Imagine a symphony orchestra where each musician plays their own tune without listening to others. The result would be chaotic and dissonant, right? Similarly, in the business world, when decision-making happens in silos and planning processes are disconnected, it’s like having a group of individuals playing their own instruments without any coordination. The harmony is lost, and the organization becomes inefficient, misses opportunities, and struggles to keep up with the fast-paced market.
Integrated Business Planning (IBP) addresses these challenges by providing a comprehensive framework that integrates strategic, operational and financial planning, analysis, and reporting to drive better business outcomes. A retail company experiences a sudden surge in online sales due to a viral social media campaign. Integrated planning incorporates supply chain planning, demand planning, and demand forecasts so the company can quickly assess the impact on inventory levels, supply chain logistics, production plans, and customer service capacity. By having real-time data at their fingertips, decision-makers can adjust their strategies, allocate resources accordingly, and capitalize on the unexpected spike in demand, ensuring customer satisfaction while maximizing revenue. This blog explores the significance of IBP in today’s modern business landscape and highlights its key benefits and implementation considerations.

Integrated business planning framework
Integrated Business Planning (IBP) is a holistic approach that integrates strategic planning, operational planning, and financial planning within an organization. IBP brings together various functions, including sales, marketing, finance, supply chain, human resources, IT and beyond to collaborate across business units and make informed decisions that drive overall business success. The term ‘IBP’ was introduced by the management consulting firm Oliver Wight to describe an evolved version of the sales and operations planning (S&OP process) they originally developed in the early 1980s.
Making up the Integrated Business Planning framework are six key pillars:
1. strategic planning.
Integrated Business Planning starts with strategic planning. The management team defines the organization’s long-term goals and objectives. This includes analyzing market trends, competitive forces, and customer demands to identify opportunities and threats. Strategic planning sets the direction for the entire organization and establishes the foundation for subsequent planning roadmap.
2. Operational planning
Operational planning focuses on translating strategic goals into actionable plans at the operational level. This involves breaking down the strategic objectives into specific targets and initiatives that different departments and functions need to execute.
For example, the sales department might develop a plan to enter new markets or launch new products, while the supply chain department focuses on inventory optimization and ensuring efficient logistics. The key is to align operational plans with the broader strategic objectives to ensure consistency and coherence throughout the organization.
3. Financial planning
Financial planning ensures that the organization’s strategic and operational plans are financially viable. It involves developing detailed financial projections, including revenue forecasts, expense budgets, and cash flow forecasts. By integrating financial planning with strategic and operational planning, organizations can evaluate financial profitability, identify potential gaps or risks, and make necessary adjustments to achieve financial targets.
4. Cross-functional collaboration
A fundamental aspect of IBP is the collaboration and involvement of various functions and departments within the organization. Rather than working in isolation, departments such as sales, marketing, finance, supply chain, human resources, and IT come together to share information, align objectives, and make coordinated decisions.
5. Data integration and analytics
IBP relies on the integration of data from different sources and systems. This may involve consolidating data from enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, supply chain management systems, and other relevant sources. Advanced analytics and business intelligence tools are utilized to analyze and interpret the data, uncovering insights and trends that drive informed decision-making.
6. Continuous monitoring and performance management
The Integrated Business Planning process requires continuous monitoring of performance against plans and targets. Key performance indicators (KPIs) are established to measure progress and enable proactive management. Regular performance reviews and reporting enable organizations to identify deviations, take corrective actions, and continuously improve their planning processes.
What are the benefits of Integrated Business Planning?
By integrating strategic, operational, and financial planning organizations can unlock the full potential of IBP and drive business success and achieve their goals.
Enhanced decision-making
IBP facilitates data-driven decision-making by providing real-time insights into various aspects of the business. By bringing together data from various departments, organizations can develop a holistic view of their operations, enabling them to make better-informed decisions.
Improved alignment
By aligning strategic objectives with operational plans and financial goals, IBP ensures that every department and employee is working towards a common vision. This alignment fosters synergy and drives cross-functional collaboration.
Agility and responsiveness
In the rapidly changing business landscape, agility is crucial. IBP allows organizations to quickly adapt to market shifts, demand fluctuations, and emerging opportunities. By continuously monitoring and adjusting plans, businesses can remain responsive and seize competitive advantages.
Optimal resource allocation
Integrated Business Planning enables organizations to optimize resource allocation across different functions. It helps identify bottlenecks, allocate resources effectively, and prioritize initiatives that yield the highest returns, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings.
Risk management
IBP facilitates proactive risk management by considering various scenarios and identifying potential risks and opportunities. By analyzing data and conducting what-if analyses, companies can develop contingency plans and mitigate risks before they materialize.
Essential steps for implementing Integrated Business Planning
Implementing an effective IBP process requires careful planning and execution that may require substantial effort and a change of management, but the rewards are well worth it. Here are some essential strategic steps to consider:
1. Executive sponsorship
Establish leadership buy-in; gain support from top-level executives who understand the value of Integrated Business Planning and can drive the necessary organizational changes. Leadership commitment, led by CFO, is crucial for successful implementation.
2. Continuous improvement
Continuously monitor and adjust; implement mechanisms to monitor performance against plans and targets. Regularly review key performance indicators (KPIs), conduct performance analysis, and generate timely reports and dashboards. Identify deviations, take corrective actions, and continuously improve the planning processes based on feedback and insights.
3. Integration of people and technology
To foster cross-functional collaboration, the organization must identify key stakeholders, break down silos, and encourage open communication among departments. Creating a collaborative culture that values information sharing and collective decision-making is essential.
Simultaneously, implementing a robust data integration system, encompassing ERP, CRM, and supply chain management systems, ensures seamless data flow and real-time updates. User-friendly interfaces, data governance, and training provide the necessary technological support. Combining these efforts cultivates an environment of collaboration and data-driven decision-making, boosting operational efficiency and competitiveness.
4. Technology
Implement advanced analytics and business intelligence solutions to streamline and automate the planning process and assist decision-making capabilities. These solutions provide comprehensive functionality, data integration capabilities, scenario planning and modeling, and real-time reporting.
Integrated Business Planning software
From a tech perspective, organizations need advanced software solutions and systems that facilitate seamless data integration and collaboration to support IBP. Here are some key components that contribute to the success of integrated business planning:
1. Corporate performance management
A platform that serves as the backbone of integrated business planning by integrating data from different departments and functions. It enables a centralized repository of information and provides real-time visibility into the entire business.
2. Business intelligence (BI) tools
Business intelligence tools play a vital role in analyzing and visualizing integrated data from multiple sources. These tools provide comprehensive insights into key metrics and help identify trends, patterns, and opportunities. By leveraging BI tools, decision-makers can quickly evaluate financial performance, make data-driven business decisions and increase forecast accuracy.
3. Collaborative planning and forecasting solutions
Collaborative planning and forecasting solutions enable cross-functional teams to work together in creating and refining plans. These planning solutions facilitate real-time collaboration, allowing stakeholders to contribute their expertise and insights. With end-to-end visibility, organizations can ensure that plans are comprehensive, accurate, and aligned with business strategy.
4. Data integration and automation
To ensure seamless data integration, organizations need to invest in data integration and automation tools. These tools enable the extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) of data from various sources. Automation streamlines data processes reduces manual effort and minimizes the risk of errors or data discrepancies.
5. Cloud-based solutions
Cloud computing offers scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, making it an ideal choice for integrated business planning. Cloud-based solutions provide a centralized platform where teams can access data, collaborate, and make real-time updates from anywhere, at any time. The cloud also offers data security, disaster recovery, and cost efficiencies compared to on-premises infrastructure.
6. Data governance and security
As organizations integrate data from multiple sources, maintaining data governance and security becomes crucial. Establishing data governance policies and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations are vital steps in maintaining data integrity and safeguarding sensitive information. Implementing robust data security measures, such as encryption and access controls, helps protect against data breaches and unauthorized access.
IBM Planning Analytics for Integrated Business Planning
IBM Planning Analytics is a highly scalable and flexible solution for Integrated Business Planning. It supports and strengthens the five pillars discussed above, empowering organizations to achieve their strategic goals and make better data-driven decisions. With its AI- infused advanced analytics and modeling capabilities, IBM Planning Analytics allows organizations to integrate strategic, operational, and financial planning seamlessly. The solution enables cross-functional collaboration by providing a centralized platform where teams from various departments can collaborate, share insights, and align their plans. IBM Planning Analytics also offers powerful data integration capabilities, allowing organizations to consolidate data from multiple sources and systems, providing a holistic view of the business. The solutions’s robust embedded AI predictive analytics uses internal and external data and machine learning to provide accurate demand forecasts. IBM Planning Analytics supports continuous monitoring and performance management by providing real-time reporting, dashboards, and key performance indicators (KPIs) that enable organizations to track progress and take proactive actions. As the business landscape continues to evolve, embracing Integrated Business Planning is no longer an option but a necessity for organizations. To succeed in this dynamic environment, businesses need an integrated approach to planning that brings all the departments and data together, creating a symphony of collaboration and coordination.
More from Artificial intelligence
Ai bundle for ibm z and linuxone.
5 min read - IT leaders have long faced a need to add compute capacity to meet the increased demands from their business. Adoption of mobile technologies and ongoing digital transformation has added to these capacity demands, and IT leaders have been forced to plan for the increasing need for compute infrastructure. We have seen that the explosion in interest and adoption of AI has led IT leaders to revisit their capacity plans. They are seeing the need for increasing compute resources at a scale…
Unlock the value of your Informix data for advanced analytics and AI with watsonx.data
3 min read - Every conversation that starts with AI ends in data. There's an urgent need for businesses to harness their data for advanced analytics and AI for competitive edge. But it’s not as simple as it sounds. Data is exploding, both in volume and in variety. According to IDC, by 2025, stored data will grow 250% across on-premises and cloud storages. With growth comes complexity—multiple data applications, formats and data silos make it harder for organizations to utilize all their data while managing costs. To unlock…
How to prevent prompt injection attacks
8 min read - Large language models (LLMs) may be the biggest technological breakthrough of the decade. They are also vulnerable to prompt injections, a significant security flaw with no apparent fix. As generative AI applications become increasingly ingrained in enterprise IT environments, organizations must find ways to combat this pernicious cyberattack. While researchers have not yet found a way to completely prevent prompt injections, there are ways of mitigating the risk. What are prompt injection attacks, and why are they a problem? Prompt…
IBM Newsletters
What Is Integrated Business Planning and Why Is It Important?

Think of modern integrated business planning, or IBP, as a mashup of supply chain optimization, financial planning and analysis (FP&A) and operational best practices, powered by a companywide culture that’s all about delivering the speed, savings and responsiveness today’s consumers demand while managing risk.
Note that IBP as a fuzzy, buzzword-laden process methodology has been around for years. It’s usually implemented by expensive consultants in sprawling, global corporations that know they need to unify siloed sales, supply, financial and operational resources — before more nimble competitors relegate them to the former Fortune 500 list.
We’re here to argue that IBP deserves a second look for any company that wants to maximize profits and minimize the risks associated with growth. No six-figure consultant required.
What Is Integrated Business Planning?
On paper, IBP is a process for aligning a company’s business goals with its finance, supply chain, product development, marketing and other operational functions. Think parts suppliers that work with automakers and need to constantly retool to accommodate design changes, or food producers operating on razor-thin margins that must manage both uncertain supply chains and fickle customer tastes.
Lag, and a competitor is standing by to take that business. Move quickly but in a disjointed manner and you may keep customers, but at the expense of higher cost of goods sold (COGS) and lower profitability.
For example, consider PickerBots, a fictional maker of custom machinery for manufacturing and warehouse operations. When the company launched in 2017, it found a niche in restaurant supply, but when that business slowed significantly in 2020 the founders decided to retool. Rather than simply changing up its marketing, the firm set out to revamp its business strategy. A top-down scenario planning exercise led to realigning its R&D, demand forecasting, profitability and revenue analysis, supply chain planning and marketing and sales strategy.
The company culture was already strong on innovative thinking, but the founders realized that the link between strategic planning and day-to-day operations could use improvement. Enter a new COO with the chops to align operations with product demand planning and sales and marketing while weighing in on financial targets and budgets.
Key Takeaways
- In a company that embraces IBP, there’s a direct line from purchasing, production and inventory to sales and marketing to financial targets and budgets.
- A key IBP benefit is that materials are bought at the right price, at the right time and in just the right quantity to fulfill market demand.
- Successful IBP delivers closer collaboration and more trust among departments, leading to improved decision-making.
- IBP may require significant cultural change and cannot be successful without unwavering commitment from the executive team.
Integrated Business Planning Explained
Many organizations mistake IBP for a supply-chain-centric exercise. While linking supply chain planning with other departments, from sales and operations through finance, is important, that’s just one element.
IBP aligns business g oals and financial t argets with decisions and execution across the entire business.
There is overlap with financial planning and analysis (FP&A). Because an IBP initiative gathers data from across the enterprise, companies get better at predictive analysis. Now, when purchasing forecasts a parts shortage, supply and operations can adjust before customers are affected.
It’s also not a one-and-done exercise. PickerBots’ new COO advises looking a minimum of 36 months out. Leaders will need to keep their eyes on that long-range plan while continually reviewing, revising and communicating financial and operating results. What supply chain gaps have opened up, and how can we close them? Do we need to update our scenario planning? Are we tracking the right financial KPIs?
A crucial element of IBP is that it integrates financials with operations. Here’s a structure that PickerBots plans to follow.
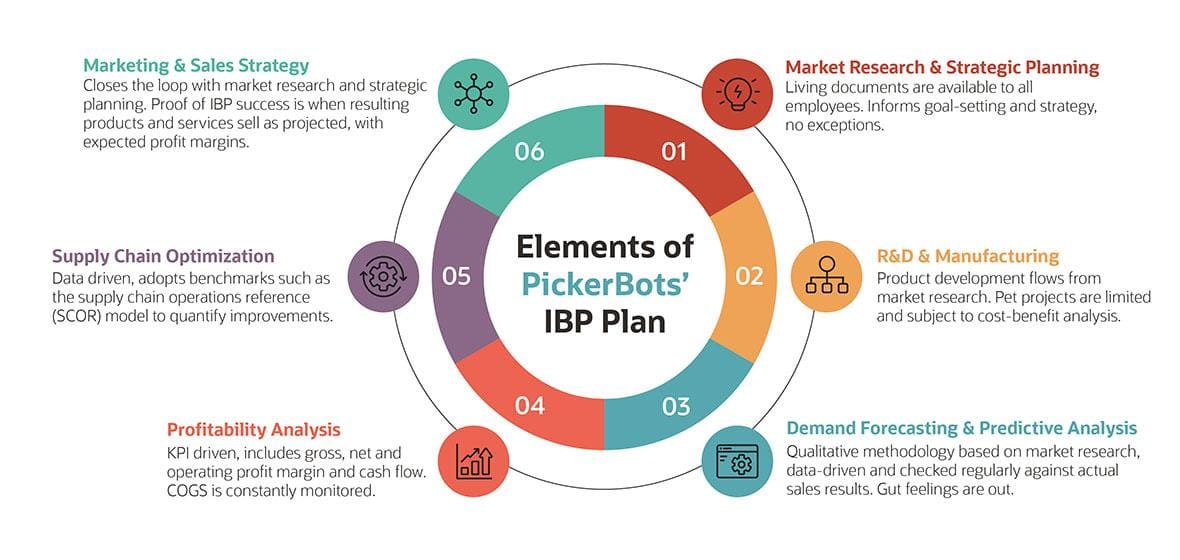
Why Is Integrated Business Planning Important?
Companies that undertake IBP realize a number of practical benefits, including reduced holding costs, more responsive customer service and demand fulfillment, shorter time to market for new products and an improved correlation between demand planning and fulfillment.
After PickerBot’s scenario planning and strategy session, the company decided to jump into the emerging collaborative robot, or cobot, market. A collaborative robot is designed to safely interact with human workers. PickerBot’s leaders believe demand will increase for “pick and place” cobots with fine motor skills for use on manufacturing lines as well as in agricultural settings.
Now that the company has its strategic direction, the COO wants to focus on three higher-level concepts before delving into more practical areas, like financial planning and analysis and supply chain optimization. That’s because without goal-setting, PickerBots won’t be able to define success.
Alignment and accountability
All executives must agree on three things: What are our corporate goals? What does success look like for each? How will I and my team contribute and be accountable?
The company’s goals are grouped into four areas: industry-focused, operations and supply chain, financial and marketing and sales. The management team will review all goals to make sure they align with strategy and are both actionable and achievable.
Industry-focused goal: Offer the most innovative cobots on the market
What success looks like: Develop a product that can match or exceed a human worker in its ability to pick fragile crops without damage.
Who will execute: The R&D team
Financial goal: Diversify revenue streams
What success looks like: Minimize dependence on one market/industry. Add a services arm to generate recurring revenue from maintenance contracts, powered by sensors built in to all new products.
Who will execute: Cross-functional led by CEO and finance
Other goals might be “control costs at each step and deliver cobots to customers on time and to specifications” with an expectation to lower COGS by 10% and raise the company’s Net Promoter Score by 25% within one year. Or for sales, “find 10 new customers for the company’s agricultural cobots and bundle maintenance contracts with each sale.” That ties back to revenue diversification.
An important point: Every manager is accountable for every goal, not just those that lie within their purviews.
Informed decisions and actions
Planning across PickerBots’ supply chain was disjointed, with engineers purchasing materials direct and little central planning or cost control. As part of the IBP process, the company will adopt sales and operations planning (S&OP) principles to improve its supply chain and logistics.
Actionable goals here include building visibility into how each department is working and tying the impact of decisions to financial goals. For example, by having R&D build in sensors that can automatically collect and transmit data on a cobot’s operational status, PickerBots can proactively perform preventative maintenance so the devices are almost never down — an important selling point and a way to contribute to maintenance income.
Organizationwide, divisions need to focus less on their own needs and view actions through the lens of all goals. That means the company needs to collect a lot of timely data and use it to issue reports so managers can make better decisions, more quickly. That may require an investment in ERP and other software.
Transparency/visibility
All department heads will take part in a monthly business review, where the group will assess progress in achieving the company’s objectives. The strategic plan is also available to all staff members, and quarterly all-hands meetings will be held to gather ideas and insights and walk through KPIs.
Four success metrics for the IBP process include:
1. Getting all stakeholders to buy in to corporate goals so that everyone agrees and understands what the business wants to achieve and how it will get there. There are clear responsibilities for each function in the pursuit of goals.
2. Basing business decisions on data. The integration of finance into product, demand and supply functions is key here, as are selecting the right KPIs.
3. Tying decision-making to outcomes and improving accountability. Because every department is responsible for providing accurate numbers and projections, there’s less risk that the CFO and finance team are left holding the bag if revenues fall short.
4. Shifting the culture to embrace cross-functional collaboration. An IBP process encourages openness and trust, and as a result more deeply engages and empowers employees. As an action item, each R&D and manufacturing team member will spend a week annually accompanying sales reps on customer calls.
What Is the Difference Between S&OP and IBP?
The term “IBP” was coined by management consultancy Oliver Wight to describe the next iteration of the sales and operations planning (S&OP) process Wight developed in the early 1980s.
The big difference between IBP and S&OP is that the latter has become the domain of supply chain and logistics specialists, particularly those involved in supply-and-demand balancing and planning. S&OP is execution-focused and involves a traditional budgeting process.
In contrast, IBP takes a more cross-functional and holistic approach to weaving business goals through every function. As a result, in theory, supply chain management is proactive and optimized.
IBP includes S&OP processes but because it involves cultural change, without executive buy-in, IBP will not be successful.
Some major differences between S&OP and IBP are:
6 Steps in the Integrated Business Planning Process
Now that its goals are set, PickerBots can take the next steps in its IBP journey.
1. Determine what is holding the company back. Is it a lack or growth or profitability? Is the product portfolio too complex? Has the business lost competitiveness in its space? For our manufacturing firm, the main problem was overfocus on one niche market.
2. Engage and educate employees. Once leadership buys in to goals, that enthusiasm must trickle down through the ranks. Unless everyone is committed to integrated business planning, success will be elusive. The COO recognizes that a formal employee engagement program will keep workers invested in the success of the business and actively working to meet strategic goals.
3. Set up a tiger team. IBP success comes from tight coordination, constant communication and accountability for KPIs. It’s a cultural shift that will take time to propagate throughout the business. To jumpstart things, PickerBots identified engaged employees within each functional area and assigned them to a daily 20-minute standup call. Now, say a shipment of RFID readers needed by manufacturing will be two weeks late. The purchasing team member shares that information promptly so that sales can manage customer expectations and finance can account for delayed revenue. If the problem recurs, the company can seek out new suppliers. No more surprises.
4. Establish a project/product prioritization process. IBP takes discipline. Only projects that forward the company’s strategic goals get resources. Same for products. That might mean sunsetting a line that’s still selling but lacks growth potential. All managers who require resources or have a product or service launch idea fill out a cost-benefit analysis template that is tailored to reveal whether expected benefits and costs align with goals. Leadership prioritizes using this process. No more sacred cows.
5. Expand the finance team’s influence. Finance needs to sit in on product planning, supply chain optimization and sales strategy meetings. Specifically, choose a finance team member well-versed in FP&A functions. FP&A professionals inform major decisions made by the executive team and collect and analyze financial data from across the organization to create reports that reveal whether goals are being met — and if not, why not? How do we fix the problem? Like many smaller firms, PickerBots doesn’t have a dedicated FP&A staffer, so the head of finance assigns an accounting team member who knows the business and has an aptitude for data collection and number crunching.
6. Adopt technology and tools to support IBP. If the forecasting process is seen as a quarterly or annual exercise imposed by finance and yielding little benefit to departments, IBP can’t succeed. Companies with static, point-in-time budgets need to adopt rolling forecasts to make sure the business stays on track. And, finance teams need to be able to easily access the data they need from each operational area. Both rolling forecasts and better use of data require technology and a commitment to transparency. You can’t manage what you can’t measure.
Traditional vs. Rolling Forecasts
5 tips to succeed at integrated business planning.
Some ways the COO plans to set PickerBots up for success include:
1. Sell IBP as a way to bring order from chaos. For example, large companies, especially those that have engaged in a number of mergers and acquisitions, may have thousands of SKUs and product codes. One big manufacturer Oliver Wight worked with used IBP to whittle 120,000 item numbers down to about 10,000 and reduce inventories by 50% while improving on-time, in-full delivery by up to 20%. For a smaller company, IBP can prevent ever getting in a situation where it needs to slash 90% of SKUs.
2. Adopt a continuous improvement mindset. All parts of any production or service system, particularly people, are interconnected, inform one another and are mutually dependent on generating successful outcomes. This practice’s origin comes from Kaizen, a Japanese term meaning “change for the better.” Originating in Japan, the business philosophy looks to continuously improve operations and involve all employees, from assembly line workers to the CEO. It’s a way to reinforce IBP.
3. Get buy-in from the CIO. PickerBots’ CIO came up through the ranks of manufacturing IT and is familiar with the concept of Total Quality Management (TQM), which has overlap with IBP. That went a long way in communicating the benefits of IBP and freeing up budget for technologies that can make IBP work, like ERP, enterprise performance management (EPM), supply chain management and real-time-capable accounting and finance software — especially important to realize the “one set of numbers” value proposition.
4. Apply risk management principles. Disasters large and small happen. While the zen of IBP skews toward positive and upbeat, make sure department heads are doing scenario planning and what-if analyses to model operational risk — like overdependence on one market. Consider assigning your tiger team a secondary function as a crisis management strike force.
5. Don’t forget HR. Labor is likely your company’s biggest operating expense, so ensure that it’s working for your IBP effort, not against it. A human resources professional can identify traits in applicants — like team players who are data driven and comfortable with transparency — that predict whether they will be contributors to IBP success.
Benefits of Integrated Business Planning
Research shows that the main benefit of implementing IBP is increased revenue, followed by forecast accuracy and improved Perfect Order Delivery rates.
Three additional key benefits:
Real-time insights: Once companies have instituted rolling forecasts, for example, finance can more quickly and accurately answer questions on spending and cash flow. Expect more accurate KPIs across the board.
Ownership: The flip side of accountability is that in a company fully embracing IBP, all employees assume responsibility for meeting all goals. So you’d better make sure that authority to make decisions is decentralized and tied to responsibility for outcomes, because there are few bigger morale killers than accountability without the power to effect success. Companies can further nurture a culture of ownership by tying rewards to meeting or exceeding goals.
Improved customer satisfaction: While more on-time, in-full deliveries make customers happy, that’s not the only way IBP improves Net Promoter Scores. Better planning yields better insights into what customers want, and a strong company culture often leads to improved customer empathy and its associated benefits.
Integrated Business Planning Adoption Challenges
Where a business starts with IBP depends on its maturity. Companies with dog-eat-dog cultures and highly siloed processes have a lot of work to do. These tend to be firms with traditional top-down management structures, static annual budgeting with little ability to generate forward-looking projections and dated business plans that are misaligned with current customer needs.
While all are thorny structural challenges, a leadership team that’s averse to placing trust and decision-making authority at lower levels of the organization is in even worse shape. Companies with autocratic, command-and-control styles must be willing to decentralize authority if they hope to realize IPB’s benefits.
Even businesses with mature, integrated processes and egalitarian cultures often get tripped up by “top down” versus “bottom up” KPI reporting and budgeting. IBP requires businesses to focus less on finance developing a top-line budget and then handing departmental budgets down from on high. Rather, they need to become comfortable with a bottom-up process, where departments start with a plan of what they want to achieve, calculate what it will cost and then feed a number up to the finance team, which uses that input to calculate the total budget.
Companies not already using at least a somewhat flexible budgeting process are likely to find this shift difficult. One way to jump-start the transformation might be a modern form of zero-based budgeting.
Steps of Zero-Based Budgeting for 2021
- Create a strategic vision for ZBB: Identify cost targets, relevant KPIs and goals.
- Evaluate business units to select ZBB candidates (also referred to as “decision units,” or any organ of the business that operates independently with its own budget).
- Start selected budgets from scratch (i.e., from zero).
- Each decision unit provides “decision packages,” which break down each activity in terms of its objective, funding needs, justification in the context of company goals, technical viability and alternative courses of action.
- Evaluate each proposed item to determine its value-add to the company and whether the entire cost is justified. What does the expenditure bring back to the company?
- Prioritize costs based on company goals. Reduce or cut expenses in areas that no longer produce significant value.
- Allocate funds among areas that are productive and aligned with the business’s growth drivers.
Elements of Integrated Business Planning
Integrated business planning takes place at a regular cadence; every month is most common, so we’ll use that in our example.
These steps are standard for IBP consultants, adaptable to most industries and bake in the PickerBots COO’s virtuous cycle of market research and strategic planning, R&D and manufacturing, demand forecasting and predictive analysis, profitability analysis, supply chain optimization and marketing and sales strategy.
1. Product management review. This includes all elements of product portfolio management. A cross-functional team meets monthly to review the overall status of all of product-related projects: Are they on track? Have we identified new risks and opportunities? Are the most high-value products or services prioritized? The goal is aligning the product portfolio with business goals and making sure needed raw materials and manufacturing floor capacity are lined up. Product managers revise as needed and publish an updated master plan, along with the resources it’ll take to deliver any changes.
2. Demand planning picks it up. This is a cross-functional process that helps businesses meet customer demand for products while minimizing excess inventory and avoiding supply chain disruptions. Demand planning can increase profitability and customer satisfaction and lead to efficiency gains. This team brings together members of sales, marketing and finance to determine whether they’re targeting the right markets, the right way. They work up an optimized demand plan. Relevant KPIs include sales forecast accuracy, inventory turns, fill rates and order fulfillment lead times.
3. Then, the ball goes to the supply planning team. These supply chain experts work out the optimal way to meet projected demand in a cost-effective way. The key is to have visibility into complex supply chains; a formal supply chain visibility (SCV) project helps spot and fix weaknesses, such as inventory shortfalls or order fulfillment issues, before they become major problems. Lower cost of goods sold (COGS) is the North star.
4. The integrated reconciliation team pulls together the initial product, demand and supply plans and consolidates them into one holistic business plan based on a 24- or 36-month projection; for iterative updates, teams highlight material changes. Decisions that could not be made by individual teams are prepared for executive review.
5. The executive team resolves conflicts and rolls the updated plan out to the entire company.
Integrated Business Planning Components
The components of integrated business planning comprise three buckets: Plan, execute and monitor and adjust.
Specific actions falling into each bucket vary depending on the consultancy or technology supplier. Some are more aligned with supply chain planning, while others center on S&OP or financial planning with plug-ins to other functional areas. Others are very industry-specific.
Let’s look at Oracle’s IBPX (Integrated Business Planning and Execution) for Manufacturing solution as an example. Key components include:
- Top-down and bottom-up, driver-based planning and forecasting
- Risk modeling for M&A and strategic initiatives
- Full financial statement structure for strategic and operational planning
- Predictive and prescriptive analytics and planning
- A preseeded S&OP process
- Near-real-time demand and supply balancing
- Real-time backlog management
- Automation of predictions and correction actions based on actuals
- AI-enabled operational planning, such as for sales territories and quotas
- IoT and sensor data flows integrated with automated decisions
Items like backlog management and enhanced support for IoT and sensor data are important to manufacturers like PickerBots. A retailer might be more interested in advanced inventory management. What’s important is that any solution, whether purchased as a suite or pulled together by an integrator or in-house team, supports the ability to do long- and medium-range and short-term planning based on a single, up-to-date data set that’s accessible to all authorized stakeholders.
Also look for the ability to easily model “what-if” scenarios, robust budgeting and costing and a roadmap to advanced technologies like AI and predictive analytics.
Integrated Business Planning Examples
We mentioned the Oliver Wight customer that whittled 120,000 SKUs down to about 10,000. That firm, Uponor Group, looked to IBP after a string of acquisitions left it with swelling inventories, an extremely complex portfolio and a lack of communication between siloed functions and far-flung locations. The Finnish company sells products for drinking water delivery as well as radiant heating and cooling equipment and has 3,900 employees in 30 countries. Uponor had a hard time getting a singular view of financial information across its subsidiaries, and each unit had its own practices for inventory management. Small events, such as holidays, would drive some sites to build up “just in case” inventory, and double-stocking in warehouses was common. Subsidiaries in different countries had different SKUs for the same items, and R&D was localized, with no collaboration across the company.
Upinor focused first on its supply chain and implemented S&OP processes, then advanced to IBP the following year. The results have been an increase in net sales of $1.1 billion euros, a 30% improvement in on-time in-full deliveries, a 50% reduction in inventories and increased visibility.
U.S.-based technology provider Juniper Networks also undertook an IBP project focused on implementing a digital supply chain with IBP, where the business planning process would extend S&OP throughout the supply chain, product and customer portfolios, customer demand and strategic planning.
Since undertaking the project, Juniper’s lead-time attainment is up 55%. and its inventory costs are down by 15%, allowing it to realize a positive ROI on the IBC project.
History of Integrated Business Planning
Oliver Wight developed S&OP in the 1980s as a methodology for a client that wanted to balance supply-and-demand volume. In the years since, the process evolved to integrate financials, inventory and new-product introductions.
The consultancy renamed S&OP as integrated business planning in the late 1990s to reflect the process of integrating all functions of the business behind one optimized plan. Since then, a newer term, “enterprise integrated business planning,” has emerged. EIBP includes scenario planning and extended supply chain collaboration and discusses how large companies will adopt new technologies, such as AI, big data and advanced analytics.
#1 Cloud ERP Software
Applications of Integrated Business Planning
IBP makes planning and operations much more transparent, so it’s ideal for companies moving to “just in time” manufacturing. It’s also predictive, once a company builds up some data. That can help with customer satisfaction.
PickerBots, as an example, found that it typically sees constrained supply chain capacity for motherboards in Q3. With that insight, sales and marketing can work to encourage customers to take delivery of systems in Q2 or Q4, manufacturing can prebuild products and supply chain leaders can work on alternate sources for parts that pose challenges.
Looking ahead to the future of IBP, we expect it to help companies:
- Work on ever-longer-range strategy planning, modeling and M&A activities with a higher degree of confidence.
- Detect and notify stakeholders of unanticipated events before they impact the business by using advanced technologies, including real-time sensor information and machine learning (ML) pattern recognition.
As companies build comfort with automation, advanced IBP systems can be set to take action based on analysis without human intervention. Consider a chain of bakeries; a system plugged into a long-range weather forecast system might detect a tropical storm that could raise the price of vanilla and automatically order extra.
Cloud-based technology such as ERP underpins all these advances. For example, PickerBots always set its sales goals monthly. But often these plans were delayed to let the executive team review and approve any changes, meaning operations was caught unawares. A tool like NetSuite Planning and Budgeting automates planning processes and centralizes company financial and operational data, so finance teams can disseminate updates quickly.
The next frontier? Expending IBP to business partners and suppliers, even customers. But first, companies need to get their own cultural and technology houses in order.
Business Strategy

Business Process Automation: Ultimate Guide
A well-run business is always analyzing business processes and finding ways to make them more efficient. It also searches for ways to review, update, change, replace or eliminate its processes on a regular basis in order to…

Trending Articles

Learn How NetSuite Can Streamline Your Business
NetSuite has packaged the experience gained from tens of thousands of worldwide deployments over two decades into a set of leading practices that pave a clear path to success and are proven to deliver rapid business value. With NetSuite, you go live in a predictable timeframe — smart, stepped implementations begin with sales and span the entire customer lifecycle, so there’s continuity from sales to services to support.
Before you go...
Discover the products that 37,000+ customers depend on to fuel their growth.
Before you go. Talk with our team or check out these resources.
Want to set up a chat later? Let us do the lifting.
NetSuite ERP
Explore what NetSuite ERP can do for you.
Business Guide
Complete Guide to Cloud ERP Implementation
A better way to drive your business
Managing the availability of supply to meet volatile demand has never been easy. Even before the unprecedented challenges created by the COVID-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine, synchronizing supply and demand was a perennial struggle for most businesses. In a survey of 54 senior executives, only about one in four believed that the processes of their companies balanced cross-functional trade-offs effectively or facilitated decision making to help the P&L of the full business.
That’s not because of a lack of effort. Most companies have made strides to strengthen their planning capabilities in recent years. Many have replaced their processes for sales and operations planning (S&OP) with the more sophisticated approach of integrated business planning (IBP), which shows great promise, a conclusion based on an in-depth view of the processes used by many leading companies around the world (see sidebar “Understanding IBP”). Assessments of more than 170 companies, collected over five years, provide insights into the value created by IBP implementations that work well—and the reasons many IBP implementations don’t.
Understanding IBP
Integrated business planning is a powerful process that could become central to how a company runs its business. It is one generation beyond sales and operations planning. Three essential differentiators add up to a unique business-steering capability:
- Full business scope. Beyond balancing sales and operations planning, integrated business planning (IBP) synchronizes all of a company’s mid- and long-term plans, including the management of revenues, product pipelines and portfolios, strategic projects and capital investments, inventory policies and deployment, procurement strategies, and joint capacity plans with external partners. It does this in all relevant parts of the organization, from the site level through regions and business units and often up to a corporate-level plan for the full business.
- Risk management, alongside strategy and performance reviews. Best-practice IBP uses scenario planning to drive decisions. In every stage of the process, there are varying degrees of confidence about how the future will play out—how much revenue is reasonably certain as a result of consistent consumption patterns, how much additional demand might emerge if certain events happen, and how much unusual or extreme occurrences might affect that additional demand. These layers are assessed against business targets, and options for mitigating actions and potential gap closures are evaluated and chosen.
- Real-time financials. To ensure consistency between volume-based planning and financial projections (that is, value-based planning), IBP promotes strong links between operational and financial planning. This helps to eliminate surprises that may otherwise become apparent only in quarterly or year-end reviews.
An effective IBP process consists of five essential building blocks: a business-backed design; high-quality process management, including inputs and outputs; accountability and performance management; the effective use of data, analytics, and technology; and specialized organizational roles and capabilities (Exhibit 1). Our research finds that mature IBP processes can significantly improve coordination and reduce the number of surprises. Compared with companies that lack a well-functioning IBP process, the average mature IBP practitioner realizes one or two additional percentage points in EBIT. Service levels are five to 20 percentage points higher. Freight costs and capital intensity are 10 to 15 percent lower—and customer delivery penalties and missed sales are 40 to 50 percent lower. IBP technology and process discipline can also make planners 10 to 20 percent more productive.
When IBP processes are set up correctly, they help companies to make and execute plans and to monitor, simulate, and adapt their strategic assumptions and choices to succeed in their markets. However, leaders must treat IBP not just as a planning-process upgrade but also as a company-wide business initiative (see sidebar “IBP in action” for a best-in-class example).
IBP in action
One global manufacturer set up its integrated business planning (IBP) system as the sole way it ran its entire business, creating a standardized, integrated process for strategic, tactical, and operational planning. Although the company had previously had a sales and operations planning (S&OP) process, it had been owned and led solely by the supply chain function. Beyond S&OP, the sales function forecast demand in aggregate dollar value at the category level and over short time horizons. Finance did its own projections of the quarterly P&L, and data from day-by-day execution fed back into S&OP only at the start of a new monthly cycle.
The CEO endorsed a new way of running regional P&Ls and rolling up plans to the global level. The company designed its IBP process so that all regional general managers owned the regional IBP by sponsoring the integrated decision cycles (following a global design) and by ensuring functional ownership of the decision meetings. At the global level, the COO served as tiebreaker whenever decisions—such as procurement strategies for global commodities, investments in new facilities for global product launches, or the reconfiguration of a product’s supply chain—cut across regional interests.
To enable IBP to deliver its impact, the company conducted a structured process assessment to evaluate the maturity of all inputs into IBP. It then set out to redesign, in detail, its processes for planning demand and supply, inventory strategies, parametrization, and target setting, so that IBP would work with best-practice inputs. To encourage collaboration, leaders also started to redefine the performance management system so that it included clear accountability for not only the metrics that each function controlled but also shared metrics. Finally, digital dashboards were developed to track and monitor the realization of benefits for individual functions, regional leaders, and the global IBP team.
A critical component of the IBP rollout was creating a company-wide awareness of its benefits and the leaders’ expectations for the quality of managers’ contributions and decision-making discipline. To educate and show commitment from the CEO down, this information was rolled out in a campaign of town halls and media communications to all employees. The company also set up a formal capability-building program for the leaders and participants in the IBP decision cycle.
Rolled out in every region, the new training helps people learn how to run an effective IBP cycle, to recognize the signs of good process management, and to internalize decision authority, thresholds, and escalation paths. Within a few months, the new process, led by a confident and motivated leadership team, enabled closer company-wide collaboration during tumultuous market conditions. That offset price inflation for materials (which adversely affected peers) and maintained the company’s EBITDA performance.
Our research shows that these high-maturity IBP examples are in the minority. In practice, few companies use the IBP process to support effective decision making (Exhibit 2). For two-thirds of the organizations in our data set, IBP meetings are periodic business reviews rather than an integral part of the continuous cycle of decisions and adjustments needed to keep organizations aligned with their strategic and tactical goals. Some companies delegate IBP to junior staff. The frequency of meetings averages one a month. That can make these processes especially ineffective—lacking either the senior-level participation for making consequential strategic decisions or the frequency for timely operational reactions.
Finally, most companies struggle to turn their plans into effective actions: critical metrics and responsibilities are not aligned across functions, so it’s hard to steer the business in a collaborative way. Who is responsible for the accuracy of forecasts? What steps will be taken to improve it? How about adherence to the plan? Are functions incentivized to hold excess inventory? Less than 10 percent of all companies have a performance management system that encourages the right behavior across the organization.
By contrast, at the most effective organizations, IBP meetings are all about decisions and their impact on the P&L—an impact enabled by focused metrics and incentives for collaboration. Relevant inputs (data, insights, and decision scenarios) are diligently prepared and syndicated before meetings to help decision makers make the right choices quickly and effectively. These companies support IBP by managing their short-term planning decisions prescriptively, specifying thresholds to distinguish changes immediately integrated into existing plans from day-to-day noise. Within such boundaries, real-time daily decisions are made in accordance with the objectives of the entire business, not siloed frontline functions. This responsive execution is tightly linked with the IBP process, so that the fact base is always up-to-date for the next planning iteration.
A better plan for IBP
In our experience, integrated business planning can help a business succeed in a sustainable way if three conditions are met. First, the process must be designed for the P&L owner, not individual functions in the business. Second, processes are built for purpose, not from generic best-practice templates. Finally, the people involved in the process have the authority, skills, and confidence to make relevant, consequential decisions.
Design for the P&L owner
IBP gives leaders a systematic opportunity to unlock P&L performance by coordinating strategies and tactics across traditional business functions. This doesn’t mean that IBP won’t function as a business review process, but it is more effective when focused on decisions in the interest of the whole business. An IBP process designed to help P&L owners make effective decisions as they run the company creates requirements different from those of a process owned by individual functions, such as supply chain or manufacturing.
One fundamental requirement is senior-level participation from all stakeholder functions and business areas, so that decisions can be made in every meeting. The design of the IBP cycle, including preparatory work preceding decision-making meetings, should help leaders make general decisions or resolve minor issues outside of formal milestone meetings. It should also focus the attention of P&L leaders on the most important and pressing issues. These goals can be achieved with disciplined approaches to evaluating the impact of decisions and with financial thresholds that determine what is brought to the attention of the P&L leader.
The aggregated output of the IBP process would be a full, risk-evaluated business plan covering a midterm planning horizon. This plan then becomes the only accepted and executed plan across the organization. The objective isn’t a single hard number. It is an accepted, unified view of which new products will come online and when, and how they will affect the performance of the overall portfolio. The plan will also take into account the variabilities and uncertainties of the business: demand expectations, how the company will respond to supply constraints, and so on. Layered risks and opportunities and aligned actions across stakeholders indicate how to execute the plan.
Would you like to learn more about our Operations Practice ?
Trade-offs arising from risks and opportunities in realizing revenues, margins, or cost objectives are determined by the P&L owner at the level where those trade-offs arise—local for local, global for global. To make this possible, data visible in real time and support for decision making in meetings are essential. This approach works best in companies with strong data governance processes and tools, which increase confidence in the objectivity of the IBP process and support for implementing the resulting decisions. In addition, senior leaders can demonstrate their commitment to the value and the standards of IBP by participating in the process, sponsoring capability-building efforts for the teams that contribute inputs to the IBP, and owning decisions and outcomes.
Fit-for-purpose process design and frequency
To make IBP a value-adding capability, the business will probably need to redesign its planning processes from a clean sheet.
First, clean sheeting IBP means that it should be considered and designed from the decision maker’s perspective. What information does a P&L owner need to make a decision on a given topic? What possible scenarios should that leader consider, and what would be their monetary and nonmonetary impact? The IBP process can standardize this information—for example, by summarizing it in templates so that the responsible parties know, up front, which data, analytics, and impact information to provide.
Second, essential inputs into IBP determine its quality. These inputs include consistency in the way planners use data, methods, and systems to make accurate forecasts, manage constraints, simulate scenarios, and close the loop from planning to the production shopfloor by optimizing schedules, monitoring adherence, and using incentives to manufacture according to plan.
Determining the frequency of the IBP cycle, and its timely integration with tactical execution processes, would also be part of this redesign. Big items—such as capacity investments and divestments, new-product introductions, and line extensions—should be reviewed regularly. Monthly reviews are typical, but a quarterly cadence may also be appropriate in situations with less frequent changes. Weekly iterations then optimize the plan in response to confirmed orders, short-term capacity constraints, or other unpredictable events. The bidirectional link between planning and execution must be strong, and investments in technology may be required to better connect them, so that they use the same data repository and have continuous-feedback loops.
Authorize consequential decision making
Finally, every IBP process step needs autonomous decision making for the problems in its scope, as well as a clear path to escalate, if necessary. The design of the process must therefore include decision-type authority, decision thresholds, and escalation paths. Capability-building interventions should support teams to ensure disciplined and effective decision making—and that means enforcing participation discipline, as well. The failure of a few key stakeholders to prioritize participation can undermine the whole process.
Decision-making autonomy is also relevant for short-term planning and execution. Success in tactical execution depends on how early a problem is identified and how quickly and effectively it is resolved. A good execution framework includes, for example, a classification of possible events, along with resolution guidelines based on root cause methodology. It should also specify the thresholds, in scope and scale of impact, for operational decision making and the escalation path if those thresholds are met.

Transforming supply chains: Do you have the skills to accelerate your capabilities?
In addition to guidelines for decision making, the cross-functional team in charge of executing the plan needs autonomy to decide on a course of action for events outside the original plan, as well as the authority to see those actions implemented. Clear integration points between tactical execution and the IBP process protect the latter’s focus on midterm decision making and help tactical teams execute in response to immediate market needs.
An opportunity, but no ‘silver bullet’
With all the elements described above, IBP has a solid foundation to create value for a business. But IBP is no silver bullet. To achieve a top-performing supply chain combining timely and complete customer service with optimal cost and capital expenditures, companies also need mature planning and fulfillment processes using advanced systems and tools. That would include robust planning discipline and a collaboration culture covering all time horizons with appropriate processes while integrating commercial, planning, manufacturing, logistics, and sourcing organizations at all relevant levels.
As more companies implement advanced planning systems and nerve centers , the typical monthly IBP frequency might no longer be appropriate. Some companies may need to spend more time on short-term execution by increasing the frequency of planning and replanning. Others may be able to retain a quarterly IBP process, along with a robust autonomous-planning or exception engine. Already, advanced planning systems not only direct the valuable time of experts to the most critical demand and supply imbalances but also aggregate and disaggregate large volumes of data on the back end. These targeted reactions are part of a critical learning mechanism for the supply chain.
Over time, with root cause analyses and cross-functional collaboration on systemic fixes, the supply chain’s nerve center can get smarter at executing plans, separating noise from real issues, and proactively managing deviations. All this can eventually shorten IBP cycles, without the risk of overreacting to noise, and give P&L owners real-time transparency into how their decisions might affect performance.
P&L owners thinking about upgrading their S&OP or IBP processes can’t rely on textbook checklists. Instead, they can assume leadership of IBP and help their organizations turn strategies and plans into effective actions. To do so, they must sponsor IBP as a cross-functional driver of business decisions, fed by thoughtfully designed processes and aligned decision rights, as well as a performance management and capability-building system that encourages the right behavior and learning mechanisms across the organization. As integrated planning matures, supported by appropriate technology and maturing supply chain–management practices, it could shorten decision times and accelerate its impact on the business.
Elena Dumitrescu is a senior knowledge expert in McKinsey’s Toronto office, Matt Jochim is a partner in the London office, and Ali Sankur is a senior expert and associate partner in the Chicago office, where Ketan Shah is a partner.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

To improve your supply chain, modernize your supply-chain IT

Supply-chain resilience: Is there a holy grail?
- my. Inchainge
- Integrated Business Planning
What is Integrated Business Planning (IBP)? And what are the similarities, but also differences when compared to S&OP? In this article, Inchainge discusses everything you need to know about IBP.
What is integrated business planning (IBP)?
Integrated Business Planning (IBP) is the business planning process that extends the principles of Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) throughout the value chain . It is to create a bridge between strategy and execution. IBP is a next step for companies that already have an S&OP process in place. It is a next step because it integrates the Financial Planning Cycle. The financial function will become part of this cross-functional process. In most companies the business owner of this process will change as well.
Similarities between IBP and S&OP
Integrated Business Planning and Sales and Operations Planning have several similarities between them. These are as follows:
- Monthly process
- Cross-functional approach
- Driven by business strategy
- Tactical planning at an aggregated level
Differences between IBP and S&OP
However, Integrated Business Planning includes content on top of Sales and Operations Planning:
- Financial function involved
- Integration financial planning cycle, like financial budget and forecast
- From volume planning to volume and value planning
- It drives the overall business performance
How does the IBP process work?
Companies have an annual budget cycle, based on their strategic plans and targets. The annual budget projects planned revenues and costs for the year.
In traditional S&OP companies go through a monthly process during which they project for the next 6 to 24 months where demand will go, and what resources need to be available to meet that demand. When gaps are discovered between expected demand and available resources looking this far ahead into the future, this often provides ample time to balance supply and demand, so that by the time real customer orders are submitted, demand can be met.
Suppose that during this monthly S&OP cycle, one would also look 6 to 24 months into the future where expected revenues and costs will go. And how these financial figures would look compared to the annually budgeted revenues and cost. Most likely gaps will occur here as well between the annually budgeted numbers and the monthly updated numbers. Actions could then be taken to address these gaps. Integrating a financial view. When this happens, we actually practice IBP. In IBP the relationship with the financial performance management cycle is very important. Budget and financial forecasting must be aligned and integrated with the steps from the original S&OP cycle.
The challenges of IBP
IBP is a next step in maturity after companies have implemented a proper S&OP process. Integrating finance sounds simple but is not easy at all. People from the physical supply chain side of the business, often speak a different language than people who operate on the financial side. Supply chain people often speak about units, products, and product families, whereas financial people often speak about money, currencies, etc. That also causes both functional areas to be assessed differently with the KPIs that they use. This calls for other participants in the IBP process, compared to participants in the S&OP process.
The 8 common pitfalls when implementing IBP
Be aware of the following risks related to integrated business planning:
- Lack of commitment in some of the needed departments
- If the S&OP process was not yet implemented or stable, IBP is too big of a step
- Targets and forecasts are mixed
- Information not available
- Discussion about numbers instead of the underlying assumptions
- Discussing only short horizon instead of midterm
- Too granular plans and discussions
- Thorough understanding of trade-offs is lacking
Want to know more? Experience IBP!
Because IBP is simple but not easy, a real-life experience creates enormous value for learning about this topic. The participants will feel and recognize the important issues in this process. In our business simulation game, The Cool Connection , we have incorporated the most important functions and decisions.
In this business game the team is forced to make a yearly financial budget and quarterly forecasts. The objective is to close the gaps between prediction (the budget and forecasts) on one hand and attained performance on the other. The best performing teams are both profitable and predictable at the same time. In business game The Cool Connection the team is almost experiencing a real-life IBP process.
Besides our business games, you can learn more in our articles about topics such as Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) , strategic alignment and external alignment and collaboration .
Now you know
Now you know that IBP is a next step for companies that already have an S&OP process in place, by integrating the financial planning cycle in this cross-functional process. IBP prompts companies to include planned revenues and costs in their annual budget cycle. Budget and financial forecasting must be aligned and integrated with the steps from the original S&OP cycle. Integrating finance sounds simple but is not easy at all. Supply chain people and finance people tend to speak a different language. Make sure to be aware of the 8 common pitfalls when implementing IBP.
You might want to learn more about

Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, attitudes, and preferences. There are many ways to learn but what works best? And why does it matter? In this article, Inchainge discusses everything you need to know about learning.

The Cool Connection
The Cool Connection is an innovative web-based business simulation game. It engages participants in making strategic decisions in the management of a manufacturing company of personal care products. Working in teams of four, participants will represent the functional roles of sales, purchasing, supply chain management and finance. They will be confronted with various real-life, real-time dilemmas.

- Total Cost of Ownership
When buying new equipment, the price tag only tells you part of the story. Energy costs, maintenance, and repair fees are often several times higher than the initial price! But often these are left unconsidered and hold nasty surprises further down the line. Calculating the Total Cost of Ownership is an important step when planning new investments.

- Strategic Alignment
Understanding what strategic alignment really is and why it is important can make the difference between being a successful company and failing. Due to its complexity, the supply chain often faces challenges in aligning its strategy properly and working as one. In this article, Inchainge discusses everything you need to know about strategic alignment.
- External Alignment and Collaboration
In an increasingly global and connected world, companies rarely execute supply chain operations themselves, but must outsource certain tasks. To make sure that supply chains across several companies run smoothly, external alignment is essential. In this article, we’ll discuss everything you need to know about external alignment.
Dive into our knowledge base
- Key Performance Indicators
- Sales & Operations Planning
- Blended learning
- Delivery formats and scalability
- Experiential learning
- Flipped classroom
- Learning cycle
- Soft skills
- Building (virtual) teams
- Leadership skills
Supply chain
- Data analytics
- End-to-end Supply Chain Management
- LARG Supply Chain
- Logistics footprint
- Omnichannel
- Supply Chain
- Supply Chain Finance
- Supply Chain Management
- Supply Chain Risk management
- Supply Chain Volatility
- The Bullwhip Effect
- Sustainability
- Carbon footprint
- Circular Economy
- Does Green Governance drive the ride to a sustainable future?
- Everything You Need To Know About Eco-Efficiency
- Greenwashing: Everything you need to know
- Is it possible to measure the Triple Bottom Line?
- Sustainability v/s Circularity
- The 3Ps Series: People
- The 3Ps Series: Planet
- The 3Ps Series: Prosperity
- The Butterfly Diagram
- The Value Hill
- What are the 3Ps of Sustainability?
- What do we know about the Triple Bottom Line?
- Value Chain
Privacy Overview
Integrated Business Planning
For integrating functional plans, deploying business strategy, and driving business management, what is integrated business planning (ibp).
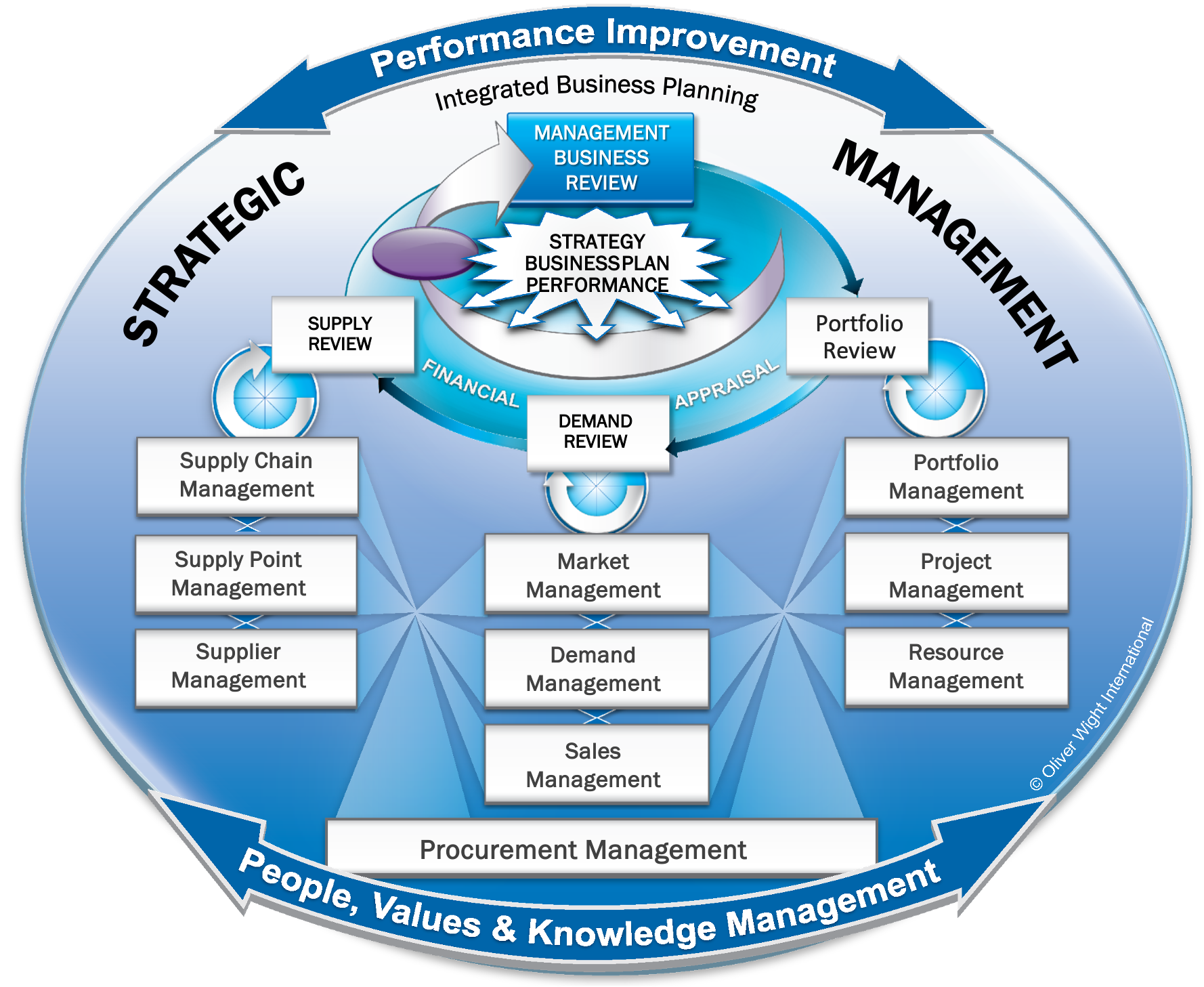
Integrated Business Planning (IBP) is a common-sense process designed for effective decision-making and led by your leadership team. True business integration means senior management can plan and manage the entire organization over a 24-36 month horizon, aligning strategic and tactical plans each month, and allocating critical resources, people, equipment, inventory, materials, time, and money; to satisfy your customers in the most profitable way.
Integrated Business Planning represents the evolution of Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) from the supply and demand balancing process developed in the early 1980s. Today it is a process that drives the alignment of all functions across an organization, models and creates readiness for alternate outcomes, drives deployment of strategy, and enhances collaboration across supply chains.
What is the difference between S&OP and IBP?
There are many differences between Sales & Operations Planning and Integrated Business Planning, but firstly it’s important to note that IBP is not a supply chain process ; it has a much broader reach. IBP is the process that connects your strategy and business plan to ensure both are delivered.
The purpose of IBP is not to drive a better forecast with which supply chain can plan. It is the process that brings focus to the deployment of your business strategy and provides a framework for effective decision-making to drive growth.
It's also much more than just a monthly meeting. IBP is a company framework to surface and solve problems and continually re-optimize plans as circumstances change. IBP enables businesses to create an aligned, cross-functional plan for the future, based upon key assumptions. These assumptions, documented and updated each month, are based on insights.
Read our white paper to learn more about what sets Integrated Business Planning apart from Sales & Operations Planning.

Looking for help with IBP software?
Oliver Wight IBP Powered by Board is a holistic solution combining Oliver Wight's industry-leading Class A and implementation change management processes with Board software. Fully align people, processes, and technology and embed IBP and its benefits for years to come.
This offering combines IBP technology and process in one package for rapid time to value. You will benefit from Oliver Wight consulting and education + Board Intelligent Planning Platform + specialist implementation services.
Find out more.
How mature is your organization's true level of maturity in IBP?
Before embarking on any performance improvement program, it is imperative to identify your organization's true level of maturity. The Oliver Wight Maturity Model characterizes an organization as being in one of four key phases of maturity: Co-ordination, Business Process Control, Automation, or Integration. Assess your business maturity in Integrated Business Planning using our free online self-assessment tool .
Assess your business maturity
How you can benefit from Integrated Business Planning
Early identification of gaps in the business plan and strategy deployment, creating time to close them
An integrated view of performance and projection of your business over a 24-36 month horizon
Alignment of functional operating plans and financial projections with ‘one set of numbers’
Application of scenario planning and modelling to areas of your business where there may be uncertainty or impact
Increased responsiveness to uncertainties and unplanned events to minimize negative impacts and seize opportunities
Creation of transparency and clear accountability across the business/organization
Simplification of the budgeting or annual planning process
Integration of strategy deployment with operational plans
Increased employee engagement and efficiency
Growth in revenue
Reduced costs
Improved customer service
Reduced inventory
Visibility of planned product changes, future demand from sales and marketing, supply chain performance, planned supply chain capability and flexibility, plus bottom-up plans and the actions and decisions required to deliver ‘best for business' outcomes
You should consider Integrated Business Planning for your business if:
You are constantly in ‘fire-fighting’ mode
You have a misaligned management team
You are continually missing the financial plan
You are experiencing rapid growth and can no longer manage effectively using an informal process
Your budgeting process is ‘painful’
You are struggling to get on top of service issues
You cannot keep up with growth in demand
You have excessive inventory
You are experiencing excessive rework and cost
Departments or sites are working in silos
There is no ‘single source of truth’ or ‘single set of numbers’ to run the business
You feel like you never have time to look at the strategy
There is poor deployment and execution of the strategic plan
You have poor employee engagement
You feel like you are not getting a return on the effort put into your existing S&OP/IBP process
How we can help
A diagnostic assessment of your current S&OP or IBP process, including its effectiveness and identifying any performance issues
Transfer of our knowledge to your people so they can create and manage an effective IBP process
Change management – plan, monitor, and support the implementation of change and its impact on your people
Facilitate the design of an IBP process to best fit your organization and its needs
Scoping of an action plan to address issues and take advantage of the opportunities identified, including resourcing, timelines, and performance improvement expectations
Coach IBP process users as you introduce the new ways of working
Assess and validate that your IBP process has achieved a Class A level of effectiveness – firmly embedded as the ‘way you do things’ and delivering the benefits you wanted
Integrated Business Planning is a cutting edge process which creates cross-functional alignment and enables businesses to re-focus to meet the ever-changing environment. IBP generates readiness for alternative outcomes, enhances collaboration, and ultimately drives deployment of strategy in an uncertain world. The chosen process of some of the world’s most progressive and best-known organizations, IBP is a common-sense process that maximizes profit and enables leaders to manage risk with confidence.
Integrated business planning resources to help you improve.
White papers & case studies
Videos & webinars
Get in touch
Upcoming courses.
11 Jun 2024
Virtual (English)
Integrated Business Planning – Introduction, Overview, and Current Best Practice
More information +
10 Sep 2024
08 Oct 2024
Virtual (French)
French Integrated Business Planning Workshop
12 Nov 2024
Latest white papers & case studies

The IBP advantage: a roadmap for marketing and product teams to collaboratively deliver success

Doom looms or opportunity awaits

Assumptions Management Part 2: Structural Integrity

Navigating the decision: behavior, empowerment, and integration to support the information revolution

From complexity to simplicity: The power of aligning people, process, and technology

Assumptions Management Part 1: Controlling your future in an uncertain world

Five key factors to speed up your successful IBP journey: Intelligent solutions meet your integrated process.

Gehen Sie Fake News nicht auf den Leim.

Transformer son S&OP en IBP

Navigating Uncertainty: Is Your IBP Process Fit for the Future?

Scenario Planning Trigger Points – Creating an Integrated Response to Scenarios

Getting the Most From Integrated Business Planning
Latest books

The Transition from Sales and Operations Planning to Integrated Business Planning - Second Edition

The Oliver Wight Class A Standard for Business Excellence

Le Standard Classe A d’Oliver Wight pour l’Excellence en Entreprise

Der Class A Standard für Business Excellence nach Oliver Wight
El Estándar de Clase A para la Excelencia Empresarial de Oliver Wight

Orchestrating Success: Improve Control of the Business with Sales & Operations Planning

Enterprise Sales and Operations Planning

An Executive's Guide to Achieving Class A Business Excellence
Latest videos and webinars
Balancing planning (ibp) and execution (itp) in rapidly changing socioeconomic environments.
Flavio Pietrocola, Oliver Wight Partner, explains how to find the right balance between Planning (IBP) and Execution (ITP) in this disruptive and rapidly changing world.
How to steer a company through the D-VUCAD world? (in German)
This podcast episode discusses how to steer companies through volatile, unpredictable times and what modern control instruments and technologies there are that companies should use.
Managing Change through Effective Implementation of Integrated Business Planning
Oliver Wight Partner, Gary Connors explains the five common failure modes in implementing Integrated Business Planning and how to manage changes through IBP.
Moving to E2E Supply Chain Management with IBP coordination
Watch the video to see Oliver Wight's CEO Les Brookes explains how to drive End-to-End supply chain transformation with IBP.
Eminox Ltd: What was it like working with Oliver Wight?
Oliver Wight Partner, Dawn Dent spoke to Eminox's Managing Director Mark Runciman, who shares his experience of working with Oliver Wight.
The Digital Supply Chain podcast
Supply Chain Resilience with Integrated Business Planning - a chat with SAP and Oliver Wight.
IBP: Driving Growth, Increasing Productivity & Improving Customer Service
Oliver Wight’s Paul Ducie joins Olivehorse Consulting to discuss how to assess your organization’s maturity, and define the correct approach for implementation.
Dynamic Integrated Business Planning: aligning process and tools to meet the challenges of an everch
The right collaboration between process and tools can deliver the IBP promise efficiently and dynamically.
The Enemies of Effective Measures
Does your business truly understand measuring and analysis? Do you apply the data and learn from it? Or are there conflicting or biased measures happening behind the scenes?
What business leaders are talking about today
Oliver Wight's Andy Walker and EY's Jocelyn Hallum discuss what business leaders are talking about today.
Financial Planning with IBP: Creating one process for your business
Join Oliver Wight Partners Monte Maritz & Lucy Jacobs for this webinar in our ongoing series focused on the evolution of Integrated Business Planning.
Data accuracy in the healthcare industry
Oliver Wight Partners Gary Connors and Steve Rowntree lift the lid on why data accuracy (or inaccuracy) is so prevalent in the healthcare industry.
Solving your most complex planning challenges

Explore Industry Research
What do Gartner, Forrester, and IDC have in common? They all named Anaplan a planning leader.
Your success is the heart of our success

Hear from our customers at Anaplan Connect 2024
Join us for a day of connected inspiration from your industry-leading peers who have found the answer in agile, connected enterprise planning.
Transform how you see, plan and lead your business
Get started today.
Explore on-demand demos to discover how our modeling and planning capabilities are designed to meet the specific and unique needs of your business.
Transform how you see, plan, and lead your business
We’d love to find out how we can help you
Events, training, and content for your planning journey

Visit our blog and newsroom
Your hub for Anaplan updates, insights, perspectives, and innovations.
Powerful partnerships to drive your digital transformation and deliver game-changing strategies.
Solutions for your business, your industry, from the world’s leading alliances.
What is IBP? Process, Strategy & Benefits
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
The platform for orchestrating performance.

Integrated business planning (IBP) continues to grow in popularity and adoption. And no wonder—when implemented, it provides a solid foundation to meet key goals. But with many stakeholders and processes involved, it’s not always easy. Where should you start in order to succeed on your journey to true IBP?
What is Integrated Business Planning (IBP)
Integrated business planning — the subject of a new report from the Association for Finance Professionals (AFP) — is a single holistic plan that seamlessly connects strategic plans with sales plans, operational plans, and financial plans while balancing practical constraints about the availability of resources and funding with the business’s financial objectives.
Benefits of Integrated Business Planning
When you’re looking for IBP best practices, a great place to begin is by taking advice from experts like Ken Caron and Ken Olsen of Deloitte. In a webinar (now available on demand), they shared their definition of IBP, discussed some core ideas behind it , and described how you can kick-start your efforts to incorporate IBP into your enterprise. We’ve recapped some of their message here, starting with an important question: Why should a company do IBP? They offered three reasons:
- Alignment and accountability. Instead of spending time and energy debating which plan to follow, all stakeholders agree on one plan—and understand their role in accomplishing the goals of that plan.
- Better decisions and actions. The structured process that comes from a well-built IBP approach enables companies to focus on making better-informed decisions and taking the best action based on those decisions.
- Increased visibility. IBP enables companies to incorporate insights from supply chain projections, financial projects, and strategic plans. And the more insights incorporated into projects, the better informed a company’s decisions will be, which, in turn, will be more likely to contribute to business goals like profitability and efficiency.
So now that you know the potential benefits of IBP, where should you begin?
6 Tips to Succeed at Integrated Business Planning
You need executive alignment and a clear vision before starting anything else. Find an executive willing to sponsor your efforts, “sell” the process, align stakeholders, and consult on change management. When you have a champion in high places, you’re on the right track.
IBP is a journey, so you need a roadmap of prioritized actions that drive quick wins and sustainable benefits. But before you can plan that roadmap, you need to understand the basic elements of an IBP framework, which we detail below, along with the benefits each element brings to the table.
- Effective governance. Clear roles, decision rights, policies, and incentives create an atmosphere that enables everyone to work together as an organized unit to achieve the company’s mission.
- Clear mission. A defined aim sets the path for IBP and defines what IBP will deliver.
- Organized process. When processes are cross-functional and designed to align the organization toward one desired outcome, you can focus on meeting the goal instead of maintaining the process.
- Right talent. Build a talent base with the skills and core competencies essential to IBP, such as strategic planning, financial planning, and supply chain planning . With skilled and experienced employees on board, you’ll be able to more effectively implement IBP across the enterprise.
- Insightful analytics. With access to real-time analytics, you can run “what-if” scenarios, quickly respond to disruptions and market adjustments, and make insight-driven decisions the core of your business planning. This helps you be proactive and stay ahead of your market instead of relying on reactive decisions.
- Powerful technology. Since IBP is a cross-functional initiative, you need an agile, flexible, cloud-based technology to provide a central platform for IBP collaboration and execution.
In their webinar, our two Deloitte experts are joined by Vivek Soneja, Global Head of Supply Chain Solutions at Anaplan. They discuss how you can make IBP a success, as well as some common reasons why IBP initiatives fail. To learn more about how you can succeed at IBP, watch the webinar.
Strengthen the connection between business and supply chain
- Explore catalog
- SAP Certification
- SAP Learning Class
- Redeem Activation Code
- SAP S/4HANA
- Customer Experience
- Network and Spend Management
- Supply Chain Management
- HR and People Engagement with SAP SuccessFactors
Training course schedule
Where to start with SAP Training
- Buy a one exam attempt subscription
- Buy a six exam attempt subscription
- List of valid certifications
- Validate your certification

Redeem activation code

Access your subscription
- Value of SAP Training and Adoption
- How to book training online
- Available training methods

Maximize your training budget with an SAP Preferred Card
Was this information useful, have questions visit the help center, this browser is not supported.
SAP Training Shop is not currently supported on Internet Explorer. For a premium experience please use an alternative browser.
Discover SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain
Introduction to Planning Processes
1 hr 2 mins
After completing this unit, you will be able to:
- Outline processes covered by SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain solution
- Describe Planning Processes and Planning Levels within the Supply Chain Planning Matrix
- Leverage SAP Best Practices for SAP IBP
- Identify SAP IBP benefits
Introduction to SAP Integrated Business Planning
Using SAP IBP for Supply Chain
1 hr 55 mins
Demand Planning
Inventory Planning and Optimization
1 hr 25 mins
Supply Planning
Exception Management
Record of Achievement
Pass all the quizzes and receive a digital badge.

Discovering SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain
Share your recently acquired knowledge across your social and professional networks.
SAP Learning Group
Join our SAP Learning Group moderated by an SAP Learning expert. Ask your questions about your digital learning journeys, prepare successfully for your SAP Certification exams, and collaborate with other learners to reach your learning goals.

SAP Learning Class
Sap ibp platform features and time series based heuristics planning, sap ibp advanced configuration.
Integrated Business Planning
Accelerating supply chain planning and orchestration
Integrated Business Planning for modern, dynamic supply chains
Integrated Business Planning (IBP) is a comprehensive planning solution developed to provide core analytics, visibility, collaboration, and execution capabilities. IBP helps organizations across industries achieve real orchestration of their supply chain in order to retain control of costs and services delivered.
Featured Integrated Business Planning Resources
Product overviews, discover more about integrated business planning, optimize costs.
Reduce transportation, overtime, and inventory holding costs
Supply chain orchestration
Coordinate stakeholders from across operations and the business unit
Rapid insights
Accelerated time-to-value analytics and development pipelines
Maximum data growth
Reduced data complexity and sourcing introduces high levels of data maturity and consensus
Unified solutions
Centralized data across Infor OS and apps, your API ecosystem, and third-party application data
Synchronize supply and demand imbalances
Align production with demand
Miminize risks
Reduce stockouts and associated service fines or lost sales
S&OP process workflows
Align departments and stakeholders.
- Multi-tenant cloud solution
- Integrated notes functionality
- Embedded S&OP process
- Integrated geography reports
Industry templates and aligned KPIs
Edit existing widgets, workbenches, and workflows or create new ones.
- 180+ pre-builts views
- 40+ pre-built workflows
- Prebuilt workflows
Highly configurable sales & operations planning environment
Balance demand and supply plans with robust tools.
- Collaborative, social platform
- S&OP process workflow and alerts
- Advanced scenario management
- Financial reconciliation
- Assumptions and amendment auditability
IBP productivity by the numbers
Additional ibp resources.
Infor Supply Chain Planning
EXECUTIVE BRIEF
Achieving end-to-end supply chain collaboration and visibility in F&B manufacturing
A buyer’s guide to supply chain management software
Related products, infor demand planning.
Achieve superior forecast accuracy
Infor Supply Planning
Optimize operations across the supply chain
Infor Production Scheduling
Improve agility and operational efficiency across the supply chain
Achieve perfect order fulfillment at the lowest possible cost
Infor Nexus
Connect supply chain partners with a single source of truth
Industry ERP solutions
Transform business-critical operations with a cloud ERP solution made for your industry
A robust cloud operating platform for accelerating innovation throughout the enterprise ecosystem
Let's Connect
Contact us and we'll have a Business Development Representative contact you within 24 business hours
By clicking “Submit” you agree that Infor will process your personal data provided in the above form for communicating with you as our potential or actual customer or a client as described in our Privacy Policy .
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Asking the better questions that unlock new answers to the working world's most complex issues.
Trending topics
AI insights
EY Center for Board Matters
EY podcasts
EY webcasts
Operations leaders
Technology leaders
EY helps clients create long-term value for all stakeholders. Enabled by data and technology, our services and solutions provide trust through assurance and help clients transform, grow and operate.
EY.ai - A unifying platform
Strategy, transaction and transformation consulting
Technology transformation
Tax function operations
Climate change and sustainability services
EY Ecosystems
EY Nexus: business transformation platform
Discover how EY insights and services are helping to reframe the future of your industry.
Case studies
How Mojo Fertility is helping more men conceive
26-Sep-2023 Lisa Lindström
Strategy and Transactions
How a cosmetics giant’s transformation strategy is unlocking value
13-Sep-2023 Nobuko Kobayashi
How a global biopharma became a leader in ethical AI
15-Aug-2023 Catriona Campbell
We bring together extraordinary people, like you, to build a better working world.
Experienced professionals
EY-Parthenon careers
Student and entry level programs
Talent community
At EY, our purpose is building a better working world. The insights and services we provide help to create long-term value for clients, people and society, and to build trust in the capital markets.
Press release
EY announces launch of artificial intelligence platform EY.ai following US$1.4b investment
13-Sep-2023 Rachel Lloyd
EY reports record global revenue results of just under US$50b
Doris Hsu from Taiwan named EY World Entrepreneur Of The Year™ 2023
09-Jun-2023 Lauren Mosery
No results have been found
Recent Searches

How do you steady the course of your IPO journey in a changing landscape?
EY Global IPO Trends Q1 2024 provides insights, facts and figures on the IPO market and implications for companies planning to go public. Learn more.
How can the moments that threaten your transformation define its success?
Leaders that put humans at the center to navigate turning points are 12 times more likely to significantly improve transformation performance. Learn More.

Artificial Intelligence
EY.ai - a unifying platform
Select your location
close expand_more
Back to EY and Pegasystems

EY and Pegasystems Alliance
Integrated business planning solution.
Integrated Business Planning (IBP) is a complete planning process from EY and Pegasystems that drives efficiency and accuracy by providing visibility into key business functions and aligning them around a single strategy.
Making complex planning simpler and smarter
Proper planning for a business’s growth and needs requires that all facets of an organization have access to one source of truth—one vision, one plan, and one set of numbers from which to plan.
The Integrated Business Planning (IBP) solution from the EY-Pega Alliance helps organizations meet their most complex challenges through a comprehensive approach that combines EY’s process improvement and business transformation acumen with the speed to value supported by Pega’s intelligent automation platform. EY-Pega IBP identifies the overall business process, finds where relevant data resides on all systems of record, then distills that information into meaningful content that guides smarter decisions. Benefits include a faster system of planning that provides better-quality data, as well as greater transparency, synchronization, collaboration and responsiveness across the organization
The EY organization’s methodology for approaching IBP, combined with the powerful Pega platform, allows businesses to realize value on an accelerated timeline – in many cases, a matter of mere weeks. That baseline of value can be established and then spread. That’s because the EY team’s approach is to break IBP into multiple stages, using Pega capabilities to provide incremental value quickly and build upon it, rather than backloading business benefits to the conclusion of a lengthy implementation.
Further, EY-Pega IBP doesn’t require discarding an organization’s existing tools, whether it be the demand optimization system or sourcing management system. Instead, organizations can “wrap and renew” as Pega leverages the data from existing tools that may be siloed to provide a more consistent, effective method of planning. Planning documents from spreadsheets or legacy systems can be pulled, parsed and processed in a more meaningful way.
With IBP, businesses can achieve tangible results derived from the ability to:
- Enable change with hands-on coaching and accelerators
- Transform processes with reliable tools
- Integrate finance to achieve a single aligned plan
- Mitigate short-term disruptions
- Challenge the mentality of “the way we used to operate”
- Complement organizational capabilities
- Leverage digital planning technologies
- Drive effective planning with analytics
Ultimately, the better business decisions enabled by EY-Pega IBP can help organizations improve revenues as they get more product to their customers, decrease production and supply chain costs, and better manage their suppliers so that they secure reduced inventory cost and the proper amount of product they need. Complex planning becomes simpler, faster, better and smarter.

- Connect with us
- Our locations
- Legal and privacy
- Open Facebook profile
- Open X profile
- Open LinkedIn profile
- Open Youtube profile
EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients.

- All Products
- Supply Chain Management
- SAP Integrated Business Planning

SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain
What is sap integrated business planning for supply chain.
Plan for a sustainable, risk-resilient future with the SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain (SAP IBP) solution. Speed responsiveness and stay ahead of change with supply chain analytics, what-if simulations, alerts, and more.
Powered by SAP HANA, this cloud-based solution combines sales and operations planning (S&OP), forecasting and demand, response and supply, demand-driven replenishment, and inventory planning.
- Automated, tightly coordinated supply chain planning processes
- Advanced machine learning algorithms and planning capabilities
- Native integration with SAP Supply Chain Control Tower and other solutions
- Watch an overview video
2023 annual customer report for SAP IBP
What were the highlights for SAP IBP over the past year? Dive in to find out.
- Read the report
See how customers are succeeding with SAP
Forecasting demand for the future of mobility.
See how ZF Friedrichshafen meets demand for its intelligent products with an integrated ecosystem of planning applications.
- Read the customer story
Optimizing inventory and service levels globally
Explore how Hyundai Mobis is reducing excess inventory and being more responsive to customer needs.
Enhancing sustainable production with data forecasting
Learn how DMK Group unified data processes on one platform so business units can track inventory data.
Building an intelligent digital supply chain
Learn how Microsoft harnessed big data, machine learning, and IoT to build a connected and predictive digital supply chain.
Product awards
What are analysts saying about planning and the sustainable, risk-resilient supply chain, building visibility with supply chain planning.
Read the Oxford Economics research into building visibility and collaboration in supply chain planning to avoid risk.
Tapping the power of AI for supply chain planning
Read what IDC has to say about how forward-thinking companies are using AI to make sense of their data and conquer supply chain complexity.
Frequently asked questions
What is SAP IBP?
The SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain (SAP IBP) solution is a cloud-based supply chain planning solution that scales to accommodate business growth and integrates with other SAP and third-party systems. It integrates key aspects of the planning process including demand, supply, inventory, and sales and operations planning (S&OP). Designed to help you streamline planning and improve performance, SAP IBP supports data-driven decision-making and simplified collaboration to increase operational efficiency. This is accomplished with help from advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and powerful optimization algorithms that enable real-time visibility, better forecasting, and faster decision-making across the entire supply chain.
Which modules are part of SAP IBP?
- Demand management: SAP IBP integrates historical data, market trends, and advanced predictive analytics so that you can generate more accurate demand forecasts.
- Response and supply planning: SAP IBP takes capacity constraints, lead times, and inventory levels into account so that you can optimize production and distribution plans and more efficiently meet customer demands.
- Inventory management: SAP IBP helps you maintain optimal inventory levels by balancing the trade-offs between carrying costs, stockouts, and service levels.
- Sales and operations planning: SAP IBP provides a unified platform for collaborative planning, allowing different departments to align on strategic goals and operational plans.
- Demand-driven replenishment: SAP IBP supports DDMRP for strategically positioning inventory buffers in the supply chain to absorb variability and uncertainty.
- Supply chain control tower: SAP IBP supports the real-time supply chain visibility and enhanced analytics you need to quickly respond to changing market conditions and customer requirements.
Who uses SAP IBP?
More than 1,000 companies worldwide use SAP IBP to streamline supply chain and planning processes. Ranging from large multinational corporations to medium-sized enterprises, these companies span a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, retail, consumer goods, pharmaceuticals, automotive, aerospace, and many others. Some of the key users of SAP IBP include:
- Supply chain managers: They use SAP IBP to optimize supply chain processes, improve visibility, and monitor and control inventory levels.
- Demand planners: They use SAP IBP to forecast customer demand accurately, align supply with demand, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
- Sales and operations planners: They use SAP IBP to align sales, marketing, and operations teams to execute integrated business plans and achieve financial targets.
- Inventory managers: They use SAP IBP to optimize inventory levels, minimize carrying costs, and improve working capital efficiency.
- Executives and decision-makers: They use SAP IBP to gain insights into the overall health of the business, make data-driven decisions, and drive strategic initiatives.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain (SAP IBP) solution is a cloud-based supply chain planning solution that scales to accommodate business growth and integrates with other SAP and third-party systems. It integrates key aspects of the planning process including demand, supply, inventory, and sales and operations planning (S&OP).
Integrated Business Planning (IBP) is a holistic approach that integrates strategic planning, operational planning, and financial planning within an organization. IBP brings together various functions, including sales, marketing, finance, supply chain, human resources, IT and beyond to collaborate across business units and make informed ...
March 15, 2021. Think of modern integrated business planning, or IBP, as a mashup of supply chain optimization, financial planning and analysis (FP&A) and operational best practices, powered by a companywide culture that's all about delivering the speed, savings and responsiveness today's consumers demand while managing risk.
One global manufacturer set up its integrated business planning (IBP) system as the sole way it ran its entire business, creating a standardized, integrated process for strategic, tactical, and operational planning. Although the company had previously had a sales and operations planning (S&OP) process, it had been owned and led solely by the supply chain function.
SAP Integrated Business Planning (IBP) is a cloud-based solution that helps you optimize your supply chain, sales, inventory, and financial processes. Learn how to use the SAP IBP add-in for Microsoft Excel, explore the features and benefits of SAP IBP, and discover how to integrate it with SAP S/4HANA Cloud.
Learning Journey for SAP IBP for Supply Chain. This cloud-based solution combines S&OP, forecasting and demand, response and supply, demand-driven replenishment, and inventory planning. Take advantage of powerful supply chain analytics, what-if simulations, alerts, and more to stay ahead of change and improve responsiveness.
SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain enables businesses to centralize demand, supply, inventory, sales, and operations planning on one platform to create more efficient and resilient supply chains. With embedded analytics, what-if simulations, alerts, and other machine learning capabilities, you can quickly identify and respond to ...
Integrated business planning (IBP) is a process for translating desired business outcomes into financial and operational resource requirements, with the overarching objective of maximizing profit and / or cash flow, while cutting down risk. The business outcomes, on which IBP processes focus, can be expressed in terms of the achievement of the ...
SAP IBP provides applications to facilitate the following: Balancing of demand and supply. Harmonization of planning across corporate functions through organizational visibility and alignment. Responsive planning with advanced algorithms, optimization, and what-if scenario simulation planning. Demand-driven supply chain planning based on demand ...
Integrated Business Planning (IBP) is the business planning process that extends the principles of Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) throughout the value chain. It is to create a bridge between strategy and execution. IBP is a next step for companies that already have an S&OP process in place. It is a next step because it integrates the ...
Integrated Business Planning (IBP) is a common-sense process designed for effective decision-making and led by your leadership team. True business integration means senior management can plan and manage the entire organization over a 24-36 month horizon, aligning strategic and tactical plans each month, and allocating critical resources, people ...
What is Integrated Business Planning (IBP) Integrated business planning — the subject of a new report from the Association for Finance Professionals (AFP) — is a single holistic plan that seamlessly connects strategic plans with sales plans, operational plans, and financial plans while balancing practical constraints about the availability ...
Why SAP Integrated Business Planning. Meet future demand profitably with SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain (SAP IBP). Powered by SAP HANA in-memory technology, this cloud-based solution combines sales and operations planning (S&OP), forecasting and demand, response and supply, demand-driven replenishment, and inventory planning.
SAP IBP Advanced Configuration. Start exploring IBP configuration of master data objects and planning areas, key figures, currency and UOM conversion, and progress to more advanced topics. Discover the power of SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain with this comprehensive learning journey. Learn from experts and boost your career.
The SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain (SAP IBP) solution is a cloud-based supply chain planning solution that scales to accommodate business growth and integrates with other SAP and third-party systems. It integrates key aspects of the planning process including demand, supply, inventory, and sales and operations planning (S&OP).
Integrated Business Planning (IBP) is a comprehensive planning solution developed to provide core analytics, visibility, collaboration, and execution capabilities. IBP helps organizations across industries achieve real orchestration of their supply chain in order to retain control of costs and services delivered.
Integrated Business Planning (IBP) is a complete planning process from EY and Pegasystems that drives efficiency and accuracy by providing visibility into key business functions and aligning them around a single strategy. Making complex planning simpler and smarter.
This document. SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain. What's New. Applications and Features of SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain . Example: Integrated Planning Process with Unified Planning Area. Administration. Identity and Access Management. Working with Web Applications. Business Applications.
IBP2 is a team of integrated business planning experts with real world experience who recognize that a complete and comprehensive approach is the right path to lasting change. Our service offerings include…. Process Evaluation & Effective Practices. Technology Selection and Solution Architecture. Process Facilitation &.
Dynamic Norm Calculations using Rolling Aggregation in SAP IBP in Supply Chain Management Blogs by Members 08-16-2021; Calculate rolling 15 Weeks of Average - Keyfigure Calculation in IBP in Supply Chain Management Q&A 05-28-2020; Supply planning-heuristic issue in Supply Chain Management Q&A 11-19-2018
The SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain (SAP IBP) solution is a cloud-based supply chain planning solution that scales to accommodate business growth and integrates with other SAP and third-party systems. It integrates key aspects of the planning process including demand, supply, inventory, and sales and operations planning (S&OP).
SAP IBP for inventory. SAP IBP for response and supply. SAP IBP for sales and operations. Supply Chain Control Tower. Productive Use: No. Size: 256 GB virtual instance. Number of users: up to 10 concurrent users. Customer-defined planning areas: up to 5. Customer data: up to 50 million Total Planning Points*.
The SAP Integrated Business Planning for Supply Chain (SAP IBP) solution is a cloud-based supply chain planning solution that scales to accommodate business growth and integrates with other SAP and third-party systems. It integrates key aspects of the planning process including demand, supply, inventory, and sales and operations planning (S&OP).