- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search


Multiply and divide fractions - Problem-Solving Investigation - Year 6
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
7 March 2019
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

This in-depth maths investigation is an open-ended problem solving activity for Year 6 children. It can be used to support teaching towards the objective: multiply and divide fractions.
In-depth Investigation: Mixed up fractions Children add a pair of fractions, multiply the same pair, then find the difference between the two answers, looking for patterns.
This investigation will develop maths meta-skills, support open-ended questioning and logical reasoning, and enable children to learn to think mathematically and articulate mathematical ideas.
This problem-solving investigation is part of our Year 6 Decimals and Fractions block. Each Hamilton maths block contains a complete set of planning and resources to teach a term’s worth of objectives for one of the National Curriculum for England’s maths areas.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Get this resource as part of a bundle and save up to 36%
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place.
Multiply and Divide (Year 6 Decimals and Fractions)
This bundle provides three days of teaching that cover the objective: **Multiply and divide fractions** *Teaching Presentation* The teaching presentation includes starter activities, whole class teaching, group activities, practice sheets and mastery questions. It can be used on a variety of interactive whiteboards. *Practice Worksheets* The procedural fluency practice worksheets are differentiated for children working towards Age Related Expectations (ARE), at ARE and at greater depth. *Problem-Solving Investigation* This in-depth maths investigation will develop maths meta-skills, and enable children to learn to think mathematically and articulate mathematical ideas. *Extra Support* The extra support activity is designed to be used by a teacher or a TA with children who need extra support. This teaching is part of Hamilton’s [Year 6 Decimals and Fractions](https://www.hamilton-trust.org.uk/maths/year-6-maths/decimals-and-fractions-2/) block. Each Hamilton maths block contains a complete set of planning and resources to teach a term’s worth of objectives for one of the National Curriculum for England’s maths areas.
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

Compare and order fractions
Your child will compare fractions and put them in size order.
They will be able to do this with proper fractions (i.e. fractions less than one) and fractions that are greater than one (i.e. improper fractions or mixed numbers ). For example:
is greater than is greater than
Calculate with mixed numbers and fractions with different denominators
Your child will learn to add and subtract fractions with different denominators (bottom numbers). They will do this by finding equivalent fractions that have the same denominator. For example:
+ = + =
They will use objects, diagrams, and symbols to solve problems with mixed numbers and fractions, and to explain how they have solved a problem.
Multiply and simplify proper fractions
Your child will be able to multiply pairs of proper fractions (i.e. fractions smaller than 1) together, and then write the answer in its simplest form.
× = =
Your child will use objects, diagrams, and symbols in their calculations.
Divide proper fractions by whole numbers
Proper fractions are fractions with a value of less than 1. Your child will be able to divide these kinds of fractions by whole numbers. For example:
Your child will do this using objects, diagrams, and symbols.
Understand the link between fractions, division, and decimals
To find of 36cm, you would divide 36 by 4 (36cm ÷ 4 = 9 cm). If you know of an unknown length is 36cm and you want to find the whole length, you would multiply 36 by 4 (36cm × 4 = 144cm).
Use numbers with 3 decimal places
Your child will understand the value of each digit in numbers with 3 decimal places. They will also be able to multiply and divide numbers by 10, 100, and 1000, giving answers up to 3 decimal places. For example:
9 ÷ 1000 = 0.009 0·734 × 100 = 73.4
Your child will divide decimal numbers by 1-digit whole numbers. At first, they will learn this in practical contexts involving measures and money (for example, 0.65m ÷ 5 = 0.13m).

Multiply numbers with decimal places
Your child will learn to multiply 1-digit numbers with up to 2 decimal places by whole numbers. For example:
2.75 × 2 = 5.5
They will start with simple examples, such as 0.4 × 2 = 0.8, in practical contexts such as using money.
Use written division methods where appropriate
Your child will use written division methods (like long division and short division) in cases where the answer has up to 2 decimal places. You can find out more about these methods on our YouTube channel: see How to do long division and How to do short division .
Round numbers to estimate answers
Your child will round numbers and estimate answers to check their answers to decimal calculations. For example:
2.56 × 5.3 ≈ 2.5 × 5 = 12.5 So, when your child works out the question exactly, they will expect their result to be roughly 12.5. If they get an answer like 1350, they will know something has gone wrong!
Use equivalences between simple fractions, decimals, and percentages
How to help at home
There are lots of ways you can help your child to understand fractions. Here are just a few ideas.
1. Help your child calculate with fractions
They could separate the whole numbers and the fractional parts:
First, add the whole numbers: 3 + 2 = 5. Then, add the fractional parts: + = . Finally, add the whole number and fractional parts together to create a mixed number: 5 .
They could turn each mixed number into an improper fraction, then add the improper fractions together, and finally convert the answer back into a mixed number:
First, convert 3 into an improper fraction: . Then, convert 2 into an improper fraction: . Then, add the improper fractions together: + = . Finally, turn the answer back into a mixed number: = 5 .
The same strategies can be applied to subtracting fractions using mixed numbers.
2. Multiply and divide with fractions
In this example, the half is shown on the left by splitting the shape vertically into two equal pieces. The same shape will then be drawn to represent quarters , this time split horizontally into four equal pieces. The diagrams will then be added together to divide the shape into eighths:
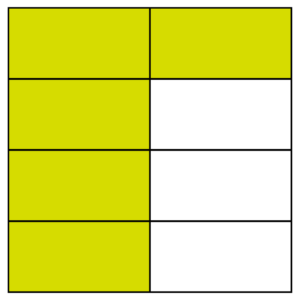
The answer can be found where the half and the quarter overlap to make one eighth :
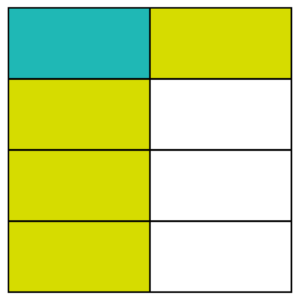
Fraction Calculations in School

3. Calculate with decimals
Your child will continue to practise adding and subtracting with decimal numbers up to 3 decimal places. They will have to understand the effect of multiplying and dividing decimal numbers by 10, 100, 1000, and so on.
Place value charts are a great way to visualise these changes:

Help your child to understand that dividing by 10 means getting ten times smaller, dividing by 100 means getting a hundred times smaller, and so on. The same concept applies to multiplication, but the other way around.
Calculate with numbers that have 3 decimal places in the real world. For example, when you fill the car with petrol, ask your child to tell you what the number is by explaining how many tenths, hundredths, or thousandths it has. Can they round the total price or the total amount of petrol to the nearest whole number, tenth, or hundredth? For example:
If you have 56.784 litres of petrol, you could round to the nearest litre (57L), tenth (56.8L), or hundredth (56.78L).
Money and measures are great for practising using numbers with 2 decimal places. You could show your child your shopping receipt with the total hidden. Ask your child to work out the total cost of the shopping receipt. How much change you would be given if you paid using, for instance, a £10 note?
4. Link fractions, decimals, and percentages
It is important your child understands that decimals and percentages are just other ways to show fractions.
Fraction, Decimal, and Percentage Treasure Hunt

Practise matching percentages, decimals, and fractions on a fun treasure hunt.
5. Multiply fractions and mixed numbers by whole numbers
Your child will multiply proper fractions and mixed numbers by whole numbers.
6. Percentages
Your child will continue to work with percentages. Talk about how ‘percent’ means ‘number of parts per hundred’.
Sales at the shops can provide great real-life opportunities to work with percentages. For example, you could ask your child to help you work out the sale price of an item. If there is 30% off a T-shirt and the full price is £9.99, what is 30% of the full price and what is the sale price?
- Age 3–4 (Early Years)
- Age 4–5 (Reception)
- Age 5–6 (Year 1)
- Age 6–7 (Year 2)
- Age 7–8 (Year 3)
- Age 8–9 (Year 4)
- Age 9–10 (Year 5)
- Age 10–11 (Year 6)
- Year 1 (age 5–6)
- Year 2 (age 6–7)
- Year 3 (age 7–8)
- Year 4 (age 8–9)
- Year 5 (age 9–10)
- Year 6 (age 10–11)
- Help with times tables
- Ratio & proportion
- Learning to tell the time
- Numicon parent guide
- MyMaths parent guide
- Maths activity books

COMMENTS
To be able to solve a range of division problems that involve fractions. These were created for a Year 6 SATs revision session to ensure that pupils were getting repetitive practice . The pupils can work their way from red to green and then continue on to an extension activity. The worksheets cover multiplying and dividing fractions with equal ...
Reasoning and Problem Solving Step 12: Divide Fractions by Integers 1 National Curriculum Objectives: Mathematics Year 6: (6F2) Use common factors to simplify fractions; use common multiples to express fractions in the same denomination Mathematics Year 6: (6F5b) Divide proper fractions by whole numbers [for example, 1/3 ÷ 2 = 1/6 ...
This comprehensive teaching pack has been written in line with Version 3.0 of the White Rose Maths scheme of learning for year 6 autumn term block 4 small step 2: Multiply Fractions by Fractions. Included in the pack is an easy-to-follow PowerPoint containing fluency, reasoning and problem-solving activities for your children to work through together. The accompanying activity sheets follow ...
Here are 24 free fractions questions for Year 6, a perfect resource to use with pupils in the run up to the KS2 Maths SATs in May. In addition to the questions, we’ve also included useful background information on the fractions knowledge Year 6 pupils need to acquire by the end of KS2. This includes the key vocabulary, concepts and fraction ...
Accept any 8 pairs of proper and improper fractions which multiply together to give the correct answer, for example: 6 13 78. x =. 3 8 24. 9b. He has multiplied both 17 and 13 by 6, instead of multiplying 17 by 6 and 13 by 7. The answer should be: 102 11 or 1. 91 91. Reasoning and Problem Solving – Multiply Fractions by Fractions ANSWERS.
Use these cards to extend your pupils\' understanding in an interesting way. These Challenge Cards provide a range of maths mastery activities based around the Year 6 objective, multiply simple pairs of proper fractions, writing the answer in its simplest form. The above video may be from a third-party source.
This in-depth maths investigation is an open-ended problem solving activity for Year 6 children. It can be used to support teaching towards the objective: multiply and divide fractions. In-depth Investigation: Mixed up fractions. Children add a pair of fractions, multiply the same pair, then find the difference between the two answers, looking ...
Mathematics Year 6: (6F2) Use common factors to simplify fractions; use common multiples to express fractions in the same denomination Mathematics Year 6: (6F3) Compare and order fractions, including fractions > 1 Mathematics Year 6: (6F4) Add and subtract fractions with different denominators and mixed numbers, using the concept of equivalent ...
Reasoning and Problem Solving – Four Rules with Fractions – Teaching Information. 1a. 2 + 4 + 2 = 1 4. 5 5 5 5. number in the answer to make the calculation correct. D. 1b. 3 – 2 ) x 6 = 8. 4 4 4 16.
Fractions in Year 6 (age 10–11) In Year 6, your child will solve lots of problems involving fractions, decimals, and percentages. They will simplify fractions using common factors and will practise multiplying fractions. The key words for this section are common factor, numerator , denominator , improper fraction, and mixed number.