CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free

Class 9 Mathematics Statistics Assignments
We have provided below free printable Class 9 Mathematics Statistics Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 9 Mathematics Statistics . These Assignments for Grade 9 Mathematics Statistics cover all important topics which can come in your standard 9 tests and examinations. Free printable Assignments for CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Statistics , school and class assignments, and practice test papers have been designed by our highly experienced class 9 faculty. You can free download CBSE NCERT printable Assignments for Mathematics Statistics Class 9 with solutions and answers. All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Mathematics Statistics Class 9. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Mathematics Statistics class 9 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 9 Mathematics Statistics Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Mathematics Statistics Class 9 Assignments Pdf Download
We have provided below the biggest collection of free CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Class 9 Mathematics Statistics . Students and teachers can download and save all free Mathematics Statistics assignments in Pdf for grade 9th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 9 important questions and answers for Mathematics Statistics as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year. All test papers and question banks for Class 9 Mathematics Statistics and CBSE Assignments for Mathematics Statistics Class 9 will be really helpful for standard 9th students to prepare for the class tests and school examinations. Class 9th students can easily free download in Pdf all printable practice worksheets given below.
Topicwise Assignments for Class 9 Mathematics Statistics Download in Pdf
Advantages of Class 9 Mathematics Statistics Assignments
- As we have the best and largest collection of Mathematics Statistics assignments for Grade 9, you will be able to easily get full list of solved important questions which can come in your examinations.
- Students will be able to go through all important and critical topics given in your CBSE Mathematics Statistics textbooks for Class 9 .
- All Mathematics Statistics assignments for Class 9 have been designed with answers. Students should solve them yourself and then compare with the solutions provided by us.
- Class 9 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Mathematics Statistics chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf
- Class 9 Mathematics Statistics question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams
Frequently Asked Questions by Class 9 Mathematics Statistics students
At https://www.cbsencertsolutions.com, we have provided the biggest database of free assignments for Mathematics Statistics Class 9 which you can download in Pdf
We provide here Standard 9 Mathematics Statistics chapter-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Mathematics Statistics in Grade 9, all topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here topic-wise Mathematics Statistics Grade 9 question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material.
We have provided the best collection of question bank and practice tests for Class 9 for all subjects. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts

Class 9 Malayalam Assignments

Class 9 Mathematics Polynomials Assignments

Class 9 Mathematics Linear Equations In Two Variables Assignments
AssignmentsBag.com
Assignments For Class 9 Mathematics Statistics
Assignments for Class 9 Mathematics Statistics have been developed for Standard 9 students based on the latest syllabus and textbooks applicable in CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools. Parents and students can download the full collection of class assignments for class 9 Mathematics Statistics from our website as we have provided all topic wise assignments free in PDF format which can be downloaded easily. Students are recommended to do these assignments daily by taking printouts and going through the questions and answers for Grade 9 Mathematics Statistics. You should try to do these test assignments on a daily basis so that you are able to understand the concepts and details of each chapter in your Mathematics Statistics book and get good marks in class 9 exams.
Key Concepts for Class 9 Mathematics Statistics
• There are two types of data (i) Primary (ii) Secondary • We can represent the data by (i) ungrouped and grouped frequency distribution. • Data can also represent by (i) bar graph (ii) Histogram (iii) Frequency polygons * Class mark of grouped data is lower limit + upper limit /2 * Measure of central tendencies by mean, median, mode. * Mean (x) = sum of all observations/total no. of observations If observations denoted by and their occurrence i.e. frequency is denoted by then mean is (x̅) = Σfixi/Σfi * Median: Arrange the observations in ascending or descending order then if numbers of observations (n) are odd then then median is (n+1/2)th term. If no. of observations (n) are even then median is average of and th terms. * Mode: The observation whose frequency is greatest. * Mode = 3 median – 2 mean.
Class 9 Mathematics Statistics Assignments
Class 9 mathematics statistics important questions and answers.
Question. Tally marks are used to find ………….
Question. Find the median of 37, 31, 42, 43, 46, 25, 39, 45, 32
Question. The following marks were obtained by the students in a test. 81, 72, 90, 90, 86, 85, 92, 70, 71, 83, 89, 95, 85, 79, 62 What is the range?
Question. If x, x 2 ……….x n are n values of a variable X such that
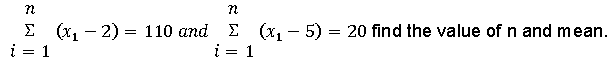
n=30, mean = 17/3
Question. In a histogram, each class rectangle is constructed with base as (a) frequency (b) class interval (c) range (d) size of the class
Question. If the mean of 2, 4, 6, 8, x, y is 5 then find the value of x+y.
Question. The mean of 10 numbers is 20, If 5 is subtracted from every number, what will be the new mean.
Question. Find the mode of following series. 25, 23, 22, 22, 24, 27, 27, 25, 23, 22, 26, 32
Question. Write the class mark of 90-110 group.
Question. Find the mean of first 10 even natural no.
Question. If the median of a series of data is 3 and mean is 2 then find the mode.
Question. If the mean of the following distribution is 6, then find the value of p. x 2 4 6 10 p+5 f 3 2 3 1 2
Question. If the ratio of mean and median of a certain data is 2:3, then find the ratio of its mode and mean.
Question. Calculate the mean for the following distribution. x 5 6 7 8 9 f 4 8 14 11 3
Question. Find the value of p, if the mean of following distribution is 20.
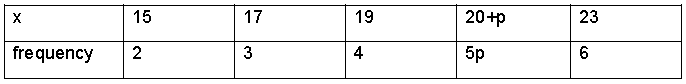
Question. The mean of 5 numbers is 18. If one number is excluded, their mean is 16, find the excluded number.
Question. The following observations have been arranged in ascending order. If the median of the data is 63, find the value of x. 29, 32, 48, 50, x, x+2, 72, 78, 84, 95
Question. Find the median of the following data 19, 25, 59, 48, 35, 31, 30, 32, 51. If 25 is replaced by 52, what will be the new median.
Question. Find the value of x and y in following distribution if it known that the mean of the distribution is 1.46.
Question. If the mean of five observations x, x+2, x+4, x+6, x+8 is 11 find the mean of first three observation.
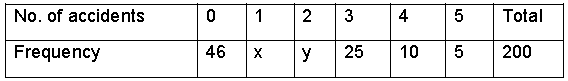
Question. Given below is a cumulative frequency distribution table showing the age of people living in a locality. Age in years No. of persons Above 108 0 Above 96 1 Above 84 3 Above 72 5 Above 60 20 Above 48 158 Above 36 427 Above 24 809 Above 12 1026 Above 0 1124 Prepare a frequency distribution table.

Question. The marks scored by 55 students in a test are given below :

Question. The mean monthly salary of 10 members of a group is Rs. 1445, one more member whose monthly salary is Rs. 1500 has joined the group. Find the mean monthly salary of 11 members of the group.
Question. The mean of 200 items was 50. Later on, it was discovered that the two items were misread as 92 and 8 instead of 192 and 88. Find the correct mean.
Assignments for Class 9 Mathematics Statistics as per CBSE NCERT pattern
All students studying in Grade 9 Mathematics Statistics should download the assignments provided here and use them for their daily routine practice. This will help them to get better grades in Mathematics Statistics exam for standard 9. We have made sure that all topics given in your textbook for Mathematics Statistics which is suggested in Class 9 have been covered ad we have made assignments and test papers for all topics which your teacher has been teaching in your class. All chapter wise assignments have been made by our teachers after full research of each important topic in the textbooks so that you have enough questions and their solutions to help them practice so that they are able to get full practice and understanding of all important topics. Our teachers at https://www.assignmentsbag.com have made sure that all test papers have been designed as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and examination pattern. These question banks have been recommended in various schools and have supported many students to practice and further enhance their scores in school and have also assisted them to appear in other school level tests and examinations. Its easy to take print of thee assignments as all are available in PDF format.
Some advantages of Free Assignments for Class 9 Mathematics Statistics
- Solving Assignments for Mathematics Statistics Class 9 helps to further enhance understanding of the topics given in your text book which will help you to get better marks
- By solving one assignment given in your class by Mathematics Statistics teacher for class 9 will help you to keep in touch with the topic thus reducing dependence on last minute studies
- You will be able to understand the type of questions which are expected in your Mathematics Statistics class test
- You will be able to revise all topics given in the ebook for Class 9 Mathematics Statistics as all questions have been provided in the question banks
- NCERT Class 9 Mathematics Statistics Workbooks will surely help you to make your concepts stronger and better than anyone else in your class.
- Parents will be able to take print out of the assignments and give to their child easily.
All free Printable practice assignments are in PDF single lick download format and have been prepared by Class 9 Mathematics Statistics teachers after full study of all topics which have been given in each chapter so that the students are able to take complete benefit from the worksheets. The Chapter wise question bank and revision assignments can be accessed free and anywhere. Go ahead and click on the links above to download free CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Statistics Assignments PDF.

You can download free assignments for class 9 Mathematics Statistics from https://www.assignmentsbag.com
You can get free PDF downloadable assignments for Grade 9 Mathematics Statistics from our website which has been developed by teachers after doing extensive research in each topic.
On our website we have provided assignments for all subjects in Grade 9, all topic wise test sheets have been provided in a logical manner so that you can scroll through the topics and download the worksheet that you want.
You can easily get question banks, topic wise notes and questions and other useful study material from https://www.assignmentsbag.com without any charge
Yes all test papers for Mathematics Statistics Class 9 are available for free, no charge has been put so that the students can benefit from it. And offcourse all is available for download in PDF format and with a single click you can download all assignments.
https://www.assignmentsbag.com is the best portal to download all assignments for all classes without any charges.
Related Posts

Assignments For Class 6 Computer Science

Assignments For Class 9 Mathematics Measures of central Tendency

Beginning Letter Sounds Assignments Download PDF
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 - Statistics
- NCERT Solutions

CBSE Class 9 NCERT Solutions For Maths Chapter 14 Statistics - Free PDF Download
Chapter 14 Maths Class 9 Statistics is one of the most important chapters of the entire Maths syllabus. It also carries good marks, so learning this chapter correctly is necessary. Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 Statistics is thus highly important from the examination’s perspective. The chapter covers data from the statistical aspect, grouping data, presenting data in a specific manner, the idea of primary and secondary data, developing grouped frequency distribution tables, and so on.
To efficiently help Class 9 students understand the basic concepts of Mathematics Chapter 14 Statistics, we have provided NCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 9 Maths Chapter 12- Statistics in the pdf format. Students can download the pdf through the link below to practice the questions anytime at their convenience.
Topics Covered in Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 - Statistics
Introduction To Statistics
Collection of Data
Presentation of Data
Graphical Representation of Data - Bar, Histogram, and Frequency Polygon
Measures of Central Tendency

Exercises under NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 Statistics
Ncert solutions for class 9 maths chapter 14, "statistics," deals with the concepts related to the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. the chapter consists of the following exercises: exercise 14.1: this exercise discusses the range of a given data set and the calculation of mean, median, and mode. exercise 14.2: this exercise covers cumulative frequency and frequency distribution tables. exercise 14.3: this exercise explains the graphical representation of data using histograms and frequency polygons. exercise 14.4: this exercise deals with the calculation of cumulative frequency, quartiles, and interquartile range., access ncert solutions for class 9 mathematics chapter 14 – statistics, exercise 14.1.
1. Give five examples of data that you can collect from day to day life.
Ans: In our day-to-day life, we collect the following data.
i. Number of boys and girls in our classroom.
ii. Rainfall in Mumbai in the last \[{\text{10}}\] months.
iii. The number of hours we study daily.
iv. Number of runs scored by Virat Kohli.
v. Number of times we exercise in a week.
2. Classify the data in Q 1 above as primary or secondary data.
Ans: Primary data is information gathered by the investigator himself with a specific goal in mind, whereas secondary data is information gathered from a source that already has the information stored.
The data in \[2\]and \[4\] can be classified as secondary data, while the data in \[1,3\]and \[5\] can be classified as primary data.
Exercise 14.2
1. The blood group of \[30\] students of class VIII are recorded as follows:
A, B, O, O, AB, O, A, O, B, A, O, B, A, O, O,
A, AB, O, A, A, O, O, AB, B, A, O, B, A, B, O.
Represent this data in the form of a frequency distribution table. Which is the most common, and which is the rarest, blood group among these students?
Ans: It can be observed that \[9\]students have their blood group as A, \[6\]as B, \[3\]as AB and \[12\] as O.
Therefore, the blood group of \[30\] students of the class can be represented as follows.
Hence, from the above table it is clear that the most common blood group is O (maximum number of students) and the rarest blood group is AB (minimum number of students).
2. The distance (in km) of \[40\] engineers from their residence to their place of work were found as follows:
5 3 10 20 25 11 13 7 12 31
19 10 12 17 18 11 32 17 16 2
7 9 7 8 3 5 12 15 18 3
12 14 2 9 6 15 15 7 6 12
Construct a grouped frequency distribution table with class size 5 for the data given above taking the first interval as \[0 - 5\] (\[5\] not included). What main feature do you observe from this tabular representation?

The classes in the table are not overlapping. Also, \[36\] out of \[40\] Engineers have their houses below\[{\text{20km}}\]distance.
3. The relative humidity (in %) of a certain city for a month of \[30\] days was as follows:
i. Construct a grouped frequency distribution table with classes \[84 - 86,86 - 88\]
Ans: We need to create a grouped frequency distribution table with a class size of two. \[84 - 86,86 - 88\]and \[88 - 90\].
By observing the data given above, the required table can be constructed as follows:
ii. Which month or season do you think this data is about?
Ans: The relative humidity is high, as can be seen. As a result, the data is for a month during the rainy season.
iii. What is the range of this data?
Ans: Range of data = Maximum value − Minimum value
\[ = 99.2 - 84.9 = 14.3\]
4. The heights of \[50\] students, measured to the nearest centimeters, have been found to be as follows:
161 150 154 165 168 161 154 162 150 151
162 164 171 165 158 154 156 172 160 170
153 159 161 170 162 165 166 168 165 164
154 152 153 156 158 162 160 161 173 166
161 159 162 167 168 159 158 153 154 159
i. Represent the data given above by a grouped frequency distribution table, taking the class intervals as \[160 - 165,165 - 170\]etc.
Ans: The class intervals and \[160 - 165,165 - 170\]so on must be taken into account when creating a grouped frequency distribution table. The needed table can be built as follows using the data provided above.
ii. What can you conclude about their heights from the table?
Ans: It is observed that more than \[50\% \] of the students are shorter than \[165{\text{cm}}\].
5. A study was conducted to find out the concentration of sulphur dioxide in the air in parts per million (ppm) of a certain city. The data obtained for \[30\] days is as follows:
0.03 0.08 0.08 0.09 0.04 0.17
0.16 0.05 0.02 0.06 0.18 0.20
0.11 0.08 0.12 0.13 0.22 0.07
0.08 0.01 0.10 0.06 0.09 0.18
0.11 0.07 0.05 0.07 0.01 0.04
i. Make a grouped frequency distribution table for this data with class intervals as \[0.00 - 0.04,0.04 - 0.08\] and so on.
ii. For how many days, was the concentration of Sulphur dioxide more than \[0.11\] parts per million?
Ans: The number of days with a SO 2 concentration greater than 0.11 is equal to the number of days with a concentration between \[0.12 - 0.16,0.16 - 0.20\] and \[0.20 - 0.24\].
Required number of days \[ = 2 + 4 + 2 = 8\]
Therefore, the concentration of SO 2 is more than \[0.11\]ppm, for \[8\]days.
6. Three coins were tossed \[30\] times simultaneously. Each time the number of heads occurring was noted down as follows:
0 1 2 2 1 2 3 1 3 0
1 3 1 1 2 2 0 1 2 1
3 0 0 1 1 2 3 2 2 0
Prepare a frequency distribution table for the data given above.
Ans: The desired frequency distribution table can be produced as follows by examining the above data.
7. The value of π up to 50 decimal places is given below:
3.14159265358979323846264338327950288419716939937510
i. Make a frequency distribution of the digits from \[0\] to \[9\] after the decimal point.
Ans: The required table can be generated as follows by observing the digits following the decimal point:
ii. What are the most and the least frequently occurring digits?
Ans: The table above shows that the lowest frequency is 2 of digit 0, while the highest frequency is 8 of digit 3 and 9. As a result, 3 and 9 are the most often occurring digits, whereas 0 is the least frequently occurring digit.
8. Thirty children were asked about the number of hours they watched TV programmes in the previous week. The results were found as follows:
1 6 2 3 5 12 5 8 4 8
10 3 4 12 2 8 15 1 17 6
3 2 8 5 9 6 8 7 14 12
i. Make a grouped frequency distribution table for this data, taking class width 5 and one of the class intervals as \[5 - 10.\]
Ans: Our class interval will be \[0 - 5,5 - 10,10 - 15\]....
The grouped frequency distribution table can be constructed as follows:
ii. How many children watched television for \[15\] or more hours a week?
Ans: The number of children who watched TV for \[15\] hours or more per week is 2 (i.e., the number of children in the \[15 - 20\] class interval).
9. A company manufactures car batteries of a particular type. The lives (in years) of \[40\] such batteries were recorded as follows:
2.6 3.0 3.7 3.2 2.2 4.1 3.5 4.5
3.5 2.3 3.2 3.4 3.8 3.2 4.6 3.7
2.5 4.4 3.4 3.3 2.9 3.0 4.3 2.8
3.5 3.2 3.9 3.2 3.2 3.1 3.7 3.4
4.6 3.8 3.2 2.6 3.5 4.2 2.9 3.6
Construct a grouped frequency distribution table for this data, using class intervals of size 0.5 starting from the intervals \[2 - 2.5\].
Ans: Starting with the class interval 22.5, a grouped frequency table with a class size of 0.5 must be formed.
Therefore, class intervals will be \[2 - 2.5,2.5 - 3,3 - 3.5\]
By observing the data given above, the required grouped frequency distribution table can be constructed as follows:
Exercise 14.3
1. A survey conducted by an organisation for the cause of illness and death among the women between the ages \[15 - 44\] (in years) worldwide, found the following figures (in %)
i. Represent the information given above graphically.
Ans: The graph of the information presented above can be produced as follows by depicting causes on the x-axis and family fatality rate on the y-axis, and selecting an acceptable scale (1 unit = 5% for the y axis).
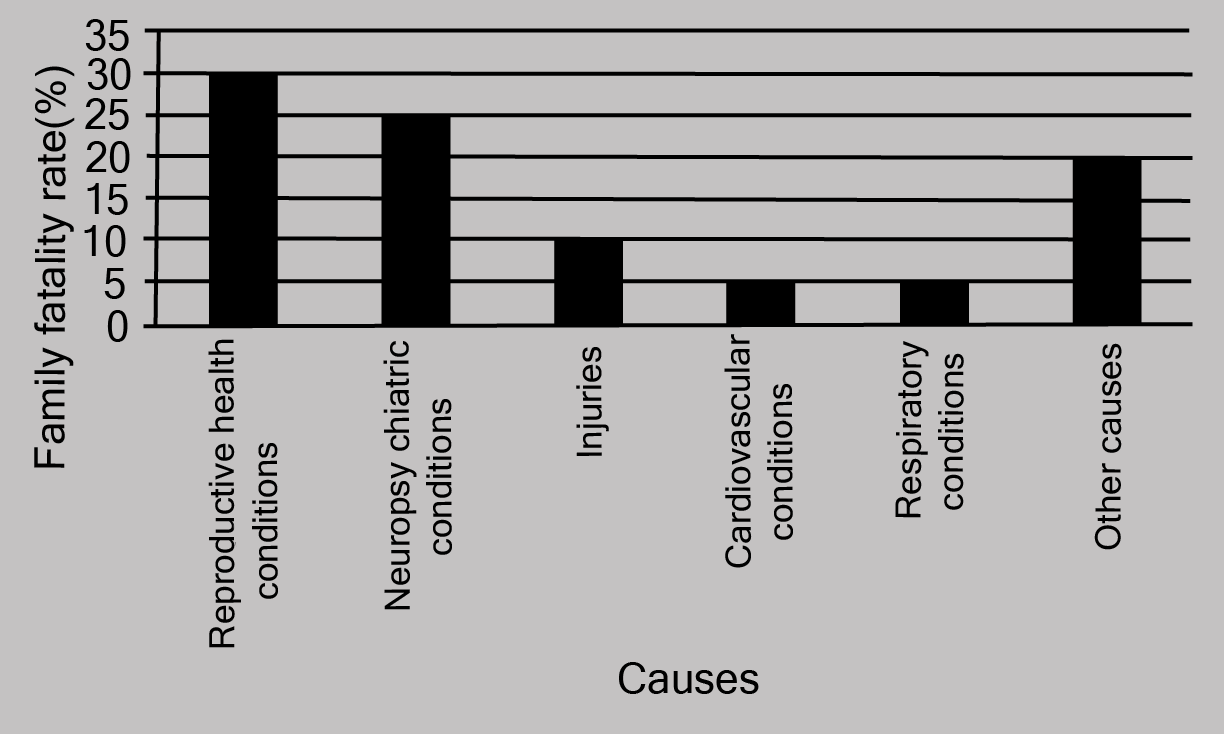
All the rectangle bars are of the same width and have equal spacing between them.
ii. Which condition is the major cause of women’s ill health and death worldwide?
Ans: Reproductive health issues are the leading cause of women's illness and mortality globally, affecting 31.8% of women.
iii. Try to find out, with the help of your teacher, any two factors which play a major role in the cause in (ii) above being the major cause
Ans: The factors are as follows:
a. Lack of medical facilities
b. Lack of correct knowledge of treatment
2. The following data on the number of girls (to the nearest ten) per thousand boys in different sections of Indian society is given below:
i. Represent the information above by a bar graph.
Ans: The graph of the information presented above may be built by choosing an appropriate scale (1 unit = 100 girls for the y-axis) and representing section (variable) on the x-axis and number of girls per thousand boys on the y-axis.
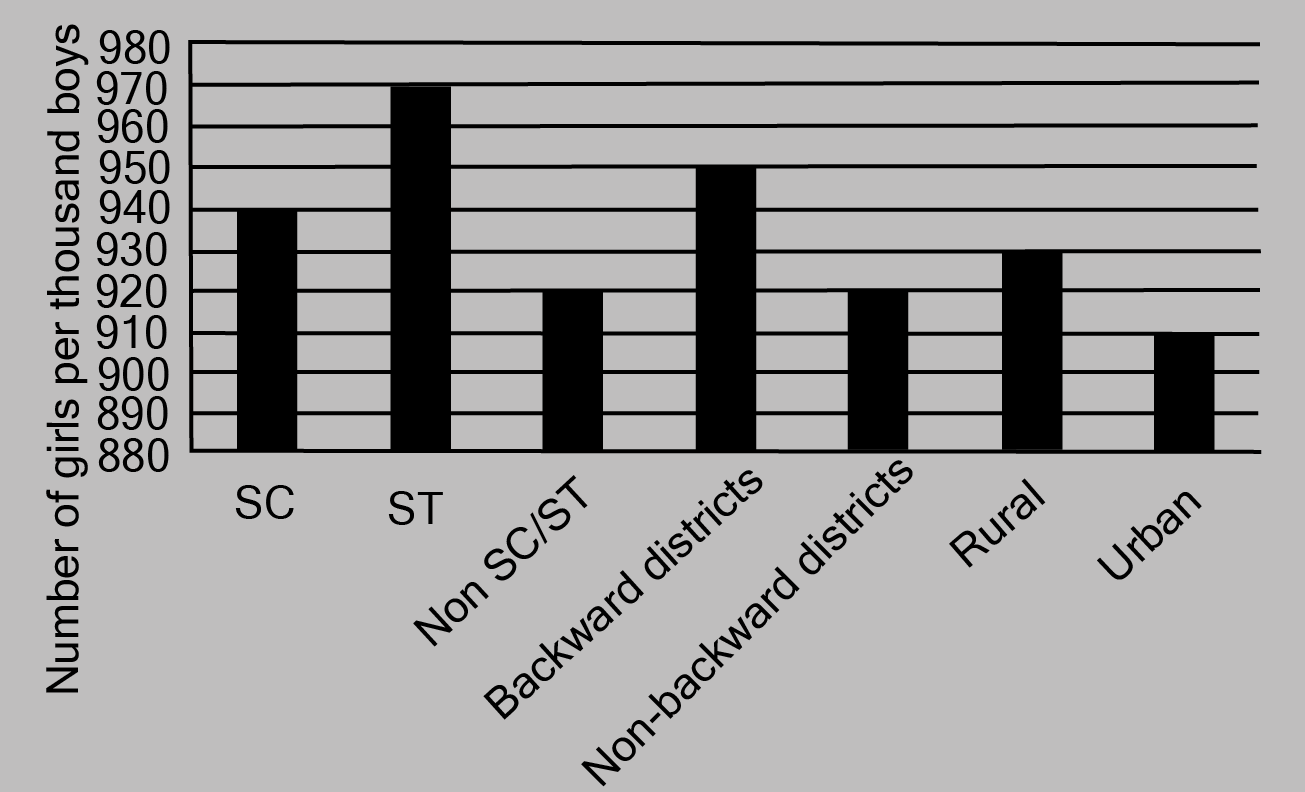
Here, all the rectangle bars are of the same length and have equal spacing in between them.
ii. In the classroom discuss what conclusions can be arrived at from the graph.
Ans: The largest number of females per thousand boys (i.e., 970) is found in ST, while the lowest number of girls per thousand boys (i.e., 910) is found in urban areas.
In addition, the number of females per thousand boys is higher in rural regions than in cities, in backward districts than in non-backward districts, and in SC and ST districts than in non-SC/ST districts.
3. Given below are the seats won by different political parties in the polling outcome of a state assembly elections:
i. Draw a bar graph to represent the polling results.
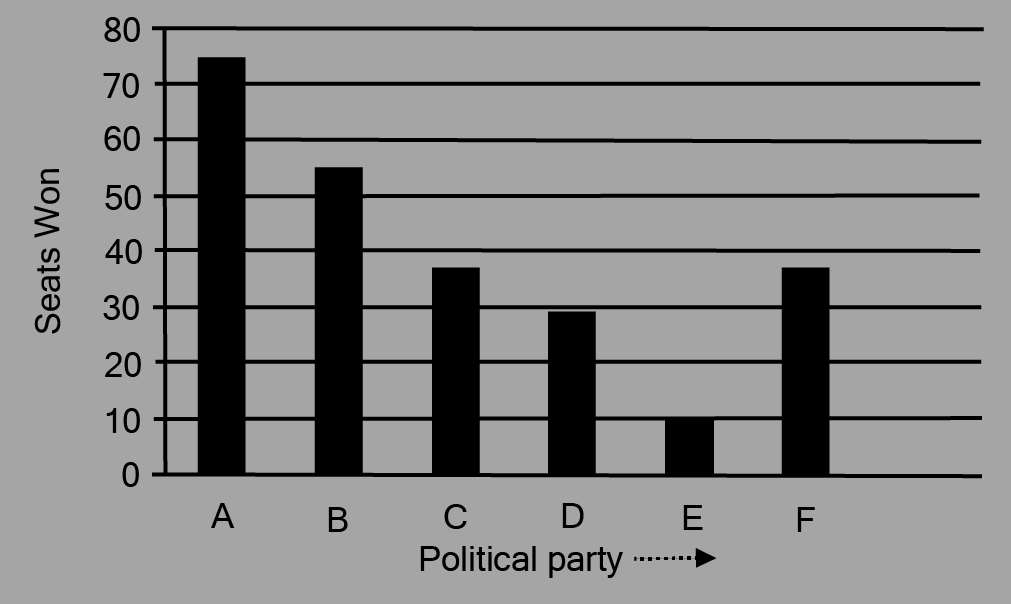
ii. Which political party won the maximum number of seats?
Ans: From the above graph it is clear that Political party ‘A’ won the maximum number of seats.
4. The length of\[40\] leaves of a plant are measured correct to one millimeter, and the obtained data is represented in the following table:
i. Draw a histogram to represent the given data.
Ans: The length of leaves is represented in a discontinuous class interval with a difference of \[1\] between them, as can be seen. To make the class intervals continuous, \[\dfrac{1}{2} = 0.5\] must be added to each upper class limit and \[0.5\] must be subtracted from the lower class limits.
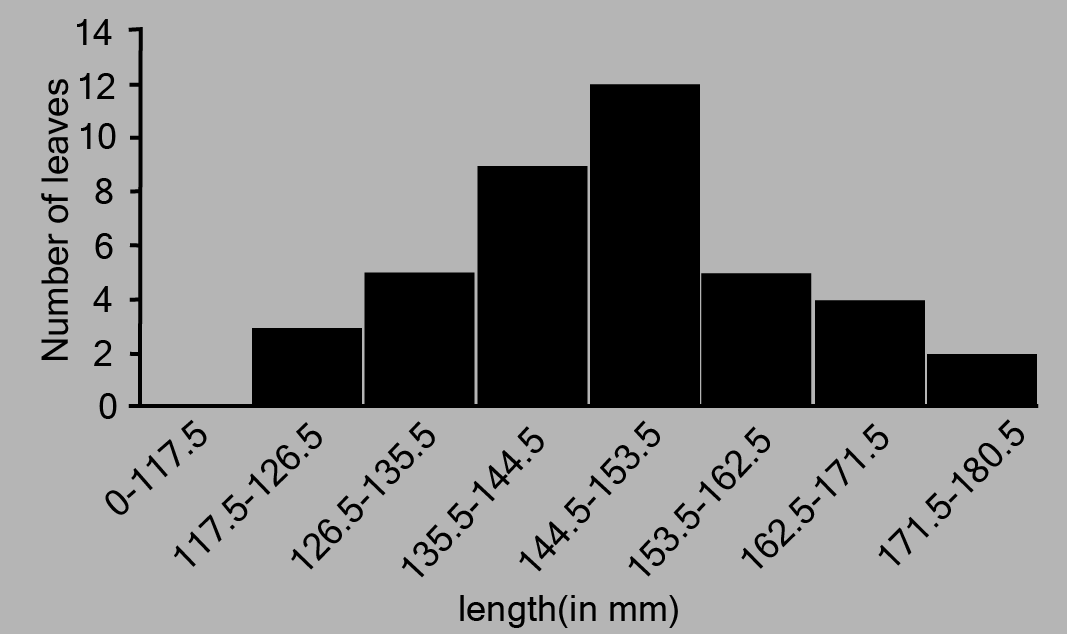
The above histogram may be built using the length of leaves on the x-axis and the number of leaves on the y-axis.
On the y-axis, one unit symbolises two leaves.
ii. Is there any other suitable graphical representation for the same data?
Ans: Frequency polygon is another good graphical representation of this data.
iii. Is it correct to conclude that the maximum number of leaves are 153 mm long? Why?
Ans: No, because the maximum number of leaves (i.e.\[12\]) has a length of \[144.5{\text{mm}}\] to \[153.5{\text{mm}}\] It is not necessary for all of them to be \[153{\text{mm}}\]long.
5. The following table gives the life times of neon lamps:
\[\boxed{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{\text{ Length (in hours) }}}&{{\text{ Number of lamps}}} \\ {300 - 400}&{14} \\ {400 - 500}&{56} \\ {500 - 600}&{60} \\ {600 - 700}&{86} \\ {700 - 800}&{74} \\ {800 - 900}&{62} \\ {900 - 1000}&{48} \\ {}&{} \end{array}}\]
i. Represent the given information with the help of a histogram.
Ans: The histogram of the given data may be produced by plotting the life duration (in hours) of neon lamps on the x-axis and the number of lamps on the y-axis. Here,1
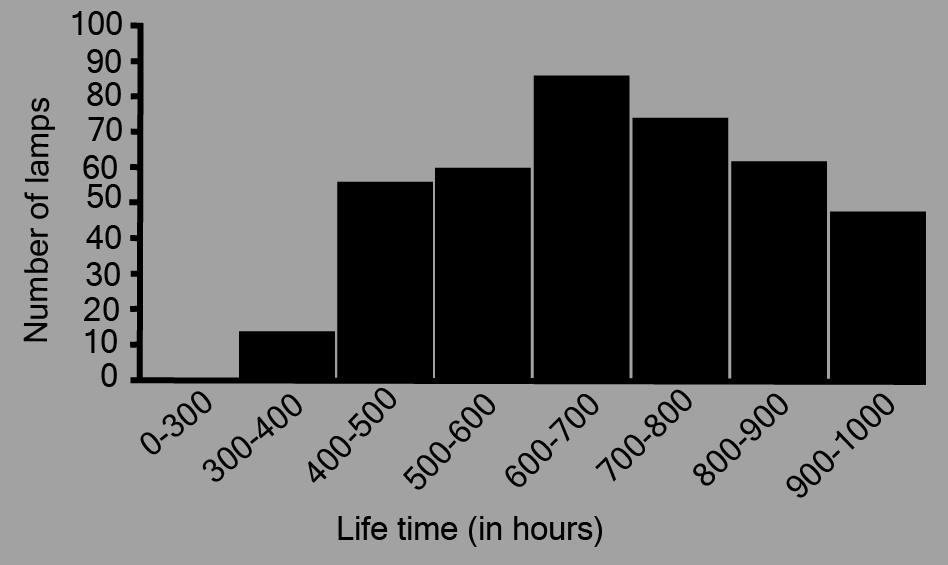
Here, 1 unit on the y-axis represents 10 lamps.
ii. How many lamps have a lifetime of more than \[700\] hours?
Ans: It may be deduced that the number of neon lamps with a lifetime more than \[700\]is equal to the sum of the numbers of neon lamps with lifetimes of \[700,800\]and \[900\]. As a result, there are \[184\] neon bulbs with a lifetime of more than \[700\] hours \[(74 + 62 + 48 = 184)\].
6. The following table gives the distribution of students of two sections according to the mark obtained by them:
Represent the marks of the students of both the sections on the same graph by two frequency polygons. From the two polygons compare the performance of the two sections.
Ans: We can find the class marks of the given class intervals by using the following formula.
\[{\text{Class mark = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Upper class limit + Lower class limit}}}}{2}\]
The frequency polygon can be constructed as follows, with class markings on the x-axis and frequency on the y-axis, and an appropriate scale \[(1{\text{ unit = 3 for the y - axis}})\].
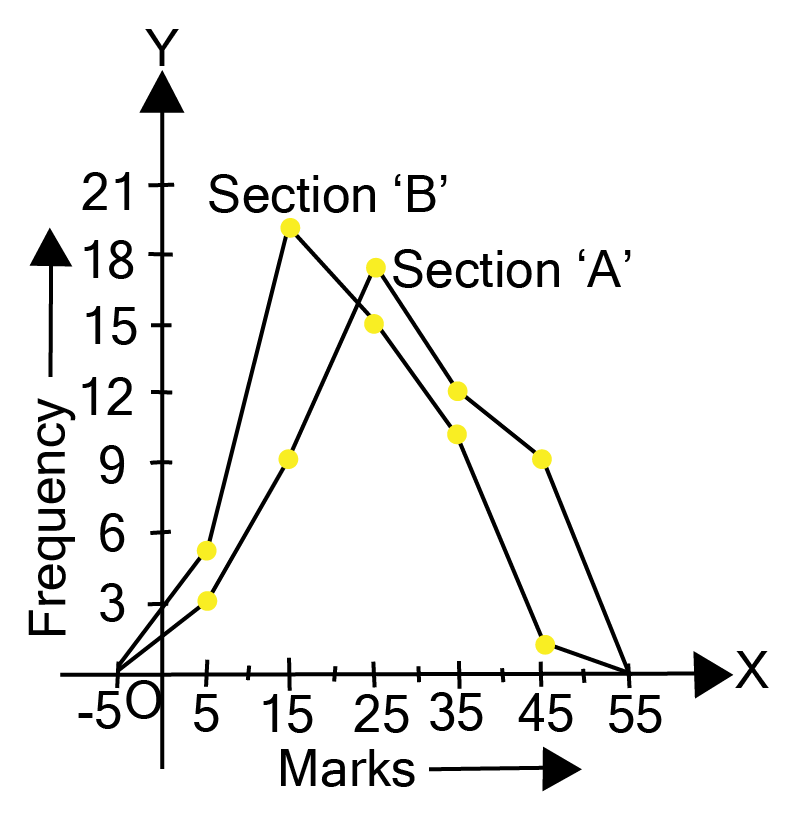
It can be observed that the performance of students of section ‘A’ is better than the students of section ‘B’ in terms of good marks.
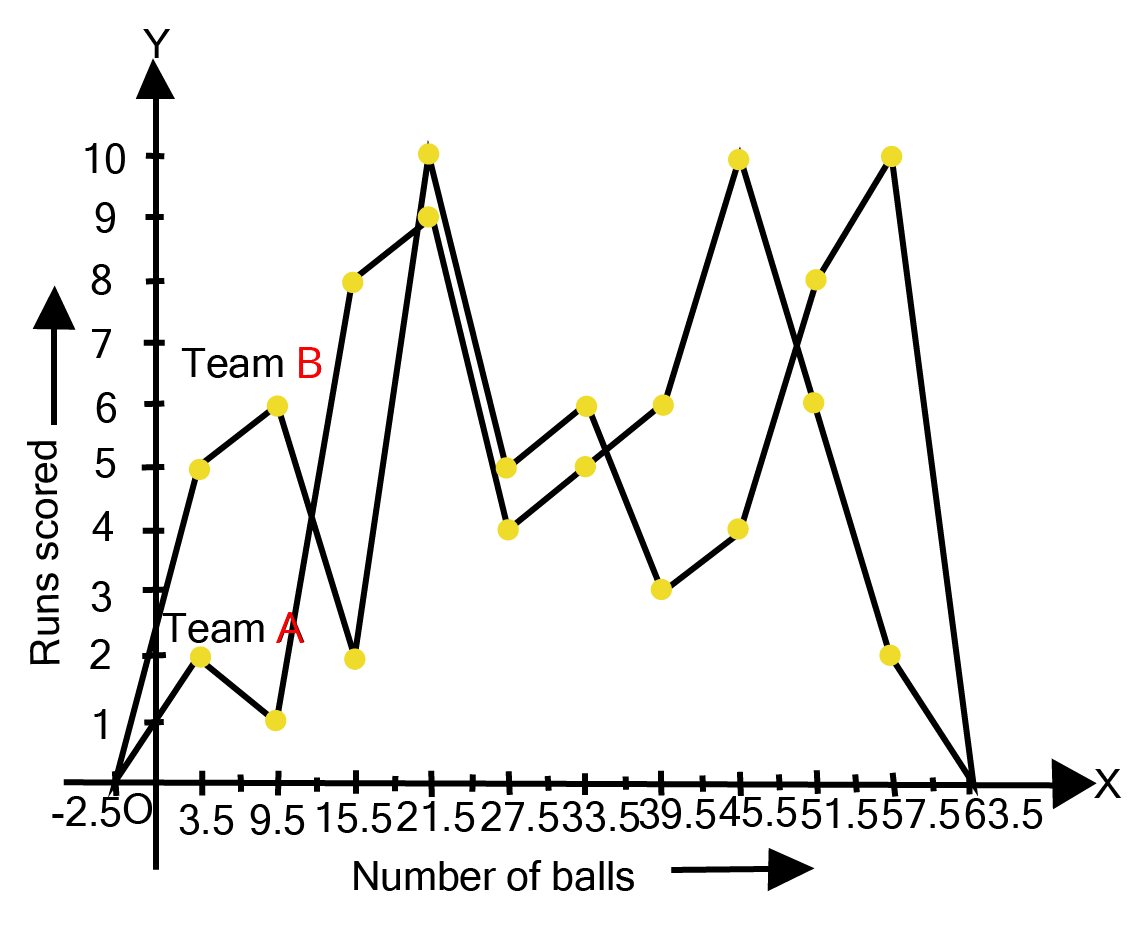
7. The runs scored by two teams A and B on the first 60 balls in a cricket match are given below:
\[\boxed{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{\text{ }}\underline {{\text{Number of balls}}} {\text{ }}}&{{\text{ }}\underline {{\text{Class mark}}} {\text{ }}}&{{\text{ }}\underline {{\text{Team A}}} {\text{ }}}&{{\text{ }}\underline {{\text{Team B}}} {\text{ }}} \\ {0.5 - 6.5}&{3.5}&2&5 \\ {6.5 - 12.5}&{9.5}&1&6 \\ {12.5 - 18.5}&{15.5}&8&2 \\ {18.5 - 24.5}&{21.5}&9&{10} \\ {24.5 - 30.5}&{27.5}&4&5 \\ {30.5 - 36.5}&{33.5}&5&6 \\ {36.5 - 42.5}&{39.5}&6&3 \\ {42.5 - 48.5}&{45.5}&{10}&4 \\ {48.5 - 54.5}&{51.5}&6&8 \\ {54.5 - 60.5}&{57.5}&2&{10} \\ {}&{}&{}&{} \end{array}}\]
Represent the data of both the teams on the same graph by frequency polygons.
(Hint: First make the class intervals continuous.)
Ans: A frequency polygon can be created by plotting class grades on the x-axis and running times on the y-axis.
8. A random survey of the number of children of various age groups playing in park was found as follows:
\[\boxed{\begin{array}{*{0}{c}} {\underline {{\text{Age (in years)}}} }&{\underline {{\text{Number of children }}} } \\ {{\text{1 - 2}}}&{\text{5}} \\ {{\text{2 - 3}}}&{\text{3}} \\ {{\text{3 - 5}}}&{\text{6}} \\ {{\text{5 - 7}}}&{{\text{12}}} \\ {{\text{7 - 10}}}&{\text{9}} \\ {{\text{10 - 15}}}&{{\text{10}}} \\ {{\text{15 - 17}}}&{\text{4}} \end{array}}\]
Draw a histogram to represent the data above.
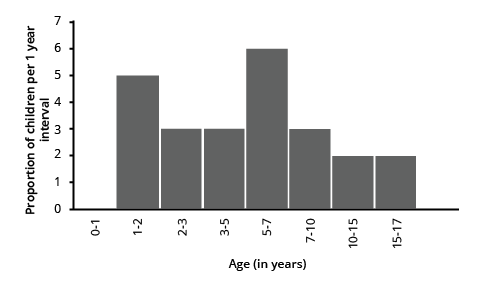
9. \[100\] surnames were randomly picked up from a local telephone directory and a frequency distribution of the number of letters in the English alphabet in the surnames was found as follows:
i. Draw a histogram to depict the given information.
The histogram can be generated using the number of letters on the x-axis and the fraction of the number of surnames per 2 letters interval on the y-axis, as well as an acceptable scale (1 unit = 4 students for the y axis).
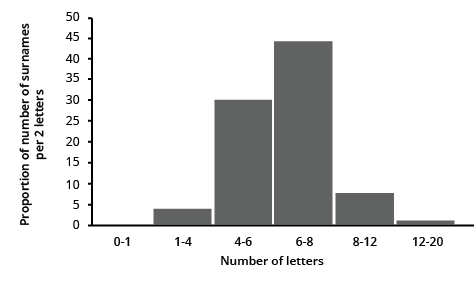
ii. Write the class interval in which the maximum number of surnames lie.
Ans: The maximum number of surnames in the class interval is 6-8 since it contains 44 surnames, which is the maximum for this data.
Exercise 14.4
1. The following number of goals was scored by a team in a series of \[10\] matches:
\[2,3,4,5,0,1,3,3,4,3\] Find the mean, median and mode of these scores.
Ans: The number of goals scored by the team is
\[2,3,4,5,0,1,3,3,4,3\]
\[{\text{Mean of data = }}\dfrac{{{\text{sum of all observations}}}}{{{\text{total number of observations}}}}\]
\[{\text{Mean score = }}\dfrac{{2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 0 + 1 + 3 + 3 + 4 + 3}}{{10}}\]
\[{\text{Mean score = }}\dfrac{{28}}{{10}} = 2.8\]
\[ = 2.8{\text{ goals}}\]
Arranging the number of goals in ascending order,
\[0,{\text{ }}1,\,{\text{ }}2,{\text{ }}3,{\text{ }}3,{\text{ }}4,{\text{ }}4,\;5\]
The total number of observations is \[10\], an even number. As a result, the median score will be the mean of the \[\dfrac{{10}}{2}\] i.e., \[{5^{{\text{th}}}}\]and \[\dfrac{{10}}{2} + 1\]i.e.,\[{6^{{\text{th}}}}\] observations in ascending or descending order.
\[{\text{Median score = }}\dfrac{{{5^{{\text{th}}}}{\text{ observation + }}{{\text{6}}^{{\text{th}}}}{\text{ observation}}}}{2}\]
\[ = \dfrac{{3 + 3}}{2} = \dfrac{6}{2} = 3\]
The data mode is the observation having the highest frequency in the data.
As a result, the data's mode score is \[3\] because the data's maximum frequency is \[4\].
2. In a mathematics test given to \[15\] students, the following marks (out of \[100\]) are recorded: \[41,39,48,52,46,62,54,40,96,52,98,40,42,52,60\] Find the mean, median and mode of this data.
Ans: In a mathematics test, \[15\] students received the following grades:
\[{\text{41, 39, 48, 52, 46, 62, 54, 40, 96, 52, 98, 40, 42, 52, 60}}\]
\[ = \dfrac{{{\text{41 + 39 + 48 + 52 + 46 + 62 + 54 + 40 + 96 + 52 + 98 + 40 + 42 + 52 + 60}}}}{{15}}\]
\[ = \dfrac{{{\text{822}}}}{{15}} = 54.8\]
Arranging the scores obtained by \[15\] students in an ascending order,
\[{\text{39, 40, 40, 41, 42, 46, 48, 52, 52, 52, 54, 60, 62, 96, 98}}\]
The total number of observations is \[{\text{15}}\], an odd number. As a result, the median score will be \[\dfrac{{{\text{15 + 1}}}}{2} = \] \[{8^{{\text{th}}}}\] observations in ascending or descending order.
Therefore, median score of data \[ = 52\]
As a result, the data's mode score is \[52\] because the data's maximum frequency is \[3\].
3. The following observations have been arranged in ascending order. If the median of the data is \[63\], find the value of x. \[{\text{29, 32, 48, 50, x, x + 2, 72, 78, 84, 95}}\]
Ans: The total number of observations is \[{\text{10}}\], an even number. As a result, the median score will be the mean of \[\dfrac{{10}}{2} + 1\] i.e., \[5\]and \[\dfrac{{10}}{2} + 1\]i.e., \[{6^{{\text{th}}}}\] observations in ascending or descending order.
Therefore, \[{\text{Median score = }}\dfrac{{{5^{{\text{th}}}}{\text{ observation + }}{{\text{6}}^{{\text{th}}}}{\text{ observation}}}}{2}\]
= \[63 = \dfrac{{{\text{x + x + 2}}}}{2}\]
= \[63 = \dfrac{{{\text{2x + 2}}}}{2}\]
= \[63 = {\text{x + 1}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{x = 62}}\]
4. Find the mode of \[{\text{14, 25, 14, 28, 18, 17, 18, 14, 23, 22, 14, 18}}{\text{.}}\]
Ans: Arranging the data in an ascending order,
\[{\text{14, 14, 14, 14, 17, 18, 18, 18, 22, 23, 25, 28}}\]
In the presented data, the number \[{\text{14}}\] has the highest frequency, i.e. \[{\text{14}}\], as noticed.
As a result, the given data's mode is \[{\text{14}}\].
5. Find the mean salary of \[{\text{60}}\] workers of a factory from the following table:
Ans: We know that,
\[{\text{Mean = }}\dfrac{{\sum\limits_{}^{} {{f_i}{x_i}} }}{{\sum\limits_{}^{} {{f_i}} }}\]
And the value of \[\sum\limits_{}^{} {{f_i}{x_i}} \]and \[\sum\limits_{}^{} {{f_i}} \]can be calculated as follows:
\[{\text{Mean salary = }}\dfrac{{305000}}{{60}}\]
Therefore, mean salary of \[60\]workers is Rs. \[5083.33\]
6. Give one example of a situation in which
i. The mean is an appropriate measure of central tendency.
Ans: When a set of data has a few observations that are significantly different from the rest of the data, it is preferable to calculate the median rather than the mean, as the median provides a better approximation of the average in this case.
Consider the following example: the heights of a family's members are represented by the following data.
\[6{\text{154}}{\text{.9 cm, 162}}{\text{.8 cm, 170}}{\text{.6 cm, 158}}{\text{.8 cm, 163}}{\text{.3 cm, 166}}{\text{.8 cm, 160}}{\text{.2 cm}}\]
In this case, it can be observed that the observations in the given data are close to each other. Therefore, the mean will be calculated as an appropriate measure of central tendency.
ii. The mean is not an appropriate measure of central tendency, but the median is an appropriate measure of central tendency.
Ans: The following data represents the marks obtained by \[12\]students in a test.
\[{\text{48, 59, 46, 52, 54, 46, 97, 42, 49, 58, 60, 99}}\]
It can be seen in this situation that some observations are considerably different from other observations. As a result, the median will be used as a suitable measure of central tendency in this case.
A Brief Overview of Class 9 Maths Chapter 14- Statistics
Statistics refers to the study of data interpretation, analysis, collection, and organisation. In various fields like industrial, scientific, or societal problems, Statistics is conventional and is used to measure statistical population and other model processes. Statistics deal with all the aspects of data, including the planning of the data and its collection to design various experiments and surveys.
In Class 9 Chapter 14, Maths, Mean, Median, and Mode are the three important measures of central tendency. Any data's mean can be calculated using the direct, assumed mean, and step deviation methods.
What are Grouped and Ungrpued Data?
Grouped Data
When raw data are grouped into different classes or categories, it is termed Grouped data.
Ungrouped Data
Ungrouped data is data that is in its raw or original form. These observations are hence not classified into any groups.
Maths Class 9 Chapter 14: Important Definitions
Frequency:
The total number of times a particular data or observation occurs in the data.
Class Interval:
All the data in a list/series can be divided and placed into groups or class intervals so that all the observations present in that particular range belong to only that group.
Class Width = Upper-Class limit – Lower Class limit
Mean:
The average of “n” numbers can be calculated by dividing the sum of all the
numbers by n.
It is the most frequently appearing observation. In the case of a class interval, the class
with the highest frequency is the modal class.
The value of observation in the middle is called the median.
If the number of observations is odd (n observations), then median=[(n+1)/2] th observation.
If n is even the median = average of (n/2) th and [(n+1)/2] th observation.
Bar graphs are the pictorial representation of data. In it, uniform width bars are drawn on an axis (say, X-axis) by keeping equal spacing among all, depicting the variable. On another axis, the second variable is represented, and the heights of the bars depend on this variable.
Histograms are special Bar graphs. They are used for continuous class intervals on an axis (usually X-axis).
Frequency Polygon
Frequency polygon is a very special way of representing data. It is usually shown when a trend is shown. It requires a large set of data.
A frequency polygon is nothing but data representation using Histograms, connecting the mid-points of upper-side bars by a line segment. The obtained figure is in the shape of a polygon, which is why it is called a Frequency Polygon.
We Cover All The Exercises in The Chapter Statistics Given Below
Kindly note solved example are not copied as questions are good to go, extra questions for practice.
1. Find the mean of the following marks obtained out of 50 by 5 students of Class 9th of a given school.
30, 35, 40, 47, 24
2. Consider the following marks obtained by the 10 student's in the English test as
30, 35, 40, 47, 24, 37, 24, 22, 43, and 33.
Find the highest and lowest marks from the above data.
3. The height of 9 students of a class in cm is given. Find the median of the following data.
155, 160, 145, 149, 150, 147, 152, 144, and 148.
Key Benefits of Referring To NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 14
Key Benefits Of NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Solutions By Vedantu:
The solutions are created by the subject experts in simple language, keeping in mind the average age group of the students.
The solutions are explained in a step-wise manner to help the students understand the concepts easily.
The solutions are prepared strictly as per the latest NCERT solutions.
The content is kept concise, brief, and self-explanatory.
Few solutions are explained in images to facilitate the understanding of the concept.
It is handy and serves as the best revision note during exam revision.
The solutions, if practised frequently, help students to enhance their problem-solving as well as time-management skills.
Why Choose Vedantu?
Vedantu’s solutions are presented by experienced teachers in a pretty easy language so that they can be easily understood by the students. The best part is all the questions and answers are available on the official website only. It is completely free and can be accessed by all. The best part of Vedantu is that all the solutions are available on its official website and various study materials. The materials you need are just a click away. So, sign up today and carry on learning with the best.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 - Statistics, provided by Vedantu, is a valuable tool for Class 9 students. It helps introduce Maths concepts in an accessible manner. The provided solutions and explanations simplify complex ideas, making it easier for Class 9 Students to understand the material. By using Vedantu's resources, Students can develop a deeper understanding of NCERT concepts. These solutions are a helpful aid for Grade 9 students, empowering them to excel in their studies and develop a genuine appreciation for Statistics.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 - Statistics
1. How can we find the median of grouped data?
From the class intervals and the corresponding frequency, write the cumulative frequency(cf) in the third column. On finding n/2, locate the median class whose cumulative frequency is greater than and nearest to n/2.
Now Median = l + (((n/2) - cf) / f) h
Where l = lower limit of the median class
n = no. of observations
cf = cumulative frequency of the class preceding the median class
f = frequency of the median class
h = class size ( where class sizes are equal)
2. What is the relationship between mean, median and mode of a data set?
In the case of any data set, the mean, median and mode are related by the following equation:
Mode = 3 Median - 2 Mean
Any problem on central tendency, that is mean, median and mode can be solved using this formula or a spin-off from the same.
3. Give five examples of data that you can collect from your day-to-day life.
Five examples from day-to-day life:
Number of students in our class
Number of fans in our school
Electricity bills for our house for the last two years
Election results obtained from television or newspapers
Literacy rate figures obtained from the Educational Survey
4. What are the three measures of central tendency for ungrouped data?
The three measures of central tendency are Mean, Median and mode.
5. When are frequency polygons used?
Frequency polygons are used when data is very large and continuous. It is generally used to compare two different sets of data of the same nature. For example, comparing the performance of two different sections of the same class.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths
Ncert solutions for class 9.
WorksheetsBag.com
Worksheets For Class 9 Mathematics Statistics
Statistics Class 9 Worksheet with Solutions have been designed as per the latest pattern for CBSE, NCERT and KVS for Grade 9. Students are always suggested to solve printable worksheets for Mathematics Statistics Grade 9 as they can be really helpful to clear their concepts and improve problem solving skills. We at worksheetsbag.com have provided here free PDF worksheets for students in standard 9 so that you can easily take print of these test sheets and use them daily for practice. All worksheets are easy to download and have been designed by teachers of Class 9 for benefit of students and is available for free download.
Mathematics Statistics Worksheets for Class 9
We have provided chapter-wise worksheets for class 9 Mathematics Statistics which the students can download in Pdf format for free. This is the best collection of Mathematics Statistics standard 9th worksheets with important questions and answers for each grade 9th Mathematics Statistics chapter so that the students are able to properly practice and gain more marks in Class 9 Mathematics Statistics class tests and exams.
Chapter-wise Class 9 Mathematics Statistics Worksheets Pdf Download
1. Collection of Data 2. Presentation of Data 3. Graphical Representation of Data 4. Measures of Central Tendency • Statistics is the area of study that deals with the collection presentation, analysis and interpretation of data. • Data: Facts or figures, collected with a definite purpose, are called data. • There are two types of data (i) Primary (ii) Secondary • We can represent the data by (i) ungrouped and grouped frequency distribution. • Data can also represent by (i) bar graph (ii) Histogram (iii) Frequency polygons • Class mark of grouped data is lower limit upper limit/2 • Measure of central tendencies by mean, median, mode. • Mean: (x̅) = sum of all observations/Total no. of observations • · If observations denoted by and their occurrence i.e. frequency is denoted by then mean is (x̅) = Σ (x̅) = Σ fixi / Σ h • Median: Arrange the observations in ascending or descending order then if numbers of observations (n) are odd then then median is n+1/2 term. If no. of observations (n) are even, then median is average of • Mode: The observation whose frequency is greatest. • Mode = 3 median – 2 mean
Mathematics Statistics Worksheets for Class 9 as per CBSE NCERT pattern
Parents and students are welcome to download as many worksheets as they want as we have provided all free. As you can see we have covered all topics which are there in your Class 9 Mathematics Statistics book designed as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and examination pattern. These test papers have been used in various schools and have helped students to practice and improve their grades in school and have also helped them to appear in other school level exams. You can take printout of these chapter wise test sheets having questions relating to each topic and practice them daily so that you can thoroughly understand each concept and get better marks. As Mathematics Statistics for Class 9 is a very scoring subject, if you download and do these questions and answers on daily basis, this will help you to become master in this subject.
Benefits of Free Statistics Class 9 Worksheet with Solutions
- You can improve understanding of your concepts if you solve NCERT Class 9 Mathematics Statistics Worksheet,
- These CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Statistics worksheets can help you to understand the pattern of questions expected in Mathematics Statistics exams.
- All worksheets for Mathematics Statistics Class 9 for NCERT have been organized in a manner to allow easy download in PDF format
- Parents will be easily able to understand the worksheets and give them to kids to solve
- Will help you to quickly revise all chapters of Class 9 Mathematics Statistics textbook
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Statistics Workbook will surely help to improve knowledge of this subject
These Printable practice worksheets are available for free download for Class 9 Mathematics Statistics. As the teachers have done extensive research for all topics and have then made these worksheets for you so that you can use them for your benefit and have also provided to you for each chapter in your ebook. The Chapter wise question bank and revision worksheets can be accessed free and anywhere. Go ahead and click on the links above to download free CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Statistics Worksheet PDF.

You can download free worksheets for Class 9 Mathematics Statistics from https://www.worksheetsbag.com
You can get free PDF downloadable worksheets for Grade 9 Mathematics Statistics from our website which has been developed by teachers after doing extensive research in each topic.
On our website we have provided worksheets for all subjects in Grade 9, all topic wise test sheets have been provided in a logical manner so that you can scroll through the topics and download the worksheet that you want.
You can easily get question banks, topic wise notes and questions and other useful study material from https://www.worksheetsbag.com without any charge
Yes all test papers for Mathematics Statistics Class 9 are available for free, no charge has been put so that the students can benefit from it. And offcourse all is available for download in PDF format and with a single click you can download all worksheets.
https://www.worksheetsbag.com is the best portal to download all worksheets for all classes without any charges.
Related Posts
Worksheets for class 11 entrepreneurship.

Blends Learning Worksheets Download PDF


Dot to Dot 1 to 10 Worksheets Download PDF

NCERT curriculum (for CBSE/ICSE) Class 9 - Statistics
Unlimited worksheets.
Every time you click the New Worksheet button, you will get a brand new printable PDF worksheet on Statistics . You can choose to include answers and step-by-step solutions.
Unlimited Online Practice
Unlimited adaptive online practice on Statistics . Practice that feels like play! Get shields, trophies, certificates and scores. Master Statistics as you play.
Unlimited Online Tests
Take unlimited online tests on Statistics . Get instant scores and step-by-step solutions on submission. Make sure you always get your answers right in Statistics .
Contents: Statistics
Statistics - Questions related to Statistics
- Assignments

Spring 2024

Time and Location
Mon. & Wed. 12:30 PM - 1:20 PM Pacific Time Jordan Hall room 040 (420-040)
Week 1: Introduction and Acoustic Phonetics
Deliverables
- Assignment 1 released on Mon 4.1.24.
Lecture 1 (Mon 4.1.24)
Course introduction.
lecture slides
Lecture 2 (Wed 4.3.24)
Phonetics: Articulatory phonetics. Acoustics. ARPAbet transcription. Readings:
- J+M Draft Edition Appendix H: Phonetics, online pdf
- Fun read (optional). The Art of Language Invention . David J Peterson. 2015.
Week 2: Speech Synthesis / Text to Speech (TTS)
Course Project Overview released on Mon 4.8.24.
Lecture 3 (Mon 4.8.24)
Some history of ASR, TTS, and dialog. TTS Overview. Text normalization. Letter-to-sound. Prosody. Readings:
- J+M Draft Edition Chapter 16.6: TTS online pdf
Lecture 4 (Wed 4.10.24)
Foundations of TTS: Data collection. Evaluation. Signal processing. Concatenative and parametric approaches. Readings:
- J+M Draft Edition Chapter 16.6: TTS (cont’d) online pdf
Week 3: Course project + TTS with deep learning
- Assignment 1 due by Monday 4.15.24 11:59PM Pacific.
- Assignment 2 released on Monday 4.15.24.
Lecture 5 (Mon 4.15.24)
Course project overview and Q&A. Social meaning extraction as supervised machine learning. Readings:
- Rajesh Ranganath, Dan Jurafsky, and Daniel A. McFarland. . Detecting friendly, flirtatious, awkward, and assertive speech in speed-dates . Computer Speech and Language. 2013.
Lecture 6 (Wed 4.17.24)
Deep learning for TTS. Readings:
- Wang, Y., Skerry-Ryan, R.J., Stanton, D., Wu, Y., Weiss, R.J., Jaitly, N., Yang, Z., Xiao, Y., Chen, Z., Bengio, S. and Le, Q., Tacotron: Towards end-to-end speech synthesis . arXiv. 2017.
- Oord, A.V.D., Dieleman, S., Zen, H., Simonyan, K., Vinyals, O., Graves, A., Kalchbrenner, N., Senior, A. and Kavukcuoglu, K. Wavenet: A generative model for raw audio . arXiv. 2016.
- Ren, Y., Ruan, Y., Tan, X., Qin, T., Zhao, S., Zhao, Z., and Liu, T. Y. Fastspeech: Fast, robust and controllable text to speech . Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32. 2019.
Deep Learning Preliminaries. Review on your own as needed depending on your experience so far with deep learning models:
- J+M Draft Edition Chapter 7: Neural Networks and Neural Language Models. pdf
- J+M Draft Edition Chapter 9: RNNs and LSTMs. pdf
- J+M Draft Edition Chapter 10: Transformers and Large Language Models. pdf
- The Illustrated Transformer – Jay Alammar – Visualizing machine learning one concept at a time
Week 4: Speech to Text / Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
- Course Project Proposal due by Wednesday 4.24.24 11:59PM Pacific.
Lecture 7 (Mon 4.22.24)
Speech recognition overview: Noisy channel model. Word error rate metrics. Hidden Markov models (HMMs). Readings:
- J+M Draft Edition Chapter 16.1, 16.2, 16.3, 16.5: Automatic Speech Recognition online pdf
- J+M Draft Edition. Appendix A pdf
- J+M Draft Edition. Appendix B pdf
- Koenecke, A., Nam, A., Lake, E., Nudell, J., Quartey, M., Mengesha, Z., Toups, C., Rickford, J.R., Jurafsky, D. and Goel, S. Racial disparities in automated speech recognition . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2020.
- J+M Draft Edition Chapter 3: N-gram Language Models. pdf
- Lecture videos on introductory NLP including language modeling youtube
Lecture 8 (Wed 4.24.24)
Speech recognition: HMM-DNN systems. Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC). End-to-end neural ASR. Readings:
- Hinton, Geoffrey, et al. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: The shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal processing magazine. 2012.
- J+M Draft Edition Chapter 16.4: CTC online pdf
- Graves, A., and Jaitly, N. Towards end-to-end speech recognition with recurrent neural networks. ICML . 2014.
- Maas, A. , Xie, Z. , Jurafsky, D., & Ng, A. Lexicon-free conversational speech recognition with neural networks. ACL-HLT . 2015. (* indicates equal contribution)
- Chan, W., Jaitly, N., Le, Q.V. and Vinyals, O. Listen, attend and spell: A neural network for large vocabulary conversational speech recognition ICASSP. 2016. arXiv preprint.
- Prabhavalkar, R., Hori, T., Sainath, T. N., Schlüter, R., and Watanabe, S. End-to-end speech recognition: A survey . IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing. 2023.
Week 5: State-of-the-art ASR and customizing ASR for products
- Assignment 2 due by Wednesday 5.1.24 11:59PM Pacific.
Lecture 9 (Mon 4.29.24)
State-of-the-art deep learning approaches for speech recognition. Conformer. Whisper. Fine tuning base models. Readings:
- Gulati, A., Qin, J., Chiu, C.C., Parmar, N., Zhang, Y., Yu, J., Han, W., Wang, S., Zhang, Z., Wu, Y. and Pang, R. Conformer: Convolution-augmented transformer for speech recognition . arXiv. 2020. 2.TBD
Lecture 10 (Wed 5.1.24)
Guest Lecture: Ello : A case study in building spoken language products. Readings:
- T. Bluche, M. Primet, & T. Gisselbrecht. Small-Footprint Open-Vocabulary Keyword Spotting with Quantized LSTM Networks .ArXiv. 2020.
- K. Audhkhasi, A. Rosenberg, A. Sethy, B. Ramabhadran, & B. Kingsbury. End-to-End ASR-free Keyword Search from Speech . IEEE J. Signal Processing 2017.
- N. Sacchi, A. Nanchen, M. Jaggi, & M. Cerňak. Open-Vocabulary Keyword Spotting with Audio and Text Embeddings . Interspeech 2019.
Week 6: Foundation models and non-English languages
- Assignment 3 released on Mon 5.6.24.
Lecture 11 (Mon 5.6.24)
Guest Lecture: Foundation models for spoken language. Dr. Karen Livescu Readings
- Baevski, A., Zhou, Y., Mohamed, A., & Auli, M. Wav2vec 2.0: A framework for self-supervised learning of speech representations . Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 33. 2020.
Lecture 12 (Wed 5.8.24)
Week 7: non-english spoken language understanding cont’d + project check-ins, lecture 13 (mon 5.13.24), lecture 14 (wed 5.15.24).
Project check-ins during class. Each group will speak for ~2 minutes about progress and planned work
Week 8: Introduction to spoken dialog + project check-ins
- Assignment 3 due by Monday 5.20.24 11:59PM Pacific.
Lecture 15 (Mon 5.20.24)
Lecture 16 (wed 5.22.24).
Overview of dialog: Human conversation. Task-oriented dialog. Dialog system design. GUS and frame-based dialog systems. Readings:
- J+M Draft Edition Chapter 15: Dialogue Systems and Chatbots, online pdf
Week 9: Spoken dialog with LLMs
- Course Project Milestone due by Monday 5.27.24 11:59PM Pacific.
Memorial Day. NO CLASS (Mon 5.27.24)
Lecture 17 (wed 5.29.24).
Guest lecture: Developing spoken dialog systems with LLMs. Gridspace .
Week 10 : Spoken dialog development & final poster session
Lecture 18 (mon 6.3.24).
Case study: Alexa Skills Kit in the era of LLMs. Readings:
- Understand Custom Skills . You do not need to cover adding visual components to skills.
- Interaction Model Design
Final project poster session (Wed 6.5.24)
Present posters at in-person session during lecture time. Location TBD
Course Project Report due by Saturday 6.8.24 by 11:59 PM Pacific. No late days allowed
- ICSE Class 9
- Class 9 Selina Solutions
- Class 9 Maths Concise Selina Solutions
- Chapter 18 Statistics
Concise Selina Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 18- Statistics
The Selina solutions for the questions given in Chapter 18, Statistics, of the Class 9 Selina textbooks are available here. In this chapter students learn about the topic of Statistics in detail. Students can easily score full marks in the exams by solving all the questions present in the Selina textbook.
The Class 9 Selina solutions are very easy to understand. These Class 9 Selina solutions maths cover all the exercise questions included in the book and are according to the syllabus prescribed by the ICSE or CISCE. Here, the PDF of the Class 9 maths Chapter 18 Selina solutions is available which can be downloaded as well as viewed online. Students can also avail these Selina solutions and download it for free to practice them offline as well.
Download PDF of Selina Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 18:- Download Here

Exercise 18(A)
1. State which of the following variables are continuous and which are discrete:
(a) Number of children in your class
(b) Distance travelled by a car
(c) Sizes of shoes
(e) Number of patients in a hospital
(a) Discrete variable.
(b) Continuous variable.
(c) Discrete variable.
(d) Continuous variable.
(e) Discrete variable.
2. Given below are the marks obtained by 30 students in an examination:
Taking class intervals 1 – 10, 11 – 20, ….., 41 – 50; make a frequency table for the above distribution.
The frequency table for the given distribution is
3. The marks of 24 candidates in the subject mathematics are given below:
The maximum marks are 50. Make a frequency distribution taking class intervals 0 – 10, 10-20, …….
In the above frequency distribution, the marks 30 are present in the class of interval 30 – 40 and not in the interval 20 – 30. Similarly, marks 40 are present in the class of interval 40 – 50 and not in 30 – 40.
4. Fill in the blanks:
(a) A quantity which can very from one individual to another is called a ………….
(b) Sizes of shoes are ……….. variables.
(c) Daily temperatures is ……….. variable.
(d) The range of the data 7, 13, 6, 25, 18, 20, 16 is …………
(e) In the class interval 35 – 46; the lower limit is ………. and upper limit is ………
(f) The class mark of class interval 22 – 29 is ………. .
(a) Variable.
(b) Discrete variables.
(c) Continuous variable.
(d) The range is 25 – 6 = 19
(e) Lower limit is 35 and upper limit is 46
(f) The class mark is 22 – 29 = (22 + 29)/2
5. Find the actual lower class limits, upper class limits and the mid-values of the classes: 10 – 19, 20 – 29, 30 – 39 and 40 – 49.
For the class interval: 10 – 19,
Lower class limit is 10
Upper class limit is 19
So, the mid-value is (10 + 19)/2 = 14.5
For the class interval: 20 – 29,
Lower class limit is 20
Upper class limit is 29
So, the mid-value is (20 + 29)/2 = 24.5
For the class interval: 30 – 39,
Lower class limit is 30
Upper class limit is 39
So, the mid-value is (30 + 39)/2 = 34.5
For the class interval: 40 – 49,
Lower class limit is 40
Upper class limit is 49
So, the mid-value is (40 + 49)/2 = 44.5
6. Find the actual lower and upper class limits and also the class marks of the classes:
1.1 – 2.0, 2.1 -3.0 and 3.1 – 4.0.
For the class interval: 1.1 – 2.0,
The lower class limit is 1.1 and the upper class limit is 2.0
Hence, the class mark is (1.1 + 2.0)/2 = 1.55
For the class interval: 2.1 – 3.0
The lower class limit is 2.1 and the upper class limit is 3.0
Hence, the class mark is (2.1 + 3.0)/2 = 2.55
For the class interval: 3.1 – 4.0
The lower class limit is 3.1 and the upper class limit is 4.0
Hence, the class mark is (3.1 + 4.0)/2 = 3.55
7. Use the table given below to find:
(a) The actual class limits of the fourth class.
(b) The class boundaries of the sixth class.
(c) The class mark of the third class.
(d) The upper and lower limits of the fifth class.
(e) The size of the third class.
(a) The actual class limits of the fourth class will be: 44.5 – 49.5.
(b) The class boundaries of the sixth class will be: 54.5 – 59.5
(c) The class mark of the third class will be the average of the lower limit and the upper limit of the class interval
Hence, the class mark is (40 + 44)/2 = 84/2 = 42
(d) The upper and lower limits of the fifth class are 54 and 50 respectively
(e) The size of the third class is (44 – 40 + 1) = 5
8. Construct a cumulative frequency distribution table from the frequency table given below:
(i)The cumulative frequency distribution table is
(ii)The cumulative frequency distribution table is
9. Construct a frequency distribution table from the following cumulative frequency distribution:
(i)The frequency distribution table is as below:
(ii)The frequency distribution table is as below:
10. Construct a frequency table from the following data:
The frequency table is as below:
11. Construct the frequency distribution table from the following cumulative frequency table:
(i) State the number of students in the age group 10 – 13.
(ii) State the age-group which has the least number of students.
The frequency distribution table is as below:
(i) The number of students in the age group 10 – 13 is 103
(ii) The age group which has the least number of students is 7 – 10
12. Fill in the blanks in the following table:
13. The value of π upto 50 decimal place is
3.14159265358979323846264338327950288419716939937510
(i) Make a frequency distribution table of digits from 0 to 9 after the decimal place.
(ii) Which are the most and least occurring digits?
(i) The frequency distribution table of digits from 0 to 9 after the decimal place is as below:
Most occurring digits are 3 and 9
Least occurring digits are 0
Exercise 18(B)
1. Construct a frequency polygon for the following distribution:
The frequency polygon for the given data is shown below:

Steps for construction:
(i) Draw a histogram for the given data.
(ii) Mark the mid-point at the top of each rectangle of the histogram drawn.
(iii) Also, mark the mid-point of the immediately lower class-interval and mid-point of the immediately higher class-interval.
(iv) Lastly, join the consecutive mid-points marked by straight lines to obtain the required frequency polygon.
2. Construct a combined histogram and frequency polygon for the following frequency distribution:
The combined histogram and frequency polygon for the given data is shown below:

3. Construct a frequency polygon for the following data:
As the class intervals are inclusive, let’s first convert them into the exclusive form.
The frequency polygon for the given data is shown as below:

4. The daily wages in a factory are distributed as follows:
Draw a frequency polygon for this distribution.

5. (i) Draw frequency polygons for each of the following frequency distribution:
(a) using histogram
(b) without using histogram
(a) Using Histogram:

(iv) Lastly, join the consecutive mid-points marked by straight lines to obtain the required frequency polygon.
(b) Without using Histogram:
(i) Find the class mark (mid-value) of each given class-interval.
Using, Class mark = mid-value = (Upper limit + Lower limit)/2
(ii) On a graph paper, mark class marks along X-axis and frequencies along Y-axis.
(iii) On this graph paper, mark points taking values of class-marks along X-axis and the values of their corresponding frequencies along Y-axis.
(iv) Draw line segments joining the consecutive points marked in step (3) above.

5. (ii) Draw frequency polygons for each of the following frequency distribution:

Selina Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 18- Statistics
The Chapter 18, Statistics, contains 2 exercises and the Solutions given here contains the answers for all the questions present in these exercises. Let us have a look at some of the topics that are being discussed in this chapter.
18.1 Introduction
18.2 Variable
18.3 Tabulation of data
18.4 Frequency
18.5 Frequency distribution table
18.6 Types of frequency distributions
18.7 Class intervals and class limits
18.8 Cumulative frequency and cumulative frequency table
18.9 Graphical representation of data
18.10 Graphical representation of continuous frequency distribution
Statistics is a branch of Mathematics that is concerned with how information is collected, organised, presented, summarised and then analysed so the conclusion may be drawn from the information. Read and learn the Chapter 18 of Selina textbook to get to know more about Statistics. Learn the Selina Solutions for Class 9 effectively to attain excellent result in the examination.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Students and teachers can download and save all free Mathematics Statistics assignments in Pdf for grade 9th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 9 important questions and answers for Mathematics Statistics as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year. All test papers and question banks for Class 9 Mathematics Statistics and CBSE ...
Key Concepts for Class 9 Mathematics Statistics. • There are two types of data (i) Primary (ii) Secondary. • We can represent the data by (i) ungrouped and grouped frequency distribution. • Data can also represent by (i) bar graph (ii) Histogram (iii) Frequency polygons. * Class mark of grouped data is lower limit + upper limit /2.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14.1. Ex 14.1 Class 9 Maths Question 1. Give five examples of data that you collect from your day-to-day life. Solution: Following are the five examples which are related to day-to-day life : Number of girl students in our class. Number of computer sets in our computer lab.
Important Questions & Solutions of Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 - Statistics. Question 1. Give three examples of data which you can get from your day-to-day life. Solution: Here are the three examples which are related to our day-to-day life : The number of boys in a sports team. Electricity bills for last one year.
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 - CBSE Download Free PDF *According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 12. NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 Statistics are the best ways to strengthen a student's skills and knowledge. It contains all the relevant study material that can help them score well in the CBSE examinations.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 - Statistics, provided by Vedantu, is a valuable tool for Class 9 students. It helps introduce Maths concepts in an accessible manner. The provided solutions and explanations simplify complex ideas, making it easier for Class 9 Students to understand the material.
Solution 1. (i) By representing causes on x axis and family fatality rate on y axis and choosing an appropriate scale (1 unit = 5% for y axis) we can draw the graph of information given above, as following. All the rectangle bars are of same width and having equal spacing between them.
Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 7 Statistics The topics and sub-topics in NCERT Class 9 Maths Text Book Chapter 14 Statistics: Statistics Introduction Collection Of Data Presentation Of Data Graphical Representation Of Data Measures Of Central Tendency Summary IMPORTANT QUESTIONS VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS 1. Mean of 20 observations is 17. […]
Chapter-wise Class 9 Mathematics Statistics Worksheets Pdf Download. 1. Collection of Data. 2. Presentation of Data. 3. Graphical Representation of Data. 4. Measures of Central Tendency.
CBSE Class 9 Maths Notes Chapter 14 Statistics. 1. Primary and Secondary Data: When the information was collected by the investigator herself or himself with a definite objective in her or his mind, the data obtained is called primary data. When the information was gathered from a source which already had the information stored, the data ...
Statistics is used in the study and manipulation of data, including ways to gather, review, analyse and draw conclusions from data. Statistics Class 9 Notes are the premier study tool that will help students get a complete overview of chapter 14 given in the CBSE math textbook.
Class 9 - Statistics problems, online practice, tests, worksheets, quizzes, and teacher assignments.
Q.1: Give one example of a condition in which: (i) the mean is a proper measure of central tendency. (ii) the mean is not a proper measure of central tendency but the median is a proper measure of central tendency. Q.2: Find the mean, median mode of 14, 25, 14, 28, 18, 17, 18, 14, 23, 22, 14, 18. Q.3: The relative humidity (in %) of a certain ...
Project check-ins during class. Each group will speak for ~2 minutes about progress and planned work. Week 8: Introduction to spoken dialog + project check-ins. Deliverables. Assignment 3 due by Monday 5.20.24 11:59PM Pacific. Lecture 15 (Mon 5.20.24) Project check-ins during class. Each group will speak for ~2 minutes about progress and ...
5/6 2. By solving one assignment given in your class by Mathematics Statistics teacher for class 9 will help you to keep in touch with the topic thus reducing dependence on last minute studies 3. You will be able to understand the type of questions which are expected in your Mathematics Statistics class test 4. You will be able to revise all topics given in the ebook for Class 9 Mathematics ...
6:00-9:00 p.m. in-class instruction . room tbd . the only assignment for the first classs is to review the syllabus. if you have questions about the syllabus or how the course is structured, ask the questions in class. after the first lecture you will be divided into , small sections ("law firms"). once in your law firm, you will be paired up
Selina Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 18- Statistics. Statistics is a branch of Mathematics that is concerned with how information is collected, organised, presented, summarised and then analysed so the conclusion may be drawn from the information. Read and learn the Chapter 18 of Selina textbook to get to know more about Statistics.