photosynthesis is one of the primary sources of energy for living organisms. The fossilized photosynthetic fuels account for almost 90% of the energy in the world (Johnson, 2016). Cellular respiration is a process that takes place in the living organism and converts nutrients into energy. This essay will examine photosynthesis and cellular respiration separately and identify similarities, differences, and interconnectedness between two processes. Two processes are similar in that they both deals with energy, but they are different because one process involves catabolic reactions and another anabolic one.
The purpose of photosynthesis is to convert atmospheric carbon dioxide into carbohydrates using light energy. The light splits one of the reactants, water in the mesophyll of the leaf into oxygen, electrons, and protons during the light-dependent phase (Johnson, 2016). Then carbon dioxide enters the mesophyll of the leaf through openings, stomata, during the light-independent phase. These two reactions differ in light utilization and molecules production. The first reaction products are oxygen, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) that are used as energy storages, while by the end of the second reaction, the carbohydrate is obtained, and molecules mentioned above are used (Flügge et al., 2016). Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplast with the light-dependent reaction taking place in the thylakoid membrane, and light-independent reaction in the stroma. The energy produced in the light reaction is used to fix carbon dioxide and produce carbohydrates while oxygen is released outside. According to the following equation of the photosynthesis, C → O2 + 2H20 + photons (CH2O)n + electrons + O2 carbon monoxide and water are transferred into carbohydrates under the light with the release of atmospheric oxygen.
The purpose of cellular respiration is to convert nutrients into energy. The reactants of the respiration are glucose circulating in the blood and oxygen obtained from breathing, while the product is ATP. Cellular respiration starts from glycolysis in the mitochondria’s stroma, where the glucose is broken down into pyruvate (Bentley & Connaughton, 2017). Then it continues with the citric acid cycle that generates ATP, NADH, and FADH2. In the final stage, the electron transport chain uses these molecules to generate more ATP. The energy produced is then used for metabolic processes in the organism, while carbon dioxide is released with breathing (BBC Bitesize, n.d.). According to the following equation of the cellular respiration, C → 6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O the glucose is broken down into carbon dioxide and water with the presence of oxygen.
There are two main differences between photosynthesis and cellular respiration. The first one is the anabolic process, during which complex compounds are synthesized, while the second one is catabolic, which involves breaking down the compounds (Panawala, 2017). The second crucial difference is that photosynthesis is found only in chloroplasts, while cellular respiration is found in any living cell, making it a universal process. There are also two main similarities between photosynthesis and respiration. The first similarity is that both processes involve the production of ATP (Stauffer et al., 2018). The second similarity is that both processes utilize ATP but for different purposes.
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are connected in such a way that they allow to perform metabolic functions normally. Moreover, these processes help to regulate the concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. If photosynthesis stopped occurring, the level of oxygen would drop dramatically This would lead to deaths of all living organisms whose lives depend on this molecule. Whereas if cellular respiration stopped happening, living creatures would not be able to generate energy and sustain life.
To conclude, photosynthesis plays a crucial role in maintaining life on Earth. Photosynthesis uses light energy to produce oxygen, while cellular respiration uses oxygen to break down complex molecules and provide energy. These processes are different in their metabolic nature, but similar in terms of energy storage. If photosynthesis did not exist, the life for oxygen-dependent creatures would become extinct. Similarly, in the case of cellular respiration disappearing, living organisms would not be able to produce energy.
BBC Bitesize . (n.d.). Respiration. 2020. Web.
Bentley, M., & Connaughton, V, P. (2017). A simple way for students to visualize cellular respiration: Adapting the board game MousetrapTM to model complexity . CourseSource. 4, 1-6. Web.
Flügge, W., Westhoff, P., & Leister, D. (2016). Recent advances in understanding photosynthesis. F1000 Research, 5, 1-10.
Johnson, M. P. (2016). Photosynthesis. Essays Biochemistry , 60 (3), 255-273.
Panawala, L. (2017). Difference between photosynthesis and respiration. IE PEDIAA. Web.
Stauffer S., Gardner A., Ungu D.A.K., López-Córdoba A., & Heim M. (2018). Cellular respiration. In Labster virtual lab experiments: Basic biology (pp. 43-55). Springer.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, February 21). Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration. https://ivypanda.com/essays/photosynthesis-and-cellular-respiration/
"Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration." IvyPanda , 21 Feb. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/photosynthesis-and-cellular-respiration/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration'. 21 February.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration." February 21, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/photosynthesis-and-cellular-respiration/.
1. IvyPanda . "Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration." February 21, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/photosynthesis-and-cellular-respiration/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration." February 21, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/photosynthesis-and-cellular-respiration/.
- Photosynthesis Rate Determination From the Oxygen Gas Evolution
- Biology: Photosynthesis and Respiration
- The Complexity of Photosynthesis and Respiration
- Glycolysis Process in Yeast and in Human
- Photosynthesis, Fermentation, and Enzyme Activity
- Planting Bamboo: The Role of Photosynthesis
- Runaway Photosynthesis and Its Effects on Life in the Universe
- Anaerobic Respiration and Its Applications
- Cell Energy Metabolism Controls
- Recent Advances in Artificial Photosynthesis
- Transgenic Organisms and Evolution
- Punctuated Equilibrium: Arguments for and Against
- Aspects of Biology Techniques
- Shapes of Cells and Their Functions
- From the Chemical Components to the Whole Body

- Why Does Water Expand When It Freezes
- Gold Foil Experiment
- Faraday Cage
- Oil Drop Experiment
- Magnetic Monopole
- Why Do Fireflies Light Up
- Types of Blood Cells With Their Structure, and Functions
- The Main Parts of a Plant With Their Functions
- Parts of a Flower With Their Structure and Functions
- Parts of a Leaf With Their Structure and Functions
- Why Does Ice Float on Water
- Why Does Oil Float on Water
- How Do Clouds Form
- What Causes Lightning
- How are Diamonds Made
- Types of Meteorites
- Types of Volcanoes
- Types of Rocks

Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
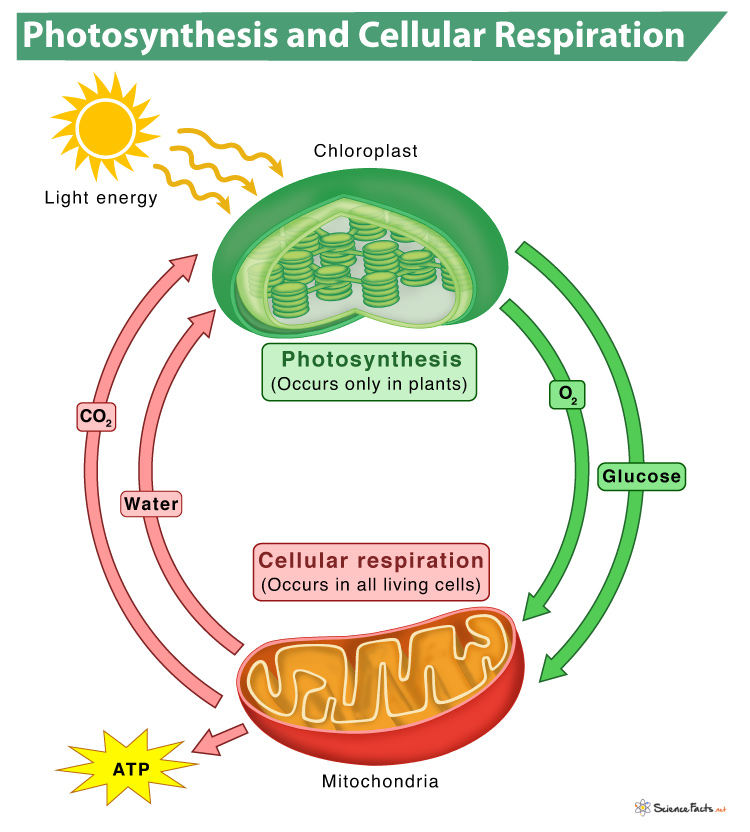
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are the two essential life processes on Earth that help living organisms survive. They are interrelated such that the products of one process are the reactants of the other and thus work in a cycle.
How are Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Related
Photosynthesis is a process by which green plants and algae make food in the form of carbohydrates (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) using water (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), and chlorophyll in the presence of sunlight as the energy source. Water and oxygen are produced as byproducts. In contrast, cellular respiration breaks down carbohydrates produced through photosynthesis and uses oxygen to produce energy and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide is again utilized during photosynthesis to continue the cycle.
The relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration can be best understood using the chemical equations given below:
Photosynthesis: 6CO 2 + 12H 2 O + sunlight → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 + 6H 2 O
Cellular Respiration: C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 → 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + ATP (energy)
Thus, photosynthesis is just the opposite process of cellular respiration, and they work in a circle.
Both processes are essential parts of the carbon cycle . While cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide in the environment, photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The exchange of CO 2 and O 2 during photosynthesis and cellular respiration helps recycle carbon dioxide in the biosphere . It keeps oxygen and carbon dioxide levels stable.
Compare and Contrast between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Although interrelated in nature, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are different in many ways.
How are Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Different
How are photosynthesis and cellular respiration similar.
Despite the two processes being opposite, they share some similarities.
- They involve multiple complex steps and many same molecules such as oxygen (O 2 ), carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), water (H 2 O), glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
- Exchange of gases
- Series of redox reactions involving enzymes
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are the two basic metabolic processes that work together to drive all cellular activities. All the primary producers in a food chain produce food by photosynthesis. In contrast, cellular respiration occurs in all living organisms on Earth. Food gets oxidized to obtain energy as ATP, which powers almost all the cellular processes. Also, the products of one process are utilized by another, creating a balance in nature.
Ans . Oxygen is released as a byproduct in photosynthesis, whereas, in cellular respiration, oxygen helps to oxidize glucose to liberate energy.
- Just Breathe: An Introduction to Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration – Orise.orau.gov
- Difference Between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration – Researchgate.net
- Steps of cellular respiration – Khanacademy.org
- Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis – Flexbooks.ck12.org
Article was last reviewed on Wednesday, August 31, 2022
Related articles
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Popular Articles

Join our Newsletter
Fill your E-mail Address
Related Worksheets
- Privacy Policy
© 2024 ( Science Facts ). All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.8: Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 13280

How do trees help you breathe?
Recall that trees release oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis. And you need oxygen to breathe. Do you know why? So your cells can perform cellular respiration and make ATP.
Connecting Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
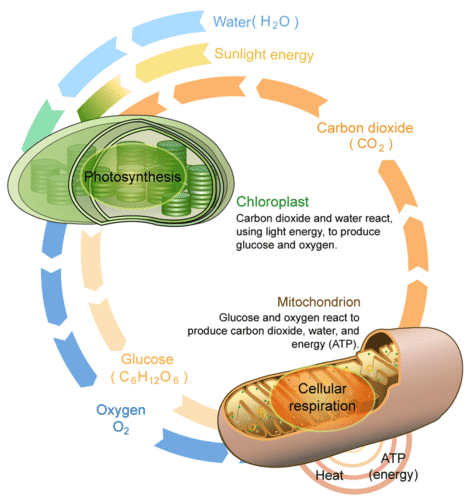
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are connected through an important relationship. This relationship enables life to survive as we know it. The products of one process are the reactants of the other. Notice that the equation for cellular respiration is the direct opposite of photosynthesis :
- Cellular Respiration: C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 → 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O
- Photosynthesis: 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2
Photosynthesis makes the glucose that is used in cellular respiration to make ATP. The glucose is then turned back into carbon dioxide, which is used in photosynthesis. While water is broken down to form oxygen during photosynthesis, in cellular respiration oxygen is combined with hydrogen to form water. While photosynthesis requires carbon dioxide and releases oxygen, cellular respiration requires oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. It is the released oxygen that is used by us and most other organisms for cellular respiration. We breathe in that oxygen, which is carried through our blood to all our cells . In our cells, oxygen allows cellular respiration to proceed. Cellular respiration works best in the presence of oxygen. Without oxygen, much less ATP would be produced.
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis are important parts of the carbon cycle. The carbon cycle is the pathways through which carbon is recycled in the biosphere. While cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide into the environment, photosynthesis pulls carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere. The exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen during photosynthesis (Figure below) and cellular respiration worldwide helps to keep atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide at stable levels.
- The equation for cellular respiration is the direct opposite of photosynthesis.
- The exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen thorough photosynthesis or cellular respiration worldwide helps to keep atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide at stable levels.
Explore More
Use the resource below to answer the questions that follow.
- Photosynthesis and Respiration at http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JEnjph9miK4 (3:46)
- What is needed for photosynthesis to occur? Be specific.
- What is needed for cellular respiration to occur?
- What is ATP?
- Do autotrophs need to carry out cellular respiration? Why or why not?
- How are the equations for photosynthesis and cellular respiration related?
- What keeps atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide at stable levels?
- Biology Difference Between
- Difference Between Photosynthesis And Respiration

Difference Between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Plants release oxygen which is a by-product of photosynthesis, and we breathe in oxygen so that our cells can carry out cellular respiration and generate ATP.
Respiration and photosynthesis are biological reactions in the environment that complement each other. Both are similar reactions that occur in a specific manner. In the process of respiration, oxygen and glucose yield water and carbon dioxide, while carbon dioxide and water yield glucose and oxygen during the process of photosynthesis.
Both cellular respiration and photosynthesis are parts of a mutually beneficial relationship. Photosynthesis cannot occur without cellular respiration and cellular respiration certainly cannot occur without photosynthesis.
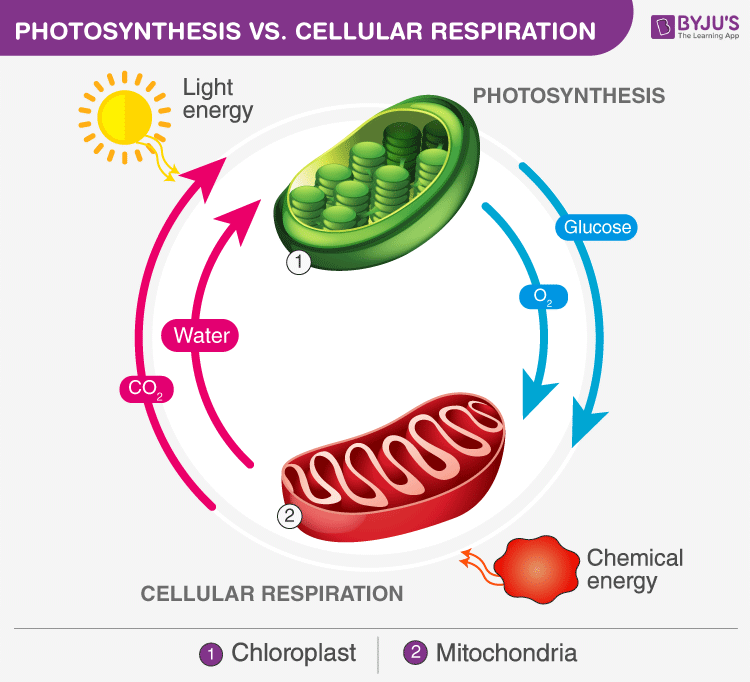
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are in many respects the “reverse” of one another. Photosynthesis is an anabolic process, whereas cellular respiration is a catabolic process. Let us explore more differences between cellular respiration and photosynthesis
Differences between Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
Also Read: Aerobic Respiration
To know more about cellular respiration and photosynthesis, visit BYJU’S.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
Vry good app is this
This is very helpful. I got an answer here from the questions in my lil’ sis module.
I like this program and I would like to do my best to participate
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Home — Essay Samples — Science — Light — Photosynthesis Process
Photosynthesis Process
- Categories: Light Photosynthesis
About this sample

Words: 423 |
Published: Feb 12, 2019
Words: 423 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Works Cited
- Campbell, N. A., & Reece, J. B. (2008). Photosynthesis and cellular respiration. In Biology (8th ed., pp. 190-220). Benjamin-Cummings Publishing Company.
- Taiz, L., & Zeiger, E. (2010). Photosynthesis: Carbon reactions. In Plant physiology (5th ed., pp. 174-207). Sinauer Associates.
- Raven, P. H., Evert, R. F., & Eichhorn, S. E. (2016). Photosynthesis and respiration. In Biology of Plants (8th ed., pp. 186-229). W. H. Freeman and Company.
- Niyogi, K. K. (1999). Photoprotection revisited: Genetic and molecular approaches. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 50, 333-359. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.333
- Siedow, J. N., & Day, D. A. (2000). Respiration and photorespiration. In Plant physiology (3rd ed., pp. 500-548). Academic Press.
- Allen, J. F. (2002). Photosynthesis and cellular respiration considered as coupled redox cycles: A chemiosmotic bridge linking two epochs. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 357(1426), 707-717. doi:10.1098/rstb.2001.0993
- Geigenberger, P. (2003). Response of plant metabolism to too little oxygen. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 6(3), 247-256. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(03)00038-8
- Foyer, C. H., & Noctor, G. (2005). Redox homeostasis and antioxidant signaling: A metabolic interface between stress perception and physiological responses. The Plant Cell, 17(7), 1866-1875. doi:10.1105/tpc.105.033589
- Sharkey, T. D. (2005). Effects of moderate heat stress on photosynthesis: Importance of thylakoid reactions, rubisco deactivation, reactive oxygen species, and thermotolerance provided by isoprene. Plant, Cell & Environment, 28(3), 269-277. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01324.x
- Sweetlove, L. J., & Fernie, A. R. (2018). The impact of oxidative stress on metabolism: A compartmental analysis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 1647. doi:10.3389/fpls.2018.01647

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Science

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1184 words
4 pages / 2197 words
3 pages / 1456 words
1 pages / 639 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Light
The light bulb greatly changed the world in many ways that continue to affect how individuals experience their lives today. Long ago using natural sources, for example, candles, lamps, and firewood were common ways of [...]
Imagine a world with no light. We use light in our everyday lives. That’s why the importance of light bulb can not be overestimated. Without it we would would have to use oil lamps and candles, and that would be hard. If we [...]
Light arrives on our planet after a speedy trip from the Sun, 149 million km (93 million miles away). Light travels at 186,000 miles (300,000 km) per second, so the light you’re seeing now was still tucked away in the Sun about [...]
The use of candles for light and heat is known to have existed in ancient times. The remains of candles have been found in the caves of France. It is believed that cavemen used them while painting and etching on the walls. It is [...]
A Led lights are a short either long bunch of huge-brightness Led lights. They give a luminous, extensive and forcing pole of light ahead, behind or to the side. They feed a powerful profit for dark driving or when fluorescent [...]
As a multimedia student author knows the lighting cost for video production is so high. As a result, he thought If he can do a research about the low cost lighting, it will be helpful for others. And he asked some production [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Critical Thinking Questions
- ATP and NADPH are forms of chemical energy produced from the light dependent reactions to be used in the light independent reactions that produce sugars.
- ATP and NADPH are forms of chemical energy produced from the light independent reactions, to be used in the light dependent reactions that produce sugars.
- ATP and NADPH are forms of chemical energy produced from the light dependent reactions to be used in the light independent reactions that produce proteins.
- ATP and NADPH are forms of chemical energy produced from the light dependent reactions to be used in the light independent reactions that use sugars as reactants.
- NADPH and ATP molecules are produced during the light-independent reactions and are used to power the light-dependent reactions.
- Sugar and ATP are produced during the light-dependent reactions and are used to power the light-independent reactions.
- Carbon dioxide and NADPH are produced during the light-independent reactions and are used to power the light-dependent reactions.
- NADPH and ATP molecules are produced during the light-dependent reactions and are used to power the light-independent reactions.
Examine the illustration of the photosynthesis equation. How does the equation relate to both photosynthesis and cellular respiration, and what is the connection between the two processes?
- Photosynthesis utilizes energy to build carbohydrates, while cellular respiration metabolizes carbohydrates.
- Photosynthesis utilizes energy to metabolize carbohydrates, while cellular respiration builds carbohydrates.
- Photosynthesis and cellular respiration both utilize carbon dioxide and water to produce carbohydrates.
- Photosynthesis and cellular respiration both metabolize carbohydrates to produce carbon dioxide and water.
- When photons strike photosystem (PS) I, pigments pass the light energy to chlorophyll, molecules that excite electrons, which are then passed to the electron transport chain. The cytochrome complex then transfers protons across the thylakoid membrane and transfers electrons from PS-II to PS-I. The products of the light-dependent reaction are used to power the Calvin cycle to produce glucose.
- When photons strike photosystem (PS) II, pigments pass the light energy to chlorophyll a molecules that in turn excite electrons, which are then passed to the electron transport chain. The cytochrome complex transfers protons across the thylakoid membrane and transfers electrons from PS-I to PS-II. The products of the light-dependent reaction are used to power the Calvin cycle to produce glucose.
- When photons strike photosystem (PS) II, pigments pass the light energy to chlorophyll a molecules that excite electrons, which are then passed to the electron transport chain. The cytochrome complex transfers protons across the thylakoid membrane and transfers electrons from PS-II to PS-I. The products of the light-dependent reaction are used to power the Calvin cycle to produce glucose.
- When photons strike photosystem (PS) II, pigments pass the light energy to chlorophyll a molecules that excite electrons, which are then passed to the electron transport chain. The cytochrome complex transfers protons across the thylakoid membrane and transfers electrons from PS II to PS I. The products of the light-independent reaction are used to power the Calvin cycle to produce glucose.
- Because UV rays and X-rays are high-energy waves, they penetrate the tissues and thus damage cells.
- Because UV rays and X-rays are long-wavelength waves, they penetrate the tissues and thus damage cells.
- Because UV rays and X-rays are low-energy waves, they cannot penetrate tissues and thus damage cells.
- Because UV rays and X-rays are low-frequency waves, they can penetrate tissues and thus damage cells.
- Photosynthesis is not possible.
- Photosynthesis is possible.
- Photosynthesis is possible only with blue light.
- Photosynthesis is possible only with green light.
- After splitting water in PS-I, high-energy electrons are delivered through the chloroplast electron transport chain to PS-II.
- After the photosynthesis reaction, released products like glucose help in the transfer of electrons from PS-II to PS-I.
- After splitting water in PS-II, high-energy electrons are delivered through the chloroplast electron transport chain to PS-I.
- After the completion of the light-dependent reactions, the electrons are transferred from PS-II to PS-I.
- This event will have no effect on the rate of photosynthesis in the leaf.
- Photosynthesis in the leaf will slow down or possibly stop.
- Photosynthesis in the leaf will increase exponentially.
- Photosynthesis in the leaf will first decrease and then increase.
- The product of the Calvin cycle is glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate and RuBP is regenerated.
- The product of the Calvin cycle is glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate and RuBisCO is regenerated.
- The product of the Calvin cycle is a 3-PGA molecule and glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate is regenerated.
- The product of the Calvin cycle is glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate and oxygen is regenerated.
- by using CAM photosynthesis and by closing stomatal pores during the night
- by using CAM photosynthesis and by opening stomatal pores during the night
- by using CAM photosynthesis and by keeping stomatal pores closed at all times
- by bypassing CAM photosynthesis and by keeping stomatal pores closed at night
- The prey of lions are generally herbivores, which depend on heterotrophs.
- The prey of lions are generally smaller carnivorous animals, which depend on non-photosynthetic organisms.
- The prey of lions are generally herbivores, which depend on autotrophs.
- The prey of lions are generally autotrophs, which depend onother autotrophs.
- It takes three turns to fix enough oxygen to export one G3P molecule.
- It takes three turns to produce RuBisCO as an end product.
- It takes three turns to produce ATP and NADPH for fixation of G3P.
- It takes three turns to fix enough carbon to export one G3P molecule.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/biology-ap-courses/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Julianne Zedalis, John Eggebrecht
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Biology for AP® Courses
- Publication date: Mar 8, 2018
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/biology-ap-courses/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/biology-ap-courses/pages/8-critical-thinking-questions
© Jan 8, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
According to the following equation of the photosynthesis, C → O2 + 2H20 + photons (CH2O)n + electrons + O2 carbon monoxide and water are transferred into carbohydrates under the light with the release of atmospheric oxygen. The purpose of cellular respiration is to convert nutrients into energy. The reactants of the respiration are glucose ...
Almost a reverse of what cellular respiration exhibits; photosynthesis combines carbon dioxide molecules and water obtained from its roots, and captures light energy to start the chemical process in which it creates energy and its byproducts. Its "waste" byproducts include that of glucose, and oxygen gas which exits from the leaves.
Photosynthesis and aerobic cellular respiration are key metabolic pathways. Photosynthesis is essential to all life on earth; both plants and animals depend on it (Figure 8.2 8. 2 ) . It is the only biological process that can capture energy that originates in outer space (sunlight) and convert it into chemical compounds (carbohydrates) that ...
The carbon dioxide is again utilized during photosynthesis to continue the cycle. The relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration can be best understood using the chemical equations given below: Equations. Photosynthesis: 6CO 2 + 12H 2 O + sunlight → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 + 6H 2 O. Cellular Respiration: C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 → ...
Cellular respiration involves the breakdown of glucose and the storage of the energy received into the molecule ATP. Plants create their own energy through photosynthesis and also use cellular respiration to produce ATP. Animals must rely on the sugars that they've gathered from plants to supply their mitochondria material to produce ATP.
Cellular Respiration: C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 → 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O. Photosynthesis: 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2. Photosynthesis makes the glucose that is used in cellular respiration to make ATP. The glucose is then turned back into carbon dioxide, which is used in photosynthesis. While water is broken down to form oxygen during ...
On a simplified level, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are opposite reactions of each other. In photosynthesis, solar energy is harvested as chemical energy in a process that converts water and carbon dioxide to glucose. Oxygen is released as a byproduct. In cellular respiration, oxygen is used to break down glucose, releasing chemical ...
The photosynthesis equation is CO2 (carbon dioxide)+H2O (water)+light energy=C6H12O6 (glucose) & O2 (oxygen). Cellular respiration is a process plants use at night for energy. This happens in the mitochondria's of plant cells. The resources needed for this are energy, carbon dioxide, water, and heat. Cellular respiration is the inverse of ...
On a simplified level, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are opposite reactions of each other. In photosynthesis, solar energy is harvested as chemical energy in a process that converts water and carbon dioxide to glucose. Oxygen is released as a byproduct. In cellular respiration, oxygen is used to break down glucose, releasing chemical ...
Cellular respiration is a process that happens inside an organism's cells. This process releases energy that can be used by the organism to live and grow. Many food molecules are broken down into glucose, a simple sugar. Glucose is used in cellular respiration. Glucose and oxygen are inputs of cellular respiration.
This process is called photosynthesis and occurs in the chloroplast of the plant cell. Plants take in carbon dioxide through tiny openings or pores in their leaves called stomata. Special cells in the leaves of plants called guard cells open and close the stomata. Cellular respiration is a process that occurs in the mitochondria of all organisms.
Chapter 3 - Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration. 35224. The atom is the smallest and most fundamental unit of matter. It consists of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Atoms combine to form molecules, which are chemical structures consisting of at least two atoms held together by a chemical bond. In plants, animals, and many other types of ...
Conclusion: Unraveling the Mysteries of Life's Energy Flow. In conclusion, photosynthesis and cellular respiration stand as integral processes in the symphony of life. Their orchestrated dance ensures the continuous flow of energy, sustaining the diverse forms of life on our planet. The unique adaptations seen in C4 and CAM pathways in ...
Differences between Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis. Occurs in all living organisms. Occurs only in phototrophs (all green plants, algae and some bacteria). The entire process occurs in Mitochondria. The entire process occurs in Chloroplasts. Glucose and oxygen are the reactants of this process.
During photosynthesis, a chemical change occurs in chloroplasts, and plants turn carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) into glucose and oxygen (O2). Cellular respiration occurs in EVERY LIVING CELL. Without it, plants would not have access to the energy in the sugar (glucose). Without energy, life cannot be maintained.
Photosynthesis: 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2. Photosynthesis makes the glucose that is used in cellular respiration to make ATP. The glucose is then turned back into carbon dioxide, which is used in photosynthesis. While water is broken down to form oxygen during photosynthesis, in cellular respiration oxygen is combined with hydrogen ...
The Cellular respiration and photosynthesis form a critical cycle of energy and matter that supports the continued existence of life on earth. Describe the stages of cellular respiration and photosynthesis and their interaction and interdependence including raw materials, products, and amount of ATP or glucose produced during each phase.
This occurred in several different projects, including the cellular respiration lab involving the respiration rate of germinating seeds, the potato core lab and the photosynthesis lab. In these labs, we were able to identify the biological processes that required energy for the different processes to take place to allow germination to occur.
Photosynthesis in the leaf will first decrease and then increase. 30 . Carbon, in the form of CO 2, must be taken from the atmosphere and attached to an existing organic molecule in the Calvin cycle. Therefore, the carbon is bound to the molecule. The products of the cycle only occur because of the added carbon.
Photosynthesis is the process through which plants make their food by converting light energy into chemical energy. Likewise, respiration is the process of burning sugars to provide energy for growth and reproduction of the plants. In this experiment, the effect of temperature on CO2 concentration in water containing Elodea was studied to see ...
Match. Shelby_Harris4444. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like how are photosynthesis and cellular respiration interdependent?, do all living organisms preform photosynthesis?, do all living organisms preform cellular respiration? and more.