How to Write a Competitive Analysis for Your Business Plan

11 min. read
Updated January 3, 2024
Do you know who your competitors are? If you do, have you taken the time to conduct a thorough competitor analysis?
Knowing your competitors, how they operate, and the necessary benchmarks you need to hit are crucial to positioning your business for success. Investors will also want to see an analysis of the competition in your business plan.
In this guide, we’ll explore the significance of competitive analysis and guide you through the essential steps to conduct and write your own.
You’ll learn how to identify and evaluate competitors to better understand the opportunities and threats to your business. And you’ll be given a four-step process to describe and visualize how your business fits within the competitive landscape.
- What is a competitive analysis?
A competitive analysis is the process of gathering information about your competitors and using it to identify their strengths and weaknesses. This information can then be used to develop strategies to improve your own business and gain a competitive advantage.
- How to conduct a competitive analysis
Before you start writing about the competition, you need to conduct your analysis. Here are the steps you need to take:

1. Identify your competitors
The first step in conducting a comprehensive competitive analysis is to identify your competitors.
Start by creating a list of both direct and indirect competitors within your industry or market segment. Direct competitors offer similar products or services, while indirect competitors solve the same problems your company does, but with different products or services.
Keep in mind that this list may change over time. It’s crucial to revisit it regularly to keep track of any new entrants or changes to your current competitors. For instance, a new competitor may enter the market, or an existing competitor may change their product offerings.
2. Analyze the market
Once you’ve identified your competitors, you need to study the overall market.
This includes the market size , growth rate, trends, and customer preferences. Be sure that you understand the key drivers of demand, demographic and psychographic profiles of your target audience , and any potential market gaps or opportunities.
Conducting a market analysis can require a significant amount of research and data collection. Luckily, if you’re writing a business plan you’ll follow this process to complete the market analysis section . So, doing this research has value for multiple parts of your plan.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
3. Create a competitive framework
You’ll need to establish criteria for comparing your business with competitors. You want the metrics and information you choose to provide answers to specific questions. (“Do we have the same customers?” “What features are offered?” “How many customers are being served?”)
Here are some common factors to consider including:
- Market share
- Product/service offerings or features
- Distribution channels
- Target markets
- Marketing strategies
- Customer service
4. Research your competitors
You can now begin gathering information about your competitors. Because you spent the time to explore the market and set up a comparison framework—your research will be far more focused and easier to complete.
There’s no perfect research process, so start by exploring sources such as competitor websites, social media, customer reviews, industry reports, press releases, and public financial statements. You may also want to conduct primary research by interviewing customers, suppliers, or industry experts.
You can check out our full guide on conducting market research for more specific steps.
5. Assess their strengths and weaknesses
Evaluate each competitor based on the criteria you’ve established in the competitive framework. Identify their key strengths (competitive advantages) and weaknesses (areas where they underperform).
6. Identify opportunities and threats
Based on the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, identify opportunities (areas where you can outperform them) and threats (areas where they may outperform you) for your business.
You can check out our full guide to conducting a SWOT analysis for more specific questions that you should ask as part of each step.
- How to write your competitive analysis
Once you’ve done your research, it’s time to present your findings in your business plan. Here are the steps you need to take:
1. Determine who your audience is
Who you are writing a business plan for (investors, partners, employees, etc.) may require you to format your competitive analysis differently.
For an internal business plan you’ll use with your team, the competition section should help them better understand the competition. You and your team will use it to look at comparative strengths and weaknesses to help you develop strategies to gain a competitive advantage.
For fundraising, your plan will be shared with potential investors or as part of a bank loan. In this case, you’re describing the competition to reassure your target reader. You are showing awareness and a firm understanding of the competition, and are positioned to take advantage of opportunities while avoiding the pitfalls.
2. Describe your competitive position
You need to know how your business stacks up, based on the values it offers to your chosen target market. To run this comparison, you’ll be using the same criteria from the competitive framework you completed earlier. You need to identify your competitive advantages and weaknesses, and any areas where you can improve.
The goal is positioning (setting your business up against the background of other offerings), and making that position clear to the target market. Here are a few questions to ask yourself in order to define your competitive position:
- How are you going to take advantage of your distinctive differences, in your customers’ eyes?
- What are you doing better?
- How do you work toward strengths and away from weaknesses?
- What do you want the world to think and say about you and how you compare to others?
3. Visualize your competitive position
There are a few different ways to present your competitive framework in your business plan. The first is a “positioning map” and the second is a “competitive matrix”. Depending on your needs, you can use one or both of these to communicate the information that you gathered during your competitive analysis:
Positioning map
The positioning map plots two product or business benefits across a horizontal and vertical axis. The furthest points of each represent opposite extremes (Hot and cold for example) that intersect in the middle. With this simple chart, you can drop your own business and the competition into the zone that best represents the combination of both factors.
I often refer to marketing expert Philip Kohler’s simple strategic positioning map of breakfast, shown here. You can easily draw your own map with any two factors of competition to see how a market stacks up.
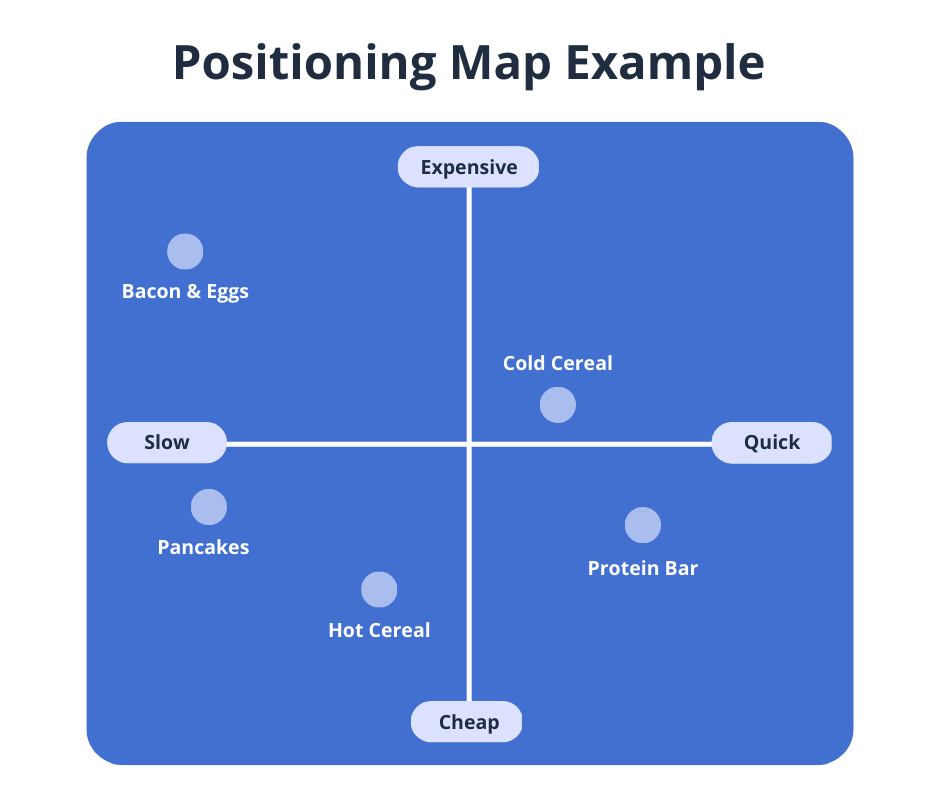
It’s quite common to see the price on one axis and some important qualitative factor on the other, with the assumption that there should be a rough relationship between price and quality.
Competitive matrix
It’s pretty common for most business plans to also include a competitive matrix. It shows how different competitors stack up according to the factors identified in your competitive framework.
How do you stack up against the others? Here’s what a typical competitive matrix looks like:

For the record, I’ve seen dozens of competitive matrices in plans and pitches. I’ve never seen a single one that didn’t show that this company does more of what the market wants than all others. So maybe that tells you something about credibility and how to increase it. Still, the ones I see are all in the context of seeking investment, so maybe that’s the nature of the game.
4. Explain your strategies for gaining a competitive edge
Your business plan should also explain the strategies your business will use to capitalize on the opportunities you’ve identified while mitigating any threats from competition. This may involve improving your product/service offerings, targeting underserved market segments, offering more attractive price points, focusing on better customer service, or developing innovative marketing strategies.
While you should cover these strategies in the competition section, this information should be expanded on further in other areas of your business plan.
For example, based on your competitive analysis you show that most competitors have the same feature set. As part of your strategy, you see a few obvious ways to better serve your target market with additional product features. This information should be referenced within your products and services section to back up your problem and solution statement.
- Why competition is a good thing
Business owners often wish that they had no competition. They think that with no competition, the entire market for their product or service will be theirs. That is simply not the case—especially for new startups that have truly innovative products and services. Here’s why:
Competition validates your idea
You know you have a good idea when other people are coming up with similar products or services. Competition validates the market and the fact that there are most likely customers for your new product. This also means that the costs of marketing and educating your market go down (see my next point).
Competition helps educate your target market
Being first-to-market can be a huge advantage. It also means that you will have to spend way more than the next player to educate customers about your new widget, your new solution to a problem, and your new approach to services.
This is especially true for businesses that are extremely innovative. These first-to-market businesses will be facing customers that didn’t know that there was a solution to their problem . These potential customers might not even know that they have a problem that can be solved in a better way.
If you’re a first-to-market company, you will have an uphill battle to educate consumers—an often expensive and time-consuming process. The 2nd-to-market will enjoy all the benefits of an educated marketplace without the large marketing expense.
Competition pushes you
Businesses that have little or no competition become stagnant. Customers have few alternatives to choose from, so there is no incentive to innovate. Constant competition ensures that your marketplace continues to evolve and that your product offering continues to evolve with it.
Competition forces focus & differentiation
Without competition, it’s easy to lose focus on your core business and your core customers and start expanding into areas that don’t serve your best customers. Competition forces you and your business to figure out how to be different than your competition while focusing on your customers. In the long term, competition will help you build a better business.
- What if there is no competition?
One mistake many new businesses make is thinking that just because nobody else is doing exactly what they’re doing, their business is a sure thing. If you’re struggling to find competitors, ask yourself these questions.
Is there a good reason why no one else is doing it?
The smart thing to do is ask yourself, “Why isn’t anyone else doing it?”
It’s possible that nobody’s selling cod-liver frozen yogurt in your area because there’s simply no market for it. Ask around, talk to people, and do your market research. If you determine that you’ve got customers out there, you’re in good shape.
But that still doesn’t mean there’s no competition.
How are customers getting their needs met?
There may not be another cod-liver frozen yogurt shop within 500 miles. But maybe an online distributor sells cod-liver oil to do-it-yourselfers who make their own fro-yo at home. Or maybe your potential customers are eating frozen salmon pops right now.
Are there any businesses that are indirect competitors?
Don’t think of competition as only other businesses that do exactly what you do. Think about what currently exists on the market that your product would displace.
It’s the difference between direct competition and indirect competition. When Henry Ford started successfully mass-producing automobiles in the U.S., he didn’t have other automakers to compete with. His competition was horse-and-buggy makers, bicycles, and railroads.
Do a competitive analysis, but don’t let it derail your planning
While it’s important that you know the competition, don’t get too caught up in the research.
If all you do is track your competition and do endless competitive analyses, you won’t be able to come up with original ideas. You will end up looking and acting just like your competition. Instead, make a habit of NOT visiting your competition’s website, NOT going into their store, and NOT calling their sales office.
Focus instead on how you can provide the best service possible and spend your time talking to your customers. Figure out how you can better serve the next person that walks in the door so that they become a lifetime customer, a reference, or a referral source.
If you focus too much on the competition, you will become a copycat. When that happens, it won’t matter to a customer if they walk into your store or the competition’s because you will both be the same.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
- Don't let competition derail planning
Related Articles
6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

24 Min. Read
The 10 AI Prompts You Need to Write a Business Plan

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

10 Min. Read
How to Write the Company Overview for a Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Discover how today’s most successful IT leaders stand out from the rest. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Read the report .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project planning |
- How to create a competitive analysis (w ...
How to create a competitive analysis (with examples)

Competitive analysis involves identifying your direct and indirect competitors using research to reveal their strengths and weaknesses in relation to your own. In this guide, we’ll outline how to do a competitive analysis and explain how you can use this marketing strategy to improve your business.
Whether you’re running a business or playing in a football game, understanding your competition is crucial for success. While you may not be scoring touchdowns in the office, your goal is to score business deals with clients or win customers with your products. The method of preparation for athletes and business owners is similar—once you understand your strengths and weaknesses versus your competitors’, you can level up.
What is a competitive analysis?
Competitive analysis involves identifying your direct and indirect competitors using research to reveal their strengths and weaknesses in relation to your own.
![competitive edge business plan example [inline illustration] What is a competitive analysis (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/c1a37dfd-53a8-44c4-b57b-10fc6a332ba1/inline-project-planning-competitive-analysis-example-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Direct competitors market the same product to the same audience as you, while indirect competitors market the same product to a different audience. After identifying your competitors, you can use the information you gather to see where you stand in the market landscape.
What to include in a competitive analysis
The purpose of this type of analysis is to get a competitive advantage in the market and improve your business strategy. Without a competitive analysis, it’s difficult to know what others are doing to win clients or customers in your target market. A competitive analysis report may include:
A description of your company’s target market
Details about your product or service versus the competitors’
Current and projected market share, sales, and revenues
Pricing comparison
Marketing and social media strategy analysis
Differences in customer ratings
You’ll compare each detail of your product or service versus the competition to assess strategy efficacy. By comparing success metrics across companies, you can make data-driven decisions.
How to do a competitive analysis
Follow these five steps to create your competitive analysis report and get a broad view of where you fit in the market. This process can help you analyze a handful of competitors at one time and better approach your target customers.
1. Create a competitor overview
In step one, select between five and 10 competitors to compare against your company. The competitors you choose should have similar product or service offerings and a similar business model to you. You should also choose a mix of both direct and indirect competitors so you can see how new markets might affect your company. Choosing both startup and seasoned competitors will further diversify your analysis.
Tip: To find competitors in your industry, use Google or Amazon to search for your product or service. The top results that emerge are likely your competitors. If you’re a startup or you serve a niche market, you may need to dive deeper into the rankings to find your direct competitors.
2. Conduct market research
Once you know the competitors you want to analyze, you’ll begin in-depth market research. This will be a mixture of primary and secondary research. Primary research comes directly from customers or the product itself, while secondary research is information that’s already compiled. Then, keep track of the data you collect in a user research template .
Primary market research may include:
Purchasing competitors’ products or services
Interviewing customers
Conducting online surveys of customers
Holding in-person focus groups
Secondary market research may include:
Examining competitors’ websites
Assessing the current economic situation
Identifying technological developments
Reading company records
Tip: Search engine analysis tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush can help you examine competitors’ websites and obtain crucial SEO information such as the keywords they’re targeting, the number of backlinks they have, and the overall health of their website.
3. Compare product features
The next step in your analysis involves a comparison of your product to your competitors’ products. This comparison should break down the products feature by feature. While every product has its own unique features, most products will likely include:
Service offered
Age of audience served
Number of features
Style and design
Ease of use
Type and number of warranties
Customer support offered
Product quality
Tip: If your features table gets too long, abbreviate this step by listing the features you believe are of most importance to your analysis. Important features may include cost, product benefits, and ease of use.
4. Compare product marketing
The next step in your analysis will look similar to the one before, except you’ll compare the marketing efforts of your competitors instead of the product features. Unlike the product features matrix you created, you’ll need to go deeper to unveil each company’s marketing plan .
Areas you’ll want to analyze include:
Social media
Website copy
Press releases
Product copy
As you analyze the above, ask questions to dig deeper into each company’s marketing strategies. The questions you should ask will vary by industry, but may include:
What story are they trying to tell?
What value do they bring to their customers?
What’s their company mission?
What’s their brand voice?
Tip: You can identify your competitors’ target demographic in this step by referencing their customer base, either from their website or from testimonials. This information can help you build customer personas. When you can picture who your competitor actively targets, you can better understand their marketing tactics.
5. Use a SWOT analysis
Competitive intelligence will make up a significant part of your competitor analysis framework, but once you’ve gathered your information, you can turn the focus back to your company. A SWOT analysis helps you identify your company’s strengths and weaknesses. It also helps turn weaknesses into opportunities and assess threats you face based on your competition.
During a SWOT analysis, ask yourself:
What do we do well?
What could we improve?
Are there market gaps in our services?
What new market trends are on the horizon?
Tip: Your research from the previous steps in the competitive analysis will help you answer these questions and fill in your SWOT analysis. You can visually present your findings in a SWOT matrix, which is a four-box chart divided by category.
6. Identify your place in the market landscape
The last step in your competitive analysis is to understand where you stand in the market landscape. To do this, you’ll create a graph with an X and Y axis. The two axes should represent the most important factors for being competitive in your market.
For example, the X-axis may represent customer satisfaction, while the Y-axis may represent presence in the market. You’ll then plot each competitor on the graph according to their (x,y) coordinates. You’ll also plot your company on this chart, which will give you an idea of where you stand in relation to your competitors.
This graph is included for informational purposes and does not represent Asana’s market landscape or any specific industry’s market landscape.
![competitive edge business plan example [inline illustration] Identify your place in the market landscape (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/fb2a8437-bb5e-4f0c-b5d0-91d67116bebe/inline-project-planning-competitive-analysis-example-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Tip: In this example, you’ll see three companies that have a greater market presence and greater customer satisfaction than yours, while two companies have a similar market presence but higher customer satisfaction. This data should jumpstart the problem-solving process because you now know which competitors are the biggest threats and you can see where you fall short.
Competitive analysis example
Imagine you work at a marketing startup that provides SEO for dentists, which is a niche industry and only has a few competitors. You decide to conduct a market analysis for your business. To do so, you would:
Step 1: Use Google to compile a list of your competitors.
Steps 2, 3, and 4: Use your competitors’ websites, as well as SEO analysis tools like Ahrefs, to deep-dive into the service offerings and marketing strategies of each company.
Step 5: Focusing back on your own company, you conduct a SWOT analysis to assess your own strategic goals and get a visual of your strengths and weaknesses.
Step 6: Finally, you create a graph of the market landscape and conclude that there are two companies beating your company in customer satisfaction and market presence.
After compiling this information into a table like the one below, you consider a unique strategy. To beat out your competitors, you can use localization. Instead of marketing to dentists nationwide like your competitors are doing, you decide to focus your marketing strategy on one region, state, or city. Once you’ve become the known SEO company for dentists in that city, you’ll branch out.
![competitive edge business plan example [inline illustration] Competitive analysis framework (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/56c32354-f525-4610-9250-f878ea0b9f26/inline-project-planning-competitive-analysis-example-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
You won’t know what conclusions you can draw from your competitive analysis until you do the work and see the results. Whether you decide on a new pricing strategy, a way to level up your marketing, or a revamp of your product, understanding your competition can provide significant insight.
Drawbacks of competitive analysis
There are some drawbacks to competitive analysis you should consider before moving forward with your report. While these drawbacks are minor, understanding them can make you an even better manager or business owner.
Don’t forget to take action
You don’t just want to gather the information from your competitive analysis—you also want to take action on that information. The data itself will only show you where you fit into the market landscape. The key to competitive analysis is using it to problem solve and improve your company’s strategic plan .
Be wary of confirmation bias
Confirmation bias means interpreting information based on the beliefs you already hold. This is bad because it can cause you to hold on to false beliefs. To avoid bias, you should rely on all the data available to back up your decisions. In the example above, the business owner may believe they’re the best in the SEO dental market at social media. Because of this belief, when they do market research for social media, they may only collect enough information to confirm their own bias—even if their competitors are statistically better at social media. However, if they were to rely on all the data available, they could eliminate this bias.
Update your analysis regularly
A competitive analysis report represents a snapshot of the market landscape as it currently stands. This report can help you gain enough information to make changes to your company, but you shouldn’t refer to the document again unless you update the information regularly. Market trends are always changing, and although it’s tedious to update your report, doing so will ensure you get accurate insight into your competitors at all times.
Boost your marketing strategy with competitive analysis
Learning your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses will make you a better marketer. If you don’t know the competition you’re up against, you can’t beat them. Using competitive analysis can boost your marketing strategy and allow you to capture your target audience faster.
Competitive analysis must lead to action, which means following up on your findings with clear business goals and a strong business plan. Once you do your competitive analysis, you can use the templates below to put your plan into action.
Related resources

What is stakeholder analysis and why is it important?
Understanding dependencies in project management

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
5 Sources of Competitive Advantage to Drive Growth

- 10 Nov 2020
From chariot races and jousting tournaments to playground games and professional sports, competition is an age-old force that drives humans to evolve and outpace their competitors.
Competition in business is no exception, and it can make or break your organization. While it's often uncomfortable and scary to witness another business profit from your company's weaknesses, competition can also push your business to evolve into a better version of itself.
How do you gain an edge to drive growth for your organization? Here are five sources of competitive advantage to leverage for your business strategy.
Access your free e-book today.
Sources of Competitive Advantage
1. product attribute differentiation.
One way to gain an advantage over competitors is by differentiating your product from theirs. Ask yourself: What makes my offering unique? Why would consumers want to purchase my product instead of my competitors’?
Countless attributes can set your product apart. Here are some to consider:
- Better customer service
- More variety
- Faster or cheaper shipping
- Color and aesthetics
- Brand identity
- Atmosphere of brick-and-mortar locations
- Source of goods
Whole Foods Market is one example of a company that differentiates its products using brand identity, atmosphere, and sourcing. Whole Foods’ competitors are other natural food chains, such as Trader Joe’s and Sprouts Farmers Market, along with big names in the grocery space, including Stop & Shop and Wegman’s.
Whole Foods stands out in the crowded natural foods market as the first and only certified organic national grocery store in the United States. Its brand identity centers on the integrity of its natural and organically sourced foods. It also cultivates an in-store atmosphere that makes grocery shopping feel purposeful and is a step up from some of its competitors' traditional grab-and-go shopping experience.
Like Whole Foods, find the attributes that differentiate your product from others and make them central to your brand’s identity.

2. Customers’ Willingness to Pay
The way you price your products or services can set you apart from your competitors. When doing so, it’s vital to understand your customers’ willingness to pay .
Willingness to pay (WTP) is the maximum price a customer is willing to pay for a product or service. It can be a specific dollar amount or a price range.
By determining your customers’ WTP, you can ensure you’re maximizing profit without turning away customers.
In the context of competition, it’s important to view willingness to pay as a strategic tool. If your customers are willing to pay the same amount for your and your competitors’ products, consider what can be shifted to increase their willingness to pay for yours.
For example, business support system company CSG reports that 47 percent of consumers are willing to pay more for products that are sustainably sourced. Among those consumers, five percent are willing to pay double the price for a sustainable product over a non-sustainable one.
With the knowledge that certain factors could cause your customers’ willingness to pay to increase, you can strategically implement changes that give your business a competitive edge.
Alternatively, if your competitor provides a product at the very top of customers’ willingness to pay, you can gain a competitive advantage by offering a lower price. Tread cautiously, because doing so could start a price war in which you both continue to drop prices to win customers.
3. Price Discrimination
With an understanding of your customers’ willingness to pay, you may find that different types of customers are willing to pay different amounts for your products. In such cases, it can be useful to employ price discrimination, which can be a valuable tool for expanding your company’s reach when competing with others.
“Price discrimination is one of the most common and powerful price strategies for companies,” says Harvard Business School Professor Bharat Anand in the online course Economics for Managers .
In the course, Anand presents several examples of price discrimination, including reduced prices for students, seniors, and veterans. These “special case” prices present an opportunity for your company to earn customers whose willingness to pay may be lower than that of its typical customers.
It’s worth noting that a lower price doesn’t always win consumers over—selecting a strategic price is crucial, but it’s just one factor they consider when determining which product to buy.
4. Bundled Pricing
Another pricing strategy that can prove to be advantageous is bundled pricing.
Bundled pricing is the practice of selling two or more products together in a “bundle,” for which the cost is different than that of purchasing all of the items separately.
Cable companies often leverage bundling. Purchasing voice, video, and data services together often grants the customer a lower price than if they were to purchase the services individually.
“How you think about the logic of pricing should depend on willingness to pay,” Anand says in Economics for Managers . He presents the example of bundling childcare and theater tickets.
“Put two products together that, when consumed jointly, increase consumers’ willingness to pay,” he says. “You might be able to increase the price for both just because it has so much more value for consumers.”
The way you price your products should be strategic, purposeful, and give your business a leg up over its competitors.
5. Human Capital
A company is only as strong as its people. As such, hiring, training, and retaining a team of skilled employees is a competitive advantage for any business.
Putting in the time and care to select outstanding candidates for open positions, train current employees, offer professional development opportunities, and create a culture wherein people feel supported and challenged can pay off.
Gallup reports that business units with highly engaged employees see a 21 percent increase in profit over their less-engaged counterparts.
Employee engagement has been especially important during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic , as many businesses have closed physical offices and transitioned to remote work. By finding ways to effectively engage your team in a virtual setting , you can make them feel supported and empowered from afar.

Positioning Your Business for Success
Differentiating your product, creating a pricing strategy, and investing in your employees can be the difference between rising to the top of your market and being driven out by a competitor.
By taking a strategy course , such as Economics for Managers , you can bolster your skills in these areas and see competition not as a looming threat, but as a catalyst for growth.
Do you want to learn more about positioning your business for success in a competitive market? Explore our eight-week Economics for Managers course and other online strategy courses to hone your skills.

About the Author
How to Write a Competitive Edge for Business
- Small Business
- Business Communications & Etiquette
- Business Writing
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
Outline & Sample of a Marketing Plan
How to write a preface for a business plan, how to write a marketing analysis report.
- What Factors Make the Difference Between a Good Business Plan & an Excellent One?
- Definition of a SWOT Analysis
Establishing your competitive edge is an important part of the feasibility study you do prior to writing your startup business plan or your year-end strategic planning for next year's business expansion. It entails research into your competition, how their products differs from yours, how their operations differ from yours and how their marketing differs from yours. Your research should also include the demographics and buying habits of your target customer so you can identify or create your competitive advantage.
SWOT Analysis
List the qualities of your product, business operations, marketing and customer base. Then list how those qualities compare to your competition and what you can do to best that competitor. Once you have a list of qualities that give you a competitive advantage, perform a SWOT analysis, which is taking each point and determining the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats associated with that product, operational system, marketing campaign or customer base.
Writing a description of your competitive edge, and how you will achieve and maintain it, may require revision and refining of your initial vision. This is why you put in research and evaluation time to identify holes in your planning and fantasies in your decision making prior to writing. Competitive edge is an elusive reality. Self-deception destroys many businesses because it leads you to think you have enough money, time, product superiority, operational superiority and marketing savvy to blow your competition out of the water.
A discussion of your competitive edge can be part of the section of your business plan that deals with the description of your company, or it can be the introduction to your marketing plan. It is also useful as a basis for your brochures, website copy and marketing presentations. Describe your product, and compare its strengths and weaknesses with respect to the competition's products. Then, indicate how your company compares to the competition and what opportunities or threats you have identified. Describe your target customers, their needs and buying habits, and why your product appeals to them. Then indicate your marketing plans for targeting and attracting those customers by educating them about the superiority of your product and services relative to those of your competition.
Reality Check
Always get an outside opinion before you deliver your description to an investor, bank or customer. Organizations such as the Service Corps of Retired Executives, known as SCORE, can provide you with unbiased advice regarding the reality of your assumptions so you have the opportunity to revise your description of your competitive edge, if needed. A clear and factual vision is one of the best competitive edges you can develop.
- Entrepreneur: Market Strategies
- Marketing MO: Competitive Positioning
Victoria Duff specializes in entrepreneurial subjects, drawing on her experience as an acclaimed start-up facilitator, venture catalyst and investor relations manager. Since 1995 she has written many articles for e-zines and was a regular columnist for "Digital Coast Reporter" and "Developments Magazine." She holds a Bachelor of Arts in public administration from the University of California at Berkeley.
Related Articles
Quick step process business plan, how to write a comprehensive business plan, how to pitch a business plan, how to write a business case for action, what does a business plan consist of, how to write a business plan for a sole proprietorship, main steps in business planning, how to write a compelling marketing letter that actually gets read, how to write the perfect business plan, most popular.
- 1 Quick Step Process Business Plan
- 2 How to Write a Comprehensive Business Plan
- 3 How to Pitch a Business Plan
- 4 How to Write a Business Case for Action
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Competitive Advantage?
- How It Works
- How To Build It
- Competitive vs. Comparative Advantage
The Bottom Line
- Business Essentials
Competitive Advantage Definition With Types and Examples
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dd453b82d4ef4ce8aac2e858ed00a114__alexandra_twin-5bfc262b46e0fb0026006b77.jpeg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
Competitive advantage refers to factors that allow a company to produce goods or services better or more cheaply than its rivals. These factors allow the productive entity to generate more sales or superior margins compared to its market rivals. Competitive advantages are attributed to a variety of factors including cost structure, branding , the quality of product offerings, the distribution network , intellectual property, and customer service.
Key Takeaways
- Competitive advantage is what makes an entity's products or services more desirable to customers than that of any other rival.
- Competitive advantages can be broken down into comparative advantages and differential advantages.
- Comparative advantage is a company's ability to produce something more efficiently than a rival, which leads to greater profit margins.
- A differential advantage is when a company's products are seen as both unique and of higher quality, relative to those of a competitor.
Investopedia / Michela Buttignol
Understanding Competitive Advantage
Competitive advantages generate greater value for a firm and its shareholders because of certain strengths or conditions. The more sustainable the competitive advantage, the more difficult it is for competitors to neutralize the advantage. The two main types of competitive advantages are comparative advantage and differential advantage.
A comparative advantage is when a firm can produce products more efficiently and at a lower cost than its competitors.
A differential advantage is when a firm's products or services differ from its competitors' offerings and are seen as superior. Advanced technology, patent-protected products or processes, superior personnel, and strong brand identity are all drivers of differential advantage. These factors support wide margins and large market shares.
For example, Apple is famous for creating innovative products, such as the iPhone, and supporting its market leadership with savvy marketing campaigns to build an elite brand. Another example is major drug companies. They can market branded drugs at high price points because they are protected by patents.
The term "competitive advantage" traditionally refers to the business world, but can also be applied to a country, organization, or even a person who is competing for something.
How To Build a Competitive Advantage
To build a competitive advantage, a company can use one of three main methods:
- Cost: Provide offerings at the lowest price
- Differentiation: Provide offerings that are superior in quality, service, or features
- Specialization: Provide offerings narrowly tailored to a focused market
Competing on price can be effective, but if you slash prices too much you risk decreasing profit margins to an untenable level. Many firms opt instead to differentiate themselves in other ways, which helps preserve or expand their profit margin.
Benefits of a Competitive Advantage
When a company creates a durable competitive advantage, it sets itself apart from the competition and provides value to customers as well as stakeholders. By producing a desirable product or service that is better or more cost-effective than its competitors,' the company can make more sales, generate more revenue, and enjoy greater profits.
Strategies to Build a Competitive Advantage
To build a competitive advantage, a company must know what sets it apart from its competitors and then focus its message, service, and products with that difference in mind. Here are several strategies companies use to build a competitive advantage:
- Research the market : Market research helps a company identify and define its target market, which can guide it in developing the most effective advantage.
- Identify strengths : A company can find its unique strengths, especially relative to competitors, by reviewing products, services, features, positioning, and branding.
- Evaluate finances : Companies can take a close look at their financial performance to spot profit centers and areas of stability, using financial statements and ratios.
- Review operations : How efficient is a company's operations? Where is it effective, and where is there room for improvement? Consider customer service as well as production and supply chain management.
- Consider human resources : The talent a company can attract as employees and leadership can make an important difference in the success of the business. Evaluating company culture, hiring, and staffing practices can help.
Competitive Advantage vs. Comparative Advantage
A firm's ability to produce a good or service more efficiently than its competitors, which leads to greater profit margins, creates a comparative advantage. Rational consumers will choose the cheaper of any two perfect substitutes offered. For example, a car owner will buy gasoline from a gas station that is 5 cents cheaper than other stations in the area. For imperfect substitutes, like Pepsi versus Coke, higher margins for the lowest-cost producers can eventually bring superior returns.
Economies of scale , efficient internal systems, and geographic location can also create a comparative advantage.
Comparative advantage does not imply a better product or service. It only shows the firm can offer a product or service of the same value at a lower price.
For example, a firm that manufactures a product in China may have lower labor costs than a company that manufactures in the U.S., so it can offer an equal product at a lower price. In the context of international trade economics, opportunity cost determines comparative advantages.
Amazon ( AMZN ) is an example of a company focused on building and maintaining a comparative advantage. The e-commerce platform has a level of scale and efficiency that is difficult for retail competitors to replicate, allowing it to rise to prominence largely through price competition.
How Do I Know If a Company Has a Competitive Advantage?
If a business can increase its market share through increased efficiency or productivity, it would have a competitive advantage over its competitors.
How Can a Company Increase Its Competitive Advantage?
Lasting competitive advantages tend to be things competitors cannot easily replicate or imitate. Warren Buffet calls sustainable competitive advantages economic moats , which businesses can figuratively dig around themselves to entrench competitive advantages. This can include strengthening one's brand, raising barriers to new entrants (such as through regulations), and the defense of intellectual property.
Why Do Larger Companies Often Have Competitive Advantages?
Competitive advantages that accrue from economies of scale typically refer to supply-side advantages, such as the purchasing power of a large restaurant or retail chain. But advantages of scale also exist on the demand side—they are commonly referred to as network effects . This happens when a service becomes more valuable to all of its users as the service adds more users. The result can often be a winner-take-all dynamic in the industry.
How Is Competitive Advantage Different From Comparative Advantage?
Comparative advantage mostly refers to international trade. It posits that a country should focus on what it can produce and export relatively the cheapest—thus if one country has a competitive advantage in producing both products A & B, it should only produce product A if it can do it better than B and import B from some other country.
A company's competitive advantage is the way it excels compared to its rivals. This advantage may be through cost leadership, differentiation, or focus. Identifying a company's competitive advantage helps show how it is positioned to be more successful than its competitors, creating more revenue and generating greater profits.
Young African Leaders Initiative. " Action Your Business Growth: The Importance of Knowing Your Competitive Advantage ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Market Research and Competitive Analysis ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/foreign_flags-5bfc316d46e0fb00511ac08a.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

Culture Development
Competitive advantage examples: strategic edge.
- February 26, 2024
In the business world, gaining a competitive advantage is crucial for success. It allows companies to differentiate themselves from their competitors and create a strategic edge in the market. In this article, we will explore the concept of competitive advantage, its importance in business, different types of competitive advantages, strategies for building and maintaining it, measuring its effectiveness, and the challenges companies face in gaining a competitive advantage.

Understanding Competitive Advantage
Competitive advantage refers to the factors that set a business apart from others in the industry and allow it to outperform its competitors. These factors can include a unique product or service offering, lower costs, better customer service, or superior technology. A company with a competitive advantage can attract more customers, increase market share, and ultimately achieve higher profitability.
Let’s dive deeper into the concept of competitive advantage and explore its various dimensions.
Defining Competitive Advantage
Competitive advantage can be defined as the “strategic edge” that a company possesses over its rivals in the market. It is the unique combination of strengths, capabilities, and resources that enable a business to deliver superior value to its customers.
One aspect of competitive advantage is having a unique product or service offering. This can be achieved through innovation, research, and development , or simply by providing a solution to a customer problem that no other company has addressed. For example, a company that develops a groundbreaking technology or a disruptive business model can gain a significant competitive advantage.
Another dimension of competitive advantage is cost leadership. By having lower costs than competitors, a company can offer its products or services at a more affordable price, attracting price-sensitive customers. This can be achieved through economies of scale, efficient operations, or strategic partnerships that reduce costs. For instance, a company that has established a global supply chain network can benefit from lower production costs and pass on the savings to customers.
Customer service is also a critical factor in gaining a competitive advantage. By providing exceptional customer experiences, a company can build strong relationships with its customers, leading to increased loyalty and repeat business. This can be achieved through personalized interactions, quick problem resolution, or proactive communication. For example, a company that invests in training its employees to deliver exceptional service or uses advanced customer relationship management systems can differentiate itself from competitors.
Lastly, superior technology can give a company a competitive advantage. By leveraging advanced technology, a company can streamline its operations, enhance product quality, or create innovative solutions that competitors cannot replicate easily. This can be achieved through continuous research and development, strategic partnerships with technology providers, or proprietary technology that is difficult to imitate. For instance, a company that develops cutting-edge software or hardware can gain a significant competitive advantage in the technology industry.
Importance of Competitive Advantage in Business
Having a competitive advantage is essential for business success. It allows companies to differentiate themselves from competitors and establish a strong position in the market. A competitive advantage gives a company the ability to attract and retain customers, increase market share, and achieve sustainable growth and profitability.

One of the key benefits of having a competitive advantage is the ability to attract more customers. When a company offers something unique or superior to its competitors, customers are more likely to choose that company over others. This can result in increased sales and market share.
Furthermore, a competitive advantage enables a company to build customer loyalty. When customers perceive a company as providing better value, they are more likely to become repeat customers and recommend the company to others. This can lead to a strong customer base and a positive brand reputation.
Another advantage of having a competitive edge is the ability to command higher prices. When customers perceive a company’s products or services as superior, they are often willing to pay a premium for them. This can lead to higher profit margins and increased profitability.
Lastly, a competitive advantage provides a company with a buffer against external threats. When a company has a unique offering or a cost advantage, it is less vulnerable to price wars, market fluctuations, or new entrants. This can provide stability and sustainability in the long run.
In conclusion, competitive advantage is a crucial element for business success. It encompasses various dimensions such as unique product offerings, cost leadership, exceptional customer service, and superior technology. By leveraging these factors, companies can differentiate themselves from competitors, attract more customers, and achieve sustainable growth and profitability.
Types of Competitive Advantage
When it comes to gaining a competitive edge in the market, there are various strategies that companies can pursue. Let’s explore some of the most common types of competitive advantages in more detail.
Cost Advantage
A cost advantage is a key strategy that many companies employ to stay ahead of their competitors. It occurs when a company can produce and deliver its products or services at a lower cost compared to its rivals. This can be achieved through a variety of means, such as economies of scale, efficient operations, or access to cheaper resources.
By having a cost advantage, a company can offer its products or services at lower prices than its competitors. This attracts price-sensitive customers who are always on the lookout for the best deals. As a result, the company can gain a larger market share and increase its overall profitability.
For example, a manufacturing company that has invested in advanced technology and streamlined its production processes may be able to produce goods at a lower cost per unit compared to its competitors. This allows them to offer their products at a more competitive price point, attracting budget-conscious customers and potentially driving their competitors out of the market.
Differentiation Advantage
While cost advantage focuses on offering products or services at a lower price, differentiation advantage revolves around providing unique and superior offerings that are perceived as valuable by customers. This strategy aims to set a company apart from its competitors by offering something that others cannot easily replicate.
There are several ways in which a company can achieve differentiation. One approach is through product design, where a company invests in creating visually appealing and user-friendly products that stand out in the market. Another approach is through product features, where a company adds unique functionalities or enhancements that provide additional value to customers.
Quality is also a crucial aspect of differentiation. By ensuring that their products or services are of superior quality compared to their competitors, a company can build a reputation for excellence and attract customers who are willing to pay a premium for top-notch offerings.
Innovation is another avenue for differentiation. By constantly pushing the boundaries and introducing new and groundbreaking products or services, a company can capture the attention of customers who are looking for the latest and most cutting-edge solutions.
Finally, branding plays a significant role in differentiation. By building a strong brand identity and cultivating a positive brand image, a company can create a unique position in the market and establish an emotional connection with its customers.
For instance, a tech company that focuses on creating sleek and innovative products with advanced features can differentiate itself from its competitors who offer more generic and outdated offerings. This differentiation allows the company to attract loyal customers who value the unique benefits it provides and are willing to pay a premium price for its products.
In conclusion, both cost advantage and differentiation advantage are essential strategies for companies seeking to gain a competitive edge. While cost advantage focuses on offering products or services at a lower price, differentiation advantage revolves around providing unique and superior offerings that are perceived as valuable by customers. By understanding and leveraging these types of competitive advantages, companies can position themselves for long-term success in the market.
Building a Competitive Advantage
Building a competitive advantage requires careful planning and execution. It involves developing strategies that set a company apart from its competitors. By creating a unique position in the market, companies can attract customers and achieve long-term success.
There are several strategies that companies can use to develop a strategic edge:
Strategies for Developing Competitive Advantage
- Innovation: Developing new and unique products or services that meet customer needs and preferences. Innovation is crucial in today’s fast-paced business environment, as it allows companies to stay ahead of the competition and capture new market opportunities.
- Quality: Delivering products or services of superior quality compared to competitors. Quality is a key differentiator in many industries, as customers are willing to pay a premium for products that meet their expectations and provide value.
- Customer Service: Providing exceptional customer service and building strong relationships with customers. Companies that prioritize customer service create loyal customers who are more likely to recommend their products or services to others.
- Efficiency: Optimizing operations and processes to reduce costs and improve productivity. By streamlining operations, companies can lower their expenses and allocate resources more effectively, giving them a competitive advantage in terms of pricing and profitability.
- Brand Building: Creating a strong brand identity and reputation that resonates with customers. A well-established brand can differentiate a company from its competitors and create a sense of trust and loyalty among customers.
However, building a competitive advantage is not a one-time effort. Once a strategic edge is established, it is important for companies to continuously maintain and enhance it. This can be achieved through ongoing innovation, continuous improvement of products or services, investment in research and development, staying ahead of market trends, and adapting to changes in customer preferences and needs.
By constantly evolving and staying relevant, companies can ensure that their competitive advantage remains strong and sustainable.
Measuring Competitive Advantage
Measuring the effectiveness of a company’s competitive advantage is essential to evaluate its performance and make informed strategic decisions. Here are some key performance indicators (KPIs) that can be used to measure competitive advantage:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Market Share: The proportion of the market that a company occupies compared to its competitors.
- Customer Satisfaction: The level of satisfaction customers have with a company’s products or services.
- Profit Margins: The difference between revenue and costs, indicating the profitability of a company.
- Brand Equity: The perceived value and strength of a brand in the market.
Benchmarking and Competitive Analysis
Benchmarking and competitive analysis are also useful tools for measuring competitive advantage. By comparing performance metrics and strategies with those of competitors, companies can identify areas for improvement and develop effective strategies for gaining a strategic edge.
Challenges in Gaining Competitive Advantage
Despite its importance, gaining a competitive advantage is not without challenges. Here are some common obstacles that companies face:
Market Saturation and Competition
In highly competitive markets, it can be challenging for companies to differentiate themselves and gain a competitive advantage. The saturation of the market and intense competition can make it difficult to attract customers and achieve sustainable profitability.
Rapid Technological Changes
The rapid advancements in technology can pose challenges in gaining and maintaining a competitive advantage. Companies must continuously adapt to new technologies, invest in research and development, and stay abreast of industry trends to stay ahead of competitors.
Conclusion:
Competitive advantage is a critical factor in business success. To thrive in a competitive market, companies must understand the concept of competitive advantage, pursue strategies to build and maintain it, measure its effectiveness, and overcome challenges. By doing so, they can gain a strategic edge and position themselves for long-term growth and profitability.
Related Stories
- April 17, 2024
Understanding the Organizational Culture Profile: A Deeper Look into Core Values
Culture statement examples: inspiring your business growth.
- April 16, 2024
Fostering a Healthy Organizational Culture: Key Strategies and Benefits
What can we help you find.
Discover top guides, trends, tips and expertise from AIO Writers
7 Competitive Advantage Examples for Business Success
Julia McCoy

Imagine stepping into a ring where everyone’s fighting to be number one. That’s the business world for you, and having a competitive advantage is like knowing a secret move that puts you ahead of the others. But what are your competitive advantages?
We’re about to explore the different types of competitive advantage in business and how companies shine by reducing expenses smartly and offering distinctive value that makes them the preferable choice of consumers.
We’re talking real-world competitive advantage examples where companies have turned the tables in their favor using these strategies.
Additionally, we’ll delve into the significance of embracing innovation and adjusting to worldwide shifts, vital for maintaining a competitive advantage.
So buckle up; it’s time to learn how to stay ahead in the game.
Table Of Contents:
What is a competitive advantage, cost leadership, product differentiation, strong brand, technological superiority, access to capital, what is competitive advantage and example, what is an example of a company with a competitive advantage, what is chick-fil-a’s competitive advantage.
Competitive advantage refers to unique attributes or capabilities that allow a business to outshine its competitors, attract more customers, and achieve higher profitability. These advantages are essential for businesses aiming to establish themselves as leaders in their respective markets.
A company’s competitive edge might stem from various sources such as innovative technology, exceptional customer service, or even a strategic geographic location.

Competitive advantage definition from Investopedia
Types of Competitive Advantage
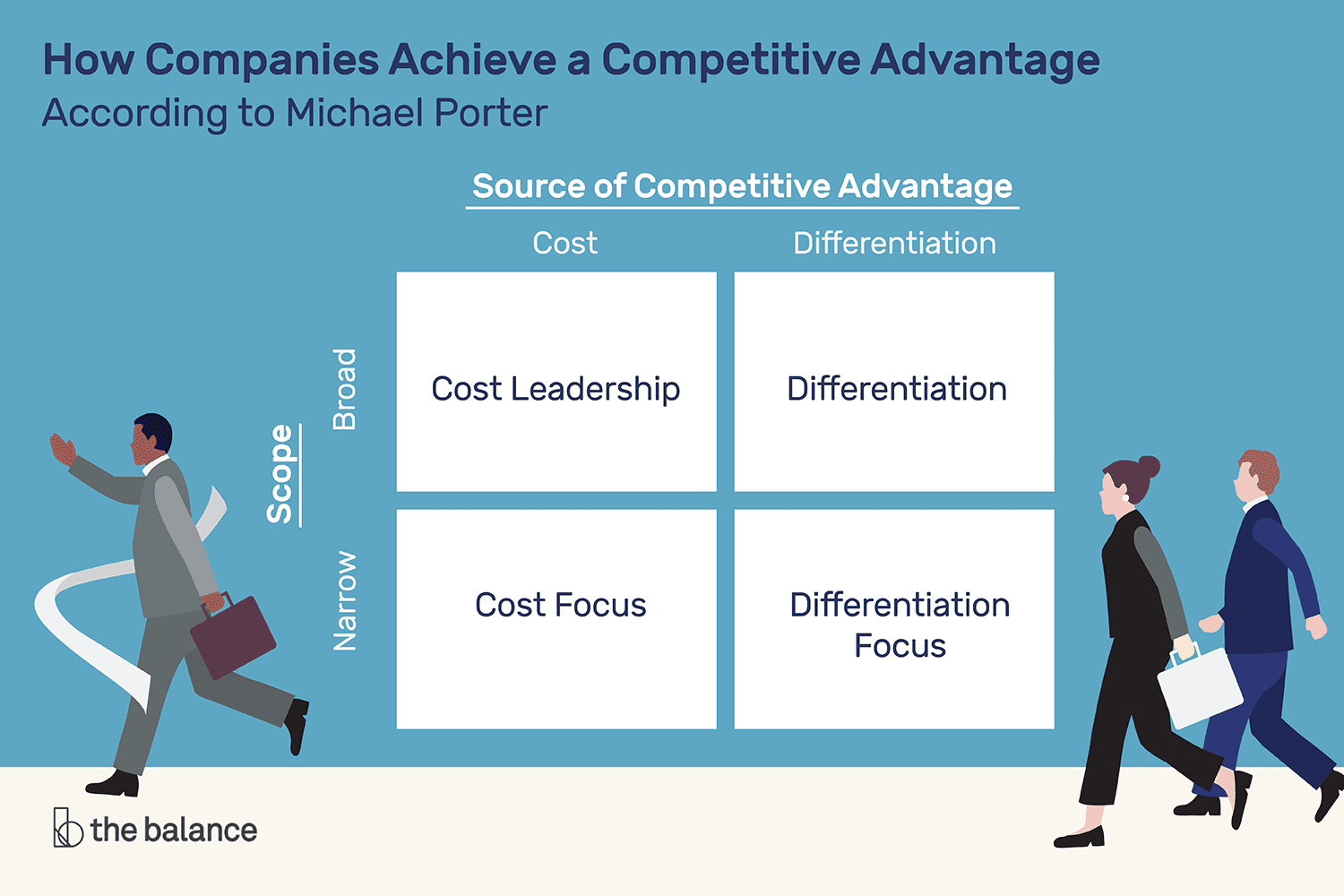
Michael Porter , a world-renowned authority on business competitiveness, identified three fundamental strategies that companies can adopt to secure enduring advantages. These strategies are cost leadership , differentiation , and focus .
Cost leadership is all about making and selling stuff that’s cheaper than the other guys.
Differentiation is about creating products that truly stand out from the crowd.
Focus is where you hone in on specific market segments and offer them something unique and tailored to their needs.
Let’s break down these three competitive advantage examples.
In cost leadership, it’s all about becoming the lowest-cost producer in your industry. Think Walmart or IKEA. These industry giants excel in trimming expenses from every angle, while still maintaining a decent level of quality. They buy in bulk, optimize operations, and pass these savings to their customers.
Even smaller enterprises can engage in this approach by focusing on efficiency and expanding their operations as opportunities arise. The key? Streamlining processes and negotiating better deals with suppliers to lower production costs.
Differentiation is when you make your product or service stand out because it has something unique. Apple, with its pioneering gadgets and a brand that epitomizes sophistication and cutting-edge technology, truly excels in carving out a distinctive niche.
There are three types of product differentiation: vertical, horizontal, and mixed.
Vertical differentiation is all about clear-cut advantages like price or quality that set a product apart.
Horizontal differentiation, on the other hand, zooms in on consumer tastes like packaging, flavor, or color.
Mixed differentiation blends both approaches — highlighting a mix of objective and subjective product characteristics.
To nail differentiation, think deeply about what makes your offering special — be it design, features, customer service, or technology — and then shout it from the rooftops (or market it wisely online).
Remember: Different doesn’t always mean better for everyone but it means better for your target audience.
A focus strategy involves targeting a specific niche market rather than trying to appeal to the masses. This could mean specializing in gluten-free baked goods if you’re a bakery or eco-friendly apparel if you’re into fashion retailing.
The beauty of focus strategies lies in understanding and serving your chosen segment so well that competitors simply can’t keep up because they’re spread too thin catering to broader markets.
Warby Parker, by really honing in on the specific desires and necessities of its target audience, has managed to secure a substantial niche despite aggressive rivalry from bigger eyewear corporations.
Gaining an edge over competitors requires not just following one path but often blending these strategies smartly based on changing market dynamics.
Source: The Balance
Cost leadership, product differentiation, and focus are generic competitive advantages. Porter has also identified three specific types of competitive advantage: strong brand , technological superiority , and access to capital .
For any company, establishing a robust brand is essential. It not only boosts the effectiveness of advertising but also fosters a deeper emotional bond with consumers.
A powerful brand transcends mere logos and names; it’s a community built on ideas, values, and beliefs, evoking inspiration and uniqueness. It’s the go-to choice for consumers, meeting their expectations effortlessly and staying attuned to evolving social and consumer trends.
To build a strong brand, you first need a clear purpose beyond profit-making. This purpose defines why your business exists. Then, you analyze competitors, identify your target audience, and formulate a strategy.
Crafting a compelling brand story follows — communicate your values, vision, and mission.
Next, shape or refine your brand identity with a strong name, recognizable logo, and unique tone of voice.
Consistency is key here — your messaging, storytelling, and promotional efforts should consistently align with your brand’s purpose.
New technology is a fantastic opportunity to revamp business models and streamline operations for better efficiency.
When technological prowess delivers specific perks like automation or data-driven innovations, it becomes a powerful competitive advantage.
Investing in research and development to unveil new products can also capture consumers’ attention and propel a company to the forefront of the digital landscape, setting it apart from rivals.
There’s a myriad of ways to leverage technology for that competitive edge. For instance, using data to understand both customers and employees better can inform strategic decisions. Cloud services enable the storage of vast amounts of data, while artificial intelligence helps with thorough analysis, leading to enhanced efficiency, cost savings, and superior customer experiences.
Apps serve as vital conduits for seamless interactions between a company and its clientele across various platforms.
Cognitive technologies like machine learning and speech recognition streamline processes that once relied on human input.
Furthermore, cybersecurity is crucial in today’s tech-driven world, safeguarding against cyber threats and ensuring the protection of sensitive customer data.
Large companies across various industries, including manufacturing, space exploration, and healthcare, frequently leverage this form of competitive advantage.
Access to capital denotes the availability of funds, equipment, and materials necessary for the production and distribution of goods. It encompasses resources for storage, refunds for defective products, and funding for marketing endeavors.
Small businesses often grapple with challenges in securing capital to launch products or expand sales. Conversely, large enterprises benefit from ample financial resources for advertising, research and development, and infrastructure — positioning them to outpace competitors.
With access to capital, market leaders can effortlessly raise funds and reinvest additional resources to scale production or venture into new markets.
Now, let’s look at real-world competitive advantage examples and explore how renowned companies have pushed their brands to the forefront of their respective industries.
Real-World Competitive Advantage Examples
Discover how industry giants like Amazon, Apple, Walmart, Tesla, Starbucks, Nike, and Netflix have used their competitive advantage to leave market competitors in the dust.
Walmart has become synonymous with savings, but it’s not just about low prices for customers. They achieve this through a relentless focus on efficiency — from logistics to negotiations with suppliers. By prioritizing efficiency, they manage to offer lower prices than their rivals while still keeping their profit margins healthy.
Another factor that turned into Walmart’s competitive edge is its strategic placement of stores in remote areas. By catering to small towns with limited retail options, Walmart effectively monopolized these markets, making it challenging for competitors to establish a foothold. This presence in hard-to-reach locations, coupled with competitive pricing and quality service, solidified Walmart’s dominance in numerous underserved communities.
Walmart’s use of technology for inventory management is especially noteworthy — it uses automation to gain a competitive advantage in the retail space. Automation plays a crucial role in streamlining operations throughout the company’s distribution centers and stores. From product transportation and sorting to packaging and checkout processes, Walmart employs automation technologies to enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Scan-and-go kiosks in stores reduce wait times, while automation in distribution centers, powered by robotics and artificial intelligence, optimizes supply chain processes, ensuring accuracy and speed. Thanks to AI, Walmart shelves are stocked efficiently while avoiding overordering — saving millions annually.
In essence, Walmart’s strategy turns cost-saving into its most potent weapon against competition.

If there’s one company that knows how to stand out, it’s Apple. Their approach? Deliver products so unique that they set the standard for what consumers expect in quality and design.
This isn’t just about having sleek gadgets; Apple backs up its designs with robust ecosystems like iOS and exclusive services such as iTunes and the App Store which lock users into their world seamlessly.
No doubt, Apple’s biggest competitive edge is its strong brand reputation — built over many years of delivering high-quality products with clean, intuitive designs. This brand equity not only distinguishes Apple in the global market but also fosters strong customer loyalty. With consistent brand recognition and a seamless ecosystem of interconnected devices and services, customers often opt for additional Apple products, reinforcing the company’s market dominance.
Technological innovation is the core of Apple’s success, as the company continually pushes boundaries with groundbreaking products like the iPod, MacBook, and iPhone. Through substantial investments in research and development, Apple maintains its position at the forefront of technological advancement, consistently introducing cutting-edge features and functionalities to captivate consumers. In 2022 alone, Apple allocated over $25 billion to R&D, showcasing its unwavering commitment to innovation.
Apple continually reshapes the market landscape, not merely by keeping pace but by establishing new benchmarks in innovation and user experience.

Amazon’s success stems from a multifaceted approach to competitive advantage.
First, the company prioritizes cost leadership — focusing on customer satisfaction over immediate profits.
Recognizing the significance of delivery costs, Amazon pioneered free shipping for purchases exceeding $25, a move that significantly enhanced customer appeal and boosted sales. This strategy was further amplified with the introduction of Amazon Prime, providing expedited two-day delivery for time-sensitive customers.
Amazon also employs product differentiation to stand out in the market. Offering an unparalleled selection of goods, the company serves both buyers and sellers through its expansive marketplace. This broad product assortment caters to diverse consumer needs, ranging from everyday essentials to specialized items, aligning with Amazon’s customer-centric ethos and enhancing service convenience.
Amazon maintains a focus on technological superiority to elevate customer service standards. The platform’s user-friendly interface, coupled with features like enhanced search functionality, personalized suggestions, and one-click ordering, prioritizes ease of use for customers.
Lastly, Amazon extends its technological prowess through its subsidiary AWS, offering cloud computing services to individuals, businesses, and governments to diversify its revenue streams and cement its position as a leader in the tech industry.

Nike’s success in the sports apparel and footwear industry is attributed to its product differentiation and efficient brand management.
Nike boasts unparalleled brand awareness, driven by its iconic swish logo and slogan “Just Do It” which has solidified its status as a household name. Endorsements from high-profile athletes like Michael Jordan and Tiger Woods further amplify Nike’s visibility and resonance with consumers.
Central to Nike’s strategy is a relentless pursuit of innovation, exemplified by its dedicated research division called The Nike Sports Research Lab. Through innovation, Nike continuously expands its product range to cater to diverse demographics, including women, teenagers, and children, ensuring its offerings align with evolving market trends and customer preferences.
Notable innovations like the Nike Fuel Band, which tracks daily activities, and Nike By You, a customization service for footwear and sportswear, enhance customer engagement and foster brand loyalty by offering personalized experiences unmatched by competitors.

Starbucks has become a household name by focusing on product differentiation, emphasizing the quality of its offerings to attract a clientele of middle to upper-class individuals. The strategic placement of Starbucks stores in bustling urban centers, suburban retail districts, and university campuses enhances accessibility and reinforces its brand image as a place where customers can relax and socialize outside of home and work.
By curating inviting store environments, offering complimentary WiFi, and providing exceptional service alongside a diverse product range, Starbucks creates a distinct customer experience that sets it apart from competitors.
With a massive global presence spanning over 80 countries and a uniform visual identity maintained across its stores worldwide, Starbucks has built a strong brand identity symbolized by the iconic Siren logo. This concerted effort to maintain consistency across locations reinforces the brand’s reputation and ensures a seamless customer experience regardless of geographical location.
Lastly, Starbucks has turned corporate social responsibility (CSR) into a competitive advantage — demonstrating a commitment to environmental sustainability that further enhances its positive brand image and fosters long-term customer loyalty.

Netflix maintains a sustainable competitive advantage through a cost leadership strategy, prioritizing low operational costs and affordable pricing to attract a broad customer base.
With over two decades of experience in the streaming industry, Netflix has developed a robust infrastructure on a large scale, positioning itself ahead of newer competitors entering the market. Rather than focusing on niche segments, Netflix adopts a global approach, aiming to expand its customer reach worldwide and solidify its market presence.
Investment in research and development plays a pivotal role in Netflix’s strategy, driving innovation and addressing customer needs effectively. Through initiatives like the Dynamic Optimizer and the introduction of offline viewing capabilities, Netflix optimizes content delivery and enhances user experience.
Continuous refinement of its recommendation algorithm also enables Netflix to personalize content suggestions according to viewing habits, further enhancing customer engagement and retention.
Unlike its rivals that offer mostly in-house titles, Netflix implements a differentiation strategy by offering original content alongside licensed third-party videos. By working directly with producers and leveraging subscriber data to inform content creation and pricing decisions, Netflix delivers value to its audience while maintaining cost efficiency.
This approach has enabled Netflix to produce compelling content targeted at specific viewer interests, fostering customer loyalty and cementing a sustainable competitive advantage in the streaming industry.

Tesla took electric cars from a niche novelty to a must-have status among environmentally conscious consumers.
Rather than targeting all car buyers, Tesla focused on affluent individuals looking for luxury without compromising on eco-friendliness.
Tesla’s biggest competitive advantage is its technological prowess, continuously integrating cutting-edge innovations into its vehicles. With a focus on software-driven functionality, Tesla can collect and analyze data from its vehicles, allowing for continuous improvement and refinement of features such as autopilot.
The use of artificial intelligence further reinforces Tesla’s position at the forefront of autonomous driving technology, with neural networks trained using real-world data captured by Tesla owners.
Like Apple’s approach to product excellence, Tesla has built a reputation for delivering high-quality, stylish automobiles that defy traditional expectations of electric cars. The introduction of the Tesla Roadster shattered stereotypes, showcasing that electric vehicles can be both fast and visually appealing.
Tesla’s vertical integration strategy, particularly in battery production, also provides a significant competitive advantage. The establishment of the Gigafactory drastically reduced battery manufacturing costs through economies of scale, waste reduction, and process optimization.
This strategic move not only enables Tesla to produce more batteries than all other car manufacturers combined but also facilitates continuous improvements in battery quality and chemical composition, further solidifying its dominance in the electric vehicle market.
FAQs – Competitive Advantage Examples
A competitive advantage makes a firm’s goods or services better than its rivals. Apple stands out with its unique ecosystem.
Amazon dominates its industry by delivering a vast selection, quick shipping, and stellar customer service.
This fast-food giant shines through top-notch customer service and quality eats. Their secret sauce? Treating patrons like gold.
Stepping into the business ring, knowing your secret move matters. That’s where competitive advantage examples shine.
Key takeaways? Cost leadership and differentiation are not just buzzwords; they’re game changers. Innovation keeps you ahead, while globalization opens doors but demands agility.
Sustaining your edge means adapting, evolving, and never settling for yesterday’s win.
To sum up: stay sharp, be unique, and always look forward. The right strategy isn’t just about leading today; it’s about staying ahead tomorrow.

Written by Julia McCoy

UNLOCK YOUR POTENTIAL
Long headline that highlights value proposition of lead magnet.
Grab a front row seat to our video masterclasses, interviews, case studies, tutorials, and guides.
What keyword do you want to rank for?
Discover RankWell ® your SEO best friend
Our proprietary suite of SEO tools, aka RankWell®, offers marketers real-time, deep SEO insights. From keyword ranking difficulty scores to audits on improving your content, our full-service SEO tool suite is your content's best friend.
Get a free topic report that has every insight you need to outrank the competition.
By clicking Sign Up, you agree with our Terms and Conditions.
%20(1).png)
How to Write a Competitor Analysis for a Business Plan (with AI in 2023)

Competitor analysis is a critical component of any business plan. It helps you understand the landscape of your industry, identify opportunities for growth and differentiation, and craft strategies that take advantage of your competitors' weaknesses.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to conduct a comprehensive competitor analysis, including how to leverage AI tools like Bizway to make the process more efficient and effective.
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a Competitor Analysis
1. identify your competitors.
Understanding your competitive landscape begins with pinpointing who your direct and indirect competitors are.
Points to Consider
- Direct Competitors : Those who offer similar products/services in the same market.
- Indirect Competitors : Businesses targeting your customer base with different offerings.
- Utilize market research and customer feedback to list competitors.
- Identify geographical considerations - local, regional, or global competitors.
2. Analyze Their Products/Services
A thorough examination of competitors’ offerings unveils potential areas for differentiation and enhancement in your product/service line.
- Feature comparisons.
- Pricing structures.
- Unique Selling Propositions (USPs).
- Adopt a customer-centric approach to understand how consumers perceive competitors’ offerings.
- Identify gaps in their product/service lines that you could explore.
3. Assess Their Marketing Strategy
Understanding competitors’ marketing approaches aids in crafting a superior, data-driven marketing strategy.
- Target audience.
- Key messages and value propositions.
- Channel effectiveness and presence.
- Use social listening tools to gauge their social media effectiveness.
- Analyze the SEO performance of competitors’ websites.
4. Examine Their Sales Strategy
Investigating sales channels and tactics employed by competitors reveals market penetration strategies and potential areas for diversification.
- Distribution channels.
- Pricing and sales tactics.
- Customer relationship management.
- Secret shop to observe sales tactics and customer experiences.
- Review customer feedback on their purchasing experience.
5. Analyze Their Strengths and Weaknesses
Identifying what competitors excel in and fall short on enables strategic decision-making in exploiting market opportunities.
- Operational efficiency.
- Customer service quality.
- Brand reputation and loyalty.
- Conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) for each competitor.
- Leverage customer reviews and testimonials to gauge reputation.
Using AI for Competitor Analysis
Automated data collection.
AI automates the harvesting of data from myriad sources, ensuring robust research while saving time.
- Use AI tools to scrape and aggregate data from competitors' websites, social media, and customer review platforms.
- Ensure the data is categorized and stored systematically for easy analysis.
Real-Time Updates
AI provides a competitive edge by monitoring and reporting real-time updates on competitor activities.
- Set up AI monitoring for specific competitor activity: product launches, PR releases, or marketing campaigns.
- Ensure to leverage real-time data to inform swift strategic adjustments.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics via AI deciphers patterns and anticipates future competitor moves, positioning your business proactively.
- Leverage AI to analyze historical data for predicting future trends.
- Utilize these insights to anticipate and formulate preemptive strategies.
Using Bizway for Competitor Analysis and Business Planning
One such AI tool that can revolutionize your competitor analysis process is Bizway . Bizway is an AI-powered business planning and research app that can help you research your competitors and write your entire competitor analysis with just a few clicks. Moreover, Bizway can assist you in writing your entire business plan, saving you time and providing you with expert-level planning documents.
With Bizway, you can automate the process of generating clear, concise planning docs across all areas of business, from an SEO Content Plan to User Onboarding Plan. It also helps fill knowledge gaps in areas of business you're not well-versed in.
So, whether you're a solopreneur, a small business owner, or an aspiring entrepreneur still in school, Bizway is the AI assistant you need to take your business planning to the next level.
Gerrard + Bizway AI Assistant
Start automating your business growth, today⚡
Create your first AI assistant & project in minutes.⚡
.png)
Bizway is brought to you by Landmark Labs Ltd.
©2024 Bizway Labs
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
Small Business Tools
Write the Competition Section: Business Plan Writing
Aayushi Mistry
- December 21, 2023
11 Min Read

What is the Competition Section?
Your business plan includes a lot of operational sections. Every section holds a different importance. In that case, competition is one of the most fundamental aspects of your business. And so, it needs to be added to your business plan. The section that explains your competition is your competition section.
While deciding where to add the competition section, pay attention to the flow of your business plan. Moreover, it also depends on the priority. So, it must come next to your objective, problem statement , product/services, and target audience.
Why Do You Need a Competition Section in Your Business Plan?
The why of your business plan depends on your purpose-
If your purpose is to direct your business growth:
Your competition status can play as your reference point. Here, the competition section serves as a medium for understanding your competition. So, you can develop strategic positioning.
This can help you and your team to look at comparative strengths and weaknesses exclusively. So, you can easily come to the strategies that work in your favor, and give you a competitive advantage .
If your purpose is to create a business plan to seek investment:
You must add it to inform your investors about your competition, market position, and brand promise.
You need to describe the competition to reassure probable investors that you know and understand your competition. And that you are ready to take advantage of opportunities and avoid the pitfalls.
Apart from this, your purpose also makes a difference in how to write your competition section in your business plan. However, the difference is minor, and the effect of it is profound.
How to write a competition section in your business plan?
Regardless of your purpose mentioned above, you have to include all the steps mentioned below. Wherever there is the need for that ‘minor’ change, we will include it under the same step.
While following this step, we suggest you take action side by side. So, it becomes easier to implement. Moreover, before putting up your competition section, be ready with your competition data.
Also, make sure that you have conducted a competitive analysis and processed data of at least 5 competition companies. Once you have everything you need, you can go through the following steps-
1. Determining and Documenting Your Business Position
Regardless of your purpose, you will have to follow this step. And there isn’t any major difference here. You need to know your business position in the market and document it properly. However, we will first talk about the determining part. And then, document it for the competition part of your business plan.
How to determine your market position?
Gather crucial details for your company and your competitors’ companies. When you have all the data, you compare them. And put it up on the competition graph.
The details you will need include:
- Sales Figures
- Profit margins
- Distributors
You can also add the marketing column if you find the need. Here, your goal is to make clear positions with respect to your target markets.
However, there are two most reliable ways to determine your position:
1. Position Mapping Graph
You can do this for 5 main aspects of your business-
- For product characters
- The quality of products/services
- The number of products/services
- For user/customer friendliness
You can either put all the points in the same graph or use a separate graph for each.
How to do this?

- Get graph paper and divide it into 4 quadrants
- Add your parameter(s)
- Start plotting your and your competition’s point
2. Competitive Matrix
A competitive matrix is a method that helps you determine your competitive advantages. Usually, you put together this tool to note your market credibility. It is an industry analysis tool that compares the characteristics of you and your competition.
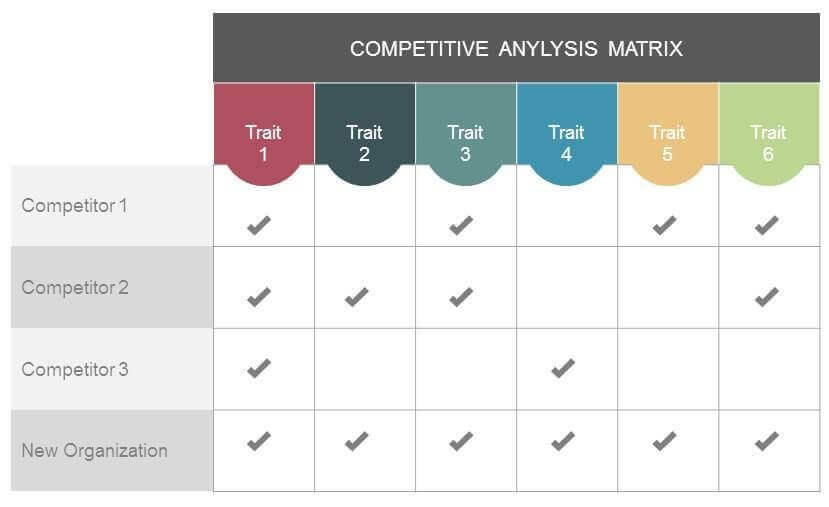
How to do it?
- You draw out a matrix
- Position your company and competitors, at the top, the horizontal blocks
- Put all the aspects you want to compete with, in the vertical blocks
- Put the tick marks to draw the competition
How to document in the competition section for your business plan?
Once you complete the determination, the documentation is quite easy. In fact, you can put the final graphs in your draft. It will not only give color and variety but also make it easy to understand.
While you put all the graphs together, you have to explain your competition and the parameters that you have selected. Moreover, you can go ahead and explain why the companies are your competition. Also, explain why you picked particular parameters.
Mention the date and time frame in your graphs. It makes it easier to have a deeper knowledge of your competition.
Basically, the documentation is journaling the process of drawing the graphs. You may not want to add every detail. As that could make the entire section a little longer than expected. But at the same time, don’t leave out the important details.
As for the difference, you can follow the same process for both purposes. Only make sure that your draft for your investors has been relatively concise. As for your company draft, you can add as many details as you want.
Why is this step important?
When you follow this step, the process of putting the competition section for your business plan is literally half done. It brings you the clarity that you, your team, and your investors need to make your business successful.
2. Determine and Draft Your Competitive Advantages
Determining the competitive advantage.
This process may look hard. But it is not. In fact, it just includes one step to the above one. It can be done side by side while you are drawing the comparison and putting them together in different graphs.
You have to note and add the points where you are doing better (or can do) better than your competition. And then, note how that bonus point can bring you an advantage(s).
Drafting your competitive advantage
You have to note down your bonus points and explain them in detail. You can use those graphs too for more clarity and variety. It is better that you make this up to the point. If you are writing for the investors, they might just want the rounded points after seeing the graphs.
And if you are using it for directive purposes, even then, it is good to have a well-rounded point. However, you might need the back details along the way ahead. So, you can note it down too.
With this step, you became assertive about your success and future in the market.
If brought in front of your investors, they quickly get a clear idea of whether to invest in your business or not. In a way, it helps you store their faith in your business.
And if you are only planning to put the direction of your company’s success, it gives you a clear picture of your strengths and opportunities. In a way, it restores your faith in your product/services.
3. Put in the customers’ review
This step is just like putting that final nail in the coffin! Plus, regardless of the purpose of your business plan, this step and section remain the same. Even more interesting, it takes less time than the two above-mentioned steps.
Here’s how you do it-
- Find out the reviews and ratings of all the competitors, you had begun the process with.
- Be discreet. Don’t only add the good points or the bad points. Add the good, the bad, and the average rating and reviews.
- You can go ahead and make three sections named- The Good, The Bad, and The Average.
- Add 10-12 reviews in total and put them in the respective sections (3 or 4 in each).
- You can find reviews from search engines, social media, websites, forums, and magazines.
- If you want authentic reviews and have enough time and resources, you can even run surveys. Or contact agencies that run unbiased surveys.
How to draft it-
- Put them just the way they are, even if they have typos. Try not to tamper with them.
- Add them at the end of the competition section for your business plan.
Why is this step important
- To add more clarity and favor to your business.
- Gives a chunk of customer points of view.
- Restores your, your team’s, and your investor’s faith in your company.
Basic Template
And that’s all about the competition section in the business plan. We hope we have given you all the information that you needed. However, regardless of how you find notes, we have listed the FAQs for the competition section for a business plan. You can refer to it for questions that look similar to yours.
FAQs for your competition section
What if we think that our business does not have competition?
Ideally, every business has competition. If not directly, then indirectly. Basically, there are three types of competition- Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary.
Primary: The business that has similar products/services as you and, serves the same target audience.
Secondary: The high-end or low-end services/products as you. There may be a slight change in the target audience, depending on the spending capacity location and more.
Tertiary: They have completely different products/services but satisfy the same needs of your target audience.
So, if you think that you don’t have primary competition. Look closely, you may have a secondary or tertiary competition.
What if that time my competition changes?
You have to run the test from the start and draft the section from scratch. It may be the same even when you want to add and remove the parameter.
Do we need a separate team to draw a competition analysis and draft it in the business plan?
Not importantly. However, it is important for everyone involved in your team to be qualified and have adequate experience. If you think that your team doesn’t have that, you can form or hire a separate team.
How long should the competition section be in the business plan?
It should be detailed. But it must not take up most part of your business plan. Moreover, it also depends on the number of other sections you are adding. And it also depends on what these other sections are. In any case, there is no harm in being concise. No matter who the reader is, we all prefer a quick read.
Where else can we showcase this analysis?
You can use this analysis in marketing and sales strategies. You can even use it to further research and develop your product/services.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
About the Author

Since childhood, I was in awe of the magic that words bring. But while studying computer science in college, my world turned upside down. I found my calling in being a copywriter and I plunged into a world of words. Since then, there is no looking back. Even today, nothing excites me to find out the wonders the words can bring!
Related Articles

What is a Competitive Advantage? Explained with Examples

Everything You Need to Know About Pricing Strategy
What is SWOT Analysis & How to Conduct it
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

31+ SAMPLE Competition Business Plan in PDF | MS Word
Competition business plan | ms word, 31+ sample competition business plan, what is a competitive business plan, different types of competitive strategies, basic elements of a competitive business plan, how to write a competitive business plan, what are some examples of competitive business plans, what are the key elements in a competitive business plan that should be included, what are the primary factors of competitive advantage, what are the main competitive forces in business.

Competition Business Plan Template

Competition Business Plan Checklist

Competition Business Plan Example
Competition Score Business Plan

Printable Competition Business Plan

Innovation Competition Student Business Plan

Competition Business Plan in PDF

Competition Youth Business Plan

Formal Competition Business Plan
Company Profile Competition Business Plan

Competition Education Business Plan

Standard Competition Business Plan

Global Business Plan Competition to Promote Entrepreneurship
Competition Student Business Plan

Competition Annual Business Plan

Competition Business Plan Format

Competition Entry Business Plan

Competition For Unity Youth Councils Business Plan

Simple Competition Business Plan

Competition Registration Form Business Plan

Competition Eligibility Statement Business Plan

Competition Marketplace Business Plan

Competition Winners Business Plan
Competition Society For Biomaterials Business Plan

Sample Competition Business Plan

Competition Annual Student Business Plan

Competition University Business Plan

Basic Competition Business Plan

Entrepreneurship Through Business Plan Competition
Draft Competition Business Plan

Competition For High School Students Business Plan

Competition Business Plan in DOC
1. low cost provider strategies, 2. broad differentiation strategies, 3. focused low-cost and differentiation strategies, 4. best-cost provider strategies, step 1: create a concise summary , step 2: develop market analysis and sales/marketing strategy, step 3: include a competitor analysis, step 4: review and execute the competitive business plan, share this post on your network, file formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 5+ sample investment company business plan in pdf.

What do you do when you have tons of spare cash lying around your home or burning a hole in your wallet or expensive jeans pocket? For some people, the…
41+ SAMPLE Unit Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
As a teacher, you might know about every school policy, the steps to keep classrooms safe for intellectual development, how to set up an organized classroom, and the proposed…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
Plan Projections
ideas to numbers .. simple financial projections
Home > Business Plan > Competition in a Business Plan

Competition in a Business Plan
… there is competition in the target market …
Who is the Competition?
By carrying out a competitor analysis a business will be able to identify its own strengths and weaknesses, and produce its own strategy. For example a review of competitor products and prices will enable a business to set a realistic market price for its own products. The competition section of the business plan aims to show who you are competing with, and why the benefits your product provides to customers are better then those of the competition; why customers will choose your product over your competitors.
- Who are our competitors?
- What are the competitors main products and services?
- What threats does the competitor pose to our business?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of our competitors?
- What are the objectives in the market place of the competitors?
- What strategies are the competitors using?
- What is the competitors market share?
- What market segments do the competitors operate in?
- What do customers think of the competition?
- What does the trade think of the competitor?
- What makes their product good?
- Why do customers buy their product?
- What problems do customers have with the product?
- What is the competitors financial strength?
- What resources do the competition have available?
The focus is on how well the customer benefits and needs are satisfied compared to competitors, and not on how the features of the product compare. For example, key customer benefits might include affordability, can be purchased online, or ease of use, but not a technical feature list.
Competition Presentation in the Business Plan
The business plan competitor section can be presented in a number of formats including a competitor matrix, but an informative way of presenting is using Harvey balls . Harvey balls allow you to grade each customer benefit from zero to four, and to show a comparison of these benefits to your main competitor products. The competitors might be individual identified companies, or a generic competitor such as ‘fast food restaurants’.
In the example below, the key benefits of the product are compared against three main competitors. Each row represents a key benefit to the customer, the first column represents your business, and the remaining three columns each represent a chosen competitor.
The investor will want to understand that your product has the potential to take a major share of the chosen target market by being shown that it is sufficiently competitive for a number of key customer benefits.
This is part of the financial projections and Contents of a Business Plan Guide , a series of posts on what each section of a simple business plan should include. The next post in this series will deal with the competitive advantages the business has in the chosen target market.
About the Author
Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Plan Projections. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University.
You May Also Like
- Skip to content.
- Jump to Page Footer.
Webinar: Foreign Investment in 2024
Discover the secrets to prospecting and selecting relevant investors, and unlock the potential of international funding opportunities. Our expert speakers provide invaluable insights on engaging with investors, creating an international investment strategy, and navigating term sheet negotiations.

Defining your competitive edge: Product positioning in your target market
Highlights (click to read).
- It’s critical to create a competitive edge for your product within your target market.
- To distinguish and position your product, be the first in the market and leverage your expertise to establish leadership.
- Work constantly to maintain your competitive edge.
- Quality, customer service and price do not provide a competitive edge.
Define your competitive edge by finding different ways of being unique in the marketplace. By differentiating your product, service, personnel or brand, you can establish a unique position in your market.
In today’s crowded market, many products can more easily mimic each other in terms of their attributes and offered benefits. The following strategies can help to distinguish your offering in the market and create a competitive edge.
Be first in the market
Buyers tend to stay with what they know. By being first to market, you will be able to take advantage of having no competition with your offering (also known as the first-mover advantage). However, it can take time to gain market acceptance of new ideas, and being first does not last forever.
Leverage your expertise: Establish leadership
Being perceived as an expert in your market bestows on you a level of trust, which transfers to your products. You can establish leadership in different areas, such as technology, science or sales. Develop your reputation and expertise with knowledge-sharing activities, such as writing blogs, articles or white papers, or presenting webinars.
Focus your market expertise
Establish your expertise by focusing on one particular niche to develop market specialization. Your market-specific expertise will set you apart from the competition. For example, instead of concentrating on a wide market encompassing all doctors, zero in on a niche within that market, such as pediatricians. This would enable you to specialize in, and appeal to, a pediatrician’s particular needs. Otherwise, your offering may not hold enough appeal to the wider audience to give you an advantage over your competition.
Make your products stand out as new and improved
Study your competitors and learn how they target a market problem. Ensure that the problem is an important one, and that your solution is better. Then reposition this market problem with your own unique solution. You can capitalize on your competitors’ marketing, but make sure to position your product as the“next generation.” For example, when microwave ovens were flooding the market, new entrants adjusted their positioning by marketing their products as “speed cookers” that evenly cooked food, a significant improvement over their microwave counterparts.
Note : By identifying market problems , you might see a problem/solution in a different way than your competitors, which will give you an advantage.
How to maintain your competitive edge
Once you have defined your competitive edge, you must work to maintain that upper hand. Your competitors will constantly work to improve their products and build their expertise, and so should you. Strive to ensure that your product continually solves your customers’ problems in new ways. By focusing on this goal, you can stay ahead of your competitors.
What is not a competitive edge
Avoid focusing on the following areas or characteristics, as they will not set you apart from your competition.
Quality and customer orientation
Although it is important to manufacture good quality products and be customer-oriented, these factors will not set you apart from the competition. Since your product is on the market, the tacit understanding is that the quality is good.
Customer service
It is assumed that you will work diligently to ensure customer satisfaction. This alone will not keep those customers coming back to you. According to Jack Trout, in Differentiate or Die , it was found that 40% of satisfied customers would change brands without looking back.
Although pricing your products below market price might attract some buyers, it will not differentiate your product for long. Being cheaper than an alternative will not position you as unique. It will place you in a weak position because your competition could change their price to match yours at any time.
Breadth of line
Based on the success of “superstores,” you might be tempted to become“everything to everyone.” However, this is not differentiation. You might solve some problems for some customers, but it is more likely that you will not fully solve any customers’ problems.
Provide a specific solution to ensure that you solve real problems for a specific target market .
Summary: It’s critical to create a competitive edge for your product within your target market and to work hard to maintain this position against your competition.
Product positioning: stress your unique value, positioning: creating an image of your product in your target customer’s mind, product positioning and positioning your startup: customer validation stage, sign up for our monthly startup resources newsletter about building high-growth companies..
- Enter your email *
You may unsubscribe at any time. To find out more, please visit our Privacy Policy .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are the steps you need to take: 1. Identify your competitors. The first step in conducting a comprehensive competitive analysis is to identify your competitors. Start by creating a list of both direct and indirect competitors within your industry or market segment. Direct competitors offer similar products or services, while indirect ...
The organization also experiences higher customer satisfaction ratings, which also contributed to higher sales performance. 9. Quality. Quality contributes to customer satisfaction and an organization's reputation, which both factor into a company's competitive advantage. Quality control programs, maintenance, technology and customer feedback ...
Perform a SWOT Analysis of your competitors. 1. Identify Your Direct and Indirect Competitors. First things first — identify all your business competitors and list them. You can make the final list later, but right now jot down all the competitors including new competitors.
You decide to conduct a market analysis for your business. To do so, you would: Step 1: Use Google to compile a list of your competitors. Steps 2, 3, and 4: Use your competitors' websites, as well as SEO analysis tools like Ahrefs, to deep-dive into the service offerings and marketing strategies of each company.
1. Brand. Strong Branding is one of the strongest sustainable competitive advantages. A lot goes into making a brand like building customer relationships, quality service/product, time, and money. But when the company is identified as a brand in the market, it brings you a positional advantage. And at the same time, your sales become easier and ...
This article is part of a series on how to write a great business plan. The Competitive Analysis section of your business plan is devoted to analyzing your competition--both your current ...
Your competitive advantage makes your product or brand more attractive to customers than your direct competition. Think about why your product or brand is a natural choice for customers. Your competitive advantage is the deciding factor that closes sales. For example, you might offer your product at a lower price than your competition.
5. Human Capital. A company is only as strong as its people. As such, hiring, training, and retaining a team of skilled employees is a competitive advantage for any business. Putting in the time and care to select outstanding candidates for open positions, train current employees, offer professional development opportunities, and create a ...
This list of competitive advantages highlights a few of the most common strategies businesses have used to get that competitive edge. 1. First-mover advantage. First movers can gain a significant ...
Competitive analysis is a type of market research. It's the process of evaluating and understanding the strengths and weaknesses of competitors in your market. It involves gathering and analyzing data on competitors' products, pricing, marketing strategies, distribution channels, and customer base. Doing a competitive analysis helps you ...
Writing. A discussion of your competitive edge can be part of the section of your business plan that deals with the description of your company, or it can be the introduction to your marketing ...
Competitive advantages are conditions that allow a company or country to produce a good or service at a lower price or in a more desirable fashion for customers. These conditions allow the ...
Competitive advantage can be defined as the "strategic edge" that a company possesses over its rivals in the market. It is the unique combination of strengths, capabilities, and resources that enable a business to deliver superior value to its customers. One aspect of competitive advantage is having a unique product or service offering.
Competitive advantage definition from Investopedia Types of Competitive Advantage. Michael Porter, a world-renowned authority on business competitiveness, identified three fundamental strategies that companies can adopt to secure enduring advantages.These strategies are cost leadership, differentiation, and focus.. Cost leadership is all about making and selling stuff that's cheaper than the ...
Examples of things which might give your business a competitive or unfair advantage include the following: Patents. First to market. Barriers to entry. Available funds and working capital. Key partnerships and relationships. Access to expertise, special skills and talents.
There are several factors that contribute to building and maintaining a competitive edge in business. Recruiting is the first step, followed by training, managing, and rewarding employees. When it comes to getting ahead in business, getting - and sustaining - a lead on your competitors is crucial. Hiring consultants to advise on people ...
Competitor analysis is a critical component of any business plan. It helps you understand the landscape of your industry, identify opportunities for growth and differentiation, and craft strategies that take advantage of your competitors' weaknesses. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to conduct a comprehensive competitor analysis, including ...
Also, make sure that you have conducted a competitive analysis and processed data of at least 5 competition companies. Once you have everything you need, you can go through the following steps-. 1. Determining and Documenting Your Business Position. Regardless of your purpose, you will have to follow this step.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan. 1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively. 2.
Key Highlights. A competitive advantage is what sets a company apart from its competitors, in the eyes of its consumers. These advantages allow a company to achieve and maintain superior margins, a better growth profile, or greater loyalty among current customers. A competitive advantage is often referred to as a "protective moat.".
Executive Summary: One of the fundamental elements of a competitive business plan is the executive summary. It provides a clear and concise summary of the document which focuses the intentions of the executives or managers of a business firm or organiation that will be discussed in the overall plan. It should be a compelling part of the plan as it illustrates the mission statement of the ...
Here are three real-life examples of competitive landscape analysis from different industries: Customer Service/Conversational Marketing Software Industry: In this sector, Zendesk emerged as a leader, characterized by its low Alexa Rank and high Twitter follower count, indicating strong online presence and engagement.
For example, key customer benefits might include affordability, can be purchased online, or ease of use, but not a technical feature list. Competition Presentation in the Business Plan. The business plan competitor section can be presented in a number of formats including a competitor matrix, but an informative way of presenting is using Harvey ...
Study your competitors and learn how they target a market problem. Ensure that the problem is an important one, and that your solution is better. Then reposition this market problem with your own unique solution. You can capitalize on your competitors' marketing, but make sure to position your product as the"next generation.".