122 Inflation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best inflation topic ideas & essay examples, 👍 good essay topics on inflation, ⭐ simple & easy inflation essay titles, 💡 interesting topics to write about inflation.
- Problem of China’s Inflation With the increase in oil prices, energy costs have increased, and this has resulted into an increase in the prices of products manufactured in the industries. In 2009 the government made a policy to increase […]
- Inflation and Deflation and Their Outcomes That is the money in the hands of the consumers is more causing an increase in the aggregate demand. On the other side, the lender of the money loses some value of the money given […] We will write a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts 808 writers online Learn More
- Increasing Inflation Impact on Individuals In simpler terms, inflation is the rise in the cost of living due to an exaggerated increase in commodity prices. This is because the rate of savings will be lower than the inflation resulting in […]
- The Relationship Between Money Supply and Inflation It is evidenced that changing the money supply through the central banks leads to a control of the inflationary situations in the same economy.
- Inflation in the United Kingdom According to the Bank of England, inflation occurs when the demand exceeds the ability by the economy’s capacity to produce goods and services.
- Inflation and High-Interest Rates When a company borrows in a country with higher interest rates, the risk of inflation and currency depreciation grows, but the debt of this company is the same.
- Inflation Effect on Japan’s and Mexico’s Economies Thus, the study aimed to establish the influence of inflation and FDI on the GDP of a developed country, developing country, and the world.
- The Price Deviations and Inflation Rates As seen from the table, the price deviations and inflation rates vary significantly depending on the item, season, and any global events that affect the economy.
- The Economic Disparity and Inflation It is essential to emphasize that the economic consequences of the pandemic are severe and are due in the main to inflation.
- US Economy: Navigating Debt, Inflation, and Recession Risks Today, the US is the world’s largest debtor and also the largest economy, market, and investor. Household debt can become a severe problem for the economy if exceeds their dead and accumulated wealth.
- Unemployment Rate: Impact on GDP and Inflation In such a way, the scenario shows it is vital to preserve the balance and avoid decisions focusing on only one aspect of the economy.
- The Inflation Dynamics in the Canadian Context According to the report, the economy only functions well when inflation is stable and predictable and is in an unhealthy state otherwise.inflation has been stable in the country over the last 25 years because of […]
- “Expected and Realized Inflation…” by Binder & Kamdar At the same time, the key focus of adaptive expectations is on the past rates of realized inflation and the factors that caused it.
- Inflation at the International Monetary Fund Anchoring inflation expectations, which is a condition in which inflation is regarded near the Central Bank target and typically matches what consumers anticipate, is one of the other possible measures. The pandemic appears to be […]
- How the Federal Reserve Controls Inflation According to the author of the article, the crisis became the impetus for developing new strategies for controlling the level of inflation.
- Inflation: Types and Negative Effects The mentioned type of inflation can stimulate the economy and increase demand for jobs, but at the same time, it raises the prices and is usually more expensive than cost-push inflation.
- Fiscal Policy and Inflation in Canada According to the report, in order to protect the country from the long-lasting consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic and the recently emerged effects of the Russian-Ukraine war, Canadian policy-makers implemented fiscal policies, but their efficacy […]
- Walmart Has Been Negatively Impacted by Inflation The employment issues caused by the pandemic and increased prices for goods handling forced the company to consider the option of automation for business processes.
- “Inflation Hits the Fastest Pace Since 1981, at 8.5% Through March” by Koeze Further on, the predictions reveal that the inflation rate is expected to stabilize due to a decrease in the price of used cars and apparel.
- Inflation Rates and the Value of the Dollar Projected Social Security benefits at the retirement age of 65 years are 48,580 The current age is 25 years Retirement age is 65 years =40 years The annual inflation rate is at 3% Utilizing the […]
- Inflation’s Impact on Fixed Income By taking a diversified approach to fixed income investing, investors can better manage the risks associated with interest rates as well as inflation and increase the yield in their bond portfolios.
- How Economic Crises Affect Inflation Beliefs A feature of the article is the study by the authors of the consequences of inflationary crises and comparison with pre-existing crises to calculate the level of the crisis as a whole.
- Inflation: What Is It and Inflation in the USA Inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods, works, and services of the country’s population and businesses or an extended period. This kind of inflation is considered the best because it occurs […]
- Inflation Crisis in China for Financial Managers As a financial manager running my company, the rise in prices of commodities will decrease the purchasing power of the foreign currency used by investors and potential customers across the globe.
- Unemployment and Inflation Relation However, the level of unemployment and its prevailing types can differ significantly depending on the state of the economies of countries and the policies they use to combat unemployment.
- Unanticipated and Participated Inflation The first inflation outcome refers to income recipients hurt by inflation as there is a forcible price level increase that does not coincide with their income increase proportionally.
- Interest Rate and Inflation Impact on Exchange Rate The second observation point to be made pertains to the differences in the exchange rate of NZDUSD among the two viable.
- Inflation and Deflation Effects on the US and Saudi Stock Markets Inflation is traditionally defined as a consistent rise in the price rates within a specific industry or in the entire economy of the state, which is triggered by a rapid increase in demand: “Inflation is […]
- Treasury Inflation-Protected Security Refers This ensures that the real rate of interest is determined beforehand, and it adjusts automatically to the increase in the inflation rate.
- Significance of Inflation to Corporate Finance The argument goes on that with elevated inflation rates, there is always a chance to cut down on interest rates as compared to instances when the inflation rates are low and interest rates need to […]
- UAE and GCC Economic Analysis: Inflation and Unemployment This is explained by the fact that UAE is less dependent on oil trade, hence, the inflation and unemployment rate in the UAE is lower in comparison with the countries of GCC.
- Government Spending Stimulation in the Fight Against Inflation The equilibrium point is a point where the value of is money adjusted thereby creating an equilibrium in the quantity of money supplied and that of the quantity of money demanded.
- How the Inflation Gauge Was Faulty in the Past In other words, the goal of the CPI, when prices change, is to measure the percentage change if the spending by the consumers to be as well off as they were before.
- Inflation in the US Business Industry Inflation can be measured in the following ways; Monetary inflation; caused by increase in the increase in the amount of money in circulation in an economy.
- How Should Monetary Authorities React to Higher Inflation Therefore, the best alternative for monetary authorities to react to higher inflation is to reduce its regulatory influence in private enterprises and banks and limit the amount of money supply in the country. Therefore, the […]
- Gasoline Prices, Rates of Unemployment, Inflation, and Economic Growth The data which has been queried from the database are related to gasoline prices in California, the unemployment rate in the US, the inflation rate in the US, and Real GDP.
- Federal Reserve System: Inflation The article ‘Inflation and the Federal Reserve’ by Richard Cook; this source can be used to describe the central threat of inflation and identify the principal steps to be developed by central banks, government, and […]
- The US and the Philippines: Unemployment and Inflation In cyclical terms, this rising inflation is actually the product and not the cause of these record-high oil prices and the idea that the U.S.had failed to think of the above-discussed alternatives to the energy […]
- Interest Rate and Inflation in Netherlands As interest rate rises, demand for debt falls as cost of capital will increase and growth rate declined. As, more funds is shifting to Market B, central bank may raise the bank rate to stabilise […]
- Monetary Policy in an Economy: Inflation Inflation can be defined as a persistent rise in the general level of prices or alternatively, a persistent fall in the value of money.
- Dollarization the Main Tool to Reduce Inflation In general, wouldollarization’ means the substitution of hard currency for the domestic currency as the medium of exchange, and above all as the store of value, in a large part of the domestic economy, so […]
- Inflation Targeting in Emerging Countries Inflation Targeting is the public announcement of numerical targets for inflation for the year. Some emerging market countries that engage in inflation targeting have gone too far in the limitation of exchange rate flexibility, with […]
- Future Inflation and Growth Figures The increase in real GDP in the first half of 2007 was the same as that in the second half of 2006: at an annual rate of 2.25%.
- “Inflation Rise Hits US Consumers” BBC Article The main focus of the article’s concern is the inflation rise that US economics experiences now and the impact it has on US consumer spending.
- Inflation Dynamics: Mistakes in the Forecaster’s Behavior In this case, the authors of the article pay attention to the evaluation of the Phillips curve and understanding its advantages and drawbacks.
- Saudi Arabia and Inflation: Past, Present, Future What is the role of the Saudi Central Bank about inflation? What is the historical inflation trend in Saudi?
- Inflation Expectations: Households and Forecasters The New Keynesian formula that the authors of the paper were trying to create, in its turn was supposed to provide justification for the lack of forecast efficacy in determining the changes in inflation rates, […]
- Inflation Targeting in Emerging Economies Debates supporting the concept of inflation targeting are premised on the idea that recession remains as a greater challenge relative to the state of high inflation. The basis of inflation targeting is always to monitor […]
- The Federal Reserve and the Inflation Problem Louis in 2005, it was noted that the economic hero of the inflationary decades was the then chairman of the Fed, Paul Volcker.
- Economics and the Great Inflation in US and Japan In the 1990s and the early years of the 21st century, the federal reserve policy makers opted to adopt the mop-up-after strategy-policy of letting the bubbles burst and then mopping up there after.
- Inflation Tradeoffs and the Phillips Curve In the findings, Lucas concluded that the there is a direct relationship and variance in the tradeoff between full employment and inflation rate at a particular level of input in the countries studied.
- Inflation and Unemployment in the United States In the 21st century, there are so many issues in the economy of the United States. This is increasing the demand for skilled workers by the day as opposed to the unskilled.
- Unemployment and Inflation Issues In most cases, if one is suffering structural unemployment, it is as a result of improvement in a certain area, or a change in the way things are done.
- Fluctuations in Inflation and Employment Debate surrounded what is termed the multiplier effect: are they higher for tax cuts or government spending, the differences in multiplier effect from different tax cuts, Incentive impact from tax cuts.
- Inflation in the 1970s In such a case, the reduced injections into the circular flow of the economy trim down the demand, which reduces inflation, and the general growth of the economy reduces significantly.
- Inflation Causes: Structuralism and Monetarism One of the features of this kind of inflation is a rapid rise in the price level with the currency loosing its value.
- The Effects of Inflation Targeting In theory inflation targeting is straightforward: the impending rate of inflation is predicted by the central bank, later on it is juxtaposed with the target rates which the government considers as appropriate for the economy […]
- The Euro Zone’s Rising Inflation and Unemployment Rate However, the euro zone found itself in a predicament from late 2009 after the economic downturns that faced some countries in the euro zone.
- Inflation Tax – Printing More Money to Cover the War Expenses The subsequent encroachment of inflation diminishes the value of money hence even if people had more money, the value of their cash was meaningless, a phenomenon similar to tax collection, which reduces the total amount […]
- Economic Condition of Singapore: Inflation Hits 5.2% in March Some of the effects of high inflation rate that has been felt in the economy are the increase of the housing prices, and cost of fuel increased by approximately 5%, thereby increasing the cost of […]
- Inflation Is Here to Stay, as Prices Will Always Go Up Monetary policy refers to the actions pursued by the central bank of a country to regulate the amount of money supply in the economy.
- Effect of a Permanent Increase in Oil Price on Inflation and Output During the same year, the alterations in the price of oil were activated by a change in the supply of the same commodity in the market place.
- Consumer Price Index: Measuring Inflation In this case, the volumes of money being circulated exceeds the supply of goods and services in the same market thus leading to an upward adjustment of prices in order to absorb the extra monies […]
- The Cause of China’s Inflation The supply is affected by the increase of prices of food in the global market, whereby, the Chinese government finds it difficult to satisfy the food demand of the increasing population of the Chinese population.
- China’s Economic Growth and Inflation On the road to becoming the second largest economy, China has experienced growth rates of about 10% in the last 30 years making it to top the list of the fastest growing economies.
- Evaluate Government Policies to Reduce the Rate of Inflation The rate of inflation is the adjustment in the index of price in a single year to a new one expressed in percentages.
- The Current Impact of Inflation and Unemployment on Germany’s Political/Economic System It is notable to recognize the fact that the rate of savings in the nation is quite high causing a dip in the rate of inflation.
- Inflation in Saudi Arabia This paper, using the quarterly data from 1980 to 2010, examines the causes behind the inflation in Saudi, its effects, and the effectiveness of the counter-strategies and policies the Saudi government has put in place […]
- Inflation Rates in Sweden The recession of the early 1990s was largely responsible for the drop in inflation rates. As per the theoretical model of money supply and inflation, increases in money supply will lead to inflationary pressures.
- China Currency Policy and Inflation The sphere of inflation in China relates to the consumer price index which has recorded a rising orientation in the near past.
- Current News of Economics: The Global Inflation Inflation has affected the total demand for goods and services in the economy, thus exceeding the supply. This means that you would have to pay more for the same amount of goods and services you […]
- Analysis of Unemployment and Inflation in the United States This was at the height of the recession that continues to grapple the country with major negative implications in the economy.
- GDP, Unemployment, Inflation, and Economic Growth
- Absolute and Relative Anti-Inflation Reputation: Evidence From the Bond Markets
- World Inflation and Monetary Accommodation in Eight Countries
- Can Demography Improve Inflation Forecasts? The Case of Sweden
- Accounting for Post-Crisis Inflation and Employment: A Retro Analysis
- Unravelling India’s Inflation and Policy Puzzles
- Inflation and Financial Market Performance: What Have We Learned in the Past Ten Years?
- Administered Inflation and Business Pricing: Another Look
- The Historical Relationship Between Inflation and Political Rebellion: What It Might Teach Us About Neoliberalism
- America’s Only Peacetime Inflation: The 1970s
- Sectoral Inflation and the Phillips Curve: What Has Changed Since the Great Recession?
- Analyzing the Relationship Between Inflation Rate and Per Capita GDP Growth
- Banks, Lies, and Bricks: The Determinants of Home Value Inflation in Spain During the Housing Boom
- Capacity Utilization and Unemployment Rates: Are They Complements or Substitutes?
- Fast vs. Gradual Policies to Control Inflation
- Bond Market Inflation Expectations in Industrial Countries: Historical Comparisons
- Inflation and Monetary Velocity in Latin America
- What Drives the Relationship Between Inflation and Price Dispersion: Market Power vs. Price Rigidity
- How Much Did Speculation Contribute to the Recent Food Price Inflation?
- MAPI: Model for Analysis and Projection of Inflation in France
- Budget Deficit, Inflation, and Debt Sustainability: Evidence From Turkey
- Monetarism: Printing Money to Curb Inflation
- Capacity Constraints, Inflation, and the Transmission Mechanism: Forward-Looking vs. Myopic Policy Rules
- When Did Inflation Expectations in the Euro Area De-Anchor?
- Capturing the Link Between M3 Growth and Inflation in the Euro Zone
- Implementing Monetary Cooperation Through Inflation Targeting
- German Great Inflation: Summary & Analysis
- The Maastricht Inflation Criterion: On the Effect of the European Union Expansion
- What Unemployment Rates Tell Us About the Future Inflation
- Applying Foreign Exchange Interventions as an Additional Instrument Under Inflation Targeting: The Case of Ukraine
- China’s Economic Slowdown and International Inflation Dynamics
- The Impact of Inflation Targeting on the Real Economy of Developing and Emerging Countries
- Effects of Inflation on Business: The Good and the Bad
- U.S. Inflation Dynamics: What Drives Them Over Different Frequencies
- Structural Inflation and the 1994 ‘Monetary’ Crisis in China
- Macroeconomic Aggregate Model for Analysis of Inflation and Stabilization of the Russian Economy
- Cyclical vs. Acyclical Inflation: A Deeper Dive
- The Inflation-Output Nexus: Empirical Evidence From India, Brazil, and South Africa
- Forecasting Inflation Using Constant Gain Least Squares
- Stopping Hyperinflation: Lessons From the German Inflation Experience of the 1920s
- Modeling and Forecasting Inflation in Japan
- Globalization and Inflation Dynamics: The Impact of Increased Competition
- The Relationship Between Inflation and Economic Growth: A Multi-Country Empirical Analysis
- How Does Monetary Policy Influence Inflation and Employment?
- Assessing the Gap Between Observed and Perceived Inflation in the Euro Area
- Unanticipated Inflation, Devaluation, and Output in Latin America
- Inflation and Economic Growth Nexus in BRICS: Evidence From ARDL Bound Testing Approach
- Bootstrapping Covariate Unit Root Tests: An Application to Inflation Rates
- Fiscal Dominance and Inflation Targeting: Lessons From Brazil
- Inflation and the Gig Economy: E-Tailing and Self-Employment Rise in Disrupting the Phillips Curve
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 25). 122 Inflation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/inflation-essay-topics/
"122 Inflation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 25 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/inflation-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '122 Inflation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 25 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "122 Inflation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/inflation-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "122 Inflation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/inflation-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "122 Inflation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/inflation-essay-topics/.
- Economic Topics
- Financial Crisis Paper Topics
- National Debt Research Topics
- Banking Research Ideas
- Money Research Ideas
- Forecasting Questions
- Macroeconomics Topics
- Budget Ideas
- Accountancy Titles
- Cash Flow Paper Topics
- Monopolistic Competition Essay Titles
- Private Equity Research Ideas
- Auditing Paper Topics
- Economic Crisis Essay Titles
- Intangible Assets Essay Topics

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium

100 Inflation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Inflation is a key economic indicator that affects the purchasing power of consumers and the overall health of an economy. As such, it is a popular topic for essays and research papers in economics, finance, and related fields. If you are looking for inspiration for your next inflation essay, look no further. Here are 100 inflation essay topic ideas and examples to help you get started:
- The causes and effects of inflation
- The relationship between inflation and unemployment
- The impact of inflation on interest rates
- The role of the Federal Reserve in controlling inflation
- The differences between demand-pull and cost-push inflation
- The effects of hyperinflation on a country's economy
- The impact of inflation on fixed income earners
- The relationship between inflation and the stock market
- The effects of inflation on real estate prices
- The impact of inflation on international trade
- The role of inflation expectations in shaping economic behavior
- The effects of inflation on poverty and income inequality
- The impact of inflation on retirement savings
- The relationship between inflation and economic growth
- The effects of inflation on consumer spending
- The role of inflation in shaping monetary policy decisions
- The impact of inflation on business investment
- The effects of inflation on government finances
- The relationship between inflation and currency exchange rates
- The impact of inflation on the cost of living
- The effects of inflation on social welfare programs
- The role of inflation in causing economic recessions
- The impact of inflation on international competitiveness
- The effects of inflation on the environment
- The relationship between inflation and financial stability
- The role of inflation in shaping government policy decisions
- The impact of inflation on entrepreneurship and innovation
- The effects of inflation on consumer confidence
- The relationship between inflation and technological advancement
- The impact of inflation on the healthcare industry
- The effects of inflation on the education sector
- The role of inflation in shaping consumer behavior
- The impact of inflation on the agricultural sector
- The relationship between inflation and social mobility
- The effects of inflation on urban development
- The role of inflation in shaping labor market dynamics
- The impact of inflation on small businesses
- The effects of inflation on the tourism industry
- The relationship between inflation and government regulations
- The impact of inflation on infrastructure development
- The role of inflation in shaping energy policy
- The effects of inflation on the manufacturing sector
- The relationship between inflation and the digital economy
- The impact of inflation on the gig economy
- The effects of inflation on the sharing economy
- The role of inflation in shaping consumer preferences
- The impact of inflation on the automotive industry
- The relationship between inflation and the housing market
- The effects of inflation on the retail sector
- The impact of inflation on the hospitality industry
- The role of inflation in shaping supply chain dynamics
- The effects of inflation on the fashion industry
- The relationship between inflation and the art market
- The impact of inflation on the entertainment industry
- The effects of inflation on the music industry
- The role of inflation in shaping the sports industry
- The relationship between inflation and the gaming industry
- The impact of inflation on the film industry
- The effects of inflation on the publishing industry
- The role of inflation in shaping the food and beverage industry
- The impact of inflation on the beauty and personal care industry
- The effects of inflation on the health and wellness industry
- The relationship between inflation and the pharmaceutical industry
- The impact of inflation on the technology industry
- The effects of inflation on the telecommunications industry
- The role of inflation in shaping the media industry
- The relationship between inflation and the advertising industry
- The impact of inflation on the e-commerce industry
- The effects of inflation on the transportation industry
- The role of inflation in shaping the logistics industry
- The impact of inflation on the energy industry
- The effects of inflation on the renewable energy industry
- The relationship between inflation and the oil and gas industry
- The impact of inflation on the mining industry
- The effects of inflation on the construction industry
- The role of inflation in shaping the real estate industry
- The relationship between inflation and the property market
- The impact of inflation on the architecture and design industry
- The effects of inflation on the engineering industry
- The role of inflation in shaping the manufacturing industry
- The effects of inflation on the aerospace industry
- The relationship between inflation and the defense industry
- The impact of inflation on the security industry
- The effects of inflation on the law enforcement industry
- The role of inflation in shaping the healthcare industry
- The impact of inflation on the medical devices industry
- The effects of inflation on the biotechnology industry
- The role of inflation in shaping the life sciences industry
- The impact of inflation on the education industry
- The effects of inflation on the e-learning industry
- The relationship between inflation and the edtech industry
- The impact of inflation on the publishing industry
- The effects of inflation on the media and entertainment industry
- The role of inflation in shaping the sports and recreation industry
- The relationship between inflation and the leisure and travel industry
- The impact of inflation on the tourism and hospitality industry
- The effects of inflation on the food and beverage industry
- The role of inflation in shaping the retail and consumer goods industry
These are just a few examples of the many possible topics you could explore in an inflation essay. Whether you are interested in the macroeconomic implications of inflation or its effects on specific industries, there is no shortage of interesting and important questions to investigate. So pick a topic that interests you, do some research, and start writing!
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
114 Inflation Essay Topics
🏆 best essay topics on inflation, ✍️ inflation essay topics for college, 👍 good inflation research topics & essay examples, 🎓 most interesting inflation research titles, ❓ essay questions on inflation.
- The Inflation Impact on Society
- The Mechanisms of Inflation
- A Political Cartoon About Canada’s Inflation by MacKay
- Inflation: Causes, Problems, Impacts on Economy
- Malaysia’s Inflation
- Income Inflation: Absorption Costing vs. Variable
- Nominal Anchor: Monetary Targeting and Inflation
- Inflation in the UK The Bank of England raised its interest rates in response to the inflation increase and forecast inflation to reach a value just above two percent in two years.
- Measuring Inflation: Article Analysis Fluctuating in a seemingly unpredictable way, inflation rates are shaped by a range of factors, one of which is the change in the cost of living.
- The United States Inflation Rate Inflation is expressed primarily in the depreciation of money, which depreciates in relation to gold, commodities, and foreign currencies.
- Measuring Inflation: Consumer Price Index The article examines the consumer price index as the main instrument for measuring inflation in the United States, analyzes its advantages and disadvantages.
- The Ethical Repercussions Inflation Has Had on Businesses This paper analyzes the ethical repercussions inflation has had on businesses and the impacts that inflation has had on consumers and other businesses.
- How Raising Interest Rates Helps Fight Inflation and High Prices There is a mutual relationship between business and government where the government regulates the environment in which business operates.
- Exploration of Price Increase and Inflation Over the Years The paper discusses how inflation affected prices in 2021 and previous periods of inflation. It helps scientists understand how important inflation is.
- The Impact of Taxation and Inflation in the U.S. Carl Szabo’s article “Democrats want you to keep paying more” from the RealClear Policy website discusses how the current government makes Americans pay more.
- Real vs. Inflationary Growth: What’s the Difference? Real growth and inflation are associated with the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). GDP is the total market worth of a nation’s products and services during a specific period.
- The Unemployment and Inflation Causes in Australia The change in the Australian 2021 indicator of unemployment is the representation of cyclical unemployment since it lasted less than a year.
- Grades Inflation and Educational Services Quality In the modern education system, the quality of educational services has become the most relevant topic. The rating system aims to improve the differentia of academic performance.
- Inflation, Oil Prices, and How the President May Influence Them Inflation and oil prices are actual modern themes, as they are directly connected with the incomes and wealth of most people.
- How to Cure Inflation: Summary Inflation leads to increased prices. Although wages grow, the taxes increase. In the end, people do not have more money to spend on goods.
- Inflation and Increase in Money Supply Even though the increase in the money supply might stimulate the economy, it is a dangerous strategy, and the Federal Reserve has to act with caution.
- Inflation and Consumer Price Indexes The paper provides an example of a country that has implemented hyperinflation and explains the impact of this economic policy on the economy.
- The US Federal Reserve on Employment and Inflation The paper analyzes the statement of Federal Reserve, how it affects the economy, why the general public criticizes it, and what the future looks like if strategic changes are made.
- Federal Reserve System, Inflation, and Wage-Price Spiral An important indicator that can cause a policy shift toward a more stringent monetary policy would be the wage-price spiral.
- Inflation and Control Policies in the United Kingdom Inflation is a highly contentious issue. This is due to its economic implications. Inflation has the potential of crippling a country’s economy.
- The Problem of Inflation: Crucial Aspects Of primary importance is the recognition that inflation is not an unnatural or harmful mechanism for a country’s economy.
- Inflation and Unemployment in Bavaria Considering the normal state of the economy and the existing level of employment close to full, the President of Bavaria is not recommended to pursue an expansionary fiscal policy.
- Inflation in the Real Estate Industry This paper will cover the real estate industry in the US, as it might be affected by the increased inflation rates, as the demand for housing is not increasing as quickly.
- Balance of Payments, Inflation and Exchange Rate Balance of payments, inflation, and the exchange rate are the main driving forces of the UK economy, as well as in other countries.
- Inflation in India and China The growth of the Asian economies, more specifically China and India have allowed the examination of inflation in both countries.
- Zimbabwe Inflation Now Over 1 Million Percent In Zimbabwe, the national-average real wages are raised well above their historical trends, but faster inflation has reduced real wages back to trend levels.
- China Faces Inflation Pressure Inflation is essentially the rise in general price of goods and services over a period of time in economics. It is more commonly referred to as price inflation in now.
- Inflation in the United Kingdom’s Economy Global Positioning System is a system comprised of satellites capable of broadcasting certain signals used primarily for navigation in both the private and the military sectors.
- Mugabenomics as a Cause of Inflation in Zimbabwe The paper outlines the primary challenges of Zimbabwe economic system and provides a consistent account of inefficient economic strategies that disrupt the country’s well-being.
- Today’s Inflation and the Great Inflation of the 1970s
- Accelerating Inflation and the Distribution of Household Savings Incentives
- Perceived Inflation and Reality: Understanding the Difference
- Alternative Instruments for Hedging Inflation Risk in the Banking Industry
- Making Sense of Consumers’ Inflation Perceptions and Expectations
- Evaluating Inflation Targeting Based on the Distribution of Inflation and Inflation Volatility
- Global Inflation Dynamics: Regularities and Forecasts
- Contract Duration, Inflation Uncertainty, and the Welfare Effects of Inflation
- Advanced Economy Inflation: The Role of Global Factors
- Central Banks’ Inflation Forecasts: The Problem of Conditioning on Fixed Short-Term Interest Rates
- Who Is Suffering the Most From Rising Inflation?
- Conflict Inflation: Estimating the Contributions to Wage Inflation in Australia During the 1990s
- Adaptive Models and Heavy Tails With an Application to Inflation Forecasting
- The Main Strategies to Deal With Inflation in Business
- Does Inflation Harm Economic Growth?
- High Inflation and the Nominal Anchors of an Open Economy
- Euro Area Inflation: Aggregation Bias and Convergence
- Adopting Inflation Targeting: Practical Issues for Emerging Market Countries
- Causality Nexus Between Economic Growth, Inflation, and Innovation
- Analyzing Inflation: Monetary and Real Theories
- Deflating Inflation Expectations: The Implications of Inflation’s Simple Dynamics
- Forecasting Inflation: The Relevance of Higher Moments
- Inflation and Financial Market Performance: What Have We Learned in the Last Ten Years
- Commodity Prices and Inflation in the Middle East, North Africa, and Central Asia
- Analyzing the Connection Between Inflation and Unemployment
- Administered Prices, Inflation, and the Business Cycle
- Core Inflation and Inflation Targeting in a Developing Economy
- Baffling Inflation: Cost-push Inflation Theories in the Late 1950s United States
- America’s Historical Experience With Low Inflation
- Right Balance Between Growth and Inflation
- Admissible Monetary Aggregates and UK Inflation Targeting
- Estimating the Optimal Inflation Target From Trends in Relative Prices
- Causality Between Inflation and Inflation Uncertainty in South Africa
- Analyzing Factors Affecting U.S. Food Price Inflation
- Forecasting Inflation Using Economic Indicators: The Case of France
- Central Bank Independence and Inflation: Good News and Bad News
- Deflation and Inflation Trends in Japan
- Anticipated Inflation and Interest Rates in an Open Economy
- Financial Conditions and Density Forecasts for US Output and Inflation
- Arch and Structural Breaks in United States Inflation
- Has U.S. Inflation Really Become Harder to Forecast?
- Challenges for Adopting Inflation Targeting Regime in Egypt
- Demographic Transition and Inflation in Emerging Economies
- High Inflation: Resource Misallocations and Growth Effects
- Australian Wage and Price Inflation: 1971-1994
- Consumer Attitudes and the Epidemiology of Inflation Expectations
- Food Inflation and the Consumption Patterns of U.S. Households
- Inflation and Asset Returns in a Monetary Economy
- Discovering the Link Between Inflation Rates and Inflation Uncertainty
- Inflation and Deflationary Biases in Inflation Expectations
- What Are the Reasons for High and Persistent Inflation in the Country?
- How Does Inflation Affect Savings and Investment?
- How Is Inflation Used as a Measure of Economic Performance?
- What Is the Monetarist View of Inflation?
- Does Inflation Lead to a Rapid Increase in Unemployment?
- Whom Does Inflation Hurt the Most?
- What Measures of Inflation Are Used Today?
- Why Does Increased Interest Rate Not Increase Inflation?
- Why Does an Increase in the “Cost of Money” Not Mean an Increase in Inflation?
- What Methods Are Used to Control Inflation?
- What Happens to the Equilibrium Interest Rate When Inflation Is Expected to Decrease?
- Why Are Economists Concerned About Inflation?
- How Can Government Policies Be Used to Reduce Inflation in a Country?
- What Is Natural Rate of Inflation?
- How Can Cost-Push and Demand-Pull Inflation Be Caused by a Fall in the Exchange Rate?
- What Is the Condition of Low and Stable Inflation Called?
- How Does Inflation Affect Cash Flows?
- In Which Decade Was the Highest Rate of Inflation in the United States?
- Does Inflation Always Benefit Debtors and Hurt Creditors?
- Can the Introduction of a New Banknote Cause Inflation?
- How Does the Government Directly and Indirectly Create Inflation?
- What Are the Macroeconomic Effects of Inflation?
- How Does Unexpected Inflation Affect Creditors, Debtors, and Savers?
- Can Inflation Occur With Non-fiat Money?
- What Is the Effect of Inflation on Our Financial Assets?
- Why Does Inflation Harmful to the Economy?
- Could Inflation Be a Problem for Some Low- And Middle-Income Countries?
- What Does the Phillips Curve Show During Inflation?
- How Can an Inflation Tax Explain the Creation of Inflation by a Central Bank?
- What Type of Inflation Will Cause Stagflation?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2023, May 7). 114 Inflation Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/inflation-essay-topics/
"114 Inflation Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 7 May 2023, studycorgi.com/ideas/inflation-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2023) '114 Inflation Essay Topics'. 7 May.
1. StudyCorgi . "114 Inflation Essay Topics." May 7, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/inflation-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "114 Inflation Essay Topics." May 7, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/inflation-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2023. "114 Inflation Essay Topics." May 7, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/inflation-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Inflation were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 8, 2024 .
Home — Essay Samples — Economics — Political Economy — Inflation
Essays on Inflation
Inflation essay topics and outline examples, essay title 1: understanding inflation: causes, effects, and economic policy responses.
Thesis Statement: This essay provides a comprehensive analysis of inflation, exploring its root causes, the economic and societal effects it generates, and the various policy measures employed by governments and central banks to manage and mitigate inflationary pressures.
- Introduction
- Defining Inflation: Concept and Measurement
- Causes of Inflation: Demand-Pull, Cost-Push, and Monetary Factors
- Effects of Inflation on Individuals, Businesses, and the Economy
- Inflationary Policies: Central Bank Actions and Government Interventions
- Case Studies: Historical Inflationary Periods and Their Consequences
- Challenges in Inflation Management: Balancing Growth and Price Stability
Essay Title 2: Inflation and Its Impact on Consumer Purchasing Power: A Closer Look at the Cost of Living
Thesis Statement: This essay focuses on the effects of inflation on consumer purchasing power, analyzing how rising prices affect the cost of living, household budgets, and the strategies individuals employ to cope with inflation-induced challenges.
- Inflation's Impact on Prices: Understanding the Cost of Living Index
- Consumer Behavior and Inflation: Adjustments in Spending Patterns
- Income Inequality and Inflation: Examining Disparities in Financial Resilience
- Financial Planning Strategies: Savings, Investments, and Inflation Hedges
- Government Interventions: Indexation, Wage Controls, and Social Programs
- The Global Perspective: Inflation in Different Economies and Regions
Essay Title 3: Hyperinflation and Economic Crises: Case Studies and Lessons from History
Thesis Statement: This essay explores hyperinflation as an extreme form of inflation, examines historical case studies of hyperinflationary crises, and draws lessons on the devastating economic and social consequences that result from unchecked inflationary pressures.
- Defining Hyperinflation: Thresholds and Characteristics
- Case Study 1: Weimar Republic (Germany) and the Hyperinflation of 1923
- Case Study 2: Zimbabwe's Hyperinflationary Collapse in the Late 2000s
- Impact on Society: Currency Devaluation, Poverty, and Social Unrest
- Responses and Recovery: Stabilizing Currencies and Rebuilding Economies
- Preventative Measures: Policies to Avoid Hyperinflationary Crises
Inflation Reduction Act in The Frame of Macroeconomic Challenges
The oscillating tides of the american economy, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Analyzing The Inflation Reduction Act
Report on inflation and its causes, the rise of inflation rate in the us, iflation and its causes, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Methods to Control Inflation
The grade inflation, inflation: a deceitful solution to debt, how to control inflation in pakistan, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
Main Factors of Inflation in Singapore
Effects of inflation on commercial banks’ lending: a case of kenya commercial bank limited, food inflation in the republic of india, the issue of unemployment and inflation in colombia, the theory and policy of macroeconomics on inflation rate, socio-economic conditions in 'what is poverty' by jo goodwin parker, non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment (nairu), targeting zero inflation and increase of government spending as a way of curbing recession, howa spiraling inflation has impacted the venezuelan economy, how venezuela has been affected by inflation, effects of inflation on kenya commercial banks lending, exploring theories of inflation in economics, about fuel prices: factors, impacts, and solutions, exploring the implications of the inflation reduction act, the impact of inflation reduction act on the international economic stage, relevant topics.
- Unemployment
- Penny Debate
- Supply and Demand
- American Dream
- Real Estate
- Minimum Wage
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Essay on Inflation: Types, Causes and Effects
Essay on Inflation!
Essay on the Meaning of Inflation:
Inflation and unemployment are the two most talked-about words in the contemporary society. These two are the big problems that plague all the economies. Almost everyone is sure that he knows what inflation exactly is, but it remains a source of great deal of confusion because it is difficult to define it unambiguously.
Inflation is often defined in terms of its supposed causes. Inflation exists when money supply exceeds available goods and services. Or inflation is attributed to budget deficit financing. A deficit budget may be financed by additional money creation. But the situation of monetary expansion or budget deficit may not cause price level to rise. Hence the difficulty of defining ‘inflation’ .
Inflation may be defined as ‘a sustained upward trend in the general level of prices’ and not the price of only one or two goods. G. Ackley defined inflation as ‘a persistent and appreciable rise in the general level or average of prices’ . In other words, inflation is a state of rising price level, but not rise in the price level. It is not high prices but rising prices that constitute inflation.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is an increase in the overall price level. A small rise in prices or a sudden rise in prices is not inflation since these may reflect the short term workings of the market. It is to be pointed out here that inflation is a state of disequilibrium when there occurs a sustained rise in price level.
It is inflation if the prices of most goods go up. However, it is difficult to detect whether there is an upward trend in prices and whether this trend is sustained. That is why inflation is difficult to define in an unambiguous sense.
Let’s measure inflation rate. Suppose, in December 2007, the consumer price index was 193.6 and, in December 2008 it was 223.8. Thus the inflation rate during the last one year was 223.8 – 193.6/193.6 × 100 = 15.6%.
As inflation is a state of rising prices, deflation may be defined as a state of falling prices but not fall in prices. Deflation is, thus, the opposite of inflation, i.e., rise in the value or purchasing power of money. Disinflation is a slowing down of the rate of inflation.
Essay on the Types of Inflation :
As the nature of inflation is not uniform in an economy for all the time, it is wise to distinguish between different types of inflation. Such analysis is useful to study the distributional and other effects of inflation as well as to recommend anti-inflationary policies.
Inflation may be caused by a variety of factors. Its intensity or pace may be different at different times. It may also be classified in accordance with the reactions of the government toward inflation.
Thus, one may observe different types of inflation in the contemporary society:
(a) According to Causes:
i. Currency Inflation:
This type of inflation is caused by the printing of currency notes.
ii. Credit Inflation:
Being profit-making institutions, commercial banks sanction more loans and advances to the public than what the economy needs. Such credit expansion leads to a rise in price level.
iii. Deficit-Induced Inflation:
The budget of the government reflects a deficit when expenditure exceeds revenue. To meet this gap, the government may ask the central bank to print additional money. Since pumping of additional money is required to meet the budget deficit, any price rise may be called deficit-induced inflation.
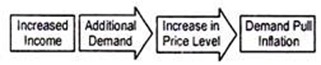
iv. Demand-Pull Inflation:
An increase in aggregate demand over the available output leads to a rise in the price level. Such inflation is called demand-pull inflation (henceforth DPI). But why does aggregate demand rise? Classical economists attribute this rise in aggregate demand to money supply.
If the supply of money in an economy exceeds the available goods and services, DPI appears. It has been described by Coulborn as a situation of “too much money chasing too few goods” .
Note that, in this region, price level begins to rise. Ultimately, the economy reaches full employment situation, i.e., Range 3, where output does not rise but price level is pulled upward. This is demand-pull inflation. The essence of this type of inflation is “too much spending chasing too few goods.”
v. Cost-Push Inflation:
Inflation in an economy may arise from the overall increase in the cost of production. This type of inflation is known as cost-push inflation (henceforth CPI). Cost of production may rise due to increase in the price of raw materials, wages, etc. Often trade unions are blamed for wage rise since wage rate is not market-determined. Higher wage means higher cost of production.
Prices of commodities are thereby increased. A wage-price spiral comes into operation. But, at the same time, firms are to be blamed also for the price rise since they simply raise prices to expand their profit margins. Thus we have two important variants of CPI: wage-push inflation and profit-push inflation. Anyway, CPI stems from the leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve.

The price level thus determined is OP 1 . As aggregate demand curve shifts to AD 2 , price level rises to OP 2 . Thus, an increase in aggregate demand at the full employment stage leads to an increase in price level only, rather than the level of output. However, how much price level will rise following an increase in aggregate demand depends on the slope of the AS curve.
Causes of Demand-Pull Inflation :
DPI originates in the monetary sector. Monetarists’ argument that “only money matters” is based on the assumption that at or near full employment, excessive money supply will increase aggregate demand and will thus cause inflation.
An increase in nominal money supply shifts aggregate demand curve rightward. This enables people to hold excess cash balances. Spending of excess cash balances by them causes price level to rise. Price level will continue to rise until aggregate demand equals aggregate supply.
Keynesians argue that inflation originates in the non-monetary sector or the real sector. Aggregate demand may rise if there is an increase in consumption expenditure following a tax cut. There may be an autonomous increase in business investment or government expenditure. Governmental expenditure is inflationary if the needed money is procured by the government by printing additional money.
In brief, an increase in aggregate demand i.e., increase in (C + I + G + X – M) causes price level to rise. However, aggregate demand may rise following an increase in money supply generated by the printing of additional money (classical argument) which drives prices upward. Thus, money plays a vital role. That is why Milton Friedman believes that inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon.
There are other reasons that may push aggregate demand and, hence, price level upwards. For instance, growth of population stimulates aggregate demand. Higher export earnings increase the purchasing power of the exporting countries.
Additional purchasing power means additional aggregate demand. Purchasing power and, hence, aggregate demand, may also go up if government repays public debt. Again, there is a tendency on the part of the holders of black money to spend on conspicuous consumption goods. Such tendency fuels inflationary fire. Thus, DPI is caused by a variety of factors.
Cost-Push Inflation Theory :
In addition to aggregate demand, aggregate supply also generates inflationary process. As inflation is caused by a leftward shift of the aggregate supply, we call it CPI. CPI is usually associated with the non-monetary factors. CPI arises due to the increase in cost of production. Cost of production may rise due to a rise in the cost of raw materials or increase in wages.
Such increases in costs are passed on to consumers by firms by raising the prices of the products. Rising wages lead to rising costs. Rising costs lead to rising prices. And rising prices, again, prompt trade unions to demand higher wages. Thus, an inflationary wage-price spiral starts.
This causes aggregate supply curve to shift leftward. This can be demonstrated graphically (Fig. 11.4) where AS 1 is the initial aggregate supply curve. Below the full employment stage this AS curve is positive sloping and at full employment stage it becomes perfectly inelastic. Intersection point (E 1 ) of AD 1 and AS 1 curves determines the price level.
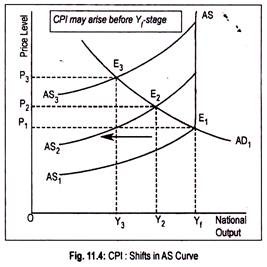
Now, there is a leftward shift of aggregate supply curve to AS 2 . With no change in aggregate demand, this causes price level to rise to OP 2 and output to fall to OY 2 .
With the reduction in output, employment in the economy declines or unemployment rises. Further shift in the AS curve to AS 2 results in higher price level (OP 3 ) and a lower volume of aggregate output (OY 3 ). Thus, CPI may arise even below the full employment (Y f ) stage.
Causes of CPI :
It is the cost factors that pull the prices upward. One of the important causes of price rise is the rise in price of raw materials. For instance, by an administrative order the government may hike the price of petrol or diesel or freight rate. Firms buy these inputs now at a higher price. This leads to an upward pressure on cost of production.
Not only this, CPI is often imported from outside the economy. Increase in the price of petrol by OPEC compels the government to increase the price of petrol and diesel. These two important raw materials are needed by every sector, especially the transport sector. As a result, transport costs go up resulting in higher general price level.
Again, CPI may be induced by wage-push inflation or profit-push inflation. Trade unions demand higher money wages as a compensation against inflationary price rise. If increase in money wages exceeds labour productivity, aggregate supply will shift upward and leftward. Firms often exercise power by pushing up prices independently of consumer demand to expand their profit margins.
Fiscal policy changes, such as an increase in tax rates leads to an upward pressure in cost of production. For instance, an overall increase in excise tax of mass consumption goods is definitely inflationary. That is why government is then accused of causing inflation.
Finally, production setbacks may result in decreases in output. Natural disaster, exhaustion of natural resources, work stoppages, electric power cuts, etc., may cause aggregate output to decline.
In the midst of this output reduction, artificial scarcity of any goods by traders and hoarders just simply ignite the situation.
Inefficiency, corruption, mismanagement of the economy may also be the other reasons. Thus, inflation is caused by the interplay of various factors. A particular factor cannot be held responsible for inflationary price rise.
Essay on the Effects of Inflation :
People’s desires are inconsistent. When they act as buyers they want prices of goods and services to remain stable but as sellers they expect the prices of goods and services should go up. Such a happy outcome may arise for some individuals; “but, when this happens, others will be getting the worst of both worlds.” Since inflation reduces purchasing power it is bad.
The old people are in the habit of recalling the days when the price of say, meat per kilogram cost just 10 rupees. Today it is Rs. 250 per kilogram. This is true for all other commodities. When they enjoyed a better living standard. Imagine today, how worse we are! But meanwhile, wages and salaries of people have risen to a great height, compared to the ‘good old days’. This goes unusually untold.
When price level goes up, there is both a gainer and a loser. To evaluate the consequence of inflation, one must identify the nature of inflation which may be anticipated and unanticipated. If inflation is anticipated, people can adjust with the new situation and costs of inflation to the society will be smaller.
In reality, people cannot predict accurately future events or people often make mistakes in predicting the course of inflation. In other words, inflation may be unanticipated when people fail to adjust completely. This creates various problems.
One can study the effects of unanticipated inflation under two broad headings:
(i) Effect on distribution of income and wealth
(ii) Effect on economic growth.
(a) Effects of Inflation on Income and Wealth Distribution :
During inflation, usually people experience rise in incomes. But some people gain during inflation at the expense of others. Some individuals gain because their money incomes rise more rapidly than the prices and some lose because prices rise more rapidly than their incomes during inflation. Thus, it redistributes income and wealth.
Though no conclusive evidence can be cited, it can be asserted that following categories of people are affected by inflation differently:
i. Creditors and Debtors:
Borrowers gain and lenders lose during inflation because debts are fixed in rupee terms. When debts are repaid their real value declines by the price level increase and, hence, creditors lose. An individual may be interested in buying a house by taking a loan of Rs. 7 lakh from an institution for 7 years.
The borrower now welcomes inflation since he will have to pay less in real terms than when it was borrowed. Lender, in the process, loses since the rate of interest payable remains unaltered as per agreement. Because of inflation, the borrower is given ‘dear’ rupees, but pays back ‘cheap’ rupees.
However, if in an inflation-ridden economy creditors chronically loose, it is wise not to advance loans or to shut down business. Never does it happen. Rather, the loan- giving institution makes adequate safeguard against the erosion of real value.
ii. Bond and Debenture-Holders:
In an economy, there are some people who live on interest income—they suffer most.
Bondholders earn fixed interest income:
These people suffer a reduction in real income when prices rise. In other words, the value of one’s savings decline if the interest rate falls short of inflation rate. Similarly, beneficiaries from life insurance programmes are also hit badly by inflation since real value of savings deteriorate.
iii. Investors:
People who put their money in shares during inflation are expected to gain since the possibility of earning business profit brightens. Higher profit induces owners of firms to distribute profit among investors or shareholders.
iv. Salaried People and Wage-Earners:
Anyone earning a fixed income is damaged by inflation. Sometimes, unionized worker succeeds in raising wage rates of white-collar workers as a compensation against price rise. But wage rate changes with a long time lag. In other words, wage rate increases always lag behind price increases.
Naturally, inflation results in a reduction in real purchasing power of fixed income earners. On the other hand, people earning flexible incomes may gain during inflation. The nominal incomes of such people outstrip the general price rise. As a result, real incomes of this income group increase.
v. Profit-Earners, Speculators and Black Marketeers:
It is argued that profit-earners gain from inflation. Profit tends to rise during inflation. Seeing inflation, businessmen raise the prices of their products. This results in a bigger profit. Profit margin, however, may not be high when the rate of inflation climbs to a high level.
However, speculators dealing in business in essential commodities usually stand to gain by inflation. Black marketeers are also benefited by inflation.
Thus, there occurs a redistribution of income and wealth. It is said that rich becomes richer and poor becomes poorer during inflation. However, no such hard and fast generalizations can be made. It is clear that someone wins and someone loses from inflation.
These effects of inflation may persist if inflation is unanticipated. However, the redistributive burdens of inflation on income and wealth are most likely to be minimal if inflation is anticipated by the people.
With anticipated inflation, people can build up their strategies to cope with inflation. If the annual rate of inflation in an economy is anticipated correctly people will try to protect them against losses resulting from inflation.
Workers will demand 10 p.c. wage increase if inflation is expected to rise by 10 p.c. Similarly, a percentage of inflation premium will be demanded by creditors from debtors. Business firms will also fix prices of their products in accordance with the anticipated price rise. Now if the entire society “learns to live with inflation” , the redistributive effect of inflation will be minimal.
However, it is difficult to anticipate properly every episode of inflation. Further, even if it is anticipated it cannot be perfect. In addition, adjustment with the new expected inflationary conditions may not be possible for all categories of people. Thus, adverse redistributive effects are likely to occur.
Finally, anticipated inflation may also be costly to the society. If people’s expectation regarding future price rise become stronger they will hold less liquid money. Mere holding of cash balances during inflation is unwise since its real value declines. That is why people use their money balances in buying real estate, gold, jewellery, etc.
Such investment is referred to as unproductive investment. Thus, during inflation of anticipated variety, there occurs a diversion of resources from priority to non-priority or unproductive sectors.
b. Effect on Production and Economic Growth :
Inflation may or may not result in higher output. Below the full employment stage, inflation has a favourable effect on production. In general, profit is a rising function of the price level. An inflationary situation gives an incentive to businessmen to raise prices of their products so as to earn higher doses of profit.
Rising price and rising profit encourage firms to make larger investments. As a result, the multiplier effect of investment will come into operation resulting in higher national output. However, such a favourable effect of inflation will be temporary if wages and production costs rise very rapidly.
Further, inflationary situation may be associated with the fall in output, particularly if inflation is of the cost-push variety. Thus, there is no strict relationship between prices and output. An increase in aggregate demand will increase both prices and output, but a supply shock will raise prices and lower output.
Inflation may also lower down further production levels. It is commonly assumed that if inflationary tendencies nurtured by experienced inflation persist in future, people will now save less and consume more. Rising saving propensities will result in lower further outputs.
One may also argue that inflation creates an air of uncertainty in the minds of business community, particularly when the rate of inflation fluctuates. In the midst of rising inflationary trend, firms cannot accurately estimate their costs and revenues. Under the circumstance, business firms may be deterred in investing. This will adversely affect the growth performance of the economy.
However, slight dose of inflation is necessary for economic growth. Mild inflation has an encouraging effect on national output. But it is difficult to make the price rise of a creeping variety. High rate of inflation acts as a disincentive to long run economic growth. The way the hyperinflation affects economic growth is summed up here.
We know that hyperinflation discourages savings. A fall in savings means a lower rate of capital formation. A low rate of capital formation hinders economic growth. Further, during excessive price rise, there occurs an increase in unproductive investment in real estate, gold, jewellery, etc.
Above all, speculative businesses flourish during inflation resulting in artificial scarcities and, hence, further rise in prices. Again, following hyperinflation, export earnings decline resulting in a wide imbalance in the balance of payments account.
Often, galloping inflation results in a ‘flight’ of capital to foreign countries since people lose confidence and faith over the monetary arrangements of the country, thereby resulting in a scarcity of resources. Finally, real value of tax revenue also declines under the impact of hyperinflation. Government then experiences a shortfall in investible resources.
Thus, economists and policy makers are unanimous regarding the dangers of high price rise. But the consequence of hyperinflation is disastrous. In the past, some of the world economies (e.g., Germany after the First World War (1914-1918), Latin American countries in the 1980s) had been greatly ravaged by hyperinflation.
The German Inflation of 1920s was also Catastrophic:
During 1922, the German price level went up 5,470 per cent, in 1923, the situation worsened; the German price level rose 1,300,000,000 times. By October of 1923, the postage of the lightest letter sent from Germany to the United States was 200,000 marks.
Butter cost 1.5 million marks per pound, meat 2 million marks, a loaf of bread 200,000 marks, and an egg 60,000 marks Prices increased so rapidly that waiters changed the prices on the menu several times during the course of a lunch!! Sometimes, customers had to pay double the price listed on the menu when they observed it first!!!
During October 2008, Zimbabwe, under the President-ship of Robert G. Mugabe, experienced 231,000,000 p.c. (2.31 million p.c.) as against 1.2 million p.c. price rise in September 2008—a record after 1923. It is an unbelievable rate. In May 2008, the cost of price of a toilet paper itself and not the costs of the roll of the toilet paper came to 417 Zimbabwean dollars.
Anyway, people are harassed ultimately by the high rate of inflation. That is why it is said that ‘inflation is our public enemy number one’. Rising inflation rate is a sign of failure on the part of the government.
Related Articles:
- Essay on the Causes of Inflation (473 Words)
- Cost-Push Inflation and Demand-Pull or Mixed Inflation
- Demand Pull Inflation and Cost Push Inflation | Money
- Essay on Inflation: Meaning, Measurement and Causes
What is inflation?

Inflation refers to a broad rise in the prices of goods and services across the economy over time, eroding purchasing power for both consumers and businesses. In other words, your dollar (or whatever currency you use for purchases) will not go as far today as it did yesterday. To understand the effects of inflation, take a commonly consumed item and compare its price from one period with another. For example, in 1970, the average cup of coffee cost 25 cents; by 2019, it had climbed to $1.59. So for $5, you would have been able to buy about three cups of coffee in 2019, versus 20 cups in 1970. That’s inflation, and it isn’t limited to price spikes for any single item or service; it refers to increases in prices across a sector, such as retail or automotive—and, ultimately, a country’s economy.
Get to know and directly engage with senior McKinsey experts on inflation.
Ondrej Burkacky is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Munich office, Axel Karlsson is a senior partner in the Stockholm office, Fernando Perez is a senior partner in the Miami office, Emily Reasor is a senior partner in the Denver office, and Daniel Swan is a senior partner in the Stamford office.
In a healthy economy, annual inflation is typically in the range of two percentage points, which is what economists consider a signal of pricing stability. And there can be positive effects of inflation when it’s within range: for instance, it can stimulate spending, and thus spur demand and productivity, when the economy is slowing down and needs a boost. Conversely, when inflation begins to surpass wage growth, it can be a warning sign of a struggling economy.
Inflation affects consumers most directly, but businesses can also feel the impact. Here’s a quick explanation of the differences in how inflation affects consumers and companies:
- Households, or consumers, lose purchasing power when the prices of items they buy, such as food, utilities, and gasoline, increase.
- Companies lose purchasing power, and risk seeing their margins decline , when prices increase for inputs used in production, such as raw materials like coal and crude oil , intermediate products such as flour and steel, and finished machinery. In response, companies typically raise the prices of their products or services to offset inflation, meaning consumers absorb these price increases. For many companies, the trick is to strike a balance between raising prices to make up for input cost increases while simultaneously ensuring that they don’t rise so much that it suppresses demand, which is touched on later in this article.
How is inflation measured?
Statistical agencies measure inflation by first determining the current value of a “basket” of various goods and services consumed by households, referred to as a price index. To calculate the rate of inflation, or percentage change, over time, agencies compare the value of the index over one period to another, such as month to month, which gives a monthly rate of inflation, or year to year, which gives an annual rate of inflation.
For example, in the United States, that country’s Bureau of Labor Statistics publishes its Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures the cost of items that urban consumers buy out of pocket. The CPI is broken down by regions and is reported for the country as a whole. The Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index —published by the US government’s Bureau of Economic Analysis—takes into account a broader range of consumers’ expenditures, including healthcare. It is also weighted by data acquired through business surveys.

Introducing McKinsey Explainers : Direct answers to complex questions
What are the main causes of inflation.
There are two primary types, or causes, of inflation:
- Demand-pull inflation occurs when the demand for goods and services in the economy exceeds the economy’s ability to produce them. For example, when demand for new cars recovered more quickly than anticipated from its sharp dip at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, an intervening shortage in the supply of semiconductors made it hard for the automotive industry to keep up with this renewed demand. The subsequent shortage of new vehicles resulted in a spike in prices for new and used cars.
- Cost-push inflation occurs when the rising price of input goods and services increases the price of final goods and services. For example, commodity prices spiked sharply during the pandemic as a result of radical shifts in demand, buying patterns, cost to serve, and perceived value across sectors and value chains. To offset inflation and minimize impact on financial performance, industrial companies were forced to consider price increases that would be passed on to their end consumers.
Learn more about McKinsey's Pricing practice.
How does inflation today differ from historical inflation?
In January 2022, inflation in the United States accelerated to 7.5 percent, its highest level since February 1982, as a result of soaring energy costs , labor mismatches , and supply disruptions . But inflation is not a new phenomenon; countries have weathered inflation throughout history.
A common comparison to the current inflationary period is with that of the post–World War II era , when price controls, supply problems, and extraordinary demand fueled double-digit inflation gains—peaking at 20 percent in 1947—before subsiding at the end of the decade, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. Consumption patterns today have been similarly distorted, and supply chains have been disrupted by the pandemic.
The period from the mid-1960s through the early 1980s, sometimes called “The Great Inflation,” saw some of the highest rates of inflation, with a peak of 14.8 percent in 1980. To combat this inflation, the Federal Reserve raised interest rates to nearly 20 percent. Some economists attribute this episode partially to monetary policy mistakes rather than to other purported causes, such as high oil prices. The Great Inflation signaled the need for public trust in the Federal Reserve’s ability to lessen inflationary pressures.
How does inflation affect pricing?
When inflation occurs, companies typically pay more for input materials . One way for companies to offset losses and maintain gross margins is by raising prices for consumers, but if price increases are not executed thoughtfully, companies can damage customer relationships, depress sales, and hurt margins. An exposure matrix that assesses which categories are exposed to market forces, and whether the market is inflating or deflating, can help companies make more informed decisions.
Done the right way, recovering the cost of inflation for a given product can strengthen relationships and overall margins. There are five steps companies can take to ADAPT (Adjust, Develop, Accelerate, Plan, and Track) to inflation:
- Adjust discounting and promotions and revisit other aspects of sales unrelated to the base price, such as lengthened production schedules or surcharges and delivery fees for rush or low-volume orders.
- Develop the art and science of price change . Don’t make across-the-board price changes; rather, tailor pricing actions to account for inflation exposure, customer willingness to pay, and product attributes.
- Accelerate decision making tenfold . Establish an “inflation council” that includes dedicated cross-functional, inflation-focused decision makers who can act nimbly and quickly on customer feedback.
- Plan options beyond pricing to reduce costs . Use “value engineering” to reimagine your portfolio and provide cost-reducing alternatives to price increases.
- Track execution relentlessly . Create a central supporting team to address revenue leakage and to manage performance rigorously.
Beyond pricing, a variety of commercial and technical levers can help companies deal with price increases in an inflationary market , but other sectors may require a more tailored response to pricing. In the chemicals industry, for instance, category managers contending with soaring prices of commodities can make the following five moves to save their companies money:
- Gain a full understanding of supply–market dynamics and outlook . Understand and track the elements that trigger price increases and rescind these increases once those drivers are no longer applicable.
- Ensure that suppliers can clearly articulate the impact that price increases in the market have on suppliers’ prices . In times of upward price pressure, sellers often overstate the share of raw materials in input costs, taking the opportunity to inflate their margins. Using cleansheet methodology to identify and challenge these situations is important.
- View unavoidable price increases as temporary surcharges, not the new future state . This mechanism, partly psychological in nature, is very effective in dealing with the stickiness of price increases because it shifts the burden of proof to the supplier.
- Prioritize cross-functional initiatives . When prices are high, the impact of yield improvements, waste reduction, or substitutions can be amplified. If any are available, now is the time to make them a priority.
- Work with sales to pass on price increases . Category managers work closely with finance and commercial teams to shed light on pure market effects and their impact on the prices of goods sold, while ensuring that the right arguments are advanced to pass market-price increases to customers.
Learn more about our Financial Services , Advanced Electronics , Operations , and Growth, Marketing & Sales practices.
What is the difference between inflation and deflation?
If inflation is one extreme of the pricing spectrum, deflation is the other. Deflation occurs when the overall level of prices in an economy declines and the purchasing power of currency increases. It can be driven by growth in productivity and the abundance of goods and services, by a decrease in aggregate demand, or by a decline in the supply of money and credit.
Generally, moderate deflation positively affects consumers’ pocketbooks, as they are able to purchase more with less money. However, deflation can be a sign of a weakening economy, leading to recessions and depressions. While inflation reduces purchasing power, it also reduces the value of debt. During a period of deflation, on the other hand, debt becomes more expensive. Additionally, consumers can protect themselves to an extent during periods of inflation. For instance, consumers who have allocated their money into investments can see their earnings grow faster than the rate of inflation. During episodes of deflation, however, investments, such as stocks, corporate bonds, and real-estate investments, become riskier.
A recent period of deflation in the United States occurred between 2007 and 2008, referred to by economists as the Great Recession. In December 2008, more than half of executives surveyed by McKinsey expected deflation in their countries, and 44 percent expected to decrease the size of their workforces.
When taken to their extremes, both inflation and deflation can significantly and negatively affect consumers, businesses, and investors.
For more in-depth exploration of these topics, see McKinsey’s Operations Insights collection. Learn more about Operations consulting , and check out operations-related job opportunities if you’re interested in working at McKinsey.
Articles referenced include:
- “ How business operations can respond to price increases: A CEO guide ,” March 11, 2022, Andreas Behrendt , Axel Karlsson , Tarek Kasah, and Daniel Swan
- “ Five ways to ADAPT pricing to inflation ,” February 25, 2022, Alex Abdelnour , Eric Bykowsky, Jesse Nading, Emily Reasor , and Ankit Sood
- “ How COVID-19 is reshaping supply chains ,” November 23, 2021, Knut Alicke , Ed Barriball , and Vera Trautwein
- “ Navigating the labor mismatch in US logistics and supply chains ,” December 10, 2021, Dilip Bhattacharjee , Felipe Bustamante, Andrew Curley, and Fernando Perez
- “ Coping with the auto-semiconductor shortage: Strategies for success ,” May 27, 2021, Ondrej Burkacky , Stephanie Lingemann, and Klaus Pototzky

Want to know more about inflation?
Related articles.

What is supply chain?

How business operations can respond to price increases: A CEO guide

Five ways to ADAPT pricing to inflation

Economic essays on inflation
- Definition – Inflation – Inflation is a sustained rise in the cost of living and average price level.
- Causes Inflation – Inflation is caused by excess demand in the economy, a rise in costs of production, rapid growth in the money supply.
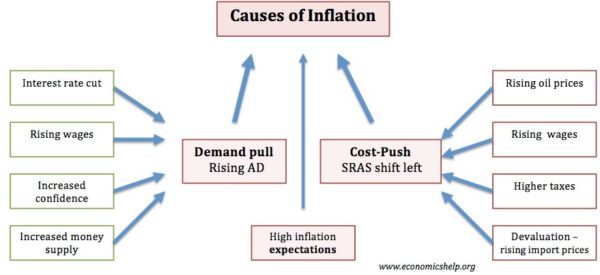
- Costs of Inflation – Inflation causes decline in value of savings, uncertainty, confusion and can lead to lower investment.
- Problems measuring inflation – why it can be hard to measure inflation with changing goods.
- Different types of inflation – cost-push inflation, demand-pull inflation, wage-price spiral,
- How to solve inflation . Policies to reduce inflation, including monetary policy, fiscal policy and supply-side policies.
- Trade off between inflation and unemployment . Is there a trade-off between the two, as Phillips Curve suggests?
- The relationship between inflation and the exchange rate – Why high inflation can lead to a depreciation in the exchange rate.
- What should the inflation target be? – Why do government typically target inflation of 2%
- Deflation – why falling prices can lead to negative economic growth.
- Monetarist Theory – Monetarist theory of inflation emphasises the role of the money supply.
- Criticisms of Monetarism – A look at whether the monetarist theory holds up to real-world scenarios.
- Money Supply – What the money supply is.
- Can we have economic growth without inflation?
- Predicting inflation
- Link between inflation and interest rates
- Should low inflation be the primary macroeconomic objective?
See also notes on Unemployment
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Government
Essay Samples on Inflation
How to reduce inflation: the role of monetary policy and measures.
Inflation, the persistent rise in the general price level, poses challenges for individuals, businesses, and economies as a whole. Controlling and reducing inflation is a crucial objective for policymakers seeking to maintain stable economic conditions. There are several ways how to reduce inflation and this...
- Monetary Policy
Unraveling Theories of Inflation in Economics and Its Problem Nature
Inflation is the continual rise in prices, this is also known as a monetary problem. There are different monetary policies in order to keep inflation below a certain level one of these consist of inflation targeting which allows banks to keep a good stability on...
- Economic Problem
How to Reduce Unemployment: What the Government Can Do for People
Unemployment is defined as 'People willing and able to work at the current rate of pay but who are unable to find a job'. There are a number of types of unemployment, including structural, cyclical, seasonal and frictional unemployment. Unemployment is a key measure of...
- Unemployment
Teachers And Professional Athletes Are Paid Differently: Teachers Should Be Paid More
Is it fair that Teachers and Professional Athletes are paid differently? I think the real question should be if they can even be categorized the same. I don't believe the wages of the two can even compare, simply because who is to say one is...
The Political Stance on Raising the Minimum Wage
The lowest wage permitted by law or by a special agreement is a country’s Minimum wage [1]. With a population of 7.6 billion people in the world of whom 2.5 billion live on less than $2 a day [2]. The cost of water in the...
- Minimum Wage
Stressed out with your paper?
Consider using writing assistance:
- 100% unique papers
- 3 hrs deadline option
Minimum Wage: The Slow Increase and Development History
Politicians had been advocating for minimum salary growth often over the previous couple of years and elections. Most Democrats argue for growth at the same time as Republicans generally oppose it. Democrats say we want a boom in the minimal salary to raise human beings...
The Effects of Inflation on a Financial Situation of People
Have you ever thought about how inflation can affect us in a financial sense? This paper will go in-depth and explain the causes of inflation and how it affects consumer behavior, income, investment, and business. In this paper we will go over the methods on...
- Financial Crisis
Understanding Inflation'S Dangers To Philippine Economy
Throughout the most parts of the world, consistent efforts are placed to reduce skyrocketing inflation rates to fall on targeted bands of an economy. Motivated by the convention that inflation bring harmful effects. In the Philippines’ inflation rate soared up to 6.7% for months September...
- Philippines
How Does Inflation Affect the Imbalance of Payments
Inflation rate is a significant variable in economy and affected nation’s balance of payments. It is determined as a stable increase in the overall price level of goods and services in the economy. According to Quah and Vahey (1995), inflation rate is general increase in...
- World Economy
Perception Of Ofw Children On The Inflation In Saudi Arabia
Introduction The economy is a man-made organization with the purpose of satisfying human wants by using limited or scarce resources available and known to a society (Aggarwal & Devi, 2002). It encompasses all of the activities involved in the production and distribution of goods and...
- Saudi Arabia
Effect Of Rupee Depreciation On Indian Economy
Lower value of Currency leads to rattle the economic growth of every small scale to large scale business affecting the population adversely. The terms Inflation, Price Hike, Imports, and taxes can’t remain untouched with the inclusion of Currency Depreciation for any country. Ultimately the financial...
Best topics on Inflation
1. How to Reduce Inflation: the Role of Monetary Policy and Measures
2. Unraveling Theories of Inflation in Economics and Its Problem Nature
3. How to Reduce Unemployment: What the Government Can Do for People
4. Teachers And Professional Athletes Are Paid Differently: Teachers Should Be Paid More
5. The Political Stance on Raising the Minimum Wage
6. Minimum Wage: The Slow Increase and Development History
7. The Effects of Inflation on a Financial Situation of People
8. Understanding Inflation’S Dangers To Philippine Economy
9. How Does Inflation Affect the Imbalance of Payments
10. Perception Of Ofw Children On The Inflation In Saudi Arabia
11. Effect Of Rupee Depreciation On Indian Economy
- Police Brutality
- Gun Control
- American Flag
- Presidential Debate
- Declaration of Independence
- Free Speech
- Franklin D. Roosevelt
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.


Facing down a surprising U.S. inflation surge
Kennedy School experts in public finance and economic policy weigh in on the causes and responses to the highest American consumer price jump in three decades.
Inflation in the United States has jumped to the highest level in 30 years, reaching 6.2% in October as measured by the Consumer Price Index. The COVID-19 pandemic has fueled consumer demand for goods and services at a time when supply lines are constrained and many industries have been affected by staff shortages. The inflation surge has generated intense political debate on the causes and the appropriate response.
We asked several economists and public finance experts at Harvard Kennedy School—all of whom have held senior federal government economics roles—to offer brief perspectives on how they view the underlying issues and the key policy choices facing the Biden administration and Congress.
- Linda Bilmes - Inflation's impact at the state and local level
- Karen Dynan - Weighing the uncertainties
- Jeffrey Frankel - Inflation Do's and Don'ts
- Jason Furman - Supply and demand challenges
- Lawrence H. Summers - Biden team needs to signal its concern about inflation
Inflation risks also lie ahead for state and local governments

On the revenue side, income and sales tax receipts will largely keep pace with inflation, so moderate inflation is unlikely to have a major impact. However, if inflation leads to sharply higher interest rates that lead to a stock market sell-off, then states that are highly dependent on capital gains taxes (such as California and New Jersey) may suffer. Another area of vulnerability could be property taxes, especially states where increases in assessed values or in property taxes are capped, as with California’s Prop. 13. These prevent rising house prices feeding through into state revenues, and are also the major revenue source for local governments.
On the expense side, the biggest risk is rising wages, which consume the largest share of state budgets. We could see public sector unions pushing for a return of “CPI-plus” language in new labor agreements. This would automatically bake in the cost of higher inflation to local expenditures. In addition, high inflation could significantly weaken state pension plans, many of which assume that future wage increases will be only 2%. Most of the current generation of local pension managers have little experience with inflation. They need to begin adjusting their portfolios now to prevent erosion of their asset bases.
Linda Bilmes is the Daniel Patrick Moynihan Lecturer in Public Policy and previously served as Assistant Secretary of Commerce.
What's certain is just how many uncertainties lie ahead

What is not clear is how quickly these issues will resolve. The size and persistence of demand/supply imbalances has repeatedly surprised us, in part because virus caseloads have stayed unexpectedly high. We have only a limited understanding of why so many would-be workers are staying out of the labor force, making it hard to predict how many will return and how quickly. We are not sure how much inflation expectations have risen (a critical determinant of whether higher inflation sticks) because of measurement difficulties.
This uncertainty makes it difficult for monetary policymakers to know when they need to begin raising rates to avoid letting inflation stay at undesirably high levels. Given that they may need to revise their views quickly based on incoming data, it is especially important that they communicate the high degree of uncertainty. Surprising financial markets with an abrupt unexpected change in policy could lead to a rapid decline in asset prices that causes a significant setback in the economic recovery.
Karen Dynan is a professor of the practice of economics and former chief economist of the U.S. Treasury.

Some inflation-fighting do's and don'ts

Let’s start with two don'ts.
- Don’t do what Federal Reserve Chair Arthur Burns and President Richard Nixon did in 1971, in order to help the president’s reelection: They responded to moderate 5% to 6 % inflation with a combination of rapid monetary stimulus and doomed wage-price controls. The lid was blown off the boiling pot a few years later; the inflation rate jumped above 12%.
- Don’t do what Donald Trump did on April 2, 2020 , to help out American oil producers: He persuaded Saudi Arabia that OPEC must cut oil output and raise prices.
- Continue to fight in the Senate for a fully funded social spending bill (“Build Back Better”).
- Let imports into the country more easily. They are a safety valve for an overheated economy. Trump put up a lot of import tariffs , which raise prices to consumers—sometimes directly, as with washing machines, and sometimes indirectly, as with steel and aluminum, which are important inputs into autos and countless other goods. With or without foreign reciprocation, U.S. trade liberalization could bring prices down quickly in many supply-constrained sectors.
- Similarly, facilitating orderly immigration would help alleviate the shortage of workers that employers in some sectors are experiencing.
- Further vaccination would increase the supply of labor, through several possible channels. One channel would be to keep children in school, allowing more parents to go back to work. Another channel is to alleviate worker’s fears of infection in the workplace.
Jeffrey Frankel is the James W. Harpel Professor of Capital Formation and Growth and was a member of the Council of Economic Advisors from 1983-1984 and 1996-1999.
Supply and demand—and the Federal Reserve’s key role

Economists like to explain everything with demand and supply, and the concepts work well here. Demand is likely to remain high, fueled by households with healthy balance sheets, continued fiscal support, and very low interest rates. No one knows how long it will take supply to recover, or even whether it will fully recover, but it could be at least a year. The combination of strong demand and weak supply will likely keep inflation uncomfortably high.
President Biden can do a little about inflation by helping with port capacity and other supply-chain measures. Even better would be dropping President Trump’s tariffs on China. But these steps would only be small. The main agency charged with controlling inflation is the Federal Reserve. They are right to continue to be focused on the millions of people without jobs but should recalibrate towards incorporating more concern for inflation into their policy stance, including setting a default of more rate increases in 2022, something it can call off if inflation and/or employment is well below what we are currently expecting.
Jason Furman is the Aetna Professor of the Practice of Economic Policy and previously was chair of the Council of Economic Advisors under President Obama.
Biden team needs to signal its determination to address inflation

Simultaneously, the Administration should signal that a concern about inflation will inform its policies generally. Measures already taken to reduce port bottlenecks may have limited effect but are a clear positive step. Buying inexpensively should take priority over buying American. Tariff reduction is the most important supply-side policy the administration could undertake to combat inflation. Raising fossil fuel supplies, such as the recent deployment of the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, is crucial. And financial regulators need to step up and be attentive to the pockets of speculative excess that are increasingly evident in financial markets.
Excessive inflation and a sense that it was not being controlled helped elect Richard Nixon and Ronald Reagan, and risks bringing Donald Trump back to power. While an overheating economy is a relatively good problem to have compared to a pandemic or a financial crisis, it will metastasize and threaten prosperity and public trust unless clearly acknowledged and addressed.
Lawrence H. Summers is Charles W. Eliot University Professor , Weil Director of the Mossavar-Rahmani Center for Business and Government, and president emeritus of Harvard University. His government positions included Secretary of the Treasury in the Clinton Administration and Director of the National Economic Council under President Obama. Portions of this essay were excerpted from a Washington Post column .
Banner image by AP Photo/Noah Berger; inline image by Xinhua via Getty Images; faculty portraits by Martha Stewart
More from HKS
Helping homeowners during the covid-19 pandemic: lessons from the great recession, democratizing the federal regulatory process: a blueprint to strengthen equity, dignity, and civic engagement through executive branch action, economic inequality and insecurity: policies for an inclusive economy.
Get smart & reliable public policy insights right in your inbox.
- Free Samples
- Premium Essays
- Editing Services Editing Proofreading Rewriting
- Extra Tools Essay Topic Generator Thesis Generator Citation Generator GPA Calculator Study Guides Donate Paper
- Essay Writing Help
- About Us About Us Testimonials FAQ
Essays on inflation
- Studentshare
- TERMS & CONDITIONS
- PRIVACY POLICY
- COOKIES POLICY
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essay Examples >
- Essays Topics >
- Essay on Government
Free Inflation Argumentative Essay Example
Type of paper: Argumentative Essay
Topic: Government , Inflation , Economics , Money , Economy , Policy , Taxes , Shopping
Words: 1200
Published: 08/06/2021
ORDER PAPER LIKE THIS
Inflation is the continuous increase in the general price levels of commodities in the economy over a period. It is identified with the market fall of the value of money in a particular economy. This recurring price increase erodes the purchasing power of money creating economic distortions and uncertainty (Sargent 2002). Inflation may also be described as a sudden increase in supply of money in a given economy. This results to each unit of currency buying fewer commodities thus a reduction in the purchasing power per unit of money. It can also be viewed as an increase in the supply of money at a rate that is higher than the rate of production in the country's economy. When this price increase is gradual and irregular, it leads to creeping inflation. This is healthy for the economy. It stimulates the economy encouraging social and economic progress. It also makes it easier to adjust relative prices such as salaries employees receive.
While mild and gradual inflation is considered to be an indicator of a healthy economy, inflation above this slow rate has a negative impact in the economy. Taxes imposed to citizens increases with increases in supply of money to the economy. This makes people become more willing to spend because of two main reasons: to purchase commodities before they increase in price and to avoid paying tax on holding currencies. This results to the increase in demand for different commodities thus raising their prices as dictated by price mechanism. This strengthens the rate of inflation and increases the velocity of money; a process referred to as a vicious cycle and is difficult to harness, leading to hyperinflation (Laubach, Mishk, 2001). High inflation rates and hyperinflation lead to bad economic times. As prices rise, the purchasing power of a currency unit decreases thus leading to an increase in uncertainty. This encourages purchasing greasing the vicious cycle while at the same time discouraging savings and investments. Unequal redistribution of money will result. People who receive fixed incomes will continue receiving the same amount which in turn reduces their purchasing power while those on flexible incomes will be able to adjust to inflation. Money will thus be redistributed from those with fixed incomes to those with flexible income. If the inflation rate is higher compared to that abroad, it will lead to deficits in balance of payment resulting from international trade.
Unless it has gone far out of hand, inflation is a controllable. Several approaches can be used to control this. The federal reserve of the U.S counters inflation rates by different fiscal and monetary policies. Fiscal policies come in the form of federal budgeting policies and taxation. However, most market watchers look at financial policies to stabilize the economy. In the US, The Federal Reserve Board's Open Market Committee FOMC is in charge of implementing monetary policies (Sargent 2002). They are charged with the responsibility of limiting or increasing the amount of money circulating in the economy. They make money easier to come by thus encouraging spending to spur economic growth or make it harder to come by when growth rates reach unsustainable levels.
In general, Central Banks in all economies fight inflation by setting high interest rates and reducing the supply of money in the economy. Income policies/ wage and price control policies can be introduced to fight inflation rates. This process all the same has negative effects including distortion of the overall functioning of the economy as it encourages shortages and decrease in quality of commodities. There are several ways used to measure inflation. Consumer Price Index (CPI) is widely used. This approach measures the average prices of a fixed basket of goods and services. This basket of goods reflects what a typical family buys to achieve some desired standard of living in a given period. In the USA, the base set is currently 1982-1984. This base period is adjusted after a given number of years. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) compiles it on a monthly basis. They weigh each item in the basket according to its total household expenditure share in the base period in order to reflect changes in the index periodically to represent the current household cost of living (Sargent 2002). The items are grouped into eight categories which include: housing, apparel, education and communication medical care and transportation. The three main CPI used are: CPI for all urban consumers, Chained CPI for all urban consumers and CPI for urban wage earners and clerical workers.
Producer Price Indexes (PPI) is another method of measuring inflation by the federal government. It measures average changes in price domestic producers receive for their output using weights attached to their output. It covers virtually all industries. It is compiled monthly by the BLS. Personal Consumption expenditure (PCE) is another method of measuring inflation. The Bureau of Economic Analysis computes it on a monthly basis from the National Income and Products Account NIPA.
Inflation has different economic costs. It has a huge impact on savers, as they lose confidence in money as a real value of saving. It may also lead to higher demand of wages as people anticipate to maintain their current living conditions. Inflation also has an impact on a country's competitiveness and unemployment rate. When a country experiences higher inflation rate than another, it leads to loss in competitiveness worsening their performance in trade. This results to increase in unemployment rate.
Business planning and investment can be disrupted by inflation. Budgeting is made hard due to uncertainties created by rise in prices and costs.Inflation has a couple of other positive consequences associated with it. A stable low rate can allow organizations to raise their revenues, prices and profits and their workers can anticipate an increase in their wages as result (Laubach, Mishk, 2001). Low stable inflation can also help reduce the real value of outstanding debts. A good example is mortgage beneficiaries who benefit from inflation to reduce the real burden on their mortgage.
Fluctuation in exchange rates can also have effects on inflation. Fall in value of the domestic currency against other currencies causes higher import prices. Rising of labor costs that are greater than the improvement in productivity also results into inflation. It is difficult to forecast inflation. Some of the reasons behind this include: volatile energy prices, change in value of currency in relation to other foreign currencies, change in indirect government taxes, volatile food prices and uncertain growth of demand Inflation is a natural phenomenon that a healthy economy must experience. Too high inflation rates and zero inflation rates are, however, harmful to the economy. The government is the entity vested with the responsibility of controlling inflation. When it fails to control it, such negligence will be equated to stealing from its people (Sargent 2002).
Laubach, T. Mishk, F. (2001). Inflation Targeting: Lessons from the International Experience. New Jersey. Princeton University Press. Sargent, T. (2002). The Conquest of American Inflation Princeton paperbacks. New Jersey. Princeton University Press, 2002

Cite this page
Share with friends using:
Removal Request

Finished papers: 1535
This paper is created by writer with
ID 278935128
If you want your paper to be:
Well-researched, fact-checked, and accurate
Original, fresh, based on current data
Eloquently written and immaculately formatted
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Get your papers done by pros!
Other Pages
Real estate personal statements, altruism case studies, stylists case studies, oprah winfrey case studies, bedroom case studies, spirituality case studies, haiti case studies, bill gates case studies, cricket case studies, public transport case studies, bartow essays, connell essays, faradays essays, fria essays, century aluminum essays, herman miller essays, denuded essays, tenet healthcare essays, cisplatin essays, dorsalis essays, g6pd essays, example of presidential approval essay, free research paper on greece euro crisis, naturalistic studies course work examples, human resource process case study example, theme analysis literature review example, evidence based research article evaluations and applications essay, good example of a1 c essay, free research paper on roberto cavalli brand history, free essay about tort case, free book review about finnish lessons what can the world learn from educational change in finland, example of literary theory and william shakespeares merchant of venice essay, the intention to continue teaching civics and citizenship education among teachers literature review examples, free research paper on police discretion, good example of how the practice of community policing can be applied to homeland security and counter terrorism essay, free the price of civilization book review sample, good airline airport operations course work example, good example of quot as the internet rewires our brains quot review article review, free essay on comparison between the film and the book frankenstein, free essay about alexander calder, free research paper about the nullification crisis of 1832, good essay about strayer, good critical thinking about springdale shopping survey.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
Inflation surged higher in March, reversing some progress made in cooling prices
The fight to reduce inflation has struck a rough patch in recent months.
Consumer prices rose 3.5% in March compared to a year ago, accelerating markedly from the previous month and reversing some of the progress achieved in a two-year fight to cool inflation, U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics data showed. The finding matched economists' expectations.
Price increases have cooled dramatically from a peak of about 9%, but inflation still stands more than a percentage point higher than the Federal Reserve's target rate of 2%.
A spike in housing and gasoline prices at the outset of this year has helped prolong the nation's bout of elevated inflation. Meanwhile, economic performance has been robust, boosting consumer demand and putting upward pressure on prices.
The latest finding indicated an uptick from the 3.2% annual inflation rate recorded in February.
Core inflation -- a closely watched measure that strips out volatile food and energy prices -- increased 3.8% over the year ending in March, holding steady from the previous month, the data showed.
More than half of the monthly increase in consumer prices owed to an uptick in gasoline and housing costs, the BLS said.
Offering relief for households, the prices of some grocery staples dropped over the year ending in March. The prices of breakfast cereal, rice and pasta each fell more than a percentage point over that period.
Prices also dropped more than 4% for breakfast sausage and ham over the past year. Apple prices fell more than 10% over that period.
Beef prices, however, increased at more than double the pace of overall inflation over the past year.
At a meeting last month, the Fed opted to keep rates highly elevated in response to stubborn inflation. The Fed Funds rate remains between 5.25% and 5.5%, matching its highest level since 2001.
"On inflation, it's too soon to say whether the recent readings represent more than just a bump," Fed Chair Jerome Powell told a business conference at Stanford University last week.
"Given the strength of the economy and progress on inflation so far, we have time to let the incoming data guide our decisions on policy," Powell added.
The Fed said last month that it still intends to make three interest rate cuts this year.
Related Stories

Interest rates could soar above 8%, Dimon warns
- Apr 8, 1:09 PM

JPMorgan CEO warns of risks not seen since WWII
- Apr 8, 6:18 AM

Fed chair Powell says no rate cuts soon
- Apr 3, 3:10 PM
Interest rate cuts would lower borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, potentially triggering a burst of economic activity through greater household spending and company investment.
But the Fed risks a rebound of inflation if it cuts interest rates too quickly, since stronger consumer demand could lead to an acceleration of price increases.

In recent days, some business leaders and policymakers have voiced concern about the outlook for inflation.
In his annual shareholder letter on Monday, JPMorgan Chase CEO Jamie Dimon warned that a host of factors, including government spending and global trading shocks, could make the final leg of inflation's path down to normal levels much more difficult than many observers expect.
Speaking at a meeting of the Shadow Open Market Committee in New York City last week, Fed Governor Michelle Bowman said she sees "a number of upside risks to inflation."
The rough patch for inflation in recent months has coincided with strong economic performance, despite persistently high interest rates meant to slow economic activity.
Employers hired 303,000 workers last month, blowing past economist expectations of 214,000 jobs added, according to a report from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics on Friday.
The hiring far surpassed the average number of jobs added each month over the previous year, suggesting an acceleration in performance for one of the key metrics used to assess the nation's economic health.
Last week, Powell referred to surveys of consumer and business sentiment that suggest inflation is widely expected to return to normal levels.
"The public does believe -- and it's a good thing, because it's true -- that inflation will go back down to 2%," Powell said. "That's very reassuring but that's partly because of the very strong action we took and also because of our ongoing commitment to actually return inflation to 2% over time."
"And that is our commitment," Powell added.
Related Topics

Higher gas and rents keep US inflation elevated, likely delaying Fed rate cuts
- Apr 9, 5:46 PM

Stock market today: Asia stocks rise with market focus on signs of interest rate cut
- Apr 7, 11:25 PM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events
Advertisement
Supported by
Inflation Was Hotter Than Expected in March, Unwelcome News for the Fed
The surprisingly stubborn reading raised doubts about when — and even whether — the Federal Reserve will be able to start cutting interest rates this year.
- Share full article

+3.8% excluding
food and energy
+3.5% in March

By Jeanna Smialek
A closely watched measure of inflation remained stronger than expected in March, worrying news for Federal Reserve officials who have become increasingly concerned that their progress on lowering price increases might be stalling.
The surprisingly stubborn inflation reading raised doubts among economists about when — and even whether — the Fed will be able to start cutting interest rates this year.
The Consumer Price Index climbed 3.8 percent on an annual basis after stripping out food and fuel prices, which economists do in order to get a better sense of the underlying inflation trend. That “core” index was stronger than the 3.7 percent increase economists had expected, and unchanged from 3.8 percent in February. The monthly reading was also stronger than what economists had forecast.
Counting in food and fuel, the inflation measure climbed 3.5 percent in March from a year earlier, up from 3.2 percent in February and faster than what economists anticipated. A rise in gas prices contributed to that inflation number.
This week’s inflation figures come at a critical juncture for the Fed. Central bankers have been hoping to confirm that warmer-than-expected inflation figures at the start of the year were just a seasonal quirk, not evidence that inflation is getting stuck well above the 2 percent target. Wednesday’s report offers little comfort that the quick early 2024 readings have not lasted.
“It is what it is: It’s a stronger-than-expected number, and it’s showing that those price pressures are strong across goods and services,” said Blerina Uruci, chief U.S. economist at T. Rowe Price. “It’s problematic for the Fed. I don’t see how they can justify a June cut with this strong data.”
Policymakers have made it clear in recent months that they want to see further evidence that inflation is cooling before they cut interest rates. Fed officials raised borrowing costs to 5.3 percent in 2022 and mid-2023, which they think is high enough to meaningfully weigh on the economy. Central bankers forecast in March that they would cut interest rates three times this year.
But Fed officials do not want to cut rates before they are confident inflation is on track to return to normal. Lowering borrowing costs too early or too much would risk allowing price increases to pick back up. And if households and businesses come to expect inflation to remain slightly higher, officials worry that could make it even harder to stamp out down the road.
That threat of lingering inflation has become a more serious concern for policymakers since the start of the year. Inflation flatlined in January and February after months of steady declines, raising some alarm at the Fed and among forecasters. Going into the year, investors expected the Fed to cut rates sharply in 2024 — perhaps five or six times, to about 4 percent — but have steadily dialed back those expectations .
Stocks dropped sharply after the inflation release as investors further pared back their expectations for lower rates. Following the report, market pricing suggested that many investors now expect just one or two cuts his year.
The S&P 500 and the tech-heavy Nasdaq composite each closed nearly 1 percent lower on Wednesday. The Russell 2000 index, which tracks smaller companies, was down nearly 3 percent.
Investors would like to see lower interest rates, which tend to bolster prices for assets like stocks. But the Fed might struggle to explain why it is cutting rates at the current moment: Not only is inflation showing signs of getting stuck well above the central bank’s target, but the economy is growing at a fairly rapid pace and employers are hiring at a robust clip.
In short, the Fed’s policies do not appear to have pushed America to the brink of a recession — and in fact, there are signs that they may not be having as much of an effect as policymakers had expected when it comes to growth.
While the Fed officially targets Personal Consumption Expenditures inflation , a separate measure, the Consumer Price Index report released on Wednesday comes out earlier and includes data that feeds into the other metric. That makes it a closely watched signal of how price pressures are shaping up.
The inflation report’s details offered little reason to dismiss the gauge’s continued stubbornness as a fluke. They showed that housing inflation remains firm, auto insurance costs picked up at a rapid pace and apparel prices climbed.

Monthly changes in March
Motor vehicle insurance
Gasoline (all types)
Motor vehicle repair
Hospital services
Meats, poultry, fish, eggs
Electricity
All items excl. food and energy
Tobacco products
Rent of primary residence
Nonalcoholic beverages
Food away from home
Medical care commodities
Fruits, vegetables
Alcoholic beverages
Physicians’ services
Piped utility gas service
Dairy products
New vehicles
Airline fares
Cereals, bakery products
Used cars, trucks

Motor vehicle maintenance and repair
Meats, poultry, fish and eggs
All items excluding food and energy
Tobacco and smoking products
Nonalcoholic beverages and materials
Fruits and vegetables
Dairy and related products
Cereals and bakery products
Used cars and trucks
In a development that is likely to be especially notable for Fed officials, a measure of services inflation contributed to the pickup in annual inflation. Policymakers watch those prices closely, because they can reflect the strength of the underlying economy and because they tend to persist over time.
The question, increasingly, is whether Fed officials can cut interest rates at all this year in a world where inflation appears to be flatlining.
Ms. Uruci said that with every month inflation stays stubborn, the Fed may need to see more convincing evidence — and a more sustained return to deceleration — to feel confident that price increases are genuinely coming under control.
Kathy Bostjancic, Nationwide’s chief economist, predicted that rate cuts could now be delayed to this autumn, if they happen in 2024 at all.
“We now think September, if they start to cut rates, is more likely than July,” Ms. Bostjancic said. The new report “shakes the confidence that inflation is on this downward trend.”
If the Fed does not cut rates soon, the election could make the start of reductions more politically fraught. Central bankers are independent of the White House and typically insist that they do not make policy with an eye on the political calendar.
Still, cutting in the months just before the election could put policymakers under a partisan spotlight : Former President Donald J. Trump, the presumptive Republican nominee, has already painted possible rate cuts as a political ploy to help Democrats. Lower rates tend to help incumbents, since they bolster the economy.
But the current economic moment is a politically complicated one.
Consumers dislike rapidly rising prices, and inflation has been dogging President Biden’s approval ratings for months. That said, consumers have become less concerned about them in recent months as the pace of inflation has come down from its peak in 2022.
At the same time, some Americans are chafing against high interest rates, the medicine the Fed uses to cure rapid inflation because they make it more expensive to borrow to buy a house or make other large purchases.
Mr. Biden has struck a concerned tone about high prices and tough housing affordability conditions in recent months, while pinning at least some of the blame for recent rapid inflation on corporations.
He reiterated that message on Wednesday, while saying that he still expects to see rate cuts this year. Mr. Biden’s comments amounted to a forecast rather than a prescription, but they were unusual coming from a White House that usually avoids talking about Fed policy out of respect for the central bank’s independence.
“We have dramatically reduced inflation down from 9 percent to close to 3 percent,” Mr. Biden also noted.
Jeanna Smialek covers the Federal Reserve and the economy for The Times from Washington. More about Jeanna Smialek

Essay on Inflation In Philippines
Students are often asked to write an essay on Inflation In Philippines in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Inflation In Philippines
What is inflation.
Inflation means the prices of things we buy are going up. In the Philippines, when prices rise, it becomes harder for people to afford food, clothes, and other items. This can happen when there’s too much money to spend but not enough goods, or when the cost to make products goes higher.
Inflation in the Philippines
The Philippines often experiences inflation. This can be due to natural disasters affecting crops, changes in global oil prices, or government actions. When inflation occurs, Filipino families might struggle to buy what they need, which can be tough for everyone.
Effects on Daily Life
Because of inflation, families in the Philippines might have to change how they spend money. They may buy less food or cheaper items to save money. Sometimes, even going to school or getting healthcare can become more expensive, making life challenging for many people.
250 Words Essay on Inflation In Philippines
Understanding inflation in the philippines.
Inflation means the increase in prices of things we buy, like food, clothes, and toys. In the Philippines, just like in other countries, prices can go up over time. This can make life hard for families, especially if they don’t have a lot of money.
Causes of Inflation
In the Philippines, inflation can happen for many reasons. Sometimes, if there’s a problem with growing food or if there’s a big storm, there might not be enough of it, and this can make prices go up. Also, if the money in the Philippines becomes less valuable compared to other countries’ money, things that come from other countries can become more expensive.
Effects of Inflation
When prices go up, it’s tough for people. They might not be able to buy as much with their money, and this can be stressful. Parents might have to work more to earn more money, and sometimes, kids might not get new toys or clothes as often.
What the Government Does
The government in the Philippines tries to control inflation. They can change how much money is in the economy or make rules about prices to help keep them from going up too fast. They do this because they want to make sure that people can afford what they need.
Inflation in the Philippines is a challenge that affects everyone. It’s important to understand why it happens and how it changes the way people live. While it can be tough when prices go up, the government works to manage inflation for the good of the country.
500 Words Essay on Inflation In Philippines
Inflation is when the prices of things we buy go up. Imagine you could buy a toy car for one peso last year, but this year the same car costs two pesos. That’s inflation: the money you have buys less than before. This can happen with toys, food, clothes, and almost everything. In the Philippines, like in many countries, inflation affects how people live because they need more money to buy the same things.
Causes of Inflation in the Philippines
In the Philippines, inflation happens for a few reasons. Sometimes, when there are not enough goods like rice or vegetables, prices go up because many people want these items but there aren’t enough for everyone. This is called “demand-pull inflation.” Another reason is “cost-push inflation,” which is when the cost to make products goes up. For example, if the price of gas increases, it costs more to deliver goods to stores, so the prices of these goods go up.
Also, when the money value in the Philippines goes down compared to other countries’ money, things we buy from other countries become more expensive. This is known as “imported inflation.”
Effects of Inflation on People
Inflation can make life hard for families. Parents have to spend more money on the same things, so they might have less money left for saving or for fun activities. Kids might notice that their allowance doesn’t buy as much candy or toys as it used to. If inflation is high, people might worry about prices going up even more and rush to buy things, which can make inflation worse.
How the Government Handles Inflation
The government of the Philippines tries to control inflation to make sure prices don’t rise too fast. The Central Bank of the Philippines can change interest rates, which is like changing the cost of borrowing money. If it’s more expensive to borrow money, people and businesses might spend less, and this can help slow down inflation.
The government can also use policies to help make sure there is enough supply of goods. For example, they can encourage farmers to grow more rice or make it easier for stores to get products from other countries when there’s not enough supply in the Philippines.
What Can People Do?
People can also do things to handle inflation. Families can plan their spending and look for better prices before buying something. It’s important to learn about money and how to use it wisely, especially when prices are going up.
Inflation in the Philippines is when prices rise and money buys less. It can be caused by not enough goods, higher costs to make products, or the country’s money value changing. Inflation affects how people live, but the government and people can take steps to manage it. By understanding what inflation is and how it works, even school students can be better prepared to deal with it in their daily lives.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Cold War
- Essay on Cold Weather
- Essay on Inequality In Society
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Essay on Inflation in Pakistan for Students
by Pakiology | Mar 22, 2024 | Essay | 0 comments
In this essay on inflation in Pakistan, we will look at the causes, effects, and solutions to this issue that has been affecting the country for decades. The term ‘inflation’ refers to a sustained rise in the prices of goods and services in an economy. In Pakistan, inflation has been a major concern since the late 1990s, with the Consumer Price Index (CPI) reaching a peak in 2023. We will explore the various factors that have contributed to inflation in Pakistan, its economic effects, and what can be done to address the issue.
Page Contents
Essay on Inflation Outlines
Causes of inflation in pakistan, effects of inflation, solution to control inflation.
- Introduction
Inflation in Pakistan is caused by several factors, which can be divided into two main categories: domestic and external. The main domestic causes of inflation are an increase in money supply, an increase in government spending, an increase in indirect taxes, and a decrease in economic growth.
The most significant contributor to inflation in Pakistan is an increase in the money supply. When there is too much money chasing after too few goods, prices rise, creating a situation known as demand-pull inflation. An increase in the money supply can be caused by the central bank printing more money or by the government borrowing more money from the public.
In addition, higher government spending can lead to inflation. This occurs when the government prints more money to finance its expenditure or borrows from the public and transfers the cost of this additional spending to businesses and consumers. This leads to higher prices for goods and services. Indirect taxes are another major factor that contributes to inflation in Pakistan. When indirect taxes are increased, prices of goods and services also increase, leading to an overall rise in prices.
Finally, low economic growth can also cause inflation in Pakistan. A weak economy reduces people’s purchasing power, forcing them to buy less, which reduces demand and leads to lower prices. However, when economic growth stalls, businesses are unable to sell their products at the same price as before, leading to a rise in prices.
Overall, inflation in Pakistan is caused by a combination of domestic and external factors. These include an increase in money supply, higher government spending, increases in indirect taxes, and a decrease in economic growth.
The effects of inflation on the economy can be both positive and negative. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, meaning that each unit of currency is worth less than it was before. This means that, as the cost of living increases, people can purchase fewer goods and services for the same amount of money. As a result, their standard of living decreases.
Inflation also reduces the real return on investments and savings, which can have a detrimental effect on economic growth. When inflation is high, people prefer to save their money rather than invest in a business or other activities. This reduces the availability of capital and results in slower economic growth.
In addition to decreasing standards of living, inflation can lead to unemployment if companies are not able to increase wages at the same rate as prices rise. This can lead to an increase in poverty, as people struggle to afford necessities. Furthermore, when prices rise faster than wages, it puts pressure on government budgets and can increase public debt.
Inflation can also cause the value of the local currency to depreciate against foreign currencies. This has a direct impact on the cost of imports and makes domestic goods less competitive in international markets. It can also have an indirect impact on exports, as it reduces the competitiveness of local producers in foreign markets.
Inflation is a serious issue in Pakistan, and it needs to be addressed to improve the country’s economic conditions. The following are some of the measures that can be taken to control inflation in Pakistan:
1. Fiscal policy: A strong fiscal policy is necessary for controlling inflation. The government should increase its revenue by implementing taxes on the wealthy and reducing public spending. This will help reduce budget deficits, which will result in lower inflation.
2. Monetary policy: The State Bank of Pakistan should adopt a tighter monetary policy to control inflation. It should raise interest rates so that investors have an incentive to save rather than spend, thus curbing demand-pull inflation.
3. Supply-side measures: There should be an increase in the production of essential commodities and products to meet the demand of consumers. This will help reduce prices and inflation in the long run.
4. Subsidies: The government should provide subsidies to those who are suffering due to the high prices of essential items. This will help them cope with the rising cost of living and ensure that they have access to essential goods and services.
5. Stabilizing exchange rate: A stable exchange rate between foreign currencies and the rupee is necessary for controlling inflation. The State Bank of Pakistan should strive to keep the rupee’s value stable by using currency swaps and other methods.
These measures can go a long way in controlling inflation in Pakistan. By taking these measures, the government can help improve the country’s economic condition and create an environment conducive to investment and growth.
What is inflation in simple words?
Inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.
What are the 4 main causes of inflation?
The 4 main causes of inflation are: Demand-pull inflation: when there is an increase in demand for goods and services that outstrip the economy’s ability to produce them. Cost-push inflation: when the cost of production increases, causing companies to raise prices to maintain their profit margins. Built-in inflation: when businesses expect prices to rise and build that expectation into their prices, causing a self-fulfilling cycle of inflation. Imported inflation: when the cost of imported goods increases, leading to higher prices for consumers.
What are the 5 main causes of inflation?
The 4 main causes of inflation are: 1. Demand-pull inflation 2. Cost-push inflation 3. Built-in inflation 4. Imported inflation 5. Monetary inflation
What is inflation introduction?
Inflation is a phenomenon that has been observed throughout history. It refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.
Find more Essays on the following Topics
Ask Your Questions
You might like, democracy in pakistan essay with quotations.
Explore the evolution, challenges, and progress of democracy in Pakistan in this in-depth essay. Gain insights into...
Problems of Karachi Essay | 200 & 500 Words
Explore the multifaceted challenges faced by Karachi in this comprehensive essay. From overpopulation to traffic...
A True Muslim Essay With Quotations 2023
A true Muslim essay is about the qualities of a true Muslim and how they embody the teachings of Islam in their daily...
Health is Wealth Essay For Students
In this essay, we explore why health is wealth and why it is crucial to prioritize our physical and mental well-being...
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- class-9-notes
- Friendship quotes
- Scholarships
- Science News
- Study Abroad
- Study in Australia
- SZABMU MDCAT
- UHS Past MCQs
- Universities

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Economic Condition of Singapore: Inflation Hits 5.2% in March. Some of the effects of high inflation rate that has been felt in the economy are the increase of the housing prices, and cost of fuel increased by approximately 5%, thereby increasing the cost of […] Inflation Is Here to Stay, as Prices Will Always Go Up.
Here are 100 inflation essay topic ideas and examples to help you get started: The causes and effects of inflation. The relationship between inflation and unemployment. The impact of inflation on interest rates. The role of the Federal Reserve in controlling inflation. The differences between demand-pull and cost-push inflation.
Inflation is a highly contentious issue. This is due to its economic implications. Inflation has the potential of crippling a country's economy. The Problem of Inflation: Crucial Aspects. Of primary importance is the recognition that inflation is not an unnatural or harmful mechanism for a country's economy.
Inflation Essay Topics and Outline Examples Essay Title 1: Understanding Inflation: Causes, Effects, and Economic Policy Responses. Thesis Statement: This essay provides a comprehensive analysis of inflation, exploring its root causes, the economic and societal effects it generates, and the various policy measures employed by governments and central banks to manage and mitigate inflationary ...
Essay on Inflation! Essay on the Meaning of Inflation: Inflation and unemployment are the two most talked-about words in the contemporary society. These two are the big problems that plague all the economies. Almost everyone is sure that he knows what inflation exactly is, but it remains a source of great deal of confusion because it is difficult to define it unambiguously. Inflation is often ...
Inflation Essay and Research Paper Examples 🗨️ More than 30000 essays Find the foremost Inflation essay introductions, questions to get results! ... Essay topics. Inflation is the measurement of how much more costly a collection of goods and services has gotten over time, generally a year. It's possible that it's one of the most well ...
Article (5 pages) Inflation refers to a broad rise in the prices of goods and services across the economy over time, eroding purchasing power for both consumers and businesses. In other words, your dollar (or whatever currency you use for purchases) will not go as far today as it did yesterday. To understand the effects of inflation, take a ...
UK inflation since 1989. Definition - Inflation - Inflation is a sustained rise in the cost of living and average price level. Causes Inflation - Inflation is caused by excess demand in the economy, a rise in costs of production, rapid growth in the money supply. Costs of Inflation - Inflation causes decline in value of savings ...
Understanding Inflation'S Dangers To Philippine Economy. Throughout the most parts of the world, consistent efforts are placed to reduce skyrocketing inflation rates to fall on targeted bands of an economy. Motivated by the convention that inflation bring harmful effects. In the Philippines' inflation rate soared up to 6.7% for months ...
The inflation rate for May 2005 was 2.80%, this is down from 3.51% in April and 3.15% for March. The average inflation rate from May 2005 to January 2000 was 2.79% ("Inflation rate," 2005). Therefore, this current inflation rate was not wholly unexpected.
And if you're also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic. ... 500 Words Essay on Inflation Introduction to Inflation. Inflation is a complex economic phenomenon that affects every aspect of our lives, from the cost of living to the value of money. It is defined as the rate at which the ...
December 01, 2021. Inflation in the United States has jumped to the highest level in 30 years, reaching 6.2% in October as measured by the Consumer Price Index. The COVID-19 pandemic has fueled consumer demand for goods and services at a time when supply lines are constrained and many industries have been affected by staff shortages.
Inflation - Free Essay Examples And Topic Ideas. Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and subsequently, purchasing power is decreasing. This increase in prices is generally measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and can be caused by various factors such as an increase in the money ...
INFLATION 1. Inflation happens in an economy when there is a rise of level of goods and services, due to an increase in the volume of money in an economy over a period of time. It is also referred to as an (erosion) in the value of an economy's currency. When inflation is high, it affects the entire economy.
Words: 607. Page: 1. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Cite this essay. Download. While increasing demand is generally great news for an economy, a lagged supply chain can cause Inflation.
The Inflation is one of the most popular assignments among students' documents. If you are stuck with writing or missing ideas, scroll down and find inspiration in the best samples. Inflation is quite a rare and popular topic for writing an essay, but it certainly is in our database.
Impact of Inflation on the Economy. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Giving people the resources and ability to learn about how things are going in our economy is an extremely important thing. One issue that is especially prevalent in ...
Inflation is the continuous increase in the general price levels of commodities in the economy over a period. It is identified with the market fall of the value of money in a particular economy. This recurring price increase erodes the purchasing power of money creating economic distortions and uncertainty (Sargent 2002).
Economists expect the inflation rate to have increased 3.5% in March compared to the same month a year ago. The finding would mark an acceleration from the 3.2% annual inflation rate recorded in ...
Alas, the story thus far in 2024 is not quite so cheerful. Growth has remained robust but, partly as a result, inflation is looking stickier. The Federal Reserve faces a dilemma about whether to ...
Introduction. Inflation, a crucial economic indicator, refers to the sustained rise in the general level of prices for goods and services. It erodes purchasing power, causing distress among the population, particularly those with fixed incomes. In India, inflation has been a persistent issue, influencing both the economic and social fabric of ...
Counting in food and fuel, the inflation measure climbed 3.5 percent in March from a year earlier, up from 3.2 percent in February and faster than what economists have anticipated. A rise in gas ...
Conclusion. Inflation in the Philippines is when prices rise and money buys less. It can be caused by not enough goods, higher costs to make products, or the country's money value changing. Inflation affects how people live, but the government and people can take steps to manage it. By understanding what inflation is and how it works, even ...
In this essay on inflation in Pakistan, we will look at the causes, effects, and solutions to this issue that has been affecting the country for decades. The term 'inflation' refers to a sustained rise in the prices of goods and services in an economy. In Pakistan, inflation has been a major concern since the late 1990s, with the Consumer ...