
Reading & Math for K-5
- Kindergarten
- Learning numbers
- Comparing numbers
- Place Value
- Roman numerals
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Order of operations
- Drills & practice
- Measurement
- Factoring & prime factors
- Proportions
- Shape & geometry
- Data & graphing
- Word problems
- Children's stories
- Leveled Stories
- Context clues
- Cause & effect
- Compare & contrast
- Fact vs. fiction
- Fact vs. opinion
- Main idea & details
- Story elements
- Conclusions & inferences
- Sounds & phonics
- Words & vocabulary
- Reading comprehension
- Early writing
- Numbers & counting
- Simple math
- Social skills
- Other activities
- Dolch sight words
- Fry sight words
- Multiple meaning words
- Prefixes & suffixes
- Vocabulary cards
- Other parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Capitalization
- Narrative writing
- Opinion writing
- Informative writing
- Cursive alphabet
- Cursive letters
- Cursive letter joins
- Cursive words
- Cursive sentences
- Cursive passages
- Grammar & Writing
Breadcrumbs
- Word Problems
- 4 Operations

Download & Print Only $5.70

4 Operations: Mixed word problems
Add / subtract / multiply / divide.
Students use the 4 basic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) to solve these word problems. Some questions will have more than one step. Mixing word problems encourages students to read and think about the questions rather than recognizing a pattern to the solutions.

These worksheets are available to members only.
Join K5 to save time, skip ads and access more content. Learn More
More word problem worksheets
Explore all of our math word problem worksheets , from kindergarten through grade 5.
What is K5?
K5 Learning offers free worksheets , flashcards and inexpensive workbooks for kids in kindergarten to grade 5. Become a member to access additional content and skip ads.
Our members helped us give away millions of worksheets last year.
We provide free educational materials to parents and teachers in over 100 countries. If you can, please consider purchasing a membership ($24/year) to support our efforts.
Members skip ads and access exclusive features.
Learn about member benefits
This content is available to members only.
- Forgot Password?
4th Grade Resources - Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems.
Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 x 7 as a statement that 35 is 5 times as many as 7 and 7 times as many as 5. Represent verbal statements of multiplicative comparisons as multiplication equations.
Multiply or divide to solve word problems involving multiplicative comparison, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem, distinguishing multiplicative comparison from additive comparison.
Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding.
Newest 4th Grade Resources - Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems.
(Click on a resource to see our full catalog)
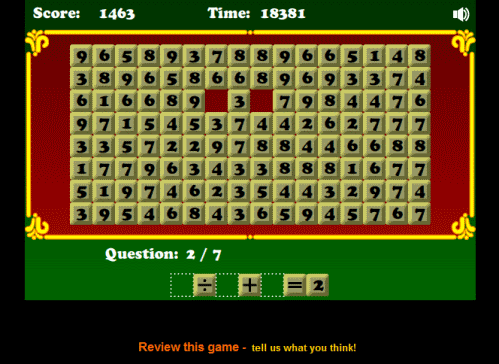
Operator Arithmetic
Use the four operators to solve multi-step equations
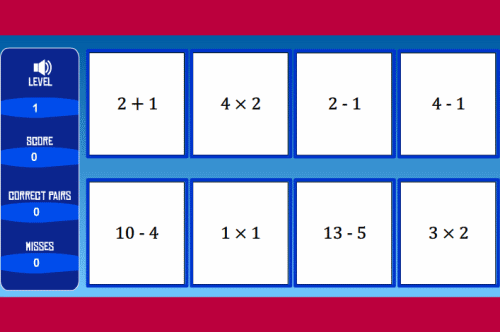
Mixed matching
Match pairs of equivalent equations to score points

Balloon Pop Mixed Operators
Pop ballons with mixed operators from smallest to largest
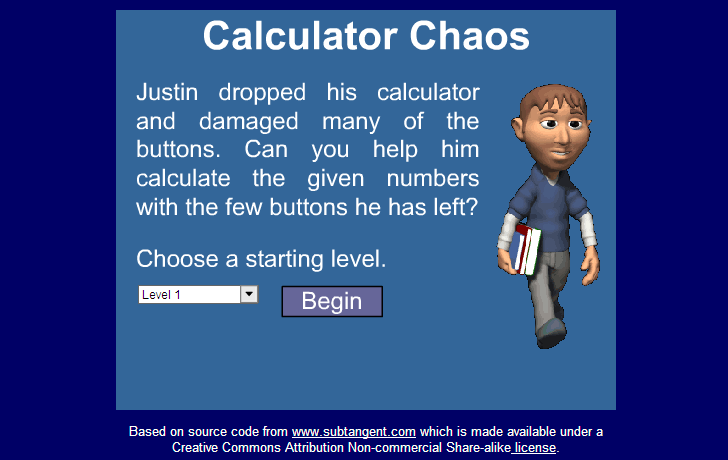
Calculator Chaos
Use knowledge of operations to solve several math problems using a single set of numbers.

Rate and keep track of your favorite activities! Sign Up to Rate Activities!
Create an Account!
Please pick a grade, elementary school math games, middle school math games, elementary school videos, middle school videos, elementary school worksheets, middle school worksheets, elementary school activities, middle school activities.
HIGH SCHOOL
- ACT Tutoring
- SAT Tutoring
- PSAT Tutoring
- ASPIRE Tutoring
- SHSAT Tutoring
- STAAR Tutoring
GRADUATE SCHOOL
- MCAT Tutoring
- GRE Tutoring
- LSAT Tutoring
- GMAT Tutoring
- AIMS Tutoring
- HSPT Tutoring
- ISAT Tutoring
- SSAT Tutoring
Search 50+ Tests
Loading Page
math tutoring
- Elementary Math
- Pre-Calculus
- Trigonometry
science tutoring
Foreign languages.
- Mandarin Chinese
elementary tutoring
- Computer Science
Search 350+ Subjects
- Video Overview
- Tutor Selection Process
- Online Tutoring
- Mobile Tutoring
- Instant Tutoring
- How We Operate
- Our Guarantee
- Impact of Tutoring
- Reviews & Testimonials
- Media Coverage
- About Varsity Tutors
Common Core: 3rd Grade Math : Solving Problems Involving the Four Operations, and Identifying and Explaining Patterns in Arithmetic
Study concepts, example questions & explanations for common core: 3rd grade math, all common core: 3rd grade math resources, example questions, example question #1 : solve two step word problems using the four operations: ccss.math.content.3.oa.d.8.

Example Question #2 : Solving Problems Involving The Four Operations, And Identifying And Explaining Patterns In Arithmetic

Example Question #1 : Solving Problems Involving The Four Operations, And Identifying And Explaining Patterns In Arithmetic

Example Question #4 : Solving Problems Involving The Four Operations, And Identifying And Explaining Patterns In Arithmetic

Example Question #5 : Solving Problems Involving The Four Operations, And Identifying And Explaining Patterns In Arithmetic

Now we need to add the watermelon, strawberries, and raspberries together to find our total.

Example Question #2 : Solve Two Step Word Problems Using The Four Operations: Ccss.Math.Content.3.Oa.D.8

Example Question #7 : Solving Problems Involving The Four Operations, And Identifying And Explaining Patterns In Arithmetic

To find the total number of flyers that she hung we add the amount of flyers on the east side and the amount on the west side.

Example Question #8 : Solving Problems Involving The Four Operations, And Identifying And Explaining Patterns In Arithmetic

Example Question #9 : Solving Problems Involving The Four Operations, And Identifying And Explaining Patterns In Arithmetic

Now we need to add up our number of balls, stuffed animals and ropes to find our total.
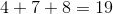
To find the total amount of laps that he swam, we need to add up the laps that he did each day.

Report an issue with this question
If you've found an issue with this question, please let us know. With the help of the community we can continue to improve our educational resources.
DMCA Complaint
If you believe that content available by means of the Website (as defined in our Terms of Service) infringes one or more of your copyrights, please notify us by providing a written notice (“Infringement Notice”) containing the information described below to the designated agent listed below. If Varsity Tutors takes action in response to an Infringement Notice, it will make a good faith attempt to contact the party that made such content available by means of the most recent email address, if any, provided by such party to Varsity Tutors.
Your Infringement Notice may be forwarded to the party that made the content available or to third parties such as ChillingEffects.org.
Please be advised that you will be liable for damages (including costs and attorneys’ fees) if you materially misrepresent that a product or activity is infringing your copyrights. Thus, if you are not sure content located on or linked-to by the Website infringes your copyright, you should consider first contacting an attorney.
Please follow these steps to file a notice:
You must include the following:
A physical or electronic signature of the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf; An identification of the copyright claimed to have been infringed; A description of the nature and exact location of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright, in \ sufficient detail to permit Varsity Tutors to find and positively identify that content; for example we require a link to the specific question (not just the name of the question) that contains the content and a description of which specific portion of the question – an image, a link, the text, etc – your complaint refers to; Your name, address, telephone number and email address; and A statement by you: (a) that you believe in good faith that the use of the content that you claim to infringe your copyright is not authorized by law, or by the copyright owner or such owner’s agent; (b) that all of the information contained in your Infringement Notice is accurate, and (c) under penalty of perjury, that you are either the copyright owner or a person authorized to act on their behalf.
Send your complaint to our designated agent at:
Charles Cohn Varsity Tutors LLC 101 S. Hanley Rd, Suite 300 St. Louis, MO 63105
Or fill out the form below:
Contact Information
Complaint details.

- Activities Index
- 50 Great Activities for Any Classroom
- QQI Activity Descriptions
- Legal & Fees
- Privacy Policy
- The Four Operations (QQI)
- The Four Operations (10QQI)
- The Four Operations (QQI Count Down)
- The Four Operations (QQI Relay)
- The Four Operations (QQI BINGO)
- The Four Operations (QQI Worksheets)
- The Four Operations (Video)
- Timestables Square (QQI)
- Grid Multiplication (QQI)
- Missing Numbers (QQI)
- Missing Numbers (10QQI)
- Missing Numbers (QQI Count Down)
- Missing Numbers (QQI Relay)
- Missing Numbers (QQI BINGO)
- Missing Numbers (QQI Worksheets)
- Order of Operations (QQI)
- Order of Operations (10QQI)
- Order of Operations (QQI Count Down)
- Order of Operations (QQI Relay)
- Order of Operations (QQI BINGO)
- Order of Operations (QQI Worksheets)
- Powers of Ten (QQI)
- Powers of Ten (10QQI)
- Powers of Ten (QQI Count Down)
- Powers of Ten (QQI Relay)
- Powers of Ten (QQI BINGO)
- Powers of Ten (QQI Worksheets)
- Decimal Operations (QQI)
- Decimal Operations (10QQI)
- Decimal Operations (QQI Count Down)
- Decimal Operations (QQI Relay)
- Decimal Operations (QQI BINGO)
- Decimal Operations (QQI Worksheets)
- Rounding (QQI)
- Rounding (10QQI)
- Rounding (QQI Count Down)
- Rounding (QQI Relay)
- Rounding (QQI BINGO)
- Rounding (QQI Worksheets)
- Products and Sums (QQI)
- Products and Sums (10QQI)
- Cancelling Fractions (QQI)
- Cancelling Fractions (10QQI)
- Cancelling Fractions (QQI Count Down)
- Cancelling Fractions (QQI Relay)
- Cancelling Fractions (QQI BINGO)
- Cancelling Fractions (QQI Worksheets)
- Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions (QQI)
- Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions (10QQI)
- Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions (QQI Count Down)
- Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions (QQI Relay)
- Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions (QQI BINGO)
- Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions (QQI Worksheets)
- Fractions of Amounts (QQI)
- Fractions of Amounts (10QQI)
- Fractions of Amounts (QQI Count Down)
- Fractions of Amounts (QQI Relay)
- Fractions of Amounts (QQI BINGO)
- Fractions of Amounts (QQI Worksheets)
- Fraction Arithmetic (QQI)
- Fraction Arithmetic (10QQI)
- Fraction Arithmetic (QQI Count Down)
- Fraction Arithmetic (QQI Relay)
- Fraction Arithmetic (QQI BINGO)
- Fraction Arithmetic (QQI Worksheets)
- Fraction Decimal Conversions Drill
- Percentages of Amounts (QQI)
- Percentages of Amounts (10QQI)
- Percentages of Amounts (QQI Count Down)
- Percentages of Amounts (QQI Relay)
- Percentages of Amounts (QQI BINGO)
- Percentages of Amounts (QQI Worksheets)
- Percentage of Amounts (Video)
- Writing Numbers as a Percentage (QQI)
- Writing Numbers as a Percentage (10QQI)
- Writing Numbers as a Percentage (QQI Count Down)
- Writing Numbers as a Percentage (QQI Relay)
- Writing Numbers as a Percentage (QQI BINGO)
- Writing Numbers as a Percentage (QQI Worksheets)
- Writing Numbers as a Percentage (Video)
- Percentage Change (QQI)
- Percentage Change (10QQI)
- Percentage Change (QQI Count Down)
- Percentage Change (QQI Relay)
- Percentage Change (QQI Worksheets)
- Percentage Change (Video)
- Increase and Decrease by a Percentage (QQI)
- Increase and Decrease by a Percentage (10QQI)
- Increase and Decrease by a Percentage (QQI Count Down)
- Increase and Decrease by a Percentage (QQI Relay)
- Increase and Decrease by a Percentage (QQI BINGO)
- Increase and Decrease by a Percentage (QQI Worksheets)
- Increase and Decrease by a Percentage (Video)
- Compound Interest and Simple Interest (QQI)
- Compound Interest and Simple Interest (10QQI)
- Compound Interest and Simple Interest (QQI Count Down)
- Compound Interest and Simple Interest (QQI Relay)
- Compound Interest and Simple Interest (QQI BINGO)
- Compound Interest and Simple Interest (QQI Worksheets)
- Compound Interest and Simple Interest (Video)
- Overall Percentage Change (QQI)
- Overall Percentage Change (10QQI)
- Overall Percentage Change (QQI Count Down)
- Overall Percentage Change (QQI Relay)
- Overall Percentage Change (QQI BINGO)
- Overall Percentage Change (QQI Worksheets)
- Reverse Percentages (QQI)
- Reverse Percentages (10QQI)
- Reverse Percentages (QQI Count Down)
- Reverse Percentages (QQI Relay)
- Reverse Percentages (QQI BINGO)
- Reverse Percentages (QQI Worksheets)
- Reverse Percentages (Video)
- Mixed Percentages (QQI)
- Mixed Percentages (10QQI)
- Mixed Percentages (QQI Count Down)
- Mixed Percentages (QQI Relay)
- Mixed Percentages (QQI BINGO)
- Mixed Percentages (QQI Worksheets)
- Number Properties (QQI)
- Product of Primes (QQI)
- Product of Primes (10QQI)
- Product of Primes (QQI Count Down)
- Product of Primes (QQI Relay)
- Product of Primes (QQI BINGO)
- Product of Primes (QQI Worksheets)
- HCF and LCM (QQI)
- HCF and LCM (10QQI)
- HCF and LCM (QQI Count Down)
- HCF and LCM (QQI Relay)
- HCF and LCM (QQI BINGO)
- HCF and LCM (QQI Worksheets)
- HCF and LCM (Video)
- 100 Square Multiples (QQI)
- 100 Square Types of Numbers (QQI)
- Standard Form Conversions (QQI)
- Standard Form Conversions (10QQI)
- Standard Form Conversions (QQI Count Down)
- Standard Form Conversions (QQI Relay)
- Standard Form Conversions (QQI BINGO)
- Standard Form Conversions 2 (QQI BINGO)
- Standard Form Conversions (QQI Worksheets)
- Standard Form Arithmetic (QQI)
- Standard Form Arithmetic (10QQI)
- Standard Form Arithmetic (QQI Count Down)
- Standard Form Arithmetic (QQI Relay)
- Standard Form Arithmetic (QQI BINGO)
- Standard Form Arithmetic (QQI Worksheets)
- Ratio (Video)
- Surds (QQI)
- Surds (10QQI)
- Surds (QQI Count Down)
- Surds (QQI Relay)
- Surds (QQI BINGO)
- Surds (QQI Worksheets)
- Collecting Like Terms (QQI)
- Collecting Like Terms (10QQI)
- Collecting Like Terms (QQI Count Down)
- Collecting Like Terms (QQI Relay)
- Collecting Like Terms (QQI BINGO)
- Collecting Like Terms (QQI Worksheets)
- Expanding Single Brackets (QQI)
- Expanding Single Brackets (10QQI)
- Expanding Single Brackets (QQI Count Down)
- Expanding Single Brackets (QQI Relay)
- Expanding Single Brackets (QQI BINGO)
- Expanding Single Brackets (QQI Worksheets)
- Factorising (QQI)
- Factorising (10QQI)
- Factorising (QQI Count Down)
- Factorising (QQI Relay)
- Factorising (QQI BINGO)
- Factorising (QQI Worksheets)
- Expanding Quadratic Brackets (QQI)
- Expanding Quadratic Brackets (10QQI)
- Expanding Quadratic Brackets (QQI Count Down)
- Expanding Quadratic Brackets (QQI Relay)
- Expanding Quadratic Brackets (QQI BINGO)
- Expanding Quadratic Brackets (QQI Worksheets)
- Factorising Quadratics (QQI)
- Factorising Quadratics (10QQI)
- Factorising Quadratics (QQI Count Down)
- Factorising Quadratics (QQI Relay)
- Factorising Quadratics (QQI BINGO)
- Factorising Quadratics (QQI Worksheets)
- Factorising Quadratic Expressions (Video)
- Factorising Four Term Expressions (Video)
- Indices (QQI)
- Indices (10QQI)
- Indices (QQI Count Down)
- Indices (QQI Relay)
- Indices (QQI BINGO)
- Indices (QQI Worksheets)
- Completing the Square (QQI)
- Completing the Square (10QQI)
- Completing the Square (QQI Count Down)
- Completing the Square (QQI Relay)
- Completing the Square (QQI BINGO)
- Completing the Square 2 (QQI BINGO)
- Completing the Square (QQI Worksheets)
- Simplifying Algebraic Fractions (Video)
- Adding and Subtracting Algebraic Fractions (Video)
- Multiplying and Dividing Algebraic Fractions (Video)
- Coordinates (GGB)
- Coordinate Battleship First Quadrant (GGB)
- Coordinate Battleship All Four Quadrants (GGB)
- 3D Coordinates (AGG)
- Solving Linear Equations (QQI)
- Solving Linear Equations (10QQI)
- Solving Linear Equations (QQI Count Down)
- Solving Linear Equations (QQI Relay)
- Solving Linear Equations (QQI BINGO)
- Solving Linear Equations (QQI Worksheets)
- Solving Equations with Algebraic Fractions (Video)
- Solving Quadratic Equations (QQI)
- Solving Quadratic Equations (10QQI)
- Solving Quadratic Equations (QQI Count Down)
- Solving Quadratic Equations (QQI Relay)
- Solving Quadratic Equations (QQI BINGO)
- Solving Quadratic Equations (QQI Worksheets)
- Solving Quadratic Equations by Factorising (Video)
- The Quadratic Formula (Video)
- Problems Involving Quadratic Equations (Video)
- Solving Simultaneous Equations (QQI)
- Solving Simultaneous Equations (10QQI)
- Solving Simultaneous Equations (QQI Count Down)
- Solving Simultaneous Equations (QQI Relay)
- Solving Simultaneous Equations (QQI Relay Fixed)
- Solving Simultaneous Equations (QQI BINGO)
- Solving Simultaneous Equations (QQI Worksheets)
- Solving Simultaneous Equations Graphically (Video)
- Simultaneous Equations by Substitution (Video)
- Simultaneous Equations by Elimination (Video)
- Simultaneous Equations - One Non-Linear (Video)
- Sequences Activity (QQI)
- Sequences (QQI)
- Sequences (10QQI)
- Sequences (QQI Count Down)
- Sequences (QQI Relay)
- Sequences (QQI BINGO)
- Sequences (QQI Worksheets)
- Generating Sequences (Video)
- General Term for Linear Sequences (Video)
- Simple Quadratic Sequences (Video)
- General Term for Quadratic Sequences (Video)
- General Term for Cubic Sequences (Video)
- Geometric Sequences (Video)
- Common Differences (QQI)
- Drawing Straight Line Graphs (GGB)
- Gradient of a Line (GGB)
- Gradient of a Line 2 (GGB)
- Parallel Lines (GGB)
- Perpendicular Lines (GGB)
- y = mx + c Activity (GGB)
- Battleships 1 (AGG)
- Battleships 2 (AGG)
- Battleships 3 (AGG)
- Find the Lines 1 (AGG)
- Regions in Graphs (Video)
- Drawing Curves (GGB)
- Quadratic Graphs Activity (GGB)
- Finding Quadratic Functions (Video)
- Graphs with a Casio GDC (Video)
- Graph Transformations 1 (GGB)
- Graph Transformations 2 (GGB)
- Graph Transformations 3 (GGB)
- Graph Transformations 4 (GGB)
- Graph Transformations 5 (GGB)
- Graph Transformations 6 (GGB)
- Functions Introductions (Video)
- Function Graphs and Important Points (Video)
- Solving Unfamiliar Equations Using Functions (Video)
- Function Notation Revision (Video)
- Composite Functions (Video)
- Inverse Functions (Video)
- Reflection Symmetry in Quadrilaterals (GGB)
- Reflection Symmetry in Triangles (GGB)
- Reflection Symmetry in Other Shapes (GGB)
- Rotational Symmetry in Quadrilaterals (GGB)
- Rotational Symmetry in Triangles (GGB)
- Rotational Symmetry in Other Shapes (GGB)
- Perimeters (GGB)
- Area of a Triangle (GGB)
- Area of a Parallelogram (GGB)
- Area of a Trapezium (GGB)
- Area of Compound Shapes (GGB)
- Perimeter and Area (GGB)
- Discovering Pi (GGB)
- Circumference of a Circle (GGB)
- Area of a Circle (GGB)
- Running Tracks (GGB)
- Circle Area Problem (GGB)
- Circles and Squares (GGB)
- Area (10QQI)
- Tilted Squares (GGB)
- Difference Between Two Squares (GGB)
- Volumes and Surface Areas (QQI)
- Volumes and Surface Areas (10QQI)
- Guess the Angle (GGB)
- Angles on a Straight Line (GGB)
- Angles around a Point (GGB)
- Angles in a Triangle (GGB)
- Angles in a Quadrilateral (GGB)
- Angles in a Regular Polygon (GGB)
- Angles on Parallel Lines (GGB)
- Striping Angles (GGB)
- Reflections (GGB)
- Reflection Challenge (GGB)
- Rotations (GGB)
- Rotation Challenge (GGB)
- Translations (GGB)
- Translation Challenge (GGB)
- Enlargements (GGB)
- Enlargement Challenge (GGB)
- Other Scale Factors (GGB)
- Which Transformation (GGB)
- How Many Transformations (GGB)
- Find Them All (AGG)
- Ultimate Challenge (GGB)
- Matrix Transformations (AGG)
- Pythagoras Theorem (QQI)
- Pythagoras Theorem (10QQI)
- Pythagoras Theorem (QQI Count Down)
- Pythagoras Theorem (QQI Relay)
- Pythagoras Theorem (QQI BINGO)
- Pythagoras Theorem (QQI Worksheets)
- Pythagoras Theorem (GGB)
- Pythagorean Triples (GGB)
- Pythagoras Proof (GGB)
- Ladders up Walls (GGB)
- Pythagoras in 3D (GGB)
- Finding the Hypotenuse Example (Video)
- Finding a Shorter Side Example (Video)
- Right Angled Trigonometry (QQI)
- Right Angled Trigonometry (10QQI)
- Right Angled Trigonometry (QQI Count Down)
- Right Angled Trigonometry (QQI Relay)
- Right Angled Trigonometry (QQI BINGO)
- Right Angled Trigonometry (QQI Worksheets)
- Discovering Trig Ratios (GGB)
- Finding Lengths (GGB)
- Finding Missing Lengths (Video)
- Finding Missing Angles (Video)
- Sine Rule (Video)
- Cosine Rule (Video)
- Sine and Cosine Rules (Video)
- Angle in the Centre vs Angle at the Circumference (GGB)
- Angle at the Centre vs Angle at the Circumference (Video)
- Angles in a Semicircle (GGB)
- Angle in a Semicircle (Video)
- Angles in Cyclic Quadrilaterals (GGB)
- Angles in a Cyclic Quadrilateral (Video)
- Angles in the Same Segment (GGB)
- Angles in the Same Segment (Video)
- Tangents (GGB)
- Tangents (Video)
- Alternate Segment Theorem (GGB)
- Intersecting Tangents (GGB)
- Intersecting Tangents (Video)
- Intersecting Chords (GGB)
- Vectors and Scalars (Video)
- Vector Notation (Video)
- Resultant Vectors (Video)
- Resultants of Column Vectors (Video)
- Scalar Multiplication (Video)
- Magnitude of a Vector (Video)
- Squares (GGB)
- Tangrams (GGB)
- Euler Line (GGB)
- Probability (QQI)
- Probability (10QQI)
- Probability Tools (Flash)
- Averages Activity (QQI)
- Listed Averages (QQI)
- Listed Averages (10QQI)
- Listed Averages (QQI Count Down)
- Listed Averages (QQI Relay)
- Listed Averages (QQI BINGO)
- Listed Averages (QQI Worksheets)
- Averages From Lists of Data (Video)
- Quartiles and Interquartile Range (Video)
- Averages from Frequency Tables (QQI)
- Averages from Frequency Tables (10QQI)
- Averages from Frequency Tables (QQI Count Down)
- Averages from Frequency Tables (QQI Relay)
- Averages from Frequency Tables (QQI BINGO)
- Averages from Frequency Tables (QQI Worksheets)
- Averages From Frequency Tables (Video)
- Averages From Grouped Frequency Tables (Video)
- Averages With A GDC (Video)
- Cumulative Frequency (Video)
- Scatter Graphs and the Mean Point (Video)
- Scatter Graphs and Linear Regression on a GDC (Video)
- Correlation and the Correlation Coefficient on a GDC (Video)
- Binomial Expansion (Video)
- Binomial Theorem (Video)
- Binomial Coefficients (Video)
- Binomial Applications (Video)
- Coordinate Geometry (QQI)
- Coordinate Geometry (10QQI)
- Equation of a Circle (AGG)
- Differentiating Polynomials (QQI)
- Differentiating Polynomials (10QQI)
- Differentiating Polynomials (QQI Count Down)
- Differentiating Polynomials (QQI Relay)
- Differentiating Polynomials (QQI BINGO)
- Differentiating Polynomials (QQI Worksheets)
- Finding Gradients of Curves (QQI)
- Finding Gradients of Curves (10QQI)
- Finding Turning Points of Curves (QQI)
- Finding Turning Points of Curves (10QQI)
- Radian and Degree Conversions (QQI)
- Radian and Degree Conversions (10QQI)
- Radian and Degree Conversions (QQI Count Down)
- Radian and Degree Conversions (QQI Relay)
- Radian and Degree Conversions (QQI BINGO)
- Radian and Degree Conversions (QQI Worksheets)
- Trigonometric Exact Values (QQI)
- Trigonometric Exact Values (10QQI)
- Trigonometric Exact Values (QQI Count Down)
- Trigonometric Exact Values (QQI Relay)
- Trigonometric Exact Values (QQI BINGO)
- Trigonometric Exact Values (QQI Worksheets)
- Graphs of Trig Functions (GGB)
- UKMT Random Question Generator
- @mathschallenge Random Questions
- School of Hard Sums Random Questions
- Random Starter of the Day
- Mathematically Possible (QQI Starter)
- Adding Challenge (QQI Starter)
- Date Starter (QQI Starter)
- Name That Number (QQI Starter)
- Matchstick Random Questions
- Choose 3 Numbers (QQI Starter)
- What's The Question (QQI Starter)
- Mathematical Words (QQI Starter)
- Number of the Day (QQI Starter)
- Anagrams and Missing Vowels (QQI Starter)
- Missing Vowels and Word Jumbles Simple Numbers (QQI)
- Tables (QQI)
- Target Boards (QQI)
- Missing Signs (QQI)
- Exploding Dots
- Easter Date
- Easter Tangrams (GGB)
- Zeller's Algorithm
- Batman Equation (AGG)
- Fermat's Last Theorem (Video)
- Pi Song (Video)
- Monty Hall Problem (Video)
- Symmetry, Reality's Riddle (Video)
- Music of the Primes (Video)
- Folding Paper (Video)
- Nature by Numbers (Video)
- Inspirations (Video)
The Four Operations
Special March offer - 7 days free unlimited access to all premium content Try Premium
- Fourth Grade
Four Operations Problems
Fourth grade four operations problems.

Filter by Grade:
Filter by subject:.
Worksheet on Word Problems on Four Operations
Practice the questions given in the worksheet on word problems on four operations i.e. addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (×) and division (÷).
Solve the following:
1. The population of a town is 198568. Out of them 45312 are men and 35678 are women. Find the number of children in the town.
2. A shopkeeper has 2425 boxes of 24 pencils each. How many pencils do all the boxes have in all?
3. Linda bought a coat for $2265 and a saree for $2150. She gave $5000 to the shopkeeper. How much money did the shopkeeper return to her?
4. The cost of 21 TV sets is $95844. Find the cost of one TV set.
5. A factory produces 24532 bulbs in a month. What is its annual production?
6. There are 145968 bags of sugar, 236487 bags of wheat and some bags of rice in a godown. It the total number of bags in the godown is 450000, find the number of bags of rice.
7. A factory manufactured 483685 toys in three weeks. The production in first week was 146345 toys and in second week 138152 toys. Find the production in the third week.
8. The cost of a sofa set is $9372. How much will 124 such sofa sets cost?
9. There are 86 rooms in a school. 4386 students study there. Equal number of students sits in each room?
10. 1575 students of a school want to go Agra by bus. If one bus can carry 75 students, how many buses are required to carry all the students?
11. The cost of a radio set is 1475. What is the cost of 35 such radio sets?
12. In an election, 52496 people voted for Ron, 44929 people for Jhon and 36824 people for Mike in a town. If everyone voted in the town, what is the total number of voters?
13. Maria bought 96 toys priced equally for $12960. The amount of $1015 is still left with her. Find the cost of each toy and the amount she had.
Answers for the worksheet on word problems on four operations are given below to check the exact answers of the above questions on addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
1. 117578 children.
2. 58200pencils.
5. 294384 bulbs.
6. 67545 bags.
7. 199188 toys.
8. $1162128
9. 51 students.
10. 21 buses.
13. $135, $13975
4th Grade Math Activities 4th Grade Math Worksheets
From Worksheet on Word Problems on Four Operations to HOME PAGE
New! Comments
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math . Use this Google Search to find what you need.
- Preschool Activities
- Kindergarten Math
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- 9th Grade Math
- 10th Grade Math
- 11 & 12 Grade Math
- Concepts of Sets
- Probability
- Boolean Algebra
- Math Coloring Pages
- Multiplication Table
- Cool Maths Games
- Math Flash Cards
- Online Math Quiz
- Math Puzzles
- Binary System
- Math Dictionary
- Conversion Chart
- Homework Sheets
- Math Problem Ans
- Free Math Answers
- Printable Math Sheet
- Funny Math Answers
- Employment Test
- Math Patterns
- Link Partners
- Privacy Policy

Recent Articles
Properties of Division | Division of Property Overview|Math Properties
Apr 04, 24 03:22 PM

Long Division | Method | Steps | Examples | Long Division Worksheets
Apr 04, 24 01:09 PM

Division of Two-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers | Dividing Larger Numbers
Apr 04, 24 09:31 AM

Dividing 3-Digit by 1-Digit Number | Long Division |Worksheet Answer
Apr 04, 24 09:30 AM

Months of the Year | List of 12 Months of the Year |Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr
Apr 02, 24 02:08 PM

© and ™ math-only-math.com. All Rights Reserved. 2010 - 2024.
2-Step Problems using 4 Operations Worksheets
Related Pages Math Worksheets Lessons for Third Grade Free Printable Worksheets
Printable “Word Problems” Worksheets Addition Word Problems 2nd Grade Word Problems Add/Subtract Word Problems Multiply/Divide Word Problems Word Problems using 4 Operations
Printable worksheets to help students solve 3rd grade word problems by representing the information in the problems visually with the help of tape diagrams or bar models. (Solve two-step word problems involving all four operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division)
Using tape diagrams, also known as bar models, is an effective visual strategy for solving two-step problems involving the four basic operations. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to solve 2-step problems using tape diagrams:
Read and Understand the Problem: Carefully read the problem to understand the context and identify the information given and what needs to be found.
Identify the Operations: Determine which operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division) are involved in the problem. Look for keywords that indicate each operation.
Break Down into Steps: Identify the main steps or operations required to solve the problem.
Draw the Tape Diagram: Represent the situation using a tape diagram. Use rectangles to represent quantities and label them accordingly.
Verify that your solution makes sense in the context of the problem. Check your calculations for accuracy.
Click on the following worksheet to get a printable pdf document. Scroll down the page for more 2-Step Problems using 4 Operations Worksheets .

More 2-Step Problems using 4 Operations Worksheets
Printable (Answers on the second page) 2-Step Problems Worksheet #1 2-Step Problems Worksheet #2 2-Step Problems Worksheet #3 2-Step Problems Worksheet #4 2-Step Problems Worksheet #5 2-Step Problems Worksheet #6 2-Step Problems Worksheet #7 2-Step Problems Worksheet #8 2-Step Problems Worksheet #9
Related Lessons & Worksheets
Solving 2-step Problems
More Printable Worksheets

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

WORD PROBLEMS - using all four operations
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
22 September 2020
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Thank you. Very useful
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
anncantwell
thank you so much for this just what I needed.
joyfulTAing
Thanks for the resource. Easily adaptable to my classes.
Thanks, very helpful.
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:


Four Operations in Math
The four basic operations in math are addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. These operations form the foundation of arithmetic and are essential for performing calculations and solving problems in various fields. In this article, we'll explore the principles, properties, and applications of each operation.
Four Operations Calculator
Addition is the process of combining two or more numbers to find their total, called the sum. This operation is represented by the plus symbol (+). For example:
Addition has the following properties:
- Commutative: a + b = b + a
- Associative: (a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
- Identity: a + 0 = a
Addition Calculations :
Subtraction.
Subtraction is the process of finding the difference between two numbers. This operation is represented by the minus symbol (-). For example:
Subtraction has the following properties:
- Non-commutative: a - b ≠ b - a (in general)
- Non-associative: (a - b) - c ≠ a - (b - c) (in general)
- Identity: a - 0 = a
Subtraction Calculations :
Multiplication.
Multiplication is the process of finding the product of two numbers. This operation is represented by the multiplication symbol (×) or an asterisk (*). For example:
Multiplication has the following properties:
- Commutative: a * b = b * a
- Associative: (a * b) * c = a * (b * c)
- Identity: a * 1 = a
- Distributive: a * (b + c) = a * b + a * c
Multiplication Calculations :
Division is the process of finding the quotient of two numbers, dividing one number by another. This operation is represented by the division symbol (÷) or a forward slash (/). For example:
Division has the following properties:
- Non-commutative: a / b ≠ b / a (in general)
- Non-associative: (a / b) / c ≠ a / (b / c) (in general)
- Identity: a / 1 = a
- Undefined for division by zero: a / 0 is undefined
Division Calculations :
Applications of the four operations.
The four basic operations are used in a wide range of mathematical and real-world applications, including:
- Calculating totals, change, and discounts in finance
- Measuring distances, areas, and volumes in geometry
- Deriving equations and solving problems in algebra
- Analyzing data and calculating probabilities in statistics
- Modeling scenarios and making predictions in various fields
The four basic operations in math - addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division - are fundamental to arithmetic and problem-solving. Understanding their principles, properties, and applications is essential for success in mathematics and various real-world contexts.
How To Use Fractions In 4-Operations
To add fractions, make sure the denominators are the same. Add the numerators together and keep the denominator the same. Simplify the result if needed.
Subtraction:
Similar to addition, ensure the denominators are identical. Subtract the numerators while keeping the denominator constant. Simplify the result if necessary.
Multiplication:
Multiply the numerators together to get the new numerator. Multiply the denominators together to get the new denominator. Simplify the resulting fraction if possible.
To divide fractions, multiply by the reciprocal of the second fraction. Invert the second fraction (swap the numerator and denominator). Then, follow the steps for multiplication.
Fractions Operations :
Get your answer in FOUR OPERATIONS math solver.
About Us | Contact | Privacy
Copyright 2022 - © FourOperations.com
SMathSmarts
A shared partnership program with HCTM and HCPS
Problem Solving Using the Four Operations
Primary Standards:
MAFS.3.OA.4.8 Solve two-step word problems using the four (addition or subtraction) operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter (symbol) standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding.
MAFS.3.OA.1.3 Use multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems in situations involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.
Connecting Standards:
MAFS.3.OA.1.4 Determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division equation relating three whole numbers. For example, determine the unknown number that makes the equation true in each of the equations 8 × ? = 48, 5 = [] ÷ 3, 6 × 6 = ?.
Content Knowledge:
In prior grades, students solved a variety of one- and two-step word problems using addition or subtraction. In 3 rd grade, with the introduction of multiplication and division, they will be challenged to solve one- and two-step problems with all four of the operations.
Knowing which operation makes sense to solve a problem is a foundational problem-solving skill. This is not achieved by identifying key words that tell students what to do, but instead, by recognizing the story situation or structure. When students understand what is happening in a story problem and know the actions of the operations, they are able to match the operation to the problem situation.
A critical skill in solving word problems is the ability to represent the problem situation with equations. In prior situations, students used symbols such as a blank space, a box, or a question mark to represent missing information. In 3 rd grade, they are introduced to the use of a letter to stand of unknowns in equations. Students may be accustomed to representing a problem with an equation, but in two-step problems they may need to build two equations as they work through the steps of the problem.
GCG 1 – Learning Goal: As a mathematician, I will be able to model and solve one-step problems; represent problems using equations with a letter for the unknown
- Step 1: Represent a problem-solving situation with an equation, using a letter for the unknown
- Step 2: Solve one-step equations, using a letter for the unknown
GCG 2 – Learning Goal: As a mathematician, I will be able to model and solve two-step problems; represent problems using equations with a letter for the unknown
- Step 1: Explain and directly model the steps of a two-step problem with concrete models or drawings
- Step 2: Represent a two-step problem-solving situation with an equation (or equations), using a letter for the unknown
- Step 3: Solve two-step problems using models, drawing, or equations
problem solving using 4 operations
All Formats
Resource types, all resource types.
- Rating Count
- Price (Ascending)
- Price (Descending)
- Most Recent
Problem solving using 4 operations
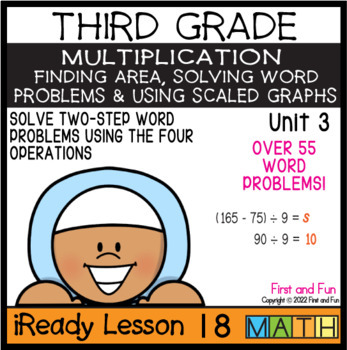
3RD GRADE SOLVE TWO-STEP WORD PROBLEMS USING THE 4 OPERATIONS iREADY LESSON 18

Two Step Word Problem Using All Four Basic Operations Math Tasks - Word Problems

- Easel Activity

4th Grade Math - Solve multistep word problems using the four operations 4 .OA.3

Solve Integers Word Problems using all 4 Operations - Learning Station BUNDLE

DIGITAL BUNDLE - Solve Integers Word Problems using all 4 Operations

2 step problem solving ( using all 4 operations ) Scavenger Hunt

Problem Solve Using the Four Operations - 3rd Grade

GRADE-3(3.OA.8) SOLVE 2-STEP WORD PROBLEMS USING THE FOUR OPERATIONS GOOGLE FORMS

- Google Slides™

Solve Integers Word Problems using all 4 Operations - Resource Pack

EXIT TICKET- SOLVE TWO-STEP WORD PROBLEMS USING THE FOUR OPERATIONS - 3.OA.8
Grade 4 Lesson Plan-Topic 6 Use Operations with Whole Numbers to Solve Problems

3rd Grade 160 Word Problems Math Problem Solving CCSS *All Standards*

GRADE 4 CSI Math Murder Mystery Activity - Fun Review of all CCSS Topics

2-Step Word Problems Using the Four Operations

TEKS 5.4B Represent and Solve Multi-Step Problems - Practice Sheets

CUBES Problem Solving Strategy Toolkit

Order of Operations 4 Decimals with Parenthesis Math Riddles Worksheets

- Google Apps™

TEKS 4 .4H and 4 .5A Represent and Solve Word Problems Task Cards

Choose the Operation : Using a Problem Solving Approach

Represent & Solve Multi-Step Problems Interactive Notebook Quick Check TEKS 5.4B

FREE 2-Step Word Problems Using the Four Operations

Word Problem Sort for 4 Operations | 3rd and 4th Grade

4th Grade Problem Solving & Input-Output Tables TEKS Exit Slips

Problem Solving Game

- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

Herbert Chanoch Kelman, 94
Everett irwin mendelsohn, 91.

Anticipate, accommodate, empower
Exploring generative ai at harvard.
Jessica McCann
Harvard Correspondent

Leaders weigh in on where we are and what’s next
The explosion of generative AI technology over the past year and a half is raising big questions about how these tools will impact higher education. Across Harvard, members of the community have been exploring how GenAI will change the ways we teach, learn, research, and work.
As part of this effort, the Office of the Provost has convened three working groups . They will discuss questions, share innovations, and evolve guidance and community resources. They are:
- The Teaching and Learning Group , chaired by Bharat Anand , vice provost for advances in learning and the Henry R. Byers Professor of Business Administration at Harvard Business School. This group seeks to share resources, identify emerging best practices, guide policies, and support the development of tools to address common challenges among faculty and students.
- The Research and Scholarship Group , chaired by John Shaw , vice provost for research, Harry C. Dudley Professor of Structural and Economic Geology in the Earth and Planetary Sciences Department, and professor of environmental science and engineering in the Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Science. It focuses on how to enable, and support the integrity of, scholarly activities with generative AI tools.
- T he Administration and Operations Group , chaired by Klara Jelinkova , vice president and University chief information officer. It is charged with addressing information security, data privacy, procurement, and administration and organizational efficiencies.

Klara Jelinkova, Bharat Anand, and John Shaw.
Photos by Kris Snibbe/Harvard Staff Photographer; Evgenia Eliseeva; and courtesy of John Shaw
The Gazette spoke with Anand, Shaw, and Jelinkova to understand more about the work of these groups and what’s next in generative AI at Harvard.
When generative AI tools first emerged, we saw universities respond in a variety of ways — from encouraging experimentation to prohibiting their use. What was Harvard’s overall approach?
Shaw: From the outset, Harvard has embraced the prospective benefits that GenAI offers to teaching, research, and administration across the University, while being mindful of the potential pitfalls. As a University, our mission is to help enable discovery and innovation, so we had a mandate to actively engage. We set some initial, broad policies that helped guide us, and have worked directly with groups across the institution to provide tools and resources to inspire exploration.
Jelinkova: The rapid emergence of these tools meant the University needed to react quickly, to provide both tools for innovation and experimentation and guidelines to ensure their responsible use. We rapidly built an AI Sandbox to enable faculty, students, and staff to experiment with multiple large language models in a secure environment. We also worked with external vendors to acquire enterprise licenses for a variety of tools to meet many different use cases. Through working groups, we were able to learn, aggregate and collate use cases for AI in teaching, learning, administration, and research. This coordinated, collective, and strategic approach has put Harvard ahead of many peers in higher education.
Anand: Teaching and learning are fundamentally decentralized activities. So our approach was to ask: First, how can we ensure that local experimentation by faculty and staff is enabled as much as possible; and second, how can we ensure that it’s consistent with University policies on IP, copyright, and security? We also wanted to ensure that novel emerging practices were shared across Schools, rather than remaining siloed.
What do these tools mean for faculty, in terms of the challenges they pose or the opportunities they offer? Is there anything you’re particularly excited about?
Anand: Let’s start with some salient challenges. How do we first sift through the hype that’s accompanied GenAI? How can we make it easy for faculty to use GenAI tools in their classrooms without overburdening them with yet another technology? How can one address real concerns about GenAI’s impact?
While we’re still early in this journey, many compelling opportunities — and more importantly, some systematic ways of thinking about them — are emerging. Various Harvard faculty have leaned into experimenting with LLMs in their classrooms. Our team has now interviewed over 30 colleagues across Harvard and curated short videos that capture their learnings. I encourage everyone to view these materials on the new GenAI site; they are remarkable in their depth and breadth of insight.
Here’s a sample: While LLMs are commonly used for Q&A, our faculty have creatively used them for a broader variety of tasks, such as simulating tutors that guide learning by asking questions, simulating instructional designers to provide active learning tips, and simulating student voices to predict how a class discussion might flow, thus aiding in lesson preparation. Others demonstrate how more sophisticated prompts or “prompt engineering” are often necessary to yield more sophisticated LLM responses, and how LLMs can extend well beyond text-based responses to visuals, simulations, coding, and games. And several faculty show how LLMs can help overcome subtle yet important learning frictions like skill gaps in coding, language literacy, or math.
Do these tools offer students an opportunity to support or expand upon their learning?
Anand: Yes. GenAI represents a unique area of innovation where students and faculty are working together. Many colleagues are incorporating student feedback into the GenAI portions of their curriculum or making their own GenAI tools available to students. Since GenAI is new, the pedagogical path is not yet well defined; students have an opportunity to make their voices heard, as co-creators, on what they think the future of their learning should look like.
Beyond this, we’re starting to see other learning benefits. Importantly, GenAI can reach beyond a lecture hall. Thoughtful prompt engineering can turn even publicly available GenAI tools into tutorbots that generate interactive practice problems, act as expert conversational aids for material review, or increase TA teams’ capacity. That means both that the classroom is expanding and that more of it is in students’ hands. There’s also evidence that these bots field more questions than teaching teams can normally address and can be more comfortable and accessible for some students.
Of course, we need to identify and counter harmful patterns. There is a risk, in this early and enthusiastic period, of sparking over-reliance on GenAI. Students must critically evaluate how and where they use it, given its possibility of inaccurate or inappropriate responses, and should heed the areas where their style of cognition outperforms AI. One other thing to watch out for is user divide: Some students will graduate with vastly better prompt engineering skills than others, an inequality that will only magnify in the workforce.
What are the main questions your group has been tackling?
Anand: Our group divided its work into three subgroups focused on policy, tools, and resources. We’ve helped guide initial policies to ensure safe and responsible use; begun curating resources for faculty in a One Harvard repository ; and are exploring which tools the University should invest in or develop to ensure that educators and researchers can continue to advance their work.
In the fall, we focused on supporting and guiding HUIT’s development of the AI Sandbox. The Harvard Initiative for Learning and Teaching’s annual conference , which focused exclusively on GenAI, had its highest participation in 10 years. Recently, we’ve been working with the research group to inform the development of tools that promise broad, generalizable use for faculty (e.g., tutorbots).
What has your group focused on in discussions so far about generative AI tools’ use in research?
Shaw: Our group has some incredible strength in researchers who are at the cutting edge of GenAI development and applications, but also includes voices that help us understand the real barriers to faculty and students starting to use these tools in their own research and scholarship. Working with the other teams, we have focused on supporting development and use of the GenAI sandbox, examining IP and security issues, and learning from different groups across campus how they are using these tools to innovate.
Are there key areas of focus for your group in the coming months?
Shaw: We are focused on establishing programs — such as the new GenAI Milton Fund track — to help support innovation in the application of these tools across the wide range of scholarship on our campus. We are also working with the College to develop new programs to help support students who wish to engage with faculty on GenAI-enabled projects. We aim to find ways to convene students and scholars to share their experiences and build a stronger community of practitioners across campus.
What types of administration and operations questions are your group is exploring, and what type of opportunities do you see in this space?
Jelinkova: By using the group to share learnings from across Schools and units, we can better provide technologies to meet the community’s needs while ensuring the most responsible and sustainable use of the University’s financial resources. The connections within this group also inform the guidelines that we provide; by learning how generative AI is being used in different contexts, we can develop best practices and stay alert to emerging risks. There are new tools becoming available almost every day, and many exciting experiments and pilots happening across Harvard, so it’s important to regularly review and update the guidance we provide to our community.
Can you talk a bit about what has come out of these discussions, or other exciting things to come?
Jelinkova: Because this technology is rapidly evolving, we are continually tracking the release of new tools and working with our vendors as well as open-source efforts to ensure we are best supporting the University’s needs. We’re developing more guidance and hosting information sessions on helping people to understand the AI landscape and how to choose the right tool for their task. Beyond tools, we’re also working to build connections across Harvard to support collaboration, including a recently launched AI community of practice . We are capturing valuable findings from emerging technology pilot programs in HUIT , the EVP area , and across Schools. And we are now thinking about how those findings can inform guiding principles and best practices to better support staff.
While the GenAI groups are investigating these questions, Harvard faculty and scholars are also on the forefront of research in this space. Can you talk a bit about some of the interesting research happening across the University in AI more broadly ?
Shaw: Harvard has made deep investments in the development and application of AI across our campus, in our Schools, initiatives, and institutes — such as the Kempner Institute and Harvard Data Science Initiative. In addition, there is a critical role for us to play in examining and guiding the ethics of AI applications — and our strengths in the Safra and Berkman Klein centers, as examples, can be leading voices in this area.
What would be your advice for members of our community who are interested in learning more about generative AI tools?
Anand: I’d encourage our community to view the resources available on the new Generative AI @ Harvard website , to better understand how GenAI tools might benefit you.
There’s also no substitute for experimentation with these tools to learn what works, what does not, and how to tailor them for maximal benefit for your particular needs. And of course, please know and respect University policies around copyright and security.
We’re in the early stages of this journey at Harvard, but it’s exciting.
Share this article
You might like.
Memorial Minute — Faculty of Arts and Sciences

How to ensure students with disabilities have an equal chance to succeed?
College accepts 1,937 to Class of 2028
Students represent 94 countries, all 50 states
Forget ‘doomers.’ Warming can be stopped, top climate scientist says
Michael Mann points to prehistoric catastrophes, modern environmental victories
Pushing back on DEI ‘orthodoxy’
Panelists support diversity efforts but worry that current model is too narrow, denying institutions the benefit of other voices, ideas

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Add / subtract / multiply / divide. Students use the 4 basic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) to solve these word problems. Some questions will have more than one step. Mixing word problems encourages students to read and think about the questions rather than recognizing a pattern to the solutions.
students to solve two-step word problems using the four operations. This mini- assessment is designed for teachers to use either in the classroom, for self -learning, or in professional development ... students for multi-step problem solving (4.OA.A.3). Standard 3.OA.D.8 and this miniassessment target - application, one of the three elements of ...
addresses problem solving with all four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted, which is at the heart of the grade 4 standards and a key component of the Major Work of the Grade. 1. It addresses coherence across grades because it completes the learning of problem solving skills using the four operations that began in
Create a free account to gain full access to the website. Save & Organize Resources. See State Standards. Manage Classes & Assignments. Sync with Google Classroom. Create Lessons. Customized Dashboard. Find lessons on Solving Problems With the Four Operations for all grades. Free interactive resources and activities for the classroom and home.
4th Grade Resources - Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 x 7 as a statement that 35 is 5 times as many as 7 and 7 times as many as 5. Represent verbal statements of multiplicative comparisons as multiplication equations. Multiply or divide to ...
Example Question #4 : Solving Problems Involving The Four Operations, And Identifying And Explaining Patterns In Arithmetic Jason loves to run and is training for a marathon at the end of the month. His training program has him running miles three times a week, and miles one time a week.
The Four Operations ( Video) A series of short videos explaining how to perform written arithmetic methods. Timestables Square ( QQI) A 10x10 square to practise you basic timestables. Grid Multiplication ( QQI) In this QQI activity you can practise multiplication skills further using the grid method. The activity shows the full solution with ...
Solving four operations problems is a great way to practice many different subjects simultaneously: addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and of course - order of operations. Here you will find our range of worksheets and resources to help your child learn to use all operations together and order and practice different problem ...
Find the cost of each toy and the amount she had. Answers for the worksheet on word problems on four operations are given below to check the exact answers of the above questions on addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Answers: 1. 117578 children. 2. 58200pencils.
Key learning points. In this lesson, we will solve a multi-step problem using all four operations; addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Licence. This content is made available by Oak National Academy Limited and its partners and licensed under Oak's terms & conditions (Collection 1), except where otherwise stated.
Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding. Identify arithmetic patterns (including patterns in the addition table or multiplication ...
Our new maths game Roll It Operations Game will give your students the practice they need to apply each of the four operations in order to solve problems involving whole numbers. Students roll two dice. They add, subtract, multiply and divide the two numbers shown on the dice (if they can). If any of the answers appear in the grid, they cover ...
These four operations worksheets include a number of different word problems for Year 5 and Year 6 children to solve. They are differentiated so they are suitable for all abilities, plus they can complete the four operation word problems in pairs. Simply take turns to select a word problem to complete. Once completed, children can ask their ...
4.9. (105) $4.50. PPT. Fourth Grade Common Core Math - Solve multistep word problems using the four operations 4.OA.A.3 Practice provides two ways for students to practice and show mastery of their ability to solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in ...
Problem Solving Using All 4 Operations https://youtu.be/MpSGFm6AUPg Playlist https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLBO60JrapqvBPUAv1cTGOEYzBhElusPLUSUBSCRIBE ...
Printable worksheets to help students solve 3rd grade word problems by representing the information in the problems visually with the help of tape diagrams or bar models. (Solve two-step word problems involving all four operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division) Using tape diagrams, also known as bar models, is an ...
Subject: Mathematics. Age range: 7-11. Resource type: Worksheet/Activity. File previews. docx, 103.55 KB. These multi -step word problems are designed to support students in gaining confidence in their abilities to solve problems using all four operations. The word problems also involve money and finding 10%. Creative Commons "Sharealike".
Fourth Grade Common Core Math - Solve multistep word problems using the four operations 4.OA.A.3 Practice provides two ways for students to practice and show mastery of their ability to solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be ...
Four Operations in Math. The four basic operations in math are addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. These operations form the foundation of arithmetic and are essential for performing calculations and solving problems in various fields. In this article, we'll explore the principles, properties, and applications of each operation.
4th Grade Worksheets - Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 x 7 as a statement that 35 is 5 times as many as 7 and 7 times as many as 5. Represent verbal statements of multiplicative comparisons as multiplication equations. Multiply or divide to ...
Step 1: Represent a problem-solving situation with an equation, using a letter for the unknown. Step 2: Solve one-step equations, using a letter for the unknown. GCG 2 - Learning Goal: As a mathematician, I will be able to model and solve two-step problems; represent problems using equations with a letter for the unknown.
Browse problem solving using 4 operations resources on Teachers Pay Teachers, a marketplace trusted by millions of teachers for original educational resources.
Shaw: From the outset, Harvard has embraced the prospective benefits that GenAI offers to teaching, research, and administration across the University, while being mindful of the potential pitfalls. As a University, our mission is to help enable discovery and innovation, so we had a mandate to actively engage.