- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

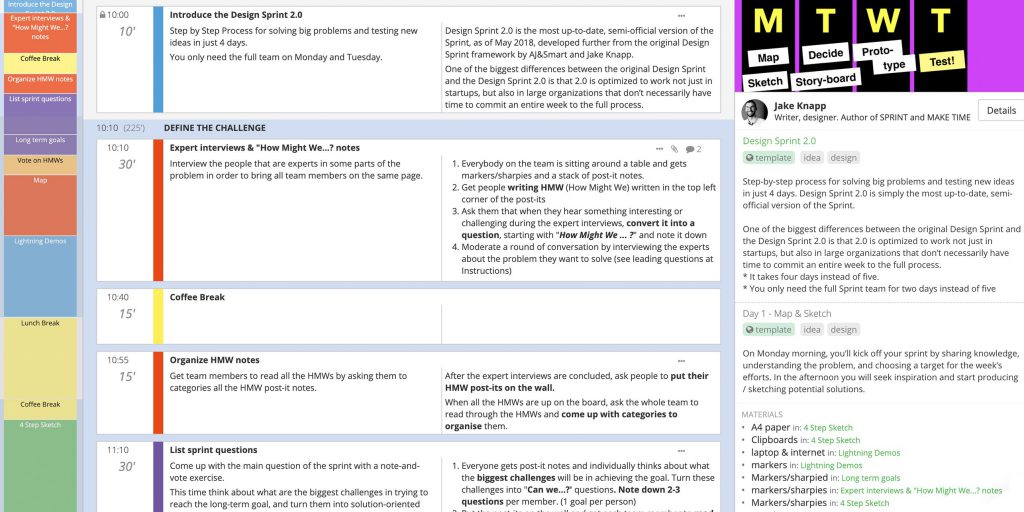
Problem-Solving Strategies and Obstacles
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Sean is a fact-checker and researcher with experience in sociology, field research, and data analytics.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Sean-Blackburn-1000-a8b2229366944421bc4b2f2ba26a1003.jpg)
JGI / Jamie Grill / Getty Images
- Application
- Improvement
From deciding what to eat for dinner to considering whether it's the right time to buy a house, problem-solving is a large part of our daily lives. Learn some of the problem-solving strategies that exist and how to use them in real life, along with ways to overcome obstacles that are making it harder to resolve the issues you face.
What Is Problem-Solving?
In cognitive psychology , the term 'problem-solving' refers to the mental process that people go through to discover, analyze, and solve problems.
A problem exists when there is a goal that we want to achieve but the process by which we will achieve it is not obvious to us. Put another way, there is something that we want to occur in our life, yet we are not immediately certain how to make it happen.
Maybe you want a better relationship with your spouse or another family member but you're not sure how to improve it. Or you want to start a business but are unsure what steps to take. Problem-solving helps you figure out how to achieve these desires.
The problem-solving process involves:
- Discovery of the problem
- Deciding to tackle the issue
- Seeking to understand the problem more fully
- Researching available options or solutions
- Taking action to resolve the issue
Before problem-solving can occur, it is important to first understand the exact nature of the problem itself. If your understanding of the issue is faulty, your attempts to resolve it will also be incorrect or flawed.
Problem-Solving Mental Processes
Several mental processes are at work during problem-solving. Among them are:
- Perceptually recognizing the problem
- Representing the problem in memory
- Considering relevant information that applies to the problem
- Identifying different aspects of the problem
- Labeling and describing the problem
Problem-Solving Strategies
There are many ways to go about solving a problem. Some of these strategies might be used on their own, or you may decide to employ multiple approaches when working to figure out and fix a problem.
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure that, by following certain "rules" produces a solution. Algorithms are commonly used in mathematics to solve division or multiplication problems. But they can be used in other fields as well.
In psychology, algorithms can be used to help identify individuals with a greater risk of mental health issues. For instance, research suggests that certain algorithms might help us recognize children with an elevated risk of suicide or self-harm.
One benefit of algorithms is that they guarantee an accurate answer. However, they aren't always the best approach to problem-solving, in part because detecting patterns can be incredibly time-consuming.
There are also concerns when machine learning is involved—also known as artificial intelligence (AI)—such as whether they can accurately predict human behaviors.
Heuristics are shortcut strategies that people can use to solve a problem at hand. These "rule of thumb" approaches allow you to simplify complex problems, reducing the total number of possible solutions to a more manageable set.
If you find yourself sitting in a traffic jam, for example, you may quickly consider other routes, taking one to get moving once again. When shopping for a new car, you might think back to a prior experience when negotiating got you a lower price, then employ the same tactics.
While heuristics may be helpful when facing smaller issues, major decisions shouldn't necessarily be made using a shortcut approach. Heuristics also don't guarantee an effective solution, such as when trying to drive around a traffic jam only to find yourself on an equally crowded route.
Trial and Error
A trial-and-error approach to problem-solving involves trying a number of potential solutions to a particular issue, then ruling out those that do not work. If you're not sure whether to buy a shirt in blue or green, for instance, you may try on each before deciding which one to purchase.
This can be a good strategy to use if you have a limited number of solutions available. But if there are many different choices available, narrowing down the possible options using another problem-solving technique can be helpful before attempting trial and error.
In some cases, the solution to a problem can appear as a sudden insight. You are facing an issue in a relationship or your career when, out of nowhere, the solution appears in your mind and you know exactly what to do.
Insight can occur when the problem in front of you is similar to an issue that you've dealt with in the past. Although, you may not recognize what is occurring since the underlying mental processes that lead to insight often happen outside of conscious awareness .
Research indicates that insight is most likely to occur during times when you are alone—such as when going on a walk by yourself, when you're in the shower, or when lying in bed after waking up.
How to Apply Problem-Solving Strategies in Real Life
If you're facing a problem, you can implement one or more of these strategies to find a potential solution. Here's how to use them in real life:
- Create a flow chart . If you have time, you can take advantage of the algorithm approach to problem-solving by sitting down and making a flow chart of each potential solution, its consequences, and what happens next.
- Recall your past experiences . When a problem needs to be solved fairly quickly, heuristics may be a better approach. Think back to when you faced a similar issue, then use your knowledge and experience to choose the best option possible.
- Start trying potential solutions . If your options are limited, start trying them one by one to see which solution is best for achieving your desired goal. If a particular solution doesn't work, move on to the next.
- Take some time alone . Since insight is often achieved when you're alone, carve out time to be by yourself for a while. The answer to your problem may come to you, seemingly out of the blue, if you spend some time away from others.
Obstacles to Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is not a flawless process as there are a number of obstacles that can interfere with our ability to solve a problem quickly and efficiently. These obstacles include:
- Assumptions: When dealing with a problem, people can make assumptions about the constraints and obstacles that prevent certain solutions. Thus, they may not even try some potential options.
- Functional fixedness : This term refers to the tendency to view problems only in their customary manner. Functional fixedness prevents people from fully seeing all of the different options that might be available to find a solution.
- Irrelevant or misleading information: When trying to solve a problem, it's important to distinguish between information that is relevant to the issue and irrelevant data that can lead to faulty solutions. The more complex the problem, the easier it is to focus on misleading or irrelevant information.
- Mental set: A mental set is a tendency to only use solutions that have worked in the past rather than looking for alternative ideas. A mental set can work as a heuristic, making it a useful problem-solving tool. However, mental sets can also lead to inflexibility, making it more difficult to find effective solutions.
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
In the end, if your goal is to become a better problem-solver, it's helpful to remember that this is a process. Thus, if you want to improve your problem-solving skills, following these steps can help lead you to your solution:
- Recognize that a problem exists . If you are facing a problem, there are generally signs. For instance, if you have a mental illness , you may experience excessive fear or sadness, mood changes, and changes in sleeping or eating habits. Recognizing these signs can help you realize that an issue exists.
- Decide to solve the problem . Make a conscious decision to solve the issue at hand. Commit to yourself that you will go through the steps necessary to find a solution.
- Seek to fully understand the issue . Analyze the problem you face, looking at it from all sides. If your problem is relationship-related, for instance, ask yourself how the other person may be interpreting the issue. You might also consider how your actions might be contributing to the situation.
- Research potential options . Using the problem-solving strategies mentioned, research potential solutions. Make a list of options, then consider each one individually. What are some pros and cons of taking the available routes? What would you need to do to make them happen?
- Take action . Select the best solution possible and take action. Action is one of the steps required for change . So, go through the motions needed to resolve the issue.
- Try another option, if needed . If the solution you chose didn't work, don't give up. Either go through the problem-solving process again or simply try another option.
You can find a way to solve your problems as long as you keep working toward this goal—even if the best solution is simply to let go because no other good solution exists.
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
Dunbar K. Problem solving . A Companion to Cognitive Science . 2017. doi:10.1002/9781405164535.ch20
Stewart SL, Celebre A, Hirdes JP, Poss JW. Risk of suicide and self-harm in kids: The development of an algorithm to identify high-risk individuals within the children's mental health system . Child Psychiat Human Develop . 2020;51:913-924. doi:10.1007/s10578-020-00968-9
Rosenbusch H, Soldner F, Evans AM, Zeelenberg M. Supervised machine learning methods in psychology: A practical introduction with annotated R code . Soc Personal Psychol Compass . 2021;15(2):e12579. doi:10.1111/spc3.12579
Mishra S. Decision-making under risk: Integrating perspectives from biology, economics, and psychology . Personal Soc Psychol Rev . 2014;18(3):280-307. doi:10.1177/1088868314530517
Csikszentmihalyi M, Sawyer K. Creative insight: The social dimension of a solitary moment . In: The Systems Model of Creativity . 2015:73-98. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-9085-7_7
Chrysikou EG, Motyka K, Nigro C, Yang SI, Thompson-Schill SL. Functional fixedness in creative thinking tasks depends on stimulus modality . Psychol Aesthet Creat Arts . 2016;10(4):425‐435. doi:10.1037/aca0000050
Huang F, Tang S, Hu Z. Unconditional perseveration of the short-term mental set in chunk decomposition . Front Psychol . 2018;9:2568. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02568
National Alliance on Mental Illness. Warning signs and symptoms .
Mayer RE. Thinking, problem solving, cognition, 2nd ed .
Schooler JW, Ohlsson S, Brooks K. Thoughts beyond words: When language overshadows insight. J Experiment Psychol: General . 1993;122:166-183. doi:10.1037/0096-3445.2.166
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.
For Business
For Individuals
10 Problem-solving strategies to turn challenges on their head

Jump to section
What is an example of problem-solving?
What are the 5 steps to problem-solving, 10 effective problem-solving strategies, what skills do efficient problem solvers have, how to improve your problem-solving skills.
Problems come in all shapes and sizes — from workplace conflict to budget cuts.
Creative problem-solving is one of the most in-demand skills in all roles and industries. It can boost an organization’s human capital and give it a competitive edge.
Problem-solving strategies are ways of approaching problems that can help you look beyond the obvious answers and find the best solution to your problem .
Let’s take a look at a five-step problem-solving process and how to combine it with proven problem-solving strategies. This will give you the tools and skills to solve even your most complex problems.
Good problem-solving is an essential part of the decision-making process . To see what a problem-solving process might look like in real life, let’s take a common problem for SaaS brands — decreasing customer churn rates.
To solve this problem, the company must first identify it. In this case, the problem is that the churn rate is too high.
Next, they need to identify the root causes of the problem. This could be anything from their customer service experience to their email marketing campaigns. If there are several problems, they will need a separate problem-solving process for each one.
Let’s say the problem is with email marketing — they’re not nurturing existing customers. Now that they’ve identified the problem, they can start using problem-solving strategies to look for solutions.
This might look like coming up with special offers, discounts, or bonuses for existing customers. They need to find ways to remind them to use their products and services while providing added value. This will encourage customers to keep paying their monthly subscriptions.
They might also want to add incentives, such as access to a premium service at no extra cost after 12 months of membership. They could publish blog posts that help their customers solve common problems and share them as an email newsletter.
The company should set targets and a time frame in which to achieve them. This will allow leaders to measure progress and identify which actions yield the best results.

Perhaps you’ve got a problem you need to tackle. Or maybe you want to be prepared the next time one arises. Either way, it’s a good idea to get familiar with the five steps of problem-solving.
Use this step-by-step problem-solving method with the strategies in the following section to find possible solutions to your problem.
1. Identify the problem
The first step is to know which problem you need to solve. Then, you need to find the root cause of the problem.
The best course of action is to gather as much data as possible, speak to the people involved, and separate facts from opinions.
Once this is done, formulate a statement that describes the problem. Use rational persuasion to make sure your team agrees .
2. Break the problem down
Identifying the problem allows you to see which steps need to be taken to solve it.
First, break the problem down into achievable blocks. Then, use strategic planning to set a time frame in which to solve the problem and establish a timeline for the completion of each stage.
3. Generate potential solutions
At this stage, the aim isn’t to evaluate possible solutions but to generate as many ideas as possible.
Encourage your team to use creative thinking and be patient — the best solution may not be the first or most obvious one.
Use one or more of the different strategies in the following section to help come up with solutions — the more creative, the better.
4. Evaluate the possible solutions
Once you’ve generated potential solutions, narrow them down to a shortlist. Then, evaluate the options on your shortlist.
There are usually many factors to consider. So when evaluating a solution, ask yourself the following questions:
- Will my team be on board with the proposition?
- Does the solution align with organizational goals ?
- Is the solution likely to achieve the desired outcomes?
- Is the solution realistic and possible with current resources and constraints?
- Will the solution solve the problem without causing additional unintended problems?

5. Implement and monitor the solutions
Once you’ve identified your solution and got buy-in from your team, it’s time to implement it.
But the work doesn’t stop there. You need to monitor your solution to see whether it actually solves your problem.
Request regular feedback from the team members involved and have a monitoring and evaluation plan in place to measure progress.
If the solution doesn’t achieve your desired results, start this step-by-step process again.
There are many different ways to approach problem-solving. Each is suitable for different types of problems.
The most appropriate problem-solving techniques will depend on your specific problem. You may need to experiment with several strategies before you find a workable solution.
Here are 10 effective problem-solving strategies for you to try:
- Use a solution that worked before
- Brainstorming
- Work backward
- Use the Kipling method
- Draw the problem
- Use trial and error
- Sleep on it
- Get advice from your peers
- Use the Pareto principle
- Add successful solutions to your toolkit
Let’s break each of these down.
1. Use a solution that worked before
It might seem obvious, but if you’ve faced similar problems in the past, look back to what worked then. See if any of the solutions could apply to your current situation and, if so, replicate them.
2. Brainstorming
The more people you enlist to help solve the problem, the more potential solutions you can come up with.
Use different brainstorming techniques to workshop potential solutions with your team. They’ll likely bring something you haven’t thought of to the table.
3. Work backward
Working backward is a way to reverse engineer your problem. Imagine your problem has been solved, and make that the starting point.
Then, retrace your steps back to where you are now. This can help you see which course of action may be most effective.
4. Use the Kipling method
This is a method that poses six questions based on Rudyard Kipling’s poem, “ I Keep Six Honest Serving Men .”
- What is the problem?
- Why is the problem important?
- When did the problem arise, and when does it need to be solved?
- How did the problem happen?
- Where is the problem occurring?
- Who does the problem affect?
Answering these questions can help you identify possible solutions.
5. Draw the problem
Sometimes it can be difficult to visualize all the components and moving parts of a problem and its solution. Drawing a diagram can help.
This technique is particularly helpful for solving process-related problems. For example, a product development team might want to decrease the time they take to fix bugs and create new iterations. Drawing the processes involved can help you see where improvements can be made.

6. Use trial-and-error
A trial-and-error approach can be useful when you have several possible solutions and want to test them to see which one works best.
7. Sleep on it
Finding the best solution to a problem is a process. Remember to take breaks and get enough rest . Sometimes, a walk around the block can bring inspiration, but you should sleep on it if possible.
A good night’s sleep helps us find creative solutions to problems. This is because when you sleep, your brain sorts through the day’s events and stores them as memories. This enables you to process your ideas at a subconscious level.
If possible, give yourself a few days to develop and analyze possible solutions. You may find you have greater clarity after sleeping on it. Your mind will also be fresh, so you’ll be able to make better decisions.
8. Get advice from your peers
Getting input from a group of people can help you find solutions you may not have thought of on your own.
For solo entrepreneurs or freelancers, this might look like hiring a coach or mentor or joining a mastermind group.
For leaders , it might be consulting other members of the leadership team or working with a business coach .
It’s important to recognize you might not have all the skills, experience, or knowledge necessary to find a solution alone.
9. Use the Pareto principle
The Pareto principle — also known as the 80/20 rule — can help you identify possible root causes and potential solutions for your problems.
Although it’s not a mathematical law, it’s a principle found throughout many aspects of business and life. For example, 20% of the sales reps in a company might close 80% of the sales.
You may be able to narrow down the causes of your problem by applying the Pareto principle. This can also help you identify the most appropriate solutions.
10. Add successful solutions to your toolkit
Every situation is different, and the same solutions might not always work. But by keeping a record of successful problem-solving strategies, you can build up a solutions toolkit.
These solutions may be applicable to future problems. Even if not, they may save you some of the time and work needed to come up with a new solution.

Improving problem-solving skills is essential for professional development — both yours and your team’s. Here are some of the key skills of effective problem solvers:
- Critical thinking and analytical skills
- Communication skills , including active listening
- Decision-making
- Planning and prioritization
- Emotional intelligence , including empathy and emotional regulation
- Time management
- Data analysis
- Research skills
- Project management
And they see problems as opportunities. Everyone is born with problem-solving skills. But accessing these abilities depends on how we view problems. Effective problem-solvers see problems as opportunities to learn and improve.
Ready to work on your problem-solving abilities? Get started with these seven tips.
1. Build your problem-solving skills
One of the best ways to improve your problem-solving skills is to learn from experts. Consider enrolling in organizational training , shadowing a mentor , or working with a coach .
2. Practice
Practice using your new problem-solving skills by applying them to smaller problems you might encounter in your daily life.
Alternatively, imagine problematic scenarios that might arise at work and use problem-solving strategies to find hypothetical solutions.
3. Don’t try to find a solution right away
Often, the first solution you think of to solve a problem isn’t the most appropriate or effective.
Instead of thinking on the spot, give yourself time and use one or more of the problem-solving strategies above to activate your creative thinking.

4. Ask for feedback
Receiving feedback is always important for learning and growth. Your perception of your problem-solving skills may be different from that of your colleagues. They can provide insights that help you improve.
5. Learn new approaches and methodologies
There are entire books written about problem-solving methodologies if you want to take a deep dive into the subject.
We recommend starting with “ Fixed — How to Perfect the Fine Art of Problem Solving ” by Amy E. Herman.
6. Experiment
Tried-and-tested problem-solving techniques can be useful. However, they don’t teach you how to innovate and develop your own problem-solving approaches.
Sometimes, an unconventional approach can lead to the development of a brilliant new idea or strategy. So don’t be afraid to suggest your most “out there” ideas.
7. Analyze the success of your competitors
Do you have competitors who have already solved the problem you’re facing? Look at what they did, and work backward to solve your own problem.
For example, Netflix started in the 1990s as a DVD mail-rental company. Its main competitor at the time was Blockbuster.
But when streaming became the norm in the early 2000s, both companies faced a crisis. Netflix innovated, unveiling its streaming service in 2007.
If Blockbuster had followed Netflix’s example, it might have survived. Instead, it declared bankruptcy in 2010.
Use problem-solving strategies to uplevel your business
When facing a problem, it’s worth taking the time to find the right solution.
Otherwise, we risk either running away from our problems or headlong into solutions. When we do this, we might miss out on other, better options.
Use the problem-solving strategies outlined above to find innovative solutions to your business’ most perplexing problems.
If you’re ready to take problem-solving to the next level, request a demo with BetterUp . Our expert coaches specialize in helping teams develop and implement strategies that work.
Boost your productivity
Maximize your time and productivity with strategies from our expert coaches.
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
8 creative solutions to your most challenging problems
5 problem-solving questions to prepare you for your next interview, what are metacognitive skills examples in everyday life, what is lateral thinking 7 techniques to encourage creative ideas, 31 examples of problem solving performance review phrases, learn what process mapping is and how to create one (+ examples), leadership activities that encourage employee engagement, can dreams help you solve problems 6 ways to try, how much do distractions cost 8 effects of lack of focus, similar articles, the pareto principle: how the 80/20 rule can help you do more with less, thinking outside the box: 8 ways to become a creative problem solver, experimentation brings innovation: create an experimental workplace, effective problem statements have these 5 components, contingency planning: 4 steps to prepare for the unexpected, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
How to improve your problem solving skills and build effective problem solving strategies

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
Effective problem solving is all about using the right process and following a plan tailored to the issue at hand. Recognizing your team or organization has an issue isn’t enough to come up with effective problem solving strategies.
To truly understand a problem and develop appropriate solutions, you will want to follow a solid process, follow the necessary problem solving steps, and bring all of your problem solving skills to the table.
We’ll first guide you through the seven step problem solving process you and your team can use to effectively solve complex business challenges. We’ll also look at what problem solving strategies you can employ with your team when looking for a way to approach the process. We’ll then discuss the problem solving skills you need to be more effective at solving problems, complete with an activity from the SessionLab library you can use to develop that skill in your team.
Let’s get to it!
What is a problem solving process?
- What are the problem solving steps I need to follow?
Problem solving strategies
What skills do i need to be an effective problem solver, how can i improve my problem solving skills.
Solving problems is like baking a cake. You can go straight into the kitchen without a recipe or the right ingredients and do your best, but the end result is unlikely to be very tasty!
Using a process to bake a cake allows you to use the best ingredients without waste, collect the right tools, account for allergies, decide whether it is a birthday or wedding cake, and then bake efficiently and on time. The result is a better cake that is fit for purpose, tastes better and has created less mess in the kitchen. Also, it should have chocolate sprinkles. Having a step by step process to solve organizational problems allows you to go through each stage methodically and ensure you are trying to solve the right problems and select the most appropriate, effective solutions.
What are the problem solving steps I need to follow?
All problem solving processes go through a number of steps in order to move from identifying a problem to resolving it.
Depending on your problem solving model and who you ask, there can be anything between four and nine problem solving steps you should follow in order to find the right solution. Whatever framework you and your group use, there are some key items that should be addressed in order to have an effective process.
We’ve looked at problem solving processes from sources such as the American Society for Quality and their four step approach , and Mediate ‘s six step process. By reflecting on those and our own problem solving processes, we’ve come up with a sequence of seven problem solving steps we feel best covers everything you need in order to effectively solve problems.
1. Problem identification
The first stage of any problem solving process is to identify the problem or problems you might want to solve. Effective problem solving strategies always begin by allowing a group scope to articulate what they believe the problem to be and then coming to some consensus over which problem they approach first. Problem solving activities used at this stage often have a focus on creating frank, open discussion so that potential problems can be brought to the surface.
2. Problem analysis
Though this step is not a million miles from problem identification, problem analysis deserves to be considered separately. It can often be an overlooked part of the process and is instrumental when it comes to developing effective solutions.
The process of problem analysis means ensuring that the problem you are seeking to solve is the right problem . As part of this stage, you may look deeper and try to find the root cause of a specific problem at a team or organizational level.
Remember that problem solving strategies should not only be focused on putting out fires in the short term but developing long term solutions that deal with the root cause of organizational challenges.
Whatever your approach, analyzing a problem is crucial in being able to select an appropriate solution and the problem solving skills deployed in this stage are beneficial for the rest of the process and ensuring the solutions you create are fit for purpose.
3. Solution generation
Once your group has nailed down the particulars of the problem you wish to solve, you want to encourage a free flow of ideas connecting to solving that problem. This can take the form of problem solving games that encourage creative thinking or problem solving activities designed to produce working prototypes of possible solutions.
The key to ensuring the success of this stage of the problem solving process is to encourage quick, creative thinking and create an open space where all ideas are considered. The best solutions can come from unlikely places and by using problem solving techniques that celebrate invention, you might come up with solution gold.
4. Solution development
No solution is likely to be perfect right out of the gate. It’s important to discuss and develop the solutions your group has come up with over the course of following the previous problem solving steps in order to arrive at the best possible solution. Problem solving games used in this stage involve lots of critical thinking, measuring potential effort and impact, and looking at possible solutions analytically.
During this stage, you will often ask your team to iterate and improve upon your frontrunning solutions and develop them further. Remember that problem solving strategies always benefit from a multitude of voices and opinions, and not to let ego get involved when it comes to choosing which solutions to develop and take further.
Finding the best solution is the goal of all problem solving workshops and here is the place to ensure that your solution is well thought out, sufficiently robust and fit for purpose.
5. Decision making
Nearly there! Once your group has reached consensus and selected a solution that applies to the problem at hand you have some decisions to make. You will want to work on allocating ownership of the project, figure out who will do what, how the success of the solution will be measured and decide the next course of action.
The decision making stage is a part of the problem solving process that can get missed or taken as for granted. Fail to properly allocate roles and plan out how a solution will actually be implemented and it less likely to be successful in solving the problem.
Have clear accountabilities, actions, timeframes, and follow-ups. Make these decisions and set clear next-steps in the problem solving workshop so that everyone is aligned and you can move forward effectively as a group.
Ensuring that you plan for the roll-out of a solution is one of the most important problem solving steps. Without adequate planning or oversight, it can prove impossible to measure success or iterate further if the problem was not solved.
6. Solution implementation
This is what we were waiting for! All problem solving strategies have the end goal of implementing a solution and solving a problem in mind.
Remember that in order for any solution to be successful, you need to help your group through all of the previous problem solving steps thoughtfully. Only then can you ensure that you are solving the right problem but also that you have developed the correct solution and can then successfully implement and measure the impact of that solution.
Project management and communication skills are key here – your solution may need to adjust when out in the wild or you might discover new challenges along the way.
7. Solution evaluation
So you and your team developed a great solution to a problem and have a gut feeling its been solved. Work done, right? Wrong. All problem solving strategies benefit from evaluation, consideration, and feedback. You might find that the solution does not work for everyone, might create new problems, or is potentially so successful that you will want to roll it out to larger teams or as part of other initiatives.
None of that is possible without taking the time to evaluate the success of the solution you developed in your problem solving model and adjust if necessary.
Remember that the problem solving process is often iterative and it can be common to not solve complex issues on the first try. Even when this is the case, you and your team will have generated learning that will be important for future problem solving workshops or in other parts of the organization.
It’s worth underlining how important record keeping is throughout the problem solving process. If a solution didn’t work, you need to have the data and records to see why that was the case. If you go back to the drawing board, notes from the previous workshop can help save time. Data and insight is invaluable at every stage of the problem solving process and this one is no different.
Problem solving workshops made easy
Problem solving strategies are methods of approaching and facilitating the process of problem-solving with a set of techniques , actions, and processes. Different strategies are more effective if you are trying to solve broad problems such as achieving higher growth versus more focused problems like, how do we improve our customer onboarding process?
Broadly, the problem solving steps outlined above should be included in any problem solving strategy though choosing where to focus your time and what approaches should be taken is where they begin to differ. You might find that some strategies ask for the problem identification to be done prior to the session or that everything happens in the course of a one day workshop.
The key similarity is that all good problem solving strategies are structured and designed. Four hours of open discussion is never going to be as productive as a four-hour workshop designed to lead a group through a problem solving process.
Good problem solving strategies are tailored to the team, organization and problem you will be attempting to solve. Here are some example problem solving strategies you can learn from or use to get started.
Use a workshop to lead a team through a group process
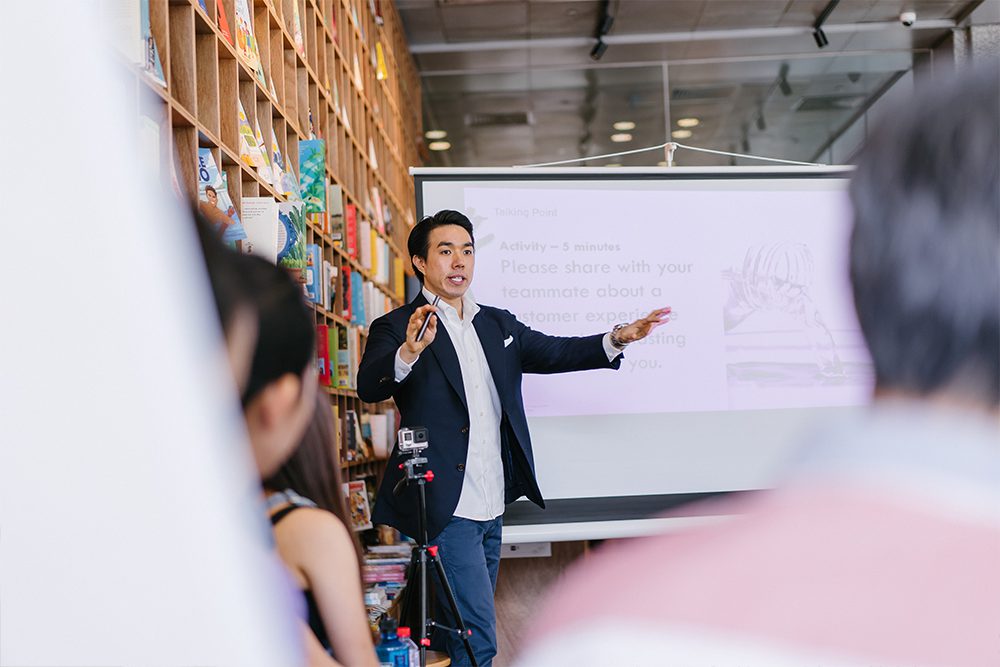
Often, the first step to solving problems or organizational challenges is bringing a group together effectively. Most teams have the tools, knowledge, and expertise necessary to solve their challenges – they just need some guidance in how to use leverage those skills and a structure and format that allows people to focus their energies.
Facilitated workshops are one of the most effective ways of solving problems of any scale. By designing and planning your workshop carefully, you can tailor the approach and scope to best fit the needs of your team and organization.
Problem solving workshop
- Creating a bespoke, tailored process
- Tackling problems of any size
- Building in-house workshop ability and encouraging their use
Workshops are an effective strategy for solving problems. By using tried and test facilitation techniques and methods, you can design and deliver a workshop that is perfectly suited to the unique variables of your organization. You may only have the capacity for a half-day workshop and so need a problem solving process to match.
By using our session planner tool and importing methods from our library of 700+ facilitation techniques, you can create the right problem solving workshop for your team. It might be that you want to encourage creative thinking or look at things from a new angle to unblock your groups approach to problem solving. By tailoring your workshop design to the purpose, you can help ensure great results.
One of the main benefits of a workshop is the structured approach to problem solving. Not only does this mean that the workshop itself will be successful, but many of the methods and techniques will help your team improve their working processes outside of the workshop.
We believe that workshops are one of the best tools you can use to improve the way your team works together. Start with a problem solving workshop and then see what team building, culture or design workshops can do for your organization!
Run a design sprint
Great for:
- aligning large, multi-discipline teams
- quickly designing and testing solutions
- tackling large, complex organizational challenges and breaking them down into smaller tasks
By using design thinking principles and methods, a design sprint is a great way of identifying, prioritizing and prototyping solutions to long term challenges that can help solve major organizational problems with quick action and measurable results.
Some familiarity with design thinking is useful, though not integral, and this strategy can really help a team align if there is some discussion around which problems should be approached first.
The stage-based structure of the design sprint is also very useful for teams new to design thinking. The inspiration phase, where you look to competitors that have solved your problem, and the rapid prototyping and testing phases are great for introducing new concepts that will benefit a team in all their future work.
It can be common for teams to look inward for solutions and so looking to the market for solutions you can iterate on can be very productive. Instilling an agile prototyping and testing mindset can also be great when helping teams move forwards – generating and testing solutions quickly can help save time in the long run and is also pretty exciting!
Break problems down into smaller issues
Organizational challenges and problems are often complicated and large scale in nature. Sometimes, trying to resolve such an issue in one swoop is simply unachievable or overwhelming. Try breaking down such problems into smaller issues that you can work on step by step. You may not be able to solve the problem of churning customers off the bat, but you can work with your team to identify smaller effort but high impact elements and work on those first.
This problem solving strategy can help a team generate momentum, prioritize and get some easy wins. It’s also a great strategy to employ with teams who are just beginning to learn how to approach the problem solving process. If you want some insight into a way to employ this strategy, we recommend looking at our design sprint template below!
Use guiding frameworks or try new methodologies
Some problems are best solved by introducing a major shift in perspective or by using new methodologies that encourage your team to think differently.
Props and tools such as Methodkit , which uses a card-based toolkit for facilitation, or Lego Serious Play can be great ways to engage your team and find an inclusive, democratic problem solving strategy. Remember that play and creativity are great tools for achieving change and whatever the challenge, engaging your participants can be very effective where other strategies may have failed.
LEGO Serious Play
- Improving core problem solving skills
- Thinking outside of the box
- Encouraging creative solutions
LEGO Serious Play is a problem solving methodology designed to get participants thinking differently by using 3D models and kinesthetic learning styles. By physically building LEGO models based on questions and exercises, participants are encouraged to think outside of the box and create their own responses.
Collaborate LEGO Serious Play exercises are also used to encourage communication and build problem solving skills in a group. By using this problem solving process, you can often help different kinds of learners and personality types contribute and unblock organizational problems with creative thinking.
Problem solving strategies like LEGO Serious Play are super effective at helping a team solve more skills-based problems such as communication between teams or a lack of creative thinking. Some problems are not suited to LEGO Serious Play and require a different problem solving strategy.
Card Decks and Method Kits
- New facilitators or non-facilitators
- Approaching difficult subjects with a simple, creative framework
- Engaging those with varied learning styles
Card decks and method kids are great tools for those new to facilitation or for whom facilitation is not the primary role. Card decks such as the emotional culture deck can be used for complete workshops and in many cases, can be used right out of the box. Methodkit has a variety of kits designed for scenarios ranging from personal development through to personas and global challenges so you can find the right deck for your particular needs.
Having an easy to use framework that encourages creativity or a new approach can take some of the friction or planning difficulties out of the workshop process and energize a team in any setting. Simplicity is the key with these methods. By ensuring everyone on your team can get involved and engage with the process as quickly as possible can really contribute to the success of your problem solving strategy.
Source external advice
Looking to peers, experts and external facilitators can be a great way of approaching the problem solving process. Your team may not have the necessary expertise, insights of experience to tackle some issues, or you might simply benefit from a fresh perspective. Some problems may require bringing together an entire team, and coaching managers or team members individually might be the right approach. Remember that not all problems are best resolved in the same manner.
If you’re a solo entrepreneur, peer groups, coaches and mentors can also be invaluable at not only solving specific business problems, but in providing a support network for resolving future challenges. One great approach is to join a Mastermind Group and link up with like-minded individuals and all grow together. Remember that however you approach the sourcing of external advice, do so thoughtfully, respectfully and honestly. Reciprocate where you can and prepare to be surprised by just how kind and helpful your peers can be!
Mastermind Group
- Solo entrepreneurs or small teams with low capacity
- Peer learning and gaining outside expertise
- Getting multiple external points of view quickly
Problem solving in large organizations with lots of skilled team members is one thing, but how about if you work for yourself or in a very small team without the capacity to get the most from a design sprint or LEGO Serious Play session?
A mastermind group – sometimes known as a peer advisory board – is where a group of people come together to support one another in their own goals, challenges, and businesses. Each participant comes to the group with their own purpose and the other members of the group will help them create solutions, brainstorm ideas, and support one another.
Mastermind groups are very effective in creating an energized, supportive atmosphere that can deliver meaningful results. Learning from peers from outside of your organization or industry can really help unlock new ways of thinking and drive growth. Access to the experience and skills of your peers can be invaluable in helping fill the gaps in your own ability, particularly in young companies.
A mastermind group is a great solution for solo entrepreneurs, small teams, or for organizations that feel that external expertise or fresh perspectives will be beneficial for them. It is worth noting that Mastermind groups are often only as good as the participants and what they can bring to the group. Participants need to be committed, engaged and understand how to work in this context.
Coaching and mentoring
- Focused learning and development
- Filling skills gaps
- Working on a range of challenges over time
Receiving advice from a business coach or building a mentor/mentee relationship can be an effective way of resolving certain challenges. The one-to-one format of most coaching and mentor relationships can really help solve the challenges those individuals are having and benefit the organization as a result.
A great mentor can be invaluable when it comes to spotting potential problems before they arise and coming to understand a mentee very well has a host of other business benefits. You might run an internal mentorship program to help develop your team’s problem solving skills and strategies or as part of a large learning and development program. External coaches can also be an important part of your problem solving strategy, filling skills gaps for your management team or helping with specific business issues.
Now we’ve explored the problem solving process and the steps you will want to go through in order to have an effective session, let’s look at the skills you and your team need to be more effective problem solvers.
Problem solving skills are highly sought after, whatever industry or team you work in. Organizations are keen to employ people who are able to approach problems thoughtfully and find strong, realistic solutions. Whether you are a facilitator , a team leader or a developer, being an effective problem solver is a skill you’ll want to develop.
Problem solving skills form a whole suite of techniques and approaches that an individual uses to not only identify problems but to discuss them productively before then developing appropriate solutions.
Here are some of the most important problem solving skills everyone from executives to junior staff members should learn. We’ve also included an activity or exercise from the SessionLab library that can help you and your team develop that skill.
If you’re running a workshop or training session to try and improve problem solving skills in your team, try using these methods to supercharge your process!
Active listening
Active listening is one of the most important skills anyone who works with people can possess. In short, active listening is a technique used to not only better understand what is being said by an individual, but also to be more aware of the underlying message the speaker is trying to convey. When it comes to problem solving, active listening is integral for understanding the position of every participant and to clarify the challenges, ideas and solutions they bring to the table.
Some active listening skills include:
- Paying complete attention to the speaker.
- Removing distractions.
- Avoid interruption.
- Taking the time to fully understand before preparing a rebuttal.
- Responding respectfully and appropriately.
- Demonstrate attentiveness and positivity with an open posture, making eye contact with the speaker, smiling and nodding if appropriate. Show that you are listening and encourage them to continue.
- Be aware of and respectful of feelings. Judge the situation and respond appropriately. You can disagree without being disrespectful.
- Observe body language.
- Paraphrase what was said in your own words, either mentally or verbally.
- Remain neutral.
- Reflect and take a moment before responding.
- Ask deeper questions based on what is said and clarify points where necessary.
Active Listening #hyperisland #skills #active listening #remote-friendly This activity supports participants to reflect on a question and generate their own solutions using simple principles of active listening and peer coaching. It’s an excellent introduction to active listening but can also be used with groups that are already familiar with it. Participants work in groups of three and take turns being: “the subject”, the listener, and the observer.
Analytical skills
All problem solving models require strong analytical skills, particularly during the beginning of the process and when it comes to analyzing how solutions have performed.
Analytical skills are primarily focused on performing an effective analysis by collecting, studying and parsing data related to a problem or opportunity.
It often involves spotting patterns, being able to see things from different perspectives and using observable facts and data to make suggestions or produce insight.
Analytical skills are also important at every stage of the problem solving process and by having these skills, you can ensure that any ideas or solutions you create or backed up analytically and have been sufficiently thought out.
Nine Whys #innovation #issue analysis #liberating structures With breathtaking simplicity, you can rapidly clarify for individuals and a group what is essentially important in their work. You can quickly reveal when a compelling purpose is missing in a gathering and avoid moving forward without clarity. When a group discovers an unambiguous shared purpose, more freedom and more responsibility are unleashed. You have laid the foundation for spreading and scaling innovations with fidelity.
Collaboration
Trying to solve problems on your own is difficult. Being able to collaborate effectively, with a free exchange of ideas, to delegate and be a productive member of a team is hugely important to all problem solving strategies.
Remember that whatever your role, collaboration is integral, and in a problem solving process, you are all working together to find the best solution for everyone.
Marshmallow challenge with debriefing #teamwork #team #leadership #collaboration In eighteen minutes, teams must build the tallest free-standing structure out of 20 sticks of spaghetti, one yard of tape, one yard of string, and one marshmallow. The marshmallow needs to be on top. The Marshmallow Challenge was developed by Tom Wujec, who has done the activity with hundreds of groups around the world. Visit the Marshmallow Challenge website for more information. This version has an extra debriefing question added with sample questions focusing on roles within the team.
Communication
Being an effective communicator means being empathetic, clear and succinct, asking the right questions, and demonstrating active listening skills throughout any discussion or meeting.
In a problem solving setting, you need to communicate well in order to progress through each stage of the process effectively. As a team leader, it may also fall to you to facilitate communication between parties who may not see eye to eye. Effective communication also means helping others to express themselves and be heard in a group.
Bus Trip #feedback #communication #appreciation #closing #thiagi #team This is one of my favourite feedback games. I use Bus Trip at the end of a training session or a meeting, and I use it all the time. The game creates a massive amount of energy with lots of smiles, laughs, and sometimes even a teardrop or two.
Creative problem solving skills can be some of the best tools in your arsenal. Thinking creatively, being able to generate lots of ideas and come up with out of the box solutions is useful at every step of the process.
The kinds of problems you will likely discuss in a problem solving workshop are often difficult to solve, and by approaching things in a fresh, creative manner, you can often create more innovative solutions.
Having practical creative skills is also a boon when it comes to problem solving. If you can help create quality design sketches and prototypes in record time, it can help bring a team to alignment more quickly or provide a base for further iteration.
The paper clip method #sharing #creativity #warm up #idea generation #brainstorming The power of brainstorming. A training for project leaders, creativity training, and to catalyse getting new solutions.
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is one of the fundamental problem solving skills you’ll want to develop when working on developing solutions. Critical thinking is the ability to analyze, rationalize and evaluate while being aware of personal bias, outlying factors and remaining open-minded.
Defining and analyzing problems without deploying critical thinking skills can mean you and your team go down the wrong path. Developing solutions to complex issues requires critical thinking too – ensuring your team considers all possibilities and rationally evaluating them.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Data analysis
Though it shares lots of space with general analytical skills, data analysis skills are something you want to cultivate in their own right in order to be an effective problem solver.
Being good at data analysis doesn’t just mean being able to find insights from data, but also selecting the appropriate data for a given issue, interpreting it effectively and knowing how to model and present that data. Depending on the problem at hand, it might also include a working knowledge of specific data analysis tools and procedures.
Having a solid grasp of data analysis techniques is useful if you’re leading a problem solving workshop but if you’re not an expert, don’t worry. Bring people into the group who has this skill set and help your team be more effective as a result.
Decision making
All problems need a solution and all solutions require that someone make the decision to implement them. Without strong decision making skills, teams can become bogged down in discussion and less effective as a result.
Making decisions is a key part of the problem solving process. It’s important to remember that decision making is not restricted to the leadership team. Every staff member makes decisions every day and developing these skills ensures that your team is able to solve problems at any scale. Remember that making decisions does not mean leaping to the first solution but weighing up the options and coming to an informed, well thought out solution to any given problem that works for the whole team.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
Dependability
Most complex organizational problems require multiple people to be involved in delivering the solution. Ensuring that the team and organization can depend on you to take the necessary actions and communicate where necessary is key to ensuring problems are solved effectively.
Being dependable also means working to deadlines and to brief. It is often a matter of creating trust in a team so that everyone can depend on one another to complete the agreed actions in the agreed time frame so that the team can move forward together. Being undependable can create problems of friction and can limit the effectiveness of your solutions so be sure to bear this in mind throughout a project.
Team Purpose & Culture #team #hyperisland #culture #remote-friendly This is an essential process designed to help teams define their purpose (why they exist) and their culture (how they work together to achieve that purpose). Defining these two things will help any team to be more focused and aligned. With support of tangible examples from other companies, the team members work as individuals and a group to codify the way they work together. The goal is a visual manifestation of both the purpose and culture that can be put up in the team’s work space.
Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligence is an important skill for any successful team member, whether communicating internally or with clients or users. In the problem solving process, emotional intelligence means being attuned to how people are feeling and thinking, communicating effectively and being self-aware of what you bring to a room.
There are often differences of opinion when working through problem solving processes, and it can be easy to let things become impassioned or combative. Developing your emotional intelligence means being empathetic to your colleagues and managing your own emotions throughout the problem and solution process. Be kind, be thoughtful and put your points across care and attention.
Being emotionally intelligent is a skill for life and by deploying it at work, you can not only work efficiently but empathetically. Check out the emotional culture workshop template for more!
Facilitation
As we’ve clarified in our facilitation skills post, facilitation is the art of leading people through processes towards agreed-upon objectives in a manner that encourages participation, ownership, and creativity by all those involved. While facilitation is a set of interrelated skills in itself, the broad definition of facilitation can be invaluable when it comes to problem solving. Leading a team through a problem solving process is made more effective if you improve and utilize facilitation skills – whether you’re a manager, team leader or external stakeholder.
The Six Thinking Hats #creative thinking #meeting facilitation #problem solving #issue resolution #idea generation #conflict resolution The Six Thinking Hats are used by individuals and groups to separate out conflicting styles of thinking. They enable and encourage a group of people to think constructively together in exploring and implementing change, rather than using argument to fight over who is right and who is wrong.
Flexibility
Being flexible is a vital skill when it comes to problem solving. This does not mean immediately bowing to pressure or changing your opinion quickly: instead, being flexible is all about seeing things from new perspectives, receiving new information and factoring it into your thought process.
Flexibility is also important when it comes to rolling out solutions. It might be that other organizational projects have greater priority or require the same resources as your chosen solution. Being flexible means understanding needs and challenges across the team and being open to shifting or arranging your own schedule as necessary. Again, this does not mean immediately making way for other projects. It’s about articulating your own needs, understanding the needs of others and being able to come to a meaningful compromise.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
Working in any group can lead to unconscious elements of groupthink or situations in which you may not wish to be entirely honest. Disagreeing with the opinions of the executive team or wishing to save the feelings of a coworker can be tricky to navigate, but being honest is absolutely vital when to comes to developing effective solutions and ensuring your voice is heard.
Remember that being honest does not mean being brutally candid. You can deliver your honest feedback and opinions thoughtfully and without creating friction by using other skills such as emotional intelligence.
Explore your Values #hyperisland #skills #values #remote-friendly Your Values is an exercise for participants to explore what their most important values are. It’s done in an intuitive and rapid way to encourage participants to follow their intuitive feeling rather than over-thinking and finding the “correct” values. It is a good exercise to use to initiate reflection and dialogue around personal values.
Initiative
The problem solving process is multi-faceted and requires different approaches at certain points of the process. Taking initiative to bring problems to the attention of the team, collect data or lead the solution creating process is always valuable. You might even roadtest your own small scale solutions or brainstorm before a session. Taking initiative is particularly effective if you have good deal of knowledge in that area or have ownership of a particular project and want to get things kickstarted.
That said, be sure to remember to honor the process and work in service of the team. If you are asked to own one part of the problem solving process and you don’t complete that task because your initiative leads you to work on something else, that’s not an effective method of solving business challenges.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
Impartiality
A particularly useful problem solving skill for product owners or managers is the ability to remain impartial throughout much of the process. In practice, this means treating all points of view and ideas brought forward in a meeting equally and ensuring that your own areas of interest or ownership are not favored over others.
There may be a stage in the process where a decision maker has to weigh the cost and ROI of possible solutions against the company roadmap though even then, ensuring that the decision made is based on merit and not personal opinion.
Empathy map #frame insights #create #design #issue analysis An empathy map is a tool to help a design team to empathize with the people they are designing for. You can make an empathy map for a group of people or for a persona. To be used after doing personas when more insights are needed.
Being a good leader means getting a team aligned, energized and focused around a common goal. In the problem solving process, strong leadership helps ensure that the process is efficient, that any conflicts are resolved and that a team is managed in the direction of success.
It’s common for managers or executives to assume this role in a problem solving workshop, though it’s important that the leader maintains impartiality and does not bulldoze the group in a particular direction. Remember that good leadership means working in service of the purpose and team and ensuring the workshop is a safe space for employees of any level to contribute. Take a look at our leadership games and activities post for more exercises and methods to help improve leadership in your organization.
Leadership Pizza #leadership #team #remote-friendly This leadership development activity offers a self-assessment framework for people to first identify what skills, attributes and attitudes they find important for effective leadership, and then assess their own development and initiate goal setting.
In the context of problem solving, mediation is important in keeping a team engaged, happy and free of conflict. When leading or facilitating a problem solving workshop, you are likely to run into differences of opinion. Depending on the nature of the problem, certain issues may be brought up that are emotive in nature.
Being an effective mediator means helping those people on either side of such a divide are heard, listen to one another and encouraged to find common ground and a resolution. Mediating skills are useful for leaders and managers in many situations and the problem solving process is no different.
Conflict Responses #hyperisland #team #issue resolution A workshop for a team to reflect on past conflicts, and use them to generate guidelines for effective conflict handling. The workshop uses the Thomas-Killman model of conflict responses to frame a reflective discussion. Use it to open up a discussion around conflict with a team.
Planning
Solving organizational problems is much more effective when following a process or problem solving model. Planning skills are vital in order to structure, deliver and follow-through on a problem solving workshop and ensure your solutions are intelligently deployed.
Planning skills include the ability to organize tasks and a team, plan and design the process and take into account any potential challenges. Taking the time to plan carefully can save time and frustration later in the process and is valuable for ensuring a team is positioned for success.
3 Action Steps #hyperisland #action #remote-friendly This is a small-scale strategic planning session that helps groups and individuals to take action toward a desired change. It is often used at the end of a workshop or programme. The group discusses and agrees on a vision, then creates some action steps that will lead them towards that vision. The scope of the challenge is also defined, through discussion of the helpful and harmful factors influencing the group.
Prioritization
As organisations grow, the scale and variation of problems they face multiplies. Your team or is likely to face numerous challenges in different areas and so having the skills to analyze and prioritize becomes very important, particularly for those in leadership roles.
A thorough problem solving process is likely to deliver multiple solutions and you may have several different problems you wish to solve simultaneously. Prioritization is the ability to measure the importance, value, and effectiveness of those possible solutions and choose which to enact and in what order. The process of prioritization is integral in ensuring the biggest challenges are addressed with the most impactful solutions.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
Project management
Some problem solving skills are utilized in a workshop or ideation phases, while others come in useful when it comes to decision making. Overseeing an entire problem solving process and ensuring its success requires strong project management skills.
While project management incorporates many of the other skills listed here, it is important to note the distinction of considering all of the factors of a project and managing them successfully. Being able to negotiate with stakeholders, manage tasks, time and people, consider costs and ROI, and tie everything together is massively helpful when going through the problem solving process.
Record keeping
Working out meaningful solutions to organizational challenges is only one part of the process. Thoughtfully documenting and keeping records of each problem solving step for future consultation is important in ensuring efficiency and meaningful change.
For example, some problems may be lower priority than others but can be revisited in the future. If the team has ideated on solutions and found some are not up to the task, record those so you can rule them out and avoiding repeating work. Keeping records of the process also helps you improve and refine your problem solving model next time around!
Personal Kanban #gamestorming #action #agile #project planning Personal Kanban is a tool for organizing your work to be more efficient and productive. It is based on agile methods and principles.
Research skills
Conducting research to support both the identification of problems and the development of appropriate solutions is important for an effective process. Knowing where to go to collect research, how to conduct research efficiently, and identifying pieces of research are relevant are all things a good researcher can do well.
In larger groups, not everyone has to demonstrate this ability in order for a problem solving workshop to be effective. That said, having people with research skills involved in the process, particularly if they have existing area knowledge, can help ensure the solutions that are developed with data that supports their intention. Remember that being able to deliver the results of research efficiently and in a way the team can easily understand is also important. The best data in the world is only as effective as how it is delivered and interpreted.
Customer experience map #ideation #concepts #research #design #issue analysis #remote-friendly Customer experience mapping is a method of documenting and visualizing the experience a customer has as they use the product or service. It also maps out their responses to their experiences. To be used when there is a solution (even in a conceptual stage) that can be analyzed.
Risk management
Managing risk is an often overlooked part of the problem solving process. Solutions are often developed with the intention of reducing exposure to risk or solving issues that create risk but sometimes, great solutions are more experimental in nature and as such, deploying them needs to be carefully considered.
Managing risk means acknowledging that there may be risks associated with more out of the box solutions or trying new things, but that this must be measured against the possible benefits and other organizational factors.
Be informed, get the right data and stakeholders in the room and you can appropriately factor risk into your decision making process.
Decisions, Decisions… #communication #decision making #thiagi #action #issue analysis When it comes to decision-making, why are some of us more prone to take risks while others are risk-averse? One explanation might be the way the decision and options were presented. This exercise, based on Kahneman and Tversky’s classic study , illustrates how the framing effect influences our judgement and our ability to make decisions . The participants are divided into two groups. Both groups are presented with the same problem and two alternative programs for solving them. The two programs both have the same consequences but are presented differently. The debriefing discussion examines how the framing of the program impacted the participant’s decision.
Team-building
No single person is as good at problem solving as a team. Building an effective team and helping them come together around a common purpose is one of the most important problem solving skills, doubly so for leaders. By bringing a team together and helping them work efficiently, you pave the way for team ownership of a problem and the development of effective solutions.
In a problem solving workshop, it can be tempting to jump right into the deep end, though taking the time to break the ice, energize the team and align them with a game or exercise will pay off over the course of the day.
Remember that you will likely go through the problem solving process multiple times over an organization’s lifespan and building a strong team culture will make future problem solving more effective. It’s also great to work with people you know, trust and have fun with. Working on team building in and out of the problem solving process is a hallmark of successful teams that can work together to solve business problems.
9 Dimensions Team Building Activity #ice breaker #teambuilding #team #remote-friendly 9 Dimensions is a powerful activity designed to build relationships and trust among team members. There are 2 variations of this icebreaker. The first version is for teams who want to get to know each other better. The second version is for teams who want to explore how they are working together as a team.
Time management
The problem solving process is designed to lead a team from identifying a problem through to delivering a solution and evaluating its effectiveness. Without effective time management skills or timeboxing of tasks, it can be easy for a team to get bogged down or be inefficient.
By using a problem solving model and carefully designing your workshop, you can allocate time efficiently and trust that the process will deliver the results you need in a good timeframe.
Time management also comes into play when it comes to rolling out solutions, particularly those that are experimental in nature. Having a clear timeframe for implementing and evaluating solutions is vital for ensuring their success and being able to pivot if necessary.
Improving your skills at problem solving is often a career-long pursuit though there are methods you can use to make the learning process more efficient and to supercharge your problem solving skillset.
Remember that the skills you need to be a great problem solver have a large overlap with those skills you need to be effective in any role. Investing time and effort to develop your active listening or critical thinking skills is valuable in any context. Here are 7 ways to improve your problem solving skills.
Share best practices
Remember that your team is an excellent source of skills, wisdom, and techniques and that you should all take advantage of one another where possible. Best practices that one team has for solving problems, conducting research or making decisions should be shared across the organization. If you have in-house staff that have done active listening training or are data analysis pros, have them lead a training session.
Your team is one of your best resources. Create space and internal processes for the sharing of skills so that you can all grow together.
Ask for help and attend training
Once you’ve figured out you have a skills gap, the next step is to take action to fill that skills gap. That might be by asking your superior for training or coaching, or liaising with team members with that skill set. You might even attend specialized training for certain skills – active listening or critical thinking, for example, are business-critical skills that are regularly offered as part of a training scheme.
Whatever method you choose, remember that taking action of some description is necessary for growth. Whether that means practicing, getting help, attending training or doing some background reading, taking active steps to improve your skills is the way to go.
Learn a process
Problem solving can be complicated, particularly when attempting to solve large problems for the first time. Using a problem solving process helps give structure to your problem solving efforts and focus on creating outcomes, rather than worrying about the format.
Tools such as the seven-step problem solving process above are effective because not only do they feature steps that will help a team solve problems, they also develop skills along the way. Each step asks for people to engage with the process using different skills and in doing so, helps the team learn and grow together. Group processes of varying complexity and purpose can also be found in the SessionLab library of facilitation techniques . Using a tried and tested process and really help ease the learning curve for both those leading such a process, as well as those undergoing the purpose.
Effective teams make decisions about where they should and shouldn’t expend additional effort. By using a problem solving process, you can focus on the things that matter, rather than stumbling towards a solution haphazardly.
Create a feedback loop
Some skills gaps are more obvious than others. It’s possible that your perception of your active listening skills differs from those of your colleagues.
It’s valuable to create a system where team members can provide feedback in an ordered and friendly manner so they can all learn from one another. Only by identifying areas of improvement can you then work to improve them.
Remember that feedback systems require oversight and consideration so that they don’t turn into a place to complain about colleagues. Design the system intelligently so that you encourage the creation of learning opportunities, rather than encouraging people to list their pet peeves.
While practice might not make perfect, it does make the problem solving process easier. If you are having trouble with critical thinking, don’t shy away from doing it. Get involved where you can and stretch those muscles as regularly as possible.
Problem solving skills come more naturally to some than to others and that’s okay. Take opportunities to get involved and see where you can practice your skills in situations outside of a workshop context. Try collaborating in other circumstances at work or conduct data analysis on your own projects. You can often develop those skills you need for problem solving simply by doing them. Get involved!
Use expert exercises and methods
Learn from the best. Our library of 700+ facilitation techniques is full of activities and methods that help develop the skills you need to be an effective problem solver. Check out our templates to see how to approach problem solving and other organizational challenges in a structured and intelligent manner.
There is no single approach to improving problem solving skills, but by using the techniques employed by others you can learn from their example and develop processes that have seen proven results.
Try new ways of thinking and change your mindset
Using tried and tested exercises that you know well can help deliver results, but you do run the risk of missing out on the learning opportunities offered by new approaches. As with the problem solving process, changing your mindset can remove blockages and be used to develop your problem solving skills.
Most teams have members with mixed skill sets and specialties. Mix people from different teams and share skills and different points of view. Teach your customer support team how to use design thinking methods or help your developers with conflict resolution techniques. Try switching perspectives with facilitation techniques like Flip It! or by using new problem solving methodologies or models. Give design thinking, liberating structures or lego serious play a try if you want to try a new approach. You will find that framing problems in new ways and using existing skills in new contexts can be hugely useful for personal development and improving your skillset. It’s also a lot of fun to try new things. Give it a go!
Encountering business challenges and needing to find appropriate solutions is not unique to your organization. Lots of very smart people have developed methods, theories and approaches to help develop problem solving skills and create effective solutions. Learn from them!
Books like The Art of Thinking Clearly , Think Smarter, or Thinking Fast, Thinking Slow are great places to start, though it’s also worth looking at blogs related to organizations facing similar problems to yours, or browsing for success stories. Seeing how Dropbox massively increased growth and working backward can help you see the skills or approach you might be lacking to solve that same problem. Learning from others by reading their stories or approaches can be time-consuming but ultimately rewarding.
A tired, distracted mind is not in the best position to learn new skills. It can be tempted to burn the candle at both ends and develop problem solving skills outside of work. Absolutely use your time effectively and take opportunities for self-improvement, though remember that rest is hugely important and that without letting your brain rest, you cannot be at your most effective.
Creating distance between yourself and the problem you might be facing can also be useful. By letting an idea sit, you can find that a better one presents itself or you can develop it further. Take regular breaks when working and create a space for downtime. Remember that working smarter is preferable to working harder and that self-care is important for any effective learning or improvement process.
Want to design better group processes?
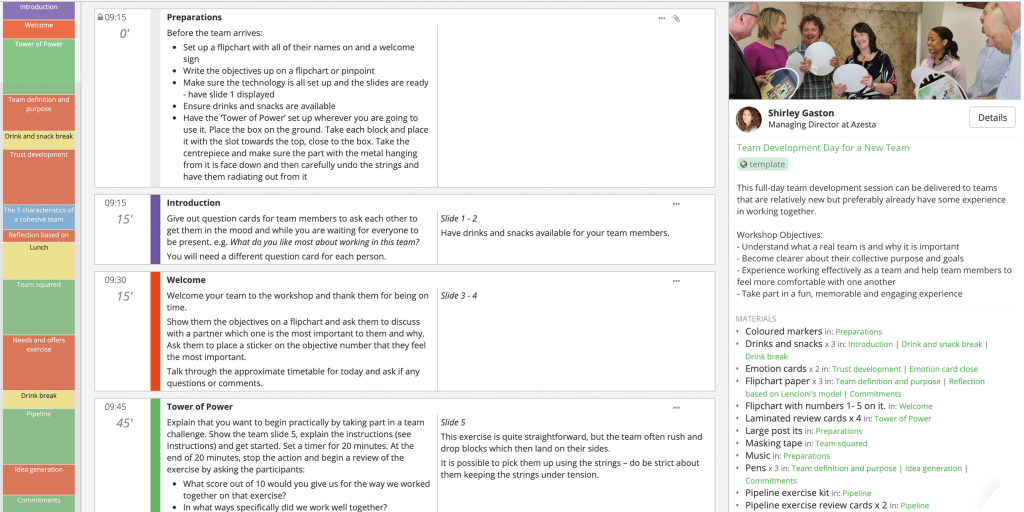
Over to you
Now we’ve explored some of the key problem solving skills and the problem solving steps necessary for an effective process, you’re ready to begin developing more effective solutions and leading problem solving workshops.
Need more inspiration? Check out our post on problem solving activities you can use when guiding a group towards a great solution in your next workshop or meeting. Have questions? Did you have a great problem solving technique you use with your team? Get in touch in the comments below. We’d love to chat!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 7 min read
What Is Problem Solving?
By the Mind Tools Content Team

We all spend a lot of our time solving problems, both at work and in our personal lives.
Some problems are small, and we can quickly sort them out ourselves. But others are complex challenges that take collaboration, creativity, and a considerable amount of effort to solve.
At work, the types of problems we face depend largely on the organizations we're in and the jobs we do. A manager in a cleaning company, for example, might spend their day untangling staffing issues, resolving client complaints, and sorting out problems with equipment and supplies. An aircraft designer, on the other hand, might be grappling with a problem about aerodynamics, or trying to work out why a new safety feature isn't working. Meanwhile, a politician might be exploring solutions to racial injustice or climate change.
But whatever issues we face, there are some common ways to tackle them effectively. And we can all boost our confidence and ability to succeed by building a strong set of problem-solving skills.
Mind Tools offers a large collection of resources to help you do just that!
How Well Do You Solve Problems?
Start by taking an honest look at your existing skills. What's your current approach to solving problems, and how well is it working? Our quiz, How Good Is Your Problem Solving? lets you analyze your abilities, and signposts ways to address any areas of weakness.
Define Every Problem
The first step in solving a problem is understanding what that problem actually is. You need to be sure that you're dealing with the real problem – not its symptoms. For example, if performance in your department is substandard, you might think that the problem lies with the individuals submitting work. However, if you look a bit deeper, the real issue might be a general lack of training, or an unreasonable workload across the team.
Tools like 5 Whys , Appreciation and Root Cause Analysis get you asking the right questions, and help you to work through the layers of a problem to uncover what's really going on.
However, defining a problem doesn't mean deciding how to solve it straightaway. It's important to look at the issue from a variety of perspectives. If you commit yourself too early, you can end up with a short-sighted solution. The CATWOE checklist provides a powerful reminder to look at many elements that may contribute to the problem, keeping you open to a variety of possible solutions.
Understanding Complexity
As you define your problem, you'll often discover just how complicated it is. There are likely several interrelated issues involved. That's why it's important to have ways to visualize, simplify and make sense of this tangled mess!
Affinity Diagrams are great for organizing many different pieces of information into common themes, and for understanding the relationships between them.
Another popular tool is the Cause-and-Effect Diagram . To generate viable solutions, you need a solid understanding of what's causing the problem.
When your problem occurs within a business process, creating a Flow Chart , Swim Lane Diagram or a Systems Diagram will help you to see how various activities and inputs fit together. This may well highlight a missing element or bottleneck that's causing your problem.
Quite often, what seems to be a single problem turns out to be a whole series of problems. The Drill Down technique prompts you to split your problem into smaller, more manageable parts.
General Problem-Solving Tools
When you understand the problem in front of you, you’re ready to start solving it. With your definition to guide you, you can generate several possible solutions, choose the best one, then put it into action. That's the four-step approach at the heart of good problem solving.
There are various problem-solving styles to use. For example:
- Constructive Controversy is a way of widening perspectives and energizing discussions.
- Inductive Reasoning makes the most of people’s experiences and know-how, and can speed up solution finding.
- Means-End Analysis can bring extra clarity to your thinking, and kick-start the process of implementing solutions.
Specific Problem-Solving Systems
Some particularly complicated or important problems call for a more comprehensive process. Again, Mind Tools has a range of approaches to try, including:
- Simplex , which involves an eight-stage process: problem finding, fact finding, defining the problem, idea finding, selecting and evaluating, planning, selling the idea, and acting. These steps build upon the basic, four-step process described above, and they create a cycle of problem finding and solving that will continually improve your organization.
- Appreciative Inquiry , which is a uniquely positive way of solving problems by examining what's working well in the areas surrounding them.
- Soft Systems Methodology , which takes you through four stages to uncover more details about what's creating your problem, and then define actions that will improve the situation.
Further Problem-Solving Strategies
Good problem solving requires a number of other skills – all of which are covered by Mind Tools.
For example, we have a large section of resources to improve your Creativity , so that you come up with a range of possible solutions.
By strengthening your Decision Making , you'll be better at evaluating the options, selecting the best ones, then choosing how to implement them.
And our Project Management collection has valuable advice for strengthening the whole problem-solving process. The resources there will help you to make effective changes – and then keep them working long term.
Problems are an inescapable part of life, both in and out of work. So we can all benefit from having strong problem-solving skills.
It's important to understand your current approach to problem solving, and to know where and how to improve.
Define every problem you encounter – and understand its complexity, rather than trying to solve it too soon.
There's a range of general problem-solving approaches, helping you to generate possible answers, choose the best ones, and then implement your solution.
Some complicated or serious problems require more specific problem-solving systems, especially when they relate to business processes.
By boosting your creativity, decision-making and project-management skills, you’ll become even better at solving all the problems you face.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Book Insights
The Back of the Napkin: Solving Problems and Selling Ideas With Pictures
Infographic
Creative Problem Solving Infographic
Infographic Transcript
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Team Management
Learn the key aspects of managing a team, from building and developing your team, to working with different types of teams, and troubleshooting common problems.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Team Briefings

Onboarding With STEPS
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
New pain points podcast - perfectionism.
Why Am I Such a Perfectionist?
Pain Points Podcast - Building Trust
Developing and Strengthening Trust at Work
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Our team values.
This Team Exercise Help Formulate Principles to Develop a Supportive Team Culture
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- Online Degree Explore Bachelor’s & Master’s degrees
- MasterTrack™ Earn credit towards a Master’s degree
- University Certificates Advance your career with graduate-level learning
- Top Courses
- Join for Free
7 Problem-Solving Skills That Can Help You Be a More Successful Manager
Discover what problem-solving is, and why it's important for managers. Understand the steps of the process and learn about seven problem-solving skills.
![problem solving and solutions [Featured Image]: A manager wearing a black suit is talking to a team member, handling an issue utilizing the process of problem-solving](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/6uiffmHlG1nCAhji06VPaV/06ef7be91702ee158c66d2caeae98607/iStock-1176251115__2_.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
1Managers oversee the day-to-day operations of a particular department, and sometimes a whole company, using their problem-solving skills regularly. Managers with good problem-solving skills can help ensure companies run smoothly and prosper.
If you're a current manager or are striving to become one, read this guide to discover what problem-solving skills are and why it's important for managers to have them. Learn the steps of the problem-solving process, and explore seven skills that can help make problem-solving easier and more effective.
What is problem-solving?
Problem-solving is both an ability and a process. As an ability, problem-solving can aid in resolving issues faced in different environments like home, school, abroad, and social situations, among others. As a process, problem-solving involves a series of steps for finding solutions to questions or concerns that arise throughout life.
The importance of problem-solving for managers
Managers deal with problems regularly, whether supervising a staff of two or 100. When people solve problems quickly and effectively, workplaces can benefit in a number of ways. These include:
Greater creativity
Higher productivity
Increased job fulfillment
Satisfied clients or customers
Better cooperation and cohesion
Improved environments for employees and customers
7 skills that make problem-solving easier
Companies depend on managers who can solve problems adeptly. Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork.
1. Analysis
As a manager , you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first. Then, you’ll use analytical skills to distinguish between ineffective and effective solutions.
2. Communication
Effective communication plays a significant role in problem-solving, particularly when others are involved. Some skills that can help enhance communication at work include active listening, speaking with an even tone and volume, and supporting verbal information with written communication.
3. Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligence is the ability to recognize and manage emotions in any situation. People with emotional intelligence usually solve problems calmly and systematically, which often yields better results.
4. Resilience
Emotional intelligence and resilience are closely related traits. Resiliency is the ability to cope with and bounce back quickly from difficult situations. Those who possess resilience are often capable of accurately interpreting people and situations, which can be incredibly advantageous when difficulties arise.
5. Creativity
When brainstorming solutions to problems, creativity can help you to think outside the box. Problem-solving strategies can be enhanced with the application of creative techniques. You can use creativity to:
Approach problems from different angles
Improve your problem-solving process
Spark creativity in your employees and peers
6. Adaptability
Adaptability is the capacity to adjust to change. When a particular solution to an issue doesn't work, an adaptable person can revisit the concern to think up another one without getting frustrated.
7. Teamwork
Finding a solution to a problem regularly involves working in a team. Good teamwork requires being comfortable working with others and collaborating with them, which can result in better problem-solving overall.
Steps of the problem-solving process
Effective problem-solving involves five essential steps. One way to remember them is through the IDEAL model created in 1984 by psychology professors John D. Bransford and Barry S. Stein [ 1 ]. The steps to solving problems in this model include: identifying that there is a problem, defining the goals you hope to achieve, exploring potential solutions, choosing a solution and acting on it, and looking at (or evaluating) the outcome.
1. Identify that there is a problem and root out its cause.
To solve a problem, you must first admit that one exists to then find its root cause. Finding the cause of the problem may involve asking questions like:
Can the problem be solved?
How big of a problem is it?
Why do I think the problem is occurring?
What are some things I know about the situation?
What are some things I don't know about the situation?
Are there any people who contributed to the problem?
Are there materials or processes that contributed to the problem?
Are there any patterns I can identify?
2. Define the goals you hope to achieve.
Every problem is different. The goals you hope to achieve when problem-solving depend on the scope of the problem. Some examples of goals you might set include:
Gather as much factual information as possible.
Brainstorm many different strategies to come up with the best one.
Be flexible when considering other viewpoints.
Articulate clearly and encourage questions, so everyone involved is on the same page.
Be open to other strategies if the chosen strategy doesn't work.
Stay positive throughout the process.
3. Explore potential solutions.
Once you've defined the goals you hope to achieve when problem-solving , it's time to start the process. This involves steps that often include fact-finding, brainstorming, prioritizing solutions, and assessing the cost of top solutions in terms of time, labor, and money.
4. Choose a solution and act on it.
Evaluate the pros and cons of each potential solution, and choose the one most likely to solve the problem within your given budget, abilities, and resources. Once you choose a solution, it's important to make a commitment and see it through. Draw up a plan of action for implementation, and share it with all involved parties clearly and effectively, both verbally and in writing. Make sure everyone understands their role for a successful conclusion.
5. Look at (or evaluate) the outcome.
Evaluation offers insights into your current situation and future problem-solving. When evaluating the outcome, ask yourself questions like:
Did the solution work?
Will this solution work for other problems?
Were there any changes you would have made?
Would another solution have worked better?
As a current or future manager looking to build your problem-solving skills, it is often helpful to take a professional course. Consider Improving Communication Skills offered by the University of Pennsylvania on Coursera. You'll learn how to boost your ability to persuade, ask questions, negotiate, apologize, and more.
You might also consider taking Emotional Intelligence: Cultivating Immensely Human Interactions , offered by the University of Michigan on Coursera. You'll explore the interpersonal and intrapersonal skills common to people with emotional intelligence, and you'll learn how emotional intelligence is connected to team success and leadership.
Build job-ready skills with a Coursera Plus subscription
- Get access to 7,000+ learning programs from world-class universities and companies, including Google, Yale, Salesforce, and more
- Try different courses and find your best fit at no additional cost
- Earn certificates for learning programs you complete
- A subscription price of $59/month, cancel anytime
Article sources
Tennessee Tech. “ The Ideal Problem Solver (2nd ed.) , https://www.tntech.edu/cat/pdf/useful_links/idealproblemsolver.pdf.” Accessed December 6, 2022.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
- The Art of Effective Problem Solving: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Learn Lean Sigma
- Problem Solving
Whether we realise it or not, problem solving skills are an important part of our daily lives. From resolving a minor annoyance at home to tackling complex business challenges at work, our ability to solve problems has a significant impact on our success and happiness. However, not everyone is naturally gifted at problem-solving, and even those who are can always improve their skills. In this blog post, we will go over the art of effective problem-solving step by step.
You will learn how to define a problem, gather information, assess alternatives, and implement a solution, all while honing your critical thinking and creative problem-solving skills. Whether you’re a seasoned problem solver or just getting started, this guide will arm you with the knowledge and tools you need to face any challenge with confidence. So let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Problem solving methodologies.
Individuals and organisations can use a variety of problem-solving methodologies to address complex challenges. 8D and A3 problem solving techniques are two popular methodologies in the Lean Six Sigma framework.
Methodology of 8D (Eight Discipline) Problem Solving:
The 8D problem solving methodology is a systematic, team-based approach to problem solving. It is a method that guides a team through eight distinct steps to solve a problem in a systematic and comprehensive manner.
The 8D process consists of the following steps:
- Form a team: Assemble a group of people who have the necessary expertise to work on the problem.
- Define the issue: Clearly identify and define the problem, including the root cause and the customer impact.
- Create a temporary containment plan: Put in place a plan to lessen the impact of the problem until a permanent solution can be found.
- Identify the root cause: To identify the underlying causes of the problem, use root cause analysis techniques such as Fishbone diagrams and Pareto charts.
- Create and test long-term corrective actions: Create and test a long-term solution to eliminate the root cause of the problem.
- Implement and validate the permanent solution: Implement and validate the permanent solution’s effectiveness.
- Prevent recurrence: Put in place measures to keep the problem from recurring.
- Recognize and reward the team: Recognize and reward the team for its efforts.
Download the 8D Problem Solving Template
A3 Problem Solving Method:
The A3 problem solving technique is a visual, team-based problem-solving approach that is frequently used in Lean Six Sigma projects. The A3 report is a one-page document that clearly and concisely outlines the problem, root cause analysis, and proposed solution.
The A3 problem-solving procedure consists of the following steps:
- Determine the issue: Define the issue clearly, including its impact on the customer.
- Perform root cause analysis: Identify the underlying causes of the problem using root cause analysis techniques.
- Create and implement a solution: Create and implement a solution that addresses the problem’s root cause.
- Monitor and improve the solution: Keep an eye on the solution’s effectiveness and make any necessary changes.
Subsequently, in the Lean Six Sigma framework, the 8D and A3 problem solving methodologies are two popular approaches to problem solving. Both methodologies provide a structured, team-based problem-solving approach that guides individuals through a comprehensive and systematic process of identifying, analysing, and resolving problems in an effective and efficient manner.
Step 1 – Define the Problem
The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause. To avoid this pitfall, it is critical to thoroughly understand the problem.
To begin, ask yourself some clarifying questions:
- What exactly is the issue?
- What are the problem’s symptoms or consequences?
- Who or what is impacted by the issue?
- When and where does the issue arise?
Answering these questions will assist you in determining the scope of the problem. However, simply describing the problem is not always sufficient; you must also identify the root cause. The root cause is the underlying cause of the problem and is usually the key to resolving it permanently.
Try asking “why” questions to find the root cause:
- What causes the problem?
- Why does it continue?
- Why does it have the effects that it does?
By repeatedly asking “ why ,” you’ll eventually get to the bottom of the problem. This is an important step in the problem-solving process because it ensures that you’re dealing with the root cause rather than just the symptoms.
Once you have a firm grasp on the issue, it is time to divide it into smaller, more manageable chunks. This makes tackling the problem easier and reduces the risk of becoming overwhelmed. For example, if you’re attempting to solve a complex business problem, you might divide it into smaller components like market research, product development, and sales strategies.
To summarise step 1, defining the problem is an important first step in effective problem-solving. You will be able to identify the root cause and break it down into manageable parts if you take the time to thoroughly understand the problem. This will prepare you for the next step in the problem-solving process, which is gathering information and brainstorming ideas.
Step 2 – Gather Information and Brainstorm Ideas
Gathering information and brainstorming ideas is the next step in effective problem solving. This entails researching the problem and relevant information, collaborating with others, and coming up with a variety of potential solutions. This increases your chances of finding the best solution to the problem.
Begin by researching the problem and relevant information. This could include reading articles, conducting surveys, or consulting with experts. The goal is to collect as much information as possible in order to better understand the problem and possible solutions.
Next, work with others to gather a variety of perspectives. Brainstorming with others can be an excellent way to come up with new and creative ideas. Encourage everyone to share their thoughts and ideas when working in a group, and make an effort to actively listen to what others have to say. Be open to new and unconventional ideas and resist the urge to dismiss them too quickly.
Finally, use brainstorming to generate a wide range of potential solutions. This is the place where you can let your imagination run wild. At this stage, don’t worry about the feasibility or practicality of the solutions; instead, focus on generating as many ideas as possible. Write down everything that comes to mind, no matter how ridiculous or unusual it may appear. This can be done individually or in groups.
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the next step in the problem-solving process, which we’ll go over in greater detail in the following section.
Step 3 – Evaluate Options and Choose the Best Solution
Once you’ve compiled a list of potential solutions, it’s time to assess them and select the best one. This is the third step in effective problem solving, and it entails weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, considering their feasibility and practicability, and selecting the solution that is most likely to solve the problem effectively.
To begin, weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each solution. This will assist you in determining the potential outcomes of each solution and deciding which is the best option. For example, a quick and easy solution may not be the most effective in the long run, whereas a more complex and time-consuming solution may be more effective in solving the problem in the long run.
Consider each solution’s feasibility and practicability. Consider the following:
- Can the solution be implemented within the available resources, time, and budget?
- What are the possible barriers to implementing the solution?
- Is the solution feasible in today’s political, economic, and social environment?
You’ll be able to tell which solutions are likely to succeed and which aren’t by assessing their feasibility and practicability.
Finally, choose the solution that is most likely to effectively solve the problem. This solution should be based on the criteria you’ve established, such as the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and your overall goals.
It is critical to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all solution to problems. What is effective for one person or situation may not be effective for another. This is why it is critical to consider a wide range of solutions and evaluate each one based on its ability to effectively solve the problem.
Step 4 – Implement and Monitor the Solution
When you’ve decided on the best solution, it’s time to put it into action. The fourth and final step in effective problem solving is to put the solution into action, monitor its progress, and make any necessary adjustments.
To begin, implement the solution. This may entail delegating tasks, developing a strategy, and allocating resources. Ascertain that everyone involved understands their role and responsibilities in the solution’s implementation.
Next, keep an eye on the solution’s progress. This may entail scheduling regular check-ins, tracking metrics, and soliciting feedback from others. You will be able to identify any potential roadblocks and make any necessary adjustments in a timely manner if you monitor the progress of the solution.
Finally, make any necessary modifications to the solution. This could entail changing the solution, altering the plan of action, or delegating different tasks. Be willing to make changes if they will improve the solution or help it solve the problem more effectively.
It’s important to remember that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to start from scratch. This is especially true if the initial solution does not effectively solve the problem. In these situations, it’s critical to be adaptable and flexible and to keep trying new solutions until you find the one that works best.
To summarise, effective problem solving is a critical skill that can assist individuals and organisations in overcoming challenges and achieving their objectives. Effective problem solving consists of four key steps: defining the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating alternatives and selecting the best solution, and implementing the solution.
You can increase your chances of success in problem solving by following these steps and considering factors such as the pros and cons of each solution, their feasibility and practicability, and making any necessary adjustments. Furthermore, keep in mind that problem solving is an iterative process, and there may be times when you need to go back to the beginning and restart. Maintain your adaptability and try new solutions until you find the one that works best for you.
- Novick, L.R. and Bassok, M., 2005. Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press.
Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.
Free Lean Six Sigma Templates
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.
5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
The Evolution of 8D Problem-Solving: From Basics to Excellence
In a world where efficiency and effectiveness are more than just buzzwords, the need for…
8D: Tools and Techniques
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way…
How to Select the Right Lean Six Sigma Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Going on a Lean Six Sigma journey is an invigorating experience filled with opportunities for…
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Solve Problems
- Laura Amico

To bring the best ideas forward, teams must build psychological safety.
Teams today aren’t just asked to execute tasks: They’re called upon to solve problems. You’d think that many brains working together would mean better solutions, but the reality is that too often problem-solving teams fall victim to inefficiency, conflict, and cautious conclusions. The two charts below will help your team think about how to collaborate better and come up with the best solutions for the thorniest challenges.
- Laura Amico is a former senior editor at Harvard Business Review.
Partner Center

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.

Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process
In this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , Simon London speaks with Charles Conn, CEO of venture-capital firm Oxford Sciences Innovation, and McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin about the complexities of different problem-solving strategies.
Podcast transcript
Simon London: Hello, and welcome to this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , with me, Simon London. What’s the number-one skill you need to succeed professionally? Salesmanship, perhaps? Or a facility with statistics? Or maybe the ability to communicate crisply and clearly? Many would argue that at the very top of the list comes problem solving: that is, the ability to think through and come up with an optimal course of action to address any complex challenge—in business, in public policy, or indeed in life.
Looked at this way, it’s no surprise that McKinsey takes problem solving very seriously, testing for it during the recruiting process and then honing it, in McKinsey consultants, through immersion in a structured seven-step method. To discuss the art of problem solving, I sat down in California with McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin and also with Charles Conn. Charles is a former McKinsey partner, entrepreneur, executive, and coauthor of the book Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything [John Wiley & Sons, 2018].
Charles and Hugo, welcome to the podcast. Thank you for being here.
Hugo Sarrazin: Our pleasure.
Charles Conn: It’s terrific to be here.
Simon London: Problem solving is a really interesting piece of terminology. It could mean so many different things. I have a son who’s a teenage climber. They talk about solving problems. Climbing is problem solving. Charles, when you talk about problem solving, what are you talking about?
Charles Conn: For me, problem solving is the answer to the question “What should I do?” It’s interesting when there’s uncertainty and complexity, and when it’s meaningful because there are consequences. Your son’s climbing is a perfect example. There are consequences, and it’s complicated, and there’s uncertainty—can he make that grab? I think we can apply that same frame almost at any level. You can think about questions like “What town would I like to live in?” or “Should I put solar panels on my roof?”
You might think that’s a funny thing to apply problem solving to, but in my mind it’s not fundamentally different from business problem solving, which answers the question “What should my strategy be?” Or problem solving at the policy level: “How do we combat climate change?” “Should I support the local school bond?” I think these are all part and parcel of the same type of question, “What should I do?”
I’m a big fan of structured problem solving. By following steps, we can more clearly understand what problem it is we’re solving, what are the components of the problem that we’re solving, which components are the most important ones for us to pay attention to, which analytic techniques we should apply to those, and how we can synthesize what we’ve learned back into a compelling story. That’s all it is, at its heart.
I think sometimes when people think about seven steps, they assume that there’s a rigidity to this. That’s not it at all. It’s actually to give you the scope for creativity, which often doesn’t exist when your problem solving is muddled.
Simon London: You were just talking about the seven-step process. That’s what’s written down in the book, but it’s a very McKinsey process as well. Without getting too deep into the weeds, let’s go through the steps, one by one. You were just talking about problem definition as being a particularly important thing to get right first. That’s the first step. Hugo, tell us about that.
Hugo Sarrazin: It is surprising how often people jump past this step and make a bunch of assumptions. The most powerful thing is to step back and ask the basic questions—“What are we trying to solve? What are the constraints that exist? What are the dependencies?” Let’s make those explicit and really push the thinking and defining. At McKinsey, we spend an enormous amount of time in writing that little statement, and the statement, if you’re a logic purist, is great. You debate. “Is it an ‘or’? Is it an ‘and’? What’s the action verb?” Because all these specific words help you get to the heart of what matters.
Want to subscribe to The McKinsey Podcast ?
Simon London: So this is a concise problem statement.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah. It’s not like “Can we grow in Japan?” That’s interesting, but it is “What, specifically, are we trying to uncover in the growth of a product in Japan? Or a segment in Japan? Or a channel in Japan?” When you spend an enormous amount of time, in the first meeting of the different stakeholders, debating this and having different people put forward what they think the problem definition is, you realize that people have completely different views of why they’re here. That, to me, is the most important step.
Charles Conn: I would agree with that. For me, the problem context is critical. When we understand “What are the forces acting upon your decision maker? How quickly is the answer needed? With what precision is the answer needed? Are there areas that are off limits or areas where we would particularly like to find our solution? Is the decision maker open to exploring other areas?” then you not only become more efficient, and move toward what we call the critical path in problem solving, but you also make it so much more likely that you’re not going to waste your time or your decision maker’s time.
How often do especially bright young people run off with half of the idea about what the problem is and start collecting data and start building models—only to discover that they’ve really gone off half-cocked.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah.
Charles Conn: And in the wrong direction.
Simon London: OK. So step one—and there is a real art and a structure to it—is define the problem. Step two, Charles?
Charles Conn: My favorite step is step two, which is to use logic trees to disaggregate the problem. Every problem we’re solving has some complexity and some uncertainty in it. The only way that we can really get our team working on the problem is to take the problem apart into logical pieces.
What we find, of course, is that the way to disaggregate the problem often gives you an insight into the answer to the problem quite quickly. I love to do two or three different cuts at it, each one giving a bit of a different insight into what might be going wrong. By doing sensible disaggregations, using logic trees, we can figure out which parts of the problem we should be looking at, and we can assign those different parts to team members.
Simon London: What’s a good example of a logic tree on a sort of ratable problem?
Charles Conn: Maybe the easiest one is the classic profit tree. Almost in every business that I would take a look at, I would start with a profit or return-on-assets tree. In its simplest form, you have the components of revenue, which are price and quantity, and the components of cost, which are cost and quantity. Each of those can be broken out. Cost can be broken into variable cost and fixed cost. The components of price can be broken into what your pricing scheme is. That simple tree often provides insight into what’s going on in a business or what the difference is between that business and the competitors.
If we add the leg, which is “What’s the asset base or investment element?”—so profit divided by assets—then we can ask the question “Is the business using its investments sensibly?” whether that’s in stores or in manufacturing or in transportation assets. I hope we can see just how simple this is, even though we’re describing it in words.
When I went to work with Gordon Moore at the Moore Foundation, the problem that he asked us to look at was “How can we save Pacific salmon?” Now, that sounds like an impossible question, but it was amenable to precisely the same type of disaggregation and allowed us to organize what became a 15-year effort to improve the likelihood of good outcomes for Pacific salmon.
Simon London: Now, is there a danger that your logic tree can be impossibly large? This, I think, brings us onto the third step in the process, which is that you have to prioritize.
Charles Conn: Absolutely. The third step, which we also emphasize, along with good problem definition, is rigorous prioritization—we ask the questions “How important is this lever or this branch of the tree in the overall outcome that we seek to achieve? How much can I move that lever?” Obviously, we try and focus our efforts on ones that have a big impact on the problem and the ones that we have the ability to change. With salmon, ocean conditions turned out to be a big lever, but not one that we could adjust. We focused our attention on fish habitats and fish-harvesting practices, which were big levers that we could affect.
People spend a lot of time arguing about branches that are either not important or that none of us can change. We see it in the public square. When we deal with questions at the policy level—“Should you support the death penalty?” “How do we affect climate change?” “How can we uncover the causes and address homelessness?”—it’s even more important that we’re focusing on levers that are big and movable.
Would you like to learn more about our Strategy & Corporate Finance Practice ?
Simon London: Let’s move swiftly on to step four. You’ve defined your problem, you disaggregate it, you prioritize where you want to analyze—what you want to really look at hard. Then you got to the work plan. Now, what does that mean in practice?
Hugo Sarrazin: Depending on what you’ve prioritized, there are many things you could do. It could be breaking the work among the team members so that people have a clear piece of the work to do. It could be defining the specific analyses that need to get done and executed, and being clear on time lines. There’s always a level-one answer, there’s a level-two answer, there’s a level-three answer. Without being too flippant, I can solve any problem during a good dinner with wine. It won’t have a whole lot of backing.
Simon London: Not going to have a lot of depth to it.
Hugo Sarrazin: No, but it may be useful as a starting point. If the stakes are not that high, that could be OK. If it’s really high stakes, you may need level three and have the whole model validated in three different ways. You need to find a work plan that reflects the level of precision, the time frame you have, and the stakeholders you need to bring along in the exercise.
Charles Conn: I love the way you’ve described that, because, again, some people think of problem solving as a linear thing, but of course what’s critical is that it’s iterative. As you say, you can solve the problem in one day or even one hour.
Charles Conn: We encourage our teams everywhere to do that. We call it the one-day answer or the one-hour answer. In work planning, we’re always iterating. Every time you see a 50-page work plan that stretches out to three months, you know it’s wrong. It will be outmoded very quickly by that learning process that you described. Iterative problem solving is a critical part of this. Sometimes, people think work planning sounds dull, but it isn’t. It’s how we know what’s expected of us and when we need to deliver it and how we’re progressing toward the answer. It’s also the place where we can deal with biases. Bias is a feature of every human decision-making process. If we design our team interactions intelligently, we can avoid the worst sort of biases.
Simon London: Here we’re talking about cognitive biases primarily, right? It’s not that I’m biased against you because of your accent or something. These are the cognitive biases that behavioral sciences have shown we all carry around, things like anchoring, overoptimism—these kinds of things.
Both: Yeah.
Charles Conn: Availability bias is the one that I’m always alert to. You think you’ve seen the problem before, and therefore what’s available is your previous conception of it—and we have to be most careful about that. In any human setting, we also have to be careful about biases that are based on hierarchies, sometimes called sunflower bias. I’m sure, Hugo, with your teams, you make sure that the youngest team members speak first. Not the oldest team members, because it’s easy for people to look at who’s senior and alter their own creative approaches.
Hugo Sarrazin: It’s helpful, at that moment—if someone is asserting a point of view—to ask the question “This was true in what context?” You’re trying to apply something that worked in one context to a different one. That can be deadly if the context has changed, and that’s why organizations struggle to change. You promote all these people because they did something that worked well in the past, and then there’s a disruption in the industry, and they keep doing what got them promoted even though the context has changed.
Simon London: Right. Right.
Hugo Sarrazin: So it’s the same thing in problem solving.
Charles Conn: And it’s why diversity in our teams is so important. It’s one of the best things about the world that we’re in now. We’re likely to have people from different socioeconomic, ethnic, and national backgrounds, each of whom sees problems from a slightly different perspective. It is therefore much more likely that the team will uncover a truly creative and clever approach to problem solving.
Simon London: Let’s move on to step five. You’ve done your work plan. Now you’ve actually got to do the analysis. The thing that strikes me here is that the range of tools that we have at our disposal now, of course, is just huge, particularly with advances in computation, advanced analytics. There’s so many things that you can apply here. Just talk about the analysis stage. How do you pick the right tools?
Charles Conn: For me, the most important thing is that we start with simple heuristics and explanatory statistics before we go off and use the big-gun tools. We need to understand the shape and scope of our problem before we start applying these massive and complex analytical approaches.
Simon London: Would you agree with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: I agree. I think there are so many wonderful heuristics. You need to start there before you go deep into the modeling exercise. There’s an interesting dynamic that’s happening, though. In some cases, for some types of problems, it is even better to set yourself up to maximize your learning. Your problem-solving methodology is test and learn, test and learn, test and learn, and iterate. That is a heuristic in itself, the A/B testing that is used in many parts of the world. So that’s a problem-solving methodology. It’s nothing different. It just uses technology and feedback loops in a fast way. The other one is exploratory data analysis. When you’re dealing with a large-scale problem, and there’s so much data, I can get to the heuristics that Charles was talking about through very clever visualization of data.
You test with your data. You need to set up an environment to do so, but don’t get caught up in neural-network modeling immediately. You’re testing, you’re checking—“Is the data right? Is it sound? Does it make sense?”—before you launch too far.
Simon London: You do hear these ideas—that if you have a big enough data set and enough algorithms, they’re going to find things that you just wouldn’t have spotted, find solutions that maybe you wouldn’t have thought of. Does machine learning sort of revolutionize the problem-solving process? Or are these actually just other tools in the toolbox for structured problem solving?
Charles Conn: It can be revolutionary. There are some areas in which the pattern recognition of large data sets and good algorithms can help us see things that we otherwise couldn’t see. But I do think it’s terribly important we don’t think that this particular technique is a substitute for superb problem solving, starting with good problem definition. Many people use machine learning without understanding algorithms that themselves can have biases built into them. Just as 20 years ago, when we were doing statistical analysis, we knew that we needed good model definition, we still need a good understanding of our algorithms and really good problem definition before we launch off into big data sets and unknown algorithms.
Simon London: Step six. You’ve done your analysis.
Charles Conn: I take six and seven together, and this is the place where young problem solvers often make a mistake. They’ve got their analysis, and they assume that’s the answer, and of course it isn’t the answer. The ability to synthesize the pieces that came out of the analysis and begin to weave those into a story that helps people answer the question “What should I do?” This is back to where we started. If we can’t synthesize, and we can’t tell a story, then our decision maker can’t find the answer to “What should I do?”
Simon London: But, again, these final steps are about motivating people to action, right?
Charles Conn: Yeah.
Simon London: I am slightly torn about the nomenclature of problem solving because it’s on paper, right? Until you motivate people to action, you actually haven’t solved anything.
Charles Conn: I love this question because I think decision-making theory, without a bias to action, is a waste of time. Everything in how I approach this is to help people take action that makes the world better.
Simon London: Hence, these are absolutely critical steps. If you don’t do this well, you’ve just got a bunch of analysis.
Charles Conn: We end up in exactly the same place where we started, which is people speaking across each other, past each other in the public square, rather than actually working together, shoulder to shoulder, to crack these important problems.
Simon London: In the real world, we have a lot of uncertainty—arguably, increasing uncertainty. How do good problem solvers deal with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: At every step of the process. In the problem definition, when you’re defining the context, you need to understand those sources of uncertainty and whether they’re important or not important. It becomes important in the definition of the tree.
You need to think carefully about the branches of the tree that are more certain and less certain as you define them. They don’t have equal weight just because they’ve got equal space on the page. Then, when you’re prioritizing, your prioritization approach may put more emphasis on things that have low probability but huge impact—or, vice versa, may put a lot of priority on things that are very likely and, hopefully, have a reasonable impact. You can introduce that along the way. When you come back to the synthesis, you just need to be nuanced about what you’re understanding, the likelihood.
Often, people lack humility in the way they make their recommendations: “This is the answer.” They’re very precise, and I think we would all be well-served to say, “This is a likely answer under the following sets of conditions” and then make the level of uncertainty clearer, if that is appropriate. It doesn’t mean you’re always in the gray zone; it doesn’t mean you don’t have a point of view. It just means that you can be explicit about the certainty of your answer when you make that recommendation.
Simon London: So it sounds like there is an underlying principle: “Acknowledge and embrace the uncertainty. Don’t pretend that it isn’t there. Be very clear about what the uncertainties are up front, and then build that into every step of the process.”
Hugo Sarrazin: Every step of the process.
Simon London: Yeah. We have just walked through a particular structured methodology for problem solving. But, of course, this is not the only structured methodology for problem solving. One that is also very well-known is design thinking, which comes at things very differently. So, Hugo, I know you have worked with a lot of designers. Just give us a very quick summary. Design thinking—what is it, and how does it relate?
Hugo Sarrazin: It starts with an incredible amount of empathy for the user and uses that to define the problem. It does pause and go out in the wild and spend an enormous amount of time seeing how people interact with objects, seeing the experience they’re getting, seeing the pain points or joy—and uses that to infer and define the problem.
Simon London: Problem definition, but out in the world.
Hugo Sarrazin: With an enormous amount of empathy. There’s a huge emphasis on empathy. Traditional, more classic problem solving is you define the problem based on an understanding of the situation. This one almost presupposes that we don’t know the problem until we go see it. The second thing is you need to come up with multiple scenarios or answers or ideas or concepts, and there’s a lot of divergent thinking initially. That’s slightly different, versus the prioritization, but not for long. Eventually, you need to kind of say, “OK, I’m going to converge again.” Then you go and you bring things back to the customer and get feedback and iterate. Then you rinse and repeat, rinse and repeat. There’s a lot of tactile building, along the way, of prototypes and things like that. It’s very iterative.
Simon London: So, Charles, are these complements or are these alternatives?
Charles Conn: I think they’re entirely complementary, and I think Hugo’s description is perfect. When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to approach. When we ideate—and that’s very similar to the disaggregation, prioritization, and work-planning steps—we do precisely the same thing, and often we use contrasting teams, so that we do have divergent thinking. The best teams allow divergent thinking to bump them off whatever their initial biases in problem solving are. For me, design thinking gives us a constant reminder of creativity, empathy, and the tactile nature of problem solving, but it’s absolutely complementary, not alternative.
Simon London: I think, in a world of cross-functional teams, an interesting question is do people with design-thinking backgrounds really work well together with classical problem solvers? How do you make that chemistry happen?
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah, it is not easy when people have spent an enormous amount of time seeped in design thinking or user-centric design, whichever word you want to use. If the person who’s applying classic problem-solving methodology is very rigid and mechanical in the way they’re doing it, there could be an enormous amount of tension. If there’s not clarity in the role and not clarity in the process, I think having the two together can be, sometimes, problematic.
The second thing that happens often is that the artifacts the two methodologies try to gravitate toward can be different. Classic problem solving often gravitates toward a model; design thinking migrates toward a prototype. Rather than writing a big deck with all my supporting evidence, they’ll bring an example, a thing, and that feels different. Then you spend your time differently to achieve those two end products, so that’s another source of friction.
Now, I still think it can be an incredibly powerful thing to have the two—if there are the right people with the right mind-set, if there is a team that is explicit about the roles, if we’re clear about the kind of outcomes we are attempting to bring forward. There’s an enormous amount of collaborativeness and respect.
Simon London: But they have to respect each other’s methodology and be prepared to flex, maybe, a little bit, in how this process is going to work.
Hugo Sarrazin: Absolutely.
Simon London: The other area where, it strikes me, there could be a little bit of a different sort of friction is this whole concept of the day-one answer, which is what we were just talking about in classical problem solving. Now, you know that this is probably not going to be your final answer, but that’s how you begin to structure the problem. Whereas I would imagine your design thinkers—no, they’re going off to do their ethnographic research and get out into the field, potentially for a long time, before they come back with at least an initial hypothesis.

Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver
Hugo Sarrazin: That is a great callout, and that’s another difference. Designers typically will like to soak into the situation and avoid converging too quickly. There’s optionality and exploring different options. There’s a strong belief that keeps the solution space wide enough that you can come up with more radical ideas. If there’s a large design team or many designers on the team, and you come on Friday and say, “What’s our week-one answer?” they’re going to struggle. They’re not going to be comfortable, naturally, to give that answer. It doesn’t mean they don’t have an answer; it’s just not where they are in their thinking process.
Simon London: I think we are, sadly, out of time for today. But Charles and Hugo, thank you so much.
Charles Conn: It was a pleasure to be here, Simon.
Hugo Sarrazin: It was a pleasure. Thank you.
Simon London: And thanks, as always, to you, our listeners, for tuning into this episode of the McKinsey Podcast . If you want to learn more about problem solving, you can find the book, Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything , online or order it through your local bookstore. To learn more about McKinsey, you can of course find us at McKinsey.com.
Charles Conn is CEO of Oxford Sciences Innovation and an alumnus of McKinsey’s Sydney office. Hugo Sarrazin is a senior partner in the Silicon Valley office, where Simon London, a member of McKinsey Publishing, is also based.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategy to beat the odds

Five routes to more innovative problem solving
How to Train Your Problem-Solving Skills
From the hiccups that disrupt your morning routines to the hurdles that define your professional paths, there is always a problem to be solved.
The good news is that every obstacle is an opportunity to develop problem-solving skills and become the best version of yourself. That’s right: It turns out you can get better at problem-solving, which will help you increase success in daily life and long-term goals.
Read on to learn how to improve your problem-solving abilities through scientific research and practical strategies.
Understanding Problem-Solving Skills
You may be surprised to learn that your problem-solving skills go beyond just trying to find a solution. Problem-solving skills involve cognitive abilities such as analytical thinking, creativity, decision-making, logical reasoning, and memory.
Strong problem-solving skills boost critical thinking, spark creativity, and hone decision-making abilities. For you or anyone looking to improve their mental fitness , these skills are necessary for career advancement, personal growth, and positive interpersonal relationships.
Core Components of Problem-Solving Skills Training
To effectively train your problem-solving skills, it’s important to practice all of the steps required to solve the problem. Think of it this way: Before attempting to solve a problem, your brain has already been hard at work evaluating the situation and picking the best action plan. After you’ve worked hard preparing, you’ll need to implement your plan and assess the outcome by following these steps:
- Identify and define problems: Recognizing and clearly articulating issues is the foundational step in solving them.
- Generate solutions: Employing brainstorming techniques helps you develop multiple potential solutions.
- Evaluate and select solutions: Using specific criteria to assess solutions helps you choose the most effective one.
- Implement solutions: Developing and executing action plans, including preparing for potential obstacles, guides you to positive outcomes.
- Review and learn from outcomes: Assessing the success of solutions and learning from the results for future improvement facilitates future success.
Strategies for Developing Problem-Solving Skills
There are many practical exercises and activities that can improve problem-solving abilities.
Cultivate a Problem-Solving Mindset
- Adopt a growth mindset: A growth mindset involves transforming phrases like “I can’t” into “I can’t yet.” Believing in the capacity to improve your skills through effort and perseverance can lead to greater success in problem-solving.
- Practice mindfulness: Mindfulness can enhance cognitive flexibility , allowing you to view problems from multiple perspectives and find creative solutions.
Enhance Core Cognitive Skills
- Strengthen your memory: Engage in activities that challenge your memory since accurately recalling information is crucial in problem-solving. Techniques such as mnemonic devices or memory palaces can be particularly effective.
- Build your critical thinking: Regularly question assumptions, evaluate arguments, and engage in activities that require reasoning, such as strategy games or debates.
Apply Structured Problem-Solving Techniques
- Use the STOP method: This stands for Stop , Think , Observe , and Plan . It's a simple yet effective way to approach any problem methodically, ensuring you consider all aspects before taking action.
- Try reverse engineering: Start with the desired outcome and work backward to understand the steps needed to achieve that result. This approach can be particularly useful for complex problems with unclear starting points.
Incorporate Technology into Your Training
- Engage with online courses and workshops: Many platforms offer courses specifically designed to enhance problem-solving skills, ranging from critical thinking to creative problem-solving techniques.
- Use cognitive training apps: Apps like Elevate provide targeted, research-backed games and workouts to improve cognitive skills including attention, processing speed, and more.
Practice with Real-World Applications and Learn from Experience
- Tackle daily challenges: Use everyday issues as opportunities to practice problem-solving. Whether figuring out a new recipe or managing a tight budget, applying your skills in real-world situations can reinforce learning.
- Keep a problem-solving journal: Record the challenges you face, the strategies you employ, and the outcomes you achieve. Reflecting on your problem-solving process over time can provide insights into your strengths and areas for improvement.
Embracing Problem-Solving as a Lifelong Journey
Since problems arise daily, it’s important to feel confident in solving them.
And you can do just that by downloading the Elevate brain training app. Elevate offers 40+ games and activities designed to improve problem-solving, communication, and other cognitive skills in a personalized way that’s backed by science. Pretty cool, right?
Consider downloading the Elevate app on Android or iOS now—it’ll be the easiest problem you solve all day.
Related Articles
How Problem-Solving Games Can Boost Your Brain
- Discover why problem-solving games are fun and effective ways to train your brain.
Improving Your Problem-Solving Skills
- Discover how to improve your problem-solving skills and make logical, informed decisions.
Best Ways to Boost Your Mental Fitness
- Mental fitness refers to your ability to sustain your overall well-being. Learn tips to improve yours.
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Discover how today’s most successful IT leaders stand out from the rest. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Read the report .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Collaboration |
- Turn your team into skilled problem sol ...
Turn your team into skilled problem solvers with these problem-solving strategies

Picture this, you're handling your daily tasks at work and your boss calls you in and says, "We have a problem."
Unfortunately, we don't live in a world in which problems are instantly resolved with the snap of our fingers. Knowing how to effectively solve problems is an important professional skill to hone. If you have a problem that needs to be solved, what is the right process to use to ensure you get the most effective solution?
In this article we'll break down the problem-solving process and how you can find the most effective solutions for complex problems.
What is problem solving?
Problem solving is the process of finding a resolution for a specific issue or conflict. There are many possible solutions for solving a problem, which is why it's important to go through a problem-solving process to find the best solution. You could use a flathead screwdriver to unscrew a Phillips head screw, but there is a better tool for the situation. Utilizing common problem-solving techniques helps you find the best solution to fit the needs of the specific situation, much like using the right tools.
Decision-making tools for agile businesses
In this ebook, learn how to equip employees to make better decisions—so your business can pivot, adapt, and tackle challenges more effectively than your competition.

4 steps to better problem solving
While it might be tempting to dive into a problem head first, take the time to move step by step. Here’s how you can effectively break down the problem-solving process with your team:
1. Identify the problem that needs to be solved
One of the easiest ways to identify a problem is to ask questions. A good place to start is to ask journalistic questions, like:
Who : Who is involved with this problem? Who caused the problem? Who is most affected by this issue?
What: What is happening? What is the extent of the issue? What does this problem prevent from moving forward?
Where: Where did this problem take place? Does this problem affect anything else in the immediate area?
When: When did this problem happen? When does this problem take effect? Is this an urgent issue that needs to be solved within a certain timeframe?
Why: Why is it happening? Why does it impact workflows?
How: How did this problem occur? How is it affecting workflows and team members from being productive?
Asking journalistic questions can help you define a strong problem statement so you can highlight the current situation objectively, and create a plan around that situation.
Here’s an example of how a design team uses journalistic questions to identify their problem:
Overarching problem: Design requests are being missed
Who: Design team, digital marketing team, web development team
What: Design requests are forgotten, lost, or being created ad hoc.
Where: Email requests, design request spreadsheet
When: Missed requests on January 20th, January 31st, February 4th, February 6th
How : Email request was lost in inbox and the intake spreadsheet was not updated correctly. The digital marketing team had to delay launching ads for a few days while design requests were bottlenecked. Designers had to work extra hours to ensure all requests were completed.
In this example, there are many different aspects of this problem that can be solved. Using journalistic questions can help you identify different issues and who you should involve in the process.
2. Brainstorm multiple solutions
If at all possible, bring in a facilitator who doesn't have a major stake in the solution. Bringing an individual who has little-to-no stake in the matter can help keep your team on track and encourage good problem-solving skills.
Here are a few brainstorming techniques to encourage creative thinking:
Brainstorm alone before hand: Before you come together as a group, provide some context to your team on what exactly the issue is that you're brainstorming. This will give time for you and your teammates to have some ideas ready by the time you meet.
Say yes to everything (at first): When you first start brainstorming, don't say no to any ideas just yet—try to get as many ideas down as possible. Having as many ideas as possible ensures that you’ll get a variety of solutions. Save the trimming for the next step of the strategy.
Talk to team members one-on-one: Some people may be less comfortable sharing their ideas in a group setting. Discuss the issue with team members individually and encourage them to share their opinions without restrictions—you might find some more detailed insights than originally anticipated.
Break out of your routine: If you're used to brainstorming in a conference room or over Zoom calls, do something a little different! Take your brainstorming meeting to a coffee shop or have your Zoom call while you're taking a walk. Getting out of your routine can force your brain out of its usual rut and increase critical thinking.
3. Define the solution
After you brainstorm with team members to get their unique perspectives on a scenario, it's time to look at the different strategies and decide which option is the best solution for the problem at hand. When defining the solution, consider these main two questions: What is the desired outcome of this solution and who stands to benefit from this solution?
Set a deadline for when this decision needs to be made and update stakeholders accordingly. Sometimes there's too many people who need to make a decision. Use your best judgement based on the limitations provided to do great things fast.
4. Implement the solution
To implement your solution, start by working with the individuals who are as closest to the problem. This can help those most affected by the problem get unblocked. Then move farther out to those who are less affected, and so on and so forth. Some solutions are simple enough that you don’t need to work through multiple teams.
After you prioritize implementation with the right teams, assign out the ongoing work that needs to be completed by the rest of the team. This can prevent people from becoming overburdened during the implementation plan . Once your solution is in place, schedule check-ins to see how the solution is working and course-correct if necessary.
Implement common problem-solving strategies
There are a few ways to go about identifying problems (and solutions). Here are some strategies you can try, as well as common ways to apply them:
Trial and error
Trial and error problem solving doesn't usually require a whole team of people to solve. To use trial and error problem solving, identify the cause of the problem, and then rapidly test possible solutions to see if anything changes.
This problem-solving method is often used in tech support teams through troubleshooting.
The 5 whys problem-solving method helps get to the root cause of an issue. You start by asking once, “Why did this issue happen?” After answering the first why, ask again, “Why did that happen?” You'll do this five times until you can attribute the problem to a root cause.
This technique can help you dig in and find the human error that caused something to go wrong. More importantly, it also helps you and your team develop an actionable plan so that you can prevent the issue from happening again.
Here’s an example:
Problem: The email marketing campaign was accidentally sent to the wrong audience.
“Why did this happen?” Because the audience name was not updated in our email platform.
“Why were the audience names not changed?” Because the audience segment was not renamed after editing.
“Why was the audience segment not renamed?” Because everybody has an individual way of creating an audience segment.
“Why does everybody have an individual way of creating an audience segment?” Because there is no standardized process for creating audience segments.
“Why is there no standardized process for creating audience segments?” Because the team hasn't decided on a way to standardize the process as the team introduced new members.
In this example, we can see a few areas that could be optimized to prevent this mistake from happening again. When working through these questions, make sure that everyone who was involved in the situation is present so that you can co-create next steps to avoid the same problem.
A SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis can help you highlight the strengths and weaknesses of a specific solution. SWOT stands for:
Strength: Why is this specific solution a good fit for this problem?
Weaknesses: What are the weak points of this solution? Is there anything that you can do to strengthen those weaknesses?
Opportunities: What other benefits could arise from implementing this solution?
Threats: Is there anything about this decision that can detrimentally impact your team?
As you identify specific solutions, you can highlight the different strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of each solution.
This particular problem-solving strategy is good to use when you're narrowing down the answers and need to compare and contrast the differences between different solutions.
Even more successful problem solving
After you’ve worked through a tough problem, don't forget to celebrate how far you've come. Not only is this important for your team of problem solvers to see their work in action, but this can also help you become a more efficient, effective , and flexible team. The more problems you tackle together, the more you’ll achieve.
Looking for a tool to help solve problems on your team? Track project implementation with a work management tool like Asana .
Related resources

Fix these common onboarding challenges to boost productivity

How Asana uses work management for organizational planning

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning

Build a cross-functional team in just 4 steps
Table of Contents
The problem-solving process, how to solve problems: 5 steps, train to solve problems with lean today, what is problem solving steps, techniques, & best practices explained.

Problem solving is the art of identifying problems and implementing the best possible solutions. Revisiting your problem-solving skills may be the missing piece to leveraging the performance of your business, achieving Lean success, or unlocking your professional potential.
Ask any colleague if they’re an effective problem-solver and their likely answer will be, “Of course! I solve problems every day.”
Problem solving is part of most job descriptions, sure. But not everyone can do it consistently.
Problem solving is the process of defining a problem, identifying its root cause, prioritizing and selecting potential solutions, and implementing the chosen solution.
There’s no one-size-fits-all problem-solving process. Often, it’s a unique methodology that aligns your short- and long-term objectives with the resources at your disposal. Nonetheless, many paradigms center problem solving as a pathway for achieving one’s goals faster and smarter.
One example is the Six Sigma framework , which emphasizes eliminating errors and refining the customer experience, thereby improving business outcomes. Developed originally by Motorola, the Six Sigma process identifies problems from the perspective of customer satisfaction and improving product delivery.
Lean management, a similar method, is about streamlining company processes over time so they become “leaner” while producing better outcomes.
Trendy business management lingo aside, both of these frameworks teach us that investing in your problem solving process for personal and professional arenas will bring better productivity.
1. Precisely Identify Problems
As obvious as it seems, identifying the problem is the first step in the problem-solving process. Pinpointing a problem at the beginning of the process will guide your research, collaboration, and solutions in the right direction.
At this stage, your task is to identify the scope and substance of the problem. Ask yourself a series of questions:
- What’s the problem?
- How many subsets of issues are underneath this problem?
- What subject areas, departments of work, or functions of business can best define this problem?
Although some problems are naturally large in scope, precision is key. Write out the problems as statements in planning sheets . Should information or feedback during a later step alter the scope of your problem, revise the statements.
Framing the problem at this stage will help you stay focused if distractions come up in later stages. Furthermore, how you frame a problem will aid your search for a solution. A strategy of building Lean success, for instance, will emphasize identifying and improving upon inefficient systems.
2. Collect Information and Plan
The second step is to collect information and plan the brainstorming process. This is another foundational step to road mapping your problem-solving process. Data, after all, is useful in identifying the scope and substance of your problems.
Collecting information on the exact details of the problem, however, is done to narrow the brainstorming portion to help you evaluate the outcomes later. Don’t overwhelm yourself with unnecessary information — use the problem statements that you identified in step one as a north star in your research process.
This stage should also include some planning. Ask yourself:
- What parties will ultimately decide a solution?
- Whose voices and ideas should be heard in the brainstorming process?
- What resources are at your disposal for implementing a solution?
Establish a plan and timeline for steps 3-5.
3. Brainstorm Solutions
Brainstorming solutions is the bread and butter of the problem-solving process. At this stage, focus on generating creative ideas. As long as the solution directly addresses the problem statements and achieves your goals, don’t immediately rule it out.
Moreover, solutions are rarely a one-step answer and are more like a roadmap with a set of actions. As you brainstorm ideas, map out these solutions visually and include any relevant factors such as costs involved, action steps, and involved parties.
With Lean success in mind, stay focused on solutions that minimize waste and improve the flow of business ecosystems.
Become a Quality Management Professional
- 10% Growth In Jobs Of Quality Managers Profiles By 2025
- 11% Revenue Growth For Organisations Improving Quality
Certified Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
- 4 hands-on projects to perfect the skills learnt
- 4 simulation test papers for self-assessment
Lean Six Sigma Expert
- IASSC® Lean Six Sigma Green Belt and Black Belt certification
- 13 Projects, 12 Simulation exams, 18 Case Studies & 114 PDUs
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Xueting Liu
Mechanical engineer student at sargents pty. ltd. ,.
A great training and proper exercise with step-by-step guide! I'll give a rating of 10 out of 10 for this training.
Abdus Salam
I have completed the Lean Six Sigma Expert Master’s Program from Simplilearn. And after the course, I could take up new projects and perform better. My average pay rate for a research position increased by 21%.
4. Decide and Implement
The most critical stage is selecting a solution. Easier said than done. Consider the criteria that has arisen in previous steps as you decide on a solution that meets your needs.
Once you select a course of action, implement it.
Practicing due diligence in earlier stages of the process will ensure that your chosen course of action has been evaluated from all angles. Often, efficient implementation requires us to act correctly and successfully the first time, rather than being hurried and sloppy. Further compilations will create more problems, bringing you back to step 1.
5. Evaluate
Exercise humility and evaluate your solution honestly. Did you achieve the results you hoped for? What would you do differently next time?
As some experts note, formulating feedback channels into your evaluation helps solidify future success. A framework like Lean success, for example, will use certain key performance indicators (KPIs) like quality, delivery success, reducing errors, and more. Establish metrics aligned with company goals to assess your solutions.
Master skills like measurement system analysis, lean principles, hypothesis testing, process analysis and DFSS tools with our Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Training Course . Sign-up today!
Become a quality expert with Simplilearn’s Lean Six Sigma Green Belt . This Lean Six Sigma certification program will help you gain key skills to excel in digital transformation projects while improving quality and ultimate business results.
In this course, you will learn about two critical operations management methodologies – Lean practices and Six Sigma to accelerate business improvement.
Our Quality Management Courses Duration And Fees
Explore our top Quality Management Courses and take the first step towards career success
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Quality Management
Lean Management
Project Management
Learn from industry experts with free masterclasses, digital marketing.
The Top 10 AI Tools You Need to Master Marketing in 2024
Unlock Digital Marketing Career Success Secrets for 2024 with Purdue University
Your Gateway to Game-changing Digital Marketing Careers in 2024 with Purdue University
Recommended Reads
Introduction to Machine Learning: A Beginner's Guide
Webinar Wrap-up: Mastering Problem Solving: Career Tips for Digital Transformation Jobs
An Ultimate Guide That Helps You to Develop and Improve Problem Solving in Programming
Free eBook: 21 Resources to Find the Data You Need
ITIL Problem Workaround: A Leader’s Guide to Manage Problems
Your One-Stop Solution to Understand Coin Change Problem
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.

From Dilemmas to Solutions: Problem-Solving Examples to Learn From
- By Daria Burnett
- May 21, 2023
Introduction to Problem-Solving
Life is full of challenges and dilemmas, both big and small.
But if there’s one skill that can help you navigate these, it’s problem-solving .
So, what exactly is problem-solving? And why is it such a crucial skill in daily life?
Understanding the Concept of Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves identifying, analyzing, and resolving challenges or difficulties.
It’s like a journey that starts with a problem and ends with a solution.
It’s a skill that’s not just used in the field of psychology but in all aspects of life.
🔥 Ready to meet your Twin Flame?
Do you know what your Twin Flame soulmate looks like? 💓
Master Wang is a "psychic artist" and a master of astrology; he's famous in China for being able to draw anyone's soulmate.
Thousands of people have found love thanks to Master Wang's gift.
Don't delay! Yes, I want my Twin Flame soulmate drawing!
Whether you’re trying to decide on the best route to work, dealing with a disagreement with a friend, or figuring out how to fix a leaky faucet, you’re using your problem-solving skills.
When you’re faced with a problem, your brain goes through a series of steps to find a solution.
This process can be conscious or unconscious and can involve logical thinking, creativity, and prior knowledge.
Effective problem-solving can lead to better decisions and outcomes, making it a valuable tool in your personal and professional life.
Related Posts:
- Your Path to Success: Best Career Options with a Psychology Degree
- Type C Personality Traits: The Power of Positivity
- Embrace the Change: Embodying the Democratic Leadership Style
Importance of Problem-Solving in Daily Life
Why is problem-solving so important in daily life? Well, it’s simple.
Problems are a part of life.
They arise in different shapes and sizes, and in different areas of life, including work, relationships, health, and personal growth.
Having strong problem-solving skills can help you navigate these challenges effectively and efficiently.
In your personal life, problem-solving can help you manage stress and conflict, make better decisions, and achieve your goals.
In the workplace, it can help you navigate complex projects, improve processes, and foster innovation.
Problem-solving is also a key skill in many professions and industries, from engineering and science to healthcare and customer service.
Don’t miss out on this unique astrological opportunity!
Are you tired of spinning your wheels and getting nowhere? Well, there’s a reason you can’t get to where you want to go.
Simply put, you’re out of sync: you're out of alignment with your astral configuration.
But: there’s a kind of map that can help you find your alignment. Think of it as your own personal blueprint to success and happiness: a personal blueprint that will help you live your most amazing life . Find out more here !
Moreover, problem-solving can contribute to your overall mental well-being.
It can give you a sense of control and agency, reduce feelings of stress and anxiety, and foster a positive attitude.
It’s also a key component of resilience, the ability to bounce back from adversity.
In conclusion, problem-solving is a fundamental skill in life.
It’s a tool you can use to tackle challenges, make informed decisions, and drive change.
By understanding the concept of problem-solving and recognizing its importance in daily life, you’re taking the first step toward becoming a more effective problem solver.
As we delve deeper into this topic, you’ll discover practical problem-solving examples, learn about different problem-solving techniques, and gain insights on how to improve your own problem-solving skills.
So, stay tuned and continue your exploration of introduction to psychology with us.
Stages of Problem-Solving
The process of problem-solving can be broken down into three key stages: identifying the problem , developing possible solutions , and implementing the best solution .
Each stage requires a different set of skills and strategies.
By understanding these stages, you can enhance your problem-solving abilities and tackle various challenges more effectively.
Identifying the Problem
The first step in problem-solving is recognizing that a problem exists.
This involves defining the issue clearly and understanding its root cause.
You might need to gather information, ask questions, and analyze the situation from multiple perspectives.
It can be helpful to write down the problem and think about how it impacts you or others involved.
For instance, if you’re struggling with time management, the problem might be that you have too many obligations and not enough time.
Or perhaps your methods of organizing your tasks aren’t effective.
It’s important to be as specific as possible when identifying the problem, as this will guide the rest of the problem-solving process.
Developing Possible Solutions
Once you’ve identified the problem, the next step is to brainstorm possible solutions.
This is where creativity comes into play.
Don’t limit yourself; even ideas that seem unrealistic or out of the box can lead to effective solutions.
Consider different strategies and approaches.
You could try using techniques like mind mapping, listing pros and cons, or consulting with others for fresh perspectives.
Remember, the goal is to generate a variety of options, not to choose a solution at this stage.
Implementing the Best Solution
The final stage of problem-solving is to select the best solution and put it into action.
Review the options you’ve developed, evaluate their potential effectiveness, and make a decision.
Keep in mind that the “best” solution isn’t necessarily the perfect one (as there might not be a perfect solution), but rather the one that seems most likely to achieve your desired outcome given the circumstances.
Once you’ve chosen a solution, plan out the steps needed to implement it and then take action.
Monitor the results and adjust your approach as necessary.
If the problem persists, don’t be discouraged; return to the previous stages, reassess the problem and your potential solutions, and try again.
Remember, problem-solving is a dynamic process that often involves trial and error.
It’s an essential skill in many areas of life, from everyday challenges to workplace dilemmas.
To learn more about the psychology behind problem-solving and decision-making, check out our introduction to psychology article.
Problem-Solving Examples
Understanding the concept of problem-solving is one thing, but seeing it in action is another.
To help you grasp the practical application of problem-solving strategies, let’s explore three different problem-solving examples from daily life, the workplace, and relationships.
Daily Life Problem-Solving Example
Imagine you’re trying to lose weight but struggle with late-night snacking.
The issue isn’t uncommon, but it’s hindering your progress towards your weight loss goal.
- Identifying the Problem : Late-night snacking is causing you to consume extra calories, preventing weight loss.
- Developing Possible Solutions : You could consider eating an earlier dinner, having a healthier snack option, or practicing mindful eating.
- Implementing the Best Solution : After trying out different solutions, you find that preparing a healthy snack in advance minimizes your calorie intake and satisfies your late-night cravings, helping you stay on track with your weight loss goal.
Workplace Problem-Solving Example
Let’s consider a scenario where a team at work is failing to meet project deadlines consistently.
- Identifying the Problem : The team is not completing projects on time, causing delays in the overall project timeline.
- Developing Possible Solutions : The team could consider improving their time management skills, using project management tools, or redistributing tasks among team members.
- Implementing the Best Solution : After trying out different strategies, the team finds that using a project management tool helps them stay organized, delegate tasks effectively, and complete projects within the given timeframe.
For more insights on effective management styles that can help in problem-solving at the workplace, check out our articles on autocratic leadership , democratic leadership style , and laissez faire leadership .
Relationship Problem-Solving Example
In a romantic relationship, conflicts can occasionally arise.
Let’s imagine a common issue where one partner feels the other isn’t spending enough quality time with them.
- Identifying the Problem : One partner feels neglected due to a lack of quality time spent together.
- Developing Possible Solutions : The couple could consider scheduling regular date nights, engaging in shared hobbies, or setting aside a specific time each day for undisturbed conversation.
- Implementing the Best Solution : The couple decides to implement a daily “unplugged” hour where they focus solely on each other without distractions. This results in improved relationship satisfaction.
For more on navigating relationship challenges, check out our articles on anxious avoidant attachment and emotional awareness .
These problem-solving examples illustrate how the process of identifying a problem, developing possible solutions, and implementing the best solution can be applied to various situations.
By understanding and applying these strategies, you can improve your problem-solving skills and navigate challenges more effectively.
Techniques for Effective Problem-Solving
As you navigate the world of problem-solving, you’ll find that there are multiple techniques you can use to arrive at a solution.
Each technique offers a unique approach to identifying issues, generating potential solutions, and choosing the best course of action.
In this section, we’ll explore three common techniques: Brainstorming , Root Cause Analysis , and SWOT Analysis .
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a free-thinking method used to generate a large number of ideas related to a specific problem.
You do this by suspending criticism and allowing your creativity to flow.
The aim is to produce as many ideas as possible, even if they seem far-fetched.
You then evaluate these ideas to identify the most beneficial solutions.
By using brainstorming, you can encourage out-of-the-box thinking and possibly discover innovative solutions to challenging problems.
Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a method used to identify the underlying causes of a problem.
The goal is to address these root causes rather than the symptoms of the problem.
This technique helps to prevent the same issue from recurring in the future.
There are several RCA methods, such as the “5 Whys” technique, where you ask “why” multiple times until you uncover the root cause of the problem.
By identifying and addressing the root cause, you tackle the problem at its source, which can lead to more effective and long-lasting solutions.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning technique that helps you identify your Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to a problem.
This approach encourages you to examine the problem from different angles, helping you understand the resources you have at your disposal (Strengths), the areas where you could improve (Weaknesses), the external factors that could benefit you (Opportunities), and the external factors that could cause problems (Threats).
With this comprehensive understanding, you can develop a well-informed strategy to solve the problem.
Each of these problem-solving techniques provides a distinct approach to identifying and resolving issues.
By understanding and utilizing these methods, you can enhance your problem-solving skills and increase your effectiveness in dealing with challenges.
For more insights into effective problem-solving and other psychological topics, explore our introduction to psychology .
Improving Your Problem-Solving Skills
Learning to solve problems effectively is a skill that can be honed with time and practice.
The following are some ways to enhance your problem-solving capabilities.
Practice Makes Perfect
The saying “practice makes perfect” holds true when it comes to problem-solving.
The more problems you tackle, the better you’ll become at devising and implementing effective solutions.
Seek out opportunities to practice your problem-solving skills both in everyday life and in more complex situations.
This could involve resolving a dispute at work, figuring out a puzzle, or even strategizing in a board game.
Each problem you encounter is a new opportunity to apply and refine your skills.
Learning from Others’ Experiences
There’s much to be gained from observing how others approach problem-solving.
Whether it’s reading about problem solving examples from renowned psychologists or discussing strategies with colleagues, you can learn valuable techniques and perspectives from the experiences of others.
Consider participating in group activities that require problem-solving, such as escape rooms or team projects.
Observe how team members identify problems, brainstorm solutions, and decide on the best course of action.
Embracing a Growth Mindset
A key component of effective problem-solving is adopting a growth mindset.
This mindset, coined by psychologist Carol Dweck, is the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through dedication and hard work.
When you embrace a growth mindset, you view challenges as opportunities to learn and grow rather than as insurmountable obstacles.
Believing in your ability to develop and enhance your problem-solving skills over time can make the process less daunting and more rewarding.
So, when you encounter a problem, instead of thinking, “I can’t do this,” try thinking, “I can’t do this yet, but with effort and practice, I can learn.”
For more on the growth mindset, you might want to check out our article on what is intrinsic motivation which includes how a growth mindset can fuel your motivation to improve.
By practicing regularly, learning from others, and embracing a growth mindset, you can continually improve your problem-solving skills and become more adept at overcoming challenges you encounter.
Interview Questions
Comprehensive Interview Guide: 60+ Professions Explored in Detail
26 Good Examples of Problem Solving (Interview Answers)
By Biron Clark
Published: November 15, 2023
Employers like to hire people who can solve problems and work well under pressure. A job rarely goes 100% according to plan, so hiring managers will be more likely to hire you if you seem like you can handle unexpected challenges while staying calm and logical in your approach.
But how do they measure this?
They’re going to ask you interview questions about these problem solving skills, and they might also look for examples of problem solving on your resume and cover letter. So coming up, I’m going to share a list of examples of problem solving, whether you’re an experienced job seeker or recent graduate.
Then I’ll share sample interview answers to, “Give an example of a time you used logic to solve a problem?”
Problem-Solving Defined
It is the ability to identify the problem, prioritize based on gravity and urgency, analyze the root cause, gather relevant information, develop and evaluate viable solutions, decide on the most effective and logical solution, and plan and execute implementation.
Problem-solving also involves critical thinking, communication, listening, creativity, research, data gathering, risk assessment, continuous learning, decision-making, and other soft and technical skills.
Solving problems not only prevent losses or damages but also boosts self-confidence and reputation when you successfully execute it. The spotlight shines on you when people see you handle issues with ease and savvy despite the challenges. Your ability and potential to be a future leader that can take on more significant roles and tackle bigger setbacks shine through. Problem-solving is a skill you can master by learning from others and acquiring wisdom from their and your own experiences.
It takes a village to come up with solutions, but a good problem solver can steer the team towards the best choice and implement it to achieve the desired result.
Watch: 26 Good Examples of Problem Solving
Examples of problem solving scenarios in the workplace.
- Correcting a mistake at work, whether it was made by you or someone else
- Overcoming a delay at work through problem solving and communication
- Resolving an issue with a difficult or upset customer
- Overcoming issues related to a limited budget, and still delivering good work through the use of creative problem solving
- Overcoming a scheduling/staffing shortage in the department to still deliver excellent work
- Troubleshooting and resolving technical issues
- Handling and resolving a conflict with a coworker
- Solving any problems related to money, customer billing, accounting and bookkeeping, etc.
- Taking initiative when another team member overlooked or missed something important
- Taking initiative to meet with your superior to discuss a problem before it became potentially worse
- Solving a safety issue at work or reporting the issue to those who could solve it
- Using problem solving abilities to reduce/eliminate a company expense
- Finding a way to make the company more profitable through new service or product offerings, new pricing ideas, promotion and sale ideas, etc.
- Changing how a process, team, or task is organized to make it more efficient
- Using creative thinking to come up with a solution that the company hasn’t used before
- Performing research to collect data and information to find a new solution to a problem
- Boosting a company or team’s performance by improving some aspect of communication among employees
- Finding a new piece of data that can guide a company’s decisions or strategy better in a certain area
Problem Solving Examples for Recent Grads/Entry Level Job Seekers
- Coordinating work between team members in a class project
- Reassigning a missing team member’s work to other group members in a class project
- Adjusting your workflow on a project to accommodate a tight deadline
- Speaking to your professor to get help when you were struggling or unsure about a project
- Asking classmates, peers, or professors for help in an area of struggle
- Talking to your academic advisor to brainstorm solutions to a problem you were facing
- Researching solutions to an academic problem online, via Google or other methods
- Using problem solving and creative thinking to obtain an internship or other work opportunity during school after struggling at first
You can share all of the examples above when you’re asked questions about problem solving in your interview. As you can see, even if you have no professional work experience, it’s possible to think back to problems and unexpected challenges that you faced in your studies and discuss how you solved them.
Interview Answers to “Give an Example of an Occasion When You Used Logic to Solve a Problem”
Now, let’s look at some sample interview answers to, “Give me an example of a time you used logic to solve a problem,” since you’re likely to hear this interview question in all sorts of industries.
Example Answer 1:
At my current job, I recently solved a problem where a client was upset about our software pricing. They had misunderstood the sales representative who explained pricing originally, and when their package renewed for its second month, they called to complain about the invoice. I apologized for the confusion and then spoke to our billing team to see what type of solution we could come up with. We decided that the best course of action was to offer a long-term pricing package that would provide a discount. This not only solved the problem but got the customer to agree to a longer-term contract, which means we’ll keep their business for at least one year now, and they’re happy with the pricing. I feel I got the best possible outcome and the way I chose to solve the problem was effective.
Example Answer 2:
In my last job, I had to do quite a bit of problem solving related to our shift scheduling. We had four people quit within a week and the department was severely understaffed. I coordinated a ramp-up of our hiring efforts, I got approval from the department head to offer bonuses for overtime work, and then I found eight employees who were willing to do overtime this month. I think the key problem solving skills here were taking initiative, communicating clearly, and reacting quickly to solve this problem before it became an even bigger issue.
Example Answer 3:
In my current marketing role, my manager asked me to come up with a solution to our declining social media engagement. I assessed our current strategy and recent results, analyzed what some of our top competitors were doing, and then came up with an exact blueprint we could follow this year to emulate our best competitors but also stand out and develop a unique voice as a brand. I feel this is a good example of using logic to solve a problem because it was based on analysis and observation of competitors, rather than guessing or quickly reacting to the situation without reliable data. I always use logic and data to solve problems when possible. The project turned out to be a success and we increased our social media engagement by an average of 82% by the end of the year.
Answering Questions About Problem Solving with the STAR Method
When you answer interview questions about problem solving scenarios, or if you decide to demonstrate your problem solving skills in a cover letter (which is a good idea any time the job description mention problem solving as a necessary skill), I recommend using the STAR method to tell your story.
STAR stands for:
It’s a simple way of walking the listener or reader through the story in a way that will make sense to them. So before jumping in and talking about the problem that needed solving, make sure to describe the general situation. What job/company were you working at? When was this? Then, you can describe the task at hand and the problem that needed solving. After this, describe the course of action you chose and why. Ideally, show that you evaluated all the information you could given the time you had, and made a decision based on logic and fact.
Finally, describe a positive result you got.
Whether you’re answering interview questions about problem solving or writing a cover letter, you should only choose examples where you got a positive result and successfully solved the issue.
Example answer:
Situation : We had an irate client who was a social media influencer and had impossible delivery time demands we could not meet. She spoke negatively about us in her vlog and asked her followers to boycott our products. (Task : To develop an official statement to explain our company’s side, clarify the issue, and prevent it from getting out of hand). Action : I drafted a statement that balanced empathy, understanding, and utmost customer service with facts, logic, and fairness. It was direct, simple, succinct, and phrased to highlight our brand values while addressing the issue in a logical yet sensitive way. We also tapped our influencer partners to subtly and indirectly share their positive experiences with our brand so we could counter the negative content being shared online. Result : We got the results we worked for through proper communication and a positive and strategic campaign. The irate client agreed to have a dialogue with us. She apologized to us, and we reaffirmed our commitment to delivering quality service to all. We assured her that she can reach out to us anytime regarding her purchases and that we’d gladly accommodate her requests whenever possible. She also retracted her negative statements in her vlog and urged her followers to keep supporting our brand.
What Are Good Outcomes of Problem Solving?
Whenever you answer interview questions about problem solving or share examples of problem solving in a cover letter, you want to be sure you’re sharing a positive outcome.
Below are good outcomes of problem solving:
- Saving the company time or money
- Making the company money
- Pleasing/keeping a customer
- Obtaining new customers
- Solving a safety issue
- Solving a staffing/scheduling issue
- Solving a logistical issue
- Solving a company hiring issue
- Solving a technical/software issue
- Making a process more efficient and faster for the company
- Creating a new business process to make the company more profitable
- Improving the company’s brand/image/reputation
- Getting the company positive reviews from customers/clients
Every employer wants to make more money, save money, and save time. If you can assess your problem solving experience and think about how you’ve helped past employers in those three areas, then that’s a great start. That’s where I recommend you begin looking for stories of times you had to solve problems.
Tips to Improve Your Problem Solving Skills
Throughout your career, you’re going to get hired for better jobs and earn more money if you can show employers that you’re a problem solver. So to improve your problem solving skills, I recommend always analyzing a problem and situation before acting. When discussing problem solving with employers, you never want to sound like you rush or make impulsive decisions. They want to see fact-based or data-based decisions when you solve problems.
Next, to get better at solving problems, analyze the outcomes of past solutions you came up with. You can recognize what works and what doesn’t. Think about how you can get better at researching and analyzing a situation, but also how you can get better at communicating, deciding the right people in the organization to talk to and “pull in” to help you if needed, etc.
Finally, practice staying calm even in stressful situations. Take a few minutes to walk outside if needed. Step away from your phone and computer to clear your head. A work problem is rarely so urgent that you cannot take five minutes to think (with the possible exception of safety problems), and you’ll get better outcomes if you solve problems by acting logically instead of rushing to react in a panic.
You can use all of the ideas above to describe your problem solving skills when asked interview questions about the topic. If you say that you do the things above, employers will be impressed when they assess your problem solving ability.
If you practice the tips above, you’ll be ready to share detailed, impressive stories and problem solving examples that will make hiring managers want to offer you the job. Every employer appreciates a problem solver, whether solving problems is a requirement listed on the job description or not. And you never know which hiring manager or interviewer will ask you about a time you solved a problem, so you should always be ready to discuss this when applying for a job.
Related interview questions & answers:
- How do you handle stress?
- How do you handle conflict?
- Tell me about a time when you failed

About the Author
Read more articles by Biron Clark
Continue Reading
15 Most Common Pharmacist Interview Questions and Answers
15 most common paralegal interview questions and answers, top 30+ funny interview questions and answers, 60 hardest interview questions and answers, 100+ best ice breaker questions to ask candidates, top 20 situational interview questions (& sample answers), 15 most common physical therapist interview questions and answers, 15 most common project manager interview questions and answers.
Science Friday
Why is solving the plastic problem so hard.
12:12 minutes
- Read Transcript
- More from this episode

One of the biggest environmental issues in our modern world is plastic, which has become integral in the manufacturing of everything from electronics to furniture. Our reliance on plastic has led to a recycling crisis: A vast amount of plastic that winds up in our recycling bins isn’t actually recyclable, and ultimately winds up in landfills.
Large companies have committed to reducing plastic packaging and cutting back on waste. But there’s still no good way to scale up the removal of plastic that already exists. Waste-eating bacteria and enzymes have been shown to work in lab settings, but the scale-up process has a long road ahead.
Judith Enck, former EPA regional administrator and founder of the organization Beyond Plastics, has dedicated her career to advocating for making plastics more recyclable and keeping toxic chemicals out of the manufacturing process. She joins guest host Maggie Koerth to talk about why plastics are such a difficult environmental issue to solve, and what makes her feel hopeful this Earth Day.
Further Reading
- Read about how big companies are trying to address the plastic waste problem via The New York Times.
- Microplastics may be a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, says a study in The New England Journal of Medicine.
- Do bottle bills work? The Public’s Radio investigates.
Donate To Science Friday
Invest in quality science journalism by making a donation to Science Friday.
Segment Guests
Judith Enck is the founder of “Beyond Plastics” in Bennington, Vermont.
Segment Transcript
The transcript of this segment is being processed. It will be available within one week after the show airs.
Meet the Producers and Host
About kathleen davis.
Kathleen Davis is a producer at Science Friday, which means she spends the week brainstorming, researching, and writing, typically in that order. She’s a big fan of stories related to strange animal facts and dystopian technology.
About Maggie Koerth
Maggie Koerth is a science journalist based in Minneapolis, Minnesota.
Explore More
Engineered bacteria might help the dream of mixed plastic recycling.
Using a combination of both chemical and biological processes, this new recycling method may eliminate the need to separate types of plastic.
Is The Plastic In Your Old Barbie Toxic?
The Barbie movie updated Barbie’s image for today's world. But if your Barbie doll was made before 2007, her plastic body might not be safe for kids.
Privacy Overview
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 10 April 2024
A hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm for solving engineering problem
- Jinwei Qiao 1 , 2 ,
- Guangyuan Wang 1 , 2 ,
- Zhi Yang 1 , 2 ,
- Xiaochuan Luo 3 ,
- Jun Chen 1 , 2 ,
- Kan Li 4 &
- Pengbo Liu 1 , 2
Scientific Reports volume 14 , Article number: 8357 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
354 Accesses
Metrics details
- Computational science
- Mechanical engineering
To overcome the disadvantages of premature convergence and easy trapping into local optimum solutions, this paper proposes an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm (named NDWPSO algorithm) based on multiple hybrid strategies. Firstly, the elite opposition-based learning method is utilized to initialize the particle position matrix. Secondly, the dynamic inertial weight parameters are given to improve the global search speed in the early iterative phase. Thirdly, a new local optimal jump-out strategy is proposed to overcome the "premature" problem. Finally, the algorithm applies the spiral shrinkage search strategy from the whale optimization algorithm (WOA) and the Differential Evolution (DE) mutation strategy in the later iteration to accelerate the convergence speed. The NDWPSO is further compared with other 8 well-known nature-inspired algorithms (3 PSO variants and 5 other intelligent algorithms) on 23 benchmark test functions and three practical engineering problems. Simulation results prove that the NDWPSO algorithm obtains better results for all 49 sets of data than the other 3 PSO variants. Compared with 5 other intelligent algorithms, the NDWPSO obtains 69.2%, 84.6%, and 84.6% of the best results for the benchmark function ( \({f}_{1}-{f}_{13}\) ) with 3 kinds of dimensional spaces (Dim = 30,50,100) and 80% of the best optimal solutions for 10 fixed-multimodal benchmark functions. Also, the best design solutions are obtained by NDWPSO for all 3 classical practical engineering problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
A clustering-based competitive particle swarm optimization with grid ranking for multi-objective optimization problems
Qianlin Ye, Zheng Wang, … Mengjiao Yu
A modified shuffled frog leaping algorithm with inertia weight
Zhuanzhe Zhao, Mengxian Wang, … Zhibo Liu

Appropriate noise addition to metaheuristic algorithms can enhance their performance
Kwok Pui Choi, Enzio Hai Hong Kam, … Weng Kee Wong
Introduction
In the ever-changing society, new optimization problems arise every moment, and they are distributed in various fields, such as automation control 1 , statistical physics 2 , security prevention and temperature prediction 3 , artificial intelligence 4 , and telecommunication technology 5 . Faced with a constant stream of practical engineering optimization problems, traditional solution methods gradually lose their efficiency and convenience, making it more and more expensive to solve the problems. Therefore, researchers have developed many metaheuristic algorithms and successfully applied them to the solution of optimization problems. Among them, Particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm 6 is one of the most widely used swarm intelligence algorithms.
However, the basic PSO has a simple operating principle and solves problems with high efficiency and good computational performance, but it suffers from the disadvantages of easily trapping in local optima and premature convergence. To improve the overall performance of the particle swarm algorithm, an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm is proposed by the multiple hybrid strategy in this paper. The improved PSO incorporates the search ideas of other intelligent algorithms (DE, WOA), so the improved algorithm proposed in this paper is named NDWPSO. The main improvement schemes are divided into the following 4 points: Firstly, a strategy of elite opposition-based learning is introduced into the particle population position initialization. A high-quality initialization matrix of population position can improve the convergence speed of the algorithm. Secondly, a dynamic weight methodology is adopted for the acceleration coefficients by combining the iterative map and linearly transformed method. This method utilizes the chaotic nature of the mapping function, the fast convergence capability of the dynamic weighting scheme, and the time-varying property of the acceleration coefficients. Thus, the global search and local search of the algorithm are balanced and the global search speed of the population is improved. Thirdly, a determination mechanism is set up to detect whether the algorithm falls into a local optimum. When the algorithm is “premature”, the population resets 40% of the position information to overcome the local optimum. Finally, the spiral shrinking mechanism combined with the DE/best/2 position mutation is used in the later iteration, which further improves the solution accuracy.
The structure of the paper is given as follows: Sect. “ Particle swarm optimization (PSO) ” describes the principle of the particle swarm algorithm. Section “ Improved particle swarm optimization algorithm ” shows the detailed improvement strategy and a comparison experiment of inertia weight is set up for the proposed NDWPSO. Section “ Experiment and discussion ” includes the experimental and result discussion sections on the performance of the improved algorithm. Section “ Conclusions and future works ” summarizes the main findings of this study.
Literature review
This section reviews some metaheuristic algorithms and other improved PSO algorithms. A simple discussion about recently proposed research studies is given.
Metaheuristic algorithms
A series of metaheuristic algorithms have been proposed in recent years by using various innovative approaches. For instance, Lin et al. 7 proposed a novel artificial bee colony algorithm (ABCLGII) in 2018 and compared ABCLGII with other outstanding ABC variants on 52 frequently used test functions. Abed-alguni et al. 8 proposed an exploratory cuckoo search (ECS) algorithm in 2021 and carried out several experiments to investigate the performance of ECS by 14 benchmark functions. Brajević 9 presented a novel shuffle-based artificial bee colony (SB-ABC) algorithm for solving integer programming and minimax problems in 2021. The experiments are tested on 7 integer programming problems and 10 minimax problems. In 2022, Khan et al. 10 proposed a non-deterministic meta-heuristic algorithm called Non-linear Activated Beetle Antennae Search (NABAS) for a non-convex tax-aware portfolio selection problem. Brajević et al. 11 proposed a hybridization of the sine cosine algorithm (HSCA) in 2022 to solve 15 complex structural and mechanical engineering design optimization problems. Abed-Alguni et al. 12 proposed an improved Salp Swarm Algorithm (ISSA) in 2022 for single-objective continuous optimization problems. A set of 14 standard benchmark functions was used to evaluate the performance of ISSA. In 2023, Nadimi et al. 13 proposed a binary starling murmuration optimization (BSMO) to select the effective features from different important diseases. In the same year, Nadimi et al. 14 systematically reviewed the last 5 years' developments of WOA and made a critical analysis of those WOA variants. In 2024, Fatahi et al. 15 proposed an Improved Binary Quantum-based Avian Navigation Optimizer Algorithm (IBQANA) for the Feature Subset Selection problem in the medical area. Experimental evaluation on 12 medical datasets demonstrates that IBQANA outperforms 7 established algorithms. Abed-alguni et al. 16 proposed an Improved Binary DJaya Algorithm (IBJA) to solve the Feature Selection problem in 2024. The IBJA’s performance was compared against 4 ML classifiers and 10 efficient optimization algorithms.
Improved PSO algorithms
Many researchers have constantly proposed some improved PSO algorithms to solve engineering problems in different fields. For instance, Yeh 17 proposed an improved particle swarm algorithm, which combines a new self-boundary search and a bivariate update mechanism, to solve the reliability redundancy allocation problem (RRAP) problem. Solomon et al. 18 designed a collaborative multi-group particle swarm algorithm with high parallelism that was used to test the adaptability of Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) in distributed computing environments. Mukhopadhyay and Banerjee 19 proposed a chaotic multi-group particle swarm optimization (CMS-PSO) to estimate the unknown parameters of an autonomous chaotic laser system. Duan et al. 20 designed an improved particle swarm algorithm with nonlinear adjustment of inertia weights to improve the coupling accuracy between laser diodes and single-mode fibers. Sun et al. 21 proposed a particle swarm optimization algorithm combined with non-Gaussian stochastic distribution for the optimal design of wind turbine blades. Based on a multiple swarm scheme, Liu et al. 22 proposed an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm to predict the temperatures of steel billets for the reheating furnace. In 2022, Gad 23 analyzed the existing 2140 papers on Swarm Intelligence between 2017 and 2019 and pointed out that the PSO algorithm still needs further research. In general, the improved methods can be classified into four categories:
Adjusting the distribution of algorithm parameters. Feng et al. 24 used a nonlinear adaptive method on inertia weights to balance local and global search and introduced asynchronously varying acceleration coefficients.
Changing the updating formula of the particle swarm position. Both papers 25 and 26 used chaotic mapping functions to update the inertia weight parameters and combined them with a dynamic weighting strategy to update the particle swarm positions. This improved approach enables the particle swarm algorithm to be equipped with fast convergence of performance.
The initialization of the swarm. Alsaidy and Abbood proposed 27 a hybrid task scheduling algorithm that replaced the random initialization of the meta-heuristic algorithm with the heuristic algorithms MCT-PSO and LJFP-PSO.
Combining with other intelligent algorithms: Liu et al. 28 introduced the differential evolution (DE) algorithm into PSO to increase the particle swarm as diversity and reduce the probability of the population falling into local optimum.
Particle swarm optimization (PSO)
The particle swarm optimization algorithm is a population intelligence algorithm for solving continuous and discrete optimization problems. It originated from the social behavior of individuals in bird and fish flocks 6 . The core of the PSO algorithm is that an individual particle identifies potential solutions by flight in a defined constraint space adjusts its exploration direction to approach the global optimal solution based on the shared information among the group, and finally solves the optimization problem. Each particle \(i\) includes two attributes: velocity vector \({V}_{i}=\left[{v}_{i1},{v}_{i2},{v}_{i3},{...,v}_{ij},{...,v}_{iD},\right]\) and position vector \({X}_{i}=[{x}_{i1},{x}_{i2},{x}_{i3},...,{x}_{ij},...,{x}_{iD}]\) . The velocity vector is used to modify the motion path of the swarm; the position vector represents a potential solution for the optimization problem. Here, \(j=\mathrm{1,2},\dots ,D\) , \(D\) represents the dimension of the constraint space. The equations for updating the velocity and position of the particle swarm are shown in Eqs. ( 1 ) and ( 2 ).
Here \({Pbest}_{i}^{k}\) represents the previous optimal position of the particle \(i\) , and \({Gbest}\) is the optimal position discovered by the whole population. \(i=\mathrm{1,2},\dots ,n\) , \(n\) denotes the size of the particle swarm. \({c}_{1}\) and \({c}_{2}\) are the acceleration constants, which are used to adjust the search step of the particle 29 . \({r}_{1}\) and \({r}_{2}\) are two random uniform values distributed in the range \([\mathrm{0,1}]\) , which are used to improve the randomness of the particle search. \(\omega\) inertia weight parameter, which is used to adjust the scale of the search range of the particle swarm 30 . The basic PSO sets the inertia weight parameter as a time-varying parameter to balance global exploration and local seeking. The updated equation of the inertia weight parameter is given as follows:
where \({\omega }_{max}\) and \({\omega }_{min}\) represent the upper and lower limits of the range of inertia weight parameter. \(k\) and \(Mk\) are the current iteration and maximum iteration.
Improved particle swarm optimization algorithm
According to the no free lunch theory 31 , it is known that no algorithm can solve every practical problem with high quality and efficiency for increasingly complex and diverse optimization problems. In this section, several improvement strategies are proposed to improve the search efficiency and overcome this shortcoming of the basic PSO algorithm.
Improvement strategies
The optimization strategies of the improved PSO algorithm are shown as follows:
The inertia weight parameter is updated by an improved chaotic variables method instead of a linear decreasing strategy. Chaotic mapping performs the whole search at a higher speed and is more resistant to falling into local optimal than the probability-dependent random search 32 . However, the population may result in that particles can easily fly out of the global optimum boundary. To ensure that the population can converge to the global optimum, an improved Iterative mapping is adopted and shown as follows:
Here \({\omega }_{k}\) is the inertia weight parameter in the iteration \(k\) , \(b\) is the control parameter in the range \([\mathrm{0,1}]\) .
The acceleration coefficients are updated by the linear transformation. \({c}_{1}\) and \({c}_{2}\) represent the influential coefficients of the particles by their own and population information, respectively. To improve the search performance of the population, \({c}_{1}\) and \({c}_{2}\) are changed from fixed values to time-varying parameter parameters, that are updated by linear transformation with the number of iterations:
where \({c}_{max}\) and \({c}_{min}\) are the maximum and minimum values of acceleration coefficients, respectively.
The initialization scheme is determined by elite opposition-based learning . The high-quality initial population will accelerate the solution speed of the algorithm and improve the accuracy of the optimal solution. Thus, the elite backward learning strategy 33 is introduced to generate the position matrix of the initial population. Suppose the elite individual of the population is \({X}=[{x}_{1},{x}_{2},{x}_{3},...,{x}_{j},...,{x}_{D}]\) , and the elite opposition-based solution of \(X\) is \({X}_{o}=[{x}_{{\text{o}}1},{x}_{{\text{o}}2},{x}_{{\text{o}}3},...,{x}_{oj},...,{x}_{oD}]\) . The formula for the elite opposition-based solution is as follows:
where \({k}_{r}\) is the random value in the range \((\mathrm{0,1})\) . \({ux}_{oij}\) and \({lx}_{oij}\) are dynamic boundaries of the elite opposition-based solution in \(j\) dimensional variables. The advantage of dynamic boundary is to reduce the exploration space of particles, which is beneficial to the convergence of the algorithm. When the elite opposition-based solution is out of bounds, the out-of-bounds processing is performed. The equation is given as follows:
After calculating the fitness function values of the elite solution and the elite opposition-based solution, respectively, \(n\) high quality solutions were selected to form a new initial population position matrix.
The position updating Eq. ( 2 ) is modified based on the strategy of dynamic weight. To improve the speed of the global search of the population, the strategy of dynamic weight from the artificial bee colony algorithm 34 is introduced to enhance the computational performance. The new position updating equation is shown as follows:
Here \(\rho\) is the random value in the range \((\mathrm{0,1})\) . \(\psi\) represents the acceleration coefficient and \({\omega }{\prime}\) is the dynamic weight coefficient. The updated equations of the above parameters are as follows:
where \(f(i)\) denotes the fitness function value of individual particle \(i\) and u is the average of the population fitness function values in the current iteration. The Eqs. ( 11 , 12 ) are introduced into the position updating equation. And they can attract the particle towards positions of the best-so-far solution in the search space.
New local optimal jump-out strategy is added for escaping from the local optimal. When the value of the fitness function for the population optimal particles does not change in M iterations, the algorithm determines that the population falls into a local optimal. The scheme in which the population jumps out of the local optimum is to reset the position information of the 40% of individuals within the population, in other words, to randomly generate the position vector in the search space. M is set to 5% of the maximum number of iterations.
New spiral update search strategy is added after the local optimal jump-out strategy. Since the whale optimization algorithm (WOA) was good at exploring the local search space 35 , the spiral update search strategy in the WOA 36 is introduced to update the position of the particles after the swarm jumps out of local optimal. The equation for the spiral update is as follows:
Here \(D=\left|{x}_{i}\left(k\right)-Gbest\right|\) denotes the distance between the particle itself and the global optimal solution so far. \(B\) is the constant that defines the shape of the logarithmic spiral. \(l\) is the random value in \([-\mathrm{1,1}]\) . \(l\) represents the distance between the newly generated particle and the global optimal position, \(l=-1\) means the closest distance, while \(l=1\) means the farthest distance, and the meaning of this parameter can be directly observed by Fig. 1 .
Spiral updating position.
The DE/best/2 mutation strategy is introduced to form the mutant particle. 4 individuals in the population are randomly selected that differ from the current particle, then the vector difference between them is rescaled, and the difference vector is combined with the global optimal position to form the mutant particle. The equation for mutation of particle position is shown as follows:
where \({x}^{*}\) is the mutated particle, \(F\) is the scale factor of mutation, \({r}_{1}\) , \({r}_{2}\) , \({r}_{3}\) , \({r}_{4}\) are random integer values in \((0,n]\) and not equal to \(i\) , respectively. Specific particles are selected for mutation with the screening conditions as follows:
where \(Cr\) represents the probability of mutation, \(rand\left(\mathrm{0,1}\right)\) is a random number in \(\left(\mathrm{0,1}\right)\) , and \({i}_{rand}\) is a random integer value in \((0,n]\) .
The improved PSO incorporates the search ideas of other intelligent algorithms (DE, WOA), so the improved algorithm proposed in this paper is named NDWPSO. The pseudo-code for the NDWPSO algorithm is given as follows:

The main procedure of NDWPSO.
Comparing the distribution of inertia weight parameters
There are several improved PSO algorithms (such as CDWPSO 25 , and SDWPSO 26 ) that adopt the dynamic weighted particle position update strategy as their improvement strategy. The updated equations of the CDWPSO and the SDWPSO algorithm for the inertia weight parameters are given as follows:
where \({\text{A}}\) is a value in \((\mathrm{0,1}]\) . \({r}_{max}\) and \({r}_{min}\) are the upper and lower limits of the fluctuation range of the inertia weight parameters, \(k\) is the current number of algorithm iterations, and \(Mk\) denotes the maximum number of iterations.
Considering that the update method of inertia weight parameters by our proposed NDWPSO is comparable to the CDWPSO, and SDWPSO, a comparison experiment for the distribution of inertia weight parameters is set up in this section. The maximum number of iterations in the experiment is \(Mk=500\) . The distributions of CDWPSO, SDWPSO, and NDWPSO inertia weights are shown sequentially in Fig. 2 .
The inertial weight distribution of CDWPSO, SDWPSO, and NDWPSO.
In Fig. 2 , the inertia weight value of CDWPSO is a random value in (0,1]. It may make individual particles fly out of the range in the late iteration of the algorithm. Similarly, the inertia weight value of SDWPSO is a value that tends to zero infinitely, so that the swarm no longer can fly in the search space, making the algorithm extremely easy to fall into the local optimal value. On the other hand, the distribution of the inertia weights of the NDWPSO forms a gentle slope by two curves. Thus, the swarm can faster lock the global optimum range in the early iterations and locate the global optimal more precisely in the late iterations. The reason is that the inertia weight values between two adjacent iterations are inversely proportional to each other. Besides, the time-varying part of the inertial weight within NDWPSO is designed to reduce the chaos characteristic of the parameters. The inertia weight value of NDWPSO avoids the disadvantages of the above two schemes, so its design is more reasonable.
Experiment and discussion
In this section, three experiments are set up to evaluate the performance of NDWPSO: (1) the experiment of 23 classical functions 37 between NDWPSO and three particle swarm algorithms (PSO 6 , CDWPSO 25 , SDWPSO 26 ); (2) the experiment of benchmark test functions between NDWPSO and other intelligent algorithms (Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) 36 , Harris Hawk Algorithm (HHO) 38 , Gray Wolf Optimization Algorithm (GWO) 39 , Archimedes Algorithm (AOA) 40 , Equilibrium Optimizer (EO) 41 and Differential Evolution (DE) 42 ); (3) the experiment for solving three real engineering problems (welded beam design 43 , pressure vessel design 44 , and three-bar truss design 38 ). All experiments are run on a computer with Intel i5-11400F GPU, 2.60 GHz, 16 GB RAM, and the code is written with MATLAB R2017b.
The benchmark test functions are 23 classical functions, which consist of indefinite unimodal (F1–F7), indefinite dimensional multimodal functions (F8–F13), and fixed-dimensional multimodal functions (F14–F23). The unimodal benchmark function is used to evaluate the global search performance of different algorithms, while the multimodal benchmark function reflects the ability of the algorithm to escape from the local optimal. The mathematical equations of the benchmark functions are shown and found as Supplementary Tables S1 – S3 online.
Experiments on benchmark functions between NDWPSO, and other PSO variants
The purpose of the experiment is to show the performance advantages of the NDWPSO algorithm. Here, the dimensions and corresponding population sizes of 13 benchmark functions (7 unimodal and 6 multimodal) are set to (30, 40), (50, 70), and (100, 130). The population size of 10 fixed multimodal functions is set to 40. Each algorithm is repeated 30 times independently, and the maximum number of iterations is 200. The performance of the algorithm is measured by the mean and the standard deviation (SD) of the results for different benchmark functions. The parameters of the NDWPSO are set as: \({[{\omega }_{min},\omega }_{max}]=[\mathrm{0.4,0.9}]\) , \(\left[{c}_{max},{c}_{min}\right]=\left[\mathrm{2.5,1.5}\right],{V}_{max}=0.1,b={e}^{-50}, M=0.05\times Mk, B=1,F=0.7, Cr=0.9.\) And, \(A={\omega }_{max}\) for CDWPSO; \({[r}_{max},{r}_{min}]=[\mathrm{4,0}]\) for SDWPSO.
Besides, the experimental data are retained to two decimal places, but some experimental data will increase the number of retained data to pursue more accuracy in comparison. The best results in each group of experiments will be displayed in bold font. The experimental data is set to 0 if the value is below 10 –323 . The experimental parameter settings in this paper are different from the references (PSO 6 , CDWPSO 25 , SDWPSO 26 , so the final experimental data differ from the ones within the reference.
As shown in Tables 1 and 2 , the NDWPSO algorithm obtains better results for all 49 sets of data than other PSO variants, which include not only 13 indefinite-dimensional benchmark functions and 10 fixed-multimodal benchmark functions. Remarkably, the SDWPSO algorithm obtains the same accuracy of calculation as NDWPSO for both unimodal functions f 1 –f 4 and multimodal functions f 9 –f 11 . The solution accuracy of NDWPSO is higher than that of other PSO variants for fixed-multimodal benchmark functions f 14 -f 23 . The conclusion can be drawn that the NDWPSO has excellent global search capability, local search capability, and the capability for escaping the local optimal.
In addition, the convergence curves of the 23 benchmark functions are shown in Figs. 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 and 19 . The NDWPSO algorithm has a faster convergence speed in the early stage of the search for processing functions f1-f6, f8-f14, f16, f17, and finds the global optimal solution with a smaller number of iterations. In the remaining benchmark function experiments, the NDWPSO algorithm shows no outstanding performance for convergence speed in the early iterations. There are two reasons of no outstanding performance in the early iterations. On one hand, the fixed-multimodal benchmark function has many disturbances and local optimal solutions in the whole search space. on the other hand, the initialization scheme based on elite opposition-based learning is still stochastic, which leads to the initial position far from the global optimal solution. The inertia weight based on chaotic mapping and the strategy of spiral updating can significantly improve the convergence speed and computational accuracy of the algorithm in the late search stage. Finally, the NDWPSO algorithm can find better solutions than other algorithms in the middle and late stages of the search.
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f1 (Dim = 30,50,100).
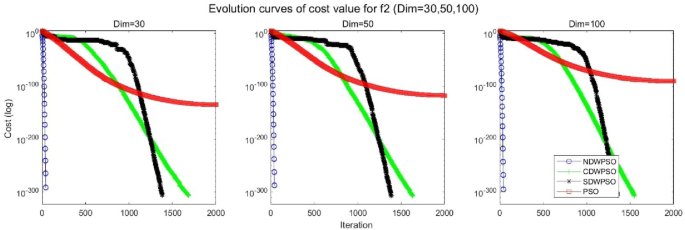
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f2 (Dim = 30,50,100).
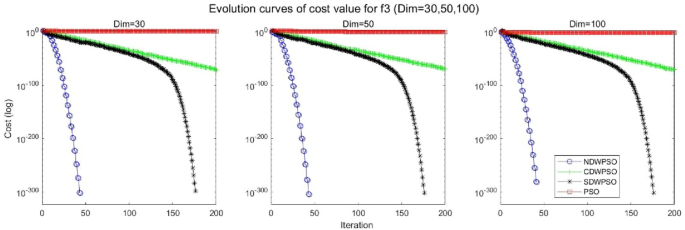
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f3 (Dim = 30,50,100).
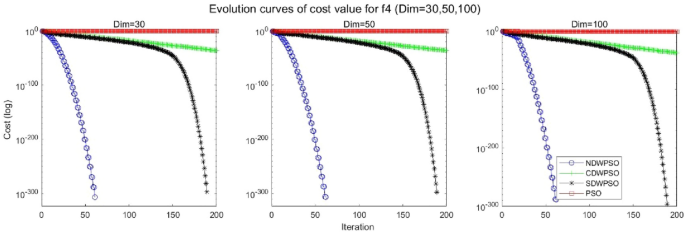
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f4 (Dim = 30,50,100).
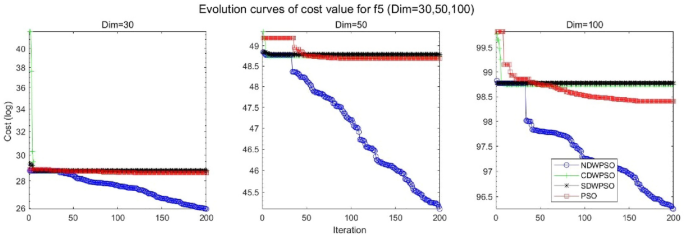
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f5 (Dim = 30,50,100).
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f6 (Dim = 30,50,100).
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f7 (Dim = 30,50,100).
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f8 (Dim = 30,50,100).
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f9 (Dim = 30,50,100).
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f10 (Dim = 30,50,100).
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f11(Dim = 30,50,100).
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f12 (Dim = 30,50,100).
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f13 (Dim = 30,50,100).
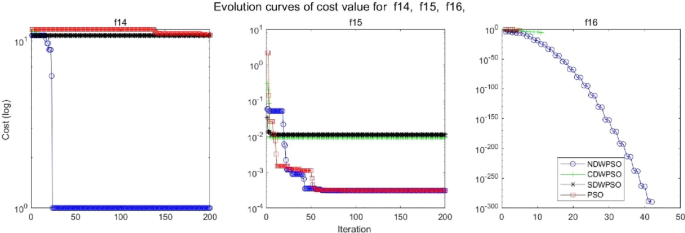
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f14, f15, f16.
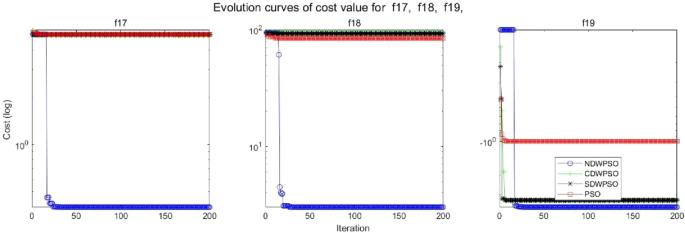
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f17, f18, f19.
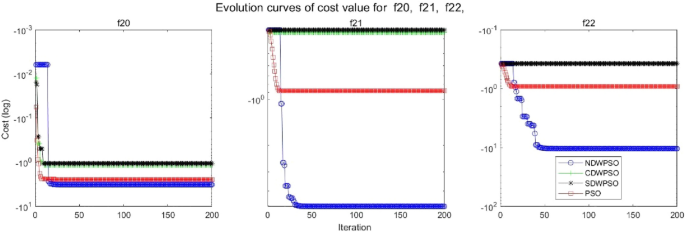
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f20, f21, f22.
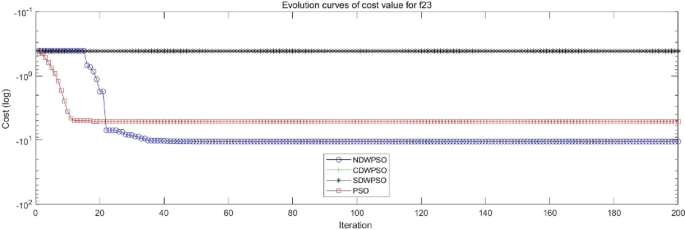
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms for f23.
To evaluate the performance of different PSO algorithms, a statistical test is conducted. Due to the stochastic nature of the meta-heuristics, it is not enough to compare algorithms based on only the mean and standard deviation values. The optimization results cannot be assumed to obey the normal distribution; thus, it is necessary to judge whether the results of the algorithms differ from each other in a statistically significant way. Here, the Wilcoxon non-parametric statistical test 45 is used to obtain a parameter called p -value to verify whether two sets of solutions are different to a statistically significant extent or not. Generally, it is considered that p ≤ 0.5 can be considered as a statistically significant superiority of the results. The p -values calculated in Wilcoxon’s rank-sum test comparing NDWPSO and other PSO algorithms are listed in Table 3 for all benchmark functions. The p -values in Table 3 additionally present the superiority of the NDWPSO because all of the p -values are much smaller than 0.5.
In general, the NDWPSO has the fastest convergence rate when finding the global optimum from Figs. 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 and 19 , and thus we can conclude that the NDWPSO is superior to the other PSO variants during the process of optimization.
Comparison experiments between NDWPSO and other intelligent algorithms
Experiments are conducted to compare NDWPSO with several other intelligent algorithms (WOA, HHO, GWO, AOA, EO and DE). The experimental object is 23 benchmark functions, and the experimental parameters of the NDWPSO algorithm are set the same as in Experiment 4.1. The maximum number of iterations of the experiment is increased to 2000 to fully demonstrate the performance of each algorithm. Each algorithm is repeated 30 times individually. The parameters of the relevant intelligent algorithms in the experiments are set as shown in Table 4 . To ensure the fairness of the algorithm comparison, all parameters are concerning the original parameters in the relevant algorithm literature. The experimental results are shown in Tables 5 , 6 , 7 and 8 and Figs. 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 and 36 .
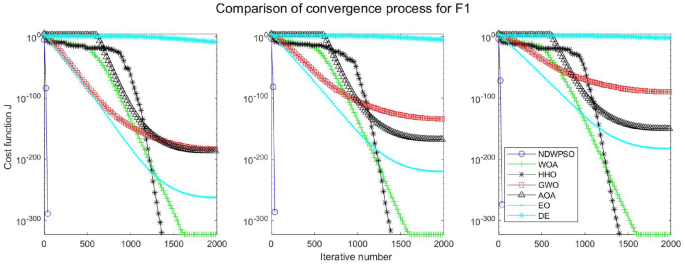
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f1 (Dim = 30,50,100).
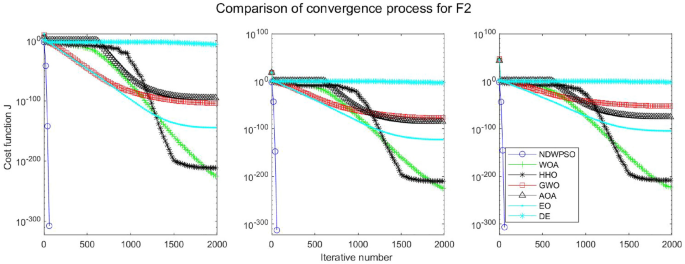
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f2 (Dim = 30,50,100).
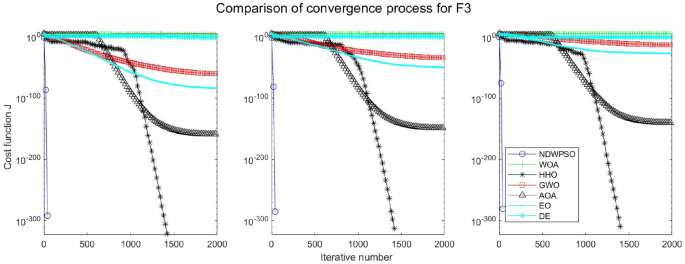
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f3(Dim = 30,50,100).
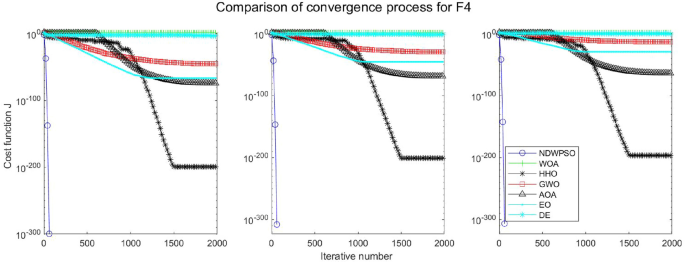
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f4 (Dim = 30,50,100).
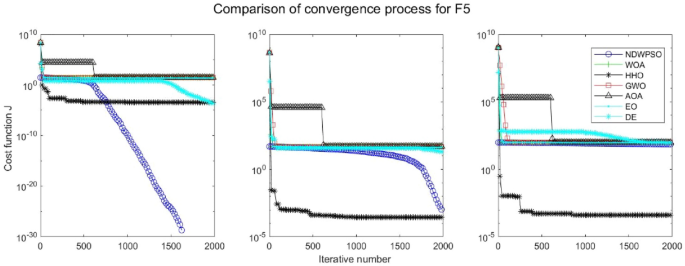
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f5 (Dim = 30,50,100).
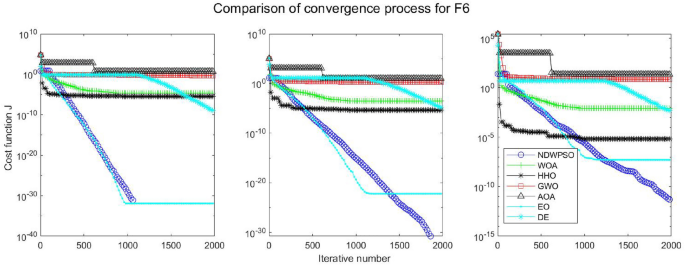
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f6 (Dim = 30,50,100).
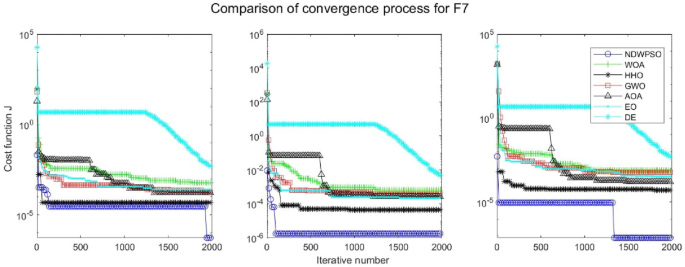
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f7 (Dim = 30,50,100).
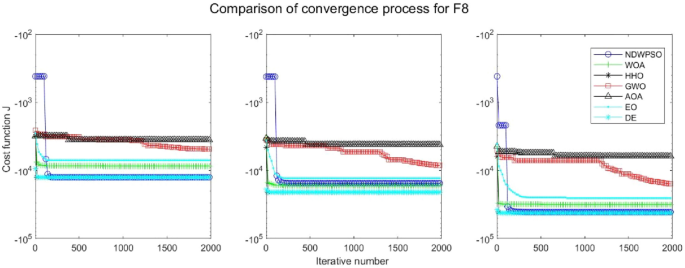
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f8 (Dim = 30,50,100).
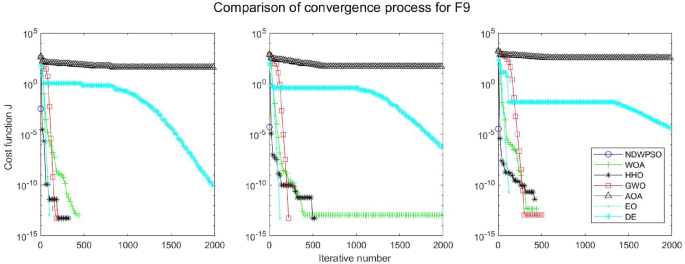
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f9(Dim = 30,50,100).
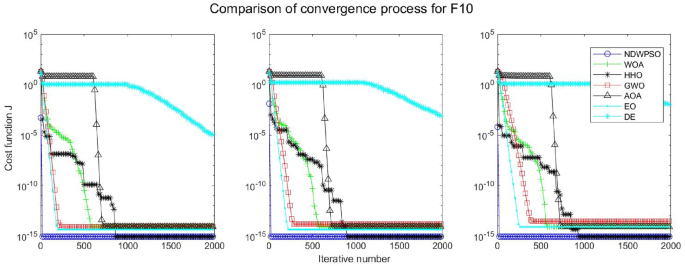
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f10 (Dim = 30,50,100).
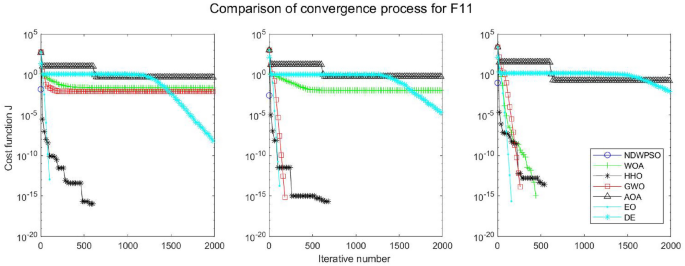
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f11 (Dim = 30,50,100).
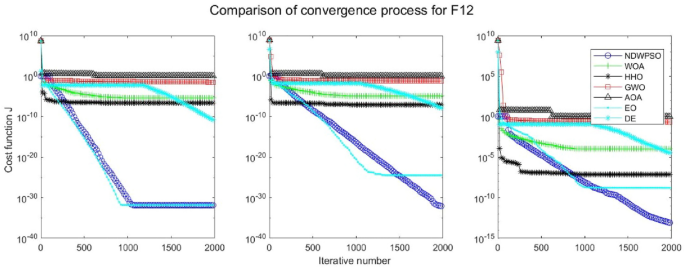
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f12 (Dim = 30,50,100).
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f13 (Dim = 30,50,100).
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f14, f15, f16.
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f17, f18, f19.
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f20, f21, f22.
Evolution curve of NDWPSO and other algorithms for f23.
The experimental data of NDWPSO and other intelligent algorithms for handling 30, 50, and 100-dimensional benchmark functions ( \({f}_{1}-{f}_{13}\) ) are recorded in Tables 8 , 9 and 10 , respectively. The comparison data of fixed-multimodal benchmark tests ( \({f}_{14}-{f}_{23}\) ) are recorded in Table 11 . According to the data in Tables 5 , 6 and 7 , the NDWPSO algorithm obtains 69.2%, 84.6%, and 84.6% of the best results for the benchmark function ( \({f}_{1}-{f}_{13}\) ) in the search space of three dimensions (Dim = 30, 50, 100), respectively. In Table 8 , the NDWPSO algorithm obtains 80% of the optimal solutions in 10 fixed-multimodal benchmark functions.
The convergence curves of each algorithm are shown in Figs. 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 and 36 . The NDWPSO algorithm demonstrates two convergence behaviors when calculating the benchmark functions in 30, 50, and 100-dimensional search spaces. The first behavior is the fast convergence of NDWPSO with a small number of iterations at the beginning of the search. The reason is that the Iterative-mapping strategy and the position update scheme of dynamic weighting are used in the NDWPSO algorithm. This scheme can quickly target the region in the search space where the global optimum is located, and then precisely lock the optimal solution. When NDWPSO processes the functions \({f}_{1}-{f}_{4}\) , and \({f}_{9}-{f}_{11}\) , the behavior can be reflected in the convergence trend of their corresponding curves. The second behavior is that NDWPSO gradually improves the convergence accuracy and rapidly approaches the global optimal in the middle and late stages of the iteration. The NDWPSO algorithm fails to converge quickly in the early iterations, which is possible to prevent the swarm from falling into a local optimal. The behavior can be demonstrated by the convergence trend of the curves when NDWPSO handles the functions \({f}_{6}\) , \({f}_{12}\) , and \({f}_{13}\) , and it also shows that the NDWPSO algorithm has an excellent ability of local search.
Combining the experimental data with the convergence curves, it is concluded that the NDWPSO algorithm has a faster convergence speed, so the effectiveness and global convergence of the NDWPSO algorithm are more outstanding than other intelligent algorithms.
Experiments on classical engineering problems
Three constrained classical engineering design problems (welded beam design, pressure vessel design 43 , and three-bar truss design 38 ) are used to evaluate the NDWPSO algorithm. The experiments are the NDWPSO algorithm and 5 other intelligent algorithms (WOA 36 , HHO, GWO, AOA, EO 41 ). Each algorithm is provided with the maximum number of iterations and population size ( \({\text{Mk}}=500,\mathrm{ n}=40\) ), and then repeats 30 times, independently. The parameters of the algorithms are set the same as in Table 4 . The experimental results of three engineering design problems are recorded in Tables 9 , 10 and 11 in turn. The result data is the average value of the solved data.
Welded beam design
The target of the welded beam design problem is to find the optimal manufacturing cost for the welded beam with the constraints, as shown in Fig. 37 . The constraints are the thickness of the weld seam ( \({\text{h}}\) ), the length of the clamped bar ( \({\text{l}}\) ), the height of the bar ( \({\text{t}}\) ) and the thickness of the bar ( \({\text{b}}\) ). The mathematical formulation of the optimization problem is given as follows:
Welded beam design.
In Table 9 , the NDWPSO, GWO, and EO algorithms obtain the best optimal cost. Besides, the standard deviation (SD) of t NDWPSO is the lowest, which means it has very good results in solving the welded beam design problem.
Pressure vessel design
Kannan and Kramer 43 proposed the pressure vessel design problem as shown in Fig. 38 to minimize the total cost, including the cost of material, forming, and welding. There are four design optimized objects: the thickness of the shell \({T}_{s}\) ; the thickness of the head \({T}_{h}\) ; the inner radius \({\text{R}}\) ; the length of the cylindrical section without considering the head \({\text{L}}\) . The problem includes the objective function and constraints as follows:
Pressure vessel design.
The results in Table 10 show that the NDWPSO algorithm obtains the lowest optimal cost with the same constraints and has the lowest standard deviation compared with other algorithms, which again proves the good performance of NDWPSO in terms of solution accuracy.
Three-bar truss design
This structural design problem 44 is one of the most widely-used case studies as shown in Fig. 39 . There are two main design parameters: the area of the bar1 and 3 ( \({A}_{1}={A}_{3}\) ) and area of bar 2 ( \({A}_{2}\) ). The objective is to minimize the weight of the truss. This problem is subject to several constraints as well: stress, deflection, and buckling constraints. The problem is formulated as follows:
Three-bar truss design.
From Table 11 , NDWPSO obtains the best design solution in this engineering problem and has the smallest standard deviation of the result data. In summary, the NDWPSO can reveal very competitive results compared to other intelligent algorithms.
Conclusions and future works
An improved algorithm named NDWPSO is proposed to enhance the solving speed and improve the computational accuracy at the same time. The improved NDWPSO algorithm incorporates the search ideas of other intelligent algorithms (DE, WOA). Besides, we also proposed some new hybrid strategies to adjust the distribution of algorithm parameters (such as the inertia weight parameter, the acceleration coefficients, the initialization scheme, the position updating equation, and so on).
23 classical benchmark functions: indefinite unimodal (f1-f7), indefinite multimodal (f8-f13), and fixed-dimensional multimodal(f14-f23) are applied to evaluate the effective line and feasibility of the NDWPSO algorithm. Firstly, NDWPSO is compared with PSO, CDWPSO, and SDWPSO. The simulation results can prove the exploitative, exploratory, and local optima avoidance of NDWPSO. Secondly, the NDWPSO algorithm is compared with 5 other intelligent algorithms (WOA, HHO, GWO, AOA, EO). The NDWPSO algorithm also has better performance than other intelligent algorithms. Finally, 3 classical engineering problems are applied to prove that the NDWPSO algorithm shows superior results compared to other algorithms for the constrained engineering optimization problems.
Although the proposed NDWPSO is superior in many computation aspects, there are still some limitations and further improvements are needed. The NDWPSO performs a limit initialize on each particle by the strategy of “elite opposition-based learning”, it takes more computation time before speed update. Besides, the” local optimal jump-out” strategy also brings some random process. How to reduce the random process and how to improve the limit initialize efficiency are the issues that need to be further discussed. In addition, in future work, researchers will try to apply the NDWPSO algorithm to wider fields to solve more complex and diverse optimization problems.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Sami, F. Optimize electric automation control using artificial intelligence (AI). Optik 271 , 170085 (2022).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Li, X. et al. Prediction of electricity consumption during epidemic period based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm. Energy Rep. 8 , 437–446 (2022).
Article Google Scholar
Sun, B. Adaptive modified ant colony optimization algorithm for global temperature perception of the underground tunnel fire. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 40 , 102500 (2022).
Bartsch, G. et al. Use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms with gene expression profiling to predict recurrent nonmuscle invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. J. Urol. 195 (2), 493–498 (2016).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bao, Z. Secure clustering strategy based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm in internet of things. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022 , 1–9 (2022).
Google Scholar
Kennedy, J. & Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of ICNN'95-International Conference on Neural Networks . IEEE, 1942–1948 (1995).
Lin, Q. et al. A novel artificial bee colony algorithm with local and global information interaction. Appl. Soft Comput. 62 , 702–735 (2018).
Abed-alguni, B. H. et al. Exploratory cuckoo search for solving single-objective optimization problems. Soft Comput. 25 (15), 10167–10180 (2021).
Brajević, I. A shuffle-based artificial bee colony algorithm for solving integer programming and minimax problems. Mathematics 9 (11), 1211 (2021).
Khan, A. T. et al. Non-linear activated beetle antennae search: A novel technique for non-convex tax-aware portfolio optimization problem. Expert Syst. Appl. 197 , 116631 (2022).
Brajević, I. et al. Hybrid sine cosine algorithm for solving engineering optimization problems. Mathematics 10 (23), 4555 (2022).
Abed-Alguni, B. H., Paul, D. & Hammad, R. Improved Salp swarm algorithm for solving single-objective continuous optimization problems. Appl. Intell. 52 (15), 17217–17236 (2022).
Nadimi-Shahraki, M. H. et al. Binary starling murmuration optimizer algorithm to select effective features from medical data. Appl. Sci. 13 (1), 564 (2022).
Nadimi-Shahraki, M. H. et al. A systematic review of the whale optimization algorithm: Theoretical foundation, improvements, and hybridizations. Archiv. Comput. Methods Eng. 30 (7), 4113–4159 (2023).
Fatahi, A., Nadimi-Shahraki, M. H. & Zamani, H. An improved binary quantum-based avian navigation optimizer algorithm to select effective feature subset from medical data: A COVID-19 case study. J. Bionic Eng. 21 (1), 426–446 (2024).
Abed-alguni, B. H. & AL-Jarah, S. H. IBJA: An improved binary DJaya algorithm for feature selection. J. Comput. Sci. 75 , 102201 (2024).
Yeh, W.-C. A novel boundary swarm optimization method for reliability redundancy allocation problems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 192 , 106060 (2019).
Solomon, S., Thulasiraman, P. & Thulasiram, R. Collaborative multi-swarm PSO for task matching using graphics processing units. In: Proceedings of the 13th Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation 1563–1570 (2011).
Mukhopadhyay, S. & Banerjee, S. Global optimization of an optical chaotic system by chaotic multi swarm particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 39 (1), 917–924 (2012).
Duan, L. et al. Improved particle swarm optimization algorithm for enhanced coupling of coaxial optical communication laser. Opt. Fiber Technol. 64 , 102559 (2021).
Sun, F., Xu, Z. & Zhang, D. Optimization design of wind turbine blade based on an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm combined with non-gaussian distribution. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021 , 1–9 (2021).
Liu, M. et al. An improved particle-swarm-optimization algorithm for a prediction model of steel slab temperature. Appl. Sci. 12 (22), 11550 (2022).
Article MathSciNet CAS Google Scholar
Gad, A. G. Particle swarm optimization algorithm and its applications: A systematic review. Archiv. Comput. Methods Eng. 29 (5), 2531–2561 (2022).
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Feng, H. et al. Trajectory control of electro-hydraulic position servo system using improved PSO-PID controller. Autom. Constr. 127 , 103722 (2021).
Chen, Ke., Zhou, F. & Liu, A. Chaotic dynamic weight particle swarm optimization for numerical function optimization. Knowl. Based Syst. 139 , 23–40 (2018).
Bai, B. et al. Reliability prediction-based improved dynamic weight particle swarm optimization and back propagation neural network in engineering systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 177 , 114952 (2021).
Alsaidy, S. A., Abbood, A. D. & Sahib, M. A. Heuristic initialization of PSO task scheduling algorithm in cloud computing. J. King Saud Univ. –Comput. Inf. Sci. 34 (6), 2370–2382 (2022).
Liu, H., Cai, Z. & Wang, Y. Hybridizing particle swarm optimization with differential evolution for constrained numerical and engineering optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 10 (2), 629–640 (2010).
Deng, W. et al. A novel intelligent diagnosis method using optimal LS-SVM with improved PSO algorithm. Soft Comput. 23 , 2445–2462 (2019).
Huang, M. & Zhen, L. Research on mechanical fault prediction method based on multifeature fusion of vibration sensing data. Sensors 20 (1), 6 (2019).
Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wolpert, D. H. & Macready, W. G. No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1 (1), 67–82 (1997).
Gandomi, A. H. et al. Firefly algorithm with chaos. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 18 (1), 89–98 (2013).
Article ADS MathSciNet Google Scholar
Zhou, Y., Wang, R. & Luo, Q. Elite opposition-based flower pollination algorithm. Neurocomputing 188 , 294–310 (2016).
Li, G., Niu, P. & Xiao, X. Development and investigation of efficient artificial bee colony algorithm for numerical function optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 12 (1), 320–332 (2012).
Xiong, G. et al. Parameter extraction of solar photovoltaic models by means of a hybrid differential evolution with whale optimization algorithm. Solar Energy 176 , 742–761 (2018).
Mirjalili, S. & Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 95 , 51–67 (2016).
Yao, X., Liu, Y. & Lin, G. Evolutionary programming made faster. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 3 (2), 82–102 (1999).
Heidari, A. A. et al. Harris hawks optimization: Algorithm and applications. Fut. Gener. Comput. Syst. 97 , 849–872 (2019).
Mirjalili, S., Mirjalili, S. M. & Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 69 , 46–61 (2014).
Hashim, F. A. et al. Archimedes optimization algorithm: A new metaheuristic algorithm for solving optimization problems. Appl. Intell. 51 , 1531–1551 (2021).
Faramarzi, A. et al. Equilibrium optimizer: A novel optimization algorithm. Knowl. -Based Syst. 191 , 105190 (2020).
Pant, M. et al. Differential evolution: A review of more than two decades of research. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 90 , 103479 (2020).
Coello, C. A. C. Use of a self-adaptive penalty approach for engineering optimization problems. Comput. Ind. 41 (2), 113–127 (2000).
Kannan, B. K. & Kramer, S. N. An augmented lagrange multiplier based method for mixed integer discrete continuous optimization and its applications to mechanical design. J. Mech. Des. 116 , 405–411 (1994).
Derrac, J. et al. A practical tutorial on the use of nonparametric statistical tests as a methodology for comparing evolutionary and swarm intelligence algorithms. Swarm Evol. Comput. 1 (1), 3–18 (2011).
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Key R&D plan of Shandong Province, China (2021CXGC010207, 2023CXGC01020); First batch of talent research projects of Qilu University of Technology in 2023 (2023RCKY116); Introduction of urgently needed talent projects in Key Supported Regions of Shandong Province; Key Projects of Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2020ME116); the Innovation Ability Improvement Project for Technology-based Small- and Medium-sized Enterprises of Shandong Province (2022TSGC2051, 2023TSGC0024, 2023TSGC0931); National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFB1705002), LiaoNing Revitalization Talents Program (XLYC2002041) and Young Innovative Talents Introduction & Cultivation Program for Colleges and Universities of Shandong Province (Granted by Department of Education of Shandong Province, Sub-Title: Innovative Research Team of High Performance Integrated Device).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences), Jinan, 250353, China
Jinwei Qiao, Guangyuan Wang, Zhi Yang, Jun Chen & Pengbo Liu
Shandong Institute of Mechanical Design and Research, Jinan, 250353, China
School of Information Science and Engineering, Northeastern University, Shenyang, 110819, China
Xiaochuan Luo
Fushun Supervision Inspection Institute for Special Equipment, Fushun, 113000, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Z.Y., J.Q., and G.W. wrote the main manuscript text and prepared all figures and tables. J.C., P.L., K.L., and X.L. were responsible for the data curation and software. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Zhi Yang .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Qiao, J., Wang, G., Yang, Z. et al. A hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm for solving engineering problem. Sci Rep 14 , 8357 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-59034-2
Download citation
Received : 11 January 2024
Accepted : 05 April 2024
Published : 10 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-59034-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Particle swarm optimization
- Elite opposition-based learning
- Iterative mapping
- Convergence analysis
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: AI and Robotics newsletter — what matters in AI and robotics research, free to your inbox weekly.
- Computer Vision
- Federated Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
- Natural Language Processing
- New Releases
- AI Dev Tools
- Advisory Board Members
- 🐝 Partnership and Promotion

Machine learning in PDEs employs neural networks to approximate solutions, with two main strategies: global-in-time optimization, like PINN and deep Ritz method, and sequential-in-time optimization, also known as neural Galerkin method. The latter updates the network representation step-by-step, using techniques like TDVP and OBTI. ML also models PDEs from data, utilizing approaches such as neural ODE, graph neural networks, neural Fourier operator, and DeepONet. Natural gradient optimization, rooted in Amari’s work, enhances gradient-based optimization by considering data geometry, leading to faster convergence. They are widely used in various fields, including neural network optimization, reinforcement learning, and PINN training.
The TENG method extends from the Time-Dependent Variational Principle (TDVP) and Optimization-Based Time Integration (OBTI). TENG optimizes the loss function using repeated tangent space approximations, enhancing accuracy in solving PDEs. Unlike TDVP, TENG minimizes inaccuracies caused by tangent space approximations over time steps. Moreover, TENG overcomes the optimization challenges of OBTI, achieving high accuracy with fewer iterations. TENG’s computational complexity is lower than that of TDVP and OBTI due to its sparse update scheme and efficient convergence, making it a promising approach for PDE solutions. Higher-order integration methods can also be seamlessly incorporated into TENG, improving accuracy.
The benchmarking of the TENG method against various approaches showcases its superiority in relative L2 error both over time and globally integrated. TENG-Heun outperforms other methods by orders of magnitude, with TENG-Euler already comparable to or better than TDVP with RK4 integration. TENG-Euler surpasses OBTI with Adam and L-BFGS optimizers, achieving higher accuracy with fewer iterations. The convergence speed of TENG-Euler to machine precision is demonstrated, contrasting starkly with OBTI’s slower convergence. Higher-order integration schemes like TENG-Heun significantly reduce errors, especially for larger time step sizes, demonstrating the efficacy of TENG in achieving high accuracy.
In conclusion, the TENG is an approach for highly accurate and efficient solving of PDEs using natural gradient optimization. TENG, including variants like TENG-Euler and TENG-Heun, outperforms existing methods, achieving machine precision in solving various PDEs. Future work involves exploring TENG’s applicability in diverse real-world scenarios and extending it to broader classes of PDEs. The wider impact of TENG spans multiple fields, including climate modeling and biomedical engineering, with potential societal benefits in environmental forecasting, engineering designs, and medical advancements.
Check out the Paper . All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter . Join our Telegram Channel , Discord Channel , and LinkedIn Gr oup .
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 40k+ ML SubReddit
For Content Partnership, Please Fill Out This Form Here..

Sana Hassan
Sana Hassan, a consulting intern at Marktechpost and dual-degree student at IIT Madras, is passionate about applying technology and AI to address real-world challenges. With a keen interest in solving practical problems, he brings a fresh perspective to the intersection of AI and real-life solutions.
- Sana Hassan https://www.marktechpost.com/author/sana-hassan/ Transforming Partial Differential Equations PDE Solutions with 'TENG': Harnessing Machine Learning for Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency
- Sana Hassan https://www.marktechpost.com/author/sana-hassan/ 'Inheritune' by UT Austin Assists Efficient Language Model Training: Leveraging Inheritance and Reduced Data for Comparable Performance
- Sana Hassan https://www.marktechpost.com/author/sana-hassan/ This AI Paper from MLCommons AI Safety Working Group Introduces v0.5 of the Groundbreaking AI Safety Benchmark
- Sana Hassan https://www.marktechpost.com/author/sana-hassan/ LMEraser: A Novel Machine Unlearning Method for Large Models Ensuring Privacy and Efficiency
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Coix: a jax-based ai framework designed for composing probabilistic programs and performing inference on them, coconut: a high-quality, large-scale dataset for next-gen segmentation models, mupt: a series of pre-trained ai models for symbolic music generation that sets the standard for training open-source symbolic music foundation models, comparative analysis of top 14 vector databases: features, performance, and scalability insights, unveiling challenges in language model performance: a study of saturation and representation degeneration, coix: a jax-based ai framework designed for composing probabilistic programs and performing inference on..., mupt: a series of pre-trained ai models for symbolic music generation that sets the..., transforming teaching: how generative ai is enhancing educator tools and methods, transforming partial differential equations pde solutions with ‘teng’: harnessing machine learning for enhanced accuracy..., mit researchers use deep learning to get a better picture of the atmospheric layer..., 6 free artificial intelligence ai courses from google, ‘inheritune’ by ut austin assists efficient language model training: leveraging inheritance and reduced data....
- AI Magazine
- Privacy & TC
- Cookie Policy
🐝 FREE AI Courses on RAG + Deployment of an Healthcare AI App + LangChain Colab Notebook all included
Thank You 🙌
Privacy Overview

Novel quantum algorithm proposed for high-quality solutions to combinatorial optimization problems
C ombinatorial optimization problems (COPs) have applications in many different fields such as logistics, supply chain management, machine learning, material design and drug discovery, among others, for finding the optimal solution to complex problems. These problems are usually very computationally intensive using classical computers and thus solving COPs using quantum computers has attracted significant attention from both academia and industry.
Quantum computers take advantage of the quantum property of superposition, using specialized qubits, that can exist in an infinite yet contained number of states of 0 or 1 or any combination of the two, to quickly solve large problems. However, when COPs involve constraints, conventional quantum algorithms like adiabatic quantum annealing struggle to obtain a near-optimal solution within the operation time of quantum computers.
Recent advances in quantum technology have led to devices such as quantum annealers and gate-type quantum devices that provide suitable platforms for solving COPs. Unfortunately, they are susceptible to noise, which limits their applicability to quantum algorithms with low computational costs.
To address this challenge, Assistant Professor Tatsuhiko Shirai and Professor Nozomu Togawa from the Department of Computer Science and Communications Engineering at Waseda University in Japan have recently developed a post-processing variationally scheduled quantum algorithm (pVSQA). Their study was published in the journal IEEE Transactions on Quantum Engineering .
"The two main methods for solving COPs with quantum devices are variational scheduling and post-processing. Our algorithm combines variational scheduling with a post-processing method that transforms infeasible solutions into feasible ones, allowing us to achieve near-optimal solutions for constrained COPs on both quantum annealers and gate-based quantum computers," explains Dr. Shirai.
The innovative pVSQA algorithm uses a quantum device to first generate a variational quantum state via quantum computation. This is then used to generate a probability distribution function which consists of all the feasible and infeasible solutions that are within the constraints of the COP.
Next, the post-processing method transforms the infeasible solutions into feasible ones, leaving the probability distribution with only feasible solutions. A classical computer is then used to calculate an energy expectation value of the cost function using this new probability distribution. Repeating this calculation results in a near-optimal solution.
The researchers analyzed the performance of this algorithm using both a simulator and real quantum devices such as a quantum annealer and a gate-type quantum device. The experiments revealed that pVSQA achieves a near-optimal performance within a predetermined time on the simulator and outperforms conventional quantum algorithms without post-processing on real quantum devices.
Dr. Shirai said, "Drastic social transformations are urgently needed to address various social issues. Examples include the realization of a carbon-neutral society to solve climate change issues and the realization of sustainable development goals to address issues such as increased energy demand and food shortage.
"Efficiently solving combinatorial optimization problems is at the heart of achieving these transformations. Our new method will play a significant role in realizing these long-term social transformations."
In conclusion, this study marks a significant step forward for using quantum computers for solving COPs, holding promise for addressing complex real-world problems across various domains.
More information: Tatsuhiko Shirai et al, Post-Processing Variationally Scheduled Quantum Algorithm for Constrained Combinatorial Optimization Problems, IEEE Transactions on Quantum Engineering (2024). DOI: 10.1109/TQE.2024.3376721
Provided by Waseda University

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how to define, generate, evaluate and implement solutions for quality problems using the four-step problem-solving process. Find resources, articles, books, case studies and webcasts on problem solving methods and tools.
Learn how to identify, analyze, and solve problems effectively with a series of tools and tips. Find out how to facilitate a problem-solving process, design a workshop agenda, and choose the right people and approaches.
Learn how to identify, define, formulate, and evaluate solutions to various problems. Find out the different problem-solving strategies, such as heuristics and algorithms, and how to apply them effectively.
Problem-solving is not a flawless process as there are a number of obstacles that can interfere with our ability to solve a problem quickly and efficiently. These obstacles include: Assumptions: When dealing with a problem, people can make assumptions about the constraints and obstacles that prevent certain solutions.
In general, effective problem-solving strategies include the following steps: Define the problem. Come up with alternative solutions. Decide on a solution. Implement the solution. Problem-solving ...
10 effective problem-solving strategies. There are many different ways to approach problem-solving. Each is suitable for different types of problems. The most appropriate problem-solving techniques will depend on your specific problem. You may need to experiment with several strategies before you find a workable solution.
6. Solution implementation. This is what we were waiting for! All problem solving strategies have the end goal of implementing a solution and solving a problem in mind. Remember that in order for any solution to be successful, you need to help your group through all of the previous problem solving steps thoughtfully.
General Problem-Solving Tools. When you understand the problem in front of you, you're ready to start solving it. With your definition to guide you, you can generate several possible solutions, choose the best one, then put it into action. That's the four-step approach at the heart of good problem solving. There are various problem-solving ...
Problem solving is the process of achieving a goal by overcoming obstacles, a frequent part of most activities. Problems in need of solutions range from simple personal tasks (e.g. how to turn on an appliance) to complex issues in business and technical fields. The former is an example of simple problem solving (SPS) addressing one issue ...
There are 4 modules in this course. Problem-solving and effective decision-making are essential skills in today's fast-paced and ever-changing workplace. Both require a systematic yet creative approach to address today's business concerns. This course will teach an overarching process of how to identify problems to generate potential ...
What is problem-solving? Problem-solving is both an ability and a process. As an ability, problem-solving can aid in resolving issues faced in different environments like home, school, abroad, and social situations, among others. As a process, problem-solving involves a series of steps for finding solutions to questions or concerns that arise ...
The A3 problem solving technique is a visual, team-based problem-solving approach that is frequently used in Lean Six Sigma projects. The A3 report is a one-page document that clearly and concisely outlines the problem, root cause analysis, and proposed solution.
How to Solve Problems. To bring the best ideas forward, teams must build psychological safety. by. Laura Amico. October 29, 2021. HBR Staff/EschCollection/Getty Images. Teams today aren't just ...
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
To discuss the art of problem solving, I sat down in California with McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin and also with Charles Conn. Charles is a former McKinsey partner, entrepreneur, executive, and coauthor of the book Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything [John Wiley & Sons, 2018].
7. Work backward. Sometimes the best way to solve a problem is to work backward to solve it. This can be helpful if you need to recreate specific events to locate the root cause of a problem. For example, a car manufacturer may want to produce a vehicle that is better than their competitor's newest model.
Enhance Core Cognitive Skills. Strengthen your memory: Engage in activities that challenge your memory since accurately recalling information is crucial in problem-solving. Techniques such as mnemonic devices or memory palaces can be particularly effective. Build your critical thinking: Regularly question assumptions, evaluate arguments, and ...
Problem solving is the process of finding a resolution for a specific issue or conflict. There are many possible solutions for solving a problem, which is why it's important to go through a problem-solving process to find the best solution. You could use a flathead screwdriver to unscrew a Phillips head screw, but there is a better tool for the ...
How to Solve Problems: 5 Steps. 1. Precisely Identify Problems. As obvious as it seems, identifying the problem is the first step in the problem-solving process. Pinpointing a problem at the beginning of the process will guide your research, collaboration, and solutions in the right direction. At this stage, your task is to identify the scope ...
Problem-Solving Skills Definition. Problem-solving skills are the ability to identify problems, brainstorm and analyze answers, and implement the best solutions. An employee with good problem-solving skills is both a self-starter and a collaborative teammate; they are proactive in understanding the root of a problem and work with others to ...
Moreover, problem-solving can contribute to your overall mental well-being. It can give you a sense of control and agency, reduce feelings of stress and anxiety, and foster a positive attitude. It's also a key component of resilience, the ability to bounce back from adversity. In conclusion, problem-solving is a fundamental skill in life.
Here are the basic steps involved in problem-solving: 1. Define the problem. The first step is to analyze the situation carefully to learn more about the problem. A single situation may solve multiple problems. Identify each problem and determine its cause. Try to anticipate the behavior and response of those affected by the problem.
Examples of Problem Solving Scenarios in the Workplace. Correcting a mistake at work, whether it was made by you or someone else. Overcoming a delay at work through problem solving and communication. Resolving an issue with a difficult or upset customer. Overcoming issues related to a limited budget, and still delivering good work through the ...
4. Implement the Solution. At this stage of problem solving, be prepared for feedback, and plan for this. When you roll out the solution, request feedback on the success of the change made. 5. Review, Iterate, and Improve. Making a change shouldn't be a one time action.
Problem-solving skills are skills that enable people to handle unexpected situations or difficult challenges at work. Organisations need people who can accurately assess problems and come up with effective solutions. In this article, we explain what problem-solving skills are, provide some examples of these skills and outline how to improve them.
Problem-Solving Approach: Design Thinking offers a systematic approach to problem-solving that can be applied to a wide range of challenges, from product design to organizational change. It helps teams break down complex problems, frame them in a human-centered way, and develop practical and effective solutions through iterative prototyping and ...
Why Is Solving The Plastic Problem So Hard? Credit: Shutterstock. One of the biggest environmental issues in our modern world is plastic, which has become integral in the manufacturing of everything from electronics to furniture. Our reliance on plastic has led to a recycling crisis: A vast amount of plastic that winds up in our recycling bins ...
The particle swarm optimization algorithm is a population intelligence algorithm for solving continuous and discrete optimization problems. It originated from the social behavior of individuals in ...
Partial differential equations (PDEs) are required for modeling dynamic systems in science and engineering, but solving them accurately, especially for initial value problems, remains challenging. Integrating machine learning into PDE research has revolutionized both fields, offering new avenues to tackle PDE complexities. ML's ability to approximate complex functions has led to algorithms ...
The proposed algorithm combines variational scheduling with post-processing to achieve near-optimal solutions to combinatorial optimization problems with constraints within the operation time of ...