Live revision! Join us for our free exam revision livestreams Watch now →
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Business news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Business Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
Study Notes

Starting a Business: Contents of a Startup Business Plan (GCSE)
Last updated 22 Mar 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
For a start-up there are usually two kinds of business plan - a simple one and a detailed one. Some businesses need to produce both.
The simple business plan is rarely shown to outsiders of the business. It is written by the entrepreneur, for the entrepreneur. The simple plan helps summarise the key aims and targets of the business and the actions required to make the business a reality. It is likely to be written in quite an informal way. What would go into the simple plan? Areas such as:
- The idea - a simple description of the proposed business
- Where the idea came from and why it is a good one
- Key targets for the business - sales, profit, growth (gives a sense of direction for the business), ideally for the next 3-4 years
- Finance required - how much from the founder, how much to be loaned over how loan and from who
- Market overview - main segments, market size (value, quantity), growth, market shares of main competitors (if known)
- How the business will operate (location, premises, staff, distribution methods)
- Cash flow forecast (important) + trading forecast
A detailed business plan is needed if a more complicated or larger business is planned as a start-up, or if the entrepreneur needs to raise money from business angels or get a substantial loan from a bank. Here is a summary of the key content:
Executive summary: a brief 1-2 page summary of the detail! Should contain nothing new, but highlight the key points
Market: a profile of the target market based on market research
Product: what it is and how it is different from the competition (the "unique selling point")
Competition: an honest description of the competition in the target market - what they do well, their weaknesses and their likely response
Protecting the idea: how the product and business can be protected from competition - e.g. patents, trademarks, distinctive approaches to marketing or distribution that competitors will find hard to replicate
Management team: a crucial area for any investor. Who is involved in the start-up and what will they be doing? What experience and expertise do they bring? Which management roles will need to be filled as the business grows?
Marketing: the key elements of the marketing mix should be explained here. Remember that for a start-up the marketing budget is likely to limited, so the plan should describe a credible approach to promoting the product and include realistic assumptions about how many customers will buy and at what price
Production /operations: this explains what is involved in the production process, what capacity is needed, who will supply the business, where it will be located etc.
Financial projections : a summary of the cash flow and trading forecasts. This section should highlight the key assumptions that have been made and also outline the main risks and opportunities in the forecasts (i.e. what might go wrong, or where things might prove better than forecast).
Sources of finance: here the figures from the cash flow forecast are taken and used to highlight what funding the business needs, and when.
Returns on investment: another key area for any investor. This is a description of how the entrepreneur expects investors to get a return on their investment. Who might eventually buy the business, when, and for how much?
- Business plan
You might also like
Business planning for a new business (revision presentation).
Teaching PowerPoints
Business Planning - Introduction
Planning a new business (gcse), the mckinsey / general electric growth share matrix, business objectives (introduction).
Topic Videos
Marketing Objectives (Introduction)
How to start an airline.
1st March 2021
Setting Business Aims & Objectives | AQA GCSE Business
Quizzes & Activities
Our subjects
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.
Business Plans
Why do businesses create plans.
It is important for any new or existing business to create a plan in order to have an understanding of how it plans to achieve its aims and objectives. There are 4 key reasons why businesses create plans:

Important for new businesses
- When Peter Jones and Theo Paphitis invested in Levi Roots Reggae Reggae Sauce, they asked to see Levi’s business plan before they committed to providing their expertise and investment.

Raising finance
- To decide whether to give finance to a business, investors and banks need in-depth financial information.
- When Facebook raised finance from venture capitalists to grow and when Snap Inc listed on the New York Stock Exchange they had to provide business plans.

Setting objectives
- A plan lets a business clearly set out what the business’ objectives are and how they are going to go about achieving them.
- These specific business objectives help firms to achieve their aims as they are measurable targets for the firm to work towards.
- It also allows a business to see which areas (growth, sales, profits etc.) they need to improve and which they are doing well on. If they fail to meet an objective then it can be easier to understand why it was not met.

Business organisation
- By detailing how functions of the business will be organised, a business plan can help improve the way that a business is run.
- A local cafe can plan its purchasing, pricing and staffing in a business plan that can help it manage its operations.
The Main Parts of a Business Plan
There are lots of different ways to structure a business plan. However, some sections are very important and are almost always included.

Executive summary
- The executive summary should be a concise overview of the entire business plan.

Mission statement
- A mission statement says what a company wants to achieve.
Products or services
- This section should clearly describe which products or services the company sells and why customers will benefit from this.
- This also may include what a product’s unique selling point (USP) is. The USP of a product or service is how this product or service is different (or unique) from the products or services offered by the competition.

Market analysis
- Analysis of competitors – Who the main competition are and where they are positioned in the market.
- Analysis of customers – The different customer segments and which of these will be the ‘target market’.

Organisation and management team
- This will outline the company’s organisation structure and provide personal details of the owners and other important personnel.

Production details
- This will outline how a firm will produce its products or provide its services.
- This includes things like the location of factories, who the suppliers will be, what materials will be needed and how much they will cost.

- Cost and profit - This includes detailed outlines of the forecasts for cost, revenue and profit.
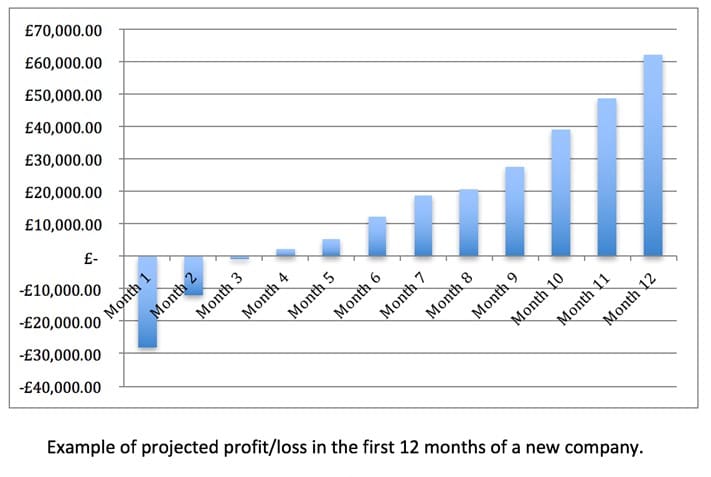
- This section usually includes a cash-flow forecast and projected profit and loss account for the first 12 months of trading.
- Sources of finance - This section often includes details of how a company will fund investment if it is required.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Business Plan
There are advantages and disadvantages of creating business plans.

- Business plans provide parameters for setting targets.
- Management can check staffing, incomes, product ranges and lots of other things against previous business plans and expansion plans.
- A business plan can be used as a benchmark against outcomes like cashflow, production outcomes or service delivery. The plan can also be compared to the behaviour of competitors and the business’ own performance in past years.

Disadvantages
- Businesses need to be flexible and able to adapt to a changing environment. A business plan may stop a company changing.
- Business plans can be costly and time consuming to make. If an entrepreneur has less time to spend designing a good product and selling to customers, then the time spent making a business plan may be negative for the business.
- Also, forecasts of revenue and profit may be misleading and lead to bad decisions.
1 Enterprise & Entrepreneurship
1.1 The Dynamic Nature of Businesses
1.1.1 The Dynamic Nature of Businesses
1.1.2 Risk & Reward
1.1.3 The Role of Business Enterprise
1.1.4 The Role of Business Enterprise 2
1.1.5 The Role of the Entrepreneur
1.1.6 End of Topic Test - Dynamic Nature of Business
1.1.7 Grade 9 - Dynamic Nature of Business
1.2 Spotting a Business Opportunity
1.2.1 Customer Needs
1.2.2 Market Research
1.2.3 Market Segmentation
1.2.4 The Competitive Environment
1.2.5 Primary & Secondary Market Research
1.2.6 End of Topic Test - Business Opportunities
1.2.7 Application Questions - Business Opportunities
1.2.8 Exam-Style Questions - Market Segmentation
1.3 Putting a Business Idea into Practice
1.3.1 Business Aims
1.3.2 Business Objectives
1.3.3 Business Revenues & Costs
1.3.4 Costs - Calculations
1.3.5 Revenue - Calculations
1.3.6 Business Profits & Break-Even Analysis
1.3.7 Profits & Losses - Calculations
1.3.8 Interest - Calculations
1.3.9 Cash & Cash Flow
1.3.10 Cash & Cash Flow 2
1.3.11 Cash Flow - Calculations
1.3.12 Sources of Business Finance
1.3.13 End of Topic Test - Business in Practice
1.3.14 Grade 9 - Business in Practice
1.3.15 Exam-Style Questions - Business in Practice
1.4 Making the Business Effective
1.4.1 The Options for Start-Up & Small Businesses
1.4.2 Limited Liability
1.4.3 Franchising & Not-For-Profits
1.4.4 Business Location
1.4.5 The Marketing Mix
1.4.6 Business Plans
1.4.7 End of Topic Test - Effective Business
1.4.8 Application Questions - Effective Business
1.4.9 Exam-Style Questions - Business Plans
1.5 Business Stakeholders
1.5.1 Business Stakeholders
1.5.2 Technology & Business
1.5.3 Legislation & Business
1.5.4 Legislation & Business 2
1.5.5 The Economy & Business
1.5.6 External Influences
1.5.7 End of Topic Test - Business Stakeholders
1.5.8 Grade 9 - Business Stakeholders
2 Building a Business
2.1 Growing the Business
2.1.1 Business Growth
2.1.2 Finance
2.1.3 Changes in Business Aims & Globalisation
2.1.4 Ethics & Business
2.1.5 The Environment & Business
2.1.6 End of Topic Test - Growing a Business
2.1.7 Application Questions - Growing a Business
2.1.8 Exam-Style Questions - Business Growth
2.2 Making Marketing Decisions
2.2.1 Product
2.2.2 Product Life Cycle
2.2.3 Price
2.2.4 Pricing Methods
2.2.5 End of Topic Test - Product & Price
2.2.6 Grade 9 - Product & Price
2.2.7 Promotion & Advertising
2.2.8 PR & Sales Promotions
2.2.9 Sponsorship & Product Placement
2.2.10 Promotional Mix
2.2.11 End of Topic Test - Promotion
2.2.12 Application Questions - Promotion
2.2.13 Exam-Style Questions - Promotional Mix
2.2.14 Place & Wholesalers
2.2.15 Direct to Consumer
2.2.16 E-commerce & M-commerce
2.3 Making Operational Decisions
2.3.1 Job Production
2.3.2 Batch & Flow Production
2.3.3 Working with Suppliers
2.3.4 Effective Supply Chains
2.3.5 Just In Time & Just In Case
2.3.6 Managing Quality
2.3.7 Total Quality Management
2.3.8 The Sales Process
2.3.9 End of Topic Test - Operational Decisions
2.3.10 Grade 9 - Operational Decisions
2.3.11 Exam-Style Questions - Managing Stock
2.4 Making Financial Decisions
2.4.1 Gross Profit & Net Profit - Definitions
2.4.2 Gross Profit - Calculations
2.4.3 Net Profit - Calculations
2.4.4 Rate of Return
2.4.5 Rate of Return - Calculations
2.4.6 Research & Financial Data
2.4.7 Marketing Data
2.4.8 Percentage Change - Calculations
2.5 Making Human Resource Decisions
2.5.1 Organisational Structures
2.5.2 Organisational Structures 2
2.5.3 Recruitment
2.5.4 Effective Recruitment
2.5.5 Training a Workforce
2.5.6 Motivating a Workforce
2.5.7 End of Topic Tests - Human Resources
2.5.8 Application Questions - Human Resources
2.5.9 Exam-Style Questions - Human Resources
Jump to other topics

Unlock your full potential with GoStudent tutoring
Affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home
Tutors are matched to your specific learning needs
30+ school subjects covered
The Marketing Mix
End of Topic Test - Effective Business

Business Plans

In this post
Business plans are used to outline the industry in which a business is working in as well as the economic structure of a company to give an idea of the financial prospects of a business. They are used primarily to organise the routes to market that a company will take and give projections on earnings and target dates for when the company expects to have a certain income.
Writing a strong business plan is important for any business, whether large or small, and is the perfect way to map out your route to success. Not only will the plan contain your aims and plans to attract new customers but it can also act as a strong tool for financial projections and help you to set out goals for your company. Throughout the units that we have already covered on this course we have seen a lot of aspects that could be included in a business plan, and including as much information as possible is key.
A lot of entrepreneurs fail to produce a clear business plan when they set up a new company and this can be a big issue further down the line. By not outlining your company and its operations you may affect the business in a negative way and be unable to keep track on the progress and route the business is taking. If you are seeking finance to launch your company it is more than likely that you will need to create a business plan to secure a loan, but this should not be thrown away once you have started the business. Your plan can be updated and adapted at any time and you must try to keep things relevant and up to date so you know the long-term aims of your company.
Why create a business plan?
Some entrepreneurs fail to create a business plan before starting a company because they feel it is a waste of time. They know what they want to do, how they want to do it and everything that is needed has been formulated in their heads. This is a very good skill to have, but without your thoughts and projections down on paper it can be very easy for them to become misinterpreted, forgotten or skewed. Simply having things thought out in your mind is not enough to convince others or explain your strategies to those you are working with. Business plans are used to organise your approach and produce a strategy that allows you the best possible chance of success. They should include:
- Information about your company so that you can plan the structure and objectives which you have
- Your relationships with others and how these can be used (e.g. banks, lenders and accountants)
- To find weaknesses in your plans and areas where you must improve
- Areas for discussion so that you can find out other people’s opinions and include them in the planning process
Some people start a business and want everything to be done immediately. With great confidence that they can do it all alone and have no input from experts, they may not stop and think about forming a clear plan that includes facts and figures to help them along the way. Doing this can be of massive detriment to any business and you need to gather as many opinions, facts and ideas as possible from those around you.
What to avoid
A business plan should include lots of information but there are a few things that should be avoided. You should put some restrictions on the long-term (over 1 year) predictions of your finances. A long-range prediction on the amount of money you will have coming into the business can be completely meaningless because it is very hard to predict how a business will perform far into the future.
Very few business plans get the figures projected spot on, so remember to give a good indication of what you expect to earn but try to be conservative with this. By exaggerating the earning potential of the company you will not be impressing anyone and this will make it difficult for you to plan your spending. Outline clear time frames and indicate your aims during these periods. Try to show what you will be working on at any time, for example if your business will take quite a lot of setting up then the first 6 months may be devoted solely to this and you should outline this in your plans and projections. Try to correctly anticipate the money and time that will be required for processes to be completed and always factor in a margin of error. By slightly exaggerating the money that will be required when completing a stage of expansion or setting more time than is needed, you will be well prepared if some unforeseen issue crops up.
Don’t just use the business plan to explain how great your product or service is. This alone will not turn your business into a big success (although it is very important). Identifying areas to improve and how you will market your company is much more important than simply relying on the uniqueness of your product.

The purpose of a business plan
Business plans are used for a variety of different reasons and the importance of these should not be underestimated. Creating a plan that is precise and includes information that is relevant to the new or existing business will ensure that ideas are implemented quickly. Without a solid business plan it will be much more difficult to judge the success of the new venture and the direction of the company will be hard for everyone to see.
Minimising risk
The risks when starting a new business can be huge. Money is invested into new businesses and time will also be spent on getting a company off the ground. Without a business plan in place, owners and employees could end up wasting their time in certain areas. Using resources inefficiently and having no clear direction for a business can lead to disaster very quickly. The best way to avoid this is with a clear outline of what the business needs to work on and what resources will be needed in order to make the venture work. A business plan will be used to set goals and objectives while losing no time in areas that do not see a large enough return on the investment.
Securing finance
Many people use business plans to secure finance for a new venture. This finance can come from several different sources such as banks, investors and start-up funds. Having a business plan that shows exactly how the business will operate and where money will be made will act as a way to convince potential investors to finance the company. With clear profits to be made and a route to market mapped clearly, investing in a business will be a much more desirable prospect for a potential investor.
Formats of business plans
There are many different formats which a business plan can be created in but the main areas to cover are:
Executive summary
Company summary, products and services, market analysis, strategy and implementation, management and personnel, financial plan.
Any business plan should include an executive summary which gives an outline of the business and the vision of the owners. Here you should briefly explain the business and its activities as well as the key areas that will help the company to succeed. A mission statement can be included to explain why your company will be unique in the market and what will give you the edge over your competitors.
You should also include some information about the financial aspirations of the company here to show the economic aims over the first few years in operation. Remember, these do not need to be hugely accurate and taking a realistic look at what can be earned is essential. It is usually best to complete the executive summary of the company last as you can include information from other sections in this part of the plan to give a good overview and concise insight into the business and your plans.
The company summary will explain key aspects of the operation of the company. This includes the owners of the business as well as where the business is located. Information about all directors must be included in this area of the plan and you should summarise their roles within the organisation. If you have any other personnel that will be involved at a senior level then they should be included also. In this part of the business plan you need to outline the funds required to set up and maintain the business also. By including information about the company’s location and operations you will be able to forecast the money required to get the company started and any investment that will be needed. Try to include a spreadsheet showing where the initial funding will come from and how much is being put into the business to start with. Remember, most new businesses make a loss in their first year due to the expenses involved in starting a new company, so be realistic. Plan the initial outlays and costs carefully and make sure you know the limits to how much you can put into the company to get started.
The location of the business can also be included here and any rent that you will be required to pay can be outlined and the costs per square foot for the company premises. Then you can go on to make projections about the sales required to cover all of your fixed costs such as office and equipment rentals.
Next we move on to explaining the things which will earn your business money – the goods and services that you have to offer. In this section you must include descriptions of what you can offer your customers and the prices you will be charging. Outline what makes your goods and services special and the key aspects that will influence potential clients and convert them into paying customers. It is also a good idea to compare your pricing structure to your competitors. It may be that you offer the same products but cheaper, or with any additional features to make your products more appealing. You should explore the need for your products and services to be better than any of the competition. As a new business you may struggle to compete unless you have something that nobody else has. By bringing to the market something which is already selling well with another company that has established its brand in the marketplace, you might struggle to take a large enough section of the market to warrant starting a whole new company. If this is the case then you must compare your pricing to your biggest competitors and ensure that you are competitive.
In this section you can also include any products and services that you may offer in the future. Explain your product development processes and how you will be able to innovate and bring new products or services to the marketplace.
Next you need to carry out some market analysis to identify your potential customers . In this section of the business plan you need to include information about your ideal customers and what sort of people they will be. Think about the earnings of your potential clients, the type of lifestyles they will live and the products and services they expect from a business. This part of your plan is great for you to use figures about your market and show any growth projections for the sector in the future.
Explain market trends and analyse the need for your goods/services in this sector. Attempt to find some facts about the disposable income of your potential customers and target certain people who will be interested in what your company offers. Think about how you will be attracting your customers and the potential for growth over the first 3 years in operation. Make estimations about the number of people in the area where you will be offering your products and services to get a good idea of how many different potential clients you can attract. Having a good understanding of your target market will give you the tools to design marketing strategies and techniques to attract the maximum number of customers to your business.
Having outlined your market and explained who your products/services will attract, it is time to explain your techniques when doing this and show how you are going to market your company. Explain the key aspects of what you offer and the main selling points that should be tailored to suit the target clients that you have in mind. Products designed for the more affluent will need to be luxurious and have an exclusivity about them, whereas items that are for people with limited incomes will need to offer greater value for money. Try to understand a clear link between the market in which you will be operating, your potential clients and the main aspects of your business which you should focus on.
Ensuring that your business suits the needs of customers is essential to getting the most customers. For example, opening up a luxury spa in an area where there is high unemployment and typically lower incomes will encounter lots of issues as the potential customers (those within a 15-mile radius) will have no need for this service and may not be able to afford what you have to offer. You will need to come up with at least five ways of promoting your business that will appeal to your target market and attract clients. Remember all of the techniques and skills we discussed on marketing and try to link what you know about your potential clients to the advertising methods you will use.
Here you can also outline the potential sales forecasts and investments which you will make when promoting your goods and services. Come up with some realistic projections about the money to be spent on advertising and increasing awareness of your brand as well as any sales targets you may wish to set. Be conservative with your sales projections as it takes time for any business to get a good level of customers and building brand awareness does not happen overnight. Your sales in year 1 will normally be fairly low and you need to take this into account when projecting your income and the amount it will cost to set up your company.
The next thing to plan is the personnel involved in your business. This will include the owners and directors as well as any senior managers that are to be involved in the company. Explain the team structure and hierarchy of your new company and the number of employees you will be hiring. Knowing the team behind the company and their individual duties will let you outline the various skills that your team possesses and establish each person’s duties within the organisation.
Outlining the duties of each person and giving a brief job description is a good way for you to understand the team dynamic and responsibilities of each member. Most new companies make the mistake of hiring too soon, but with a clear plan of the business personnel that will be involved in your company you will be able to ensure each person is needed for the business to operate. Establishing a business will require you to be frugal in your approach and employing staff that are not needed can have a terrible impact on your profits and end up costing you tens of thousands of pounds a year.
Outline the wages of your employees and then come up with some totals for staffing costs that can be used when writing your executive summary.
Your financial plan will provide a clear breakdown of all the income and outgoings of the business that you expect. These will only be projected figures so will be likely to change in reality, but you should be able to predict fairly accurately using your knowledge of costs incurred and the pricing and potential customer base for your products/services.
Make projected figures for your fixed and variable costs as well as the profits you expect to earn from sales. This will then help you to create a break-even analysis for your company that will show the amount of money required to cover all of your outgoings. Remember that your first year will have fixed and variable costs as well as additional outgoings which come from setting up your company. You will also have a limited number of sales during the first 12 months as you build up your customer base, so the projected net profit for year 1 will be lower than any other year. Try to think about the most popular goods/services you offer and come up with an average sale price for your customers. This will then help you to identify the number of customers you need in your first year to break even.
Come up with some cash flow and profit and loss charts (look over our work in Unit 1.3 to help) to project how much money you can expect to see in the business each year. This will help you to come up with clear and concise predictions for how much money you will be making in your first three years.
Reformulating a business plan
If you do ever happen to make a slight error in judgement on your initial business plan this can always be altered and the plan changed as required. The chances of figures being completely correct in your first projections are very slim and there will be certain things that you miss or random payments to be made when setting up your business which you did not account for. This is the main reason why being conservative with your income projections and adding in a ‘safety net’ figure to your costings will help you to deal with these circumstances. Business plans should be flexible and are a working document, so chopping and changing them is fine. When doing this try to use what you already have to create a new plan for the next few years rather than just altering figures to make it look like you got the initial plan correct.
Business plans are working documents, so they should be altered and added to as time goes by to determine where your company is heading and how it will get there. Being understanding of the nature of business and the fact that you will not be able to predict certain outcomes will give you an edge and allow you to put in place certain measures to help if you ever do come up against any problems.

Interested in business?
We offer a GCSE Business course that covers information on Business plans.
Learn more about our GCSE business course
Read another one of our posts
Understanding dementia: types, symptoms, and care needs.

A Comprehensive Guide to Health and Social Care Training

Understanding and Supporting Mental Health Conditions

The Role of Diet in Managing Chronic Diseases

Effective Communication Skills in Health and Social Care

Understanding Animal Training – Positive Reinforcement Techniques

Key Skills for Successful Care Home Management

Save your cart?

INTERACTIVE VIDEO
It’s time to follow the journey of Finley Thomas, an aspiring entrepreneur who dreams of opening a small local shop. Throughout the interactive video, we will follow Finley through the process of creating a well-thought-out business plan, which is essential for the success of any business venture.
- DETAILED EXPLAINER VIDEO
- 10 QUESTION MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUIZ
- 6 INTERACTIVE ACTIVITIES
- INTERACTIVE CASE STUDY
- SUPPORTING STUDENT WORKSHEETS
CASE STUDY ANALYSIS MP MECHANICS
The real-life case study explores the journey of Molly Pratt, who started her own mechanics workshop in a small town in Lincolnshire, specialising in luxury vehicles. Despite approaching a bank for a loan of £20,000 to cover the costs of specialist equipment, she was unable to afford to employ any additional staff, resulting in high levels of stress. Unfortunately, MP Mechanics closed down in January 2019 due to a lack of interest in luxury vehicle repair and Molly's difficulties in managing the workload alone.
Teacher Resources
Join your school now, featured links.
- Terms & Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
Connect with us

Sign in/up with Google
Sign in/up with Facebook
Sign in/up with Linkedin
Sign in/up with Apple
Sign in/up with Twitter
Skip to content
Get Revising
Join get revising, already a member.

GCSE Business Studies - What is a Business Plan?
A quick powerpoint explaining what a business plan is, how it is used, and why it is important to a business.
- Created by: Rhys B-M
- Created on: 05-12-11 13:13
- Business Studies
No comments have yet been made
Similar Business Studies resources:
GCSE Business Studies Worksheets 5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating Teacher recommended
Business studies GCSE- Unit 2 0.0 / 5
OCR GCSE Business Studies 2012 Specification 0.0 / 5
Cash Flow (Business Studies Revision GCSE) 3.0 / 5 based on 2 ratings
Business Studies and the Environment (GCSE BBC Bitesize Revision) 3.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
Recruitment - Business Studies (GCSE BBC Bitesize Revision) 5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating Teacher recommended
AQA Business Studies GCSE Unit 1 0.0 / 5
Economy - Business Studies (GCSE BBC Bitesize Revision) 4.0 / 5 based on 1 rating
Breaking Even (Business Studies Revision GCSE) 5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating Teacher recommended
AQA GCSE Business Studies Unit 2 5.0 / 5 based on 1 rating Teacher recommended
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Business BTEC Level 3 Extended Diploma »
- BTEC Business Q&A »
- Should I take History or Business Studies IGCSE »
- Results for GCSE »
- Is this a good A level combination? »
- Should I do geography, biology and psychology a level »
- GCSE options Computer Science vs Spanish vs Business »
- What can I do with a BTEC Level 3 in Business? »
- A level subject choices between Business, Biology and Law »
- alevel - economics vs philosophy »

All you need to know about taking a business studies GCSE!
What is business studies.
You might already know this, but Business Studies teaches all aspects of business, from operations to human resources, and things that have an effect on how well businesses perform, for example, the economy. Business Studies explains how the four pillars of business (marketing, human resources, finance and operations) work together to create a successful company.
What is a Business Studies GCSE?
Unsurprisingly, Business Studies GCSE aims to test you how well you have grasped the different areas of a business and what can impact them. Not only will you learn about different areas of business, you’ll also learn how company structures can affect productivity or what type of employment contract best suits your staff. You’ll even learn about the different influences on a business from tech to ethical and environmental considerations!

So is Business Studies a good GCSE to take?
Short answer, yes. Longer answer, let’s get into it! Business Studies gives great foundational knowledge of what it’s like to work in a business and the factors that go into making a business successful or not. The great thing about business studies is that it’s universal - the terms and concepts don’t differ depending on who or where you are! You’ll also learn a lot of transferable skills, like leadership or how to be a team player.
Doing a Business Studies GCSE is also a great way to improve your employability skills. In every business there will be different departments doing wildly different things, but having a good understanding of how a business functions means you can look at the business as a whole. This perspective is rarer than you think and it can help you bring new ideas to the table that benefit the business.
How to revise for a Business Studies GCSE?
The best way of knowing how to revise for an exam is to understand its structure; there's no point in learning formulas by heart if the questions are more essay-based. So let’s have a look at the format - the Business Studies GCSE is usually split into two exams, each with three parts:
- Part one - tests your knowledge and understanding of business concepts and issues
- Part two - asks you to apply your knowledge to a variety of contexts (case studies)
- Part three - asks you to analyse and evaluate information to demonstrate your understanding of business activity and ability to make judgements and draw conclusions (another case study)
During the first part of the exam there will usually be some short, low-mark questions, which are definition/formula based. After the first section, it's on to the higher marks, where you’ll be given a case study and need to answer a mixture of high and low marked questions.
One of our biggest tips is to know your strengths and weaknesses! If you're not much of a writer and you're getting worried about those longer answers, study the mark scheme and do as many past papers as you can get your hands on. If, on the other hand, you've got the longer marks covered, but can never remember definitions, make use of flashcards and get your friends and family to test you.
When you’re knee-deep in your preparation for your Business Studies GCSE, you’ll probably realise that having your finger on the pulse can help your grades. Reading the news or listening to news-based podcasts is a great way to cement your learning. After all, if you can apply textbook learning to real-world events, you are pretty much there!
As we said before, business is universal, so talking to your friends and family about business is a great way to ensure you've got those all-important concepts locked in. In the exam, you're likely to come across some case studies, and talking to friends and family about LinkedIn's new features or Spotify's latest marketing campaign is essentially like revising a case study out loud without even realising it!
What jobs can Business Studies GCSE get you?
Whilst no GCSE can guarantee you a job, Business Studies is great for opening doors to any sector. After all, every sector has businesses! With a business studies GCSE you could go on to do a business administration apprenticeship, or you could decide to do a business studies A level and/or related degree.
Once you’ve finished your Business Studies GCSE and you’re desperate to learn more, have a think about what areas of a business interest you most. Are you a people-person that loves to figure out what makes people tick? Think about HR! If you’re interested in the day-to-day runnings and always come up with a way to make things easier, why not look for jobs in operations? Another great thing about business is that it’s inclusive, for example, if you’re really creative but not great with numbers you could find a home in marketing.
What is a Business Administration apprenticeship?
If you're not sure whether A levels or a university degree is right for you, why not consider a Business Administration apprenticeship? You'll get to combine learning with real-world work. The apprenticeship normally takes around 18 months to complete and is a great first step into any of the following business areas:
- Human Resources
- Finance and accounting
- Secretarial
- Procurement
- Office administration
- Customer services
What’s next?
So once you’ve chosen your Business Studies GCSE, what’s next? Consider how you like to work and what the best options are for you, there are a lot out there from BTEC’s to A levels, apprenticeships and degrees.
How can we help?
We hope this article helped and you’re one step closer to working out whether a Business Studies GCSE is right for you. If you want to find out more about how to run a business, different areas within a business or even get a head start on what the Business Studies GCSE might involve - why not check out some business Virtual Work Experience programmes ?
Continue reading

What are the future prospects of T Levels? Exploring the benefits of T Levels, and building a successful career

Why should you do a Higher Technical Qualification? The future prospects of Higher Technical Qualifications (HTQs)

What is the difference between the types of apprenticeships? Your guide to exploring opportunities

Quick Links:
More From Forbes
What chess can teach us about entrepreneurship.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Peter J. Burns, III, serial entrepreneur and mentor. Two of my most significant businesses are Burns Funding and Millennial Queenmaker.
As a successful serial entrepreneur, I get asked a lot of questions. But one question I don’t get asked enough is, “How can I teach my son or daughter to be a successful entrepreneur?”
My answer would be simple: Buy them a chessboard.
I taught myself how to play chess when I was 8 years old. No one in my family played at the time. But I took to it like a duck to water. I loved the strategy. As I began starting businesses, I learned that my ability to craft strategies on the chess board carried over to entrepreneurship.
Here are some lessons I've learned from being successful at chess that have helped me become a successful entrepreneur.
Your Best Look Yet At The New iPhone 16
Trump media stock djt at risk of a new short selling plunge, ryan garcia what s ostarine and how could a boxer use it to cheat, plan multiple moves ahead, but also be ready to adjust..
What I like about chess is that it is extremely important that you not only plan several moves ahead but also observe and plot based on your opponent and their moves. In business, this means you plan your strategy, but you remain willing to adjust based on the competitive marketplace.
If you want to be good, work at it.
People who are good at chess worship the game and devote their entire lives to it. I was that way. I structured my life around chess, joined clubs, joined the YMCA and joined every organization that I could possibly think of. I started playing adults right away because they were more challenging.
Long story short, I was more than just a passing participant. I was a very serious chess player and it got to the point where I was able to actually play multiple players at the same time on different boards. The game appealed to me because of my ability to process information very quickly. Chess became a way for me to think clearly about what would happen if I did this and then did that. That approach became ingrained in me at a very early age.
In business, embrace a business that you are passionate about. And then do whatever it takes to make the business a success. That may mean getting up at 4 a.m. or working late into the night. Bring passion to your work, and your work will bring passion to your life.
Learn to read your opponent.
Chess is about how you read your opponent. They can react badly if you have taken a piece in a move that they didn't see coming. This might be an opportunity to make a bold move that will lead to a checkmate.
What I also do is learn to prod their defenses, to find out where their weak point is. If their ego suffered, I would hit it 10 times harder and that would cause them to lose their concentration. In chess, the one that capitalizes on their opponent’s mistakes is the one that wins.
In a business meeting, for example, I have developed the ability to read the room, and then use assets. I might use my sense of humor, for example, to distract them from my intelligence. They underestimate me, which helps me achieve my business objectives.
Understand your assets and what you are willing to sacrifice.
The chess board itself is really like your business career. You have your queen and king, which you really have to protect. They are your assets. At the same time, you should be willing to sacrifice your pawns for a greater objective.
In business, do you know what you need to protect and what you are willing to sacrifice? Maybe there are certain products and services that you are willing to give away in exchange for selling others, which will exponentially grow your business. Take inventory of your assets, and know what you are willing to sacrifice.
Be observant and learn from others.
It's important to learn from your mistakes when playing chess. But it’s even more important to learn what your opponent is successfully doing so you can incorporate their moves in future games. You may not play them again, but it will certainly help you against other opponents.
This happens in business all the time when we see strategies being successfully deployed in our industry, as well as other industries. But we may be too focused on our own business. Be observant, just like you would be in a chess match.
Don’t let them read your emotions.
In chess, you don't get to talk. It is pure strategy. You checkmate your opponent as quickly as possible. You learn by doing it. It's almost like you are an artificial intelligence being, learning and improving every time you play an opponent. We become akin to a computer because there's no emotion in chess. Once the emotion comes in chess, you might lose the game because whoever messes up first loses. If you are a good chess player, you will win by attrition because they made a mistake, and you capitalize on it. It's the same in business.
In sum, I recommend looking at the game of chess and embracing the strategies that you can matriculate into your business environment. I found it's worked really well for me over the years. It taught me to think logically, and it also taught me to apply emotional intelligence to my business acumen.
Forbes Business Council is the foremost growth and networking organization for business owners and leaders. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Take action
- Report an antitrust violation
- File adjudicative documents
- Find banned debt collectors
- View competition guidance
- Competition Matters Blog
New HSR thresholds and filing fees for 2024
View all Competition Matters Blog posts
We work to advance government policies that protect consumers and promote competition.
View Policy
Search or browse the Legal Library
Find legal resources and guidance to understand your business responsibilities and comply with the law.
Browse legal resources
- Find policy statements
- Submit a public comment

Vision and Priorities
Memo from Chair Lina M. Khan to commission staff and commissioners regarding the vision and priorities for the FTC.
Technology Blog
Consumer facing applications: a quote book from the tech summit on ai.
View all Technology Blog posts
Advice and Guidance
Learn more about your rights as a consumer and how to spot and avoid scams. Find the resources you need to understand how consumer protection law impacts your business.
- Report fraud
- Report identity theft
- Register for Do Not Call
- Sign up for consumer alerts
- Get Business Blog updates
- Get your free credit report
- Find refund cases
- Order bulk publications
- Consumer Advice
- Shopping and Donating
- Credit, Loans, and Debt
- Jobs and Making Money
- Unwanted Calls, Emails, and Texts
- Identity Theft and Online Security
- Business Guidance
- Advertising and Marketing
- Credit and Finance
- Privacy and Security
- By Industry
- For Small Businesses
- Browse Business Guidance Resources
- Business Blog
Servicemembers: Your tool for financial readiness
Visit militaryconsumer.gov
Get consumer protection basics, plain and simple
Visit consumer.gov
Learn how the FTC protects free enterprise and consumers
Visit Competition Counts
Looking for competition guidance?
- Competition Guidance
News and Events
Latest news, ftc order bans former pioneer ceo from exxon board seat in exxon-pioneer deal.
View News and Events
Upcoming Event
Older adults and fraud: what you need to know.
View more Events
Sign up for the latest news
Follow us on social media
--> --> --> --> -->

Playing it Safe: Explore the FTC's Top Video Game Cases
Learn about the FTC's notable video game cases and what our agency is doing to keep the public safe.
Latest Data Visualization
FTC Refunds to Consumers
Explore refund statistics including where refunds were sent and the dollar amounts refunded with this visualization.
About the FTC
Our mission is protecting the public from deceptive or unfair business practices and from unfair methods of competition through law enforcement, advocacy, research, and education.
Learn more about the FTC

Meet the Chair
Lina M. Khan was sworn in as Chair of the Federal Trade Commission on June 15, 2021.
Chair Lina M. Khan
Looking for legal documents or records? Search the Legal Library instead.
- Cases and Proceedings
- Premerger Notification Program
- Merger Review
- Anticompetitive Practices
- Competition and Consumer Protection Guidance Documents
- Warning Letters
- Consumer Sentinel Network
- Criminal Liaison Unit
- FTC Refund Programs
- Notices of Penalty Offenses
- Advocacy and Research
- Advisory Opinions
- Cooperation Agreements
- Federal Register Notices
- Public Comments
- Policy Statements
- International
- Office of Technology Blog
- Military Consumer
- Consumer.gov
- Bulk Publications
- Data and Visualizations
- Stay Connected
- Commissioners and Staff
- Bureaus and Offices
- Budget and Strategy
- Office of Inspector General
- Careers at the FTC
Fact Sheet on FTC’s Proposed Final Noncompete Rule
- Competition
- Office of Policy Planning
- Bureau of Competition
The following outline provides a high-level overview of the FTC’s proposed final rule :
- Specifically, the final rule provides that it is an unfair method of competition—and therefore a violation of Section 5 of the FTC Act—for employers to enter into noncompetes with workers after the effective date.
- Fewer than 1% of workers are estimated to be senior executives under the final rule.
- Specifically, the final rule defines the term “senior executive” to refer to workers earning more than $151,164 annually who are in a “policy-making position.”
- Reduced health care costs: $74-$194 billion in reduced spending on physician services over the next decade.
- New business formation: 2.7% increase in the rate of new firm formation, resulting in over 8,500 additional new businesses created each year.
- This reflects an estimated increase of about 3,000 to 5,000 new patents in the first year noncompetes are banned, rising to about 30,000-53,000 in the tenth year.
- This represents an estimated increase of 11-19% annually over a ten-year period.
- The average worker’s earnings will rise an estimated extra $524 per year.
The Federal Trade Commission develops policy initiatives on issues that affect competition, consumers, and the U.S. economy. The FTC will never demand money, make threats, tell you to transfer money, or promise you a prize. Follow the FTC on social media , read consumer alerts and the business blog , and sign up to get the latest FTC news and alerts .
Press Release Reference
Contact information, media contact.
Victoria Graham Office of Public Affairs 415-848-5121
- Updated Terms of Use
- New Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Closed Captioning Policy
Quotes displayed in real-time or delayed by at least 15 minutes. Market data provided by Factset . Powered and implemented by FactSet Digital Solutions . Legal Statement .
This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed. ©2024 FOX News Network, LLC. All rights reserved. FAQ - New Privacy Policy
Biden's new student loan forgiveness plan would cost an extra $84 billion: report
Eliminating unpaid interest on student loans alone costs approximately $58 billion.

Much of the new plan is already covered under SAVE, but key new provisions raise the price tag considerably. ( iStock )
President Joe Biden's new student debt elimination proposal would bring relief for millions more Americans, but a Penn Wharton Budget Model (PWBM) analysis shows it could add another $84 billion to an already costly plan.
The Biden Administration released a formal proposal to provide student debt relief to over 30 million borrowers. The new plan also proposes to eliminate accrued interest for 23 million borrowers and automatically discharge debt for borrowers eligible for loan forgiveness under SAVE, closed school discharge or other forgiveness programs, even if not enrolled. Additionally, student debt for borrowers who entered repayment for 20 or more years would be discharged. The plan would also provide relief to borrowers who experience hardship in paying back their loans.
"These distinct forms of debt relief are designed for borrowers struggling with their loans – and that's a lot of people," Under Secretary of Education James Kvaal said. "There are 25 million borrowers whose interest is growing faster than they can pay it down. That fact alone shows how badly President Biden's student loan relief is needed."
PWBM said that the new plan would cost an extra $84.06 billion on top of the $475 billion price tag for the Saving on a Valuable Education (SAVE) Plan, bringing the total cost to around $559 billion for both plans.
The biggest cost of the plan is waiving up to $20,000 for millions of borrowers whose balances have grown because of unpaid interest. That part of the plan is estimated to cost roughly $58 billion. The second-largest cost, $19 billion, stems from eliminating student debt for borrowers in repayment for 20 years or more (or 25 years with graduate student debt).
Private student loan borrowers can't benefit from federal loan relief. But you could lower your monthly payments by refinancing to a lower interest rate. Visit Credible to speak with an expert and get your questions answered.
BUY A HOME IN THESE STATES TO GET STUDENT LOAN DEBT RELIEF
Student loan cancellation keeps coming
More people are becoming eligible for student loan cancellation as they hit 10 years of payments. Since the launch of SAVE, nearly 8 million borrowers have received relief, including 4.5 million with a $0 monthly payment. Student loan forgiveness has reached millions even as the Supreme Court blocked Biden's original debt forgiveness plan last June.
The latest round of cancellations targets $7.4 billion in student loans for 277,000 borrowers, the Department of Education said in a statement . This brings the total debt forgiven over Biden's presidency to $153 billion.
Biden's SAVE plan could lower borrowers' monthly payments to zero dollars, reduce monthly costs in half and save those who make payments at least $1,000 yearly. Yet roughly three out of four borrowers who make $75,000 or less annually, and would benefit from the SAVE plan, still need to be enrolled, according to a recent Student Debt Crisis Center (SDCC) survey .
If you can qualify for a student loan refinance at a lower rate than you're currently paying, there are usually no downsides to refinancing. You can use Credible to compare student loan refinancing rates from multiple private lenders at once without affecting your credit score.
HOMEOWNERS COULD SAVE TENS OF THOUSANDS IN DAMAGES BY USING SMART DEVICES
Biden student loan forgiveness plan faces legal challenge
Republican-led states filed suit against President Joe Biden and the U.S. Department of Education to stop the SAVE Plan. A total of 18 states have joined one of two lawsuits challenging the plan.
The lawsuits seek to halt the SAVE plan immediately, arguing that the U.S. Department of Education has no authority to alter student loan repayment plans. This would cancel more than $156 billion in student loan debt .
The lawsuit also argues that the U.S. Supreme Court determined that Biden's original forgiveness program violated federal law and that only Congress can authorize the forgiveness of student loans involving taxpayer money.
A statement from the Education Department said Congress gave the agency the authority to define the terms of income-driven repayment plans.
If you hold private student loans, you won't be enrolled in a federal income-driven repayment plan, but you could refinance your loans to a lower rate. Visit Credible to compare options from different lenders without affecting your credit score.
MORTGAGE LOAN LIMIT RISES ABOVE $1.1M AS HOME PRICES SURGE
Have a finance-related question, but don't know who to ask? Email The Credible Money Expert at [email protected] and your question might be answered by Credible in our Money Expert column.
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Business Plan Group Activity for GCSE Business Students.
Subject: Business and finance
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Lesson (complete)
Last updated
22 February 2018
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
christinalangsdale
Found this very useful and more engaging than my original lesson plan !
businessteacher1
Thank you for the review - I plan to share more resources on TES over the coming weeks and months, if there are any topics you think would be good for me to focus on please let me know - [email protected]
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
A retired Microsoft exec and his wife fell in love with RVing during the pandemic. Now he's using AI to help you plan your next road trip.
- Scott Lengel, a former Microsoft CTO, launched an AI-powered RV road trip planner, AdventureGenie.
- He said when he got into RVing during the pandemic, he couldn't find a great planning tool.
- AdventureGenie recommends custom routes, campsites, and activities based on user preferences.

Scott Lengel and his wife, Lisa, were Marriott people.
After spending 23 years as a CTO at Microsoft , Lengel retired in 2017, at which point he and his wife knew they wanted to travel the world. They visited places like Cambodia, Vietnam, and India, typically traveling by plane and staying in hotels — often Marriotts.
Then the pandemic hit.
Suddenly, they were stuck at home in South Carolina. That's when the couple realized, "We really haven't seen the good old US of A."
Up until that point, they'd never even been camping .
"We figured if ever there was a time to go RVing, to go camping, this would be it," Lengel told Business Insider.
So they rented an RV and set off for Nashville with a couple of good friends. "We just had a blast," Lengel said. "Hanging around the campsite and the campfire and eating and beverages, and just the camaraderie. We just fell in love with the lifestyle of camping in one week."
Within six months, they purchased an RV of their own and started taking it all over. But when the couple tried to plan a six-week, multi-stop road trip to the national parks of the Southwest, they realized it was actually pretty challenging and that the existing resources were not great.
"There has to be a better way," they thought.
A couple of years later, in May 2023, Lengel launched AdventureGenie — an AI-powered RV trip planner. Lengel, who serves as chairman and CEO, said that in less than a year, AdventureGenie has attracted more than 10,000 users, and not just RVers, but also people traveling in cars on all kinds of road trips.
AI can customize trip planning
AdventureGenie is one of many AI-powered trip-planning tools that have popped up over the past couple of years. It's been featured on lists of the best RV- and road-trip planning AI tools.
Related stories
AdventureGenie is set up to help people plan their trips in three phases, which Lengel said was based on talking to thousands of people about how they plan their trips.
First, you can shape your trip. You can tell AdventureGenie things like where you want to start, where you want to end, how many miles you want to drive in a day, and any places you know you want to stop along the way. AdventureGenie will create a custom route based on your preferences and what the program knows about you, either from what you've told it or from past trips you've planned.
Second, you can select your campsites. AdventureGenie uses AI to compile information about campsites and make recommendations based on your preferences. In addition to generating an overall score on a campsite, AdventureGenie also generates a score that is unique to you, indicating how likely a specific campground is to meet your personal needs.
Third, is finding things to do. For instance, if it knows you like eating at local restaurants, hiking, and biking, as Lengel and his wife do, it can point out those attractions.
The biggest thing AI brings to AdventureGenie's trip planning is the customization, Lengel said. Instead of looking up a generic road trip planner that is the first hit served to everyone on Google, AdventureGenie can create itineraries that are unique to you.
"It feels as if you have a copilot or a travel planner sitting by your side and knows what you're looking for and customizes it for you," Lengel said.
He said that when RVers first use AdventureGenie the "jaw-dropping" moment for them is when it fills in the blanks on a trip with stops along the way.
In the past, if you wanted to road trip from South Carolina to Yellowstone, you'd have to look at a map and try to plot out stops based on how many miles a day you want to drive. But you'd also have to manually figure out whether those stops have campsites that suit your needs, or if they have any other attractions that make them worth passing through, or how far off the highway they are.
Lengel said new AdventureGenie users often say it saves them so much time planning their trip just by filling in their route.
"That's pretty darn rewarding for us," he said.
From Microsoft to tech startup
Lengel, who came out of retirement to launch AdventureGenie, said working on this startup has been a major change of pace from his days at Microsoft, which he also loved.
"We're a startup at our core, and it's a lot different than when I was working for an organization that had 150,000 employees and an incredible budget," he said. "We all wear lots of hats, which has been exciting, thrilling, and even challenging from time to time."
These days, he and his wife are on the road three out of four weeks a month, though now it's usually for work, visiting trade shows and meeting with RV user groups.
However, they do still make a point to do some fun things, too.
When Lengel spoke to BI, he was sitting in his RV in the Florida Keys, with a view of the ocean right out his window .
Watch: Marriott International's Tina Edmundson tells Insider that the travel mindset has changed since the pandemic
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
GCSE; Edexcel; Business plans - Edexcel The role and importance of a business plan. A business plan is an essential part of starting any business. Entrepreneurs create business plans to help them ...
A business plan is a written document that describes a business, its objectives, its strategies, the market it is in and its financial forecasts. The business plan has many functions, from securing external funding to measuring success within the business. Benefits of business planning to a start-up. The main reasons why a start-up should ...
A business plan is a document produced by the owner at start-up, which provides forecasts of items such as: The business idea ( sub-topic 1.1.1) The business aims and objectives ( sub-topic 1.3.1) The target market ( sub-topic 1.2.2) The forecast revenues, costs and profits ( sub-topic 1.3.2) The cash-flow forecast ( sub-topic 1.3.5)
Reasons for Developing a Business Plan. A business plan sets out key aspects of a business and how the owners intend it to develop. Producing a business plan helps reduce the risk associated with starting a new business and can help the owners raise finance. A business plan forces the owner to think about every aspect of the business and ...
Business Plans Explained - GCSE and A Level Business Revision 📝 This video explains what a business plan is, includes the contents of a business plan as we...
How the business will operate (location, premises, staff, distribution methods) Cash flow forecast (important) + trading forecast; A detailed business plan is needed if a more complicated or larger business is planned as a start-up, or if the entrepreneur needs to raise money from business angels or get a substantial loan from a bank. Here is a ...
A business plan is an essential part of starting any business. Entrepreneurs create business plans to help them consider all of the elements they are going to need for their new business to be a ...
Businesses need to be flexible and able to adapt to a changing environment. A business plan may stop a company changing. Business plans can be costly and time consuming to make. If an entrepreneur has less time to spend designing a good product and selling to customers, then the time spent making a business plan may be negative for the business.
📚 Explore More with BizWizard:Redefine the learning experience over at https://www.bizzwizard.co.uk a platform designed for both teachers and students. Brin...
The purpose of a business plan. Business plans are used for a variety of different reasons and the importance of these should not be underestimated. Creating a plan that is precise and includes information that is relevant to the new or existing business will ensure that ideas are implemented quickly. Without a solid business plan it will be ...
The lesson outlines all the specification points of Business Plans within the GCSE (9-1) Edexcel Business Studies course (useful for other exam boards too) This lesson teaches the following content: The role and importance of a business plan: to identify:the business idea; business aims and objectives; target market (market research); forecast ...
The interactive video introduces students to business plans and their importance for a successful venture. The video follows the journey of Finley Thomas, an entrepreneur who wants to open a local shop, as he creates a business plan. Important sections of a business plan, such as the business idea, people, aims and objectives, market research, finances, and business location, are discussed.
- the business idea - what product or service the business will provide (this is usually the first section of a business plan) - the business' aims and objectives - using the SMART principles - target market - determined through market research - revenue forecast - projected costs and profit - cash flow forecast - sources of finance - long-term and short-term finance - location - where the ...
A quick powerpoint explaining what a business plan is, how it is used, and why it is important to a business. GCSE Business Studies - What is a Business Plan? Powerpoint Presentation 155.89 Kb.
A business plan explains how a business intends to achieve its objectives. It may be written before the business starts, or when planning a major change to the way an existing business operates. A good business plan will include the following: operate, i.e. worker, equipment, Planning is a vital part in the successful start-up and development ...
GCSE Business. Our extensive collection of resources is the perfect tool for students aiming to ace their exams and for teachers seeking reliable resources to support their students' learning journey. Here, you'll find an array of revision notes, topic questions, fully explained model answers, past exam papers and more, meticulously organized ...
So let's have a look at the format - the Business Studies GCSE is usually split into two exams, each with three parts: Part one - tests your knowledge and understanding of business concepts and issues. Part two - asks you to apply your knowledge to a variety of contexts (case studies) Part three - asks you to analyse and evaluate information ...
Max with ads (Monthly Plan) Formerly HBO Max, now just Max, this streaming service is the US home of premium content from HBO and Warner Bros. Since the rebranding, it's now also the home of ...
zip, 914 Bytes. pdf, 59.95 KB. pptx, 1.99 MB. This lesson / resource is from Unit 1 - Understanding Business Activity and looks specifically at Business Plans . I normally teach this in Year 10 and it has been designed for GCSE with the following learning objectives: Know what a Business Plan is and why a person might write one.
In business, embrace a business that you are passionate about. And then do whatever it takes to make the business a success. That may mean getting up at 4 a.m. or working late into the night.
The Biden administration moved Tuesday to reclassify marijuana as a lower-risk substance, a person familiar with the plans told CNN, a historic move that acknowledges the medical benefits of ...
Fewer than 1% of workers are estimated to be senior executives under the final rule. Specifically, the final rule defines the term "senior executive" to refer to workers earning more than $151,164 annually who are in a "policy-making position.". The FTC estimates that banning noncompetes will result in: Reduced health care costs: $74 ...
Starbucks is brewing a turnaround plan that involves speedier service and expanding the number of promotions after its most recent quarter was "disappointing," in the words of its own chief ...
Business plan. A business plan is a document that sets out the aims and objectives of a business and how it plans to achieve them. A business plan can be used to work out whether your business is ...
That fact alone shows how badly President Biden's student loan relief is needed." PWBM said that the new plan would cost an extra $84.06 billion on top of the $475 billion price tag for the Saving ...
A business plan observation sheet for the potential investor to peer mark the business plan. A completed business plan observation sheet A homework sheet. This resources has been designed for GCSE Business Studies and can be used for the new AQA GCSE Business (8132) for exams 2019 - it covers 3.1.6 Business Plans but can be used for any Level 2 ...
Here are some of the best 529 college savings plans for tax benefits and how to choose a 529 plan in 2024. 1. Bright Start Direct-Sold College Savings Program (Illinois) Bright Start Direct-Sold ...
Scott Lengel and his wife, Lisa, were Marriott people. After spending 23 years as a CTO at Microsoft, Lengel retired in 2017, at which point he and his wife knew they wanted to travel the world ...