110 Economic Growth Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best economic growth topic ideas & essay examples, 👍 good essay topics on economic growth, ⭐ simple & easy economic growth essay titles.
- The Importance of Service Industries in Economic Growth The pursuit of service economy, which dictates the specialization in the service industries, is one of the newest economic concepts that ensure the realization of the economic growth.
- ICT and Economic Growth The study of knowledge economy highlights the significance of ICT and learning in the creation of wealth and competitive advantage in the global economy. We will write a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts 808 writers online Learn More
- Traffic Congestion Impact on Dubai’s Economic Growth In many urban centers, an efficient and functioning public transport system is essential to the economic and social development of the society.
- Challenges to Sustainable Economic Growth in Africa In addition to the frequent outbreaks of conflict and instability among African states, the rapid increase in the continent’s population poses a threat to economic development.
- Sustainable Development’ and Economic Growth’ Relationship The concepts of sustainable development and economic growth are interconnected with the aim of protecting the available wealth of the earth and at the same time creating more opportunities towards satisfaction of human needs.
- Social Equality and Economic Growth Social equality provides individuals with equal opportunities to contribute to the growth of the economy. Equality also ensures that the potential of the society is fully exploited to enhance the development of the entire community.
- The Relationship between Political Stability & Economic Growth The government is very crucial to stability and economic development in a country because it holds the responsibility of developing legislation.
- Economic Growth in Canada Between 1990 and 2000 In addition, the paper discusses the sources of the economic growth data and the formula the country uses for making calculations of its various economic indicators like the GDP.
- Education, Human Capital, and Economic Growth In the broad sense, it is an intensive productive factor of economic development, including the educated part of the labor resources, knowledge, tools of intellectual and managerial work, and the environment of living and working.
- Ibn Khaldun’s Umran Theory and Economic Growth Although the subject matter is typically viewed as the means of explaining the development of the contemporary society from the perspective of the cause-and-effect concept; however, the specified approach is a common misconception and a […]
- Relationship Between Population and Economic Growth Consequently, Solow argues that the rate of population growth will be equal to the rate of economic growth in steady states.
- Poor Economic Growth in Uganda The country’s fiscal policies are not effective and the ability of the government to control the money supply is significantly low.
- Entrepreneurship and Economic Growth Entrepreneurship capital is the main factor in the neoclassical production function which is the ability of economic representatives to start new organizations.
- Economic Growth and Environment Relation Although the relevance of the EKC and the focus on the stages of development as the important factors to speak about the relationship between the economic growth and environment are highly debatable issues, it is […]
- The Impact of Automation and Robotization on Long-Run Economic Growth Due to the increased use of robotics and AI in the production industries, it is imperative to understand the contribution of mechanization in the economic world.
- Sogo Shosha’s Impact on Japan’s Economic Growth At the time, Japan had limited access to foreign markets, and the Sogo Shosha companies offered an important bridge between Japan and the rest of the world.
- Foreign Aid and Economic Growth in Developing States The paper under analysis covers the topic of the relationship between foreign aid and economic growth in developing countries. There is a raging debate on the real effect of foreign aid on developing countries, and […]
- External Debt and Economic Growth by Al Kharusi and Ada The journal article “External Debt and Economic Growth: The Case of Emerging Economy” by Sami Al Kharusi and Mbah Stella Ada highlights some of the impacts of external debts on a nation’s economic growth.
- Economic Growth and Role of Government The economy is a crucial aspect of any nation, and the role of government in its sustainable development is hard to overestimate.
- A Staple Theory of Economic Growth Further, it compares the staple approach with other frameworks of economic growth; and, eventually, suggests the applicability of a staple approach to the historical case of Canada.
- Who Reduces Economic Growth in Africa This is due to the fact that the financial assistance provided by the West to the countries of Africa is not gratuitous, but leads to the formation of state debt.
- Panama: Quality of Life and Economic Growth The inflation rate in the country is an indicator of the degree of depreciation of money. In the United States of America, this indicator is significantly higher and is 0.1%.
- Economic, Productivity Growth, and Free Trade The article by Saleem et al.is closely connected to the topic of factors contributing to productivity growth as researchers explored the impact of innovation and total factor productivity in Pakistan’s economic environment.
- Environmental Policy’s Impact on Economic Growth One common belief about the environmental policy is that it results in layoffs as well as closure of plants and reduces the level of competition in the market.
- Economic Growth and Unemployment Relationship in the USA The corresponding figures characterize the structure of economic dynamics and the diversification of the labor market. The research limitation is the multifactorial nature of economic growth and unemployment indicators.
- Family Business Promoting Economic Growth The primary goal of the article is to assess the role of the family business in the economic growth of Saudi Arabia.
- Nigeria’s Economic Evolution and Future Growth The Federal Republic of Nigeria is a country located in the western part of the African Continent. The paper is going to tackle the economic evolution and the current economic status of Nigeria.
- Latitude Can Cause Long-Run Economic Growth Differences Across Countries The researchers found that there was a clear relationship between the prevalence of disease, especially malaria, as well as the productivity of agriculture in tropical zones, and the low economic growth rate.
- Economic Growth and Inequality: Finding Linkages National policy makers and the development economists have been interested in the study of the interface between growth and equality in the past, but recently there have been a revival of this subject.
- Economic Growth of Morocco in the Context of Sustainable Development However, the labor share of GDP is the highest in the upper-middle-income sector which demonstrates the growth of a strong middle class in the country.
- Ten-Year Economic Growth of Australia The aim of this report is to show the status of the economy of Australia. The number of young people in the country constitutes the greater percentage of the population.
- Climate Change and Economic Growth The graph displays the levels of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and the years before our time with the number 0 being the year 1950.
- Vietnam’s Economic Growth and Poverty & Inequality A significant part of the population was active in employment, and this means that the numerous income-generating activities improved the economy of this country.
- History of the Kenyan Economy: Stimulating the Economic Growth Through Various Means Political influence on monetary and fiscal policies of the country by the end of the century facilitated the continued stagnation of the Kenyan economy.
- John M. Quigley: Urban Diversity and Economic Growth The article reviews the part that the traditional scale economies and diversities in the improvement of the economic growth. The diversity of cities should therefore be valued as factor contributing to economic growth.
- U.S. Automobile Industry as a Large Segment of the National Economic Growth The main indicators of stability and efficiency in work were the factors for the oligopoly of the automobile market in the United States.
- Gasoline Prices, Rates of Unemployment, Inflation, and Economic Growth The data which has been queried from the database are related to gasoline prices in California, the unemployment rate in the US, the inflation rate in the US, and Real GDP.
- Concept of Economic Growth Development is a term that can be used to explain the way the resources are put to efficient use as the greater the positive usage of resources; the more the state of development.
- Economic Growth & Developing Countries Sponsorship of trademarks will help the general public identifying the owner of goods in the market as also the availability of goods and services in the market and can protect people against false practices.
- An Initial Examination of Correlates of Economic Growth The variable of choice is REGION because of the numerical values assigned to Southeast Asia and the OECD countries. Finally, the fourth variable is degree of participation in foreign trade.
- Early Economic Growth in America and Its Causes Nor was the dominant ideology appreciably affected by the novel and radical doctrines that penetrated the intellectual barriers of the nation in the early twentieth century, as the shift in the tide of immigration carried […]
- Irish Economic Growth and Standard of Living Ireland today being named as ‘Celtic Tiger’ for the economic boom it has experienced from 1990s to 2001 and then from 2003 to 2006, which has changed the fate of this poor economy to be […]
- Walmart Inc.’s Training and Development for Economic Growth In turn, the key deliverable that the exercise mentioned above is expected to produce will be represented by a rise in the quality of communication between employees and managers.
- Economic Growth and Technological Change It is suggested that the combination of these ideologies enhances the freedoms of individuals, and allows the economy of the country to develop at a rapid rate.
- “Economic Growth: International Edition” by David Weil At the beginning of this chapter, David Weil discusses the role of technologies in increasing economic growth and productivity. This notion is used to describe a situation when the arrival of new technologies harms both […]
- Economic Growth Damage in Developing Countries During the creation of the European single currency, the EMU left the fiscal policy to the individual member states. Subsidization of agricultural products in developed countries leads to overproduction and thus affecting the trade cycle.
- Economic Growth: Problems in Different Countries The author analyzes the political and legal situation in the developing countries and devises two principles in integrating and blending informal and legal systems of property ownership.
- Australia’s Economic Growth and International Trade An IMF report has revealed that the relaxation of inflexible labor laws can lead to a decline in the rate of unemployment.
- Economics: “The Elusive Quest for Growth” by Easterly In this case, it is arguable that technology has resulted in growth from the leaping effects in production and industrial efficiency.
- Globalization Impact on China’s Economic Growth This is because descriptive research is the most appropriate research design in a study that makes use of a hypothesis and research objectives and questions. In this case, a pilot study will be conducted prior […]
- Economic Growth and Land Reform in Developing Countries The most common land reform approach is state-controlled land reforms where the state seeks to promote land redistribution to contribute to the socio-economic development of a country.
- Higher Education Financing and Economic Growth Throughout the article, the author uses data to show that increasing government spending on higher education has a negative impact on economic growth, and it leads to a decrease in the number of students joining […]
- Political Systems as Factors of Economic Growth In the 20th century, many events that transformed the global political structure had occurred: the collapse of the bipolar system of international relationships, development of independent sovereign states with the communist historical background, regime changes […]
- Saudi Arabian Human Capital and Economic Growth The current situation poses a significant risk for the future, as it is unclear whether or not the country will be able to take its place on the global oil market again nor what the […]
- Southeast Asia: Energy Security and Economic Growth The Southeast Asian peninsula is made up of the countries that are geographically positioned south of China, north of Australia, and east of India. The metropolitans are extensions of the cities to the periphery as […]
- China’s Law, Finance, and Economic Growth Nexus Besides providing the reflection of the status quo of China’s economic phenomenon aspect, section 3 offers recommendations that the country can establish to address the wanting legal protection of minority shareholders.
- Saudi Arabian Economic Growth Effect on Foreign Direct Investment The study is important because many studies that have analyzed the relationship between economic growth and FDI have examined the effect of FDI on economic growth.
- Economic, Financial and Social Growth Prospects of the UAE According to the latest information on the state’s progress, the premises for the growth of the international business in the UAE have been set rather successfully, with a range of areas, where international organisations may […]
- US Economic Growth: Projected Trends for 2016-2018 According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis, the United States is one of the largest economies in the globe. This fact explains why the country is the largest economy in the world today.
- Economic Growth in Kenya: Past and Future Challenges To ensure that the country attracts more investment, the government has put in place strategies to make the country investment conducive for both local and foreign investors, mainly from the United States and the Middle […]
- Multinational Firms Impacts on the Economic Growth Although Byres affirms that MNCs may have a positive economic impact on their host countries, he says the economic sectors that align with their operations benefit from the companies, at the expense of other economic […]
- Role of Supply-side Policies in Balanced Economic Growth Considering the drawbacks of economic growth as a measure of performance for economies such as failing to record productivity in the black markets, Keith asserts that all nations endeavour to ensure a balanced economic growth.
- Kenya: Economic Growth and Health Care System As a result of the projects financed by the international lending organizations, Kenya has seen a growth in the percentage of children accessing free basic education.
- Gross Domestic Product and Economic Growth For instance, the business sector is responsible for the production of goods and services which have to be consumed for production to continue.
- Economic Growth of Singapore from 1965 to 2008 It is a country located south of Johor, one of the Malaysian state, and it is also to the north of the Equator.
- Supply Policies’ Role in Economic Growth Despite the flexibility aspect, the role of the government in the implementation of the supply side policies cannot be ruled out.
- China’s Export-Led Economic Growth and Development Supporters of China’s export-led growth strategy believe that the approach has enabled the country to improve its economic fortunes in the last three decades.
- Remittances Role in Spurring Global Economic Growth It is necessary to lower the cost of sending remittances in order to increase the annual amount by recovering the excess that is used to cater for the exorbitant costs imposed by money transfer companies.
- Economic Growth by David Weil Another factor the author explains in a more in-depth manner in the book is the method of the comparison made in the determination of the level of economic growth.
- Cuba’s Quest for Economic Growth However, this has not had much impact on the development of the country due to inefficiencies in the government. It is important to note that the private sector is restricted in Cuba and the government […]
- Industrialization and Modern Economic Growth in India and China The other theory suggests that the de-industrialization of Indias economy was a result of the British victory in foreign markets for cottage made manufactures, followed by its penetration in the India’s home market with cheap […]
- Economic Growth and the Living Standards This arose from the high rate of economic growth as a result of the high rate of industrial revolution and technological progress.
- The Relationship Between Economic Growth and Development To this end, the author is going to discuss the relationship between economic development and economic growth Economic Development Overview Economic development is characterised by the initiatives put in place to spearhead improvement of the […]
- Etihad Airways to Collaborate With Maharashtra Government for Economic Growth The main issue of the article is an establishment of collaborative bonds between Etihad Airways and the government of Maharashtra. The opportunity to extend the purposes of the transitional services by launching the first touristic […]
- Effect of Civil War on Economic Growth The sources will provide data about the state of Sudan before the civil war and the state of the economy after the war.
- Effect of Civil War on Economic Growth: Evidence From Sudan Of greater essence in the paper is the collection of a set of data and literature that will help in linking the scale of violence and instability caused by the civil war in Sudan and […]
- Sustaining Australia’s Rate of Economic Growth The Australian Bureau of Statistics declared that in the year 2005-06 to 2009-10 witnessed the increase of 21% in the GVA of mining industry in Australia.
- Services Industries’ Role in Building Economic Growth Overview of the task There is a compelling need to highlight the importance of services economy which policy makers and entrepreneurs alike can benefit from, by making use of the economic and business potential in […]
- Services Industries and Economic Growth Importance of technology in the service industry Another reason for building service economy is because of the technological advancement in the service industry.
- United Arab Emirates Vision 2021: Economic and Social Prosperity The national interest is to be proactive in responding to challenges affecting the people of the UAE and to leave a legacy of prosperity and stability.
- Economic Growth and Development Differences between economic growth and economic development When compared to economic development as we are to witness shortly, economic growth is a simpler and narrower subject.
- China’s Economic Growth and Financial Development It is the wish of every country to realize improved and sustainable economic growth and financial development in order to improve the living standards of the greatest majority among its citizenry.
- Democracy and Economic Growth: Asia-Pacific Region Experiences Kalpana and Jolly describe that to date, communication industry in the Asia-pacific area have been boosted by flexible and mobile networks and the relevant maintenance of data systems. The maintenance of high economic growth reduces […]
- Has Globalisation Led To Economic Growth? However, the benefits of globalization in promotion of economic growth outweigh the negative effects that it has in economic growth of a country.
- Australia’s Economic Growth One of the main dangers which awaits Australia as a result of the reduction of the Asian demand in its resources is the reduction in the investment.
- Economic History of Canada: How Did the Settlers Facilitate Economic Growth? The study of economic history of Canada involves the analysis of the prevalent economic institutions and industries. The major analytical part of the paper will concentrate on the role of settlers in developing the economy.
- Impact of Economic Growth on Environmental Sustainability Because of constant development of the richest economies, such as the United Kingdom, and United States, the consumption levels of the global population surpass the actual amount of natural resources that the Earth has prepared […]
- Institutional Reforms and China’s Economic Growth The paper also evaluates some of the issues that China has to do in order to maintain the country’s future economic growth and development.
- Building Economic Growth: Service Industries Significance For example, service industries form the largest category in the Australian and Canadian economy in regards to employment, and businesses. In addition, the need for organizations to develop their service offerings is due to the […]
- Services Industries Are Important in Building Economic Growth Ettlie Rosenthal postulates that a customer is always engaged in provision of a service, and the reaction of the customer to the service affects the quality.
- India’s Highs and Lows in Economic Growth India in particular has become one of the fastest growing countries in the world after China and the country shows signs of maintaining the growth momentum in a sustainable manner.
- International Trade Policy and Economic Growth Realization Similarly, the labor, which is the human asset employed in the realization of this output of cooperation, will necessitate the international bodies to observe and regulate all the players in the international trade.
- Technology Progress in Realising Sustainable Economic Growth Because of the growth theory and the development theory having fostered the process of technological advancement as the core reason for economic growth, most of the Asian economies have embarked on the initiative.
- The Economic Growth of China and India The new infrastructure invested in China and the increase in credit in India show that there is a bigger growth of credit in India than in China.
- China’s Rapid Economic Growth This piece of work gives a critical discussion of the various factors that are associated with the rapid economic growth in China in the last three decades and their implications in the country as well […]
- Rising Oil Prices’ Effects on Economic Growth Increase in production costs and the decrease in consumption expenditure caused by the rise in oil prices prompt producers to reduce outputs.
- The Role of the State in Encouraging Economic Growth Despite the call for minimization of the role of the state in regulating trade and other economic activities by proponents of trade liberalization following the demise of the Cold War in 1980s and 1990s,it is […]
- Theories of Economic Growth Too, despite highlighting the plight of the global poor, most of these activities are executed with the aim of increasing the foreign aid to the poor.
- China’s Economic Growth and Inflation On the road to becoming the second largest economy, China has experienced growth rates of about 10% in the last 30 years making it to top the list of the fastest growing economies.
- Effects of China’s Economic Growth on Sub-Saharan Africa On the same note, trading with China has led to increase in prices of raw materials that are produced by countries in Sub-Saharan Africa thus leading to expansion of Gross Domestic Product.
- China’s Economic Growth Since 1978 The article by Wang and Yao, however, sought to use data of China’s human capital stock to analyze the economic growth of the country. China’s involvement in the global economy subjected it to the effects […]
- Relationship between Economic Growth and Nation’s Health Ascertaining the influence of economic growth in health care is necessary for policy makers since such an intimate understanding of the relationship between economic growth and population health will enable them to formulate astute policies […]
- External Financing and Economic Growth The main reason why investors may decide to pull out of a country in the course of their stay is loss of faith in that country’s economy.
- Kenya’s Economic Growth The level of increase in output of services and goods is used as a measure of economic growth. Kenya’s government has been trying to be ahead of population growth, and this has been favored by […]
- Economic Growth in Hong Kong and Singapore As a result, support for investment and exports is one of the most successful methods that have been used to encourage economic growth for typical firms in Hong Kong and Singapore.
- Economic Growth and Crises in Historical Perspective Describing the concepts history, contributors and the how the changes occurred in the economic history In line with the World of Economics, economic thought began with the onset of industrialization.
- Colombia’s Improved Business Climate: Foreign Investment and Economic Growth Political instability in the country can be traced to the middle of the twentieth century after the assassination of the country’s president in the year 1948.
- Rapid Economic Growth and Industrialization in Japan In Asia, Japan was the first country to exhibit a marked positive growth after the damage caused to the nation following the world war.
- Key Drivers of China’s Rapid Economic Growth and the Global Impacts The resulting graduates therefore worked in the manufacturing sectors of the economy and thus led to the improvement of the quantity and quality of outputs.
- Is China’s Economy Another Bubble? The fact that China is expected to contribute to about a third of the world’s growth this year makes the issue a global concern.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 26). 110 Economic Growth Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/economic-growth-essay-topics/
"110 Economic Growth Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 26 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/economic-growth-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '110 Economic Growth Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 26 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "110 Economic Growth Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/economic-growth-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "110 Economic Growth Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/economic-growth-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "110 Economic Growth Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 26, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/economic-growth-essay-topics/.
- Acquisition Essay Ideas
- Bureaucracy Paper Topics
- Antitrust Law Research Topics
- Business Structure Titles
- Capitalism Paper Topics
- Economic Topics
- Growth Strategy Titles
- Macroeconomics Topics
- Performance Indicators Essay Topics
- Manufacturing Essay Topics
- Research and Development Essay Topics
- Social Development Essay Topics
- Technology Essay Ideas
- Scientist Paper Topics
- Urbanization Ideas

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium

114 Economic Growth Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Economic growth is a crucial aspect of any country's development and prosperity. It refers to the increase in the production of goods and services in an economy over time, leading to higher income levels and improved living standards for the population. As such, economic growth is a key indicator of a country's overall economic health and can have a significant impact on various sectors such as employment, investment, and international trade.
When it comes to writing an essay on economic growth, there are countless topics and examples to explore. Whether you are a student looking for inspiration for your next assignment or a researcher looking to delve deeper into the subject, here are 114 economic growth essay topic ideas and examples to get you started:
- The impact of technological advancements on economic growth
- The role of infrastructure development in fostering economic growth
- The relationship between education and economic growth
- The effects of government policies on economic growth
- The importance of innovation in driving economic growth
- The impact of globalization on economic growth
- The role of entrepreneurship in stimulating economic growth
- The effects of population growth on economic development
- The relationship between income inequality and economic growth
- The impact of natural resources on economic growth
- The effects of demographic changes on economic growth
- The role of monetary policy in promoting economic growth
- The impact of fiscal policy on economic growth
- The effects of trade liberalization on economic growth
- The relationship between financial development and economic growth
- The role of foreign direct investment in driving economic growth
- The effects of corruption on economic growth
- The impact of environmental sustainability on economic growth
- The relationship between healthcare and economic growth
- The effects of social capital on economic development
- The role of institutions in fostering economic growth
- The impact of urbanization on economic growth
- The effects of inflation on economic development
- The relationship between government debt and economic growth
- The role of technology transfer in promoting economic growth
- The effects of labor market regulations on economic growth
- The impact of political stability on economic development
- The relationship between property rights and economic growth
- The role of foreign aid in fostering economic growth
- The effects of currency devaluation on economic development
- The impact of financial crises on economic growth
- The relationship between education and human capital formation
- The role of public-private partnerships in promoting economic growth
- The effects of international trade agreements on economic development
- The impact of automation on economic growth
- The relationship between economic growth and poverty reduction
- The role of economic diversification in fostering sustainable growth
- The effects of demographic transitions on economic development
- The impact of climate change on economic growth
- The relationship between energy consumption and economic development
- The role of regional integration in promoting economic growth
- The effects of government corruption on economic development
- The impact of social welfare programs on economic growth
- The relationship between financial inclusion and economic development
- The role of job creation in driving economic growth
- The effects of income redistribution on economic development
- The impact of agricultural productivity on economic growth
- The relationship between industrialization and economic development
- The role of foreign exchange reserves in promoting economic growth
- The effects of trade protectionism on economic development
- The impact of technological diffusion on economic growth
- The relationship between economic growth and environmental degradation
- The role of sustainable development goals in fostering economic growth
- The effects of population aging on economic development
- The impact of digital transformation on economic growth
- The relationship between financial literacy and economic development
- The role of social entrepreneurship in promoting economic growth
- The effects of income mobility on economic development
- The impact of public investments on economic growth
- The relationship between economic growth and social cohesion
- The role of gender equality in fostering economic development
- The effects of cultural diversity on economic growth
- The impact of technological adoption on economic development
- The relationship between economic growth and income distribution
- The role of inclusive growth in promoting sustainable development
- The effects of financial inclusion on economic growth
- The impact of digital infrastructure on economic development
- The relationship between economic growth and public health
- The role of social capital in fostering economic development
- The effects of labor market flexibility on economic growth
- The impact of consumer spending on economic development
- The relationship between economic growth and political stability
- The role of human capital development in promoting economic growth
- The effects of urbanization on sustainable development
- The impact of transportation infrastructure on economic growth
- The relationship between economic growth and social mobility 77
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
Economics Essay Examples

Ace Your Essay With Our Economics Essay Examples
Published on: Jun 6, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

Share this article
Are you struggling to understand economics essays and how to write your own?
It can be challenging to grasp the complexities of economic concepts without practical examples.
But don’t worry!
We’ve got the solution you've been looking for. Explore quality examples that bridge the gap between theory and real-world applications. In addition, get insightful tips for writing economics essays.
So, if you're a student aiming for academic success, this blog is your go-to resource for mastering economics essays.
Let’s dive in and get started!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is an Economics Essay?
An economics essay is a written piece that explores economic theories, concepts, and their real-world applications. It involves analyzing economic issues, presenting arguments, and providing evidence to support ideas.
The goal of an economics essay is to demonstrate an understanding of economic principles and the ability to critically evaluate economic topics.
Why Write an Economics Essay?
Writing an economics essay serves multiple purposes:
- Demonstrate Understanding: Showcasing your comprehension of economic concepts and their practical applications.
- Develop Critical Thinking: Cultivating analytical skills to evaluate economic issues from different perspectives.
- Apply Theory to Real-World Contexts: Bridging the gap between economic theory and real-life scenarios.
- Enhance Research and Analysis Skills: Improving abilities to gather and interpret economic data.
- Prepare for Academic and Professional Pursuits: Building a foundation for success in future economics-related endeavors.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
If youâre wondering, âhow do I write an economics essay?â, consulting an example essay might be a good option for you. Here are some economics essay examples:
Short Essay About Economics
A Level Economics Essay Examples
Here is an essay on economics a level structure:
Band 6 Economics Essay Examples
Here are some downloadable economics essays:
Economics essay pdf
Economics essay introduction
Economics Extended Essay Examples
In an economics extended essay, students have the opportunity to delve into a specific economic topic of interest. They are required to conduct an in-depth analysis of this topic and compile a lengthy essay.
Here are some potential economics extended essay question examples:
- How does foreign direct investment impact economic growth in developing countries?
- What are the factors influencing consumer behavior and their effects on market demand for sustainable products?
- To what extent does government intervention in the form of minimum wage policies affect employment levels and income inequality?
- What are the economic consequences of implementing a carbon tax to combat climate change?
- How does globalization influence income distribution and the wage gap in developed economies?
IB Economics Extended Essay Examples
IB Economics Extended Essay Examples
Economics Extended Essay Topic Examples
Extended Essay Research Question Examples Economics
Tips for Writing an Economics Essay
Writing an economics essay requires specific expertise and skills. So, it's important to have some tips up your sleeve to make sure your essay is of high quality:
- Start with a Clear Thesis Statement: It defines your essay's focus and argument. This statement should be concise, to the point, and present the crux of your essay.
- Conduct Research and Gather Data: Collect facts and figures from reliable sources such as academic journals, government reports, and reputable news outlets. Use this data to support your arguments and analysis and compile a literature review.
- Use Economic Theories and Models: These help you to support your arguments and provide a framework for your analysis. Make sure to clearly explain these theories and models so that the reader can follow your reasoning.
- Analyze the Micro and Macro Aspects: Consider all angles of the topic. This means examining how the issue affects individuals, businesses, and the economy as a whole.
- Use Real-World Examples: Practical examples and case studies help to illustrate your points. This can make your arguments more relatable and understandable.
- Consider the Policy Implications: Take into account the impacts of your analysis. What are the potential solutions to the problem you're examining? How might different policies affect the outcomes you're discussing?
- Use Graphs and Charts: These help to illustrate your data and analysis. These visual aids can help make your arguments more compelling and easier to understand.
- Proofread and Edit: Make sure to proofread your essay carefully for grammar and spelling errors. In economics, precision and accuracy are essential, so errors can undermine the credibility of your analysis.
These tips can help make your essay writing journey a breeze. Tailor them to your topic to make sure you end with a well-researched and accurate economics essay.
To wrap it up , writing an economics essay requires a combination of solid research, analytical thinking, and effective communication.
You can craft a compelling piece of work by taking our examples as a guide and following the tips.
However, if you are still questioning "how do I write an economics essay?", it's time to get professional help from the best essay writing service - CollegeEssay.org.
Our economics essay writing service is always ready to help students like you. Our experienced economics essay writers are dedicated to delivering high-quality, custom-written essays that are 100% plagiarism free.
Also try out our AI essay writer and get your quality economics essay now!
Barbara P (Literature)
Barbara is a highly educated and qualified author with a Ph.D. in public health from an Ivy League university. She has spent a significant amount of time working in the medical field, conducting a thorough study on a variety of health issues. Her work has been published in several major publications.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Essay on Economic Growth: Top 13 Essays | Economics
Here is a compilation of essays on ‘Economic Growth’ for class 9, 10, 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Economic Growth’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on Economic Growth
Essay Contents:
- The New (Endogenous) Economic Growth Theory
Essay # 1. Introduction to Economic Growth:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Various theories, viewpoints and models have been presented from time to time to account for the sources of economic growth and the determinants of economic development. To most people, a theory is a contention that is impractical and has no factual support.
For the economist, however, a theory is a systematic explanation of interrelationships among economic variables and its purpose is to explain causal relationships among these variables. Usually a theory is used not only to understand the world better but also to provide a basis for policy. This essay discusses a few of the major theories of economic development, from which emerged alternative approaches to economic development.
The earliest students of development economics were the mercantilists. Mercantilists were a group of traders. They believed that exports were always good for a country because exports implied inflow of precious metals (such as gold and silver). By contrast, imports were harmful for a country because imports implied outflow of precious metals. So, in their view, growth and development of a nation depended on its accumulation of precious metals.
Essay # 2. Adam Smith and Economic Growth :
The mercantilist view was challenged by Adam Smith (1723-1790), the Father of Economics, in 1776. Smith, in his Wealth of Nations, pointed out that the mercantilist view contained a major fallacy. International trade is just like a two-person zero-sum game in which one country’s gains is the other country’s loss. So two trading nations cannot have trade surplus (or favourable balance of trade) at the same time. In the late 18th century Smith argued that the true wealth of a nation is not its accumulated gold and silver hut its labour power— the human factor of production.
And the wealth of nation depended on two main factors:
(i) The productivity of labour, and
(ii) The proportion of productive labour in the total labour force (i.e., the labour force participation rate).
Smith believed that division of labour, specialisation, and exchange were the true springs of economic growth.
Smith argued that in a market-based (competitive) economy, with no collusion, cartel or monopoly, each individual, by acting in his (her) own interest, promoted the public interest. A producer who charges more than others will not find buyers, a worker who asks more than the going wages will not get job, and an employer who pays less than the market wage (i.e., the wages competitors pay) will not find anyone to work.
It was as if an invisible hand were behind the self-interest of capitalists, merchants, landlords and workers, directing their actions toward maximum economic growth. So Smith advocated a laissez-faire (non-interference of government in economic matters) and free trade policy as two growth-promoting measures.
Essay # 3. The Classical Theory of Economic Stagnation :
The classical theory, based on the work of David Ricardo (1772-1823), had a pessimistic view about the possibility of sustained economic growth. For Ricardo, who assumed little continuing technical progress, growth was limited by scarcity of land. A major tenet of Ricardo was the law of diminishing returns.
For him, diminishing returns due to population growth and a fixed supply of land threatened economic growth. Since Ricardo believed that technical change or improved production techniques could only temporarily avert the operation of the law of diminishing returns, increasing capital was seen as the only way to offset this long-run threat.
However, any fall in the rate of capital accumulation would lead to eventual stagnation. Ricardian stagnation might result in a Marxian scenario, in which wages and investment would be maintained only if property were confiscated by society and payments to private capitalists and landlords stopped.
Essay # 4. Marx’s Theory of Economic Development :
Marx (1818-83) predicted that the capitalist system would in the initial stage grow due to increased profit (surplus value which was the result of exploitation of labour) and would provide funds for accumulation. But since wages were pegged at the subsistence level, due to the existence of a huge reserve army of unemployed, the capitalists would suffer from a realisation crisis. They would not be able to realise the profits embodied in already produced goods. And, according to Marx, the under consumption of the masses is the root cause of all crises.
Marx, in fact, made certain predictions about the growth, maturity and stagnation of capitalism. He predicted that the capitalist system would ultimately collapse for want of markets and would yield place to socialism.
Unfortunately, history has not obliged Marx. The year 1989 saw the collapse of socialism (especially in erstwhile USSR and its satellite countries) and with it the abandonment of the centralised planning system and the emergence of newborn post-socialist countries.
All these countries have embraced the market system which is now thought to be a more efficient mechanism for solving society’s economic problems, promoting faster economic growth and improving the living standards of the people.
Essay # 5. Rostow’s Stages of Economic Grow th:
By criticizing Marx’s stages of growth, viz, feudalism, capitalism and socialism, Walter W. Rostow sets forth a new historical synthesis about the beginnings of modern economic growth on six continents.
His economic stages are:
(i) The traditional society,
(ii) The preconditions for takeoff,
(iii) The takeoff,
(iv) The drive to maturity, and
(v) The age of high mass consumption.
The most important stage is the third one, i.e., the takeoff stage. In order to reach that stage a country must save and invest at least 10 -12% of its national income. Many Western countries had already reached the stage when Rostow’s book appeared. Many underdeveloped countries reached the stage later (mainly under the influence of planning).
Essay # 6. Vicious Circle Theory of Economic Growth :
The vicious circle theory presented by Ragnar Nurkse in his book- The Problems of Capital Formation in Underdeveloped Countries, 1953) indicates that poverty perpetuates itself in mutually reinforcing vicious circles on both the supply and demand sides. In fact, low per capita income is both the cause and the effect of poverty.
A. Supply Side :
At low levels of income, people cannot save much. Shortage of capital leads to low productivity of labour, which perpetuates low levels of income. Thus the circle is complete, as shown in Fig. 1. A country is poor because it was previously so poor that it could not save and invest. Or, as Jeffrey Sachs (2005) explains the poverty trap: ‘Poverty itself is the cause of economic stagnation.’
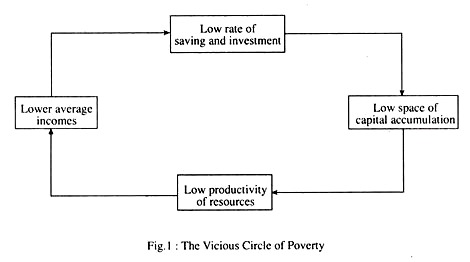
In short, various obstacles to development are self-enforcing. Low levels of income prevent saving, retard capital growth, hinder productivity growth and keep income low. Successful development may require taking steps to break the chain at various points. By contrast, as countries get richer they save more, creating a virtuous circle in which high sayings rates lead to faster growth. A country is rich because it was rich in the past. Or a rich country is likely to become richer in the future.
B. Demand Side:
In addition, due to the narrow size of the domestic market for light consumer goods (such as shoes, textiles, radio, etc.) there is hardly any incentives for potential entrepreneurs to investment. Lack of invest means low factor productivity and continued low income. A country is poor because it was so poor in the past that it could not provide the market to spur investment.
Essay # 7. Balanced Vs. Unbalanced Economic Growth :
A major debate in the areas of development economics from the 1940s through the 1960s concerned balanced growth versus unbalanced growth. The term balanced growth has been used in different senses. The meaning of the term may vary from the absurd requirement that all sectors grow at the same rate to the more sensible plan that a minimum attention has to be given to all major sectors—industry, agriculture, and services.
Balanced Growth :
The main advocate of the doctrine of balanced growth was Nurkse. To him, balanced growth means the synchronized application of capital to a wide range of different industries. Nurkse considers this strategy as the only escape route from the vicious circle of poverty (underdevelopment).
Big Push Thesis :
The advocates of the Nurkseian doctrine support the big push thesis, arguing that a strategy of gradualism is bound to fail. A substantial effort is needed to overcome the inertia inherent in a stagnant economy. According to Paul N. Rosenstein-Rodan (1943), the factors that contribute to economic growth—such as demand and investment in infrastructure—do not increase smoothly but are subject to sizable jumps or indivisibilities. These indivisibilies result from flows created in the investment market by external economies (positive externalities), that is, cost advantages enjoyed by one firm due to output expansion by another firm.
These benefits spillover to society as a whole, or to some members of it, rather than to the investor concerned. This means that the social profitability of this investment exceeds its private profitability. Furthermore, unless the government intervenes, total private investment will be grossly inadequate compared to society’s needs.
Indivisibility in Infrastructure :
For Rosenstein-Rodan, a major indivisibility is in infrastructure, such as power, transport and communications. This basic social capital reduces costs to other industries.
Indivisibility in Demand :
The indivisibility arises from the interdependence of investment decisions; that is, a prospective investor is uncertain whether the output from his investment projects will find a market. This problem can be solved if a number of industries are set up so that new producers become each other’s customers and create additional markets through increased incomes. Complementary demand reduces the risk of not finding a market. Reducing interdependent risks increases the incentive to invest.
Hirschman’s Strategy of Unbalanced Growth:
A. O. Hirschman develops (1958) the idea of unbalanced investment to complement existing imbalances. In his view, deliberately unbalancing the economy, in line with a predesigned strategy, is the best path for economic growth. He argues that the big push theory cannot be applied to less developed countries (LDCs) because they do not have the skills needed to launch such a massive effort. The scarcest resource in LDCs is the decision-making input, i.e., entrepreneurship, not capital. Economic development is held in check not by shortage of savings, but by that of risk-takers and decision-makers.
In Hischman’s view, low-income countries need a development strategy that spurs investment decisions. He suggests that since physical resources and managerial skills and abilities are scarce in LDCs, a big push is sensible only in strategically selected industries within the economy. Growth is then likely to spread from one sector to another (similar to Rostow’s concept of leading and lagging sectors).
However, it is not in the Tightness of things to leave investment decisions solely to individual entrepreneurs in the market. The reason is that the profitability of different investment projects may depend on the order in which they are undertaken. For example, the return from a car factory may be 12%, and that from a steel plant 10%. However, if the car factory is set up first, its return is likely to be low due to shortage of steel.
However, if the steel plant is set up, the returns to the car factory may increase in the next period from 12 to 15%. This means that society would be better off investing in the steel plant first and the car factory next, rather than making independent decisions based on the market. So planners and policy-makers need to consider the interdependence of one investment project with another so that they maximise overall social profitability.
They need to make that investment which promotes the maximum investment. Investment should be concentrated in those industries which have the strongest linkages—both backward (to enterprises that sell inputs to the industry) and forward (to units that buy output from the industry).
The steel industry, for instance, may be accorded the maximum priority by the planners because it has backward linkages with coal and iron ore industries, and forward linkages with car and engineering industries. So there is need for making public investment in steel industry which has a strong investment potential in the sense that it is likely to spur private investment. Similarly, public investment in power and transport will increase productivity and thus encourage investment in various other industries.
Critique of Unbalanced Growth :
One main drawback of unbalanced growth approach is that it fails to stress the importance of agricultural investments. According to Hirschman, agriculture does not stimulate linkage formation so directly as other industries.
However, empirical studies indicate that agriculture has substantial linkages to other sectors. Moreover, as Johnston and Mellor have pointed out, agricultural growth makes vital contributions to the non-agricultural sector through increased food supplies, added foreign exchange, labour supply, capital transfer and wider markets.
The truth is that there is no conflict between these two strategies of development. An optimum strategy must combine some elements of balance as well as imbalance. As E. Wayne Nafziger has opined- ‘What constitutes the proper investment balance among sectors requires careful analysis. In some instances, imbalances may be essential for compensating for existing imbalances. By contrast, Hirschman’s unbalanced growth should have some kind of balance as an ultimate aim.’
Essay # 8. Underdevelopment as Coordination Failure :
To some modern economists underdevelopment is result of coordination failure. This is why the theory of big push or critical minimum effort or balanced growth has been put forward. The coordination failure problem leads to multiple equilibria, as has been suggested by M. P. Todaro.
The basic point is that benefits an economic agent receives from taking an action depends positively on how many other agents are expected to take the same action or the extent of these actions. For example, price a farmer can expect to receive for his output depends on the number of intermediaries who are active in channel of distribution which, in turn, depends on number of other farmers who specialise in the same product.
Likewise, fertility decision need in effect to be coordinated across families. All are better if average fertility rate declines. But any one family may be worse off by being only one to have fewer children. The reason is that in rural areas children are a source of labour power for agricultural families. So if only one family adopts the small family norm it will have to hire workers from the external labour market by paying higher wages.
In Fig. 2 the S-shaped privately rational decision function YY first increase at a increasing rate and the at a decreasing rate.
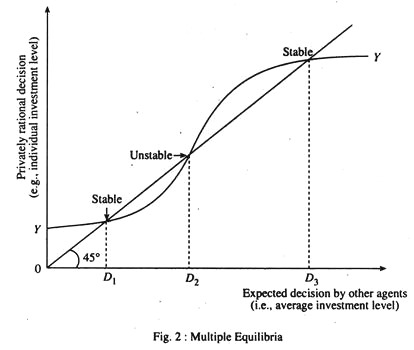
This shape reflects typical nature of complementariness. For example, some economic agents may take complementary action such investing even if others in the economy do not, particularly when interactions are expected through foreigners, say, through exporting. If in this case one or a few agents take action, each agent may be isolated from others. So spillovers may be minimum.
Thus the curve YY does not rise quickly at first as more agents take the decision to invest. But after enough invest there may be a cumulative effect, in which most agents begin to provide external benefits to neighbouring agents and the curve rises at a much faster rate. Finally, after most potential investors have been seriously affected and most important gains have been realised the curve starts to rise at a decreasing rate.
In Fig. 2 function YY cuts the 45° line three times. Thus there is possibility of multiple equilibria. Of these D 1 and D 3 are stable equilibria. The reason is that if expectations were slightly changed to a little above or below these-levels economic agents (investors) would adjust their behaviour in such a way as to bring the economy back to equilibrium levels. In each case YY function cuts 45° line from above. This is the hallmark of a stable equilibrium.
The intermediate equilibrium at D 2 cuts YY function from below. So it is unstable. This is because if a few less entrepreneurs were expected to invest equilibrium would be D 1 and if a few more, equilibrium would shift to D 3 .
Therefore, D 2 may be treated as chance equilibrium, i.e., it could be an equilibrium only by chance. Thus in practice we can think of an unstable equilibrium such as a D 2 as ways of dividing ranges of expectations over which a higher or lower stable equilibrium will hold sway.
Thus there is need for coordinating investment decisions when the value (rate of relation) of one investment depends on the presence or the extent of other investments. All are better off with more investors or higher rate of investment.
But this cannot be achieved only through market system. So there is need for government intervention. It is possible to achieve the desired outcome only under the influence of certain types of government policies. Difficulties of investment coordination give rise to government-led strategies for industrialisation.
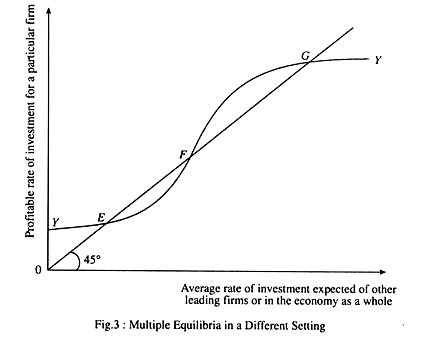
Technology Spillover :
The investment coordination perspective explains the nature and extent of problems posed when technology has spread effects, i.e., development of technology by one firm has favourable effects on other firms, i.e., positive externality.
Now suppose we show average rate of investment expected of other key firms or in the economy as a whole on the horizontal axis or profitable rate of investment for a particular firm on the vertical axis, given what other firms are expected to invest on average. In this case points where the YY the curve crosses 45° line in Fig. 2 depict equilibrium investment rates.
Then due to direct relation between investment and growth, the economy may get struck in a low growth rate largely because its expected rate of investment is likely to be low. Changing expectations may not be sufficient if it is more profitable for a firm to wait for others to invest rather than to take the lead and become a ‘pioneer’ investor. In that case there is need for government policy in addition to a change of expectation of investors.
This is why attention to the presence of multiple equilibria is so important. Market forces can bring us to one of these equilibria but they are not sufficient to ensure that no equilibrium will be achieved and they offer no mechanism to move from a bad equilibrium to a good one.
In general when jointly profitable investment may not be made without coordination multiple equilibria may exist in which the same individuals with access to same resources and technologies could find themselves in either a good or bad situation. For example, the extent of effort of each firm in a developing region puts to increase the rate of technological transfer depends on effort put by other firms.
No doubt bring in modern technology from abroad often has spillover effects for other firms. But the presence of multiple equilibria subject to making better technology available is a necessary but not a sufficient condition to achieve faster economic growth and consequent improvement in the living standards of the people.
Essay # 9. The Lewis Model of Economic Growth :
In the Lewis model, economic growth occurs due to an increase in the size of the industrial sector, which accumulates capital, relative to the subsistence agricultural sector, which does not accumulate any capital. The source of capital in the industrial sector is profits from the low wages paid in unlimited supply of surplus labour from traditional agriculture. An unlimited supply of labour available to the industrial sector facilitates capital accumulation and economic growth.
Urban industrialists increase their labour supply by attracting workers from agriculture who migrate to urban areas when wages there exceed rural wages. Lewis elaborates this point while explaining labour transfer from agricultural to industry in a newly industrializing country. Industrial expansion would come to a halt when labour shortages develop in rural areas.
The significance of the Lewis model is that growth takes place as a result of structural change. An economy consisting mainly of a subsistence agricultural sector (which does not save) is transformed into one predominantly in the modern capitalist sector (which alone saves). As the relative size of the capitalist sector grows, the ratio of profits and other surplus to national income grows.
Essay # 10. The Fei-Ranis Modification of Lewis Model of Economic Growth :
In John Fei and Gustav Ranis, in their modification of the Lewis model, contend that the agricultural sector must grow, through technical progress, for output to grow as fast as population; technical change increases output per hectare to compensate for the growing pressure of labour on land, which is a fixed resource. As with the Lewis model, the advent of fully commercialized agriculture and industry ends industrial growth (or what Fei-Ranis calls the take-off into self-sustained growth).
Essay # 11. Baran’s Neo-Marxist Thesis :
Paul A. Baran incorporated Lenin’s concepts of imperialism and international class conflict into his theory of economic growth and stagnation. For Baran LDCs were unlikely to achieve growth and development because of Western economic and political domination, especially in the colonial period.
Capitalism arose not through the growth of small competitive firms at home but through the transfer from abroad of advanced monopolistic business. Baran felt that as capitalism took hold, the bourgeoisie (business and middle classes) in LDCs, lacking the strength to spearhead thorough institutional change for major capital accumulation, would have to seek allies among other classes.
From Marxian perspective Baran writes:
What is decisive is that economic development in underdeveloped countries is profoundly inimical to the dominant interests in the advanced capitalist countries. The backward world has always represented the indispensable hinterland of the highly developed capitalist West.
The only way out of the impasse may be worker and peasant revolution, expropriating land and capital, and establishing a new regime based on collective effort and the creed of the predominance of interests of society over the interests of a selected few.
Essay # 12. Dependency Theory of Economic Growth :
According to A. G. Frank, a major dependency theorist, underdevelopment is not simply non-development, but is a unique type of socioeconomic structure that results from the dependency of the underdeveloped country on advanced capitalist countries.
This results from foreign capital removing a surplus from the dependent economy to the advanced country by structuring the underdeveloped economy in an ‘external orientation’ that includes the export of primary products, the import of manufactures, and dependent industrialisation. As Frank states- ‘It is capitalism, world and national, which produced under development in the past and still generates underdevelopment in the present.’
Frank’s dependency approach maintains that countries become underdeveloped through integration into, not isolation from, the international capitalist system. However, despite some evidence supporting Frank, he does not give adequately demonstration that withdrawing from the capitalist system results in faster economic development.
Unequal Exchange :
According to dependency theorists, the same process of capitalism that brought development to the presently advanced capitalists countries resulted in the underdevelopment of the dependent periphery. The global system is such that the development of part of the system occurs at the expense of other parts. Underdevelopment of the periphery is the Siamese twin of development of the centre.
Centre-periphery trade is characterised by unequal exchange. This may refer to deterioration in the peripheral country’s terms of trade. It may also refer to unequal bargaining power in investment, transfer of technology, taxation, and relations with multinational corporations. According to S. Amin, unequal exchange means the exchange of products whose production involves wage differentials greater than those of productivity.
The Neoclassical Counterrevolution :
The neoclassical counterrevolution to Marxian and dependency theory emphasised reliance on the market, private initiative, and deregulation in LDCs. Neoclassical growth theory emphasised the importance of increased saving and capital formation for economic development and for empirical measures of sources of growth. The neoclassical model predicts that incomes per capita between rich and poor countries will converge. But empirical studies do not support this prediction.
This is why N. G. Mankiw and others propose an augmented Solow neoclassical model which includes human capital as an additional explanatory variable to physical capital and labour. The Washington institutions of the World Bank, IMF, and US Government have applied neoclassical analysis in their policy-based lending to LDCs.
Essay # 13. The New (Endogenous) Economic Growth Theory :
The new (endogenous) growth theory developed by Paul Romer arose from concerns that neoclassical economists neglected the explanations of technical change and accepted the unrealistic assumption of perfect competition. For Mankiw, Romer, and Weil, human capital and for Romer, endogenous (originating internally) technology, when added to physical capital and labour in neoclassical growth theory, are important factors contributing to economic growth.
One reason is that although there are diminishing returns to physical capital, there are constant returns to all (human and physical) capital. The new growth theory, however, does no better than an enhanced neoclassical model in measuring the sources of economic growth.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Trade and Economic Growth | International Economics
- Solow’s Neoclassical Growth Model | Economic Growth | Economics
- Essay on Human Capital | Economic Growth | Economics
- Difference between Economic Growth and Economic Development
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Economic Growth, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2331
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
- Causes of Economic Growth
The topic of economic growth, and how to drive economic growth, is an important one for policy makers and businessmen alike. Indeed, especially after the 2007-2008 financial crisis in which many previously healthy economies fell into recession, economic growth has emerged as one of the most concepts in the current policy climate.
Traditionally, the factors of economic growth are embodied in the GDP equation: AD=C+I+G+X-M (Mankiw, 2008). John Maynard Keynes, a famous economist, was really the first to develop this equation for factors that drive economic growth. In this conceptualization, aggregate demand is the product of five different factors: consumption, investment, government spending, exports and imports (Mankiw, 2006).
Consumption is the first factor or cause of economic growth. Consumption in this context is limited to personal consumption; that is, consumption among private individuals for purchases of goods and services. Consumption can also be divided into different types of goods such as durable goods, nondurable goods, and commodities (Mankiw, 2006). Durable goods are large-ticket items such as cars, computers, and the purchase of appliances. Nondurable goods are typically goods such as food and clothing that have a limited consumption time; non-durable goods also includes trip to restaurants and other establishments such as those typically found in the mall. Finally, commodities are also included under the category of consumption. Commodities include the purchase of metals such as gold and silver.
Overall, consumption plays a key role in driving economic growth for more developed economies. For example, consumption traditionally composes 60-70% of gross domestic product in the United States; consumption also plays a substantive role in the economic growth of Europe. The reason consumption plays a greater role in driving growth in developed economies is, for the most part, they have higher per-capita income levels that translate into greater disposable income. At the same time, these economies also tend to be free-market economies where the offering of credit to consumers is an important way to promote economic growth.
The second main element of economic growth is investment. Individuals or corporations can engage in investment. Businesses typically make investments in capital equipment such as computers, machinery, buildings, or other goods related to the production of goods and services. Investment, however, is not limited to large businesses. Small-to-medium sized businesses may also engage in investment in such items as cars, trucks, or equipment used for accounting and investing.
Regardless the size or stage of economic growth, investment tends to play a major role in economic growth. This is especially true in the case of China. Since 1979, the Chinese economy has registered double-digit growth levels. Investment has played a key role in driving this growth. Indeed, the level of investment in China has varied between 50-65% of the country’s total GDP. This was because firms did not have any where to put their money, and decided to (over) invest in capacity such as building new houses, new factories, or investing in factory equipment to increase production. Regardless of the size and stage of economy, investment plays a key role in driving economic growth. This is especially because corporate investment is linked to other variables in the growth equation such as hiring, consumption, and exports.
The third major factor of growth is government spending. Government spending includes government purchase of goods and services that are used for government or public purposes. For example, the government may spend money to construct roads for driving, may build schools and employ teachers from tax dollars, and may purchase missile protection systems to protect people from foreign attack. Keynes posited that government expenditure could be a particularly powerful source of economic growth, particularly during times when the private sector did not spend on investment, thus also denting possible consumption expenditures (Mankiw, 2008). This was purported to be the case in the United States and other countries after the 2007-2008 financial crisis. Numerous countries introduced “stimulus” packages that pledged government expenditures in key areas such as infrastructure, education, and health in order to promote economic growth after it cratered. Although there is mixed evidence regarding the efficacy of government expenditure to drive economic growth (known in the literature as the “multiple”), many governments used it to effect.
The fourth and fifth growth drivers are related: imports and exports. Imports are goods and services that are purchased from abroad. Imports are the only growth category that is subtracted in the GDP identity. That is, the total amount a nation imports from abroad is subtracted from growth because this represents expenditures on goods and services purchased from foreign economies. Exports are an important driver of economic growth. Exports represent goods and services that are purchased by foreign individuals abroad. Exports have a positive contribution to economic growth. Indeed, exports played a key role in the development of many Asian economies in the 1970s and 1980s. Known collectively as the Asian “Tigers”, countries such as Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Hong Kong, and China developed their economies through producing lower-priced goods and selling them abroad. The problem with using exports as a main growth strategy is two-fold: 1) as a country’s economy develops, wages and other production costs naturally rise meaning that exports become more and more expensive; 2) being competitive with exports usually mean having a cheaper currency that can lead to political problems.
- Per-capita growth and living standards
Gross domestic product (GDP), whether in the aggregate or on a per-capita basis, is a statistic under rhetorical fire. Indeed, the measure is a good approximation of the value of goods and services produced in a country over a defined period of time. The measure, however, is an incomplete measure of how individuals fare in the economy whether that be as a function of living standards or their general satisfaction. In defense of GDP, it makes no claim to inform the latter issues; GDP is primarily used by governments across the world because it is easier to calculate than other more inclusive statistics (IMF, 2011). At the same time, however, it does tend to privilege economic growth as the most important economic metric. This essay will argue, based on the data provided for four countries, that per-capita GDP is not necessarily a good proxy to measure living standards in a country (Nielsen, 2011).
First, a quick methodological word on how per-capita GDP is calculated. Per-capita GDP is essentially a disaggregated measure of total GDP on an individual basis (World Bank, 2012). That is, in order to calculate the per-capita GDP for any country one takes the aggregate level of GDP output in goods and services and divides it by the total population size (IMF,2011). Thus, per-capita GDP does not fundamentally represent what each person in the economy “earns” but rather each person’s share in a country’s economic output (IMF,2011). This is an important distinction, particularly when trying to assess whether per-capita GDP is a good proxy for living standards in a country.
Looking at the data one can see how distortions in the calculation method may lead to a somewhat misleading impression of an individual’s standard of living in a country. Qatar is the country with the highest per-capital level of all four countries. There are two different measures for each country: The United Nations per-capita statistic, which essentially measures per-capita GDP in local currency meaning that countries with a weaker currency will register a lower per-capita GDP; the IMF measure which essentially measures per-capita from the same base currency meaning that it strips out differences in per-capita GDP due to currency fluctuations (Nielsen, 2011). The UN ranks Qatar fourth based on per-capita GDP; the IMF ranks Qatar first based on per-capita GDP- the difference between the two means that Qatar’s currency was likely weaker versus other currencies. Despite Qatar’s high ranking on a per-capita basis, the country has a lower human development ranking: 37 th . The dissonance between these statistics is a function of what they are measuring. Qatar is a rich country due to rich natural gas deposits located in the country (EIU Qatar, 2011). At the same time, the country has a relatively small population (roughly average for other Gulf nations) that means a high per-capita GDP level built off the country’s large aggregate GDP. The Human Development Index, on the other hand, is a broad-based index that measures individuals’ access to education, health, and other social resources (UN,2011). Thus, the measure does not focus on the size of the economy, but rather the resources individuals can take advantage of in the country. The dissonance of Qatar’s three measures could have the following interpretation: Although Qatar is certainly a “rich” country in the aggregate, individuals do not have similar access to resources in the health, educational, and social sphere, or the ability to develop at the same rate. This difference gets a the operationalization of “standard of living” because such a measure does not simply measure a country’s economic output, but the goods and services that an individual enjoys, including public goods that make up a substantive proportion of .
Equatorial Guinea would provide a similar example. Equatorial Guinea is a country blessed with abundant oil resources. The country discovered significant oil reserves off the western coast of the country leading to significant economic growth after the discovery. The country shares a similar profile to Qatar: A country with a relatively small population (total population in the country is around 700,000) and abundant natural resources that registers a high per-capita GDP, although the two measures (UN and IMF) have greater distance (EIU Equatorial Guinea, 2012). The true economic level of the country is blunted by the cross-sectional nature of the data presented; looking at time-series data would show how economic growth has skyrocketed in Guinea. However, similar to the case of Guinea, the country ranks substantially lower in the Human Development Index: 136 th . This significant dissonance might signify two things. First, the relative newness of the country’s riches where economic growth has led to a substantial boost, while government expenditures on public goods and other services have lagged behind (EIU Equatorial Guinea, 2012). Second, and somewhat related, the country likely suffers from the “Dutch Disease” where oil revenue essentially crowds out investment in other areas. In any sense, one could rightly say that Equatorial Guinea has economic development, but a low standard of living, particularly for those individuals
Finally, we have the two countries of the United Kingdom and South Korea. Of all the countries profiled in this exercise, the United Kingdom likely has the highest aggregate level of economic output. At the same time, however, the country also boasts a larger population (roughly 62 million in 2011). Thus, the ranking of 27 th and 24 th , respectively, demonstrate a mature economy with a substantial population- something not seen in the economic upstarts of Qatar and Equatorial Guinea (EIU UK, 2012). The UK, however, is the only country that boasts a Human Development Index roughly equal to the per-capita level. Overall, the UN ranks the country 28 th , marginally on par with the rankings of the per-capital level. Although there is no rule that a country should rank similarly across the three categories, it may show a greater balance in how resources are distributed. That is, the government stepping in to actually provide infrastructure, health, and educational services roughly on par with the level of economic development.
South Korea is the last country examined, and the main anomaly. South Korea arguably registered the fastest rate of economic development in history during the 1960s and 1970s. However, since the “miracle on the Han (river)” during that time, the country’s economic growth rate has slowed down, entering a more mature phase of economic development (EIU South Korea, 2012). Overall, the country ranks 36 th and 27 th , respectively, for per-capita economic level; this level is below Qatar and the UK, while higher than the average of Guinea’s two per-capita measures. Unlike the other three countries, however, South Korea boasts a higher UN Human Development Index than its per-capita GDP scores. Since South Korea has a similar ranking to countries such as Canada and Japan, it might be interesting to take a look on which factors the country is ranked higher. The country’s strength in the rankings is predicated on four factors: 1) longevity (a function of the country’s single-payer health care system); 2) education level (a high mandatory education level); 3) high cellular phone penetration rate; 4) lower level of income equality than the other four countries (UN, 2012). Together, these factors lifted South Korea into a category of countries typically reserved for advanced economies.
Overall, the data show limited correlation between per-capita income level and the human development index. This is not to say that the two are not related: high standards of living, particularly those found in northern European countries, are predicated on strong economies. However, a high level of economic , whether it be aggregate or per-capita, is not a sufficient condition to ensure a high standard of living. Indeed, the government and private enterprise must work together to provide goods and services that improves an individual’s ability to live and succeed in society. This is particularly true in the age of increasing income inequality of countries. A simple improvement in economic growth will not translate to a better standard of living if the largesse from such growth is limited to only certain individuals in the economy. Countries should also be concerned about rapid increases in per-capita growth that does not translate into an increase in living standards for the population at large.
Works Cited:
Economist Intelligence Unit. (2012). Equatorial Guinea. Available at: www.eiu.com
Economist Intelligence Unit. (2012). Qatar. Available at: www.eiu.com
Economist Intelligence Unit. (2012). South Korea. Available at: www.eiu.com
Economist Intelligence Unit. (2012). United Kingdom. Available at: www.eiu.com
International Monetary Fund (2011). Explanation of per-capita growth calculation methods.
Mankiw, G. (2008) Economics. Cengage: Boston.
Mankw, G. (2006). Macroeconomics. Cengage: Boston.
Nielsen, L. (2011). Classification of Countries Based on Their Level of Development: How It is Done and How it Could Be Done. IMF Working Paper. Available at: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/wp/2011/wp1131.pdf.
World Bank. Measurement of living standards and equality. Available at: http://siteresources.worldbank.org/ECAEXT/Resources/publications/Making-Transition-Work-for-Everyone/appendix+A.pdf.
United Nations. Human Development Index Explanation. Available at: http://hdr.undp.org/en/reports/global/hdr2011/.
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Public Justice of Erin Brockovich, Essay Example
The West vs. China in Fukuzawa Yukichi’s Thought, Essay Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371

Macro Economic Essays
These are a collection of essays written for my economic blogs.
Exchange Rate Essays
- Effects of a falling Dollar
- Why Dollar keeps falling
- Discuss Policies to Stop the Dollar Falling
- Does Devaluation Cause Inflation?
- Benefits and Costs of Falling Dollar
- Reasons for Falling Dollar
- The Dollar as the World’s Reserve Currency
Economic Growth Essays
- Evaluate Benefits of Economic Growth
- Essays on Recessions
- Causes of Recessions
- Problems of Recovering from a Recession
- What can Increase Long-Run Economic Growth?
- Discuss Effect of a fall in the Savings Ratio
Inflation Essays
- Discuss the Difficulties of Controlling Inflation
- Should the aim of the Government be to Attain Low Inflation?
- Explain What Can Cause a Sustained Increase in the Rate of Inflation
- Reasons for low inflation in the UK
- Inflation Explained
- Difficulties of Inflation targeting
- Hyperinflation
Unemployment Essays
- Explain what is meant by Natural Rate of Unemployment?
- Should the Main Macro Economic Aim of the Government be Full Employment?
- The True Level of Unemployment in the UK
- What explains low inflation and low unemployment in the UK?
Demand Side Policies
- Discuss effect of Expansionary demand-side policies on Balance of Payments and Environment
- Effects of a Falling Stock Market
- How do Mortgage Defaults affect and Economy?
- Discuss the effect of increased Government spending on education
- Phillips Curve – Trade-off between Inflation and Unemployment
Development Economics
- Why Growth may not benefit developing countries
- Does Aid Increase Economic Welfare?
- Problems of Free Trade for Developing Economies
Fiscal Policy
- Will US Economy benefit from Tax Cuts?
- Can Fiscal Policy solve Unemployment?
- Explain Reasons for UK Current Account Deficit
- Benefits of Globalisation for Developing and Developed Countries
Monetary Policy
- Discuss Effects of an Increase in Interest Rates
- How MPC set Interest Rates
- Benefits of High-Interest Rates (and recessions)
- Who Sets interest rates – Markets or Bank of England?
Economic History
- Economics of the 1920s
- What Caused Wall Street Crash of 1929?
- UK economy under Mrs Thatcher
- Economy of the 1970s
- Lawson Boom of the 1980s
- UK recession of 1991
- The great recession 2008-13
General Economic Essays
- The Dismal Science
- Difference Between Economists and Non Economists
- War and Recessions
- The Economics of Fear
- The Economics of Happiness
- Can UK and US avoid Recession?
- 3 Of the Worst Economic Policies
- Overvalued Housing Markets
- What Went Wrong with US Economy?
- Problem with Bailing out financial sector
- Problems of Personal Debt
- Problem of Inflation
- National Debt in the UK
- How To Survive a Recession
- Can A recession be a good thing?
Chinese Economy
- Problems of Chinese Economic Growth
- Should we worry about a strong China
- Chinese Growth and Costs of Growth
- Chinese Interest Rates and Economic Growth
Model essays

- A2 model essays
- AS model essays
- Top 10 Reasons For Studying Economics
- Inflation explained by Victor Borge
- Funny Exam Answers
- Humorous look at Subprime crisis
78 Economic Growth Essay Topics
🏆 best essay topics on economic growth, 📚 economic growth research paper examples, 🎓 most interesting economic growth research titles, 💡 simple economic growth essay ideas.
- Hospitality Industry in Economic Growth and Development
- Sustainability of Economic Growth
- Institutions and Economic Growth
- Social Determinants of Health: Economic Growth Effect
- Joseph Schumpeter’s Evolutionary Approach to Economic Growth
- Moral Dimensions of Economic Growth
- Debt Burden and Sustainable Economic Growth in Nigeria
- Whether Infinite Economic Growth Is Possible The author believes that there is a number of reasons why endless economic development is impossible in practice.
- Bangladesh: Stimulating Economic Growth It is crucial to address the digital literacy level in rural Bangladesh to stimulate economic growth, as it is deficient nowadays.
- Transportation Developments and Subsequent Economic Growth From 1865 to 1900 This essay discusses the main factors of increasing economic growth through transportation, and the reasons for such a connection are presented.
- Operations, Cash Budgets, and Economic Growth The purpose of working capital management is to ensure that an entity has sufficient funds to cover operational expenses and short-term maturing debts at any given point in time.
- Deficit Spending and Economic Growth To gain an in-depth understanding of the economic outcomes of the Great Recession and other financial catastrophes, it is crucial to grasp the concept of deficit spending.
- Timor-Leste: Effects of Tourism on the Economic Growth The tourism sector in Timor-Leste, just like in any other Southeast Asian countries has an immense potential to contribute to the country’s economic growth.
- Long-Term Economic Growth in the East Asian States Although immigrants contribute positively to the economic status of East Asia, they cause overpopulation, native culture erosion, low wages, and unemployment.
- United Kingdom-Ghana Economic Growth Disparities The purpose of this paper is to explore some of the contributing factors that have led to economic growth disparities between the United Kingdom and Ghana.
- Economic Growth of East Asian States: The Impact of Foreign Workers Foreign workers perform essential skills and have affirmative productivity influences, thus, are integral to the long-term economic growth of East Asian states.
- Economic Issues: Factors of Production Growth and Unemployment Rates Assessing the factors such as the rates of production growth, the selected financial systems, and the rates of unemployment is essential for determining the threat to the state economy.
- Sports Facilities Development for Economic Growth Sports facilities do not contribute to the economic growth of the urban environment in their vicinity. There is no correlation between existing capacity and economic benefits.
- Trade in Environmental Goods and Economic Growth This paper analyzes how trading in environmental-friendly goods and services may be important in improving the quality of the environment and promoting economic development.
- What Is the Best Way to Stimulate Economic Growth? The examples of economic growth and downturns and economic theories propose different solutions to overcome financial crisis and stabilize economic situation in a country.
- China’s and India’s Economic Growth Experiences China is a country that has been in a position to have poverty reduction this has been due to the strategies that have been used in the country by the Chinese people.
- Trends and Projections of the United States Economic Growth The economic growth rate of a country is not constant over time, but it exhibits phases of expansion, stagnation, and decline.
- The Industrial Revolution and Economic Growth The Industrial Revolution began to lay the foundation for the first market economies where goods were sold and purchased, resulting in the exchange and accumulation of wealth.
- The Industrial Revolution and Economic Growth History The Industrial Revolution had an impact on various spheres of European society. Its primary consequence was urbanization; people started to move to cities to find jobs.
- The Relationship Between Unemployment and Economic Growth Among the factors that define economic growth and development, human resources and unemployment are considered to be the most vital.
- Industrial Revolution’s Input to Economic Growth The industrial revolution created many working places all over the United Kingdom, whereas the population of the state became more educated and competent.
- Dubai’s Economic Growth and Laziness of Poor The unprecedented growth of Dubai’s economy started in the 1970s. Dubai’s success provides an important lesson in the importance of human capital development.
- Economic Growth Factors in Australia External factors such as Consumer Price Index (CPI), consumer behavior, and inflation rate play a very important role in stimulating economic growth.
- Global Warming Problems due to Economic Growth This paper investigates if it is possible to deal with global warming by reducing CO2 emissions and energy consumption without any threats to economic development.
- China’s Economic Growth and Manufacturing The enhanced economic growth, which China is currently experiencing, coexists with a drop in the manufacturing entrepreneurships’ performance.
- Trade Openness and Economic Growth’s Relationship In the article “The Relationship Between Trade Openness and Economic Growth,” authors discover aspects of measuring trade openness and its impact on economic growth.
- Economic Growth and Market Dynamics Gross domestic product (GDP) is a measure of the value of all services and goods produced in a certain period of time.
- Economic Growth and Expansion The acquisition of smaller companies, as well as creating mergers with the companies helps considerably when it comes to choosing an appropriate risk management strategy.
- Absorptive Capacity and the Effects of Foreign Direct Investment on Economic Growth
- Background Factors Facilitating Economic Growth Using Linear Regression and Soft Regression
- Accounting for the Decline in AFDC Caseloads: Welfare Reform or Economic Growth
- Defense Spending and Economic Growth in Turkey
- Building the Skills for Economic Growth and Competitiveness in Sri Lanka
- Capital Account Liberalization and Economic Growth in Developing Economies
- Accumulation, Technical Progress, and Increasing Returns in the Economic Growth of East Asia
- Rebalancing China’s Economic Growth: Some Insights From Japan’s Experience
- Achieving Sustainable Economic Growth and Development in Communities Across the United States
- China’s Economic Growth 1978-2025: What We Know Today About China’s Economic Growth Tomorrow
- Beyond Economic Growth: The Genuine Progress of Hong Kong From 1968 to 2010
- Economic Growth and Capital Flows in European Countries in Pre and Post-crisis Periods
- Adjustment Policies and Economic Growth in Developing Countries
- Linear and Nonlinear Causality Between Sectoral Electricity Consumption and Economic Growth
- Africa’s Recent Economic Growth: What Are the Contributing Factors
- Financial Development and Economic Growth: An Egg-and-Chicken Problem
- Banking Sector Development and Economic Growth in Central and Southeastern Europe Countries
- Measuring Intangible Capital and Its Contribution to Economic Growth in Europe
- Crime, Justice, and Growth in South Africa: Toward a Plausible Contribution From Criminal Justice to Economic Growth
- Optimal Economic Growth With Recursive Preferences: Decreasing Rate of Time Preference
- Aging and Economic Growth: The Role of Factor Markets and Fundamental Pension Reforms
- Challenge Facing China’s Economic Growth in Its Aging but Not Affluent Era
- Breaking Down the Barriers to Technological Progress: How U.S. Policy Can Promote Higher Economic Growth
- Finding the Cointegration and Causal Linkages Between Electricity Production and Economic Growth in Pakistan
- Accounting for Agricultural Decline With Economic Growth in Taiwan
- Labor Markets and Economic Growth: Lessons From Korea’s Industrialization, 1970-1990
- Bank and Non-Bank Financial Deepening and Economic Growth: The Nigerian Experience (1981–2010)
- Migrant Workers’ Remittances and Economic Growth: The Role of Financial Development
- Capital Flows and Economic Growth Across Spectral Frequencies: Evidence From Turkey
- Breaking Boundaries: Economic Growth in Canada in Relation to Immigration
- Population Growth and Endogenous Technological Change: Australian Economic Growth in the Long Run
- Addressing Smart Economic Growth by Specific Policies in the European Higher Education Area
- Determining the Relationship Between Financial Development and Economic Growth
- Capital Quality Improvement and the Sources of Economic Growth in the Euro Area
- Economic Growth and Climate Change in a Decentralized Economy
- Biodiversity and Economic Growth: Stabilization Versus Preservation of the Ecological Dynamics
- Living Standard and Economic Growth: The Relationship Through the Nonparametric Approach
- Agglomeration Economies, Economic Growth and the New Economic Geography in Mexico
- Financial Deepening and Economic Growth in Developing Countries
- Banking Structure and Regional Economic Growth
- A Causal Relationship Between Fossil Fuel Consumption and Economic Growth in the World
- Bridging and Bonding Social Capital: Which Type Is Good for Economic Growth
- China’s Eighteenth-Century Economic Growth and Imperial Power
- Financial Sector Development and Economic Growth
- British Economic Growth 1856-1973: The Post-War Period in Historical Perspective
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, June 5). 78 Economic Growth Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/economic-growth-essay-topics/
"78 Economic Growth Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 5 June 2022, studycorgi.com/ideas/economic-growth-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) '78 Economic Growth Essay Topics'. 5 June.
1. StudyCorgi . "78 Economic Growth Essay Topics." June 5, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/economic-growth-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "78 Economic Growth Essay Topics." June 5, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/economic-growth-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "78 Economic Growth Essay Topics." June 5, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/economic-growth-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Economic Growth were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on December 28, 2023 .
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Government
Essay Samples on Economic Growth
Importance of entrepreneurship: economic growth and societal transformation.
Importance of entrepreneurship transcends its role as a mere business activity; it stands as a driving force behind innovation, economic growth, and societal transformation. Entrepreneurship fosters the creation of new products, services, and industries, while also generating employment opportunities and catalyzing economic development. This essay...
- Economic Growth
- Entrepreneurship
Economic Success and Development: China Case Analysis
At present, many growing nations give a boost to the economic development. China is a correct example. After opening reform, Chinese economic system has saved rapid development for 30 years, which has already grown to third largest economies in the world. China is a massive...
- Economic Development
- History of China
Immigration as a Boost for Economic Growth Productivity in America
When discussing immigration, it is a controversy filled with myths and is overall a touchy topic in today’s society, along with it being a relevant issue to this day. Many argue that immigrants in America are criminals, steal jobs, and are burdens some native-born. On...
- Immigration
- Immigration in America
Aging Population and Economic Growth: An Uneasy Relationship
The silver tsunami is coming. Goldstein (as cited in Kye & Arenas, 2014) estimated that the median age of the world population will rise by 11.4 years from 2000 to 2050. This phenomena can be attributed to the increase in lifespan and the decrease in...
Exploring the Link Between British Culture and Economic Success
O'riordan categorized values in many types as for instance business values, political values, and spiritual values and so on. However, business values are the most relatively greater strengths. In modern Britain, affected by industrial recession, wherever concern over jobs and growth seems to dominate public...
Stressed out with your paper?
Consider using writing assistance:
- 100% unique papers
- 3 hrs deadline option
Agriculture in the United States and the Role It Plays in the Country
Agriculture or farming is a major part of the lives of people and animals around the world everyday. From the clothes we put on when we get up in the morning, to the food we eat and drink throughout our day, to the bed we...
- Agriculture
- Organic Farming
Renewable Energy Development and Economic Growth
The growth of adoption of renewable energies is affected primarily by its many motivations as well as limitations in applications. In rural areas, this adoption is found to be shaped by additional modifiers that are endemic to poverty, such as steep necessity for cost-effectiveness, social...
- Renewable Energy
Potential Development Of Tanjung Buton Industrial Area Against Increasing Job Opportunities
Development is very important to create a just and prosperous society and to achieve a better standard of living for the people. The purpose of development in essence is to increase economic growth oriented to creating as many jobs as possible, creating social justice, and...
- Vocational Education
Sweatshops And Their Contribution Into Economic Growth Of Developing Countries
Sweatshops are highly practiced in undeveloped countries. This is due to the economy might be poor hence high rate of unemployment. Large companies enable communities to attain employment by assembling companies for manual jobs. Manual jobs can be tiresome however one gets a living to...
- Developing Country
Analysis of the Advantages of Asian Economy and How It Can Be Applied to Belgium
About ASEAN We’ve have spoken about this topic multiple times during Asian Business classes. An organization that unifies the Southern part of Asia. ASEAN was discovered on August 8th 1967 in Thailand. The main finders of this organization is Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore and of course...
Analysis of the GDP Growth in United Kingdom During the 2019
Gross Domestic Product, or GDP, is the total market value of goods and services produced in a country during a given time period. Economists use GDP to measure a country’s economy to see how well they are doing. There are different types of GDP measurements...
- Gross Domestic Product
- United Kingdom
Defense Spending, Nato, And Economic Growth In North Macedonia And Albania
Introduction The issue of defense spending and correlation with economic growth has been an debatable issue with no unification on whether defense spending affects economic growth on developing countries or not. As mentioned by Jaroslav Usiak, Radoslav Ivancik (2014), defense spending belongs to the very...

Comparison of New England and Chesapeake
Colonies are not always the same they have their differences, that makes them unique from one another. Usually they differ from economically, religiously, and their societal structure which is common we are not all the same in this world. New England and Chesapeake are very...
- New England
The Relationship Between Economic Growth and Wildlife Conservation in Africa
Economic growth “is how much of goods/services are consumed by one person in a particular population size over a period of time”. Economic growth has an inverse link with wildlife or nature conservation which is “the protection of animal species and their homes” because it...
- Conservation
An Op-Ed on Life and Debt and Bad Samaritans
Any country has its way of development. Some countries maintain to thrive in a quickly changing environment, and some have difficulties. Often, IMF and World Bank, which is supported by developed countries, tend to guide underdeveloped countries to make progress by introducing neo-liberalism policies. However,...
- Life and Debt
Poverty Reduction and Shared Prosperity Development
Sustainable development does not merely imply to the economic growth but is composed of peace, healthy and dignified human life, human capital development, proper social safety net and environmental sustainability. Economic growth along with proper education, better health status, social cohesion, fair distribution of public...
- Sustainability
Gross Domestic Product of the United States of America
The United States GDP in the second quarter was a total of $5,335,067 million. GDP is a total monetary or market value of all the finished goods and services produced within a country's borders within a specific time period. GDP does not take into account...
- Macroeconomics
Promotion of a Wider Economic Diversification for Rentier States
The Economic and Financial Committee (ECOFIN), second of the six committees of the United Nations General Assembly, has always been vigilant about economic growth and development issues. This committee has continued its assistance to developing countries with the opportunity to prosper along with financial aid....
- The United Nations
Sleep Deprivation: An Economic Catastrophe
Sleep deprivation has now been classified by Medsleep–a network of Canadian clinics–as an “emerging global epidemic” (“Sleep Deprivation”). In the past fifty years, our average sleep duration has decreased by nearly two hours (“Sleep Deprivation”). In the United States, the average sleep duration has dropped...
- Sleep Deprivation
The Struggle of Economic Growth in the Monopolistic Society
The article I chose discusses the Monopoly problem we have in America. The article I’m choosing to discuss is “America has a Monopoly Problem” by John Mauldin. In this article he brings light to the fact that a greater portion of America’s economy consists of...
The Impacts of French and Indian War
Their war between the French and Indians between 1754 and 1763. These war it was as a result of various reasons main being in need of territory, resources and trade routes. Both wanted to control fur trade and expected one day they will send settlers...
- French and Indian War
Unity and Economical Focus of Mexican Revolution
Mexico during the early 20th century was a state of unease, high tension and resentment as a result of land exhaustion, political unrest, economic and social inequality. There is still some unease regarding the validity of the Mexican Revolution from 1910-1920. As there were various...
The Import and Export Culture of Italy
Italy is in Southern Europe, right next to the Mediterranean Sea. Italy is one of the most prosperous countries in the world. Its influence on other countries has spread well beyond its borders. Italy is bordered by the Adriatic Sea on the east coast and...
The Renourishment and Reconstruction of the Folly Beach
Folly Island, 20km south of Charleston, South Carolina, is a barrier island. It has marketed itself and its beach as the “Edge of America,” and attracts thousands of tourists each year. Folly Beach is Folly Island’s most valuable resource. Folly Beach acts as a barrier...
- Natural Environment
Development Through Dictatorship A Focus on the Economic Reforms of Park Chung-hee
Looking at Korea today, it is hard to imagine a time where they were not at the forefront of economic prosperity and innovation. However, following the conclusion of the Korean War, it possessed virtually no industry and was riff with political, and economic crisis. This...
- Dictatorship
Global Health and Macroeconomics Are Interrelated
Health Status vs. Economy Health has a special place in the economy of a country. The wealth of a nation is measured by the health status of its citizens. Thus, health performance and economic performance go hand in hand. Health issues directly affect education, labor...
- Public Health
Evaluation of the Success of the Plan Colombia
Plan Colombia aimed to rescue the Colombian economy. The US foreign aid program for Colombia has been compared to the Marshall Plan in its “scale relative to the beneficiary’s size” (Mendez 2017, p.2). Firstly, this essay with outline the history of Plan Colombia and its...
The Changes and Development in Texas' Economy
Introduction Texas is a state in the South of the United States with Austin as its capital. Texas borders Arkansas to the Northeast, New Mexico to the West, Mexico and Gulf of Mexico to the Southwest and East and Louisiana to the East. This essay...
The SWOT Analysis of the Florida State
The state of Florida has one of the biggest economies in the United States. The economic growth rate in Florida has been impressive and has outpaced the average growth rate in the United States (Office, 2018). Small businesses form the backbone of the economy in...
- SWOT Analysis
Improving Economic Growth with Coporate Social Responsibility
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) refers to the awareness, acceptance and management of the wider implications of corporate decisions. (Michalaska, 2019). CSR is “the responsibility of a company for the totality of its impact” (Chandler, 2001) European commission states that it is expected from companies to...
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Social Responsibility
Foreign Policy of Bhutan Towards South Asia: A Study Case of Economic Policy
Introduction Background study Foreign Policy is a significant part of international studies. Foreign policy has been defined in different ways thus, the definition of the term has remained unclear and a debatable topic (Beach, 2019). For example, Herman has defined foreign policy as the different...
- Foreign Policy
- Globalization
Guanxi - The Way To Engage More With The Business Culture Of Chinese
China has one fifth of the world’s consumer. China’s economic growth and living standards of the people is growing fast in recent years. Business people from all around the globe are interested to have a business in China or work with Chinese since in the...
Japan's Economic Miracle: How the Nation Revived After World War II
Japan’s Economic “Miracle” The conventions of a society provide the way said society will act and be. These conventions structure the framework that a society is based on, and therefore is the foundation for the roles that people play in their context. Understanding the different...
Examining Economic Growth in Senor and Singer's Start-Up Nation
Book Review of Start-up Nation Synopsis and Evaluation In the eye-opening and inspirational novel Start-up Nation: The Story of Israel’s Economic Miracle, authors Senor and Singer have explained how Israel successfully flourished as an economic center of the world by having the most start-up companies...
Analysis Of China's Economy Current State And Future
China was under communism ruled by Mao ZeDong since 1949 to 1976 and classified Maoism for Socialism. China is known as one of the largest countries in the world due to their huge number of populations, being second largest economy in nominal GDP, being one...
Pillars Of Economic Growth And Their Impact On Canadian Economy
There are four pillars of economic development. Infrastructure In infrastructure, different kind of levels like Highways, rails, ports, power, water, broadband, fuel and real estate are included. If any country has these essential resources that country automatically be a developed country by using these resources....
Success And Failures Of The Initiative
As mentioned previously regarding the initiatives made by IKEA complying to the UN Sustainable Development Goals, generally all initiatives taken are proven to be a success, but however there are several obstacles that they have faced. Affordable and clean energyAs stated in the report, energy...
The Role Of Banking Institutions In Any Economy
The banking institution is one of the most significant financial intermediaries in any economy. Its main purpose is to allocate funds from the areas of surplus to the areas of deficit. It also helps to get small amounts of deposits from individual small depositors and...
The Concepts I Learnt From Cocktail Party Economics
From reading Cocktail Party Economics, there are a lot of concepts which I had found interesting, shocking, and even obvious. The idea in the first few chapters is to just give an introduction about the vocabulary of an economist. This is where I learnt that...
- Book Review
- Consumerism
Prospect Of Public Private Partnerships (PPP) In Bangladesh
Introduction Bangladesh has been one the fastest growing economies in the recent couple of decades with massive infrastructure and development works being in progress. Throughout the period, much of the growth, has come from the private sector while public sector has lagged behind in the...
- Role of Government
Significance Of Foreign Direct Investment In Economic Growth
This project report researches the heading of causal connection between foreign direct investment (FDI) and economic development in BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) nations utilizing direct relapse system from BRICS nations, shows bidirectional short run causal connection among GDP and FDI. Introduction There...
The Imbalance Between Us And Our World
In man's struggle with nature to reach the top, we have achieved many milestones that overall separate from our animal counterparts. However, in our pursuit of growth, we have made our world suffer. This can sometimes go to show that taking action to grow just...
- Environmental Issues
Environmental Health And Standard Of Living
Introduction Our planet is continuously attempting to reach the “smart” living standards of the developed world due to which there is a widespread concern that this is negatively impacting the environment. The struggle to reach this higher standard of living has become the cause for...
- Environmental Protection
Best topics on Economic Growth
1. Importance of Entrepreneurship: Economic Growth and Societal Transformation
2. Economic Success and Development: China Case Analysis
3. Immigration as a Boost for Economic Growth Productivity in America
4. Aging Population and Economic Growth: An Uneasy Relationship
5. Exploring the Link Between British Culture and Economic Success
6. Agriculture in the United States and the Role It Plays in the Country
7. Renewable Energy Development and Economic Growth
8. Potential Development Of Tanjung Buton Industrial Area Against Increasing Job Opportunities
9. Sweatshops And Their Contribution Into Economic Growth Of Developing Countries
10. Analysis of the Advantages of Asian Economy and How It Can Be Applied to Belgium
11. Analysis of the GDP Growth in United Kingdom During the 2019
12. Defense Spending, Nato, And Economic Growth In North Macedonia And Albania
13. Comparison of New England and Chesapeake
14. The Relationship Between Economic Growth and Wildlife Conservation in Africa
15. An Op-Ed on Life and Debt and Bad Samaritans
- Gun Control
- Police Brutality
- Gerrymandering
- Conspiracy Theory
- Kamala Harris
- Fire Safety
- Alien and Sedition Acts
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
Economic Growth Essays
Deng’s economic revolution, international agricultural development: a comprehensive perspective, women in canada’s economic evolution, the environmental crisis in your closet, the beneficial impact of walmart on our community, the impact of international trade on emerging economies, the belt and road: its significance to china’s vision as the world power, the cost of brexit, the world bank: promoting sustainable development globally, the car wash application project, role of decision-making in economic growth, economic growth and its impact on american society in the early 20th century, open borders are better than closed borders, rostow’s development phases, the impact of natural disasters on emerging economies, popular essay topics.
- American Dream
- Artificial Intelligence
- Black Lives Matter
- Bullying Essay
- Career Goals Essay
- Causes of the Civil War
- Child Abusing
- Civil Rights Movement
- Community Service
- Cultural Identity
- Cyber Bullying
- Death Penalty
- Depression Essay
- Domestic Violence
- Freedom of Speech
- Global Warming
- Gun Control
- Human Trafficking
- I Believe Essay
- Immigration
- Importance of Education
- Israel and Palestine Conflict
- Leadership Essay
- Legalizing Marijuanas
- Mental Health
- National Honor Society
- Police Brutality
- Pollution Essay
- Racism Essay
- Romeo and Juliet
- Same Sex Marriages
- Social Media
- The Great Gatsby
- The Yellow Wallpaper
- Time Management
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Violent Video Games
- What Makes You Unique
- Why I Want to Be a Nurse
- Send us an e-mail

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Economic growth
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Economics essays
- Reading time: 12 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 14 October 2015*
- File format: Text
- Words: 3,523 (approx)
- Number of pages: 15 (approx)
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 3,523 words. Download the full version above.
1. Introduction:
Economic growth, which reflects the overall performance of a country, is one of the most important macroeconomic goals that a country seeks to achieve and maintain. Economic growth in one-way or another refers to the increase of the country’s potential GDP. It must be sustained in order for economic development to be achieved (Desmond, et al, 2012).
Besides taxes as an instrument of fiscal policy, governments might use their expenditures, as another instrument, to achieve economic growth. ‘Public expenditure was born out of revenue allocation which refers to the redistribution of fiscal capacity between the various levels of government or the disposition of responsibilities between tiers of the government’ (Okoro, 2013). Therefore, understanding the relationship between the government expenditures and revenues and the implementation of an efficient fiscal policy is necessary to give a clear indication of how effective the government’s policies used in managing the country’s resources, establishing price stability and maintaining sustainable economic growth (Hamdi and Sabia, 2013).
In the past two decades, the Palestinian economy was going through fluctuating behavior. It was affected by different social and political situations. Gross domestic product (GDP) the most important indicator of economic growth varied with different percentages over these two decades. For example, in 1996-1999 GDP reached its maximum in 1999 with US$4,534.9 million with 8% growth rate while GDP was US$3,744 million with a growth rate of 14% in 1997. Moreover, GDP started and continued to decrease as a result of Israeli military measures during the years of the second intifada (2000-2004). In fact, it reached its minimum in 2002 with US$3,301.4 million with a rate of -13% growth. This fluctuating behavior continued where GDP started to improve in the following two years (2004-2005) where it reached US$4,559.5 million in 2005 with 9% growth. However, it started to decrease back in 2006-2007 to reach US$4,554.1 million with growth rate of 5% only. After that, GDP started recovering and continued to increase (2008-2012) and reached the maximum in 2012 with US$6,797.3 million and 6% growth (Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, 2013).
Therefore, it can be said that Palestine, as an occupied small country, has a very fragile and sensitive political, economical and social situation due to the Israeli occupation. Much attention should be paid to the Palestinian economy, in particular to the governmental policies used in order to analyze the reasons and effects of such a fragile economy on the other aspects of life. Government expenditures and its components, as an example of such policies, will be studied and analyzed through this study to give an indication of how effective the Palestinian policy makers’ strategies in managing and controlling the Palestinian economy and resources.
2. Theoretical Background and Literature Review:
One of the definitions of economic growth is ‘the increase in the total output of an economy that happens as a result of a society acquiring new resources or learning to produce more using the existing ones’. ‘New resources may refer to an increase in capital stock or in labor force’. ‘Accumulation of capital and technological advances are two of the most important sources of economic growth’ (Case, Oster and Fair, 2012). According to McConnel, Brue and Flynn (2009) economic growth is ‘an outward shift in the production possibilities curve that results from an increase in resource supplies or quality or an improvement in technology’ or it’s ‘an increase in real GDP or in real GDP per capita over some period of time’. This study uses the definition of economic growth as an increase in real GDP.
Economic growth can be measured by comparing real GDP for different years. Real GDP is defined as ‘the value of total production of farms, factories, shops and offices of a country measured in the prices of a single year’. One of the main approaches for calculating GDP is the expenditure approach which equals ‘the sum of consumption expenditure, investment, government spending on goods and services and net exports’ (Parkin, Powell and Matthews, 2005).
Government spending (expenditure), which will be the main focus of the study, is the acquisition of goods and services either for current use, to directly satisfy individual or collective needs of the members or for future benefits such as infrastructure investment. It includes all government consumption and investment but excludes transfer payments made by a state (Barro and Grilli, 1994).
There have been several schools of thoughts regarding the impact of government expenditure on the economic growth. The classical school viewed that countries with higher government expenditure would experience lower economic growth (Ricardo, 1821). While the Keynesians viewed that the increase in government expenditure leads to higher economic growth (Keynes, 1936). However, the neo- classical viewed that there is no long run impact of government expenditures on the economic growth rate (Solow, 1956). Wagner (1893) argued that there is a positive correlation between economic growth and government activity in the long run (Wagner’s law or the law of increasing state spending). Moreover, Economists of Endogenous Growth Theory such as Barro (1990) suggested that government expenditure induces economic growth.
There have been several studies interested in the impact of government expenditure on economic growth. For example, Mohammadi, Maleki and Gashti (2012) analyzed the effect of governmental expenditure composition on the Economic development of economic cooperation organization countries ECO: Iran, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Turkey annually for (1995-2009). They focused on three types of government expenditures: health expenditure, education and defense. The real per capita of GDP in period t was the dependent variable where real per capita of GDP in period t-1, government expenditure on health to GDP ratio in period t, government expenditure on education to GDP ratio in period t, government expenditure on defense to GDP ratio in period t, the investment in period t, total of Population growth rate, technological growth and the depreciation rate in period t and other financial variables as a share of GDP in period t formed the independent variables. The dynamic panel data method, the generalized method of moments (GMM) and the Sargan test were conducted. The results showed that the health expenditure has significant and negative effect on growth, educational expenditure has significant and positive effect and the governmental defense expenditure has significant and positive effect on the economic development of ECO countries.
Moreover, Dao (2012) using cross sectional data, analyzed the impact of the growth of the share of various government expenditure programs in the GDP on economic growth in 28 developing countries (Argentina, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Brazil, Bulgaria, Colombia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Egypt Arab Republic, Hungary, India, Iran, Israel, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Lithuania, Madagascar, Moldova, Poland, Portugal, Russian Federation, Slovak Republic, Slovenia, South Africa, Tajikistan, Thailand and Ukraine) for 3 years (2008-2010). The dependent variable in this study was per capita GDP growth while the growth of per capita public health expenditure in the GDP, growth of per capita public spending on education in the GDP, population growth, growth of the share of total health expenditure in the GDP and the share of gross capital formation in the GDP formed the independent variables. Data for all variables were obtained from the World Development Indicators (2008 and 2010). Least square multiple regression analysis and t-test were used to estimate the specified model. Results showed that the share of gross physical capital formation in the GDP is not significant, developing countries in which the government continues to increase per capita spending for health care and education relative to income are expected to grow faster and that the growth of the share of total health expenditure in the GDP also influences per capita GDP growth of countries included in this study.
Also, Yu, Fan and Saurkar (2009) assessed the impact of the composition of government spending on economic growth in 44 developing countries 44 developing countries (1980-2004). The aggregate national GDP were used as the dependent variable while the explanatory variables included labor, gross capital stock, and capital stock of various government expenditures. Total government expenditures and its composition were collected from the International Monetary Fund’s Government Finance Statistics (GFS) Yearbook sectors. The World Development Indicators (World Bank, 2006) were used for exchange rates. Dynamic GMM model and a panel data set for 44 developing countries, Dickey-Fuller unit root test and Levin-Lin-Chu (2002), Im-Pesaran-Shin (2003) and Hadri Lagrange Multiplier (2000) panel unit root tests were also conducted. Results showed that the various types of government spending have different impact on economic growth. In Africa, government spending in human capital was particularly strong in promoting economic growth. In Asia, capital, agriculture, and education expenditure promotes economic growth. In Latin America, none of the government spending items has any significant impact on economic growth.
3. Problem Statement:
This study will be designed to highlight one of the fiscal policies’ instruments and how it can be used in managing the Palestinian resources and maintaining the stability of the Palestinian economy. The main question that will be answered: what is the relationship between the government expenditures and the economic growth in Palestine? This will be achieved by answering the following sub-questions:
o How does the gross domestic product (GDP) in Palestine change over the period of 1996-2012? o What is the impact of employment as an indicator for the labor force on GDP for the period? o What is the impact of capital, which will be estimated using the Incremental Capital Output Ratio (ICOR) approach on GDP for the period? o What is the impact of technology on GDP for the period? o How do government expenditures change over the period? o What is the impact of the overall government expenditures on the GDP for the period? o What are the components of the government expenditures? o How much does each component form as a percentage of the overall government expenditures? o What effect does each component has on GDP for the period? o What are the recommendations that can be extracted from the results of the study and how would they benefit the competent authorities?
4. The Objectives of the Study:
The main objective of the study will be to analyze the impact of government expenditures as a total and its components on the Palestinian economic growth. Moreover, the specific goals to be achieved are:
o Estimating capital using the ICOR approach for the period. o Observing how GDP, labor, capital, and government expenditures change over (1996-2012). o Identifying the components of the government expenditures for the period. o Calculating the percentage each component form of the total government expenditures for the period. o Estimating an econometric model where GDP is a function of labor, capital, technology and total government expenditures. o Estimating an econometric model where GDP is a function of labor, capital, technology and the four components of government expenditures (wages and salaries expenditures, non-wage expenditures, development expenditures and net lending). o Analyzing the effect of each component on the overall government expenditures and GDP for the period. o Analyzing the impact of the overall government expenditures on the GDP for the period. o Comparing the effect of labor force, capital, technology and components of government expenditures on GDP for the period. o Suggesting some recommendations and address them to the competent authorities to inhance the palestinain economy through this instrument (government expenditures). 5. The Importance of the Study:
Since the Palestinian economy is directly connected to the Israeli economy, this limits the Palestinian policy makers’ options in setting up the policies needed to enhance the Palestinian economy. Monetary policies are not an option in the case of Palestine since it’s an occupied country and has no full control over the currency. The Palestinian don’t have their own currency, instead they are forced to use the Israeli currency (shekel). However, government expenditures and taxes are two tools of fiscal policies that can be used to achieve the desired economic growth in Palestine. Government expenditures are more controlled by the Palestinian authorities, which give them the preference over the other instruments of fiscal policy in this study. Since part of the taxes are under the control of the Israeli authorities in certain circumstances and up to certain levels, the recommendations that will come out of this study will be more effective in the case of government expenditures rather than taxes. Israel can affect the Palestinian economy in two different ways; directly through taxes’ collection prevention, since they have control over the international borders, and indirectly by tax revenues’ base reduction (Issac, et al, 2011).
This study will be directly addressed to the Palestinian policy makers, mainly the Ministry of Finance. This study will help the policy makers in the Ministry of Finance to take into their consideration the effect of the government expenditures on the economic growth when they formulate and create the Palestinian Authority budget. This will make the budget more effective and the Palestinian resources will be allocated in a more efficient and productive way. This study will also be very helpful to the Ministry of Planning in setting up the social, economical, financial and political plans that would enhance the overall performance of the country in the previously mentioned fields. Since there is a direct relationship between GDP and unemployment rate, this fiscal policy instrument will be very helpful for Ministry of Labor in preparing its annual strategies in decreasing the unemployment rates. In addition, this study will benefit the Ministry of National Economy in choosing the projects that should be given licenses, in particular, the ones that enhance the economy growth the most. In addition, this will help the individuals as being part of the labor force to determine how and where to invest their money so as to help in achieving better GDP growth.
6. The Scope and Limitations of the Study:
This study will be analyzing the impact of government expenditures as a total and its components on the economic growth in Palestine (1996-2012). It will have an important limitation, which will be the shortness of the time series that will be taken in analyzing the impact of the government expenditures on the GDP. The time series coverage will be (1996-2012) since the Palestinian Authority was established in 1994 as a result of the Oslo Accords between the Palestine Liberation Organization and Israel. The data available in the Palestinian Ministries and the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (PCBS) start mostly from 1996.
7. The Methodology:
The study will be based on secondary annual data (1996-2012) of total government expenditures and its components from the Ministry of Finance whereas the GDP, capital (estimated using the ICOR approach) and employment to be taken from the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics.
This study will be consisting of two models. The dependent variable of the first model will be the GDP whereas the independent variables will be capital, labor force, technology and total government expenditures (Mohammadi, Maleki and Gashti (2012). As for the second model GDP will be the dependent variable while labor, capital, technology and the components of government expenditures will be the independent variables (Bader, 2012). According to the Ministry of Finance (2013) government expenditures in Palestine are divided into four types; expenditures on wages and salaries, non- wage expenditures, net lending and development expenditures. These four types will form the independent variables of the second model. The stationarity of the two models will be first tested using Augmented Dickey-Fuller and Phillips-Perron unit root test for stationarity. Then the impact of government expenditures as a total and its components on the GDP will be examined using multiple regression analysis where the R2, F-test and t- test will be calculated. Moreover, other tests will be performed such as White test of heteroscedasticity, Ramsey RESET test, Durbin-Watson test of autocorrelation.
The models to be used in this study are:
Model 1: GDP= f(L, K, T, G) Where: L: labor. K: capital. T: technology. G: total government expenditure.
Model2: GDP= f(L, K, T, Wexp, NWexp, NL, Dexp) L: labor. K: capital. T: technology. Wexp: Wages and salaries expenditures. NWexp: non-wages expenditures. NL: Net lending. Dexp: development expenditures.
8. Contents of the Study:
This study will consist of five chapters. Chapter one will contain seven sections: the introduction, the problem, the objectives, the importance, the scope and limitations, the methodology and finally the contents of the study. Chapter two will outline the theoretical background and a literature review of previous studies that have the same problem of this study. Chapter three will be a detailed descriptive analysis of the data on the variables of interest focusing on the allocation of the government expenditures. Chapter four will be analyzing the data statistically. It will contain detailed description of the methodology of the study with the models to be estimated addressed in functional forms using symbols representing the dependent variable along with the independent variables. Finally, the estimated models will be discussed and tested economically and statistically in order to highlight the impact of government expenditures along with its components on economic growth. Chapter five will give the final conclusions of the study and the recommendations that will be addressed to the competent authorities.
References:
Bader, M. (2012). ‘The Effect of Education on Economic Growth in Jordan: An Econometric Study (1976 ‘ 2007) “The Modified Version”. Administrative Sciences, Volume 39, No. 1.
Barro, R. (1990). ‘Government Spending in a Simple Model of Endogenous Growth’. Journal of Political Economy. Vol. 98(5), pp. S103-S125. As in Altaf, N., Khan, S. (2013). ‘Impact of Government Expenditure on Economic Growth in Assam: An Econometric Study. Shodh Anusandhan Samachar, Vol. IV, Issue-1, PP.10-21. Accessed on November 14, 2013 from: http://www.shodhanusandhann.com/WebGallery/201365246_NISHAD%20ALTAF%20ECONOMICS%20PAPER.pdf
Barro, R., Grilli, V. (1994). European Macroeconomics. Macmillan. London. As in Modebe, N., Okafor, R., Onwumere, J., Ibe, G. (2012). ‘Impact of Recurrent and Capital Expenditure on Nigeria’s Economic Growth’. European Journal of Business and Management, Vol 4, No.19. Accessed on November 10, 2013 from: http://www.iiste.org/Journals/index.php/EJBM/article/download/3586/3635
Case, E., Fair, R., Oster, S. (2012). Principles of macroeconomics, 10th ed. Prentice Hall. USA. Accessed on December 20, 2013 from: http://www.econ.cmu.ac.th/teacher/nisit/files/Principles%20of%20Macroeconomics.pdf
Dao, M. (2012). ‘Government Expenditure and Growth in Developing Countries’. Progress in Development Studies, pp. 77’82. Accessed on December 2, 2013 from: http://pdj.sagepub.com/content/12/1/77.full.pdf
Desmond, N., Titus, O., Timothy, O., Odiche, N. (2012). ‘Effects of Public Expenditure on Economic Growth in Nigeria: A Disaggregated Time Series Analysis’. International Journal of Management Sciences and Business Research, Vol. 1, Issue 7. Accessed on November 10, 2013 from: http://www.ijmsbr.com/Volume 1,Issue 7 (6) Andy.pdf
Hamdi, H., Sbia, R. (2013). ‘Re-examining Government Revenues, Government Spending and Economic Growth in GCC Countries’. The Journal of Applied Business Research, Vol. 29, No. 3 . Accessed on November 14, 2013 from: http://journals.cluteonline.com/index.php/JABR/article/download/7777/7841
Issac, J., Cail, M., Siaj, M., Hilal, J. (2011). ‘The Economic Costs of the Israeli Occupation for the Occupied Palestinian Territory’. A bulletin published by the Palestinian Ministry of National Economy in Cooperation with the Applied Research Institute- Jerusalem (ARIJ). Accessed on November 15, 2013 from: http://www.mne.gov.ps/pdf/EconomiccostsofoccupationforPalestine.pdf
Keynes, M. (1936). General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money. Macmillan, London. As in Desmond, N., Titus, O., Timothy, O., Odiche, N. (2012). ‘Effects of Public Expenditure on Economic Growth in Nigeria: A Disaggregated Time Series Analysis’. International Journal of Management Sciences and Business Research, Vol. 1, Issue 7. Accessed on November 10, 2013 from: http://www.ijmsbr.com/Volume 1,Issue 7 (6) Andy.pdf
McConnel, R., Brue, L., Flynn, M. (2009). Economics: Principles, Problems and Policies, 18th ed. McGraw-Hill/ Irwin, New York, USA. Accessed on January 10 , 2014 from: http://dc479.4shared.com/download/go0lfX_7/Economics_-_Mcconnell_Brue_Fly.pdf?tsid=20140110-121402-d3c477f5
Ministry of Finance (2013), Definitions and terms, Accessed on December 10, 2013 from: http://www.pmof.ps/en/web/guest/86
Mohammadi, T., Maleki, B., Gashti, H. (2012). ‘The effect of government expenditure composition on economic growth: Evidence on ECO countries’. Economics and Finance Review, Vol. 2(5) pp. 14 ‘ 21.Accessed on December 3, 2013 from: http://www.businessjournalz.org/articlepdf/EFR_2403july2512c.pdf
Okoro, A. (2013). ‘Government Spending and Economic growth in Nigeria (1980-2011)’. Global Journal of Management and Business Research Economics and Commerce, Vol. 13, Issue 5. Accessed on November 10, 2013 from: https://globaljournals.org/GJMBR_Volume13/4-Government-Spending-and-Economic.pdf
Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics (2013), Guide to Palestinian Statistics, National Accounts (GDP), 2004 is the Base Year, Accessed on November 5, 2013 from: http://www.pcbs.gov.ps/Portals/_Rainbow/Documents/MajorConstantE1994-2011.htm
Parkin, M., Powell, M., Matthews, K. (2005). Economics, 6th ed. Pearson Education Limited 2005. Spain, Madrid. Accessed on December 20, 2013 from: http://dc168.4shared.com/download/stSc3xoY/50204016-PARKIN-Economics-6e.pdf?tsid=20131220-185323-e76f8ce3
Ricardo, D. (1821). The Principles of Political Economy and Taxation, Third Edition, John Murray, Albemarle Street, London. As in Altaf, N., Khan, S. (2013). ‘Impact of Government Expenditure on Economic Growth in Assam: An Econometric Study. Shodh Anusandhan Samachar, Vol. IV, Issue-1, PP.10-21. Accessed on November 14, 2013 from: http://www.shodhanusandhann.com/WebGallery/201365246_NISHAD%20ALTAF%20ECONOMICS%20PAPER.pdf
Wagner, A. (1893). Grundlegung der Politischen Okonomie. Teil I: Grundlagen der Volkswirtschaft. C.F. Wintersche Verlagshandlung. As in Kuckuck, J. (2012). ‘Testing Wagners’s Law at Different Stages of Economic Development: A Historical Analysis of Five Western European Countries’. Institute Of Empirical Economic Research. Osnabrueck University. Germany. Accessed on December 20, 2013 from: http://www.iew.uni-osnabrueck.de/WP_91.pdf
Yu, B., Fan, S., Saurkar, A. (2009). ‘Does Composition of Government Spending Matter to Economic Growth’? Contributed Paper prepared for presentation at the International Association of Agricultural Economists Conference, Beijing, China, August 16-22. Accessed on November 29, 2013 from: http://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/51684/2/IAAE%20government%20spending.pdf
...(download the rest of the essay above)
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Economic growth . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/economics-essays/essay-economic-growth/> [Accessed 08-04-24].
These Economics essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on Essay.uk.com at an earlier date.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Zoology essays
Home — Essay Samples — Economics — Economic Development — What is Economic Growth
What is Economic Growth
- Categories: Economic Development Economic Growth
About this sample

Words: 593 |
Published: Dec 18, 2018
Words: 593 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Works Cited:
- Barry, S. (2010). “Do No Harm”: In Defense of John Q. Journal of Medical Humanities, 31(4), 345–358.
- Breen, J. (2015). John Q: A Question of Ethics. Journal of Religion and Film, 19(1), 1–19.
- Clouser, K. D. (2005). John Q and the Healthcare System: A Philosophical Analysis. Theoretical Medicine and Bioethics, 26(3), 203–216.
- Codey, R. (2002, February 21). Hollywood and Heart Transplants. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2002/02/21/opinion/hollywood-and-heart-transplants.html
- Delgado, R. (2002, March 22). John Q. Wall Street Journal.
- Filkins, L. (2002, March 10). Father Takes Hostages to Get Son’s Heart Transplant. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2002/03/10/movies/father-takes-hostages-to-get-son-s-heart-transplant.html
- John Q. (2002). [Motion Picture]. United States: New Line Cinema.
- John Q. (2018). In IMDb.
- McNamara, M. (2002, February 15). A Life-and-Death Crisis Gets Hollywood Treatment in ‘John Q.’ Los Angeles Times. https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-2002-feb-15-et-mcnamara15-story.html
- Pekmezovic, A. (2015). Movie John Q and the Socioeconomic Environment of Health Care in the United States. Serbian Journal of Management, 10(2), 249–259.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Economics

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
7 pages / 2969 words
2.5 pages / 1026 words
2.5 pages / 1030 words
2.5 pages / 1097 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Spier, F. (2015). Big history and the future of humanity. Somerset, UK: Wiley.Takagi, E., & Saito, Y. (2015). Older parents’ loneliness and family relationships in Japan. Ageing International, 40(4), 353-375. [...]
In our world, the government will often want people to see the good things in their country instead of the details including poverty, racial discrimination, social and economic issues, and so much more. During the Great [...]
Entrepreneurs are someone that founds and venture a small business while acknowledging the risks and rewards of it rather than working as an employee. They are commonly seen as an innovator, a source of fresh ideas, goods and [...]
In discussing the role of entrepreneurship in economic development, this essay essay recognizes that entrepreneurs play an essential role in the progress of a country. Their skills, talent, and hard work are [...]
John Steele Gordon for the past 20 years has been a very highly experienced specialist in the business field. As well as being an author of many scholarly books, he was a contributing editor to American Heritage, written by John [...]
The 2008-09 crisis provided a fertile ground for emerging economies of the world to cooperate and collaborate to hedge against such a scenario. Thus, BRIC (and later BRICS) was born. However, each country had a fixed agenda to [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
EconomicGrowth →
No results found in working knowledge.
- Were any results found in one of the other content buckets on the left?
- Try removing some search filters.
- Use different search filters.
Home / Essay Samples / Government / Economy / Economic Growth
Economic Growth Essay Examples
The significance of globalization for indian economy.
With the start of changes to change the Indian economy in July of 1991, another segment has unfurled for India and her at least billion people. This season of money related change has immensely influenced the as a rule budgetary enhancement of essentially all noteworthy...
Positive and Negative Affects of Automation on the Us Economy
Over the past few decades, US firms are investing more in capital, such as in industrial robots, automation and machinery than in human workers, which is a major factor of economic growth. In fact, many macroeconomic variables come into account when explaining the long run...
Engineering Economics Assignment: Green Growth
The problem of sustaining a growing population using scarce and finite resources is a challenge for many economists, government officials, business managers, consumers and other stake holders. This paper is an individual study that reviews the concept and types of different mechanisms for economy-wide “green...
Gross Domestic Product Isn't a Comprehensive Measure
Almost all nations across the world use GDP as an indicator of economic growth and development and only recently there has been much debate about whether or not GDP is an accurate measure of growth. GDP is the final value of the goods and services...
Roaring 20s: Decade of Prosperity and Growth
The 20's marked a decade of prosperity and growth. It was a time of transition in culture and in society. It took place in Canada, the UK and particularly the United States, the most notable countries. Metropolitan towns developed and the economy was high for...
Main Sources of Economic Growth of Israel
If one were to point towards a true oasis in the sands — a true example of order growing out of chaos — whose economy practically grew from the ground up to not only survive but thrive, one would point to Israel. Surrounded by enemies...
The Effects of the James Bay Project on Quebec
During the nineteenth century, Quebec faced a dramatic period of change in hopes of establishing its national identity which influenced the James Bay Project. The James Bay Project resulted in a change of traditional life for the Cree and Inuit communities of Northern Quebec. The...
The Thoughts & Ideas of Al-ghazali in the Field of Economics & Economic Growth
The Muslim world, as of today, suffers from the rise of the contemporary economic system adopted by the world. The vicious circle of poverty, inequality, inadequate resource distribution and the huge network of conventional financiers, working towards bettering the society by implementing an interest-based model...
Economic Growth and Demographic Changes in Mena Region
Demographic change brings unique opportunities and challenges to centers of global poverty that is marked by high fertility and engines of globa1growth that is marked by rapid aging. The variegated accomplishment of neighborhood policymakers in taking care of open worries through network effort and open...
Analysis of the Slovenian Agricultural Sector Cooperating with the Tourism Industry by Creating Sustainable Economic Growth
The project called “Green Supply Chains” has started in 2015 in the capital of Slovenia, Ljubljana, in the pipeline for pretentious the title of European Green Capital 2016. The project has spread to entire Central Slovenia region by 2017, connecting Ljubljana restaurants and hoteliers presented...
Trying to find an excellent essay sample but no results?
Don’t waste your time and get a professional writer to help!
You may also like
- Constitution
- Gentrification
- Transportation
- Declaration of Independence
- Social Security
- Reign of Terror
- Crimea Crisis
- Minimum Wage Essays
- Taxation Essays
- Affordable Care Act Essays
- Student Loans Essays
- Unemployment Essays
- Compensation Essays
- Crisis Essays
- Gross Domestic Product Essays
- Inflation Essays
- Financial Crisis Essays
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->