Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree

The Top 10 Most Interesting Mental Health Research Topics
In the United States, the majority of people have been diagnosed with at least one mental disorder. Once considered shameful, mental health issues are now being discussed more openly through various online platforms, such as the best mental health podcasts and blogs, which have made information more accessible. As a result, more people are seeking forms of mental healthcare and researchers are learning even more.
While research on mental health has come a long way, there is still a long way to go in destigmatizing mental health conditions and spreading mental health awareness. If you are looking for mental health research paper topics and are struggling to narrow down your list, take a look at the top 10 most interesting mental health research topics to help get you started.
Find your bootcamp match
What makes a strong mental health research topic.
The best way for you to develop a strong mental health research topic is by first having a specific and well-defined area of interest. Your research topic should provide a clear and simple roadmap to help you focus your research paper. Additionally, consider your audience and the topic’s significance within the mental health field. What does it contribute?
Tips for Choosing a Mental Health Research Topic
- Choose a topic that is interesting to you. You may be writing to share your findings with your peers, but your topic should excite you first and foremost. You will spend a significant amount of time on it, so it should be work you are eager to dive into.
- Choose a fresh approach. There is an extensive amount of mental health research conducted by mental health professionals. Use your research skills to choose a topic that does more than just restate the same facts and information. Say something that hasn’t been said before.
- Choose a topic that matters. The topic you choose should make a contribution to all the mental health education and research that already exists. Approach your topic in a way that ensures that it’s of significance within the field.
- Choose a topic that challenges you. A sure-fire way to find out if your topic meets the criteria of being interesting, fresh, and significant, is if it challenges you. If it’s too easy, then there must be enough research available on it. If it’s too difficult, it’s likely unmanageable.
- Choose a topic that’s manageable. You should aim to choose a topic that is narrow enough in its focus that it doesn’t overwhelm you. Consider what’s feasible for you to dedicate to the research in terms of resources and time.
What’s the Difference Between a Research Topic and a Research Question?
The purpose of a research topic is to let the reader know what specific area of mental health research your paper will focus on. It is the territory upon which your research paper is based. Defining your topic is typically the initial step of any research project.
A research question, on the other hand, narrows down the scope of your research and provides a framework for the study and its objectives. It is based on the research topic and written in the form of a question that the research paper aims to answer. It provides the reader with a clear idea of what’s to be expected from the research.
How to Create Strong Mental Health Research Questions
To create a strong research question, you need to consider what will help guide the direction your research takes. It is an important part of the process and requires strong research methods . A strong research question clearly defines your work’s specific focus and lets your audience know exactly what question you intend to answer through your research.
Top 10 Mental Health Research Paper Topics
1. the effects of social media platforms on the mental well-being of children.
The effects of social media platforms on the mental well-being of children is a research topic that is especially significant and relevant today. This is due to the increasing usage of online social networks by children and adolescents. Evidence shows a correlation between social media usage and increased self-harming behaviors, anxiety, and psychological distress.
2. The Psychology of Gender Identity, Inclusivity, and Diversity
With the conversations surrounding gender and identity in recent times, a research topic on the psychology of gender identity, inclusivity, and diversity is a good option. Our understanding of gender now, in the 21st century, has evolved and gender identity has become non-binary, more inclusive, and more diverse.
3. The Psychological Effects of Social Phobia on Undergraduate Students
Some of the most common mental illnesses in the United States are phobias, so the topic of the psychology and effects of phobias is interesting and relevant to the majority of people. There are various categories of phobias that have been identified by the American Psychiatric Association that you could choose to focus on.
4. Eating Disorders Among Teenagers and Adolescents
Eating disorders among teenagers and adolescents in the United States are prevalent, especially among young women. The statistics surrounding mental health issues show that 10 in 100 young women suffer from eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa and bulimia, as well as a preoccupation with food and body dysmorphia.
5. The Correlation Between Childhood Learning Disabilities and Mental Health Problems in Adulthood
When groups of people with learning disorders (LD) were compared with groups that had no known history of LD, a correlation between childhood LD and mental health issues in adulthood was found. This research is important because it helps us to understand how childhood LD increases mental health risks in adulthood and affects emotional development.
6. How Mental Disorder is Glamorized and Sensationalized in Modern Media
Shows and movies centered around the depiction of mental illness have become more popular in recent years. The portrayal of characters with mental illnesses can often be damaging and fail to take into account the complexities of mental disorders, which often leads to stigmatization and discrimination, and a reluctance to seek mental health care.
7. The Relationship Between Self-esteem and Suicide Rates Among Adolescents
A relationship between self-esteem and suicide rates among adolescents has been found when looking into their suicidal tendencies. This is more so the case with any individual who already suffers from a mental health issue. Low self-esteem has been linked to increased levels of depression and suicide ideation, leading to higher chances of suicide attempts among adolescents.
8. Destigmatizing Mental Illness and Mental Disorders
The rates at which people are diagnosed with mental illnesses are high. Even so, their portrayal in the media has resulted in the belief that those who suffer from a mental health issue or live in mental health facilities are dangerous. Conducting research on abnormal psychology topics and destigmatizing mental illness and mental disorders is important for mental health education.
9. Psychological Trauma and the Effects of Childhood Sexual Abuse
Mental health statistics show that most abuse happens in childhood, causing long-lasting psychological trauma. The type of trauma caused by child abuse and childhood sexual abuse affects development in infants and children. It has been linked to higher levels of depression, anxiety, guilt, sexual issues, dissociative patterns, and relationship issues, to name a few.
10. Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Psychological Well-Being
There is no doubt about the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and COVID-19 confinement on psychological well-being. The threat to public health, the social and economic stresses, and the various reactions by governments and individuals have all caused unexpected mental health challenges. This has affected behaviors, perceptions, and the ways in which people make decisions.
Other Examples of Mental Health Research Topics and Questions
Mental health research topics.
- How trauma affects emotional development in children
- The impact of COVID-19 on college students
- The mental effects of bullying
- How the media influences aggression
- A comparative analysis of the differences in mental health in women and mental health in men
Mental Health Research Questions
- Are digital therapy sessions as impactful as face-to-face therapy sessions for patients?
- What are the best methods for effectively using social media to unite and connect all those suffering from a mental health issue in order to reduce their isolation?
- What causes self-destructive behavior in some children?
- Can introducing mental health topics in the school curriculum help to create understanding and reduce the stigmatization of mental disorders?
- What are the most effective methods to improve brain health and emotional intelligence as we go through the aging process?
Choosing the Right Mental Health Research Topic
When choosing the right mental health research question, it is essential to figure out what single issue you want to focus on within the broader topic of mental conditions. The narrower your scope, the easier it will be to conduct thorough and relevant research. Vagueness can lead to information overload and a lack of clear direction.
However, even though it needs to be specific, your research question must also be complex enough to allow you to develop your research. If it’s too narrow in its focus, you won’t give yourself enough room to flesh out your findings as you build on your research. The key is to find the middle ground between the two.
Mental Health Research Topics FAQ
A mental disorder refers to any of the various conditions that affect and alter our behavior, thoughts, and emotions. More than half of Americans get diagnosed with a mental disorder at some point in their lives. They are common and manageable with the right support. Some mental illnesses are occasional, such as postpartum depression, while others are long-term, such as panic attacks.
Mental health research raises awareness of mental health disorders and promotes mental health care. It provides support and evidence for the effectiveness of mental health services and programs designed for psychiatric patients and those with mental health disorders. The information provided by the research helps us better understand mental illnesses and how best to approach treatment plans.
Behavioral health and emotional health are part of a person’s overall mental health since they are all interlinked and each one affects the other. When we speak of mental health, we are referring to behavioral, cognitive, and emotional well-being, which can also affect physical health.
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), the five main categories of mental illness include dementia, mood disorders such as bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders, feeding and eating disorders, and personality disorders such as obsessive-compulsive disorder.
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Thesis Helpers
Find the best tips and advice to improve your writing. Or, have a top expert write your paper.
230 Current Mental Health Research Topics For Top Dissertation

Mental health characterizes our emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It involves the taking of multiple approaches to care for these different areas.
Medical news today notes that our mental health determines how we handle stress, relate to other people, and make healthy and articulate choices.
Mental health research is fast becoming one of the most researched areas in health. With this, so many research works can be chosen from this field. Therefore, as a student writing your essay on mental health, you must conduct extensive research for sufficient information.
Structure Of Mental Health Research Paper Or Essay
Students often have ample information on the chosen mental health nursing research topics, but the challenge they often encounter is properly arranging these topics to communicate knowledge effectively. We’ve prepared a mental illness research paper outline to improve your research paper.
- Abstract. Your abstract provides a summary of the area your topic will be based on and what the aim and objectives of this topic focus are. Your abstract is like a door that leads to your research, so you need to make it interesting and informative.
- Introduction. The introduction is the foremost part of your research paper or essay. Your introduction should always be straightforward, touching across all the relevant information that will be further pieced out subsequently.
- Body. This is the actual content of your research paper or essay. In the body, you are expected to assemble all the various subtitles related and relevant to your topic of interest. All your opinions, findings, research methodology, and discussions will be contained in the body. To create a rich, high quality research paper or essay, the body of your writing must examine relevant data.
- Conclusion. Your conclusion is the part where you are expected to summarise your arguments, thereby restating your thesis. By doing this, you’re bringing everything you’ve examined into consciousness again to remind your readers of the main issues and how it has been developed in the course of your writing.
- Reference List. In the course of your essay, you must have used different sources. As you go along, you should therefore ensure that you keep notes of the books, journals, articles you have read, ensuring that the reference style goes with what your university and college recommend for your class. This way, you’ll stick with what your school dictates as the reference style and be praised by your teachers or professors at the end of the school year. Your references also have to be current.
By using this structure your thesis or dissertation will be way more clear.
Characteristics Of Mental Health Essay
How do you recognize a good essay? How do you know that everyone will welcome your contributions to the mental health essays? It would help if you considered these tips:
- Clear Grammar. In other words, your diction must be grand yet easily understood. If it’s difficult for one to efficiently and thoroughly grasp your work, it’s not great work, and the essay’s purpose could be jeopardized. It would help if you communicated in simple language.
- Conciseness. Conciseness is simply communicating in as few words as possible. As the soul of communication, brevity makes your words last longer in the minds of readers. To achieve this, erase superfluous or elaborative words, be pointed in your writing, and make your sentences too passive.
- Depth and Arguments. Your arguments must be intellectually in depth and high level. With different mental health topics to write about, you need to explore a topic whose arguments you can profoundly develop. With this, you’ll be able to turn the ideas into something exciting and engaging. To create a good essay or an engaging one, this is something your readers look forward to.
- Clear Structure. You must structure your work to relate well with your mental illness research topics. This is the only way to make your readers follow your thoughts without stress. Thus, your essay or paper must have an introduction, a body, the conclusion, and a reference list.
This brief guide should help you have an idea of what a professor is looking for. And now here is a helpful list of topics to consider when writing your bachelor thesis or about mental health in general:
Research Questions About Mental Health
Since the subject, mental health is quite vast and includes our emotional, psychological, and social well-being, below are some of the best mental health research questions that allow the student to focus on a particular field of research.
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of delivering mental health care virtually?
- Can mental health conditions limit how a person engages with technology?
- How can physicians maximize the combination of existing treatment options with virtual mental health procedures?
- Have virtual interventions been proven safe?
- What are the measures put in place to ensure that mental health platforms are safe?
- What different effects will the adoption of virtual meetups have on the patients’ appointment time?
- Are virtual therapies as effective as physical therapies?
- Can one ascertain total satisfaction from standard elements of therapy through virtual meetups?
- Does virtual interaction create better avenues for minorities as compared to traditional interface?
- Can the different virtual platforms be used to reach out to people with mental health problems effectively?
- Does obesity affect mental health?
- What are the possible symptoms of mental illness in family members?
- At what point do people with mental illness become destructive?
- What are the causes of anorexia?
- Why does a person with mental illness begin to cut themselves?
- How easily can one treat post-traumatic stress?
- Does childbirth lead to depression?
- Are mental illnesses more prevalent in men or women?
- Is ADHD a mental illness?
- What are the causes of ADHD in young adults?
- Are mental illnesses prevalent in survivors of war?
- Can OCD be termed a mental illness?
- How can one tell when a person begins to develop obsessive-compulsive disorder?
- Are movies, games, etc., some of the leading causes of depression in young adults?
- How can one quickly ascertain if they’re mentally ill or not?
- What are the side effects of drug abuse on mental health?
- A study into medically proven ways of curing ADHD.
- The impacts of ADHD on Young adults.
- A study of the mental effects of excessive consumption of Marijuana
- How ADHD and autism affect young people in the 21st century.
- The mental challenges of living with learning disabilities.
Mental Health Research Paper Topics
Mental health is the psychological and emotional part of human health. Good mental health suggests good cognitive, behavioral, and emotional wellbeing. The following mental health research topics will provide multiple avenues for students to base their research topics on:
- The relationship between depression and weight loss
- The rise of eating disorders in teenagers and adolescents
- The glamorization of mental illness in modern media
- Why is it still somewhat taboo to speak openly about mental health?
- The lasting psychological trauma of rape
- PTSD in modern-day youth
- How positive portrayals of mental illness in movies have helped destigmatize it
- Violence in video games and violence in real life: is there a link between the two?
- The effects of victim-blaming on rape victims
- Is mental illness hereditary?
- why mental health education is relevant in our society
- ADHD in adults: regular, or a problem?
- Harmful misconceptions about OCD
- The relationship between physical health and mental wellness
- Is postpartum depression a modern illness?
- Why is a bipolar disorder more than a mood swing disorder
- The relationship between childhood bullying and self-esteem issues in adults
- Is mental illness more prevalent in men or women?
- Advances in mental health education and research in the last decade
- Living with mental health in the age of social media
- Mental health and Nollywood: a study of mental illness portrayal in Nollywood
- Mental health and social media: how social media has helped to destigmatize mental illness
- Why schools should have functioning guidance counselors for students and teachers
- The importance of including mental health topics in the school curriculum
- The need to create safe spaces for people living with mental health issues.
Mental Health Topics To Write About
Your mental health deals with several health disorders, including mood disorders, anxiety disorders, eating disorders, and personality disorders. In case your mental health research topics are based on the categorical aspects of mental health, the following are research topics on mental health that you can write about:
- What is mental health?
- Destigmatizing mental health discussions
- Mental health education in Nigerian societies
- Can exposure to violent games and movies cause people to become killers?
- Are sociopaths born or made?
- The importance of self-affirmation to goal achievement
- Why therapy isn’t only for the mentally ill
- Why you have to love yourself to be able to receive love from others
- Living with social anxiety
- Overcoming low self-esteem
- Why OCD is not just about an obsession with keeping things clean
- How self-loathing makes us self-destructive
- The benefits of mental health support groups
- How to handle bullying when your child is the aggressor
- Why do we need time for ourselves
- Is your friend group toxic?
- On low self-esteem and managing relationships
- Why it’s insensitive to refer to the mentally ill as crazy
- Why do we sometimes feel unloved?
- Why it is helpful to have supportive friends and family when going through a hard time
- Medically proven ways to deal with a constant depressive episode
- Why depression pills should be regulated
- Why everyone needs access to pills to relax anxiety
- The importance of antidepressants to neurotics
- How to successfully manage the challenges of living with mental health challenges
Mental Illness Research Paper Topics
Mental illness is a range of mental conditions that affect the mind, how we think, our behaviors. If you’ve been looking for the best mental illness research paper topics, your search stops here. Find below mental illness topics to help with your research:
- The difference between depression and sadness
- Similarities between bipolar disorder
- Treating mental disorders using medication: a study on the pros and cons
- The effects of postpartum depression on family members
- The relationship between bullying and eating disorders
- Common misconceptions about mental illness
- Mental illness in the media: positive influence or harmful perpetuation of stereotypes?
- A study on serial killers: how their childhoods shaped who they became
- Self-esteem issues as a trigger for eating disorders
- A study on the compulsive nature of kleptomania
- A study on how movies shape our perception of mental illness
- Identifying signs and symptoms of sociopathy in children
- A study on the relationship between paranoia and impulsive actions
- The relationship between suicide and low self-esteem
- Genetics and mental illness: a study on mental illness in three generations of family members
- A study on how past traumatic events shape our present
- Why eating disorders are mental disorders
- The portrayal of mental illness in the media in the past fifty years
- Improvements in mental illness diagnosis and treatment in the past century
- Examining the effects of mental illness on the lives of teenagers: a qualitative study
- Examining the impacts of antidepressants in curbing depression
- A study into the root cause of mental health challenges in young adults
- Investigating the causes of mental illness in 80+ adults
- The lingering cases of mental health challenges in older people
- The need for the free accessibility of mental health facilities by students.
Research Topics In Psychiatry
Psychiatry is a vast field of study in medicine. Any psychiatry topics must make the research journey more straightforward. That said, the following are interesting topics in psychiatry:
- Defects of tobacco addiction on the human brain
- Treating schizophrenia: most effective ways
- ADHD: more prevalent in adults than children?
- Perfectionism and OCD: Where do we draw the line?
- Why we should look out for symptoms of depression
- How has the raid of COVID-19 affected the mental health of people?
- What are the factors that provoke depression?
- Bipolar disorders as symptoms of mental illness
- What is the potency of talk therapy in relating to suicidal patients
- Anxiety disorder: symptoms and remedies
- Practical measures in overcoming alcohol abuse in men
- Depression: cyberbullying as a tool for enhancing depressive tendencies in young adults
- The adverse effect of antidepressants on brain activities
- Genetics: A yardstick for determining mental health illness
- Lack of sleep as a tool for building anxiety
- Stress as a buildup for depression
- Side effects of psychiatric treatments on older people
- The effects of COVID-19 on brain activity
- Preventing the excessive usage of sedatives in young adults
- Aging as a measure of depression
- Treating mental illness: Applying classical soul music as a means in the 21st century
- Child mental disorders: curbing unhealthy family relationships
- Postpartum depression is the leading cause of mental illness amongst women
- A study on the distinction between Bipolar I and Bipolar II
- The need for the destigmatization of psychiatric patients
Research Topics In Mental Health Nursing
Mental health nursing is a highly essential field of study that should be considered:
- The challenges involved in psychiatric nursing care
- Mental health risks involved in working with psychiatric patients
- Merits and demerits of mental health nursing careers
- Self-discipline in psychiatry nursing fields
- Nursing ethics: what a nurse should know
- Approaches to nursing theories
- Talk therapy in nursing fields
- Dealing with exposed trauma: a typical nursing experience
- Psychiatry nursing: a walk in the park?
- Limitation of responsibilities by nurses on psychiatric patients
- The essence of skilled nurses in clinical psychology
- Effective patients’ recovery: the roles of nurses in present-day psychiatry
- Practical application of nursing experience in psychiatry wards
- Forbidden practices in nursing homes
- Is psychiatry nursing predominantly a woman’s job?
- Promoting nursing staff shortage in health sectors
- Evaluating anti stigmatization by nurses in psychiatric wards
- Damning effects of psychiatric nursing on nurses
- Mental health illness: are nurses exempted?
- Nursing practices applied in treating children and adults
- Helpful ways mental health nurses administer care to patients
- Ways care for mental health patients can be improved in the hospitals
- Effective ways of caring for mental health patients
- Why mental health nursing should be a specialized healthcare role
- Importance of mental health nursing
- Why mental health nursing should be prioritized as a specialist role
Critical Analysis Research Paper Topics In Mental Health
The following are some critically analyzed paper topics in mental health that will make your research more accessible and give more depth to your essay.
- Problems related to physical and mental health issues in men and women
- Supporting children’s mental health in the 21st century
- Bipolar disorder problem as a mental health challenge
- Mental health and eating disorders
- A mental health project: a research methodology on curbing mental illnesses
- Connecting poverty and mental health problems
- Mental health counseling: a way in the wilderness
- Mental health administration: a necessity in present-day lives
- Mental health and spirituality
- Effects of marijuana on mental health
- The critical role of school psychology in the mental health movement
- Code of ethics for mental health professions worldwide
- Mental health counselors: professionalism in workplaces
- Mental health benefits in the employee benefits packages
- Eliminating stigmatization in mental health diagnoses
- Community mental health as a tool for curbing disorders
- Mental health counselor: a much-needed remedy
- Mental health issues in the criminal justice system
- Refugees and their mental health
- Medical ethics in mental health care
- Child’s mental health and depression in adulthood: a qualitative study
- Transitions in late life: a typical study of mental health concerns
- Mental health nursing: health and illness
- Mental health specialist jobs and career
- Mental health: screening and assessment of nursing personnel
- The role of female mental health in socio-cultural conditions
- Schizophrenia: a dominant mental health disorder
- Mental health practice model for public institutions
- Mental health: research methodologies issues
- Mental health strategies at the workplace
Good Research Questions About Mental Health
Good research questions must be willing to provide concise and thorough answers. Over time, researchers have generated questions that border on mental health that have proven highly effective.
- Should the use of antidepressants be accessible to children?
- Why do people need access to mental health care?
- What is the importance of prioritizing mental health care?
- Is self-care the same as mental health care?
- Is there a correlation between self-care and mental health care?
- How to prioritize mental health
- The study of the growing mental health challenge amongst young adults
- Growth of depression in third-world countries
- The effects of poverty on mental health
- A study on the effects of mental health education on the treatment of the mentally ill
- Institutionalized bullying in schools and its effects on students’ mental health
- The importance of mother’s mental health in the aftermath of childbirth
- Addressing mental health problems in children below the age of ten
- The effects of sudden environmental changes on childrens’ mental health
- The focus on mental health in the wake of the covid-19 pandemic
- Harmful effects of social media on the mental health of Nigerian youth
- Fostering mental health discourse among males
- Trolling and cancel culture and their effects on the mental health of their victims
- The benefits of mental health apps in the lives of individuals
- Measures to promote mental health awareness in religious spheres
Mental Illness Thesis Ideas
By nature, there are several mental illness thesis ideas you can explore. The following are proven great thesis ideas that concern mental health.
- Addressing inadequate measures to combat mental illness in Nigerian societies
- A study on the marginalization of the mentally ill in the society
- Mental illness stigma and seeking help: how mental health stigma affects
- The effects of mental illness stigma in people’s seeking of treatment
- Embracing mental illness discourse in schools and the workplace
- Why mental illness is an illness and not a figment of the imagination
- The relationship between mental illness and violence
- The relationship between childhood abuse and mental illness
- The benefits of support systems to the mentally ill
- Mental illness and the perpetuation of gun violence among youth in the united states
- A study of mental illness portrayals in Nigerian media
- Mental illness portrayals in Nigerian media: harmful or beneficial?
- A study on the harmful effects of certain medications on mental disorders
- Tackling common misconceptions about mental disorders among members of the older generation
- Advancements in mental illness treatment methods
- Breakthroughs in mental illness research in the 50s and 60s
- A study on ethically questionable mental health research experiments in the last 50 years
- Living with mental illness in the age of toxic internet culture
- The increase in cases of depression and anxiety in youths between the early 2000s and late 2010s
- Mental illness and criminality: a study on the relationship between the two
- Drug abuse: a study on how college students engage in drugs
- A study of the nicotine content of harmful drugs
- A critical study of the early stage of mental illness in patients.
Need Help With Your Thesis?
Suppose you are a college or university student who needs high-level advanced psychology dissertation help in preparing for your thesis deadlines and require thesis help from experts in this field. Be assured that we have professional writers online who are professors, teachers, and native writers from various fields. They can assist you in preparing high-quality research works, proofreading, editing, and writing services, all at a cheap rate. You can be sure of custom-written works that will secure you high grades.
Make PhD experience your own
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Program Finder
- Admissions Services
- Course Directory
- Academic Calendar
- Hybrid Campus
- Lecture Series
- Convocation
- Strategy and Development
- Implementation and Impact
- Integrity and Oversight
- In the School
- In the Field
- In Baltimore
- Resources for Practitioners
- Articles & News Releases
- In The News
- Statements & Announcements
- At a Glance
- Student Life
- Strategic Priorities
- Inclusion, Diversity, Anti-Racism, and Equity (IDARE)
- What is Public Health?
Research and Practice
- Mental Health Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Origins of Mental Health
- Job Openings
- Faculty Profiles
- PET Alumni Profiles - Postdocs
- PET Alumni Profiles - Predocs
- Trainee Profiles
- NIMH T32 Mental Health Services and Systems Training Grant
- Funded Training Program in Data Integration for Causal Inference in Behavioral Health
- Aging and Dementia Funded Training Program
- COVID-19 and Mental Health Research
- Mental Health Resources During COVID-19
- News and Media
Social Determinants of Mental and Behavioral Health
- Our Work in Action
- Global Mental Health
- Related Faculty
- Courses of Interest
- Training and Funding Opportunities
- Mental Health in the Workplace: A Public Health Summit
Autism and Developmental Disabilities
- Alumni Newsletters
- Alumni Updates
- Postdoctoral Fellows
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) Students in Mental Health
- Master of Health Science (MHS) Students in Mental Health
- In the News
- Past Seminars 2020-21 AY: Wednesday Seminar Series
- Make a Gift
- Available Datasets
Research Areas
The Department of Mental Health covers a wide array of topics related to mental health, mental illness, and substance abuse. We emphasize ongoing research that enriches and stimulates the teaching programs. All students and fellows are encouraged to participate in at least one research group. Faculty and students from multiple disciplines work together within and across several major research areas:
Faculty are working to understand the distribution, causes and consequences of autism and developmental disabilities as well as the impact of public health policy on children and families.
Global Mental Health faculty develop, implement and evaluate measures and interventions to assess and meet mental health needs of communities around the world, with a focus on developing nations.
Mental Health and Aging
Faculty in the Mental Health and Aging Research Area conduct observational and intervention research aimed at enhancing cognitive and mental well being in older adults.
Mental Health and COVID-19
Understanding how mental health evolves as a result of this serious global pandemic will inform prevention and treatment strategies moving forward.
Mental Health in the Workplace
At the Bloomberg School of Public Health, which houses the only department of mental health in a school of public health, we have a unique ability to define both the problems and potential solutions.
Mental Health Services and Policy
Faculty in this area study mental health and behavioral health services and supports in communities, educational institutions and employment settings. They aim to reduce risk, and provide effective long-term treatment.
The Methods program area develops and applies innovative qualitative and quantitative methods for public mental health research, with a focus on statistical methods and economic models.
Prevention Research
The Prevention Research faculty develop, test, refine and bring to scale prevention programs directed at a range of mental health and behavioral problems in children, adolescents, adults and the elderly.
Psychiatric and Behavioral Genetic Epidemiology
Faculty in this area research genetic factors and how they interact with the physical and social environment to affect the risk for mental disorders.
Psychiatric Epidemiology
Faculty in this area study the occurrence and distribution of mental and behavioral disorders across people, space and time, and examine the causes to develop support and treatment strategies.
School-based Mental Health
The Department of Mental Health views the education and schools as a key public health context. Multiple faculty members partner with local school systems to develop, refine, and test preventive interventions for school-aged children and aim to promote mental health as well as positive social, emotional, and behavioral development.
Social Determinants of Mental & Behavioral Health Area emphasizes the role of multilevel social and structural factors in shaping mental and behavioral health, such as stigma, social networks, structural racism and policies on housing, drug control, and criminal justice domestically and internationally.
Substance Use Epidemiology
Faculty in this area study the etiology and natural history of substance use, and develop and evaluate interventions to prevent and control substance use disorders.
The Department of Mental Health has projects focused on various aspects of violence such as suicide, intimate partner violence , and youth violence. Faculty and students from multiple disciplines work together within and across several major research areas.
Centers and Institutes
The department houses several school-based centers, and has a significant role in many others across the school. These are described below. Centers help bring together faculty, students, and community partners across multiple departments and schools to meet their particular missions in pursuit of improving public mental health.
- Moore Center for the Prevention of Child Sexual Abuse
- Wendy Klag Center for Autism and Developmental Disabilities
- Center on Aging and Health
- Center for Mental Health and Addiction Policy Research
- Suicide Prevention
Our Students and Faculty Work in Action
The Johns Hopkins COVID-19 Mental Health Measurement Working Group developed key questions to add to existing large domestic and international surveys to measure the mental health impact of the pandemic.

Insights in Public Mental Health: 2022
Loading... Editorial 08 February 2024 Editorial: Insights in public mental health: 2022 Wulf Rössler 698 views 0 citations
Original Research 05 September 2023 The Columbia-suicide severity rating scale: validity and psychometric properties of an online Spanish-language version in a Mexican population sample Fernando Austria-Corrales , 11 more and Igor Galynker 982 views 0 citations
Review 23 June 2023 Indigenous mental healthcare and human rights abuses in Nigeria: The role of cultural syntonicity and stigmatization Adegboyega Ogunwale , 1 more and Oladayo Bifarin 3,186 views 1 citations
Original Research 02 March 2023 Psychological distress, intimate partner violence and substance use in a representative sample from Mexico: A structural equation model Paola Adanari Ortega Ceballos , 4 more and Berenice Pérez Amezcua 1,261 views 0 citations
Perspective 28 February 2023 Trans-diagnostic determinants of psychotherapeutic treatment response: The pressing need and new opportunities for a more systematic way of selecting psychotherapeutic treatment in the age of virtual service delivery Barna Konkolÿ Thege , 2 more and Kathleen D. Askland 815 views 0 citations
Loading... Original Research 23 February 2023 Time trends in mental health indicators in Germany's adult population before and during the COVID-19 pandemic Elvira Mauz , 9 more and Julia Thom 13,234 views 20 citations
Original Research 13 February 2023 Treatment with Soteria-elements in acute psychiatry—Effectiveness for acutely ill and voluntarily treated patients Philine Fabel , 3 more and Maria C. Jockers-Scherübl 937 views 0 citations
Original Research 20 January 2023 Assessing perceptions of resilience: The understanding from network analysis Rong Liu and Wenjie Duan 1,786 views 2 citations
Original Research 22 December 2022 Reach and perceived effectiveness of a community-led active outreach postvention intervention for people bereaved by suicide Nicole T. M. Hill , 8 more and Ashleigh Lin 2,269 views 0 citations
Original Research 15 December 2022 Attitudes toward the pandemic and COVID-19 vaccination intention among German university students and the general population: Results from two cross-sectional surveys Sabrina Baldofski , 5 more and Christine Rummel-Kluge 828 views 3 citations
Original Research 14 December 2022 Sleep disturbances, depressive symptoms, and cognitive efficiency as determinants of mistakes at work in shift and non-shift workers Hyewon Yeo , 5 more and Seog Ju Kim 1,616 views 4 citations
Perspective 06 December 2022 The wellbeing pandemic: Outline of a contested terrain and a proposed research agenda Steven J. Jackson , 2 more and Daniel Porter 3,065 views 0 citations
Perspective 04 November 2022 Recent developments on psychological factors in medically unexplained symptoms and somatoform disorders Ricarda Mewes 3,091 views 6 citations
Original Research 28 October 2022 Prevalence and characteristics of registered falls in a Belgian University Psychiatric Hospital Lynn de Smet , 5 more and Marc De Hert 1,585 views 3 citations
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Browse Articles
The impact of mindfulness apps on psychological processes of change: a systematic review
- Natalia Macrynikola
- John Torous
Mental health and psychosocial interventions in the context of climate change: a scoping review
- Alessandro Massazza
- Emma L. Lawrance
Mental health outcomes, literacy and service provision in low- and middle-income settings: a systematic review of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Kayonda Hubert Ngamaba
- Laddy Sedzo Lombo
- Cheyann Heap
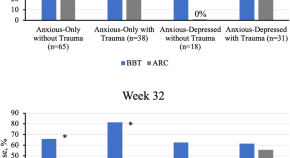
Impact of trauma exposure and depression comorbidity on response to transdiagnostic behavioral therapy for pediatric anxiety and depression
- Felix Angulo
- Pauline Goger
- V. Robin Weersing
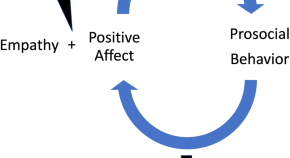
The effect of psilocybin on empathy and prosocial behavior: a proposed mechanism for enduring antidepressant effects
- Kush V. Bhatt
- Cory R. Weissman
Author Correction: Loneliness and suicide mitigation for students using GPT3-enabled chatbots
- Bethanie Maples
- Merve Cerit
Natural language processing of multi-hospital electronic health records for public health surveillance of suicidality
- Ariel Cohen
- Richard Delorme
Association between continuity of care and attendance of post-discharge follow-up after psychiatric emergency presentation
- Ben Hoi-Ching Wong
- Petrina Chu
- Dennis Ougrin
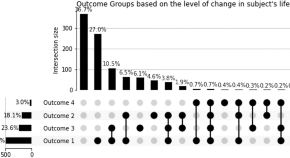

Loneliness and suicide mitigation for students using GPT3-enabled chatbots
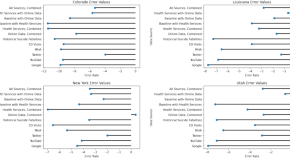
Predicting state level suicide fatalities in the united states with realtime data and machine learning
- Devashru Patel
- Steven A. Sumner
- Munmun De Choudhury
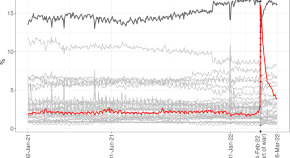
Effects of stress on pain in females using a mobile health app in the Russia-Ukraine conflict
- Aliaksandr Kazlou
- Kateryna Bornukova
- Sarah Garfinkel
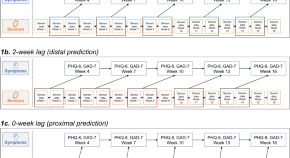
Differential temporal utility of passively sensed smartphone features for depression and anxiety symptom prediction: a longitudinal cohort study
- Caitlin A. Stamatis
- Jonah Meyerhoff
- David C. Mohr
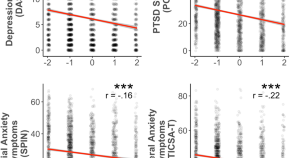
Specific topics, specific symptoms: linking the content of recurrent involuntary memories to mental health using computational text analysis
- Ryan C. Yeung
- Myra A. Fernandes
Investigating the reciprocity between cognition and behavior in adaptation to large-scale disasters
- Tiffany Junchen Tao
- Wai Kai Hou
A systematic review on automated clinical depression diagnosis
- Kaining Mao
Managing expectations with psychedelic microdosing
Microdosing psychedelics is a growing practice among recreational users, claimed to improve several aspects of mental health, with little supporting empirical research. In this comment, we highlight the potential role of expectations and confirmation bias underlying therapeutic effects of microdosing, and suggest future avenues of research to address this concern.
- Omer A. Syed
- Benjamin Tsang
Technical and clinical considerations for electroencephalography-based biomarkers for major depressive disorder
- Leif Simmatis
- Emma E. Russo
- Nardin Samuel

Natural language processing analysis of the psychosocial stressors of mental health disorders during the pandemic
- María P. Raveau
- Julián I. Goñi
- Susana Eyheramendy
Systematic review of machine learning in PTSD studies for automated diagnosis evaluation

An automatic speech analytics program for digital assessment of stress burden and psychosocial health
- Amanda M. Y. Chu
- Benson S. Y. Lam
- Mike K. P. So
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychiatry
Mental Health Prevention and Promotion—A Narrative Review
Associated data.
Extant literature has established the effectiveness of various mental health promotion and prevention strategies, including novel interventions. However, comprehensive literature encompassing all these aspects and challenges and opportunities in implementing such interventions in different settings is still lacking. Therefore, in the current review, we aimed to synthesize existing literature on various mental health promotion and prevention interventions and their effectiveness. Additionally, we intend to highlight various novel approaches to mental health care and their implications across different resource settings and provide future directions. The review highlights the (1) concept of preventive psychiatry, including various mental health promotions and prevention approaches, (2) current level of evidence of various mental health preventive interventions, including the novel interventions, and (3) challenges and opportunities in implementing concepts of preventive psychiatry and related interventions across the settings. Although preventive psychiatry is a well-known concept, it is a poorly utilized public health strategy to address the population's mental health needs. It has wide-ranging implications for the wellbeing of society and individuals, including those suffering from chronic medical problems. The researchers and policymakers are increasingly realizing the potential of preventive psychiatry; however, its implementation is poor in low-resource settings. Utilizing novel interventions, such as mobile-and-internet-based interventions and blended and stepped-care models of care can address the vast mental health need of the population. Additionally, it provides mental health services in a less-stigmatizing and easily accessible, and flexible manner. Furthermore, employing decision support systems/algorithms for patient management and personalized care and utilizing the digital platform for the non-specialists' training in mental health care are valuable additions to the existing mental health support system. However, more research concerning this is required worldwide, especially in the low-and-middle-income countries.
Introduction
Mental disorder has been recognized as a significant public health concern and one of the leading causes of disability worldwide, particularly with the loss of productive years of the sufferer's life ( 1 ). The Global Burden of Disease report (2019) highlights an increase, from around 80 million to over 125 million, in the worldwide number of Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) attributable to mental disorders. With this surge, mental disorders have moved into the top 10 significant causes of DALYs worldwide over the last three decades ( 2 ). Furthermore, this data does not include substance use disorders (SUDs), which, if included, would increase the estimated burden manifolds. Moreover, if the caregiver-related burden is accounted for, this figure would be much higher. Individual, social, cultural, political, and economic issues are critical mental wellbeing determinants. An increasing burden of mental diseases can, in turn, contribute to deterioration in physical health and poorer social and economic growth of a country ( 3 ). Mental health expenditure is roughly 3–4% of their Gross Domestic Products (GDPs) in developed regions of the world; however, the figure is abysmally low in low-and-middle-income countries (LMICs) ( 4 ). Untreated mental health and behavioral problems in childhood and adolescents, in particular, have profound long-term social and economic adverse consequences, including increased contact with the criminal justice system, lower employment rate and lesser wages among those employed, and interpersonal difficulties ( 5 – 8 ).
Need for Mental Health (MH) Prevention
Longitudinal studies suggest that individuals with a lower level of positive wellbeing are more likely to acquire mental illness ( 9 ). Conversely, factors that promote positive wellbeing and resilience among individuals are critical in preventing mental illnesses and better outcomes among those with mental illness ( 10 , 11 ). For example, in patients with depressive disorders, higher premorbid resilience is associated with earlier responses ( 12 ). On the contrary, patients with bipolar affective- and recurrent depressive disorders who have a lower premorbid quality of life are at higher risk of relapses ( 13 ).
Recently there has been an increased emphasis on the need to promote wellbeing and positive mental health in preventing the development of mental disorders, for poor mental health has significant social and economic implications ( 14 – 16 ). Research also suggests that mental health promotion and preventative measures are cost-effective in preventing or reducing mental illness-related morbidity, both at the society and individual level ( 17 ).
Although the World Health Organization (WHO) defines health as “a state of complete physical, mental, and social wellbeing and not merely an absence of disease or infirmity,” there has been little effort at the global level or stagnation in implementing effective mental health services ( 18 ). Moreover, when it comes to the research on mental health (vis-a-viz physical health), promotive and preventive mental health aspects have received less attention vis-a-viz physical health. Instead, greater emphasis has been given to the illness aspect, such as research on psychopathology, mental disorders, and treatment ( 19 , 20 ). Often, physicians and psychiatrists are unfamiliar with various concepts, approaches, and interventions directed toward mental health promotion and prevention ( 11 , 21 ).
Prevention and promotion of mental health are essential, notably in reducing the growing magnitude of mental illnesses. However, while health promotion and disease prevention are universally regarded concepts in public health, their strategic application for mental health promotion and prevention are often elusive. Furthermore, given the evidence of substantial links between psychological and physical health, the non-incorporation of preventive mental health services is deplorable and has serious ramifications. Therefore, policymakers and health practitioners must be sensitized about linkages between mental- and physical health to effectively implement various mental health promotive and preventive interventions, including in individuals with chronic physical illnesses ( 18 ).
The magnitude of the mental health problems can be gauged by the fact that about 10–20% of young individuals worldwide experience depression ( 22 ). As described above, poor mental health during childhood is associated with adverse health (e.g., substance use and abuse), social (e.g., delinquency), academic (e.g., school failure), and economic (high risk of poverty) adverse outcomes in adulthood ( 23 ). Childhood and adolescence are critical periods for setting the ground for physical growth and mental wellbeing ( 22 ). Therefore, interventions promoting positive psychology empower youth with the life skills and opportunities to reach their full potential and cope with life's challenges. Comprehensive mental health interventions involving families, schools, and communities have resulted in positive physical and psychological health outcomes. However, the data is limited to high-income countries (HICs) ( 24 – 28 ).
In contrast, in low and middle-income countries (LMICs) that bear the greatest brunt of mental health problems, including massive, coupled with a high treatment gap, such interventions remained neglected in public health ( 29 , 30 ). This issue warrants prompt attention, particularly when global development strategies such as Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) realize the importance of mental health ( 31 ). Furthermore, studies have consistently reported that people with socioeconomic disadvantages are at a higher risk of mental illness and associated adverse outcomes; partly, it is attributed to the inequitable distribution of mental health services ( 32 – 35 ).
Scope of Mental Health Promotion and Prevention in the Current Situation
Literature provides considerable evidence on the effectiveness of various preventive mental health interventions targeting risk and protective factors for various mental illnesses ( 18 , 36 – 42 ). There is also modest evidence of the effectiveness of programs focusing on early identification and intervention for severe mental diseases (e.g., schizophrenia and psychotic illness, and bipolar affective disorders) as well as common mental disorders (e.g., anxiety, depression, stress-related disorders) ( 43 – 46 ). These preventive measures have also been evaluated for their cost-effectiveness with promising findings. In addition, novel interventions such as digital-based interventions and novel therapies (e.g., adventure therapy, community pharmacy program, and Home-based Nurse family partnership program) to address the mental health problems have yielded positive results. Likewise, data is emerging from LMICs, showing at least moderate evidence of mental health promotion intervention effectiveness. However, most of the available literature and intervention is restricted mainly to the HICs ( 47 ). Therefore, their replicability in LMICs needs to be established and, also, there is a need to develop locally suited interventions.
Fortunately, there has been considerable progress in preventive psychiatry over recent decades, including research on it. In the light of these advances, there is an accelerated interest among researchers, clinicians, governments, and policymakers to harness the potentialities of the preventive strategies to improve the availability, accessibility, and utility of such services for the community.
The Concept of Preventive Psychiatry
Origins of preventive psychiatry.
The history of preventive psychiatry can be traced back to the early 1900's with the foundation of the national mental health association (erstwhile mental health association), the committee on mental hygiene in New York, and the mental health hygiene movement ( 48 ). The latter emphasized the need for physicians to develop empathy and recognize and treat mental illness early, leading to greater awareness about mental health prevention ( 49 ). Despite that, preventive psychiatry remained an alien concept for many, including mental health professionals, particularly when the etiology of most psychiatric disorders was either unknown or poorly understood. However, recent advances in our understanding of the phenomena underlying psychiatric disorders and availability of the neuroimaging and electrophysiological techniques concerning mental illness and its prognosis has again brought the preventive psychiatry in the forefront ( 1 ).
Levels of Prevention
The literal meaning of “prevention” is “the act of preventing something from happening” ( 50 ); the entity being prevented can range from the risk factors of the development of the illness, the onset of illness, or the recurrence of the illness or associated disability. The concept of prevention emerged primarily from infectious diseases; measures like mass vaccination and sanitation promotion have helped prevent the development of the diseases and subsequent fatalities. The original preventive model proposed by the Commission on Chronic Illness in 1957 included primary, secondary, and tertiary preventions ( 48 ).
The Concept of Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Prevention
The stages of prevention target distinct aspects of the illness's natural course; the primary prevention acts at the stage of pre-pathogenesis, that is, when the disease is yet to occur, whereas the secondary and tertiary prevention target the phase after the onset of the disease ( 51 ). Primary prevention includes health promotion and specific protection, while secondary and tertairy preventions include early diagnosis and treatment and measures to decrease disability and rehabilitation, respectively ( 51 ) ( Figure 1 ).

The concept of primary and secondary prevention [adopted from prevention: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary by Bauman et al. ( 51 )].
The primary prevention targets those individuals vulnerable to developing mental disorders and their consequences because of their bio-psycho-social attributes. Therefore, it can be viewed as an intervention to prevent an illness, thereby preventing mental health morbidity and potential social and economic adversities. The preventive strategies under it usually target the general population or individuals at risk. Secondary and tertiary prevention targets those who have already developed the illness, aiming to reduce impairment and morbidity as soon as possible. However, these measures usually occur in a person who has already developed an illness, therefore facing related suffering, hence may not always be successful in curing or managing the illness. Thus, secondary and tertiary prevention measures target the already exposed or diagnosed individuals.
The Concept of Universal, Selective, and Indicated Prevention
The classification of health prevention based on primary/secondary/tertiary prevention is limited in being highly centered on the etiology of the illness; it does not consider the interaction between underlying etiology and risk factors of an illness. Gordon proposed another model of prevention that focuses on the degree of risk an individual is at, and accordingly, the intensity of intervention is determined. He has classified it into universal, selective, and indicated prevention. A universal preventive strategy targets the whole population irrespective of individual risk (e.g., maintaining healthy, psychoactive substance-free lifestyles); selective prevention is targeted to those at a higher risk than the general population (socio-economically disadvantaged population, e.g., migrants, a victim of a disaster, destitute, etc.). The indicated prevention aims at those who have established risk factors and are at a high risk of getting the disease (e.g., family history of psychiatric illness, history of substance use, certain personality types, etc.). Nevertheless, on the other hand, these two classifications (the primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention; and universal, selective, and indicated prevention) have been intended for and are more appropriate for physical illnesses with a clear etiology or risk factors ( 48 ).
In 1994, the Institute of Medicine (IOM) Committee on Prevention of Mental Disorders proposed a new paradigm that classified primary preventive measures for mental illnesses into three categories. These are indicated, selected, and universal preventive interventions (refer Figure 2 ). According to this paradigm, primary prevention was limited to interventions done before the onset of the mental illness ( 48 ). In contrast, secondary and tertiary prevention encompasses treatment and maintenance measures ( Figure 2 ).

The interventions for mental illness as classified by the Institute of Medicine (IOM) Committee on Prevention of Mental Disorders [adopted from Mrazek and Haggerty ( 48 )].
Although the boundaries between prevention and treatment are often more overlapping than being exclusive, the new paradigm can be used to avoid confusion stemming from the common belief that prevention can take place at all parts of mental health management ( 48 ). The onset of mental illnesses can be prevented by risk reduction interventions, which can involve reducing risk factors in an individual and strengthening protective elements in them. It aims to target modifiable factors, both risk, and protective factors, associated with the development of the illness through various general and specific interventions. These interventions can work across the lifespan. The benefits are not restricted to reduction or delay in the onset of illness but also in terms of severity or duration of illness ( 48 ).On the spectrum of mental health interventions, universal preventive interventions are directed at the whole population without identifiable risk factors. The interventions are beneficial for the general population or sub-groups. Prenatal care and childhood vaccination are examples of preventative measures that have benefited both physical and mental health. Selective preventive mental health interventions are directed at people or a subgroup with a significantly higher risk of developing mental disorders than the general population. Risk groups are those who, because of their vulnerabilities, are at higher risk of developing mental illnesses, e.g., infants with low-birth-weight (LBW), vulnerable children with learning difficulties or victims of maltreatment, elderlies, etc. Specific interventions are home visits and new-born day care facilities for LBW infants, preschool programs for all children living in resource-deprived areas, support groups for vulnerable elderlies, etc. Indicated preventive interventions focus on high-risk individuals who have developed minor but observable signs or symptoms of mental disorder or genetic risk factors for mental illness. However, they have not fulfilled the criteria of a diagnosable mental disorder. For instance, the parent-child interaction training program is an indicated prevention strategy that offers support to children whose parents have recognized them as having behavioral difficulties.
The overall objective of mental health promotion and prevention is to reduce the incidence of new cases, additionally delaying the emergence of mental illness. However, promotion and prevention in mental health complement each other rather than being mutually exclusive. Moreover, combining these two within the overall public health framework reduces stigma, increases cost-effectiveness, and provides multiple positive outcomes ( 18 ).
How Prevention in Psychiatry Differs From Other Medical Disorders
Compared to physical illnesses, diagnosing a mental illness is more challenging, particularly when there is still a lack of objective assessment methods, including diagnostic tools and biomarkers. Therefore, the diagnosis of mental disorders is heavily influenced by the assessors' theoretical perspectives and subjectivity. Moreover, mental illnesses can still be considered despite an individual not fulfilling the proper diagnostic criteria led down in classificatory systems, but there is detectable dysfunction. Furthermore, the precise timing of disorder initiation or transition from subclinical to clinical condition is often uncertain and inconclusive ( 48 ). Therefore, prevention strategies are well-delineated and clear in the case of physical disorders while it's still less prevalent in mental health parlance.
Terms, Definitions, and Concepts
The terms mental health, health promotion, and prevention have been differently defined and interpreted. It is further complicated by overlapping boundaries of the concept of promotion and prevention. Some commonly used terms in mental health prevention have been tabulated ( Table 1 ) ( 18 ).
Commonly used terms in mental health prevention.
Mental Health Promotion and Protection
The term “mental health promotion” also has definitional challenges as it signifies different things to different individuals. For some, it means the treatment of mental illness; for others, it means preventing the occurrence of mental illness; while for others, it means increasing the ability to manage frustration, stress, and difficulties by strengthening one's resilience and coping abilities ( 54 ). It involves promoting the value of mental health and improving the coping capacities of individuals rather than amelioration of symptoms and deficits.
Mental health promotion is a broad concept that encompasses the entire population, and it advocates for a strengths-based approach and tries to address the broader determinants of mental health. The objective is to eliminate health inequalities via empowerment, collaboration, and participation. There is mounting evidence that mental health promotion interventions improve mental health, lower the risk of developing mental disorders ( 48 , 55 , 56 ) and have socioeconomic benefits ( 24 ). In addition, it strives to increase an individual's capacity for psychosocial wellbeing and adversity adaptation ( 11 ).
However, the concepts of mental health promotion, protection, and prevention are intrinsically linked and intertwined. Furthermore, most mental diseases result from complex interaction risk and protective factors instead of a definite etiology. Facilitating the development and timely attainment of developmental milestones across an individual's lifespan is critical for positive mental health ( 57 ). Although mental health promotion and prevention are essential aspects of public health with wide-ranging benefits, their feasibility and implementation are marred by financial and resource constraints. The lack of cost-effectiveness studies, particularly from the LMICs, further restricts its full realization ( 47 , 58 , 59 ).
Despite the significance of the topic and a considerable amount of literature on it, a comprehensive review is still lacking that would cover the concept of mental health promotion and prevention and simultaneously discusses various interventions, including the novel techniques delivered across the lifespan, in different settings, and level of prevention. Therefore, this review aims to analyze the existing literature on various mental health promotion and prevention-based interventions and their effectiveness. Furthermore, its attempts to highlight the implications of such intervention in low-resource settings and provides future directions. Such literature would add to the existing literature on mental health promotion and prevention research and provide key insights into the effectiveness of such interventions and their feasibility and replicability in various settings.
Methodology
For the current review, key terms like “mental health promotion,” OR “protection,” OR “prevention,” OR “mitigation” were used to search relevant literature on Google Scholar, PubMed, and Cochrane library databases, considering a time period between 2000 to 2019 ( Supplementary Material 1 ). However, we have restricted our search till 2019 for non-original articles (reviews, commentaries, viewpoints, etc.), assuming that it would also cover most of the original articles published until then. Additionally, we included original papers from the last 5 years (2016–2021) so that they do not get missed out if not covered under any published review. The time restriction of 2019 for non-original articles was applied to exclude papers published during the Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic as the latter was a significant event, bringing about substantial change and hence, it warranted a different approach to cater to the MH needs of the population, including MH prevention measures. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in the flooding of novel interventions for mental health prevention and promotion, specifically targeting the pandemic and its consequences, which, if included, could have biased the findings of the current review on various MH promotion and prevention interventions.
A time frame of about 20 years was taken to see the effectiveness of various MH promotion and protection interventions as it would take substantial time to be appreciated in real-world situations. Therefore, the current paper has put greater reliance on the review articles published during the last two decades, assuming that it would cover most of the original articles published until then.
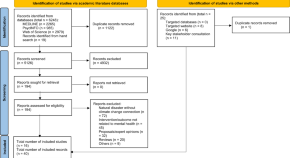
The above search yielded 320 records: 225 articles from Google scholar, 59 articles from PubMed, and 36 articles from the Cochrane database flow-diagram of records screening. All the records were title/abstract screened by all the authors to establish the suitability of those records for the current review; a bibliographic- and gray literature search was also performed. In case of any doubts or differences in opinion, it was resolved by mutual discussion. Only those articles directly related to mental health promotion, primary prevention, and related interventions were included in the current review. In contrast, records that discussed any specific conditions/disorders (post-traumatic stress disorders, suicide, depression, etc.), specific intervention (e.g., specific suicide prevention intervention) that too for a particular population (e.g., disaster victims) lack generalizability in terms of mental health promotion or prevention, those not available in the English language, and whose full text was unavailable were excluded. The findings of the review were described narratively.
Interventions for Mental Health Promotion and Prevention and Their Evidence
Various interventions have been designed for mental health promotion and prevention. They are delivered and evaluated across the regions (high-income countries to low-resource settings, including disaster-affiliated regions of the world), settings (community-based, school-based, family-based, or individualized); utilized different psychological constructs and therapies (cognitive behavioral therapy, behavioral interventions, coping skills training, interpersonal therapies, general health education, etc.); and delivered by different professionals/facilitators (school-teachers, mental health professionals or paraprofessionals, peers, etc.). The details of the studies, interventions used, and outcomes have been provided in Supplementary Table 1 . Below we provide the synthesized findings of the available research.
The majority of the available studies were quantitative and experimental. Randomized controlled trials comprised a sizeable proportion of the studies; others were quasi-experimental studies and, a few, qualitative studies. The studies primarily focussed on school students or the younger population, while others were explicitly concerned with the mental health of young females ( 60 ). Newer data is emerging on mental health promotion and prevention interventions for elderlies (e.g., dementia) ( 61 ). The majority of the research had taken a broad approach to mental health promotion ( 62 ). However, some studies have focused on universal prevention ( 63 , 64 ) or selective prevention ( 65 – 68 ). For instance, the Resourceful Adolescent Program (RAPA) was implemented across the schools and has utilized cognitive-behavioral and interpersonal therapies and reported a significant improvement in depressive symptoms. Some of the interventions were directed at enhancing an individual's characteristics like resilience, behavior regulation, and coping skills (ZIPPY's Friends) ( 69 ), while others have focused on the promotion of social and emotional competencies among the school children and attempted to reduce the gap in such competencies across the socio-economic classes (“Up” program) ( 70 ) or utilized expressive abilities of the war-affected children (Writing for Recover (WfR) intervention) ( 71 ) to bring about an improvement in their psychological problems (a type of selective prevention) ( 62 ) or harnessing the potential of Art, in the community-based intervention, to improve self-efficacy, thus preventing mental disorders (MAD about Art program) ( 72 ). Yet, others have focused on strengthening family ( 60 , 73 ), community relationships ( 62 ), and targeting modifiable risk factors across the life course to prevent dementia among the elderlies and also to support the carers of such patients ( 61 ).
Furthermore, more of the studies were conducted and evaluated in the developed parts of the world, while emerging economies, as anticipated, far lagged in such interventions or related research. The interventions that are specifically adapted for local resources, such as school-based programs involving paraprofessionals and teachers in the delivery of mental health interventions, were shown to be more effective ( 62 , 74 ). Likewise, tailored approaches for low-resource settings such as LMICs may also be more effective ( 63 ). Some of these studies also highlight the beneficial role of a multi-dimensional approach ( 68 , 75 ) and interventions targeting early lifespan ( 76 , 77 ).
Newer Insights: How to Harness Digital Technology and Novel Methods of MH Promotion and Protection
With the advent of digital technology and simultaneous traction on mental health promotion and prevention interventions, preventive psychiatrists and public health experts have developed novel techniques to deliver mental health promotive and preventive interventions. These encompass different settings (e.g., school, home, workplace, the community at large, etc.) and levels of prevention (universal, selective, indicated) ( 78 – 80 ).
The advanced technologies and novel interventions have broadened the scope of MH promotion and prevention, such as addressing the mental health issues of individuals with chronic medical illness ( 81 , 82 ), severe mental disorders ( 83 ), children and adolescents with mental health problems, and geriatric population ( 78 ). Further, it has increased the accessibility and acceptability of such interventions in a non-stigmatizing and tailored manner. Moreover, they can be integrated into the routine life of the individuals.
For instance, Internet-and Mobile-based interventions (IMIs) have been utilized to monitor health behavior as a form of MH prevention and a stand-alone self-help intervention. Moreover, the blended approach has expanded the scope of MH promotive and preventive interventions such as face-to-face interventions coupled with remote therapies. Simultaneously, it has given way to the stepped-care (step down or step-up care) approach of treatment and its continuation ( 79 ). Also, being more interactive and engaging is particularly useful for the youth.
The blended model of care has utilized IMIs to a varying degree and at various stages of the psychological interventions. This includes IMIs as a supplementary approach to the face-to-face-interventions (FTFI), FTFI augmented by behavior intervention technologies (BITs), BITs augmented by remote human support, and fully automated BITs ( 84 ).
The stepped care model of mental health promotion and prevention strategies includes a stepped-up approach, wherein BITs are utilized to manage the prodromal symptoms, thereby preventing the onset of the full-blown episode. In the Stepped-down approach, the more intensive treatments (in-patient or out-patient based interventions) are followed and supplemented with the BITs to prevent relapse of the mental illness, such as for previously admitted patients with depression or substance use disorders ( 85 , 86 ).
Similarly, the latest research has developed newer interventions for strengthening the psychological resilience of the public or at-risk individuals, which can be delivered at the level of the home, such as, e.g., nurse family partnership program (to provide support to the young and vulnerable mothers and prevent childhood maltreatment) ( 87 ); family healing together program aimed at improving the mental health of the family members living with persons with mental illness (PwMI) ( 88 ). In addition, various novel interventions for MH promotion and prevention have been highlighted in the Table 2 .
Depiction of various novel mental health promotion and prevention strategies.
a/w, associated with; A-V, audio-visual; b/w, between; CBT, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy; CES-Dep., Center for Epidemiologic Studies-Depression scale; CG, control group; FU, follow-up; GAD, generalized anxiety disorders-7; IA, intervention arm; HCWs, Health Care Workers; LMIC, low and middle-income countries; MDD, major depressive disorders; mgt, management; MH, mental health; MHP, mental health professional; MINI, mini neuropsychiatric interview; NNT, number needed to treat; PHQ-9, patient health questionnaire; TAU, treatment as usual .
Furthermore, school/educational institutes-based interventions such as school-Mental Health Magazines to increase mental health literacy among the teachers and students have been developed ( 80 ). In addition, workplace mental health promotional activities have targeted the administrators, e.g., guided “e-learning” for the managers that have shown to decrease the mental health problems of the employees ( 102 ).
Likewise, digital technologies have also been harnessed in strengthening community mental health promotive/preventive services, such as the mental health first aid (MHFA) Books on Prescription initiative in New Zealand provided information and self-help tools through library networks and trained book “prescribers,” particularly in rural and remote areas ( 103 ).
Apart from the common mental disorders such as depression, anxiety, and behavioral disorders in the childhood/adolescents, novel interventions have been utilized to prevent the development of or management of medical, including preventing premature mortality and psychological issues among the individuals with severe mental illnesses (SMIs), e.g., Lets' talk about tobacco-web based intervention and motivational interviewing to prevent tobacco use, weight reduction measures, and promotion of healthy lifestyles (exercise, sleep, and balanced diets) through individualized devices, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular disorders ( 83 ). Similarly, efforts have been made to improve such individuals' coping skills and employment chances through the WorkingWell mobile application in the US ( 104 ).
Apart from the digital-based interventions, newer, non-digital-based interventions have also been utilized to promote mental health and prevent mental disorders among individuals with chronic medical conditions. One such approach in adventure therapy aims to support and strengthen the multi-dimensional aspects of self. It includes the physical, emotional or cognitive, social, spiritual, psychological, or developmental rehabilitation of the children and adolescents with cancer. Moreover, it is delivered in the natural environment outside the hospital premises, shifting the focus from the illness model to the wellness model ( 81 ). Another strength of this intervention is it can be delivered by the nurses and facilitate peer support and teamwork.
Another novel approach to MH prevention is gut-microbiota and dietary interventions. Such interventions have been explored with promising results for the early developmental disorders (Attention deficit hyperactive disorder, Autism spectrum disorders, etc.) ( 105 ). It works under the framework of the shared vulnerability model for common mental disorders and other non-communicable diseases and harnesses the neuroplasticity potential of the developing brain. Dietary and lifestyle modifications have been recommended for major depressive disorders by the Clinical Practice Guidelines in Australia ( 106 ). As most childhood mental and physical disorders are determined at the level of the in-utero and early after the birth period, targeting maternal nutrition is another vital strategy. The utility has been expanded from maternal nutrition to women of childbearing age. The various novel mental health promotion and prevention strategies are shown in Table 2 .
Newer research is emerging that has utilized the digital platform for training non-specialists in diagnosis and managing individuals with mental health problems, such as Atmiyata Intervention and The SMART MH Project in India, and The Allillanchu Project in Peru, to name a few ( 99 ). Such frameworks facilitate task-sharing by the non-specialist and help in reducing the treatment gap in these countries. Likewise, digital algorithms or decision support systems have been developed to make mental health services more transparent, personalized, outcome-driven, collaborative, and integrative; one such example is DocuMental, a clinical decision support system (DSS). Similarly, frameworks like i-PROACH, a cloud-based intelligent platform for research outcome assessment and care in mental health, have expanded the scope of the mental health support system, including promoting research in mental health ( 100 ). In addition, COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in wider dissemination of the applications based on the evidence-based psycho-social interventions such as National Health Service's (NHS's) Mind app and Headspace (teaching meditation via a website or a phone application) that have utilized mindfulness-based practices to address the psychological problems of the population ( 101 ).
Challenges in Implementing Novel MH Promotion and Prevention Strategies
Although novel interventions, particularly internet and mobile-based interventions (IMIs), are effective models for MH promotion and prevention, their cost-effectiveness requires further exploration. Moreover, their feasibility and acceptability in LMICs could be challenging. Some of these could be attributed to poor digital literacy, digital/network-related limitations, privacy issues, and society's preparedness to implement these interventions.
These interventions need to be customized and adapted according to local needs and context, for which implementation and evaluative research are warranted. In addition, the infusion of more human and financial resources for such activities is required. Some reports highlight that many of these interventions do not align with the preferences and use the pattern of the service utilizers. For instance, one explorative research on mental health app-based interventions targeting youth found that despite the burgeoning applications, they are not aligned with the youth's media preferences and learning patterns. They are less interactive, have fewer audio-visual displays, are not youth-specific, are less dynamic, and are a single touch app ( 107 ).
Furthermore, such novel interventions usually come with high costs. In low-resource settings where service utilizers have limited finances, their willingness to use such services may be doubtful. Moreover, insurance companies, including those in high-income countries (HICs), may not be willing to fund such novel interventions, which restricts the accessibility and availability of interventions.
Research points to the feasibility and effectiveness of incorporating such novel interventions in routine services such as school, community, primary care, or settings, e.g., in low-resource settings, the resource persons like teachers, community health workers, and primary care physicians are already overburdened. Therefore, their willingness to take up additional tasks may raise skepticism. Moreover, the attitudinal barrier to moving from the traditional service delivery model to the novel methods may also impede.
Considering the low MH budget and less priority on the MH prevention and promotion activities in most low-resource settings, the uptake of such interventions in the public health framework may be lesser despite the latter's proven high cost-effectiveness. In contrast, policymakers may be more inclined to invest in the therapeutic aspects of MH.
Such interventions open avenues for personalized and precision medicine/health care vs. the traditional model of MH promotion and preventive interventions ( 108 , 109 ). For instance, multivariate prediction algorithms with methods of machine learning and incorporating biological research, such as genetics, may help in devising tailored, particularly for selected and indicated prevention, interventions for depression, suicide, relapse prevention, etc. ( 79 ). Therefore, more research in this area is warranted.
To be more clinically relevant, greater biological research in MH prevention is required to identify those at higher risk of developing given mental disorders due to the existing risk factors/prominent stress ( 110 ). For instance, researchers have utilized the transcriptional approach to identify a biological fingerprint for susceptibility (denoting abnormal early stress response) to develop post-traumatic stress disorders among the psychological trauma survivors by analyzing the expression of the Peripheral blood mononuclear cell gene expression profiles ( 111 ). Identifying such biological markers would help target at-risk individuals through tailored and intensive interventions as a form of selected prevention.
Similarly, such novel interventions can help in targeting the underlying risk such as substance use, poor stress management, family history, personality traits, etc. and protective factors, e.g., positive coping techniques, social support, resilience, etc., that influences the given MH outcome ( 79 ). Therefore, again, it opens the scope of tailored interventions rather than a one-size-fits-all model of selective and indicated prevention for various MH conditions.
Furthermore, such interventions can be more accessible for the hard-to-reach populations and those with significant mental health stigma. Finally, they play a huge role in ensuring the continuity of care, particularly when community-based MH services are either limited or not available. For instance, IMIs can maintain the improvement of symptoms among individuals previously managed in-patient, such as for suicide, SUDs, etc., or receive intensive treatment like cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) for depression or anxiety, thereby helping relapse prevention ( 86 , 112 ). Hence, such modules need to be developed and tested in low-resource settings.
IMIs (and other novel interventions) being less stigmatizing and easily accessible, provide a platform to engage individuals with chronic medical problems, e.g., epilepsy, cancer, cardiovascular diseases, etc., and non-mental health professionals, thereby making it more relevant and appealing for them.
Lastly, research on prevention-interventions needs to be more robust to adjust for the pre-intervention matching, high attrition rate, studying the characteristics of treatment completers vs. dropouts, and utilizing the intention-to-treat analysis to gauge the effect of such novel interventions ( 78 ).
Recommendations for Low-and-Middle-Income Countries
Although there is growing research on the effectiveness and utility of mental health promotion/prevention interventions across the lifespan and settings, low-resource settings suffer from specific limitations that restrict the full realization of such public health strategies, including implementing the novel intervention. To overcome these challenges, some of the potential solutions/recommendations are as follows:
- The mental health literacy of the population should be enhanced through information, education, and communication (IEC) activities. In addition, these activities should reduce stigma related to mental problems, early identification, and help-seeking for mental health-related issues.
- Involving teachers, workplace managers, community leaders, non-mental health professionals, and allied health staff in mental health promotion and prevention is crucial.
- Mental health concepts and related promotion and prevention should be incorporated into the education curriculum, particularly at the medical undergraduate level.
- Training non-specialists such as community health workers on mental health-related issues across an individual's life course and intervening would be an effective strategy.
- Collaborating with specialists from other disciplines, including complementary and alternative medicines, would be crucial. A provision of an integrated health system would help in increasing awareness, early identification, and prompt intervention for at-risk individuals.
- Low-resource settings need to develop mental health promotion interventions such as community-and school-based interventions, as these would be more culturally relevant, acceptable, and scalable.
- Utilizing a digital platform for scaling mental health services (e.g., telepsychiatry services to at-risk populations) and training the key individuals in the community would be a cost-effective framework that must be explored.
- Infusion of higher financial and human resources in this area would be a critical step, as, without adequate resources, research, service development, and implementation would be challenging.
- It would also be helpful to identify vulnerable populations and intervene in them to prevent the development of clinical psychiatric disorders.
- Lastly, involving individuals with lived experiences at the level of mental health planning, intervention development, and delivery would be cost-effective.
Clinicians, researchers, public health experts, and policymakers have increasingly realized mental health promotion and prevention. Investment in Preventive psychiatry appears to be essential considering the substantial burden of mental and neurological disorders and the significant treatment gap. Literature suggests that MH promotive and preventive interventions are feasible and effective across the lifespan and settings. Moreover, various novel interventions (e.g., internet-and mobile-based interventions, new therapies) have been developed worldwide and proven effective for mental health promotion and prevention; such interventions are limited mainly to HICs.
Despite the significance of preventive psychiatry in the current world and having a wide-ranging implication for the wellbeing of society and individuals, including those suffering from chronic medical problems, it is a poorly utilized public health field to address the population's mental health needs. Lately, researchers and policymakers have realized the untapped potentialities of preventive psychiatry. However, its implementation in low-resource settings is still in infancy and marred by several challenges. The utilization of novel interventions, such as digital-based interventions, and blended and stepped-care models of care, can address the enormous mental health need of the population. Additionally, it provides mental health services in a less-stigmatizing and easily accessible, and flexible manner. More research concerning this is required from the LMICs.
Author Contributions
VS, AK, and SG: methodology, literature search, manuscript preparation, and manuscript review. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.898009/full#supplementary-material
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Mental Health News
Featured content, explore mental health news, more in trending.
Children’s Mental Health Research
- Mental health in the community
- Different data sources
- National data sets
Research on children’s mental health in the community
Project to learn about youth – mental health.

The Project to Learn About Youth – Mental Health (PLAY-MH) analyzed information collected from four communities. The focus was to study attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and other externalizing and internalizing disorders, as well as tic disorders in school-aged children. The purpose was to learn more about public health prevention and intervention strategies to support children’s health and development.

Read about the results of the Play-MH study
Study questions included:
- What percentage of children in the community had one or more externalizing, internalizing, or tic disorders?
- How frequently did these disorders appear together?
- What types of treatment were children receiving in their communities?
This project used the same methodology as the original Project to Learn about ADHD in Youth (PLAY) project. Read more about the original study approach here .
Other research
Read more about research on
- Tourette syndrome
CDC and partner agencies are working to understand the prevalence of mental disorders in children and how they impact their lives. Currently, it is not known exactly how many children have any mental disorder, or how often different disorders occur together, because no national dataset is available that looks at all mental, emotional, or behavioral disorders together.
Research on prevalence
What is It and Why is It Important?
Using different data sources
Healthcare providers, public health researchers, educators, and policy makers can get information about the prevalence of children’s mental health disorders from a variety of sources. Data sources, such as national surveys, community-based studies, and administrative claims data (like healthcare insurance claims), use different study methods and provide different types of information, each with advantages and disadvantages. Advantages and disadvantages for different data sources include the following:
- National surveys have large sample sizes that are needed to create estimates at the national and state levels. However, they also generally use a parent’s report of the child’s diagnosis, which means that the healthcare provider has to give an accurate diagnosis and the parent has to accurately remember what it was.
- Community-based studies offer the opportunity to observe children’s symptoms, which means that even children who have not been diagnosed or do not have the right diagnosis could be found. However, these studies are typically done in small geographic areas, so findings are not necessarily the same in other communities.
- Administrative claims are typically very large datasets with information on diagnosis and treatment directly from the providers, which allows tracking changes over time. Because they are recorded for billing purposes, diagnoses or services that would not be reimbursed from the specific health insurance might not be recorded in the data.
Using different sources of data together provides more information because it is possible to describe the following:
- Children with a diagnosed condition compared to children who have the same symptoms, but are not diagnosed
- Differences between populations with or without health insurance
- How estimates for mental health disorders change over time
Read more about using different data sources.

National data on children’s mental health
A comprehensive report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Mental Health Surveillance Among Children — United States, 2013 – 2019 , described federal efforts on monitoring mental disorders, and presented estimates of the number of children with specific mental disorders as well as for positive indicators of mental health. The report was developed in collaboration with the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA ), the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH ), and the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA ). It represents an update to the first ever cross-agency children’s mental health surveillance report in 2013.
Read a summary of the findings for the current report using data from 2012-2019
Read a summary of the findings for the first report using data from 2005-2011 .
The goal is now to build on the strengths of federal agencies serving children with mental disorders to:
- Develop better ways to document how many children have these disorders,
- Better understand the impacts of mental disorders,
- Inform needs for treatment and intervention strategies, and
- Promote the mental health of children.
This report is an important step on the road to recognizing the impact of childhood mental disorders and developing a public health approach to address children’s mental health.
Holbrook JR, Bitsko RB, Danielson ML, Visser SN. Interpreting the Prevalence of Mental Disorders in Children: Tribulation and Triangulation. Health Promotion Practice. Published online November 15, 2016 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27852820 .
To receive email updates about this topic, enter your email address:
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
For younger women, mental health now may predict heart health later
Study suggests anxiety and depression could offer an early warning of cardiovascular risk in this traditionally low-risk group.
Younger women are generally thought to have a low risk of heart disease, but new research urges clinicians to revisit that assumption, especially for women who suffer from certain mental health conditions. A new study being presented at the American College of Cardiology's Annual Scientific Session found that having anxiety or depression could accelerate the development of cardiovascular risk factors among young and middle-aged women.
The study draws new attention to the importance of cardiovascular screening and preventive care as rates of cardiovascular risk factors rise and heart attacks become more common in younger people. Anxiety and depression have also become more prevalent in recent years, especially since the COVID-19 pandemic.
The researchers reported that younger women with anxiety or depression were nearly twice as likely to develop high blood pressure, high cholesterol or diabetes over a 10-year period compared with women who did not have these mental health conditions, putting them nearly on par with men of the same age in terms of heart disease risk.
"We often feel that young women are the 'safe group' with regards to cardiovascular disease because the incidence of cardiovascular disease is quite low due to the protective effects of estrogen in this group," said Giovanni Civieri, MD, cardiologist, research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, doctoral student at the University of Padua in Italy and the study's lead author. "But this study suggests that if a younger woman has depression or anxiety, we should start screening for cardiovascular risk factors to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular disease."
The researchers analyzed health records of 71,214 people participating in the Mass General Brigham Biobank, a research program of the Mass General Brigham health system. People who had heart disease or who were diagnosed with anxiety or depression after the study began were excluded.
During the 10-year follow-up period, 38% of participants developed high blood pressure, high cholesterol and/or diabetes. According to the analysis, those with a history of anxiety or depression before the study period were about 55% more likely to develop one or more of these risk factors than people without anxiety or depression. This finding was most pronounced among women under the age of 50 with anxiety or depression, who were nearly twice as likely to develop cardiovascular risk factors compared with any other group.
In terms of absolute risk, young women overall showed the lowest rates of cardiovascular risk factors of any group, which was expected based on findings from previous studies and what is known about the protective effects of estrogen in pre-menopausal women. However, anxiety and depression were associated with a much higher relative risk among young women than was seen in other groups.
"Once a young woman has depression or anxiety, her absolute risk is comparable to a young male," Civieri said. "There is a sort of a catch-up phenomenon where depression and anxiety increase the risk that would otherwise be very low."
To study the potential drivers behind this relationship, the researchers examined the metabolic activity of stress-related brain regions in a subset of participants who had undergone brain scans. The results indicated that younger women with anxiety or depression showed relatively large increases in stress-related neural activity.
"The question is: Why are anxiety and depression associated with heightened gains in risk among younger females? This is something we are continuing to study," Civieri said.
Although anxiety and depression are separate conditions, they were grouped together in the study because they are both associated with increased cardiovascular risk and they share common neurobiological pathways, meaning they are thought to affect health in similar ways.
It is unknown whether mental health treatments, such as antidepressant medications or psychotherapy, could help reduce cardiovascular risk, researchers said. However, once a person has high blood pressure, high cholesterol or diabetes, Civieri said that well-established treatments such as statins and blood pressure-lowering drugs can effectively reduce the risk of serious cardiac events.
- Heart Disease
- Mental Health Research
- Cholesterol
- Hypertension
- Mental Health
- Postpartum depression
- Breast cancer
- Personalized medicine
Story Source:
Materials provided by American College of Cardiology . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Heart Disease Risk: More Than One Drink a Day
- Unlocking Supernova Stardust Secrets
- Why Do Some Memories Become Longterm?
- Cell Division Quality Control 'Stopwatch'
- What Controls Sun's Differential Rotation?
- Robot, Can You Say 'Cheese'?
- Researchers Turn Back the Clock On Cancer Cells
- Making Long-Term Memories: Nerve-Cell Damage
- A Solar Cell You Can Bend and Soak in Water
- 'Cosmic Cannibals': Fast-Moving Jets in Space
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.

Transforming the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses.
Información en español
Celebrating 75 Years! Learn More >>
- Health Topics
- Brochures and Fact Sheets
- Help for Mental Illnesses
- Clinical Trials
Caring for Your Mental Health
Esta página también está disponible en español .
Mental health includes emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It is more than the absence of a mental illness—it’s essential to your overall health and quality of life. Self-care can play a role in maintaining your mental health and help support your treatment and recovery if you have a mental illness.
How can I take care of my mental health?
Self-care means taking the time to do things that help you live well and improve both your physical health and mental health. This can help you manage stress, lower your risk of illness, and increase your energy. Even small acts of self-care in your daily life can have a big impact.
Here are some self-care tips:
- Get regular exercise. Just 30 minutes of walking every day can boost your mood and improve your health. Small amounts of exercise add up, so don’t be discouraged if you can’t do 30 minutes at one time.
- Eat healthy, regular meals and stay hydrated. A balanced diet and plenty of water can improve your energy and focus throughout the day. Pay attention to your intake of caffeine and alcohol and how they affect your mood and well-being—for some, decreasing caffeine and alcohol consumption can be helpful.
- Make sleep a priority . Stick to a schedule, and make sure you’re getting enough sleep. Blue light from devices and screens can make it harder to fall asleep, so reduce blue light exposure from your phone or computer before bedtime.
- Try a relaxing activity. Explore relaxation or wellness programs or apps, which may incorporate meditation, muscle relaxation, or breathing exercises. Schedule regular times for these and other healthy activities you enjoy, such as listening to music, reading, spending time in nature, and engaging in low-stress hobbies.
- Set goals and priorities. Decide what must get done now and what can wait. Learn to say “no” to new tasks if you start to feel like you’re taking on too much. Try to appreciate what you have accomplished at the end of the day.
- Practice gratitude. Remind yourself daily of things you are grateful for. Be specific. Write them down or replay them in your mind.
- Focus on positivity . Identify and challenge your negative and unhelpful thoughts.
- Stay connected. Reach out to friends or family members who can provide emotional support and practical help.
Self-care looks different for everyone, and it is important to find what you need and enjoy. It may take trial and error to discover what works best for you.
Learn more about healthy practices for your mind and body .
When should I seek professional help?
Seek professional help if you are experiencing severe or distressing symptoms that have lasted 2 weeks or more, such as:
- Difficulty sleeping
- Changes in appetite or unplanned weight changes
- Difficulty getting out of bed in the morning because of mood
- Difficulty concentrating
- Loss of interest in things you usually find enjoyable
- Inability to complete usual tasks and activities
- Feelings of irritability, frustration, or restlessness
How can I find help?
If you have concerns about your mental health, talk to a primary care provider. They can refer you to a qualified mental health professional, such as a psychologist, psychiatrist, or clinical social worker, who can help you figure out the next steps. Find tips for talking with a health care provider about your mental health.
You can learn more about getting help on the NIMH website. You can also learn about finding support and locating mental health services in your area on the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration website.
If you or someone you know is struggling or having thoughts of suicide, call or text the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or chat at 988lifeline.org . This service is confidential, free, and available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. In life-threatening situations, call 911.
Suicide is preventable—learn about warning signs of suicide and action steps for helping someone in emotional distress.
Featured videos
GREAT: Helpful Practices to Manage Stress and Anxiety: Learn about helpful practices to manage stress and anxiety. GREAT was developed by Dr. Krystal Lewis, a licensed clinical psychologist at NIMH.
Getting to Know Your Brain: Dealing with Stress: Test your knowledge about stress and the brain. Also learn how to create and use a “ stress catcher ” to practice strategies to deal with stress.
Guided Visualization: Dealing with Stress: Learn how the brain handles stress and practice a guided visualization activity.
Mental Health Minute: Stress and Anxiety in Adolescents: Got 60 seconds? Take a mental health minute to learn about stress and anxiety in adolescents.
Featured fact sheets
- NIH Wellness Toolkits : NIH provides toolkits with strategies for improving your emotional health and social health .
- MedlinePlus: How to Improve Mental Health : MedlinePlus provides health information and tips for improving your mental health.
- CDC: Emotional Well-Being : CDC provides information on how to cope with stress and promote social connectedness.
- SAMHSA: How to Cope : SAMHSA offers tips for taking care of your well-being and connecting with others for support.
Last Reviewed: February 2024
Unless otherwise specified, the information on our website and in our publications is in the public domain and may be reused or copied without permission. However, you may not reuse or copy images. Please cite the National Institute of Mental Health as the source. Read our copyright policy to learn more about our guidelines for reusing NIMH content.
- Accessibility Options:
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Search
- Skip to footer
- Office of Disability Services
- Request Assistance
- 305-284-2374
- High Contrast
- School of Architecture
- College of Arts and Sciences
- Miami Herbert Business School
- School of Communication
- School of Education and Human Development
- College of Engineering
- School of Law
- Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science
- Miller School of Medicine
- Frost School of Music
- School of Nursing and Health Studies
- The Graduate School
- Division of Continuing and International Education
- People Search
- Class Search
- IT Help and Support
- Privacy Statement
- Student Life
- University of Miami
- Division of University Communications
- Office of Media Relations
- Miller School of Medicine Communications
- Hurricane Sports
- UM Media Experts
- Emergency Preparedness
Explore Topics
- Latest Headlines
- Arts and Humanities
- People and Community
- All Topics A to Z
Related Links
- Subscribe to Daily Newsletter
- Social Networks
- For the Media
- Find University Experts
- News and Info
- People and Culture
- Benefits and Discounts
- More Life@TheU Topics
- About Life@the U
- Connect and Share
- Faculty and Staff Events
- Student Events
- TheU Creates (Arts and Culture Events)
- Undergraduate Students: Important Dates and Deadlines
- Submit an Event
- Miami Magazine
- Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science
- Student Affairs
- More News Sites
- UM NEWS HOME
Psychology professor leads field in HIV and mental health research
By Adrianne Gonzalez 03-29-2024
Steven Safren , professor of psychology and director of the Center for HIV and Research in Mental Health (CHARM) at the University of Miami, was recognized by the Faculty Senate with the 2023–24 Distinguished Faculty Scholar Award for a lifetime of distinguished accomplishments in clinical practice and research.
After joining the University of Miami faculty in 2015, Safren founded CHARM — an interdisciplinary center between the College of Arts and Sciences, Miller School of Medicine, and the School of Nursing and Health Studies. Funded by the National Institute of Mental Health, the center is designated as a full HIV/AIDS facility and one of seven in the nation.
Nominated for the Distinguished Faculty Scholar Award by Philip M. McCabe , professor and chair of the Department of Psychology, Safren is lauded for his exceptional proactivity, extensive funding success, and leadership in the field. “He is a truly exceptional scholar, teacher, and University citizen. He has my highest recommendation,” said McCabe.
Safren earned his Ph.D. in clinical psychology from the University at Albany State University of New York and trained at Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School specializing in cognitive behavior therapy.
Reflecting on his most memorable moments at the University of Miami, Safren emphasizes his pride in witnessing his students' achievements during the commencement ceremonies and believes that both students and graduates must narrow their focus. “ Find a piece of what you are studying that you really enjoy, and do more of that,” he shared.
The 2023–24 Faculty Senate Awards Ceremony will be held in person on Monday, April 8, at 5 p.m. on the Coral Gables Campus. Learn more about the awards ceremony.
This profile is part of a 2023–24 Faculty Senate Awards series recognizing all awardees.
Faculty Affairs
Office of the provost, information and resources, browse people at um, faculty events, borwse upcoming events, faculty senate.

University of Miami News Sub
- Coral Gables , FL 33124
- 305-284-2211 305-284-2211
- UM News and Events
- Alumni & Friends
- University Hotline
Tools and Resources
- Academic Calendar
- Department Search
- Parking & Transportation
- social-facebook
- social-twitter
- social-youtube
- social-instagram
Copyright: 2024 University of Miami. All Rights Reserved. Emergency Information Privacy Statement & Legal Notices Title IX & Gender Equity Website Feedback
Individuals with disabilities who experience any technology-based barriers accessing the University’s websites or services can visit the Office of Workplace Equity and Inclusion .
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
When Teens Visit Doctors, Increasingly the Subject is Mental Health

By Matt Richtel
Increasingly, doctor visits by adolescents and young adults involve mental health diagnoses, along with the prescription of psychiatric medications.
That was the conclusion of a new study that found that in 2019, 17 percent of outpatient doctor visits for patients ages 13 to 24 in the United States involved a behavioral or mental health condition, including anxiety, depression, suicidal ideation, self-harm or other issues. That figure rose sharply from 2006, when just 9 percent of doctor’s visits involved psychiatric illnesses.
The study , published Thursday in JAMA Network Open, also found a sharp increase in the proportion of visits involving psychiatric medications. In 2019, 22.4 percent of outpatient visits by the 13-24 age group involved the prescription of at least one psychiatric drug, up from 13 percent in 2006.
The Big Picture
The study is the latest evidence in a shift in the kinds of ailments affecting children, adolescents and young adults. For many decades, their health care visits involved more bodily ailments, such as broken bones, viruses and drunken-driving injuries. Increasingly, however, doctors are seeing a wide variety of behavioral and mental health issues.

The reasons are not entirely clear. Some experts have said that modern life presents a new kind of mental pressure, even as society has limited the risks of physical ailments.
The latest study does not posit a reason for the shift. But the pandemic alone was not to blame, it noted. “These findings suggest the increase in mental health conditions seen among youth during the pandemic occurred in the setting of already increasing rates of psychiatric illness,” wrote the authors, a pediatrician and psychiatrist at Harvard Medical School. “Treatment and prevention strategies will need to account for factors beyond the direct and indirect effects of the pandemic.”
The Numbers
The analysis was drawn from the National Ambulatory Care Survey, which asks a sample of clinicians from across the country about the reasons for patient visits. Between 2006 and 2019, patients aged 13 to 24 made 1.1 billion health care visits, of which 145 million involved mental health issues. But the share of mental-health-related visits rose each year, the study found, as did the prescription of psychiatric medications, including stimulants, antipsychotics, mood stabilizers and anti-anxiety drugs.
The study found that antidepressants had the greatest increase, but it did not specify the exact level, said Dr. Florence T. Bourgeois, a pediatrician at Boston Children’s Hospital, an associate professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School and a co-author of the paper.
The prescription patterns leave an open question, she said.
“We can’t differentiate whether this speaks to the severity of conditions or changes in prescribing attitudes and trends,” she said. Either way, she added, “We are treating these conditions aggressively.”
Matt Richtel is a health and science reporter for The Times, based in Boulder, Colo. More about Matt Richtel
Managing Anxiety and Stress
Stay balanced in the face of stress and anxiety with our collection of tools and advice..
How are you, really? This self-guided check-in will help you take stock of your emotional well-being — and learn how to make changes .
These simple and proven strategies will help you manage stress , support your mental health and find meaning in the new year.
First, bring calm and clarity into your life with these 10 tips . Next, identify what you are dealing with: Is it worry, anxiety or stress ?
Persistent depressive disorder is underdiagnosed, and many who suffer from it have never heard of it. Here is what to know .
If you notice drastic shifts in your mood during certain times of the year, you could have seasonal affective disorder. Here are answers to your top questions about the condition .
How much anxiety is too much? Here is how to establish whether you should see a professional about it .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Top 10 Mental Health Research Paper Topics. 1. The Effects of Social Media Platforms on the Mental Well-Being of Children. The effects of social media platforms on the mental well-being of children is a research topic that is especially significant and relevant today. This is due to the increasing usage of online social networks by children and ...
Good mental health suggests good cognitive, behavioral, and emotional wellbeing. The following mental health research topics will provide multiple avenues for students to base their research topics on: The relationship between depression and weight loss. The rise of eating disorders in teenagers and adolescents.
Health Topics. The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), the lead federal agency for research on mental disorders, offers basic information on mental disorders, a range of related topics, and the latest mental health research. It is not the intention of NIMH to provide specific medical advice, but rather to provide users with information ...
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) is the Nation's leader in research on mental disorders, supporting research to transform the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses. ... Updates about mental health topics, including NIMH news, upcoming events, mental disorders, funding opportunities, and research. Innovation Speaker Series.
On World Mental Health Day 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared mental health a fundamental human right that should be accessible to everyone, regardless of location or background. In support of WHO's mission, we have compiled a list of leading article collections advancing mental health research.
Topics of Psychology Research Related to Human Cognition. Some of the possible topics you might explore in this area include thinking, language, intelligence, and decision-making. Other ideas might include: Dreams. False memories. Attention. Perception.
Research Areas. The Department of Mental Health covers a wide array of topics related to mental health, mental illness, and substance abuse. We emphasize ongoing research that enriches and stimulates the teaching programs. All students and fellows are encouraged to participate in at least one research group. Faculty and students from multiple ...
Maternal positive mental health during pregnancy impacts the hippocampus and functional brain networks in children. Using a longitudinal dataset, the authors investigated the effects of maternal ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly influenced the world. In wave after wave, many countries suffered from the pandemic, which caused social instability, hindered global growth, and harmed mental health. Although research has been published on various mental health issues during the pandemic, some profound effects on mental health are ...
This editorial initiative of particular relevance, led by Dr. Wulf Rössler, Specialty Chief Editor of the Public Mental Health section, is focused on new insights, novel developments, current challenges, latest discoveries, recent advances and future perspectives in the field of Public Mental Health. The Research Topic solicits brief, forward ...
Microdosing psychedelics is a growing practice among recreational users, claimed to improve several aspects of mental health, with little supporting empirical research. In this comment, we ...
Impact on mental health. Mental health is defined as a state of well-being in which people understand their abilities, solve everyday life problems, work well, and make a significant contribution to the lives of their communities [].There is debated presently going on regarding the benefits and negative impacts of social media on mental health [9,10].
Research also suggests that mental health promotion and preventative measures are cost-effective in preventing or reducing mental illness-related morbidity, both at the society and individual level . ... Despite the significance of the topic and a considerable amount of literature on it, a comprehensive review is still lacking that would cover ...
Mental health is a state of mind characterized by emotional well-being, good behavioral adjustment, relative freedom from anxiety and disabling symptoms, and a capacity to establish constructive relationships and cope with the ordinary demands and stresses of life. ... Topics in Psychology. Explore how scientific research by psychologists can ...
The Division of Neuroscience and Basic Behavioral Science (DNBBS) at the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) supports research on basic neuroscience, genetics, and basic behavioral science. These are foundational pillars in the quest to decode the human mind and unravel the complexities of mental illnesses. At NIMH, we are committed to supporting and conducting genomics research as a ...
Plain-language explanations of how our mental health and behavior play a role in everyday issues such as: aging, depression, eating disorders, emotional health, marriage and divorce, parenting, sexuality, sleep, stress and trauma. ... Topics in Psychology. Explore how scientific research by psychologists can inform our professional lives ...
Mental health. Mental health is a state of mental well-being that enables people to cope with the stresses of life, realize their abilities, learn well and work well, and contribute to their community. It has intrinsic and instrumental value and is integral to our well-being. At any one time, a diverse set of individual, family, community and ...
NIMH launched a five-year research study called RECOUP-NY to promote the mental health of New Yorkers from communities hard-hit by COVID-19. The study will test the use of a new care model called Problem Management Plus (PM+) that can be used by non-specialists. A study funded by NIMH is examining the use of mobile apps to address mental health ...
Heath psychology topics can look at a range of issues related to health, illness, and healthcare. It may include such things as eating disorders, weight management, diet, exercise, stress coping, women's health, and more. Health psychology, also known as medical psychology or behavioral medicine, focuses on how biology, psychology, behavior ...
The Experts Agree: What You Eat Can Directly Impact Stress and Anxiety. Unsung Hero Spotlight: Rest for Resistance. Mental Health Insights. Stay up to date on the latest mental health news with trustworthy and accurate reporting from Verywell Mind's team of board-certified physicians, health journalists, and industry experts.
Mental health is a state of mental well-being that enables people to cope with the stresses of life, realize their abilities, learn well and work well, and contribute to their community. It is an integral component of health and well-being that underpins our individual and collective abilities to make decisions, build relationships and shape ...
A comprehensive report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Mental Health Surveillance Among Children — United States, 2013 - 2019, described federal efforts on monitoring mental disorders, and presented estimates of the number of children with specific mental disorders as well as for positive indicators of mental health.
March 28, 2024. Source: American College of Cardiology. Younger women are generally thought to have a low risk of heart disease, but new research urges clinicians to revisit that assumption ...
SHARE: Behavioral Health. Behavioral health problems, which include mental health and substance use disorders, are among the most common conditions seen in primary care settings. AHRQ provides data to quantify these challenges, tools and resources for screening and treatment, and funding for behavioral health research.
Exclusive articles about Mental health. Roughly one in three people will experience panic attacks at some point during their lives. But there is good news: They usually pass in 10 - 15 minutes, and you can use a few techniques to manage them, say experts Cindy Aaronson PhD and Justin Feinstein PhD. Posted Aug 2021.
Eat healthy, regular meals and stay hydrated. A balanced diet and plenty of water can improve your energy and focus throughout the day. Pay attention to your intake of caffeine and alcohol and how they affect your mood and well-being—for some, decreasing caffeine and alcohol consumption can be helpful. Make sleep a priority.
By Adrianne Gonzalez 03-29-2024. Steven Safren, professor of psychology and director of the Center for HIV and Research in Mental Health (CHARM) at the University of Miami, was recognized by the Faculty Senate with the 2023-24 Distinguished Faculty Scholar Award for a lifetime of distinguished accomplishments in clinical practice and research.
Between 2006 and 2019, patients aged 13 to 24 made 1.1 billion health care visits, of which 145 million involved mental health issues. But the share of mental-health-related visits rose each year ...