Revolutionize Your Research with Jenni AI

Literature Review Generator
Welcome to Jenni AI, the ultimate tool for researchers and students. Our AI Literature Review Generator is designed to assist you in creating comprehensive, high-quality literature reviews, enhancing your academic and research endeavors. Say goodbye to writer's block and hello to seamless, efficient literature review creation.

Loved by over 1 million academics

Endorsed by Academics from Leading Institutions
Join the Community of Scholars Who Trust Jenni AI

Elevate Your Research Toolkit
Discover the Game-Changing Features of Jenni AI for Literature Reviews
Advanced AI Algorithms
Jenni AI utilizes cutting-edge AI technology to analyze and suggest relevant literature, helping you stay on top of current research trends.
Get started

Idea Generation
Overcome writer's block with AI-generated prompts and ideas that align with your research topic, helping to expand and deepen your review.
Citation Assistance
Get help with proper citation formats to maintain academic integrity and attribute sources correctly.

Our Pledge to Academic Integrity
At Jenni AI, we are deeply committed to the principles of academic integrity. We understand the importance of honesty, transparency, and ethical conduct in the academic community. Our tool is designed not just to assist in your research, but to do so in a way that respects and upholds these fundamental values.
How it Works
Start by creating your account on Jenni AI. The sign-up process is quick and user-friendly.
Define Your Research Scope
Enter the topic of your literature review to guide Jenni AI’s focus.
Citation Guidance
Receive assistance in citing sources correctly, maintaining the academic standard.
Easy Export
Export your literature review to LaTeX, HTML, or .docx formats
Interact with AI-Powered Suggestions
Use Jenni AI’s suggestions to structure your literature review, organizing it into coherent sections.
What Our Users Say
Discover how Jenni AI has made a difference in the lives of academics just like you

· Aug 26
I thought AI writing was useless. Then I found Jenni AI, the AI-powered assistant for academic writing. It turned out to be much more advanced than I ever could have imagined. Jenni AI = ChatGPT x 10.

Charlie Cuddy
@sonofgorkhali
· 23 Aug
Love this use of AI to assist with, not replace, writing! Keep crushing it @Davidjpark96 💪

Waqar Younas, PhD
@waqaryofficial
· 6 Apr
4/9 Jenni AI's Outline Builder is a game-changer for organizing your thoughts and structuring your content. Create detailed outlines effortlessly, ensuring your writing is clear and coherent. #OutlineBuilder #WritingTools #JenniAI

I started with Jenni-who & Jenni-what. But now I can't write without Jenni. I love Jenni AI and am amazed to see how far Jenni has come. Kudos to http://Jenni.AI team.

· 28 Jul
Jenni is perfect for writing research docs, SOPs, study projects presentations 👌🏽

Stéphane Prud'homme
http://jenni.ai is awesome and super useful! thanks to @Davidjpark96 and @whoisjenniai fyi @Phd_jeu @DoctoralStories @WriteThatPhD
Frequently asked questions
What exactly does jenni ai do, is jenni ai suitable for all academic disciplines, is there a trial period or a free version available.
How does Jenni AI help with writer's block?
Can Jenni AI write my literature review for me?
How often is the literature database updated in Jenni AI?
How user-friendly is Jenni AI for those not familiar with AI tools?
Jenni AI: Standing Out From the Competition
In a sea of online proofreaders, Jenni AI stands out. Here’s how we compare to other tools on the market:
Feature Featire
COMPETITORS
Advanced AI-Powered Assistance
Uses state-of-the-art AI technology to provide relevant literature suggestions and structural guidance.
May rely on simpler algorithms, resulting in less dynamic or comprehensive support.
User-Friendly Interface
Designed for ease of use, making it accessible for users with varying levels of tech proficiency.
Interfaces can be complex or less intuitive, posing a challenge for some users.
Transparent and Flexible Pricing
Offers a free trial and clear, flexible pricing plans suitable for different needs.
Pricing structures can be opaque or inflexible, with fewer user options.
Unparalleled Customization
Offers highly personalized suggestions and adapts to your specific research needs over time.
Often provide generic suggestions that may not align closely with individual research topics.
Comprehensive Literature Access
Provides access to a vast and up-to-date range of academic literature, ensuring comprehensive research coverage.
Some may have limited access to current or diverse research materials, restricting the scope of literature reviews.
Ready to Transform Your Research Process?
Don't wait to elevate your research. Sign up for Jenni AI today and discover a smarter, more efficient way to handle your academic literature reviews.
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

Automate your literature review with AI

Table of Contents
Traditional methods of literature review can be susceptible to errors . Whether it’s overcoming human bias ">human bias or sifting through an incredibly large amount of scientific research being published today. Not to forget all the papers that have already been published in the past 100 years. Putting both together makes a heap of information that is humanly impossible to sift through. At least do so in an efficient way.
Thanks to artificial intelligence, long and tedious literature reviews are becoming quick and comprehensive. No longer do researchers have to spend endless hours combing through stacks of books and journals.
In this blog post, we'll dive deep into the world of automating your literature review with AI, exploring what a literature review is, why it's so crucial, and how you can harness AI tools to make the process more effective.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is essentially the foundation of a scientific research project, providing a comprehensive overview of existing knowledge on a specific topic. It gives an overview of your chosen topic and summarizes key findings, theories, and methodologies from various sources.
This critical analysis not only showcases the current state of understanding but also identifies gaps and trends in the scientific literature. In addition, it also shows your understanding of your field and can help provide credibility to your research paper .
Types of literature review
There are several types of literature reviews but for the most part, you will come across five versions. These are:
1. Narrative review: A narrative review provides a comprehensive overview of a topic, usually without a strict methodology for selection.
2. Systematic review: Systematic reviews are a strategic synthesis of a topic. This type of review follows a strict plan to identify, evaluate, and critique all relevant research on a topic to minimize bias.
3. Meta-analysis: It is a type of systematic review that uses research data from multiple articles to draw quantitative conclusions about a specific phenomenon.
4. Scoping review: As the name suggests, the purpose of a scoping review is to study a field, highlight the gaps in it, and underline the need for the following research paper.
5. Critical review: A critical literature review assesses and critiques the strengths and weaknesses of existing literature, challenging established ideas and theories.
Benefits of using literature review AI tools?
Using literature review AI tools can be a complete game changer in your research. They can make the literature review process smarter and hassle-free. Here are some practical benefits:
AI tools for literature review can skim through tons of research papers and find the most relevant one for your topic in no time, thus saving you hours of manual searching.
Comprehensive insights
No matter how complex the topic is or how long the research papers are, AI tools can find key insights like methodology, datasets, limitations, etc, by simply scanning the abstracts or PDF documents.
Eliminate bias
AI doesn't have favorites. Based on the data it’s fed, it evaluates research papers objectively and reduces as much bias in your literature review as possible.
Faster research questions
AI tools present loads of research papers in the same place. Some AI tools let you create visual maps and connections, thus helping you identify gaps in existing literature and arriving at your research question faster.
Consistency
AI tools ensure your review is consistently structured and formatted . They can also check for proper grammar and citation style, which is crucial for scholarly writing.
Multilingual support
There are heaps of non-native English-speaking researchers who can struggle with understanding scientific jargon in English. AI tools with multilingual support can help such academicians conduct their literature review in their own language.
How to write a literature review with AI
Now that we understand the benefits of a literature review using artificial intelligence, let's explore how you can automate the process. Literature reviews with AI-powered tools can save you countless hours and allow a more comprehensive and systematic approach. Here's one process you can follow:
Choose the right AI tool
Several AI search engines like Google Scholar, SciSpace, Semantic Scholar help you find the most relevant papers semantically. Or in other words even without the right keywords. These tools understand the context of your search query and deliver the results.
Find relevant research papers
Once you input your research question or keywords into a search engine like Google Scholar, Semantic Scholar, or SciSpace, it scours millions of papers worth of databases to find relevant articles. After that, you can narrow your search results to a certain time period, journals, number of citations, and other parameters for more accuracy.
Analyze the search results
Now that you have your list of relevant academic papers, the next step would be reviewing these results. A lot of AI-powered tools for literature review will often provide summaries along with the paper. Some sophisticated tools also help you gather key points from multiple papers at once and let you ask questions regarding that topic. This way, you can get an understanding of the topic and further have a better understanding of your field.
Organize your collection
Whether you’re writing a literature review or your paper, you will need to keep track of your references. Using AI tools, you can efficiently organize your findings, store them in reference managers, and instantly generate citations automatically, saving you the hassle of manually formatting references.
Write the literature review
Now that you’ve done your groundwork, you can start writing your literature review. Although you should be doing this yourself, you can use tools like paraphrasers, grammar checkers, and co-writers to help you refine your academic writing and get your point across with more clarity.
Best AI Tools for Literature Review
Since generative AI and ChatGPT came into the picture, there are heaps of AI tools for literature review available out there. Some of the most comprehensive ones are:
SciSpace is a valuable tool to have in your arsenal. It has a repository of 270M+ papers and makes it easy to find research articles. You can also extract key information to compare and contrast multiple papers at the same time. Then, go on to converse with individual papers using Copilot, your AI research assistant.
Love using SciSpace tools? Enjoy discounts! Use SR40 (40% off yearly) and SR20 (20% off monthly). Claim yours here 👉 SciSpace Premium
Research Rabbit
Research Rabbit is a research discovery tool that helps you find new, connected papers using a visual graph. You can essentially create maps around metadata, which helps you not only explore similar papers but also connections between them.
Iris AI is a specialized tool that understands the context of your research question, lets you apply smart filters, and finds relevant papers. Further, you can also extract summaries and other data from papers.
If you already don’t know about ChatGPT , you must be living under a rock. ChatGPT is a chatbot that creates text based on a prompt using natural language processing (NLP). You can use it to write the first draft of your literature review, refine your writing, format it properly, write a research presentation, and many more things.
Things to keep in mind when using literature review AI tools
While AI-powered tools can significantly streamline the literature review process, there are a few things you should keep in mind while employing them:
Quality control
Always review the results generated by AI tools. AI is powerful but not infallible. Ensure that you do further analysis by yourself and determine that the selected research articles are indeed relevant to your research.
Ethical considerations
Be aware of ethical concerns, such as plagiarism and AI writing. Use of AI is still frowned upon so make sure you do a thorough check for originality of your work, which is vital for maintaining academic integrity.
Stay updated
The world of AI is ever-evolving. Stay updated on the latest advancements in AI tools for literature review to make the most of your research.
In conclusion
Artificial intelligence is a game-changer for researchers, especially when it comes to literature reviews. It not only saves time but also enhances the quality and comprehensiveness of your work. With the right AI tool and a clear research question in hand, you can build an excellent literature review.
A few more good reads for you!
Types of Essays in Academic Writing
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
You might also like

Introducing SciSpace’s Citation Booster To Increase Research Visibility

How To Write An Argumentative Essay

Beyond Google Scholar: Why SciSpace is the best alternative
RAxter is now Enago Read! Enjoy the same licensing and pricing with enhanced capabilities. No action required for existing customers.
Your all in one AI-powered Reading Assistant
A Reading Space to Ideate, Create Knowledge, and Collaborate on Your Research
- Smartly organize your research
- Receive recommendations that cannot be ignored
- Collaborate with your team to read, discuss, and share knowledge
From Surface-Level Exploration to Critical Reading - All in one Place!
Fine-tune your literature search.
Our AI-powered reading assistant saves time spent on the exploration of relevant resources and allows you to focus more on reading.
Select phrases or specific sections and explore more research papers related to the core aspects of your selections. Pin the useful ones for future references.
Our platform brings you the latest research related to your and project work.
Speed up your literature review
Quickly generate a summary of key sections of any paper with our summarizer.
Make informed decisions about which papers are relevant, and where to invest your time in further reading.
Get key insights from the paper, quickly comprehend the paper’s unique approach, and recall the key points.
Bring order to your research projects
Organize your reading lists into different projects and maintain the context of your research.
Quickly sort items into collections and tag or filter them according to keywords and color codes.
Experience the power of sharing by finding all the shared literature at one place.
Decode papers effortlessly for faster comprehension
Highlight what is important so that you can retrieve it faster next time.
Select any text in the paper and ask Copilot to explain it to help you get a deeper understanding.
Ask questions and follow-ups from AI-powered Copilot.
Collaborate to read with your team, professors, or students
Share and discuss literature and drafts with your study group, colleagues, experts, and advisors. Recommend valuable resources and help each other for better understanding.
Work in shared projects efficiently and improve visibility within your study group or lab members.
Keep track of your team's progress by being constantly connected and engaging in active knowledge transfer by requesting full access to relevant papers and drafts.
Find papers from across the world's largest repositories

Testimonials
Privacy and security of your research data are integral to our mission..

Everything you add or create on Enago Read is private by default. It is visible if and when you share it with other users.

You can put Creative Commons license on original drafts to protect your IP. For shared files, Enago Read always maintains a copy in case of deletion by collaborators or revoked access.

We use state-of-the-art security protocols and algorithms including MD5 Encryption, SSL, and HTTPS to secure your data.
AI Literature Review Generator
Effortlessly generate comprehensive literature reviews with our AI-powered tool, saving time and enhancing research quality.
2M+ Professionals choose us
AI Review Benefits
Time-saving.
Generate detailed literature reviews in less time, allowing you to focus on research and analysis.
Enhanced Quality
Produce comprehensive and high-quality literature reviews with the assistance of advanced AI algorithms.
Improved Efficiency
Streamline your research process by efficiently generating literature reviews using AI technology.
AI Literature Review Generator Benefits
Efficient research.
AI writing tools offer a comprehensive database for literature review, accelerating the research process. By providing access to a vast collection of scholarly articles, these tools save time and effort that would otherwise be spent on manual searches. Researchers can swiftly identify relevant sources, enhancing the efficiency of their literature review process.
Moreover, the ability to filter search results based on specific criteria ensures that the retrieved content aligns with the research requirements. This precision in sourcing information streamlines the review process, enabling researchers to focus on analyzing and synthesizing the gathered data.

Enhanced Content Quality
Utilizing AI tools for writing elevates the quality of literature reviews by offering advanced language processing capabilities. These tools facilitate the identification of key themes, trends, and insights within the literature, enabling researchers to produce more in-depth and well-structured reviews.
Additionally, the automated citation and referencing features ensure accuracy and consistency in academic writing, saving researchers from the tedious task of manually managing citations. This not only enhances the overall quality of the literature review but also reduces the likelihood of errors.

Collaborative Capabilities
Online writing tools foster seamless collaboration among researchers by providing features for shared document editing and real-time feedback. This collaborative environment promotes effective teamwork, allowing multiple contributors to collectively work on the literature review, share insights, and provide constructive feedback.
Furthermore, these tools offer version history tracking, ensuring transparency and accountability in the collaborative writing process. With the ability to track changes and contributions, researchers can easily monitor the evolution of the literature review and attribute specific contributions to team members.

Best AI Writing Tools - Useful Tips
Utilize advanced features.
When using the best AI tools for writing, explore advanced features such as natural language processing and sentiment analysis to gain deeper insights from the literature. These features can help in identifying underlying emotions, biases, and perspectives within the reviewed content, adding depth to the analysis.
Moreover, leverage the data visualization capabilities offered by AI writing tools to present the literature review findings in an engaging and comprehensible manner, enhancing the overall impact of the research.
Continuous Learning
Stay updated with the latest advancements in AI writing tools for authors to harness the full potential of these technologies. Regularly explore new features, updates, and best practices to optimize the efficiency and effectiveness of literature review generation.
Engaging in continuous learning ensures that researchers remain at the forefront of utilizing AI tools for writing, empowering them to leverage cutting-edge capabilities for producing high-quality literature reviews.
Optimize Collaboration
Maximize the collaborative benefits of AI writing tools by establishing clear communication channels and defining roles within the research team. Effective communication ensures that all team members are aligned with the literature review goals and enables streamlined coordination in the review process.
Additionally, establish regular checkpoints to review the progress and address any challenges, fostering a collaborative environment that maximizes the collective expertise of the research team.
Customize Search Parameters
Tailor the search parameters within AI literature review generators to align with the specific research objectives. By customizing search filters based on publication dates, relevance, or specific keywords, researchers can refine the search results to precisely match the requirements of the literature review.
This customization enhances the accuracy and relevance of the retrieved literature, ensuring that the generated review is comprehensive and aligned with the research focus.
Utilize Citation Management
Effectively utilize the citation management features offered by AI writing tools for authors to streamline the referencing process. Organize and manage citations seamlessly, ensuring adherence to the required citation styles and formatting guidelines throughout the literature review.
By leveraging these citation management capabilities, researchers can maintain consistency and accuracy in citing sources, enhancing the credibility and scholarly integrity of the literature review.
How to use Article Generator
Choose a template.
Select the necessary template from the template gallery.

Provide more details
Fill out the carefully selected inputs to create the best quality of output content.
Enjoy the results
Copy, save for later, rate the output or hit regenerate button.

AI Literature Review Generator Examples
Discover the power of AI literature review generators with these practical examples showcasing their effectiveness in generating comprehensive and insightful literature reviews tailored to specific research queries.
Craft a comprehensive literature review addressing the impact of AI in medical research, highlighting the advancements, challenges, and future implications of AI integration in healthcare.
AI literature review generators provide a valuable resource for synthesizing the extensive body of medical research related to artificial intelligence. By inputting specific keywords such as 'AI in healthcare' and 'medical research advancements,' the tool swiftly retrieves a diverse range of scholarly articles, enabling the identification of key themes and insights.
The generated literature review encompasses a comprehensive analysis of the impact of AI in medical research, encapsulating the advancements, challenges, and future implications of AI integration in healthcare. Through the tool's advanced natural language processing capabilities, the review delves into the underlying perspectives, sentiments, and potential biases within the analyzed literature, providing a nuanced understanding of the subject matter.
Furthermore, the AI writing tool streamlines the citation and referencing process, ensuring the accurate attribution of sources and adherence to citation guidelines. The collaborative features of the tool facilitate seamless teamwork, allowing multiple researchers to collectively contribute to the literature review, share insights, and refine the analysis.
The generated literature review is presented with compelling data visualizations, effectively conveying the synthesized information in a visually engaging format. This example underscores the efficacy of AI literature review generators in producing comprehensive and insightful reviews tailored to specific research queries, showcasing their indispensable role in advancing medical research and scholarly discourse.
Create a literature review exploring the intersection of AI and environmental studies, focusing on the applications, implications, and ethical considerations of AI technologies in environmental research and conservation.
For researchers delving into the intersection of AI and environmental studies, AI literature review generators offer a robust platform for consolidating a diverse array of scholarly resources. By inputting targeted keywords such as 'AI applications in environmental research' and 'ethical considerations of AI in conservation,' the tool retrieves an extensive range of literature, enabling the synthesis of key insights and perspectives.
The generated literature review provides a comprehensive exploration of the applications, implications, and ethical considerations of AI technologies in environmental studies and conservation. Leveraging the tool's advanced features, the review delves into the nuanced perspectives and sentiments within the analyzed content, enhancing the depth of the analysis.
Moreover, the citation management capabilities of the AI writing tool ensure the seamless organization and adherence to citation guidelines, maintaining the scholarly integrity of the review. The collaborative environment facilitated by the tool allows researchers to collectively contribute to the literature review, fostering an environment of shared insights and collaborative refinement.
The literature review is presented with impactful data visualizations, effectively conveying the synthesized information in an engaging manner. This example exemplifies the effectiveness of AI literature review generators in generating comprehensive and insightful reviews tailored to specific research queries, illustrating their pivotal role in advancing environmental research and fostering informed discourse.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an ai literature review generator, how do ai writing tools benefit literature review creation, what are some examples of ai-powered writing assistance tools, why use ai-powered writing tools for literature review generation, how can ai writing tools improve the quality of literature reviews, where can i find the best ai writing tools for literature review creation, join 1,000,000+ creators and professionals from trusted companies by choosing us, .css-1d7fhal{margin:0;font-family:"roboto","helvetica","arial",sans-serif;font-weight:400;font-size:1rem;line-height:1.5;letter-spacing:0.00938em;max-width:700px;}@media (min-width:0px){.css-1d7fhal{font-size:24px;font-weight:600;line-height:32px;font-family:'__inter_6eddd9','__inter_fallback_6eddd9';}}@media (min-width:744px){.css-1d7fhal{font-size:45px;font-weight:600;line-height:52px;font-family:'__inter_6eddd9','__inter_fallback_6eddd9';}} have a task that has no tool our chat knows how to do it.

Literature Review AI
Ai-powered literature review tool.
- Conduct academic research: Use the Literature Review AI to get a comprehensive overview of the current state of research on your topic. This tool can highlight gaps in the existing literature and suggest potential directions for future research.
- Prepare a research proposal: Use this tool to conduct a literature review as part of your research proposal. It can help you identify key theories, arguments, and findings related to your research question.
- Write a thesis or dissertation: The Literature Review AI can help you write the literature review section of your thesis or dissertation, saving you time and effort in the research process.
- Stay updated on the latest research: Use this tool to stay updated on the latest research in your field. It can help you identify recent studies and trends that are relevant to your work.
New & Trending Tools
Ai text message responder, chemistry expert ai.

Free Online Literature Review Generator
It’s free and easy to use. A simple upload of your content and your Literature Reviews are autogenerated.
Create Literature Reviews by repurposing audio or video content
The AI works fully automated
No prompt engineering required
Experience the power of AI without needing prompts
Train your AI to exactly sound like you
You can train your AI on a piece of content of yours
Autogenerate Literature Reviews
Create Literature Reviews based on the best templates from top-marketers. You will get your insights in the best format possible.
Extracted from your existing content
Work with your team, edit and download Literature Reviews
Literature Reviews that sound like you
You can train your Free Online Literature Review Generator to sound like you, so you Literature Reviews are always in your own tone and style—the opposite of generating generic-sounding content out of thin air.
AI-based content repurposing for your Literature Reviews
Creating Literature Reviews is part of every good content marketing strategy. And now it has become even more accessible with Free Online Literature Review Generator.

The best Free Online Literature Review Generator.
Create Literature Reviews based on your insights, and that sounds like you inside Unifire, thanks to all the Free Online Literature Review Generator’s unique AI-powered features.
Your content is generated based on the best creator templates and hook frameworks.
Collaboration
Unifire is built for collaboration. Live editing, unlimited team members and workspaces included.
Train your AI
AI’s that can sound like you and learn your own writing style. From vocabulary to sentence structure.
What are Literature Reviews?
Literature reviews are critical assessments of existing research on a specific topic. They synthesize key findings, identify trends, and highlight gaps in the literature, guiding future research directions and informing readers about the current state of knowledge.
How to use the Free Online Literature Review Generator
It couldn’t be easier: Upload a piece of content, audio or video. Let the tool transcribe it and produce your Literature Reviews.
You can upload audio & video files, directly or via a link. After 2-4 mins you will receive your transcript. Autogenerated.
Auto transcription
We have the best transcription running in the background. 97% accuracy on even the most technical topics speaks for itself.
Edit your transcription
No AI is 100% perfect. So, we let you edit your transcript before hitting the generate content button.
Autogeneration
Free Online Literature Review Generator automatically generates your Literature Reviews, based on the best templates we could find. So your content is in the best shape when you get it.
Edit & Collaborate
Free Online Literature Review Generator is entirely collaborative and comes with unlimited team seats, workspaces and a full collaborative suite.
Once you’re ready to distribute, simply copy & paste your content into your favourite tools.
Questions about the Free Online Literature Review Generator
It’s free for your first upload. You get 900 credits every month for free to use.
This is dependent on the length of your upload. If you upload 5 hours it will create much more content than if you upload only 5 mins.
Yes, you can train the AI to adopt your own tone & style. This includes sentence structures, vocabulary and more.
Some of the best Free Online Literature Review Generator include Jasper, Reword, Anyword, and others.
Book Title Generator for creating perfect Book Titles
Youtube description maker for creating perfect youtube descriptions, ai book title generator for creating perfect book titles, youtube title generator for creating perfect youtube titles, youtube video transcript generator free for creating perfect transcripts, ai personal statement writer for creating perfect statements, book hashtag generator for creating perfect book hashtags, ai book creator for creating perfect book content, ai outline writer for creating perfect outlines, hook sentence generator for creating perfect hook sentences, your literature reviews deserve to be perfect, and so does the rest of your content.
Repurpose and scale content whether you are a seasoned marketer or a total novice.
Screen, analyse and summarise articles faster with Scholarcy
Try it for free, subscribe today.
Scholarcy is used by students around the world to read and analyse research papers in less time. Upload your articles to Scholarcy to:
- Cut your reading time in half and feel more in control
- Identify the papers that matter in less time
- Jump straight to the most important information
- Compare a collection of articles more easily
With Scholarcy Library, you can import all your papers and search results, and quickly screen them with the automatically generated ‘key takeaway’ headline.
Take the stress out of your literature review
While there are lots of tools that help you discover articles for your research, how do you analyse and synthesise the information from all of those papers?
3 easy ways to import articles
Scholarcy lets you quickly import your articles for screening and analysing.
Import papers in PDF, Word, HTML and LaTeX format
Import search results from PubMed or any service that provides results in RIS or BibTeX format
Import publisher RSS feeds
Build your literature matrix in minutes
Our Excel export feature generates a literature synthesis matrix for you, so you can
Compare papers side by side for their study sizes, key contributions, limitations, and more.
Export literature-review ready data in Excel, Word, RIS or Markdown format
Integrates with your reference manager and ‘second brain’ tools such as Roam, Notion and Obsidian
Carrying out a systematic review?
Scholarcy breaks papers down into our unique summary flashcard format.
The Study subjects and analysis tab shows you study population, intervention, outcome, and statistical analyses from the paper.
And the Excel synthesis matrix generated shows the key methods and quantitative findings of each paper, side by side.
Build a knowledge graph from your papers
If you’re a fan of the latest generation of knowledge management tools such as Roam or Obsidian , you’ll love our Markdown export.
This creates a knowledge graph of all the papers in your library by connecting them via key terms, methods, and shared citations.
What People Are Saying
“Quick processing time, successfully summarized important points.”
“It’s really good for case study analysis, thank you for this too.”
“I love this website so much it has made my research a lot easier thanks!”
“The instant feedback I get from this tool is amazing.”
“Thank you for making my life easier.”
Privacy Overview
Literary Analysis Maker
The literary analysis maker is an AI-powered online tool that can generate literary analysis in just a few seconds! It can help college and high school students with literary criticism assignments, saving time and effort. In addition, our generator can help students improve their literary analysis skills and serve as a source of inspiration!
Try our literary analysis maker right now to see how it works!
- ✒️ What Is Literary Analysis?
- 💫 Tool Benefits
- 💡 Ideas for Literary Analysis
- ✍️ Literary Analysis Prompts
- 📋 Literary Analysis Structure
🔗 References
✒️ what does literary analysis mean.
Literary analysis is a written evaluation of the elements of a literary work, for example, a poem, short story, novel, etc. It aims to deepen one's understanding of the work's ideas and impact on the readers.
Literary analysis is not just about summarizing what you read . It involves deconstructing the artwork to evaluate its parts, including plot, character, setting, theme, style, and symbolism. This assignment provides an opportunity to learn more about the underlying meanings of a literary work and see how its elements help the author convey the intended message.
💫 Literary Analysis Maker: Benefits
The literary analysis essay writer has a lot of benefits for its users. Check the table below to learn more!
💡 What to Write a Literary Analysis on?
If you are wondering what to write a literary analysis on, do not panic! Below, we've listed all the important elements of literary analysis with brief instructions on how to evaluate them.
✍️ Literary Analysis Essay Prompts
Looking for some inspiration? You are on the right page! Check our writing prompts on literary analysis to find a lot of fresh ideas!
To Kill a Mockingbird Literary Criticism Essay
In your essay on To Kill a Mockingbird , you can discover and analyze autobiographical elements. Note how Harper Lee uses characters like Atticus Finch and Scout in her novel to reflect experiences from her own life, particularly surrounding discrimination, racism, and rape. Discuss how the novel's setting, historical context, symbolism, and imagery reinforce Lee's core message.
Hamlet Literary Analysis Essay
To write a good analysis of Shakespeare's Hamlet , investigate dialogues, soliloquies, and the play's vivid and rich language filled with rhetorical devices . You can devote particular attention to such literary devices as allusion and metaphors and add your point of view on the impact of Hamlet on the audience.
The Great Gatsby Literary Criticism Essay
Analyze the significance of the clock in F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby as a symbol of time, focusing on its multi-faceted meaning and its impact on the characters and themes. Discuss how the clock represents Gatsby's attempt to control time and its connection to his ultimate fate.
A Raisin in the Sun Literary Analysis Essay
In a literary analysis essay on A Raisin in the Sun , you can analyze the theme of dreams in this novel. Discuss the characters of Ruth, Lena, Travis, Beneatha, and Walter, focusing on the personal dreams they yearn to achieve. Evaluate how the Younger family's dreams are affected by social, economic, and emotional circumstances.
Lord of the Flies Literary Analysis Essay
In your essay, analyze William Golding's portrayal of human nature in Lord of the Flies , focusing on the influence of the environment on people's behavior. Examine the character developments of Ralph, Jack, Simon, and others, revealing their experiences on an island that show both good and evil potential within each individual.
📋 How to Structure a Literary Analysis
The structure of literary criticism consists of 3 key parts: the introduction, main body, and conclusion. Check the table below to see what to include in each part.
❓ Literary Analysis Free: FAQ
Updated: Mar 28th, 2024
- Discovering Evidence for a Literary Analysis Essay – San José State University Writing Center
- Writing about Literature – Fordham University
- Literary Criticism – UTA Libraries
- Writing Your Literary Analysis – University of Hawaii
- Literary Analysis – Appalachian State University
- Free Essays
- Writing Tools
- Lit. Guides
- Donate a Paper
- Referencing Guides
- Free Textbooks
- Tongue Twisters
- Job Openings
- Expert Application
- Video Contest
- Writing Scholarship
- Discount Codes
- IvyPanda Shop
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Copyright Principles
- DMCA Request
- Service Notice
Our literary analysis maker will help you break down any piece of literature! Get a detailed review of the plot, narrative techniques, and other text elements in a few clicks. Additionally, read the guide to discover excellent literary analysis prompts and examples.
Article Review Generator
Here is your article critique :
Writing an article review can become a daunting task for any student. It requires analyzing the article's content, evaluating it, and sharing personal insights. Stuck with summarizing the article rather than criticizing it? Use this article review generator!
- ️🎤 What Is This Review Generator?
- ️👑 Article Review Generator Benefits
- ️🤔 When to Use the Tool
- ️✍️ How to Write an Article Review
- ️❓ Article Review Generator Free: FAQ
- ️🔗 References
🎤 What Is the Article Review Generator?
Our online article review generator is an excellent solution for crafting comprehensive reviews. It offers in-depth analysis while ensuring that the main ideas from the article are effectively highlighted. The tool allows students to focus on critical evaluation and personal insights rather than getting bogged down in summarization.
An article review is a piece that critically evaluates and analyzes a scholarly article or research paper. It involves summarizing the article's main points, assessing its strengths and weaknesses, and providing personal opinion.

You may need to write an article analysis:
- To provide a critique of a specific article or paper.
- To contribute to academic discourse by evaluating scholarly work.
- To improve your writing skills via summarizing, analyzing, and critiquing complex texts.
- To deepen understanding of a topic.
- To prepare for future research projects.
👑 Online Article Review Generator: 6 Benefits
Many benefits make our article review summary generator stand out. For example, it is:
🤔 When to Use the Article Reviewer Tool?
Our tool is not only helpful in writing article reviews, but it also comes in handy for a variety of other purposes. Here are some cases when you can use the article review summary generator:
- Analyze the article's strengths and weaknesses.
- Quickly understand the key points and arguments of the article.
- Get a new perspective on the article's content and structure.
- Generate a concise summary of an article.
- Understand complex articles more effectively.
- Improve writing skills .
- Be informed about current developments.
- Prepare for exams or presentations.
- Facilitate collaboration during group projects.
- Get multiple article summaries for the literature review.

✍️ How to Write an Article Review
You can always use our online article review generator to analyze and evaluate an article quickly. However, if you have time and want to enhance your academic writing skills, you might want to consider writing the review yourself. To help you with this, we've prepared a step-by-step guide for crafting a comprehensive article review .
Step 1 – Preparation
You should clearly understand the task's purpose to prepare for an article review. An article review is more than just a summary or sharing your personal opinion ; it involves a critical analysis and evaluation of the content.
Here are some crucial steps that will help you be fully prepared for writing an article review:
- Assess the title. Before delving into the article, consider what the title suggests about the content and the potential focus of the author's argument.
- Analyze the structure. Subheadings can offer a roadmap of the article's structure and organization. Focus on them to get an overview of the key topics and themes that the author will address.
- Understand the main idea. Identify the central argument or thesis of the article. This is the primary claim or position that the author is asserting.
- Analyze the abstract. The abstract provides a condensed summary of the entire article, offering a glimpse into the main arguments, research methodology, and conclusions.
Step 2 – Reading
Correctly reading an article is essential for making a well-informed evaluation , so don't underestimate this step. Take notes or use highlighters to keep track of the information you might refer to later. We recommend paying attention to:
- Intended audience . Determine who the article is addressing. Consider the level of expertise, interests, and background knowledge the author assumes about the readers.
- Author's purpose. Is the author aiming to summarize existing research, present a new argument, or refute others' claims?
- Key terms. Note whether the author defines key terms or concepts. A clear definition of terms helps in understanding the author's arguments effectively.
- Facts and opinions. Differentiate between factual information and the author's views. Assess the reliability and validity of the information presented.
- Central arguments and conclusions. Assess their clarity, coherence, and the extent to which they are supported by evidence and analysis.
- Methodology and results. Examine the methods and expected results in the article. Assess the credibility of the research and the reported findings' clarity.
- Visual aids. If the article includes illustrations or charts, assess their effectiveness in conveying information and supporting the content.
Step 3 – Outlining & Drafting
Creating an outline for an article review can help you organize your ideas and guarantee that your review is well-structured and coherent. Usually, the outline includes an introduction, the body of the review, and a conclusion.
When writing an outline, work on your thesis statement . A thesis statement is a sentence or two that presents the main argument you are making about the article. It is the central point that you will support and develop throughout your review.
After finishing your outline, you can move on to writing a draft. These are the main components for each section of an article review:
- Hook (attention-grabbing opening).
- Background information on the article.
- Thesis statement.
- Summary of the article.
- Analysis and evaluation.
- Restated thesis statement.
- Summary of your main points.
- Final evaluation of the article.
- Suggestions for further research or areas for improvement.
Step 4 – Writing
The final stage of writing an article critique involves reviewing and polishing the draft. It is important to revise the piece and check for any mistakes or inconsistencies. Additionally, we recommend double-checking all citations and references and ensuring they are carefully formatted according to the requirements provided in the assignment.
During the review and polishing process, consider the following:
- Review title. Consider creating a suitable title for the article review if a title is not provided. A good article review title should convey the text's main focus, include keywords, and hint at what readers can expect from the review.
- Reference list. Include a reference list to acknowledge and give credit to the sources you have used in your review. Even if the review only references the article being analyzed, the reference list should include this article.
❓ Article Review Generator Free: FAQ
❓ what is an article review.
An article review critically evaluates and analyzes a scholarly article or research paper. It summarizes the main points, critiques the methodology, and discusses the significance and potential limitations of the work. Article reviews are a common assignment among high school and college students.
❓ How to write an article review?
Writing an article review starts with thorough preparation and understanding of the article's context. Then, carefully read the article to identify critical points and evaluate the author's arguments. Finally, provide a well-reasoned and supported assessment of the article's overall quality and contribution. You can always use our article review generator for the best summary and evaluation.
❓ Where is the literature review in an article?
The literature review in an article is typically situated after the introduction or in the body section. It draws a comprehensive overview of existing research relevant to the article's topic. However, not all article reviews require a literature review. It's better to consult the professor or review guidelines to determine if a literature review is necessary for the specific assignment.
❓ How to start an article review?
To begin an article review, start by introducing the article's title, author, and publication date. Provide a brief overview of the article's main topic and purpose. Consider setting the context by explaining the topic's significance and the article's relevance to the field. Lastly, state your thesis or main argument regarding the article's quality and contribution.
🔗 References
- How to Write an Article Review (with Sample Reviews) - wikiHow
- Research Guides: Introduction to Research: Humanities and Social Sciences: Critical Reviews
- How to Review a Journal Article | University of Illinois Springfield
- Research Guides: Writing Help: The Article Review

AI-Based Literature Review Resources

STEM Librarian

Brainstorming
- ChatGPT ChatGPT is useful for brainstorming new ideas and it helps if your prompts are detailed and provide plenty of context.
- Copilot Use Copilot to generate alternative viewpoints, unique angles, or unexpected twists.
- Gemini If you have a basic idea, Gemini can help find fresh perspectives on it.
- Perplexity You may get better responses if you click Focus and select Academic, which allows you to search in published academic papers.
- Hypothesis Maker HyperWrite's Hypothesis Maker is an AI-driven tool that generates a hypothesis based on your research question.
Searching the Literature
- Research Rabbit Research Rabbit is a good place to start to get an overview of the field and explore citation networks to identify important authors. It allows you to visualize citation chains by network or timeline.
- Litmaps Litmaps allows you to search the literature using citation maps and seedmaps that allow you to discover key authors, spot research gaps. Upload a paper and map top connected authors, and search by momentum to see which papers are being cited fastest,
- Consensus Consensus lists and summarizes papers it finds into single sentence summaries with clickable endnotes to references from Semantic Scholar. Categorizes methodology, citation activity, and journal rigor. Consensus meter calculates number of papers supporting or negating research question. Filter useful studies by year, citation count, method, controlled studies, human studies.
- SciSpace Search, summarize/TLDR, add columns to compare articles and article sections to create a synthesis matrix, upload papers into MyLibrary, highlight sections of paper and ask questions about it. Includes citation generattor, paraphraser, ai detector.
Summarizing and Synthesizing the Literature
- AskYourPDF You can upload and ask questions of PDFs to create an interactive reading experience that provides an alternative to skimming and browsing.
- docAnalyzer.ai Ask questions and receive precise answers in real time. docAnalyzer.ai offers dynamic, context-aware interactions with one or multiple PDFs, powered by AI research for superior document analysis.
- Explainpaper Explainpaper allows you to highlight text for explanations and to ask follow-up questions.
- Humata Summarize and question literature, and Humata provides answers with citations, and allows you to compare documents.
- TLDR This Upload text for explanation, summarize any piece of text into concise, easy to digest content, and use the browser extension to summarize webpages.
- Notably Summarize secondary research, evaluate it, and look for gaps in knowledge to fill with more secondary or primary research.
Citing the Literature
- Bibliography.com Bibliography.com offers a user-friendly interface and a comprehensive database where users can seamlessly input source information, select the desired citation style, and generate accurate citations with ease.
- Citation Machine This artificial intelligence citation generator allows you to cite websites, books, journals, newspapers, films, videos, databases, blogs, and much more.
- EduBirdie This tool features a simple interface and step-by-step guide to help authors with citation formatting and creation.
- Opendemia The open-source nature of this tool allows users to modify and adapt the tool to their specific needs like notes taking, upload images and cite, making it a versatile option for researchers and developers.
- Petal Petal Citation Generator automatically creates citations for sources in over 10,000 styles, such as Harvard, MLA, APA, IEEE, AMA, Chicago, ACS, Vancouver.
- Quetext Citation Generator Quetext offers a straightforward interface and a comprehensive source input method, allowing users to quickly and easily create citations for their research papers, essays, and other written works.
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 10:56 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ttu.edu/c.php?g=1398054
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Find academic sources for your next paper
Finish Your Research in Minutes. Save Your Sleep.
Paste your essay to find, summarize, and add credible sources. (That's something Google Scholar can't do!)
200m+ research papers
Precise search filters
Just paste your essay

Join 10,000+ students saving 100s of hours
See Sourcely in action 👇

Please wait. This may take a minute...
If it takes longer than a minute, try again.
Text exceeds 300 characters. Click here to upgrade to SourcelyPRO for unlimited characters
Success: Scroll Down to see results
Publications From
Minimum Citations
Include Keywords
Exclude Keywords
Results for...

Publication Year:
Publication Venue:
Edit your papers with Yomu AI
Seamless Transition from Sources to Masterpiece
Congratulations on finding the perfect sources for your academic paper! Now, take the next step towards crafting a flawless masterpiece with Yomu. Our AI writing assistant is your guide to refined, error-free writing. Edit your paper like a pro with real-time feedback and efficient writing tools. From research to writing, Yomu & Sourcely are your all-in-one solution for academic excellence.
Sources about
Discover more sources for your essay today, sources about .

Trusted By Academics From
Why trust us? Because we are trusted by the absolute best academic institutions, including Harvard, MIT, and Stanford, among others
POWERFUL FEATURES
Fed up with scrolling through pages of search results? Our source-finding tool simplifies the process so you can find your sources quickly and easily.

Paste Your Essay
Simply paste your essay or paragraph and let Sourcely do the rest!

Get Credible Summaries
Save time and effort by quickly getting a general overview/summary of a source material
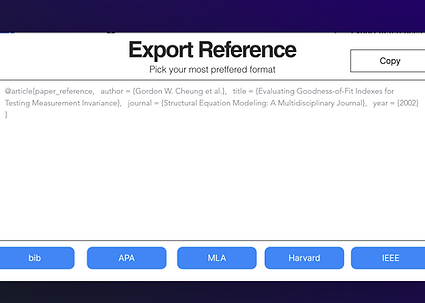.png)
Export References
Save time and ensure accuracy by exporting your sourced references in various formats, making citation and bibliography creation a breeze.
_edited.jpg)
F ind Sources
Hit the button, and watch Sourcely find all suitable sources.

Free PDF Downloads
Sourcely also allows users to download free PDFs of many of the sources it lists.
.png)
Advanced Filters
Tailor your source discovery by applying advanced filters, such as publication year, authorship, relevance, and more.
PRICING & PLANS
Sourcely is an investment in your academic career, but we know that budgets can be tight. That's why we strive to keep wallet-friendly prices, with monthly plans starting at just $9 per month or yearly plans at $87 - affordable for everyone.
Pay Per Use
Sourcelyfree.
- Skip hours of Manual Research!
- Assured Credibility of Sources
- Only UP TO 300 characters :(
- Quality results for 300 characters
SourcelyPRO Monthly
- Quick and Easy Source-finding
- Ease of Pasting your Entire Essay
- Skip Tedious Manual Research!
- Generate Credible Summaries
- PDF Downloads of Sources
- Search Millions of Sources
- Filter by Year of Publication
SourcelyPRO Yearly
- All features of the Monthly plan
- Save 20% Off the Monthly Plan
- One purchase, endless benefits
- Lock it in before price increases!
- Pro Yearly users suggest features
- Equal to $7.25/month
SourcelyPRO 2000 Words
- Skip tedious Manual Research!
- Total of 2,000 words
Trusted by researchers and organizations around the world
Over 10,000 students, researchers, and industry experts use Sourcely
See what they're saying

10,000 students helped

100,000 hours saved

Narrative Essay Writer AcademicHelp

FREE AND USER-FRIENDLY ESSAY WRITING
Efficient Essay Generation
Reliable Scholarly Sources
Accurate MLA/APA Citations
Are you a struggling narrative essay writer.
Oh, the narrative essay—the bane of many a student’s existence! You just wrapped up one assignment, and bam, another one drops onto your desk. Sound familiar? This cycle can really wear you down, especially when it comes to narrative essays.
Narrative essays are tough for a few reasons. They require you to be a great storyteller within a structured academic framework, which is more complex than it sounds. You need to engage your reader with a story that’s not just interesting but also well-organized and coherent. This type of writing stretches your creative muscles while demanding compliance with strict academic rules—a challenging combination even for the most experienced students.
Adding to the problem, narrative essays require a deep dive into personal experience, asking you to reflect and articulate your thoughts and feelings. This shift from objective analysis to personal storytelling can be jarring. It asks more of you than just research and facts; it requires introspection and a strong, authentic voice.
Remember, developing your unique writing style and voice is a journey that involves plenty of practice and patience. It’s perfectly normal to find narrative essays difficult at first. Most writers, even professionals, have faced these challenges and worked through them over time. If you’re feeling stuck, remember that every essay is an opportunity to improve and refine your skills. Each paragraph you write is a step toward becoming not just a proficient writer but a compelling storyteller. Keep pushing forward, and don’t be afraid to ask for feedback or help. One way to get support when writing is to use our Narrative Essay Generator by AcademicHelp.
Why Use a Personal Narrative Generator?
All is great, but isn’t it better to compose the essay yourself since you know the requirements like no one else? Well, using an essay maker tool is like day and night in this regard. Why would you count 263×730, if you can just use a calculator?
Firstly, a narrative generator helps spark ideas. Starting can be the hardest part of writing, especially when facing a blank page. This tool can offer initial guidance on themes or experiences you might want to explore. It acts like a muse, generating initial thoughts that lead to a fully fleshed-out story. This can be game-changing for writers who may feel overwhelmed by the infinite possibilities a narrative essay presents.
Secondly, these generators help structure your stories. A well-structured narrative flows smoothly, keeps the reader engaged, and ensures that the story unfolds in a coherent manner. The generator can suggest an outline that balances the introduction, body, and conclusion, helping create a clear path for your narrative. This is key for keeping the narrative focused and making sure that it delivers the intended message or emotion. For many writers, structuring a story can be as challenging as writing it, so having a tool that lays out the framework is helpful, to say the least.
Moreover, using a narrative generator can save time. For students juggling multiple assignments or writers on tight deadlines, these tools can speed up the writing process by providing quick, structured, and thoughtful input that can be further customized or expanded upon. This efficiency in academic or professional settings is often lacking due to limited time. By reducing the time spent on planning and initial drafting, writers can allocate more time to refining and polishing their narratives.
What Our Narrative Report Generator Has to Offer
Nobody is willing to purchase a cat in a bag. We want you to know what you’re getting after you decide to use our Narrative Essay Generator, so let’s break it down.
- Quick and Easy Essay Generation . Obviously, that’s the main point. We get how hard it can be to gather your thoughts, create an engaging narrative, spice it up with fancy vocabulary, polish it extensively, and finally submit the assignment. The Narrative Essay Writer by AcademicHelp will be there to support you and provide the necessary basis for your text so that you won’t be tiresomely staring at the screen.
- Variety of Scholarly Sources . Our platform provides access to a broad selection of scholarly materials across many subjects. This feature allows you to support your arguments with solid evidence and insights from established sources, which makes your narrative more convincing and well-prepared.
- MLA/APA Citations . Managing citations is such a bore since there are so many rules to catch up with. Our tool simplifies this aspect by automatically formatting your references correctly in MLA or APA styles. This will save you both time and effort, so you can put your energy into perfecting the paper itself.
Types of Essays a Narrative Report Maker Can Handle
It’s important to remember that narrative essays come in various flavors, each with its unique twist. Can AcademicHelp’s Essay Generator be a lifesaver for students and help with your writing process? Spoiler – yes, it can!
First, the personal narrative essay invites you to share a personal experience in a way that offers insight or a lesson learned. This type is all about emotional resonance, making the reader feel as though they’ve walked a mile in your shoes. If you’re having trouble coming up with ideas, using an essay generator will help.
Next, the descriptive narrative essay focuses on painting a vivid picture. It aims to transport the reader to a time and place through rich, detailed descriptions. Here, it’s less about the plot and more about immersing the reader in the scene. It can be hard to know where to start, but we got you.
Another one is the historical narrative, which tells the story of historical events through a compelling narrative lens, often adding personal or imagined details to factual events to make history come alive. Our tool can handle citations and references, so just put it into your instructions. Easy-peasy!
AcademicHelp’s Essay Generator can help in crafting these types of essays by providing structured outlines and helpful prompts that guide you in developing your story, especially when you don’t really know where to start. Whether you need help organizing your thoughts, finding the right words, or sticking to the narrative style, this tool makes sure your essay is well-composed and engaging. This way, the writing process is smoother and more approachable, and this is just what any student wants.
THE BEST NARRATIVE ESSAY WRITER EXPERIENCE

How do you write a narrative essay?
Writing a narrative essay involves telling a story with a clear point of view. Start by choosing an engaging topic, then outline your story’s plot, introduce the characters, set the scene, and write using vivid details and personal reflections to engage your audience.
What are the 5 parts of a narrative essay?
It depends! Still, the five key parts of a narrative essay are the introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution. These elements work together to create a compelling story arc that guides the reader through the events and experiences described.
What are the 3 types of narrative essays?
There are three main types of narrative essays: personal narratives, which tell a story from the writer's life; fictional narratives, which involve invented stories; and narrative nonfiction, which recounts true events in a storytelling format.
How do you start a narrative?
Start a narrative with a hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a striking quote, a shocking fact, or an intriguing question. Set the tone and provide a glimpse into the setting or characters to draw readers into the story.
How long is a narrative essay?
A narrative essay typically ranges from 500 to 2,000 words, depending on the assignment’s requirements. It should be long enough to develop the story fully but concise enough to keep the reader engaged throughout.
Remember Me
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
- Collections
- Support PDR
Search The Public Domain Review
Professor Megalow’s Dinosaur Bones Richard Owen and Victorian Literature
By Richard Fallon
Richard Owen, the Victorian scientist who first named the “dinosaurs”, claimed that he could identify an animal, even an extinct one, from inspecting a single bone. Richard Fallon revisits other Owen-inspired fictions — by R. D. Blackmore, William Makepeace Thackeray, and Charles Kingsley — and finds literature layered with scientific, religious, and political interventions, spurred by the discovery of prehistoric life.
May 2, 2024

“Professor Owen—On his Favourite Hobby”, colour zincograph by F. Gillot from the cover of an 1870 issue of The Period: An Illustrated Review of What Is Going On — Source .
Richard Owen, known today for coining the term “dinosaur” and founding London’s Natural History Museum, was Victorian Britain’s most celebrated comparative anatomist. He was also — to put it diplomatically — a divisive figure. Writing in 1851, one of his various scientific nemeses, Thomas Henry Huxley, considered it “astonishing with what an intense feeling of hatred Owen is regarded by the majority of his contemporaries”. 1 Yet, when one of his chief admirers, Richard Doddridge (R. D.) Blackmore, based a character in his latest novel on Owen, that character was intended to epitomize the famous naturalist’s “common sense, kindness and humility”. 2 Huxley and Blackmore were evidently seeing very different Owens.
We will return to Blackmore’s intriguing but now largely forgotten novel, The Remarkable History of Sir Thomas Upmore, Bart., M.P., Formerly Known as “Tommy Upmore” (1884), in which Owen is transmuted into the kindly “Professor Megalow”. First, however, it must be asked why the man attracted such variety, and intensity, of feeling. In other words, why did so many fellow naturalists hate his guts? And why did so many titans of literary culture — including not just Blackmore but also Charles Dickens, William Makepeace Thackeray, and many others — find his recondite investigations into zoology and palaeontology so profoundly inspiring?

“Dinner in the Iguanodon ”. On New Year’s Eve, 1853, Owen presides over a meal celebrating the construction of model prehistoric animals at the Crystal Palace in Sydenham. Illustration after Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins from an issue of Illustrated London News that same year — Source .
Owen rose up from relatively unglamorous family roots in Lancaster, becoming curator, professor, and finally — in 1842 — conservator of London’s well-stocked Hunterian Museum of the Royal College of Surgeons. Superintendency of the natural history collections of the British Museum followed in 1856. Across both spaces, Owen had access to the finest zoological and palaeontological treasures of the ever-growing and ever-acquisitive British Empire. In addition to providing us with the dinosaurs, Owen’s accomplishments included the reconstruction of the New Zealand moa and the giant South American ground sloth Mylodon , pioneering work on the gorilla, and — both before and after the publication of Charles Darwin’s On the Origin of Species (1859) — he postulated innovative if arcane theories of life’s natural development through time. 3 Museums were his speciality: Owen’s orchestration of the opening of the Natural History Museum in 1881, absorbing scientific collections formerly housed at the British Museum, capped an illustrious career.
Nonetheless, Owen’s egotism and inscrutability made him enemies in the scientific world from the start. This habit of acquiring adversaries eventually became a serious problem. In the late 1850s, tensions with the rising star Huxley were already foreboding future ill; in 1864, a powerful group calling itself the X Club formed to take charge of science’s role in society and stuck a more persistent thorn in Owen’s side. This influential group of secular scientific naturalists, whose members included Huxley as well as Herbert Spencer, stood for much that Owen detested. Their agnosticism and naturalistic interpretation of evolutionary processes — sometimes understood as driven by what Spencer termed “survival of the fittest”, or what Darwin called “natural selection” — were anathema to Owen’s theistic evolutionism, in which humans represent the apex of God’s providentially unfolding plan. Charles Kingsley’s classic children’s story The Water-Babies (1863) memorably satirized one of the most public clashes between Owen and Huxley, in which the former attempted to distance humans biologically from apes, while the latter, stressing our humble animal descent, did just the reverse.

Linley Sambourne depicts opponents Owen (left) and Huxley (right) in an 1885 edition of Charles Kingsley’s The Water-Babies — Source .

Owen dines at the Palaeontographical Society, accompanied by those prehistoric creatures whose fossil bones he knew so intimately. 19th-century lithograph by A. Orton after E. C. Rye — Source .
In addition to espousing a more compartmentalized view of the relationship between science and religion than Owen, and a less compartmentalized view of the relationship between humanity and other animals, those naturalists who came to form the X Club distrusted his pervasive influence over scientific culture. As such, many opposed his ambitious proposals for a separate Natural History Museum. Although he got his museum in the end, acolytes of Darwin and Huxley wrote much of the subsequent history, creating a caricature of Owen as a bigoted obscurantist. Notably, Darwin’s statue currently holds pride of place over Owen’s in the latter’s own museum.
Owen, however, enjoyed propagandistic powers of his own. He came to number leading politicians and members of the royal family among his intimate friends and whipped up excitement for his work in lectures and publications for general readers. Particularly integral to his reputation was the notion that Owen could identify an animal, even an extinct one, from a single bone. His most sensational feat concerned a broken femur found in New Zealand. When it was presented to Owen in 1839, he declared that this femur belonged to a then-unidentified ostrich-like bird. In 1843, further specimens vindicated his apparently audacious prediction and revealed that New Zealand had, indeed, once been infested by these giant, flightless moa birds, which Owen dubbed Dinornis . Contemporaries found this story of scientific wizardry utterly enchanting. The reality, which Owen’s media machine smothered with increasing severity, was slightly more mundane: John Rule, the surgeon who presented Owen with the femur, had already provided evidence for its avian origin.

Late in life, holding the famous femur in one hand and caressing a moa in another, Owen relives the high point of his career. Halftone after J. Smit after a photograph, ca. 1877 — Source .
Most of Owen’s contemporaries, however, knew nothing of John Rule. As his career thrived in the 1840s, Owen befriended more and more star-studded litterateurs, many of whose works he voraciously consumed in snatches of spare time. This was an era when palaeontological reconstruction, geological time, and extinction were thrilling and still relatively novel notions. Pre-Darwinian controversies over “development” (or, to use a more recognisable term, evolution) raged, while the largely Christian community of British naturalists continued to construct sophisticated ways of making sense of Earth’s history via liberal interpretation of the Book of Genesis — and vice versa. Owen, for his part, was happy to frame his work (or have others frame it) as confirming that even the most apparently monstrous prehistoric creatures were the products of God’s benign design, mysteriously unfolding over sublime aeons of deep time.
Owen’s ability to resurrect these strange animals from inadequate materials struck several leading novelists as an apt analogy for their own literary methods. “How can I tell the feelings in a young lady’s mind; the thoughts in a young gentleman’s bosom?” asks the narrator of William Makepeace Thackeray’s The Newcomes (1854–55). His justification is palaeontological: “As Professor Owen . . . takes a fragment of a bone, and builds an enormous forgotten monster out of it, wallowing in primæval quagmires . . . so the novelist puts this and that together: from the footprint finds the foot; from the foot, the brute who trod on it; from the brute, the plant he browsed on, the marsh in which he swam”. 4 For Thackeray, this quasi-scientific pedigree — not entirely proposed in jest — was gratifying, implying as it did that his gigantic works were painstakingly researched and planned.
Dickens was even closer to Owen. His periodicals, including Household Words , published Owen’s articles and promoted the naturalist’s ideas, from his moa mythmaking to his esoteric concept of the ideal “archetype” underlying all vertebrate forms. Nor did Dickens’ novels escape his friend’s osseous influence. Direct reference to Owen in Our Mutual Friend (1864–65) is admittedly limited to a droll description of the complacent Mrs Podsnap, a “fine woman for Professor Owen” possessing “quantity of bone, neck and nostrils like a rocking-horse”; nonetheless, as literary scholars like Gowan Dawson have shown, an Owenian language of palaeontological reassembly pervades this last of Dickens’ completed novels. 5 Not least in scenes including the bone collector Mr Venus and the wooden-legged Silas Wegg, the question of conjuring the whole from the part comes to symbolize, as in Thackeray’s The Newcomes , the task of the Victorian serial novelist, who must prove that isolated fragments are all integral contributions to a harmonious and insightful end product.

Satirical lithograph dating roughly to the 1840s: in a parody of the dagger scene in Macbeth , the dreaming palaeontologist is visited by creatures that he has perhaps, in waking life, striven to reconstruct — Source .
Thackeray and Dickens were just two of the famous authors who extolled Owen in his glory days. In 1884, R. D. Blackmore — to return, as promised, to Sir Thomas Upmore — gave Owen, in the form of “Professor Megalow”, a more prominent role than any author of fiction had ever attempted before, and at a time when the man himself was passing out of fashion. Although he only retired from the Natural History Museum the previous year, Owen’s scientific authority had been besieged for decades. Alienating Darwin and X Clubbers like Huxley had resulted in him being sidelined from many cutting-edge evolutionary discussions of later Victorian science, even if Owen continued to publish elaborate, lavishly illustrated zoological and palaeontological “memoirs” and monographs.
The two Richards — Owen and Blackmore — were fast friends (and fellow chess aficionados), living not far from each other in what is now the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames. Blackmore had previously shot to fame with Lorna Doone: A Romance of Exmoor (1869), a historical romance set in the seventeenth century which remains in print today. 6 Sir Thomas Upmore , which stands out among the author’s otherwise substantially rural literary oeuvre, has not enjoyed similar success, and the reasons are not far to seek. The Saturday Review ’s critic called it “neither allegory nor novel, neither satire nor romance, but a mixture – not altogether a successful mixture – of all four”. 7 Despite, or because of, this generic confusion, it is highly interesting to a present-day reader.
The titular character of Blackmore’s allegorico-romantico-satirico novel, like many fellow Victorian narrators, undertakes an upwardly mobile journey to gentlemanliness. The son of a soap manufacturer, young Tommy Upmore courts Laura, the beautiful daughter of Lady Twentifold of Twentifold Towers. To win the respect of the aristocratic Laura’s politically-obsessed brother, Roland, he must also win a seat as Conservative MP and fight off the onslaughts of Liberals pursuing a dramatic reform agenda. What distinguishes this novel from comparable realist works is its highly fantastic element: due to his body’s abnormal density, Tommy can fly, or rather float. At the end of the novel, he literally rises up above the party-political din in the House of Commons to unite Britain’s politicians in nationalistic fervour.

Watercolour by Ernest Griset depicting Richard Owen (seated) and the mineralogist Bryce Wright, ca. 1873 — Source .
Despite its protagonist’s ability to float above divisions, Sir Thomas Upmore is hardly a conciliatory novel. Although not as diehard a Tory as Roland, Tommy is shocked at the radical progressive reforms proposed by their Liberal foes (led by the smooth-talking Panclast): “grand measures were being prepared, for a fine subversion of established things; Liberal statesmen being quite convinced by their own condition, that the universe was wrong”. 8 Their nefarious plans include the abolition of land ownership, the secession of Britain’s strategic and colonial territories, and even the restitution of plundered artefacts. In addition to swiping at socialists and anarchists, Blackmore caricatured the reforming aims of prime minister W. E. Gladstone’s Liberal government, in power since 1880. In the eyes of the Saturday Review , the novel’s Panclast was “as like Mr. Gladstone as one pea is like another”. 9
Science is central to the novel’s conservative political intervention. Blackmore skewers “Professor Brachipod” and the collective of evolutionists brought in to investigate Tommy’s remarkable floating abilities. Insensitive to the boy’s feelings and quick to speculate baselessly about the origin of his powers, these “scientists” — a neologism Blackmore accompanies with scare quotes to indicate his distaste — are impious champions of scientific naturalism, like those men comprising the X Club. Blackmore’s targets are indicated not just by the scientists’ menacing association with vivisection, but also when they help overthrow the traditional classical curriculum of Tommy’s school, replacing it with a new, scientistic syllabus. Both the necessity of vivisection and the need for scientific instruction to accompany — or even replace — classical education, were standard talking points for men such as Huxley.
If Tommy mocks his scientific teachers’ incompetence in the field of ancient Greek and Latin, patrician Lady Twentifold is concerned by something deeper: the apparent atheism of the modern approaches to science they promulgate. “Who brought up this tree?” she asks, gesturing to a grand oak. While some, Tommy observes, would say “Nature”, “Science”, or “Accident”, she prefers to say “that the Almighty made it so”. 10 Luckily for both, a more positive model for the scientific practitioner is at hand: Professor Megalow, “whose name shall never be out-rubbed by time”, and whose face, when Tommy first encounters it, appears “the kindest and grandest I had ever seen”. 11

Photomechanical portrait of Richard Owen, ca. 1880s — Source .
Megalow is nothing like Brachipod (or their equally oddly named colleagues Jargoon, Chocolous, and Mullicles). A devout Christian, softly spoken, reluctant to construct premature hypotheses, and uninterested in fame or lucre, he dispenses wisdom to Tommy throughout the latter’s career. That Blackmore intended to flatter his friend is undeniable: he even wrote to Owen, asking permission to do so. Megalow was meant to be so recognisable “that the public . . . will exclaim at once ‘this must be Professor Owen’”. 12
As the title of an early chapter indicates, Megalow understands “True Science”. He is Blackmore’s ideal scientific practitioner, albeit one at odds with the times. “Even upon subjects, he understands more thoroughly than any other man yet born”, Tommy observes, Megalow “speaks (when he does speak at all) with more doubt, and diffidence, and humility, than a school-girl does, who knows nothing about it, except from one of his own books”. 13 Tommy’s old schoolmaster, the classics-obsessed Dr Rumbelow, calls him “a genuine acolyte of that glorious sage, Pythagoras”. 14 Himself an enthusiast and one-time tutor of classical literature, as well as a conservative in both politics and religion, Blackmore represented Owen as a reassuring and responsible steward of the era’s dramatic scientific advances.
Megalow’s standout scene takes place when Tommy and Laura help him to excavate a “Deino-Saurian” from a cliff face. It is tempting to suggest that this set piece reflects a growing interest in dinosaurs, catalysed by fossils unearthed in the United States during the 1870s and 1880s, including Brontosaurus and Stegosaurus . Owen himself, after all, had coined “dinosaur” back in 1842 and Megalosaurus was even one of the creatures included in his definition. For most of the nineteenth century, however, general audiences were surprisingly indifferent to the term “dinosaur” and Blackmore’s pedantic spelling suggests that the fossil is to be understood as some rather obscure animal. An arguably more pertinent reference point here is the moa: just as Owen had, according to the myth, predicted the form of the moa and been vindicated years later, the “Deino-Saurian” discovery acts as “tangible proof” of Megalow’s “inductions, published in a treatise ten years ago”. 15
Owen’s life-like restoration of Megalosaurus , one of the gigantic extinct creatures he included in his category “Dinosauria” and the origin of the name of Blackmore’s “Professor Megalow”. Illustration from Owen’s Geology and Inhabitants of the Ancient World (1854) — Source .

Detail from an 1863 engraving by C. G. Lewis after T. J. Barker of notables gathered at Buckingham Palace. Gladstone (left, seated) gestures to a military treaty, while Owen (right, with Dickens at his left shoulder), examines an invention — Source .
Strikingly, Megalow’s method is presented as a third way not just in science but also in the era’s polarized politics. In an otherwise polemical and reactionary novel, Megalow’s Liberal — and worse, “Rad” (Radical) — allegiance is repeatedly stressed. As the ultra-Tory Roland thunders, “[how] can such a great man as the Professor ever have become a Liberal?” 16 Indeed, while far from being a revolutionary, the real Owen’s early career had been steeped in the liberal Conservatism of reformist prime minister Robert Peel, who even commissioned a painting of Owen to hang in his country seat, Drayton Manor. In later decades, the Liberal doyen Gladstone himself became a major ally in Owen’s quest to establish the Natural History Museum, as well as supplementing the ageing anatomist’s pension and array of titles.
Admittedly, Tommy’s tolerance for his mentor’s inconvenient political beliefs is enabled by the latter’s reluctance to act upon them: Megalow “was not at all a partisan, or active politician, but quietly held his opinions, upon reasons which satisfied him, and therefore cannot have been weak ones”. 17 Attempting conciliation, Tommy concludes that the party governing Britain, “[w]hether it be Radical, or Tory, matters little to the average Englishman; so long as it acts with courage, candour, common sense, and consistency”. 18 (And, presumably, doesn’t meddle with landowners or the country’s colonial possessions.)
Sir Thomas Upmore is a fascinating and bizarre text (and, as readers will have noticed, an excellent repository of Victorian character names, including those of Tommy’s father Bucephalus, his friend Bill Chumps, and the formidable Lord Grando Crushbill). Far more so than its young leads and their somewhat perfunctory romance, Professor Megalow lingers with us as the novel’s most compelling character. A modest master of rarefied induction, and unwilling to pursue scientific theories with disruptive social consequences, he represents a safe pair of hands to usher in scientific modernity. This was something of the impression Blackmore absorbed in conversation with his accomplished friend, Owen, making Sir Thomas Upmore one of the century’s greatest love letters to one of its most controversial men of science.
Notes Show Notes
- Leonard Huxley, Life and Letters of Thomas Henry Huxley , 2 vols (London: Macmillan, 1900), I, 93.
- Letter quoted in undated catalogue of manuscript material for sale by Maggs Bros of London, “English Literature of the 19th and 20th Centuries … Part I”, no. 443, 30. Available here .
- For a classic study of Owen’s complex relationship with evolutionary thought, see Evelleen Richards, “A Question of Property Rights: Richard Owen’s Evolutionism Reassessed”, British Journal for the History of Science , vol. 20 (1987): 129–171.
- William Makepeace Thackeray, The Newcomes: Memoirs of a Most Respectable Family , 2 vols (London: Bradbury and Evans, 1855), II, 81.
- Gowan Dawson, “Dickens, Dinosaurs, and Design”, Victorian Literature and Culture , vol. 44 (2016): 761–778.
- For a concise modern biography of Blackmore, see Charlotte Mitchell, “Blackmore, Richard Doddridge (1825–1900), Novelist and Fruit Farmer”, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography , 23 Sep., 2004. Available here .
- “Two Novels”, Saturday Review , vol. 57 (1884): 755.
- R. D. Blackmore, The Remarkable History of Sir Thomas Upmore, Bart., M.P., Formerly Known as “Tommy Upmore” (London: Sampson Low, Marston, 1894 [1884]), 386.
- “Two Novels”, 755–756.
- Blackmore, The Remarkable History of Sir Thomas Upmore , 392.
- Ibid., 30–31.
- Maggs Bros, “English Literature of the 19th and 20th Centuries”, 30.
- Blackmore, The Remarkable History of Sir Thomas Upmore , 257.
- Ibid., 254.
- Ibid., 245.
- Ibid., 352.
- Ibid., 440.
Public Domain Works
- Internet Archive
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Google Books
- Internet Archive (volume 1)
- Internet Archive (volume 2)
Further Reading
For twenty years, the X Club was the most powerful network in Victorian science -- the men succeeded each other in the presidency of the Royal Society for a dozen years. Barton's group biography traces the roots of their success and the lasting effects of their championing of science against those who attempted to limit or control it, along the way shedding light on the social organization of science, the interactions of science and the state, and the places of science and scientific men in elite culture in the Victorian era.

Nineteenth-century palaeontologists boasted that, shown a single bone, they could identify or even reconstruct the extinct creature it came from with infallible certainty ― “Show me the bone, and I will describe the animal!” Show Me the Bone tells the story of the rise and fall of this famous claim. In so doing, Gowan Dawson reveals how decisively the practices of the scientific elite were ― and still are ― shaped by their interactions with the general public.

When the term “dinosaur” was coined in 1842, it referred to fragmentary British fossils. In subsequent decades, American discoveries — including Brontosaurus and Triceratops — proved that these so-called “terrible lizards” were in fact hardly lizards at all. Unlike previous scholars, who have focused on displays in American museums, Richard Fallon argues that literature was critical in turning these extinct creatures into cultural icons. Popular authors skillfully related dinosaurs to wider concerns about empire, progress, and faith; some of the most prominent, like Arthur Conan Doyle and Henry Neville Hutchinson, also disparaged elite scientists, undermining distinctions between scientific and imaginative writing. The rise of the dinosaurs thus accompanied fascinating transatlantic controversies about scientific authority.

In the mid-1850s, no scientist in the British Empire was more visible than Richard Owen. But, a century and a half later, Owen remains largely obscured by the shadow of the most famous Victorian naturalist of all, Charles Darwin. With this innovative biography, Nicolaas A. Rupke resuscitates Owen's reputation. Arguing that Owen should no longer be judged by the evolution dispute that figured in only a minor part of his work, Rupke stresses context, emphasizing the importance of places and practices in the production and reception of scientific knowledge.
The Public Domain Review receives a small percentage commission from sales made via the links to Bookshop.org (10%) and Amazon (4.5%). Thanks for supporting the project! For more recommended books, see all our “ Further Reading ” books, and browse our dedicated Bookshop.org stores for US and UK readers.
Richard Fallon is a postdoctoral researcher at the Natural History Museum and a knowledge exchange fellow at the University of Nottingham. His research focuses on literary culture’s relationship with geology and palaeontology. Richard received his doctorate in English from the University of Leicester in 2019 and completed a Leverhulme Trust Early Career Fellowship at the University of Birmingham in 2023. His books Reimagining Dinosaurs in Late Victorian and Edwardian Literature (Cambridge University Press) and Creatures of Another Age (Richmond, VA: Valancourt Books) were published in 2021.
The text of this essay is published under a CC BY-SA license, see here for details.
- Science & Medicine
If You Liked This…

Get Our Newsletter
Our latest content, your inbox, every fortnight

Prints for Your Walls
Explore our selection of fine art prints, all custom made to the highest standards, framed or unframed, and shipped to your door.
Start Exploring
{{ $localize("payment.title") }}
{{ $localize('payment.no_payment') }}
Pay by Credit Card
Pay with PayPal
{{ $localize('cart.summary') }}
Click for Delivery Estimates
Sorry, we cannot ship to P.O. Boxes.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Our Literature Review Generator is an AI-powered tool that streamlines and simplifies the creation of literature reviews by automatically collecting, analyzing, summarizing, and synthesizing all the relevant academic sources on a specific topic within the parameters you define. It saves you additional time by highlighting themes, trends, and ...
Creates a comprehensive academic literature review with scholarly resources based on a specific research topic. HyperWrite's AI Literature Review Generator is a revolutionary tool that automates the process of creating a comprehensive literature review. Powered by the most advanced AI models, this tool can search and analyze scholarly articles, books, and other resources to identify key themes ...
Finds Good Matches: A literature review generator is designed to find the most relevant literature according to your research topic. The expertise of these software tools allows users to ease the process of finding relevant scholarly articles, making it more accurate and faster than doing it manually. Reduces Errors and Improves Quality: Humans ...
AI-Powered Literature Review Generator. Generate high-quality literature reviews fast with our AI tool. Summarize papers, identify key themes, and synthesize conclusions with just a few clicks. The AI reviews thousands of sources to find the most relevant info for your topic.
Welcome to Jenni AI, the ultimate tool for researchers and students. Our AI Literature Review Generator is designed to assist you in creating comprehensive, high-quality literature reviews, enhancing your academic and research endeavors. Say goodbye to writer's block and hello to seamless, efficient literature review creation.
This makes it a perfect match for those who specifically need help with tough papers, such as literature reviews, research abstracts, and analysis essays. Why Use the Free Online Literature Review Generator With our Free Online Literature Review you will be able to finish your literature review assignments in just a few minutes.
Generate a comprehensive literature review based on a given research topic. HyperWrite's Literature Review Generator is an AI-powered tool that helps you conduct a thorough literature review on any given research topic. Leveraging advanced AI models, this tool searches for scholarly articles, books, and other relevant sources, summarizes their main points, methodologies, and findings, and ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Okay - with the why out the way, let's move on to the how. As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter.
3. Zotero. A big part of many literature review workflows, Zotero is a free, open-source tool for managing citations that works as a plug-in on your browser. It helps you gather the information you need, cite your sources, lets you attach PDFs, notes, and images to your citations, and create bibliographies.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
Organize your collection. Whether you're writing a literature review or your paper, you will need to keep track of your references. Using AI tools, you can efficiently organize your findings, store them in reference managers, and instantly generate citations automatically, saving you the hassle of manually formatting references.
Simplify literature reviews and find answers to your questions about any research paper seamlessly. Discover, read, and understand research papers effortlessly with Enago Read, your AI-powered companion for academic research. ... Enago Read is an AI assistant that speeds up the literature review process, offering summaries and key insights to ...
An AI literature review generator is a tool that uses artificial intelligence to automatically create literature reviews. Justdone.ai provides one of the best AI writing tools for literature review generation, making it easier and faster to create high-quality content.
Searches scholarly articles based on a research question or specific topic, then compiles them into high-quality writing with references. HyperWrite's Literature Review AI is an innovative tool that simplifies the process of conducting a literature review. By harnessing the power of advanced AI models, this tool searches millions of scholarly articles related to your research question or topic ...
How to use the Free Online Literature Review Generator. It couldn't be easier: Upload a piece of content, audio or video. Let the tool transcribe it and produce your Literature Reviews. Upload. You can upload audio & video files, directly or via a link. After 2-4 mins you will receive your transcript.
Build your literature matrix in minutes. Our Excel export feature generates a literature synthesis matrix for you, so you can. Compare papers side by side for their study sizes, key contributions, limitations, and more. Export literature-review ready data in Excel, Word, RIS or Markdown format. Integrates with your reference manager and ...
Our literary analysis essay generator is based on AI algorithms, allowing you to get original and customized results. ⏱️ Fast: ... Our literary analysis maker will help you break down any piece of literature! Get a detailed review of the plot, narrative techniques, and other text elements in a few clicks. Additionally, read the guide to ...
Our online article review generator is an excellent solution for crafting comprehensive reviews. It offers in-depth analysis while ensuring that the main ideas from the article are effectively highlighted. The tool allows students to focus on critical evaluation and personal insights rather than getting bogged down in summarization.
This artificial intelligence citation generator allows you to cite websites, books, journals, newspapers, films, videos, databases, blogs, and much more. EduBirdie. This tool features a simple interface and step-by-step guide to help authors with citation formatting and creation. Opendemia.
100% free: Generate unlimited summaries without paying a penny Accurate: Get a reliable and trustworthy summary of your original text without any errors No signup: Use it without giving up any personal data Secure: No summary data is stored, guaranteeing your privacy Speed: Get an accurate summary within seconds, thanks to AI Flexible: Adjust summary length to get more (or less) detailed summaries
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
Find Sources for Free. AI-powered literature sourcing tool that quickly retrieves relevant texts based on user input. With advanced natural language processing techniques, it provides easy access to diverse information sources, saving time and effort. Get help from Sourcely AI.
This can be game-changing for writers who may feel overwhelmed by the infinite possibilities a narrative essay presents. Secondly, these generators help structure your stories. A well-structured narrative flows smoothly, keeps the reader engaged, and ensures that the story unfolds in a coherent manner. The generator can suggest an outline that ...
Richard Owen, the Victorian scientist who first named the "dinosaurs", claimed that he could identify an animal, even an extinct one, from inspecting a single bone. Richard Fallon revisits other Owen-inspired fictions — by R. D. Blackmore, William Makepeace Thackeray, and Charles Kingsley — and finds literature layered with scientific, religious, and political interventions, spurred by ...