Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.
What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
- Example 2
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , 9 steps to publish a research paper, what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., presenting research data effectively through tables and figures, ethics in science: importance, principles & guidelines .
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Good Research Question (w/ Examples)
What is a Research Question?
A research question is the main question that your study sought or is seeking to answer. A clear research question guides your research paper or thesis and states exactly what you want to find out, giving your work a focus and objective. Learning how to write a hypothesis or research question is the start to composing any thesis, dissertation, or research paper. It is also one of the most important sections of a research proposal .
A good research question not only clarifies the writing in your study; it provides your readers with a clear focus and facilitates their understanding of your research topic, as well as outlining your study’s objectives. Before drafting the paper and receiving research paper editing (and usually before performing your study), you should write a concise statement of what this study intends to accomplish or reveal.
Research Question Writing Tips
Listed below are the important characteristics of a good research question:
A good research question should:
- Be clear and provide specific information so readers can easily understand the purpose.
- Be focused in its scope and narrow enough to be addressed in the space allowed by your paper
- Be relevant and concise and express your main ideas in as few words as possible, like a hypothesis.
- Be precise and complex enough that it does not simply answer a closed “yes or no” question, but requires an analysis of arguments and literature prior to its being considered acceptable.
- Be arguable or testable so that answers to the research question are open to scrutiny and specific questions and counterarguments.
Some of these characteristics might be difficult to understand in the form of a list. Let’s go into more detail about what a research question must do and look at some examples of research questions.
The research question should be specific and focused
Research questions that are too broad are not suitable to be addressed in a single study. One reason for this can be if there are many factors or variables to consider. In addition, a sample data set that is too large or an experimental timeline that is too long may suggest that the research question is not focused enough.
A specific research question means that the collective data and observations come together to either confirm or deny the chosen hypothesis in a clear manner. If a research question is too vague, then the data might end up creating an alternate research problem or hypothesis that you haven’t addressed in your Introduction section .
The research question should be based on the literature
An effective research question should be answerable and verifiable based on prior research because an effective scientific study must be placed in the context of a wider academic consensus. This means that conspiracy or fringe theories are not good research paper topics.
Instead, a good research question must extend, examine, and verify the context of your research field. It should fit naturally within the literature and be searchable by other research authors.
References to the literature can be in different citation styles and must be properly formatted according to the guidelines set forth by the publishing journal, university, or academic institution. This includes in-text citations as well as the Reference section .
The research question should be realistic in time, scope, and budget
There are two main constraints to the research process: timeframe and budget.
A proper research question will include study or experimental procedures that can be executed within a feasible time frame, typically by a graduate doctoral or master’s student or lab technician. Research that requires future technology, expensive resources, or follow-up procedures is problematic.
A researcher’s budget is also a major constraint to performing timely research. Research at many large universities or institutions is publicly funded and is thus accountable to funding restrictions.
The research question should be in-depth
Research papers, dissertations and theses , and academic journal articles are usually dozens if not hundreds of pages in length.
A good research question or thesis statement must be sufficiently complex to warrant such a length, as it must stand up to the scrutiny of peer review and be reproducible by other scientists and researchers.
Research Question Types
Qualitative and quantitative research are the two major types of research, and it is essential to develop research questions for each type of study.
Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research questions are specific. A typical research question involves the population to be studied, dependent and independent variables, and the research design.
In addition, quantitative research questions connect the research question and the research design. In addition, it is not possible to answer these questions definitively with a “yes” or “no” response. For example, scientific fields such as biology, physics, and chemistry often deal with “states,” in which different quantities, amounts, or velocities drastically alter the relevance of the research.
As a consequence, quantitative research questions do not contain qualitative, categorical, or ordinal qualifiers such as “is,” “are,” “does,” or “does not.”
Categories of quantitative research questions
Qualitative research questions.
In quantitative research, research questions have the potential to relate to broad research areas as well as more specific areas of study. Qualitative research questions are less directional, more flexible, and adaptable compared with their quantitative counterparts. Thus, studies based on these questions tend to focus on “discovering,” “explaining,” “elucidating,” and “exploring.”
Categories of qualitative research questions
Quantitative and qualitative research question examples.

Good and Bad Research Question Examples
Below are some good (and not-so-good) examples of research questions that researchers can use to guide them in crafting their own research questions.
Research Question Example 1
The first research question is too vague in both its independent and dependent variables. There is no specific information on what “exposure” means. Does this refer to comments, likes, engagement, or just how much time is spent on the social media platform?
Second, there is no useful information on what exactly “affected” means. Does the subject’s behavior change in some measurable way? Or does this term refer to another factor such as the user’s emotions?
Research Question Example 2
In this research question, the first example is too simple and not sufficiently complex, making it difficult to assess whether the study answered the question. The author could really only answer this question with a simple “yes” or “no.” Further, the presence of data would not help answer this question more deeply, which is a sure sign of a poorly constructed research topic.
The second research question is specific, complex, and empirically verifiable. One can measure program effectiveness based on metrics such as attendance or grades. Further, “bullying” is made into an empirical, quantitative measurement in the form of recorded disciplinary actions.
Steps for Writing a Research Question
Good research questions are relevant, focused, and meaningful. It can be difficult to come up with a good research question, but there are a few steps you can follow to make it a bit easier.
1. Start with an interesting and relevant topic
Choose a research topic that is interesting but also relevant and aligned with your own country’s culture or your university’s capabilities. Popular academic topics include healthcare and medical-related research. However, if you are attending an engineering school or humanities program, you should obviously choose a research question that pertains to your specific study and major.
Below is an embedded graph of the most popular research fields of study based on publication output according to region. As you can see, healthcare and the basic sciences receive the most funding and earn the highest number of publications.
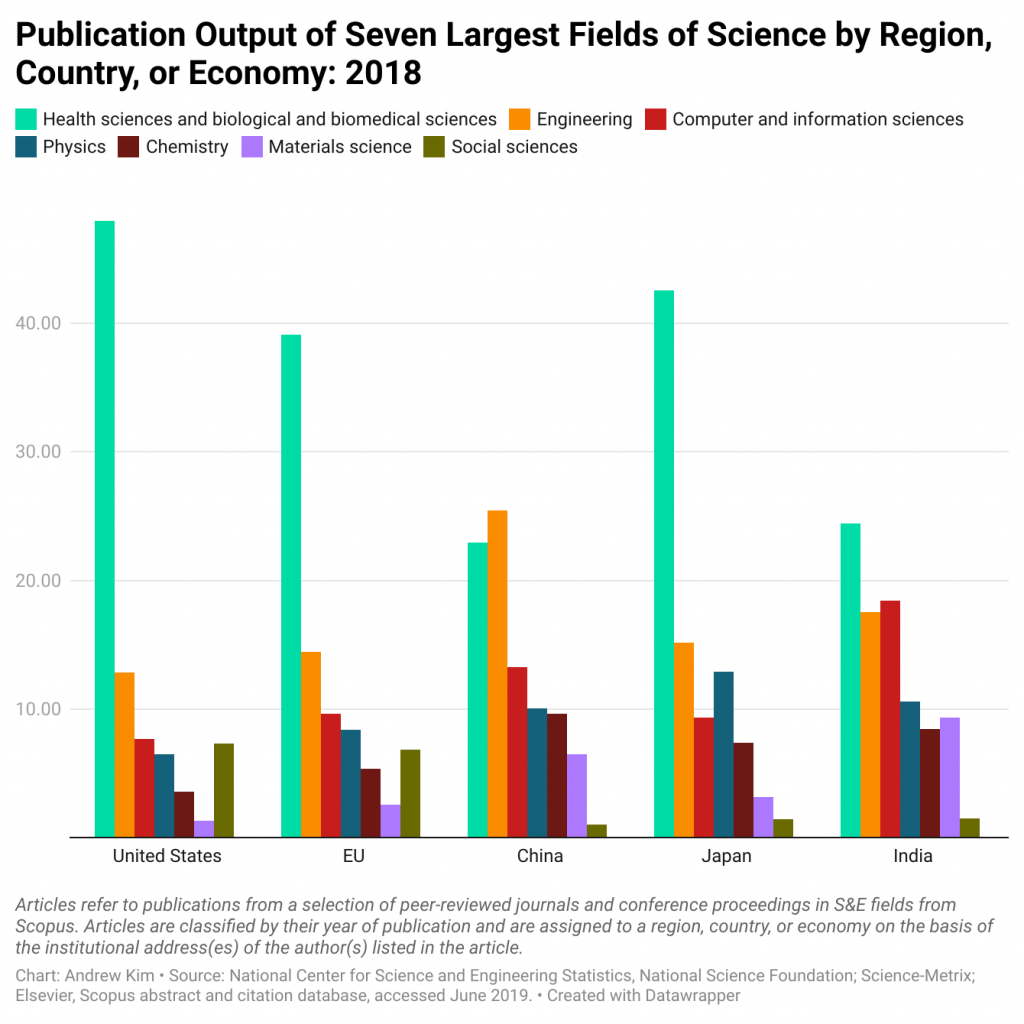
2. Do preliminary research
You can begin doing preliminary research once you have chosen a research topic. Two objectives should be accomplished during this first phase of research. First, you should undertake a preliminary review of related literature to discover issues that scholars and peers are currently discussing. With this method, you show that you are informed about the latest developments in the field.
Secondly, identify knowledge gaps or limitations in your topic by conducting a preliminary literature review . It is possible to later use these gaps to focus your research question after a certain amount of fine-tuning.
3. Narrow your research to determine specific research questions
You can focus on a more specific area of study once you have a good handle on the topic you want to explore. Focusing on recent literature or knowledge gaps is one good option.
By identifying study limitations in the literature and overlooked areas of study, an author can carve out a good research question. The same is true for choosing research questions that extend or complement existing literature.
4. Evaluate your research question
Make sure you evaluate the research question by asking the following questions:
Is my research question clear?
The resulting data and observations that your study produces should be clear. For quantitative studies, data must be empirical and measurable. For qualitative, the observations should be clearly delineable across categories.
Is my research question focused and specific?
A strong research question should be specific enough that your methodology or testing procedure produces an objective result, not one left to subjective interpretation. Open-ended research questions or those relating to general topics can create ambiguous connections between the results and the aims of the study.
Is my research question sufficiently complex?
The result of your research should be consequential and substantial (and fall sufficiently within the context of your field) to warrant an academic study. Simply reinforcing or supporting a scientific consensus is superfluous and will likely not be well received by most journal editors.

Editing Your Research Question
Your research question should be fully formulated well before you begin drafting your research paper. However, you can receive English paper editing and proofreading services at any point in the drafting process. Language editors with expertise in your academic field can assist you with the content and language in your Introduction section or other manuscript sections. And if you need further assistance or information regarding paper compositions, in the meantime, check out our academic resources , which provide dozens of articles and videos on a variety of academic writing and publication topics.
- (855) 776-7763
Training Maker
All Products
Qualaroo Insights
ProProfs.com
- Sign Up Free
Do you want a free Survey Software?
We have the #1 Online Survey Maker Software to get actionable user insights.
How To Write a Good Research Question: Guide with Definition, Tips & Examples

Sameer Bhatia
Founder and CEO - ProProfs
Review Board Member
Sameer Bhatia is the Founder and Chief Executive Officer of ProProfs.com. He believes that software should make you happy and is driven to create a 100-year company that delivers delightfully ... Read more
Sameer Bhatia is the Founder and Chief Executive Officer of ProProfs.com. He believes that software should make you happy and is driven to create a 100-year company that delivers delightfully smart software with awesome support. His favorite word is 'delight,' and he dislikes the term 'customer satisfaction,' as he believes that 'satisfaction' is a low bar and users must get nothing less than a delightful experience at ProProfs. Sameer holds a Masters in Computer Science from the University of Southern California (USC). He lives in Santa Monica with his wife & two daughters. Read less

Market Research Specialist
Emma David, a seasoned market research professional, specializes in employee engagement, survey administration, and data management. Her expertise in leveraging data for informed decisions has positively impacted several brands, enhancing their market position.

Research questions form the backbone of any study, guiding researchers in their search for knowledge and understanding. Framing relevant research questions is the first essential step for ensuring the research is effective and produces valuable insights.
In this blog, we’ll explore what research questions are, tips for crafting them, and a variety of research question examples across different fields to help you formulate a well-balanced research questionnaire.
Let’s begin.
What Is a Research Question?
A research question is a specific inquiry or problem statement guiding a research study, outlining the researcher’s intention to investigate. Think of it as a roadmap for your paper or thesis – it tells you exactly what you want to explore, giving your work a clear purpose.
A good research question not only helps you focus your writing but also guides your readers. It gives them a clear idea of what your research is about and what you aim to achieve. Before you start drafting your paper and even before you conduct your study, it’s important to write a concise statement of what you want to accomplish or discover.
This sets the stage for your research and ensures your work is focused and purposeful.
Why Are Research Questions Important?
Research questions are the cornerstone of any academic or scientific inquiry. They serve as a guide for the research process, helping to focus the study, define its goals, and structure its methodology.
Below are some of its most significant impacts, along with hypothetical examples to help you understand them better:
1. Guidance and Focus
Research questions provide a clear direction for the study, enabling researchers to narrow down the scope of their investigation to a manageable size. Research efforts can become scattered and unfocused without a well-defined question without a well-defined question, leading to wasted time and resources.
For example, consider a researcher interested in studying the effects of technology on education. A broad interest in technology and education could lead to an overwhelming range of topics to cover. However, by formulating a specific research question such as, “ How does the use of interactive digital textbooks in high school science classes affect students’ learning outcomes?” the researcher can focus their study on a specific aspect of technology in education, making the research more manageable and directed.
2. Defining the Research Objectives
A well-crafted research question helps to clearly define what the researcher aims to discover, examine, or analyze. This clarity is crucial for determining the study’s objectives and ensures that every step of the research process contributes toward achieving these goals.
For example, in a study aimed at understanding the impact of remote work on employee productivity, a research question such as “ Does remote work increase productivity among information technology professionals? ” directly sets the objective of the study to measure productivity levels among a specific group when working remotely.
3. Determining the Research Methodology
The research question influences the choice of methodology, including the design, data collection methods, and analysis techniques. It dictates whether the study should be qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods and guides the selection of tools and procedures for conducting the research.
For example, in a research question like “ What are the lived experiences of first-generation college students? ” a qualitative approach using interviews or focus groups might be chosen to gather deep, nuanced insights into students’ experiences. In contrast, a question such as “ What percentage of first-generation college students graduate within four years?” would require a quantitative approach, possibly utilizing existing educational data sets for analysis.
4. Enhancing Relevance and Contribution
A well-thought-out research question ensures that the study addresses a gap in the existing literature or solves a real-world problem. This relevance is crucial for the contribution of the research to the field, as it helps to advance knowledge, inform policy, or offer practical solutions.
For example, in a scenario where existing research has largely overlooked the environmental impacts of single-use plastics in urban waterways, a question like “ What are the effects of single-use plastic pollution on the biodiversity of urban waterways?” can fill this gap, contributing valuable new insights to environmental science and potentially influencing urban environmental policies.
5. Facilitating Data Interpretation and Analysis
Clear research questions help in structuring the analysis, guiding the interpretation of data, and framing the discussion of results. They ensure that the data collected is directly relevant to the questions posed, making it easier to draw meaningful conclusions.
For example, in a study asking, “ How do social media algorithms influence political polarization among users? ” the data analysis would specifically focus on the mechanisms of algorithmic content delivery and its effects on user behavior and political views. This focus makes it straightforward to interpret how algorithm-induced echo chambers might contribute to polarization.
Types of Research Questions
Understanding the different types of research questions is essential for researchers to effectively design and conduct studies that align with their research objectives and methodologies
These questions can be broadly categorized into three main types: quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method research questions.
Let’s explore each type in-depth, along with some examples.
Type A: Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research involves the collection and analysis of numerical data to answer specific research questions or hypotheses. It focuses on quantifying relationships, patterns, and phenomena, often using statistical methods for analysis. Quantitative research questions are typically structured and aim to explore relationships between variables or assess the impact of interventions.
Quantitative research questions can again be subcategorized into three distinct types:
1. Descriptive Questions :
Descriptive questions aim to describe characteristics, behaviors, or phenomena within a population. These questions often start with words like “ how much ,” “ how many ,” or “ what is the frequency of .” They provide a snapshot of a particular situation or phenomenon.
Example: “ What is the average age of first-time homebuyers in the United States?”
2. Comparative Questions :
Comparative questions seek to compare two or more groups, conditions, or variables to identify differences or similarities. They often involve the use of statistical tests to determine the significance of observed differences or associations.
Example: “Is there a significant difference in academic performance between students who receive tutoring and those who do not?”
3. Relationship Questions:
Relationship questions explore the associations or correlations between variables. They aim to determine the strength and direction of relationships, allowing researchers to assess the predictive power of one variable on another.
Example: “What is the relationship between exercise frequency and levels of anxiety among adults?”
Type B: Qualitative Research Questions
Qualitative research involves the exploring and understanding of complex phenomena through an in-depth examination of individuals’ experiences, behaviors, and perspectives. It aims to uncover meaning, patterns, and underlying processes within a specific context, often through techniques such as interviews, observations, and content analysis.
Types of qualitative research questions:
1. Exploratory Questions:
Exploratory questions seek to understand a particular phenomenon or issue in depth. They aim to uncover new insights, perspectives, or dimensions that may not have been previously considered.
Example: “What are the experiences of LGBTQ+ individuals in accessing healthcare services in rural communities?”
2. Descriptive Questions:
Descriptive questions aim to provide a detailed description or portrayal of a phenomenon or social context. They focus on capturing the intricacies and nuances of a particular situation or setting.
Example: “What are the communication patterns within multicultural teams in a corporate setting?”
3. Explanatory Questions:
Explanatory questions delve into the underlying reasons, mechanisms, or processes that influence a phenomenon or behavior. They aim to uncover the ‘why’ behind observed patterns or relationships.
Example: “What factors contribute to employee turnover in the hospitality industry?”
Type C: Mixed-Methods Research Questions
Mixed-methods research integrates both quantitative and qualitative approaches within a single study, allowing researchers to gain a comprehensive understanding of a research problem. Mixed-method research questions are designed to address complex phenomena from multiple perspectives, combining the strengths of both quantitative and qualitative methodologies.
Types of Mixed-Methods Research Questions:
1. Sequential Questions:
Sequential questions involve the collection and analysis of quantitative and qualitative data in separate phases or stages. The findings from one phase inform the design and implementation of the subsequent phase.
Example: “Quantitatively, what are the prevalence rates of mental health disorders among adolescents? Qualitatively, what are the factors influencing help-seeking behaviors among adolescents with mental health concerns?”
2. Concurrent Questions:
Concurrent questions involve the simultaneous collection and analysis of quantitative and qualitative data. Researchers triangulate findings from both methods to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research problem.
Example: “How do students’ academic performance (quantitative) correlate with their perceptions of school climate (qualitative)?”
3. Transformative Questions:
Transformative questions aim to use mixed-methods research to bring about social change or inform policy decisions. They seek to address complex societal issues by combining quantitative data on prevalence rates or trends with qualitative insights into lived experiences and perspectives.
Example: “What are the barriers to accessing healthcare services for underserved communities, and how can healthcare policies be redesigned to address these barriers effectively?”
Steps to Developing a Good Research Question
Developing a good research question is a crucial first step in any research endeavor. A well-crafted research question serves as the foundation for the entire study, guiding the researcher in formulating hypotheses, selecting appropriate methodologies, and conducting meaningful analyses.
Here are the steps to developing a good research question:
Identify a Broad Topic
Begin by identifying a broad area of interest or a topic that you would like to explore. This could stem from your academic discipline, professional interests, or personal curiosity. However, make sure to choose a topic that is both relevant and feasible for research within the constraints of your resources and expertise.
Conduct Preliminary Research
Before refining your research question, conduct preliminary research to familiarize yourself with existing literature and identify gaps, controversies, or unanswered questions within your chosen topic. This step will help you narrow down your focus and ensure that your research question contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
Narrow Down Your Focus
Based on your preliminary research, narrow down your focus to a specific aspect, problem, or issue within your chosen topic. Consider the scope of your study, the availability of resources, and the feasibility of addressing your research question within a reasonable timeframe. Narrowing down your focus will help you formulate a more precise and manageable research question.
Define Key Concepts and Variables
Clearly define the key concepts, variables, or constructs that are central to your research question. This includes identifying the main variables you will be investigating, as well as any relevant theoretical or conceptual frameworks that will guide your study. Clarifying these aspects will ensure that your research question is clear, specific, and focused.
Formulate Your Research Question
Based on your narrowed focus and defined key concepts, formulate your research question. A good research question is concise, specific, and clearly articulated. It should be phrased in a way that is open-ended and leads to further inquiry. Avoid vague or overly broad questions that are difficult to answer or lack clarity.
Consider the Type of Research
Consider whether your research question is best suited for quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods research. The type of research question will influence your choice of methodologies, data collection techniques, and analytical approaches. Tailor your research question to align with the goals and requirements of your chosen research paradigm.
Evaluate the Significance and Relevance
Evaluate the significance and relevance of your research question within the context of your academic discipline, field of study, or practical implications. Consider how your research question fills gaps in knowledge, addresses practical problems, or advances theoretical understanding. A good research question should be meaningful and contribute to the broader scholarly conversation.
Refine and Revise
Finally, refine and revise your research question based on feedback from colleagues, advisors, or peers. Consider whether the question is clear, feasible, and likely to yield meaningful results. Be open to making revisions as needed to ensure that your research question is well-constructed and aligned with the goals of your study.
Examples of Research Questions
Below are some example research questions from various fields to provide a glimpse into the diverse array of inquiries within each field.
1. Psychology Research Questions:
- How does childhood trauma influence the development of personality disorders in adulthood?
- What are the effects of mindfulness meditation on reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression?
- How does social media usage impact self-esteem among adolescents?
- What factors contribute to the formation and maintenance of romantic relationships in young adults?
- What are the cognitive mechanisms underlying decision-making processes in individuals with addiction?
- How does parenting style affect the development of resilience in children?
- What are the long-term effects of early childhood attachment patterns on adult romantic relationships?
- What role does genetics play in the predisposition to mental health disorders such as schizophrenia?
- How does exposure to violent media influence aggressive behavior in children?
- What are the psychological effects of social isolation on mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic?
2. Business Research Questions:
- What are the key factors influencing consumer purchasing behavior in the e-commerce industry?
- How does organizational culture impact employee job satisfaction and retention?
- What are the strategies for successful international market entry for small businesses?
- What are the effects of corporate social responsibility initiatives on brand reputation and consumer loyalty?
- How do leadership styles influence organizational innovation and performance?
- What are the challenges and opportunities for implementing sustainable business practices in emerging markets?
- What factors contribute to the success of startups in the technology sector?
- How do economic fluctuations affect consumer confidence and spending behavior?
- What are the impacts of globalization on supply chain management practices?
- What are the determinants of successful mergers and acquisitions in the corporate sector?
3. Education Research Questions:
- What teaching strategies are most effective for promoting student engagement in online learning environments?
- How does socioeconomic status impact academic achievement and educational attainment?
- What are the barriers to inclusive education for students with disabilities?
- What factors influence teacher job satisfaction and retention in urban schools?
- How does parental involvement affect student academic performance and school outcomes?
- What are the effects of early childhood education programs on later academic success?
- How do culturally responsive teaching practices impact student learning outcomes in diverse classrooms?
- What are the best practices for implementing technology integration in K-12 education?
- How do school leadership practices influence school climate and student outcomes?
- What interventions are most effective for addressing the achievement gap in STEM education?
4. Healthcare Research Questions:
- What are the factors influencing healthcare-seeking behavior among underserved populations?
- How does patient-provider communication affect patient satisfaction and treatment adherence?
- What are the barriers to implementing telemedicine services in rural communities?
- What interventions are effective for reducing hospital readmissions among elderly patients?
- How does access to healthcare services impact health disparities among marginalized communities?
- What are the effects of nurse staffing levels on patient outcomes in acute care settings?
- How do socioeconomic factors influence access to mental healthcare services?
- What are the best practices for managing chronic disease patients in primary care settings?
- What are the impacts of healthcare reform policies on healthcare delivery and patient outcomes?
- How does cultural competence training for healthcare providers affect patient trust and satisfaction?
5. Computer Science Research Questions:
- What are the security vulnerabilities of blockchain technology, and how can they be mitigated?
- How can machine learning algorithms be used to detect and prevent cyber-attacks?
- What are the privacy implications of data mining techniques in social media platforms?
- How can artificial intelligence be used to improve medical diagnosis and treatment?
- What are the challenges and opportunities for implementing edge computing in IoT systems?
- How can natural language processing techniques be applied to improve human-computer interaction?
- What are the impacts of algorithmic bias on fairness and equity in decision-making systems?
- How can quantum computing algorithms be optimized for solving complex computational problems?
- What are the ethical considerations surrounding the use of autonomous vehicles in transportation systems?
- How does the design of user interfaces influence user experience and usability in mobile applications?
Create a Compelling Research Question With the Given Examples
Understanding research questions is essential for any successful research endeavor. We’ve explored the various research questions – quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods – each with unique characteristics and purposes.
Through various examples, tips, and strategies, we’ve seen how research questions can be tailored to specific fields of study.
By following these guidelines, we are confident that your research questions will be well-designed, focused, and capable of yielding valuable insights.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some good research question examples.
Good research questions are clear, specific, relevant, and feasible. For example, “How does childhood trauma influence the development of personality disorders in adulthood?”
What are some examples of good and bad research questions?
Good research questions are focused and relevant, such as “What factors influence employee job satisfaction in the hospitality industry?” Bad research questions are vague or trivial, like “What is the favorite color of employees in the hospitality industry?”
Watch: How to Create a Survey Using ProProfs Survey Maker

About the author
Emma David is a seasoned market research professional with 8+ years of experience. Having kick-started her journey in research, she has developed rich expertise in employee engagement, survey creation and administration, and data management. Emma believes in the power of data to shape business performance positively. She continues to help brands and businesses make strategic decisions and improve their market standing through her understanding of research methodologies.
Popular Posts in This Category

Margin of Error: An Ultimate Guide

Customer Satisfaction Survey [2024 Quick Guide with Questions]

How to Use Surveys for Content Marketing

Customer Segmentation: A Hands-on Guide for Businesses

How to Write Quantitative Research Questions: Types With Examples
Omnichannel Customer Engagement 101: Every Business Owner Should Know
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write a Research Question

Academic writing and research require a distinct focus and direction. A well-designed research question gives purpose and clarity to your research. In addition, it helps your readers understand the issue you are trying to address and explore.
Every time you want to know more about a subject, you will pose a question. The same idea is used in research as well. You must pose a question in order to effectively address a research problem. That's why the research question is an integral part of the research process. Additionally, it offers the author writing and reading guidelines, be it qualitative research or quantitative research.
In your research paper , you must single out just one issue or problem. The specific issue or claim you wish to address should be included in your thesis statement in order to clarify your main argument.
A good research question must have the following characteristics.

- Should include only one problem in the research question
- Should be able to find the answer using primary data and secondary data sources
- Should be possible to resolve within the given time and other constraints
- Detailed and in-depth results should be achievable
- Should be relevant and realistic.
- It should relate to your chosen area of research
While a larger project, like a thesis, might have several research questions to address, each one should be directed at your main area of study. Of course, you can use different research designs and research methods (qualitative research or quantitative research) to address various research questions. However, they must all be pertinent to the study's objectives.
What is a Research Question?

A research question is an inquiry that the research attempts to answer. It is the heart of the systematic investigation. Research questions are the most important step in any research project. In essence, it initiates the research project and establishes the pace for the specific research A research question is:
- Clear : It provides enough detail that the audience understands its purpose without any additional explanation.
- Focused : It is so specific that it can be addressed within the time constraints of the writing task.
- Succinct: It is written in the shortest possible words.
- Complex : It is not possible to answer it with a "yes" or "no", but requires analysis and synthesis of ideas before somebody can create a solution.
- Argumental : Its potential answers are open for debate rather than accepted facts.
A good research question usually focuses on the research and determines the research design, methodology, and hypothesis. It guides all phases of inquiry, data collection, analysis, and reporting. You should gather valuable information by asking the right questions.
Why are Research Questions so important?
Regardless of whether it is a qualitative research or quantitative research project, research questions provide writers and their audience with a way to navigate the writing and research process. Writers can avoid "all-about" papers by asking straightforward and specific research questions that help them focus on their research and support a specific thesis.
Types of Research Questions

There are two types of research: Qualitative research and Quantitative research . There must be research questions for every type of research. Your research question will be based on the type of research you want to conduct and the type of data collection.
The first step in designing research involves identifying a gap and creating a focused research question.
Below is a list of common research questions that can be used in a dissertation. Keep in mind that these are merely illustrations of typical research questions used in dissertation projects. The real research questions themselves might be more difficult.
Example Research Questions

The following are a few examples of research questions and research problems to help you understand how research questions can be created for a particular research problem.
Steps to Write Research Questions

You can focus on the issue or research gaps you're attempting to solve by using the research questions as a direction.
If you're unsure how to go about writing a good research question, these are the steps to follow in the process:
- Select an interesting topic Always choose a topic that interests you. Because if your curiosity isn’t aroused by a subject, you’ll have a hard time conducting research around it. Alos, it’s better that you pick something that’s neither too narrow or too broad.
- Do preliminary research on the topic Search for relevant literature to gauge what problems have already been tackled by scholars. You can do that conveniently through repositories like Scispace , where you’ll find millions of papers in one place. Once you do find the papers you’re looking for, try our reading assistant, SciSpace Copilot to get simple explanations for the paper . You’ll be able to quickly understand the abstract, find the key takeaways, and the main arguments presented in the paper. This will give you a more contextual understanding of your subject and you’ll have an easier time identifying knowledge gaps in your discipline.
Also: ChatPDF vs. SciSpace Copilot: Unveiling the best tool for your research
- Consider your audience It is essential to understand your audience to develop focused research questions for essays or dissertations. When narrowing down your topic, you can identify aspects that might interest your audience.
- Ask questions Asking questions will give you a deeper understanding of the topic. Evaluate your question through the What, Why, When, How, and other open-ended questions assessment.
- Assess your question Once you have created a research question, assess its effectiveness to determine if it is useful for the purpose. Refine and revise the dissertation research question multiple times.
Additionally, use this list of questions as a guide when formulating your research question.
Are you able to answer a specific research question? After identifying a gap in research, it would be helpful to formulate the research question. And this will allow the research to solve a part of the problem. Is your research question clear and centered on the main topic? It is important that your research question should be specific and related to your central goal. Are you tackling a difficult research question? It is not possible to answer the research question with a simple yes or no. The problem requires in-depth analysis. It is often started with "How" and "Why."
Start your research Once you have completed your dissertation research questions, it is time to review the literature on similar topics to discover different perspectives.
Strong Research Question Samples
Uncertain: How should social networking sites work on the hatred that flows through their platform?
Certain: What should social media sites like Twitter or Facebook do to address the harm they are causing?
This unclear question does not specify the social networking sites that are being used or what harm they might be causing. In addition, this question assumes that the "harm" has been proven and/or accepted. This version is more specific and identifies the sites (Twitter, Facebook), the type and extent of harm (privacy concerns), and who might be suffering from that harm (users). Effective research questions should not be ambiguous or interpreted.
Unfocused: What are the effects of global warming on the environment?
Focused: What are the most important effects of glacial melting in Antarctica on penguins' lives?
This broad research question cannot be addressed in a book, let alone a college-level paper. Focused research targets a specific effect of global heating (glacial melting), an area (Antarctica), or a specific animal (penguins). The writer must also decide which effect will have the greatest impact on the animals affected. If in doubt, narrow down your research question to the most specific possible.
Too Simple: What are the U.S. doctors doing to treat diabetes?
Appropriately complex: Which factors, if any, are most likely to predict a person's risk of developing diabetes?
This simple version can be found online. It is easy to answer with a few facts. The second, more complicated version of this question is divided into two parts. It is thought-provoking and requires extensive investigation as well as evaluation by the author. So, ensure that a quick Google search should not answer your research question.
How to write a strong Research Question?

The foundation of all research is the research question. You should therefore spend as much time as necessary to refine your research question based on various data.
You can conduct your research more efficiently and analyze your results better if you have great research questions for your dissertation, research paper , or essay .
The following criteria can help you evaluate the strength and importance of your research question and can be used to determine the strength of your research question:
- Researchable
- It should only cover one issue.
- A subjective judgment should not be included in the question.
- It can be answered with data analysis and research.
- Specific and Practical
- It should not contain a plan of action, policy, or solution.
- It should be clearly defined
- Within research limits
- Complex and Arguable
- It shouldn't be difficult to answer.
- To find the truth, you need in-depth knowledge
- Allows for discussion and deliberation
- Original and Relevant
- It should be in your area of study
- Its results should be measurable
- It should be original
Conclusion - How to write Research Questions?
Research questions provide a clear guideline for research. One research question may be part of a larger project, such as a dissertation. However, each question should only focus on one topic.
Research questions must be answerable, practical, specific, and applicable to your field. The research type that you use to base your research questions on will determine the research topic. You can start by selecting an interesting topic and doing preliminary research. Then, you can begin asking questions, evaluating your questions, and start your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace ResearchGPT . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, read, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1-Research Questions
6. Developing Your Research Question
Because of all their influence, you might worry that research questions are very difficult to develop. Sometimes it can seem that way. But we’ll help you get the hang of it and, luckily, none of us has to come up with perfect ones right off. It’s more like doing a rough draft and then improving it. That’s why we talk about developing research questions instead of just writing them.
Steps for Developing a Research Question
The steps for developing a research question, listed below, can help you organize your thoughts.
Step 1: Pick a topic (or consider the one assigned to you).
Step 2: Write a narrower/smaller topic that is related to the first.
Step 3: List some potential questions that could logically be asked in relation to the narrow topic.
Step 4: Pick the question that you are most interested in.
Step 5: Change the question you’re interested in so that it is more focused and specific.
MOVIE: Developing Research Questions
As you view this short video on how to develop research questions, think about the steps. Which step do you think is easiest? Which do you think is the hardest?
Once you know the steps and their order, only three skills are involved in developing a research question:
- Imagining narrower topics about a larger one,
- Thinking of questions that stem from a narrow topic, and
- Focusing questions to eliminate their vagueness.
Every time you use these skills, it’s important to evaluate what you have produced—that’s just part of the process of turning rough drafts into more finished products.

ACTIVITY: Developing a Research Question
Maybe you have a topic in mind but aren’t sure how to form a research question around it. The trick is to think of a question related to your topic but not answerable with a quick search. Also, try to be specific so that your research question can be fully answered in the final product for your research assignment.
ACTIVITY: Thinking of Questions
For each of the narrow topics below, think of a research question that is logically related to that topic. (Remember that good research questions often, but not always, start with “Why” or “How” because questions that begin that way usually require more analysis.)
- U.S. investors’ attitudes about sustainability
- College students’ use of Snapchat
- The character Scout in To Kill a Mockingbird
- Nature-inspired nanotechnologies
- Marital therapy
After you think of each research question, evaluate it by asking whether it is:
- Logically related to the topic
- In question form
- Not answerable with a quick Google search
- Specific, not vague
Sometimes the first draft of a research question is still too broad, which can make your search for sources more challenging. Refining your question to remove vagueness or to target a specific aspect of the topic can help.
ACTIVITY: Focusing Questions
The first draft research questions below are not focused enough. Read them and identify at least one area of vagueness in each. Check your vagueness with what we identified. It’s great if you found more than we did because that can lead to research questions of greater specificity. See the bottom of the page for our answers.
First Drafts of Research Questions:
- Why have most electric car company start-ups failed?
- How do crabapple trees develop buds?
- How has NASA helped America?
- Why do many first-time elections soon after a country overthrows a dictator result in very conservative elected leaders?
- How is music composed and performed mostly by African-Americans connected to African-American history?
ANSWER TO ACTIVITY: Focusing Questions
Some answers to the “Focusing Questions” Activity above are:
Question 1: Why have most electric car company start-ups failed? Vagueness: Which companies are we talking about? Worldwide or in a particular country?
Question 2: How do crabapple trees develop buds? Vagueness: There are several kinds of crabapples. Should we talk only about one kind? Does it matter where the crabapple tree lives?
Question 3: How has NASA helped America? Vagueness: NASA has had many projects. Should we should focus on one project they completed? Or projects during a particular time period?
Question 4: Why do many first-time elections soon after a country overthrows a dictator result in very conservative elected leaders? Vagueness: What time period are we talking about? Many dictators have been overthrown and many countries have been involved. Perhaps we should focus on one country or one dictator or one time period.
Question 5: How is music composed and performed mostly by African-Americans connected to African-American history? Vagueness: What kinds of music? Any particular performers and composers? When?
Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research Copyright © 2015 by Teaching & Learning, Ohio State University Libraries is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- How it works
How to Write the Research Questions – Tips & Examples
Published by Owen Ingram at August 13th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
Conducting research and writing an academic paper requires a clear direction and focus.
A good research question provides purpose to your research and clarifies the direction. It further helps your readers to understand what issue your research aims to explore and address.
If you are unsure about how to write research questions, here is a list of the attributes of a good research question;
- The research question should contain only a single problem
- You should be able to find the answer to it using primary and secondary data sources
- You should be able to address it within the time limit and other constraints
- Can attain in-depth and detailed results
- Relevant and applicable
- Should relate to your chosen field of research
Whenever you want to discover something new about a topic , you will ask a question about it. Therefore, the research question is important in the overall research process and provides the author with the reading and writing guidelines.
In a research paper or an essay, you will need to create a single research question that highlights just one problem or issue. The thesis statement should include the specific problem you aim to investigate to establish your argument’s central position or claim.
A larger project such as a dissertation or thesis , on the other hand, can have multiple research questions, but every question should focus on your main research problem . Different types of research will help you answer different research questions, but they should all be relevant to the research scope.
How to Write a Research Question
Steps to develop your research question.
- Choose a topic with a wide range of published literature
- Read and skim relevant articles to find out different problems and issues
- Specify a theoretical or practical research problem that your research question will address
- Narrow down the focus of your selected core niche

Example Research Question (s)
Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem.
Types of Research Questions
There are two main types of research; quantitative and qualitative research . Both types of research require research questions. What research question you will answer is dependent on the type of research you wish to employ.
The first part of designing research is to find a gap and create a fully focused research question.
The following table shows common research questions for a dissertation project. However, it is important to note that these examples of dissertation research questions are straightforward, and the actual research questions may be more complicated than these examples.
What data collection method best suits your research?
- Find out by hiring an expert from ResearchProspect today!
- Despite how challenging the subject may be, we are here to help you.
Steps to Write Research Questions
The research question provides you with a path and focuses on the real problem and the research gap you aim to fill. These are steps you need to take if you are unsure about how to write a research question:
Choose an Interesting Topic
Choose a topic of research according to your interest. The selected topic should be neither too broad nor too narrow.
Do Preliminary Research on the Topic
Find articles, books, journals, and theses relevant to your chosen topic. Understand what research problem each scholar addressed as part of their research project.
Consider your Audience
It is necessary to know your audience to develop focused research questions for your essay or dissertation. You can find aspects of your topic that could be interesting to your audience when narrowing your topic.
Start Asking Questions
What, why, when, how, and other open-ended questions will provide in-depth knowledge about the topic.
Evaluate your Question
After formulating a research question, evaluate to check its effectiveness and how it can serve the purpose. Revise and refine the dissertation research question.
- Do you have a clear research question?
It would help if you formed the research question after finding a research gap. This approach will enable the research to solve part of the problem.
- Do you have a focused research question?
It is necessary that the research question is specific and relating to the central aim of your research.
- Do you have a complex research question?
The research question cannot be answered by yes or no but requires in-depth analysis. It often begins with “How” or “Why.”
Begin your Research
After you have prepared dissertation research questions, you should research the existing literature on similar topics to find various perspectives.
Also See: Formulation of Research Question
If you have been struggling to devise research questions for your dissertation or are unsure about which topic would be suitable for your needs, then you might be interested in taking advantage of our dissertation topic and outline service, which includes several topic ideas in your preferred area of study and a 500/1000 words plan on your chosen topic. Our topic and outline service will help you jump-start your dissertation project.
Find out How Our Topics & Outline Service Can Help You!
Tips on How to Write a Strong Research Question
A research question is the foundation of the entire research. Therefore, you should spend as much time as required to refine the research question.
If you have good research questions for the dissertation, research paper , or essay, you can perform the research and analyse your results more effectively. You can evaluate the strength of the research question with the help of the following criteria. Your research question should be;
Intensive and Researchable
- It should cover a single issue
- The question shouldn’t include a subjective judgment
- It can be answerable with the data analysis or research=
Practical and Specific
- It should not include a course of action, policy, or solution
- It should be well-defined
- Answerable within research limits
Complicated and Arguable
- It should not be simple to answer
- Need in-depth knowledge to find facts
- Provides scope for debate and deliberation
Unique and Relevant
- It should lie in your field of study
- Its results should be contributable
- It should be unique
Conclusion – How to Write Research Questions
A research question provides a clear direction for research work. A bigger project, such as a dissertation, may have more than one research question, but every question should focus on one issue only.
Your research questions should be researchable, feasible to answer, specific to find results, complex (for Masters and PhD projects), and relevant to your field of study. Dissertation research questions depend upon the research type you are basing your paper on.
Start creating a research question by choosing an interesting topic, do some preliminary research, consider your audience, start asking questions, evaluating your question, and begin your research.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over. You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over.
You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
Place Order
Frequently Asked Questions
How are research questions written.
Research questions are written by:
- Identifying your topic.
- Considering what you want to explore.
- Making questions clear and concise.
- Ensuring they’re researchable.
- Avoiding bias or leading language.
- Focusing on one main idea per question.
What are examples of research questions?
- Does regular exercise improve mental well-being in adults over 50?
- How do online courses impact student engagement compared to traditional classes?
- What are the economic effects of prolonged pandemic lockdowns?
- How does early childhood nutrition influence academic performance in later life?
- Does urban green space reduce stress levels?
How to write a research question?
- Identify a specific topic or issue of interest.
- Conduct preliminary research to understand existing knowledge.
- Narrow the focus to address gaps or unresolved issues.
- Phrase the question to be clear, concise, and researchable.
- Ensure it is specific enough for systematic investigation.
How to formulate my research questions for my geography dissertation?
- Identify a geographical topic or phenomenon of interest.
- Review existing literature to find gaps.
- Consider spatial, temporal, environmental, or societal aspects.
- Ensure questions are specific, feasible, and significant.
- Frame questions to guide methodology: quantitative, qualitative, or mixed.
- Seek feedback from peers/advisors.
You May Also Like
This article is a step-by-step guide to how to write statement of a problem in research. The research problem will be half-solved by defining it correctly.
How to write a hypothesis for dissertation,? A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested with the help of experimental or theoretical research.
Here we explore what is research problem in dissertation with research problem examples to help you understand how and when to write a research problem.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Questions
Definition:
Research questions are the specific questions that guide a research study or inquiry. These questions help to define the scope of the research and provide a clear focus for the study. Research questions are usually developed at the beginning of a research project and are designed to address a particular research problem or objective.
Types of Research Questions
Types of Research Questions are as follows:
Descriptive Research Questions
These aim to describe a particular phenomenon, group, or situation. For example:
- What are the characteristics of the target population?
- What is the prevalence of a particular disease in a specific region?
Exploratory Research Questions
These aim to explore a new area of research or generate new ideas or hypotheses. For example:
- What are the potential causes of a particular phenomenon?
- What are the possible outcomes of a specific intervention?
Explanatory Research Questions
These aim to understand the relationship between two or more variables or to explain why a particular phenomenon occurs. For example:
- What is the effect of a specific drug on the symptoms of a particular disease?
- What are the factors that contribute to employee turnover in a particular industry?
Predictive Research Questions
These aim to predict a future outcome or trend based on existing data or trends. For example :
- What will be the future demand for a particular product or service?
- What will be the future prevalence of a particular disease?
Evaluative Research Questions
These aim to evaluate the effectiveness of a particular intervention or program. For example:
- What is the impact of a specific educational program on student learning outcomes?
- What is the effectiveness of a particular policy or program in achieving its intended goals?
How to Choose Research Questions
Choosing research questions is an essential part of the research process and involves careful consideration of the research problem, objectives, and design. Here are some steps to consider when choosing research questions:
- Identify the research problem: Start by identifying the problem or issue that you want to study. This could be a gap in the literature, a social or economic issue, or a practical problem that needs to be addressed.
- Conduct a literature review: Conducting a literature review can help you identify existing research in your area of interest and can help you formulate research questions that address gaps or limitations in the existing literature.
- Define the research objectives : Clearly define the objectives of your research. What do you want to achieve with your study? What specific questions do you want to answer?
- Consider the research design : Consider the research design that you plan to use. This will help you determine the appropriate types of research questions to ask. For example, if you plan to use a qualitative approach, you may want to focus on exploratory or descriptive research questions.
- Ensure that the research questions are clear and answerable: Your research questions should be clear and specific, and should be answerable with the data that you plan to collect. Avoid asking questions that are too broad or vague.
- Get feedback : Get feedback from your supervisor, colleagues, or peers to ensure that your research questions are relevant, feasible, and meaningful.
How to Write Research Questions
Guide for Writing Research Questions:
- Start with a clear statement of the research problem: Begin by stating the problem or issue that your research aims to address. This will help you to formulate focused research questions.
- Use clear language : Write your research questions in clear and concise language that is easy to understand. Avoid using jargon or technical terms that may be unfamiliar to your readers.
- Be specific: Your research questions should be specific and focused. Avoid broad questions that are difficult to answer. For example, instead of asking “What is the impact of climate change on the environment?” ask “What are the effects of rising sea levels on coastal ecosystems?”
- Use appropriate question types: Choose the appropriate question types based on the research design and objectives. For example, if you are conducting a qualitative study, you may want to use open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed responses.
- Consider the feasibility of your questions : Ensure that your research questions are feasible and can be answered with the resources available. Consider the data sources and methods of data collection when writing your questions.
- Seek feedback: Get feedback from your supervisor, colleagues, or peers to ensure that your research questions are relevant, appropriate, and meaningful.
Examples of Research Questions
Some Examples of Research Questions with Research Titles:
Research Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
- Research Question : What is the relationship between social media use and mental health, and how does this impact individuals’ well-being?
Research Title: Factors Influencing Academic Success in High School
- Research Question: What are the primary factors that influence academic success in high school, and how do they contribute to student achievement?
Research Title: The Effects of Exercise on Physical and Mental Health
- Research Question: What is the relationship between exercise and physical and mental health, and how can exercise be used as a tool to improve overall well-being?
Research Title: Understanding the Factors that Influence Consumer Purchasing Decisions
- Research Question : What are the key factors that influence consumer purchasing decisions, and how do these factors vary across different demographics and products?
Research Title: The Impact of Technology on Communication
- Research Question : How has technology impacted communication patterns, and what are the effects of these changes on interpersonal relationships and society as a whole?
Research Title: Investigating the Relationship between Parenting Styles and Child Development
- Research Question: What is the relationship between different parenting styles and child development outcomes, and how do these outcomes vary across different ages and developmental stages?
Research Title: The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy in Treating Anxiety Disorders
- Research Question: How effective is cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating anxiety disorders, and what factors contribute to its success or failure in different patients?
Research Title: The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity
- Research Question : How is climate change affecting global biodiversity, and what can be done to mitigate the negative effects on natural ecosystems?
Research Title: Exploring the Relationship between Cultural Diversity and Workplace Productivity
- Research Question : How does cultural diversity impact workplace productivity, and what strategies can be employed to maximize the benefits of a diverse workforce?
Research Title: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- Research Question: How can artificial intelligence be leveraged to improve healthcare outcomes, and what are the potential risks and ethical concerns associated with its use?
Applications of Research Questions
Here are some of the key applications of research questions:
- Defining the scope of the study : Research questions help researchers to narrow down the scope of their study and identify the specific issues they want to investigate.
- Developing hypotheses: Research questions often lead to the development of hypotheses, which are testable predictions about the relationship between variables. Hypotheses provide a clear and focused direction for the study.
- Designing the study : Research questions guide the design of the study, including the selection of participants, the collection of data, and the analysis of results.
- Collecting data : Research questions inform the selection of appropriate methods for collecting data, such as surveys, interviews, or experiments.
- Analyzing data : Research questions guide the analysis of data, including the selection of appropriate statistical tests and the interpretation of results.
- Communicating results : Research questions help researchers to communicate the results of their study in a clear and concise manner. The research questions provide a framework for discussing the findings and drawing conclusions.
Characteristics of Research Questions
Characteristics of Research Questions are as follows:
- Clear and Specific : A good research question should be clear and specific. It should clearly state what the research is trying to investigate and what kind of data is required.
- Relevant : The research question should be relevant to the study and should address a current issue or problem in the field of research.
- Testable : The research question should be testable through empirical evidence. It should be possible to collect data to answer the research question.
- Concise : The research question should be concise and focused. It should not be too broad or too narrow.
- Feasible : The research question should be feasible to answer within the constraints of the research design, time frame, and available resources.
- Original : The research question should be original and should contribute to the existing knowledge in the field of research.
- Significant : The research question should have significance and importance to the field of research. It should have the potential to provide new insights and knowledge to the field.
- Ethical : The research question should be ethical and should not cause harm to any individuals or groups involved in the study.
Purpose of Research Questions
Research questions are the foundation of any research study as they guide the research process and provide a clear direction to the researcher. The purpose of research questions is to identify the scope and boundaries of the study, and to establish the goals and objectives of the research.
The main purpose of research questions is to help the researcher to focus on the specific area or problem that needs to be investigated. They enable the researcher to develop a research design, select the appropriate methods and tools for data collection and analysis, and to organize the results in a meaningful way.
Research questions also help to establish the relevance and significance of the study. They define the research problem, and determine the research methodology that will be used to address the problem. Research questions also help to determine the type of data that will be collected, and how it will be analyzed and interpreted.
Finally, research questions provide a framework for evaluating the results of the research. They help to establish the validity and reliability of the data, and provide a basis for drawing conclusions and making recommendations based on the findings of the study.
Advantages of Research Questions
There are several advantages of research questions in the research process, including:
- Focus : Research questions help to focus the research by providing a clear direction for the study. They define the specific area of investigation and provide a framework for the research design.
- Clarity : Research questions help to clarify the purpose and objectives of the study, which can make it easier for the researcher to communicate the research aims to others.
- Relevance : Research questions help to ensure that the study is relevant and meaningful. By asking relevant and important questions, the researcher can ensure that the study will contribute to the existing body of knowledge and address important issues.
- Consistency : Research questions help to ensure consistency in the research process by providing a framework for the development of the research design, data collection, and analysis.
- Measurability : Research questions help to ensure that the study is measurable by defining the specific variables and outcomes that will be measured.
- Replication : Research questions help to ensure that the study can be replicated by providing a clear and detailed description of the research aims, methods, and outcomes. This makes it easier for other researchers to replicate the study and verify the results.
Limitations of Research Questions
Limitations of Research Questions are as follows:
- Subjectivity : Research questions are often subjective and can be influenced by personal biases and perspectives of the researcher. This can lead to a limited understanding of the research problem and may affect the validity and reliability of the study.
- Inadequate scope : Research questions that are too narrow in scope may limit the breadth of the study, while questions that are too broad may make it difficult to focus on specific research objectives.
- Unanswerable questions : Some research questions may not be answerable due to the lack of available data or limitations in research methods. In such cases, the research question may need to be rephrased or modified to make it more answerable.
- Lack of clarity : Research questions that are poorly worded or ambiguous can lead to confusion and misinterpretation. This can result in incomplete or inaccurate data, which may compromise the validity of the study.
- Difficulty in measuring variables : Some research questions may involve variables that are difficult to measure or quantify, making it challenging to draw meaningful conclusions from the data.
- Lack of generalizability: Research questions that are too specific or limited in scope may not be generalizable to other contexts or populations. This can limit the applicability of the study’s findings and restrict its broader implications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications. If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Research Paper Guides
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- How to Write a Research Question: Types & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
How to Write a Research Question: Types & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A research question is the main query that researchers seek to answer in their study. It serves as the basis for a scholarly project such as research paper, thesis or dissertation. A good research question should be clear, relevant and specific enough to guide the research process. It should also be open-ended, meaning that it allows for multiple possible answers or interpretations.
If you have located your general subject and main sources but still aren’t quite sure about the exact research questions for your paper, this guide will help you out. First, we will explore the concept of it together, so you could answer it in your work. Then some simple steps on composing your inquiry will be suggested. In the end, we will draw your attention to some specific details which can make your work good or bad. Sometimes it’s just easier to delegate all challenging tasks to a reliable research paper service . StudyCrumb is a trustable network of qualified writers ready to efficiently solve students’ challenges.
What Is a Good Research Question: Full Definition
Good research questions provide a concise definition of a problem. As a scholar, your main goal at the beginning is to select the main focus. It should be narrow enough so you could examine it within your deadline. Your work should be focused on something specific. Otherwise, it will require too much work and might not produce clear answers. At the same time your answer should be arguable and supported by data you’ve collected. Take a look at this example:

How to Write a Research Question: Step-By-Step Guide
In this section we will examine the process of developing a research question. We will guide you through it, step by step. Keep in mind that your subject should be important for your audience. So it requires some preliminary study and brainstorming. Let’s take a closer look at the main steps.
Step 1. Choose a Broad Topic for Your Research Paper Question
First, you need to decide on your general direction. When trying to identify your research paper questions, it is better to choose an area you are really interested in. You should be able to obtain enough data to write something about this topic. Therefore, do not choose something out of your reach. At the same time, your broad topic should not be too simple. Research paper questions that can be answered without any study would hardly make any sense for your project.
Step 2. Do Preliminary Reading Before Starting Your Research Question
Next, it is time we explore the context of the selected topic. You wouldn’t want to choose research questions that have already been examined and answered in detail. On the other hand, choosing a topic that is a complete ‘terra incognita’ might be a bridge too far for your project. Browse through available sources that are related to this topic. You should try and find out what has been discovered about it before. Do you see a gap that you can fill with your study? You can proceed with developing your exact inquiry! Have no time for in-depth topic exploration? Leave this task to professionals. Entrust your “ write my research paper ” order to StudyCrumb and get a top-notch work.
Step 3. Consider an Audience for Your Research Question
It is good to know your reader well to be able to convey your ideas and results to them in the best possible way. Before writing research questions for your projects, you might need to perform a brief analysis of your audience. That's how you'll be able to understand what is interesting for them and what is not. This will allow you to make better decisions when narrowing your broad topic down. Select a topic that is interesting for your reader! This would contribute much to the success for writing a research paper .
Step 4. Start Asking a Good Research Question
After you have considered your options, go ahead and compose the primary subject of your paper. What makes a good research question? It should highlight some problematic and relevant aspects of the general topic. So, after it is answered, you should have obtained some new valuable knowledge about the subject. Typically scholars start narrowing down their general topic by asking ‘how’, ‘why’ or ‘what’s next’ questions. This approach might help you come up with a great idea quickly.
Step 5. Evaluate Your Research Question
Finally, after you have composed a research paper question, you should take a second look at it and see if it is good enough for your paper. It would be useful to analyze it from the following sides:
- Is it clear for your audience?
- Is it complex enough to require significant study?
- Is it focused on a certain aspect of your general topic?
You might use the help of your peers or your friends at this step. You can also show it to your tutor and ask for their opinion.
Types of Research Questions: Which to Choose
A number of research questions types are available for use in a paper. They are divided into two main groups:
Qualitative questions:
- Explanatory
- Ethnographic
Quantitative questions:
- Descriptive
- Comparative
- Relationship based.
Selecting a certain type would impact the course of your study. We suggest you think about it carefully. Below you can find a few words about each type. Also, you can seek proficient help from academic experts. Buy a research paper from real pros and forget about stress once and for all.
Qualitative Research Questions: Definition With Example
When doing qualitative research, you are expected to aim to understand the different aspects and qualities of your target problem. Therefore, your thesis should focus on analyzing people’s experience, ideas and reflections rather than on obtaining some statistical data and calculating trends. Thus, this inquiry typically requires observing people’s behavior, interacting with them and learning how they interpret your target problem. Let’s illustrate this with an example:

What Is Contextual Research Questions
Contextual research revolves around examining your subject in its natural, everyday environment. It may be watching animals living in their usual habitats or people doing their normal activities in their familiar surroundings (at home, at school or at office). This academic approach helps to understand the role of the context. You'll be able to better explain connections between your problem, its environment and outcomes. This type of inquiry ought to be narrow enough. You shouldn’t have to examine each and every aspect of the selected problem in your paper. Consider this example:

Definition and Sample of Evaluative Research Questions
Evaluative research is performed in order to carefully assess the qualities of a selected object, individual, group, system or concept. It typically serves the purpose of collecting evidence that supports or contradicts solutions for a problem. This type of inquiry should focus on how useful a certain quality is for solving the problem. To conduct such study, you need to examine selected qualities in detail. Then, you should assume whether they match necessary criteria. It might include some quantitative methods such as collecting statistics. Although, the most important part is analyzing the qualities. If you need some examples, here’s one for you:

Explanatory Research Questions: Definition With Example
Your paper can be dedicated to explaining a certain phenomenon, finding its reasons and important relationships between it and other important things. Your explanatory research question should aim to highlight issues, uncertainties and problematic aspects of your subject. So, your study should bring clarity about these qualities. It should show how and why they have developed this way. An explanation may include showing causes and effects of issues in question, comparing the selected phenomenon to other similar types and showing whether the selected qualities match some predefined criteria. If you need some examples, check this one:

Generative Research Questions
This type of research is conducted in order to better understand the subject. With its help, you can find some new solutions or opportunities for improvement. Therefore, its main purpose is to develop a theoretical basis for further actions. You need to compose your generative research questions in a way that facilitates obtaining new ideas. It would help to begin with asking ‘why’, ‘what is the relationship between the subject and the problems X, Y, and Z’, ‘what can be improved here’, ‘how we can prevent it’ and so on. Need relevant examples? We’ve got one for you:

Ethnographic Research Question
Ethnography research is focused on a particular group of people. The aim is to study their behavior, typical reactions to certain events or information, needs, preferences or habits. Important parameters of this group which are most relevant to your general subject are taken into consideration. These are age, sex, language, religion, ethnicity, social status and so on. Main method in this case is first-hand observation of people from the selected group during an extended period of time. If you need strong examples, here’s one:

Quantitative Research Questions: Full Definition With Examples
Quantitative research deals with data – first of all, it is numeric data. It involves mathematical calculations and statistical analysis. It helps to obtain knowledge which is mostly expressed in numbers, graphs and tables. Unlike the qualitative type, the purpose of quantitative research is finding patterns, calculating probabilities, testing causal relationships and making predictions. It is focused on testing theories and hypotheses. (We have the whole blog on what is a hypothesis .) It is mostly used in natural and social sciences. These are: chemistry, biology, psychology, economics, sociology, marketing, etc. Here are a couple of examples:

Descriptive Research Questions: Definition With Example
This is probably the most widespread type of quantitative research question. Such inquiries seek to explain when, where, why, or how something occurred. They describe it accurately and systematically. These inquiries typically start with ‘what’. You are expected to use various methods to investigate one or more variables and determine their dependencies. Note, however, that you cannot control or manipulate any of these variables. You can only observe and measure them. Looking for some interesting examples? Here is one:

Definition of Comparative Research Questions
Comparative research question is used to highlight different variables and provide numerical evidence. This type is based on comparing one object, parameter or issue with another one of a similar kind. It can help to discover the differences between two or more groups by examining their outcome variables. Take a look at these two examples:

Relationship Research Questions
We conduct this type of research when we need to make it clear whether one parameter of a selected object causes another one. A relationship based quantitative research question should help us to explore and define trends and interactions between two or more variables. Are these two things mutually dependent? What kind of dependence is it? How has it developed? And what are possible outcomes of this connection? Here is an example of relationship-based quantitative research questions:

Research Questions Examples: Free
This section contains a number of helpful examples of research questions. Feel free to use them as inspiration to create your own questions and conduct productive study. Let’s start with two simple ones:

Are you interested in well written and inspiring questions? Do you want to learn what to avoid in your study? Just stay with us – there will be more of them below.
Examples of Good and Bad Research Questions
Everyone is interested in getting the best possible appraisal for their study. Choosing a topic which doesn't suit your specific situation may be discouraging. Thus, the quality of your paper might get affected by a poor choice. We have put together some good and bad examples so that you could avoid such mistakes.
Good Research Questions Examples
It is important to include clear terms into your questions. Otherwise, it would be difficult for you to plan your investigation properly. Also, they must be focused on a certain subject, not multiple ones. And finally, it should be possible to answer them. Let’s review several good examples:

Examples of Bad Research Questions
It is difficult to evaluate qualities of objects, individuals or groups if your purpose is not clear. This is why you shouldn’t create unclear research questions or try to focus on many problems at once. Some preliminary study might help to understand what you should focus on. Here are several bad examples:

In case you may need some information about the discussion section of a research paper example , find it in our blog.
Final Thoughts on Research Questions
In this article we have made a detailed review of the most popular types of research questions. We described peculiarities. We also provided some tips on conducting various kinds of study. Besides, a number of useful examples have been given for each category of questions.
Feel free to check out essay writing services. We have experienced writers who can help you compose your paper in time. They will absolutely ensure the high quality of your text.
Frequently Asked Questions About Research Questions
1. what is an example of a weak research question.
Here is an example of the weakest research question:
An answer would be simply making a list of species that inhabit the country. This subject does not require any actual study to be conducted. There is nothing to calculate or analyze here.
2. What is the most effective type of research question?
Most effective type of research question is the one that doesn't have a single correct answer. However, you should also pay close attention to your audience. If you need to create a strong effect, better choose a topic which is relevant for them.
3. What is a good nursing research question?
If you need an idea for a nursing research question, here are a few helpful examples you could use as a reference:
4. What are some sociological research questions?
Sociological questions are the ones that examine the social patterns or a meaning of a social phenomenon. They could be qualitative or quantitative. They should target groups of people with certain parameters, such as age or income level. Keep in mind that type of study usually requires collecting numerous data about your target groups.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like

The Right Questioning: Steps on Writing A Research Question
Read this article to understand the steps for writing a good research question and how it impacts the overall quality of a research study.
A good research question is required for any research to offer direction and purpose. It will assist you in determining the type of information to gather, the methods to utilize for data analysis, and the resources to examine.
Coming up with the appropriate research question can be extremely difficult for everyone. This is not a skill that comes naturally; rather, it is something that must be studied and learned.
As the saying goes, practice makes perfect.
This article intends to provide you with important information on crafting the right research questions by providing you with a step-by-step guide with examples.
What is a research question?
A research topic is a specific problem, issue, or phenomenon that a research study attempts to examine. It is an important part of the research process since it guides the study design and methods while also ensuring that the research is targeted and relevant. It should be a clear, focused, and short statement.
Typically, research questions are established following a literature review to discover gaps in current knowledge or to validate the necessity for more study in a certain field. They may be adjusted and altered when new information is exposed during the research process, but they must stay focused on the underlying topic or problem being examined.
What is a strong research question?
A strong research question is a targeted inquiry that defines a problem, topic, or issue to be explored and it should describe the important concepts or variables to be studied in a research. A strong research question has to be:
- Feasible: The research question should be empirically feasible. This implies that the question should be answerable through data collecting and analysis, utilizing quantitative and/or qualitative data, or by reading scholarly literature. If such information is unavailable, you should reconsider your question;
- Interesting: The research question should be intriguing to both the researcher and the larger academic community;
- Specific: The research question should be specific, short, and targeted. It should be detailed enough to lead the research process and limit the scope of the research;
- Focused: A focused research question is crucial as it ensures that resources are used efficiently, offers clear direction for the research project, and contributes to the production of meaningful results that are relevant to the subject of research.
- Relevant: The research question should be pertinent to the subject of study and address current and pressing problems;
- Ethical: The study question must be ethical, which means it must not cause harm or violate the rights of any persons or organizations.
Types of research question
Descriptive.
These questions are designed to describe a specific phenomenon, circumstance, or group. They are frequently used to collect basic information on a subject, such as its frequency, distribution, or characteristics.
Example: What are the characteristics of individuals who use public transportation in a large urban area?
Exploratory
These are questions designed to assist you in understanding more about a subject. The goal of asking an exploration question is to learn more about a topic without bias or prior preconceptions.
Example: What impact does personal technology have on today’s youth?
Comparative
These questions aim to find similarities, differences, or correlations between two or more groups, phenomena, or variables. Comparative research questions are frequently used to investigate the impact of multiple interventions or treatments, as well as to compare the features or results of different groups or populations.
Example: What are the disparities in depression rates between male and female teenage populations in urban and rural areas?
Relationship-based
Relationship-based research questions are a form of research question that focuses on investigating the relationships and links between different variables, ideas, or occurrences. These research questions attempt to explore the connections and interactions of many components, as well as to uncover patterns and trends in the data.
Example: What is the relationship between teenage social media use and self-esteem?
Predictive research questions are research questions that attempt to predict the probability of a specific occurrence or outcome based on the connection among several variables or circumstances. In domains such as economics, psychology, and epidemiology, these types of questions are frequently used to construct models and hypotheses that might assist foresee future trends or behavior.
Example: What is the likelihood of consumers purchasing a product after seeing it promoted by a celebrity?
Evaluative research questions are a form of research question that focuses on determining the efficacy, influence, or worth of a certain intervention, program, policy, or practice. These research questions attempt to ascertain the extent to which a certain intervention accomplished its intended goals or results, as well as to discover any unintended consequences or bad impacts.
Example: What effect does a new medicine have on lowering the symptoms of a certain medical condition when compared to normal treatment?
Steps on writing a good research question
Add visual impact to your posters with scientific illustrations and graphics.
Mind the Graph helps you to convey the significance of your research, making sure you’re including the right graphics and illustrations to make your poster even more successful. The correct visuals will emphasize your key findings and implications for a simple comprehension.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Unlock Your Creativity
Create infographics, presentations and other scientifically-accurate designs without hassle — absolutely free for 7 days!
About Jessica Abbadia
Jessica Abbadia is a lawyer that has been working in Digital Marketing since 2020, improving organic performance for apps and websites in various regions through ASO and SEO. Currently developing scientific and intellectual knowledge for the community's benefit. Jessica is an animal rights activist who enjoys reading and drinking strong coffee.
Content tags
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Writing Survey Questions
Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions. Creating good measures involves both writing good questions and organizing them to form the questionnaire.
Questionnaire design is a multistage process that requires attention to many details at once. Designing the questionnaire is complicated because surveys can ask about topics in varying degrees of detail, questions can be asked in different ways, and questions asked earlier in a survey may influence how people respond to later questions. Researchers are also often interested in measuring change over time and therefore must be attentive to how opinions or behaviors have been measured in prior surveys.
Surveyors may conduct pilot tests or focus groups in the early stages of questionnaire development in order to better understand how people think about an issue or comprehend a question. Pretesting a survey is an essential step in the questionnaire design process to evaluate how people respond to the overall questionnaire and specific questions, especially when questions are being introduced for the first time.
For many years, surveyors approached questionnaire design as an art, but substantial research over the past forty years has demonstrated that there is a lot of science involved in crafting a good survey questionnaire. Here, we discuss the pitfalls and best practices of designing questionnaires.
Question development
There are several steps involved in developing a survey questionnaire. The first is identifying what topics will be covered in the survey. For Pew Research Center surveys, this involves thinking about what is happening in our nation and the world and what will be relevant to the public, policymakers and the media. We also track opinion on a variety of issues over time so we often ensure that we update these trends on a regular basis to better understand whether people’s opinions are changing.
At Pew Research Center, questionnaire development is a collaborative and iterative process where staff meet to discuss drafts of the questionnaire several times over the course of its development. We frequently test new survey questions ahead of time through qualitative research methods such as focus groups , cognitive interviews, pretesting (often using an online, opt-in sample ), or a combination of these approaches. Researchers use insights from this testing to refine questions before they are asked in a production survey, such as on the ATP.
Measuring change over time
Many surveyors want to track changes over time in people’s attitudes, opinions and behaviors. To measure change, questions are asked at two or more points in time. A cross-sectional design surveys different people in the same population at multiple points in time. A panel, such as the ATP, surveys the same people over time. However, it is common for the set of people in survey panels to change over time as new panelists are added and some prior panelists drop out. Many of the questions in Pew Research Center surveys have been asked in prior polls. Asking the same questions at different points in time allows us to report on changes in the overall views of the general public (or a subset of the public, such as registered voters, men or Black Americans), or what we call “trending the data”.
When measuring change over time, it is important to use the same question wording and to be sensitive to where the question is asked in the questionnaire to maintain a similar context as when the question was asked previously (see question wording and question order for further information). All of our survey reports include a topline questionnaire that provides the exact question wording and sequencing, along with results from the current survey and previous surveys in which we asked the question.
The Center’s transition from conducting U.S. surveys by live telephone interviewing to an online panel (around 2014 to 2020) complicated some opinion trends, but not others. Opinion trends that ask about sensitive topics (e.g., personal finances or attending religious services ) or that elicited volunteered answers (e.g., “neither” or “don’t know”) over the phone tended to show larger differences than other trends when shifting from phone polls to the online ATP. The Center adopted several strategies for coping with changes to data trends that may be related to this change in methodology. If there is evidence suggesting that a change in a trend stems from switching from phone to online measurement, Center reports flag that possibility for readers to try to head off confusion or erroneous conclusions.
Open- and closed-ended questions
One of the most significant decisions that can affect how people answer questions is whether the question is posed as an open-ended question, where respondents provide a response in their own words, or a closed-ended question, where they are asked to choose from a list of answer choices.
For example, in a poll conducted after the 2008 presidential election, people responded very differently to two versions of the question: “What one issue mattered most to you in deciding how you voted for president?” One was closed-ended and the other open-ended. In the closed-ended version, respondents were provided five options and could volunteer an option not on the list.
When explicitly offered the economy as a response, more than half of respondents (58%) chose this answer; only 35% of those who responded to the open-ended version volunteered the economy. Moreover, among those asked the closed-ended version, fewer than one-in-ten (8%) provided a response other than the five they were read. By contrast, fully 43% of those asked the open-ended version provided a response not listed in the closed-ended version of the question. All of the other issues were chosen at least slightly more often when explicitly offered in the closed-ended version than in the open-ended version. (Also see “High Marks for the Campaign, a High Bar for Obama” for more information.)
Researchers will sometimes conduct a pilot study using open-ended questions to discover which answers are most common. They will then develop closed-ended questions based off that pilot study that include the most common responses as answer choices. In this way, the questions may better reflect what the public is thinking, how they view a particular issue, or bring certain issues to light that the researchers may not have been aware of.
When asking closed-ended questions, the choice of options provided, how each option is described, the number of response options offered, and the order in which options are read can all influence how people respond. One example of the impact of how categories are defined can be found in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in January 2002. When half of the sample was asked whether it was “more important for President Bush to focus on domestic policy or foreign policy,” 52% chose domestic policy while only 34% said foreign policy. When the category “foreign policy” was narrowed to a specific aspect – “the war on terrorism” – far more people chose it; only 33% chose domestic policy while 52% chose the war on terrorism.
In most circumstances, the number of answer choices should be kept to a relatively small number – just four or perhaps five at most – especially in telephone surveys. Psychological research indicates that people have a hard time keeping more than this number of choices in mind at one time. When the question is asking about an objective fact and/or demographics, such as the religious affiliation of the respondent, more categories can be used. In fact, they are encouraged to ensure inclusivity. For example, Pew Research Center’s standard religion questions include more than 12 different categories, beginning with the most common affiliations (Protestant and Catholic). Most respondents have no trouble with this question because they can expect to see their religious group within that list in a self-administered survey.
In addition to the number and choice of response options offered, the order of answer categories can influence how people respond to closed-ended questions. Research suggests that in telephone surveys respondents more frequently choose items heard later in a list (a “recency effect”), and in self-administered surveys, they tend to choose items at the top of the list (a “primacy” effect).
Because of concerns about the effects of category order on responses to closed-ended questions, many sets of response options in Pew Research Center’s surveys are programmed to be randomized to ensure that the options are not asked in the same order for each respondent. Rotating or randomizing means that questions or items in a list are not asked in the same order to each respondent. Answers to questions are sometimes affected by questions that precede them. By presenting questions in a different order to each respondent, we ensure that each question gets asked in the same context as every other question the same number of times (e.g., first, last or any position in between). This does not eliminate the potential impact of previous questions on the current question, but it does ensure that this bias is spread randomly across all of the questions or items in the list. For instance, in the example discussed above about what issue mattered most in people’s vote, the order of the five issues in the closed-ended version of the question was randomized so that no one issue appeared early or late in the list for all respondents. Randomization of response items does not eliminate order effects, but it does ensure that this type of bias is spread randomly.
Questions with ordinal response categories – those with an underlying order (e.g., excellent, good, only fair, poor OR very favorable, mostly favorable, mostly unfavorable, very unfavorable) – are generally not randomized because the order of the categories conveys important information to help respondents answer the question. Generally, these types of scales should be presented in order so respondents can easily place their responses along the continuum, but the order can be reversed for some respondents. For example, in one of Pew Research Center’s questions about abortion, half of the sample is asked whether abortion should be “legal in all cases, legal in most cases, illegal in most cases, illegal in all cases,” while the other half of the sample is asked the same question with the response categories read in reverse order, starting with “illegal in all cases.” Again, reversing the order does not eliminate the recency effect but distributes it randomly across the population.
Question wording
The choice of words and phrases in a question is critical in expressing the meaning and intent of the question to the respondent and ensuring that all respondents interpret the question the same way. Even small wording differences can substantially affect the answers people provide.
[View more Methods 101 Videos ]
An example of a wording difference that had a significant impact on responses comes from a January 2003 Pew Research Center survey. When people were asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule,” 68% said they favored military action while 25% said they opposed military action. However, when asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule even if it meant that U.S. forces might suffer thousands of casualties, ” responses were dramatically different; only 43% said they favored military action, while 48% said they opposed it. The introduction of U.S. casualties altered the context of the question and influenced whether people favored or opposed military action in Iraq.
There has been a substantial amount of research to gauge the impact of different ways of asking questions and how to minimize differences in the way respondents interpret what is being asked. The issues related to question wording are more numerous than can be treated adequately in this short space, but below are a few of the important things to consider:
First, it is important to ask questions that are clear and specific and that each respondent will be able to answer. If a question is open-ended, it should be evident to respondents that they can answer in their own words and what type of response they should provide (an issue or problem, a month, number of days, etc.). Closed-ended questions should include all reasonable responses (i.e., the list of options is exhaustive) and the response categories should not overlap (i.e., response options should be mutually exclusive). Further, it is important to discern when it is best to use forced-choice close-ended questions (often denoted with a radio button in online surveys) versus “select-all-that-apply” lists (or check-all boxes). A 2019 Center study found that forced-choice questions tend to yield more accurate responses, especially for sensitive questions. Based on that research, the Center generally avoids using select-all-that-apply questions.
It is also important to ask only one question at a time. Questions that ask respondents to evaluate more than one concept (known as double-barreled questions) – such as “How much confidence do you have in President Obama to handle domestic and foreign policy?” – are difficult for respondents to answer and often lead to responses that are difficult to interpret. In this example, it would be more effective to ask two separate questions, one about domestic policy and another about foreign policy.
In general, questions that use simple and concrete language are more easily understood by respondents. It is especially important to consider the education level of the survey population when thinking about how easy it will be for respondents to interpret and answer a question. Double negatives (e.g., do you favor or oppose not allowing gays and lesbians to legally marry) or unfamiliar abbreviations or jargon (e.g., ANWR instead of Arctic National Wildlife Refuge) can result in respondent confusion and should be avoided.
Similarly, it is important to consider whether certain words may be viewed as biased or potentially offensive to some respondents, as well as the emotional reaction that some words may provoke. For example, in a 2005 Pew Research Center survey, 51% of respondents said they favored “making it legal for doctors to give terminally ill patients the means to end their lives,” but only 44% said they favored “making it legal for doctors to assist terminally ill patients in committing suicide.” Although both versions of the question are asking about the same thing, the reaction of respondents was different. In another example, respondents have reacted differently to questions using the word “welfare” as opposed to the more generic “assistance to the poor.” Several experiments have shown that there is much greater public support for expanding “assistance to the poor” than for expanding “welfare.”
We often write two versions of a question and ask half of the survey sample one version of the question and the other half the second version. Thus, we say we have two forms of the questionnaire. Respondents are assigned randomly to receive either form, so we can assume that the two groups of respondents are essentially identical. On questions where two versions are used, significant differences in the answers between the two forms tell us that the difference is a result of the way we worded the two versions.

One of the most common formats used in survey questions is the “agree-disagree” format. In this type of question, respondents are asked whether they agree or disagree with a particular statement. Research has shown that, compared with the better educated and better informed, less educated and less informed respondents have a greater tendency to agree with such statements. This is sometimes called an “acquiescence bias” (since some kinds of respondents are more likely to acquiesce to the assertion than are others). This behavior is even more pronounced when there’s an interviewer present, rather than when the survey is self-administered. A better practice is to offer respondents a choice between alternative statements. A Pew Research Center experiment with one of its routinely asked values questions illustrates the difference that question format can make. Not only does the forced choice format yield a very different result overall from the agree-disagree format, but the pattern of answers between respondents with more or less formal education also tends to be very different.
One other challenge in developing questionnaires is what is called “social desirability bias.” People have a natural tendency to want to be accepted and liked, and this may lead people to provide inaccurate answers to questions that deal with sensitive subjects. Research has shown that respondents understate alcohol and drug use, tax evasion and racial bias. They also may overstate church attendance, charitable contributions and the likelihood that they will vote in an election. Researchers attempt to account for this potential bias in crafting questions about these topics. For instance, when Pew Research Center surveys ask about past voting behavior, it is important to note that circumstances may have prevented the respondent from voting: “In the 2012 presidential election between Barack Obama and Mitt Romney, did things come up that kept you from voting, or did you happen to vote?” The choice of response options can also make it easier for people to be honest. For example, a question about church attendance might include three of six response options that indicate infrequent attendance. Research has also shown that social desirability bias can be greater when an interviewer is present (e.g., telephone and face-to-face surveys) than when respondents complete the survey themselves (e.g., paper and web surveys).
Lastly, because slight modifications in question wording can affect responses, identical question wording should be used when the intention is to compare results to those from earlier surveys. Similarly, because question wording and responses can vary based on the mode used to survey respondents, researchers should carefully evaluate the likely effects on trend measurements if a different survey mode will be used to assess change in opinion over time.
Question order
Once the survey questions are developed, particular attention should be paid to how they are ordered in the questionnaire. Surveyors must be attentive to how questions early in a questionnaire may have unintended effects on how respondents answer subsequent questions. Researchers have demonstrated that the order in which questions are asked can influence how people respond; earlier questions can unintentionally provide context for the questions that follow (these effects are called “order effects”).
One kind of order effect can be seen in responses to open-ended questions. Pew Research Center surveys generally ask open-ended questions about national problems, opinions about leaders and similar topics near the beginning of the questionnaire. If closed-ended questions that relate to the topic are placed before the open-ended question, respondents are much more likely to mention concepts or considerations raised in those earlier questions when responding to the open-ended question.
For closed-ended opinion questions, there are two main types of order effects: contrast effects ( where the order results in greater differences in responses), and assimilation effects (where responses are more similar as a result of their order).
An example of a contrast effect can be seen in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in October 2003, a dozen years before same-sex marriage was legalized in the U.S. That poll found that people were more likely to favor allowing gays and lesbians to enter into legal agreements that give them the same rights as married couples when this question was asked after one about whether they favored or opposed allowing gays and lesbians to marry (45% favored legal agreements when asked after the marriage question, but 37% favored legal agreements without the immediate preceding context of a question about same-sex marriage). Responses to the question about same-sex marriage, meanwhile, were not significantly affected by its placement before or after the legal agreements question.
Another experiment embedded in a December 2008 Pew Research Center poll also resulted in a contrast effect. When people were asked “All in all, are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the way things are going in this country today?” immediately after having been asked “Do you approve or disapprove of the way George W. Bush is handling his job as president?”; 88% said they were dissatisfied, compared with only 78% without the context of the prior question.
Responses to presidential approval remained relatively unchanged whether national satisfaction was asked before or after it. A similar finding occurred in December 2004 when both satisfaction and presidential approval were much higher (57% were dissatisfied when Bush approval was asked first vs. 51% when general satisfaction was asked first).
Several studies also have shown that asking a more specific question before a more general question (e.g., asking about happiness with one’s marriage before asking about one’s overall happiness) can result in a contrast effect. Although some exceptions have been found, people tend to avoid redundancy by excluding the more specific question from the general rating.
Assimilation effects occur when responses to two questions are more consistent or closer together because of their placement in the questionnaire. We found an example of an assimilation effect in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in November 2008 when we asked whether Republican leaders should work with Obama or stand up to him on important issues and whether Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders or stand up to them on important issues. People were more likely to say that Republican leaders should work with Obama when the question was preceded by the one asking what Democratic leaders should do in working with Republican leaders (81% vs. 66%). However, when people were first asked about Republican leaders working with Obama, fewer said that Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders (71% vs. 82%).
The order questions are asked is of particular importance when tracking trends over time. As a result, care should be taken to ensure that the context is similar each time a question is asked. Modifying the context of the question could call into question any observed changes over time (see measuring change over time for more information).
A questionnaire, like a conversation, should be grouped by topic and unfold in a logical order. It is often helpful to begin the survey with simple questions that respondents will find interesting and engaging. Throughout the survey, an effort should be made to keep the survey interesting and not overburden respondents with several difficult questions right after one another. Demographic questions such as income, education or age should not be asked near the beginning of a survey unless they are needed to determine eligibility for the survey or for routing respondents through particular sections of the questionnaire. Even then, it is best to precede such items with more interesting and engaging questions. One virtue of survey panels like the ATP is that demographic questions usually only need to be asked once a year, not in each survey.
U.S. Surveys
Other research methods, sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- EXPLORE Random Article
How to Write a Research Question
Last Updated: April 20, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Danielle Blinka, MA, MPA . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 75,817 times.
A research question helps you narrow your research and write a clear, arguable thesis. Your research question needs to be concise, arguable, and focused on your particular topic. Before writing your research question, narrow down your topic and brainstorm possible questions. Then, select the best question and craft it into a good research question. As another option, choose the type of research question that fits your purpose and format your question to fit that style.
Research Questions

Narrowing Your Topic

- When you decide on a research question for your work, it's best to run it by your instructor.

- For instance, great topics for a high school paper might include family dynamics during the civil war, body image among teens, or type 2 diabetes.
- If you're doing a college-level project, a good topic might be the environment's influence on human development, cultural influences on a poet's work, or the ethics of technological advancements.
- In some cases, your topic may be provided to you, such as when you're writing a paper for a class. You can still use the same process for narrowing your topic and selecting a research question.

- The purpose of this research is to learn more, not gather sources. That means it's okay to check sites like Wikipedia, which aren't typically considered reliable sources.

- What, why, and how questions make the best research questions.
- Write down the first questions that come to mind without worrying if they'll make a good research question. You can always revise your question later to make it better.
- For example, let's say you chose body image among teens as your topic. You might write questions like, “How does social media impact body image?” “How does the amount of time spent on Instagram relate to a teen's sense of self-worth?” “Are peers or family members a bigger influence on body image in teens?” and “What factors make teens more likely to have a poor body image?”
- Similarly, you might write a college paper about the ethics of technological advancements. Questions you might ask include, "How is social media altering the culture of society?" "How does screen time alter the brain's neural processing?" and "How might current advancements affect society over the next 25 years?"
Tip: If you find yourself drawn to a particular question, don't keep brainstorming potential questions. Instead, start evaluating the question that interests you to figure out if it might be right for your research project.
Crafting an Effective Research Question

- As an example, the question "What jobs will humans lose to robots over the next 50 years?" may be too difficult to answer. Instead, you might ask, "How has the field of robotics changed the manufacturing industry?"
Tip: When choosing your question, consider your skill level and purpose. If you're doing this project for a class, how will it be graded? What are your instructor's expectations? Additionally, make sure your question fits the scope of the assignment.

- Is this question clear enough to guide my research?
- Is this question specific?
- Does this question allow for research and analysis?
- Can I answer this question based on current research? If so, could I easily find the answer by looking at basic reference works (which means the question is too easy to answer), or will it require more in-depth analysis using multiple sources?
- Has this question already been answered?
- Can I answer the question in an objective manner, based on evidence?
- Can I answer this question in the time I have allotted for this project?

- “What factors cause teens to have poor body image?” is better stated “What environmental and social factors contribute to poor body image in teens?”
- “How does T.S. Elliot use symbolism?” becomes “Why does T.S. Elliot use tea as a symbol in 'The Lovesong of J. Alfred Prufrock?'”
- “What happened to family dynamics during the civil war?” can be narrowed to “How did the fracturing of families during the civil war affect society?”
- "How does screen time alter the brain's neural processing?" might be narrowed to "How does spending 2 hours a day on social media impact neural processing in preteens?"

- For instance, questions like, "What season of the year do parrots typically breed?" or "What era did William Wordsworth write?" are not great research questions because they are too easy to answer.
- The research question “Are peers or family members a bigger influence on body image in teens?” is arguable because you could make a case for either peers or family members having a greater influence on teenagers. Similarly, “Why does T.S. Elliot use tea as a symbol in 'The Lovesong of J. Alfred Prufrock?'” is arguable because different critics may have varying interpretations of the poem.
- As another example, "How does spending 2 hours a day on social media impact neural processing in preteens?" is debatable because you can focus on different effects. It's possible to interpret these effects differently, depending on your stance on the issue.
Tip: Research your question and see what comes up. If you feel like the search results effectively cover what you want to say, then you might want to pick a different question.
Choosing a Type of Research Question

- "What environmental factors cause birds to move nests?"
- "What changes to the habitat can encourage parrots to mate?"
- "What political conditions contributed to the start of the War of 1812?"
- "What symbols does T.S. Elliot use in 'The Lovesong of J. Alfred Prufrock?'”

- "If two different plants are both provided the same amount of sunlight and fertilizer, will they grow at the same rate?"
- "If two identical solutions are exposed to different quantities of an element, will they show equal or different reactions?"
- "If two test subjects are asked to perform a task alone and then together, how will collaboration affect their outcome?"

- "Will the introduction of a new plant to a biodome affect the ecosystem?"
- "Does changing team assignments cause workers to lose morale?"
- "Do metered ramps on highways change driver behavior?"
Community Q&A
- Make sure your research question is narrow enough to write a specific paper. If it's too broad, your paper will be too general and vague to make a clear point. A narrow research question will help you write a focused paper. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- A clear, specific research question will help you create a good thesis for your paper. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- If you're doing your research as part of a class assignment, talk to your instructor if you're having trouble writing your research question. Tell them what you're considering and ask them for guidance. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libraries.indiana.edu/sites/default/files/Develop_a_Research_Question.pdf
- ↑ https://www.pewresearch.org/our-methods/u-s-surveys/writing-survey-questions/
- ↑ https://cirt.gcu.edu/research/develop/tutorials/question
- ↑ https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/how-to-write-a-research-question
About this article

To write a research question, start by writing a list of open-ended questions that relate to the topic you're researching. For example, if your topic was social media, your questions might look something like "How does social media impact body image?" or "What impact does social media have on our culture?" Next, choose the question that interests you the most, and try to make it as specific as possible. Also, make sure it can't be easily answered since you want a topic that you can thoroughly examine. For more advice, like how to choose a topic to research, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
Reader Success Stories
Apr 7, 2022
Did this article help you?
- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
'ZDNET Recommends': What exactly does it mean?
ZDNET's recommendations are based on many hours of testing, research, and comparison shopping. We gather data from the best available sources, including vendor and retailer listings as well as other relevant and independent reviews sites. And we pore over customer reviews to find out what matters to real people who already own and use the products and services we’re assessing.
When you click through from our site to a retailer and buy a product or service, we may earn affiliate commissions. This helps support our work, but does not affect what we cover or how, and it does not affect the price you pay. Neither ZDNET nor the author are compensated for these independent reviews. Indeed, we follow strict guidelines that ensure our editorial content is never influenced by advertisers.
ZDNET's editorial team writes on behalf of you, our reader. Our goal is to deliver the most accurate information and the most knowledgeable advice possible in order to help you make smarter buying decisions on tech gear and a wide array of products and services. Our editors thoroughly review and fact-check every article to ensure that our content meets the highest standards. If we have made an error or published misleading information, we will correct or clarify the article. If you see inaccuracies in our content, please report the mistake via this form .
How to write better ChatGPT prompts in 5 steps

ChatGPT is the generative artificial intelligence (AI) tool that's taken the world by storm. While there's always the possibility it will simply make stuff up , there's a lot you can do when crafting prompts to ensure the best possible outcome. That's what we'll be exploring in this how-to.
In this article, we'll show you how to write prompts that encourage the large language model (LLM) that powers ChatGPT to provide the best possible answers.
Also: Have 10 hours? IBM will train you in AI fundamentals - for free
Writing effective prompts, known as prompt engineering, has even become its own highly-paid discipline . Who knows? These tips could help you build the skills to become one of those highly paid prompt engineers. Apparently, these gigs can pay from $175,000 to $335,000 per year.
How to write effective ChatGPT prompts
1. talk to the ai like you would a person.
One of the more interesting things I had to get used to when working with ChatGPT is that you don't program it, you talk to it. As a formally trained programmer, I've had to leave a lot of habits by the wayside when engaging with AI. Talking to it (and with it) requires a mindset shift.
When I say talk to it like a person, I mean talk to it like you would a co-worker or team member. If that's hard to do, give it a name. Alexa is taken, so maybe think of it as "Bob". This naming helps because when you talk to Bob, you might include conversational details, little anecdotes that give your story texture.
Also: How to use ChatGPT to write code
When talking to a person, it would be natural for them to miss your point initially and require clarification, or veer away from the topic at hand and need to be wrangled back. You might need to fill in the backstory for them, or restate complex questions based on the answers they give you.
This is called interactive prompting. Don't be afraid to ask multi-step questions: ask, get a response, and based on that response, ask another question. I've done this myself, sometimes 10 or 20 times in a row, and gotten very powerful results. Think of this as having a conversation with ChatGPT.
2. Set the stage and provide context
Writing a ChatGPT prompt is more than just asking a one-sentence question. It often involves providing relevant background information to set the context of the query.
Let's say that you want to prepare for a marathon (for the record, I do not run, dance, or jump -- this is merely an example). You could ask ChatGPT:
How can I prepare for a marathon?
However, you'll get a far more nuanced answer if you add that you're training for your first marathon. Try this instead:
I am a beginner runner and have never run a marathon before, but I want to complete one in six months. How can I prepare for a marathon?
By giving the AI more information, you're helping it return a more focused answer. Even with ChatGPT's help, there's no way I'm going to run a marathon (unless I'm doing it with a V-Twin motor under my seat). Here are two more examples of questions that provide context:
I am planning to travel to Spain in a few months and would like to learn some basic Spanish to help me communicate with local residents. I am looking for online resources that are suitable for beginners and provide a structured and comprehensive approach to learning the language. Can you recommend some online resources for learning Spanish as a beginner?
In this case, rather than just asking about learning resources, the context helps focus the AI on learning how to communicate on the ground with local residents. Here's another example:
I am a business owner interested in exploring how blockchain technology can be used to improve supply chain efficiency and transparency. I am looking for a clear and concise explanation of the technology and examples of how it has been used in the context of supply chain management. Can you explain the concept of blockchain technology and its potential applications in supply chain management?
In this example, rather than just asking for information on blockchain and how it works, the focus is specifically on blockchain for supply chain efficiency and how it might be used in a real-world scenario.
Also: How to use Image Creator from Microsoft Designer (formerly Bing Image Creator) Lastly, let's get into how to construct a detailed prompt.
One note: I limit the answer to 500 words because ChatGPT seems to break when asked to produce somewhere between 500 and 700 words, leaving stories mid-sentence and not resuming properly when asked to continue. I hope future versions provide longer answers, because premises like this can generate fun story beginnings:
Write a short story for me, no more than 500 words. The story takes place in 2339, in Boston. The entire story takes place inside a Victorian-style bookstore that wouldn't be out of place in Diagon Alley. Inside the store are the following characters, all human: The proprietor: make this person interesting and a bit unusual, give them a name and at least one skill or characteristic that influences their backstory and possibly influences the entire short story. The helper: this is a clerk in the store. His name is Todd. The customer and his friend: Two customers came into the store together, Jackson and Ophelia. Jackson is dressed as if he's going to a Steampunk convention, while Ophelia is clearly coming home from her day working in a professional office. Another customer is Evangeline, a regular customer in the store, in her mid-40s. Yet another customer is Archibald, a man who could be anywhere from 40 to 70 years old. He has a mysterious air about himself and seems both somewhat grandiose and secretive. There is something about Archibald that makes the others uncomfortable. A typical concept in retail sales is that there's always more inventory "in the back," where there's a storeroom for additional goods that might not be shown on the shelves where customers browse. The premise of this story is that there is something very unusual about this store's "in the back." Put it all together and tell something compelling and fun.
You can see how the detail provides more for the AI to work with. First, feed "Write me a story about a bookstore" into ChatGPT and see what it gives you. Then feed in the above prompt and you'll see the difference.
3. Tell the AI to assume an identity or profession
One of ChatGPT's coolest features is that it can write from the point of view of a specific person or profession. In a previous article, I showed how you can make ChatGPT write like a pirate or Shakespeare , but you can also have it write like a teacher, a marketing executive, a fiction writer -- anyone you want.
Also: How ChatGPT can rewrite and improve your existing code
For example, I can ask ChatGPT to describe the Amazon Echo smart home device, but to do so from the point of view of a product manager, a caregiver, and a journalist in three separate prompts:
From the point of view of its product manager, describe the Amazon Echo Alexa device. From the point of view of an adult child caring for an elderly parent, describe the Amazon Echo Alexa device. From the point of view of a journalist, describe the Amazon Echo Alexa device.
Try dropping these three prompts into ChatGPT to see its complete response.
I've pulled a few lines from ChatGPT's responses, so you can see how it interprets different perspectives. From the product manager identity: I can confidently say that this is one of the most innovative and revolutionary products in the smart home industry.
From the caregiver identity: The device's ability to set reminders and alarms can be particularly helpful for elderly individuals who may have trouble remembering to take their medication or attend appointments.
Also: 5 ways to explore the use of generative AI at work
And from the journalist identity: From a journalistic perspective, the Echo has made headlines due to privacy concerns surrounding the collection and storage of user data.
You can see how different identities allow the AI to provide different perspectives as part of its response. To expand this, you can let the AI do a thought experiment. Let's look at some of the issues that went into the creation of something like Alexa:
The year is 2012. Siri has been out for the iPhone for about a year, but nothing like an Alexa smart home device has been released. The scene is an Amazon board meeting where the Echo smart assistant based on Alexa has just been proposed. Provide the arguments, pro and con, that board members at that meeting would have been likely to discuss as part of their process of deciding whether or not to approve spending to invest in developing the device. Feel free to also include participation by engineering design experts and product champions, if that provides more comprehensive perspective.
It's also good to know that making minor changes to your prompts can significantly change ChatGPT's response. For example, when I changed the phrase, "Provide the arguments, pro and con, that..." to "Provide the pro and con arguments as dialogue, that...," ChatGPT rewrote its answer, switching from a list of enumerated pros and cons to an actual dialogue between participants.
4. Keep ChatGPT on track
As mentioned above, ChatGPT has a tendency to go off the rails, lose track of the discussion, or completely fabricate answers.
There are a few techniques you can use to help keep it on track and honest.
One of my favorite things to do is ask ChatGPT to justify its responses. I'll use phrases like "Why do you think that?" or "What evidence supports your answer?" Often, the AI will simply apologize for making stuff up and come back with a new answer. Other times, it might give you some useful information about its reasoning path. In any case, don't forget to apply the tips I provide for having ChatGPT cite sources .
Also: My two favorite ChatGPT Plus features and the remarkable things I can do with them
If you have a fairly long conversation with ChatGPT, you'll start to notice that the AI loses the thread. Not that that's unique to AIs -- even in extended conversations with humans, someone is bound to get lost. That said, you can gently guide the AI back on track by reminding it what the topic is, as well as what you're trying to explore.
5. Don't be afraid to play and experiment
One of the best ways to up your skill at this craft is to play around with what the chatbot can do.
Try feeding ChatGPT a variety of interesting prompts to see what it will do with them. Then change them up and see what happens. Here are five to get you started:
- Imagine you are a raindrop falling from the sky during a thunderstorm. Describe your journey from the moment you form in the cloud to the moment you hit the ground. What do you see, feel, and experience?
- You are a toy that has been left behind in an attic for decades. Narrate your feelings, memories of playtimes past, and your hopes of being rediscovered.
- Write the final diary entry of a time traveler who has decided to settle down in a specific era, explaining why they chose that time and what they've learned from their travels.
- Imagine a dialogue between two unlikely objects, like a teacup and a wristwatch, discussing the daily routines and challenges they face.
- Describe a day in an ant colony from the perspective of an ant. Dive deep into the politics, challenges, and social structures of the ant world.
Pay attention not only to what the AI generates, but how it generates what it does, what mistakes it makes, and where it seems to run into limits. All of that detail will help you expand your prompting horizons.
More prompt-writing tips
- Feel free to re-ask the question. ChatGPT will often change its answer with each ask.
- Make small changes to your prompts to guide it into giving you a better answer.
- ChatGPT will retain its awareness of previous conversations as long as the current page is open. If you leave that page, it will lose awareness. To be clear, ChatGPT will also sometimes lose the thread of the conversation without reason, so be aware you may need to start over from time to time.
- Similarly, opening a new page will start the discussion with fresh responses.
- Be sure to specify the length of the response you want. Answers over about 500 words sometimes break down.
- You can correct and clarify prompts based on how the AI answered previously. If it's misinterpreting you, you may be able to just tell it what it missed and continue.
- Rephrase questions if ChatGPT doesn't want to answer what you're asking. Use personas to elicit answers that it might not otherwise want to give.
- If you want sources cited , tell it to support or justify its answers.
- ChatGPT custom instructions are now available to free users. You can give ChatGPT a set of prompts that are always available , so you don't have to retype them.
- Keep experimenting.
- Consider getting the ChatGPT Plus subscription . You can then use your own data for powerful analytics . You can also pull data from the Web .
- Try asking the same question of Gemini (formerly Bard) or Copilot (formerly Bing Chat). Both will interpret your prompts differently and answer differently. This is effectively getting a second opinion on your prompt, and can give you alternate perspectives.
- Ask for examples. If you want to see how well ChatGPT understands what you're asking for, ask it "Can you give me three examples of how that works?" or similar questions.
- Ask it to repeat parts of your original requests back to you. For example, if you feed it an article to analyze, you can tell it something like, "Just to be sure you understand, please echo back the first three headlines," or "I want to be sure you understand what I mean, so summarize the main conflict discussed in this article."
- Sometimes ChatGPT just fails. Keep trying, but also be willing to give up and move on to other tools. It's not perfect...yet.
What type of prompts work best with ChatGPT?
Part of what makes ChatGPT so compelling is you can ask it almost anything. That said, keep in mind that it's designed to provide written answers. If you want a list of websites, you're better off talking to Google.
Also: How to use DALL-E 3 in ChatGPT
If you want some form of computation, talk to Wolfram Alpha . Give ChatGPT open-ended prompts, encourage creativity, and don't be afraid to share personal experiences or emotions. Plus, keep in mind that the AI's knowledge ends in 2021 for ChatGPT 3.5 and December 2023 for ChatGPT 4 in ChatGPT Plus.
How can I adjust the complexity of ChatGPT responses?
You can directly specify the complexity level by including it in your prompt. Add "... at a high school level" or "... at a level intended for a Ph.D. to understand" to the end of your question. You can also increase complexity of output by increasing the richness of your input. The more you provide in your prompt, the more detailed and nuanced ChatGPT's response will be. You can also include other specific instructions, like "Give me a summary," "Explain in detail," or "Provide a technical description."
Also: How does ChatGPT actually work?
You can also pre-define profiles. For example, you could say "When evaluating something for a manager, assume an individual with a four-year business college education, a lack of detailed technical understanding, and a fairly limited attention span, who likes to get answers that are clear and concise. When evaluating something for a programmer, assume considerable technical knowledge, an enjoyment of geek and science fiction references, and a desire for a complete answer. Accuracy is deeply important to programmers, so double-check your work."
If you ask ChatGPT to "explain C++ to a manager" and "explain C++ to a programmer," you'll see how the responses differ.
What do I do if ChatGPT refuses to answer or I don't like its answer?
There are some guardrails built into ChatGPT. It tends to shut down if you ask it political questions, for example. That's what's built into the system. While you might be able to tease out an answer, it's probably not going to provide great value. That said, feel free to keep trying with different phrasing or perspectives.
You can follow my day-to-day project updates on social media. Be sure to subscribe to my weekly update newsletter on Substack , and follow me on Twitter at @DavidGewirtz , on Facebook at Facebook.com/DavidGewirtz , on Instagram at Instagram.com/DavidGewirtz , and on YouTube at YouTube.com/DavidGewirtzTV .
More on AI tools
Google releases two new free resources to help you optimize your ai prompts, humane ai pin: what went wrong and how it can be fixed (before it's too late), how to get started with meta ai in facebook, instagram, and more.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Start with a broad topic. A broad topic provides writers with plenty of avenues to explore in their search for a viable research question. Techniques to help you develop a topic into subtopics and potential research questions include brainstorming and concept mapping.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
How to write a research question. Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question. Steps. Explanation. Topic selection. Choose a broad topic, such as "learner support" or "social media influence" for your study.
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
How to write research questions. Follow these steps when writing a research question: 1. Select a general topic. The first step to writing a research question is to choose a broad topic for your question. This can be something like "1920s novels" or "effects of technology." It's helpful to select something you are interested in and want to know ...
It can be difficult to come up with a good research question, but there are a few steps you can follow to make it a bit easier. 1. Start with an interesting and relevant topic. Choose a research topic that is interesting but also relevant and aligned with your own country's culture or your university's capabilities.
Most professional researchers focus on topics they are genuinely interested in studying. Writers should choose a broad topic about which they genuinely would like to know more. An example of a general topic might be "Slavery in the American South" or "Films of the 1930s.". Do some preliminary research on your general topic.
5. Facilitating Data Interpretation and Analysis. Clear research questions help in structuring the analysis, guiding the interpretation of data, and framing the discussion of results. They ensure that the data collected is directly relevant to the questions posed, making it easier to draw meaningful conclusions.
There are two types of research: Qualitative research and Quantitative research. There must be research questions for every type of research. Your research question will be based on the type of research you want to conduct and the type of data collection. The first step in designing research involves identifying a gap and creating a focused ...
A strong research question must be researchable, original, complex, and relevant. Here are five simple steps that can make the entire process easier. Identify a broad topic from your areas of interest, something that is relevant, and you are passionate about since you'll be spending a lot of time conducting your research.
The steps for developing a research question, listed below, can help you organize your thoughts. Step 1: Pick a topic (or consider the one assigned to you). Step 2: Write a narrower/smaller topic that is related to the first. Step 3: List some potential questions that could logically be asked in relation to the narrow topic.
To learn how to use these tools responsibly, see our AI writing resources page. Step 4: Create a research design. The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you'll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of ...
Hannah, a writer and editor since 2017, specializes in clear and concise academic and business writing. She has mentored countless scholars and companies in writing authoritative and engaging content. A research question is a question that a research project seeks to answer. Learn how to craft an effective research question with our step-by ...
Steps to Develop your Research Question. Choose a topic with a wide range of published literature. Read and skim relevant articles to find out different problems and issues. Specify a theoretical or practical research problem that your research question will address. Narrow down the focus of your selected core niche.
Here are some steps to consider when choosing research questions: Identify the research problem: Start by identifying the problem or issue that you want to study. This could be a gap in the literature, a social or economic issue, or a practical problem that needs to be addressed. ... How to Write Research Questions. Guide for Writing Research ...
We've covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are: To choose a research question and review the literature. To plan your paper structure and draft an outline. To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
How to Write a Research Question: Step-By-Step Guide. In this section we will examine the process of developing a research question. We will guide you through it, step by step. Keep in mind that your subject should be important for your audience. So it requires some preliminary study and brainstorming. Let's take a closer look at the main steps.
Steps on writing a good research question. STEP EXAMPLE; 1. Identify the general topic. Healthcare. 2. Conduct a literature review. Examine existing studies on the usage of remote medicine. 3. Narrow your focus and develop a precise research question that addresses a gap or problem in the latest research.
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
Question development. There are several steps involved in developing a survey questionnaire. The first is identifying what topics will be covered in the survey. For Pew Research Center surveys, this involves thinking about what is happening in our nation and the world and what will be relevant to the public, policymakers and the media.
question may develop into a series of questions that lead to your conclusion. These steps are used to. connect the dots for your reader, s howing the way to your solutions. Taking the time to ...
The purpose of this research is to learn more, not gather sources. That means it's okay to check sites like Wikipedia, which aren't typically considered reliable sources. 4. Write a list of open-ended questions about your topic. Do a brainstorming session to generate questions you may have based on your research.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Don't be afraid to ask multi-step questions: ask, get a response, and based on that response, ask another question. I've done this myself, sometimes 10 or 20 times in a row, and gotten very ...