An Educational Blog
My Teaching Journey

An Educational Blog Pages
- Sample Page
Reflecting on My Own Math Experiences
Hi thank you so much for being here..
Welcome! I am so glad you have come across this post! My name is Julia Park and I am a senior at Millersville University! I am an Early Childhood Education major and I have learned so much so far! If you have a moment, feel free to check out my previous blog posts!
In my last post, I shared information about learning centers in math class! In this post, I will be reflecting on my mathematical journey. My experiences in math have really shaped the way I teach my students.
My Early Math Memories
I believe that early math experiences can really shape a child’s mindset towards mathematics. It has definitely shaped mine. Unfortunately, it has been a long journey of growing my interest in math, and I am still working on it!
When I was in elementary school, even up until my time at Millersville, math has been a huge struggle for me. I have grown up with the incredibly damaging misconception that you have to be a “math person” to excel in math. A lot of my peers had the same mindset, which made it even harder to let go of those limiting thoughts.
I discussed this in my growth mindset blog post , but “math people” do not exist! I have my own reasons as to why I thought there were math people, but children’s experiences often vary. I think my fixed mindset was formed from experiences with not-so-nice teachers, the pressure of time limits and the need for accuracy in class, and a lack of hands-on learning. Those are just a few ideas of why I think I have had a tough time with math and I will be discussing more ideas later in this post!
Although it was hard to get through math class sometimes, I am really grateful that I have had these experiences because I can learn from them and relate to my own students. I want my students to feel comfortable with asking for help and to know that it is possible to learn and grow in many ways!
What I Have Learned From Past Teachers
Through my time as a student in math class, I have had many different experiences with a variety of teachers. I want to share the good and the bad of what I have gone through because I think it is beneficial for teachers to reflect on all experiences related to learning. We can take what we learn to inform our own teaching practices.
Positive approaches I have learned from teachers:
- Providing assistance outside of class
- Using a hands-on learning approach
- Giving time to practice skills in class
- Utilizing interactive math games
- Facilitating class discussions
- Being kind and encouraging when a student is struggling
Approaches of teachers that were difficult for me:
- Focusing on accuracy only and not effort
- Putting pressure on students to turn in extensive assignments with a limited amount of time
- Teaching new concepts too fast
- Using too many lectures and PowerPoint presentations
- Not having time to reflect on concepts in class
- Being intimidating when a student is struggling
Every student learns differently. These experiences are unique to me and not everyone will be able to relate to what I have taken from my past math classes. However, I think it is important to recognize that although one strategy might work for one student, it might not work for another student. This notion emphasizes the need for differentiation. I will be discussing differentiation more in the next section.
Strategies I Want to Use to Teach Math
As I finish this semester at Millersville University, I am leaving with so many new ways of teaching math that I was not even aware of previously. I have a new passion for making math class fun and interesting for my students. The following are some examples of strategies I would love to incorporate in my future math class:
- My math instruction will be differentiated based on my students’ needs. I will monitor their progress through various assessments and observations to modify or individualize my instruction when needed.
- Hands-on learning will be included to increase the engagement and participation of my students. I want to make math fun and exciting!!
- Class discussions will be a huge part of my mathematics instruction. Discussions in math class promote a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts in children.
- I would love to try to use interactive notebooks to organize my students’ learning and create engaging experiences. I had not heard of these notebooks until this year and I love them!
- Technology , manipulatives , and children’s literature are just a few tools I plan on using to enhance mathematics instruction for my students.
- Parent involvement is very important for a child’s education and I will consistently keep in contact with families to increase this involvement.
- I am very passionate about modeling a growth mindset for my students. I want my students to believe in themselves and in their ability to grow.
- I will strive to create a safe and welcoming environment for my students. I want them to be comfortable with sharing their ideas and to not fear making mistakes. To do this, I will value effort just as much as accuracy.
Mistakes Are Learning Opportunities!
One of the biggest lessons I have learned throughout my time at Millersville is that making mistakes is okay. I used to put so much pressure on myself to be perfect and know everything, but that is not healthy. Teachers are not robots made to feed information to students. Instead, we have a purpose to learn alongside our students and to welcome mistakes as learning opportunities.
I am much more comfortable now being honest with my students in moments of uncertainty. I would rather figure something out with them than provide them with the wrong information. It’s really fun to explore ideas with students and work together toward a common goal. These experiences with students are valuable and strengthen the student-teacher relationship. When children trust their teachers, they are more engaged, motivated, and feel an increased amount of comfort when reaching out for help and sharing their thoughts with others.
Check out my blog post about growth mindset to learn more about the importance of making mistakes and the value of having a positive mindset in math class!
Thank you so much for reading!
I had a blast sharing my mathematical experiences with you all! I have grown so much through the years and I can’t wait to keep growing as I gain more experience. I hope you learned about some ways you can teach mathematics in your own classroom! Thank you for reading. I sincerely appreciate it!
Published by
Hi! I am Julia Park and I'm a junior at Millersville University. I am currently studying Early Childhood Education. I am so excited to share my journey through my new blog! View all posts by Julia Park
- Our Mission
2 Ways to Encourage Reflection on Math Concepts
Open-ended questions guide students to participate and to think mathematically, which cements their learning.

For many students, math is a subject where every question has one (and only one) correct answer. If a student is asked, “What is two plus two?” the only acceptable response is “Four.”
What if students were also asked, “Why does two plus two equal four?” Reflection questions like this, which are purposely open-ended, do not have a single correct answer. Instead, these questions remove the fear of being wrong and encourage mathematical thinking, participation, and growth.
“Reflection questions are important for students and help move the focus from performance to learning,” says Stanford professor Jo Boaler , who believes that “assessment plays a key role in the messages given to students about their potential, and many classrooms need to realign their assessment approach in order to encourage growth instead of fixed mindsets among students.”
In addition to performance-focused questions and assessments (“What is the total sum of the interior angles of a triangle?”), you can ask open-ended reflection questions that encourage mathematical thinking and participation (“Why do you think the total sum of the interior angles of a triangle always equals 180 degrees?”). The second question shifts the focus from performance toward thinking, learning, and engaging with mathematics without the fear of being wrong.
How can you incorporate reflection questions into your math lessons? Try these two useful strategies.
Which One Doesn’t Belong?
If you grew up watching Sesame Street , you probably remember the “One of These Things Is Not Like the Others” segment, where viewers had to identify one object out of a set of four that did not belong. This simple activity helps children to identify similarities and differences, and this type of thinking can be extended to learning math.
Which One Doesn’t Belong? (WODB) math activities present students with four different visual graphics that are all similar and different from each other in some way. This four-quadrant activity is my go-to for getting whole-class participation, as each option can be argued as the correct answer.

Observe the photo above of a WODB activity showing the numbers 22, 33, 44, and 50, and identify which choice does not belong and explain why. Since the graphics are purposely ambiguous and have overlapping similarities and differences, there is no single correct answer. One student might conclude that 50 doesn’t belong because it is the only number not divisible by 11. Another student may also believe that 50 doesn’t belong but for a different reason, namely that it is the only number with two different digits. A third student might conclude that 33 doesn’t belong because it is the only odd number. With this one graphic, you can easily spark a deep mathematical discussion where all students are eager to participate and share their thinking without any fear of being wrong.
WODB activities can be used for any math topic and can include images, numbers, charts, and graphs. They can also be used as formative assessments where students write their responses on sticky notes and stick them on the graphic that is projected at the front of the classroom.
Think-Notice-Wonder
Writing about math helps students organize their thoughts, use important vocabulary terms, and express their ideas in depth—which leads to deeper understanding.
Think-Notice-Wonder (TNW) activities are open-ended writing prompts where students are required to complete I think… , I notice… , I wonder… , based on a given graphic related to a math topic.

For example, students observe the soda and popcorn price graphic above and are prompted: What do you think? What do you notice? What do you wonder?
Encourage your students to think deeply for a minute or two before putting their thoughts into writing. They can share their ideas about the relationship between the price of a bag of popcorn and a soda based on size. They can verbalize how they perceive the proportional relationship to behave, wonder about which option provides the most value, and question how the prices were determined in the first place.
Since TNW writing activities are open-ended and do not have a correct answer, they encourage full group participation. Teachers often have students share their responses in a math journal notebook, but you can also use this free TNW student response template .
If you are looking for free images and graphics to use as TNW writing prompts, here are a few helpful resources:
- Find math-related graphics and images using Google Image Search and display them at the front of your classroom.
- Access and share teacher-created TNW activities on Twitter by searching the math education hashtags, including #ITeachMath, #MTBoS, and #NoticeWonder.
- Free stock photo websites such as Unsplash have an excellent collection of photos that relate to math topics, including estimation, three-dimensional figures, and mathematical patterns in nature.
When you add more reflection questions into your math lessons, students will have more opportunities to participate and engage in mathematical thinking without fear, which leads to a most-desired outcome—accessibility and growth.
Reflections: Students in Math Class
Published by patrick honner on June 14, 2012 June 14, 2012
At the end of the term I ask students to write simple reflections on their experiences from the year: what they learned about math, about the world, about themselves. It’s one of the many ways I get students writing in math class .
It’s a great way to model reflection as part of the learning process, and it’s also a good way for me to get feedback about the student experience.
Mostly, it’s fun! I love sharing and discussing the reflections with students, and it always results in great end-of-year conversations.
Here are some of my favorites.
After learning a little more about math, I think math is created rather than discovered. This makes mathematicians and scientists the creators, not merely the seekers.
I learned a lot of things from my classmates that I wouldn’t have learned if I were to just study on my own.
I have learned that I still have very much to learn about myself.
Mathematics is magical; it can lead you to a dead end, but then it can miraculously open up an exit.
Learning how to think of things in three dimensions completely changed the way I saw math.
By seeing algebraic and geometric interpretations, I learned how to communicate math in more ways.
The process which turns a difficult problem into a relatively easy problem is the beauty of math.
One of the best parts of reflection is how much it gets you thinking about the future. Plenty of food for thought here.
For more resources, see my Writing in Math Class page.
Related Posts
- Writing in Math Class
- Writing in Math Class: Peer Review
- Why Write in Math Class?
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
patrick honner
Math teacher in Brooklyn, New York
Hilary · August 7, 2012 at 3:39 pm
These are great!
admin · August 8, 2012 at 1:18 am
Yeah, inspiring and thoughtful stuff. It’s a great way to make kids conscious of the role of reflection in learning while getting some practical teaching advice, too.
The key is to get the students writing and reflecting on a regular basis. By the end of the year, the students will have great things to say plus the tools and motivaiton to say them.
Annette · June 17, 2018 at 5:09 pm
I know this is an old post, but this is truly inspiring and I hope you encourage students to continue doing reflections!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Currently you have JavaScript disabled. In order to post comments, please make sure JavaScript and Cookies are enabled, and reload the page. Click here for instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your browser.
Resources Teaching Writing
Math that connects where we’re going to where we’ve been — quanta magazine.
My latest column for Quanta Magazine is about the power of creative thinking in mathematics, and how understanding problems from different perspectives can lead us to surprising new conclusions. It starts with one of my Read more…
Workshop — The Geometry of Statistics
I’m excited to present The Geometry of Statistics tonight, a new workshop for teachers. This workshop is about one of the coolest things I have learned over the past few years teaching linear algebra and Read more…
People Tell Me My Job is Easy
People tell me my job is easy. You get summers off. You only work nine months of the year. You’re done at 3 pm. You get paid to babysit. Students at that school won’t succeed Read more…
Follow Mr Honner
Get every new post delivered to your Inbox
Join other followers:

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the complete ib extended essay guide: examples, topics, and ideas.
International Baccalaureate (IB)

IB students around the globe fear writing the Extended Essay, but it doesn't have to be a source of stress! In this article, I'll get you excited about writing your Extended Essay and provide you with the resources you need to get an A on it.
If you're reading this article, I'm going to assume you're an IB student getting ready to write your Extended Essay. If you're looking at this as a potential future IB student, I recommend reading our introductory IB articles first, including our guide to what the IB program is and our full coverage of the IB curriculum .
IB Extended Essay: Why Should You Trust My Advice?
I myself am a recipient of an IB Diploma, and I happened to receive an A on my IB Extended Essay. Don't believe me? The proof is in the IBO pudding:
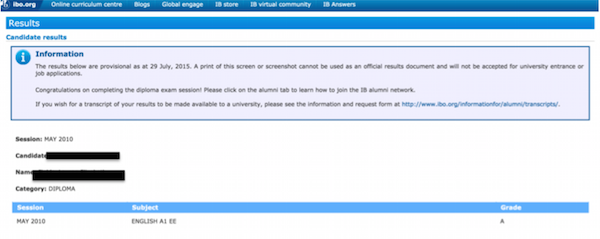
If you're confused by what this report means, EE is short for Extended Essay , and English A1 is the subject that my Extended Essay topic coordinated with. In layman's terms, my IB Diploma was graded in May 2010, I wrote my Extended Essay in the English A1 category, and I received an A grade on it.
What Is the Extended Essay in the IB Diploma Programme?
The IB Extended Essay, or EE , is a mini-thesis you write under the supervision of an IB advisor (an IB teacher at your school), which counts toward your IB Diploma (learn more about the major IB Diploma requirements in our guide) . I will explain exactly how the EE affects your Diploma later in this article.
For the Extended Essay, you will choose a research question as a topic, conduct the research independently, then write an essay on your findings . The essay itself is a long one—although there's a cap of 4,000 words, most successful essays get very close to this limit.
Keep in mind that the IB requires this essay to be a "formal piece of academic writing," meaning you'll have to do outside research and cite additional sources.
The IB Extended Essay must include the following:
- A title page
- Contents page
- Introduction
- Body of the essay
- References and bibliography
Additionally, your research topic must fall into one of the six approved DP categories , or IB subject groups, which are as follows:
- Group 1: Studies in Language and Literature
- Group 2: Language Acquisition
- Group 3: Individuals and Societies
- Group 4: Sciences
- Group 5: Mathematics
- Group 6: The Arts
Once you figure out your category and have identified a potential research topic, it's time to pick your advisor, who is normally an IB teacher at your school (though you can also find one online ). This person will help direct your research, and they'll conduct the reflection sessions you'll have to do as part of your Extended Essay.
As of 2018, the IB requires a "reflection process" as part of your EE supervision process. To fulfill this requirement, you have to meet at least three times with your supervisor in what the IB calls "reflection sessions." These meetings are not only mandatory but are also part of the formal assessment of the EE and your research methods.
According to the IB, the purpose of these meetings is to "provide an opportunity for students to reflect on their engagement with the research process." Basically, these meetings give your supervisor the opportunity to offer feedback, push you to think differently, and encourage you to evaluate your research process.
The final reflection session is called the viva voce, and it's a short 10- to 15-minute interview between you and your advisor. This happens at the very end of the EE process, and it's designed to help your advisor write their report, which factors into your EE grade.
Here are the topics covered in your viva voce :
- A check on plagiarism and malpractice
- Your reflection on your project's successes and difficulties
- Your reflection on what you've learned during the EE process
Your completed Extended Essay, along with your supervisor's report, will then be sent to the IB to be graded. We'll cover the assessment criteria in just a moment.

We'll help you learn how to have those "lightbulb" moments...even on test day!
What Should You Write About in Your IB Extended Essay?
You can technically write about anything, so long as it falls within one of the approved categories listed above.
It's best to choose a topic that matches one of the IB courses , (such as Theatre, Film, Spanish, French, Math, Biology, etc.), which shouldn't be difficult because there are so many class subjects.
Here is a range of sample topics with the attached extended essay:
- Biology: The Effect of Age and Gender on the Photoreceptor Cells in the Human Retina
- Chemistry: How Does Reflux Time Affect the Yield and Purity of Ethyl Aminobenzoate (Benzocaine), and How Effective is Recrystallisation as a Purification Technique for This Compound?
- English: An Exploration of Jane Austen's Use of the Outdoors in Emma
- Geography: The Effect of Location on the Educational Attainment of Indigenous Secondary Students in Queensland, Australia
- Math: Alhazen's Billiard Problem
- Visual Arts: Can Luc Tuymans Be Classified as a Political Painter?
You can see from how varied the topics are that you have a lot of freedom when it comes to picking a topic . So how do you pick when the options are limitless?

How to Write a Stellar IB Extended Essay: 6 Essential Tips
Below are six key tips to keep in mind as you work on your Extended Essay for the IB DP. Follow these and you're sure to get an A!
#1: Write About Something You Enjoy
You can't expect to write a compelling essay if you're not a fan of the topic on which you're writing. For example, I just love British theatre and ended up writing my Extended Essay on a revolution in post-WWII British theatre. (Yes, I'm definitely a #TheatreNerd.)
I really encourage anyone who pursues an IB Diploma to take the Extended Essay seriously. I was fortunate enough to receive a full-tuition merit scholarship to USC's School of Dramatic Arts program. In my interview for the scholarship, I spoke passionately about my Extended Essay; thus, I genuinely think my Extended Essay helped me get my scholarship.
But how do you find a topic you're passionate about? Start by thinking about which classes you enjoy the most and why . Do you like math classes because you like to solve problems? Or do you enjoy English because you like to analyze literary texts?
Keep in mind that there's no right or wrong answer when it comes to choosing your Extended Essay topic. You're not more likely to get high marks because you're writing about science, just like you're not doomed to failure because you've chosen to tackle the social sciences. The quality of what you produce—not the field you choose to research within—will determine your grade.
Once you've figured out your category, you should brainstorm more specific topics by putting pen to paper . What was your favorite chapter you learned in that class? Was it astrophysics or mechanics? What did you like about that specific chapter? Is there something you want to learn more about? I recommend spending a few hours on this type of brainstorming.
One last note: if you're truly stumped on what to research, pick a topic that will help you in your future major or career . That way you can use your Extended Essay as a talking point in your college essays (and it will prepare you for your studies to come too!).
#2: Select a Topic That Is Neither Too Broad nor Too Narrow
There's a fine line between broad and narrow. You need to write about something specific, but not so specific that you can't write 4,000 words on it.
You can't write about WWII because that would be a book's worth of material. You also don't want to write about what type of soup prisoners of war received behind enemy lines, because you probably won’t be able to come up with 4,000 words of material about it. However, you could possibly write about how the conditions in German POW camps—and the rations provided—were directly affected by the Nazis' successes and failures on the front, including the use of captured factories and prison labor in Eastern Europe to increase production. WWII military history might be a little overdone, but you get my point.
If you're really stuck trying to pinpoint a not-too-broad-or-too-narrow topic, I suggest trying to brainstorm a topic that uses a comparison. Once you begin looking through the list of sample essays below, you'll notice that many use comparisons to formulate their main arguments.
I also used a comparison in my EE, contrasting Harold Pinter's Party Time with John Osborne's Look Back in Anger in order to show a transition in British theatre. Topics with comparisons of two to three plays, books, and so on tend to be the sweet spot. You can analyze each item and then compare them with one another after doing some in-depth analysis of each individually. The ways these items compare and contrast will end up forming the thesis of your essay!
When choosing a comparative topic, the key is that the comparison should be significant. I compared two plays to illustrate the transition in British theatre, but you could compare the ways different regional dialects affect people's job prospects or how different temperatures may or may not affect the mating patterns of lightning bugs. The point here is that comparisons not only help you limit your topic, but they also help you build your argument.
Comparisons are not the only way to get a grade-A EE, though. If after brainstorming, you pick a non-comparison-based topic and are still unsure whether your topic is too broad or narrow, spend about 30 minutes doing some basic research and see how much material is out there.
If there are more than 1,000 books, articles, or documentaries out there on that exact topic, it may be too broad. But if there are only two books that have any connection to your topic, it may be too narrow. If you're still unsure, ask your advisor—it's what they're there for! Speaking of advisors...

Don't get stuck with a narrow topic!
#3: Choose an Advisor Who Is Familiar With Your Topic
If you're not certain of who you would like to be your advisor, create a list of your top three choices. Next, write down the pros and cons of each possibility (I know this sounds tedious, but it really helps!).
For example, Mr. Green is my favorite teacher and we get along really well, but he teaches English. For my EE, I want to conduct an experiment that compares the efficiency of American electric cars with foreign electric cars.
I had Ms. White a year ago. She teaches physics and enjoyed having me in her class. Unlike Mr. Green, Ms. White could help me design my experiment.
Based on my topic and what I need from my advisor, Ms. White would be a better fit for me than would Mr. Green (even though I like him a lot).
The moral of my story is this: do not just ask your favorite teacher to be your advisor . They might be a hindrance to you if they teach another subject. For example, I would not recommend asking your biology teacher to guide you in writing an English literature-based EE.
There can, of course, be exceptions to this rule. If you have a teacher who's passionate and knowledgeable about your topic (as my English teacher was about my theatre topic), you could ask that instructor. Consider all your options before you do this. There was no theatre teacher at my high school, so I couldn't find a theatre-specific advisor, but I chose the next best thing.
Before you approach a teacher to serve as your advisor, check with your high school to see what requirements they have for this process. Some IB high schools require your IB Extended Essay advisor to sign an Agreement Form , for instance.
Make sure that you ask your IB coordinator whether there is any required paperwork to fill out. If your school needs a specific form signed, bring it with you when you ask your teacher to be your EE advisor.
#4: Pick an Advisor Who Will Push You to Be Your Best
Some teachers might just take on students because they have to and aren't very passionate about reading drafts, only giving you minimal feedback. Choose a teacher who will take the time to read several drafts of your essay and give you extensive notes. I would not have gotten my A without being pushed to make my Extended Essay draft better.
Ask a teacher that you have experience with through class or an extracurricular activity. Do not ask a teacher that you have absolutely no connection to. If a teacher already knows you, that means they already know your strengths and weaknesses, so they know what to look for, where you need to improve, and how to encourage your best work.
Also, don't forget that your supervisor's assessment is part of your overall EE score . If you're meeting with someone who pushes you to do better—and you actually take their advice—they'll have more impressive things to say about you than a supervisor who doesn't know you well and isn't heavily involved in your research process.
Be aware that the IB only allows advisors to make suggestions and give constructive criticism. Your teacher cannot actually help you write your EE. The IB recommends that the supervisor spends approximately two to three hours in total with the candidate discussing the EE.
#5: Make Sure Your Essay Has a Clear Structure and Flow
The IB likes structure. Your EE needs a clear introduction (which should be one to two double-spaced pages), research question/focus (i.e., what you're investigating), a body, and a conclusion (about one double-spaced page). An essay with unclear organization will be graded poorly.
The body of your EE should make up the bulk of the essay. It should be about eight to 18 pages long (again, depending on your topic). Your body can be split into multiple parts. For example, if you were doing a comparison, you might have one third of your body as Novel A Analysis, another third as Novel B Analysis, and the final third as your comparison of Novels A and B.
If you're conducting an experiment or analyzing data, such as in this EE , your EE body should have a clear structure that aligns with the scientific method ; you should state the research question, discuss your method, present the data, analyze the data, explain any uncertainties, and draw a conclusion and/or evaluate the success of the experiment.
#6: Start Writing Sooner Rather Than Later!
You will not be able to crank out a 4,000-word essay in just a week and get an A on it. You'll be reading many, many articles (and, depending on your topic, possibly books and plays as well!). As such, it's imperative that you start your research as soon as possible.
Each school has a slightly different deadline for the Extended Essay. Some schools want them as soon as November of your senior year; others will take them as late as February. Your school will tell you what your deadline is. If they haven't mentioned it by February of your junior year, ask your IB coordinator about it.
Some high schools will provide you with a timeline of when you need to come up with a topic, when you need to meet with your advisor, and when certain drafts are due. Not all schools do this. Ask your IB coordinator if you are unsure whether you are on a specific timeline.
Below is my recommended EE timeline. While it's earlier than most schools, it'll save you a ton of heartache (trust me, I remember how hard this process was!):
- January/February of Junior Year: Come up with your final research topic (or at least your top three options).
- February of Junior Year: Approach a teacher about being your EE advisor. If they decline, keep asking others until you find one. See my notes above on how to pick an EE advisor.
- April/May of Junior Year: Submit an outline of your EE and a bibliography of potential research sources (I recommend at least seven to 10) to your EE advisor. Meet with your EE advisor to discuss your outline.
- Summer Between Junior and Senior Year: Complete your first full draft over the summer between your junior and senior year. I know, I know—no one wants to work during the summer, but trust me—this will save you so much stress come fall when you are busy with college applications and other internal assessments for your IB classes. You will want to have this first full draft done because you will want to complete a couple of draft cycles as you likely won't be able to get everything you want to say into 4,000 articulate words on the first attempt. Try to get this first draft into the best possible shape so you don't have to work on too many revisions during the school year on top of your homework, college applications, and extracurriculars.
- August/September of Senior Year: Turn in your first draft of your EE to your advisor and receive feedback. Work on incorporating their feedback into your essay. If they have a lot of suggestions for improvement, ask if they will read one more draft before the final draft.
- September/October of Senior Year: Submit the second draft of your EE to your advisor (if necessary) and look at their feedback. Work on creating the best possible final draft.
- November-February of Senior Year: Schedule your viva voce. Submit two copies of your final draft to your school to be sent off to the IB. You likely will not get your grade until after you graduate.
Remember that in the middle of these milestones, you'll need to schedule two other reflection sessions with your advisor . (Your teachers will actually take notes on these sessions on a form like this one , which then gets submitted to the IB.)
I recommend doing them when you get feedback on your drafts, but these meetings will ultimately be up to your supervisor. Just don't forget to do them!

The early bird DOES get the worm!
How Is the IB Extended Essay Graded?
Extended Essays are graded by examiners appointed by the IB on a scale of 0 to 34 . You'll be graded on five criteria, each with its own set of points. You can learn more about how EE scoring works by reading the IB guide to extended essays .
- Criterion A: Focus and Method (6 points maximum)
- Criterion B: Knowledge and Understanding (6 points maximum)
- Criterion C: Critical Thinking (12 points maximum)
- Criterion D: Presentation (4 points maximum)
- Criterion E: Engagement (6 points maximum)
How well you do on each of these criteria will determine the final letter grade you get for your EE. You must earn at least a D to be eligible to receive your IB Diploma.
Although each criterion has a point value, the IB explicitly states that graders are not converting point totals into grades; instead, they're using qualitative grade descriptors to determine the final grade of your Extended Essay . Grade descriptors are on pages 102-103 of this document .
Here's a rough estimate of how these different point values translate to letter grades based on previous scoring methods for the EE. This is just an estimate —you should read and understand the grade descriptors so you know exactly what the scorers are looking for.
Here is the breakdown of EE scores (from the May 2021 bulletin):
How Does the Extended Essay Grade Affect Your IB Diploma?
The Extended Essay grade is combined with your TOK (Theory of Knowledge) grade to determine how many points you get toward your IB Diploma.
To learn about Theory of Knowledge or how many points you need to receive an IB Diploma, read our complete guide to the IB program and our guide to the IB Diploma requirements .
This diagram shows how the two scores are combined to determine how many points you receive for your IB diploma (3 being the most, 0 being the least). In order to get your IB Diploma, you have to earn 24 points across both categories (the TOK and EE). The highest score anyone can earn is 45 points.
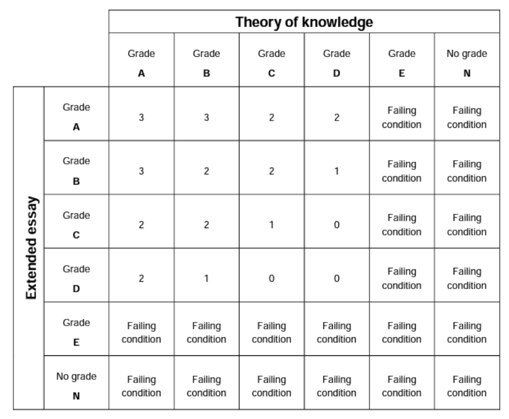
Let's say you get an A on your EE and a B on TOK. You will get 3 points toward your Diploma. As of 2014, a student who scores an E on either the extended essay or TOK essay will not be eligible to receive an IB Diploma .
Prior to the class of 2010, a Diploma candidate could receive a failing grade in either the Extended Essay or Theory of Knowledge and still be awarded a Diploma, but this is no longer true.
Figuring out how you're assessed can be a little tricky. Luckily, the IB breaks everything down here in this document . (The assessment information begins on page 219.)
40+ Sample Extended Essays for the IB Diploma Programme
In case you want a little more guidance on how to get an A on your EE, here are over 40 excellent (grade A) sample extended essays for your reading pleasure. Essays are grouped by IB subject.
- Business Management 1
- Chemistry 1
- Chemistry 2
- Chemistry 3
- Chemistry 4
- Chemistry 5
- Chemistry 6
- Chemistry 7
- Computer Science 1
- Economics 1
- Design Technology 1
- Design Technology 2
- Environmental Systems and Societies 1
- Geography 1
- Geography 2
- Geography 3
- Geography 4
- Geography 5
- Geography 6
- Literature and Performance 1
- Mathematics 1
- Mathematics 2
- Mathematics 3
- Mathematics 4
- Mathematics 5
- Philosophy 1
- Philosophy 2
- Philosophy 3
- Philosophy 4
- Philosophy 5
- Psychology 1
- Psychology 2
- Psychology 3
- Psychology 4
- Psychology 5
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 1
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 2
- Social and Cultural Anthropology 3
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 1
- Sports, Exercise and Health Science 2
- Visual Arts 1
- Visual Arts 2
- Visual Arts 3
- Visual Arts 4
- Visual Arts 5
- World Religion 1
- World Religion 2
- World Religion 3

What's Next?
Trying to figure out what extracurriculars you should do? Learn more about participating in the Science Olympiad , starting a club , doing volunteer work , and joining Student Government .
Studying for the SAT? Check out our expert study guide to the SAT . Taking the SAT in a month or so? Learn how to cram effectively for this important test .
Not sure where you want to go to college? Read our guide to finding your target school . Also, determine your target SAT score or target ACT score .
Want to improve your SAT score by 160 points or your ACT score by 4 points? We've written a guide for each test about the top 5 strategies you must be using to have a shot at improving your score. Download it for free now:

As an SAT/ACT tutor, Dora has guided many students to test prep success. She loves watching students succeed and is committed to helping you get there. Dora received a full-tuition merit based scholarship to University of Southern California. She graduated magna cum laude and scored in the 99th percentile on the ACT. She is also passionate about acting, writing, and photography.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

My Reflection in Mathematics in the Modern World

Related Papers
Cheryl Praeger
as the wonderings about the status of school mathematics are becoming louder and louder, the need for a revision of our reasons can no longer be ignored. In what follows, I respond to this need by taking a critical look at some of the most popular arguments for the currently popular slogan, “Mathematics for all.” This analysis is preceded by a proposal of how to think about mathematics so as to loosen the grip of clichés and to shed off hidden prejudice. It is followed by my own take on the question of what mathematics to teach, to whom, and how.
Ten pages paper, will be presented at '5th International …
Mette Andresen
As the time enters the 21st century, sciences such as those of theoretical physics, complex system and network, cytology, biology and economy developments change rapidly, and meanwhile, a few global questions constantly emerge, such as those of local war, food safety, epidemic spreading network, environmental protection, multilateral trade dispute, more and more questions accompanied with the overdevelopment and applying the internet, · · · , etc. In this case, how to keep up mathematics with the developments of other sciences? Clearly, today's mathematics is no longer adequate for the needs of other sciences. New mathematical theory or techniques should be established by mathematicians. Certainly, solving problem is the main objective of mathematics, proof or calculation is the basic skill of a mathematician. When it develops in problem-oriented, a mathematician should makes more attentions on the reality of things in mathematics because it is the main topic of human beings.
Amarnath Murthy
There is nothing in our lives, in our world, in our universe, that cannot be expressed with mathematical theories, numbers, and formulae. Mathematics is the queen of science and the king of arts; to me it is the backbone of all systems of knowledge. Mathematics is a tool that has been used by man for ages. It is a key that can unlock many doors and show the way to different logical answers to seemingly impossible problems. Not only can it solve equations and problems in everyday life, but it can also express quantities and values precisely with no question or room for other interpretation. There is no room for subjectivity. Though there is a lot of mathematics in politics, there is no room for politics in mathematics. Coming from a powerful leader two + two can not become five it will remain four. Mathematics is not fundamentally empirical —it does not rely on sensory observation or instrumental measurement to determine what is true. Indeed, mathematical objects themselves cannot be observed at all! Mathematics is a logical science, cleanly structured, and well-founded. Mathematics is obviously the most interesting, entertaining, fascinating, exciting, challenging, amazing, enthralling, thrilling, absorbing, involving, fascinating, mesmerizing, satisfying, fulfilling, inspiring, mindboggling, refreshing, systematic, energizing, satisfying, enriching, engaging, absorbing, soothing, impressive, pleasing, stimulating, engrossing, magical, musical, rhythmic, artistic, beautiful, enjoyable, scintillating, gripping, charming, recreational, elegant, unambiguous, analytical, hierarchical, powerful, rewarding, pure, impeccable, useful, optimizing, precise, objective, consistent, logical, perfect, trustworthy, eternal, universal subject in existence full of eye catching patterns.
Journal of Humanistic Mathematics
Gizem Karaali
Katja Lengnink
Mathematics plays a dominant role in today's world. Although not everyone will become a mathematical expert, from an educational point of view, it is key for everyone to acquire a certain level of mathematical literacy, which allows reflecting and assessing mathematical processes important in every day live. Therefore the goal has to be to open perspectives and experiences beyond a mechanical and tight appearance of the subject. In this article a framework for the integration of reflection and assessment in the teaching practice is developed. An illustration through concrete examples is given.
Swapna Mukhopadhyay
Michele Emmer
It is no great surprise that mathematical structures and ideas, conceived by human beings, can be applied extremely effectively to what we call the "real" world. We need only to think of physics, astronomy, meteorology, telecommunications, biology, cryptography, and medicine. But that's not all mathematics has always had strong links with music, literature, architecture, arts, philosophy, and more recently with theatre and cinema
Liliya Samigullina
The article considers mathematics as a way of teaching reasoning in symbolic non-verbal communication. Particular attention is paid to mathematical ways of thinking when studying the nature and its worldview. The nature is studied through the theory of experimental approval of scientific concepts of algorithmic and nonalgorithmic "computing". Various discoveries are analyzed and the role of mathematics in the worldview is substantiated. The greatest value of mathematics is development of knowledge in order to express it in abstract language of mathematics and natural science, i.e., to move to the meta-pedagogical level of understanding of problems
RELATED PAPERS
cdyteninhbinh.vn
The Astronomical Journal
Rene Mendez
harry yulianto
Conjuntura Austral
Camilo Pereira Carneiro F°
Laura Winkens
Clinical Cardiology
Jeffrey Roseman
Jurnal Ilmiah Medicamento
Ni Putu Udayana Antari , Ni Made Dharma Shantini Suena
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
C. Johan van der Westhuizen
Irina Antonova
Journal of Geophysical Research
Hugh Christian
Acta Haematologica
Ida Carmosino
Geoarchäologie
Lukas Werther
Revista Binacional Brasil-Argentina: Diálogo entre as ciências
Joelma Alves Rodrigues
New Covenant Publications International Ltd
Bibliomania 777
Michael Scofield
Ridho Ar-Rasyid
Ridho ar-rasyid
Revista do Centro de Estudos Portugueses
Elizangela Pinheiro
Afyon Kocatepe Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi
Nurgül Kurt
Bubungan Tinggi: Jurnal Pengabdian Masyarakat
Romauli Nainggolan
Experimental Eye Research
Toshifumi Itano
Materials Today: Proceedings
Sushila Srivastava
American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education
Claire Anderson
Social Aspects of Population Health
Elena Zemlyanova
Journal of Marine Science and Engineering
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Home — Essay Samples — Science — Mathematics in Everyday Life — Mathematics In Everyday Life: Most Vital Discipline
Mathematics in Everyday Life: Most Vital Discipline
- Categories: Mathematics in Everyday Life
About this sample

Words: 795 |
Published: Mar 14, 2019
Words: 795 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Works Cited
- Benacerraf, P. (1991). Mathematics as an object of knowledge. In P. Benacerraf & H. Putnam (Eds.), Philosophy of mathematics: Selected readings (pp. 1-13). Cambridge University Press.
- EdReady. (n.d.). Home. Retrieved from https://www.edready.org/
- Puttaswamy, T. K. (2012). Engineering mathematics. Dorling Kindersley (India) Pvt. Ltd.
- Steen, L. A. (Ed.). (2001). Mathematics today: Twelve informal essays. Springer Science & Business Media.
- Suter, B. W. (2012). Mathematics education: A critical introduction. Bloomsbury Academic.
- Tucker, A. W. (2006). Applied combinatorics. John Wiley & Sons.
- Vakil, R. (2017). A mathematical mosaic: Patterns & problem solving. Princeton University Press.
- Wolfram MathWorld. (n.d.). MathWorld--The web's most extensive mathematics resource. Retrieved from http://mathworld.wolfram.com/
- Wu, H. H. (2011). The mis-education of mathematics teachers. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 77(1), 1-20.
- Ziegler, G. M., & Aigner, M. (2012). Proofs from THE BOOK. Springer Science & Business Media.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Science

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 423 words
1 pages / 610 words
1 pages / 649 words
1 pages / 470 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Mathematics in Everyday Life
Background information on field experience school: Miami Coral Park Senior High School has 2,891 students of which 92% are Hispanic, 2% are Black, 4% White, and 2% Asian. 13% of the school’s students are ELL/LEP. The grades [...]
In this 'Mathematics in Architecture' essay, the researcher delves into the question if it is possible for architecture to stand alone without the help of mathematics? This research paper will also determine how Mathematics is [...]
Algebra, a branch of mathematics that involves symbols, equations, and variables, is often met with mixed feelings among students. Some see it as a challenging and abstract subject, while others recognize its practicality and [...]
Golden ration is a common mathematical ratio existing in the nature that is used to construct compositions in design work. The Golden ratio describes the perfectly symmetrical relationship between two proportions. It has been in [...]
This paper will be a summary of my findings in answering the questions, “how large can a set with zero ‘length’ be?”. Throughout this paper I will be explaining facts regarding the Cantor set. The Cantor set is the best example [...]
“In mathematics the Pythagorean theorem, also known as pythagoras theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle.” Stephanie J. Morris says “This famous theorem is named for the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Guide on How to Write a Reflection Paper with Free Tips and Example

A reflection paper is a very common type of paper among college students. Almost any subject you enroll in requires you to express your opinion on certain matters. In this article, we will explain how to write a reflection paper and provide examples and useful tips to make the essay writing process easier.
Reflection papers should have an academic tone yet be personal and subjective. In this paper, you should analyze and reflect upon how an experience, academic task, article, or lecture shaped your perception and thoughts on a subject.
Here is what you need to know about writing an effective critical reflection paper. Stick around until the end of our guide to get some useful writing tips from the writing team at EssayPro — a research paper writing service
What Is a Reflection Paper
A reflection paper is a type of paper that requires you to write your opinion on a topic, supporting it with your observations and personal experiences. As opposed to presenting your reader with the views of other academics and writers, in this essay, you get an opportunity to write your point of view—and the best part is that there is no wrong answer. It is YOUR opinion, and it is your job to express your thoughts in a manner that will be understandable and clear for all readers that will read your paper. The topic range is endless. Here are some examples: whether or not you think aliens exist, your favorite TV show, or your opinion on the outcome of WWII. You can write about pretty much anything.
There are three types of reflection paper; depending on which one you end up with, the tone you write with can be slightly different. The first type is the educational reflective paper. Here your job is to write feedback about a book, movie, or seminar you attended—in a manner that teaches the reader about it. The second is the professional paper. Usually, it is written by people who study or work in education or psychology. For example, it can be a reflection of someone’s behavior. And the last is the personal type, which explores your thoughts and feelings about an individual subject.
However, reflection paper writing will stop eventually with one very important final paper to write - your resume. This is where you will need to reflect on your entire life leading up to that moment. To learn how to list education on resume perfectly, follow the link on our dissertation writing services .
Unlock the potential of your thoughts with EssayPro . Order a reflection paper and explore a range of other academic services tailored to your needs. Dive deep into your experiences, analyze them with expert guidance, and turn your insights into an impactful reflection paper.


Free Reflection Paper Example
Now that we went over all of the essentials about a reflection paper and how to approach it, we would like to show you some examples that will definitely help you with getting started on your paper.
Reflection Paper Format
Reflection papers typically do not follow any specific format. Since it is your opinion, professors usually let you handle them in any comfortable way. It is best to write your thoughts freely, without guideline constraints. If a personal reflection paper was assigned to you, the format of your paper might depend on the criteria set by your professor. College reflection papers (also known as reflection essays) can typically range from about 400-800 words in length.
Here’s how we can suggest you format your reflection paper:

How to Start a Reflection Paper
The first thing to do when beginning to work on a reflection essay is to read your article thoroughly while taking notes. Whether you are reflecting on, for example, an activity, book/newspaper, or academic essay, you want to highlight key ideas and concepts.
You can start writing your reflection paper by summarizing the main concept of your notes to see if your essay includes all the information needed for your readers. It is helpful to add charts, diagrams, and lists to deliver your ideas to the audience in a better fashion.
After you have finished reading your article, it’s time to brainstorm. We’ve got a simple brainstorming technique for writing reflection papers. Just answer some of the basic questions below:
- How did the article affect you?
- How does this article catch the reader’s attention (or does it all)?
- Has the article changed your mind about something? If so, explain how.
- Has the article left you with any questions?
- Were there any unaddressed critical issues that didn’t appear in the article?
- Does the article relate to anything from your past reading experiences?
- Does the article agree with any of your past reading experiences?
Here are some reflection paper topic examples for you to keep in mind before preparing to write your own:
- How my views on rap music have changed over time
- My reflection and interpretation of Moby Dick by Herman Melville
- Why my theory about the size of the universe has changed over time
- How my observations for clinical psychological studies have developed in the last year
The result of your brainstorming should be a written outline of the contents of your future paper. Do not skip this step, as it will ensure that your essay will have a proper flow and appropriate organization.
Another good way to organize your ideas is to write them down in a 3-column chart or table.

Do you want your task look awesome?
If you would like your reflection paper to look professional, feel free to check out one of our articles on how to format MLA, APA or Chicago style
Writing a Reflection Paper Outline
Reflection paper should contain few key elements:
Introduction
Your introduction should specify what you’re reflecting upon. Make sure that your thesis informs your reader about your general position, or opinion, toward your subject.
- State what you are analyzing: a passage, a lecture, an academic article, an experience, etc...)
- Briefly summarize the work.
- Write a thesis statement stating how your subject has affected you.
One way you can start your thesis is to write:
Example: “After reading/experiencing (your chosen topic), I gained the knowledge of…”
Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs should examine your ideas and experiences in context to your topic. Make sure each new body paragraph starts with a topic sentence.
Your reflection may include quotes and passages if you are writing about a book or an academic paper. They give your reader a point of reference to fully understand your feedback. Feel free to describe what you saw, what you heard, and how you felt.
Example: “I saw many people participating in our weight experiment. The atmosphere felt nervous yet inspiring. I was amazed by the excitement of the event.”
As with any conclusion, you should summarize what you’ve learned from the experience. Next, tell the reader how your newfound knowledge has affected your understanding of the subject in general. Finally, describe the feeling and overall lesson you had from the reading or experience.
There are a few good ways to conclude a reflection paper:
- Tie all the ideas from your body paragraphs together, and generalize the major insights you’ve experienced.
- Restate your thesis and summarize the content of your paper.
We have a separate blog post dedicated to writing a great conclusion. Be sure to check it out for an in-depth look at how to make a good final impression on your reader.
Need a hand? Get help from our writers. Edit, proofread or buy essay .
How to Write a Reflection Paper: Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: create a main theme.
After you choose your topic, write a short summary about what you have learned about your experience with that topic. Then, let readers know how you feel about your case — and be honest. Chances are that your readers will likely be able to relate to your opinion or at least the way you form your perspective, which will help them better understand your reflection.
For example: After watching a TEDx episode on Wim Hof, I was able to reevaluate my preconceived notions about the negative effects of cold exposure.
Step 2: Brainstorm Ideas and Experiences You’ve Had Related to Your Topic
You can write down specific quotes, predispositions you have, things that influenced you, or anything memorable. Be personal and explain, in simple words, how you felt.
For example: • A lot of people think that even a small amount of carbohydrates will make people gain weight • A specific moment when I struggled with an excess weight where I avoided carbohydrates entirely • The consequences of my actions that gave rise to my research • The evidence and studies of nutritional science that claim carbohydrates alone are to blame for making people obese • My new experience with having a healthy diet with a well-balanced intake of nutrients • The influence of other people’s perceptions on the harm of carbohydrates, and the role their influence has had on me • New ideas I’ve created as a result of my shift in perspective
Step 3: Analyze How and Why These Ideas and Experiences Have Affected Your Interpretation of Your Theme
Pick an idea or experience you had from the last step, and analyze it further. Then, write your reasoning for agreeing or disagreeing with it.
For example, Idea: I was raised to think that carbohydrates make people gain weight.
Analysis: Most people think that if they eat any carbohydrates, such as bread, cereal, and sugar, they will gain weight. I believe in this misconception to such a great extent that I avoided carbohydrates entirely. As a result, my blood glucose levels were very low. I needed to do a lot of research to overcome my beliefs finally. Afterward, I adopted the philosophy of “everything in moderation” as a key to a healthy lifestyle.
For example: Idea: I was brought up to think that carbohydrates make people gain weight. Analysis: Most people think that if they eat any carbohydrates, such as bread, cereal, and sugar, they will gain weight. I believe in this misconception to such a great extent that I avoided carbohydrates entirely. As a result, my blood glucose levels were very low. I needed to do a lot of my own research to finally overcome my beliefs. After, I adopted the philosophy of “everything in moderation” as a key for having a healthy lifestyle.
Step 4: Make Connections Between Your Observations, Experiences, and Opinions
Try to connect your ideas and insights to form a cohesive picture for your theme. You can also try to recognize and break down your assumptions, which you may challenge in the future.
There are some subjects for reflection papers that are most commonly written about. They include:
- Book – Start by writing some information about the author’s biography and summarize the plot—without revealing the ending to keep your readers interested. Make sure to include the names of the characters, the main themes, and any issues mentioned in the book. Finally, express your thoughts and reflect on the book itself.
- Course – Including the course name and description is a good place to start. Then, you can write about the course flow, explain why you took this course, and tell readers what you learned from it. Since it is a reflection paper, express your opinion, supporting it with examples from the course.
- Project – The structure for a reflection paper about a project has identical guidelines to that of a course. One of the things you might want to add would be the pros and cons of the course. Also, mention some changes you might want to see, and evaluate how relevant the skills you acquired are to real life.
- Interview – First, introduce the person and briefly mention the discussion. Touch on the main points, controversies, and your opinion of that person.
Writing Tips
Everyone has their style of writing a reflective essay – and that's the beauty of it; you have plenty of leeway with this type of paper – but there are still a few tips everyone should incorporate.
Before you start your piece, read some examples of other papers; they will likely help you better understand what they are and how to approach yours. When picking your subject, try to write about something unusual and memorable — it is more likely to capture your readers' attention. Never write the whole essay at once. Space out the time slots when you work on your reflection paper to at least a day apart. This will allow your brain to generate new thoughts and reflections.
- Short and Sweet – Most reflection papers are between 250 and 750 words. Don't go off on tangents. Only include relevant information.
- Clear and Concise – Make your paper as clear and concise as possible. Use a strong thesis statement so your essay can follow it with the same strength.
- Maintain the Right Tone – Use a professional and academic tone—even though the writing is personal.
- Cite Your Sources – Try to cite authoritative sources and experts to back up your personal opinions.
- Proofreading – Not only should you proofread for spelling and grammatical errors, but you should proofread to focus on your organization as well. Answer the question presented in the introduction.
'If only someone could write my essay !' you may think. Ask for help our professional writers in case you need it.
Do You Need a Well-Written Reflection Paper?
Then send us your assignment requirements and we'll get it done in no time.
How To Write A Reflection Paper?
How to start a reflection paper, how long should a reflection paper be, related articles.
%20(2).webp)
- Blogs @Oregon State University
Ecampus Course Development and Training
Providing inspiration for your online class.

Reflection Assignments in Math Courses

Reflection assignments as an active learning strategy are commonly seen in humanities courses. The purpose of this writing is to share an example of how simple reflection activities can make a huge impact in two math courses. MTH 251 Differential Calculus covers five units, with one exam for each unit, counting 14% of the final grade. Before students attempt to take the unit exam, they are assigned to read textbook readings, watch instructor-created lecture videos, work on Canvas-based homework assignment and Adaptive Learning based practice assignments in Knewton Lab online platform. After assignment due date expires, students are assigned to complete a weekly written homework reflection. The weekly homework and the weekly homework reflection together count for 14% of final grade in this course, weighing the same as each of the unit exams.
MTH 341 Linear Algebra I has ten weekly modules. Each week, students read textbook assigned readings, watch lecture videos created by the instructor (Dr. ), complete post-reading questions in quiz format, work on graded group discussion questions to solve math problems in small groups, complete written homework individually, and in the following week, complete a written homework response activity individually in discussion format.
The written homework reflection in MATH 251 and the written homework response in MATH 341 are both reflection activities designed to optimize student learning success, through comparing their own homework solutions with answer keys and evaluate whether they did it correctly or incorrectly and analyze where they did it wrong and how to get it right. The purpose of such weekly reflection is to help students develop meta-cognitive skills related to their learning. By looking back at students’ own work and learning from their mistakes, they develop an understanding of what is the proper way to solve a problem and what is not the proper way for solving a particular math problem. It also prompts students to plan for proper action in the future and exercises students’ executive functioning skills (CAST, 2018). Here is what the instructions for the weekly reflection look like: 1. First answer the weekly prompt: Reflecting on the Unit 1 module, which topics did you struggle with the most? 2. Download the written homework solutions PDF: (Solution for each written homework in pdf format is attached here.) 3. Look over the solutions and compare to your submitted homework. Look for any problems where your solution differs from the posted solution.
- why you struggled with certain problems
- why each solution makes sense now
- what your misunderstanding was
- what will you do in the future when solving problems similar to these?
- what strategies will help you?
- what did you learn by making a mistake?
- what did you learn from looking at the solutions?
- If you are still confused about a problem, ask a question. DO NOT simply list which problems you got wrong.
- If your solutions are all correct then in the discussion board please discuss the problem that you found the most challenging. Describe what specific tasks helped you to complete that problem. Be as detailed as you can about your solution process.
Students not only posted their own reflections, but they also comment on or answer other students’ reflections as well. Additionally, the instructor and the four TAs in the course responded actively to students’ reflections, which makes the reflection more valuable since students get encouragement, praises, or corrections from the instructor and teaching assistants. Again, feedback from experts is critical in the success of a reflection activity (Vandenbussche, 2018)
Image 1: How reflection usually looks like and How reflection should look like ( Image Source )
Many students were reflecting on what they did wrong and asked for help. Some were reflecting on their time management in completing the homework assignments. And we were glad to see students completing homework, evaluating their own work, analyzing where they did wrong, and planning for future improvement. Overall, the purpose of this assignment is accomplished!

(Image by Dave_Here )
A great benefit that comes from these weekly reflection activities is increased or sustained homework completion rate. For MTH 251 winter 2021 week 1 to week 7, over 85% of students completed the weekly homework and the reflection activity on average. For MTH 341 Fall 20 week 1 to week 7, over 90% of students on average completed the weekly homework and the reflection assignments. All math teachers love to see their students practice with homework assignments before they attempt to take the quizzes or exams! And evidence-based research tells us that deliberate practice with targeted feedback promotes mastery learning (Ambrose et al., 2010).
So, if it works in math courses, it will work in Chemistry, Biology, Physics, Engineering and other STEM courses too! If you’re interested in implementing this technique in your teaching and have questions about setting it up, feel free to contact us. We’d love to help you figure out the easiest way to set it up in your course.
Ambrose, S.A., Bridges, M.W., DiPietro, M., Lovettt, M.C. , Norman, M.K., & The Eberly Center for Teaching Excellence at Carnegie Mellon University. (2010). How learning works: Seven research-based principles for smart teaching. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass
CAST. (2018). UDL Guidelines. Retrieved from https://udlguidelines.cast.org/
Vandenbussche, B. (2018). Reflecting for learning. Retrieved from https://educationaltoolsportal.eu/en/tools-for-learning/reflecting-learning

Leave a reply Cancel reply
Contact info.

K-5 Math Centers
K-5 math ideas, 3rd grade math, need help organizing your k-5 math block, student math reflection activities that deepen understanding.

There are 4 essential components that make up a meaningful math block . Let’s focus on the last one, student math reflection.
Even though this seems simple enough, this was the area where I struggled.
Have you ever been so focused on the other parts of your lesson that you forget to give your students time to reflect on what they learned? That was me.
Until I thought back on my own personal experiences, I don’t think I understood the power of student reflection at the time. However, I knew how it felt to be rushed through a new PD or training without being given time to think about what I learned, so why was I doing the same thing to my students?

After I had that realization, I searched for quick and effective ways to close my lessons with a reflection.
I knew this was a critical component to an effective lesson cycle, but I just couldn’t figure out everything I needed to make it happen.
In my search for the “perfect” way to get students to reflect, I asked myself these two questions:
- How can I gauge what my students understood from the lesson I taught?
- How can I give my students time to reflect in a short period of time?
So, let me share 3 easy ways to implement student math reflection activities in your classroom:
Activity #1: Two Sentence Wrap Up
What Is It?
A 2 sentence wrap-up is a quick and insightful way to close a lesson. After a lesson, students write two sentences that summarize what they learned. The sentences should:
Sentence 1: Tell what the student learned
Sentence 2: Share an example of the learning
How Does It Work?
The sentences can be recorded in student journals or on a piece of paper. If you’re working with younger students, you can have them draw a picture and label it.
Teaching Tip:
Sentence frames are helpful tools because they provide a scaffold for writing. Display the following sentence frames on your board:
Today I learned ____.
A ____ is an example of a ____ because ____.

Activity #2: Traffic Light or Thermostat
Images like a thermostat or a traffic light can give your students a visual to help them express how much they understand.
Traffic Light: An image of a traffic light with the 3 circles( red, yellow, and green)
Thermostat: An image of a thermostat set at 3 levels (high. medium, and low)
After your lesson, students circle or color the image that best describes how well they feel they understood the lesson. They can even write a sentence or two to provide more details.
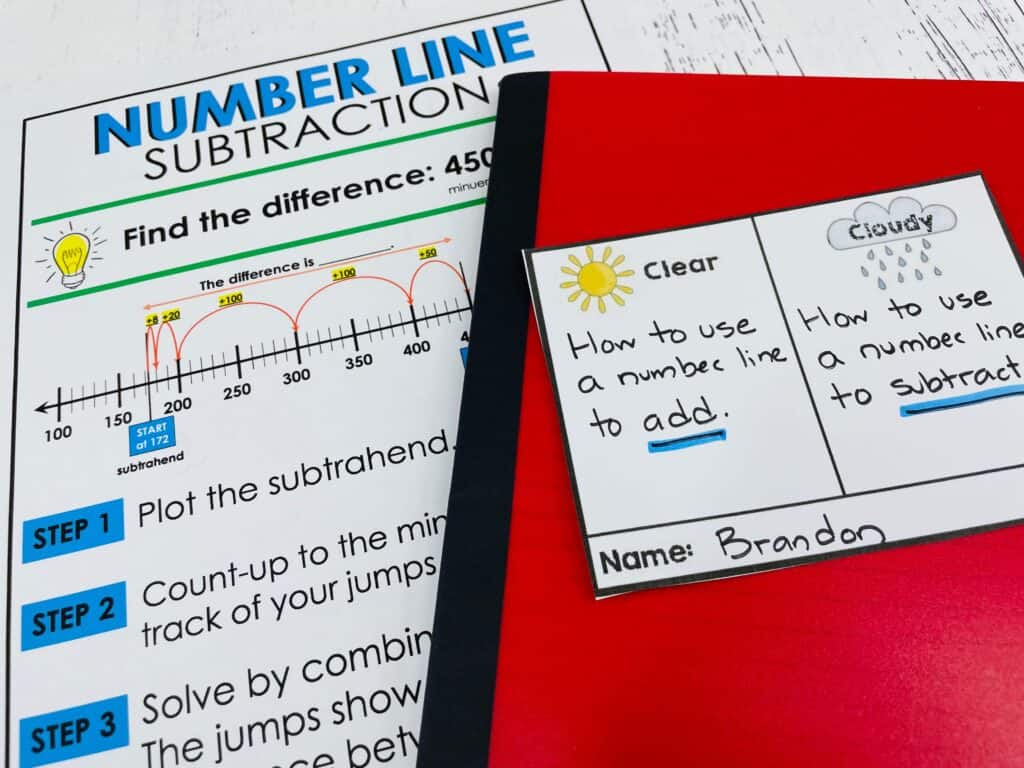
Activity #3: Clear and Cloudy
Clear or Cloudy is a reflection activity where children communicate what is clear (what they understand) and what is cloudy (what they’re having trouble understanding). This is a very simple way to get students to reflect on their learning.
At the end of your lesson, give each student a “Clear or Cloudy” sheet. Ask them to record one thing that was clear and one thing that was cloudy. After students complete their sheets, collect and review their responses to inform further instruction.
Easily Add Math Reflection Time into Your Instruction
Give your students time to step back and think about what they learned. This will allow them the opportunity to identify what they did well, decide what they found interesting, and pinpoint where they need more support.
Grab my Math Student Reflections and get your students to start reflecting on their learning now!
Want Your Students to Start Reflecting in Your Classroom? Get My FREE Student Math Reflections!
If you want to know how to get your students to think about their learning with student math reflections and found the activities in this post helpful, please share on Pinterest!
- Read more about: K-5 Math Ideas
You might also like...

Reflect and Reset: Tips for Becoming a Better Math Teacher

5 Math Mini-Lesson Ideas that Keep Students Engaged

A Rigorous Elementary Math Curriculum for Busy Teachers

Culturally Responsive Teaching: What Every Math Teacher Needs to Know

What We Offer:
Follow us here:.

- Aug 12, 2019
Math: Reflective Math Journaling Prompts
Updated: Aug 18, 2023
I am a HUGE groupie of Dr. Yeap Ban Har. If you have ever heard him discuss a lesson, he has a very specific structure that allows students to collaborate and evaluate. He begins by choosing a thoughtful problem that allows students to solve in multiple ways. The classroom lesson continues in this manner:
Exploration with Observation (10 minutes): Students work to solve the problem presented. They use manipulatives, paper and express their methods in their math journals as an investigative response, if needed. Dr. Ban Har encourages students to solve in more than 2 ways.
Structured Discussion with Sharing of Methods (10 minutes): Dr. Ban Har asks students to share out their methods. As students share, he records their methods using examples, words and pictures. He expresses no judgement on these methods and allows students to see if they are similar or that they work properly.
Reflection or Journaling with Interaction (10 minutes): Students then take a moment to process what has happened this point in the lesson. This can be by reading through part of the textbook and analyzing what the author did. They can also do this by writing in their interactive math journals. However, the prompts should vary based on the type of problem. Check out the graphic below to see the types of prompts he suggests.

Guided Practice (10 minutes): Guided Practice is an opportunity for students to try out the methods discussed with a partner. Students work to solve problems using the various methods. If they need help, they receive assistance from the teacher through questioning.
Independent Practice (10 minutes): Often lessons end without students having an opportunity to process the information on their own. Independent Practice allows students to use the various methods and make sense of problems. Due to the fact that students are working collaboratively throughout the lesson, this independent time is vital to help students finish the lesson.
Dr. Ban Har mentions that Reflection or Journaling can move after Guided Practice, if needed. That allows students to practice and reflect throughout the lesson. If you would like a copy of the lesson structure and the Journal Prompts, click below to access your own printable prompts. These would be great to cut out and glue in a student math journal to remind students how to journal. You can also find out more about how I set up math journals in this blog post here .
If you are interested in more from Dr. Ban Har, check out his blog at http://banhar.blogspot.com/
Recent Posts
Unlocking Equivalent Fractions with Multiplication Charts
Sir Cumference and All the King's Tens
Partnering with Parents in a Hybrid School Setting
Thanks for submitting!
Consortium to Promote Reflection in Engineering Education
Campus: green river college, 9. math test reflection essay.
Educator: Mike Kenyon, Faculty, Mathematics Context: Out of class; MATH 141 Pre-Calculus Keywords: mathematics, essays Student Activity Time: 30 minutes
After completing an exam, students wrote a reflection essay about how the test went.
Introducing the Reflection Activity
One way to prompt students to think about their test performance is to simply ask for their first response to the test and their score. An educator used post-exam essays to prompt students to reflect on and articulate their reactions about the exam and their score. The purpose of this activity is to assist students in verbalizing their concerns, thoughts, and reactions to their graded exam.
The educator administered the regularly scheduled math exam, graded it, and returned the test to students with a solution key. The educator offered students a chance to earn a small portion of their homework grade by completing an essay about how the exam went and their reactions to it. The educator required students to write at least one double-spaced, typed page for their essay. Students often turned in reworked problems with the essay. The educator then graded the student’s submission and included a short 2-3 sentence response to their essay. The response generally included validation, answers to open questions, or recommendations that would assist the student in the future.
The educator used the information shared in the students’ essays in individual interactions with them, either in class or during office hours. When multiple students expressed similar concerns, the educator chose to respond to those concerns in class. As a result, students experienced an opportunity to articulate their successes, misconceptions and errors on the exam. Students often take action based on the educator’s response and suggestions, such as visiting office hours or the tutoring center to improve future exam performance.
Recreating the Reflection Activity
< Back to Green River College

Reflect a Point
Across x axis, y axis and other lines.
A reflection is a kind of transformation . Conceptually, a reflection is basically a 'flip' of a shape over the line of reflection.
Reflections are opposite isometries , something we will look below.
--> image and its preimage . -->