Motivation Theories Essay
Introduction, theories of motivation – elton mayo, abraham maslow, theories’ application in creative technology, motivation theory in marketing, motivation tools and techniques, references list.
Motivation is the force that drives people into action and encourages them into exerting more effort towards carrying out something. Motivated employees feel more comfortable and will have feelings of happiness and fulfillment. Besides, motivated workers tend to produce quality results, and are more productive than their counterparts are.
Different factors exist that can determine how an individual is motivated; for instance, everyone has basic needs like; food and shelter which can be catered for by pay. However, other diverse motivators exist that stimulate people into action. A creative environment can encourage motivation especially in design where a high level of creativity is critical.
Some workers will do well given the problem solving nature of their jobs and support initiative against challenges. Besides, creative staff will find the diverse nature of their occupation encouraging because they have the opportunity to try special responsibilities.
According to Elton Mayo, employees are not only motivated by pay, but could also be highly motivated if their social needs are fulfillment especially when they are at the workplace (Sheldrake, 2003). Mayo introduced a new way of looking at employees and argued that managers and supervisors need to have an interest in employees. This involves valuing their opinions and treating them in a worthwhile manner by recognizing that they take pride in inter-personal interactions.
While coming up with the theory, Mayo experimented at the Western Electric Hawthorne factory in Chicago. He separated two groups of women employees and viewed the outcome to productivity intensity in varying environments like working conditions and lighting. Contrary to his expectations, he was surprised to note the productivity of the employees improved or remained constant even with varying lighting and other working conditions. He then concluded that employees are highly motivated by various factors.
Among his top picks are better communication between employees and their managers. When employees feel there exists consultation on their roles and responsibilities with the managers, they tend to perform better also if given the chance to give feedback.
The second factor he discovered was the fact that employees responded very well to increased manager participation in their working lives. Besides the two, Mayo also identified teamwork as a motivator in working environments. He stated that corporate and businesses should reorganize to encourage teamwork, which is a theory that closely links to paternalistic management style.
In the 1950’s, Abraham Maslow with Frederick Herzberg came up with the neo-human relations school. According to Montana and Charnov (2008), “The school focused on employees’ psychological needs” (p. 408). In his theory, Maslow illustrates five stages in human needs that workers need to fulfill at the workplace.
Maslow then structured the needs into a hierarchy. When a lower need is fulfilled that an employee will be motivated to the next stage or need. For instance, a person threatened by hunger will have a great motivation to achieve a basic wage to satisfy the need to eat by buying food. in this sense, the person will have less motivation towards getting a formal or secure employment.
At the bottom, of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, physiological needs are the lowest and the most basic; this involves the basic needs of humans, which he argued must be satisfied to sustain life. After the physiological needs are satisfied, attention now shifts towards safety.
In a job environment, this could mean the workers are motivated to such things like living in a safe area, secure job and medical insurance as well as saving for the future. Mackay (2007) noted that “If employees feel there is not enough security provided by their jobs, higher needs will remain unattended” (p.281). Social needs are third in the hierarchy.
Maslow’s theory explains that once the lower levels are satisfied, social needs become a motivator as people have other needs for friends or the need to belong. Esteem needs come after employees feeling the need to be recognized and build their reputation. At the peak of the hierarchy, Maslow describes that this is where people pursue the need to self -actualize.
However, Montana and Charnov (2008) state that “Maslow’s theory stipulates that need to self- actualize is not fully realized as people are constantly pursuing changing endeavors” (p.191). The needs here are mostly related to truth, justice and meaning.
In creative businesses, such as website design, businesses should strive towards giving incentives that meet the needs of the staff to motivate them to progress up the hierarchy.
Furthermore, Maslow’s theory dictates that, it is essential for managers to realize that workers respond differently to different incentives to increase output. Besides, all workers progress up the hierarchy at different paces. According to Mayo’s theory, creative employees should be encouraged to work in teams. Sheldrake (2003) found out that “creativity seems to be strengthened by teamwork” (p.122).
When applying motivation theories in marketing, few changes are necessary. As explained by O’Neil and Drillings (1994) “different employees in different departments will be motivated by different incentives” (p.233). In the marketing of merchandise, high levels of motivation are required from the staff.
A good salary package and attractive benefits attracted from the sales will be necessary in ensuring maximum productivity is reached. On the contrary, employees in creative fields require a serene working environment among other incentives to maximize on productivity.
Pleasure technique is one of the oldest. The tool ensures a pleasurable reward for productivity and in turn creates motivation in employees to become more productive, besides when employees feel that their efforts are being rewarded they will tend to produce more and more.
According to Daft and Lane (2007) “performance incentives play a key role in ensuring high levels of motivation” (p. 102). It works best by creating an appeal to people’s selfishness, and by giving employees an opportunity to earn more, you as an employer will earn more.
In addition, setting deadlines will help achieve more as workers will tend to realize more productivity and are able to concentrate more when nearing a deadline. This can be achieved by creation of smaller deadlines that lead to a bigger result. It is important for managers to encourage team spirit and create an environment of teamwork.
Mackay (2007) noted that “when people work in a team they tend to be more effective” (p. 253) and besides, they don’t want to pull others down by not putting enough effort. Encouraging creativity is very essential, as employees feel more comfortable within an optimistic environment. The last tool for effective motivation is communication. Managers should uphold open channels of communication. This enables one to fix the problems as soon as they arise and it creates a better working environment.
It is important for every business to take note of the theory to implement. Depending on its line of trade, various incentives may be given to employees to maximize production.
Daft, R. L., & Lane, P. G. (2007). The leadership experience . Florence, KY: Cengage Learning
Mackay, A. (2007). Motivation, Ability and Confidence Building in People . London: Taylor & Francis
Montana, P. J., &Charnov, B. H. (2008). Management. Hauppauge, NY: Barron’s Educational Series
O’Neil, H. F., Drillings, M. (1994). Motivation: Theory and Research. New York, NY: Routledge
Sheldrake, J. (2003). Management theory . Florence, KY: Cengage Learning
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 28). Motivation Theories. https://ivypanda.com/essays/motivation-theories/
"Motivation Theories." IvyPanda , 28 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/motivation-theories/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Motivation Theories'. 28 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Motivation Theories." February 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/motivation-theories/.
1. IvyPanda . "Motivation Theories." February 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/motivation-theories/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Motivation Theories." February 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/motivation-theories/.
- An Analysis on Elton John’s Candle in the Wind 1997 Song
- George Elton Mayo’s Outlook
- Miss Brodie and Miss Mackay - Difference in Education Idea
- Miss Brodie and Miss Mackay’s Ideas of Education
- “Reality TV...” Article by Joanne Morreale
- Technology and Society Relations
- Comparison of Ball Scene in "Emma" With Frat Party Scene in "Clueless"
- Mayo Clinic: Marketing of the Healthcare System
- "Emma" by Jane Austen: Main Character Analysis
- Healthcare Institutions: Problems Facing Management
- Leadership and Cultural Differences
- Career Planning and Succession Management
- Running of Multinational Internet Firm
- Time Management Theories and Models Report
- Examination of the Portfolio Approach to IT Projects

20 Most Popular Theories of Motivation in Psychology

The many approaches to defining what drives human behavior are best understood when considering the very purpose of creating them, be it increased performance, goal pursuit, resilience, or relapse prevention, to name a few.
There is nothing more practical than a good theory.
There is no single motivation theory that explains all aspects of human motivation, but these theoretical explanations do often serve as the basis for the development of approaches and techniques to increase motivation in distinct areas of human endeavor.
This article briefly summarizes existing theories of motivation and their potential real-world applications.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Goal Achievement Exercises for free . These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients create actionable goals and master techniques to create lasting behavior change.
This Article Contains:
What is motivation psychology, theories of motivation, content theories of motivation, process theories of motivation, cognitive theories of motivation, motivational theories in business, motivational theories in sports psychology, textbooks on motivation, a take-home message.
Motivation psychologists usually attempt to show how motivation varies within a person at different times or among different people at the same time. The purpose of the psychology of motivation is to explain how and why that happens.
Broad views of how to understand motivation were created by psychologists based on various types of analyses. Cognitive analyses, behavioral anticipation, and affective devices are often used to account for motivation in terms of expecting an end-state or goal.
Motivation psychology is a study of how biological, psychological, and environmental variables contribute to motivation. That is, what do the body and brain contribute to motivation; what mental processes contribute; and finally, how material incentives, goals, and their mental representations motivate individuals.
Psychologists research motivation through the use of two different methods. Experimental research is usually conducted in a laboratory and involves manipulating a motivational variable to determine its effects on behavior.
Correlational research involves measuring an existing motivational variable to determine how the measured values are associated with behavioral indicators of motivation.
Whether you think you can, or think you can’t, you’re right.
Henry Ford, 1863–1947
To be motivated means to be moved into action. We are induced into action or thought by either the push of a motive or the pull of an incentive or goal toward some end-state. Here a motive is understood as an internal disposition that pushes an individual toward a desired end-state where the motive is satisfied, and a goal is defined as the cognitive representation of the desired outcome that an individual attempts to achieve.
While a goal guides a behavior that results in achieving it, an incentive is an anticipated feature of the environment that pulls an individual toward or away from a goal. Incentives usually enhance motivation for goal achievement. Emotions act like motives as well. They motivate an individual in a coordinated fashion along multiple channels of affect, physiology, and behavior to adapt to significant environmental changes.
See our discussion of the motivation cycle and process in the blog post entitled What is Motivation .

In short, content theories explain what motivation is, and process theories describe how motivation occurs.
There are also a large number of cognitive theories that relate to motivation and explain how our way of thinking and perceiving ourselves and the world around us can influence our motives.
From self-concept, dissonance and mindset to values, orientation and perceived control, these theories explain how our preference toward certain mental constructs can increase or impair our ability to take goal-directed action.
Theories of motivation are also grouped by the field of human endeavor they apply to. Several theories relate to motivating employees where incentives and needs take a central stage as well as theories used in sports and performance psychology where affect is considered a more prominent driver of human behavior. Some of these theories are also applied to education and learning.
Read our insightful post on motivation in education .
The self-concordance model of goal setting differentiates between four types of motivation (Sheldon & Elliot, 1999). These are:
External motivation
Goals are heavily guided by external circumstances and would not take place without some kind of reward or to prevent a negative outcome.
For example, an individual who clocks extra hours in their day job purely to receive a bigger paycheck.
Introjected motivation
Goals are characterized by self-image or ego-based motivation, reflecting the need to keep a certain self-image alive.
For example, our worker in the example above staying longer in the office so that they are perceived as a ‘hard worker’ by their manager and co-workers.
Identified motivation
The actions needed to accomplish the goal are perceived as personally important and meaningful, and personal values are the main drivers of goal pursuit.
For example, the worker putting in extra hours because their personal values align with the objective of the project they are working on.
Intrinsic motivation
When a behavior is guided by intrinsic motivation, the individual strives for this goal because of the enjoyment or stimulation that this goal provides. While there may be many good reasons for pursuing the goal, the primary reason is simply the interest in the experience of goal pursuit itself.
For example, the worker spends more time at their job because they enjoy and are energized by using their skills in creativity and problem-solving.
Goals guided by either identified or intrinsic motivation can be considered self-concordant. A self-concordant goal is personally valued, or the process towards the goal is enjoyable and aligns with interests. Self-concordant goals are associated with higher levels of wellbeing, enhanced positive mood, and higher levels of life satisfaction compared to non-self-concordant goals.

Maslow’s theory of the hierarchy of needs, Alderfer’s ERG theory, McClelland’s achievement motivation theory, and Herzberg’s two-factor theory focused on what motivates people and addressed specific factors like individual needs and goals.
Maslow’s theory of the hierarchy of needs
The most recognized content theory of motivation is that of Abraham Maslow, who explained motivation through the satisfaction of needs arranged in a hierarchical order. As satisfied needs do not motivate, it is the dissatisfaction that moves us in the direction of fulfillment.
Needs are conditions within the individual that are essential and necessary for the maintenance of life and the nurturance of growth and well-being. Hunger and thirst exemplify two biological needs that arise from the body’s requirement for food and water. These are required nutriments for the maintenance of life.
The body of man is a machine which winds its own spring.
J. O. De La Mettrie
Competence and belongingness exemplify two psychological needs that arise from the self’s requirement for environmental mastery and warm interpersonal relationships. These are required nutriments for growth and well-being.
Needs serve the organism, and they do so by:
- generating wants, desires, and strivings that motivate whatever behaviors are necessary for the maintenance of life and the promotion of growth and well-being, and
- generating a deep sense of need satisfaction from doing so.
Maslow’s legacy is the order of needs progressing in the ever-increasing complexity, starting with basic physiological and psychological needs and ending with the need for self-actualization. While basic needs are experienced as a sense of deficiency, the higher needs are experienced more in terms of the need for growth and fulfillment.

Alderfer’s ERG theory
Alderfer’s theory of motivation expands on the work of Maslow and takes the premise of need categories a bit further. He observes that when lower needs are satisfied, they occupy less of our attention, but the higher needs tend to become more important, the more we pursue them.
He also observed a phenomenon that he called the frustration-regression process where when our higher needs are thwarted, we may regress to lower needs. This is especially important when it comes to motivating employees.
When a sense of autonomy or the need for mastery is compromised, say because of the structure of the work environment, the employee may focus more on the sense of security or relatedness the job provides.
McClelland’s achievement motivation theory
McClelland took a different approach to conceptualize needs and argued that needs are developed and learned, and focused his research away from satisfaction. He was also adamant that only one dominant motive can be present in our behavior at a time. McClelland categorized the needs or motives into achievement, affiliation, and power and saw them as being influenced by either internal drivers or extrinsic factors.
Among all the prospects which man can have, the most comforting is, on the basis of his present moral condition, to look forward to something permanent and to further progress toward a still better prospect.
Immanuel Kant
The drive for achievement arises out of the psychological need for competence and is defined as a striving for excellence against a standard that can originate from three sources of competition: the task itself, the competition with the self, and the competition against others.
High need for achievement can come from one’s social environment and socialization influences, like parents who promote and value pursuit and standards of excellence, but it can also be developed throughout life as a need for personal growth towards complexity (Reeve, 2014).
Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene theory
Herzberg’s two-factor theory, also known as motivation-hygiene theory, was originally intended to address employee motivation and recognized two sources of job satisfaction. He argued that motivating factors influence job satisfaction because they are based on an individual’s need for personal growth: achievement, recognition, work itself, responsibility, and advancement.
On the other hand, hygiene factors, which represented deficiency needs, defined the job context and could make individuals unhappy with their job: company policy and administration, supervision, salary, interpersonal relationships, and working conditions.
Motivation theories explained in 10 minutes – EPM
Process theories like Skinner’s reinforcement theory, Victor Vroom’s expectancy theory, Adams’ equity theory, and Locke’s goal-setting theory set out to explain how motivation occurs and how our motives change over time.
Reinforcement theory
The most well-known process theory of motivation is the reinforcement theory, which focused on the consequences of human behavior as a motivating factor.
Based on Skinner’s operant conditioning theory , it identifies positive reinforcements as promoters that increased the possibility of the desired behavior’s repetition: praise, appreciation, a good grade, trophy, money, promotion, or any other reward (Gordon, 1987).
It distinguished positive reinforcements from negative reinforcement and punishment, where the former gives a person only what they need in exchange for desired behavior, and the latter tries to stop the undesired behavior by inflicting unwanted consequences.
See our articles on Positive Reinforcement in the Workplace and Parenting Children with Positive Reinforcement .
Other process motivation theories combine aspects of reinforcement theory with other theories, sometimes from adjacent fields, to shine a light on what drives human behavior.
Adams’ equity theory of motivation
For example, Adams’ equity theory of motivation (1965), based on Social Exchange theory, states that we are motivated when treated equitably, and we receive what we consider fair for our efforts.
It suggests that we not only compare our contributions to the amount of rewards we receive but also compare them to what others receive for the same amount of input. Although equity is essential to motivation, it does not take into account the differences in individual needs, values, and personalities, which influence our perception of inequity.
Vroom’s expectancy theory
Victor Vroom’s expectancy theory (1964), on the other hand, integrates needs, equity, and reinforcement theories to explain how we choose from alternative forms of voluntary behavior based on the belief that decisions will have desired outcomes. Vroom suggests that we are motivated to pursue an activity by appraising three factors:
- Expectancy that assumes more effort will result in success
- Instrumentality that sees a connection between activity and goal
- Valence which represents the degree to which we value the reward or the results of success.
Locke’s goal-setting theory
Finally, Locke and Latham’s (1990) goal-setting theory, an integrative model of motivation, sees goals as key determinants of behavior. Possibly the most widely applied, the goal-setting theory stresses goal specificity, difficulty, and acceptance and provides guidelines for how to incorporate them into incentive programs and management by objectives (MBO) techniques in many areas.
Lock’s recipe for effective goal setting includes:
- Setting of challenging but attainable goals. Too easy or too difficult or unrealistic goals don’t motivate us.
- Setting goals that are specific and measurable. These can focus us toward what we want and can help us measure the progress toward the goal.
- Goal commitment should be obtained. If we don’t commit to the goals, then we will not put adequate effort toward reaching them, regardless of how specific or challenging they are.
- Strategies to achieve this could include participation in the goal-setting process, the use of extrinsic rewards (bonuses), and encouraging intrinsic motivation through providing feedback about goal attainment. It is important to mention here that pressure to achieve goals is not useful because it can result in dishonesty and superficial performance.
- Support elements should be provided. For example, encouragement, needed materials and resources, and moral support.
- Knowledge of results is essential. Goals need to be quantifiable, and there needs to be feedback.
There are several articles on effective goal setting in our blog series that cover Locke’s theory and it’s many applications.

They address specific cognitive phenomena that can influence motivation, represent a particular factor of motivation, describe a form of expression of motivation, or explain a process through which it can occur or be enhanced.
The list of cognitive phenomena is by no means comprehensive, but it does give us a taste of the complexity of human motivation and includes references for those who want to read further into more nuanced topics:
- Plans (Carver, Scheier, & Weintraub, 1998)
- Goals (Locke & Latham, 2002)
- Implementation intentions (Gollwitzer, 1999)
- Deliberative versus implementation mindsets (Gollwitzer & Kinney, 1989)
- Promotion versus prevention orientations (Higgins, 1997)
- Growth versus fixed mindsets (Dweck, 2006)
- Dissonance (Festinger, 1957; Harmon-Jones & Mills, 1999)
- Self-efficacy (Bandura, 1986)
- Perceived control (Skinner, 1996)
- Reactance theory (Brehm, 1966)
- Learned helplessness theory (Miller & Seligman, 1975)
- Mastery beliefs (Diener & Dweck, 1978)
- Attributions (Wiener, 1986)
- Values (Eccles & Wigfield, 2002)
- Self-concept (Markus, 1977)
- Possible selves (Oyserman, Bybee, & Terry, 2006)
- Identity (Eccles, 2009)
- Self-regulation (Zimmerman, 2000)
- Self-control (Baumeister & Tierney, 2011)
There are also several different approaches to understanding human motivation which we have discussed in greater detail in our article on Benefits and Importance of Motivation which amass a large body of motivational studies and are currently attracting a lot of attention in contemporary research in motivational science, namely intrinsic motivation (Ryan & Deci, 2000) and the flow theory (Csíkszentmihályi, 1975).

In addition to the Two Factor theory and equity theory, some theories focus on autonomy, wellbeing, and feedback as core motivational aspects of employees’ performance; theories X, Y and Z, and the Hawthorne effect, respectively.
Theory X and Theory Y
Douglas McGregor proposed two theories, Theory X and Theory Y, to explain employee motivation and its implications for management. He divided employees into Theory X employees who avoid work and dislike responsibility and Theory Y employees who enjoy work and exert effort when they have control in the workplace.
He postulated that to motivate Theory X employees, the company needs to enforce rules and implement punishments. For Theory Y employees, management must develop opportunities for employees to take on responsibility and show creativity as a way of motivating. Theory X is heavily informed by what we know about intrinsic motivation, and the role satisfaction of basic psychological needs plays in effective employee motivation.
In response to this theory, a third theory, Theory Z, was developed by Dr. William Ouchi. Ouchi’s theory focuses on increasing employee loyalty to the company by providing a job for life and focusing on the employee’s well-being. It encourages group work and social interaction to motivate employees in the workplace.
The Hawthorne Effect
Elton Mayo developed an explanation known as the Hawthorne Effect that suggested that employees are more productive when they know their work is being measured and studied.

Download 3 Free Goals Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients create actionable goals and master techniques for lasting behavior change.
Download 3 Free Goals Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
There are also several theories on motivation that are used in sports and performance psychology. The core concept in understanding motivation from the performance perspective is how physiological and psychological arousal accompanies behavior.
Arousal is basically a form of mobilization of energy and activation either before or while engaged in the behavior. Arousal occurs in different modes. Physiological arousal refers to the excitement of the body, while psychological arousal is about how subjectively aroused an individual feels.
When we say that our palms are sweaty or our heart is pounding, it implies physiological arousal. When we feel tense and anxious, it signifies psychological arousal.
Robert Thayer (1989) evolved the theory of psychological arousal into two dimensions: energetic arousal and tense arousal, composed of energetic and tense dimensions. Energetic arousal is associated with positive affect, while tense arousal is associated with anxiety and fearfulness.

Tense arousal can be divided further into two types of anxiety: trait anxiety and state anxiety. One refers to the degree we respond to the environment in general negatively and with worry, while state anxiety refers to feelings of apprehension that occur in response to a particular situation.
Arousal originates from several sources. It can be generated by a stimulus that has an arousing function and a cue function. But background stimuli that do not capture our attention also increase arousal.
Thayer found that arousal varies with time of day, for many of us being highest around noon and lower in the morning and evening. Coffee, for example, can boost arousal, as can an instance of being evaluated during exams, music performance, or sports competitions.
Arousal also depends on more complex variables like novelty, complexity, and incongruity. The interaction of various stimuli explains why sometimes arousal increases behavioral efficiency and in other instances, decreases it.
Optimal functioning hypothesis
The zone of optimal functioning hypothesis in sports psychology identifies a zone of optimal arousal where an athlete performs best (Hanin, 1989). As arousal increases, performance on a task increases and then decreases, as can be seen on the inverted-U arousal–performance relationship diagram below.
According to the zone of optimal functioning hypothesis, each individual has her preferred area of arousal based on cognitive or somatic anxiety. The Yerkes–Dodson law explains further that the high point of the inverted-U or arousal–performance relationship depends on the complexity of the task being performed.

Several theories have been proposed to explain the relationship between the inverted-U nature of the arousal–performance relationship.
Hull–Spence drive theory
The classic Hull–Spence drive theory emphasizes how arousal affects performance with little regard for any cognitive awareness by the individual. Also known as drive reduction theory, it postulates that human behavior could be explained by conditioning and reinforcement.
This oversimplification is part of the reason why more nuanced and complex cognitive theories have largely replaced the theory. The cusp catastrophe model in sports psychology, arousal-biased competition theory, processing efficiency theory, and attentional control theory are more concerned with the cognitive aspects of arousal and how this affects behavioral efficiency.
Arousal-biased competition theory
Mather and Sutherland (2011) developed an arousal-biased competition theory to explain the inverted-U arousal–performance relationship. It suggests that arousal exhibits biases toward information that is the focus of our attention.
Arousal effects and therefore increases the priority of processing important information and decrease the priority of processing less critical information. The presence of arousal improves the efficiency of behavior that concerns a crucial stimulus, but it is done at the expense of the background stimuli.
Two memory systems theory
Metcalfe and Jacobs (1998) postulated the existence of two memory systems that influence the level of arousal we experience: a cool memory system and a hot memory system, each in a different area of the brain. The cool system, located in the hippocampus, serves the memory of events occurring in space and time and would allow us to remember where we parked our car this morning.
The hot system in the amygdala serves as the memory of events that occur under high arousal. Metcalfe and Jacobs theorized that the hot system remembers the details of stimuli that predict the onset of highly stressful or arousing events, such as events that predict danger and is responsible for the intrusive memories of individuals who have experienced extremely traumatic events.
Processing efficiency theory
The processing efficiency theory of Eysenck and Calvo theorized on how anxiety, expressed as worry, can influence performance. Preoccupation with being evaluated and being concerned about one’s performance turns to worry, which takes up working memory capacity and causes performance on cognitive tasks to decline (Eysenck & Calvo, 1992).

17 Tools To Increase Motivation and Goal Achievement
These 17 Motivation & Goal Achievement Exercises [PDF] contain all you need to help others set meaningful goals, increase self-drive, and experience greater accomplishment and life satisfaction.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
Here are a suggested book references for tertiary-level study of motivation for those who want to dive deeper into some of these topics:
1. Understanding Motivation and Emotion – Johnmarshall Reeve

IT provides a toolbox of practical interventions and approaches for use in a wide variety of settings.
Available on Amazon .
2. Motivation: Theories and Principles – Robert C. Beck

It covers a broad range of motivational concepts from both human and animal theory and research, with an emphasis on the biological bases of motivation.
3. Motivation – Lambert Deckers

How motivation is the inducement of behavior, feelings, and cognition.
4. Motivation and Emotion Evolutionary Physiological, Developmental, and Social Perspectives – Denys A. deCatanzaro

5. Motivation: A Biosocial and Cognitive Integration of Motivation and Emotion – Eva Dreikurs Ferguson

These include hunger and thirst, circadian and other biological rhythms, fear and anxiety, anger and aggression, achievement, attachment, and love.
6. Human Motivation – Robert E. Franken

7. The Psychology of Action: Linking Cognition and Motivation to Behavior – Peter M. Gollwitzer and John Bargh

These programs are effectively mapping the territory, providing new findings, and suggesting innovative strategies for future research.
8. Motivation and Self-Regulation Across the Life Span – Jutta Heckhausen and Carol S. Dweck

9. Reclaiming Cognition: The Primacy of Action, Intention, and Emotion (Journal of Consciousness Studies) – Rafael Nunez and Walter J. Freeman

This leads to the claim that cognition is representational and best explained using models derived from AI and computational theory. The authors depart radically from this model.
10. Motivation: Theory, Research, and Applications – Herbert L. Petri and John M. Govern

The book clearly presents the advantages and drawbacks to each of these explanations, allowing readers to draw their own conclusions.
11. Intrinsic & Extrinsic Motivation: The Search for Optimal Motivation and Performance – Carol Sansone and Judith M. Harackiewicz

12. The Psychobiology of Human Motivation (Psychology Focus) – Hugh Wagner

It starts from basic physiological needs like hunger and thirst, to more complex aspects of social behavior like altruism.
There is no shortage of explanations for what constitutes human motivation, and the research on the topic is as vast and dense as the field of psychology itself. Perhaps the best course of action is to identify the motivational dilemma we’re trying to solve and then select one approach to motivation if only to try it out.
By annihilating desires you annihilate the mind. Every man without passions has within him no principle of action, nor motive to act.
Claude Adrien Helvetius, 1715–1771
As Dan Kahneman argues, teaching psychology is mostly a waste of time unless we as students can experience what we are trying to learn or teach about human nature and can deduce if it is right for us.
Then and only then, can we choose to act on it, move in the direction of change, or make a choice to remain the same. It’s all about experiential learning and connecting the knowledge we acquire to our own experience.
What motivational theory do you find most useful?
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Goal Achievement Exercises for free .
- Image 1 : Maslow pyramid adapted from “Renovating the Pyramid of Needs: Contemporary Extensions Built upon Ancient Foundations” by D. T. Kenrick et al., 2010, Perspectives on Psychological Science, 5, 292–314 (see p. 293), and from “A Theory of Human Needs Should Be Human-Centered, Not Animal-Centered: Commentary on Kenrick et al. (2010)” by S. Kesebir et al., 2010, Perspectives on Psychological Science, 5, 315–319 (see p. 316), and from “Human Motives, Happiness, and the Puzzle of Parenthood: Commentary on Kenrick et al. (2010)” by S. Lyubormirsky & J. K. Boehm, 2010, Perspectives on Psychological Science, 5, 327–334.
- Adams, J. S. (1965). Inequity in social exchange. Advances in experimental social psychology (Vol. 2, pp. 267-299). New York, NY: Academic Press.
- Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action. In D. Marks (Ed.), The health psychology reader (pp. 23-28). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Sage.
- Baumeister, R. F., & Tierney, J. (2011). Willpower: Rediscovering the greatest human strength. New York, NY: Penguin.
- Brehm, J. (1966). A theory of psychological reactance . New York, NY: Academic Press.
- Carver, C. S., Scheier, M. F., & Weintraub, J. K. (1989). Assessing coping strategies: A theoretically based approach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 56 (2), 267-283.
- Csíkszentmihályi, M. (1975). Beyond boredom and anxiety: The experience of play in work and games. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
- Diener, C. I., & Dweck, C. S. (1978). An analysis of learned helplessness: Continuous changes in performance, strategy, and achievement cognitions following failure. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 36 (5), 451-462.
- Dweck, C. S. (2006). Mindset: The new psychology of success. New York, NY: Balantine Books.
- Eccles, J. (2009). Who am I and what am I going to do with my life? Personal and collective identities as motivators of action. Educational Psychologist, 44 (2), 78-89.
- Eccles, J. S., & Wigfield, A. (2002). Motivational beliefs, values, and goals. Annual Review of Psychology, 53 (1), 109-132.
- Eysenck, M. W., & Calvo, M. G. (1992). Anxiety and performance: The processing efficiency theory. Cognition & Emotion, 6 (6), 409-434.
- Festinger, L. (1957). A theory of cognitive dissonance . Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Gollwitzer, P. M. (1999). Implementation intentions: strong effects of simple plans. American Psychologist, 54 (7), 493-503.
- Gollwitzer, P. M., & Kinney, R. F. (1989). Effects of deliberative and implemental mind-sets on illusion of control. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 56 (4), 531-542.
- Gordon, R. M. (1987). The structure of emotions . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
- Hanin, Y. L. (1989). Interpersonal and intragroup anxiety in sports. In D. Hackfort & C. D. Spielberger (Eds.), Anxiety in sports: An international perspective (pp. 19-28). New York, NY: Hemisphere.
- Harmon-Jones, E., & Mills, J. (Eds.). (1999). Science conference series. Cognitive dissonance: Progress on a pivotal theory in social psychology. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Higgins, E. T. (1997). Beyond pleasure and pain. American Psychologist, 52 (12), 1280-1300.
- Kenrick, D. T., Griskevicius, V., Neuberg, S. L., & Schaller, M. (2010). Renovating the pyramid of needs: Contemporary extensions built upon ancient foundations. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 5 (3), 292-314.
- Kesebir, S., Graham, J., & Oishi, S. (2010). A theory of human needs should be human-centered, not animal-centered: Commentary on Kenrick et al. (2010). Perspectives on Psychological Science, 5 (3), 315-319.
- Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (1990). A theory of goal setting & task performance . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
- Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (2002). Building a practically useful theory of goal setting and task motivation: A 35-year odyssey. American Psychologist, 57 (9), 705-717.
- Lyubomirsky, S., & Boehm, J. K. (2010). Human motives, happiness, and the puzzle of parenthood: Commentary on Kenrick et al.(2010). Perspectives on Psychological Science, 5 (3), 327-334.
- Markus, H. (1977). Self-schemata and processing information about the self. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 35 (2), 63-78.
- Mather, M., & Sutherland, M. R. (2011). Arousal-biased competition in perception and memory. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 6 (2), 114-133.
- Metcalfe, J., & Jacobs, W. J. (1998). Emotional memory: The effects of stress on “cool” and “hot” memory systems. In D. L. Medin (Ed.), The psychology of learning and motivation: Advances in research and theory (Vol. 38, pp. 187-222). New York, NY: Academic Press.
- Miller, W. R., & Seligman, M. E. (1975). Depression and learned helplessness in man. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 84 (3), 228-238.
- Oyserman, D., Bybee, D., & Terry, K. (2006). Possible selves and academic outcomes: How and when possible selves impel action. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 91 (1), 188-204.
- Reeve, J. (2014). Understanding motivation and emotion (6th ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
- Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist, 55 (1), 68-78.
- Sheldon, K. M., & Elliot, A. J. (1999). Goal striving, need satisfaction, and longitudinal well-being: The self-concordance model. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 76(3) , 482–497.
- Skinner, E. A. (1996). A guide to constructs of control. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 71 (3), 549-570.
- Thayer, R. L. (1989). The experience of sustainable landscapes. Landscape Journal, 8 (2), 101-110.
- Vroom, V. H. (1964). Work and motivation. New York, NY: Wiley.
- Wiener, B. (1986). Attribution, emotion, and action. In R. M. Sorrentino & E. T. Higgins (Eds.), Handbook of motivation and cognition: Foundations of social behavior (pp. 281–312). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
- Zimmerman, B. J. (2000). Attaining self-regulation: A social cognitive perspective. In M. Boekaerts, P. R. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 13-39). San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
Hi Nicole, I love this site! I am a PhD student but in international development, not psychology and my methodology is multi-disciplinary, but that is quite difficult I am finding now I am looking at psychology! I have been sent down a path by an Australian academic about the role of action to motivation to action – do you have any good references to recommend on this? Thx, Sue Cant, Charles Darwin University
It sounds like you’re delving into an exciting interdisciplinary study! The role of action and motivation is indeed a key topic in psychology and relevant to international development too.
First, you might find “ Self-Determination Theory ” by Richard M. Ryan and Edward L. Deci interesting. It delves into the relationship between motivation, action, and human behavior, exploring how our needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness influence our motivation and actions.
Another reference to consider is “ Mindset: The New Psychology of Success ” by Carol S. Dweck. It explores the concept of “growth mindset” and how our beliefs about our abilities can impact our motivation to act and overcome challenges.
These references should provide a good starting point for understanding the psychological aspects of action and motivation. I hope they prove useful for your research!
Best of luck with your PhD journey!
Kind regards, Julia | Community Manager
I enjoyed the fact that there is plenty information, if I were to write an essay on Motivation.
It’s so informative and inclusive! I just wonder if there are relevant theories on how to motivate communities (e.g. residents, companies, experts) to participate in decision-making (e.g. protection of cultural heritage)? Thank you!
Glad you liked the article! I’m not sure if there are theories that specifically cover this (they may be more in sociology and a bit beyond my expertise). But I’d recommend having a read of my article on positive communities. If you follow some of the references throughout, I suspect you’ll find some great resources and advice, particularly on participative decision-making: https://positivepsychology.com/10-traits-positive-community/
Hope this helps a little!
– Nicole | Community Manager
Deci and Ryans Self Determination Theory needs to be discussed… NOT just given an afterthought. Their argument that human behaviour is driven by the 3 fundamental needs of 1) Affiliation 2) Competence and 3) Self Determination is supported by developmental science (attachment theory, Tomosello’s cross species work, developmental work on competence and learning, and finally the huge body of work on intrinsic motivation and self-regulation.
This overview is well written but appears to have a big hole in it.
Hi Dr. Martin,
Thanks for your comment. We agree SDT is a powerful theory, and it has many different applications. We’ve addressed these in depth in some of our other articles on the topic:
Self-Determination Theory of Motivation: Why Intrinsic Motivation Matters – https://positivepsychology.com/self-determination-theory/ 21 Self-Determination Skills and Activities to Utilize Today: https://positivepsychology.com/self-determination-skills-activities/ Intrinsic Motivation Explained: 10 Factors & Real-Life Examples: https://positivepsychology.com/intrinsic-motivation-examples/
Hey Nicole. This summary is amazing and pin points what I’m looking for. In the case where I have to evaluate this theory for example Maslow’s hierarchy theory in relation to an organization’s needs. How do I go about that or what’s the best way to do so?
Hi Deborah,
So glad you enjoyed the article. Could you please give a little more information about what you’re looking to do? For instance, are you looking for a theory you can apply to assess individual employees’ motivation at work? Note that not all of the theories discussed here are really applicable to an organizational context (e.g., I would personally avoid Maslow’s hierarchy for this), so it would be helpful to have a little more information.
Yes. Precisely that. I am looking for theories that I am adapt to do an intervention , implementation and evaluation of employee motivation in an organization. And how exactly these theories are implemented.
Thank you Nicole. Excellent summary of available theories. Could you tell me please which may be the best theory to explain involvement in extremism and radicalization?
Glad you liked the article. Research on motivations underlying extremism and radicalization tend to point to our beliefs having a central role. This paper by Trip et al. (2019) provides an excellent summary of the thinking in this space. It looks at the factors from an REBT perspective. It addresses a whole range of motivational perspectives including uncertainty-identity theory and integrated threat theory.
I hope this article is helpful for you.
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Victor Vroom’s Expectancy Theory of Motivation
Motivation is vital to beginning and maintaining healthy behavior in the workplace, education, and beyond, and it drives us toward our desired outcomes (Zajda, 2023). [...]

SMART Goals, HARD Goals, PACT, or OKRs: What Works?
Goal setting is vital in business, education, and performance environments such as sports, yet it is also a key component of many coaching and counseling [...]

How to Assess and Improve Readiness for Change
Clients seeking professional help from a counselor or therapist are often aware they need to change yet may not be ready to begin their journey. [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (48)
- Coaching & Application (57)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (24)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (45)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (27)
- Positive Communication (20)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (16)
- Positive Psychology (33)
- Positive Workplace (36)
- Productivity (16)
- Relationships (49)
- Resilience & Coping (35)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (37)
- Strengths & Virtues (30)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)

- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
3 Goal Achievement Exercises Pack
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Motivational Theories, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 595
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Part of a manager’s duties in the workplace involves motivating employees. A manager who successfully motivates his or her employees will be able to reap the benefits tied to better employee performance. A manager who unsuccessfully motivates employees earns the consequences of a poorly functioning organization. Managers can apply different motivational theories to assist them in motivating staff. Three motivational theories, Expectancy Theory, Reinforcement Theory, and Adam’s Equity Theory of Motivation, are useful tools for motivating employees.
Expectancy Theory points to the relationship between motivation and outcome (“Expectency Theory” n.d.). Essentially, the theory states that people will work hard when they expect the outcome of their hard work to be positive (“Expectency Theory” n.d.). As such, expectancy theory states that motivating people should come down to three things (“Expectency Theory” n.d.). First, motivation is a factor of effort (“Expectency Theory” n.d.). In order to motivate others, employers should encourage the belief that more effort equals better performance. Second, employers should encourage the belief that better performance will lead to better rewards (“Expectency Theory” n.d.).Finally, employers should focus on the outcome by making sure that the reward is attractive to the employee (“Expectency Theory” n.d.).
Expectancy theory has both pros and cons when managers use it in the application of performance improvement. First, since expectancy theory is dependent upon individual perspective, the outcome is dependent on each employee’s individual perspective. If the manager has an understanding of the perspective, it will be successful; otherwise it will fail miserably. If managers want to see the results of expectancy theory, they can utilize several tools. First they can use a reward system that is closely tied to pay-for-performance (“Expectency Theory” n.d.). Second, they can use training to instill the belief that added effort will lead to better performance.
A second motivational theory, Reinforcement Theory, states that individuals behaviors are a function of the consequences (“Reinforcement Theory” n.d.). In other words, an individual will repeat behaviors that lead to positive consequences and fail to repeat behaviors that lead to negative consequences (“Reinforcement Theory” n.d.). Management should be sure to tie the consequence directly to the behavior in order to see the results.
While Reinforcement Theory can be helpful to managers, it has been criticized for failing to focus on the causes of individuals’ behavior. On the positive side, the theory can be a strong tool for analyzing the controlling mechanisms of human behavior (“Reinforcement Theory” n.d.). Under this theory, managers can use several tools to motivate individuals’ behavior including positive reinforcement or negative reinforcement (“Reinforcement Theory” n.d.).
The third motivational theory is Adam’s Equity Theory of Motivation. This theory states that employees will strive to achieve equity between them and their coworkers (buzz). This can be achieved when the outcome to input ratio is equal for all employees (buzz). Managers can implement this theory by tying rewards to performance and by setting goals effectively for workers (buzz).
Adam’s Equity Theory can work in situations where the work employees perform is easy to measure and compare. When employees perform similar, standardized procedures, managers can easily compare the data. However, sometimes employees perform job duties that may not tie directly to a quantifiable measure. In cases such as this, equity theory falls short.
Motivated employees will work harder. This hard work leads to a more profitable company. Motivation theories explain ways managers can ensure that their organizations are more profitable. With proper application, both employees and managers can reap the benefits.
Expectency Theory: Motivate Your Team by Linking Effort With Outcome. (n.d.) Retrieved from http://www.lacpa.org.lb/Includes/Images/Docs/TC/TC341.pdf
Reinforcement Theory of Motivation. (n.d.). Retreived from http://www.managementstudyguide.com/reinforcement-theory-motivation.htm
Equity Theory of Motivation. (n.d.) Retreived from http://www.buzzle.com/articles/equity-theory-of-motivation.html
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
A Wishing Well Premise, Article Review Example
A Brief History of Soap, Essay Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Motivation: The Driving Force Behind Our Actions
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Emily Roberts
- Improvement
The term motivation describes why a person does something. It is the driving force behind human actions. Motivation is the process that initiates, guides, and maintains goal-oriented behaviors.
For instance, motivation is what helps you lose extra weight, or pushes you to get that promotion at work. In short, motivation causes you to act in a way that gets you closer to your goals. Motivation includes the biological , emotional , social , and cognitive forces that activate human behavior.
Motivation also involves factors that direct and maintain goal-directed actions. Although, such motives are rarely directly observable. As a result, we must often infer the reasons why people do the things that they do based on observable behaviors.
Learn the types of motivation that exist and how we use them in our everyday lives. And if it feels like you've lost your motivation, do not worry. There are many ways to develop or improve your self-motivation levels.
Press Play for Advice on Motivation
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares an exercise you can use to help you perform your best. Click below to listen now.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
What Are the Types of Motivation?
The two main types of motivation are frequently described as being either extrinsic or intrinsic.
- Extrinsic motivation arises from outside of the individual and often involves external rewards such as trophies, money, social recognition, or praise.
- Intrinsic motivation is internal and arises from within the individual, such as doing a complicated crossword puzzle purely for the gratification of solving a problem.
A Third Type of Motivation?
Some research suggests that there is a third type of motivation: family motivation. An example of this type is going to work when you are not motivated to do so internally (no intrinsic motivation), but because it is a means to support your family financially.
Why Motivation Is Important
Motivation serves as a guiding force for all human behavior. So, understanding how motivation works and the factors that may impact it can be important for several reasons.
Understanding motivation can:
- Increase your efficiency as you work toward your goals
- Drive you to take action
- Encourage you to engage in health-oriented behaviors
- Help you avoid unhealthy or maladaptive behaviors, such as risk-taking and addiction
- Help you feel more in control of your life
- Improve your overall well-being and happiness
Click Play to Learn More About Motivation
This video has been medically reviewed by John C. Umhau, MD, MPH, CPE .
What Are the 3 Components of Motivation?
If you've ever had a goal (like wanting to lose 20 pounds or run a marathon), you probably already know that simply having the desire to accomplish these things is not enough. You must also be able to persist through obstacles and have the endurance to keep going in spite of difficulties faced.
These different elements or components are needed to get and stay motivated. Researchers have identified three major components of motivation: activation, persistence, and intensity.
- Activation is the decision to initiate a behavior. An example of activation would be enrolling in psychology courses in order to earn your degree.
- Persistence is the continued effort toward a goal even though obstacles may exist. An example of persistence would be showing up for your psychology class even though you are tired from staying up late the night before.
- Intensity is the concentration and vigor that goes into pursuing a goal. For example, one student might coast by without much effort (minimal intensity) while another student studies regularly, participates in classroom discussions, and takes advantage of research opportunities outside of class (greater intensity).
The degree of each of these components of motivation can impact whether you achieve your goal. Strong activation, for example, means that you are more likely to start pursuing a goal. Persistence and intensity will determine if you keep working toward that goal and how much effort you devote to reaching it.
Tips for Improving Your Motivation
All people experience fluctuations in their motivation and willpower . Sometimes you feel fired up and highly driven to reach your goals. Other times, you might feel listless or unsure of what you want or how to achieve it.
If you're feeling low on motivation, there are steps you can take to help increase your drive. Some things you can do to develop or improve your motivation include:
- Adjust your goals to focus on things that really matter to you. Focusing on things that are highly important to you will help push you through your challenges more than goals based on things that are low in importance.
- If you're tackling something that feels too big or too overwhelming, break it up into smaller, more manageable steps. Then, set your sights on achieving only the first step. Instead of trying to lose 50 pounds, for example, break this goal down into five-pound increments.
- Improve your confidence . Research suggests that there is a connection between confidence and motivation. So, gaining more confidence in yourself and your skills can impact your ability to achieve your goals.
- Remind yourself about what you've achieved in the past and where your strengths lie. This helps keep self-doubts from limiting your motivation.
- If there are things you feel insecure about, try working on making improvements in those areas so you feel more skilled and capable.
Causes of Low Motivation
There are a few things you should watch for that might hurt or inhibit your motivation levels. These include:
- All-or-nothing thinking : If you think that you must be absolutely perfect when trying to reach your goal or there is no point in trying, one small slip-up or relapse can zap your motivation to keep pushing forward.
- Believing in quick fixes : It's easy to feel unmotivated if you can't reach your goal immediately but reaching goals often takes time.
- Thinking that one size fits all : Just because an approach or method worked for someone else does not mean that it will work for you. If you don't feel motivated to pursue your goals, look for other things that will work better for you.
Motivation and Mental Health
Sometimes a persistent lack of motivation is tied to a mental health condition such as depression . Talk to your doctor if you are feeling symptoms of apathy and low mood that last longer than two weeks.
Theories of Motivation
Throughout history, psychologists have proposed different theories to explain what motivates human behavior. The following are some of the major theories of motivation.
The instinct theory of motivation suggests that behaviors are motivated by instincts, which are fixed and inborn patterns of behavior. Psychologists such as William James, Sigmund Freud , and William McDougal have proposed several basic human drives that motivate behavior. They include biological instincts that are important for an organism's survival—such as fear, cleanliness, and love.
Drives and Needs
Many behaviors such as eating, drinking, and sleeping are motivated by biology. We have a biological need for food, water, and sleep. Therefore, we are motivated to eat, drink, and sleep. The drive reduction theory of motivation suggests that people have these basic biological drives, and our behaviors are motivated by the need to fulfill these drives.
Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs is another motivation theory based on a desire to fulfill basic physiological needs. Once those needs are met, it expands to our other needs, such as those related to safety and security, social needs, self-esteem, and self-actualization.
Arousal Levels
The arousal theory of motivation suggests that people are motivated to engage in behaviors that help them maintain their optimal level of arousal. A person with low arousal needs might pursue relaxing activities such as reading a book, while those with high arousal needs might be motivated to engage in exciting, thrill-seeking behaviors such as motorcycle racing.
The Bottom Line
Psychologists have proposed many different theories of motivation . The reality is that there are numerous different forces that guide and direct our motivations.
Understanding motivation is important in many areas of life beyond psychology, from parenting to the workplace. You may want to set the best goals and establish the right reward systems to motivate others as well as to increase your own motivation .
Knowledge of motivating factors (and how to manipulate them) is used in marketing and other aspects of industrial psychology. It's an area where there are many myths, and everyone can benefit from knowing what works with motivation and what doesn't.
Nevid JS. Psychology: Concepts and Applications .
Tranquillo J, Stecker M. Using intrinsic and extrinsic motivation in continuing professional education . Surg Neurol Int. 2016;7(Suppl 7):S197-9. doi:10.4103/2152-7806.179231
Menges JI, Tussing DV, Wihler A, Grant AM. When job performance is all relative: How family motivation energizes effort and compensates for intrinsic motivation . Acad Managem J . 2016;60(2):695-719. doi:10.5465/amj.2014.0898
Hockenbury DH, Hockenbury SE. Discovering Psychology .
Zhou Y, Siu AF. Motivational intensity modulates the effects of positive emotions on set shifting after controlling physiological arousal . Scand J Psychol . 2015;56(6):613-21. doi:10.1111/sjop.12247
Mystkowska-Wiertelak A, Pawlak M. Designing a tool for measuring the interrelationships between L2 WTC, confidence, beliefs, motivation, and context . Classroom-Oriented Research . 2016. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-30373-4_2
Myers DG. Exploring Social Psychology .
Siegling AB, Petrides KV. Drive: Theory and construct validation . PLoS One . 2016;11(7):e0157295. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0157295
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Motivation: Introduction to the Theory, Concepts, and Research
- First Online: 03 May 2018
Cite this chapter

- Paulina Arango 4
Part of the book series: Literacy Studies ((LITS,volume 15))
1583 Accesses
2 Citations
Motivation is a psychological construct that refers to the disposition to act and direct behavior according to a goal. Like most of psychological processes, motivation develops throughout the life span and is influenced by both biological and environmental factors. The aim of this chapter is to summarize research on the development of motivation from infancy to adolescence, which can help understand the typical developmental trajectories of this ability and its relation to learning. We will start with a review of some of the most influential theories of motivation and the aspects each of them has emphasized. We will also explore how biology and experience interact in this development, paying special attention to factors such as: school, family, and peers, as well as characteristics of the child including self-esteem, cognitive development, and temperament. Finally, we will discuss the implications of understanding the developmental trajectories and the factors that have an impact on this development, for both teachers and parents.
- Achievement
- Motivational theories
- Influences on motivation
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
This is not intended to be an exhaustive review of motivational theories. For a more detailed review see: (Dörnyei and Ushioda 2013 ; Eccles and Wigfield 2002 ; Wentzel and Miele 2009 ; Wigfield et al. 2007 ).
For more information on the development of motivation in adults you can see: Carstensen 1993 ; Kanfer and Ackerman 2004 ; Wlodkowski 2011 .
Atkinson, J. W. (1957). Motivational determinants of risk taking behavior. Psychological Review, 64 (6), 359–372. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0043445 .
Article Google Scholar
Atkinson, J. W., & Raynor, J. O. (1978). Personality, motivation, and achievement . Oxford: Hemisphere.
Google Scholar
Aunola, K., Leskinen, E., Onatsu-Arvilommi, T., & Nurmi, J. E. (2002). Three methods for studying developmental change: A case of reading skills and self-concept. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 72 (3), 343–364. https://doi.org/10.1348/000709902320634447 .
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory . Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Bandura, A. (1991). Self-regulation of motivation through anticipatory and self-reactive mechanisms. In R. A. Dienstbier (Ed.), Perspectives on motivation: Nebraska symposium on motivation (Vol. 38, pp. 69–164). Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control . New York: Freeman.
Bandura, A. (1999). A social cognitive theory of personality. In L. Pervin & O. John (Eds.), Handbook of personality (2nd ed., pp. 154–196). New York: Guilford.
Bandura, A., Barbaranelli, C., Caprara, G. V., & Pastorelli, C. (2001). Self-efficacy beliefs as shapers of children’s aspirations and career trajectories. Child Development, 72 (1), 187–206. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00273 .
Bechara, A., Damasio, H., & Damasio, A. R. (2000). Emotion, decision making and the orbitofrontal cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 10 (3), 295–307. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/10.3.295 .
Boulton, M. J., Don, J., & Boulton, L. (2011). Predicting children’s liking of school from their peer relationships. Social Psychology of Education, 14 (4), 489–501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11218-011-9156-0 .
Bradley, R. H., & Corwyn, R. F. (2002). Socioeconomic status and child development. Annual Review of Psychology, 53 (1), 371–399. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135233 .
Brechwald, W. A., & Prinstein, M. J. (2011). Beyond homophily: A decade of advances in understanding peer influence processes. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 21 (1), 166–179. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-7795.2010.00721.x .
Buss, D. M. (2008). Human nature and individual differences. In S. E. Hampson & H. S. Friedman (Eds.), The handbook of personality: Theory and research (pp. 29–60). New York: The Guilford Press.
Cain, K. M., & Dweck, C. S. (1989). The development of children’s conceptions of Intelligence; A theoretical framework. In R. J. Sternberg (Ed.), Advances in the psychology of human intelligence (Vol. 5, pp. 47–82). Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Cain, K., & Dweck, C. S. (1995). The relation between motivational patterns and achievement cognitions through the elementary school years. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 41 (1), 25–52.
Carlson, C. L., Mann, M., & Alexander, D. K. (2000). Effects of reward and response cost on the performance and motivation of children with ADHD. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 24 (1), 87–98. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005455009154 .
Carstensen, L. L. (1993, January). Motivation for social contact across the life span: A theory of socioemotional selectivity. In Nebraska symposium on motivation (Vol. 40, pp. 209–254).
Catalano, R. F., Berglund, M. L., Ryan, J. A., Lonczak, H. S., & Hawkins, J. D. (2004). Positive youth development in the United States: Research findings on evaluations of positive youth development programs. The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, 591 (1), 98–124. https://doi.org/10.1177/0002716203260102 .
Coll, C. G., Bearer, E. L., & Lerner, R. M. (2014). Nature and nurture: The complex interplay of genetic and environmental influences on human behavior and development . Mahwah: Psychology Press.
Collins, W. A., Maccoby, E. E., Steinberg, L., Hetherington, E. M., & Bornstein, M. H. (2000). Contemporary research on parenting: The case for nature and nurture. American Psychologist, 55 (2), 218–232. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003–066X.55.2.218 .
Conger, R. D., Wallace, L. E., Sun, Y., Simons, R. L., McLoyd, V. C., & Brody, G. H. (2002). Economic pressure in African American families: A replication and extension of the family stress model. Developmental Psychology, 38 (2), 179. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012–1649.38.2.179 .
Connell, J. P. (1985). A new multidimensional measure of children’s perception of control. Child Development, 56 (4), 1018–1041. https://doi.org/10.2307/1130113 .
Damasio, A. R., Everitt, B. J., & Bishop, D. (1996). The somatic marker hypothesis and the possible functions of the prefrontal cortex [and discussion]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 351 (1346), 1413–1420. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.1996.0125 .
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (2000). The “what” and “why” of goal pursuits: Human needs and the self–determination of behavior. Psychological Inquiry, 11 (4), 227–268. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327965PLI1104_01 .
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (2002a). The paradox of achievement: The harder you push, the worse it gets. In J. Aronson (Ed.), Improving academic achievement: Impact of psychological factors on education (pp. 61–87). San Diego: Academic Press.
Chapter Google Scholar
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (2002b). Self–determination research: Reflections and future directions. In E. L. Deci & R. M. Ryan (Eds.), Handbook of self–determination theory research (pp. 431–441). Rochester: University of Rochester Press.
Dörnyei, Z., & Ushioda, E. (2013). Teaching and researching: Motivation . London: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315833750 .
Book Google Scholar
Dweck, C. S. (2002). The development of ability conceptions. In A. Wigfield & J. S. Eccles (Eds.), Development of achievement motivation (pp. 57–88). San Diego: Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978–012750053–9/50005–X .
Eccles, J. S. (1987). Gender roles and women’s achievement–related decisions. Psychology of Women Quarterly, 11 (2), 135–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471–6402.1987.tb00781.x .
Eccles, J. S. (1993). School and family effects on the ontogeny of children’s interests, self–perceptions, and activity choice. In J. Jacobs (Ed.), Nebraska symposium on motivation, 1992: Developmental perspectives on motivation (pp. 145–208). Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Eccles, J. S., & Harold, R. D. (1993). Parent–school involvement during the early adolescent years. Teachers’ College Record, 94 , 568–587.
Eccles, J. S., & Wigfield, A. (1995). In the mind of the actor: The structure of adolescents’ achievement task values and expectancy–related beliefs. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 21 (3), 215–225. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167295213003 .
Eccles, J. S., & Wigfield, A. (2002). Motivational beliefs, values, and goals. Annual Review of Psychology, 53 (1), 109–132. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135153 .
Eccles, J. S., Wigfield, A., Harold, R., & Blumenfeld, P. B. (1993). Age and gender differences in children’s self– And task perceptions during elementary school. Child Development, 64 (3), 830–847. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467–8624.1993.tb02946.x .
Eccles, J. S., Wigfield, A., & Schiefele, U. (1998). Motivation to succeed. In W. Damon (Series Ed.) & N. Eisenberg (Vol. Ed.), Handbook of Child Psychology (5th ed. Vol. 3, pp. 1017–1095). New York: Wiley.
Eccles–Parsons, J., Adler, T. F., & Kaczala, C. M. (1982). Socialization of achievement attitudes and beliefs: Parental influences. Child Development, 53 (2), 310–321. https://doi.org/10.2307/1128973 .
Eccles–Parsons, J., Adler, T. F., Futterman, R., Goff, S. B., Kaczala, C. M., Meece, J. L., et al. (1983). Expectancies, values, and academic behaviors. In J. T. Spence (Ed.), Achievement and achievement motivation (pp. 75–146). San Francisco: Freeman.
Eggen, P. D., & Kauchak, D. P. (2007). Educational psychology: Windows on classrooms . Virginia: Prentice Hall.
Ernst, M. (2014). The triadic model perspective for the study of adolescent motivated behavior. Brain and Cognition, 89 , 104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2014.01.006 .
Ernst, M., & Fudge, J. L. (2009). A developmental neurobiological model of motivated behavior: Anatomy, connectivity and ontogeny of the triadic nodes. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 33 (3), 367–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.10.009 .
Ernst, M., & Paulus, M. P. (2005). Neurobiology of decision making: A selective review from a neurocognitive and clinical perspective. Biological Psychiatry, 58 (8), 597–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.06.004 .
Ernst, M., Pine, D. S., & Hardin, M. (2006). Triadic model of the neurobiology of motivated behavior in adolescence. Psychological Medicine, 36 (03), 299–312. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291705005891 .
Ernst, M., Romeo, R. D., & Andersen, S. L. (2009). Neurobiology of the development of motivated behaviors in adolescence: A window into a neural systems model. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 93 (3), 199–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2008.12.013 .
Fredricks, J. A., & Eccles, J. S. (2002). Children’s competence and value beliefs from childhood through adolescence: Growth trajectories in two male–sex–typed domains. Developmental Psychology, 38 (4), 519–533. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012–1649.38.4.519 .
Fredricks, J. A., & Eccles, J. S. (2004). Parental influences on youth involvement in sports. In M. R. Weiss (Ed.), Developmental sport and exercise psychology: A lifespan perspective (pp. 145–164). Morgantown: Fitness Information Technology.
Freud, S. (1920). Beyond the pleasure principle . London: The Hogarth Press and the Institute of Psychoanalysis.
Friedel, J. M., Cortina, K. S., Turner, J. C., & Midgley, C. (2007). Achievement goals, efficacy beliefs and coping strategies in mathematics: The roles of perceived parent and teacher goal emphases. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 32 (3), 434–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2006.10.009 .
Furrer, C., & Skinner, E. (2003). Sense of relatedness as a factor in children’s academic engagement and performance. Journal of Educational Psychology, 95 (1), 148–162. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022–0663.95.1.148 .
Gallardo, L. O., Barrasa, A., & Guevara–Viejo, F. (2016). Positive peer relationships and academic achievement across early and midadolescence. Social Behavior and Personality: An International Journal, 44 (10), 1637–1648. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.2016.44.10.1637 .
Glenn, S., Dayus, B., Cunningham, C., & Horgan, M. (2001). Mastery motivation in children with down syndrome. Down Syndrome Research and Practice, 7 (2), 52–59. https://doi.org/10.3104/reports.114 .
Gniewosz, B., Eccles, J. S., & Noack, P. (2015). Early adolescents’ development of academic self-concept and intrinsic task value: The role of contextual feedback. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 25 (3), 459–473. https://doi.org/10.1111/jora.12140 .
Gunderson, E. A., Ramirez, G., Levine, S. C., & Beilock, S. L. (2012). The role of parents and teachers in the development of gender–related math attitudes. Sex Roles, 66 (3–4), 153–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-011-9996-2 .
Guthrie, J. T., Wigfield, A., & Perencevich, K. C. (Eds.). (2004). Motivating reading comprehension: Concept oriented reading instruction . Mahwah: Erlbaum. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781410610126 .
Harackiewicz, J. M., Barron, K. E., & Elliot, A. J. (1998). Rethinking achievement goals: When are they adaptive for college students and why? Educational Psychologist, 33 (1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326985ep3301_1 .
Heckhausen, H. (1987). Emotional components of action: Their ontogeny as reflected in achievement behavior. In D. Gîrlitz & J. F. Wohlwill (Eds.), Curiosity, imagination, and play (pp. 326–348). Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Heckhausen, J. (2000). Motivational psychology of human development: Developing motivation and motivating development . Amsterdam: Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4115(00)80003-5 .
Hokoda, A., & Fincham, F. D. (1995). Origins of children’s helpless and mastery achievement patterns in the family. Journal of Educational Psychology, 87 (3), 375–385. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.87.3.375 .
Hull, C. L. (1943). Principles of behavior: An introduction to behavior theory . Oxford: Appleton-Century Company, Incorporated.
Jacobs, J. E., & Eccles, J. S. (2000). Parents, task values, and real-life achievement-related choices. In C. Sansone & J. M. Harackiewicz (Eds.), Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation: The search for optimal motivation and performance (pp. 405–439). San Diego: Academic Press.
Jacobs, J. E., Lanza, S., Osgood, D. W., Eccles, J. S., & Wigfield, A. (2002). Changes in children’s self-competence and values: Gender and domain differences across grades one through twelve. Child Development, 73 (2), 509–527. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00421 .
Jacobs, J. E., Davis-Kean, P., Bleeker, M., Eccles, J. S., & Malanchuk, O. (2005). I can, but I don’t want to. The impact of parents, interests, and activities on gender differences in math. In A. Gallagher & J. Kaufman (Eds.), Gender differences in mathematics: An integrative psychological approach (pp. 246–263). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
James, W. (1963). Psychology . New York: Fawcett.
Kahne, J., Nagaoka, J., Brown, A., O’Brien, J., Quinn, T., & Thiede, K. (2001). Assessing after-school programs as contexts for youth development. Youth & Society, 32 (4), 421–446. https://doi.org/10.1177/0044118X01032004002 .
Kanfer, R., & Ackerman, P. L. (2004). Aging, adult development, and work motivation. Academy of Management Review, 29 (3), 440–458. https://doi.org/10.5465/AMR.2004.13670969 .
Karbach, J., Gottschling, J., Spengler, M., Hegewald, K., & Spinath, F. M. (2013). Parental involvement and general cognitive ability as predictors of domain-specific academic achievement in early adolescence. Learning and Instruction, 23 , 43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2012.09.004 .
King, R. B., & Ganotice, F. A., Jr. (2014). The social underpinnings of motivation and achievement: Investigating the role of parents, teachers, and peers on academic outcomes. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 23 (3), 745–756. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-013-0148-z .
Kleinginna, P. R., Jr., & Kleinginna, A. M. (1981). A categorized list of motivation definitions, with a suggestion for a consensual definition. Motivation and Emotion, 5 (3), 263–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00993889 .
Lee, J., & Shute, V. J. (2010). Personal and social-contextual factors in K–12 academic performance: An integrative perspective on student learning. Educational Psychologist, 45 (3), 185–202. 1080/00461520.2010.493471 .
Lee, V. E., & Smith, J. (2001). Restructuring high schools for equity and excellence: What works . New York: Teachers College Press.
Linnenbrink, E. A. (2005). The dilemma of performance-approach goals: The use of multiple goal contexts to promote students’ motivation and learning. Journal of Educational Psychology, 97 (2), 197–213. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.97.2.197 .
Logan, M., & Skamp, K. (2008). Engaging students in science across the primary secondary interface: Listening to the students’ voice. Research in Science Education, 38 (4), 501–527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11165-007-9063-8 .
Mantzicopoulos, P., French, B. F., & Maller, S. J. (2004). Factor structure of the pictorial scale of perceived competence and social acceptance with two pre-elementary samples. Child Development, 75 (4), 1214–1228. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2004.00734.x .
Marjoribanks, K. (2002). Family and school capital: Towards a context theory of students’ school outcomes . Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-9980-1 .
Maslow, A. H. (1943). A theory of human motivation. Psychological Review, 50 (4), 370–396. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0054346 .
McDougal, W. (1908). An introduction to social psychology . Boston: John W. Luce and Co..
McInerney, D. M. (2008). Personal investment, culture and learning: Insights into school achievement across Anglo, aboriginal, Asian and Lebanese students in Australia. International Journal of Psychology, 43 (5), 870–879. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207590701836364 .
Midgley, C. (Ed.). (2014). Goals, goal structures, and patterns of adaptive learning . Abingdon: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781410602152 .
Murdock, T. B., Hale, N. M., & Weber, M. J. (2001). Predictors of cheating among early adolescents: Academic and social motivations. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 26 (1), 96–115. https://doi.org/10.1006/ceps.2000.1046 .
National Research Council. (2004). Engaging schools: Fostering high school students’ motivation to learn . Washington, DC: National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.5860/choice.42–1079 .
Nelson, R. M., & DeBacker, T. K. (2008). Achievement motivation in adolescents: The role of peer climate and best friends. The Journal of Experimental Education, 76 (2), 170–189. https://doi.org/10.3200/JEXE.76.2.170-190 .
Niccols, A., Atkinson, L., & Pepler, D. (2003). Mastery motivation in young children with Down’s syndrome: Relations with cognitive and adaptive competence. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 47 (2), 121–133. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2788.2003.00452.x .
Nicholls, J. G. (1979). Development of perception of own attainment and causal attributions for success and failure in reading. Journal of Educational Psychology, 71 (1), 94–99. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.71.1.94 .
Nicholls, J. G., & Miller, A. T. (1984). The differentiation of the concepts of difficulty and ability. Child Development, 54 (4), 951–959. https://doi.org/10.2307/1129899 .
Patrick, H., Anderman, L. H., Ryan, A. M., Edelin, K. C., & Midgley, C. (2001). Teachers’ communication of goal orientations in four fifth-grade classrooms. The Elementary School Journal, 102 (1), 35–58. Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/1002168 .
Pavlov, I. P. (2003). Conditioned reflexes . Mineola: Courier Corporation.
Pesu, L. A., Aunola, K., Viljaranta, J., & Nurmi, J. E. (2016a). The development of adolescents’ self-concept of ability through grades 7–9 and the role of parental beliefs. Frontline Learning Research, 4 (3), 92–109. https://doi.org/10.14786/flr.v4i3.249 .
Pesu, L., Viljaranta, J., & Aunola, K. (2016b). The role of parents’ and teachers’ beliefs in children’s self-concept development. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 44 , 63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2016.03.001 .
Petri, H. L., & Govern, J. M. (2012). Motivation: Theory, research, and application . Belmont: Wadsworth Publishing.
Pintrich, P. R. (2000). Multiple goals, multiple pathways: The role of goal orientation in learning and achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology, 92 (3), 544–555. 10.I037//0022-O663.92.3.544 .
Pintrich, P. R. (2003). A motivational science perspective on the role of student motivation in learning and teaching contexts. Journal of Educational Psychology, 95 (4), 667. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.95.4.667 .
Pintrich, P. R., & Maehr, M. L. (2004). Advances in motivation and achievement: Motivating students, improving schools (Vol. 13). Bingley: Emerald Grup Publishing Limited.
Ratelle, C. F., Guay, F., Larose, S., & Senécal, C. (2004). Family correlates of trajectories of academic motivation during a school transition: A semiparametric group-based approach. Journal of Educational Psychology, 96 (4), 743. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.96.4.743 .
Roeser, R. W., Eccles, J. S., & Sameroff, A. J. (1998). Academic and emotional functioning in early adolescence: Longitudinal relations, patterns, and prediction by experience in middle school. Development and Psychopathology, 10 (02), 321–352.
Roeser, R. W., Marachi, R., & Gelhbach, H. (2002). A goal theory perspective on teachers’ professional identities and the contexts of teaching. In C. M. Midgley (Ed.), Goals, goal structures, and patterns of adaptive learning (pp. 205–241). Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Rotter, J. B. (1966). Generalized expectancies for internal versus external control of reinforcement. Psychological Monographs: General and Applied, 80 (1), 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0092976 .
Ryan, A. M. (2001). The peer group as a context for the development of young adolescents’ motivation and achievement. Child Development, 72 (4), 1135–1150. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00338 .
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2002). An overview of self-determination theory: An organismic-dialectical perspective. In E. L. Deci & R. M. Ryan (Eds.), Handbook of self-determination theory research (pp. 3–33). Rochester: University of Rochester Press.
Schunk, D. H., & Pajares, F. (2002). The development of academic self-efficacy. In A. Wigfield & J. S. Eccles (Eds.), Development of achievement motivation (pp. 15–32). San Diego: Academic Press.
Schunk, D. H., Meece, J. R., & Pintrich, P. R. (2012). Motivation in education: Theory, research, and applications . Harlow: Pearson Higher Ed.
Shell, D. F., Colvin, C., & Bruning, R. H. (1995). Self-efficacy, attribution, and outcome expectancy mechanisms in reading and writing achievement: Grade-level and achievement-level differences. Journal of Educational Psychology, 87 (3), 386–398. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.87.3.386 .
Shin, H., & Ryan, A. M. (2014). Friendship networks and achievement goals: An examination of selection and influence processes and variations by gender. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 43 (9), 1453–1464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-014-0132-9 .
Simpkins, S. D., Fredricks, J. A., & Eccles, J. S. (2012). Charting the Eccles’ expectancy-value model from mothers’ beliefs in childhood to youths’ activities in adolescence. Developmental Psychology, 48 (4), 1019–1032. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0027468 .
Simpson, R. D., & Oliver, J. (1990). A summary of major influences on attitude toward and achievement in science among adolescent students. Science Education, 74 (1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.3730740102 .
Sjaastad, J. (2012). Sources of inspiration: The role of significant persons in young people’s choice of science in higher education. International Journal of Science Education, 34 (10), 1615–1636. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500693.2011.590543 .
Skinner, B. F. (1963). Operant behavior. American Psychologist, 18 (8), 503–515. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0045185 .
Skinner, E. A. (1995). Perceived control, motivation, and coping . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Skinner, E. A., Chapman, M., & Baltes, P. B. (1988). Control, meansends, and agency beliefs: A new conceptualization and its measurement during childhood. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54 (1), 117–133. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.54.1.117 .
Skinner, E. A., Gembeck-Zimmer, M. J., & Connell, J. P. (1998). Individual differences and the development of perceived control. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 6 (2/3. Serial No. 254), 1–220.
Stipek, D., Recchia, S., McClintic, S., & Lewis, M. (1992). Self-evaluation in young children. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development , 57 (1. Serial No. 226) 1–97.
Swarat, S., Ortony, A., & Revelle, W. (2012). Activity matters: Understanding student interest in school science. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 49 (4), 515–537. https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.21010 .
Tenenbaum, H. R., & Leaper, C. (2003). Parent-child conversations about science: The socialization of gender inequities? Developmental Psychology, 39 (1), 34–47. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.39.1.34 .
Thorndike, E. L. (1927). The law of effect. The American Journal of Psychology, 39 (1/4), 212–222. https://doi.org/10.2307/141541310.2307/1415413 .
Ushioda, E. (2007). Motivation, autonomy and sociocultural theory. In P. Benson (Ed.), Learner autonomy 8: Teacher and learner perspectives (pp. 5–24). Dublin: Authentik.
Vallerand, R. J. (1997). Toward a hierarchical model of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 29 , 271–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60019-2 .
Vedder-Weiss, D., & Fortus, D. (2013). School, teacher, peers, and parents’ goals emphases and adolescents’ motivation to learn science in and out of school. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 50 (8), 952–988. https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.21103 .
Véronneau, M. H., Vitaro, F., Brendgen, M., Dishion, T. J., & Tremblay, R. E. (2010). Transactional analysis of the reciprocal links between peer experiences and academic achievement from middle childhood to early adolescence. Developmental Psychology, 46 (4), 773. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019816 .
Volkow, N. D., Wang, G. J., Newcorn, J. H., Kollins, S. H., Wigal, T. L., Telang, F., & Wong, C. (2011). Motivation deficit in ADHD is associated with dysfunction of the dopamine reward pathway. Molecular Psychiatry, 16 (11), 1147–1154. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2010.97 .
Wang, M. T., & Eccles, J. S. (2012). Social support matters: Longitudinal effects of social support on three dimensions of school engagement from middle to high school. Child Development, 83 (3), 877–895. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2012.01745.x .
Wang, M. T., & Sheikh-Khalil, S. (2014). Does parental involvement matter for student achievement and mental health in high school? Child Development, 85 (2), 610–625. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12153 .
Weiner, B. (1985). An attributional theory of achievement motivation and emotion. Psychological Review, 92 (4), 548–573. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.92.4.548 .
Weiner, B., Frieze, I., Kukla, A., Reed, L., Rest, S., & Rosenbaum, R. M. (1987). Perceiving the causes of success and failure. In E. E. Jones, D. E. Kanouse, H. H. Kelley, R. E. Nisbett, S. Valins, & B. Weiner (Eds.), Attribution: Perceiving the causes of behavior (pp. 95–120). Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Weisz, J. P. (1984). Contingency judgments and achievement behavior: Deciding what is controllable and when to try. In J. G. Nicholls (Ed.), The development of achievement motivation (pp. 107–136). Greenwich: JAI Press.
Wentzel, K. R. (1998). Social relationships and motivation in middle school: The role of parents, teachers, and peers. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90 (2), 202–209. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.90.2.202 .
Wentzel, K. R. (2000). What is it that I’m trying to achieve? Classroom goals from a content perspective. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 25 (1), 105–115. https://doi.org/10.1006/ceps.1999.1021 .
Wentzel, K. (2002). Are effective teachers like good parents? Teaching styles and student adjustment in early adolescence. Child Development, 73 (1), 287–301. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00406 .
Wentzel, K. R. (2005). Peer relationships, motivation, and academic performance at school. In C. S. Dweck & A. J. Elliot (Eds.), Handbook of competence and motivation (pp. 279–296). New York: Guilford Press.
Wentzel, K. R., & Miele, D. B. (Eds.). (2009). Handbook of motivation at school . New York: Routledge.
Wentzel, K. R., & Muenks, K. (2016). Peer influence on students’ motivation, academic achievement, and social behavior. In K. R. Wentzel & G. B. Ramani (Eds.), Handbook of social influences in school contexts: Social-emotional, motivation, and cognitive outcomes (pp. 13–30). New York: Routledge.
Wentzel, K. R., Battle, A., Russell, S. L., & Looney, L. B. (2010). Social supports from teachers and peers as predictors of academic and social motivation. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 35 (3), 193–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2010.03.002 .
Wigfield, A., & Eccles, J. (1992). The development of achievement task values: A theoretical analysis. Developmental Review, 12 (3), 265–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-2297(92)90011-P .
Wigfield, A., & Eccles, J. S. (2000). Expectancy–value theory of achievement motivation. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 25 (1), 68–81. https://doi.org/10.1006/ceps.1999.1015 .
Wigfield, A., & Eccles, J. S. (2002). The development of competence beliefs and values from childhood through adolescence. In A. Wigfield & J. S. Eccles (Eds.), Development of achievement motivation (pp. 92–120). San Diego: Academic Press.
Wigfield, A., & Tonks, S. (2004). The development of motivation for reading and how it is influenced by CORI. In J. T. Guthrie, A. Wigfield, & K. C. Perencevich (Eds.), Motivating reading comprehension: Concept-oriented reading instruction (pp. 249–272). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
Wigfield, A., & Wagner, A. L. (2005). Competence, motivation, and identity development during adolescence. In A. J. Elliot & C. S. Dweck (Eds.), Handbook of competence and motivation (pp. 222–239). New York: Guilford Press.
Wigfield, A., Eccles, J. S., Yoon, K. S., Harold, R. D., Arbreton, A. J., Freedman-Doan, C., & Blumenfeld, P. C. (1997). Change in children’s competence beliefs and subjective task values across the elementary school years: A 3-year study. Journal of Educational Psychology, 89 (3), 451. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.89.3.451 .
Wigfield, A., Eccles, J. S., Schiefele, U., Roeser, R. W., & Davis-Kean, P. (2006). Development of achievement motivation . In N. Eisenberg, W. Damon & R.M. Lerner (Vol. 3, pp.933–1002). Hoboken: Wiley. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470147658.chpsy0315 .
Wigfield, A., Eccles, J. S., Schiefele, U., Roeser, R. W., & Davis‐Kean, P. (2007). Development of achievement motivation . Hoboken: Wiley.
Wigfield, A., Eccles, J. S., Roeser, R. W., & Schiefele, U. (2008). Development of achievement motivation. In W. Damon, R. M. Lerner, D. Kuhn, R. S. Siegler, & N. Eisenberg (Eds.), Child and adolescent development: An advanced course (pp. 406–434). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Wlodkowski, R. J. (2011). Enhancing adult motivation to learn: A comprehensive guide for teaching all adults . San Francisco: Wiley.
Woodworth, R. S. (1918). Dynamic Psychology . New York: Columbia University Press.
Yeung, W. J., Linver, M. R., & Brooks–Gunn, J. (2002). How money matters for young children's development: Parental investment and family processes. Child Development, 73 (6), 1861–1879. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.t01-1-00511 .
Zimmerman, B. J., & Martinez-Pons, M. (1990). Student differences in self-regulated learning: Relating grade, sex, and giftedness to self-efficacy and strategy use. Journal of Educational Psychology, 82 (1), 51–59. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.82.1.51 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Escuela de Psicología, Universidad de los Andes, Santiago, Chile
Paulina Arango
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Paulina Arango .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
School of Education, Universidad de los Andes, Las Condes, Chile
Pelusa Orellana García
Institute of Literature, Universidad de los Andes, Las Condes, Chile
Paula Baldwin Lind
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Arango, P. (2018). Motivation: Introduction to the Theory, Concepts, and Research. In: Orellana García, P., Baldwin Lind, P. (eds) Reading Achievement and Motivation in Boys and Girls. Literacy Studies, vol 15. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75948-7_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75948-7_1
Published : 03 May 2018
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-75947-0
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-75948-7
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Theories of Motivation
Motivation describes the wants or needs that direct behavior toward a goal, but, why do we do the things we do? What motivations underlie our behaviors? Is motivation an inherited trait or is motivation influenced by reinforcement and consequences that strengthen some behaviors and weaken others? Is the key to motivating learners a lesson plan that captures their interest and attention? In other words, is motivation something innate that we are born with that can be strengthened by reinforcers external to the learning task, or is it something interwoven with the learning process itself?
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation
Some motives are biological, like our need for food or water. However, the motives that we will be more interested in are more psychological. In general, we discuss motivation as being intrinsic (arising from internal factors) or extrinsic (arising from external factors). Intrinsically motivated behaviors are performed because of the sense of personal satisfaction that they bring, while extrinsically motivated behaviors are performed in order to receive something from others.

Video 6.1.1. Extrinsic vs Intrinsic Motivation explains the difference and provides examples of these types of motivation.
Think about why you are currently in college. Are you here because you enjoy learning and want to pursue an education to make yourself a more well-rounded individual? If so, then you are intrinsically motivated. However, if you are here because you want to get a college degree to make yourself more marketable for a high-paying career or to satisfy the demands of your parents, then your motivation is more extrinsic in nature.
In reality, our motivations are often a mix of both intrinsic and extrinsic factors, but the nature of the mix of these factors might change over time (often in ways that seem counter-intuitive). There is an old adage: “Choose a job that you love, and you will never have to work a day in your life,” meaning that if you enjoy your occupation, work doesn’t seem like . . . well, work. Some research suggests that this isn’t necessarily the case (Daniel & Esser, 1980; Deci, 1972; Deci, Koestner, & Ryan, 1999). According to this research, receiving some sort of extrinsic reinforcement (i.e., getting paid) for engaging in behaviors that we enjoy leads to those behaviors being thought of as work no longer providing that same enjoyment. As a result, we might spend less time engaging in these reclassified behaviors in the absence of any extrinsic reinforcement. For example, Odessa loves baking, so in her free time, she bakes for fun. Oftentimes, after stocking shelves at her grocery store job, she often whips up pastries in the evenings because she enjoys baking. When a coworker in the store’s bakery department leaves his job, Odessa applies for his position and gets transferred to the bakery department. Although she enjoys what she does in her new job, after a few months, she no longer has much desire to concoct tasty treats in her free time. Baking has become work in a way that changes her motivation to do it. What Odessa has experienced is called the overjustification effect—intrinsic motivation is diminished when extrinsic motivation is given. This can lead to extinguishing intrinsic motivation and creating a dependence on extrinsic rewards for continued performance (Deci et al., 1999).
Other studies suggest that intrinsic motivation may not be so vulnerable to the effects of extrinsic reinforcements, and in fact, reinforcements such as verbal praise might actually increase intrinsic motivation (Arnold, 1976; Cameron & Pierce, 1994). In that case, Odessa’s motivation to bake in her free time might remain high if, for example, customers regularly compliment her baking or cake decorating skills.
These apparent discrepancies in the researchers’ findings may be understood by considering several factors. For one, physical reinforcement (such as money) and verbal reinforcement (such as praise) may affect an individual in very different ways. In fact, tangible rewards (i.e., money) tend to have more negative effects on intrinsic motivation than do intangible rewards (i.e., praise). Furthermore, the expectation of the extrinsic motivator by an individual is crucial: If the person expects to receive an extrinsic reward, then intrinsic motivation for the task tends to be reduced. If, however, there is no such expectation, and the extrinsic motivation is presented as a surprise, then intrinsic motivation for the task tends to persist (Deci et al., 1999).
In addition, culture may influence motivation. For example, in collectivistic cultures, it is common to do things for your family members because the emphasis is on the group and what is best for the entire group, rather than what is best for any one individual (Nisbett, Peng, Choi, & Norenzayan, 2001). This focus on others provides a broader perspective that takes into account both situational and cultural influences on behavior; thus, a more nuanced explanation of the causes of others’ behavior becomes more likely. (You will learn more about collectivistic and individualistic cultures when you learn about social psychology.)
In educational settings, students are more likely to experience intrinsic motivation to learn when they feel a sense of belonging and respect in the classroom. This internalization can be enhanced if the evaluative aspects of the classroom are de-emphasized and if students feel that they exercise some control over the learning environment. Furthermore, providing students with activities that are challenging, yet doable, along with a rationale for engaging in various learning activities can enhance intrinsic motivation for those tasks (Niemiec & Ryan, 2009). Consider Hakim, a first-year law student with two courses this semester: Family Law and Criminal Law. The Family Law professor has a rather intimidating classroom: He likes to put students on the spot with tough questions, which often leaves students feeling belittled or embarrassed. Grades are based exclusively on quizzes and exams, and the instructor posts the results of each test on the classroom door. In contrast, the Criminal Law professor facilitates classroom discussions and respectful debates in small groups. The majority of the course grade is not exam-based but centers on a student-designed research project on a crime issue of the student’s choice. Research suggests that Hakim will be less intrinsically motivated in his Family Law course, where students are intimidated in the classroom setting, and there is an emphasis on teacher-driven evaluations. Hakim is likely to experience a higher level of intrinsic motivation in his Criminal Law course, where the class setting encourages inclusive collaboration and a respect for ideas, and where students have more influence over their learning activities.
Think About It
Schools often use concrete rewards to increase adaptive behaviors. How might this be a disadvantage for students intrinsically motivated to learn? What are the educational implications of the potential for concrete rewards to diminish intrinsic motivation for a given task?
We would expect to see a shift from learning for the sake of learning to learning to earn some reward. This would undermine the foundation upon which traditional institutions of higher education are built. For a student motivated by extrinsic rewards, dependence on those may pose issues later in life (post-school) when there are not typically extrinsic rewards for learning.
Like motivation itself, theories of it are full of diversity. For convenience in navigating through the diversity, we have organized the theories around two perspectives about motion. The first set of theories focuses on the innateness of motivation. These theories emphasize instinctual or inborn needs and drives that influence our behavior. The second set of theories proposes cognition as the source of motivation. Individual motivation is influenced by thoughts, beliefs, and values. The variation in these theories is due to disagreement about which cognitive factors are essential to motivation and how those cognitive factors might be influenced by the environment.

Innate Motivation Theories
First, we will describe some early motivational theories that focus on innate needs and drives. Not all of these theories apply to the classroom, but learning about them will show you how different theorists have approached the issue of motivation. You are sure to find some elements of your own thinking about motivation in each of them. We will examine instinct theory, drive theory, and arousal theory as early explanations of motivation. We will also discuss the behavioral perspective on motivation and the deficiency-growth perspective, as exemplified by Maslow’s hierarchy of needs.
Cognitive Theories of Motivation
Cognitive theories of motivation assume that behavior is a result of cognitive processes. These theories presume that individuals are interpreting information and making decisions, not just acting on basic needs and drives. Cognitive motivation theories share strong ties with the cognitive and social learning theories that we discussed previously. We will examine several cognitive motivation theories: interest, attribution theory, expectancy-value theory, and self-efficacy theory. All emphasize that learners need to know, understand, and appreciate what they are doing in order to become motivated. Then, along with these cognitive motivation theories, we will examine a motivational perspective called self-determination theory, which attempts to reconcile cognitive theory’s emphasis on intrinsic motivation with more traditional notions of human needs and drives.
Video 6.1.2. Instincts, Arousal, Needs, Drives provides a brief overview of some of the major motivational theories.
Candela Citations
- Theories of Motivation . Authored by : Nicole Arduini-Van Hoose. Provided by : Hudson Valley Community College. Retrieved from : . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Educational Psychology. Authored by : Kelvin Seifert and Rosemary Sutton. Provided by : The Saylor Foundation. Retrieved from : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/educationalpsychology. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Educational Psychology. Authored by : Borlin. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Psychology 2e. Authored by : Rose M. Spielman, William J. Jenkins, Marilyn D. Lovett. Provided by : Open Stax. Retrieved from : https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Extrinsic vs Intrinsic Motivation. Provided by : ASCatRIT. Retrieved from : https://youtu.be/kUNE4RtZnbk. License : All Rights Reserved
Educational Psychology Copyright © 2020 by Nicole Arduini-Van Hoose is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Behav Sci (Basel)

Work Motivation: The Roles of Individual Needs and Social Conditions
Thuy thi diem vo.
1 Department of Business Administration, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, No. 43, Section 4, Keelung Road, Da’an District, Taipei City 106335, Taiwan; wt.ude.tsutn.liam@31880701d (T.T.D.V.); wt.ude.tsutn.liam@nehcwc (C.-W.C.)
Kristine Velasquez Tuliao
2 Graduate Institute of Human Resource Management, National Central University, No. 300, Zhongda Road, Zhongli District, Taoyuan City 320317, Taiwan
Chung-Wen Chen
Associated data.
The data that support this study are publicly available.
Work motivation plays a vital role in the development of organizations, as it increases employee productivity and effectiveness. To expand insights into individuals’ work motivation, the authors investigated the influence of individuals’ competence, autonomy, and social relatedness on their work motivation. Additionally, the country-level moderating factors of those individual-level associations were examined. Hierarchical linear modeling (HLM) was used to analyze data from 32,614 individuals from 25 countries, obtained from the World Values Survey (WVS). Findings showed that autonomy and social relatedness positively impacted work motivation, while competence negatively influenced work motivation. Moreover, the individual-level associations were moderated by the country-level religious affiliation, political participation, humane orientation, and in-group collectivism. Contributions, practical implications, and directions for further research were then discussed.
1. Introduction
Work motivation is considered an essential catalyst for the success of organizations, as it promotes employees’ effective performance. To achieve an organization’s objectives, the employer depends on the performance of their employees [ 1 ]. However, insufficiently motivated employees perform poorly despite being skillful [ 1 , 2 ]. Employers, therefore, need their employees to work with complete motivation rather than just showing up at their workplaces [ 3 ]. Work motivation remains a vital factor in organizational psychology, as it helps explain the causes of individual conduct in organizations [ 4 ]. Consequently, studies on the factors that encourage work motivation can contribute to the theoretical underpinnings on the roots of individual and practical social conditions that optimize individuals’ performance and wellness [ 5 ].
Several decades of research have endeavored to explain the dynamics that initiate work-related behavior. The primary factor examining this aspect is motivation, as it explains why individuals do what they do [ 6 ]. The basic psychological needs have represented a vital rationalization of individual differences in work motivation. Psychological needs are considered natural psychological nutrients and humans’ inner resources. They have a close relationship with individual conduct and have a strong explicit meaning for work performance [ 7 , 8 ]. Different needs are essential drivers of individual functioning due to the satisfaction derived from dealing with them [ 9 ]. In addition to individual-level antecedents, the social context has also been regarded to have implications for work motivation. Social exchange and interaction among individuals accentuate the importance of work motivation as something to be studied with consideration of contextual factors [ 10 ].
Significant contributions have been made to the socio-psychological perspective of work motivation ( Table 1 ). However, current literature shows three deficiencies. First, over 150 papers utilize the key approaches of psychological needs to justify motivational processes in the workplace [ 11 ], which justifies the vital role of psychological needs in interpreting individual work motivation. The association between psychological needs and work motivation has often been implicitly assumed; however, the influence of psychological needs on work motivation has been inadequately tested [ 8 ]. The verification of the extent and the direction of influence will provide a better understanding of, and offer distinct implications for, the facilitation of work motivation. In examining the influence of psychological needs on work motivation, this paper mainly focuses on the intrinsic aspect of motivation. The study of Alzahrani et al. (2018) [ 12 ] argued that although intrinsic motivation is more efficient than extrinsic motivation, researchers have mostly neglected it.
Several investigated predictors of work motivation in general and intrinsic motivation in particular.
Second, there is no study examining the country-level moderating effects of social conditions and national cultures on individual relationships between psychological needs and work motivation. Pinder (2014) [ 20 ] argued that contextual practices could influence variables at the individual level. Culture is a crucial factor influencing motivation [ 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 ]. Researchers (e.g., [ 19 ]) have further suggested that both the proximal social situations (e.g., workgroup) and the distal social situations (e.g., cultural values) in which humans operate influence their need for satisfaction and their motivation type. Intrinsic motivation interacts with prosocial motivation in judging work performance [ 21 ]. By including the social conditions in the framework, prosocial motivation is considered. Prosocial motivation refers to the desire to help and promote the welfare of others [ 22 , 23 ]. The study of Shao et al. (2019) [ 24 ] proposed that prosocial motivation promotes employee engagement in particular organizational tasks. Researchers often consider prosocial motivation as a pattern of intrinsic motivation [ 23 ]. This implies that when intrinsic motivation is investigated, prosocial motivation should be examined together to obtain a comprehensive understanding.
Third, there are few studies using a considerable number of cross-national samples to investigate factors influencing work motivation. A cross-cultural analysis makes the findings more objective by minimizing individual bias towards any particular culture. Therefore, the examination of the study is crucial to expanding insights on the influence of social situations on the individual associations between psychological needs and work motivation.
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
2.1. work motivation: a conceptual background.
Work motivation is considered “a set of energetic forces that originate both within as well as beyond an individual’s being, to initiate work-related behavior, and to determine its form direction intensity and duration” [ 20 ]. Nicolescu and Verboncu (2008) [ 25 ] argued that work motivation contributes directly and indirectly to employees’ performance. Additionally, research (e.g., [ 26 ]) has postulated that work motivation could be seen as a source of positive energy that leads to employees’ self-recognition and self-fulfillment. Therefore, work motivation is an antecedent of the self-actualization of individuals and the achievement of organizations.
Literature has identified several models of work motivation. One of the primary models is Maslow’s (1954) [ 27 ] need hierarchy theory, which proposes that humans fulfill a set of needs, including physiological, safety and security, belongingness, esteem, and self-actualization. Additionally, Herzberg’s (1966) [ 28 ] motivation-hygiene theory proposed that work motivation is mainly influenced by the job’s intrinsic challenge and provision of opportunities for recognition and reinforcement. More contemporary models also emerged. For instance, the study of Nicolescu and Verboncu (2008) [ 25 ] has categorized the types of motivation into four pairs, including positive-negative, intrinsic-extrinsic, cognitive-affective, and economic-moral spiritual. Additionally, Ryan and Deci [ 29 ] focused on intrinsic motivation and extrinsic motivation.
With the existence of numerous factors that relate to work motivation, this paper mainly focuses on intrinsic motivation. Previous research found that emotional intelligence and interpersonal relationship quality predict individuals’ intrinsic motivation [ 14 ]. Additionally, the study of Lin (2020) [ 13 ] argued that personal factors, including age, gender, educational level, living setting, health status, and family support, impact people’s intrinsic motivation. To understand more about intrinsic motivation, the authors examined individuals’ psychological needs. Fulfillment of the basic needs is related to wellness and effective performance [ 7 ]. Since intrinsic motivation results in high-quality creativity, recognizing the factors influencing intrinsic motivation is important [ 5 ].
Although a significant number of important contributions have been made regarding intrinsic motivation, self-determination theory is of particular significance for this study. Self-determination theory (SDT) postulates that all humans possess a variety of basic psychological needs. One of the primary crucial needs is the need for competence [ 30 , 31 ], which makes individuals feel confident and effective in their actions. Additionally, the need for autonomy [ 32 ] is one of the important psychological needs, which makes people satisfied with optimal wellness and good performance obtained as a result of their own decisions. Moreover, SDT proposed the crucial importance of interpersonal relationships and how social forces can influence thoughts, emotions, and behaviors [ 33 ]. This means that the psychological need for social relatedness [ 34 ] also plays a significant role in human’s psychological traits. Individuals need to be cared for by others and care for others to perceive belongingness. The need for relatedness can motivate people to behave more socially [ 35 ].
Prior research (e.g., [ 36 ]) has explored self-determination theory and related theories as approaches to work motivation and organizational behavior. The study of Van den Broeck et al. (2010) [ 37 ] emphasized grasping autonomy, competence, and relatedness at workplaces. This paper contributes to the exhaustive understanding of intrinsic work motivation influenced by further examining the impact of these three factors on work motivation as well as the moderating effects of social contexts.
2.2. Main Effect
2.2.1. individuals’ competence and work motivation.
Competence is “the collective learning in the organization, especially how to coordinate diverse production skills and integrate multiple streams of technologies” [ 38 ]. The study of Hernández-March et al. (2009) [ 39 ] argued that a stronger competence was commonly found in university graduates rather than those without higher education. Competence has been considered a significant factor of work motivation that enhances productivity and profits. Harter’s (1983) [ 40 ] model of motivation proposed that competence enhances motivation because competence promotes flexibility for individuals [ 41 ]. Likewise, Patall et al. (2014) [ 42 ] indirectly argued that competence positively affects work motivation. Individuals become more engaged in activities that demonstrate their competence [ 6 ]. When people perceive that they are competent enough to attain goals, they generally feel confident and concentrate their efforts on achieving their objectives as soon as possible for their self-fulfillment.
Individuals’ competence positively relates to their work motivation.
2.2.2. Individuals’ Autonomy and Work Motivation
Autonomy is viewed as “self-determination, self-rule, liberty of rights, freedom of will and being one’s own person” [ 43 ]. Reeve (2006) [ 44 ] argued that autonomy is a primary theoretical approach in the study of human motivation and emotion. Autonomy denotes that certain conduct is performed with a sense of willingness [ 30 ]. Several researchers (e.g., [ 45 ]) investigated the positive relationship between individuals’ autonomy and work motivation. When humans are involved in actions because of their interest, they fully perform those activities volitionally [ 36 ]. Dickinson (1995) [ 46 ] also proposed that autonomous individuals are more highly motivated, and autonomy breeds more effective outcomes. Moreover, when individuals have a right to make their own decisions, they tend to be more considerate and responsible for those decisions, as they need to take accountability for their actions. Bandura (1991) [ 47 ] has argued that humans’ ability to reflect, react, and direct their actions motivates them for future purposes. Therefore, autonomy motivates individuals to work harder and overcome difficulties to achieve their objectives.
Individuals’ autonomy positively relates to their work motivation.
2.2.3. Individuals’ Social Relatedness and Work Motivation
The psychological need for social relatedness occurs when an individual has a sense of being secure, related to, or understood by others in the social environment [ 48 ]. The relatedness need is fulfilled when humans experience the feeling of close relationships with others [ 49 ]. Researchers (e.g., [ 34 ]) have postulated that the need for relatedness reflects humans’ natural tendency to feel associated with others, such as being a member of any social groups, or to love and care as well as be loved and cared for. Prior studies have shown that social relatedness strongly impacts motivation [ 50 , 51 , 52 ]. Social relatedness offers people many opportunities to communicate with others, making them more motivated at the workplace, aligning them with the group’s shared objectives. Marks (1974) [ 53 ] suggested that social relatedness encourages individuals to focus on community welfare as a reference for their behavior, resulting in enhanced work motivation. Moreover, when individuals feel that they relate to and are cared for by others, their motivation can be maximized since their relatedness need is fulfilled [ 54 ]. Therefore, establishing close relationships with others plays a vital role in promoting human motivation [ 55 ]. When people perceive that they are cared for and loved by others, they tend to create positive outcomes for common benefits to deserve the kindness received, thereby motivating them to work harder.
Individuals’ social relatedness positively relates to their work motivation.
Aside from exploring the influence of psychological needs on work motivation, this paper also considers country-level factors. Previous research (e.g., [ 56 ]) has examined the influence of social institutions and national cultures on work motivation. However, the moderating effects of country-level factors have to be investigated, given the contextual impacts on individual needs, attitudes, and behavior. Although social conditions provide the most common interpretation for nation-level variance in individual work behaviors [ 57 ], few cross-national studies examine social conditions and individual work behaviors [ 56 ]. Hence, this paper investigates the moderating effects, including religious affiliation, political participation, humane orientation, and in-group collectivism, on the psychological needs-work motivation association.
A notable theory to explain the importance of contextual factors in work motivation that is customarily linked with SDT is the concept of prosocial motivation. Prosocial motivation suggests that individuals have the desire to expend efforts in safeguarding and promoting others’ well-being [ 58 , 59 ]. It is proposed that prosocial motivation strengthens endurance, performance, and productivity, as well as generates creativity that encourages individuals to develop valuable and novel ideas [ 21 , 60 ]. Prosocial motivation is found to interact with intrinsic motivation in influencing positive work outcomes [ 21 , 61 ]. However, there are few studies examining the effects of prosocial motivation on work motivation [ 62 ].
Utilizing the concept of prosocial motivation and examining it on a country-level, this paper suggests that prosocial factors promote basic psychological needs satisfaction that reinforces motivational processes at work. Therefore, prosocial behaviors and values may enhance the positive impact of individuals’ basic psychological needs, including competence, autonomy, and social relatedness, on work motivation.
2.3. Moderating Effects
2.3.1. religious affiliation.
Religions manifest values that are usually employed as grounds to investigate what is right and wrong [ 63 ]. Religious affiliation is considered prosocial because it satisfies the need for belongingness and upholds collective well-being through gatherings to worship, seek assistance, and offer comfort within religious communities. Hence, religious affiliation promotes the satisfaction of individuals’ psychological needs, which directs motivation at work and life in general. Research (e.g., [ 64 ]) has argued that religious affiliation is an essential motivational component given its impact on psychological processes. The study of Simon and Primavera (1972) [ 65 ] investigated the relationship between religious affiliation and work motivation. To humans characterized by competence, autonomy, and social relatedness, attachment to religious principles increases their motivation to accomplish organizational goals. Religious membership will increase the influence of psychological needs on work motivation. The tendency of individuals affiliated with any religion to be demotivated is lower compared to those who are not. Individuals with religious affiliations also tend to work harder as the virtue of hard work is aligned with religious principles. Accordingly, religious affiliation may enhance the positive association between individuals’ psychological needs and work motivation.
2.3.2. Political Participation
Political participation, indicated by people’s voting habits, plays a crucial role in ensuring citizens’ well-being and security [ 66 ]. Political participation encourages shared beliefs and collective goals among individuals [ 67 ]. The communication and interaction among people help them grasp the government’s developmental strategies, motivating them to work harder. Political participation is a collective pursuit that makes societal members feel more confident, socially related, and motivated at work to achieve communal targets. Increased political participation reinforces effective public policy to enhance its members’ welfare, congruent with the perspectives of prosocial motivation. The prosocial values and behaviors derived from political participation satisfy human needs and interact positively with intrinsic motivation. Therefore, political participation may strengthen the positive influence of individuals’ competence, autonomy, and social relatedness on work motivation. Conversely, poor political participation is perceived as a separation from the society that may lead to demotivation. In a society with poor political participation, an individualistic mentality is encouraged, thereby decreasing the desire to pursue cooperative endeavors.
2.3.3. Humane Orientation
GLOBE characterizes humane orientation as “the degree to which an organization or society encourages and rewards individuals for being fair, altruistic, generous, caring, and kind to others” [ 68 ]. Research (e.g., [ 69 , 70 ]) has argued that a high humane orientation encourages members to develop a strong sense of belonging, commit to fair treatment, and manifest benevolence. The desire to help others or enhance others’ well-being indicates prosocial values and behaviors [ 71 , 72 ]. Since humane orientation is correlated with philanthropy and promotes good relations, this cultural value may enhance work motivation. Fairness, which is derived from a humane-oriented society, is one of the most vital influences on work motivation [ 1 ]. Moreover, altruism, promoted by humane-oriented societies, encourages individuals to sacrifice individual interests for shared benefits. Altruism then encourages attachment to others’ welfare and increases resources needed for prosocial behaviors such as work [ 73 , 74 ]. Members of humane-oriented countries view work in a positive light—it is an opportunity for them to perform altruistic behaviors and engage in collective actions. Therefore, people are more likely to work harder for common interests in humane-oriented societies. In such conditions, individuals with competence, autonomy, and social relatedness will be more motivated to work. By contrast, a less humane-oriented society gives prominence to material wealth and personal enjoyment [ 75 ]. Although this may be perceived as a positive influence on the association between psychological needs and work motivation, such an individualistic mindset works against the prosocial factors that further motivate individuals.
2.3.4. In-Group Collectivism
House et al. (2004) [ 68 ] defined in-group collectivism as “the degree to which individuals express pride, loyalty, and cohesiveness in their organizations or families”. Collectivistic cultures indicate the need for individuals to rely on group membership for identification [ 76 ]. High collectivism enhances equity, solidarity, loyalty, and encouragement [ 77 , 78 ]. Humans living in a collectivist culture are interdependent and recognize their responsibilities towards each other [ 79 ]. In-group collectivism transfers the concepts of social engagement, interdependence with others, and care for the group over the self (e.g., [ 79 , 80 , 81 ], thereby motivating individuals to work harder for the common interests. Oyserman et al. (2002) [ 82 ] have further argued that individualistic values encourage an independent personality, whereas collectivistic values form an interdependent one. Therefore, in-group collectivism is a prosocial value that emphasizes the importance of reciprocal relationships and encourages people to work harder to benefit the group. By contrast, low collectivism promotes individual interests and personal well-being while neglecting the value of having strong relations with others [ 70 ]. Considering that in-group collectivism promotes individuals’ prosocial behaviors of individuals, people who are competent, autonomous, and socially related to collective societies are less likely to be demotivated at the workplace. Consequently, in-group collectivism may intensify the positive influence of individuals’ competence, autonomy, and social relatedness on their work motivation.
(a–d): The positive relationship between individuals’ competence and their work motivation is enhanced as religious affiliation (a), political participation (b), humane orientation (c), and in-group collectivism (d) increase.
(a–d): The positive relationship between individuals’ autonomy and their work motivation is enhanced as religious affiliation (a), political participation (b), humane orientation (c), and in-group collectivism (d) increase.
(a–d): The positive relationship between individuals’ social relatedness and their work motivation is enhanced as religious affiliation (a), political participation (b), humane orientation (c), and in-group collectivism (d) increase.
3.1. Sample
The data came from the seventh wave (2017–2021) of the World Values Survey (WVS) [ 83 ], which examines humans’ beliefs and values. This survey is performed every five years to explore changes in people’s values and perceptions. Face-to-face interviews, or phone interviews for remote areas, were conducted by local organizations. Almost 90 percent of the world’s population is represented in the WVS. At least 1000 individuals were selected as respondents to exhibit each nation’s population. Further information regarding the WVS can be reached at the WVS website ( http://www.worldvaluessurvey.org , accessed on 14 October 2021).
The samples of this study were based on the availability of national-level data for the moderators and individual-level data for the measures of independent and dependent variables. Respondents without answers on the individual measures and corresponding country-level data were excluded from the analysis. The final data included 32,614 respondents in 25 countries aged 18 and above. The 25 countries included Argentina, Australia, Brazil, China, Colombia, Ecuador, Egypt, Germany, Greece, Guatemala, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Iran, Japan, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Philippines, Russia, South Korea, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey, and the USA.
3.2. Dependent Variable
Consistent with previous researchers (e.g., [ 84 ]), the authors used four items to gauge individual work motivation, namely “Indicate how important work is in your life”, “People who do not work turn lazy”, “Work is a duty towards society”, and “Work should always come first, even if it means less spare”. The first item was measured on a scale from 1 to 4, in which lower scores indicate a higher level of work importance. The other three items were gauged on a scale from 1 to 5 (1 indicating strongly agree and 5 indicating strongly disagree). The scores for each item were reverse coded, and the mean scores were computed so that higher scores indicate greater work motivation.
3.3. Independent Variables
The independent variables of this study include individuals’ competence, autonomy, and social relatedness. First, people’s competence was measured by the item “What is the highest educational level that you attained” on a scale from 0 to 8, in which higher scores indicate a higher level of educational attainment. The authors used the item to gauge individual competence, as a capacity for learning is highlighted in the examination of competence [ 39 ]. Second, a scale from 1 to 10 was utilized to measure the item “How much freedom of choice and control”, which represented individual autonomy (1 indicating no choice at all and 10 indicating a great deal of choice). The authors used the item to gauge people’s autonomy as this item indicates the degree to which individual can make their own decisions. Finally, the individual’s social relatedness was gauged by twelve items, representing twelve types of organizations where individuals are active/inactive members or do not belong. The twelve items were measured on a scale from 0 to 2 (0 indicating do not belong, 1 indicating inactive member, and 2 indicating active member). The mean score of the twelve items represents the individual’s social relatedness. The membership in organizations represents social relatedness, as this indicates the reciprocal relationship between the individual and the organization through their mutual rights, responsibilities, and obligations towards each other [ 85 ].
3.4. Moderators
The four country-level moderators in this study were religious affiliation, political participation, humane orientation, and in-group collectivism. Similar to prior research (e.g., [ 86 ]), the authors used the percentage of the country’s population with religious affiliation obtained from Pew Research Center 2015 [ 87 ]. Secondly, the index of voter turnout collected from the International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance [ 88 ] was utilized to gauge political participation. Voting habits are an indicator of an individual’s presence in their country’s life, and a nation with a high index of voter turnout illustrates its substantial degree of political participation [ 89 ]. Finally, two cultural values, including humane orientation and in-group collectivism, were obtained from the GLOBE study [ 68 ]. The authors used scores on cultural practices as the moderators for this study because they indicate the actual behaviors as “the way things are done in this culture” [ 68 ].
3.5. Control Variables
Several individual-level and country-level elements related to the dependent variable were considered control variables. The effects of gender, marital status, age, and income level were accounted for, as these four variables are basic personal factors that may impact individual’s motivation [ 90 ]. Gender (1 indicating male and 0 indicating female) and marital status (1 indicating married and 0 indicating other status) were dummy coded. Moreover, age was measured in years, while income level was gauged using a scale from 1 representing the lowest group to 10 representing the highest group. Along with the above individual-level controls, education and family strength were treated as country-level control variables. Education and family are primary institutions that shape individuals’ motivation [ 91 , 92 ]. Similar to prior researchers (e.g., [ 93 ]), education was computed as two-thirds of the adult literacy rate attained from the UNESCO Institute for Statistics 2020 [ 94 ] and one-third of the mean years of schooling obtained from the Human Development Report 2020 [ 95 ]. This score is commonly approved as representing access to education in a country [ 42 ]. Regarding family strength, the score was quantified by the ratio of divorces to marriages per 1000 members of the population consistent with previous researchers (e.g., [ 93 ]). The data was obtained from the United Nations Demographic Yearbook [ 96 ].
3.6. Measurement and Analysis
To perform the descriptive statistics, cross-level correlations, scale reliability, confirmatory factor analysis, convergent validity, and discriminant validity, the authors utilized SPSS software.
The framework of this study considers independent variables, dependent variables, and moderators at different levels. Thus, the authors used a hierarchical linear model (HLM) [ 97 ] to test the hypotheses. HLM was defined as a “complex form of ordinary least squares (OLS) regression that is used to analyze variance in the outcome variables when the predictor variables are at varying hierarchical levels” [ 98 ]. This technique evaluates the impacts of higher-level outcomes on lower-level ones while preserving an appropriate degree of analysis [ 99 ]. HLM has been employed in several cross-level studies (e.g., [ 100 , 101 ]).
Table 2 presents a matrix of correlations and sample statistics from the individual-level to country-level variables. Table 3 and Table 4 report convergent and discriminant validity test results, respectively. Finally, Table 5 illustrates results for hypotheses testing using HLM. Three models are presented in the table: those of individual-level main effects and control variables (Model 1), those of country-level main effects (Model 2), and country-level moderating effects (Model 3).
Descriptive statistics, cross-level correlations and scale reliability a,b,c .
a n = 32,614 level 1; n = 25, level 2. b * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. c The reliability found in the parentheses is expressed as Cronbach’s alpha for scales with ≥four items.
Convergent validity.
Discriminant validity—Fornell and Larcker’s criterion.
* p < 0.05.
HLM results: (The DV is work motivation) a,b .
a , n = 32,614 level 1; n = 25, level 2. b , †, p < 0.10, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
For the confirmatory factor analysis, previous research (e.g., [ 102 , 103 , 104 ]) suggested that analysis of each variable requires at least three items. Factor analysis using statistical software will provide imprecise results if there are fewer than three items per variable [ 105 ]. Therefore, the authors only performed Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) for social relatedness and work motivation.
To assess the measurement, convergent and discriminant validity were tested. Composite Reliability (CR) and Average Variance Extracted (AVE) were performed to illustrate convergent validity. The study of Hair et al. (2019) [ 106 ] suggested that CR is required to be above a threshold of 0.7. On the other hand, the AVE value should be higher than a threshold of 0.5 [ 107 ]. As shown in Table 3 , CR is acceptable while AVE is slightly lower than a threshold of 0.5. Despite the limitation of AVE, the acceptable result of the discriminant validity is achieved. The discriminant validity was tested using Fornell and Larcker (1981)’s criterion [ 107 ]. This proposes that the square root of the AVE of any latent variable should be higher than its correlation with any other construct. The result of the discriminant validity test indicates that all the two latent constructs have a square root of AVE higher than its correlation with the other construct, as presented in Table 4 .
The authors argued that individuals’ competence (H1), autonomy (H2), and social relatedness (H3) positively relate to their work motivation. However, the findings only supported H2 (β2 = 0.036, p < 0.001) and H3 (β3 = 0.042, p < 0.001). In contrast, the findings presented that H1 was also significant, but in the opposite direction compared with our original prediction. The result suggests that individuals’ competence negatively relates to their work motivation.
In Hypotheses 4a–d, we proposed that higher levels of religious affiliation (4a), political participation (4b), humane orientation (4c), and in-group collectivism (4d) strengthen the relationship described in H1. However, the results only demonstrated support for the two hypotheses, H4c (γ13 = 0.032, p < 0.001) and H4d (γ14 = 0.042, p < 0.001). In contrast, the findings presented that H4a was also significant, but opposite our initial prediction. This different result proposes that a higher level of religious affiliation weakens the association between individuals’ competence and work motivation.
In Hypotheses 5a–d, the authors argued that the higher levels of religious affiliation (5a), political participation (5b), humane orientation (5c), and in-group collectivism (5d) enhance the positive relationship between individuals’ autonomy and their work motivation. However, the results only supported the two hypotheses H5b (γ22 = 0.012, p < 0.05) and H5c (γ23 = 0.012, p < 0.1), while H5a and H5d were not significant.
In Hypotheses 6a–d, the authors argued that the higher levels of religious affiliation (6a), political participation (6b), humane orientation (6c), and in-group collectivism (6d) enhance the positive relationship between individuals’ social relatedness and their work motivation. However, the results only supported H6c (γ33 = 0.019, p < 0.01). In contrast, the findings indicated that H6d was also significant, but in the opposite direction compared to our initial hypothesis. The different result suggests that higher in-group collectivism weakens the positive association between individuals’ social relatedness and work motivation. Figure 1 , Figure 2 , Figure 3 , Figure 4 and Figure 5 represent the significant moderators of the associations examined.

The association between competence and work motivation at different levels of humane orientation.

The association between competence and work motivation at different levels of in-group collectivism.

The association between autonomy and work motivation at different levels of political participation.

The association between autonomy and work motivation at different levels of humane orientation.

The association between social relatedness and work motivation at different levels of humane orientation.
Regarding the statistical results of the control variables, gender, marital status, and age consistently indicated significant positive relationships with work motivation across three models. On the other hand, family strength indicated a significant negative association to work motivation only in Model 1.
5. Discussion
The study’s objective was to examine the influence of individuals’ competence, autonomy, and social relatedness on their work motivation, as well as the impact of country-level moderators, including religious affiliation, political participation, humane orientation, and in-group collectivism on their relationships. Seven primary findings are crucial in this research. First, people’s autonomy and social relatedness positively relate to their work motivation. This result is in line with the findings of prior researchers (e.g., [ 45 , 52 ]), postulating that humans’ autonomy and social relatedness breeds work motivation. The study of Theurer et al. (2018) [ 108 ] argued that, among motivational elements, autonomy had been found to greatly predict positive work motivation. When people feel they have enough control over their activities, they are more confident and motivated to work. Along with autonomy, humans’ social relatedness promotes communal benefits, thereby motivating people to work harder for their organization. Second, the association between individual competence and work motivation is moderated by cultural values, including humane orientation and in-group collectivism. The findings are consistent with the viewpoints of prior researchers (e.g., [ 69 , 70 , 77 , 78 ]), namely that a society with higher levels of humane orientation and in-group collectivism strengthens altruism, solidarity, loyalty, and the encouragement of individuals, which results in work motivation. Consequently, there will be an increase in the differences in individuals’ competence and work motivation if they live in a society with greater humane orientation and in-group collectivism. Third, political participation and humane orientation moderate the relationship between individual autonomy and work motivation. These results are in line with the investigations of prior researchers (e.g., [18,45), which found that social circumstances and cultural practices promote people’s motivation. Accordingly, the differences in individuals’ autonomy based on their work motivation will be enhanced if they belong to nations with higher political participation and humane orientation. Fourth, the association between social relatedness and work motivation is moderated by humane orientation. Accordingly, in a humane-oriented society, the differences in individuals’ social relatedness based on their work motivation will be strengthened.
The remaining findings were contrary to the original propositions. Pinder (2014) [ 20 ] argued that it is possible to find that contextual practices can influence variables at the individual level in the opposite prediction in motivation research. Fifth, individuals’ competence negatively influences their work motivation. This finding proposes that more competent individuals are less motivated at work. One possible interpretation of this opposite result is that, when the majority of the organization members recognize individuals’ competence, these individuals may perceive that it is not necessary to devote most of their time and energy to work anymore. These individuals may believe that no matter how unwillingly they perform, they are still competent enough because of their prior achievements. Additionally, competent individuals recognize that they have already sacrificed their enjoyment of life for their previous successes; therefore, they tend to offset this by investing their valuable time in other aspects. This is consistent with other researchers’ investigations (e.g., [ 109 ]), which found that low-skilled individuals are more often compelled to engage in regular work activities and are more easily motivated than others. By contrast, highly competent individuals tend to be motivated by challenging tasks and improving themselves through further education. Sixth, the relationship between competence and work motivation is negatively moderated by religious affiliation. This finding suggests that religious affiliation weakens the association between individuals’ competence and work motivation. One possible explanation for this finding is that strong religious beliefs are the foundation for virtuous living [ 110 ]. Individuals with religious affiliation usually employ religious principles to guide their behavior, regardless of their competence. In other words, both competent and incompetent individuals tend to be more motivated at the workplace if they are affiliated with any religion, thereby diminishing the influence of competence in work motivation. Seventh, the relationship between social relatedness and work motivation is negatively moderated by in-group collectivism. This result proposes that a higher degree of in-group collectivism weakens the association between individuals’ social relatedness and work motivation. One possible explanation for this is that, under an in-group collective society, people put more weight on mutual relationships and encourage acts that may build up the solidarity of groups. Since in-group collectivism is viewed as a social attachment in which people emphasize the group over the self (e.g., [ 79 , 80 , 81 ]), individuals are fairly conscious of their responsibility to the group regardless of their social relatedness. Both socially related and unrelated individuals belonging to in-group collective cultures tend to work harder for common goals. Accordingly, the influence of individuals’ social relatedness on their work motivation is reduced.
6. Limitations and Future Research
Despite its significant contributions, this study has its limitations. The use of secondary data represents the fact that the data collection process was beyond the authors’ control. However, the collection of cross-national data is time-consuming and costly. The authors used the available data but strove for the efficient use of multilevel data. The secondary data also limited the measurement of individual-level factors based on the available data. Moreover, it is quite complex to gauge an individual’s work motivation appropriately, since personal work motivation may not be one-dimensional. Nevertheless, the authors made efforts to employ the measurements utilized by prior research. Moreover, it is complicated to measure social factors such as political participation. There are challenges in investigating social contexts due to the absence of direct measurements [ 111 ]. This compels the authors to identify substitute measurements for this study. Finally, this study covered 25 samples from 25 countries with different characteristics. Despite the attempt of this study to include the most relevant social conditions in the framework, the influence of other national differences and cultural sensitivities were not considered.
This paper directs further research considering that several frameworks and approaches should be employed to better examine motivation [ 112 ]. First, as some of the results were opposite to the original propositions based on the theoretical foundations employed, combining different concepts and approaches is necessary to enhance perspectives of psychological needs and social issues. For instance, the relationship between competence and work motivation can be further investigated by employing other theories to understand their association better. Similarly, the moderating effects of social contexts such as religious affiliation and in-group collectivism should be further examined to obtain a more in-depth comprehension of the roles of contextual circumstances and cultural values in individual-level relationships. Additionally, self-determination theory and the concept of prosocial motivation may be used to explore motivation towards specific behavior in organizations, such as organizational citizenship and proactive behaviors. Organizational context, such as rewards, training, and culture, can be considered as part of the framework to enhance the conception of work motivation.
7. Conclusions
This study has utilized a multilevel framework to examine the influence of psychological needs and social context on work motivation. Through this research, a deeper understanding of the roles of competence, autonomy, and social relatedness, as well as social situations and cultural values on work motivation, is achieved. The contrary findings call for integrating other concepts and approaches towards a more comprehensive knowledge of work motivation.
Along with the theoretical contribution, the study’s findings offer practical implications. The satisfaction of psychological needs promotes self-motivation, which creates positive outcomes. Hence, organizations can provide programs and activities to promote employees’ autonomy and social relatedness as this will enhance their work motivation. Employee empowerment can be advocated by encouraging them to make their own decisions at the workplace, providing constructive criticisms rather than instilling the fear of failure. Additionally, managers should encourage solidarity, support, and mutual care among employees. Putting more weight on employees’ fulfillment of needs will further increase employees’ motivation, thereby diminishing costs related to stress or turnover [ 50 ]. To establish a novel mechanism towards promoting work motivation in the entire nation, the government should pay attention to the political structure and conditions that encourage citizens’ participation. Additionally, a culture of humane orientation should be promoted in the workplace and society so that solidarity, kind assistance, and altruism among communities as well as among individuals can be strengthened. For instance, teamwork should be encouraged for employees to help each other overcome difficulties at the workplace or share responsibilities with their colleagues. This will motivate people to work harder for collective goals, contributing to the development of organizations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.T.D.V. and K.V.T.; data collection, T.T.D.V.; methodology, T.T.D.V. and K.V.T.; formal analysis, T.T.D.V. and K.V.T.; resources, K.V.T. and C.-W.C.; writing-original draft, T.T.D.V. and K.V.T.; writing-review, editing & proofreading, T.T.D.V., K.V.T. and C.-W.C.; visualization, K.V.T.; supervision, K.V.T. and C.-W.C.; project administration, K.V.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
This paper does not receive funding from any individuals or organizations.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Home — Essay Samples — Psychology — Motivation — Theory of Motivational: Context and Process Theories
Theory of Motivational: Context and Process Theories
- Categories: Maslow'S Hierarchy of Needs Motivation
About this sample

Words: 2206 |
12 min read
Published: Aug 1, 2022
Words: 2206 | Pages: 5 | 12 min read
Table of contents
Context theories, process theories, maslow's hierarchy of needs, alderfer's erg theory, motivator-hygiene theory, mcclelland's learned needs theory, expectancy theory.
- Their expectancy, which means how much they accept that advancing exertion will prompt a given degree of performance
- Their instrumentality, or how much they accept that a given degree of execution will bring about specific results or rewards
- Their valence, which is the degree to which the normal results are alluring or unattractive
Equity Theory
Goal-setting theory, reinforcement theory.
- Positive Reinforcement − Positive reinforcement clarifies that, when a worker gives positive and necessary conduct, the reaction towards them should be certain. This invigorates the event of conduct. Reward to a representative who performs well fortifies his/her longing to perform better in view of the positive aftereffects of doing as such. Honda Company always encourages their employees' behavior and performance through a system of praise and rewards.
- Negative Reinforcement −Negative reinforcement happens when certain deterrent(s) or obstruction(s) is expelled and the employee(s) reacts to ideal conduct after such expulsion. For example, a worker who drives from a long separation wraps up a couple of undertakings quicker than wanted; in any case, when he is advised by the administrator to take the ventures home for a few days and complete them, it animates him/her to function true to form. By evacuating the negative improvements, the ideal conduct is fortified.
- Punishment − Punishment alludes to forcing negative outcomes or expelling positive results with the end goal of averting employees from rehashing unwanted and uncalled-for practices. It can, in this way, be both positive and negative. For example, Honda Company cut in the wages of an employee who misses work. The loss of income constitutes the punishment for missing work.
- Extinction − Extinction alludes to stifling educated conduct by retaining uplifting feedback or reward that has empowered the conduct.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Psychology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 660 words
3 pages / 1449 words
3 pages / 1571 words
2 pages / 717 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Motivation
Living life as a student-athlete is no easy feat by any definition of the world. You’re constantly trying to balance your social life, your athletics, and your grades. The training sessions are a killer and trying to do any [...]
Motivation serves as a driving force that compels individuals to pursue their goals and desires. In the case of Macbeth, the protagonist's motivation is rooted in his ambition to seize power and fulfill the prophecy of becoming [...]
In William Shakespeare's play "Julius Caesar," the character of Brutus is a multifaceted and complex individual. Known for his involvement in the conspiracy against Caesar, Brutus is a character who possesses both admirable and [...]
Motivation is something that is sought out by everyone in some form or another. It is a driving force that causes us to want to do better or to change something that we might be doing. Motivational speaker Nick Vujicic talks [...]
Flowers for Algernon by Daniel Keyes suggests when putting with the motivation you will have to strive in order to complete the goal. During the book, Charlie was faced with 3 main stages of life to make it to his end goal which [...]
In the following essay, I will be talking about how coaches, teachers and instructors can create two different climates, the mastery climate and the competitive climate and how this can impact sports performance. A mastery [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
9.1 Early Theories of Motivation
- What are the basic principles of Frederick Taylor’s concept of scientific management?
Motivation is the set of forces that prompt a person to release energy in a certain direction. As such, motivation is essentially a need- and want-satisfying process. A need is best defined as the gap between what is and what is required . Similarly, a want is the gap between what is and what is desired . Unsatisfied needs and wants create a state of tension that pushes (motivates) individuals to practice behavior that will result in the need being met or the want being fulfilled. That is, motivation is what pushes us to move from where we are to where we want to be, because expending that effort will result in some kind of reward.
Rewards can be divided into two basic categories: intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic rewards come from within the individual—things like satisfaction, contentment, sense of accomplishment, confidence, and pride. By contrast, extrinsic rewards come from outside the individual and include things like pay raises, promotions, bonuses, prestigious assignments, and so forth. Exhibit 9.3 illustrates the motivation process.
Successful managers are able to marshal the forces to motivate employees to achieve organizational goals. And just as there are many types of gaps between where organizations are and where they want to be, there are many motivational theories from which managers can draw to inspire employees to bridge those gaps. In this chapter, we will first examine motivational theories that grew out of the industrial revolution and early ideas of organizational psychology. Then we will examine needs-based theories and more contemporary ideas about employee motivation like equity, expectancy, goals, and reinforcement theories. Finally, we will show you how managers are applying these theories in real-world situations.
How can managers and organizations promote enthusiastic job performance, high productivity, and job satisfaction? Many studies of human behavior in organizations have contributed to our current understanding of these issues. A look at the evolution of management theory and research shows how managers have arrived at the practices used today to manage human behavior in the workplace. A sampling of the most influential of these theorists and research studies are discussed in this section.
Frederick Taylor’s Scientific Management
One of the most influential figures of the classical era of management, which lasted from about 1900 to the mid-1930s, was Frederick W. Taylor , a mechanical engineer sometimes called the “father of scientific management .” Taylor’s approach to improved performance was based on economic incentives and the premise that there is “one best way” to perform any job. As a manager at the Midvale and Bethlehem Steel companies in Philadelphia in the early 1900s, Taylor was frustrated at the inefficiency of the laborers working in the mills.
Convinced that productivity could be improved, Taylor studied the individual jobs in the mill and redesigned the equipment and the methods used by workers. Taylor timed each job with a stopwatch and broke down every task into separate movements. He then prepared an instruction sheet telling exactly how each job should be done, how much time it should take, and what motions and tools should be used. Taylor ’s ideas led to dramatic increases in productivity in the steel mills and resulted in the development of four basic principles of scientific management:
- Develop a scientific approach for each element of a person’s job.
- Scientifically select, train, teach, and develop workers.
- Encourage cooperation between workers and managers so that each job can be accomplished in a standard, scientifically determined way.
- Divide work and responsibility between management and workers according to who is better suited to each task.
Taylor published his ideas in The Principles of Scientific Management. His pioneering work vastly increased production efficiency and contributed to the specialization of labor and the assembly-line method of production. Taylor’s approach is still being used nearly a century later in companies such as UPS , where industrial engineers maximize efficiency by carefully studying every step of the delivery process looking for the quickest possible way to deliver packages to customers. Though Taylor’s work was a giant step forward in the evolution of management, it had a fundamental flaw in that it assumed that all people are primarily motivated by economic means. Taylor’s successors in the study of management found that motivation is much more complex than he envisioned.
Concept Check
- How did Frederic Taylor’s studies contribute to the early understanding of human motivation?
- How are Taylor’s insights still seen in today’s management practices?
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introduction-business/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Lawrence J. Gitman, Carl McDaniel, Amit Shah, Monique Reece, Linda Koffel, Bethann Talsma, James C. Hyatt
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introduction to Business
- Publication date: Sep 19, 2018
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-business/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-business/pages/9-1-early-theories-of-motivation
© Apr 5, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Table of Contents
What are motivation theories, popular motivational theories, conclusion , theories of motivation: a comprehensive guide.

Motivation drives an individual to go beyond the normal level and achieve success with great energy and enthusiasm. It pushes people to come out of their comfort zone, perform well, and be productive for their personal or professional growth. Theories of motivation allow management to understand the behavior of their employees based on their passion and interest. They put them in situations that lead to better progress of individuals and the organization as a whole.
Motivation theories refer to the study of the development of inspiration to achieve certain aims at a professional or personal level. It means the theories help identify the process of learning and understanding an individual's motivation to achieve a particular result. Motivation theories are helpful in several fields, including sociology, psychology, and business management.
The theories are beneficial and widely applicable in management to identify the factors inspiring employees. Consequently, they aid in enhancing the productivity and profit of individuals and organizations.
Here are some popular motivational theories to find the factors that motivate individuals:
Maslow's Theory Of Hierarchical Needs
Any individual cannot focus on complex requirements until their basic requirements have not been fulfilled. Maslow’s theory outlines this hierarchy by creating a pyramid to portray the process of individuals fulfilling their basic needs before progressing to the higher level needs. These needs are generally categorized into five types, including
- Psychological Needs: It is about the basic survival needs that are needed in our daily life routine, such as food, shelter, water, clothes and so on. Psychological needs can only be fulfilled by the individual’s income.
- Safety Requirements: Safety needs refer to the needs that make individuals feel secure and protected. Protection from deprivation, employment security, health, property and other factors are included in safety requirements.
- Social Needs: They cover the individual’s sense of belonging. Everyone strives to associate with people and organizations to connect, affiliate, and join groups and communities. They indulge in team-building activities.
- Self-Esteem Needs: Individuals have a quest for recognition and respect. It makes them feel confident in their area and boosts self-esteem. This esteem can be fostered by acknowledging the employees' achievements and providing positive feedback.
- Self-Actualization Needs: Self-actualization is the highest phase of Maslow’s theory that trains individuals to have long-term complex goals to reach this level. The need inspires workers to deliver effective tasks, learn more, and work for their personal development in challenging fields.

Mcclelland's Theory Of Needs
The theory affirms the three motivating drivers that every individual needs, though each would vary with the type of personality. The management must understand employees' behavior of striving for their specific needs and motivate them accordingly. The three dominant needs are as follows:
1. Achievement:
Some people have a hunger to be successful and get recognition. They always strive for competition to achieve higher standards in their work environment. Furthermore, they seek quick acknowledgment of their progress to be consistent in their result-based efforts.
2. Affiliation:
The theory claims that individuals want to be associated and accepted in groups. The theory aids management in understanding their employees' striving for growth within the team and building interpersonal skills, strengthening the relations between coworkers so that they can encourage them accordingly.
Some desire control of their work and are interested in leading others at their workplace. They incorporate their leadership skills to distribute work, coordinate events, and inspire coworkers.
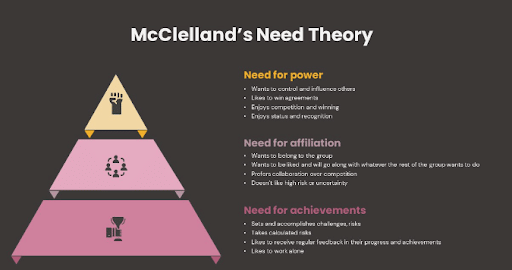
Become a Project Management Professional
- 6% Growth In Jobs Of Project Management Profiles By 2024
- 22 Million Jobs Estimated For Project Management Professionals By 2027
PMP® Certification Training
- Access to Digital Materials from PMI
- 12 Full-Length Simulation Test Papers (180 Questions Each)
Post Graduate Program in Project Management
- Receive Post Graduate Program Certificate and Alumni Association Membership from UMass Amherst
- 8X higher live interaction in live online classes by industry experts
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Katrina Tanchoco
Shell - manila ,.
The interactive sessions make a huge difference as I'm able to ask for further clarifications. The training sessions are more engaging than the self-paced modules, it's easier now that i first decided to take up the online classroom training, and then followed it up with the self-paced learning (online and readings).
PHC Business Manager , Midlands and Lancashire Commissioning Support Unit
I wanted to transition into the Project Management field and wanted the right opportunity to do so. Thus, I took that leap forward and enrolled in this course. My learning experience was fantastic. It suited my learning style.
Incentive Theory
The theory determines that rewards or punishments influence employees' work behavior. Therefore, these are the primary motivators for individuals performing certain tasks and achieving specific results. For instance,
- Bonus: It refers to the reward that is given to the employees for their exceptional performance.
- Opportunity: It is a type of incentive given to individuals through paid training or continuing education to enhance their knowledge and build their skills.
- Promotion: Providing a higher position or salary can make employees feel their importance and growth.
- Paid off: Providing compensation for taking leave as additional holidays on emergency needs or planned trips can make employees feel satisfied.

Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory
The theory states that two factors influence satisfaction or dissatisfaction:
- Hygiene Factors: Satisfaction can be influenced by factors like professional relations, policies, working environment, attitude of the supervisor. If these factors are fine, they can motivate employees and vice versa.
- Motivators Factors: Motivating factors, including recognition, personal growth, achievements, career and responsibilities, are crucial for employees. Acknowledging these enhances job satisfaction.
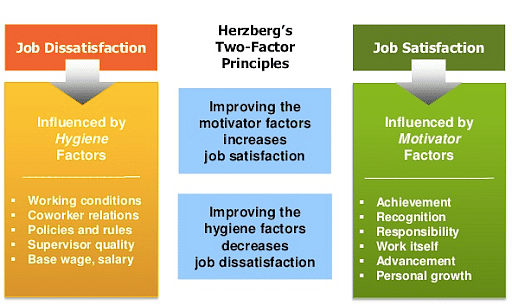
Vroom's Expectancy Theory
The theory states that expectations for the future can have a major impact on an individual’s motivation. It means that conscious choices from the options given can boost pleasure and decrease pain. The factors that influence motivation are:
- Expectancy: It implies that Increased efforts bring success. It means if you work hard, you will get better outcomes.
- Instrumentality: Getting incentives or rewards if you meet performance expectations.
- Valence: It refers to how an employee gives importance to the expected results.
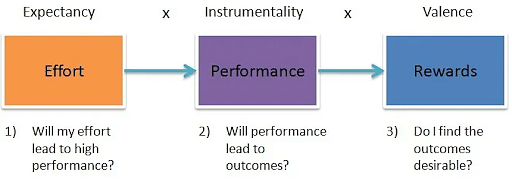
McGregor’s Theory X And Theory Y
McGregor introduced Mcgregor’s theory in his book named ‘The Human Side of Enterprise.’ In the book, he stated two styles of management, i.e.,
1. Theory X:
The theory incorporates micromanaging individuals who have low motivation, are incapable of performing well, dislike their work, avoid work and responsibility and so on. Micromanagement gets the task done appropriately by using an authoritarian style of management.
2. Theory Y:
The theory states that managers can use a decentralized and participative management approach for people who are enthusiastic towards their work, take responsibility for their work or do not need to be supervised to get the task done appropriately.
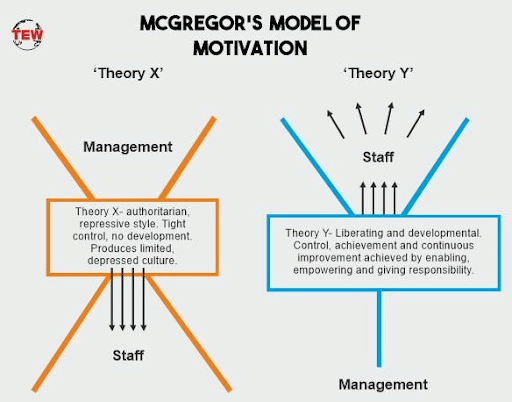
Alderfer’s Erg Theory
The theory liquidized Maslow’s five hierarchy of needs into three categories, i.e., existence, growth and relatedness, along with physiological and materialistic desires (such as affection, clothing, food, water, etc.). It focuses on the following:
- Existence: It involves the basic needs for living, like food and shelter.
- Growth: It determines the intrinsic need for personal development aligned with self-esteem, achievement, and confidence. It requires problem-solving skills, creativity and morality.
- Relatedness: It involves interpersonal relationships, such as social interactions, terms with family members, belongings or love-related needs.
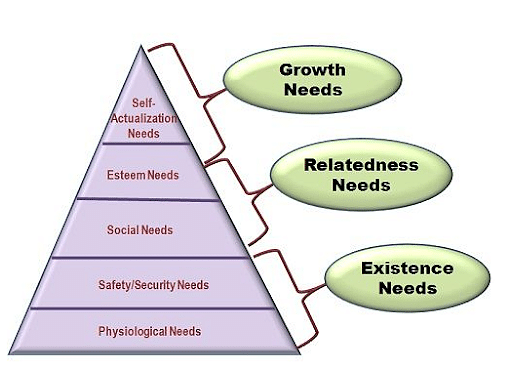
Theories of motivation aid management teams in bringing out the best ways to achieve organizational goals and work toward the desired outcomes. If we apply the theories of motivation successfully, it helps to bring positiveness, support, and inspire the employees efficiently, leading to the growth of individuals, teams and the entire organization.
Want to build experts in your teams but do not know how to apply the theories? Join the PMP Certification Training Course to be a successful project management professional. The training involves practice sessions with an updated PMP examination preparation. Join now to upskill!
1. What are the theories of motivation?
Theories of motivation help understand the factors that motivate individuals to perform efficiently toward their specific goals. It helps management to influence individuals to achieve the result effectively.
2. Who is the father of motivation theory?
An American psychologist, Abraham Maslow, is popularly known as the father of motivation theory.
3. What is Maslow's motivation theory?
Maslow’s motivation theory determines the five fundamental needs of individuals. It incorporates physiological, safety, love and belongingness (social need), esteem and self-actualization needs. Individuals cannot switch to their complex high-level needs before fulfilling these fundamental needs.
Our Project Management Courses Duration And Fees
Project Management Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
Learn from Industry Experts with free Masterclasses
Project management.
How to Successfully Ace the PMP Exam on Your First Attempt in 2024
Career Masterclass: How to Successfully Ace the PMP Exam on Your First Attempt in 2024
Career Fast-track
Panel Discussion: The Startup Career Strategy - The Highs and Lows
Recommended Reads
An Introduction to Project Management: A Beginner’s Guide
The Basic Principles of Project Management
What is Agile Project Management?
Project Management Interview Guide
PMP Study: 3 Types of Contracts in Project Management
What Is Project Management?
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >
8 The Motivational Theory of Emotions
- Published: November 2014
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Having an emotion customarily involves appraising a stimulus a particular way, feeling a particular way, and being motivated to act a particular way. These three aspects offer distinctive entry points for explaining what emotions are. Philosophers have so far built their accounts primarily around appraisals and feelings. As a result, two research programs have dominated the philosophy of emotions over the past forty years: Cognitivism and Perceptualism. The objective of this paper is to introduce a new Motivational Theory of Emotions, which replaces the primacy of the appraisal and feeling aspects of emotions with the primacy of their motivational dimension. The core proposal is that emotions are action control systems designed to prioritize the pursuit of some goals over others. The Motivational Theory will be shown to explain how emotions motivate better than Cognitivism and Perceptualism, and to offer solutions to two outstanding problems in the philosophy of emotions: explaining the intentionality of emotions and explaining how emotions differ from one another.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Motivation Theory in marketing. When applying motivation theories in marketing, few changes are necessary. As explained by O'Neil and Drillings (1994) "different employees in different departments will be motivated by different incentives" (p.233). In the marketing of merchandise, high levels of motivation are required from the staff.
Mukaddes, Rashed, & Samad, 2010) We begin by looking at three early motivation theories: Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg. Motivation/Hygiene theory and Victor Vroom's Expectancy theory ...
Maslow's theory of the hierarchy of needs, Alderfer's ERG theory, McClelland's achievement motivation theory, and Herzberg's two-factor theory focused on what motivates people and addressed specific factors like individual needs and goals. ... if I were to write an essay on Motivation. Reply. Sunny on July 20, 2022 at 02:14 . It's so ...
As such, expectancy theory states that motivating people should come down to three things ("Expectency Theory" n.d.). First, motivation is a factor of effort ("Expectency Theory" n.d.). In order to motivate others, employers should encourage the belief that more effort equals better performance. Second, employers should encourage the ...
This paper explores theories of motivation, including instinct theory, arousal theory, incentive theory, intrinsic theory, extrinsic theory, the ARCS model, self-determination theory, expectancy-value theory, and goal-orientation theory. Each theory is described in detail, along with its key concepts, assumptions, and implications for behavior.
In expectancy‐value theory, motivation is a function of the expectation of success and perceived value. Attribution theory focuses on the causal attributions learners create to explain the results of an activity, and classifies these in terms of their locus, stability and controllability. Social‐ cognitive theory emphasises self‐efficacy ...
Theories. The term motivation describes why a person does something. It is the driving force behind human actions. Motivation is the process that initiates, guides, and maintains goal-oriented behaviors. For instance, motivation is what helps you lose extra weight, or pushes you to get that promotion at work.
Motivation is often taken for granted in psychology, perhaps because it is hidden beneath the actions we take. The relative visibility of our actions and the relative invisibility of their motivational underpinnings may explain why some researchers—such as many who study cognition, intelligence, or personality—do not see their phenomena as arising from and importantly influenced by motivation.
This theory focuses on how interpretations of the reasons for success or failure in an event affect motivation for future events. Weiner identified that the most frequent achievement attributions relate to ability, effort, task difficulty, and luck. These attributions can be classified in three causal dimensions.
The first set of theories focuses on the innateness of motivation. These theories emphasize instinctual or inborn needs and drives that influence our behavior. The second set of theories proposes cognition as the source of motivation. Individual motivation is influenced by thoughts, beliefs, and values.
Motivation, the psychological construct 'invented' to describe the mechanism by which individuals and groups choose particular behaviour and persist with it, has a history going back millennia in all cultures. Ancient Greek, Roman, Egyptian, Indian, Chinese, and Indigenous cultures from all continents developed rubrics about positively ...
First, over 150 papers utilize the key approaches of psychological needs to justify motivational processes in the workplace ... Although a significant number of important contributions have been made regarding intrinsic motivation, self-determination theory is of particular significance for this study. Self-determination theory (SDT) postulates ...
Context Theories. Content (or need) theory of motivation centers around factors inside to the person that empowers and direct conduct. As a rule, such theory sees motivation as the result of inside drives that constrain a person to act or move (henceforth, 'persuade') close as per the general inclination of individual needs.
Motivation Theory The Implementation of Motivation in. PAGES 4 WORDS 1071. Motivation Theory: The Implementation of Motivation in the Workplace. Motivation lends a hand to one to achieve goals and can be either intrinsic or extrinsic (TheManager.org, 2001). In multiple theories, motivation is the need to decrease pain or increase one's happiness.
According to Maslow's Need Hierarchy Theory, the source of motivation is "both a theory of human motives by classifying basic human needs in a hierarchy, and a theory of human motivation that relates these needs to general behavior" (Wahba, 1976, p. 213). In other words, Maslow's theory organizes individual needs from basic to complex.
In this essay, I aim to highlight and analyse three of the most well-known theories of motivation in relation to social class disparity within the UK workplace, and try to offer solutions to this problem using the three theories of motivation. These three theories are McClelland's Need for Achievement Theory, McGregor's Theory X and Y, and ...
Motivation is the set of forces that prompt a person to release energy in a certain direction. As such, motivation is essentially a need- and want-satisfying process. ... A look at the evolution of management theory and research shows how managers have arrived at the practices used today to manage human behavior in the workplace. A sampling of ...
Motivational Theories Essay. Motivation is the force that makes us do things, whether accomplishing personal goals or completing tasks at work. Most people are motivated as a result of their individual needs being satisfied, which gives them the inspiration to perform specific behaviors for which they receive rewards (Kinicki & Williams, 2011).
Download. Essay, Pages 7 (1664 words) Views. 636. Maslow and Herzberg both came up with motivation theories which have been widely used in explaining human psychology over the years. These theories however differ and a proper understanding is required in order to determine the ideology in each. While Maslow concentrated on personal motivation ...
Theories of motivation help understand the factors that motivate individuals to perform efficiently toward their specific goals. It helps management to influence individuals to achieve the result effectively. 2. Who is the father of motivation theory? An American psychologist, Abraham Maslow, is popularly known as the father of motivation ...
The Motivational Theory will be shown to explain how emotions motivate better than Cognitivism and Perceptualism, and to offer solutions to two outstanding problems in the philosophy of emotions: explaining the intentionality of emotions and explaining how emotions differ from one another.
The dictionary defines motivation as "the reason why somebody does something or behaves in a particular way" (Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary of Current English, 2000, p1128). Many theorists over the years starting from the industrial revolution have analysed what makes workers work harder. This essay will illustrate why there are ...
Arousal theory of motivation: This theory suggests that people carry out some specific actions in order to increase or decrease their levels of arousal. More clearly we can say, that this theory motivates us in order to maintain our arousal level at an optimum point, not below it, not higher. A clear example of application of this theory could ...