John F. Kennedy
John F. Kennedy, the 35 th U.S. president, negotiated the Nuclear Test-Ban Treaty and initiated the Alliance for Progress. He was assassinated in 1963.


Quick Facts
U.s. navy service, u.s. congressman and senator, wife and children, 1960 presidential campaign, u.s. president, assassination and death, release of assassination documents, who was john f. kennedy.
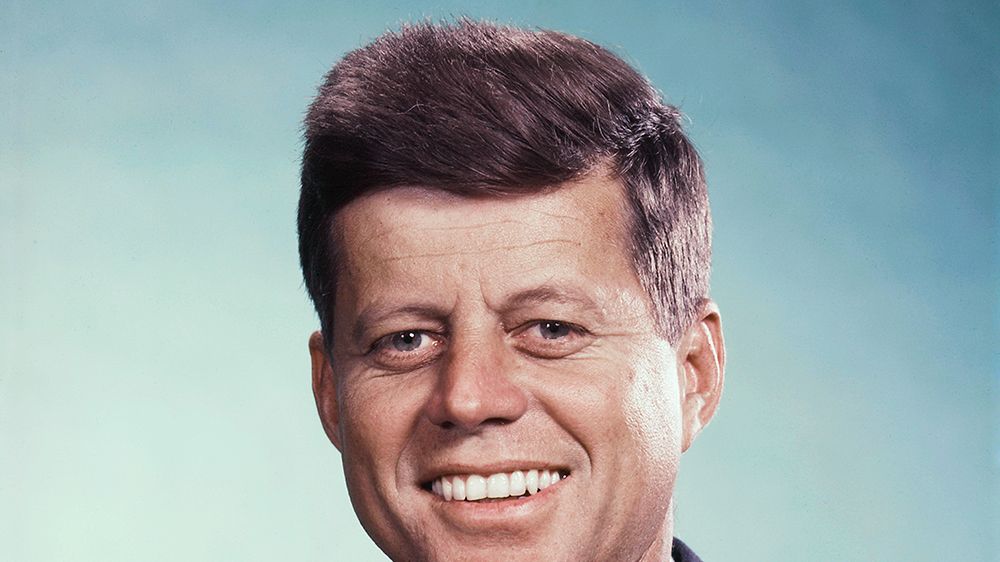
John F. Kennedy served in both the U.S. House of Representatives and U.S. Senate before becoming the 35 th American president in 1961. While in the White House, Kennedy faced a number of foreign crises, especially in Cuba and Berlin, but managed to secure such achievements as the Nuclear Test-Ban Treaty and the Alliance for Progress. On November 22, 1963, Kennedy was assassinated while riding in a motorcade in Dallas. He was 46 years old.
FULL NAME: John Fitzgerald Kennedy BORN: May 29, 1917 DIED: November 22, 1963 BIRTHPLACE: Brookline, Massachusetts SPOUSE: Jaqueline Kennedy (1953-1963) CHILDREN: Caroline Kennedy , John F. Kennedy Jr. , and Patrick Kennedy ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Gemini

John Fitzgerald Kennedy was born on May 29, 1917, in Brookline, Massachusetts. Both the Fitzgeralds and the Kennedys were wealthy and prominent Irish Catholic families in Boston. John’s paternal grandfather, P.J. Kennedy, was a wealthy banker and liquor trader, and his maternal grandfather, John E. Fitzgerald, nicknamed “Honey Fitz,” was a skilled politician who served as a congressman and as the mayor of Boston. Kennedy’s mother, Rose Elizabeth Fitzgerald , was a Boston debutante, and his father, Joseph Kennedy Sr. , was a successful banker who made a fortune on the stock market after World War I. Joe Kennedy Sr. went on to a government career as chairman of the Securities and Exchange Commission and as an ambassador to Great Britain.
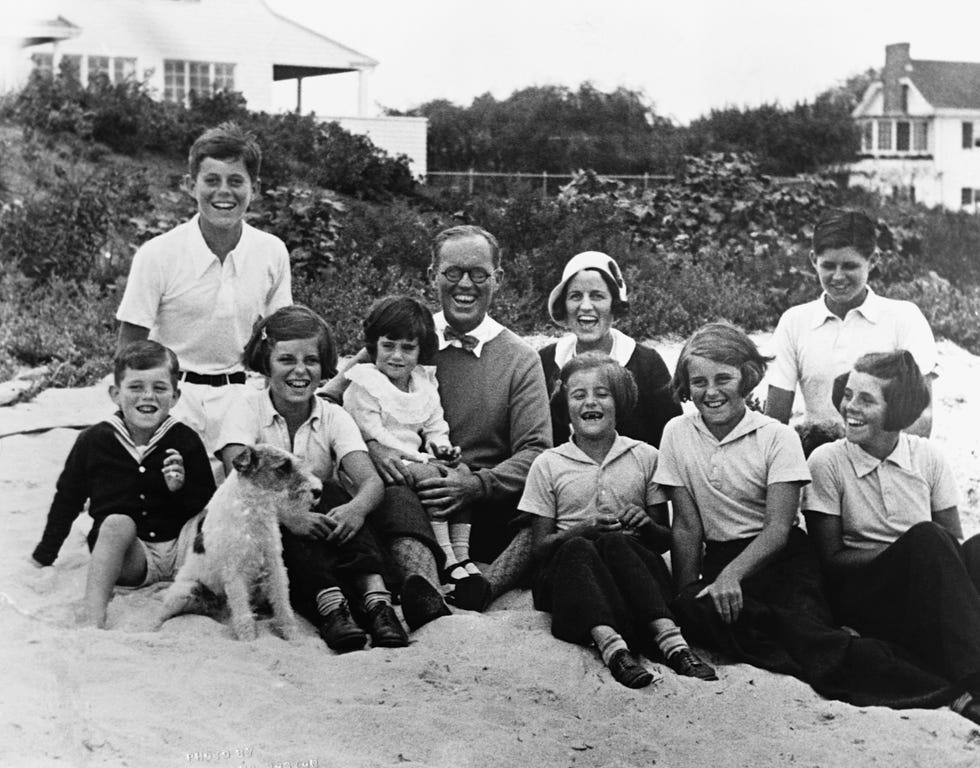
John, nicknamed “Jack,” was the second oldest of a group of nine extraordinary siblings. His brothers and sisters include Special Olympics founder Eunice Kennedy Shriver, U.S. Attorney General Robert Kennedy , and Ted Kennedy , one of the most powerful senators in American history. The Kennedy children remained close-knit and supportive of each other throughout their entire lives.

Joseph and Rose largely spurned the world of Boston socialites into which they had been born to focus instead on their children’s education. Joe Sr. in particular obsessed over every detail of his kids’ lives, a rarity for a father at that time. As a family friend noted, “Most fathers in those days simply weren’t that interested in what their children did. But Joe Kennedy knew what his kids were up to all the time.”
Joe Sr. had great expectations for his children, and he sought to instill in them a fierce competitive fire and the belief that winning was everything. He entered his children in swimming and sailing competitions and chided them for finishing in anything but first place. John’s sister, Eunice, later recalled, “I was 24 before I knew I didn’t have to win something every day.” John bought into his father’s philosophy that winning was everything. “He hates to lose at anything,” Eunice said. “That’s the only thing Jack gets really emotional about—when he loses.”
Despite his father’s constant reprimands, young Kennedy was a poor student and a mischievous boy. He attended a Catholic boys’ boarding school in Connecticut called Canterbury, where he excelled at English and history—the subjects he enjoyed—but nearly flunked Latin, in which he had no interest. Despite his poor grades, Kennedy continued on to Choate, an elite Connecticut preparatory school. Although he was obviously brilliant, evidenced by the extraordinary thoughtfulness and nuance of his work on the rare occasions when he applied himself, Kennedy remained at best a mediocre student, preferring sports, girls, and practical jokes to coursework.
His father wrote to him by way of encouragement, “If I didn’t really feel you had the goods, I would be most charitable in my attitude toward your failings... I am not expecting too much, and I will not be disappointed if you don’t turn out to be a real genius, but I think you can be a really worthwhile citizen with good judgment and understanding.” John was, in fact, very bookish in high school, reading ceaselessly but not the books his teachers assigned.
He was also chronically ill during his childhood and adolescence; he suffered from severe colds, the flu, scarlet fever, and even more severe, undiagnosed diseases that forced him to miss months of school at a time and occasionally brought him to the brink of death.

After graduating from Choate and spending one semester at Princeton University, Kennedy transferred to Harvard University in 1936. There, he repeated his by then well-established academic pattern, excelling occasionally in the classes he enjoyed but proving only an average student due to the omnipresent diversions of sports and women. Handsome, charming, and blessed with a radiant smile, Kennedy was incredibly popular with his Harvard classmates. His friend Lem Billings recalled, “Jack was more fun than anyone I’ve ever known, and I think most people who knew him felt the same way about him.” Kennedy was also an incorrigible womanizer. He wrote to Billings during his sophomore year, “I can now get tail as often and as free as I want, which is a step in the right direction.”
Nevertheless, as an upperclassman, Kennedy finally grew serious about his studies and began to realize his potential. His father had been appointed ambassador to Great Britain, and on an extended visit in 1939, John decided to research and write a senior thesis on why Britain was so unprepared to fight Germany in World War II . An incisive analysis of Britain’s failures to meet the Nazi challenge, the paper was so well-received that upon Kennedy’s graduation in 1940 it was published as a book, Why England Slept , selling more than 80,000 copies. Kennedy’s father sent him a cablegram in the aftermath of the book’s publication: “Two things I always knew about you one that you are smart two that you are a swell guy love dad.”
Shortly after graduating from Harvard, Kennedy joined the U.S. Navy and was assigned to command a patrol torpedo boat in the South Pacific. On August 2, 1943, his boat, PT-109 , was rammed by a Japanese warship and split in two. Two sailors died, and Kennedy badly injured his back. Hauling another wounded sailor by the strap of his life vest, Kennedy led the survivors to a nearby island, where they were rescued six days later. The incident earned him the Navy and Marine Corps Medal for “extremely heroic conduct” and a Purple Heart for the injuries he suffered.
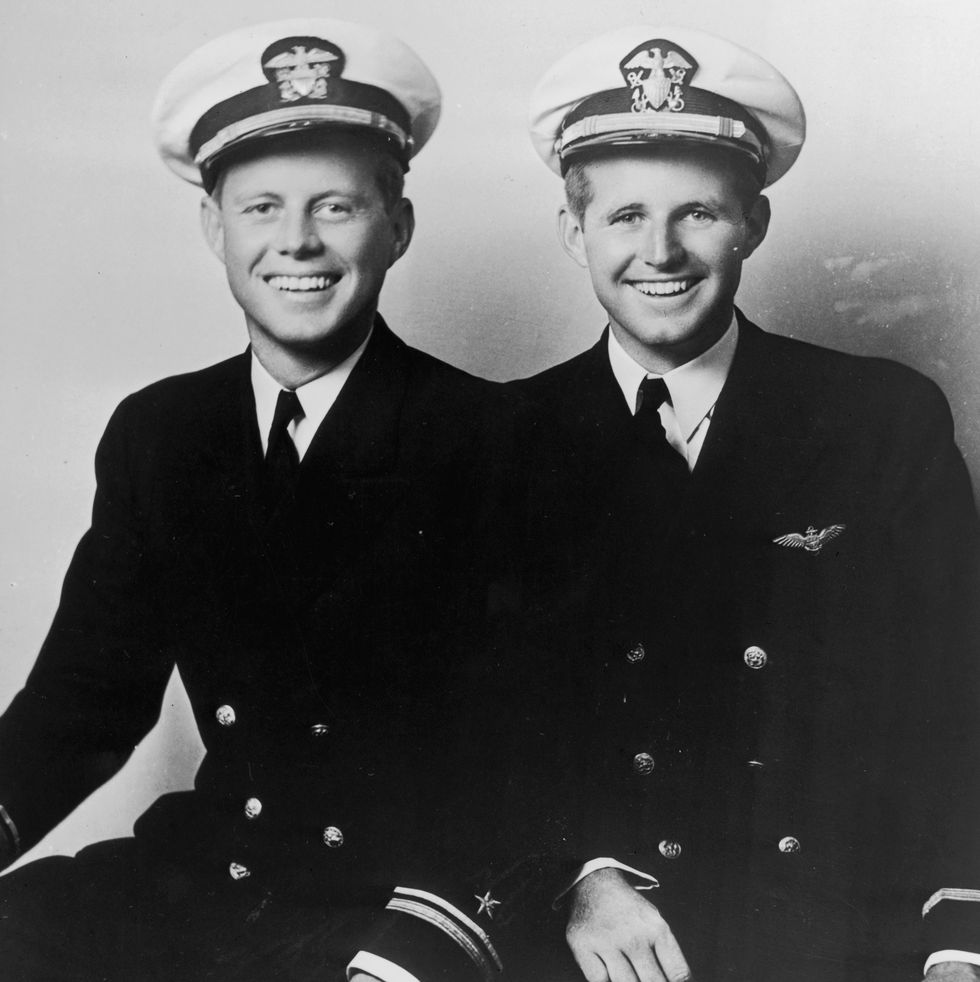

However, Kennedy’s older brother, Joe Jr., who had also joined the Navy, wasn’t so fortunate. A pilot, he died when his plane blew up in August 1944. Handsome, athletic, intelligent, and ambitious, Joseph Kennedy Jr. had been pegged by his father as the one among his children who would some day become president of the United States. In the aftermath of Joe Jr.’s death, John took his family’s hopes and aspirations for his older brother upon himself.
Upon his discharge from the Navy, John worked briefly as a reporter for Hearst Newspapers. Then in 1946, at the age of 29, he decided to run for the U.S. House of Representatives from a working-class district of Boston, a seat being vacated by Democrat James Michael Curly. Bolstered by his status as a war hero, his family connections, and his father’s money, the young Democrat won the election handily.
However, after the glory and excitement of publishing his first book and serving in World War II, Kennedy found his work in Congress incredibly dull. Despite serving three terms, from 1946 to 1952, Kennedy remained frustrated by what he saw as stifling rules and procedures that prevented a young, inexperienced representative from making an impact. “We were just worms in the House,” he later recalled. “Nobody paid attention to us nationally.”
In 1952, seeking greater influence and a larger platform, Kennedy challenged Republican incumbent Henry Cabot Lodge for his seat in the U.S. Senate. Once again backed by his father’s vast financial resources, Kennedy hired his younger brother Robert as his campaign manager. Robert put together what one journalist called “the most methodical, the most scientific, the most thoroughly detailed, the most intricate, the most disciplined and smoothly working state-wide campaign in Massachusetts history—and possibly anywhere else.”
In an election year in which Republicans gained control of both houses of Congress, Kennedy nevertheless won a narrow victory, giving him considerable clout within the Democratic Party. According to one of his aides, the decisive factor in Kennedy’s victory was his personality: “He was the new kind of political figure that people were looking for that year, dignified and gentlemanly and well-educated and intelligent, without the air of superior condescension.”
Kennedy continued to suffer frequent illnesses during his career in the Senate. While recovering from one surgery, he wrote another book, profiling eight senators who had taken courageous but unpopular stances. Profiles in Courage won the 1957 Pulitzer Prize for biography, and Kennedy remains the only American president to win a Pulitzer Prize.
Otherwise, Kennedy’s eight-year Senate career was relatively undistinguished. Bored by the Massachusetts-specific issues on which he had to spend much of his time, Kennedy was more drawn to the international challenges posed by the Soviet Union’s growing nuclear arsenal and the Cold War battle for the hearts and minds of Third World nations.
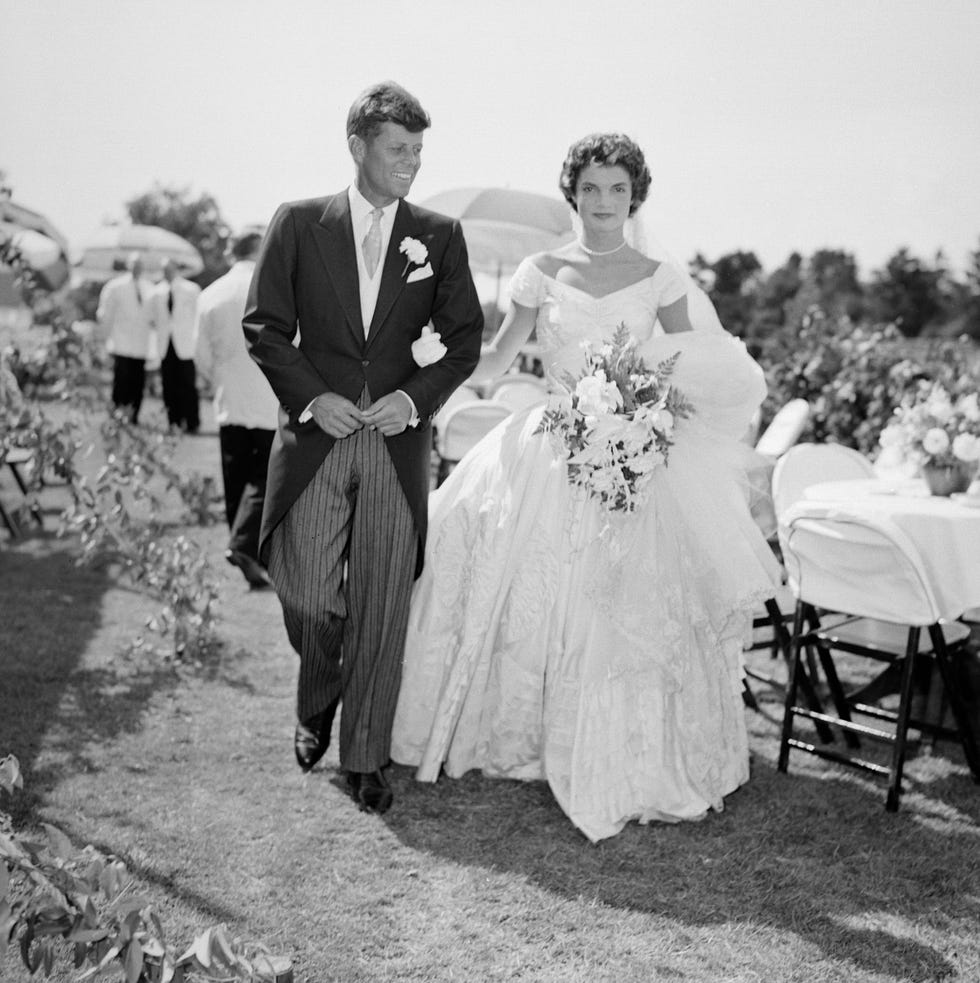

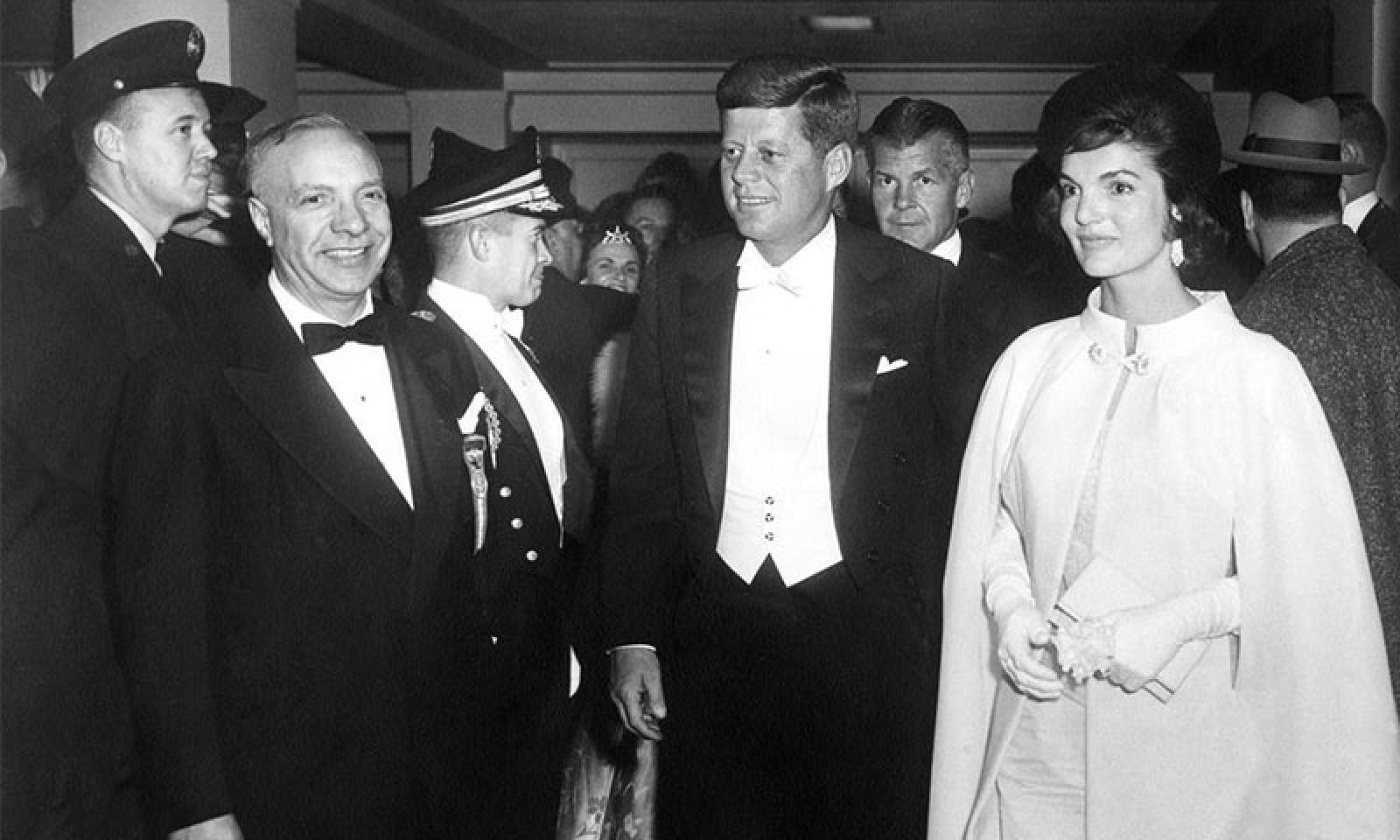
Shortly after his Senate election, Kennedy met a beautiful young woman named Jacqueline Bouvier at a dinner party and, in his own words, “leaned across the asparagus and asked her for a date.” They were married on September 12, 1953, until John’s death a decade later.
The couple first expected to become parents in 1956, but Jackie delivered a stillborn girl they intended to name Arabella. John and Jackie then welcomed their daughter, Caroline , in November 1957 and their son John Jr. in November 1960. In August 1963, their son Patrick was born prematurely and died two days after his birth.
In 1956, Kennedy was very nearly selected as Democratic presidential candidate Adlai Stevenson’s running mate but was ultimately passed over for Estes Kefauver from Tennessee. Four years later, Kennedy decided to run for president himself.
In the 1960 Democratic primaries, Kennedy outmaneuvered his main opponent, Hubert Humphrey, with superior organization and financial resources. Selecting Senate Majority Leader Lyndon B. Johnson as his running mate, Kennedy faced Vice President Richard Nixon in the general election. The election turned largely on a series of televised national debates in which Kennedy bested Nixon, an experienced and skilled debater, by appearing relaxed, healthy, and vigorous in contrast to his pallid and tense opponent.
On November 8, 1960, Kennedy defeated Nixon by a razor-thin margin to become the 35 th president of the United States of America. Kennedy’s election was historic in several respects. At the age of 43, he was the second youngest American president in history, second only to Theodore Roosevelt , who assumed the office at 42. He was also the first Catholic president and the first president born in the 20 th century.
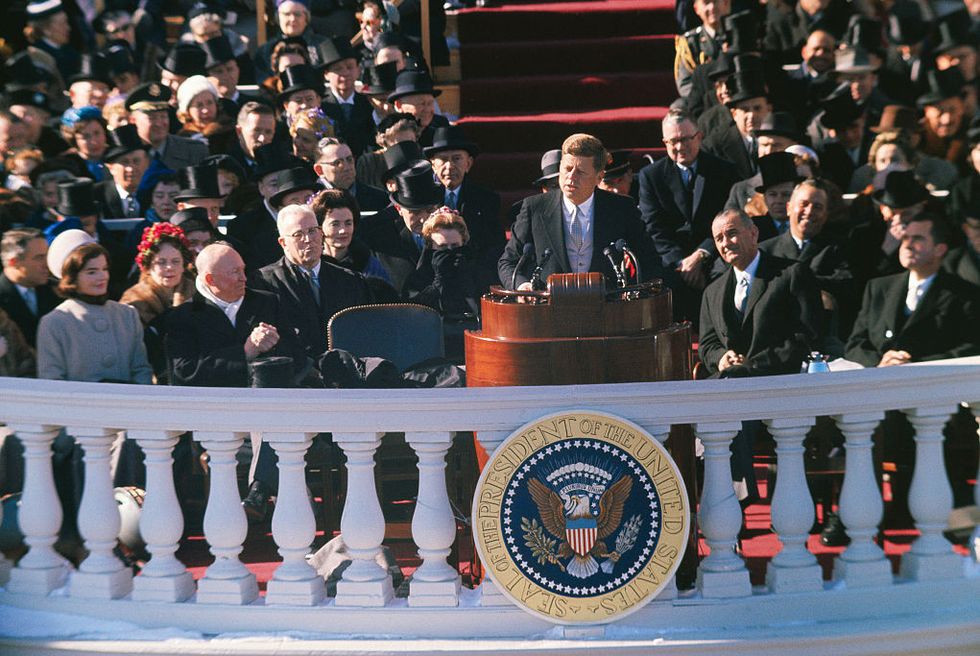

Delivering his legendary inaugural address on January 20, 1961, Kennedy sought to inspire all Americans to more active citizenship. “Ask not what your country can do for you,” he famously said. “Ask what you can do for your country.” During his brief tenure as president, Kennedy did much for America.
Foreign Affairs
Kennedy’s greatest accomplishments came in the arena of foreign affairs. Capitalizing on the spirit of activism he had helped to ignite, Kennedy created the Peace Corps by executive order in 1961. By the end of the century, over 170,000 Peace Corps volunteers would serve in 135 countries. Also in 1961, Kennedy created the Alliance for Progress to foster greater economic ties with Latin America, in hopes of alleviating poverty and thwarting the spread of communism in the region.
Kennedy also presided over a series of international crises. On April 15, 1961, he authorized a covert mission to overthrow leftist Cuban leader Fidel Castro with a group of 1,500 CIA-trained Cuban refugees. Known as the Bay of Pigs Invasion , the mission proved an unmitigated failure, causing Kennedy great embarrassment.
In August 1961, to stem massive waves of emigration from Soviet-dominated East Germany to American ally West Germany via the divided city of Berlin, Nikita Khrushchev ordered the construction of the Berlin Wall , which became the foremost symbol of the Cold War.
However, the greatest crisis of the Kennedy administration was the Cuban Missile Crisis of October 1962. Discovering that the Soviet Union had sent ballistic nuclear missiles to Cuba, Kennedy blockaded the island and vowed to defend the United States at any cost. After several of the tensest days in history, during which the world seemed on the brink of nuclear annihilation, the Soviet Union agreed to remove the missiles in return for Kennedy’s promise to not invade Cuba and to remove American missiles from Turkey.
Eight months later, in June 1963, Kennedy successfully negotiated the Nuclear Test-Ban Treaty with Great Britain and the Soviet Union, helping to ease Cold War tensions. It was one of his proudest accomplishments.

Domestic Policy
President Kennedy’s record on domestic policy was rather mixed. Taking office in the midst of a recession, he proposed sweeping income tax cuts, raising the minimum wage, and instituting new social programs to improve education, health care, and mass transit. However, hampered by lukewarm relations with Congress, Kennedy only achieved part of his agenda: a modest increase in the minimum wage and watered down tax cuts.
The most contentious domestic issue of Kennedy’s presidency was civil rights . Constrained by Southern Democrats in Congress who remained stridently opposed to civil rights for Black citizens, Kennedy offered only tepid support for civil rights reforms early in his term.
Nevertheless, in September 1962, Kennedy sent his brother Attorney General Robert Kennedy to Mississippi to use the National Guard and federal marshals to escort and defend civil rights activist James Meredith as he became the first Black student to enroll at the University of Mississippi on October 1, 1962.
Near the end of 1963, in the wake of the March on Washington and Martin Luther King Jr. ’s “I Have a Dream” speech , Kennedy finally sent a civil rights bill to Congress. One of the last acts of his presidency and his life, Kennedy’s bill eventually passed as the landmark Civil Rights Act in 1964.
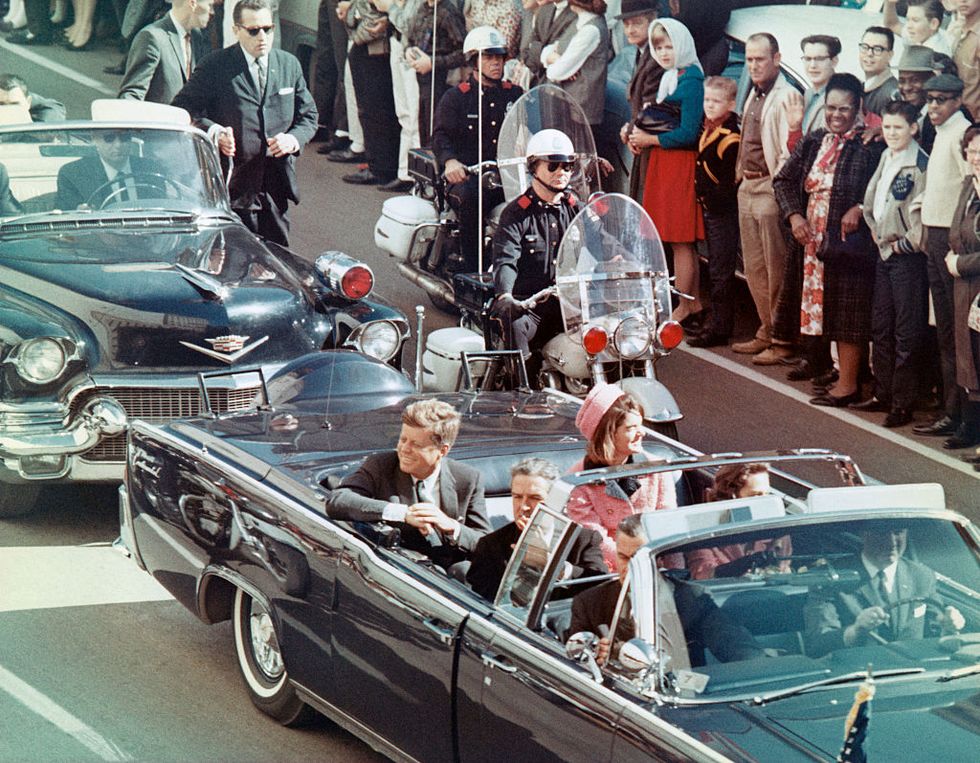

On November 21, 1963, President Kennedy flew to Fort Worth, Texas, for a campaign appearance. The next day, November 22, Kennedy, along with his wife and Texas governor John Connally, rode through cheering crowds in downtown Dallas in a Lincoln Continental convertible. From an upstairs window of the Texas School Book Depository building, a 24-year-old warehouse worker named Lee Harvey Oswald , a former Marine with Soviet sympathies, fired upon the car, hitting the president twice. Kennedy died at Dallas’ Parkland Memorial Hospital shortly thereafter at age 46.
A Dallas nightclub owner named Jack Ruby assassinated Oswald days later while he was being transferred between jails. The death of President Kennedy was an unspeakable national tragedy, and to this date, many people remember with unsettling vividness the exact moment they learned of his death. While conspiracy theories have swirled ever since Kennedy’s assassination, the official version of events remains the most plausible: Oswald acted alone.
For few former presidents is the dichotomy between public and scholarly opinion so vast. To the American public, as well as his first historians, Kennedy is a hero—a visionary politician who, if not for his untimely death, might have averted the political and social turmoil of the late 1960s. In public-opinion polls, Kennedy consistently ranks with Thomas Jefferson and Abraham Lincoln as among the most beloved American presidents of all time. Critiquing this outpouring of adoration, many more recent Kennedy scholars have derided Kennedy’s womanizing and lack of personal morals and argued that, as a leader, he was more style than substance.
In the end, no one can ever truly know what type of president Kennedy would have become had he finished out his first term or been reelected. Nor can we say how the course of history might have been different had he lived into old age. As historian Arthur Schlesinger Jr. wrote , it was “as if Lincoln had been killed six months after Gettysburg or Franklin Roosevelt at the end of 1935 or Truman before the Marshall Plan.”
The most enduring image of Kennedy’s presidency, and of his whole life, is that of Camelot , the idyllic castle of the legendary King Arthur . As his wife, Jackie Kennedy, said after his death, “There’ll be great presidents again, and the Johnsons are wonderful—they’ve been wonderful to me—but there’ll never be another Camelot again.”
On October 26, 2017, President Donald Trump ordered the release of 2,800 records related to John F. Kennedy’s assassination. The move came at the expiration of a 25-year waiting period signed into law in 1992, which allowed the declassification of the documents provided that doing so wouldn’t hurt intelligence, military operations, or foreign relations.
Trump’s release of the documents came on the final day he was legally allowed to do so. However, he didn’t release all of the documents, as officials from the FBI, CIA, and other agencies had successfully lobbied for the chance to review particularly sensitive material for an additional 180 days.
- For time and the world, do not stand still. Change is the law of life. And those who look only to the past, or the present, are certain to miss the future.
- Forgive your enemies, but never forget their names.
- We need men who can dream of things that never were and not ask why.
- If we cannot now end our differences, at least we can help make the world safe for diversity.
- Ask not what your country can do for you. Ask what you can do for your country.
- A man does what he must—in spite of personal consequences, in spite of obstacles, and dangers, and pressures—and that is the basis of all human morality.
- The times are too grave, the challenge too urgent, and the stakes too high—to permit the customary passions of political debate. We are not here to curse the darkness, but to light the candle that can guide us through that darkness to a safe and sane future... For the world is changing. The old era is ending. The old ways will not do.
- If a free society cannot help the many who are poor, it cannot save the few who are rich.
- The cost of freedom is always high—and Americans have always paid it. And one path we shall never choose and that is the path of surrender or submission.
- We choose to go to the moon in this decade and do the other things, not because they are easy, but because they are hard.
- The greater our knowledge increases, the greater our ignorance unfolds.
- Let every nation know, whether it wishes us well or ill, that we shall pay any price, bear any burden, meet any hardship, support any friend, oppose any foe, in order to assure the survival and the success of liberty.
- Those who make peaceful revolution impossible will make violent revolution inevitable.
- [O]ur most basic common link is that we all inhabit this small planet. We all breathe the same air. We all cherish our children’s future. And we are all mortal.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us !
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us
U.S. Presidents

Oppenheimer and Truman Met Once. It Went Badly.

Who Killed JFK? You Won’t Believe Us Anyway

Jimmy Carter

Inside Jimmy and Rosalynn Carter’s 77-Year Love

Abraham Lincoln

Who Is Walt Nauta, the Man Indicted with Trump?

Hunter Biden and Other Presidential Problem Kids

Controversial Judge Aileen Cannon Not Out Just Yet

Barack Obama

10 Celebrities the Same Age as President Joe Biden

- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
John F. Kennedy
By: History.com Editors
Updated: April 16, 2024 | Original: October 29, 2009

Elected in 1960 as the 35th president of the United States, 43-year-old John F. Kennedy became one of the youngest U.S. presidents, as well as the first Roman Catholic to hold the office. Born into one of America’s wealthiest families, he parlayed an elite education and a reputation as a military hero into a successful run for Congress in 1946 and for the Senate in 1952.
As president, Kennedy confronted mounting Cold War tensions in Cuba, Vietnam and elsewhere. He also led a renewed drive for public service and eventually provided federal support for the growing civil rights movement. His assassination on November 22, 1963, in Dallas, Texas, sent shockwaves around the world and turned the all-too-human Kennedy into a larger-than-life heroic figure. To this day, historians continue to rank him among the best-loved presidents in American history.
John F. Kennedy’s Early Life
Born on May 29, 1917, in Brookline, Massachusetts, John F. Kennedy (known as Jack) was the second of nine children. His parents, Joseph and Rose Kennedy, hailed from two of Boston’s most prominent Irish Catholic political families. Despite persistent health problems throughout his childhood and teenage years (he would later be diagnosed with a rare endocrine disorder called Addison’s disease), Jack led a privileged youth. He attended private schools such as Canterbury and Choate and spent summers in Hyannis Port on Cape Cod.
Joe Kennedy, a hugely successful businessman and an early supporter of Franklin D. Roosevelt , was appointed chairman of the Securities and Exchange Commission in 1934 and named U.S. ambassador to Great Britain in 1937. As a student at Harvard University, Jack traveled in Europe as his father’s secretary. His senior thesis about Britain’s unpreparedness for war was later published as an acclaimed book, Why England Slept (1940).

Watch the three-episode documentary event, Kennedy . Available to stream now.
Did you know? John F. Kennedy's Senate career got off to a rocky start when he refused to condemn Senator Joseph McCarthy, a personal friend of the Kennedy family whom the Senate voted to censure in 1954 for his relentless pursuit of suspected communists. In the end, though he planned to vote against McCarthy, Kennedy missed the vote when he was hospitalized after back surgery.
Jack joined the U.S. Navy in 1941 and two years later was sent to the South Pacific, where he was given command of a Patrol-Torpedo (PT) boat. In August 1943, a Japanese destroyer struck the craft, PT-109, in the Solomon Islands. Kennedy helped some of his marooned crew back to safety and was awarded the Navy and Marine Corps Medal for heroism. His older brother, Joe Jr., was not so fortunate: He was killed in August 1944 when his Navy airplane exploded on a secret mission against a German rocket-launching site. A grieving Joe Sr. told Jack it was his duty to fulfill the destiny once intended for Joe Jr.—to become the first Catholic president of the United States.
JFK’s Beginnings in Politics
Abandoning plans to be a journalist, Jack left the Navy by the end of 1944. Less than a year later, he returned to Boston, preparing a run for Congress in 1946. As a moderately conservative Democrat, and backed by his father’s fortune, Jack won his party’s nomination handily and carried the mostly working-class Eleventh District by nearly three to one over his Republican opponent in the general election. He entered the 80th Congress in January 1947, at the age of 29, and immediately attracted attention (as well as some criticism from older members of the Washington establishment) for his youthful appearance and relaxed, informal style.
Kennedy won reelection to the House of Representatives in 1948 and 1950, and in 1952 ran successfully for the Senate, defeating the popular Republican incumbent Henry Cabot Lodge Jr. On September 12, 1953, Kennedy married the beautiful socialite and journalist Jacqueline (Jackie) Lee Bouvier. Two years later, he was forced to undergo a painful operation on his back. While recovering from the surgery, Jack wrote another best-selling book, Profiles in Courage , which won the Pulitzer Prize for biography in 1957. (The book was later revealed to be mostly the work of Kennedy’s longtime aide, Theodore Sorenson.)
Kennedy’s Road to Presidency
After nearly earning his party’s nomination for vice president (under Adlai Stevenson) in 1956, Kennedy announced his candidacy for president on January 2, 1960. He defeated a primary challenge from the more liberal Hubert Humphrey and chose the Senate majority leader, Lyndon Johnson of Texas, as his running mate. In the general election, Kennedy faced a difficult battle against his Republican opponent, Richard Nixon, a two-term vice president under the popular Dwight D. Eisenhower .
Offering a young, energetic alternative to Nixon and the status quo, Kennedy benefited from his performance (and telegenic appearance) in the first-ever televised presidential debates, watched by millions of viewers. In November’s election, Kennedy won by a narrow margin—fewer than 120,000 out of some 70 million votes cast—becoming the youngest man and the first Roman Catholic to be elected president of the United States.
With his beautiful young wife and their two small children (Caroline, born in 1957, and John Jr., born just weeks after the election), Kennedy lent an unmistakable aura of youth and glamour to the White House . In his inaugural address, given on January 20, 1961, the new president called on his fellow Americans to work together in the pursuit of progress and the elimination of poverty, but also in the battle to win the ongoing Cold War against communism around the world. Kennedy’s famous closing words expressed the need for cooperation and sacrifice on the part of the American people: “Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country.”
Kennedy’s Foreign Policy Challenges
An early crisis in the foreign affairs arena occurred in April 1961, when Kennedy approved the plan to send 1,400 CIA-trained Cuban exiles in an amphibious landing at the Bay of Pigs in Cuba. Intended to spur a rebellion that would overthrow the communist leader Fidel Castro , the mission ended in failure, with nearly all of the exiles captured or killed.
That June, Kennedy met with Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev in Vienna to discuss the city of Berlin, which had been divided after World War II between Allied and Soviet control. Two months later, East German troops began erecting a wall to divide the city. Kennedy sent an army convoy to reassure West Berliners of U.S. support, and would deliver one of his most famous speeches in West Berlin in June 1963.
Kennedy clashed again with Khrushchev in October 1962 during the Cuban missile crisis . After learning that the Soviet Union was constructing a number of nuclear and long-range missile sites in Cuba that could pose a threat to the continental United States, Kennedy announced a naval blockade of Cuba.
The tense standoff lasted nearly two weeks before Khrushchev agreed to dismantle Soviet missile sites in Cuba in return for America’s promise not to invade the island and the removal of U.S. missiles from Turkey and other sites close to Soviet borders. In July 1963, Kennedy won his greatest foreign affairs victory when Khrushchev agreed to join him and Britain’s Prime Minister Harold Macmillan in signing a nuclear test ban treaty. In Southeast Asia, however, Kennedy’s desire to curb the spread of communism led him to escalate U.S. involvement in the conflict in Vietnam, even as privately he expressed his dismay over the situation.
Kennedy’s Leadership at Home
During his first year in office, Kennedy oversaw the launch of the Peace Corps, which would send young volunteers to underdeveloped countries all over the world. Otherwise, he was unable to achieve much of his proposed legislation during his lifetime, including two of his biggest priorities: income tax cuts and a civil rights bill. Slow to commit himself to the civil rights cause, events forced Kennedy into action, spurring him to send federal troops to support the desegregation of the University of Mississippi after riots there left two dead and many others injured. The following summer, Kennedy announced his intention to propose a comprehensive civil rights bill and endorsed the massive March on Washington that took place that August.
Kennedy held enormous popularity, both at home and abroad, and his family drew famous comparisons to King Arthur’s court at Camelot. His brother Bobby served as his attorney general, while the youngest Kennedy son, Edward (Ted), was elected to Jack’s former Senate seat in 1962. Jackie Kennedy became an international icon of style, beauty and sophistication, though stories of her husband’s numerous marital infidelities (and his personal association with members of organized crime) would later emerge to complicate the Kennedys’ idyllic image.
JFK’s Assassination
On November 22, 1963, the president and his wife landed in Dallas; he had spoken in San Antonio, Austin and Fort Worth the day before. From the airfield, the party then traveled in a motorcade to the Dallas Trade Mart, the site of Jack’s next speaking engagement. Shortly after 12:30 p.m., as the motorcade passed through downtown Dallas, shots rang out . Bullets struck Kennedy twice, in the neck and head; he was pronounced dead shortly after arriving at a nearby hospital.
Authorities arrested 24-old Lee Harvey Oswald, known to have Communist sympathies, for the killing. But he was shot and fatally wounded two days later by local nightclub owner Jack Ruby while being led to jail. Almost immediately, alternative theories of Kennedy’s assassination emerged—including conspiracies allegedly run by the KGB , the Mafia and the U.S. military-industrial complex, among others. A presidential commission led by Chief Justice Earl Warren concluded that Oswald had acted alone, but speculation and debate over the assassination have persisted.

HISTORY Vault: U.S. Presidents
Stream U.S. Presidents documentaries and your favorite HISTORY series, commercial-free

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500

John F. Kennedy
The 35th President of the United States
The biography for President Kennedy and past presidents is courtesy of the White House Historical Association.
John F. Kennedy was the 35th President of the United States (1961-1963), the youngest man elected to the office. On November 22, 1963, when he was hardly past his first thousand days in office, JFK was assassinated in Dallas, Texas, becoming also the youngest President to die.
On November 22, 1963, when he was hardly past his first thousand days in office, John Fitzgerald Kennedy was killed by an assassin’s bullets as his motorcade wound through Dallas, Texas. Kennedy was the youngest man elected President; he was the youngest to die.
Of Irish descent, he was born in Brookline, Massachusetts, on May 29, 1917. Graduating from Harvard in 1940, he entered the Navy. In 1943, when his PT boat was rammed and sunk by a Japanese destroyer, Kennedy, despite grave injuries, led the survivors through perilous waters to safety.
Back from the war, he became a Democratic Congressman from the Boston area, advancing in 1953 to the Senate. He married Jacqueline Bouvier on September 12, 1953. In 1955, while recuperating from a back operation, he wrote Profiles in Courage, which won the Pulitzer Prize in history.
In 1956 Kennedy almost gained the Democratic nomination for Vice President, and four years later was a first-ballot nominee for President. Millions watched his television debates with the Republican candidate, Richard M. Nixon. Winning by a narrow margin in the popular vote, Kennedy became the first Roman Catholic President.
His Inaugural Address offered the memorable injunction: “Ask not what your country can do for you–ask what you can do for your country.” As President, he set out to redeem his campaign pledge to get America moving again. His economic programs launched the country on its longest sustained expansion since World War II; before his death, he laid plans for a massive assault on persisting pockets of privation and poverty.
Responding to ever more urgent demands, he took vigorous action in the cause of equal rights, calling for new civil rights legislation. His vision of America extended to the quality of the national culture and the central role of the arts in a vital society.
He wished America to resume its old mission as the first nation dedicated to the revolution of human rights. With the Alliance for Progress and the Peace Corps, he brought American idealism to the aid of developing nations. But the hard reality of the Communist challenge remained.
Shortly after his inauguration, Kennedy permitted a band of Cuban exiles, already armed and trained, to invade their homeland. The attempt to overthrow the regime of Fidel Castro was a failure. Soon thereafter, the Soviet Union renewed its campaign against West Berlin. Kennedy replied by reinforcing the Berlin garrison and increasing the Nation’s military strength, including new efforts in outer space. Confronted by this reaction, Moscow, after the erection of the Berlin Wall, relaxed its pressure in central Europe.
Instead, the Russians now sought to install nuclear missiles in Cuba. When this was discovered by air reconnaissance in October 1962, Kennedy imposed a quarantine on all offensive weapons bound for Cuba. While the world trembled on the brink of nuclear war, the Russians backed down and agreed to take the missiles away. The American response to the Cuban crisis evidently persuaded Moscow of the futility of nuclear blackmail.
Kennedy now contended that both sides had a vital interest in stopping the spread of nuclear weapons and slowing the arms race–a contention which led to the test ban treaty of 1963. The months after the Cuban crisis showed significant progress toward his goal of “a world of law and free choice, banishing the world of war and coercion.” His administration thus saw the beginning of new hope for both the equal rights of Americans and the peace of the world.
For more information about President Kennedy, please visit the John F. Kennedy Library and Museum.
Learn more about John F. Kennedy’s spouse, Jacqueline Lee Bouvier Kennedy .
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.

Life of John F. Kennedy
Growing up in the kennedy family.
Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy, who was a very disciplined and organized woman, made the following entry on a notecard, when her second child was born:
John Fitzgerald Kennedy Born Brookline, Mass. (83 Beals Street) May 29, 1917

In all, Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy would have nine children, four boys and five girls. She kept notecards for each of them in a small wooden file box and made a point of writing down everything from a doctor’s visit to the shoe size they had at a particular age. John Fitzgerald Kennedy was named in honor of Rose’s father, John Francis Fitzgerald, the Boston Mayor popularly known as Honey Fitz. Before long, family and friends called this small blue-eyed baby, Jack. Jack was not a very healthy baby, and Rose recorded on his notecard the childhood diseases from which he suffered, such as: "whooping cough, measles, chicken pox."
On February 20, 1920 when Jack was not yet three years old, he became sick with scarlet fever, a highly contagious and then potentially life-threatening disease. His father, Joseph Patrick Kennedy, was terrified that little Jack would die. Mr. Kennedy went to the hospital every day to be by his son’s side, and about a month later Jack took a turn for the better and recovered. But Jack was never very healthy, and because he was always suffering from one ailment or another his family used to joke about the great risk a mosquito took in biting him – with some of his blood the mosquito was almost sure to die!
When Jack was three, the Kennedys moved to a new home a few blocks away from their old house in Brookline, a neighborhood just outside of Boston. It was a lovely house with twelve rooms, turreted windows, and a big porch. Full of energy and ambition, Jack’s father worked very hard at becoming a successful businessman. When he was a student at Harvard College and having a difficult time fitting in as an Irish Catholic, he swore to himself he would make a million dollars by the age of 35. There was a lot of prejudice against Irish Catholics in Boston at that time, but Joseph Kennedy was determined to succeed. Jack’s great-grandparents had come from Ireland and managed to provide for their families, despite many hardships. Jack’s grandfathers did even better for themselves, both becoming prominent Boston politicians. Jack, because of all his family had done, could enjoy a very comfortable life. The Kennedys had everything they needed and more. By the time Jack was eight there were seven children altogether. Jack had an older brother, Joe; four sisters, Rosemary, Kathleen, Eunice, and Patricia; and a younger brother, Robert. Jean and Teddy hadn’t been born yet. Nannies and housekeepers helped Rose run the household.

At the end of the school year, the Kennedy children would go to their summer home in Hyannis Port on Cape Cod where they enjoyed swimming, sailing, and playing touch football. The Kennedy children played hard, and they enjoyed competing with one another. Joseph Sr. encouraged this competition, especially among the boys.
He was a father with very high expectations and wanted the boys to win at sports and everything they tried. As he often said, "When the going gets tough, the tough get going." But sometimes these competitions went too far. One time when Joe suggested that he and Jack race on their bicycles, they collided head-on. Joe emerged unscathed while Jack had to have twenty-eight stitches. Because Joe was two years older and stronger than Jack, whenever they fought, Jack would usually get the worst of it. Jack was the only sibling who posed any real threat to Joe’s dominant position as the oldest child.
Jack was very popular and had many friends at Choate, a boarding school for adolescent boys in Connecticut. He played tennis, basketball, football, and golf and also enjoyed reading. His friend Lem Billings remembers how unusual it was that Jack had a daily subscription to the New York Times . Jack had a "clever, individualist mind," his Head Master once noted, though he was not the best student. He did not always work as hard as he could, except in history and English, which were his favorite subjects.
"Now Jack," his father wrote in a letter one day, "I don’t want to give the impression that I am a nagger, for goodness knows I think that is the worse thing any parent can be, and I also feel that you know if I didn’t really feel you had the goods I would be most charitable in my attitude toward your failings. After long experience in sizing up people I definitely know you have the goods and you can go a long way…It is very difficult to make up fundamentals that you have neglected when you were very young, and that is why I am urging you to do the best you can. I am not expecting too much, and I will not be disappointed if you don’t turn out to be a real genius, but I think you can be a really worthwhile citizen with good judgment and understanding."
Jack graduated from Choate and entered Harvard in 1936, where Joe was already a student. Like his brother Joe, Jack played football. He was not as good an athlete as Joe but he had a lot of determination and perseverance. Unfortunately, one day while playing he ruptured a disk in his spine. Jack never really recovered from this accident and his back continued to bother him for the rest of his life. The two eldest boys were attractive, agreeable, and intelligent young men and Mr. Kennedy had high hopes for them both. However, it was Joe who had announced to everyone when he was a young boy that he would be the first Catholic to become President. No one doubted him for a moment. Jack, on the other hand, seemed somewhat less ambitious. He was active in student groups and sports and he worked hard in his history and government classes, though his grades remained only average.
Late in 1937, Mr. Kennedy was appointed United States Ambassador to England and moved there with his whole family, with the exception of Joe and Jack who were at Harvard. Because of his father’s job, Jack became very interested in European politics and world affairs. After a summer visit to England and other countries in Europe, Jack returned to Harvard more eager to learn about history and government and to keep up with current events. Joe and Jack frequently received letters from their father in England, who informed them of the latest news regarding the conflicts and tensions that everyone feared would soon blow up into a full-scale war. Adolph Hitler ruled Germany and Benito Mussolini ruled Italy. They both had strong armies and wanted to take land from other countries. On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland and World War II began.
By this time, Jack was a senior at Harvard and decided to write his thesis on why Great Britain was unprepared for war with Germany. It was later published as a book called Why England Slept. In June 1940, Jack graduated from Harvard. His father sent him a cablegram from London: "TWO THINGS I ALWAYS KNEW ABOUT YOU ONE THAT YOU ARE SMART TWO THAT YOU ARE A SWELL GUY LOVE DAD."
World War II and a Future in Politics
Soon after graduating, both Joe and Jack joined the Navy. Joe was a flyer and sent to Europe, while Jack was made Lieutenant (Lt.) and assigned to the South Pacific as commander of a patrol torpedo boat, the PT-109.

Lt. Kennedy had a crew of twelve men whose mission was to stop Japanese ships from delivering supplies to their soldiers. On the night of August 2, 1943, Lt. Kennedy’s crew patrolled the waters looking for enemy ships to sink. A Japanese destroyer suddenly became visible. But it was traveling at full speed and headed straight at them. Holding the wheel, Lt. Kennedy tried to swerve out of the way, but to no avail. The much larger Japanese warship rammed the PT-109, splitting it in half and killing two of Lt. Kennedy’s men. The others managed to jump off as their boat went up in flames. Lt. Kennedy was slammed hard against the cockpit, once again injuring his weak back. Patrick McMahon, one of his crew members, had horrible burns on his face and hands and was ready to give up. In the darkness, Lt. Kennedy managed to find McMahon and haul him back to where the other survivors were clinging to a piece of the boat that was still afloat. At sunrise, Lt. Kennedy led his men toward a small island several miles away. Despite his own injuries, Lt. Kennedy was able to tow Patrick McMahon ashore, a strap from McMahon’s life jacket clenched between his teeth. Six days later two native islanders found them and went for help, delivering a message Jack had carved into a piece of coconut shell. The next day, the PT-109 crew was rescued. Jack’s brother Joe was not so lucky. He died a year later when his plane blew up during a dangerous mission in Europe.
When he returned home, Jack was awarded the Navy and Marine Corps Medal for his leadership and courage. With the war finally coming to an end, it was time to choose the kind of work he wanted to do. Jack had considered becoming a teacher or a writer, but with Joe’s tragic death suddenly everything changed. After serious discussions with Jack about his future, Joseph Kennedy convinced him that he should run for Congress in Massachusetts' eleventh congressional district, where he won in 1946. This was the beginning of Jack’s political career. As the years went on, John F. Kennedy, a Democrat, served three terms (six years) in the House of Representatives, and in 1952 he was elected to the US Senate.
Soon after being elected senator, John F. Kennedy, at 36 years of age, married 24 year-old Jacqueline Bouvier, a writer with the Washington Times-Herald . Unfortunately, early on in their marriage, Senator Kennedy’s back started to hurt again and he had two serious operations. While recovering from surgery, he wrote a book about several US Senators who had risked their careers to fight for the things in which they believed. The book, called Profiles in Courage , was awarded the Pulitzer Prize for biography in 1957. That same year, the Kennedys’ first child, Caroline, was born.
John F. Kennedy was becoming a popular politician. In 1956 he was almost picked to run for vice president. Kennedy nonetheless decided that he would run for president in the next election.
He began working very long hours and traveling all around the United States on weekends. On July 13, 1960 the Democratic party nominated him as its candidate for president. Kennedy asked Lyndon B. Johnson, a senator from Texas, to run with him as vice president. In the general election on November 8, 1960, Kennedy defeated the Republican Vice President Richard M. Nixon in a very close race. At the age of 43, Kennedy was the youngest man elected president and the first Catholic. Before his inauguration, his second child, John Jr., was born. His father liked to call him John-John.
John F. Kennedy Becomes The 35th President of the United States
John F. Kennedy was sworn in as the 35th president on January 20, 1961. In his inaugural speech he spoke of the need for all Americans to be active citizens. "Ask not what your country can do for you, ask what you can do for your country," he said. He also asked the nations of the world to join together to fight what he called the "common enemies of man: tyranny, poverty, disease, and war itself." President Kennedy, together with his wife and two children, brought a new, youthful spirit to the White House. The Kennedys believed that the White House should be a place to celebrate American history, culture, and achievement. They invited artists, writers, scientists, poets, musicians, actors, and athletes to visit them. Jacqueline Kennedy also shared her husband's interest in American history. Gathering some of the finest art and furniture the United States had produced, she restored all the rooms in the White House to make it a place that truly reflected America’s history and artistic creativity. Everyone was impressed and appreciated her hard work. The White House also seemed like a fun place because of the Kennedys’ two young children, Caroline and John-John. There was a pre-school, a swimming pool, and a tree-house outside on the White House lawn. President Kennedy was probably the busiest man in the country, but he still found time to laugh and play with his children. However, the president also had many worries. One of the things he worried about most was the possibility of nuclear war between the United States and the Soviet Union. He knew that if there was a war, millions of people would die. Since World War II, there had been a lot of anger and suspicion between the two countries but never any shooting between Soviet and American troops. This 'Cold War', which was unlike any other war the world had seen, was really a struggle between the Soviet Union's communist system of government and the United States' democratic system. Because they distrusted each other, both countries spent enormous amounts of money building nuclear weapons. There were many times when the struggle between the Soviet Union and the United States could have ended in nuclear war, such as in Cuba during the 1962 missile crisis or over the divided city of Berlin. President Kennedy worked long hours, getting up at seven and not going to bed until eleven or twelve at night, or later. He read six newspapers while he ate breakfast, had meetings with important people throughout the day, and read reports from his advisers. He wanted to make sure that he made the best decisions for his country. "I am asking each of you to be new pioneers in that New Frontier," he said. The New Frontier was not a place but a way of thinking and acting. President Kennedy wanted the United States to move forward into the future with new discoveries in science and improvements in education, employment and other fields. He wanted democracy and freedom for the whole world. One of the first things President Kennedy did was to create the Peace Corps. Through this program, which still exists today, Americans can volunteer to work anywhere in the world where assistance is needed. They can help in areas such as education, farming, health care, and construction. Many young men and women have served as Peace Corps volunteers and have won the respect of people throughout the world.
President Kennedy was also eager for the United States to lead the way in exploring space. The Soviet Union was ahead of the United States in its space program and President Kennedy was determined to catch up. He said, "No nation which expects to be the leader of other nations can expect to stay behind in this race for space." Kennedy was the first president to ask Congress to approve more than 22 billion dollars for Project Apollo, which had the goal of landing an American man on the moon before the end of the decade. President Kennedy had to deal with many serious problems here in the United States. The biggest problem of all was racial discrimination. The US Supreme Court had ruled in 1954 that segregation in public schools would no longer be permitted. Black and white children, the decision mandated, should go to school together. This was now the law of the land. However, there were many schools, especially in southern states, that did not obey this law. There was also racial segregation on buses, in restaurants, movie theaters, and other public places.
Thousands of Americans joined together, people of all races and backgrounds, to protest peacefully this injustice.
Martin Luther King Jr. was one of the famous leaders of the movement for civil rights. Many civil rights leaders didn’t think President Kennedy was supportive enough of their efforts. The President believed that holding public protests would only anger many white people and make it even more difficult to convince the members of Congress who didn't agree with him to pass civil rights laws. By June 11, 1963, however, President Kennedy decided that the time had come to take stronger action to help the civil rights struggle. He proposed a new Civil Rights bill to the Congress, and he went on television asking Americans to end racism. "One hundred years of delay have passed since President Lincoln freed the slaves, yet their heirs, their grandsons, are not fully free," he said. "This Nation was founded by men of many nations and backgrounds…[and] on the principle that all men are created equal." President Kennedy made it clear that all Americans, regardless of their skin color, should enjoy a good and happy life in the United States.
The President is Shot
On November 21, 1963, President Kennedy flew to Texas to give several political speeches. The next day, on November 22, as his car drove slowly past cheering crowds in Dallas, shots rang out. Kennedy was seriously wounded and died a short time later. Within a few hours of the shooting, police arrested Lee Harvey Oswald and charged him with the murder. On November 24, another man, Jack Ruby, shot and killed Oswald, thus silencing the only person who could have offered more information about this tragic event. The Warren Commission was organized to investigate the assassination and to clarify the many questions which remained.
The Legacy of John F. Kennedy
President Kennedy's death caused enormous sadness and grief among all Americans. Most people still remember exactly where they were and what they were doing when they heard the news. Hundreds of thousands of people gathered in Washington for the President's funeral, and millions throughout the world watched it on television. As the years have gone by and other presidents have written their chapters in history, John Kennedy's brief time in office stands out in people's memories for his leadership, personality, and accomplishments. Many respect his coolness when faced with difficult decisions--like what to do about Soviet missiles in Cuba in 1962. Others admire his ability to inspire people with his eloquent speeches. Still others think his compassion and his willingness to fight for new government programs to help the poor, the elderly and the ill were most important. Like all leaders, John Kennedy made mistakes, but he was always optimistic about the future. He believed that people could solve their common problems if they put their country's interests first and worked together.
Biography of John F. Kennedy, 35th President of the U.S.
His term was cut short by his assassination on Nov. 22, 1963 in Dallas
- U.S. Presidents
- Important Historical Figures
- Native American History
- American Revolution
- America Moves Westward
- The Gilded Age
- Crimes & Disasters
- The Most Important Inventions of the Industrial Revolution
- African American History
- African History
- Ancient History and Culture
- Asian History
- European History
- Latin American History
- Medieval & Renaissance History
- Military History
- The 20th Century
- Women's History
- M.A., History, University of Florida
- B.A., History, University of Florida
John F. Kennedy (May 29, 1917–Nov. 22, 1963), the first U.S. president born in the 20th century, was born to a wealthy, politically connected family . Elected as the 35th president in 1960, he took office on Jan. 20, 1961, but his life and legacy were cut short when he was assassinated on Nov. 22, 1963, in Dallas. Though he served as president for less than three years, his brief term coincided with the height of the Cold War, and his tenure was marked by some of the biggest crises and challenges of the 20th century.
Fast Facts: John F. Kennedy
- Known For : First U.S. president born in the 20th century, known for the fiasco of The Bay of Pigs early in his term, his highly praised response to the Cuban Missile Crisis, as well as his assassination on Nov. 22, 1963.
- Also Known As : JFK
- Born : May 29, 1917 in Brookline, Massachusetts
- Parents : Joseph P. Kennedy Sr., Rose Fitzgerald
- Died : Nov. 22, 1963 in Dallas, Texas
- Education : Harvard University (BA, 1940), Stanford University Graduate School of Business (1940–1941)
- Published Works : Profiles in Courage
- Awards and Honors : Navy and Marine Corps Medal, Purple Heart, Asiatic-Pacific Campaign Medal, Pulitzer Prize for Biography (1957)
- Spouse : Jacqueline L. Bouvier (m. Sept. 12, 1953–Nov. 22, 1963)
- Children : Caroline, John F. Kennedy, Jr.
- Notable Quote : "Those who make peaceful revolution impossible make violent revolution inevitable."
Kennedy was born on May 29, 1917, in Brookline, Massachusetts. He was sickly as a child and continued to have health problems for the rest of his life. He attended private schools including Choate and Harvard (1936–1940), where he majored in political science. An active and accomplished undergraduate, Kennedy graduated cum laude.
Kennedy's father was the indomitable Joseph Kennedy. Among other ventures, he was the head of the SEC and the ambassador to Great Britain. His mother was a Boston socialite named Rose Fitzgerald. He had nine siblings including Robert Kennedy, who he appointed as the U.S. attorney general. Robert Kennedy was assassinated in 1968 . In addition, his brother Edward Kennedy was a senator from Massachusetts who served from 1962 until his death in 2009.
Kennedy married Jacqueline Bouvier, a wealthy socialite and photographer, on Sept. 12, 1953. Together they had two children: Caroline Kennedy and John F. Kennedy, Jr. Another son, Patrick Bouvier Kennedy, died on Aug. 9, 1963, two days after his birth.
Military Career
Kennedy was originally turned down by both the Army and Navy because of his back pain and other medical problems. He didn’t give up, and with the help of his father’s political contacts, he was accepted into the Navy in 1941. He made it through the Navy Officer Candidate School but then failed another physical. Determined not to spend his military career sitting behind a desk, he again called upon his father's contacts. With their help, he managed to get into a new PT boat training program.
After completing the program, Kennedy served in the Navy during World War II and rose to the rank of lieutenant. He was given command of PT-109 . When the boat was rammed by a Japanese destroyer, he and his crew were thrown into the water. He was able to swim four hours to save himself and a fellow crewman, but he aggravated his back in the process. He received the Purple Heart and the Navy and Marine Corps Medal for his military service and was hailed for his heroism.
House of Representatives
Kennedy worked for a time as a journalist before running for the House of Representatives. Now considered a Navy war hero, Kennedy was elected to the House in November 1946. This class also included another former Navy man whose career arc would eventually intersect with Kennedy’s— Richard M. Nixon . Kennedy served three terms in the House—he was reelected in 1948 and 1950—where he gained a reputation as a somewhat conservative Democrat.
He did show himself to be an independent thinker, not always following the party line, such as in his opposition to the Taft-Hartley Act, an anti-union bill that passed both the House and Senate overwhelmingly during the 1947-1948 session. As a freshman member of the minority party in the House and not a member of any of the committees of jurisdiction, there was little else Kennedy could do other than speak against the bill, which he did.
U.S. Senate
Kennedy was later elected to the U.S. Senate—defeating Henry Cabot Lodge II, who would later become the Republican U.S. vice presidential candidate on the 1960 ticket alongside Nixon—where he served from 1953 to 1961. Again, he did not always vote with the Democratic majority.
Kennedy had more impact in the Senate than in the House. For example, in late spring 1953, he gave three speeches on the Senate floor outlining his New England economic plan, which he said would be good for New England and the nation as a whole. In the speeches, Kennedy called for a diversified economic base for New England and the U.S., with job training and technical assistance for the workers and relief from harmful tax provisions for the firms.
In other areas, Kennedy:
- Distinguished himself as a national figure in the debate and vote on building the St. Lawrence Seaway ;
- Used his position on the Senate Labor Committee to push for an increase in the minimum wage and to protect union rights in an environment where Congress was trying to strip unions of any power to bargain effectively;
- Joined the Foreign Relations Committee in 1957, where he supported Algerian independence from France and sponsored an amendment that would provide aid to Russian satellite nations;
- Introduced an amendment to the National Defense Education Act to eliminate the requirement that aid recipients sign a loyalty oath.
During his time in the Senate, Kennedy also authored "Profiles in Courage," which won a Pulitzer Prize for biography in 1957, although there was some question about its true authorship.
Election of 1960
In 1960, Kennedy was nominated to run for the presidency against Nixon, who was by then Dwight D. Eisenhower 's vice president. During Kennedy's nominating speech, he set forward his ideas of a "New Frontier." Nixon made the mistake of meeting Kennedy in debates—the first televised presidential debates in U.S. history—during which Kennedy came off as young and vital.
During the campaign, both candidates worked to win support from the growing suburban population. Kennedy sought to pull together key elements of Franklin D. Roosevelt 's coalition of the 1930s—urban minorities, ethnic voting blocs, and organized labor—win back conservative Catholics who had deserted the Democrats to vote for Eisenhower in 1952 and 1956, and hold his own in the south. Nixon emphasized the record of the Eisenhower years and promised to keep the federal government from dominating the free market economy and the lives of Americans.
At the time, some sectors expressed concern that a Catholic president, which Kennedy would be, would be beholden to the Pope in Rome. Kennedy confronted the issue in a speech before the Greater-Houston Ministerial Association, in which he said: "I believe in an America where the separation of church and state is absolute; where no Catholic prelate would tell the President—should he be Catholic—how to act, and no Protestant minister would tell his parishioners for whom to vote."
The anti-catholic feeling remained strong among some sectors of the populace, but Kennedy won by the smallest margin of popular votes since 1888, 118,574 votes. However, he received 303 electoral votes .
Events and Accomplishments
Domestic policy: Kennedy had a tough time getting many of his domestic programs through Congress. However, he did get an increased minimum wage, better Social Security benefits, and an urban renewal package passed. He created the Peace Corps, and his goal to get to the moon by the end of the 1960s found overwhelming support.
On the Civil Rights front, Kennedy initially did not challenge Southern Democrats. Martin Luther King, Jr. believed that only by breaking unjust laws and accepting the consequences could African-Americans show the true nature of their treatment. The press reported daily on the atrocities occurring due to nonviolent protest and civil disobedience. Kennedy used executive orders and personal appeals to aid the movement. His legislative programs, however, would not pass until after his death.
Foreign affairs: Kennedy's foreign policy began in failure with the Bay of Pigs debacle of 1961. A small force of Cuban exiles was to lead a revolt in Cuba but was captured instead. America's reputation was seriously harmed. Kennedy's confrontation with Russian leader Nikita Khrushchev in June 1961 led to the construction of the Berlin Wall . Further, Khrushchev began building nuclear missile bases in Cuba. Kennedy ordered a "quarantine" of Cuba in response. He warned that any attack from Cuba would be seen as an act of war by the USSR. This standoff led to the dismantling of the missile silos in exchange for promises that the U.S. would not invade Cuba. Kennedy also agreed to a Nuclear Test Ban Treaty in 1963 with Great Britain and the USSR.
Two other important events during his term were the Alliance for Progress (the U.S. provided aid to Latin America) and the problems in Southeast Asia. North Vietnam was sending troops through Laos to fight in South Vietnam. The South's leader, Ngo Dinh Diem, was ineffective. America increased its military advisers from 2,000 to 16,000 during this time. Diem was overthrown but new leadership was no better. When Kennedy was killed, Vietnam was approaching a boiling point.
Assassination
Kennedy's three years in office were somewhat turbulent, but by 1963 he was still popular and thinking about running for a second term. Kennedy and his advisers felt that Texas was a state that could provide crucial electoral votes, and they made plans for Kennedy and Jackie to visit the state, with stops planned for San Antonio, Houston, Fort Worth, Dallas, and Austin. On Nov. 22, 1963, after addressing the Fort Worth Chamber of Commerce, Kennedy and the first lady boarded a plane for a brief flight to Dallas, arriving just before noon accompanied by about 30 members of the Secret Service.
They were met by a 1961 Lincoln Continental convertible limousine that would take them on a 10-mile parade route within the city of Dallas, ending at the Trade Mart, where Kennedy was scheduled to deliver a luncheon address. He never made it. Thousands lined the streets, but just before 12:30 p.m., the presidential motorcade turned right from Main Street onto Houston Street and entered Dealey Plaza.
After passing the Texas School Book Depository, at the corner of Houston and Elm, shots suddenly rang out. One shot hit Kennedy’s throat, and as he reached up with both hands toward the injury, another shot struck his head, mortally wounding him.
Kennedy's apparent assassin, Lee Harvey Oswald , was killed by Jack Ruby before standing trial. The Warren Commission was called to investigate Kennedy's death and found that Oswald had acted alone to kill Kennedy. Many argued, however, that there was more than one gunman, a theory upheld by a 1979 House Committee investigation. The FBI and a 1982 study disagreed. Speculation continues to this day.
Kennedy was important more for his iconic reputation than his legislative actions. His many inspiring speeches are often quoted. His youthful vigor and fashionable first lady was hailed as American royalty; his time in office was termed "Camelot." His assassination has taken on a mythic quality, leading many to posit about possible conspiracies involving everyone from Lyndon Johnson to the Mafia. His moral leadership of Civil Rights was an important part of the movement's eventual success.
- “ Campaign of 1960 .” JFK Library.
- “ Details You Didn't Know About the Death of JFK's Son, Patrick. .” IrishCentral.com , 4 Nov. 2018.
- “ John F. Kennedy. ” Biography.com , A&E Networks Television, 14 Jan. 2019.
- “ John F. Kennedy. ” The White House , The United States Government.
- “ JFK's Assassination Aided by His Bad Back, Records Show. ” fox8.Com , 22 Nov. 2017.
- “ JFK in Congress. ” National Archives and Records Administration , National Archives and Records Administration.
- “ John F. Kennedy: Life Before the Presidency. ” Miller Center , 22 Apr. 2018.
- 10 Things to Know About John F. Kennedy
- John F. Kennedy Printables
- Biography of Robert Kennedy, US Attorney General, Presidential Candidate
- President John F. Kennedy's Assassination
- The Aftermath of John F. Kennedy's Assassination
- Biography of John F. Kennedy Jr.
- 7 20th Century Men Who Made History
- Biography of Lyndon B. Johnson, 36th President of the United States
- Biography of Jacqueline Kennedy Onassis, First Lady
- Biography of Richard Nixon, 37th President of the United States
- JFK's Accomplishments in Education and the Space Program
- Pictures and Trivia About the Presidents of the United States
- How Many U.S. Presidents Have Been Assassinated?
- George McGovern, 1972 Democratic Nominee Who Lost in Landslide
- Who Were the Democratic Presidents of the United States?
- Top 10 Facts About LBJ, President of the US
Help inform the discussion
U.S. Presidents / John F. Kennedy
1917 - 1963
John f. kennedy.
Let the word go forth from this time and place, to friend and foe alike, that the torch has been passed to a new generation of Americans... Inaugural Address
John F. Kennedy was born into a rich, politically connected Boston family of Irish-Catholics. He and his eight siblings enjoyed a privileged childhood of elite private schools, sailboats, servants, and summer homes. During his childhood and youth, "Jack" Kennedy suffered frequent serious illnesses. Nevertheless, he strove to make his own way, writing a best-selling book while still in college at Harvard and volunteering for hazardous combat duty in the Pacific during World War II. Kennedy's wartime service made him a hero. After a short stint as a journalist, Kennedy entered politics, serving in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1947 to 1953 and the U.S. Senate from 1953 to 1961.
Life In Depth Essays
- Life in Brief
- Life Before the Presidency
- Campaigns and Elections
- Domestic Affairs
- Foreign Affairs
- Death of the President
- Family Life
- The American Franchise
- Impact and Legacy

Chicago Style
Miller Center of Public Affairs, University of Virginia. “John F. Kennedy.” Accessed April 09, 2024. https://millercenter.org/president/kennedy.
Associate Professor
Marc J. Selverstone
Marc J. Selverstone is Chair of the the Presidential Recordings Program and University of Virginia Associate Professor.
- A Companion to John F. Kennedy (editor)
- Constructing the Monolith: The United States, Great Britain, and International …
- The Presidential Recordings, Digital Edition (co-editor)
Featured Insights

Listening to the presidency
Explore audio recordings with contextual materials about events during President Kennedy's administration

The Vietnam War
Explore the additional resources that accompany the film by Ken Burns and Lynn Novick

American Forum: Rose Kennedy
Barbara Perry discusses her biography on JFK’s mother, Rose Kennedy
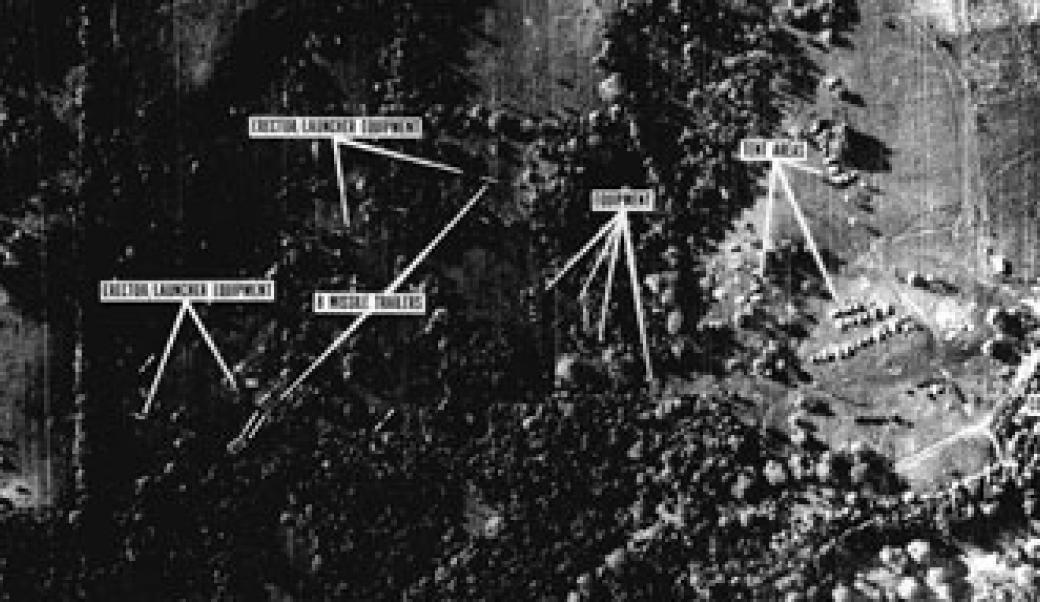

JFK and the Cuban Missile Crisis
Secret recordings that reveal what President Kennedy was thinking—and the advice he was receiving—during the Cuban Missile Crisis

January 20, 1961: Inaugural Address
May 25, 1961: the goal of sending a man to the moon, june 11, 1963: address on civil rights, secret white house tapes.

Meeting on Berlin
Meeting on soviet arms shipments to cuba, meeting on u-2 incident, photo gallery, jfk's inauguration.
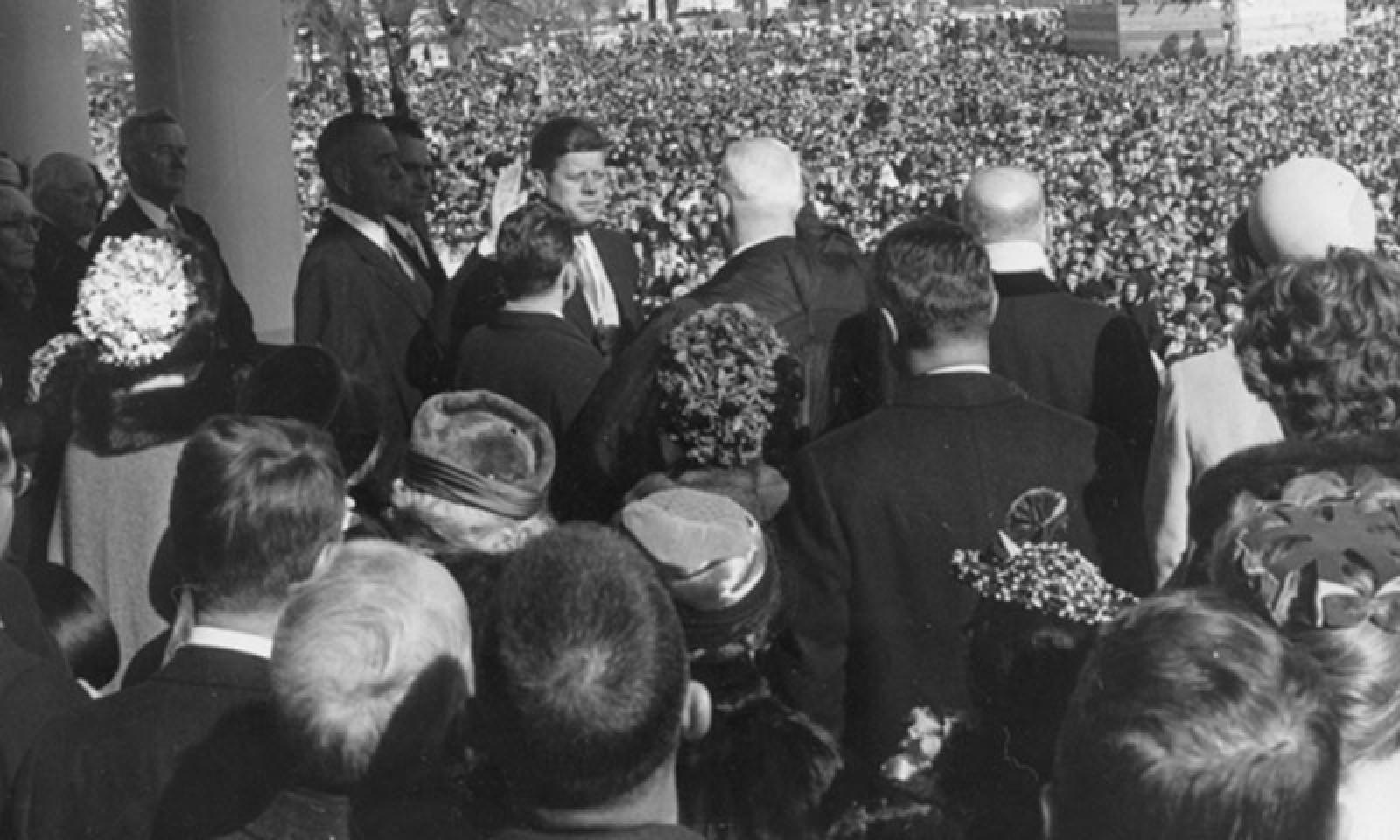

JFK takes the oath of office
John F. Kennedy was inaugurated as the 35th President of the United States on January 20, 1961.

JFK delivers his Inaugural Address
JFK's Inaugural Address is best know for these words: "Ask not what your country can do for you—ask what you can do for your country."
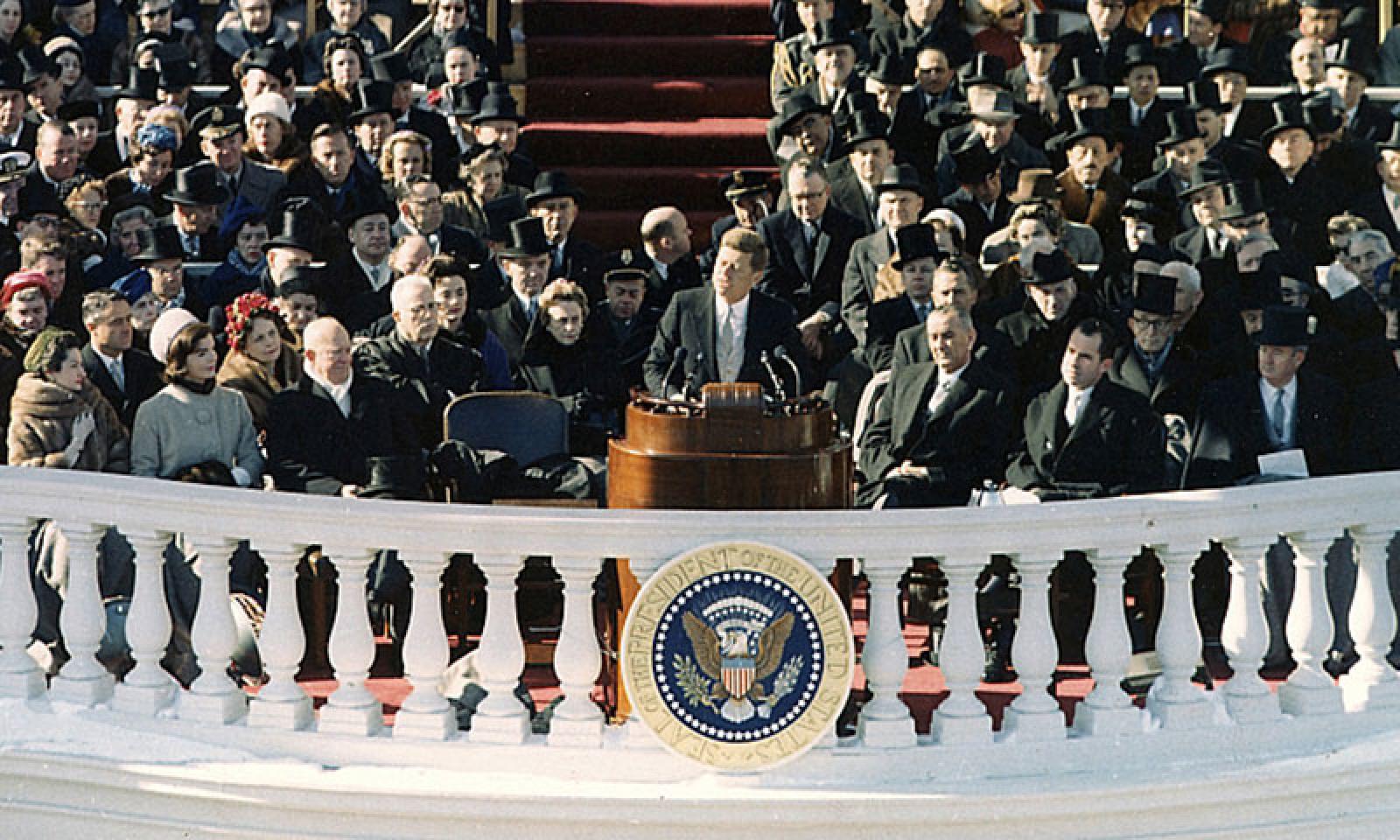

Kennedy's Inaugural Address focused on the hope and youth that his administration brought to Washington.
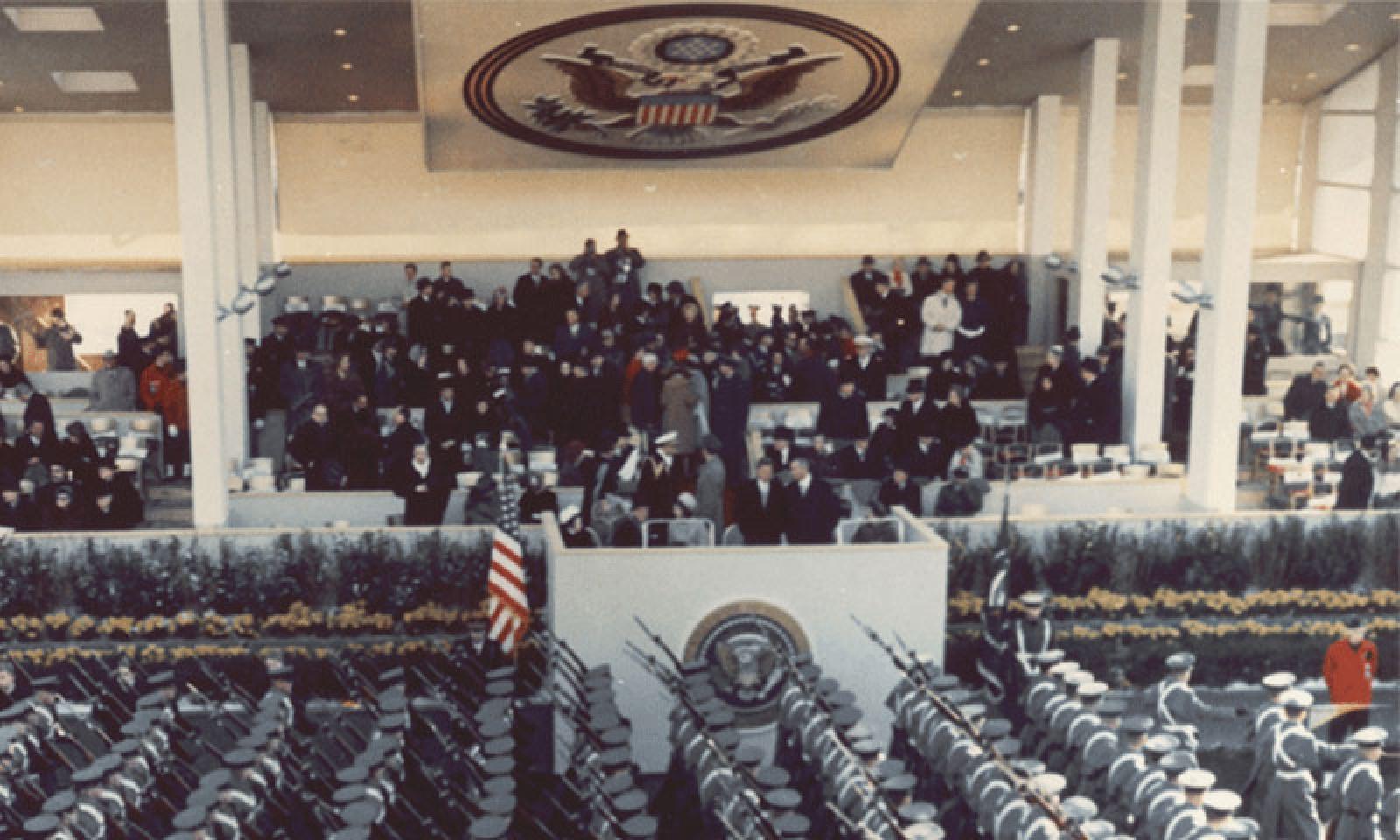

Inaugural Parade
The President and First Lady watch the Inaugural Parade from the official reviewing stand.
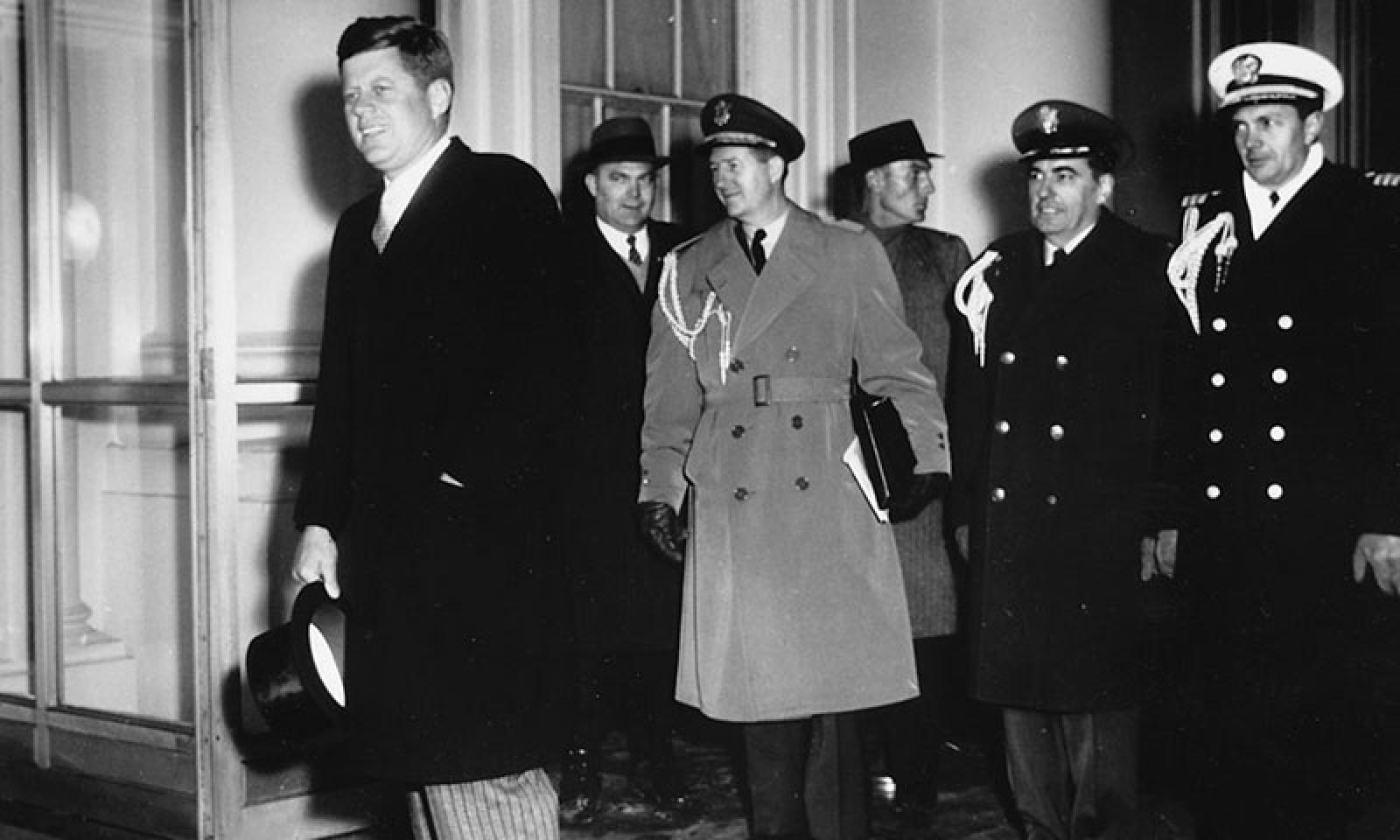

Returning to the White House
President Kennedy returns to the White House after taking the oath of office.

Arriving at the Inaugural Ball
The President and First Lady arrive for the Inaugural Ball.
Featured Video

Why Vietnam?
Miller Center expert Marc Selverstone discusses the evolution of American interests in the Vietnam War
Featured Publications

Biography Online

John F Kennedy Biography

Born on May 1917, John F. Kennedy came from an illustrious political family; his father Joseph Kennedy was a leading member of the Democratic Party, and Joseph encouraged John F. Kennedy in his political ambitions after the war.
John graduated from Harvard after completing a thesis on “Appeasement in Munich.” His thesis was later converted into a successful book: Why England Slept (1940).

On Jack Paar Tonight Show
Before America joined the war, John joined the Navy and saw action throughout the Pacific theatre. In August 1943, his boat was rammed by Japanese destroyer Amagiri . John F Kennedy was later decorated for his outstanding bravery in rescuing a fellow crewman; he was also awarded the Purple Heart for an incident later in the war. Afterwards, Kennedy was modest about his actions, saying he felt a bit embarrassed as it resulted from a botched military action.
In 1946, he won a seat in Boston for the US House of Representatives, and in 1952 got himself elected to the US Senate, defeating the incumbent Republican.

In 1956, he was nearly chosen to be the Vice Presidential candidate for Adlai Stevenson. The national exposure raised his profile, and in 1960 he was selected to be the Democratic nomination for the Presidency.
In 1960, in a very tight election, John F. Kennedy narrowly defeated the much-fancied Republican, Richard Nixon. It was a memorable election with many millions glued to the TV in the pre-election hustings. John F. Kennedy came across very well on TV and looked more relaxed and professional on camera.

During his inauguration, JFK gave a memorable speech, where he famously encouraged citizens to help the nation become strong again.
“Ask not what your country can do for you – ask what you can do for your country.”
He also called for greater internationalism.
“We will make clear that America’s enduring concern is for both peace and freedom; that we are anxious to live in harmony with the Russian people; that we seek no conquests, no satellites, no riches; that we seek only the day when nation shall not lift up sword against nation, neither shall they learn war any more.”
One of his early acts was to establish the Peace Corps – a volunteer programme run by the US government, it allowed young Americans to travel abroad and serve in developing countries. Kennedy hoped it would change foreign perceptions of Americans and give Americans a greater sense of international solidarity.
In 1961, after pressure from the CIA, Kennedy reluctantly ordered the Bay of Pigs invasion of Cuba. It was mostly led by Cuban exiles with minimal US support. They hope to overthrow the Communist Fidel Castro. However, the invasion was a failure leading to embarrassing negotiations with Fidel Castro’s Cuba. Despite been reluctant to go along with the policy, he accepted his responsibilty for its failure.
In 1962, figures in the US Department of Defense and Joint Chief of Staff proposed ‘Operation Northwoods’ which involved the CIA planning ‘false flag’ operations to stage attacks on US targets and claim Cuba was responsible – to create an opportunity to start a war against Cuba. Kennedy rejected the proposals but his reluctance to fully commit to removing Castro led to resentment amongst some CIA officers and Cuban exiles who felt Kennedy was insufficiently committed to removing Castro.
Cuban Missile Crisis
In 1962, the world came extraordinarily close to nuclear war during the Cuban Missile Crisis. The Soviet Union moved missiles to Cuba, which was seen as very provocative (despite the US have nuclear weapons in NATO ally Turkey. Many in the American military were keen on a pre-emptive airstrike on the missile bases, but Kennedy chose a more cautious diplomatic approach.
Kennedy found a way to offer Khrushchev a way out without losing face. After several days of tense negotiation, an agreement was reached where the Soviet Union would remove missiles from Cuba in return for a US promise not to invade Cuba. The US also secretly removed weapons from Turkey to pacify the Soviets. His careful handling of the situation was widely praised. It led to the establishment of a direct Moscow-Washington hotline and for a few years, tensions between the Cold War antagonists were reduced.
During his brief presidency, John F. Kennedy oversaw an escalation of US involvement in Vietnam, which included sending 16,000 military advisers to the country. Later, Kennedy’s Secretary of Defence Robert McNamara said Kennedy considered pulling out of Vietnam in 1963 and believes that if Kennedy had survived, American involvement would have ended. Tapes showed that Kennedy’s former Vice-President, Lyndon Johnson later criticised Kennedy’s opinion that America should withdraw.
Civil rights

Meeting with leaders of March on Washington August 1963
Kennedy was a supporter of civil rights, but when elected in 1960, American society was deeply divided with entrenched opposition to the end of segregation and racism. Kennedy was torn between the need to retain the support of white southern democrat voters and a wish to promote civil rights. He supported voter registration drives, appointed African Americans to positions within his administration and promoted Thurgood Marshall to the Second Circuit court of Appeals in New York.
However, this was insufficient to tackle the much larger injustices. During the 1960s, the civil rights movement led by Martin Luther King became disappointed with JFK’s apparent non-committal stance, instead, they took non-violent direct action to highlight the injustice of segregation and civil rights leaders. This often led to shocking images – shown on tv, of police brutality against civil rights activists. A turning point was 3 May 1963, where police in Birmingham unleased shocking brutality on protestors. This galvanised Kennedy to take more direct action sending federal marshals to the south in order to prevent racial violence getting out of hand. On 11 June 1963, Kennedy made a televised address to the nation where he spoke clearly in favour of the need to pass civil rights legislation
“The heart of the question is — whether all Americans are to be afforded equal rights and equal opportunities. Whether we are going to treat our fellow Americans as we want to be treated… One hundred years of delay have passed since President Lincoln freed the slaves, yet their heirs, their grandsons, are not fully free….” – J.F. Kennedy
Although he did not live to see his promise enacted, it was a turning point in his presidency with a clear commitment made. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 outlawed racial segregation.

Ich Bin Ein Berliner

JFK’s handwriting
In June 1963, Kennedy made a memorable speech in West Berlin to a crowd of up to 450,000. He criticised the Soviets for their divisive wall and stated:
“Freedom has many difficulties and democracy is not perfect, but we have never had to put a wall up to keep our people in… All free men, wherever they may live, are citizens of Berlin, and therefore, as a free man, I take pride in the words “Ich bin ein Berliner!”
His speech was very well received by people living in West Berlin, who felt surrounded by the Berlin Wall and Communist East Germany. The Soviet authorities were less enamoured of his speech which they felt was confrontational.
Assassination
John F. Kennedy was assassinated in November 1963. Lee Harvey Oswald was arrested and put on trial for his murder. However, before he could reach trial, Lee Harvey Oswald was himself killed by Jack Ruby. Lee Harvey Oswald always pleaded his innocence and many believe the assassination was a wider conspiracy. His death left a large void in American politics that was never adequately filled. Though Johnson did enact civil rights legislation and a form of welfare state, which many see as something Kennedy was keen to do. His brother Robert F. Kennedy was assassinated in 1968 whilst seeking the democratic presidential nomination.
Citation: Pettinger, Tejvan . “ John F. Kennedy Biography ”, Oxford, UK. www.biographyonline.net , Last updated 25 March 2020. Originally published 11 Feb 2013.
The Kennedy Half-Century

The Kennedy Half-Century at Amazon
Quotes by J F Kennedy
“The men who create power make an indispensable contribution to the Nation’s greatness, but the men who question power make a contribution just as indispensable, especially when that questioning is disinterested, for they determine whether we use power or power uses us.”
John F. Kennedy, Amherst College, Oct 26, 1963 – Source JFK Library, Boston, Mass.
“And so, my fellow Americans: ask not what your country can do for you – ask what you can do for your country. My fellow citizens of the world: ask not what America will do for you, but what together we can do for the freedom of man.”
John F. Kennedy, Inaugural address, January 20, 1961
“War will exist until that distant day when the conscientious objector enjoys the same reputation and prestige that the warrior does today.”
“I believe in an America where the rights that I have described are enjoyed by all, regardless of their race or their creed or their national origin – where every citizen is free to think and speak as he pleases and write and worship as he pleases – and where every citizen is free to vote as he pleases, without instructions from anyone, his employer, the union leader or his clergyman.”
October 31, 1960. Online by Gerhard Peters and John T. Woolley, The American Presidency Project.
“Let every nation know, whether it wishes us well or ill, that we shall pay any price, bear any burden, meet any hardship, support any friend, oppose any foe to assure the survival and the success of liberty.”
Inaugural Address (1961)
Related pages

Famous Americans – Great Americans from the Founding Fathers to modern civil rights activists. Including presidents, authors, musicians, entrepreneurs and businesspeople.

Presidential Libraries

JFK Biography
John Fitzgerald Kennedy was born on May 29, 1917, in Brookline, Massachusetts, a few miles outside of Boston. His parents were Joseph Kennedy, a successful businessman, and Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy. He was the second of nine children. While Jack grew up with every material advantage, he suffered from a series of medical ailments but learned to underplay the effects of his illnesses.
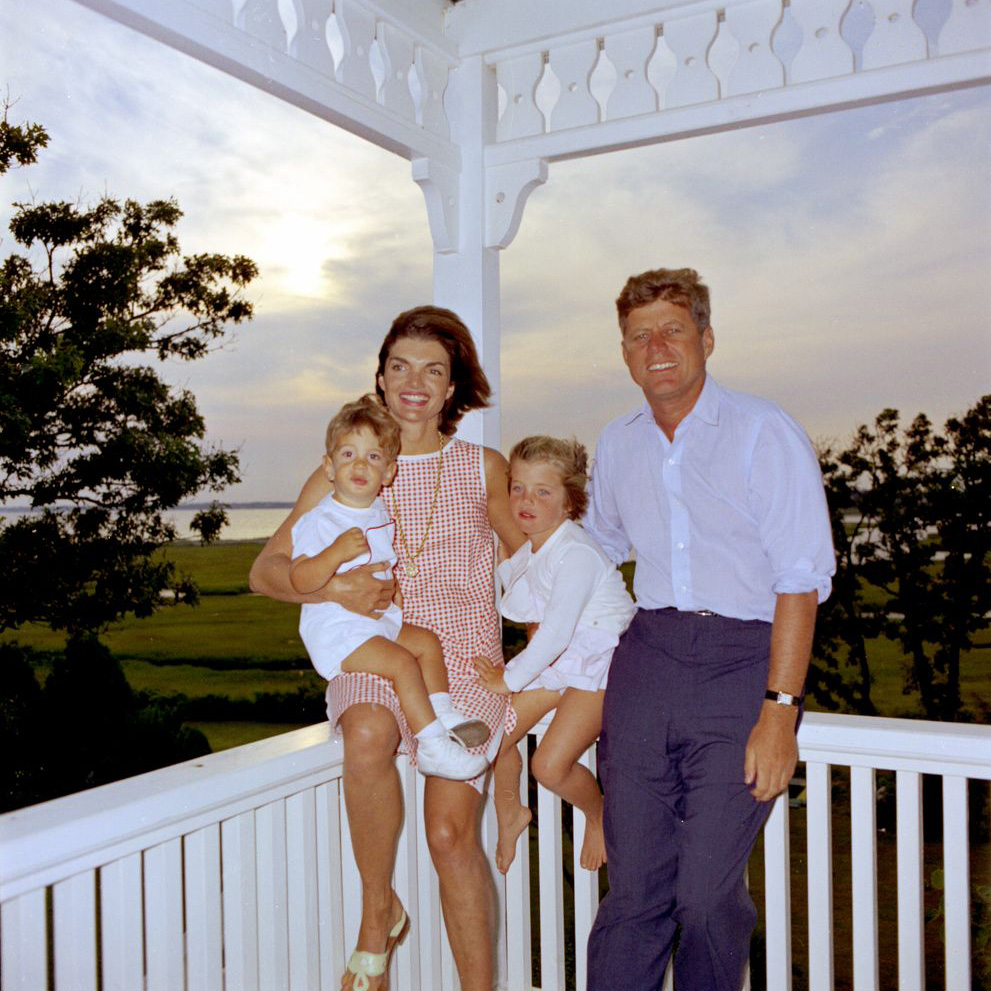

President John F. Kennedy and First Lady Jacqueline Kennedy pose for a portrait with their children, Caroline Kennedy and John F. Kennedy, Jr., on a porch in Hyannis Port, Massachusetts. August 4, 1962. John F. Kennedy Presidential Library & Museum Local Identifier: ST-C22-1-62
World War II changed Kennedy in many ways. He joined the Navy and served in the Pacific, where his PT boat was sunk by a Japanese destroyer. He never forgot his own war experience and the bravery of his Navy crew.
After the war, JFK decided to run for office. In 1946 he won election as congressman for Massachusetts and served for six years. He was elected to the U.S. Senate in 1952. In 1953 he married Jacqueline Bouvier, and their daughter, Caroline, was born in 1957, and their son, John Jr., was born in 1960.
At 43 years old, he became the youngest man elected President of the United States, defeating Richard Nixon in 1960.
One of his first actions after taking office was creating the Peace Corps, which today still sends volunteers on two-year missions to live and work with people around the globe.
The Cuban Missile Crisis in late 1962 threatened the world with possible nuclear war. The United States confronted the Soviet Union over the placement of nuclear weapons on Cuba, and in secret negotiations, Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev agreed to remove the missiles.
Kennedy challenged the U.S. to be the first country to send a man to the moon by the end of the 1960s. The United States reached President Kennedy’s goal on July 20, 1969, when the crew of Apollo 11 landed on the lunar surface.
At home, Kennedy urged an end to racial segregation and asked Congress for a civil rights bill. Before the bill could get through Congress, JFK was assassinated in Dallas, Texas, on November 22, 1963.
People remember John F. Kennedy as a President who was young and energetic. But he is also remembered as a leader who made a difference. His words and actions made people want to help others and serve their country.
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

Bernie Sanders sees red lights flashing for election

Up next for Supreme Court on abortion: Idaho

Historian sees a warning for today in post-Civil War U.S.
Congressman John Fitzgerald Kennedy (circa 1946-47) in his Congressional Office.
Courtesy of John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum, Boston
A portrait of JFK, in full
Brett Milano
Harvard Correspondent
New biography aims to chronicle a complex life amid a pivotal time for a nation
One of the revelations about John F. Kennedy in Fredrik Logevall’s new biography, “JFK: Coming of Age in the American Century, 1917‒1956,” is that the man was an excellent letter-writer and diarist. The Laurence D. Belfer Professor of International Affairs at the Harvard Kennedy School and professor of history makes effective use of the collection at the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library, part of which has become available only recently.
“He always had a knack for the English language, even if he was an indifferent student in prep school and in his first years at Harvard,” Logevall says. “His teachers, frustrated by his lack of application overall, were always impressed by his way with words. It is an interesting contrast with his older brother, Joe Jr., the family’s supposed golden child, whose writings had a more dutiful, less imaginative quality.”
The first of a two-volume set, “JFK” aims to give the clearest picture yet available of the 35th president set against the historical, political, and cultural context of a pivotal age. The book begins with great-grandfather Patrick Kennedy’s arrival in Boston during the Irish potato famine and runs through Jack’s childhood, studies at Harvard, and military duty, and finally his rise in politics in 1956, when he almost became the Democrats’ vice presidential pick. Logevall spoke with the Gazette recently about the man and the book.
Fredrik Logevall
GAZETTE: There have certainly been many books written about JFK. What were you able to find that hadn’t been found before?
LOGEVALL: You’re quite right. There are a lot of excellent books out there on various aspects of his life and career, and especially the presidency — one thinks, for example, about the many studies of the Cuban missile crisis, Civil Rights, the Bay of Pigs disaster, the marriage with Jackie, and the assassination in Dallas. But we don’t have many true biographies, even one that is a full-scale examination of the entire life and that looks closely at his early life, in particular his teens and 20s, which I believe were key years for him (as they are for most of us). Mine is a “life and times” biography that places Kennedy in his own context, that of a rising American power in world affairs. I guess the conceit of the book is that I can tell two stories together: the story of John F. Kennedy’s rise and the story of America’s rise. I believe we can better understand the first half of the so-called American Century through the lens of Kennedy’s life.
Joseph P. Kennedy Jr. (from left), Joseph P. Kennedy Sr., and John F. Kennedy in Southampton, England, July 2, 1938.
Courtesy of John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum
GAZETTE: What did you find that people have missed about JFK in the past?
LOGEVALL: One thing that people have underplayed is the degree to which he was a serious student of democracy and world affairs at an earlier point than we imagine. We tend to think of him as a callow playboy, not serious about public policy or his career until quite late, until he runs for Congress in 1946, and maybe not even then. But you can look at the papers he wrote as an undergraduate at Harvard, some of which are available, and you can look at his senior thesis which became a best-selling book [“Why England Slept”] and see a young man already thinking deeply and in sustained fashion about important issues. A second finding is that the young Jack Kennedy was in important respects his own master. Though his father was a towering force in his life and those of his eight siblings, Jack proved willing and able, to a degree I did not expect, to chart his own course. The Harvard years are interesting in this regard: In 1939‒40, as World War II began and debate raged in the U.S. about how to respond, Jack showed himself willing in a way his older brother, Joe Jr., never was to separate himself from his father. Long before Pearl Harbor, Jack had become an interventionist while his father adhered throughout to a staunch isolationist position. Later, during his political campaigns, Jack always kept the key decision-making role for himself, notwithstanding the common misconception that his father called the shots. [gz_soundcloud title=”John F. Kennedy recording for public speaking class at Harvard, 1937″ track_id=”321147626″ playlists=”” height=”350″ show_artwork=”false”] [/gz_soundcloud]
GAZETTE: Another family relationship we learn more about is with his brother Bobby, and how this became increasingly important.
LOGEVALL: Yes, the age difference between the two brothers was such — 8½ years — that in the early years, when Jack was at prep school and then at Harvard, they weren’t particularly close. But what we see especially in 1951, when they traveled together along with their sister Patricia on an extended tour of the Middle East and Asia, is that they developed a strong bond. Bobby admired his brother to no end, and Jack could now see Bobby’s intelligence and loyalty and good cheer. Then in 1952 Bobby, all of 26 at the time, came aboard to take charge of Jack’s floundering Senate campaign against Henry Cabot Lodge and helped to turn the thing around. Jack could now see just how important Bobby could be to his career, could see the powerful combination of doggedness, shrewdness, and ruthlessness that his brother possessed.
The Kennedy family at Hyannisport, Mass., 1931. Robert (from left), John, Eunice, Jean (on lap of) Joseph P. Kennedy Sr., Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy (behind) Patricia, Kathleen, Joseph, Rosemary.
Photo by Richard Sears, courtesy of the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum
GAZETTE: He was quite a complex character. He did have his playboy side, but some of his war actions can be called heroic.
LOGEVALL: Yeah, I think that is right. There is a seriousness of purpose which you see in his letters home from the South Pacific, and more dramatically in the actions he took to help save his crew after his boat, the PT-109, was rammed by a Japanese destroyer. Was there heroism there? I believe so, even if he deserves no accolades for allowing his boat to be rammed. The efforts he made in the succeeding days to try to save his crew were really quite extraordinary. We might note here as well that he came back from the war, as many of the servicemen did, with a seriousness of purpose evinced to some degree before but deepened as a result of seeing combat. He was convinced that the U.S. would need to play a leading role in world affairs, even as he also had a skepticism about the use of the military’s power that he would carry with him for the rest of his days.
GAZETTE: His coming out against Joseph McCarthy seems to be a bit of a political turning point.
LOGEVALL: Well, he never fully came out in stark opposition, which was a problem. The relationship with McCarthy was complicated, partly because of family ties. He never felt the kind of personal connection to McCarthy that Joe Sr. felt and that Bobby felt. And there were a lot of aspects of McCarthy’s political persona that he found off-putting — the disdain for senatorial good manners, the disregard for facts, for reasoning from evidence. That said, liberals at the time had good reason to be frustrated by JFK’s reluctance to really condemn McCarthy. Even in 1954, when McCarthy’s influence was in decline and the Senate held a censure vote, JFK, recovering in the hospital following a serious surgery, did not instruct his aide Ted Sorensen to register his position on the vote. He could have done so, but he didn’t, and that caused a lot of grief for him with liberals later on. He preferred to sidestep the issue, aware that there were an awful lot of Irish Catholic voters in Massachusetts who still backed McCarthy. He didn’t want to get on their bad side.
A page in Kennedy’s diary from fall 1951. The first part reads: “Oct. 3 — Paris — I talked with General Eisenhower Biddle and MacArthur at SHAEF Headquarters. Eisenhower looking very fit — seemed disturbed at news of last few days.” Lt. Kennedy on board PT 109, July 1943.
Photo by Joel Benjamin (left), courtesy of the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum
GAZETTE: The book deals a lot with the influence of World War II on his character development. Do you think he took a lot from other aspects of American life at the time, including popular culture?
LOGEVALL: To a degree, certainly. When he returned from the war and was figuring out what he wanted to do, he had a fascinating stint as a journalist. He showed good reporting instincts and could have made it a career. In this period he also liked to pal around in Hollywood, where his father had been a movie mogul in the 1920s and still had connections. Jack dated actresses like Gene Tierney and liked to be on the set, liked to go to movies. Popular music I think interested him less, and until Jackie came along he evinced little interest in art. He did like poetry, and he memorized a lot of it starting already in prep school at Choate. But the Hollywood connection is interesting to me, and probably plays some role in his later skill at using images and film to advance his political career. He was among the first politicians to see that images matter, that the right use of film can make a powerful difference. Television was a huge emerging thing as his career builds, and he had that savvy understanding of the medium and how he could use it to his advantage, kind of like FDR used radio so effectively.
GAZETTE: Many of the reviews I’ve read have focused on his womanizing, which we already knew about. Do you think that’s ultimately that important a part of his character?
LOGEVALL: Yes, the womanizing is an important part of who he is. His father led by example, carrying on with innumerable women in the 1920s and 1930s, and the older kids knew very well what was going on. Joe Sr. made clear he expected his sons to follow his ways. But I can’t have it both ways: If I’m going to argue that JFK was able to resist his father’s pressure and be his own man when it came to politics and career choices, I have to maintain that he could have broken with him on this issue too. Here he was his father’s son, with a tendency to see women as objects to be conquered. But there are paradoxes here, among them the fact that his administration took important progressive steps, establishing, for example, the President’s Commission on the Status of Women, with Eleanor Roosevelt as chair. In 1962, at the urging of the commission, Kennedy ordered federal agencies to cease sex discrimination in hiring.
Sen. John Kennedy and his then-fiancée Jacqueline Bouvier in Hyannis Port, Mass.
Photo courtesy of Harvard Fine Arts Library, Digital Images & Slides Collection
GAZETTE: In the second volume you’ll have to unravel the mystery around the assassination. Do you have a sense of how you will approach that?
LOGEVALL: There is certainly a fascination, and it shows few signs of fading. It is a vexing issue to any biographer of JFK, and it has spawned a whole cottage industry of its own. I haven’t yet written Volume 2 so I haven’t fully decided how I will proceed on this. But certainly I will talk about Lee Harvey Oswald’s background, about what led him to take this action, and will give the reader a full sense of how it all culminated in this terrible moment. And I think I will owe the reader my assessment of what I believe happened. So I will provide it. I don’t think I will get heavily into the deliberations of the Warren Commission or the various conspiracy theories that have sprouted up over the years. That’s another book, not to mention a potential morass.
GAZETTE: What do you think happened?
LOGEVALL: My reading of the evidence we have indicates pretty clearly to me that Oswald was the lone gunman. Claims to the contrary all come up short. Oswald’s associations and meetings in the weeks leading up to the assassination are worthy of investigation, however, and have been examined in recent studies. I will delve into that material and be interested to see what I find.
Interview was lightly edited for clarity and length.
Share this article
More like this.

JFK speaks from his Harvard past

A room fit for a president

Thoughts on JFK at 100
You might like.
Vermont senator warns of growing income, wealth, and political inequality

Justices to hear case on near-complete ban amid shifting legal landscape after overturn of Roe

Past is present at Warren Center symposium featuring scholars from Harvard, Emory, UConn, and University of Cambridge
Harvard announces return to required testing
Leading researchers cite strong evidence that testing expands opportunity
When will patients see personalized cancer vaccines?
Sooner than you may think, says researcher who recently won Sjöberg Prize for pioneering work in field
Finding right mix on campus speech policies
Legal, political scholars discuss balancing personal safety, constitutional rights, academic freedom amid roiling protests, cultural shifts
My Journey Through the Best Presidential Biographies

The Best Biographies of John F. Kennedy
31 Thursday Aug 2017
Posted by Steve in Best Biographies Posts , President #35 - J Kennedy
≈ 35 Comments
American history , Arthur Schlesinger Jr. , book reviews , Doris Kearns Goodwin , Geoffrey Perret , Herbert Parmet , JFK , John F Kennedy , Michael O'Brien , Nigel Hamilton , Pulitzer Prize , Richard Reeves , Robert Dallek , Ted Sorensen , Thomas Reeves , Thurston Clarke

In the end, JFK proved to be everything I hoped for – and more! Like several of the presidents who preceded him, Kennedy’s life is a biographer’s dream .
His forebears were dynamic, endlessly fascinating, occasionally unscrupulous and, from time to time, oddly dysfunctional. Kennedy himself proved to be no less interesting: he was medically infirm, an ardent bookworm, a serial philanderer, often ruthlessly pragmatic and extremely charismatic.
But after spending five-and-a-half months with JFK and experiencing his presidency nine times (three of the books did not cover his time in the Oval Office) I still find Kennedy undeservedly well-ranked by historians. But that’s a subject for another day.
* “ An Unfinished Life: JFK 1917-1963 ” by Robert Dallek (published 2003) – This comprehensive biography was the first book on JFK that I read. It also proved to be my favorite. Dallek provides a devastating early indictment of JFK’s personal behavior, but more than half of the book is reserved for Kennedy’s presidency where his personal affairs take a back seat to the nation’s issues. Overall, Dallek’s biography provides the best combination of insight, balance and color of any of the JFK biographies I encountered — 4¼ stars ( Full review here )
* “ JFK: Reckless Youth ” by Nigel Hamilton (1992) – This was intended to be the first book in a three-volume series but as a result of his “unflattering” portrayal of the Kennedy family Hamilton lost access to important research documents and, regrettably, abandoned the series. This lively 800-page narrative is riveting and provides unparalleled insight into JFK’s relationships with his older brother and his parents (who are painted in an extremely unflattering light). No other biography I read covers Kennedy’s early life better than this volume — 3¾ stars ( Full review here )
* “ Kennedy: The Classic Biography ” by Ted Sorensen (1965) – Written by Kennedy’s long-time adviser and speechwriter, the author’s proximity to JFK proves both a blessing and a curse. Sorensen’s allegiance to Kennedy is quickly obvious – and occasionally distracting – but the narrative covers events from a unique perspective. But in the end it does not provide balanced, comprehensive coverage of JFK and can only serve as the eloquent observations of a staunchly loyal aide — 3½ stars ( Full review here )
* “ John F. Kennedy: A Biography ” by Michael O’Brien (2005) – This 905-page biography is encyclopedic and provides more detail (and more perspectives) on most events than any other JFK biography. But while it is 200 pages longer than Dallek’s biography (its most comparable counterpart) it is no more potent…and its numerous nuggets of wisdom are buried beneath an avalanche of unnecessary verbosity — 3½ stars ( Full review here )
* “ Jack: A Life Like No Other ” by Geoffrey Perret (2001) – This full-scale (but lightweight, at just 400 pages) biography is easy to read and decidedly informal. Unfortunately, it also provides less insight or analysis of Kennedy than most other biographies. And while readers new to JFK may appreciate its lack of “complexity” almost everyone else will finish this biography still feeling hungry — 3 stars ( Full review here )
* “ A Question of Character: A Life of John F. Kennedy ” by Thomas Reeves (1991) – This study quickly proves to be a captivating, but flawed, critique of its subject. Devoted to exposing the hypocrisy hidden beneath Camelot’s polished veneer, it feels more bluntly partisan, and less scholarly, than Nigel Hamilton’s somewhat similar “JFK: Reckless Youth.” But where Hamilton covers three decades in about 900 pages, Reeves covers JFK’s entire life in just half of that — 3 stars ( Full review here )
* “ Jack: The Struggles of John F. Kennedy ” and “ JFK: The Presidency of John F. Kennedy ” by Herbert Parmet – This two-volume series was published between 1980 and 1983 and totals nearly 900 pages (excluding notes and bibliography). Offering a thoughtful and balanced perspective on Kennedy, this series is serious, scholarly and solid. But where it was the “go to” reference on Kennedy for years, documents which have become available since its publication have left it somewhat stale. Parmet’s writing style also leaves JFK and his family feeling a bit flat and lifeless. Imagine that ! — 3½ star (Full reviews here and here )
* “ The Fitzgeralds and the Kennedys ” by Doris Kearns Goodwin (1987) – This non-traditional biography of JFK is actually a family history which ends with a focus on John F. Kennedy – but only up to his presidential inauguration. Despite its heft (943 pages) it is engrossing, clever and insightful. Unfortunately it also left Goodwin embroiled in a plagiarism scandal. But for readers unconcerned with the author’s failure to adequately cite sources – or her awkward effort to conceal her sins – it is a wickedly entertaining and perceptive (if too friendly) treatment of Honey Fitz, Rose Kennedy and Joseph P. Kennedy. The book does not end as strongly as it starts and the weakest player (ironically) is JFK himself who receives less focus than he deserves — 4½ stars ( Full review here )
* “ A Thousand Days: JFK in the White House ” by Arthur Schlesinger Jr. (1965) – This Pulitzer Prize-winning tome (with 1,031 pages) is part memoir, part biography and part interpretive history with a nearly exclusive focus on the Kennedy presidency. The author served as Special Assistant to President Kennedy, providing him an advantageous perch from which to view JFK’s presidency. Schlesinger’s reputation as a historian is unquestioned, but his book proves dense, dry and often tedious – as well as uneven in emphasis and highly sympathetic to Kennedy. A classic, perhaps, but not a balanced account of the Kennedy presidency — 3 stars ( Full review here )
* “ President Kennedy: Profile of Power ” by Richard Reeves (1993) – This unique (and extraordinarily revealing) book follows JFK almost moment-by-moment through his presidency. But where most biographies are written from the point of view of the biographer , Reeves’s audience often views the world through Kennedy’s own eyes. Unfortunately missing from the book is much insight on Kennedy’s family and friends, and there is little analysis to be found. But for a unique point of view, and as a supplemental book on JFK, “Profile of Power” is hard to beat — 3¾ stars ( Full review here )
* “ JFK’s Last Hundred Days: The Transformation of a Man and the Emergence of a Great President ” by Thurston Clarke (2013) – Ostensibly focused on the last weeks of Kennedy’s life, this book is more comprehensive than its title suggests. Almost continuously throughout its 362 pages it reaches back in time to Kennedy’s past in order to provide unfamiliar readers with adequate context. The resulting lack of continuity, however, is perhaps the book’s greatest weakness. Most confounding, however, is the book’s failure (despite its sub-title) to demonstrate that Kennedy was on the verge of greatness when he was assassinated. Otherwise, a stimulating and enjoyable read — 3½ stars ( Full review here )
Best Biography of John F. Kennedy: “ An Unfinished Life: JFK 1917-1963 ” by Robert Dallek
Honorable Mention: “ JFK: Reckless Youth ” by Nigel Hamilton (though “incomplete”)
Share this:
35 thoughts on “the best biographies of john f. kennedy”.
August 31, 2017 at 2:55 pm
I find it interesting with all that’s been written about him, only one book was rated at 4 stars+. Looking forward to LBJ!
August 31, 2017 at 5:05 pm
Yes, that was slightly disappointing. Other than Dallek’s biography, each book I read was either too narrowly focused for a 4+ rating or was disappointing in some meaningful way. The benefit to reading several biographies (particularly in the case of JFK) is that they tended to complement each other – one making up for another’s weakness, etc.
August 31, 2017 at 5:40 pm
Enjoy your LBJ reads! Robert Caro’s series is fanastic! LBJ is fascinating! Much better books on him than on JFK in my opinion. I agree with you on JFK- his high ranking by many not deserved. Middle of the pack.
September 1, 2017 at 4:45 am
As a native Texan with no direct memory of LBJ I can’t wait to get through his life. I’m saving Caro for a few weeks so I’ll savor the moment(s) a bit more…but when I started with Washington I was really hoping Volume 5 would be out by the time I got to this point(!)
September 1, 2017 at 8:09 am
I am eagerly awaiting for Volume 5- the final volume– too. You have Johnson and Nixon coming up- a lot of good stuff on both of them. Great project!
August 31, 2017 at 7:02 pm
He’s overrated as president, but seems to be an interesting biography subject!
September 1, 2017 at 4:43 am
Indeed – an absolutely fascinating biographical subject! So I was a little surprised the biographies of him weren’t more consistently excellent.
But it seems that in the decades since his death many biographers have dedicated themselves either to tearing apart the Camelot “myth” or excessively praising/eulogizing him.
Can’t wait to see how LBJ turns out!
September 1, 2017 at 10:53 am
I’m amazed one if the top-5 biographers didn’t write on him considering his fame. I don’t care for LBJ as a president at all, but I look forward to your analysis of his biographies!
August 26, 2018 at 12:45 pm
Would the biographies on Kennedy By Michael O’Brien or Robert Dallek be what you would call a good starter birth to death biography on Kennedy if you haven’t read on him before?
August 26, 2018 at 12:57 pm
Yes – though I think Dallek’s book is by far the better (more interesting and efficient) choice. Good luck and enjoy!
September 4, 2018 at 3:33 pm
Would like to do a critical comparison of two biographies on JFK – what two would you recommend?
September 5, 2018 at 6:11 pm
Depending on what, exactly, you mean by “critical comparison” I would heartily recommend reading Dallek’s relatively traditional “An Unfinished Life” and comparing it to Goodwins’s “The Fitzgeralds and the Kennedys” which is somewhat less focused on JFK himself and more on his family – but he obviously plays a critical part in the narrative and is the emotional center of the book.
September 6, 2018 at 5:57 am
Thanks – by “critical comparison” I mean one that looks at JFK in a positive view and another in a negative view.
September 6, 2018 at 6:05 am
In that case I might suggest Ted Sorensen’s “Kennedy” as a favorable account of JFK and compare that portrait to the one provided by Nigel Hamilton’s “Reckless Youth.” I think you will find the contrast incredible.
Unfortunately the two books don’t cover the same periods of time with the same intensity (Sorensen spends much more time in JFK’s later life while Hamilton’s book focuses on his earlier years) but from what I recall, the image presented by these two books could almost be of a different person.
January 13, 2019 at 6:37 am
I agree with your statement, “I still find Kennedy undeservedly well-ranked by historians. But that’s a subject for another day.” His legacy made him an outstanding president only after his death. There is very little of consequence that came from his term in office.
January 12, 2023 at 10:51 am
(1) The U.S. was in recession when Kennedy took office. He carried out various measures to boost the economy under his own executive anti-recessionary acceleration program. Among other things, the most significant tax reforms since the New Deal were carried out including a new investment tax credit. GDP which had grown by an average of only 2.2% per annum during his predecessor Eisenhower’s presidency, expanded by an average of 5.5% from early 1961 to late 1963, when Kennedy was assassinated. Also inflation remained steady at around 1%, industrial production rose by 15% and unemployment decreased. This rate of growth continued till 1969 and hasn’t been repeated for such a sustained period yet.
(2) JFK established the Peace Corps on March 1, 1961 by Executive Order 10924.
(3) He stood up to the Soviet Union, forcing/negotiating the dismantling and removal of its nuclear weapons in Cuba.
(4) To slow down the nuclear arms race and to protect the environment from radioactive contamination, JFK began negotiations with Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev for a treaty to address these concerns. This resulted in the Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty which was signed by the governments of U.S.S.R., U.K. and the U.S. in Moscow on August 5, 1963. The provisions of the treaty prohibited nuclear testing on the ground, in the atmosphere, or underwater. All testing was to be driven underground. 125 UN member states have ratified or acceded to the treaty since then.
(5) His domestic program the “New Frontier” provided aid to cities to improve housing and transportation; a water pollution control act was passed to protect rivers and streams; social security benefits and minimum wage increased; and the most comprehensive legislation to assist farmers was carried out since 1938 which included expansion in rural electrification, soil conservation, crop insurance and farm credit.
(6) On March 6, 1961, he signed Executive Order 10925 which required government contractors to take affirmative action to ensure all employees are treated equally irrespective of their race, creed, color, or national origin. His Executive Order 11063 of November 1962 banned segregation in federally funded housing. On June 11, 1963, JFK gave his famous civil rights address calling Americans to recognize civil rights as a moral cause. His proposal to provide equal access to public schools and other facilities, and greater protection of voting rights became part of the landmark Civil Rights Act of 1964.
(7) On 10th June 1963, John F. Kennedy signed into law the Equal Pay Act of 1963 to abolish wage disparity based on sex. It amended the existing Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938. EPA was a major step towards closing the wage gap in women’s pay. Although EPA’s equal pay for equal work goals have not been completely achieved, women’s salaries via-à-vis men’s have risen dramatically since its enactment. JFK also proposed an overhaul of American immigration policy that would later lead to the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965 that abolished the quota system based on national origins with a preference system that focused on the immigrant’s skills and family relationships with US citizens.
(8) On June 10, 1963, President John F. Kennedy federalized National Guard troops and deployed them to the University of Alabama to force its desegregation. The next day, Governor Wallace yielded to the federal pressure, and two African American students—Vivian Malone and James A. Hood—successfully enrolled. In September of the same year, Wallace again attempted to block the desegregation of an Alabama public school—this time Tuskegee High School—but President Kennedy once again employed his executive authority and federalized National Guard troops. Wallace had little choice but to yield.
(9) Kennedy was an unparalleled advocate of the US Army Special Forces (i.e. the Green Berets). During JFK’s tenure as president, the Special Forces regiment grew by seven Special Forces groups. Not long after a visit to Fort Bragg in 1961 with then-Special Forces commander, Brig. Gen. William P. Yarborough, Kennedy authorized the Green Beret as the official headgear of the U.S. Army Special Forces. Today, Special Forces Soldiers still train at the school which bears his name: the United States Army John F. Kennedy Special Warfare Center and School.
Was he perfect? Hell, no. He made plenty of mistakes, both large and small. But he had a better aim than most of the lesser ‘men’ that succeeded him.
— a former US Army parachute infantryman (three tours of the sandbox) raised on a West Texas ranch, a former federal law enforcement national security special investigator with a BA in American Political Thought, a current CPA with an MS in Accountancy, and the grandson of Continental, Union and Allied Army soldiers
January 13, 2023 at 6:25 am
If you know the whole story about # 3, you would not include it. #’s 6 & 7 still are not totally used today, but have to be sued for. # 9, special forces had been trained since WWII, he merely gave them a name.
March 5, 2019 at 9:46 pm
I have to admit I haven’t been as fascinated by JFK as many others. So, in my own journey through the presidents, I chose Alan Brinkley’s biography for the American Presidents series. This series has been my go to for presidents lacking great bios or those I just wanted to “get through.” They’re all around 160 pages, often providing factual discussions that let you know what happened to the guy in his life—and little more. They are, in other words … OK.
I felt Brinkley’s book, however, was quite good. It’s portrait of JFK goes beyond factual recitation and was exceedingly well balanced. I now see JFK as admirable in some ways, far from admirable in others, and even have some understanding of how _others_ are partly responsible for the mixed views in which we hold him.
A cut above other entries in the Amer. Presidents series.
September 18, 2020 at 4:36 pm
Early reviews are encouraging:
September 19, 2020 at 5:09 pm
Indeed, everything I’ve read and heard has been positive. Can’t wait to read this one and see for myself. Trying to figure out when exactly to squeeze it in since I’m hoping my next presidential biography will be the “coming soon” biography of Jimmy Carter.
September 19, 2020 at 8:43 pm
I am also looking forward to Alter’s Carter biography. It should be the best available to date given his access to Carter. I am hoping Douglas Brinkley is willing and able to revisit Carter in the future.
January 17, 2023 at 6:14 pm
It is quite good, and the author is in the process of working on Part 2 – 1957-1963.
January 11, 2021 at 5:52 am
https://www.goodreads.com/book/show/112469.Robert_Kennedy
If you haven’t already read it, I highly recommend this biography of Bobby Kennedy by Evan Thomas.
January 11, 2021 at 8:56 am
Thanks for the suggestion. I’m exploring a couple of titles on Robert Kennedy and this is one of them! Glad to hear you liked it so much.
June 9, 2021 at 11:41 am
The independent publisher I work for is about to release a book written by one of JFK’s long-time friends about his relationship with JFK over the years. Of course it will be available on Amazon but we’re happy to send you a promo copy if you are interested?
June 9, 2021 at 2:21 pm
As a standard practice I don’t ask for or review books I haven’t purchased…but can you confirm this book is on my Upcoming Releases page? If not it sounds like it should appear there-
June 9, 2021 at 2:42 pm
Can you please let me know what you need from me to list it on your upcoming releases page? It will likely be a late June or early July release. Thanks! Michelle
June 9, 2021 at 2:52 pm
Title, author’s name, and publication date would be great. A link to publisher’s page on the book (or Amazon’s pre-publication page for the book, if there is one) would be a bonus.
June 9, 2021 at 4:01 pm
Thanks, Steve. I just now sent you an email with the details.
March 28, 2022 at 5:09 pm
I am truly surprised there is no mention of Red Faye’s “The Pleasure of His Company” a book loved by those who knew the individuals involved.
March 29, 2022 at 4:17 am
Are you surprised it isn’t mentioned because you think it’s a really good biography or because it was written by one of JFK’s friends who doesn’t work too hard to cover him fully, warts and all? (The whole thing is something like 150 pages?) Just curious
July 16, 2023 at 7:46 pm
I spoke with a friend and comrade of Joe Jr. He and others like him revere this book and its loving portrayal of JFK. They believe it captured the man like nothing else. Scholarship is a wonderful thing, but a heart felt appreciation is incredibly enjoyable and valuable.
December 22, 2022 at 10:37 am
Here is the review of another one, released in 2022. You may want to reconsider his rank, I’m biased because I have him #1 out of 45. Why? Because I am still here to write this comment and you are still here to post your blog. https://www.kennedysandking.com/john-f-kennedy-articles/last-president
March 2, 2023 at 5:40 am
I find it interesting you say Kennedy is “undeservedly well-ranked among historians” I find it quite the opposite, he’s extremely popular amongst the general public, but most historians rip into him far too much. I’ve recently been reading about Canadian-American bilateral relations and the general narrative of most historians of the 70s to 90s was that negative tensions amongst the two nations was largely Kennedy’s fault. It’s only recently that the love-to-hate-JFK tide has curbed amongst historians that, in the 2000s, there is more discussion regarding Canadian nationalism, anti-american sentiments, and more importantly the fact that Deifenbaker attempted to blackmail Kennedy, and then blamed JFK and American intervention after he lost his election in 63.
Reading the older historical accounts is such a whirlwind. Multiple historians accused Kennedy of being “arrogant” and one even said “who’s posture towards deifenbaker’s canada was that of a president stretching his legs across the border demanding a shoe shine” which is beyond ridiculous considering he actually showed a great deal of patience towards a highly nationalist prime minister that attempted to blame and blackmail him. Historians made the cat the mouse and made the mouse the cat. Madness
December 26, 2023 at 11:49 pm
Has anyone read the kennedys by Horowitz and collier to provide some insight or the kennedys by John h. Davis?thanks
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
U.S. Presidents
John f. kennedy.
35th president of the United States
John F. Kennedy, the second oldest of nine children, was born in Brookline, Massachusetts , on May 29, 1917. His father hoped that one of his children would one day become president. As a child, Kennedy had many childhood illnesses and once almost died from scarlet fever. But he grew up to be athletic and competitive, playing football for Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts. He injured his spine in college and never fully recovered from the injury.
In 1943, a Japanese warship destroyed a boat Kennedy commanded while serving in the U.S. Navy during World War II. Kennedy swam with the surviving crew members to safety several miles away, carrying one injured sailor by pulling the man’s life jacket strap by his teeth. When asked later how he became a hero, Kennedy replied: "It was easy—they sank my boat." Now a decorated World War II officer, Kennedy took up his father’s presidential hopes after his older brother, Joseph, died in combat.
Before being elected president, Kennedy represented Massachusetts in the House of Representatives and in the U.S. Senate. He married Jacqueline Bouvier in 1953, soon after he became a senator. In 1960, he was elected president of the United States by the narrowest popular voting margin in history, becoming the youngest person and the only Catholic to ever be elected president.
COLD WAR CONFLICTS
The Cold War—a period of tensions mostly between the United States and the former Soviet Union, now called Russia —dominated much of Kennedy’s presidency. First, the U.S. government secretly tried to overthrow the island of Cuba’s new leader and Soviet Union ally, Fidel Castro, in a failed mission known as the Bay of Pigs. Then the Soviet Union built a wall in Germany , dividing East Berlin, which was under control of communist Soviet Union, and West Berlin, which was supported by the democratic West. This angered Germans on both sides of the wall and citizens of nearby countries. Kennedy visited West Berlin and vowed U.S. support to the people there, stating: " Ich bin ein Berliner, " or "I am a Berliner" in German.
Cold War tensions cooled off in 1963 after the two nations signed a treaty, but the conflict would last until around 1990.
FIGHTING FOR CIVIL RIGHTS
Another issue Kennedy dealt with during his presidency was civil rights, or the idea that all U.S. citizens should have the same basic rights regardless of the color of their skin, and their religion. Kennedy wanted to pass more laws that would guarantee equal rights for all citizens.
Before Kennedy became president, the Supreme Court passed a ruling in the case of Brown v. Board of Education that schools had to desegregate, or allow white and black children to attend the same school. Kennedy publicly supported the ruling and even sent military troops to the southern states to make sure African-American kids were getting safely to school.
Near the end of Kennedy’s time in office in 1963, more than 200,000 people took part in a March on Washington during the 100th anniversary of Abraham Lincoln ’s Emancipation Proclamation speech. Civil rights leader Martin Luther King, Jr. , delivered his famous "I Have a Dream" speech from the steps of the Lincoln Memorial during the gathering.
DEATH IN DALLAS
Kennedy had only been president for a little less than three years when he was assassinated on November 22, 1963, while touring Dallas, Texas , in a presidential motorcade. Gunman Lee Harvey Oswald was charged with the death but was killed himself before he could be put on trial.
More than a hundred nations sent representatives to Kennedy’s funeral in Washington, D.C. Although he was only president for a short time, his calls for peace, justice, and national service—JFK famously said "Ask not what your country can do for you; ask what you can do for your country" when he first became president in 1961—inspired action among countless citizens during his lifetime and continue to influence others today.
• Kennedy supposedly wrote his own spy book, but he never released it.
• During stressful meetings, Kennedy liked to doodle sailboats.
• JFK donated his entire presidential salary to charity.
From the Nat Geo Kids books Our Country's Presidents by Ann Bausum and Weird But True Know-It-All: U.S. Presidents by Brianna Dumont, revised for digital by Avery Hurt
Explore more
(ad) "weird but true know-it-all: u.s. presidents", independence day, (ad) "our country's presidents".
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your California Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell My Info
- National Geographic
- National Geographic Education
- Shop Nat Geo
- Customer Service
- Manage Your Subscription
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
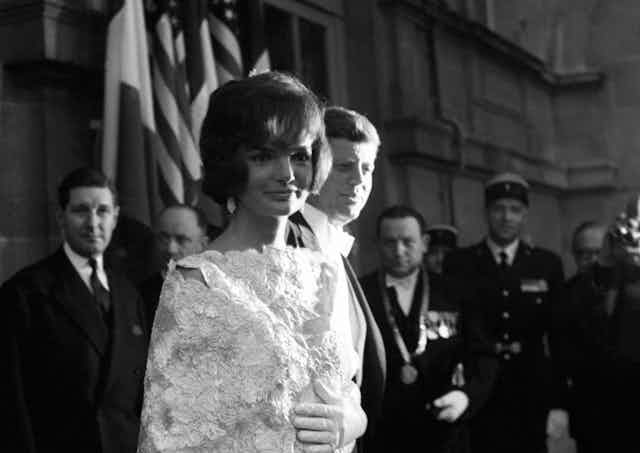

The unfinished business of John F. Kennedy’s vision for world peace
Adjunct Assistant Professor of History, Quinnipiac University
Disclosure statement
Philip A. Goduti, Jr. does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Quinnipiac University provides funding as a member of The Conversation US.
View all partners
Less than a week after her husband’s assassination in Dallas on Nov. 22, 1963, Jackie Kennedy granted an interview with esteemed political writer Theodore White for Life magazine, one of the leading national publications of its day.
Determined to protect the legacy of the fallen president, Jackie likened the unfulfilled promise of his short-lived administration to the mythical days of King Arthur’s court as portrayed in “ Camelot ,” a popular Broadway musical at the time and one of Kennedy’s favorites.
“Don’t let it be forgot,” Kennedy told White, “that for one brief, shining moment there was Camelot.”
Though historians have since revealed many of Kennedy’s shortcomings , one fact is undeniable. From his 1960 campaign against Richard Nixon to his little more than 1,000 days as president, Kennedy’s boldness defined the times.
In my view as a scholar of Kennedy’s life, he set the modern-day standard for public service that is all but absent in the 2024 presidential election dominated by the legal woes of Donald Trump and the age of 81-year-old President Joe Biden .
Kennedy’s lofty rhetoric, coupled with his energetic youth, propelled the nation into what he termed the “ New Frontier ,” the campaign slogan he used to inspire ordinary citizens to make the world a better place at a time of Cold War nuclear tensions between the U.S. and the Soviet Union.
“Let us begin anew … remembering on both sides that civility is not a sign of weakness, and sincerity is always subject to proof,” Kennedy said during his inaugural address in 1961. “Let us never negotiate out of fear. But let us never fear to negotiate.”
Decorated war hero
Part of the Camelot myth starts with Kennedy’s military service during World War II.
Due to a myriad of illnesses, Kennedy was deemed unfit to join the U.S. Army and was able to serve in the Navy only after his father, the wealthy businessman Joseph Kennedy who was U.S. ambassador to Great Britain during the early war years, intervened on his behalf. Shortly after joining the Navy, Kennedy became commander of a patrol torpedo boat stationed near the Solomon Islands in the southwestern Pacific Ocean.

On Aug. 2, 1943, a Japanese destroyer rammed his boat and sliced it in half, immediately killing two of his men. Kennedy later told an interviewer that when he saw the destroyer pass in front of him he thought, “This is how it feels to be killed.”
The 26-year-old Kennedy led his crew of 11 survivors on a 3-mile swim while towing a badly burned crew member to safety by holding a strap of a life vest between his teeth.
After several days of hiding on an uninhabited island with very little food and water, he was able to get help by etching a message on a coconut that was given to two Solomon Islanders who were patrolling the area in a canoe for Allied forces. They brought the message to a nearby British base, and Kennedy and his men were subsequently rescued.
Once safe, Kennedy sent a note home to his family saying that many people thought they were dead, but “fortunately they misjudged the durability of a Kennedy.”
Kennedy received a Purple Heart medal for being wounded in combat and remains the only U.S. president to receive the honor. JFK also earned the Navy and Marine Corps Medal for his “extremely heroic conduct” after his boat was sunk.
That coconut was later set on a wooden base and used as a paper weight on Kennedy’s desk after his narrow victory over Republican Richard M. Nixon in the 1960 presidential election .
Baptism by fire
Even though he stumbled in his first year as president, Kennedy learned, made changes and initiated bold measures such as a moral stand on civil rights and a plan for peace with the Soviet Union.
Kennedy’s first major blunder was the Bay of Pigs fiasco. Troubled by Cuban leader Fidel Castro and his relationship with Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev , Kennedy approved a U.S. invasion of the Caribbean island by using about 1,400 CIA-trained Cuban exiles who also wanted to overthrow Castro. The attempted coup was launched on April 17, 1961, and was defeated in less than two days by Cuban armed forces.
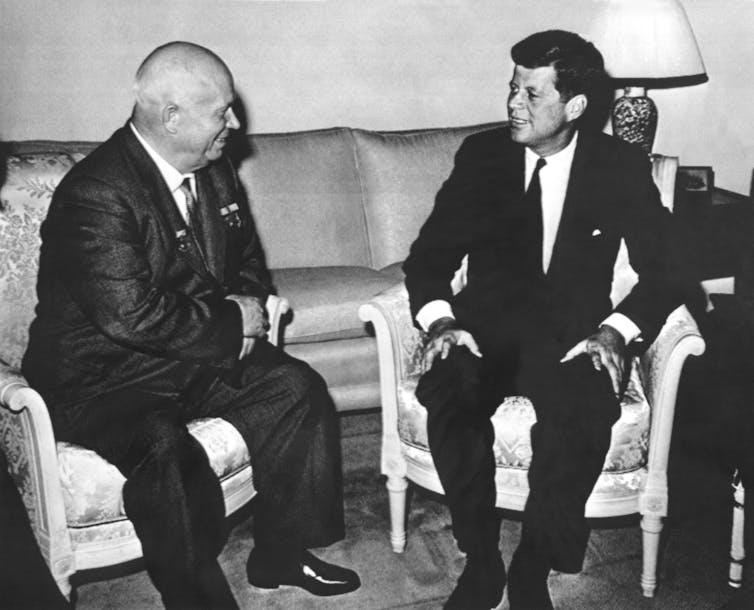

The botched invasion led Khrushchev to believe that Kennedy was young, naive and weak. That line of thinking played out two months later at the Vienna summit , where the Soviet leader demanded the removal of U.S. troops from West Berlin.
Kennedy refused, but Khrushchev retaliated by starting construction of the Berlin Wall , which became the symbol of the Cold War divisions between Western European democracies and Eastern European countries controlled by communist governments.
An unfulfilled legacy
Kennedy was a Cold Warrior, but he was also a realist.
In October 1962, Kennedy learned that the Soviet Union had placed missiles in Cuba that could strike the U.S. Kennedy’s advisers urged him to invade Cuba, this time using U.S. military forces.
On the brink of nuclear war, Kennedy ignored his advisers and enacted a naval blockade around Cuba to prevent the Soviet Union from shipping any more military supplies to Castro. It was a bold move that went against Cold War orthodoxy, which would have called for a stronger response to Khrushchev’s actions. Instead, the crisis made it clear that both sides feared nuclear retaliation from the other.
Eight months later, on June 11, 1963 , Kennedy gave a speech at American University that proposed peace with the Soviet Union.
“I am talking about genuine peace, the kind of peace that makes life on earth worth living,” he told the crowd. “For, in the final analysis, our most basic common link is that we all inhabit this small planet. We all breathe the same air. We all cherish our children’s future. And we are all mortal.”
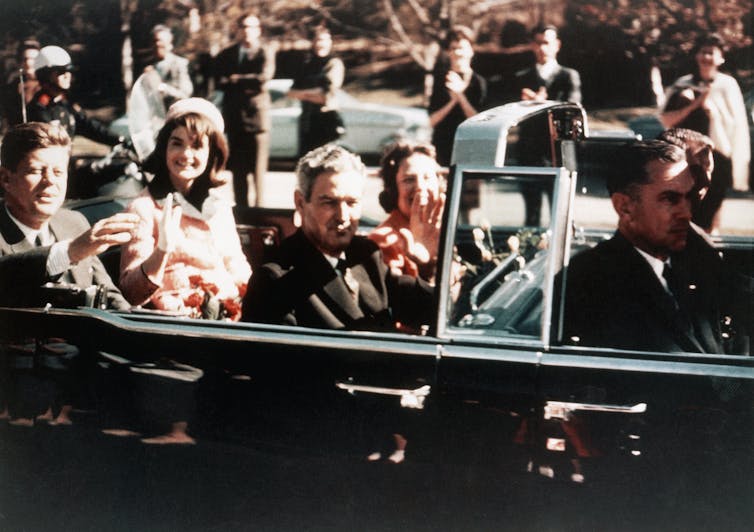

In my view, this speech is perhaps his greatest legacy, because it stressed that peace was a process and led to a limited nuclear test ban treaty . Signed in 1963 by the U.S., Great Britain and the Soviet Union, the agreement prohibited tests of nuclear weapons in the atmosphere, outer space and underwater.
It also put Kennedy and Khrushchev on a path to end Cold War tensions between the two superpowers. Those negotiations came to an abrupt halt after Kennedy’s assassination. The Cold War lasted for another 30 years until Nov. 9, 1989, when the Berlin Wall was torn down and communist regimes in Eastern Europe were booted out after free elections.
He served only 1,036 days as president, and much like the myth of Camelot, Kennedy’s legacy remains an unfulfilled dream for peace around the world.
- Nuclear weapons
- Public service
- Cuban Missile Crisis
- Nikita Kruschev
- Berlin Wall
- Bay of Pigs
- Jackie Kennedy

Deputy Social Media Producer

Research Fellow /Senior Research Fellow – Implementation Science

Associate Professor, Occupational Therapy

GRAINS RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION CHAIRPERSON

Faculty of Law - Academic Appointment Opportunities
Meet Jack Schlossberg, John F. Kennedy's 31-year-old grandson who was rumored to be dating Selena Gomez
- Jack Kennedy Schlossberg , 31, is the grandson of John F. Kennedy and the son of Caroline Kennedy.
Schlossberg is on track to follow the family tradition of becoming a lawyer.
- He's also shown that he has a sense of humor and is an avid paddleboarder.

There's a new Kennedy in town.
Jack Kennedy Schlossberg is the 31-year-old grandson of President John F. Kennedy and the son of Caroline Kennedy.
He was recently the subject of internet rumors claiming he dated pop singer Selena Gomez, 31, between 2020 and 2021.
"Never met this human sorry," Gomez, who is dating music producer Benny Blanco , commented on a post shared by a fan-made Instagram account.
Despite being known as a member of one of America's most iconic political families, Schlossberg has asserted he has no plans to enter a race of his own. However, he's already making a name for himself.
Here's what you need to know about Jack Schlossberg.
John "Jack" Bouvier Kennedy Schlossberg is the 31-year-old grandson of President John F. Kennedy and the son of Caroline Kennedy.
He was named for his maternal grandfather, John F. Kennedy, and his maternal great-grandfather, John Vernou Bouvier III.
He is the youngest child of Caroline Kennedy and designer Edwin Schlossberg, who have been married since 1986.
Kennedy came from an Irish-Catholic background, while Edwin Schlossberg was raised Jewish.
Jack Schlossberg was born in New York City on January 19, 1993.
In 2011, he graduated from The Collegiate School, a prestigious all-boys private school on the Upper West Side of Manhattan.
Caroline Kennedy and Edwin Schlossberg share two other children besides Jack: Tatiana Schlossberg, 33, and Rose Schlossberg, 35.
Schlossberg is the lone grandson of John F. Kennedy and Jacqueline Kennedy and the eldest surviving male descendant of the former president's immediate family.
Rose and Tatiana Schlossberg are both married, but Jack appears to be single.
When appearing on the "Today" show in 2022, Schlossberg shared that his sister Tatiana had recently welcomed a son named Edwin, after their father. Schlossberg also said he'd moved back to his "childhood bedroom" to be closer to his family after graduating from Harvard.
He bears a striking resemblance to his maternal uncle, John F. Kennedy Jr., who died in a plane crash in 1999.
John F. Kennedy Jr. died after an aircraft he was piloting crashed off the coast of Martha's Vineyard, Massachusetts, on July 16, 1999. His wife, Carolyn Bessette Kennedy, and her sister Lauren Bessette also perished in the accident.
The couple did not have any children together, so there were no surviving Kennedy heirs through Kennedy Jr.
After Schlossberg graduated from Yale University in 2015 with a history degree, he entered Harvard Law School in the fall of 2017 and Harvard Business School in the fall of 2018.
"I'm inspired by my family's legacy of public service," Schlossberg said in his first live interview on "Today" in 2017. "It's something that I'm very proud of."
He graduated from the university in 2022, and in April 2023 he shared that he had passed the New York State bar exam.
His mother, Caroline, passed the same bar exam in 1989. According to People , his uncle John F. Kennedy Jr. famously failed the New York bar exam twice before ultimately passing on his third try in 1990.
He appears to share his family's interest in politics and civic justice.
"I'm still trying to make my own way, figure things out, so stay tuned. I don't know what I'm going to do," he told "Today" in 2017. He again told Savannah Guthrie in 2022 that he had "no plans" to enter politics at the moment.
While he hasn't committed to a career in politics just yet, Schlossberg has taken an increasingly public role with the family's Profile in Courage Awards , which honors world leaders, and the John F. Kennedy Library Foundation.
According to People , Schlossberg has also worked as a Senate page and intern for former Secretary of State John Kerry.
Schlossberg spoke at the 2020 Democratic National Convention as a representative of his family and has appeared with his mother at many public events. In December 2022, the Harvard graduate was pictured alongside his mother and sister Tatiana meeting with Prince William at the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum.
Schlossberg has become the face of a new generation of Kennedys.
Schlossberg boasts over 101,000 followers on Instagram , where he often shares photos and videos related to his paddleboarding hobby.
He's also shown that he has a sense of humor. In July 2023, a series of light-hearted videos Schlossberg posted to Instagram about the downsides of eating at restaurants went viral .
"We have to wait there to eat something that we don't get to choose, really, what it is," Schlossberg said to the camera in one video. "We only get a few choices and you don't know what any of them are gonna taste like or what's good … and we're gonna sit there and wait for some guy to ask us a question. And we're gonna have to talk to some guy about what we wanna eat."
Secretary of State John Kerry once said of him, "A sense of humor is not genetic, but apparently in the Kennedy family, it can be inherited. In President Kennedy's grandson, Jack Schlossberg, this quality seems to abide."
- Main content

Robert F. Kennedy Jr. Says He Was Approached to Be Trump's VP
R obert F. Kennedy Jr. said this week that members of former President Donald Trump 's inner circle asked him to run as Trump's vice president.
"President Trump calls me an ultra-left radical. I'm soooo liberal that his emissaries asked me to be his VP. I respectfully declined the offer," Kennedy Jr. wrote in a post on X, formerly Twitter on Monday. "I am against President Trump, and President Biden can't win. Judging by his new website, it looks like President Trump knows who actually can beat him."
Kennedy Jr. is currently running as an independent candidate in the 2024 election after initially planning to run as a Democrat. Trump, the presumptive Republican nominee, and President Joe Biden , the Democratic incumbent, are slated for a 2020 rematch.
Kennedy is the son of former New York Democratic Sen. Robert F. Kennedy and nephew of former President John F. Kennedy.
Newsweek reached out to a spokesperson for Trump via email for comment.
The context:
Earlier this month, Trump shared a video on Truth Social speaking about Kennedy Jr.
"RFK Jr., as you know, is the most radical left candidate in the race," Trump says in the video. "But he's got some nice things about him, I happen to like him. Unfortunately, he is about the green new scam ... [he wants to] waste money doing something that nobody wants and everybody knows doesn't work."
Trump continued, "Kennedy is a radical left Democrat and always will be ... It's great for MAGA, I hope he continues to run ... But expect him to be indicted any day now, probably for environmental fraud."
What we know:
Responding to Trump's remarks earlier this month, Kennedy Jr.'s campaign Press Secretary Stefanie Spear told Newsweek via email that "If 'radical' means protecting our constitutional rights, especially freedom of speech, ending the war machine, growing small businesses, rebuilding the middle class, and reducing the national debt, then we are proudly 'radical' as Trump described."
Newsweek has reached out to Kennedy Jr.'s campaign for comment.
Shortly after Trump's criticism of Kennedy Jr. earlier this month, former federal prosecutor Ron Filipkowski responded on X saying "He's doing this because his internal polling shows RFK Jr is pulling votes from him. Especially since they now have essentially the same position on abortion and J6, and RFK Jr is more in synch with MAGA on Covid and vaccines than Trump is."
Kennedy Jr. also previously said that he believes Biden is worse of a threat to Democracy in the U.S. than Trump.
"I can make the argument that President Biden is much worse, " Kennedy Jr. said while appearing on CNN 's OutFront . "And the reason for that is President Biden is the first candidate in history, the first president in history that has used the federal agencies to censor political speech or censor his opponent."
What's next:
Kennedy Jr. recently named Nicole Shanahan as his running mate as he continues to work to get his name on the ballot in all 50 states ahead of the November election.
Trump has yet to name a vice presidential pick and a number of names have been speculated for the position.
Update, 4/15/24, 12:11 p.m. EST: This story has been updated with further information.
Update, 4/15/24, 12:52 p.m. EST: This story has been updated with further information.
Related Articles
- Michael Cohen's Legal Adviser Responds to Trump's Alleged Gag Order Breach
- Donald Trump 'Probably' Can't Get Fair Trial: Jury Consultant
- Prosecutors Eager to Put Donald Trump on Hot Seat: Legal Analyst
Start your unlimited Newsweek trial


An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
2024 Kennedy Half Dollar Products Available April 23

WASHINGTON – The United States Mint (Mint) will open sales for rolls and bags of 2024 Kennedy Half Dollar coins beginning on April 23 at noon EDT. Available product options include the following:
Both product options contain circulating quality coins from the Denver and Philadelphia Mint facilities that have never been placed in circulation. The coin rolls are wrapped in United States Mint paper coin wrap marked with a “P” or “D” for the mint of origin and “$10” for the face value of the roll. The bags are marked with a “P” or “D” for the mint of origin and “$100” for the face value of the contents.
The Mint launched the Kennedy Half Dollar coin in 1964 to commemorate President John F. Kennedy after his assassination in 1963. The coin’s obverse (heads) features the original 1964 design of President Kennedy with the inscriptions “LIBERTY,” “IN GOD WE TRUST,” and “2024.” The reverse (tails) design is based on the Presidential Coat of Arms. Inscriptions are “UNITED STATES OF AMERICA,” “E PLURIBUS UNUM,” and “HALF DOLLAR.”
To set up REMIND ME alerts for the Kennedy Half Dollar products, click on the links:
- 200-Coin Bag (product code 24KA)
- Two-Roll Set (product code 24KB)
The Kennedy Half Dollar bags and rolls are also available for purchase through the Mint’s Product Subscription Program . Subscriptions work like a magazine subscription. Once you sign up, you will receive the next product released in the series and continue to receive products until you end your enrollment. To learn more, visit usmint.gov/shop/subscriptions/ .
About the United States Mint Congress created the United States Mint in 1792, and the Mint became part of the Department of the Treasury in 1873. As the Nation’s sole manufacturer of legal tender coinage, the Mint is responsible for producing circulating coinage for the Nation to conduct its trade and commerce. The Mint also produces numismatic products, including proof, uncirculated, and commemorative coins; Congressional Gold Medals; silver and bronze medals; and silver and gold bullion coins. Its numismatic programs are self-sustaining and operate at no cost to taxpayers.
Note: To ensure that all members of the public have fair and equal access to United States Mint products, the United States Mint will not accept and will not honor orders placed prior to the official on-sale date of April 23, 2024, at noon EDT.
- Visit https://www.usmint.gov/about for information about the United States Mint.
- Visit https://catalog.usmint.gov/email-signup to subscribe to United States Mint electronic product notifications, news releases, public statements, and our monthly educational newsletter, Lessons That Make Cents .
- Sign up for RSS Feeds from the United States Mint and follow us on Facebook , Twitter , and Instagram .
United States Mint – Connecting America through Coins
A list of linkable tags for topics mentioned on this page.
- Circulating
- Half Dollar (50-Cent Piece)
- Philadelphia
- Press Release
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Accessibility
© United States Mint All Rights Reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 - November 22, 1963), often referred to as JFK, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination in 1963. He was the youngest person elected president. Kennedy served at the height of the Cold War, and the majority of his foreign policy concerned relations with the Soviet Union and Cuba.
John F. Kennedy, 35th president of the United States (1961-63), who faced a number of foreign crises, especially the Cuban missile crisis, but managed to secure such achievements as the Nuclear Test-Ban Treaty and the Alliance for Progress. He was assassinated while riding in a motorcade in Dallas.
John F. Kennedy was sworn in as the 35th president of the United States on January 20, 1961. Delivering his legendary inaugural address on January 20, 1961, Kennedy sought to inspire all Americans ...
Elected in 1960 as the 35th president of the United States, 43-year-old John F. Kennedy became the youngest man and the first Roman Catholic to hold that office. Learn about his personal and ...
John F. Kennedy was the 35th President of the United States (1961-1963), the youngest man elected to the office. On November 22, 1963, when he was hardly past his first thousand days in office ...
Soon after being elected senator, John F. Kennedy, at 36 years of age, married 24 year-old Jacqueline Bouvier, a writer with the Washington Times-Herald. Unfortunately, early on in their marriage, Senator Kennedy's back started to hurt again and he had two serious operations.
Updated on May 15, 2019. John F. Kennedy (May 29, 1917-Nov. 22, 1963), the first U.S. president born in the 20th century, was born to a wealthy, politically connected family. Elected as the 35th president in 1960, he took office on Jan. 20, 1961, but his life and legacy were cut short when he was assassinated on Nov. 22, 1963, in Dallas.
John F. Kennedy was born into a rich, politically connected Boston family of Irish-Catholics. He and his eight siblings enjoyed a privileged childhood of elite private schools, sailboats, servants, and summer homes. During his childhood and youth, "Jack" Kennedy suffered frequent serious illnesses. Nevertheless, he strove to make his own ...
John F. Kennedy, 1961. Kennedy had nearly become Stevenson's vice presidential running mate in 1956. The charismatic young New Englander's near victory and his televised speech of concession (Estes Kefauver won the vice presidential nomination) brought him into some 40 million American homes. Overnight he had become one of the best-known ...
John Fitzgerald Kennedy, often referred to as JFK, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination in 1963. He was the youngest person elected president. Kennedy served at the height of the Cold War, and the majority of his foreign policy concerned relations with the Soviet Union and Cuba.
John F. Kennedy was born into a rich, politically connected Boston family of Irish-Catholics. He and his eight siblings enjoyed a privileged childhood of elite private schools, sailboats, servants, and summer homes. During his childhood and youth, "Jack" Kennedy suffered frequent serious illnesses. Nevertheless, he strove to make his own way ...
John F. Kennedy, (born May 29, 1917, Brookline, Mass., U.S.—died Nov. 22, 1963, Dallas, Texas), 35th president of the U.S. (1961-63).The son of Joseph P. Kennedy, he graduated from Harvard University in 1940 and joined the navy the following year.He commanded a patrol torpedo (PT) boat in World War II and was gravely injured in an attack by a Japanese destroyer; he was later decorated for ...
John F Kennedy Biography. John F. Kennedy was America's second youngest elected president. He oversaw one of the most crucial moments in the Cold War (Cuban Missile Crisis) and sought to affirm America's beliefs in basic human rights by calling for civil rights legislation and an attempt to reduce poverty. Kennedy was assassinated on ...
John F. Kennedy's tenure as the 35th president of the United States began with his inauguration on January 20, 1961, and ended with his assassination on November 22, 1963. Kennedy, a Democrat from Massachusetts, took office following his narrow victory over Republican incumbent vice president Richard Nixon in the 1960 presidential election.He was succeeded by Vice President Lyndon B. Johnson.
JFK Biography. John Fitzgerald Kennedy was born on May 29, 1917, in Brookline, Massachusetts, a few miles outside of Boston. His parents were Joseph Kennedy, a successful businessman, and Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy. He was the second of nine children. While Jack grew up with every material advantage, he suffered from a series of medical ailments ...
On November 22, 1963, John F. Kennedy, the 35th president of the United States, was assassinated while riding in a presidential motorcade through Dealey Plaza in Dallas, Texas.Kennedy was in the vehicle with his wife, Jacqueline, Texas Governor John Connally, and Connally's wife, Nellie, when he was fatally shot from the nearby Texas School Book Depository by former U.S. Marine Lee Harvey Oswald.
New biography aims to chronicle a complex life amid a pivotal time for a nation. One of the revelations about John F. Kennedy in Fredrik Logevall's new biography, "JFK: Coming of Age in the American Century, 1917‒1956," is that the man was an excellent letter-writer and diarist. The Laurence D. Belfer Professor of International Affairs ...
I spent the past 24 weeks reading a dozen biographies of John F. Kennedy totaling just under 8,000 pages: six "conventional" biographies, a two-volume series and four narrowly-focused studies of Kennedy's presidency. In the end, JFK proved to be everything I hoped for - and more! Like several of the presidents who preceded him, Kennedy's…
President John F. Kennedy's youth, connections, political life, and tragic death captured the American imagination. Learn more in this mini biography. #Biogr...
John F. Kennedy, the second oldest of nine children, was born in Brookline, Massachusetts, on May 29, 1917. His father hoped that one of his children would one day become president. As a child, Kennedy had many childhood illnesses and once almost died from scarlet fever. But he grew up to be athletic and competitive, playing football for ...
John F. Kennedy (1963), Foto: Cecil W. Stoughton John Fitzgerald Kennedy, meist kurz John F. Kennedy (* 29.Mai 1917 in Brookline, Massachusetts; † 22. November 1963 in Dallas, Texas), privat „Jack" genannt, später häufig nur bei seinen Initialen JFK, war als Politiker der Demokratischen Partei von 1961 bis zu seiner Ermordung im November 1963 der 35.
A 1941 portrait of John F. Kennedy wearing his U.S. Navy uniform. Photo by Frank Turgent/Hulton Archive/Getty Images) Frank Turgent/Hulton Archive/Getty Images On Aug. 2, 1943, a Japanese ...
Kennedy's assassination, the most notorious political murder of the 20th century, remains a source of bafflement, controversy, and speculation. Portrait of Pres. John F. Kennedy by Aaron Shikler, 1970. John Kennedy was dead, but the Kennedy mystique was still alive. Both Robert and Ted ran for president (in 1968 and 1980, respectively).
John Fitzgerald Kennedy ( Brookline, Massachusetts; 29 de mayo de 1917- Dallas, Texas; 22 de noviembre de 1963) fue un político y diplomático estadounidense que se desempeñó como el trigésimo quinto presidente de los Estados Unidos. También fue conocido como Jack por sus amigos o por su sobrenombre JFK .
The inauguration of John F. Kennedy as the 35th president of the United States was held on Friday, January 20, 1961, at the East Portico of the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C. This was the 44th inauguration and marked the commencement of John F. Kennedy's and Lyndon B. Johnson's only term as president and vice president.Kennedy was assassinated 2 years, 306 days into this term, and ...
The Lost Chance for Peace and the Escalation of War in Vietnam (2003) Kaufman, Burton I. "John F. Kennedy as world leader: A perspective on the literature." Diplomatic History 17.3 (1993): 447-470. Kempe, Frederick. Berlin 1961: Kennedy, Khrushchev, and the most dangerous place on earth (2011). Kunz, Diane B.
Jack Kennedy Schlossberg is the 31-year-old grandson of President John F. Kennedy and the son of Caroline Kennedy. He was recently the subject of internet rumors claiming he dated pop singer ...
John F. Kennedy. John Fitzgerald Kennedy (tunnettiin myös lyhenteellä JFK ja lempinimellä Jack, 29. toukokuuta 1917 Brookline, Massachusetts, Yhdysvallat - 22. marraskuuta 1963 Dallas, Texas, Yhdysvallat) oli Yhdysvaltain 35. presidentti (1961-1963). Kennedy oli historian nuorin Yhdysvaltain presidentiksi valittu sekä ensimmäinen ...
Kennedy is the son of former New York Democratic Sen. Robert F. Kennedy and nephew of former President John F. Kennedy. Newsweek reached out to a spokesperson for Trump via email for comment.. The ...
The Mint launched the Kennedy Half Dollar coin in 1964 to commemorate President John F. Kennedy after his assassination in 1963. The coin's obverse (heads) features the original 1964 design of President Kennedy with the inscriptions "LIBERTY," "IN GOD WE TRUST," and "2024.". The reverse (tails) design is based on the Presidential ...