

Realism of Education
Feb 12, 2014
1.57k likes | 3.74k Views
Realism of Education. Present by Miss Kamonrat Chimpalee Mrs. Siwaporn Ratanapech Mrs. Siripun Siribunnam. Contents. Overview. Introduction. Definition of Realism. Aristotle, Thomas Aquinas, Francis Bacon, John Locke etc. Key Philosophers. Educator, Director Teacher and Student.
Share Presentation
- realist www themegallery com
- educator religious realist
- most recent
- critical reasoning

Presentation Transcript
Realism of Education Present byMiss KamonratChimpaleeMrs. SiwapornRatanapechMrs. SiripunSiribunnam
Contents Overview Introduction Definition of Realism Aristotle, Thomas Aquinas, Francis Bacon, John Locke etc. Key Philosophers Educator, Director Teacher and Student • Characteristic Technique/ media Classroom Activity www.themegallery.com
Characteristics of Realismist • Teacher • Educator Characteristics • Director • Student www.themegallery.com
Characteristic Educator Characteristic Educator Religious Realist Scientific realist
1. Realists believe nature (God) should be the principle aim of educator 2. Studying the world carefully Characteristic of Educator Religious Realist www.themegallery.com
1. Understanding of the material world through the development of methods of inquiry 2. Should clear their minds of the idols of generalization language and philosophy 3. Deduction Approach, rational thought Characteristic of Educator Scientific realist www.themegallery.com
4. Promoter a study of science and scientific method 6. Reading , Writing and Arithmetic 5. The idea of survival is and important one Characteristic of Educator Scientific realist www.themegallery.com
7. Concern for religion , patriotism and capitalism. 8. Emphasis on the practical, includes moral and character development. Characteristic of Educator Scientific realist www.themegallery.com
Characteristic of Director Religious realist 1. The school as a place where students are very happy and convenience in the ministry. 2. The promote harmony, collaboration. 3. Create an environment within the school with a good nature. 4. Promotional activities public in terest
Characteristic of Director Religious realist 5. Establishing a library that provides students with the Bible. 6. Promote the cultural heritage of their own learning 3. Create an environment within the school with a good nature. 4. Promotional activities public in terest
Characteristic of Director Scientific realist 1. The policy of producing students who are competent to practice. 2. Formalize the rules in school. 3. Encourage teachers to use the semi-experience in teaching. 4. Create environment within the school physic.
Characteristic of Director Scientific realist 5. The equality in their subordinates and social contracting. 6. In school, everyone must know the functions and duties of his intentions . 7. Audio-visual support in the classroom
Characteristic of Director Scientific realist 8. Supporting co-create Curriculumdesign andIntegration Learning. 9.Specific degrees to teach in their subject. 10. Encourages cooperation in research texts, the actual assembly.
Characteristic of Teacher Curriculum Methods. Role of the Teacher www.themegallery.com
Cultural Literacy • Reading , Writing and Arithmetic(Great Books) • Add Science, Geology, music and Art was provided student face a situation. • Physical activityhas educational value (Locke) Curriculum • Use of objects in education (Maria Montessori) • Attention to the completeperson (Locke) • Extensive use of pictures (John Amos Comenius) www.themegallery.com
Natural Law Correspondence Theory Scientific Realism The Spectator Theory Pure Theory Method Theory of Learning. • Reality and Natural • Natural Plan Correspond between Idea and Essence Scientific Method Prove Common sense www.themegallery.com
Self-evidence and Intuition Neo-ThomistEpistemology Intuition and Revelation Cause Principle Method Theory of Learning. • Synthetic or Evidence truth • Analytic or Self-Evident truth Analysis and Intuition All things have a cause
Role of teacher • Not only facts, but method of arriving at facts • Emphasis on critical reasoning through observation • Supports formal ways of teaching • Children should be given positive rewards (Locke) • Precision and order: ringing bells, time periods, daily lesson plans, pre packaged curriculum materials • Supports accountability and performance-based teaching • Scientific research and development • Most recent development: computer technology www.themegallery.com
Character of Teacher Realists emphasize the role of the teacher Humanities should be taught in ways that areconducive to cognitive development Should teach students what they need to survive. Material presented ina systematic andorganized way, Workshop, Case based Project At the very least, should teachthe essentials www.themegallery.com
Character of Student Development of Individual Talents and Abilities Natural Intelligence and Intellectual Virtues Can servicein the real world. Retention be good for a student,Scientific character. www.themegallery.com
Classroom Activity Authentic Meterial/ Audio-visual equipment. Demonstration Thinking Reinforcement
Question and Suggestion Thank You !
- More by User

Realism. by Phillip Martin. Realism. What can that possibly mean?. Realism. An “ ism ” is a suffix at the end of many English words. It comes from Greek “ ismos ” and Latin “ ismus ”. You have seen it at the end of words like optim ism , Buddh ism , rac ism , favorit ism , and terror ism .
1.41k views • 18 slides

Realism vs Anti-realism
Realism vs Anti-realism. Topics. The Problem of Unobservability The “No Miracles” Argument The Observable / Unobservable Distinction The Underdetermination Argument for Antirealism. ~ 10 -35 m. Very tiny tiny . . . tiny superstrings!. The Problem of Unobservability.
879 views • 24 slides

Annibale Carracci, “The Butcher's Shop” 1585s. Realism. Or how we stopped talking about fields of flowers in such dreadfully romantic ways.
475 views • 17 slides

Realism. Contemporary Realism Historical Fiction. There are three rules for writing a good novel. Unfortunately, nobody knows what they are. - W. Somerset Maugham
389 views • 11 slides

Realism. Realism An attempt to make art and literature resemble life. Realist painters and writers take their subjects from the world around them (instead of from idealized subjects, such as figures in mythology or folklore) and try to represent them in a lifelike manner.
580 views • 18 slides

Realism. The powers to be in the art world controlled artists’ work by approving art that showed proper technical polish and appropriate subject matter Subject matter based on history, mythology or picturesque genre Not innovative and forgetful
705 views • 47 slides

Realism. By Savannah Tappan. Moment. "The Salmon Fisher | Eilif Peterssen | Gallery | Aurlaea ." Aurlaea RSS. N.p ., n.d. Web. 26 Nov. 2012. <http://www.aurlaea.com/gallery_viewer.html?i=73>.
235 views • 7 slides

Realism. b lunt, tell-it-like-it-is focused on lives of ordinary people rejected the class system darker view of the world fate is an illusion; lives shaped by forces we cannot see or understand. Modernism. overwhelming technological changes grief over the loss of the past youth culture
349 views • 18 slides

Fundamentals of Realism
Fundamentals of Realism. Statism Survival Self-help. Statism – sovereignty and force internally. State = main actor, possessing sovereignty 1 st move of a state behaving as a realist: Est. a monopoly of legitimate use of violence. Statism – sovereignty and force externally.
386 views • 11 slides

Realism. American Literature Mrs. Sikora. I. Aspects of Realism. A. ______________________ : "the faithful representation of reality"
291 views • 6 slides

Realism . (1855-1900). Major Historical Events . 1861-1865 : American Civil War 1863 : (Jan. 1): Emancipation Proclamation (abolish slavery) 1865 : 13 th Amendment (abolish slavery) 1869 : First transcontinental railroad 1859 : Darwin’s The Origin of Species. Prominent Writers .
348 views • 9 slides

Realism. Jacques-Louis David, “The Oath of the Horatii ” 1784. Caspar David Friedrich, “Wanderer Above the Sea of Fog,” 1818 . Jean-François Millet, “The Gleaners,” 1857. Gustave Courbet, “The Stonebreakers,” 1849. Realism. resisting idealization things as they really are, appear
313 views • 7 slides

Realism. By Maxwell Patterson Art History 7 th Period Art I. Works Consulted. Brommer , Gerald F., and David Kohl. "12.3 Realism." Discovering Art History . Worcester, MA: Davis Publications, 1988. 400-09. Print.
419 views • 11 slides

Realism. Some things are independent of mind. Aristotle’s Argument for Realism.
370 views • 15 slides

Rise of Realism
Rise of Realism. Based on the experiences during the Civil War, writers turned to realistic writing in which they sought to portray real life without a Romantic, idealistic outlook on life.
227 views • 4 slides

Realism. by Phillip Martin. Realism. What can that possibly mean?. Realism. An “ ism ” is a suffix at the end of many English words. It comes from Greek “ ismos ” and Latin “ ismus ”. You have seen it at the end of words like optim ism , Buddh ism , rac ism , favorit ism , and terror ism.
305 views • 9 slides

Realism. verisimilitude ( ver -uh- si -mil- i - tood , - tyood ), noun : the appearance of truth or reality. What is realism?. Literary movement following romanticism Attempted to portray the “cultural exhuberance ” of figurative American landscape and peoples
342 views • 12 slides

Realism. American Literature. Realism. reaction to Romantic ideals of the previous generation(s). defined as "the faithful representation of reality”. Realist authors not afraid to write about REAL subjects like war, death, prostitution, etc. Realism.
298 views • 12 slides

Realism . 1865-1915 Music. Describe the moment…. Write a description of the setting of this classroom. Be as detailed as possible. Even if a detail seems too mundane to be included, include it anyway. Use as much detail as possible in your description. Similarities. Differences.
463 views • 12 slides

Realism. International Security in the Modern World Masaryk University in Brno 1-2 July 2012 V ěra Stojarová. Three phases of realism. the beginnings between the WWI and WWII, the core in the 1950s. War, peace, development, freedom.
253 views • 15 slides
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Realism-and-its-role-in-education-2203
Related Papers
Studies in the History and Philosophy of Science
Renee Raphael
Francesco Coniglione
In order to support his new science, Galileo Galilei criticized the Aristotelianism that permeated the science of his time, by endorsing Aristotle’s traditional rival, Plato, read through the mediation of Archimedes, another scientist he valued highly. This allowed him to lay the foundations of modern science, breaking with the qualitative science of peripatetic medieval philosophy. To this purpose, he built a new methodology that is justified by a worldview based upon several ontological assumptions that outline an influential metaphysics that are pivotal to science. It is uncertain whether Galileo gave these assumptions the character of a purely methodological and necessary move; anyway, subsequently they deeply marked scientific thought, and particularly influenced scientists and philosophers who were barely aware of the methodological approach of modern science. However, it would be a mistake to transform the assumptions, that are at the basis of Galileo’s methodology, into a „t...
Global Cardiology Science and Practice
Alberto Zanatta
Lucas Angioni
I discuss what Aristotle was trying to encode when he said that the object of scientific knowledge is necessary, or that what we know (scientifically) cannot be otherwise etc. The paper is meant as a continuation of previous papers-orientated towards a book on the Posterior Analytics-and thus does not discuss in much detail key passages, as the very definition of scientific knowledge in APo I.2, or passages from APo I.4 and I.6 (for these, I refer to my previous papers). This paper is mainly focused on Aristotle's references to his notion of scientific knowledge both in other passages from the APo and in other treatises. I intend to show that there is a progressive, intrinsic relation between the two requirements by which scientific knowledge is defined. It is not true that each of these requirements stems from a different source. The Causal-Explanatory requirements gives Aristotle the general heading. Then, the Necessity Requirement ranges over the explanatory relation between explanans and explanandum and thereby specifies what sort of cause is sctricly required for having scientific knowledge of a given explanandum. Now, Aristotle was also concerned with the necessary truth of the elemental predications that constitute a demonstration. My claim that the Necessity Requirement ranges over the explanatory relation does not ignore that concern, and does not deny it. My claim is that Aristotle's main focus, and main concern, consists in stressing that the explanatory factor to be captured in scientific knowledge of a given explanandum is such that cannot be otherwise.
Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics
Philobiblon
Alexandra Baneu
This article focuses on three aspects of Pelbartus of Themeswar’s position on learning: how one should prepare before beginning to study theology, which sciences should one learn in order to better understand theology and in order to pursue a magisterium in this domain and, finally, what people have to learn in order to be saved. These three lines of investigation contour a true educational program.
The Blackwell Guide to Aristotle's Nicomachean …
C. D. C. Reeve
Craig A Boyd
Michele Camerota
JSTOR is a not-for-profit service that helps scholars, researchers, and students discover, use, and build upon a wide range of content in a trusted digital archive. We use information technology and tools to increase productivity and facilitate new forms of scholarship. For more information about JSTOR, please contact [email protected].. BRILL is collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to Early Science and Medicine.
sunday S akpan
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Ponto de Vista
Revista Estudos Feministas
Laurel Kamada
Cuadernos Económicos de ICE
Fidel Rodríguez
Limnology and Oceanography
Amarjeet Singh
Eder Ortiz Roca
Ni Gusti Ayu Dasriani , Khairan Marzuki
Boletin Conser V Accion
Ricardo Rozzi
Revista de Psicoterapia
Silvia Beatriz Franchi
Avaliação de Desempenho de Tecnologias Construtivas Inovadoras: Conforto Ambiental, Durabilidade e Pós-Ocupação
Mena Cristina Marcolino Mendes
Sustainability
Jiuh-Biing Sheu
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids
Samir Romdhane
- Mathematics
Jason Papathanasiou
isingoma julius
Sociologicky Casopis-czech Sociological Review
Antonín Paleček
SSRN Electronic Journal
Andreas Tan
James Seale
Perceptual and Motor Skills
NOBORU SEKIYA
Littérature, langages et …
Flavia Aragon Ronsano
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment
Ingo Hofmann
Virginia Walter
Elizabeth Dobson
International journal of innovative technology and exploring engineering
Mugdha Kulkarni
Nanomaterials
Vineet Tirth
mohammad chahkandi
See More Documents Like This
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
4 Chapter 4: Foundational Philosophies of Education

A philosophy is often defined as the foundation upon which knowledge is based. However, when you break apart the actual word, a much different meaning emerges. Derived from the Greek “philos,” which means love , and “sophos,” which means wisdom , the actual meaning of the word philosophy is love of wisdom (Johnson et. al., 2011).
In this chapter, we will explore how traditional philosophies have evolved over time by briefly looking at three key branches of philosophy. Then, the schools of philosophy and their influence on education will be presented. Finally, you will hear from educators in the field and see how they put their “philosophies” of education into practice.
Section I: Schools of Philosophy
4.1 Essential Questions
At the end of this section, the following essential questions will be answered:
- What are the four main schools of philosophy?
- Who were the key philosophers within each school of philosophy?
- What are the key implications of each school of philosophy on education today?
There are four broad schools of thought that reflect the key philosophies of education that we know today. These schools of thought are: Idealism, Realism, Pragmatism, and Existentialism. It is important to note that idealism and realism, otherwise known as general or world philosophies, have their roots in the work of the ancient Greek philosophers: Plato and Aristotle. Whereas pragmatism and existentialism are much more contemporary schools of thought.
It is important to study each school of thought because they shape the way we approach education today. Specifically, each school of thought directly impacts how curriculum is developed, implemented, and assessed.
Idealism is a school of philosophy that emphasizes that “ideas or concepts are the essence of all that is worth knowing” (Johnson et. al., 2011, p. 87). In other words, the only true reality is that of ideas. Based on the writings of Plato, this school of philosophy encourages conscious reasoning in the mind. Furthermore, idealists look for, and value, universal or absolute truths and ideas. Consequently, idealists believe that ideas should remain constant throughout the centuries.
Key Philosophers
Plato (ca. 427 – ca. 347 BCE):

4.2 A Closer Look
- How does the Allegory of the Cave give us insight into Plato’s conception of reality?
- What are some other examples of “cave-like” thinking?
- Do you agree with Plato’s premise? Why or why not?
Socrates (ca. 470 – ca. 399 BCE):

4.3 A Closer Look
- In what ways does the Socratic Method actively engage students in the learning process?
- Do you think this method improves students understanding?
- How does this method promote higher-order thinking?
- Elementary Example: Socratic Seminar Strategies for the Second Grade Classroom
- Secondary Example: Scaffolding Discussion Skills with a Socratic Circle
Kant (1724 – 1804):

Educational Implications of Idealism
When translated to the classroom, teachers with an Idealist school of though would emphasize being role models of these absolute truths, ideas, and values. Curriculum would focus on broad ideas, particularly those contained in great works of literature and/or scriptures. Teaching methods used within idealism include: lecture, discussion, and Socratic dialogue. Essential to these teaching methods is posing questions that generate thoughts and spark connections.
Paul (n/d) suggests the following six types of Socratic questions:
- How does this relate to our discussion?

- What would be an example?
- What is another way to look at it?
- What are the consequences of that assumption?
- What was the point of this question?
Realism is a school of philosophy with origins in the work of Aristotle. This philosophy emphasizes that “reality, knowledge, and value exist independent of the human mind” (Johnson, 2011, p. 89). Realists argue for the use of the senses and scientific investigation in order to discover truth. The application of the scientific method also allows individuals to classify things into different groups based on their essential differences.
Aristotle (384 – 322 BCE):

4.4 A Closer Look
- Scientific Method Clip
Locke (1632 – 1704):
John Locke believed in the tabula rasa, or blank tablet, view of the mind. According to this view, a child’s mind is a blank slate when they are born. All the sensory experiences they have after birth fill up the slate through the impressions that are made upon the mind.
4.5 A Closer Look
- Do you agree with Locke’s claim that “at birth our minds are like a sheet of white paper?” Why or why not?
- How is this idea more similar to “nature” vs. “nurture?”
Educational Implications of Realism
Within a realist educational philosophy, the curricular focus is on scientific research and development as Realists’ consider education a matter of reality rather than speculation. The teacher role is to teach students about the world they live in. Realists view the subject expert as the source and authority for determining the curriculum.
Outcomes of this thinking in classrooms today include the appearance of standardized tests, serialized textbooks, and specialized curriculum (Johnson et. al., 2011). Teaching methods used in realism include:

- Critical thinking
- Observation
- Experimentation
Pragmatism is “a process philosophy that stresses evolving and change rather than being” (Johnson et. al., 2011, p. 91). In other words, pragmatists believe that reality is constantly changing so we learn best through experience.

According to pragmatists, the learner is constantly conversing and being changed by the environment with whom he or she is interacting. There is “no absolute and unchanging truth, but rather, truth is what works” (Cohen, 1999, p.1). Based on what is learned at any point and time, the learner or the world in which he or she is interacting can be changed.
Peirce (1839 – 1914):
Charles Sanders Peirce is one of the first pragmatic thinkers. He introduced the pragmatic method in which students are supplied a procedure for constructing and clarifying meanings. In addition, this system helps to facilitate communication among students.
Dewey (1859 – 1952):

Dewey also believed that the application of the “scientific method” could solve an array of problems. He saw ideas as the instruments to solving problems and advocated for the application of the following steps to meet this goal:
- Recognize that the problem exists.
- Clearly define the problem.
- Suggest possible solutions.
- Consider the potential consequences of the possible solutions.
- Carry out further observation and experiment leading to the solution’s acceptance or rejection. (Timm, 2020)
4.6 A Closer Look
- What did the “new” or “Romantic” side believe about education? What did the “old” or “traditional” side believe about education? Which side(s) did Dewey lean toward and why?
- What else did Dewey think we should take into account? Why is this so important to Dewey?
- Why did Dewey want to connect education with society?
- What is the question of education according to Dewey? Do you agree? Why or why not?
Educational Implications of Pragmatism
According to a Pragmatic school of thought, curriculum should be so planned in such a way that it teaches the learner how to think critically rather than what to think. Teaching should, therefore, be more exploratory in nature than explanatory. To promote this approach to teaching, students should be actively engaged in the learning process and be challenged to solve problems. The teachers job is to help support students learning by promoting questioning and problem-solving during the natural course of lesson delivery.
The curriculum is also interdisciplinary. Teaching methods used in pragmatism include:
- Hands-on problem solving
- Experimenting
- Cooperative Learning
Existentialism
Existentialism is a school of philosophy that “focuses on the importance of the individual rather than on external standards” (Johnson et. al., 2011, p. 93). Existentialists believe that our reality is made up of nothing more than our lived experiences, therefore our final realities reside within each of us as individuals. As such, the physical world has no real meaning outside our human experience and there is no objective, authoritative truth about metaphysics, epistemology, and ethics.

Kierkegaard (1813-1855):

Soren Kierkegaard was a Danish minister and philosopher. He is
considered to be the founder of existentialism.
4.7 A Closer Look
- Kierkegaard’s Philosophy
Nietzsche (1844-1900):
Friedrich Nietzcshe stressed the importance of the individuality of each person. According to Johnson et. al. (2011), his work provided a “strategy to liberate people from the oppression of feeling inferior within themselves, and a teaching of how not to judge what one is in relation to what one should be” (p. 95).

Educational Implications of Existentialism
Within an existentialist classroom, subject matter takes second place to helping the students understand and appreciate themselves for who they are as individuals. The teacher’s role is to help students accept individual responsibility for their personal thoughts, feelings, and actions. To do this, the teacher is responsible for creating an environment in which student may freely choose their own preferred way of learning by giving students latitude in their choice of subject matter.
Furthermore, answers come from within the individual in an existential classroom, not from the teacher. For this reason, Existentialists strongly oppose standardized assessments which measure or track student learning. Instead, they want the educational experience of the student to focus on creating opportunities for self-direction and self-actualization of the whole person, not just the mind (Cohen, 1999).
In an Existentialist classroom, curriculum is structured to provide students with experiences that will help unleash their own creativity and self-expression through an emphasis on teaching humanities. For example, rather than emphasizing historical events, existentialists focus upon the actions of historical individuals, each of whom provides possible models for the students’ own behavior. Math and science may be de-emphasized because their subject matter would be considered “cold,” “dry,” “objective,” and therefore less fruitful to self-awareness. In teaching art, existentialism encourages individual creativity and imagination more than copying and imitating established models.
As described above, Existentialist methods focus on the individual. Learning is self-paced, self directed, and includes a great deal of individual contact with the teacher, who relates to each student openly and honestly. Although elements of existentialism occasionally appear in public schools, this philosophy has found wider acceptance in private schools and in alternative public schools founded in the late 1960s and early 1970s.
4.8 A Closer Look
Now that you have learned about the four main schools of thought, let’s find out which one you most align to right now. In order to do this, you are going to take the quiz below. Note: Make sure to write down which school of thought you are based on your quiz results.
- What school of thought were you?
- Do you agree that you align with the school of thought identified by the quiz? Why or why not?
- What are some specific implications for you as a future teacher given the school of thought you were identified as from the quiz?
Section II: Defining your own philosophy
4.9 Essential Questions
- What is a philosophy?
- What elements do you consider to be most important to include in your philosophy of education?
- Think about the elements identified in this section, do you think all of them are essential to include when writing a philosophy of education? Why or why not?

As discussed in section one, there are several key schools of thought that reflect key philosophies of education. In this section, we are going to look at the “definition” of a philosophy. We will also explore the importance of defining your own education philosophy as a future teacher. Finally, we will identify essential elements that should be considered when writing your educational philosophy.
What is a Philosophy?
When asked to think about the following question, what comes to mind: What is a Philosophy?
Common responses include:

• A set of beliefs
• A personal platform
• Our personal thoughts
A philosophy is indeed all of these things, and so much more! According to the New Oxford American Dictionary (2005), a philosophy is “the study of the fundamental nature of knowl- edge, reality, and existence” (p. 1278).
When it comes to our educational philosophy, Webb et. al. (2010) state that our “philosophy of education enables us to recognize certain educational principles that define our views about the learner, the teacher, and the school” (p. 50). As such, it critical to determine what school of thought you most align to as this will shape the way you see the students, curriculum and educational setting.
Articulating Your Philosophy of Education
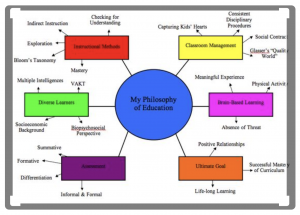
When articulating your philosophy of education, it is essential to reflect on the multiple dimension of teaching that would impact your philosophy. As demonstrated by the diagram, there are a lot of factors to consider. Take a moment to reflect on the diagram, are there any elements you feel are more important than the others? Are there elements missing that you would include? If so, what are they and why do you feel they are important?
When approaching the writing of your philosophy of education, we recommend using the following key elements to ensure that your philosophy of education is well thought out and supported, no matter which school of thought it is based upon.
- Why do you teach?
- Why have you chosen to teach elementary, secondary, or a particular content area?
- What are your values as a teacher?
- FOUNDATIONS OF EDUCATION
- What philosophy of education do you MOST align with and why (revisit Ch. 4 – Ch. 9 of your iBook)?
- How has education changed historically in the last 50/60 years (revisit Ch. 2 & Ch. 3 of your iBook)?
- What impact have movements like the civil rights had on schools (revisit Ch. 2 of your iBook)?
- How have educational policies like NCLB and the standardized testing movement impacted educators and instructional decisions/programming?
- In what ways has the increased diversity in our educational settings impacted the need for teachers to be prepared to address the needs of linguistically and culturally diverse students in their classrooms now more than ever before?
3. UNDERSTANDING OF TEACHING AND LEARNING
- What approaches, methods, pedagogy do you use and why and how are these influenced by the philosophy you MOST aligned with (revisit Ch. 4 – Ch. 9 of your iBook)?
- Which elements of effective instruction do you think are most important to apply to support ALL students learning?
- What strategies do you apply to actively engage ALL your students throughout the lesson?
- How do you motivate your students to learn?
- How do you motivate yourself to be the teacher your students need you to be?
4. CLASSROOM ENVIRONMENT
- How do you create a community of learners (revisit Ch. 1 of your iBook)?
- What is your “code of conduct” (revisit Ch. 1 of your iBook)?
- How do you engage students to limit disruptions and time off task?
- If disruptions do occur, what do you do?
5. INCLUSIVENESS
- Do you understand your own bias and how this impacts your teaching (revisit Ch. 2 of your iBook)?
- How are you effective with ALL students (revisit Ch. 2 of your iBook)?
- How do you create a culturally responsive class room environment (revisit Ch. 1 of your iBook)?
- How do you teach UNCONDITIONALLY so that all your students get the best education possible and you demonstrate respect for the customs and beliefs of the diverse student groups represented in your classroom?
- What specific strategies do you use to support diverse learners?
- In what ways do you act as an advocate for your students, their families, and the community?

Take a moment to reflect on all the information you read about educational philosophies. Your challenge is to write at least a one-page, single-spaced philosophy of education paper that summarizes your current philosophy of education.
Section III: The importance of student voices
4.10 Essential Questions
By the end of this section, the following essential questions will be answered.
- What can we learn from student voices?
- What insights might you gain from the student quotes?
- What did you learn from watching the video clips?
- What links did you make between the what the speakers shared in the video clips and the different schools of thought discussed in this chapter?
To best understand the power of an educational philosophy in practice, this section is going to provide you with two different sets of evidence. The first set of evidence comes from KSU students. The second set comes from a student and two educators in the field. As you read and listen to the information being shared, please reflect on the questions to consider. Although you do not need to document your responses to each of the questions, they have been provided to help you critical reflect on the information being presented.
4.11 Student Voices
- “My philosophical belief is that I want to prepare my children, not for the next grade or college; but for their future in society through tools learned in the classroom.” ASU16
- “I feel that after studying several popular philosophies of education my personal philosophy is a medley of all of them, making it completely mine.” DP U16
- “Every experience I have impacts the way I look at the world and I will continue to strive to keep my teaching the same while as the same time adapting to the needs of my students.” MLU16
4.12 A Closer Look
The following video provides and more in-depth look the importance of having a solid philosophy of education from a student’s point of view. As you watch this video, consider the following questions:
- What insights did you gain from the video?
- Based on the information shared, what school of thought(s) do you think influenced prior educational experiences of this student?
- What school of thought do you think this student is advocating for in the future? Why?
As demonstrated in the student voices, and video by Adora Avitak, being able to articulate your philosophy of education is essential as a future educator. For your philosophy of education shapes your delivery of academic content, but more importantly guides your beliefs when it comes to working with students. To learn more about the importance of how educators view students, let’s watch Rita Pierson.
4.7 A Closer Look
As you listen to Rita Pierson, consider the following questions:
- Based on the information shared, what school of thought(s) do you think influence this teacher?
- How might you apply what you learned from Rita Pierson to your own future practice?
Rita Pierson is such a powerful educator and advocate for students. I hope you learned a lot from her TedTalk! As we wrap up this chapter, I leave you with one final question: How will you be a champion for your future students?!
Media Attributions
- Socrates Aristotle Shakespeare Flintstone © esmemes
- Plato Quote © TraumaAndDissociation
- Socrates Quote © obscuredreamer
- Kant Quote © Butrous Foundation
- Socratic Circle © Samantha Bush
- Aristotle Quote © Mountaingoat Seventeen
- Standardized Test © Alberto G.
- Pragmatism Pic © Kristian Bjornard
- Dewey Quote © PetiteFamily93
- Existentialist Snoopy © Rob S
- Kierkegaard Quote © Max Lagace
- Nietzcshe Quote © SnD Quotes
- Glass half full © Geralt
- Thinking © GlobalUppal
- My Philosophy of Education © Kelsey F. Hawkins
To the extent possible under law, Della Perez has waived all copyright and related or neighboring rights to Social Foundations of K-12 Education , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Arts & Humanities
PowerPoint Presentation - The Philosophy of Education

Related documents

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Realism Presented by: Overview Definition of Realism Key Philosophers Effects on Education Group Activity.
Published by Leon Daniels Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Realism Presented by: Overview Definition of Realism Key Philosophers Effects on Education Group Activity."— Presentation transcript:

Perception and the External World 1 Direct Realism is the doctrine that perception puts us in direct contact with reality. “Direct” because nothing.

Empiricism Part I John Locke ( CE) George Berkeley ( CE)

Empiricism All knowledge of things in the world is a posteriori (that is, based ultimately on experience). Purely mental (i.e., a priori) operations of.

general psychology Firouz meroei milan History of Psychology 1.

Heavily influenced by Aristotle and Descartes Empiricists around his time: › Berkeley, & Hume (all Brits including Locke) Rationalists around his.

Realism And Its Place In The Education System. What is Realism? Realism believes in the world as it is. It is based on the view that reality is what we.

© Michael Lacewing Direct and representative realism Michael Lacewing

Rationalism: Knowledge Is Acquired through Reason, not the Senses We know only that of which we are certain. Sense experience cannot guarantee certainty,

Behaviorism. 1.Origin of Behaviorism 2.Structure of Stimulus - Response (and Consequence) 3.Types of Consequences –Reinforcers & Punishment 4.Task Analyses.

PHILOSOPHIES OF EDUCATION

John Locke and the Two Treatises on Government (1690)

Classical Realism Aristotle – B.C. He was a student at Plato’s Academy He opened his own school, The Lyceum. Aristotle – B.C. He was a student.

Chapter 3: Knowledge Innate Ideas and the Empiricist Theory: John Locke Introducing Philosophy, 10th edition Robert C. Solomon, Kathleen Higgins, and Clancy.
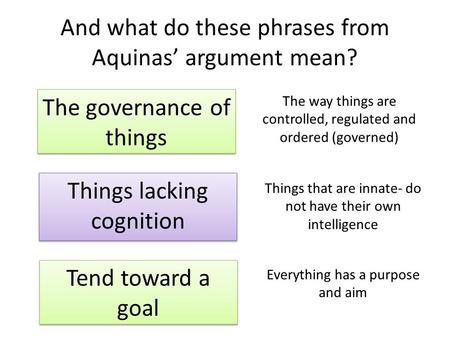
And what do these phrases from Aquinas’ argument mean? Things lacking cognition The governance of things Tend toward a goal The way things are controlled,

Modern Philosophers Rationalists –Descartes –Spinoza –Leibniz Empiricists –Locke –Berkeley –Hume Epistemology - the theory of knowledge (what and how we.

History of Atom Theory AdamClaytonMeganMorganTrenton.
Welcome to Unit 2 Seminar!

Test Review Enlightenment. Who wrote the first Encyclopedia? DIDEROT.

Agenda 1. Bellringer: One thing you’d like to see this year. (5) 2. Class Expectations and Syllabus (15) 3. Lecture: Origins of Psychology, Major Thinkers.

Psychology: The Early Years AP Psychology Ms. Desgrosellier September 16, 2009.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
realism powerpoint
All Formats
Resource types, all resource types.
- Rating Count
- Price (Ascending)
- Price (Descending)
- Most Recent
Realism powerpoint

Realism and Naturalism in American Literature Powerpoint


Realism : American Literature Digital Lesson, Google Slides , PowerPoint

- Google Apps™

Fantasy and Realism PowerPoint Lesson

Introduction to American Realism Literature PowerPoint with Notes and Videos!

Intro to Magical Realism - Google Slides - Editable - A Man With Enormous Wings

- Google Slides™

Literary Realism (Lesson Notes and PowerPoint Presentation)

Magical Realism PPT

Realism Unit: American Literature (Google Slides , PowerPoint )

Realism and Naturalism in Literature - PowerPoint and Guided Notes

Types of Literary Realism ( PowerPoint Presentation)

Realism , Regionalism, Naturalism: Digital Lesson, Google Slides , PowerPoint

Piet Mondrian PPT - Biography, Realism to Abstract, Art Themes, Craft Projects!

- PowerPoint Presentations

Unit 5: Realism , Naturalism, Civil War, Modernism PowerPoint

Realism and Fantasy Interactive Powerpoint

Realism and Yellow Journalism PowerPoint Presentation

Romanticism Realism Impressionism Notes & PPT AP European History

Art Styles PPT - Renaissance Art to Photo Realism --Companion to Final Exam--H.S.

Advanced Art History-Unit 8 Modern Art Realism through Art Nouveau- PPT

Romanticism and Realism 1800s Art Movements - Slides with Sources and Paintings

Lesson Plan for Realism Fantasy ppt

- Word Document File

Realism and Yellow Journalism Pack ( PPT , DOC, PDF)

Introduction to Magical Realism (Customizeable Google Slides )

- Internet Activities

Realism : Background Powerpoint

Arts & Humanities Romanticism and Realism Power Point

- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

solar eclipse
25 templates

academic writing
15 templates

8 templates

education technology
180 templates

32 templates

citizenship
14 templates
Artists of Realism
Artists of realism presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
The Realism movement in art sought to represent reality as it was, highlighting everyday life and ordinary people, often with a focus on social criticism and depiction of the mundane. Well... We've captured the essence of this art movement by creating a template on some of its most representative artists! This detailed presentation includes real content about the artists, the works, their characteristics and even real images of some of their most outstanding works. No matter if you use this template in an art history class or in a lecture, it will be a success.
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 35 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Presentation Transcript. Realism of Education Present byMiss KamonratChimpaleeMrs. SiwapornRatanapechMrs. SiripunSiribunnam. 1. Realists believe nature (God) should be the principle aim of educator 2. Studying the world carefully Characteristic of Educator Religious Realist www.themegallery.com. 1.
Teaching is a way to serve humankind; it is part of God's work. "Leading the student from ignorance to enlightenment is one of the greatest services one person can give to another.". The soul possesses an inner knowledge. The major goal of education was the perfection of the human being and the ultimate reunion of the soul with God.
What is the Philosophy of Realism? Dictionary: the doctrine that universals have a real objective existence represents the theory that particular things exist independently of our perception Books: It is an attitude of mind, a mode of thinking and an attempt to explain the nature of things (Dhiman. 2008) Matter has its own existence independently of our mind. A doctrine that the objects of our ...
Alexandra Baneu. This article focuses on three aspects of Pelbartus of Themeswar's position on learning: how one should prepare before beginning to study theology, which sciences should one learn in order to better understand theology and in order to pursue a magisterium in this domain and, finally, what people have to learn in order to be saved.
DEFINITION OF EDUCATION 1.Education is the process of receiving or giving systematic instruction, especially at a school or university: a course of education. 2.Education in its general sense is a form of learning in which the knowledge, skills, and habits of a group of people are transferred from one generation to the next through teaching, training, or research. 3. Education frequently takes ...
There are four broad schools of thought that reflect the key philosophies of education that we know today. These schools of thought are: Idealism, Realism, Pragmatism, and Existentialism. It is important to note that idealism and realism, otherwise known as general or world philosophies, have their roots in the work of the ancient Greek ...
Chapter 5. What is Philosophy of Education. All teachers have a personal philosophy that. colors the way they teach. Engaging in philosophy helps clarify what. they do or intend to do, justify or explain. why they do what they do in a logical, systematic manner. Understanding two important.
Realism in education seeks to teach students the logical processes that would lead them to discover mind-independent reality. One good method for discovering realist truths is the scientific ...
Realism - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Realism is a philosophical approach that believes reality is objective and external. It views the world as governed by natural laws that humans can observe and understand through their senses. Key proponents included Aristotle, Aquinas, Locke, and ...
Realism and Education - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This will help students to know the use of philosophy specifically realism in education
This thesis holds the reality, knowledge and value exist independently of the. human mind. In other words, realism rejects the idealist notion that only ideas are real. The. realist asserts, as a ...
Download ppt "Realism Presented by: Overview Definition of Realism Key Philosophers Effects on Education Group Activity." Similar presentations Perception and the External World 1 Direct Realism is the doctrine that perception puts us in direct contact with reality. "Direct" because nothing.
This PPT provides a comprehensive presentation for Modern Art Realism through Art Nouveau-and supports the teacher, in preparing students for the AP Art History Exam. The course is a finishing course for many high school students, bringing together math, science, social studies, English and foreign language that spans the school curriculum.
Realism Powerpoint Presentation - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This document defines realism and discusses several philosophers who contributed to the realist perspective. It provides an overview of realism, which is the view that objects exist independently of the mind.
The Realism movement in art sought to represent reality as it was, highlighting everyday life and ordinary people, often with a focus on social criticism and depiction of the mundane. Well... We've captured the essence of this art movement by creating a template on some of its most representative artists! This detailed presentation includes ...