

Thesis Proposal
Note: This article is partially based on the 2017-2018 MechE Graduate Student Guide (PDF) . Please check the latest guide for the most-up to date formatting requirements.
Criteria for Success
A strong thesis proposal…
- Motivates your project and introduces your audience to the state-of-the-art for the problem you’re working on.
- Explains the limitations in the current methods through literature review and/or original analysis. This should also explain why the limitations matter and why they’re the right ones to focus on.
- Clearly explains your technical approach to make specific improvements to some part of the field.
- Uses original analysis and literature to support the feasibility of the approach.
- Describes what is original about your work.
- Provides a practical outline for completing this research : a degree timeline laying out quantifiable hypotheses, experimental/numerical/theoretical techniques, and metrics for evaluation .
Structure Diagram
Meche-specific structure requirements.
Your thesis proposal should be limited to 6 pages including figures and references.
In addition, you need a cover page that (only) includes:
- tentative title of the thesis
- brief abstract
- committee chair and/or advisor should be indicated
- include their official titles, departmental affiliations, and email addresses
The purpose of your thesis proposal is to introduce your research plan to your thesis committee. You want the committee members to come away understanding what your research will accomplish, why it is needed ( motivation ), how you will do it ( feasibility & approach ), and most importantly, why it is worthy of a PhD ( significance ).
You intend to solve a real and important problem, and you are willing to dedicate years of your life to it, so use your proposal to get the committee excited about your research!
Analyze your audience
Unlike many of the papers and presentations you will write during graduate school, only a select few people will read your thesis proposal. This group will always include your PhD committee and your research advisor, and may include other interested MechE faculty or scientists and engineers at your funding source.
Therefore, you will typically have a good understanding of your audience before it is written. This can allow you to tailor your message to the technical level of your specific audience. If you aren’t sure what your audience could reasonably be expected to know, be conservative! Regardless, your audience is always looking to answer the questions: “ what is this research, how will you perform it, and why does it matter?”
While the small audience may make you less interested in committing time to your proposal, the exercise of motivating and justifying your work plan will be critical to your PhD.
Follow the standard structure for research proposals
While some variation is acceptable, don’t stray too far from the following structure. See also the Structure Diagram above.
- Introduction . Provide only the necessary information to motivate your research, and show how it fits into the broader field. What is the problem you are trying to solve? By the end of the introduction, your audience should understand the basics of what you will do and why you will do it.
- Background/Methodology . Describe the current state of the art and related research fields in sufficient technical detail. The goal is provide just enough detail to give the reader a sound understanding of the limitations and the need for new work. Do not go into detail that does not directly help in understanding your You are not trying to make your reader understand everything about the topic or demonstrate how much you know.
- Objectives . Although not strictly necessary, this section lets you summarize concrete goals of your work, and can help to serve as a checklist for yourself as you move through the process. This is best for projects that tackle many interrelated problems. Think of this as a list of concrete (quantifiable) goals that you want to accomplish.
- Proposed Work. Explain how your work will solve the problems that you have identified. How will you address the objectives above? Provide just enough technical specificity to leave the reader with a firm grasp of what you will do.
- Provide a set of time-structured goals and deliverables. While this is not strictly necessary, your committee will want a timeline when you meet with them, so it can help to start planning now. You want to graduate, so make sure that you have a plan to do so!
- This is a standard section listing references in an appropriate format (MLA, APA, etc.)
Consider the logical sequence of your sections. After the introduction, your audience should be intrigued by a key problem, and intrigued that you know how to solve it. Through the background, they learn that this problem is more difficult than they originally realized. Finally, in the proposed work they learn that your proposal addresses the additional complexity introduced in the background, and they have confidence that you can actually solve the problem.
Summarize the current research field
You need to have a strong grasp of the broader research community. How can you contribute, if you don’t know what is done and what needs to be done?
The point here is not to educate your audience, but rather to provide them with the tools needed to understand your proposal. A common mistake is to explain all of the research that you did to understand your topic and to demonstrate that you really know your field. This will bore your audience, who either already knows this information or does not see why they should care. It’s more important to show where current gaps are. Cut anything that doesn’t answer the what and why of what people are doing. Your depth of knowledge will come through in your thoughtful proposal.
Justify the significance of your work
Answer the question: “What happens if your work is successful?” Again, you are trying to convince your readers either to give you funding or to work with you for three (or more) years. Convince them that your project is worth it.
Your research doesn’t have to revolutionize your field, but you need to explain concretely how it will move your field forward. For example, “Successful development of the proposed model will enable high-fidelity simulation of boiling” is a specific and convincing motivation, compared to, “The field of boiling modeling must be transformed in order to advance research.”
Justify your research plan
Identify the steps needed to overcome your identified problem/limitation. Though your PhD will evolve over time, the tasks and timeline that you identify in your proposal will continue to help determine the trajectory of your research. A good plan now can save a lot of work a few years down the road.
A strong research plan answers three key questions:
- g., “In order to engineer material properties using mesoscopic defects, it is necessary to characterize the defects, measure how they affect material response, and identify techniques to reproducibly create the defects at specific sites within a material.”
- g., “In my PhD, I will focus on developing high-speed dynamic imaging techniques to characterize transient defect states in metallic nanowires. I will then use these techniques to measure the properties of nanowires fabricated with three different processes known to produce different defect structures.”
- How will you evaluate success in each step? These metrics should be concrete and measurable! Putting the thought into metrics now will make it easier for your committee (and yourself) to check a box and say ‘you can graduate.’
Each of these questions should be supported by details that reflect the current state of the art. Technical justification is critical to establish credibility for your plan. Reference the material that you introduced in the background section. You should even use your research plan to tailor your background section so that your committee knows just enough to believe what you’re claiming in your plan.
Based on the tasks and metrics in your plan, establish specific reflection points when you’ll revisit the scope of your project and evaluate if changes are needed.
Include alternative approaches
You won’t be able to predict all of the challenges you will encounter, but planning alternative approaches early on for major methods or decision points will prepare you to make better game-time decisions when you come up against obstacles. e.g.,
I will develop multi-pulse, femtosecond illumination for high speed imaging following Someone et al. Based on the results they have shown, I expect to be able to observe defect dynamics with micron spatial resolution and microsecond temporal resolution. If these resolutions are not achievable in the nanowire systems, I will explore static measurement techniques based on the work of SomeoneElse et al.
Resources and Annotated Examples
Annotated example 1.
This is a recent MechE thesis proposal, written in the style of an IEEE paper. 1,022 KB
Writing a Competitive Preliminary Research Proposal for an Engineering Ph.D. Degree
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Skip to main content
- Main Kingston University site
- About Kingston
- International students
- Our services
- Collaborations
- News and events

Home > Faculty of Engineering, Computing and the Environment > Research > Research degrees > Preparing a proposal
How to prepare a research proposal
A crucial part of a research application is the research proposal. This page provides some guidance on writing a research proposal and includes some suggestions on what to include and what to avoid.
Normally a proposal should be between 1,500 and 2,000 words and will include the following:
- A working title of the topic area: This should do more than convey the key words associated with the proposed research, it should describe the content and direction of your project.
- General overview of area: This should provide a brief overview of the wider background of the proposed research and identify the discipline(s) within which it falls. You might also refer to the way in which your own background gives you competences in your chosen area.
- Identification of the relevant literature: In this section you should develop your proposal to demonstrate that you are aware of the debates and issues raised in relevant bodies of literature, and provide evidence for why you believe your research is needed, using an analysis of published work. References to key articles and texts should be made to show that you appreciate their relevance to your research area. You should demonstrate that your proposed area has not been studied before, so you need to identify your niche which will lead on to the thesis preparation.
- Key research questions: Since you need to demonstrate that the topic can be completed within the normal time period allowed, you need to show that it is manageable, and so focus on key questions within your niche area.
- Aims and objectives: State specific aims and objectives of the research to be undertaken, in a logical sequence.
- Methodology: You need to show how you anticipate achieving your aims, and demonstrate an awareness of the methodological tools available to you and show some understanding of which would be suitable for your research. It may be that a qualitative method, including the analysis of interviews, is appropriate. Alternatively your approach may involve forecasting or statistical, financial or econometric modelling. In other cases you may be combining methodologies. You need to specify the approach you feel will be most appropriate. You should include a back-up plan or risk mitigation in case of unforeseen problems.
- Timescale/research planning: You need to demonstrate an awareness of the need for planning and the timescale of the research. Your timescale should be realistic, taking into account the requirement for upgrade monitoring (PhD applicants) and timely thesis submission. The timeline should show which aspects of the project you will be completing in each year of registration and the anticipated time required for each, and time for writing up the thesis (by the end of month 36 for full-time or month 72 for part-time) should be included. Please note: use month 1, 2, 3 etc in the timeplan/Gantt chart, not calendar months.
- Upgrade Monitoring Report (9-10M FT, 20-22 M PT)
- 2nd year Annual Monitoring Report (21-22M FT, 42-44M PT)
- 3rd year Annual Monitoring Report (33-34M FT, 66-68M PT)
- PhD Thesis Submission or Application for Writing Up Extension (36M FT, 72M PT)
- Apply for Research Ethics Approval (1-6M FT, 1-12M PT)
- Discipline-specific Training (1-9M FT, 1-18M PT)
- Complete Draft Literature Review (6-15M FT, 12-30M PT)
- Data Collection/field work (3-18M FT, 6-36M PT)
- Data Analysis / Experiments / Methodology (ongoing 6-36M FT, 12-72M PT)
- 1st year Internal (seminar/conference) presentation: (6-12M FT, 12-24M PT)
- 2nd year Internal/external (seminar/conference) presentation: (12-24M FT, 24-48M PT)
- 3rd year Internal (seminar/conference) presentation: (24-36M FT, 48-72M PT)
- Bibliography: You should include a short list of references to key articles and texts included in the application.
- Broad topic areas which would be unmanageable as research topics
- Vague descriptions of research areas
- Subject areas where your chosen school has no expertise.
- Plagiarism (for more information, please see Policies and regulations )
Research degrees

- How to apply

- Preparing a proposal

- Research FAQ

- Self-funded PhD project ideas

- Centre for Engineering, Environment and Society Research

- Digital Information Research Centre
- About the Faculty
- Cyber Centre of Excellence
- Undergraduate study
- Postgraduate study
- Faculties and schools
- Services for business
- How to find us
- Website accessibility
- Website feedback
- Freedom of Information
- Wider Information Set
- Privacy Notice
- Charitable status
Kingston University , Holmwood House, Grove Crescent, Kingston upon Thames KT1 2EE . Tel: +44 (0)20 8417 9000
- Department of Materials Science and Engineering
- Postgraduate study
Writing a research proposal
The key feature of your PhD is that it is yours - the topic, planning, motivation, and thinking all come from you. It will be the most challenging type of academic work you have ever done, but also the most rewarding.
The Research Proposal – an outline
The research proposal constitutes the main way in which the department evaluates the potential quality of your PhD plans. The proposal should be approximately 1,500 words in length and include:
- A provisional title
Question or hypothesis
Value of the phd, existing literature, methods of work.
The title indicates the ‘headline’ character of the PhD. It should include any key concepts, empirical focus, or lines of inquiry that you aim to pursue. For example: ‘ High entropy alloys (HEAs) for fusion: Exploration of novel processing routes and HEA stability in extreme environments’, or ‘Tailoring the Thermomechanical Properties of High Performance Aerospace & Automotive Composite Materials’.
You can negotiate changes in the title with your supervisor should you be successful, but it's important to devise a title that describes what you aspire to research – and which looks original and exciting.
You need a question or hypothesis to drive the research forward. The question/hypothesis will provide your motivation; to answer the question or prove/disprove the hypothesis.
The question/hypothesis will need to be something that has not been posed before - this may involve looking at something that nobody has looked at before, or taking a fresh approach to an existing topic or issue.
The aims of your research should be a short list of answers to the question - what will the PhD do? So, for example ‘this PhD will explore...’ or ‘by carrying out this research, I will contribute to debates about...’. The aims are broader than the questions/hypotheses; they give a prospective statement about the overall destination of the PhD and its potential impact.
The value of the PhD follows closely from the aims. Think about how the ways it might improve our understanding of materials - a new process or the generation of new materials? To whom might the PhD be interesting - scholars looking at particular challenges, or specific industries?
A short note of key existing literature situates the PhD in existing research. Literature reviews are not simply descriptive mapping exercises at PhD level - you should identify a small number of key texts and say something about how these books are important for your research, and whether they support, extend, or challenge existing work.
The resources you require can vary according to the nature of your research: access to a particular archive, specialist library, visits to specialised equipment and facilities, the use of analytical software, access to databases, training, workshop attendance and so on. It's important to list any of these resources and give a very brief account of how they will enhance the PhD.
The methods of work is a particularly important section - it's where you can discuss how you will answer your question or prove your hypothesis. It's relatively easy to ask a new question; it is more challenging to set out how you might come up with a convincing answer!
The research also needs a timetable . This should be set out over three years with clear indications of how long you will need to prepare for and carry out research (however defined) and allow time for writing up. Try to be as detailed as you can at this stage.
Each of these criteria helps the Department of Materials Science and Engineering selectors make a good judgement about your proposal. By following these criteria you will have your best chance of getting your proposal accepted.
Three more important points:
- Try to be concise. Don't write too much – be as specific as you can but not wordy. It is a difficult balance to strike.
- Bear in mind that the proposal is a starting point. If you are registered to read for a PhD you will be able to work the proposal through with your supervisor in more detail in the early months.
- Take a look at the department’s staff profiles. Can you identify possible supervisors and intellectual support networks within the department? The better able the department is to support your research, the better it will be for your proposal.
Search for PhD opportunities at Sheffield and be part of our world-leading research.
School of Engineering
Guide to writing a research proposal for an engineering phd.
An important part of your PhD application is the research proposal so we want to know what your research interests are so that we may direct your application to potential supervisors. The proposal does not need be long, but the quality should be high and no more than 2-3 pages should be sufficient. Ideally your proposal should address the points below however as long as we get a clear idea of your research interests then we can consider your application.
- Ensure that your research interests match those in the School of Engineering.
- Outline the main objectives of your research, providing details of two or three key aspects.
- State your target audience for this project.
- Explain what the main outcomes of the project are that you would want to see.
- Outline what methods/approaches you intend to use to achieve the aims of your project.
- Indicate your suggested data collection procedures, including sources and any possible difficulties.
- Explain any analytical techniques you intend to use for your research.
- Broad research areas which would be unmanageable as a PhD topic or that have no relevance to the University of Warwick research areas.
- Vague descriptions of your research interests.
How to write a research proposal
What is a research proposal.
A research proposal should present your idea or question and expected outcomes with clarity and definition – the what.
It should also make a case for why your question is significant and what value it will bring to your discipline – the why.
What it shouldn't do is answer the question – that's what your research will do.
Why is it important?
Research proposals are significant because Another reason why it formally outlines your intended research. Which means you need to provide details on how you will go about your research, including:
- your approach and methodology
- timeline and feasibility
- all other considerations needed to progress your research, such as resources.
Think of it as a tool that will help you clarify your idea and make conducting your research easier.
How long should it be?
Usually no more than 2000 words, but check the requirements of your degree, and your supervisor or research coordinator.
Presenting your idea clearly and concisely demonstrates that you can write this way – an attribute of a potential research candidate that is valued by assessors.
What should it include?
Project title.
Your title should clearly indicate what your proposed research is about.
Research supervisor
State the name, department and faculty or school of the academic who has agreed to supervise you. Rest assured, your research supervisor will work with you to refine your research proposal ahead of submission to ensure it meets the needs of your discipline.
Proposed mode of research
Describe your proposed mode of research. Which may be closely linked to your discipline, and is where you will describe the style or format of your research, e.g. data, field research, composition, written work, social performance and mixed media etc.
This is not required for research in the sciences, but your research supervisor will be able to guide you on discipline-specific requirements.
Aims and objectives
What are you trying to achieve with your research? What is the purpose? This section should reference why you're applying for a research degree. Are you addressing a gap in the current research? Do you want to look at a theory more closely and test it out? Is there something you're trying to prove or disprove? To help you clarify this, think about the potential outcome of your research if you were successful – that is your aim. Make sure that this is a focused statement.
Your objectives will be your aim broken down – the steps to achieving the intended outcome. They are the smaller proof points that will underpin your research's purpose. Be logical in the order of how you present these so that each succeeds the previous, i.e. if you need to achieve 'a' before 'b' before 'c', then make sure you order your objectives a, b, c.
A concise summary of what your research is about. It outlines the key aspects of what you will investigate as well as the expected outcomes. It briefly covers the what, why and how of your research.
A good way to evaluate if you have written a strong synopsis, is to get somebody to read it without reading the rest of your research proposal. Would they know what your research is about?
Now that you have your question clarified, it is time to explain the why. Here, you need to demonstrate an understanding of the current research climate in your area of interest.
Providing context around your research topic through a literature review will show the assessor that you understand current dialogue around your research, and what is published.
Demonstrate you have a strong understanding of the key topics, significant studies and notable researchers in your area of research and how these have contributed to the current landscape.
Expected research contribution
In this section, you should consider the following:
- Why is your research question or hypothesis worth asking?
- How is the current research lacking or falling short?
- What impact will your research have on the discipline?
- Will you be extending an area of knowledge, applying it to new contexts, solving a problem, testing a theory, or challenging an existing one?
- Establish why your research is important by convincing your audience there is a gap.
- What will be the outcome of your research contribution?
- Demonstrate both your current level of knowledge and how the pursuit of your question or hypothesis will create a new understanding and generate new information.
- Show how your research is innovative and original.
Draw links between your research and the faculty or school you are applying at, and explain why you have chosen your supervisor, and what research have they or their school done to reinforce and support your own work. Cite these reasons to demonstrate how your research will benefit and contribute to the current body of knowledge.
Proposed methodology
Provide an overview of the methodology and techniques you will use to conduct your research. Cover what materials and equipment you will use, what theoretical frameworks will you draw on, and how will you collect data.
Highlight why you have chosen this particular methodology, but also why others may not have been as suitable. You need to demonstrate that you have put thought into your approach and why it's the most appropriate way to carry out your research.
It should also highlight potential limitations you anticipate, feasibility within time and other constraints, ethical considerations and how you will address these, as well as general resources.
A work plan is a critical component of your research proposal because it indicates the feasibility of completion within the timeframe and supports you in achieving your objectives throughout your degree.
Consider the milestones you aim to achieve at each stage of your research. A PhD or master's degree by research can take two to four years of full-time study to complete. It might be helpful to offer year one in detail and the following years in broader terms. Ultimately you have to show that your research is likely to be both original and finished – and that you understand the time involved.
Provide details of the resources you will need to carry out your research project. Consider equipment, fieldwork expenses, travel and a proposed budget, to indicate how realistic your research proposal is in terms of financial requirements and whether any adjustments are needed.
Bibliography
Provide a list of references that you've made throughout your research proposal.
Apply for postgraduate study
New hdr curriculum, find a supervisor.
Search by keyword, topic, location, or supervisor name
- 1800 SYD UNI ( 1800 793 864 )
- or +61 2 8627 1444
- Open 9am to 5pm, Monday to Friday
- Student Centre Level 3 Jane Foss Russell Building Darlington Campus
Scholarships
Find the right scholarship for you
Research areas
Our research covers the spectrum – from linguistics to nanoscience
Our breadth of expertise across our faculties and schools is supported by deep disciplinary knowledge. We have significant capability in more than 20 major areas of research.
Research facilities
High-impact research through state-of-the-art infrastructure
Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

- Research Process
Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal
- 5 minute read
- 95.7K views
Table of Contents
The importance of a well-written research proposal cannot be underestimated. Your research really is only as good as your proposal. A poorly written, or poorly conceived research proposal will doom even an otherwise worthy project. On the other hand, a well-written, high-quality proposal will increase your chances for success.
In this article, we’ll outline the basics of writing an effective scientific research proposal, including the differences between research proposals, grants and cover letters. We’ll also touch on common mistakes made when submitting research proposals, as well as a simple example or template that you can follow.
What is a scientific research proposal?
The main purpose of a scientific research proposal is to convince your audience that your project is worthwhile, and that you have the expertise and wherewithal to complete it. The elements of an effective research proposal mirror those of the research process itself, which we’ll outline below. Essentially, the research proposal should include enough information for the reader to determine if your proposed study is worth pursuing.
It is not an uncommon misunderstanding to think that a research proposal and a cover letter are the same things. However, they are different. The main difference between a research proposal vs cover letter content is distinct. Whereas the research proposal summarizes the proposal for future research, the cover letter connects you to the research, and how you are the right person to complete the proposed research.
There is also sometimes confusion around a research proposal vs grant application. Whereas a research proposal is a statement of intent, related to answering a research question, a grant application is a specific request for funding to complete the research proposed. Of course, there are elements of overlap between the two documents; it’s the purpose of the document that defines one or the other.
Scientific Research Proposal Format
Although there is no one way to write a scientific research proposal, there are specific guidelines. A lot depends on which journal you’re submitting your research proposal to, so you may need to follow their scientific research proposal template.
In general, however, there are fairly universal sections to every scientific research proposal. These include:
- Title: Make sure the title of your proposal is descriptive and concise. Make it catch and informative at the same time, avoiding dry phrases like, “An investigation…” Your title should pique the interest of the reader.
- Abstract: This is a brief (300-500 words) summary that includes the research question, your rationale for the study, and any applicable hypothesis. You should also include a brief description of your methodology, including procedures, samples, instruments, etc.
- Introduction: The opening paragraph of your research proposal is, perhaps, the most important. Here you want to introduce the research problem in a creative way, and demonstrate your understanding of the need for the research. You want the reader to think that your proposed research is current, important and relevant.
- Background: Include a brief history of the topic and link it to a contemporary context to show its relevance for today. Identify key researchers and institutions also looking at the problem
- Literature Review: This is the section that may take the longest amount of time to assemble. Here you want to synthesize prior research, and place your proposed research into the larger picture of what’s been studied in the past. You want to show your reader that your work is original, and adds to the current knowledge.
- Research Design and Methodology: This section should be very clearly and logically written and organized. You are letting your reader know that you know what you are going to do, and how. The reader should feel confident that you have the skills and knowledge needed to get the project done.
- Preliminary Implications: Here you’ll be outlining how you anticipate your research will extend current knowledge in your field. You might also want to discuss how your findings will impact future research needs.
- Conclusion: This section reinforces the significance and importance of your proposed research, and summarizes the entire proposal.
- References/Citations: Of course, you need to include a full and accurate list of any and all sources you used to write your research proposal.
Common Mistakes in Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal
Remember, the best research proposal can be rejected if it’s not well written or is ill-conceived. The most common mistakes made include:
- Not providing the proper context for your research question or the problem
- Failing to reference landmark/key studies
- Losing focus of the research question or problem
- Not accurately presenting contributions by other researchers and institutions
- Incompletely developing a persuasive argument for the research that is being proposed
- Misplaced attention on minor points and/or not enough detail on major issues
- Sloppy, low-quality writing without effective logic and flow
- Incorrect or lapses in references and citations, and/or references not in proper format
- The proposal is too long – or too short
Scientific Research Proposal Example
There are countless examples that you can find for successful research proposals. In addition, you can also find examples of unsuccessful research proposals. Search for successful research proposals in your field, and even for your target journal, to get a good idea on what specifically your audience may be looking for.
While there’s no one example that will show you everything you need to know, looking at a few will give you a good idea of what you need to include in your own research proposal. Talk, also, to colleagues in your field, especially if you are a student or a new researcher. We can often learn from the mistakes of others. The more prepared and knowledgeable you are prior to writing your research proposal, the more likely you are to succeed.
Language Editing Services
One of the top reasons scientific research proposals are rejected is due to poor logic and flow. Check out our Language Editing Services to ensure a great proposal , that’s clear and concise, and properly referenced. Check our video for more information, and get started today.

- Manuscript Review
Research Fraud: Falsification and Fabrication in Research Data

Research Team Structure
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
Engineering Proposals: Free Template + 12 Proposal Writing Tips
- Digital Asset Management
- Marketing Technology
Posted by: Cinthya Soto
An engineering service proposal is a standardized document pivotal in guiding the selection of consultants. The engineering proposal is more than just a document; it’s your opportunity to showcase expertise, understanding, and value among the piles of proposals.
Whether you’re a seasoned engineering consultant or a firm stepping into the arena of important projects, your ability to craft a compelling proposal can make all the difference in placing your business ahead of the competition. After all, in 2023 alone companies sourced 39% of their revenue from RFPs .
However, mastering the creation of such a proposal is a complex task. For those wanting to successfully navigate this process, you must be ready to grasp the fundamental concepts of engineering proposals. But what exactly does that include?
In this blog, we’re covering everything there is to know about writing engineering proposals. From what to include in your engineering proposal and writing tips to engineering project proposal examples and a free engineering proposal template, we aim to help you create winning proposals .
How to Write an Engineering Proposal: What to Include
Engineering proposals serve as the critical document on which selections of engineering consultants are based. For consulting firms in the engineering sector, these proposals are the principal tool for winning new contracts. For clients or project owners, they are an invaluable resource to help them choose the best consultants. But what should be included in an engineering proposal format?
Here are the different sections you should include in your engineering proposal:
Cover Page
The cover page of your engineering proposal sets the first impression. It should include the project title, the name of the organization or individual presenting the proposal, the date, and any relevant project identification details. Make sure to keep it professional and clean to reflect the seriousness of your intentions.

Cover Letter
The cover letter personalizes your engineering proposal. It should briefly introduce your organization, express your enthusiasm for the project, and highlight the key points that make your proposal stand out. This is your opportunity to establish a connection with the reader and encourage them to read further.
Introduction
The proposal introduction serves as the executive summary of your proposal. It should include an overview of your organization, the purpose of the proposal, and a summary of what the proposal will cover.
Make sure to clearly define the problem or opportunity your proposal addresses. Essentially, the introduction clarifies the purpose of crafting the proposal. It should lay out the foundation for why the proposal is necessary.
Additionally, the introduction should provide a concise overview of the proposal’s content. This summary needs to be engaging and offer a glimpse of the detailed descriptions to follow. It reveals your core idea and outlines the strategy you intend to use in delivering your services. Here’s an example of what a successful proposal introduction looks like:

Project Background
This section delves into the details of the project. Describe the current situation, the specific problem or opportunity, and the objectives of the project. Providing a concise but thorough background helps the reader understand the context and the necessity of the proposed work.
You should illustrate the issue or situation that led to the creation of your proposal. In this section, it’s important to show a thorough comprehension of the problem at hand.
Qualifications
In this section, highlight your qualifications and experience relevant to the project. Detail your technical expertise, prior successful projects, and any unique skills or resources that make you stand out. This section reassures the client that you are capable of handling the project.
When writing this section, make sure to accurately highlight your skill set to emphasize your suitability for the project at hand. Consider this section as the part of your resume where you detail your skills and experiences.
While you should showcase your expertise, It’s also important to showcase, if relevant, your company’s proficiency and ability to successfully carry out the proposed task.

Project Team
Typically, an engineering proposal requires including details about each team member, their specific roles, and their professional backgrounds. The collective expertise of the project team often plays a critical role in the selection of a qualified engineering consultant, which is why the “Project Team” section is extremely important.
In this section, showcase the team that will work on the project. Ensure that every team member’s relevant experience is detailed in the proposal. Make sure to include brief employee bios in your RFP resumes that highlight each member’s qualifications and relevant experience. Just a few well-crafted sentences on such skills can make a significant difference.

The right tools can help in creating and formatting these bios to present a professional image. With a robust digital asset management (DAM) solution like OpenAsset , you can cut down on the hours spent creating resumes and employee bios for engineering proposals.
A notable feature for employee bios is Content Assist , powered by OpenAsset’s Generative AI. It’s designed to assist users in creating project descriptions and employee bios within OpenAsset. In simple terms, Content Assist will analyze the existing data in your OpenAsset system to create original project descriptions and employee bios.
OpenAsset and the Employee Module enhance productivity within your organization by automating the creation of employee resume documents . This helps you present your team in the best light possible and quickest way possible.
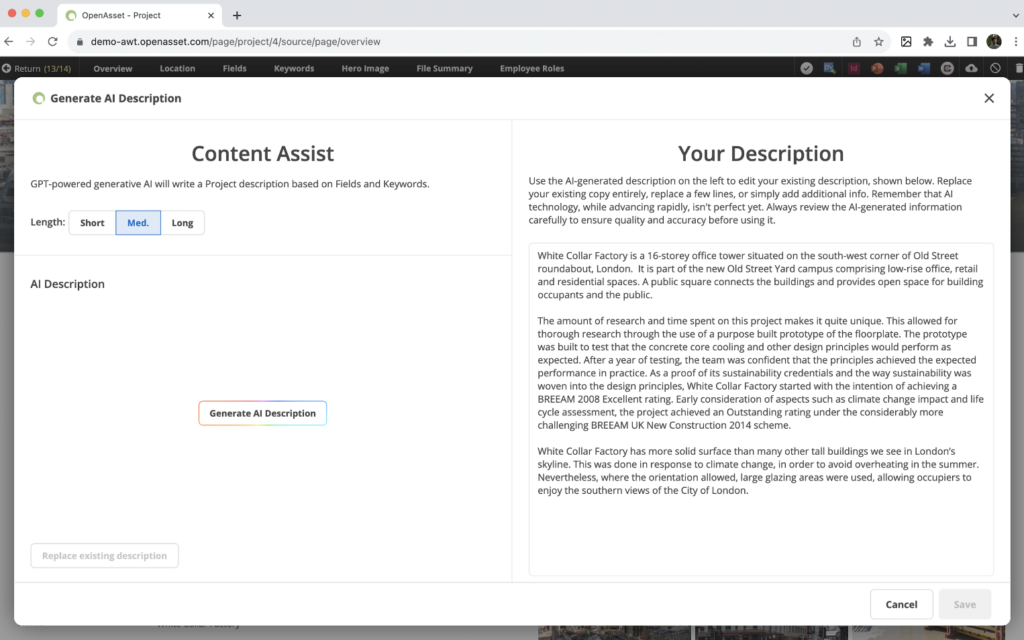
Remember, the strength of your team and how you present your team can be a significant deciding factor in winning the proposal.
Scope of Work
In the scope of work , you’ll want to detail the specific activities, deliverables, and timelines involved in the project. It’s crucial for an engineering proposal to precisely outline the project scope. Given that misunderstandings about project scope are a primary cause of project issues or failures, defining the scope with as much clarity is essential to prevent and more easily resolve problems.
Clearly outline the work that will be done, the methodologies used, and the expected outcomes. This section should align expectations and minimize misunderstandings about the project’s scope. When the scope is clearly defined, everyone involved understands the extent of work expected within the project’s framework.
Work Schedule
The work schedule section of the proposal does precisely what its name suggests: it monitors your work schedule.
Provide a detailed schedule of the project, including key milestones, deadlines, and dependencies. This section maps out the timeline for completing the project and is crucial as it informs your audience about the expected timelines and milestones.
The work schedule should be realistic and allow for some flexibility. You can enhance clarity by incorporating well-organized tables and specific time allocations. It’s also crucial to demonstrate your understanding of project management and your ability to complete the project on time.
Including a work schedule provides a professional touch to your proposal. Should you find yourself unable to stick to this schedule once the project has begun, it’s crucial to communicate any changes as soon as possible with the relevant parties.
Project Cost
Undoubtedly, the cost of engineering services holds significant weight in the decision-making process. The potential consultant is expected to define costs for each team member based on suitable hourly rates and the estimated hours needed for each stage of the project, along with a summary. While engineering associations recommend choosing consultants based on qualifications above cost, the reality is that pricing remains a key determinant.
In this section, detail the expected expenses for your project by itemizing them and assigning monetary values to each category. Break down the costs into distinct groups, such as individual labor charges per employee, material costs, and so on. Summing up these figures will provide the total cost, offering the reader a clear financial overview.
This facilitates an informed decision-making process, allowing for a thorough assessment of different factors before committing funds.
Write a Strong Proposal Conclusion
The conclusion of the proposal mirrors the concluding section of a cover letter. Here, you should explain the reasons for considering you or your team as the ideal choice for the project and provide your contact information. It’s also an opportunity to reaffirm why you or your team is the most suitable candidate for the project.
Conclude your proposal by summarizing the main points, reiterating the benefits of choosing your organization, and expressing your eagerness to work on the project. End on a positive note, inviting further discussion or questions. You want to write a compelling conclusion that will leave a lasting impression on the reader.
Expert Engineering Project Proposal Tips
To maximize your chances of winning projects with your engineering proposals, here are 12 proposal writing tips to keep in mind when crafting your next engineering proposal:
1. Read the RFP Multiple Times
Simply reading the Request for Proposal (RFP) is not enough; a deep understanding of the evaluation criteria is crucial. It’s essential to review the RFP carefully, taking in every detail beyond the basic requirements such as submission dates, formatting guidelines, and required signatures.
This thorough examination ensures you are aligned with all the requirements, conditions, and expectations outlined in the RFP. Such attentiveness not only aids in crafting a tailored response that aligns with the issuer’s needs but also minimizes the risk of non-compliance with the RFP’s requirements.
Moreover, upon reading a new RFP, it’s smart to draft a checklist detailing all essential criteria. This approach allows a good amount of time for you to make sure everything is included in your RFP response and allows you to request any necessary clarifications well in advance of the deadline.
2. Do Your Research
Undertaking comprehensive research is a cornerstone in the development of a compelling engineering proposal. This process involves gathering data, understanding industry standards, exploring the project’s context, and analyzing the potential impact of your work.
Research allows you to approach the project with a depth of knowledge that will reflect the feasibility, innovation, and planning of your proposal. It also provides a foundation for making informed decisions, identifying potential risks, and proposing effective solutions.
In essence, the research you conduct forms the backbone of a proposal that’s both convincing and achievable.
3. Create a Clear Proposal Format
If you’re wondering how to draft a proposal, starting with a clear format is a great start. Maintaining a clear engineering proposal format is fundamental to creating a structured and professional document. A standardized format ensures that the information is presented in an organized manner, making it easy for the reviewers to follow and evaluate. The format typically includes a well-defined table of contents, sections with clear headings, and a logical flow of information.
This structured approach helps display your message with precision and prevents critical elements from being overlooked. Consistency in format across various sections, such as the project background, scope, schedule, and qualifications, reinforces the overall flow of the proposal.
A well-formatted proposal not only reflects your professionalism but also helps in communicating the seriousness and preparedness of your team for the project.
4. Introduce Your Company’s Background
Introducing your company with a concise background in your engineering proposal is a critical step in setting the stage for a strong pitch. This section should provide a snapshot of your company’s history, core competencies, successes, and mission as they relate to the project in question. It’s an opportunity to establish credibility and build trust with the proposal’s reviewers.
This introduction should show the essence of your company’s identity, values, and the journey that has led to its current standing in the industry. Highlighting notable achievements, experience in similar projects, and the overarching vision can create a compelling narrative that resonates with the potential client.
A well-articulated company background serves as the foundation upon which the rest of the proposal is built, underlining why your firm is uniquely suited for the project.

5. Feature Your Team’s Talent
In an engineering proposal, it’s important to select the best employees for your RFP response . Make sure to illustrate the unique skill sets, qualifications, and experiences that each member brings to the table. You can use this section to delve into the specific talents that differentiate your team from competitors.
Detailing individual roles and how they will contribute to the success of the project not only showcases the depth of your collective proficiency but also helps build confidence in your team’s ability to deliver results. Remember to align these talents with the project requirements, demonstrating a perfect fit between your team’s capabilities and the project’s needs.
If you’re looking to generate employee resumes in minutes that demonstrate your team’s talent, a robust DAM can help you store and manage employee profiles. A DAM for engineering like OpenAsset saves you time and resources in managing your resumes. Through the use of Generative AI, you can create project descriptions and employee RFP bios.
6. Include Images and Graphics
Incorporating images and proposal graphics into your engineering proposal can significantly enhance its impact. Civil engineering projects typically require various diagrams, illustrations, and maps. This is because the essence of designs is best conveyed through visual representation for complete clarity. The same principle applies to proposals, where visual elements are crucial for demonstrating complex information clearly and effectively.
Moreover, using images to communicate visually will save reading time for the client. The reader will also appreciate the amount of effort put into preparing the engineering proposal.
Use tools like OpenAsset to seamlessly find and present visuals of projects that align closely with the prospective client’s needs or showcase your team’s qualifications. This tailored visual approach not only shows your past successes but also provides a compelling, concrete visual narrative of what you can deliver.
Moreover, AI in DAM saves you time and resources in managing your images through AI-suggested keywords, image similarity search, AI Content Assist, and more. These features:
- Reduce the time it takes to manually tag images
- Helps you build and expand taxonomies
- Gives you additional images to select from and use.
- Enables you to leverage Generative AI for project descriptions and employee RFP bios
Images are not just embellishments; they can be powerful testimonials of your work’s relevance and quality, speaking volumes more than words alone.
7. Use Clear Language
Using clear and concise language is crucial when crafting an engineering proposal. The ability to demonstrate complex ideas effectively without resorting to overly technical jargon or unnecessarily complicated explanations is a skill that cannot be overstated.
Likewise, it’s important not to assume that the readers will be familiar with the specialized jargon of your field. Take time to research the client and the reviewing committee to grasp their expertise and knowledge base. When delving into detailed technical matters, ensure you offer sufficient background to maintain inclusivity and prevent any misunderstandings.
Proposals should be accessible, ensuring that stakeholders, regardless of their technical background, can grasp the proposed concepts and see the value in them.
Your team might possess attributes such as “remarkable efficiency, strong motivation, and outstanding qualifications,” yet, it’s likely that your competitors claim the same. Such language is often so overused in proposals that they become clichéd and lose their impact.
Rather than relying on generic adjectives, prove your capabilities with concrete examples of past projects or situations that illustrate your skills in action. Even more compelling would be citing testimonials or endorsements from previous clients who can vouch for your expertise. Here’s what that could look like in your proposal:

Additionally, avoiding excessive language not only helps in maintaining the reader’s attention but also demonstrates your ability to communicate efficiently. The proposal should be as concise as possible without sacrificing completeness. Every sentence should serve a purpose, whether it’s to inform, persuade, or clarify.
8. Keep It Short
Coming across an RFP with a large page limit or no page limit might give you the impression that you should create a significantly lengthy proposal. However, it’s best to resist this urge to write a 200-page proposal.
Keep in mind, your potential client will be comparing your proposal with several others. A concise submission allows them to quickly discern the essential details. Overloading your proposal with text increases the likelihood of them skimming over key points — steer clear of dense paragraphs.
A concise proposal not only respects the reviewer’s time but also enhances readability and comprehension. It’s essential to spread your message and value proposition without unnecessary elaboration. Precision in language, clarity in presenting solutions, and conciseness in your descriptions can make a powerful impact.
Moreover, a proposal that is straight to the point is often a sign of a well-thought-out project plan and a capable, organized team that knows how to communicate. A compact and well-structured proposal often speaks volumes about your project management skills and your respect for the client’s resources and time constraints.
9. Practice Teamwork
A collaborative approach ensures that diverse expertise and perspectives contribute to a more robust and comprehensive document. It’s the teamwork among team members, with their unique skill sets and experiences, that can elevate the quality of a proposal.
Working together with your team in the proposal process can lead to innovative solutions that might not surface in a siloed work environment. Teamwork facilitates thorough cross-checking, brainstorming, and problem-solving, which are essential to addressing the complex challenges typically presented in engineering projects.
Remember, surrounding yourself with an effective team is the key to success. A collaborative culture could be what makes you stand out from the competition.
Moreover, highlighting the collaborative nature of your team within the proposal can also serve as a testament to your capability to work together, a quality often wanted by clients. It’s not just about the final product but also about demonstrating the process of how your team works together to achieve excellence.
10. Proofread and Double-Check
Proofreading and carefully double-checking your proposal is as essential as the content itself. This step ensures that your document is free from errors, which could otherwise affect the credibility of your proposal. It’s not only about catching typos or grammatical mistakes; it’s about ensuring that every figure, fact, and statement aligns with the RFP requirements and your research findings.
A proposal that is well-edited and error-free communicates attention to detail and a commitment to excellence. It’s recommended to have multiple team members review the proposal to provide fresh perspectives and catch issues that you might have overlooked.
Remember, a single mistake could raise doubts about the professionalism of your work and the quality of the project delivery. Therefore, rigorous proofreading and double-checking are necessary to validate the integrity and professionalism of your engineering proposal.
11. Meet Deadlines
Meeting deadlines is important in the context of engineering proposals. The ability to deliver on time reflects your professionalism and reliability. It’s a non-negotiable element of project management that sets the stage for how potential clients view your commitment to the project’s success.
Planning is essential to ensure deadlines are not just met, but comfortably, allowing planning for any unexpected circumstances that might arise. Missing a deadline can have significant repercussions, from damaging your reputation to disqualification from the bidding process.
However, it’s not just about avoiding the negative. Following deadlines can also enhance your standing with clients, as it demonstrates respect for their time and trust in your ability to manage the project effectively from the start.
12. Submit the Proposal on Time
Part of meeting deadlines includes submitting your proposal on time. Every RFP specifies a submission deadline that must be met. Contrary to project deadlines, which may be subject to change during a project, the cut-off date for proposal submission is non-negotiable.
Physical submissions of hard copy proposals are often marked with an actual time stamp upon receipt. If that timestamp shows your submission arrived even one second past the deadline, it will unfortunately be too late.
With the rise in digital submissions, the strict adherence to deadlines continues. Considering potential issues like slow upload speeds or internet disruptions, it’s wise to plan additional time when submitting proposals electronically.
Make sure it’s clear how the proposal will be submitted so there are no surprises. You should also ask for help when it’s needed, especially if you are facing roadblocks and don’t have much time left.
Moreover, building buffer time for reviews and potential revisions is a wise strategy. Proposal writing often shows that tasks tend to extend beyond anticipated time frames. Whether you run out of printing paper or a team member makes a last-minute change, you need to be prepared. Therefore, allowing yourself a generous timeline for the preparation and submission of the final documents can mitigate the risk of missing the deadline.
Meeting deadlines reflect your professionalism and reliability, which are critical factors in the selection process. It demonstrates your commitment to the project timeline and sets the stage for the timely execution of the work ahead. Engineering proposals are also an investment of time and money and if you miss the deadline, this investment is wasted.
Additionally, a punctual proposal suggests that your project management and organizational skills are well-tuned, giving potential clients confidence in your ability to deliver results within the specified timeframe.
Free Engineering Proposal Template
At OpenAsset, we want to provide you with valuable resources to help pave the way toward success. That’s why we’re providing a free engineering project proposal template to inspire your proposal writing journey.

Use OpenAsset for Your Engineering Services Proposal
Leveraging a robust DAM, like OpenAsset , in your engineering proposals is a game-changer. OpenAsset streamlines the process of incorporating high-quality images and project data that represent your team’s past achievements and expertise.
By using OpenAsset, you can create a visually impactful and content-rich proposal that stands out. It not only saves valuable time by organizing your assets efficiently but also ensures that you present a polished, professional, and tailored proposal to your potential clients.
OpenAsset’s DAM solution makes AEC proposals simpler, faster, and more successful. That’s why 99% of customers renew. Leverage OpenAsset to elevate your proposals and effectively demonstrate why your team is the ideal choice for any AEC project.
Ready to start creating engineering proposals that will set you apart?
Get OpenAsset DAM Insights

How to Create Winning Proposals
What to read next.

5 Inspiring Ideas for Using OpenAsset Beyond Traditional Asset Management
As a digital asset management (DAM) solution, OpenAsset has established itself as a leader for AEC professionals wanting to streamline their...

Building the Future: How AI is Transforming the AEC Industry
The architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry stands on the brink of a revolutionary shift, powered by artificial intellige...

Digital Marketing for Engineering: Strategies, Tips, and Channels
With the rise of digital channels, engineering firms are recognizing the importance of digital marketing to stand out, connect with their ta...
Visit the Health Advisories website for the latest vaccination and mask information and to Report a Case.
SJSU is Open and Operational
Campus will be open January 22–26. Visit our FAQ to learn more .
Mechanical Engineering
How to Write a Project Proposal
Contents of proposal.
A recommended template for an MS project or thesis proposal is provided at the following link, from which you can make a Google Docs copy or download a Microsoft Word file:
ME 295 and ME 299 Proposal Template
Proposal Approval Process
The project proposal must be written so that it provides a strong evidence of a student’s thorough understanding of the topic and the capabilities to carry out the work successfully. There are three levels of approvals and signatures required to ascertain that the student in fact has the understanding and capabilities to complete the project successfully. First, the proposal is reviewed, evaluated, and signed by the advisory committee. Next, the signed Proposal Evaluation Form is attached to the proposal, along with the completed Proposal Cover Sheet and submitted to the ME office for approval and signatures of the Graduate Advisor and the Department Chair. Refer to the Projects and Thesis tab for proposal deadline.
See our detailed instructions [pdf] for submitting the project proposal in DocuSign to help guide you through the process.
Proposal Deadline
The proposal must be approved by the advisory committee, the Graduate Advisor, and the Department Chair prior to the university deadline for adding a course, usually the second week of February for the Spring semester and the second week of September for the Fall semester. The add-code for the first term project is issued by the ME office only after the approved project proposal has been received. Failure to meet the deadlines can delay your graduation.
Sample Proposals
The following are some representative examples of project proposals. Your proposal may have additional requirements depending on your project committee chair.
- Sample 1 (Bicycle brake)
- Sample 2 (Collapsible cup)
- Sample 3 (Object detection)
- Sample 4 (Metamaterial)
- Sample 5 (Battery)

How to Write an Engineering Proposal
November 29, 2012 by Bernie Roseke, P.Eng., PMP 7 Comments

Engineering proposals are the industry standard document for which engineering consultant selection decisions are made. For engineering consulting firms, they are the primary method of securing new work. For the owners they are indispensible as a means to differentiate between consultants. But what are the major parts of an engineering proposal?
Project Comprehension
A typical engineering proposal will need to document superb technical comprehension of the project. In this section, the technical issues are listed and some of the alternatives discussed. This section was always the most difficult to wrap my head around, because where I came from the industry was “small enough” that they should know our qualifications. So maybe we could miss something and someone much less experienced could “out-write” us to better score in this category. From the recipient’s point of view though, it is very important that a show of technical competence be a part of the proposal, and it is not likely that any one small detail will swing the proposal in one direction.
There isn’t alot of guidance I can give you here for writing this section because this is where your technical know-how has to shine. I always write the section once, and look at it multiple times from different perspectives. Imagine each phase of the project as it would be carried out and think about what all of the relevant technical issues are.
Project Scope
An engineering proposal needs to accurately define the project scope. Because confusion related to the project scope is the leading cause of project failure (or problems), it is imperative that the scope be defined as accurately as possible so that issues do not arise. And when they do, they can be dealt with much more easily when everyone knew what work was supposed to be performed within the boundaries of the project.
Generally the stakeholders of the project interpret grey areas of the project scope in their favor. For example, if the purchase of adjacent land was not mentioned in the proposal for an interchange construction project, the owner is likely to interpret that it was included, but the engineer is likely to interpret that it was not. To the owner, it appears to be “a part of the job.” To the engineer, it appears to be overlooked and therefore not part of the project as defined.
Project Team
Normally an engineering proposal will require a description of each project member, their role on the team, and a professional resume. Naturally the strength of the project team is a factor in the selection of a qualified engineering consultant, and there isn’t much you can do about this if your competitors have more relevant experience than you.
But make sure all of the relevant experience of the team members are present. You would be surprised how good the smallest things can sound, for example an engineer spending 10 years in the field interpreting contracts may not be glamorous, but it doesn’t sound that bad on a proposal if you throw in a sentence or two on contract expertise.
Project Budget
Of course, the price of the engineering services is an important consideration. The prospective consultant should price out each member according to an appropriate charge out rate and the number of hours required for each phase, and provide a summary. Engineering associations advocate for a consultant selection based on merits rather than price, but price will always be a factor.
Related posts:

About Bernie Roseke, P.Eng., PMP
Bernie Roseke, P.Eng., PMP, is the president of Roseke Engineering . As a bridge engineer and project manager, he manages projects ranging from small, local bridges to multi-million dollar projects. He is also the technical brains behind ProjectEngineer , the online project management system for engineers. He is a licensed professional engineer, certified project manager, and six sigma black belt. He lives in Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada, with his wife and two kids.
I found this article extremely informative as a reference material for an essay on engineering writing. Iam a 58 year old engineering major at Eastern Arizona College. This just goes to show you are never too old to learn a new profession. Thank you. Sincerely Jacob Boer
Thanks Jacob,
Glad I could help. Good luck in your studies.
I am planning to do PhD in civil engineer and have been so lost how to write a proposal on the idea that I have in mind. but this seems to be really helpful. thank you.
Glad it helped!
I am writing a proposal for a masters scholarship studies and my topic is “Design specifications for Highway bridges and structures in low income and Developing countries’ But am still finding its difficult to get technical information or points to make my proposal solid or arguable .
please email to me i will give to you some document in order to do your proposal my email, [email protected]
Writing engineering proposals seems like it would be so complicated. I liked that you explained that you need to cover the scope of the project and what to do if something goes wrong. That does seem like it would be really intense. It seems like you should get someone with a lot of experience to help you out.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Project Initiation
- Project Planning
- Project Execution
- Monitoring and Controlling
- Project Closure
- Project Management Tutorial
- Project Scheduling Tutorial
- Earned Value Tutorial
- PMP Exam Tutorial
- Find Talent
- PRINCE2 Foundation
- PRINCE2 Practitioner
- PRINCE2 Professional
- IPMA Level A
- IPMA Level B
- IPMA Level C
- IPMA Level D
- Learning Videos
Certification
Recent posts.
- PMI Project Knowledge Areas, Intro
- PMI Project Knowledge Areas, Video 1: Project Integration
- Project Risk Checklist
- Creating a Risk Register
- 50 SMART Goals
- Reporting Earned Value
- Analogous Estimating
- Variance at Completion (Earned Value Analysis)
- TCPI (Earned Value Analysis)
FIND IT HERE
Subscibe to ProjectEngineer.NET channel – YouTube
- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Support Forums
- How we work
55 Engineering Research Paper Topics Worth Your Attention
Stuck with engineering research topics for your proposal? Have a look at ours and get inspired effectively!

Let’s Pick up the Most Exciting Engineering Research Topics
The main feature of engineering topics for research paper and related projects is that they mostly offer practical solutions to a specific problem. Purely theoretical engineering research is less common and is usually done only to challenge existing knowledge, theories & concepts. Which topic to choose is up to you. However, our seasoned experts would like to share some insights on how to write an engineering proposal to help you create papers that will not only earn excellent reviews from your academic advisors but also inspire you to make breakthroughs in your field.
Some Expert Insights on How to Write an Engineering Proposal
The proposal is a paper representing your project from a research angle. It should include as much information about your investigations as possible, including study plans, methods, expected outcomes, etc. Regarding revealing engineering topics, experts from our proposal writing services often recommend focusing on their impact on the current field knowledgebase and practicality if it comes to engineering application solutions development.

Important note! Adding graphics, schemes, images, and any other visuals will be especially beneficial in your engineering research project papers. It helps you reveal more topic details and add value to your PhD research proposal engineering.
How to Reveal Engineering Research Paper Topics With a Paper Structure
Remember also to stick a paper to a given structure:
- Introduction. Review the engineering topic you choose and reveal its importance. Here, you can also give a short overview of what is included in the proposal.
- Qualifications. This section is set to show you have the required skills and capabilities to conduct your research successfully. For example, if it’s a research proposal in mechanical engineering, you may mention some physical aspects of objects you will investigate.
- The background is where you discuss the topic and the problem motivating you to take it. Show how you understand the issue, its impact & causes. If it’s a research proposal for mathematics or another theoretical one, your investigation will probably be based on a theory or concept.
- The schedule section informs paper readers about the time frame you set to complete the work so they understand when to expect the result and what milestones you should go through in revealing your engineering research paper topics.
- The proposal statement is the section where you tell what exactly you are proposing regarding the topic and what you aren’t, giving readers additional information about your work. This is especially valuable if you plan to join engineering research in Princeton University or other prestigious institutions.
- Costs. This paper section shows how many resources your project requires (especially vital if it needs additional funding). The best way to do it is to divide expenses into categories and calculate the totals for each category. E.g., hardware & software, auxiliary tools, etc., if it comes to working on PhD topics in computer science or other application solutions.
- Research methodology. In PhD research proposal mechanical engineering, you present how exactly you will complete the work, discussing steps you take during the working process.
- The results section is aimed at showcasing the proposal’s outcomes. For example, if you work with research proposal topics in mechanical engineering, you can present a concept of an electronic device or offer a problem solution.
Research Proposal Topics in Electronics Engineering
It’s time to get more specific and actual topic samples. First, we will go with research proposal topics in electronics engineering.
- Understanding Effective Power Electronics Using Circuit Simulation
- Redesign of AC Electrical Motors
- Electric Vehicle Motors and Gearbox
- Benefits of Optimization in Electrical Engineering
- Electric Vehicles – A Solution to Global Pollution
- Effects of Standard Deviation on Time and Frequency Response of Gaussian Filter
- Impact of Surface on Nano-Beam Mechanical Behaviors
- Maximum Power Point Tracking Based on Differential Conductance
- Analyzing Mechanical Property of Electrically Assisted Friction Stir Welding
- High Throughput Droplet Actuation Platform
- Numerical Analysis of Mechanical Characteristics of Joint Structure of Steel Pipe Sheet Pile Foundation
- Implementation of an Improved Automatic DC Motor Speed Control Systems Using Microcontrollers
- Automated Hybrid Smart Door Control System
- Comprehensive Review of Smart Grid Ecosystem
- Solar Simulators’ Trends Overview
- Intelligent Voice Controlled Wheel Chair: Design and Implementation
- Comparative of Field Effect Transistor (FET) and Bipolar Power Transistor Performance in Amplifiers
- Development of a Low-Cost Automatic Internet of Things Extension System
- Mechanical Analysis of Thin-Walled Cylindrical Shells With Cracks
17 Great Research Proposal Topics for Civil Engineering
The civil engineering field focuses on improving infrastructure and environmental sustainability. By discovering new research ideas and presenting unique research proposal topics for civil engineering, civil engineers are able to resolve problems people couldn’t deal with before.
- Studying the Effects of Urbanization on Biodiversity
- Analyzing the Effects of Water Scarcity on Infrastructure and the Environment
- Evaluating the Feasibility of Using Drones in Construction
- Assessing the Feasibility of Using Prefabrication in Construction
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Public Transportation Systems in Reducing Carbon Emissions
- The Impacts of Infrastructure on Local Economies
- Investigating the Use of Big Data in Civil Engineering
- Impact of Ripe and Unripe Plantain Peel Ash on Strength Properties of Concrete
- The Effects of Water Scarcity on Infrastructure and the Environment
- The Effects of Natural Disasters on Transportation Infrastructure
- Evaluating the Feasibility of Using Robots in Construction
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Sustainable Transportation Infrastructure
- Investigating the Use of Blockchain Technology in Civil Engineering
- Structural Characteristics of Soilcrete Blocks
- The Use of Augmented Reality (AR) In Civil Engineering
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Sustainable Drainage Systems (SUDs)
- Analyzing the Effects of Climate Change on Infrastructure Materials
Some Good Research Proposal Topics in Mechanical Engineering
With a solid number of topics for engineering research papers in mechanics, choosing the central theme for your research will be easier. Even if you already know what area to investigate, having several research paper topics for engineering allows you to decide from which angle you will approach the issue.
- Energy and Exergy Analysis of Boiler Systems
- Effect of Delay Period on Performance of Compression Engine Running on Jatropha Fuel
- Optimum Buckling Response Model of Grp Composites
- Experimental Performance Evaluation of Charcoal-Stove
- The Detail Fabrication of a Candle Moulding Machine
- Fabrication of Metal Panel Door
- Electricity Generation Using Propeller Shaft
- The Cavitation Effect in Centrifugal Pumps
- Development of a Gas Propelled Rocket Engine
- Research on Methods for Recycling Spent Fuel for Internal Combustion Engines
- Study of Changes in the Characteristics of the Al-6’1/OCU Alloy after Annealing Process
- The Development of a Pumping Machine for Water Distribution in a High-Rise Building
- 3D Printing in the Construction of Water Supply Systems
- Repair and Rehabilitation of Faulty Air Condition
- Design and Analysis of a Microsatellite Structure in Lowearth Orbit
- A Study of Cavitation in Pumps and Flow Systems
- Design and Construction of a Digital Clock
- Effect of Injector Nozzle Holes on Diesel Engine
- Effect of Vortex in Kaplan Turbine-Using Cfd a Case Study: Rosseries Power Plant
Download Here More Engineering Research Proposal Ideas!
Get help working on engineering topics for research paper.
Working on some engineering research topics may be challenging for students needing a lot of time and effort to present qualitative proposals when they often have many other responsibilities. And this is where hiring qualified proposal writers may save them much effort. Delegating the work on your research topics to an expert makes your student’s life much easier, allowing quality outcomes with minimal time.
Specialists also know what topic information should be added to your paper and how it should be formatted. Just specify your needs and requirements and mention the main purpose for writing engineering proposal. Everything will be done well at the appointed time, so there will be no need to worry about anything. Check the list of our proposal topics and ensure you choose the most interesting one.
Take the experts’ assistance and wait a little for a paper leading to your research project approval!

Upload Files
Thank you for your request!
We will get in touch with you shortly!
Please, try one more time.
Engineering Proposals
Consulting engineers aren't the only engineers who write proposals. For instance, in academia, engineers write proposals to receive funding for their research or even to initiate a project. Some engineers produce proposals to be read and approved by management while others send proposals to specific funding agencies or clients.
Definition of Proposals
A proposal is a description of the work you will complete on a project. The details included in a proposal depend on the project's scope and who will read the document. Typically, organizations advertise a need for proposalsand consulting engineers respond to the need. However, as an engineer, you may determine that a problem exists, and therefore, propose solutions to an organization. In this case, you must first convince the agency that the problem exists before proposing your solutions.
Types of Proposals
Different types of proposals are necessary for different projects. In academia, engineers produce grant proposals or research proposals in order to receive funding from government agencies and non-profit organizations. In industry, engineers, especially consultants, write proposals or "bids." Engineers produce these proposals for the company where they are working or for other organizations.
A proposal's audience is those supporting the proposed project. The details you provide in a proposal may change, depending on your audience. For instance, if you submit a Proposal to your company's management, you may not have to include project costs or other background information. On the other hand, if you produce a proposal for an organization outside your company, you may need to provide more details. These details might include a rationale for why they should fund your project, as well as the necessary materials and costs. Before writing a proposal, you should always research your audience's background. This way, you will have a better idea about what information to include in your proposal.
General Format
You can submit a proposal in several ways, depending on your audience. For example, proposing a project to your supervisor may require a phone call or a quick e-mail. Or, you may write a short memo, outlining your ideas. On the other hand, you may have to produce a lengthy proposal that provides project background and completely describes the proposed work. Typically, you will know which format to use based on the proposal's context.
When you write a lengthy proposal, you will have to spend time conducting research before you begin writing. This research might include locating other designs and theories to refer to as examples or to critique. A proposal might also include graphics to help an audience visualize your ideas. You might incorporate other data, such as dollar figures and time schedules, so your audience knows exactly how long the project will take to complete and much it will cost them To read more, choose any of the items below:
Introduction
In the proposal's Introduction, you should provide information about the need for a proposal. In other words, here is where you state why you are writing the proposal in the first place. You should also provide an overview of what the rest of the proposal includes.
Qualifications
In the Qualifications section, you should show that you and your organization (if applicable) are skilled and capable of completing the proposed work successfully. You should view this section as a "resume" since in it, you will depict your skills and experiences. If your audience is your supervisor or other managing decision-makers, then you may not need to include this section.
In the Background section, you should depict the problem/situation that lead to your writing a proposal. Here, you should show that you thoroughly understand the problem. If your audience already knows the Background, you may not need to include this section. For example, your supervisor or other managing decision-makers may already be familiar with the specific problem. Therefore, you don't need to tell them what they already know.
Work Schedule
The Work Schedule section does exactly what its name implies: It presents the time frame in which you will complete the proposed work. This section informs your audience of what to expect from you and when. It also helps to keep you organized. If, after you begin working, you are unable to keep this schedule, you should always communicate changes in deadlines to the appropriate people.
Proposal Statement
In the Proposal Statement section, you should inform your audience of exactly what you are proposing. You should also include what you aren't proposing. For example, if you are proposing partial work on a project, state this and then verify what your work will not include.
In the Cost section, you should present what costs you anticipate your project will involve. To do this, divide your expenses into categories and provide dollar figures. For example, labor costs for each worker, materials, etc. Then, you might provide a total cost.
In the Results section, you should discuss the outcome of your proposal. The types of outcomes resulting from a proposal cover a wide range. For example, you may be creating a design, building an actual construction, or even producing a lengthy report. Be sure to state exactly what the Results will be.
The Conclusion section is similar to the ending of a cover letter. Here, you should summarize why you should be considered and how you can be contacted. You might also reiterate why you are the best person or group for the project.
Methodology
In the Methodology section, you should present how you will complete the project's work. This is similar to a Lab Report's Procedures section in that you have to discuss the steps you will have taken to reach a final goal.
Perspectives on Proposals
Dave alciatore, mechanical engineering.
Internal Proposals
"You're likely to write internal proposals if you work with a product development group in a big company. For example, you might conduct research on possible new product lines. Then, you would write a proposal to communicate that you want to pursue this product, but that it will involve testing and development. In other words, it's going to cost money. In order to get financial support, you have to write a proposal that presents your plans. This includes the benefits of the product in terms of profit."
Tom Siller, Civil Engineering
Consulting Engineers
"If you are a consulting engineer, you will work in a very competitive environment because you have to sell your services. In order to get work on a project, you have to submit a proposal or give a presentation. To do this successfully, you have to know who your client is and what that client expects."
John Mahan, Electrical Engineering
Proposal Types
"Engineers write many different types of proposals. Sometimes, a proposal has to be powerful and business-oriented. Many companies don't want to look too far into the future, not even past two years. So, you have to be very specific and down to earth. You have to tell them when exactly you will complete the work. In Phase One, you'll do x. In Phase Two, you'll do y. You should also include the benefits gained during each phase."
Citation Information
Dawn Kowalski. (1994-2024). Engineering Proposals. The WAC Clearinghouse. Colorado State University. Available at https://wac.colostate.edu/repository/writing/guides/.
Copyright Information
Copyright © 1994-2024 Colorado State University and/or this site's authors, developers, and contributors . Some material displayed on this site is used with permission.

Search form
- Academic Advising & Support
- Academic Planning & Resources
- Environmental Changemakers Certificate
- Academic Opportunities & Research
- Financial Support
- Online Forms & Resources
- Calendar & Deadlines
- Career Resources
- Clubs and Organizations
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Advisors & Coordinators
- Graduate Studies Committee
- Curricular Practical Training
- New Graduate Students
- Ph.D. Milestones
- Policies & Procedures
- Teaching Assistant FAQs
- Career Development Resources
- Engineering Student Study/Meeting Space
- Free Software
- Message From Chair
- Facts & Figures
- Undergraduate
- Faculty & Staff
- Academic Employment
- Dept Events
- Discovery News
- Student Testimonials
- Give to BME
- Seminar Series
- E-Newsletter
- Message from Chair
- CEE Affiliates
- Give to CEE
- International Center Form
- MSE Business & Forms
- MSE 298 Seminars
- MSE Diversity & Inclusion
- Support MSE@UCI
- MAE Seminars
- Corporate Affiliates
- Interdisciplinary Graduate Programs
- All faculty & staff
- Dean's Office
- Development and External Relations
- Student Affairs
- Engineering Research Management
- UC Irvine Directory
- Proposal Text and Resources
- Early Career Opportunities
- Purchasing Requests
- Reimbursements
- Purchasing & Reimbursement Mission Statement
- Business Meetings/ Entertainment Guidelines
- Service Agreements
- Travel Guidelines
- Travel Tips
- UC Policies & Procedures
- Dean's Executive Office
- Chief Administrative Officers
- Personnel Unit
- Finance Unit
- Purchasing Unit
- Computing Unit
- Facilities Unit
- Curriculum, Analytical Studies, & Accreditation (CASA)
- Communications Office
- Development and External Relations Office
- Outreach Unit
- Office of Information Technology
- Faculty Websites
- Computer Labs & Laptops
- Engineering Facilities Request Form
- Safety Procedures
- Campus Evacuation Zones
- Environmental Health & Safety
- UCI Police Department
- Helpful Links
- At Your Service
- Zot! Portal
- FAQs for Engineering Instructors
- Spring Awards
- Process Improvement
- Alumni Spotlight
- Hall of Fame
- #ANTEATERENGINEER
- Ways to Give
- UCI Engineering Alumni Society
- UC Irvine Alumni Association
- Dean's Message
- Strategic Plan
- Facts and Figures
- Henry Samueli
- School Leadership
- Engineering Leadership Council
- Accreditation
- Orange County
- Got Questions?
- Enrollment and Degrees Awarded
- How to Apply
- Prospective Students
- Newly Admitted
- Majors and Minors Offered
- Programs and Concentrations
- Accelerated Status Program
- International Fellowships
- Meet Us on the Road
- Anteater Voices
- Ph.D. and Master's Inquiry Form
- Message from the Associate Dean
- UCI Engineering-LANL Graduate Fellowships
- Research Thrusts
- Research by Department
- Research Centers, Institutes and Facilities
- Undergraduate Research
- Interdisciplinary Science and Engineering Building (ISEB)
- Contracts & Grants / ERM
Research and Proposal Development
- Annual Membership Levels
- Connect with Students
- Prototyping Services
- Sponsored Research
- External Relations Office
- Community College
- International
- IDEA - Inclusion, Diversity, Equity, Access
- Stacey Nicholas Office of Access and Inclusion
- Inclusion in Engineering Education
- Samueli Shoutouts
- Media Watch
- Dean's Report
- Social Media
- Style Guide
Research Support for the Samueli School of Engineering
The Engineering Research and Proposal Development team proactively supports faculty, researchers, and students to attract extramural funding and facilitates the advancement of the research enterprise in SSoE. The team provides the following research proposal development support:
- Coordination of large and complex grant and contract proposal efforts
- Facilitation of partnerships among investigators and connect proposal teams to research resources
- Guidance for the pursuit of new strategic research activities in response to the funding opportunity landscape and new research directions
- Timely notification of strategic funding opportunities
- Communication with funding agencies to gather input and advice on developing proposals for specific programs and centers
- Coordination with campus units to gain key insights on ongoing and future research programs
Quick Links
- Early Career Funding Opportunities
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience. Thanks!

- Funding Opportunities
- Proposal Development
Packard Fellowships for Science and Engineering Program
OVPR is actively accepting applications for this internal competition. If you are interested in applying to this program, you must submit a pre-application through the internal competitions submission portal . Pre-application requirements are listed in the announcement below.
The Office of the Vice President for Research and the Office of Advancement invite applications to the 2024 Packard Fellowships for Science and Engineering Program . The David and Lucile Packard Foundation invests in future leaders who have the freedom to take risks, explore new frontiers in their fields of study, and follow uncharted paths that may lead to groundbreaking discoveries. The program aims to support the nation's most promising early career professors to pursue their science and engineering research with few funding restrictions and limited paperwork requirements. Stony Brook University has been invited to nominate TWO candidates for the 2024 competition.
Please see below for details. If you are interested in applying, you must submit the internal competitions form by Friday, February 16, 2024 . Pre-applications for internal review and selection must be uploaded to the portal as a single PDF document. The competition code for this program is LC202414 .
WHAT DOES IT FUND: The Fellowship Program provides support for highly creative researchers early in their careers; faculty members who are well-established and well-funded are less likely to receive the award. Packard Fellows are inquisitive, passionate scientists and engineers who take a creative approach to their research, dare to think big, and follow new ideas wherever they lead. The Foundation emphasizes support for innovative individual research that involves the Fellows, their students, and junior colleagues, rather than extensions or components of large-scale, ongoing research programs.
APPLICANT REQUIREMENTS: Candidates must be faculty members who are eligible to serve as principal investigators engaged in research in the natural and physical sciences or engineering and must be within the first three years of their faculty careers (initial faculty appointments began no earlier than May 31, 2021, and no later than May 31, 2024). Disciplines that will be considered include physics, chemistry, mathematics, biology, astronomy, computer science, earth science, ocean science, and all branches of engineering. Candidates engaged in research in the social sciences will not be considered.
AWARD: $875,000 over five years.
SPONSOR DEADLINE: Nominations due March 15, 2024. Applications due April 20, 2024.
A complete pre-application should comprise of the following:
- Research statement (maximum two pages of text, prepared in 12-point font with 1-inch margins). The research statement should describe why the research is important and outline the general goals for the next five years. The statement should also indicate, in general, how funds will be used. If there are relevant figures, images or references, please include these separately on a third page.
- CV/Biosketch
- Current external research support
- Recommendation letter (no more than two pages) from the candidate's department head, which should describe firsthand knowledge of the candidate's ability to do creative research. Candidates with joint appointments may submit a single letter signed by both department heads.
Office of the Vice President for Research
Ovpr announces recipients of 2024 discovery and innovation awards.
The Office of the Vice President for Research (OVPR) is honoring 11 faculty and staff for their exceptional contributions to research, scholarship, and creative activity as part of the 2024 Discovery and Innovation Awards .
“ The winners represent the best and the brightest of our University of Iowa faculty and staff, who are making an impact across a range of disciplines,” said Marty Scholtz, vice president for research. “Their research and scholarship enhance undergraduate and graduate education on campus, and their efforts to expand the frontiers of discovery betters our community, state, and world.”
The OVPR solicited nominations from across campus for the awards, which include: Scholar of the Year, Early Career Scholar of the Year, Leadership in Research, and awards that recognize achievement in communicating scholarship with public audiences, community engagement, arts and humanities, mentorship, research administration and safety. A campuswide event on April 30 will celebrate the winners.
Faculty Awards

Jun Wang , James E. Ashton Professor and interim departmental executive officer in the College of Engineering’s
Department of Chemical and Biochemical Engineering, is the 2024 Scholar of the Year . The award celebrates nationally recognized recent achievement in outstanding research, scholarship, and/or creative activities.
Wang’s research centers on the development of novel remote sensing techniques to characterize aerosols and fires from space. He serves as the University of Iowa’s lead investigator on NASA’s TEMPO, Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring Pollution, which Time magazine named one of its best inventions of 2023.
“Professor Wang's scholarly endeavors over the past two years stand out as a paradigm of excellence, serving as an exemplary model for both emerging and seasoned faculty members to aspire toward,” said Karim Abdel-Malek, professor of biomedical engineering and director of the Iowa Technology Institute.

James Byrne , assistant professor of radiation oncology in the Carver College of Medicine ( CCOM ), is the 2024 Early Career Scholar of the Year . The award honors assistant professors who are currently involved in research, scholarship, and/or creative activity and show promise of making a significant contribution to their field.
As a physician scientist, Byrne continues to care for patients while developing novel biomedical therapies for cancer, finding inspiration in everything from latte foam to tardigrades. In his first two years as faculty at the UI, he has earned more that $2.5M in external research funding, including a K08 award from the NIH.
“Dr. Byrne’s scientific creativity stems from both an active and curious mind as well as his ability to bridge diverse fields from engineering to biology to medicine,” said Michael Henry, professor and interim director of the Holden Comprehensive Cancer Center. “These interdisciplinary boundaries are where some of the most interesting and important work is happening today.”

Donna Santillan , research professor and director of the Division of Reproductive Science Research in the CCOM Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, received the Leadership in Research Award , which recognizes research and scholarly accomplishments throughout a career.
While Santillan’s research has spanned across the field of reproductive science, she has a particular interest in the deadly diseases of pregnancy, including preeclampsia and its intergenerational effects. She designed and directs the Women’s Health Tissue Repository. Santillan’s work has been cited more than 2,700 times, and she has mentored 114 early career scientists and students, a testament to her expansive impact.
“Dr. Santillan has consistently demonstrated an unwavering commitment to fostering the professional and personal development of trainees in research, including myself,” said Banu Gumusoglu, assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology. “Her mentorship extends beyond the confines of traditional academic settings, touching the lives of many aspiring trainees from high school through residency, clinical fellowship, and faculty levels.”

Stephen Warren , professor of history and American studies in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences (CLAS), received the Distinguished Achievement in Publicly Engaged Research Award . The award recognizes an individual faculty member who has put addressing public needs and direct engagement with the public, in the service of improving quality of life through research, at the forefront of his or her academic activities.
A prolific scholar of Native American culture, Warren’s research has centered on the Shawnee people of Oklahoma for the past two decades. He has published four books and co-authored the most recent one , Replanting Cultures: Community-Engaged Scholarship in Indian Country, with Chief Benjamin Barnes of the Shawnee Tribe.
“Over the last two decades, Professor Warren has established himself as a leading community-engaged scholar, and his achievements in research and publishing demonstrate that community engagement and strong scholarship are not mutually exclusive,” said Nick Benson, director of the Office of Community Engagement. “Professor Warren’s work serves as an inspiration for researchers at Iowa and nationally who seek not only to make a difference in academia, but also in our communities.”

Kaveh Akbar , associate professor of English in CLAS, received the Distinguished Achievement in Arts and Humanities Research Award . This award honors distinguished achievement in humanities scholarship and work in the creative, visual and performing arts.
Akbar joined Iowa in 2022 to serve as the director of the English and creative writing major. In January, his new novel, Martyr!, was published to critical acclaim. Akbar previously published two prize-winning poetry collections and has served as poetry editor for The Nation since 2021.
“Akbar’s leadership in the profession and on campus continues: his transformative work in our department not only enriches the academic experiences of 700+ English and creative writing majors, but also enhances the profile of UI as ‘The Writing University,’” said Blaine Greteman, professor and departmental executive officer of the Department of English.

Cara Hamann , associate professor of epidemiology, received the Faculty Communicating ideas Award . This award recognizes excellence in communication about research and scholarship in the sciences and humanities and the study of creative, visual, and performing arts to a general audience directly or via print and electronic media.
Hamann has frequently shared her work on transportation issues, including teen driving, bike and scooter safety, and pedestrian safety, through peer-reviewed journals and extensive media outreach. Her recent op-ed, “The most deadly traffic policy you’ve never heard of leaves you vulnerable, too,” drew widespread attention to a legal loophole in crosswalk laws and appeared in more than 50 news outlets nationwide, including USA Today .
“Dr. Hamann’s work is not only academically rigorous but also accessible and impactful to a
wide audience,” said Diane Rohlman, associate dean for research in the College of Public Health. “Her ability to communicate with clarity, creativity, and passion coupled with her extensive media outreach, exemplifies how she utilizes multiple approaches to address transportation challenges impacting society.”

Bob McMurray , F. Wendell Miller Professor in the Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences, and Caroline Clay , assistant professor of acting in the Department of Theatre Arts, were recipients of the Office of Undergraduate Research (OUR) Distinguished Mentor Awards . The awards honors mentors’ dedication to making their students research experiences successful.
“I can’t imagine my research journey without Bob’s welcoming kindness, thriving lab community, and confident mentorship, and I am so deeply grateful for his impact on me,” said Hannah Franke, a psychology and linguistics major mentored by McMurray.
“I know I am far from the only student whose life has been impacted by Caroline Clay,” said Isabella Hohenadel, a second-year theatre arts major. “She deserves to be recognized of all of the wonderful work she does and how much she cares about us as students. I cannot think of anyone more deserving of recognition than her.”
Staff Awards

Angie Robertson , department administrator for CCOM’s Department of Microbiology and Immunology, received the Distinguished Research Administrator Award . The award recognizes staff members who performed exceptional service in support of research at the UI by exploring funding opportunities, assisting in grant proposal preparation, submission, post-award administration, and operational support.
In addition to overseeing every aspect of daily operations for the department, Robertson manages nearly 100 research grants for the department and three longstanding NIH T32 training grants.
“Angie plays a leading role in our department office, inspiring us to achieve all aspects of our missions ,” said Li Wu, professor and department chair. “She is innovative, collaborative, accountable, and respectful in her daily work. She exceeds any expectations and sets a great example for staff members in the department.”

Min Zhu , research specialist in the Iowa Institute for Oral Health Research (IIOHR) within the College of Dentistry, received the Distinguished Research Professional Award . The award recognizes staff members who performed exceptional service in support of research at the UI by conducting experiments, collecting, and analyzing results and performing operational duties associated with a laboratory or research program.
Zhu has worked as a lab bench scientist in the College of Dentistry since 2006, executing experimental work for grants and other research, working closely with IIOHR faculty members, overseeing lab maintenance and environmental health and safety efforts.
“Beyond her research skills, Dr. Zhu has been an exceptional mentor and educator for my students and other junior researchers,” said Liu Hong, professor of prosthodontics. “Her kindness and willingness to share her knowledge have made her a beloved figure among them.”

Curtis Iberg , manager of sterilization services in the College of Dentistry, received the Innovation in Safety Award, which celebrates exceptional and ground-breaking innovations that advance safety at the UI. Iberg led a major renovation of the College of Dentistry’s instrument processing and sterilization area, with the aim of encouraging better workflow and support for future growth.
“His innovations in workspace are a valuable asset to the greater University and demonstrates that the most important people to be involved in a space renovation are those that use the area because they can see how the facility can better function and how it can be designed for future needs,” said Kecia Leary, associate dean of clinics.
- Biomedical Engineering
- Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering
- Civil and Environmental Engineering
- Computer & Data Sciences
- Electrical, Computer and Systems Engineering
- Macromolecular Science & Engineering
- Materials Science & Engineering
- Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering
- Intranet Login
Search form
Case school of engineering.
- Global Opportunities
- Outside The Classroom
Related News
Spartan showcase: sydney schenk, case western reserve university awarded federal contract to develop and commercialize ‘live’ replacement joints, national science foundation awards prestigious early career grant to case western reserve university electrical engineering researcher, call for summer/fall 2024 scsam student fellowship program proposals.

We are excited to announce the Summer/Fall 2024 SCSAM Student Fellowship Program. The objective of this program is to provide a professional and technical development opportunity for CWRU students working on understanding the science and engineering of materials, broadly defined. In this program, students can propose new (to them) proof-of-concept experiments to advance their program of study. The applications are fashioned similar to the general user proposals of the DOE user facilities, and include four parts:
General demographic info
Scientific goal
Proposed instrument needs
Applications can be submitted by 5/12/2024 using the following LINK
Draft responses are saved prior to submission for 30 days.
If awarded, Fellows are entitled to time on the instrument(s) and engineer time for training on the instrument to conduct their experiment.
Explore related information at the Case School of Engineering
Visit our research facilities.
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS. A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Dear Colleague Letter: Funding Opportunities for Science and Engineering Research with Impact on Women's Health
March 18, 2024
Dear Colleagues:
With this Dear Colleague Letter (DCL), in response to the White House Initiative on Women's Health Research , the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) encourages the submission of research and education proposals related to women's health. Despite making up more than half of the population, women are historically understudied and underrepresented in health research. The historical exclusion of women from scientific and biomedical research studies, combined with the undervaluation of research that advances knowledge on conditions that uniquely, differentially, or disproportionately affect women, has resulted in significant knowledge and health gaps. Addressing these research gaps will ultimately advance the health, prosperity, and welfare of all.
NSF continues to support fundamental science and engineering research with implications for women's health. This DCL reaffirms NSF's commitment to fund discovery, innovation, and research translation on topics of relevance to women's health, from the molecular to the ecosystem level, including input from the full range of science, engineering, and education that NSF supports. Pioneering the next generation of discoveries in women's health will require a sustained effort focusing on the socioeconomic impact of women's health, breaking down disciplinary boundaries in carrying out the necessary research to advance understanding of relevant questions, and building a diverse STEM workforce committed to advancing women's health and the health of a citizens.
The National Science Foundation encourages the submission of fundamental research and education proposals related to women's health topics, including, but not limited to, proposals in the following areas:
- Projects that develop a well-informed citizenry and a diverse and capable STEM workforce that will pioneer the next generation of discoveries in women's health.
- Science and engineering approaches and novel computational models that elucidate factors that interact with and impact women's health, such as studies that examine the genetic, epigenetic, biological, economic, societal, and environmental determinants of women's health and cognition.
- Holistic approaches to women's health and development, including aging, by moving beyond diagnostics and disease management to include novel methods for discovery and monitoring. This includes, but is not limited to, wearable devices, and other types of sensing and imaging technologies that improve early detection, as well as telehealth platforms that broaden accessibility and promote women's health.
- Foundational and transformative research that advances our understanding of engineering biomechanics and/or mechanobiology related to women's health.
- Advanced biomanufacturing of cells, tissues, or organs relevant to women's health.
- Engineering research that advances the understanding of injury mechanisms and rehabilitation technologies for health conditions and disabilities that affect women.
- Development of validated models (living or computational) of healthy and pathological cells, tissues, and organ systems relevant to women's health that improve the understanding of these systems.
- Projects on novel computational approaches (i.e. multi-level and multiscale data, sensing, prediction) that examine the effects of women's health on mental and physical development across the life span and that support health decision making.
- Projects that foster partnerships with government, industry, nonprofits, civil society, and communities of practice to leverage, energize, and rapidly bring to society use-inspired research and innovation that may include, but are not limited to, innovations that enable fundamental research of women's health topics, and breakthrough technologies designed for women.
- Transdisciplinary approaches to environmental change challenges and opportunities to improve understanding of climate, environment, and health pathways to protect and promote women's health, such as research that elucidates mechanisms and/or prevention of pollution transport/exposure implicated in adverse health outcomes.
- Studies that assess theories and models of health, aging, disease, and disease transmission at multiple scales (populational, generational, transgenerational, and geographical), from the molecular to the ecosystem level, including the interaction of environment on molecular scale phenomena.
- Research that seeks to advance knowledge about the processes that shaped biological diversity in living and ancient human species such as effects of life history transitions on women's health; intergenerational effects of violence, stress, and maternal health; and impacts of biocultural context on women's health, reproduction, and epigenetics.
- Research to advance theory on design and management of organizations such as how gendered aging symptoms may affect women's experience at work and in other environments.
- Research and research infrastructure to advance basic knowledge in bias, prejudice, and discrimination directed toward women as well as the intersection of gender and other identities; dynamics of close interpersonal relationships and women's health; and power in relationships.
NSF welcomes proposals that broaden geographic and demographic participation to engage the full spectrum of diverse talent in STEM. Proposals from minority-serving institutions , emerging research institutions , primarily undergraduate institutions, two-year colleges, and institutions in EPSCoR-eligible jurisdictions , along with collaborations between these institutions and those in non-EPSCoR jurisdictions, are encouraged.
PROPOSAL SUBMISSION AND RELEVANT NSF PROGRAMS AND CONTACTS
This DCL does not constitute a new competition or program. Proposals submitted in response to this DCL should be prepared and submitted in accordance with guidelines in the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide (PAPPG) and instructions found in relevant NSF funding opportunities. Investigators who wish to submit proposals on any of these topics, or others related to women's health, are strongly encouraged to reach out to the cognizant NSF Program Officer(s) listed in the relevant funding opportunity to discuss the fit of their ideas to existing program. Specific programs and opportunities list these contacts. For assistance in determining program suitability for a proposal concept, researchers are encouraged to utilize the NSF "Program Suitability & Proposal Concept Tool (ProSPCT) at https://suitability.nsf.gov/s/ . Note that NSF has limitations on the scope of health-related projects that can be submitted to participating programs. More information on these limitations can be found in "Introduction, Part A: about the National Science Foundation" in the PAPPG. In addition to these limitations, investigators should also review new information regarding human subjects in NSF-funded research at https://new.nsf.gov/funding/research-involving-human-subjects .
Susan Marqusee, Assistant Director Directorate for Biological Sciences (BIO)
Dilma Da Silva, Acting Assistant Director Directorate for Computer and Information Science and Engineering (CISE)
Susan Margulies, Assistant Director Directorate for Engineering (ENG)
James Luther Moore, Assistant Director Directorate for STEM Education (EDU)
C. Denise Caldwell, Acting Assistant Director Directorate for Mathematical and Physical Sciences (MPS)
Kendra Sharp, Office Head Office of International Science and Engineering (OISE)
Alicia Knoedler, Office Head Office of Integrated Activities (OIA)
Sylvia M. Butterfield, Acting Assistant Director Directorate for Social, Behavioral and Economic Sciences (SBE)
Erwin Gianchandani, Assistant Director Directorate for Technology, Innovation and Partnerships (TIP)
Tufts Elephant Conservation Alliance proposals due
- Campus news

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Purpose. The purpose of your thesis proposal is to introduce your research plan to your thesis committee. You want the committee members to come away understanding what your research will accomplish, why it is needed ( motivation ), how you will do it ( feasibility & approach ), and most importantly, why it is worthy of a PhD ( significance ).
Writing a Research Proposal A guide for Science and Engineering students A Research Proposal has several inter-related purposes: Writing an effective research proposal also trains you in a valuable skill required to operate effectively in both academia and industry after you graduate. You are presenting a reasonable thesis idea or hypothesis, the
Sample Proposals. Before an article, report, or brief is accepted into the Undergraduate Engineering Review, the author must first submit a proposal that specifies the importance of the research, the scope and limitations of the research, and the methods for the research. Submitters should read the journal's Request for Proposals before submitting.
A research proposal is an obvious and essential part of a Ph.D. application in most parts of the world. It is an outline of your proposed project, whose aim is to present and justify your research idea and explain the practical ways in which you think this research should be implemented. It is often the first opportunity for you to communicate your ideas to attract interest from faculty ...
Example research proposal #1:"A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management". Example research proposal #2:"Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use". Title page. Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title pagethat includes: The proposed title of your project.
Normally a proposal should be between 1,500 and 2,000 words and will include the following: A working title of the topic area: This should do more than convey the key words associated with the proposed research, it should describe the content and direction of your project. General overview of area: This should provide a brief overview of the ...
The research proposal constitutes the main way in which the department evaluates the potential quality of your PhD plans. The proposal should be approximately 1,500 words in length and include: A provisional title. Question or hypothesis. Aims. Value of the PhD. Existing literature. Resources. Methods of work.
Guide to Writing a Research Proposal for an Engineering PhD. An important part of your PhD application is the research proposal so we want to know what your research interests are so that we may direct your application to potential supervisors. The proposal does not need be long, but the quality should be high and no more than 2-3 pages should ...
This chapter presents the overall process and practical guidelines for proposal development, particularly for student and novice researchers, over the course of five sections. The first section introduces how to initiate a research proposal: creating ideas from problems, idea evaluation, hypothesis, and overall development process. The second ...
The research proposals are evaluated both by your prospective advisor (who will have expertise in your subject) as well as the Doctor of Engineering Oversight Committee (who have backgrounds spanning many different areas). You need to write a proposal that is appropriate for both audiences. That is, you need to provide an overview of your ...
their research. Proposal Content • the Topic of the proposal is clearly formulated, of appropriate scope, and relevant to modern engineering research and practice. If successfully completed, it would represent an original contribution to knowledge. • the Survey of existing work provides sufficient background and context for the proposed
Doctoral students will write a research proposal document, which is limited to 30 pages (with 12 point font, single spacing, 1 inch margins all around) and should contain sections describing. the innovative claims of the proposed work and its relation to existing work, a description of at least one initial result that is mature enough to be ...
A research proposal should present your idea or question and expected outcomes with clarity and definition - the what. It should also make a case for why your question is significant and what value it will bring to your discipline - the why. What it shouldn't do is answer the question - that's what your research will do.
Your research proposal should include the following sections: Introduction, Background, Literature Review, Methodology, Budget and Timeline, and Conclusion. Writing roughly 1-2 sentences for each heading, create a mini-research proposal for this grant opportunity. Assume the department you are writing for is your own. Sample Answer Key for ...
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level project, and one for a PhD-level ...
Abstract: This is a brief (300-500 words) summary that includes the research question, your rationale for the study, and any applicable hypothesis. You should also include a brief description of your methodology, including procedures, samples, instruments, etc. Introduction: The opening paragraph of your research proposal is, perhaps, the most ...
Undertaking comprehensive research is a cornerstone in the development of a compelling engineering proposal. This process involves gathering data, understanding industry standards, exploring the project's context, and analyzing the potential impact of your work.
First, the proposal is reviewed, evaluated, and signed by the advisory committee. Next, the signed Proposal Evaluation Form is attached to the proposal, along with the completed Proposal Cover Sheet and submitted to the ME office for approval and signatures of the Graduate Advisor and the Department Chair. Refer to the Projects and Thesis tab ...
Project Comprehension. A typical engineering proposal will need to document superb technical comprehension of the project. In this section, the technical issues are listed and some of the alternatives discussed. This section was always the most difficult to wrap my head around, because where I came from the industry was "small enough" that ...
Here are real-life research proposal examples of funded research projects in the field of science and technology. Funder. Title. US Geological Survey (USGS) (Mendenhall Postdoctoral Research Fellowship) Using Integrated Population Modelling in Decision-support Tools to Connect Science and Decision Makers.
First, we will go with research proposal topics in electronics engineering. Understanding Effective Power Electronics Using Circuit Simulation. Redesign of AC Electrical Motors. Electric Vehicle Motors and Gearbox. Benefits of Optimization in Electrical Engineering. Electric Vehicles - A Solution to Global Pollution.
In academia, engineers produce grant proposals or research proposals in order to receive funding from government agencies and non-profit organizations. In industry, engineers, especially consultants, write proposals or "bids." Engineers produce these proposals for the company where they are working or for other organizations.
The Engineering Research and Proposal Development team proactively supports faculty, researchers, and students to attract extramural funding and facilitates the advancement of the research enterprise in SSoE. The team provides the following research proposal development support: Coordination of large and complex grant and contract proposal ...
The Office of Proposal Development (OPD) is committed to providing Stony Brook University's research community with high level support to identify extramural funding opportunities, build networks, and foster collaborations for the development of large, complex and innovative proposals. ... Packard Fellowships for Science and Engineering Program.
NSF Dear Colleague Letter: Funding Opportunities for Engineering Research in Quantum Information Science and Engineering Deadline for FY24 funding: ... Standard Research Proposals: Research proposals should be submitted to the Noyce program by the program's annual submission due date. Please read the solicitation for the prospective program ...
Jun Wang, James E. Ashton Professor and interim departmental executive officer in the College of Engineering's Department of Chemical and Biochemical Engineering, is the 2024 Scholar of the Year.The award celebrates nationally recognized recent achievement in outstanding research, scholarship, and/or creative activities.
This proposal requests funding for the NRC's Division on Engineering and Physical Sciences to organize ... scientific research and policy advice to the Government derives from its creation by Congress in 1863 (36 ... energies of the engineering community on significant aerospace policies and programs." In undertaking
The deadline for proposal submission is May 12th, 2024. ... provide a professional and technical development opportunity for CWRU students working on understanding the science and engineering of materials, broadly defined. In this program, students can propose new (to them) proof-of-concept experiments to advance their program of study ...
March 18, 2024. Dear Colleagues: With this Dear Colleague Letter (DCL), in response to the White House Initiative on Women's Health Research, the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) encourages the submission of research and education proposals related to women's health.Despite making up more than half of the population, women are historically understudied and underrepresented in health ...
School of Engineering Dean's Office Science and Engineering Complex Anderson Hall, Room 105 / 200 College Avenue Medford, MA 02155 617-627-3237. Undergraduate Admissions 617-627-3170. Graduate Admissions 617-627-3395. Engineering Graduate Programs 617-627-1332