Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Mental Health — Argumentative On Contact Sports

Argumentative on Contact Sports
- Categories: Mental Health
About this sample

Words: 669 |
Published: Mar 19, 2024
Words: 669 | Page: 1 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Nursing & Health

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 670 words
5 pages / 2449 words
3 pages / 1405 words
2 pages / 834 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Mental Health
The relationship between mental illness and homelessness is a deeply intertwined and complex issue that affects individuals and communities across the globe. This essay delves into the multifaceted connection between mental [...]
Mental health stigma is a pervasive issue that hinders individuals from seeking help, perpetuates myths, and marginalizes those who experience mental health challenges. This essay explores the nature of mental health stigma in [...]
Easterlin, M., Chung, P., & Leng, M. (2023). Association of Team Sports Participation With Long-term Mental Health Outcomes Among Individuals Exposed to Adverse Childhood Experiences. JAMA Pediatrics.National Public Radio (NPR). [...]
Mental illness within the criminal justice system is a complex and pressing issue that intersects legal, medical, and ethical considerations. This essay examines the challenges posed by mental illness among individuals in the [...]
“Eat your vegetables! Exercise! Get a good night's sleep!” We’ve all known to take care of our bodies since grade school P. E. class. But what about our mental health, isn’t mental health just as important as physical health? [...]
J.D. is an 8 year-old male student at Central Philadelphia elementary school whom is diagnosed with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. J.D. was referred by his physician to receive psychiatric inpatient treatment [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Should Children Be Playing Contact Sports? The Risks And Benefits Of Youth Athletics
Children playing contact sports has been a hot topic for years. Is there enough evidence to warrant pulling kids from sports completely?
We independently evaluate all recommended products and services. If you click on links we provide, we may receive compensation.

Disclaimer : Just so you know, if you order an item through one of our posts, we may get a small share of the sale.
“Do I love hockey more than I love my child?” This is the question Bennet Omalu , a neurologist and forensic pathologist, asked in his book Truth Doesn’t Have a Side . Omalu is famous for publishing groundbreaking research documenting the damaging effects of football on professional athletes in America. His research changed the way we think about contact sports. In his opinion, no person under the age of 18 should participate in contact sports. The risk, in his mind, is simply too great. In a country in love with sports, this claim has caused many parents to pause and ask hard questions about their decisions regarding their child’s participation in sports. Should all adolescents be withdrawn from contact sports completely? What is the real risk of continuing to let them play? And on the other hand, could there be risks associated with refusing to let your child play team sports?
The Risk of Joining the Team
There is no denying that there are risks associated with participating in contact sports. Recently, a Texas NBC affiliate published quotes from doctors warning against preventable injuries caused by sports. Their specific worries concerned overuse injuries (injuries caused by too much stress on a certain body part). According to the article, these injuries are so common, they’ve reached “epidemic levels.” Doctors said these injuries could be prevented, however, by scaling back on training in childhood sports. The risk of traumatic brain injury is also gaining national attention. Participating in competitive sports puts young athletes at a high risk of sustaining at least one concussion in their lifetime , according to research published by JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association in 2017 . Of the survey’s 13,088 adolescent responders, 14 percent reported sustaining at least one concussion. When responders also reported participating in competitive sports, that number increased. This isn’t surprising, considering that sports accounted for roughly half of all concussions in adolescents, according to a 2013 report published in JAMA . The good news is that concussion symptoms are typically temporary. It isn’t common for adolescents to experience lasting effects from a properly treated concussion, according to the Mayo Clinic . The real concern about concussions pertains to the risks that come with repeated or compounding concussions. One study performed pre-season cognitive testing on high school adolescents, examining for symptoms of impairment and asking students to self-report concussions. The adolescents who reported more than one concussion were more likely to exhibit cognitive, sleep, and physical symptoms . The symptoms for students reporting three or more concussions were more likely to be significantly more severe.
The Risk of Benching Your Kids
“ In many cases, it seems that a lot of the narrative has been around what contact sports can do to an individual … I think we need to … discuss the things that sports in general … can do for the individuals participating.” —Vernon Williams, MD
Keeping Kids Active and Safe
Deciding whether to withdraw kids from sports or involve them is not an easy choice. For parents who want their child to remain involved in team sports, however, there are a few guidelines they can follow to keep kids as safe as possible during practices and games. One of the first things to know is that some contact sports simply aren’t worth the risk; McLaughlin doesn’t believe there is any reason for adolescents to be involved in boxing or mixed martial arts. In these sports, hitting someone in the head is part of the strategy. “The goal of boxing is to give somebody a concussion,” he says. Outside these two sports, McLaughlin says contact sports are getting safer for children. He notes that, because we have greater awareness, it may seem like concussions are becoming more frequent, when we’re really just getting better at detecting injuries. Additionally, thanks to the research on brain injury in contact sports, rules at the high school level are changing to increase safety. To guarantee that the team a child plays for is implementing safe practices, McLaughlin advocates for high parental involvement in sports. He says it is currently lacking, but it is the only way to be certain your child is safely participating in their sport of choice. Parents should go out of their way to educate themselves on safety practices that can decrease the risk of injury in their child’s sport. In the unfortunate instance that a child is injured while playing contact sports, the right response is crucial. Specifically, parents should take action and take their child to a health professional any time the child experiences loss of consciousness or memory impairment after a hit in sports. More common symptoms include tiredness, headache, and sound and light sensitivity, but loss of conscious and loss of memory are the biggest indicators that the child needs immediate medical care, according to Davis. “If someone has any symptoms of concussion, they should be removed from play, and they shouldn’t be allowed to return to play until they’ve been cleared … by the appropriate healthcare professional,” says Williams. According to Williams, experiencing a second concussion before the first has healed poses serious risks to all athletes. Additionally, he notes that emerging research suggests sub-concussive brain injuries can add up over time to create some of the same effects a full-blown concussion can create. For this reason, he pushes for reduced blows to the head in general in contact sports. He encourages parents to discuss ideas for reducing contact during practices with coaches as well as teaching athletes proper techniques. He also encourages athletic officials to enforce the new rules that have been created to minimize risks. Lastly, Davis, who is a strong supporter of participation in team sports, believes monitoring should be non-negotiable. “One thing that I think schools really need to implement … is requiring baseline cognitive testing for anyone who is going to play a sport,” she says. “Contract with a neuropsychologist and have them do baseline paper-and-pencil testing.” This would create a baseline for all participating athletes, says Davis. That way, if they were to experience an injury like a concussion, trainers and coaches would have a starting point to measure the impact of that injury. Without this initial test, post-injury testing is inaccurate. Ultimately, it is a parent’s choice if their child will participate in team sports. If you have any concerns about your child’s unique circumstances, it is always a good idea to consult with a doctor before allowing a child to become involved in activities with a risk of physical injury. With their help and proper education, you can confidently make a decision you feel is best for your child.
What to Eat When Nothing Sounds Good – 50 Ideas + Why You May Feel This Way
How to get rid of neck fat: 7 easy and effective methods that work, 10 best polygel nail kits for a flawless at home manicure, 14 best shapewear for lower belly pooch – easy tummy-control for 2024, best lash lift kit: 12 options to try at home (2022), related articles, stay in touch.
Please subscribe to our newsletter to get the latest news in your domain of interest. Don't forget to follow us on social networks!
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Solid Ventures, Inc. All Rights Reserved.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
Frontiers for Young Minds

- Download PDF
CTE: The Hidden Risk of Playing Contact Sports

If you have ever played contact sports, you may have heard about chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). CTE is caused by repetitive head injuries leading to a progressive loss in memory and other brain skills. The lack of proper skull protection has become a leading cause of brain problems in athletes. When playing sports, we focus on competition rather than the impact of repetitive injuries. Physical sports, like football, hockey, and boxing, have all been associated with CTE. When the brain hits the skull with an intense force, a substance in brain cells called tau proteins can malfunction in a way that leads to harmful changes in thinking, behavior, and mood. Tau proteins can collect between brain cells and form structures that disrupt normal communications between the cells. We can protect our brains from CTE by limiting the number of head injuries we experience. Giving ourselves adequate recovery time following an injury, receiving medical clearance before returning to normal activities, and keeping up with our social lives throughout recovery can help prevent or minimize the negative effects of CTE.
What Is CTE?
Have you ever played a sport and hit your head by accident, maybe colliding with the ground or with another person? You might have experienced a ringing pain or a headache in the short term, but have you ever considered what repetitive hits to the head might do to your brain in the long term? When we play sports, we tend to focus on the fun parts, like the competition, teamwork, and the joy of winning. However, people usually do not consider the possible consequences of sports injuries on their mental health. Contact sports like football, soccer, boxing, as well as domestic violence and bomb blast waves, might damage the human brain more than expected, even after all the initial symptoms of the injury are gone ( Figure 1 ) [ 1 ].
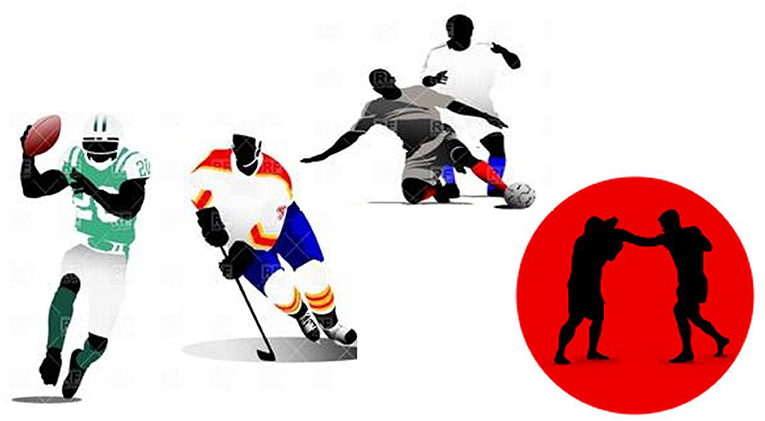

- Figure 1 - Which sports can cause CTE? High-impact sports, such as soccer, football, boxing, and hockey, can lead to the development of CTE.
- Tackling in football, hitting the head on the ice in hockey, and hitting the ground or another person’s head in soccer can all lead to head trauma and result in CTE if not appropriately treated. Although some protective gear has been created for sports, such as football and hockey, players are still susceptible to CTE. Sports administrators have added padding to arenas and courts to prevent head injuries. Additionally, coaches have emphasized good sportsmanship and proper techniques to avoid head injuries.
When a strong force hits the skull, the brain suffers damage. When the brain is damaged by a single injury, called a traumatic brain injury (TBI) , the body is affected in many different ways, depending on the intensity of the damage. When there are repeated injuries to the brain, those people are at a higher risk for developing something called chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) . Chronic stands for “long-lasting,” traumatic means “intense,” and encephalopathy refers to any process that alters the function or the structure of the brain. Severe hits can injure opposite sides of the brain, through the coup and countercoup model. How do opposite sides of the brain get injured? Well, the coup is the initial injury that occurs from a hit, while the countercoup injury occurs on the opposite side of the brain as the brain hits the inside of the skull ( Figure 2 ). When the injury is intense, the brain can develop long-term damage in multiple areas that can significantly impair brain function, possibly leading to memory loss and, in a few cases, even death.
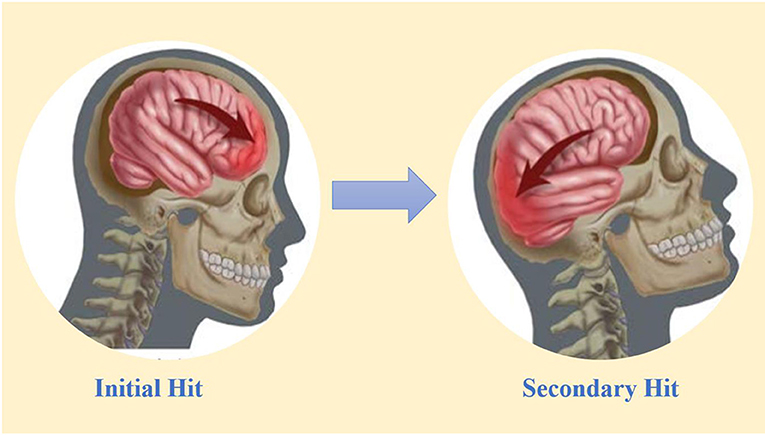
- Figure 2 - One hit can damage two parts of the brain: the coup and countercoup model.
- One hit to the brain results in a force on the skull that causes the brain to move back and forth. This motion leads to dual injuries, one in the location of the initial hit (coup) and a secondary hit on the opposite side, where the brain bounces off the inside of the skull (countercoup). Such injuries can be very damaging to the structure and function of the brain [ 1 , 2 ].
So, it seems that repeated brain injuries will begin to damage the brain permanently. In sports like football, players can have contact on almost every play. Head contact is frequent in soccer, especially when players slide tackle to get possession; frequent head-to-head contact going for a ball can knock players out. In boxing, getting hit in the head repeatedly is inevitable. Looking at these sports from this perspective, it is easy to see why so many athletes are developing CTE, and most do not realize the consequences. Some sports have less of a risk for CTE, including swimming, tennis, and even basketball. We should all consider the risks and think about brain safety before we play any activity or sport. There are always emergencies that no one can control, like bike or car accidents, but when it comes to contact sports, we need to make the right decisions for a healthier life [ 1 – 4 ].
The level of intensity of each hit influences how quickly the brain starts to deteriorate. CTE can come from one strong hit or multiple smaller hits over time. Multiple factors influence the development of CTE in response to a head injury, including genes, diet, alcohol, drugs, etc. Different people are affected in different ways, and no specific number of hits dictates whether the CTE will develop [ 1 ].
What Happens in the Brain When People Hit Their Heads Playing Sports?
The human brain needs healthy proteins for the brain cells to work and function properly. There are some proteins that we get from our diets and other proteins that are produced inside our bodies, such as the tau protein . Tau proteins are the connecting pieces that hold brain cells together. Imagine the brain is a Lego city, with thousands of tall buildings, each one representing a brain cell. If a head injury occurs while playing sports, it disrupts the brain cell structures, like an earthquake causing the Lego buildings to fall apart. Continuous hits shake the brain cells, breaking them into smaller pieces and creating a mess that we call protein aggregates. When these aggregates collect within cells, it is difficult for the tau protein to function properly. Think of a traffic jam on the streets between the Lego buildings, caused by all the fallen debris. Over time, larger protein aggregates collect through the breakdown of other brain cells. As people age, these messes become so severe that the Lego city of brain cells in the brain can no longer function in a healthy way. Diseases related to problems with tau function are called “ tauopathies .” Tauopathies do not occur in an instant but happen after multiple brain injuries occur over time. Playing contact sports can speed up this process [ 1 , 2 , 5 ] ( Figure 3 ).
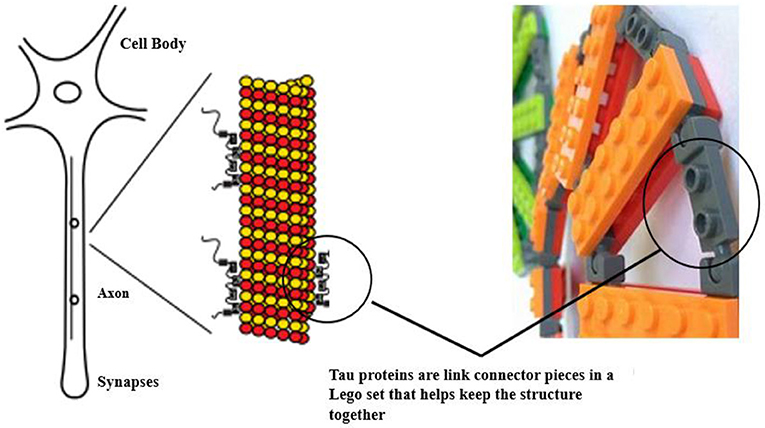
- Figure 3 - How do tau proteins relate to TBI/CTE? A brain sends messages (synapses) through brain cells or neurons.
- A neuron is made of a long central strand known as an axon, which helps carry synapses in the brain. An axon is made of smaller proteins (microtubules) represented by the red and yellow balls. Similar to Lego pieces, tau protein holds onto the microtubules to hold the neurons together. When tau proteins are broken down as in TBI or CTE, they cause destruction of the brain neuronal structure. These broken parts of tau form a mess. Too much destruction makes it hard for the body to clean up the mess. When the messes obstruct brain functions, this leads to memory loss and other problems.
How Can I Tell If I Have CTE?
CTE is hard to diagnose compared with other brain diseases. The methods usually used to look at the brain and diagnose brain diseases are called MRI and CT scans [ 6 ]. Unfortunately, these techniques are not able to show whether or not the brain has experienced CTE. You can predict that a person might have CTE if he or she has been a sports player for 10–15 years and suddenly starts acting differently or expressing unusual emotions, such as suicidal thoughts and depression. Scientists usually identify CTE after death because the brain has to be removed and examined for tau clusters to accurately diagnose CTE. Observation of degraded brain structures and decreased brain size may indicate that a person had CTE. Most of the symptoms associated with CTE also occur in people who suffer from diseases related to memory loss, including Alzheimer’s disease.
Researchers are trying to find new and efficient ways to diagnose CTE in living patients so that these people can be treated. Many methods are being studied, but one of the most promising methods is a brain-scanning technique known as positron emission tomography (PET). PET scans the brain a radioactive substance is injected into a vein. The radioactive substance allows any problems with the brain tissues to be seen. PET researchers would like to discover a specific radioactive substance that can find issues with the tau proteins in the brain. Another important method for diagnosing CTE involves identifying broken-down forms of tau in body fluids, including blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) , mucus, saliva, or urine. Detection of tau in these fluids could indicate whether CTE is likely in the patient.
How can you know if you might have a brain injury from hitting your head? Immediate symptoms, which can happen right after the injury or take up to a day to occur, include: loss of consciousness, feeling dizzy, severe headaches, blurry vision, nausea/vomiting, fatigue, trouble speaking, difficulty sleeping, loud ringing in the ears, or even a bad taste in the mouth [ 3 , 4 ].
Can CTE Be Treated?
CTE is a progressive, long-term, harmful process. At this point, there no reliable treatments for CTE. However, scientists are hoping to find some biological molecules, known as biomarkers that can be used to detect and decrease the chances of developing CTE. These biomarkers are produced by the cells of the brain, specifically when the brain is injured, and they may someday allow us to diagnose CTE and potentially cure the diseased brain.
How Can I Prevent Myself From Getting CTE?
Since there is no cure for CTE, preventing it is the best way to stop yourself from getting it. Headgear and body pads are examples of preventative methods that are meant to lower the chances of head injuries in many sports and jobs. Although helmets do not fully prevent TBI, they reduce the amount of impact. Hard surfaces on the outside of helmets are used to prevent skull fractures, while inner sections contain padding to reduce the amount of shock that the head experiences when hit. Scientists and sports medicine analysts are working on improving helmet paddings to prevent coup and countercoup injuries.
In addition to protective gear, sports administrators continue to take preventative measures to ensure the safety of players. For example, placing pads on hard surfaces in wrestling arenas and on basketball courts, to prevent head injuries. Coaches also teach players how to respect each other through sportsmanship, to avoid aggression and unnecessary injuries. Coaches have also incorporated neck stretches before, during, and after practice, to release neck tension and provide head support.
Although preventative methods are used, brain injuries still occur on a daily basis. When these injuries do happen, they must be appropriately treated. Around 85% of TBIs need about 3 weeks of recovery. One should take care of oneself until fully recovered, to prevent additional injury. Cut back on physical activity, get plenty of rest, avoid computer time, write things down, and avoid drinking alcohol. During recovery, light exercise and brain-stimulating activities are recommended to help the brain and body heal. Some examples include stretching exercises and puzzles. Following the recovery process, your doctor may have you undergo physical and mental tests to make sure your brain has gone back to its original state. These tests will ensure that you have recovered enough before you to go back to your day-to-day activities [ 1 , 2 ].
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) : ↑ Damage in the brain caused by a sudden hit to the head. TBIs can occur from accidents, sports, or other physical traumas.
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) : ↑ A disease developed after multiple traumatic brain injuries, through the breakdown of brain cells.
Coup and Countercoup Model : ↑ A model representing how an initial injury (coup) can have enough force to cause damage on the opposite side of the brain (countercoup).
Tau Protein : ↑ A protein that holds brain cells together to keep the brain structure intact.
Tauopathies : ↑ Diseases caused by the breakdown of tau proteins; Alzheimer’s disease is an example.
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) : ↑ The brain or spine fluid that scientist use to study tauopathies.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
1. ↑ Gaetz, M. 2017. The multi-factorial origins of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) symptomology in post-career athletes: the athlete post-career adjustment (AP-CA) model. Med. Hypotheses 102:130–43. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2017.03.023
2. ↑ Weston, S. 2015. School of Hard Knocks, Concussions by the Number, Center for Disease Control . Available online at: http://media.nj.com/hssportsextra/photo/concussionmainjpg-03ef39e81af937e1.jpg
3. ↑ Aldag, M., Armstrong, R. C., Bandak, F., Bellgowan, P. S. F., Bentley, T., Biggerstaff, S., et al. 2017. The biological basis of chronic traumatic encephalopathy following blast injury: a literature review. J. Neurotrauma 34:S26–43. doi: 10.1089/neu.2017.5218
4. ↑ McKee, A., Stein, T. D., Kiernan, P. T., and Alvarez, V. E. 2015. The neuropathology of chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Brain Pathol. 25:350–64. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12248
5. ↑ Turner, R. C., Lucke-Wold, B. P., Robson, M. J., Omalu, B. I., Petraglia, A. L., and Bailes, J. E. 2012. Repetitive traumatic brain injury and development of chronic traumatic encephalopathy: a potential role for biomarkers in diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment? Front. Neurol. 3:186. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2012.00186
6. ↑ Donald, CLM., Mukherjee, P., and Yuh, E. 2019. How to See Into the Brain Without Surgery! Front. Young Minds . 7:14. doi: 10.3389/frym.2019.00014

Work Hard, Play Hard
Are Contact Sports Worth the Risk? Unveiling the Truth about Concussions
by admin · February 20, 2024
Yes, contact sports are worth the risk as they offer various physical, mental, and social benefits, despite the potential for injury. Engaging in contact sports can enhance cardiovascular fitness, improve coordination and strength, promote teamwork and discipline, and boost self-confidence.
While there is always a risk of injuries such as concussions or fractures, these risks can be mitigated through proper training, protective gear, and strict adherence to rules. The benefits gained from participating in contact sports often outweigh the potential risks, especially when athletes take necessary precautions to ensure their safety.
It is crucial for individuals to weigh the risks and benefits and make an informed decision based on their personal circumstances and priorities. Overall, contact sports can be highly rewarding experiences that offer numerous advantages to participants.
Understanding The Nature Of Concussions
Table of Contents
Understanding the nature of concussions is crucial when evaluating the risks of contact sports. It’s important to weigh the potential dangers against the benefits of participating in these activities.
Concussions are a major concern in contact sports due to the potential short-term and long-term effects they can have on athletes. To fully comprehend the risks associated with these head injuries, it is crucial to understand the mechanism of concussions, as well as their short-term and long-term effects.
The Mechanism Of Concussions In Contact Sports
- When an athlete experiences a blow to the head, whether from a collision with another player or a hard surface, it can cause the brain to move within the skull.
- The impact can result in the stretching and damaging of brain cells, disrupting their normal functioning.
- This sudden movement and damage to the brain lead to the onset of a concussion.
Short-Term Effects Of Concussions
Concussions can have immediate effects on an athlete’s well-being, both physically and mentally. Some of the short-term effects include:
- Headaches: Athletes may experience severe headaches following a concussion, making it difficult to concentrate or engage in physical activities.
- Dizziness and Balance Issues: Concussions can lead to dizziness and problems with balance, affecting an athlete’s coordination and overall performance.
- Nausea and Vomiting: It is not uncommon for concussions to cause feelings of nausea and sometimes vomiting, causing further discomfort for athletes.
- Cognitive Impairment: Concussions can temporarily impair cognitive functioning, leading to difficulties with memory, concentration, and decision-making.
- Emotional Changes: Athletes may experience mood swings, irritability, and increased sensitivity due to the disruption in brain function caused by concussions.
Long-Term Effects Of Concussions
While the short-term effects of concussions are concerning, the potential long-term consequences can be even more worrisome. These may include:
- Post-Concussion Syndrome: Some athletes may develop post-concussion syndrome, an ongoing condition characterized by symptoms such as prolonged headaches, dizziness, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating.
- Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE): Although rare, repeated concussions or inadequate recovery from concussions can contribute to the development of CTE, a degenerative brain disease with long-term consequences. CTE can cause symptoms such as cognitive impairment, memory loss, depression, and behavioral changes.
- Increased Susceptibility to Future Concussions: Athletes who have previously suffered from concussions may be more prone to experiencing future concussions, even with less impact.
The nature of concussions in contact sports is complex and multi-faceted. Understanding their mechanism and the short-term and long-term effects they can have is crucial in determining whether contact sports are worth the risk for athletes. It is essential to prioritize athlete safety and take appropriate measures to prevent, diagnose, and manage concussions effectively.
The Prevalence Of Concussions In Contact Sports
Contact sports carry inherent risks, and the prevalence of concussions remains a concern. Are the dangers worth the rewards? We explore this ongoing debate.
Contact sports have always been a source of excitement and thrill for both athletes and fans. The adrenaline rush and the competitive spirit fuel the games. However, these sports also come with a significant risk: concussions. The prevalence of concussions in contact sports is a topic of concern and debate.
In this section, we will explore the statistics on concussions in professional sports, concussion rates in youth sports, and the gender disparities in concussion rates.
Statistics On Concussions In Professional Sports:
- Football: The most popular contact sport in the United States, football, also has the highest reported number of concussions. Studies indicate that around 7.4 concussions occur per 10,000 athletic exposures.
- Hockey: Known for its physicality, hockey ranks second in terms of the number of reported concussions. Both professional and amateur players are susceptible to head injuries due to the fast-paced nature of the game.
- Rugby: Considered one of the most physically demanding sports, rugby has a substantial concussion rate. With rigorous tackling and contact, players are prone to head injuries.
Concussion Rates In Youth Sports:
- Football: Despite the popularity of football among youth, the concussion rates are relatively high compared to other sports. It is essential to provide proper coaching and equipment to ensure the safety of young players.
- Soccer: Although soccer is a non-contact sport, concussion rates in youth soccer have been on the rise. Collisions during headers, accidental clashes, or falls contribute to head injuries among young athletes.
- Basketball: While basketball is generally known as a non-contact sport, collision incidents can still lead to concussions. These incidents often occur during aggressive play or accidental contact between players.
Gender Disparities In Concussion Rates:
- Female Athletes: Studies have shown that female athletes are more susceptible to concussions than their male counterparts. This could be due to differences in neck strength, hormonal influences, and playing style. Adequate precautions must be taken to protect female athletes from head injuries.
- Male Athletes: Although females are at a higher risk, it is important to note that male athletes also experience concussions. Sports like football and rugby have higher concussion rates for males due to the physicality involved.
The prevalence of concussions in contact sports highlights the need for consistent efforts to enhance player safety. By understanding the statistics on concussions in professional sports, the concussion rates in youth sports, and the gender disparities in concussion rates, we can work towards implementing better safety measures and protecting athletes from the risks associated with contact sports.
The Impact On Athletes’ Health And Well-Being
Contact sports have a significant impact on athletes’ health and well-being, raising the question: are they worth the risk? The physicality involved places players at a higher risk of injuries, potentially leading to long-term health issues.
Are Contact Sports Worth The Risk?
Throughout history, contact sports have been a significant part of our culture and entertainment. From football to boxing and everything in between, these sports have captured the attention of fans across the globe. However, it is important to consider the impact that participating in contact sports can have on the health and well-being of athletes.
In this blog post, we will explore the physical symptoms, cognitive impairments, and functional limitations that athletes may experience as a result of their involvement in contact sports.
Physical Symptoms And Challenges After Concussions:
Contact sports, such as football and rugby, often involve high-impact collisions that increase the risk of concussions for athletes. These head injuries can lead to a range of physical symptoms and challenges, including:
- Headaches: Athletes may experience persistent headaches following a concussion, which can significantly impact their daily lives.
- Dizziness and Vertigo: Concussions can cause athletes to feel dizzy or experience episodes of vertigo, affecting their balance and coordination.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some individuals may experience bouts of nausea or even vomiting as a result of a sports-related concussion.
- Sensitivity to Light and Noise: After a concussion, athletes may become sensitive to light and noise, making it difficult for them to function in everyday environments.
- Sleep Disturbances: Many athletes report changes in their sleep patterns following a concussion, experiencing either an increase or decrease in their normal sleep duration.
Cognitive Impairments And Mental Health Issues:
In addition to physical symptoms, contact sports can also lead to cognitive impairments and mental health issues among athletes. These can include:
- Memory Problems: Athletes may experience difficulties with both short-term and long-term memory following a head injury.
- Attention and Concentration Difficulties: Concussions can make it challenging for athletes to focus on tasks or sustain concentration for extended periods.
- Depression and Anxiety: Contact sports-related injuries can contribute to the development of depression and anxiety disorders in athletes.
- Mood Swings: Athletes may experience sudden changes in their mood, ranging from irritability to uncontrollable anger, as a result of head trauma.
Functional Limitations And Disability:
Contact sports injuries can also result in functional limitations and potentially even disability for athletes. Some of the functional limitations that athletes may face include:
- Joint and Muscle Pain: The repetitive impact and strain placed on the body during contact sports can lead to chronic joint and muscle pain.
- Decreased Mobility: Injuries sustained during contact sports can limit an athlete’s ability to move freely and participate in daily activities.
- Loss of Motor Skills: Severe injuries can result in the loss or impairment of motor skills, making it challenging for athletes to perform basic movements.
- Reduced Quality of Life: The cumulative effects of contact sports injuries can significantly impact an athlete’s overall quality of life and ability to engage in daily activities.
It is important to weigh the potential risks and rewards of participating in contact sports. While these sports offer excitement and physical fitness, athletes must consider the long-term consequences on their health and well-being. By understanding the physical symptoms, cognitive impairments, and functional limitations associated with contact sports, athletes can make informed decisions regarding their participation in these activities.

Credit: www.judoshop.com
Assessing The Potential Benefits Of Contact Sports
Evaluating the potential advantages of contact sports involves weighing if the risks are worth it. Understanding the potential benefits allows individuals to make an informed decision about participating in these physically demanding activities.
Engaging in contact sports may seem daunting due to the perceived risks involved. However, it is important to consider the potential benefits that these sports can offer. From physical fitness to social and psychological advantages, contact sports can play a significant role in an individual’s overall well-being.
Let’s delve into these benefits and explore why contact sports might be worth the risk.
Physical Fitness And Cardiovascular Health:
- Improved cardiovascular endurance: Engaging in contact sports requires constant movement and high-intensity actions, which can significantly enhance cardiovascular fitness.
- Increased strength and power: The nature of contact sports demands strength and power, leading to improved muscle tone and overall physical strength.
- Greater flexibility and agility: Regular practice of contact sports helps develop flexibility and agility, enabling athletes to perform quick movements and react swiftly during gameplay.
- Weight management: The high-intensity nature of contact sports often results in increased calorie expenditure, aiding in weight control and promoting overall fitness.
Development Of Skills And Teamwork:
- Skill acquisition: Contact sports provide numerous opportunities for individuals to develop and refine various skills such as hand-eye coordination, balance, and spatial awareness.
- Decision-making under pressure: Contact sports regularly involve split-second decision-making, honing an individual’s ability to think quickly and strategically amidst intense competition.
- Enhancing teamwork: Participating in contact sports requires individuals to collaborate effectively with teammates, fostering important skills such as communication, cooperation, and trust.
- Leadership and responsibility: Contact sports provide opportunities for players to assume leadership roles, fostering personal growth and a sense of responsibility.
Social And Psychological Benefits:
- Building relationships: Engaging in contact sports enables individuals to form lasting friendships and create a strong sense of camaraderie with teammates.
- Stress relief: Contact sports offer an outlet for individuals to channel their stress and frustrations, promoting mental well-being and reducing anxiety.
- Self-confidence and self-esteem: Achieving personal milestones in contact sports can boost an individual’s self-confidence and self-esteem, translating into various aspects of life.
- Discipline and determination: Contact sports require consistent discipline and dedication, instilling valuable qualities such as perseverance, determination, and resilience.
The potential benefits of contact sports are diverse and impactful. From improved physical fitness and cardiovascular health to the development of skills, teamwork, and social well-being, these sports offer a plethora of advantages. While risks must be considered, it is crucial to acknowledge the positive impact that participating in contact sports can have on individuals’ overall well-being.
So, are contact sports worth the risk? When weighing the benefits and risks, it’s clear that the potential rewards make them a worthwhile endeavor.
Mitigating And Managing Concussions
Discover effective strategies for mitigating and managing concussions in contact sports. Gain insights on whether the potential risks of participating in these sports are worth it. Explore practical and valuable tips to ensure safety and protect athletes from the damaging effects of head injuries.
Concussions are a prevalent concern in contact sports, raising questions about the overall safety of these activities. However, there are various methods available to mitigate and manage concussions effectively. This section focuses on the current evaluation and diagnosis methods, treatment options, as well as return-to-play guidelines and protocols.
Current Evaluation And Diagnosis Methods
- Medical Assessment: Qualified healthcare professionals employ a comprehensive medical assessment to evaluate athletes suspected of sustaining a concussion. This typically includes a thorough review of the athlete’s medical history, physical examination, and assessment of symptoms.
- Symptom Assessment: Healthcare providers use specialized tools and questionnaires to assess the presence and severity of concussion symptoms, aiding in the diagnosis process.
- Neurological Examination: A neurological examination is conducted to assess reflexes, coordination, balance, and cognitive function. This evaluation provides crucial information for accurate concussion diagnosis.
- Neuroimaging: While imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are usually not required, they may be used in specific cases to rule out severe complications or other potential causes of symptoms.
Treatment Options For Concussions
- Physical and Cognitive Rest: Rest is of utmost importance in concussion management. Both physical and cognitive activities should be limited initially to allow the brain to heal properly. Gradual return to regular activities is typically recommended based on the individual’s progress.
- Symptom Management: Medications may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms such as headaches, sleep disturbances, or mood changes. However, it is important to note that medication alone does not expedite the healing process.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: In some cases, cognitive rehabilitation therapy may be beneficial to address cognitive deficits and improve overall functionality.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Collaborative efforts between healthcare professionals from various disciplines, such as neurologists, neuropsychologists, and physical therapists, ensure a holistic approach to concussion treatment.
Return-To-Play Guidelines And Protocols
- Graduated Return-to-Play (RTP) Protocol: Athletes should follow a structured and stepwise RTP protocol to minimize the risk of re-injury and ensure a safe return to sports. This involves gradually reintroducing physical activities while closely monitoring symptoms and progress.
- Clearance from Healthcare Professional: Athletes must be cleared by a qualified healthcare professional, who specializes in sports concussion management, before returning to contact sports. This clearance is determined based on objective assessments, resolution of symptoms, and adherence to the RTP protocol.
- Education and Athlete Empowerment: Athletes should undergo tailored education programs to increase their awareness of concussion risks, symptoms, and the importance of reporting potential injuries promptly. Empowering athletes to prioritize their long-term health and well-being contributes to an overall safer sports environment.
By implementing these evaluation methods, treatment options, and return-to-play guidelines, the management of concussions in contact sports is continuously evolving. This systematic approach aims to ensure the well-being of athletes while allowing them to continue participating in the sports they love, under expert guidance.
Promoting Safety In Contact Sports
Contact sports present a question of whether the risk is worth it. However, promoting safety in these sports can help mitigate potential harm, ensuring athletes can enjoy the benefits of competition without compromising their well-being.
Contact sports have long been a popular form of physical activity, offering athletes the thrill of intense competition and camaraderie. However, the risks involved in these sports, such as concussions and other injuries, have raised concerns about their safety. The good news is that there are measures in place to promote safety and minimize the risks in contact sports.
Sports Equipment And Protective Gear
- High-quality sports equipment: Investing in well-made and properly fitting equipment is crucial for safety in contact sports.
- Helmets: Helmets play a vital role in protecting athletes from head injuries. They should meet appropriate safety standards and be regularly inspected for any signs of damage.
- Mouthguards: These devices protect athletes from dental and jaw injuries. Custom-fitted mouthguards offer superior protection and comfort.
- Pads and guards: Protective pads and guards are designed to reduce the risk of fractures, sprains, and other injuries in vulnerable areas such as shoulders, elbows, and knees.
- Eye protection: In sports where eye injuries are common, such as basketball or hockey, goggles or visors should be worn to safeguard the eyes.
Rule Changes And Game Modifications
- Strict enforcement of rules: Clear and consistent enforcement of rules is necessary to maintain a safe playing environment. Officials should penalize dangerous or unnecessary contact.
- Limiting contact: Certain modifications to the rules, such as restricting excessive physicality, can help reduce the risk of injuries.
- Fair play initiatives: Encouraging fair play and sportsmanship can contribute to a safer sporting environment. Teaching athletes to respect their opponents and play within the rules can minimize dangerous behaviors.
- Age-appropriate guidelines: Implementing age-specific rules and regulations ensures that young athletes are not exposed to excessive or unnecessary physical contact.
Educating Coaches, Athletes, And Parents
- Coach training programs: Coaches play a critical role in the safety of contact sports. Proper training programs should emphasize injury prevention, recognize signs of concussion, and teach safe playing techniques.
- Athlete education: Providing athletes with comprehensive information about the risks and potential consequences of contact sports enables them to make informed decisions regarding their safety.
- Parental involvement: Parents should be actively engaged in understanding the risks associated with contact sports and the steps taken to minimize them. It is essential for parents to support their child’s safety by ensuring they have appropriate equipment and encouraging adherence to safety guidelines.
By implementing these strategies, contact sports can remain a thrilling and enjoyable activity while prioritizing the safety of athletes. Remember, it is crucial to focus on proper equipment, rule changes, and educating all stakeholders to ensure the well-being of those participating in contact sports.
Balancing The Risks And Rewards
Balancing the risks and rewards in contact sports raises the question: are they worth the potential harm? The article examines the impact and value of participating in these sports, taking into account the physical consequences.
Are contact sports worth the risk? This is a question that has been debated for years, with passionate arguments on both sides of the spectrum. While contact sports offer unique physical challenges and the thrill of competition, they also come with inherent risks.
In this section, we will delve into the ethical considerations surrounding contact sports, the role of personal choice and autonomy, and the future directions in concussion research and safety measures.
Ethical Considerations In Contact Sports:
- The duty of care: Sports organizations and coaches have a responsibility to ensure the safety and well-being of athletes.
- Informed consent: Athletes should have access to comprehensive information about the risks involved in contact sports and be able to make an informed decision.
- Balancing risks and benefits: The potential physical and mental risks associated with contact sports should be weighed against the benefits they offer, such as physical fitness, teamwork, and personal growth.
- Equality and inclusivity: Ensuring that contact sports are accessible to individuals of all backgrounds and abilities is essential for promoting diversity and inclusivity.
Personal Choice And Autonomy:
- A matter of individual preference: Some individuals may find the risks of contact sports acceptable, while others may prioritize their long-term health and well-being.
- Understanding risk tolerance: People have different thresholds for risk and may be willing to accept a higher level of risk in exchange for the enjoyment and benefits derived from participating in contact sports.
- Risks and rewards: Each individual should have the freedom to make their own decision, considering their personal values, goals, and priorities.
Future Directions In Concussion Research And Safety Measures:
- Advancements in helmet technology: Ongoing research is focused on developing helmets that provide enhanced protection against concussions and traumatic brain injuries.
- Rule modifications: Sports organizations are considering rule changes to minimize the risk of concussions, such as stricter penalties for dangerous plays and head-to-head collisions.
- Early detection and treatment: Improving the methods for diagnosing and treating concussions is crucial for minimizing long-term health consequences.
- Education and awareness: Increasing awareness about concussion risks among athletes, coaches, and parents can help in identifying and addressing head injuries promptly.
The decision to participate in contact sports involves a careful consideration of the risks and rewards. Ethical considerations, personal values, and the future of research and safety measures all play significant roles in balancing the risks associated with contact sports.
Ultimately, individuals must make their own informed choices while taking into account their own circumstances and preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions For Are Contact Sports Worth The Risk
Are contact sports beneficial for overall physical fitness.
Yes, contact sports are highly beneficial for overall physical fitness as they improve strength, agility, endurance, and coordination.
What Safety Measures Are In Place To Minimize The Risk In Contact Sports?
Safety measures in contact sports include proper equipment usage, trained coaches, regular medical check-ups, and rules and regulations that prioritize player safety.
Are There Any Long-Term Consequences Of Participating In Contact Sports?
While contact sports carry some risk of injuries, proper training, precautionary measures, and prompt medical care can help minimize long-term consequences and ensure a safer sports experience.
Considering the potential risks involved, the question of whether contact sports are worth it remains complex. While they offer numerous physical and mental benefits, the potential for long-term injuries cannot be ignored. These injuries, such as concussions or other brain trauma, can have significant and lasting impacts on an individual’s health and quality of life.
It is crucial for athletes, parents, coaches, and governing bodies to prioritize safety measures and rigorous enforcement in contact sports. This includes regular medical check-ups, proper equipment, and strict adherence to rules and regulations. Additionally, continued research and advancements in technology are necessary to minimize the risks associated with contact sports.
Ultimately, the decision to participate in these sports depends on individual circumstances and personal risk tolerance. By weighing the benefits against the potential risks and taking necessary precautions, one can make an informed decision about whether contact sports are worth it.
Tags: sports
Hi, myself Adam John a professional athlete. I love to see sports and always want to find out sports-related all news on my blog. I wish this blog gives you all types of sports news.
You may also like...

What are the Most Athletic States?
September 23, 2022

What are the Four Functions of Sports in Society? Discover the Impact!
August 23, 2023

Where Can I Get an Urgent Sports Physical? Fast and Convenient Options!
September 23, 2023
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Next story Is Tennis a Hard Sport? Unlocking the Power and Grit Behind the Game
- Previous story What is Non Contact Sport? Discover the Thrill of Contact-Free Athletics
The Preventable Risks and Benefits of Contact Sports Essay Example
Since 1869, American football has been a popular sport known to anyone in the United States, although it has been known to have concussions. Most people believed it to be relatively safe. No one thought of the risk that it could bring. Recently, there has been a lot of new research suggesting that contact sports are posing a long-lasting threat to the health of its players. It has led to a lot of hesitation surrounding whether playing contact sports, like football, or even regular sports, like girl’s soccer, is worth it. Despite the risks that could come, famous football players are not worried about the hazards. Tom Brady said in interviews that they are not worried about getting a concussion. “I'm not oblivious to them. I mean, I understand the risks that, you know, come with the physical nature of our game” (Brady). While it is dangerous, contact sports are worth the risk because the pros that come with it outweigh the common danger of getting a concussion. There are many guidelines, safety precautions, and more that could decrease the chance of getting a concussion. There are also many benefits of the sport, in school, and the work industry.
Some people believe that contact sports such as football and girls' soccer are dangerous, and they refuse to play any contact sports because of the risk of concussion and CTE. They argue, for example, Paragraph 12 of “What a Lifetime of Playing Football Can Do to the Human Brain”, stating: “There are approximately 0.41 concussions per NFL game of American football: 67.7 percent of concussions involve impact by another player’s helmet.” Football is not the only sport that has interference with concussions, as girl’s soccer, which is not considered a contact sport, often hosts year-round playing, with the high school seasons, and in the off-season. It as well as football contains a high risk of getting a concussion. Removing tackling or delaying it would also be a problem, as it could lead to a higher risk of damage later in life when it is finally introduced. Although that could be the case, should you get a concussion or be at risk of CTE from repeated violent contact with the ground, or other players, there are professionals trained for these types of encounters. These professionals include doctors, referees, and other medically trained professionals for types of situations, on standby.
Football leagues in both high school and professional leagues, like the NFL, are striving for safer futures. As stated in paragraph 12 of the paper, “Heads Up Football Program Flourishing”, “The ultimate objective is to educate everyone who needs to know more about the trauma in the sport, and that when trauma happens, that the right action takes place.” Guidelines include education on CTE and concussions, (As stated previously in this essay) heat prevention and hydration, tackling with head prevention (From soccer), coaching and certification, and many more. There is always the last resort of removing tackling from football. It would drastically change the curriculum of football is traditionally played, but greatly reduce the risk of being injured.
There are also many benefits outside of contact sports. A paper called “The Social and Academic Benefits of Team Sports” has many examples of these benefits. In paragraph 3, “A University of Kansas study looking at the performance of students in grades 9 to 12 showed that more than 97% of student-athletes graduated high school, 1-% higher than those students who had never participated in sports. Athletes were also proven to have better GPA outcomes than non-athletes.” (1) Furthermore, you also have advantages in job industries, not only school and the sport itself. Some employers look for former athletes. They have persistence and work with other people better than those that haven’t engaged in playing contact sports.
The beneficial social and academic skills and the guidelines and prevention of concussions that you can incorporate into the sport outweigh the dangers of having a possibility of being injured. Examples of social and academic benefits include having a higher chance of being hired by an employer, as well as athletes’ GPAs and grade scores have also been higher. Prevention of the interferences can also be prevented or be prepared for. Professionals are trained for situations that happen in the game, like concussions. There are also a lot of guidelines recently being put in place to prevent concussions. The endangerments get superseded by all the gains rewarded in favor of only playing the sports, and there is a possibility that the hazards can be completely avoided in a few years.
Associated Press. “Heads Up Football Program Flourishing.” USA Today, 2014. Commonlit, Commonlit.org. Accessed 14 Mar. 2022.
Maslen, Paige. “The Social and Academic Benefits of Team Sports.” Edutopia, 2015. CommonLit, Commonlit.org. Accessed 14 Mar. 2022.
Resnick, Brian. “What a Lifetime of Playing Football Can Do to the Human Brain, Six things to know about the NFL, concussions, and brain damage.” Vox Media, LLC, 2019. Commonlit, Commonlit.org. Accessed 14 Mar. 2022.
Related Samples
- Persuasive Essay on Student Athletes Should Be Paid
- Feminism Essay Example: The Importance Of Female Athletic Trainers In First Division
- Exploitation Of College Athletes Research Paper
- Should College Athletes Be Paid Essay Sample
- Essay Sample on Aaron Donaldson - NFL Player
- Baseball vs Softball Essay Example
- Sports Policy in NCAA
- Essay on African American Athlete: Their Role in American Culture
- Personal Essay Sample: Reasons I Dream to Be in the NBA
- Research Paper on Biological Sex Difference and Physical Education
Didn't find the perfect sample?

You can order a custom paper by our expert writers

- Join Donate
- OUR PROGRAMS
- IN THE NEWS

Contact Sports: Yes Or No?

By Steven Schlozman, MD
Posted in: Hot Topics , Podcast , Teenagers
Topics: Child + Adolescent Development
There’s no doubt about the recommendations. Most experts in neurodevelopment suggest that kids stay away from American contact sports, like tackle football, until they are at least 14 years old.
You can also tune in this conversation wherever you get your podcasts – just search for “Shrinking It Down.”
What’s so magic about 14? We’ll get to that in a minute, but first, let’s frame the debate by putting it into a larger context. As we learn more and more about the rapidly-developing brains of childhood and adolescence, we become increasingly skittish about what we’re willing to subject those brains to in the name of sports and athletics.
The Controversy
This is certainly highly controversial. Many of us have fond memories of high school football, lacrosse, or hockey, and, depending on where in the U.S. you were born, you might even have something approaching reverence for these sports. That’s why there was a tiny but vociferous outcry when the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) officially recommended that its members suggest that kids no longer participate in Golden Gloves Boxing until at least adolescence. There aren’t many regions of the nation that have strong boxing programs, but the ones that do were, well, ready to throw a punch with that announcement.
But that’s just the tip of the iceberg. It’s easy to imagine that the AAP was setting the stage for a more sweeping commentary on all contact sports. Forty years ago, most neurodevelopmental specialists thought that brain development was slow and plodding. Now, we are aware that the developing brain changes rapidly and logorhythmically. That means that so many changes happen so quickly and so precisely in developing brains, that any injury—a concussion, for example—can significantly derail neuro-development. This is one of reasons that kids who have a single concussion are many times more likely to suffer multiple concussions. These risks seem to lessen with the onset of adolescence, but, as with professional athletes, the risks persist.
Here’s where the debate gets heated. I was actually discussing this with my old football coach, and he was incredulous. “Of course there are more concussions in college and the pros,” he said. “It’s physics! Force equals mass times accelerations. Little kids can’t run, and they don’t weigh anything. How much damage can they do?” Well, a lot, it turns out.
The Science
Researchers at Virginia Tech studied Pop Warner football players using instrumented helmets, and they found that these pre-adolescent kids were enduring hits with the same force as their teenage and adult counterparts. That finding, of course, begs a larger question: why would any age be OK for a civilized society to permit something like football? Won’t those little kids just get bigger? Won’t they just do more damage?
Yes, it’s true that the potential for more potent hits during contact sports exists among bigger kids, but as kids grow, the risks of concussion fall. And, it turns out, this isn’t related to the state of the kids’ brains—it’s instead related to the muscles in their necks. To make sense of this, let’s start by formally defining what a concussion actually is.
Think of your skull as a protective container packed with bubble wrap. The container is meant to hold the contents in place, and the bubble wrap is meant to stop the contents from getting damaged as they bang against the walls of the container. In the case of your brain, your skull provides the external and powerful protection, but that same property that makes the skull perfect for protecting the brain—the fact that the skull is hard and bony—also causes problems when your head gets knocked around. That’s because your brain sloshes about inside your skull, sort of banging up against one side or the other. So, the brain uses its own bubble wrap—in this case, the fluid in the skull—to cushion the brain inside its hard casing.
But, we all know what happens to our packages, even when they’re packed with bubble wrap, if we drop them too often. If the delivery guy throws the package onto your doorstep, that bubble wrap can only do so much. The contents of that package get damaged if they are thrown inside their box with enough force to overcome the resistance of the bubble wrap.
Now, picture two kids’ heads. These heads bash into each other in, say, a Pop Warner football game. If the force is great enough, the fluid in the skull—the bubble wrap—isn’t enough. The brain sloshes back and forth inside the skull, and the delicate neurons and connections take a beating. A concussion is defined as anytime this kind of contact leads to an altered state of consciousness, no matter how long. You don’t have to lose consciousness to have a concussion. But, you do have to feel a bit shaken up—we used to call it “having your bell rung.” There are, of course, major and minor concussions, but remember that once your brain has taken a significant beating, it is much more likely to suffer a similar beating with further contact.
I still remember a hard hit in junior high football where I got up, stared at the blurry and confused world, and then made my way to the sidelines …the other team’s sidelines. “Son, you got your bell rung,” the opposing coach laughed, and he helped to re-orient me with my own team. A play later, I was back in the game.
This happened to me when I was 12 years old, and today, most experts would recommend that I sit out the rest of the game, even be examined by a physician. But, experts are divided on what to do if this were to have happened later in my football career (as it certainly did). What if I took the same hit at age 16? Why is that different?
That brings us back to the magic age 14 as a cut-off. Contrary to what most people think, 14 isn’t set aside for any major reason other than the fact that it’s the age where most boys have at least begun puberty. This is the recommendation of Dr. Cantu and Mark Hyman in their book, Concussions and Our Kids: America’s Leading Expert on How to Protect Young Athletes and Keep Sports Safe. In fact, the authors even suggest ignoring the age, and looking instead for signs of puberty in the child. That’s because puberty correlates strongly with having a stronger neck, and the stronger the neck, the less sloshing around your brain does when you take a hard hit from contact sports. The neck absorbs the blow, and the brain stays steadier; the end result is protection against concussion. Think of this in evolutionary terms: we’re born with huge heads relative to other species—that’s because of our huge brains. However, our bodies tend to catch up to those heads around the onset of biological adolescence. Hence, 14 is the arbitrary cut-off, but it is based on the fact that most 14-year-old bodies can handle the brain that sits on top of them.
What To Do About Contact Sports?
All of this brings us back to the initial controversy about contact sports. What do you do if your child “gets her bell rung” in soccer or takes “a hard hit” to the head in football?
Here’s what the CDC has advised: it’s better to miss a game than a whole season . That is, in fact, the key message of a campaign by the CDC aimed at sports-related concussions. The CDC notes that the short-term effects of a concussion can generate additional problems that may plague a person throughout life. When young athletes have a flawed memory, they can have difficulty concentrating in school, relating to other kids, or sleeping well, and these problems therefore have long-term, devastating consequences.
Right now, as we wander through the gray zone of unclear official recommendations, the biggest danger occurs when athletes go back to the game before they fully recover from a concussion. In such a case, even a mild blow can cause second-impact syndrome, which can lead to brain swelling, brain damage, and even death. This is, of course, quite rare—high school football players aren’t dying in droves.
But why take the risk?
Teammates need to keep an eye on each other. Athletes must let everyone know if they hurt their heads. Parents should make sure that children wear the right safety gear during all practices and games, and, given the ongoing controversy, it sometimes is up to the parents to get their kids out of the game. This is, of course, awkward for parents and kids, but a long-lasting brain injury is substantially worse.
Bench your child until a health care professional who knows the return-to-play guidelines says it’s OK to play contact sports. As with all parenting, your first job is to keep your child safe.
For more information about concussions, visit the CDC at http://www.cdc.gov/TraumaticBrainInjury
Share on Social Media

Was this post helpful?

Steven Schlozman, MD
Steven Schlozman, MD, is an assistant professor of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School (HMS), course director of the psychopathology class for the MIT-HMS Program in Health, Sciences and Technology, and former co-director of the Clay Center for Youn...
To read full bio click here .
Related Posts

How to Support Youth Athletes When a Sports Injury Derails Their Season

10 Important Steps for Parenting Young Athletes

Simone Biles – Choosing Mental Health Over Defending Olympic Gold
Subscribe today, your monthly dose of the latest mental health tips and advice from the expert team at the clay center..

Quick Jumps
Improving Safety and Reducing Risk in Youth Contact Sports
Because prohibition is not a perfect answer.
Youth Contact Sports: Worth the Risk?
Concussion – no matter who you are or where you go today – is a word that has been splashed across many sports and mainstream media headlines. As such, it is a word that has provoked a collective fear and doubt in the minds of the public – perhaps most especially among parents of young athletes participating in "contact sports."
And the medical community is weighing in. A recent editorial in the journal Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research asks: "Do Orthopaedic Surgeons Belong on the Sidelines at American Football Games?" The authors answer that question with a collectively resounding "no." Their rationale is well-intended and varied – from the notion that concussions aren't the primary area of expertise for orthopedic surgeons to a physician's moral obligation to not engage in helping a sport continue if it has known risks. Though I'm not an orthopaedic surgeon, most of the associate colleagues in my practice are, and yet the tenor and tone of this piece alarmed me.
[See: 10 Concerns Parents Have About Their Kids' Health .]
My concern with the editorial comes at a time when draft legislation in Maryland calls to prohibit participation in youth/little league and Pop Warner football for anyone under the age of 14. In California, the United States Fight League – a youth martial arts program that includes grappling and limited contact striking – delegation is having great difficulty finding physicians to provide participation physicals for the participants due to health care provider concerns about the morality of youth combat sports. In this particular case, the physicians may not realize that youth pankration does not involve head strikes (this is a penalty) and all participants wear protective headgear. In fact, early evidence (based on the documentation of all participation injuries ) indicates it's a safe sport with minimal, nuisance-type strains and sprains, and no significant concussive/head injury risk. But a fear of being seen as endorsing a sport that could be perceived – whether it's actually true or not – as posing even a remote neurological risk has become unpalatable for many in the medical community.
Here's the rub: The risk of concussion , sub-concussive injury and/or long-term associated consequences is not limited to participation in the sport of football or combat sports. A number of other sport and recreational activities also involve increased, but unquantifiable, risk. In attempting to force participation prohibitions on football or other assumed "dangerous" sports, are we as a medical community missing the larger and more important opportunity to improve safety for all individuals in all sports and activities with associated neurological risk? I believe we are, and this is what concerns me.
[See: Top Reasons Children End Up in the Hospital .]
In addition, I believe there are some unintended but significant consequences of prohibition policies, especially for individuals in lower socio-economic and underserved communities. It's a widely held belief that the opportunity to participate in sport and athletic activities represents significant benefits for participants. The potential impact (were football and/or other sports with risk of concussive injury to disappear) on childhood obesity, behavioral problems, academic progress and success, and exposure to less desirable alternative "activities" with risk of brain injury is not known and may represent more danger to participants than the neurological risk. And will such a blanket prohibition policy impact different categories of people in different ways?
[See: 9 Sports Injuries That Sideline Kids .]
As doctors, we must consider public health principles – and yes, we do have a societal responsibility to protect and promote health in the population as a whole. But to date, there is insufficient evidence to justify an all-out prohibition policy on football and other contact or combat sports. Yes, there are studies and research to suggest a potential risk of participation in football (as well as other sports), but there is also high-level evidence that participation during youth doesn't confer excessive or increased long-term risk. Furthermore, many of the safety provisions in effect now weren't present before. So the fact remains that we're still learning about risk of participation, which individuals may be at highest risk and how to quantify said risk. We must also continue to be vigilant to the risks of unintended consequences. Much has been said about what contact, collision and other sports-related injuries may do to an individual who participates. We should also consider what participation in sport can do for our youth. To truly help our youth athletes right now, our attention and effort should be focused on improving safety and reducing risk, rather than prohibiting participation.
The Best Olympic Sport for Your Body Type

Tags: concussions , sports , injuries , children's health
Most Popular

Patient Advice

OTC Medicine & Health Products

health disclaimer »
Disclaimer and a note about your health ».
Sign Up for Our 3-Day Guide to Medicare
Confused about Medicare? We can help you understand the different Medicare coverage options available to help you choose the best Medicare coverage for you or a loved one.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
How chemotherapy works.
Payton Sy March 28, 2024
Stomach Bloating Causes and Relief
Tamara Duker Freuman and Gretel Schueller March 27, 2024
Medicare vs. Medicaid
David Levine March 27, 2024
Early Signs of Diabetes
Toby Smithson March 26, 2024

How to Request a Hospital Transfer
Elaine K. Howley March 26, 2024

Breastfeeding Tips
Vanessa Caceres March 22, 2024

Does Medicare Cover Home Health Care?
Paul Wynn March 21, 2024

Coming Soon: Best Senior Living Ratings
Ben Harder , Zach Adams and Joshua H. Sandefur March 18, 2024

Best Medicare Advantage Insurance 2024
U.S. News Staff March 15, 2024

How to Shop for Medicare Advantage
Lisa Zamosky and Elaine K. Howley March 15, 2024


Contact Sports – What are They and What are the Risks?
In recent times, we’ve seen scientists highlight the link between various contact sports and a number of degenerative brain injuries in players.
Recently, former Rugby Union international and All Black Carl Hayman became the latest retired player to join a class action lawsuit against World Rugby and other governing bodies, after he was formally diagnosed with early-onset dementia.
But what exactly do we mean by contact sports, and what are the exact risks facing players across the board?
What are Contact Sports?
In general terms, contact spo rts are disciplines that require or place an emphasis on physical contact between players .
This can take multiple forms, with some sports seeing a significantly higher level of collisions and impacts that involve the head.
Perhaps the two most popular contact sports in this respect are rugby and football. As we’ve already touched on, there’s a class action facing rugby’s governing bodies following a surge in the number of ex-players suffering brain injuries, with the sport requiring high impact collisions that involve the head and upper body.
Football is another impactful collision sport, and one in which players regularly head the ball or clash heads when competing in high challenges.
Because of this, a number of ex-footballers have also suffered from early-onset dementia, while a new study has been launched to investigate how the sport’s governing bodies can reduce the risk of disease in current and former players alike.
Other common and high-risk contact sports involve cricket, boxing and martial arts, the latter of which occasionally see competitors experience significant and potentially life-changing injuries.
What are the Main Risks?
While all sports have at least some forms of risk, contact sports are particularly dangerous as they’re more likely to lead to chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE).
This is caused by repetitive head injuries over time, which can trigger repeat concussions and lead to a progressive loss of memory and other degenerative brain symptoms. This is borne out by sports stars such as cricketer Will Pucovski, with the Australian opener having suffered 11 concussions by the age of 24 and faces long-term doubts over his career and future health.
Regardless, CTE is a major risk that’s associated with contact sports, while a fundamental lack of proper skull protection (particularly in disciplines like rugby, football and boxing) has been cited as a major reason why so many brain injuries occur when playing sport.
If you are injured while playing contact sport and experience some form of head or brain injury, you may also be able to make a claim for compensation.
This may be especially important if you’re a professional sportsman, as brain injury compensation can cover your loss of earnings and help provide financial support for your treatment, rehabilitation or long-term care.
You’ll just have to prove that your injuries were caused as a direct result of playing contact sport, while demonstrating that a government body should be held accountable for failing to provide adequate protection.
We hope you enjoyed the article ‘Contact Sports – What are They and What are the Risk?’ Have you ever partaken in full contact sports? Let us know!
Read more on sport below:
- 2022 NBA draft: top international prospects
- Picking the perfect football shirt: Our top tips
- Boxing vs MMA: Which is more dominant?
The Best Spots to Learn to Surf in the US
Who is the new Maryland rising tennis star? Frances Tiafoe
Jacob graduated with a Bachelor of Laws from the University of Reading. An avid footballer, he spent time under the FAW academy programme as well as Cardiff Corinthians. Later going on to play for his university and Wellington United whilst residing in New Zealand. He currently resides in Frome, Somerset. You can contact him at [email protected]

You may like

Remembering Phil Mickelson’s first Masters victory 20 years on

Talking points from the Austria Grand Prix

The Championship: Leeds Move One Step Closer

How to approach extended rosters in Counter Strike

Wales Women Football Stars – An Interview with Kayleigh Green

Championship Midweek Preview: Matchweek 42

Mobs, Violence, Discrimination: The Italian Ultra Problem

Influential Women in the Business Side of Boxing: Part 3

The Best Male Tennis Players of All Time

Players with the most goals in a Premier League season

10 of the most underrated footballers in the world right now

Chelsea’s Possible Lineup For Next Season

The Fastest Rugby Players Ever

Who is the Fastest Football Player in the World?

The 5 Biggest NBA trades so far this off-season

Who are the Highest Paid Football Managers in 2021?
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer

CHOC - Children's health hub
brought to you by CHOC Children's Hospital of Orange County
Contact sports and kids: What parents should know
Published on: November 16, 2021 Last updated: November 11, 2022
A CHOC pediatrician and sports medicine physician offers ways that parents can ensure their children's safety during contact sports.
Link: https://health.choc.org/contact-sports-and-kids-what-parents-should-know/
How to keep your children safe during the season
Each year, more than 2.6 million children, age 19 years and younger, visit the emergency room for both recreation and sports-related injuries. Kids are at greater risk than adults for sports injuries because they’re still growing and developing.
The risk for injury is even greater if the child plays a contact sport, such as basketball, football or soccer, says Dr. Matthew Kornswiet , a sports medicine physician and pediatrician in the CHOC Primary Care Network .
To help kids and teens prevent injury, Dr. Kornswiet says to make sure they follow these rules:
Wear protective gear
Make sure your children always be wearing the correct equipment for their sport before going onto the field or court. This may include pads, a helmet and a mouthguard. Frequently check equipment to make sure it is well fitting due to the use and continued growth of young athletes. If your child must wear eyeglasses while playing, they should be made of non-shattering glass to prevent eye injury.
Play by the rules
Different sports have specific safety rules like headings in soccer, headfirst slides in baseball and checking in hockey that change based on the age and level of the athletes involved. Check with your league and coaches to ensure these rules are followed correctly.
Create a safe playing field
Before your child begins to play, officials and coaches should make sure that the field or court is free of debris, holes, and other potential hazards. If the game is at night, the venue should be well lit.
Don’t overplay
Kids should take breaks often during sports to prevent overuse injuries such as growth plate injuries and stress fractures. Recommendations by The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) include taking at least 1-2 days off per week from sports and taking 3 months off of sports (in 1-month increments) each year to prevent injury.
The hours of sports your child plays per week should be less than their age in years. For example, a 10-year-old should have no more than 10 hours of sports per week. Ensure your child has eight hours of sleep or more per night too.
Consider other health conditions
Children with certain conditions, like irregular heart rhythms and bleeding disorders, may not be suited for contact sports. A preseason physical is recommended to rule out any conditions that may limit your child’s ability to participate in sports.
Warm up and tone up
Young athletes should stretch before and after every practice and game. Your child’s training focus should be on the quality of movements over the quantity of movements. Repetitive motions can put an athlete at more risk for injuries. Taking the time and learning proper techniques are important in preventing injuries in the future.
Prevent hot-weather injury
When playing outdoor sports during warmer months, make sure your child stays hydrated by drinking fluids before, during and after each game or match. Kids and teens should take a water break every 20 minutes. During extremely hot and humid conditions, it may be necessary to reduce or stop practices.
Group kids by size
Kids are less likely to be injured in a contact sport if they’re playing with opponents who are their similar size and skill level. Encourage your child’s coach to group players based on ability and size instead of by age. If this isn’t possible, the game should be modified to accommodate beginners or smaller players.
Recognize the signs of an injury
Quick treatment of a contact sports injury can prevent it from becoming more severe or causing permanent damage. Seek prompt medical treatment if your child experiences any swelling, pain over a small area, is limping, has pain that lasts when they are not playing sports or has any pain greater than a four on a scale of 10. Children should never be encouraged to play through pain.
Head injuries
Any athlete who has signs of a head injury or concussion should not return to sports until they are cleared by their physician. There is no situation that an athlete with a headache, dizziness or altered behavior should return to sports the same day as their injury.
Don’t rush back after injury
As a general rule, young athletes should have a full range of motion and no pain or swelling in the affected area before returning to sports. If your child suffers an injury, contact a sports medicine physician or your pediatrician to help them safely return to their activities.
For more health and wellness resources from the pediatric experts at CHOC, sign up for the Kids Health newsletter .
Find a CHOC Primary Care Pediatrician
From babies to teens, pediatricians from CHOC’s Primary Care Network partner with parents to offer immunizations, sick visits, sports physicals and more.
Related Articles

Mononucleosis (mono) myths debunked

Weight loss medications for treating teen obesity: What parents should know

10 quick tips for helping kids and teens maintain a healthy weight
Kidshealth newsletter.
Get “healthful” information for your family from the pediatric experts at CHOC. This monthly e-newsletter provides parenting tips on topics like nutrition, mental health and more.
The guidance on this page has been clinically reviewed by CHOC pediatric experts.

Our pediatric healthcare system is dedicated to preserving the magic of childhood.
CHOC Inside
Physical Contact Sport and Children Essay
Introduction.
When discussing the question of whether or not children should be allowed to play contact sports that may lead to head injuries, several things need to be considered. First of all, the consequences of such injuries, for example, concussions, can have both short- and long-term effects. Initial symptoms of a concussion are dizziness, tiredness, headaches, and nausea. Long-term results of suffering head trauma, if untreated, include changes in the emotional and cognitive aspects of a person. Therefore, if these effects were a completely unavoidable part of any contact sport, the logical decision would be to ban these activities.
However, with all of the risks that come with engaging in these activities, there are social and emotional factors that play a positive role in children’s lives. Participating in sports, especially team sports that involve relying on one another, develops a sense of belonging and responsibility in a child. It is also important to mention the beneficial impacts of regular physical activity that physical contact sports provide.
Another aspect of this discussion that needs to be taken into consideration is whether these consequences can be minimized or completely eliminated. Since the main argument against these sports lies within their dangers to children, the abolishment of the said dangers would be the solution. If safety is taken seriously, it will lead to fewer risks of dangerous occurrences among players. In order to achieve this safety, the coaches need to be well-trained, and the safety gear needs to fit the children properly. It is also important to allow children to have a good rest after practices and games.
In conclusion, physical contact sports may lead to head traumas, for example, concussions, and therefore they can be dangerous to a child’s developing organism. At the same time, these sports have several practical benefits (physical, emotional, and social) for children’s development. If executed properly, safety measures can minimize the harmful occurrences and their consequences. These measures include well-fitting gear, highly-educated coaches, and sufficient time for rest.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, March 30). Physical Contact Sport and Children. https://ivypanda.com/essays/physical-contact-sport-and-children/
"Physical Contact Sport and Children." IvyPanda , 30 Mar. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/physical-contact-sport-and-children/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Physical Contact Sport and Children'. 30 March.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Physical Contact Sport and Children." March 30, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/physical-contact-sport-and-children/.
1. IvyPanda . "Physical Contact Sport and Children." March 30, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/physical-contact-sport-and-children/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Physical Contact Sport and Children." March 30, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/physical-contact-sport-and-children/.
- Recovery Time Among High School Athletes with Concussion
- Concussions and Physical Activity
- Concussions Evaluation Among Young Athletes
- Neuropsychological Tests Reliability Following Concussion
- Concussion Occurring Among Football Athletes
- Concussions and Their Psychological Effects
- Concussion and Neurodegenerative Disorders' Links
- How Concussions Cause Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy?
- Athletic Training and Its Effects on the Lives
- Cross-Border Marriages Between Japan and China: Reasons and Results
- Gould et al. on Coaching Generation Z Athletes
- The Doping Scandal Documentary Analysis
- The Challenges of Being a Female Racer in a Male-Dominated Sport
- Race and Gender in Physical Education and Sports
- Kids’ Development and Impact of Sports
Essay on Importance of Sports for Students and Children
500+ words essay on importance of sports.
First of all, Sport refers to an activity involving physical activity and skill . Here, two or more parties compete against each other. Sports are an integral part of human life and there is great importance of sports in all spheres of life. Furthermore, Sports help build the character and personality of a person. It certainly is an excellent tool to keep the body physically fit. Most noteworthy, the benefits of Sports are so many that books can be written. Sports have a massive positive effect on both the mind and body.

Physical Benefits of Sports
First of all, Sports strengthen the heart. Regular Sports certainly make the heart stronger. Hence, Sport is an excellent preventive measure against heart diseases . This certainly increases the life expectancy of individuals. Furthermore, a healthy heart means a healthy blood pressure.
Sports involve physical activity of the body. Due to this physical activity, blood vessels remain clean. Sports reduces the amount of cholesterol and fats in the body. This happens because of the increase of flexibility of the wall of the blood vessels. The flexibility increases due to physical exertion, which is the result of Sports.
Furthermore, the sugar level in blood also gets lower thanks to Sports. The sugar certainly does not accumulate in the blood due to physical activity.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
A person experiences a good quality of breathing because of Sports. Sports strengthen the lungs of the body. Sports certainly escalate the lung capacity and efficiency of the body. Hence, more oxygen enters the blood which is extremely beneficial. Furthermore, there are fewer chances of developing lung diseases due to Sports.
Appropriate body weight is easy to maintain because of sports. A Sports playing person probably does not suffer from obesity or underweight problems. Sports certainly help the body remain fit and slim.
Furthermore, Sports also improves the quality of bones. A person who plays sports will have strong bones even in old age. Several scientific research reports that Sports prevent many diseases. For example, many researchers conclude that Sports prevent the development of cancer.
Other Benefits of Sports
Sport is certainly an excellent tool to build self-confidence . Playing Sports increases confidence to talk properly. A sport certainly improves the skills of communicating with others. Furthermore, the person experiences confidence in sitting, standing, and walking properly. Hence, Sports enriches the social life of an individual.
Sports bring discipline in life. It certainly teaches the values of dedication and patience. Sports also teach people how to handle failure. Furthermore, the importance of following a time schedule is also present in Sports.

Above all, Sports improves the thinking ability of individuals. Sports certainly sharpen the mind. Children who play Sports probably perform better at exams than those who don’t.
Finally, Sports reduces the stress of mind . A Sports playing person would certainly experience less depression. Sports ensure the peace of mind of those playing it. Most noteworthy, Sports brings happiness and joy in the life of individuals.
A sport is an aspect of human life that is of paramount importance. It certainly increases the quality of human life. Sports must be made mandatory in schools. This is because it is as important as education. Everyone must perform at least one Sport activity on a regular basis.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How do Sports clean blood vessels?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Sports clean blood vessels by physical activity. This physical activity certainly reduces the amount of fat and cholesterol.” } }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How Sports improves the quality of breathing?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Sports improves the quality of breathing by strengthening the lungs. This certainly results in increasing lung capacity.” } } ] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Argumentative on Contact Sports. Contact sports have long been a subject of debate, with arguments on both sides regarding their benefits and drawbacks. On one hand, proponents argue that contact sports provide numerous physical and mental health benefits, promote teamwork and discipline, and offer valuable life lessons.
The risk of traumatic brain injury is also gaining national attention. Participating in competitive sports puts young athletes at a high risk of sustaining at least one concussion in their lifetime, according to research published by JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association in 2017. Of the survey's 13,088 adolescent responders ...
If you have ever played contact sports, you may have heard about chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). CTE is caused by repetitive head injuries leading to a progressive loss in memory and other brain skills. The lack of proper skull protection has become a leading cause of brain problems in athletes. When playing sports, we focus on competition rather than the impact of repetitive injuries.
Playing contact sports helps your physical skills because it can get you in shape and lose weight. "Clearly, sports can help you reach your fitness goals and maintain a healthy weight." ("Benefits"). Contact sports can help people let go of stress and improve mental skills.
Unveiling the Truth about Concussions. by admin · February 20, 2024. Yes, contact sports are worth the risk as they offer various physical, mental, and social benefits, despite the potential for injury. Engaging in contact sports can enhance cardiovascular fitness, improve coordination and strength, promote teamwork and discipline, and boost ...
A paper called "The Social and Academic Benefits of Team Sports" has many examples of these benefits. In paragraph 3, "A University of Kansas study looking at the performance of students in grades 9 to 12 showed that more than 97% of student-athletes graduated high school, 1-% higher than those students who had never participated in sports.
There's no doubt about the recommendations. Most experts in neurodevelopment suggest that kids stay away from American contact sports, like tackle football, until they are at least 14 years old. You can also tune in this conversation wherever you get your podcasts - just search for "Shrinking It Down.".
Here's the rub: The risk of concussion, sub-concussive injury and/or long-term associated consequences is not limited to participation in the sport of football or combat sports.A number of other ...
In general terms, contact sports are disciplines that require or place an emphasis on physical contact between players. This can take multiple forms, with some sports seeing a significantly higher level of collisions and impacts that involve the head. Perhaps the two most popular contact sports in this respect are rugby and football.
Prevent hot-weather injury. When playing outdoor sports during warmer months, make sure your child stays hydrated by drinking fluids before, during and after each game or match. Kids and teens should take a water break every 20 minutes. During extremely hot and humid conditions, it may be necessary to reduce or stop practices.
Playing contact sports has also been scientifically found to stimulate the brain, so on this basis a child playing a contact sport is likely to perform better academically in class too. However ...
Although physical activity is beneficial in many ways, contact sports creates many health risks: concussions, chronic traumatic encephalopathy, brain damage, broken bones, and broken growth plates. Because of all of these risks, contact sports should be banned for people under 18. To begin, contact sports should be banned for children under 18 ...
Children should play contact sports. First, children should play contact sports because it teaches them lifelong skills such as team interaction, to obey rules, and sportsmanship. Children at this age should be exposed to these things early. Contact sports involve working together as a team to achieve their goal, which also teaches them ...
In conclusion, physical contact sports may lead to head traumas, for example, concussions, and therefore they can be dangerous to a child's developing organism. At the same time, these sports have several practical benefits (physical, emotional, and social) for children's development. If executed properly, safety measures can minimize the ...
Contact Sports Essay. Decent Essays. 984 Words. 4 Pages. Open Document. Cost of contact sports causing over hundreds of thousands injuries every year. Over 600,000 thousand athletes in contact sport are injured every year. By turning contact sports into non contact sports would reduce injuries over the year. As illustrated by Gina Kolata ...
387 Words 2 Pages. The school system is far too strict; students are not even able to play any contact sports other than football as well as wrestling. Contact sports can actually be really good for someone's physical being as well as encourage physical health. These sports can also build self esteem and self confidence.
Persuasive Essay On Contact Sports. 1213 Words | 5 Pages. Contact sports are worth the risk. They benefit students in so many ways. We should first start tackling at a young age. That would help solve some of the issues. Contact sports also help in the classroom. It helps students learn discipline and accountability in the classroom. And lastly ...
Argumentative Essay On Contact Sports. Concussions are one of the main problems that many athletes face. It can change the way the brain functions. According to Mayo Clinic, it can have short-term issues such as headaches and long-term problems. Today, many children around the ages of twelve play a contact-related sport such as tackle football ...
500+ Words Essay on Importance of Sports. First of all, Sport refers to an activity involving physical activity and skill. Here, two or more parties compete against each other. Sports are an integral part of human life and there is great importance of sports in all spheres of life. Furthermore, Sports help build the character and personality of ...
Argumentative Essay On Contact Sports. 903 Words4 Pages. Contact sports are the reason kids are getting hurt. Contact sports are good for kids. The Federal and state government should stop kids under 10 to stop playing contact sports because 45% of kids under 10 getting hurt are from contact sports and 5% of the time its ending that kids ...
According to Omalu, the high-impact contact sports like football, ice hockey, mixed martial arts and boxing place athletes at risk of brain damage. Children's brains are very vulnerable because of the concussion Therefore, many families are wondering, is it wise for the sport as well as pursuing a passion for this subject.
The short sports essay is for students in grades 7, 8, 9 and 10. Long Essay on Sports 500 Words. Sports is such an activity that it can be taken up by anyone; at any age and any point in life. Adults, children and elders - everyone alike can take part in sports. Many regard sports as a mere co-curricular or extra-curricular activity in schools.
Concussions have been a major part of this talk about the safety of certain sports. People have been questioning the safety of contact sports for years. This has been a talk since football started back in 1869 with the first version of football. Of course, things have changed from 1869 and we have new rules and new protection gear.