- 0 Shopping Cart $ 0.00 -->


How to Start a Food Cart Business: a Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners & Entrepreneurs
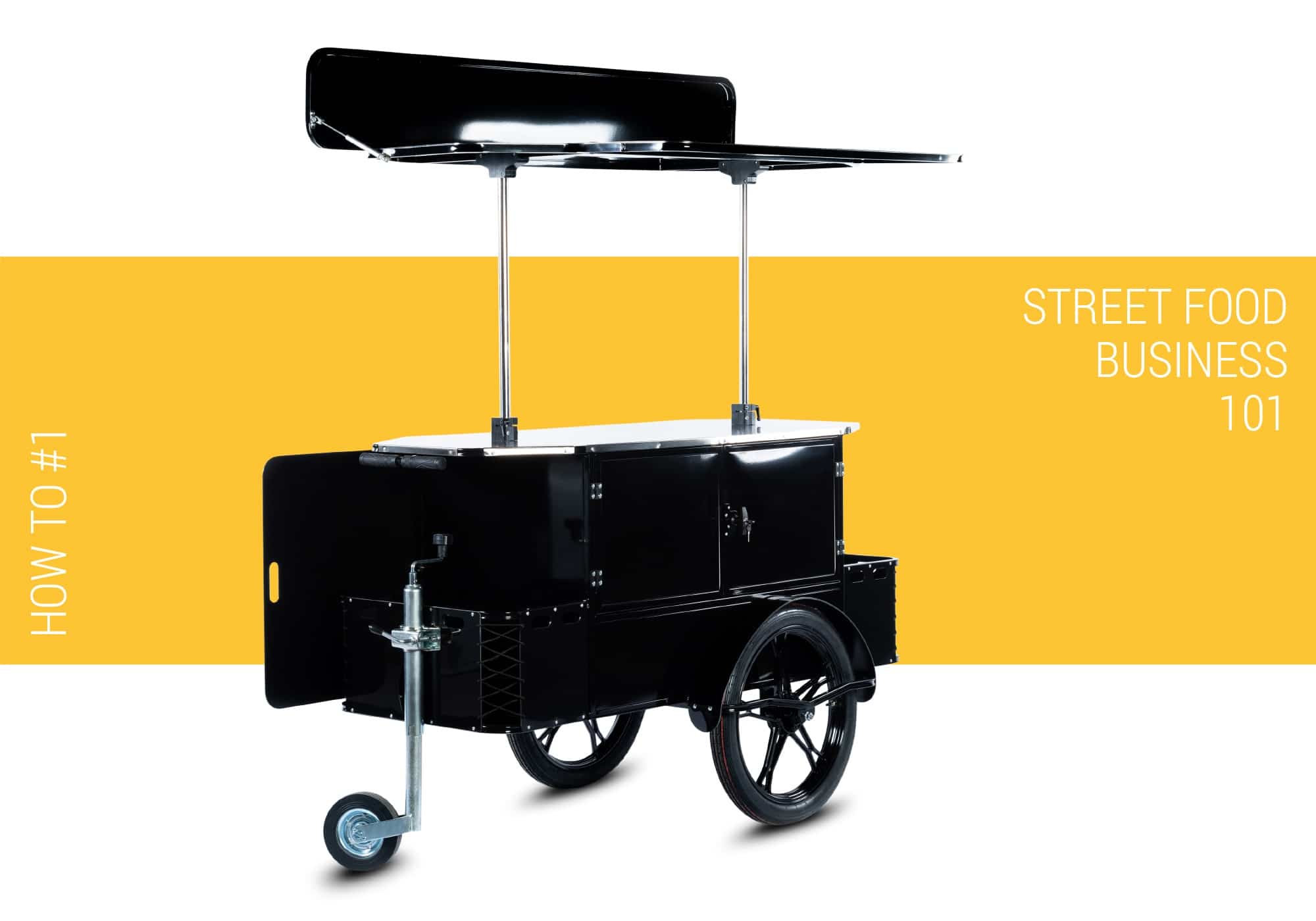

Wondering how to start a food cart business?
The timing couldn’t be better: it seems that the street food craze is sweeping the world.
From bustling cities to small towns, food on wheels is a growing trend. And it’s not just drawing street food fans, it’s bringing in big bucks too: according to Intuit , the street-food business, including food trucks and mobile food carts, is a $2.7 billion industry that has seen a 12.4% growth in the last 5 years alone!
Traders are encouraged by the growing number of urban street markets, private events and street food festivals, while the entire trend is supported by the global rise of the “foodie” culture, making the public increasingly open to new taste experiences and quality cuisine.
Which begs the question:
What Makes Street Food So Popular?
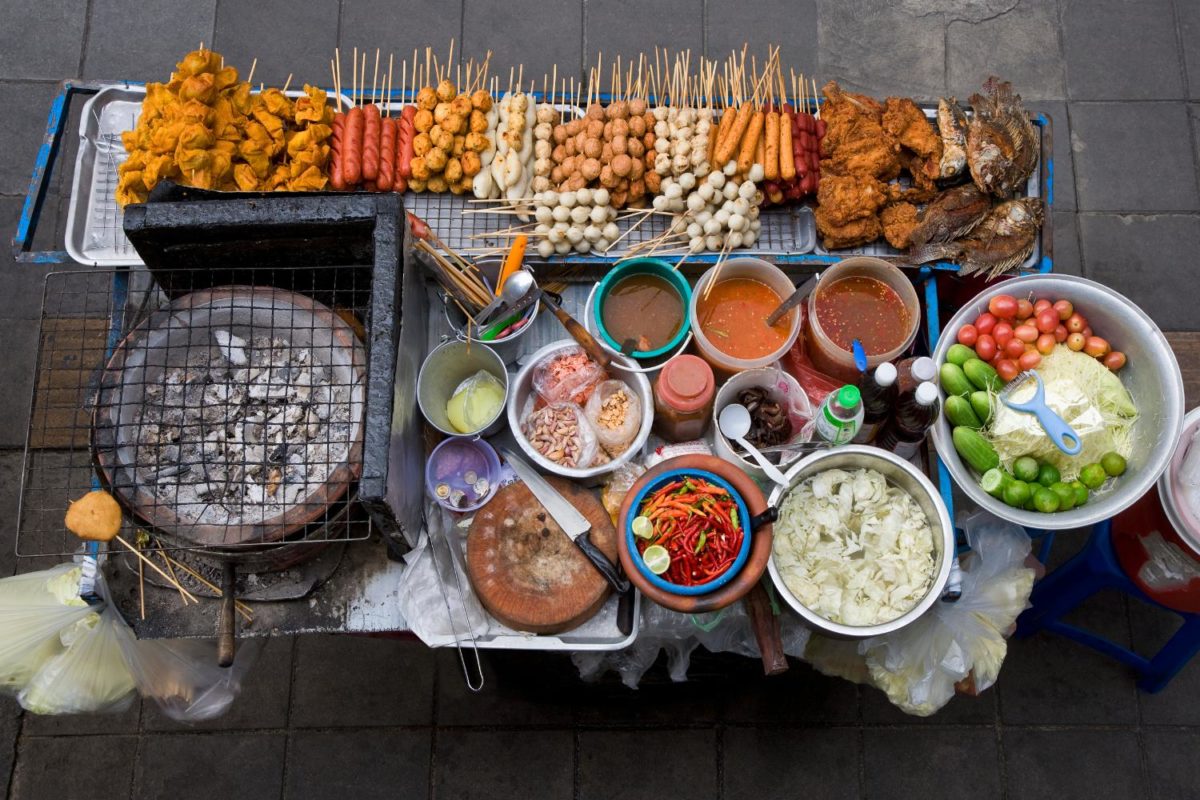

From the entrepreneur’s perspective , street food comes with important benefits such as low start-up costs and mobility. Kiosks, food carts , trailers, and food trucks have a lower overhead than restaurants and can be moved if one location does not generate enough business.
For customers , street food is convenient and cost-friendly, which makes it attractive for basically everyone: locals and tourists, students and busy professionals, frugal singles and large families.
The most popular street foods?
There are the classics: hot dogs, hamburgers, ice cream and doughnuts.
Then there are those inspired by ethnic cuisines such as tacos, empanadas, sushi and crepes. The possibilities are endless and it’s up to you, the entrepreneur, to find the dishes and recipes that will set you apart from the rest and, most importantly, that will help you build a good reputation and a loyal customer base.
But, before you decide what foods you’re going to sell, you’ll have to consider:
The PROs and CONs of a Food Cart Business
There are many advantages to starting your own food cart business, which is why a lot of people choose to do just that. The PROs include:
- Low start-up costs
- Less risky than opening up a restaurant
- The ability to be your own boss
- The flexibility to work when and where you want
- Little restaurant experience required
- The growing popularity of the street food trend
But, as with all business endeavours, there are also CONs to examine. A food cart business is no walk in the park: there’s a lot of hard work to be done and you’ll only see significant profits after your business picks up.
The biggest CONs are:
- Being self-employed can be testing for some
- Long hours, early mornings and night shifts required
- Fierce competition
- There are many regulations and laws to comply with
- Seasonal reliance
- Finding a suitable location that you’re allowed to trade in
- Customer service can be challenging if you’re a solo-preneur
From our experience as food carts manufacturers , people are attracted by affordable start-up costs and by flexibility; at the same time, the most common complaints – at least in the initial phase – are long working hours and industry volatility in terms of trends and business opportunities.
However, if you are passionate about good food and you start with solid and well-researched plan, there is every chance you could make a roaring success of your food cart start-up.
How to Start a Mobile Food Cart Business? A Step-by-Step Guide
First step: market research.
Market research involves finding out the “who, what, where, why and when” of your business, and while it’s not the most exciting part of your endeavour, it’s certainly an essential one.
It can be risky and even silly to assume that you already know the answers to these questions and then get caught out later on.
Here’s what you need to address at this stage:
Operational
- Where will you set up your food cart business?
- When will you open to ensure the best business?
- How will the weather affect your trade?
Target Market
- Who are your customers? What is their demographic?
- Competition
- Is there any competition? What do they offer?
Locations & Business Opportunities
Finding a couple of great locations will play a major factor in your success and it depends on several key factors:
- Where you’re allowed to park by law
- Where the customers are
- The prime hours for each location
Some great places and opportunities to consider for trading are:
- Office parks
- The business district
- Shopping districts or malls
- Popular tourist locations
- Sports venues
- Parks and beaches
- Bus and train stations
- College campuses
- Festivals and events
- Conferences and conventions
- Private events (weddings, birthdays, etc)
- Corporate events
Most of these locations will require permits and/or owner agreements, so make sure to check with your local authorities & institutions beforehand.
When it comes to festivals, events, conferences and conventions the best thing to do is to get in touch with organizers and lease your space well in advance.
Determining Your Food Cart Business Legal Requirements
You’ve probably noticed that most How-To guides on this subject place sorting out the legal requirements at the bottom of their To-Do list.
And here’s why: the permits and licensing requirements for food cart businesses vary from country to country, state to state, and even city to city, so making a definitive list with everything you need is close to impossible.
Only your local Health Department can provide you with the information that applies in your case.
At this stage, you’ll address issues such as:
- The street food vending regulations in your city
- Licenses and permits required
- The types of food you’ll be selling and how they’re handled, stored, thawed, and cooked
- Commissary requirements (the requirement to operate from a licensed commercial kitchen)*
- The size, make and the equipment of your street food vehicle
- The vehicle’s fresh water and waste water holding capacity
- Safe food handling course requirement
- Hygiene policies
- Pre-approval inspection of the equipment
* Most municipalities don’t allow food vendors to operate a food cart business from a residential kitchen and they require the use of a commissary – a licensed and inspected commercial kitchen.
Vendors have to report to the commissary each day of operation to prepare the food that will be served from the cart and to clean the vehicle’s equipment at the end of the day.
If you are selling prepackaged foods, you are not considered a food handler and may have less stringent requirements than if you are actually preparing foods or even scooping ice cream.
But as long as food is unwrapped, you are typically considered to be a food handler and must meet specific regulations.
While your cart or truck manufacturer will not know the nuances of each city’s requirements, they can usually help you meet specific health standards.
For example, all of our food carts are manufactured using food-grade materials for countertops and other parts/areas where food may be stored and prepared.
In addition, we work closely with each of our clients to adapt the carts’ cooking & water systems so they will meet all the health and safety standards specific to the vendor’s area.
Getting all the trading, health and safety qualifications in order will not only allow you to operate legally (and avoid hefty fines), but it will also help enforce the public’s hard earned perception that that those running a street food business are doing their utmost to meet and surpass sanitary requirements.
Basically, your legal status and reputation are on the line.
In addition to the food service permits and health requirements, you may also need to apply for:
- Business license
- State sales tax permit
- Truck/cart registration
To sort these out, the city hall or the county clerk’s office will usually point you in the right direction.
Keep in mind that before you can hit the road, health inspectors will check your vehicle. Usually, they look for:
- Proof of ownership, proper identification and license (of the vehicle)
- Proof of District-issued Food Manager Identification Card
- Food-purchase record storage and record keeping
- That your depot, commissary or service support facility meets your vending unit operation needs
- Copy of license for the service support facility and/or a recent inspection report
Food vehicles are typically inspected at least once a year by a health department inspector, sometimes randomly.
The inspector checks to see how food is stored so that it does not spoil and that it is kept at the proper temperature. All food equipment as well as sinks and water supplies are checked.
Commercial kitchens and garages in which food vehicles are kept are also inspected frequently and can be given high fines if they do not meet health and fire codes.
Some have been shut down because of too many violations. Likewise, trucks and carts have lost their licenses over repeated violations.
Editor’s Note: if you want to learn more about what it takes to launch a business, from a more general perspective, here’s a great resource to get you started: How To Start A Business: A Complete Playbook
Choosing Your Street Food Business Platform/Vehicle
Mobile street food businesses come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and deciding which is the right one for you depends on your:
- Start-up budget
- Time commitment
- Vision and the ability to fulfill it
- Experience at running a business
- Target demographic
Your options are: food stands, food carts , concession trailers and food trucks. Each of them has its own unique benefits as well as some disadvantages:
Food Stands
Food stands are essentially booths or stalls that are either temporary or mobile, and are used to sell everything from quick snacks such as bagels, pretzels and ice cream, to more elaborate meals.
Most food stands are usually operated indoors and they are an excellent choice in areas where outdoor selling is limited by cold or unpleasant weather.
Pros: low start-up and running costs, flexibility. Cons: limited trading areas, limited inventory.
Mobile Food Carts

Pros: affordable, easy to customize, easy to move between locations (they can be pulled by a bicycle/car or pushed by hand), easy to park, easy to maintain, suitable for both indoor and outdoor use, may require less licensing than a food truck. Cons: not too much space for preparing elaborate dishes.
Concession Trailers
Same as food carts, concession trailers have been around for a long time and are often found at fairs, carnivals and sporting events.
Pros: low overhead costs compared to food trucks, more space for cooking. Cons: more difficult to move between locations, require bigger parking space both on/off-duty, involve higher operating costs.
Food Trucks

We believe food carts are the best choice, especially for first-time entrepreneurs. Their size, mobility and low running costs make them ideal for starting a profitable food cart business with the potential to grow and expand at a rapid pace.
Are Food Carts Profitable?
A food cart business can be very lucrative right from the start; however, this depends on many factors such as location, footfall, weather, product type etc.
According to our customers, if you can secure a good location for your business, you can expect between 100 to 400 customers per day (during weekends, festivals and public events), bringing in anywhere from $500 to $3,000 daily.
Choosing Your Concept, Menu & Suppliers

Whether they’re food carts , concession trailers or food trucks, most successful street food businesses out there have themes or concepts that are consistently reflected in all their elements: exterior design, branding, menus and recipes.
Your concept should be a means of distinguishing you from your competition and building your niche market. And, if you get it right, it can even draw media attention to your business.
This brings us to menu planning. Choosing what kind of food you’ll prepare and sell can be a fun task, and if you look at the carts, trailers and trucks operating on the streets, you’ll find that almost anything edible can be served as street food.
But there are a lot of factors to consider when it comes to menu planning, such as:
- What foods do you know how to cook?
- What foods do you enjoy cooking?
- What are the most popular foods in your area?
- What foods can you prepare relatively fast, repeatedly and without difficulty?
- What foods could your customers take with them easily?
- What foods have a good profit margin?
- What times of day will you be open for business?
- What are you going to specialize in?
- How many items will your menu have?
- Where are you going to get the ingredients from?
After deciding on the type of food you’re going to sell, it’s time to start working on recipes and experiment with various ingredients.
Once you’ve found a few favourites, test them on your friends and family first. Don’t be afraid or dismissive of criticism: it’s better to receive it from them.
The bottom line is, don’t start out with foods you have not thoroughly tested. This means you need to perfect each recipe to be sure it has the following qualities:
- It tastes consistently good
- It’s easy to make repeatedly in large quantities.
- It’s easy to serve
- It’s easy to store & carry
Next in line is figuring out your sourcing – where will you buy your ingredients from?
Sourcing your food can be an important factor in planning your purchases, schedule and menu items.
Common sources include wholesale food distributors, food manufacturers, local and regional suppliers, green markets and farmers markets.
Determining the right quantities is another matter that you’ll need to deal with, initially by trial and error. If you have the time, spend a couple of hours observing the street food vendors in your area. How many customers do they have per hour? When’s their busiest period? This will help you estimate a potential sales volume, which you can use to draft your shopping list.
Pay special attention to foods and ingredients that lose their freshness quickly; learn which are the items you can safely keep throughout the day and how many of them you can sell before they go bad.
Creating Your Food Cart Business Plan
Despite the low start-up costs involved, jumping in to street food without any kind of plan is a sure-fire recipe for disaster. The space is extremely competitive, and you need to have a very clear idea of the niche you plan to fill before taking the plunge.
Writing a business plan isn’t a complicated job and it doesn’t have to be very long. Keep it concise, to the point and ensure that you cover each of the following topics:
- Your business’s name
- Business management: who’s going to be in charge?
- Your mission statement: in one sentence, summarize the aim of your street food business.
- Your vehicle: are you going to use a stall, a cart, a trailer or a truck?
- Start-up costs: what do you need to buy to get started? What fees to you need to pay in advance?
- The daily operational costs: how much will you spend on ingredients and what are the overhead costs on a weekly or monthly basis?
- Funding and financial projections; where do you plan to get the money from to start the business and what are your projected profits/losses for the next month, year, 2 years etc? How will you maintain the cash-flow?
- Your schedule: will you work on the business full-time or alongside your day job?
- What’s your main competition and how will you differentiate yourself from it?
- What is your marketing strategy?
- Do you have the logistics in place to deal with delivery and customer service?
If you plan to focus on events, your food cart business plan should include a clear targeting strategy. Pitch fees will vary widely, and there are a whole host of other variables to take into account including total attendance, other traders present, and the demographic of customer that will attend.
A good idea would be to create a spreadsheet with all the events and street food opportunities in your area. The amount of options available could seem daunting in the beginning, so start by thinking about what kind of event or environment you would expect to see a street food business similar to yours.
The next step would be to attend a few events yourself, taking note of the businesses that appear to be doing well and why.
As a general guide, generic fast-food businesses that focus on sales volume fare well at large music festivals and other events where the food is incidental to the main experience, whilst high-end street food traders perform better at events in which the customer will be searching for a new taste experience.
However, all the preparation in the world can’t account for the unexpected, and you will find some events simply fail to produce the expected revenue.
Your business plan should account for this, and you should always have enough spare cash in reserve to act as a safety net when you run up against the worst case scenario
Your approach to branding and marketing is a vital part of your business plan. A strong brand will help you stand out from the crowd, which is important for attracting customers as well as for securing spots at venues.
Remember: you are often selling a lifestyle with street food, so your brand should have a good slogan and a clear identity which reflects this.
Social media should obviously be central to your marketing plan and a strong Facebook and Instagram presence will help you raise your profile and create an army of online followers who you can spread your message to.
Regularly update your profiles with good quality photos as they generate a lot of interest and always display your social media handles so your customers /potential customers can connect with you
Estimating Costs: How Much Does It Cost to Start and Run a Food Cart Business?
There’s no set formula for determining how much starting a street food business is going to cost you since the niche is very broad and there are too many possibilities.
But even so, if you were to estimate, here’s a general expense breakdown:
Food Cart Business
- $3,000 – $5000 on a fully equipped food cart
- $500 – $700 on your ingredients & initial food stock,
- $400 – $ 600 on permits and registrations,
- $500 – upwards on marketing,
- $500 for the first month to park and clean the cart
- $500 in other miscellaneous costs
For comparison purposes, here are the estimates for a food truck business:
- $50,000 – $75,000 on a retrofitted food truck
- $1,000 – $1,500on initial ingredients
- $2,000 on permits and licenses,
- $2,000 for the first month of a commercial kitchen rental
- $500 for the first month of parking and maintaining the truck
- $1,800 on kitchen supplies
- $3,000 on marketing and promotion
- $2,000 on packaging
- $500 in miscellaneous costs
Huge difference, right? Regardless of your choice, you need to do the math before spending any money so that you do not run out before you get started.
Final Words of Advice
Speaking with our customers about their businesses, we’ve learnt that a background in catering or hospitality isn’t necessary to succeed – indeed, a lot of successful food cart businesses were founded by people with no prior experience of serving food.
Their biggest allies? Great food, flexibility – the ability to pivot according to the market’s trends and demands, marketing – a well-thought strategy for promoting their business across multiple channels, and outstanding customer service.
Do you have any questions concerning our food carts ? Contact us and we’ll do our best to help you out!
Get a Food Cart Quote!
Invalid value
BUSINESS GUIDES
WhatsApp us
We noticed you're visiting from United States (US). We've updated our prices to United States (US) dollar for your shopping convenience. Use Euro instead. Dismiss
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Start a Food Business: A Step-by-Step Guide

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
For many food-lovers, the ultimate dream is to open up their own food business. What many people don’t realize in the beginning is that starting a food business is no easy feat. There’s a lot of business operational skills that are necessary to get started.
But the steps below can help you understand what you'll need to start a food business, and what you should consider before you jump in.

How to start a food business in 9 steps
Step 1: assess your skills.
If you’re reading this article, we can assume that you have a food business idea in mind that you’re interested in starting. That’s great! While interest is the number one step in starting a business, you also need to take a good hard look and assess your skills and assets before jumping into starting a business.
Passion can get you a long way, but when it comes to how to start a food business you’re also going to need hard work and business smarts. While many first-time business owners don’t know everything off the bat, they know how to seek out resources for help when they bump into something they don’t know how to do or don’t understand. That’s a lesson you should learn quickly.
While much of how to start a small food business consists of concrete steps such as choosing your business structure and finding funding, there’s also the soul-searching question: Are you willing and capable to do this?
Before you start, take a moment to write down your strengths, consider your support network, and brainstorm your resources—better yet, research what resources are available to you.
Operating a food business means you’ll need to grapple with:
Hiring and firing employees
Buying from suppliers
Creating a menu
Real estate
Purchasing equipment
And so much more...
With that debate over with, it’s time to talk about the more nitty-gritty, concrete details of how to start a food business.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Step 2: Create a business plan
A business plan can have multi-fold benefits for your small food business. This is a great way to get your thoughts and plans on paper, which can be useful for you to refer back to you during the process of starting and operating your business. A business plan can also be beneficial if you’re looking for funding to start your food business.
SCORE offer great resources to help you write a business plan for your food business. It can seem intimidating to make one, but if you’re researching how to start a food business, it’s likely that you already have a lot of great thoughts to contribute to your plan. Below are a few of the steps you’ll need to take while creating a business plan.
1. Create a business budget
One of the most important parts of your business plan, especially if you’re seeking funding, is the business budget.
A business budget will include looking at all the costs you’ll need to cover to begin operation of your business, what funds you’ll need to operate the business once it’s up and running, and a more long-term look at how your business will make money and how much money you expect to make.
A few examples of the costs you’ll incur and what you need to consider while starting a food business include:
What type of food business you’re starting
Cost of employees and management team
Initial investment in food product
Design for a physical space
2. Study your competitors
As you’re putting together your business plan, you need to start looking at and assessing your competitors. The food industry is very competitive and many markets are saturated. Before you go any further in starting your small food business, you need to know who else is out there and what they’re doing.
As you’re finding your competitors, make sure to be assessing what they do well and where they’re lacking. That will tell you where there’s a hole that you can fill with your business.
This is also a great time to be looking at prices and assessing the cost of doing business and the reality of how much money you’ll be able to make.
3. Find a hole in the market
The ideal situation for starting a food business is to find a hole in the market. Where is there customer desire that no one else is filling? And just because no one is doing it, doesn’t mean there’s customer desire—to turn a profit, customers have to want it and be willing to buy it.
Finding a hole in the market will help you to decide what kind of food you want to sell and how you want to sell it. There are a variety of options to choose from when it comes to how to sell your food including:
Meal delivery
Baked goods sold to other food establishments
In-home food business
Wedding and special event catering
4. Choose a concept
When starting a food business, it’s important to decide what type of food business you want to have. The main options include: a brick-and-mortar restaurant, a food truck, and a home-based catering business.
Each of these options is a viable way to start and operate your business. You might choose to start with one type of operation in the hopes of moving to another one eventually. A food truck and home-based catering business both have complications, but tend to require less capital to get started than a full-fledged brick and mortar restaurant.
Step 3: Set up your business
Once you’ve studied your market, you know where there’s a hole that needs to be filled, and you’ve taken some time to create a business plan, you’re ready to take the first steps toward starting your food business.
1. Choose a business entity
The first step in setting up your food business is to choose a business entity. There are a few different choices and depending on your circumstances, one or the other will be right for your business.
The most common business entity for small food businesses are sole proprietorships, LLCs, and co-ops. Other business entity options includes partnerships, S-corporations, and C-corporations.
Sole proprietorship
One of the most straight-forward business structures available is the sole proprietorship. While a sole proprietorship is simple (and popular among food establishments), it’s also limited in protection. If someone gets sick eating your food and wished to do so, instead of suing your business, they’d have to sue you—and they could go after your personal assets as compensation.
An LLC is one step up from a sole proprietorship. An LLC or limited liability corporation is a legal business entity that separates the business from the owner. An LLC limits a business owner’s personal liability for the business. An LLC also provides businesses with tax efficiency and remains uncomplicated as to ownership structure, so it’s ideal for a food business owner who wants to be somewhat protected, but still have some flexibility when it comes to paying taxes.
Cooperative
A cooperative, which is more commonly known as a co-op, is a business structure that is formed and owned by multiple people. Each member or owner of the business owns a portion of the business. Co-ops are one of the most collaborative business types available and are very common among food operations, especially food production facilities, grocery stores, and farmers markets.
Choosing the right business structure for your future food business can be confusing and initially seem complicated. But, if you start your business and decide you’ve chosen the wrong structure, you can certainly change it. If that sounds like a headache, though, you can consult with a business attorney to help you decide which structure is right for your business.
2. Register your business
If your business is going to employ others, it’s recommended that you register for an EIN, or a federal employee identification number, from the IRS. If you apply online, you can get one in a matter of minutes. An EIN helps you get business loans, manage your taxes, open a business bank account, and more, so this step is highly recommended.
You’ll also probably need to register your business with the state you’re operating in. Rules for how to do this exactly vary by state, and even county, but generally this information can be found on your state’s Secretary of State website. You should do a business name search before registering your business to make sure your desired name isn’t already taken by another business in your area.
3. Register for all required licenses
One of the most important steps in starting a food business is to make sure that you’re legally licensed to prepare and sell food. There are many different certifications and licenses that are necessary for food businesses.
It’s also important to note that what licenses you need will depend upon what type of food establishment your opening, whether or not you’ll be selling alcohol, and where you’re located. Different local jurisdictions can have slightly different requirements for food establishments.
Here are some types of licenses and certifications you might need for your food business:
A food handling permit
A Certificate of Occupancy or CO for your restaurant
A liquor license or beer and wine license to sell alcohol
A food license to make and sell food out of your home
A resale license to be able to buy ingredients at wholesale
No matter what type of food business you’re starting, you’re going to need some permits and licenses. Your local government office should be able to help you figure out exactly which licenses you need for your type of business.
4. Get insurance
As a business that employs workers and has a physical location which hosts customers, you need certain types of insurance to make sure your business is covered in any situation. You might consider:
General liability insurance
Auto insurance for business vehicles
Workers’ compensation
Commercial property insurance
Mobile food vendor insurance
5. Separate your finances
No matter what type of business entity you’ve chosen for your business, it’s important to separate your personal finances from the business finances. This makes figuring out your taxes and expenses much easier.
When you start your small food business, simply start a second bank account for your business. This can be done with the institution you use for your personal banking, but if you want to switch things up, there are some newer banks allow you to open a business checking account online.
And, if you choose to, you can also get a separate credit card that’s used only for business purposes. If you use a business credit card , you’ll be able to build up your business credit (assuming you use it responsible and pay off your bills on time), which can ultimately help you secure a business loan down the line.
Step 4: Look for funding options
When you’re thinking about how to start a food business, one of the major concerns can be the funds you need to get started. The initial investment in a business can be costly and it can take months, even years, before a business is profitable.
To get started, many new food businesses ask for funding from investors, seek out loans, or ask for help from friends and family. Bank loans are one option for funding, though banks typically are hesitant to lend to first-time business owners. There are also alternate lenders you can look into.
1. Equipment loans
An equipment loan is a great option if you need to be expensive equipment for your restaurant or are looking at buying a food truck. An equipment loan is simple: You receive a loan to buy the equipment and the equipment serves as collateral. Meaning if you don’t pay back the loan, the equipment can be repossessed as payment.
This type of loan is easier to get than other types of loans.
2. Friends and family loans
If you’re starting up a food business, who better to get involved and help you out then your friends and family? If you’re saving up to get your business up and running, don’t be afraid to ask for help. Just make sure to write down a loan agreement with your lender and then to stick to it.
3. Line of credit
A line of credit is a fantastic option for someone starting a food business. A line of credit gives you access to a pool of funds. You can borrow from that fund and up to the limit of that fund anytime you need. This is a great option for a business that’s a little cash-strapped for short periods of time.
4. SBA microloan
For food businesses looking to start up a food truck business or for a restaurant that just needs a little extra cash to get going, there’s the SBA microloan. An SBA microloan is a loan of up to $50,000 that the Small Business Administration guarantees. A loan from the SBA is considered the best loan on the market due to its low interest rates and flexible repayment terms.
Step 5: Invest in product and tools
When it comes to how to start a food business, you need more than just cash and business entity to make your dream a reality: You need equipment, food supplies, and something to sell it all on.
1. Research suppliers
One of the most important relationships you form as a food business owner is with your suppliers. Your suppliers are the businesses who make sure you get the food and products you need to keep your business going.
If there’s a restaurant in your area that has closed recently, you might be able to buy their equipment or furnishings for cheap, or take on extra stock they had saved up. Your food can often be sourced locally and trade publications or professional organizations, like the National Restaurant Association, can be helpful.
Find trustworthy, reliable suppliers to make sure you’re always getting your supplies on time and for the best price. Where you source your food from can also be a selling point for your food business, since sustainable companies have become more attractive to customers recently.
2. Point of sale system
A point of sale system, or POS, is the modern version of a cash register. The POS is how your waitstaff takes down orders, charges customers, and receives payment from customers.
There are many restaurant POS systems available on the market that offer enhanced usability for your staff, including:
Square for Restaurants
TouchBistro POS
Lightspeed Restaurant POS
Loyverse POS
Some, like Square, can be great for mobile companies since you only need a card reader to do business if you have a compatible phone or tablet you can use. Others, like TouchBistro, are better for full-service restaurants that might benefit from a POS that also offers tools for customer and floor planning management. The best POS system for you will depend on your food business’s needs.
» MORE: Best POS systems for food trucks
3. Buy or rent necessary supplies
Before your restaurant can open the doors to customers, there are a lot of supplies you need to make sure the restaurant is outfitted to be inviting to customers, serving up good food, and making money for you.
Aside from your POS system, here are some examples of supplies you might need:
Kitchen appliances
Cold storage
Flatware and utensils
Furnishing for the restaurant
Cleaning supplies
Some of these you can buy in bulk, but depending on the mobility of your food business, you might want to consider renting equipment—which might work out cheaper for you. As an example, if you run a catering business, you might not need to own tons of flatware and utensils just yet. Renting on a case-by-case trial will save you money and help you understand what a practical order might be when you’re actually ready to buy.
Step 6: Hire staff
Depending on what type of food business you’re starting, you may or may not need help. But, even the smallest establishment usually hires an extra set of hands to increase production. Who you hire and how many people you hire will all depend upon your needs. For example, a food truck probably can’t fit many employees, but a large-scale restaurant will require more employees to keep the floor running smoothly.
Some examples of staff you might need include: delivery drivers, hosts, waiters, dishwashers, bartenders, and busboys. Make sure you factor hiring staff into your business plan, since you may be required to take on added costs, like purchasing workers compensation, for them.
Step 7: Set your pricing
One of the most important steps in how to start a food business is setting your pricing. Without the right price on your food products, it will be impossible to make money.
1. Do market research
One of the first steps in figuring out what you should charge for certain foods is to do market research. Go to your competitors to see what they’re serving, what their portion sizes are, and how much they’re charging.
This gives you a starting place to assess the right price for food, but it’s only a starting point. While it gives you an idea, it doesn’t give you insight into whether that business is making money or not.
You should also be mindful of emerging food trends and what that says about consumer priorities. For example, the wellness trends in food indicate that your business might do well if there’s a health-conscious market you’re able to tap into and you’re able to sell them on the health benefits of your food products.
2. Price out the cost of your product
While it’s not easy, it is possible to calculate the total cost of a dish. You’ll have to be mindful of all the tiny ingredients that go into a dish, including oil, seasonings, and garnishes. This can seem like a lot, but there are actually a number of formulas and measurements professional kitchens use to determine these figures, so be sure to study up.
Then, with a little magic and math, you’ll be able to price your product accordingly, so that you make a small profit from it, even when including the cost of labor to make, serve, and clean up the dish.
Step 8: Create an online presence
While you might think that a food business is all about food—and it is—you also need to get customers in the door and eating your food. The food industry is notoriously difficult to break into. For example, 85% of consumer packaged goods products fail within the first two years. One important step to avoiding that fate is establishing your online presence and nurturing your consumer base.
1. Social media
While food is all about the taste, many diners shop with their eyes. If you want to establish an online presence for your food business, one of the fastest ways to do that is through social media.
Instagram is a food business’s best friend. Post delicious-looking pictures of your food and customers will want to try it. Make sure you interact with consumers and encourage them to see you as a company that will be responsive to their needs.
While not every food business has a website, this can be a way to establish your credibility as a business. A website can be a place to post information for customers including menus, restaurant hours, and specials. There are a number of ways to build your small food business website, so it’s easier than ever to either sell products online or add helpful features like reservation widgets to your site.
3. Online review sites
While many a food business owner loathes review sites, it’s a necessary evil for those who have restaurants, catering businesses, and food trucks. According to a TripAdvisor survey, 94% of U.S. diners will consult online reviews before trying a restaurant. That’s the vast majority of diners. As a food business owner, you can hate the sites as much as you want, but you need to have a presence. Try offering a free perk to incentivize customers to leave reviews.
Step 9: Serve up delicious foods
When you’re thinking about how to start a small food business, the big draw is, obviously, the food. What you’ll cook, how it will taste to the diners, and what seasonal changes you’ll make to the menu. Owning a food business is only partly about the food, though—there’s also a ton of time spent on operating and managing the business. Study up to ensure success.
But, make sure you’re just as dedicated to serving up delicious foods!

Start Your Dream Business
Final thoughts
There are a wide array of food businesses you can start and competition will be tough. To help you get a leg up, make sure you consult these nine steps for starting a food business. If you pay attention to foundational steps, like creating a solid business plan and registering for all licenses you might need, you’ll put yourself in a good place for your food business to grow. So, refine that menu and get ready to feed the masses. With a little elbow grease and planning, there’s nothing you can’t do.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...

Eat App for
How it works

How to Write a Restaurant Business Plan in 2024 (Step by Step Guide with Templates)

A restaurant business plan is a framework that guides you to plan and forecast every element of restaurant management and operations.
This includes anything from your restaurant's menu design , location, financials, employee training , and a lot more.
Creating a solid business plan is important, as it helps:
- Transform your restaurant ideas into reality.
- Boosts entrepreneurial success by 16% (Harvard Business Study) .
- It equips you to navigate challenges before they arise.
- Attracts potential investors.
Planning is key to restaurant success. Without a plan, you're more likely to join the 26% of restaurants that fail within a year.
Create a business plan to set yourself up for success.
Here's how to get started.

What is a restaurant business plan?
Before writing a business plan, it is important to understand its fundamentals.
It serves as a roadmap for starting and running your restaurant , making it easy for outside parties, such as investors, to understand your objectives, vision, and plan of action for your restaurant.
The length and level of detail of business plans vary, ranging from brief synopses to large papers. Investors can benefit from clear insights and additional information provided by beginning with a concise plan and working their way up to a detailed one.
In short, a thorough description of the resources allocated to the success of your restaurant should be included in your business plan.
Steps to include in your business plan
Your restaurant and mission statement needs to reflect your brand and goals, but you don't have to start from scratch.
The Eat App Restaurant Business Plan template , created by industry professionals and packed with insider information, is your go-to manual for creating a profitable business plan.
Your finalized business plan should have 11 essential elements, no matter how you write it. Continue reading below.
1. Executive summary
A restaurant business plan should always begin with an executive summary. Why?
- 80% of venture capitalists say they read the executive summary first.
- 62% of investors say they would not continue reading a business plan if the executive summary did not capture their interest.
- A strong executive summary can increase the likelihood of securing funding by up to 40%.
An executive summary not only acts as the introduction to your restaurant business plan samples but also as a summary of the entire idea.
The main aim of an executive summary is to draw the reader (oftentimes an investor) into the rest of your business plan.
The executive summary also helps you envision the identity of your restaurant which essentially shapes the customer experience and sets you apart from competitors.
To establish a distinct identity, you need to focus on c ommon elements of an executive summary, including:
- A mission statement
- Proposed concept development
- Cuisine selection
- The overall execution
- The potential costs
- Expected return on investments (ROI)
Let's take a more in-depth look at the concept development, cuisine selection, and mission statement.
Further reading
- How to write a restaurant executive summary
Concept Development
Selecting the type of restaurant, service style, and atmosphere is the first step towards creating a unique dining experience. Whether you envision a sample menu for a:
- cozy, intimate bistro
- bustling quick-service deli
- fast-casual restaurant
- fine dining establishment
Your concept should reflect your passion and expertise in the industry.
Cuisine Selection
The cuisine you select for your restaurant can significantly influence its success.
Choosing the appropriate cuisine is vital for distinguishing your establishment from competitors and attracting your target market.
To make an informed decision, consider factors such as:
- Market demand
- Expertise and passion
- Ingredient availability
- Competition
- Profitability
- Cultural fit
- Seasonality
- Dietary restrictions and trends
In the highly competitive restaurant industry, keeping track of current and emerging cuisine trends can be a significant advantage.
Creating a mission statement
A well-constructed mission statement communicates the purpose, values, and goals of your restaurant to potential investors and customers alike.
A mission statement serves as a guiding light for decision-makers and employees, fueling their efforts to achieve your restaurant’s objectives.
To create an impactful mission statement, consider the following steps:
- Identify the purpose of the restaurant.
- Contemplate the brand’s image.
- Account for the target audience.
- Incorporate company values.
- Ensure brevity and comprehensiveness.
Related content: How to Write a Restaurant Mission Statement
Remember, your mission statement should not only differentiate your restaurant from competitors but also resonate with your target market .
2. Company description
This is where you carefully introduce the company in the restaurant business plan. Include the name of the restaurant you are launching in this field along with its address, phone number, and other important information. Then, also include the owner's information as well as a synopsis or explanation of their background. The restaurant's legal position and its short- and long-term objectives should be outlined in the second section of the company description. To demonstrate your understanding of the changes in the local food business and the reasons why the most independent restaurant investors will be successful in this market, please submit a brief market research.
Here's an example of the page layout:
Company Description
Restaurant Name: [Restaurant Name]
Location: [Restaurant Address]
Contact: [Restaurant Phone Number] | [Restaurant Email Address]
Owner: [Owner Name]
Experience: [Owner Name] has over [Number] years of experience in the restaurant industry. They have worked in various roles, including [List of Roles]. They are passionate about food and creating a memorable dining experience for their guests.
Legal Standing: [Restaurant Name] is a [Type of Legal Entity] registered in [State/Province].
3. Market analysis
The market analysis portion of the restaurant business plan is typically divided into three parts.
3.1 Industry analysis
What is your target market? What demographics will your restaurant cater to?
This section aims to explain your target market to investors and why you believe guests will choose your restaurant over others.
Comprehending your target market is key to customizing your restaurant offerings to their preferences and needs.
By diving into demographics, preferences, dining habits, and trends, you can fine-tune your concept and marketing strategy to reach and appeal to your target audience effectively.
An example of analyzing your target market
Comprehending your target market is key to customizing your restaurant offerings to their preferences and needs.
Demographics and preferences
Identifying your primary target market involves considering factors such as:
For example, a neighborhood with a high concentration of families might prefer a family-friendly restaurant with a diverse menu catering to various age groups and dietary preferences.
Conversely, a trendy urban area with a predominantly young and affluent population may gravitate towards upscale dining experiences and innovative cuisine.
Cultural and ethnic backgrounds also have a significant impact on restaurant preferences, with people from different backgrounds having distinctive tastes and customs that influence their dining choices.
By thoroughly understanding the demographics and preferences of your target market, you’ll be better equipped to create a restaurant concept that resonates with them and ultimately drives success.
Dining habits and trends
As the restaurant industry continues to evolve, staying informed about dining habits and trends is crucial for adapting your offerings and attracting customers.
For example, the rise of online ordering and delivery services has significantly influenced dining habits, with many consumers seeking the convenience of having their meals delivered to their doorstep.
Health trends have also had an impact on dining habits, with an increasing number of individuals seeking healthier options when dining out.
- How to find your restaurant's target market
3.2 Competition analysis
It's easy to assume that everyone will visit your new restaurant first, so it is important to research your competition to make this a reality.
What restaurants have already established a customer base in the area?
Take note of everything from their prices, hours, and service style to menu design to the restaurant interior.
Then explain to your investors how your restaurant will be different.
3.3 Marketing analysis
Your investors are going to want to know how you plan to market your restaurant. How will your marketing campaigns differ from what is already being done by others in the restaurant industry?
How do you plan on securing your target market? What kind of offers will you provide your guests? Make sure to list everything.
The menu is the most important part of a restaurant's debut. Your restaurant wouldn't be able to operate without it.
You most likely don't have a final draft at this time, but you should aim to create a mock-up for your restaurant business plan. You can choose a design that you can envision yourself using and add your logo to the mock-up.
- Top Free Restaurant Menu Makers
There are several resources available online if you need assistance with menu design or don't want to hire a designer.
But the price should be the most important component of your sample menu. The cost research you've completed for investors ought to be reflected in your prices. They will have a clearer idea of your restaurant's intended price range as a result. You'll quickly see how important menu engineering can be, even early on.
5. Employees
The company description section of the restaurant business plan briefly introduces the owners of the restaurant with some information about each. This section should fully flesh out the restaurant's business plan and management team.
The investors don’t expect you to have your entire team selected at this point, but you should at least have a couple of people on board. Use the talent you have chosen thus far to highlight the combined work experience everyone is bringing to the table.
6. Restaurant design
The design portion of your restaurant business plan is where you can really show off your thoughts and ideas to the investors. If you don’t have professional mock-ups of your restaurant rendered, that’s fine.
Instead, put together a mood board to get your vision across. Find pictures of a similar aesthetic to what you are looking for in your restaurant.
The restaurant design extends beyond aesthetics alone and should include everything from restaurant software to kitchen equipment.
7. Location
The location you settle on for your restaurant should be well aligned with your target market (making it easier to cater to your ideal customer) and with your business plans.
At this stage in the process, it's not uncommon to not have a specific location in mind - but you should at the very least have a few options to narrow down.
Pro Tip: When you approach your investors about potential locations, make sure to include as much information as possible about each venue and why it would be ideal for your brand.
Example for choosing an ideal location
Choosing the ideal location for your restaurant is a pivotal decision that can greatly influence your success.
To make the best choice, consider factors such as foot traffic, accessibility, and neighborhood demographics.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you’ll be better equipped to maximize visibility and attract your target market.
Foot traffic and accessibility
Foot traffic and accessibility are important factors in selecting a location that will attract customers and ensure convenience.
A high-traffic area with ample parking and public transportation options can greatly increase the likelihood of drawing in potential customers.
Additionally, making your restaurant accessible to individuals with disabilities can further broaden your customer base and promote inclusivity.
Neighborhood demographics
Analyzing neighborhood demographics can help you determine if your restaurant’s concept and cuisine will appeal to the local population.
Factors such as income levels, family structures, and cultural diversity can all influence dining preferences and habits.
By understanding the unique characteristics of the neighborhood, you can tailor your offerings and marketing efforts to resonate with the local community.
Conducting a market analysis can be a valuable step in this process.
To gather demographic data for a particular neighborhood, you can utilize resources such as the U.S. Census Bureau’s American Community Survey and reference maps.
Armed with this information, you can make informed decisions about your restaurant’s concept, menu, and pricing, ensuring that your establishment is well-positioned for success within the community.
Conducting market research will further strengthen your understanding of the local demographic.
8. Market overview
The market overview section is heavily related to the market research and analysis portion of the restaurant business plan. In this section, go into detail about both the micro and macro conditions in the area you want to set up your restaurant.
Discuss the current economic conditions that could make opening a restaurant difficult, and how you aim to counteract that. Mention all the other restaurants that could prove to be competition and what your strategy is to set yourself apart.
9. Marketing
With restaurants opening left and ride nowadays, investors are going to want to know how you will get word of your restaurant to the world.
The next marketing strategy and publicity section should go into detail on how you plan to market your restaurant before and after opening. As well as any plans you may have to bring a PR company on board to help spread the word.
Read more: How to write a restaurant marketing plan from scratch
10. External help
To make your restaurant a reality, you are going to need a lot of help. List any external companies or software you plan on hiring to get your restaurant up and running.
This includes everything from accountants and designers to suppliers that help your restaurant perform better, like POS systems and restaurant reservation systems .
Explain to your other potential investors about the importance of each and what they will be doing for your restaurant.
11. Financial analysis
The most important part of your restaurant business plan is the financial section . We would recommend hiring professional help for this given its importance.
Hiring a trained accountant will not only help you get your own financial projections and estimates in order but also give you a realistic insight into owning a restaurant.
You should have some information prepared to make this step easier for the accountant.
He/she will want to know how many seats your restaurant has, what the check average per table will be, and how many guests you plan on seating per day.
In addition to this, doing rough food cost calculations for various menu items can help estimate your profit margin per dish. This can be achieved easily with a free food cost calculator.
- Important restaurant metrics to track
A well-crafted restaurant business plan serves as a roadmap to success, guiding every aspect of the venture from menu design to employee training.
By carefully considering each component of the plan, aspiring restaurateurs can increase their chances of securing funding, attracting customers, and achieving their long-term goals.
Remember, a restaurant business plan is not just a document to satisfy investors; it is a living tool that should be revisited and updated regularly as the business grows and evolves.
By staying committed to the plan and adapting it as needed, restaurateurs can ensure that their culinary dreams have a solid foundation for success.
Share this article!
Saif Alnasur used to work in his family restaurant, but now he is a food influencer and writes about the restaurant industry for Eat App.
How to Calculate Food Cost in:...
Whether you're putting together a menu for your...

The A to Z Guide to:...
86 that dish? Camper? Kill it? In the weeds?

OpenTable vs. Resy::...
When it comes to choosing an online restaurant...
Join restaurants in 70+ countries using Eat App

Empowering restaurants, one table at a time Discover seamless dining with Eat App
- Reservation system
- Table management
- CRM and guest profiles
- Reports & trends
- Integrations
- Privacy policy
- Terms of service
- The 16 Best Reservation Systems
- Guide to Restaurant Marketing
- Guide to Customer Service
- Guide to Making a Restaurant Website
- All articles
"> "> Compare us
- Seven Rooms
- Compare All
© Eat App. All rights reserved.
How to Write a Food and Beverage Business Plan + Sample Business Plan PDF
Elon Glucklich
7 min. read
Updated February 17, 2024
Free Download: Sample Food and Beverage Business Plan Templates
The food and beverage sector is booming. Restaurant openings rose 10% in 2023 compared to 2022 — even higher than in pre-pandemic years.
From fine dining to food trucks, farmers to brewers, and wholesalers to coffee makers, there are opportunities across the food and beverage industry.
But starting a business without covering the basics — your operations plan, marketing tactics, financial strategy, and more — carries huge risks.
That’s why we recommend you write a business plan.
- Why write a food and beverage business plan?
Writing a business plan is an easy first step that you can start for free. Plus, businesses that take time to plan are significantly more successful than those that don’t.
Many food and beverage establishments fail because of one of the following:
- Poor inventory management
- Underestimated expenses
- High employee turnover
- Misjudged the size of their market
Writing a business plan can help you:
- Develop processes for managing inventory and logistics
- Understand your cash flows and create a realistic expense budget
- Budget for competitive employee pay that increases worker retention
- Analyze your competition and determine how big your market is
If you’re looking for funding from investors for your business, you’ll definitely need a business plan.
Brought to you by

Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- How to write a food and beverage business plan
Many business plans follow a standard format and you can use it as a starting point when writing your own plan. Here’s what that includes:
Executive summary
- Company summary and funding needs
- Products and services
- Marketing plan
- Management team
Financial plan
For food and beverage companies, you must give extra attention to your market analysis, operations plan, and financial forecasts.
If you’re ready to start, download a free business plan template and fill it out as you read this article.

Every business plan should include an executive summary . It’s a brief outline summarizing the plan, no more than one or two pages.
We recommend that you write the executive summary last after fleshing out the details of your plan.
Just summarize the vision for your business, describe your offerings and target market , and touch on your management team and financials. Don’t go into tons of detail — just provide a high-level sense of what you want your business to accomplish.
Opportunity: problem and solution
This section of your food and beverage business plan describes the opportunity you hope to capture.
Maybe you’re a farmer looking to diversify your revenue streams by distributing to grocery stores. Or a bar owner with high-end liquor that competitors in the market aren’t serving.
Whatever your business is, describe the gap in the market and how you aim to fill it.
If you’re operating a more common type of business, like a restaurant , you can probably keep this section short. But it’s useful to document what makes your business unique and it will help focus your sales and marketing efforts later on.
Market analysis
In a field as crowded with competitors as the food and beverage space, a detailed market analysis is essential.
Your focus should be on identifying the specific customer segments you aim to serve.
Maybe you’re a butcher with connections to fresh livestock. Will you be more successful selling directly to consumers, or should you focus on selling to grocery stores and markets in your area?
Or, you’re opening a diner. Should your menu focus on healthy meals or easy-to-make child-friendly options?
These are the types of questions that market research helps you answer. This section should detail the defining characteristics of your target market, including the demographics and preferences of your ideal customer and the size of the market you’re targeting. Market research questions specific to a food and beverage business could include:
- Business location and characteristics
- Area income
- Local food and beverage preferences
- Existing food and beverage options
Elaborate on how your food and beverage offerings align with that target market ’s needs. Remember, you can’t please everyone, so focus on a specific group of people or type of person and build out from there.
Marketing and sales
For food and beverage businesses promotions are how you stand out and seize a share of your market.
The marketing and advertising chapter of your business plan is where you’ll detail your strategies for capturing the attention — and loyalty — of the customers you identified as your target market in the previous section.
With so many options for consumers in the food and beverage space, you’ll likely have to rely on multiple marketing channels , including::
- Advertising on websites, television, and in relevant publications.
- Content marketing — developing an engaging website and writing blog content that’s search engine optimized to drive traffic to your site.
- Engaging with your customers on social media.
- Offering discounts and customer loyalty programs.
- Appearing at food and beverage industry trade shows and community events.
It doesn’t matter how delicious your recipes are, how fresh your crops are, or how innovative your cocktails are — if you don’t operate efficiently, your business probably won’t last long.
The operations strategy may be the most detailed section of your business plan, especially if you’re writing it for a bank loan or investment. This section describes how you will run your business day to day.
When writing the operations section, describe the following:
Physical space
Whether it’s a restaurant, a farm, or a food transportation business, describe the space you’re operating in, and all of the physical assets and equipment you’ll need to be successful.
If it’s a sit-down restaurant, consider including a floorplan mockup in your appendix.
Supply chain
List the suppliers and partners that get your product to customers. Think about the businesses you purchase ingredients from, the warehouses that goods are stored in, and the trucking companies that deliver your products to grocery stores.
These are your supply chain partners. It’s crucial that you maintain good relationships with them.
Production processes
How long it takes to make your product, and what materials and equipment are required. Documenting how you produce your goods or services demonstrates that you understand the costs of making them.
You may also uncover ways to produce them more quickly, or at a lesser cost.
Detail how you’ll handle matters of efficiency like order fulfillment, storage, shipping, and returns, as well as customer satisfaction. If you provide delivery services, document how you will handle the process of getting your product to customers’ homes or businesses.
List your staffing needs, training, and experience requirements for key staff. Also, document the management structure of your business.
This helps ensure that important tasks you don’t have time to monitor are being done and that workers are being supervised.
Describe investments in payment processing systems, inventory management software, and other tools that support sales or operations in your business. Cataloging your technology systems will help you determine where it might make sense to invest in upgrades for efficiency.
Take some time to write a financial plan . Create detailed financial projections, including sales , expenses , and profitability .
If that sounds intimidating, take a deep breath, and remember that financial forecasts are really just best guesses. If you’re running an existing business, you can start with your previous year’s numbers. If you’re starting, make an educated guess about where you hope to be financially a year from now.
Investors will want to see a:
- Sales forecast
- Income statement (also called a profit and loss statement )
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
If you use a tool like LivePlan , you’ll be able to build out your financial forecasts relatively quickly, even if you don’t have experience with business numbers.
Even if you aren’t seeking investment, the financial plan is crucial for understanding the viability of your business. It allows you to adjust your business model based on projected performance, and make informed decisions about where to spend your money.
- Food and beverage business plan templates and examples
If you want to see how other food and beverage businesses have created their plans, check out our free library of food and beverage business plans .
You can download all of them in Word format and jump-start your own business plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Elon is a marketing specialist at Palo Alto Software, working with consultants, accountants, business instructors and others who use LivePlan at scale. He has a bachelor's degree in journalism and an MBA from the University of Oregon.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
Related Articles

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

How to Write an Online Boutique Clothing Store Business Plan + Example Templates

How to Write a Brewery Business Plan + Free Sample Plan

How to Write a Cleaning Service Business Plan + Free Sample Plan PDF
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
13 food stall ideas to start now
Table of Contents
3. Vegan cuisine
4. bao buns, 6. tacos , 7. loaded fries, 8. ice-cream, 9. crepes and pancakes, 10. cocktails, 11. juice and smoothies, 13. bubble tea.
The days of the greasy fast food truck are quickly disappearing. In their place, we’re starting to see more and more gourmet food stalls that can produce restaurant-quality food with limited space.
That smaller size means overheads are generally quite low for food stalls, making it the perfect place for chefs to start their own businesses without having to fork out for a full restaurant.
To help inspire you, this guide will look at 13 popular food stall ideas that you can start right now, including:
- Vegan cuisine
- Loaded fries
- Crepes and pancakes
- Juice and smoothies
There will always be room for burgers in the food stall marketplace. There is considerable competition when it comes to burgers, but there are so many directions you can take that finding a niche in the market isn’t impossible.
For example, your stall could specialise in any number of these:
- Classic beef burgers.
- Chicken burgers.
- Smash burgers.
- Sloppy joes.
- Pulled pork burgers.
- Veggie burgers.
We wouldn’t recommend trying more than a couple of these options at a time. At the moment, the trend seems to be focusing on a few things that you can do exceptionally well, rather than providing an exhaustive menu.
Pizza is a crowd favourite that offers you a lot of flexibility as a food stall. A proper pizza oven is a must. But after that, all you really need is the ingredients for dough and ingredients for toppings.
That’s where the strength of a pizza stall comes into play. Your base is always the same, so you can switch up your menu with relative ease, giving you plenty of opportunities to get creative and keep offering customers something new.
The term “vegan cuisine” is definitely a broad brush stroke that can cover a whole range of different styles. But seeing as vegan food is still a smaller industry than others, it’s still separated into its own niche.
That’s not to say that it’s not popular. In fact, the number of vegans in the UK quadrupled from 2014 to 2019, so it’s a fast-growing market.
You can make a broad distinction in vegan cuisine between meat alternatives, like soy/veggie burgers, soy chicken, and seitan pulled pork, or you can just focus on normal vegan recipes in any style that you choose.
Also known as “steamed buns”, bao buns are a Chinese street food that has been growing in popularity in the UK.
It’s a type of sweet steamed bun, similar to dumplings, filled with different combinations of spiced meat and fragrant veggies.
Like pizza, wraps are particularly flexible in terms of what you decide to sell, and you can regularly change it up as you please.
Grilled chicken or falafel wraps are always a popular healthy option. But you could also other fast food wrap staples, like burritos, quesadillas, chimichungas, taquitos, or enchiladas.
Tacos are the perfect street stall food. They’re small, delicious, and relatively simple to make. And with larger companies like Taco Bell setting up more stores in the UK, there’s a proven market for them among the British public.
Loaded fries, dirty fries, cheesy chips, or poutine. Whatever you want to call it, it really boils down to putting delicious things on top of chips. And everybody loves chips.
This upgrade to classic comfort food has wide appeal and offers a lot of opportunity for new ideas and experimentation.
Although you’ll be limited by the weather, ice-cream carts and stalls are a great summertime business that will always be popular among customers.
Like some of our other examples, ice cream has seen a lot of changes in terms of what it can offer, meaning you can go in any number of directions, including:
- Classic ice cream.
- Dairy-free ice cream.
- Sundae bars.
Now that we’re in dessert territory, it’s time to mention another staple of European food stalls; crepes.
These thin pancakes are made fresh and can be filled with a variety of sweet and savoury combinations, making them a light and delicious crowd favourite.
Plus, have you ever seen crepes being made? It’s oddly satisfying, and that’s sometimes enough to attract some customers.
Your food stall doesn’t necessarily have to sell food. Pop-up cocktail stalls are a huge draw for festivals and events. Because you’re limited by space, a lot of these businesses focus on one area, like gin or whiskey cocktails, so a little market research is your best bet to find the right niche.
On the healthier side of things, juices and smoothies are a great way for customers to treat themselves while doing something good for their bodies.
You won’t be limited to drinks either. You can also sell fresh fruit and smoothie bowls at your stall. Smoothie bowls are very thick smoothies in a tub with a range of healthy toppings, so it wouldn’t require any extra ingredients or prep.
This part almost needs no explanation. It’s coffee! Loads of people want one at least some of the time, so there’s no doubting its widespread appeal. And with the variety of hot and cold coffees, you can make, it’s a good idea all year round.
The main difficulty with a coffee stall is the amount of competition you’re facing. A lot of coffee shops offer the same sort of thing, so you’ll need some way to stand out beside well-known industry giants, like Starbucks, Costa, and Caffe Nero.
Still, a bit of a novelty in the UK, bubble tea is a Taiwanese phenomenon that keeps growing in popularity. It’s basically a range of flavoured hot and cold teas with tapioca balls (bubbles) mixed in.

- Counting Up on Facebook
- Counting Up on Twitter
- Counting Up on LinkedIn
Related Resources
Bookkeeping and accounting tips for hairdressers.
As a self-employed hairdresser or salon owner, bookkeeping and accounting can be hard
What expenses can you claim as a childminder?
Being a childminder can be a great way to earn extra income or
How to get more clients as a freelance makeup artist
Whether you’re a professional makeup artist, a bridal makeup artist or a student
How to start a supported living business
Starting a supported living business is a challenging, but incredibly rewarding, way to
How To Start A Vending Machine Business In The UK
Starting a business is a great way to become your own boss and
How to start a dog daycare business
If you think dogs are a treat to be around, you’re not alone.
How to start a babysitting business
If you love spending time with children and offer to babysit for family,
How to start a cat sitting business
Did you know that 24% of the UK population own a cat? That’s
Money laundering regulations for estate agents
In December 2020, the government issued the National risk assessment of money laundering
How to sell jewellery designs to companies
Do you enjoy creating unique jewellery designs? If so, you might want to
How to become a self-employed labourer
Do you enjoy working with your hands and like the idea of being
How to start a home-based recording studio
With the advancement of technology, recording music at a professional level from home
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

A SAMPLE BUSINESS PLAN FOR SMALL FOOD BUSINESSES

Related Papers
Arditya Setyawan
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
How to create a financial forecast for a street food stall?

Creating a financial forecast for your street food stall, and ensuring it stays up to date, is the only way to maintain visibility on future cash flows.
This might sound complex, but with the right guidance and tools, creating an accurate financial forecast for your street food stall is not that hard.
In this guide, we'll cover everything from the main goal of a financial projection, the data you need as input, to the tables that compose it, and the tools that can help you build a forecast efficiently.
Without further ado, let us begin!
In this guide:
Why create and maintain a financial forecast for a street food stall?
What information is used as input to build a street food stall financial forecast, the sales forecast for a street food stall, the operating expenses for a street food stall.
- What investments are needed for a street food stall?
The financing plan of your street food stall
What tables compose the financial plan for a street food stall.
- Which tool should you use to create and maintain your street food stall's financial projections?
- Financial forecast template for a street food stall
Creating and maintaining an up-to-date financial forecast is the only way to steer the development of your street food stall and ensure that it can be financially viable in the years to come.
A financial plan for a street food stall enables you to look at your business in detail - from income to operating costs and investments - to evaluate its expected profitability and future cash flows.
This gives you the visibility needed to plan future investments and expansion with confidence.
And, when your trading environment gets tougher, having an up to date street food stall forecast enables you to detect potential upcoming financing shortfalls in advance, enabling you to make adjustments or secure financing before you run out of cash.
It’s also important to remember that your street food stall's financial forecast will be essential when looking for financing. You can be 100% certain that banks and investors will ask to see your numbers, so make sure they’re set out accurately and attractively.
Need a solid financial forecast?
The Business Plan Shop does the maths for you. Simply enter your revenues, costs and investments. Click save and our online tool builds a three-way forecast for you instantly.
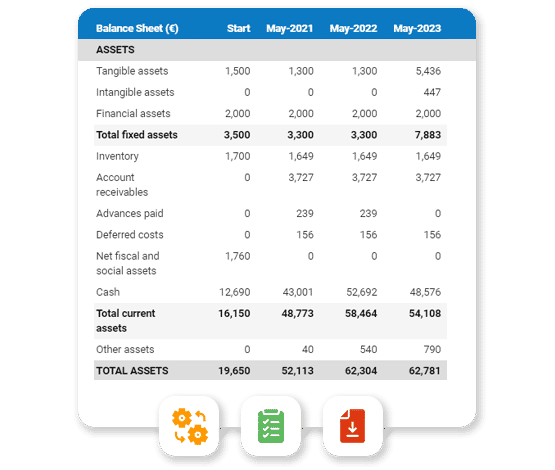
A street food stall's financial forecast needs to be built on the right foundation: your assumptions.
The data required to create your assumptions will depend on whether you are a new or existing street food stall.
If you are creating (or updating) the forecast of an existing street food stall, then your main inputs will be historical accounting data and operating metrics, and your team’s view on what to expect for the next three to five years.
If you are building financial projections for a new street food stall startup, you will need to rely on market research to form your go-to-market strategy and derive your sales forecast.
For a new venture, you will also need an itemised list of resources needed for the street food stall to operate, along with a list of equipment required to launch the venture (more on that below).
Now that you understand what is needed, let’s have a look at what elements will make up your street food stall's financial forecast.
From experience, it is usually best to start creating your street food stall financial forecast by your sales forecast.
To create an accurate sales forecast for your street food stall, you will have to rely on the data collected in your market research, or if you're running an existing street food stall, the historical data of the business, to estimate two key variables:
- The average price
- The number of monthly transactions
To get there, you will need to consider the following factors:
- Weather conditions: It is important to take into account the weather conditions when forecasting your sales. For example, during the summer months, the demand for your street food may increase due to the warmer weather and people being out and about more often. However, during the colder months, the demand may decrease, impacting your average price and number of transactions.
- Local events and festivals: Keep an eye on any local events or festivals that may be happening in your area. These events can attract a large number of people, providing a potential increase in sales for your street food stall. However, if there are multiple events happening at the same time, it may impact the number of transactions you receive as people may have more options to choose from.
- Tourism season: Depending on the location of your street food stall, the tourism season can greatly impact your sales. If your stall is located in a popular tourist destination, you may see an increase in both average price and number of transactions during peak tourist season. However, during the off-season, you may experience a decrease in sales.
- Competition: It's important to keep an eye on your competitors in the street food market. If there are other food stalls offering similar products in the same location, it may impact your average price and number of transactions. Consider adjusting your prices and offerings to stay competitive in the market.
- Local economy: The state of the local economy can also impact your sales forecast. During times of economic downturn, people may be more conscious of their spending and may opt for cheaper options. On the other hand, during a booming economy, people may be more willing to spend money on street food, potentially increasing your average price and number of transactions.
Once you have an idea of what your future sales will look like, it will be time to work on your overhead budget. Let’s see what this entails.
Need inspiration for your business plan?
The Business Plan Shop has dozens of business plan templates that you can use to get a clear idea of what a complete business plan looks like.

The next step is to estimate the expenses needed to run your street food stall on a day-to-day basis.
These will vary based on the level of sales expected, and the location and size of your business.
But your street food stall's operating expenses should include the following items at a minimum:
- Food and Ingredients: This includes the cost of purchasing all the necessary ingredients and supplies to prepare your dishes. This could include items such as meat, vegetables, spices, and packaging materials.
- Staff Costs: As a street food stall, you will likely have a small team of employees to help with food preparation, service, and cleaning. Be sure to factor in their wages, taxes, and any benefits or bonuses you offer.
- Rent/Utilities: Whether you are operating out of a food truck or a rented space, you will have to pay for rent and utilities such as electricity, water, and gas.
- Permits and Licenses: In order to legally operate your street food stall, you will need to obtain various permits and licenses. These could include health permits, food handling permits, and business licenses.
- Accountancy Fees: It is important to keep track of your finances and stay on top of tax obligations. You may need to hire an accountant to help you with bookkeeping, tax preparation, and financial planning.
- Marketing and Advertising: To attract customers, you will need to invest in marketing and advertising efforts. This could include creating flyers, social media promotions, and participating in local events.
- Insurance Costs: As a business owner, it is important to protect yourself and your business from potential risks. Be sure to budget for insurance coverage such as liability insurance and property insurance.
- Equipment Maintenance: Your street food stall will likely rely on various equipment such as grills, fryers, and refrigerators. Make sure to account for regular maintenance and repairs to keep your equipment in good working condition.
- Software Licenses: In today's digital age, you may need to invest in software to help with tasks such as inventory management, accounting, and online ordering. Be sure to budget for any necessary software licenses.
- Banking Fees: As a business owner, you will need to open a business bank account and may incur fees for services such as transactions, wire transfers, and overdrafts.
- Cleaning Supplies: Maintaining a clean and sanitary environment is crucial for a street food stall. Be sure to budget for cleaning supplies such as soap, paper towels, and disinfectants.
- Packaging Materials: If you offer take-away options, you will need to budget for packaging materials such as containers, bags, and utensils.
- Telephone/Internet: In order to communicate with customers and suppliers, you may need to have a dedicated business phone line and internet connection.
- Transportation Costs: Depending on your location, you may need to factor in transportation costs for obtaining ingredients and supplies, as well as traveling to and from events or markets.
- Training and Development: Investing in your own skills and knowledge as a street food stall owner is important for your business's success. Consider budgeting for workshops, courses, or conferences related to food, business, or marketing.
This list is, of course, not exhaustive, and you'll have to adapt it according to your precise business model and size. A small street food stall might not have the same level of expenditure as a larger one, for example.
What investments are needed to start or grow a street food stall?
Once you have an idea of how much sales you could achieve and what it will cost to run your street food stall, it is time to look into the equipment required to launch or expand the activity.
For a street food stall, capital expenditures and initial working capital items could include:
- Food Truck/Trailer: This is the most essential fixed asset for your street food stall. It includes the cost of purchasing or renting a food truck or trailer, as well as any necessary modifications or equipment installations.
- Kitchen Equipment: You will need to purchase or lease cooking and food preparation equipment, such as grills, fryers, refrigerators, and food storage containers.
- Point of Sale (POS) System: A POS system is necessary for accepting payments and tracking sales. This includes the cost of purchasing or leasing a POS system, as well as any necessary software and accessories.
- Generator/Power Supply: If your street food stall will be operating in locations without access to electricity, you will need to invest in a generator or alternative power supply to run your equipment and lighting.
- Signage and Branding: In order to attract customers and stand out among other food stalls, you may need to invest in custom signage and branding materials, such as banners, menus, and logo design.
Again, this list will need to be adjusted according to the specificities of your street food stall.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

The next step in the creation of your financial forecast for your street food stall is to think about how you might finance your business.
You will have to assess how much capital will come from shareholders (equity) and how much can be secured through banks.
Bank loans will have to be modelled so that you can separate the interest expenses from the repayments of principal, and include all this data in your forecast.
Issuing share capital and obtaining a bank loan are two of the most common ways that entrepreneurs finance their businesses.
Now let's have a look at the main output tables of your street food stall's financial forecast.
The projected profit & loss statement
The projected profit & loss shows how profitable your street food stall is likely to be in the years to come.
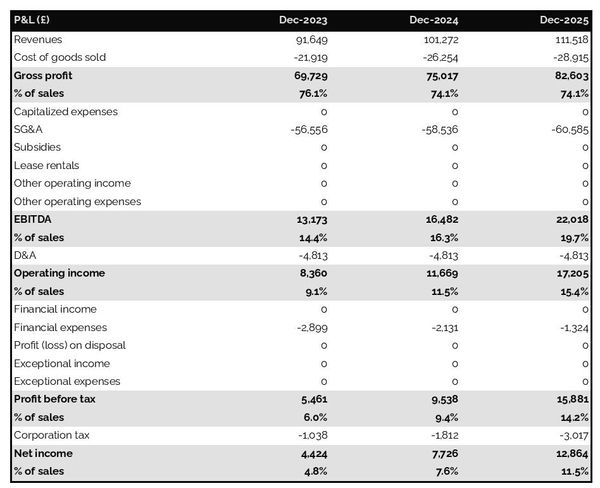
For your street food stall to be financially viable, your projected P&L should ideally show:
- Sales growing above inflation (the higher the better)
- Profit margins which are stable or expanding (the higher the better)
- A net profit at the end of each financial year (the higher the better)
This is for established street food stalls, there is some leniency for startups which will have numbers that will look a bit different than existing businesses.
The projected balance sheet
The projected balance sheet gives an overview of your street food stall's financial structure at the end of the financial year.
It is composed of three categories of items: assets, liabilities and equity:
- Assets: are what the business possesses and uses to produce cash flows. It includes resources such as cash, buildings, equipment, and accounts receivable (money owed by clients).
- Liabilities: are the debts of your street food stall. They include accounts payable (money owed to suppliers), taxes due and bank loans.
- Equity: is the combination of what has been invested by the business owners and the cumulative profits to date (which are called retained earnings). Equity is a proxy for the value of the owner's stake in the business.
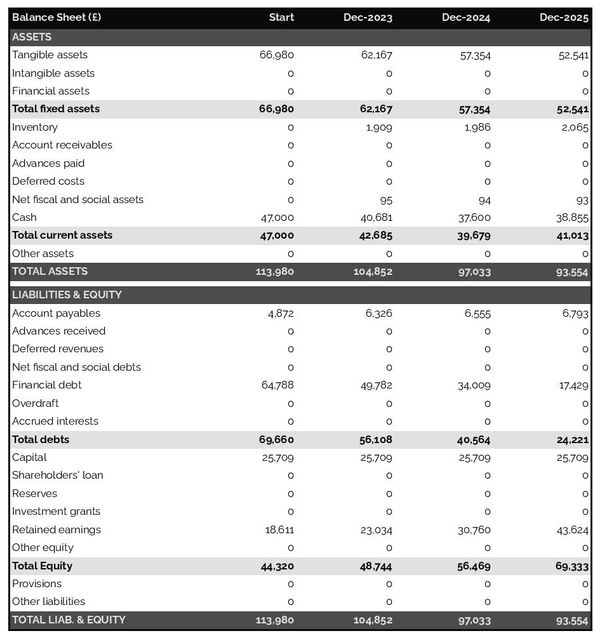
The cash flow forecast
Your street food stall's cash flow forecast shows how much cash your business is expected to consume or generate in the years to come.
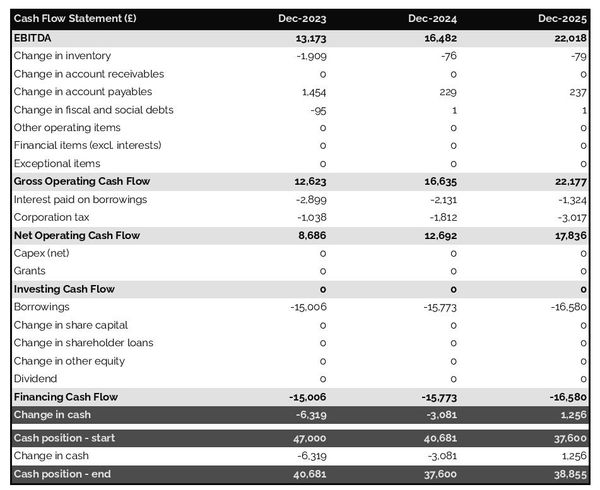
It is best practice to organise the cash flow forecast by nature to better explain where cash is used or generated by the street food stall:
- Operating cash flow: shows how much cash is generated by the operating activities
- Investing cash flow: shows how much will be invested in capital expenditure to maintain or expand the business
- Financing cash flow: shows if the business is raising new capital or repaying financiers (debt repayment, dividends)
Keeping an eye on (and regularly updating) your street food stall's cash flow forecast is key to ensuring that your business has sufficient liquidity to operate normally and to detect financing requirements as early as possible.
If you are trying to raise capital, you will normally be asked to provide a monthly cash flow forecast in your street food stall's financial plan - so that banks or investors can assess seasonal variation and ensure your business is appropriately capitalised.
Which tool should you use to create your street food stall's financial forecast?
Using the right tool or solution will make the creation of your street food stall's financial forecast much easier than it sounds. Let’s explore the main options.
Using online financial forecasting software to build your street food stall's projections
The modern and easiest way is to use professional online financial forecasting software such as the one we offer at The Business Plan Shop.
There are several advantages to using specialised software:
- You can easily create your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you without errors
- You have access to complete financial forecast templates
- You get a complete financial forecast ready to be sent to your bank or investors
- You can easily track your actual financial performance against your financial forecast, and recalibrate your forecast as the year goes by
- You can create scenarios to stress test your forecast's main assumptions
- You can easily update your forecast as time goes by to maintain visibility on future cash flows
- You have a friendly support team on standby to assist you when you are stuck
- It’s cost-efficient and much cheaper than using an accountant or consultant (see below)
If you are interested in this type of solution, you can try our forecasting software for free by signing up here .
Hiring a financial consultant or chartered accountant
Hiring a consultant or chartered accountant is also an efficient way to get a professional street food stall financial projection.
As you can imagine, this solution is much more expensive than using software. From experience, the creation of a simple financial forecast over three years (including a balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement) is likely to start around £700 or $1,000 excluding taxes.
The indicative estimate above, is for a small business, and a forecast done as a one-off. Using a financial consultant or accountant to track your actuals vs. forecast and to keep your financial forecast up to date on a monthly or quarterly basis will naturally cost a lot more.
If you choose this solution, make sure your service provider has first-hand experience in your industry, so that they may challenge your assumptions and offer insights (as opposed to just taking your figures at face value to create the forecast’s financial statements).
Why not use a spreadsheet such as Excel or Google Sheets to build your street food stall's financial forecast?
Creating an accurate and error-free street food stall financial forecast on Excel (or any spreadsheet) is very technical and requires both a strong grasp of accounting principles and solid skills in financial modelling.
Most entrepreneurs lack the expertise required to create an accurate financial forecast using spreadsheet software like Excel or Google Sheets. As a result, it is unlikely anyone will trust your numbers.
The second reason is that it is inefficient. Building forecasts on spreadsheets was the only option in the 1990s and early 2000s, nowadays technology has advanced and software can do it much faster and much more accurately.
This is why professional forecasters all use software. With the rise of AI, software is also becoming smarter at helping us detect mistakes in our forecasts and helping us analyse the numbers to make better decisions.
Finally, like everything with spreadsheets, tracking actuals vs. forecasts and updating your forecast as the year progresses is manual, tedious, error-prone, and time-consuming. Whereas financial forecasting software like The Business Plan Shop is built for this.
Use our financial projection templates for inspiration
The Business Plan Shop has dozens of financial forecasting templates available.
Our examples contain both the financial forecast, and a written business plan which presents, in detail, the company, the team, the strategy, and the medium-term objectives.
Whether you are just starting out or already have your own street food stall, looking at our template is always a good way to get ideas on how to model financial items and what to write when creating a business plan to secure funding.
- A financial forecast shows expected growth, profitability, and cash generation metrics for your street food stall.
- Tracking actuals vs. forecast and having an up-to-date financial forecast is key to maintaining visibility on your future cash flows.
- Using financial forecasting software is the modern way of creating and maintaining financial projections.
We hope that this guide helped you gain a clearer perspective on the steps needed to create the financial forecast for a street food stall. Don't hesitate to contact us if you have any questions!
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- Financial forecast example
- How to write a street food stall business plan
Know someone who runs a street food stall? Share our business guide with them!

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool ? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here
Business Advice
May 11, 2023
Small business guide: How to open a pop-up food stall

Starting a pop-up food stall counts as living the dream for lots of foodies. It lets you work for yourself, focusing on the cuisine that you love, meeting lots of new people, and showcasing your creativity. It comes with lots of challenges too of course, which is why we’ve created this mini guide to opening a pop-up food stall.
In it we’ll cover:
- What is a pop-up food stall?
- How to set up a pop-up food stall
Creating a business plan
- What paperwork you’ll need
How to market your pop-up food stall
What is a pop-up food stall.
Firstly, what is a pop-up food stall anyway? A pop-up food stall is a temporary food service establishment that is set up in a location for a short period, typically for a few hours or days, to serve food to customers.
Pop-up food stalls are often used by food vendors or entrepreneurs to test a food concept, showcase a specific cuisine, or participate in events such as food festivals, farmers' markets, or street fairs.
They’re typically small and mobile, often consisting of a food cart or a portable structure, and they may serve a variety of food items such as snacks, sandwiches, desserts, or speciality dishes.
Pop-up food stalls are especially well-known for their unique and often creative food offerings, and they provide a dynamic and vibrant dining experience for customers in temporary and unexpected locations.
Some of the advantages of starting up a pop up food stall include:
- Free publicity: Setting up a pop-up dining experience in an established venue, such as a shopping centre or at a music festival, provides instant potential visibility to a crowd seeking dining options. It can catch the attention of passersby and generate free publicity for your food.
- Cost-effective: Starting a pop-up dining experience is generally more affordable compared to establishing a permanent restaurant. Lower investment, overheads, and labour costs are incurred as pop-up dining experiences are temporary.
- Experimentation: Pop-up dining experiences provide the opportunity to test menus, themes, and pricing before committing to a permanent venue. It allows for flexibility in trying out different concepts and gauging customer preferences.
- Flexibility: Pop-ups provide the flexibility to try different locations, including different towns and cities, to identify markets for your street food. This allows for creative and strategic location choices to attract a wider customer base.
How to Set up a Pop Up Food Stall
Those are some of the benefits you can get, but do you know how to set up a pop-up food stall? They may look like they just, well, ‘pop up’, but there’s a lot of planning and preparation required to make something look as spontaneous and effortless as a successful pop-up food stall.
Let’s dive into what you’ll need to think about before you’ll be able to open up shop:
Firstly you need to consider some key aspects of what can make a successful launch:
Pop-up restaurants offer a unique opportunity to test out new culinary concepts, whether it's a specific food item like gourmet grilled cheese sandwiches or a cuisine that's not widely available in your area. By identifying gaps in the competitive landscape and tapping into rising restaurant trends, you can bring your culinary expertise and passion to life with a pop-up concept that captures the hearts of foodies. If your concept resonates with customers and receives rave reviews, you may have stumbled upon a winning idea for a lasting business.
The Location
When it comes to choosing a location for your pop-up restaurant, think outside the box to make your venture stand out and generate buzz. While street food stalls or food trucks are common options, consider unconventional venues to create a memorable experience. Hosting your pop-up in an existing venue’s kitchen during off-peak hours can help draw a crowd, while setting up in a scenic location like a city rooftop or a rustic barn can provide a picturesque backdrop for Instagram-worthy photos. You could even consider opening near an apartment complex to attract curious residents eager to try something new. Get creative with your location to make your pop-up restaurant truly unforgettable.
Your USP (unique selling point)
To stand out from the competition in a crowded street food market or an area with many dining options, you'll need to find ways to set your food stall apart. One effective approach is to create a signature recipe that is unique and memorable, while authenticity can also be a powerful selling point. If you have a compelling backstory behind your food stall, you can use it to your advantage by showcasing the quality and presentation of your product. Whether it's using fresh, homemade, ethical, sustainable, and locally sourced ingredients, or offering fast and affordable options, highlighting these unique qualities can serve as your USP and differentiate your business from the competition. Remember, finding a way to stand out from the crowd is crucial for the success of your street food stall. Whether it's through a creative and distinctive recipe, an authentic backstory, or unique qualities that appeal to your target audience, showcasing what makes your food stall special can help you attract customers and build a loyal following.
Accept payments for your business
Another key consideration is taking payments. Being a pop-up food stall means needing to be flexible and mobile. So, when it comes to payment processing for your mobile business, you need a solution that is both adaptable and secure in a potentially chaotic environment. That's where the Dojo Go card machine comes in.
Designed with mobility and flexibility in mind, the Dojo card machine is easy to use and can go wherever your business takes you. It allows you to accept payments quickly and efficiently, freeing up your time to focus on marketing campaigns and creating irresistible offers to attract customers.
With our card machine, you can have peace of mind knowing that your payment processing is safe and reliable. It offers a secure way for a food market stall owner to accept card payments, ensuring that customers' information is protected.
The Dojo Go card machine can help you streamline your mobile business operations and provide a seamless payment experience for your customers, so you can focus on growing your business and creating an exceptional customer experience.
What paperwork do you need for a pop-up food stall in the UK?
Now you’ve worked out the ‘what’ and the ‘where’, let’s look at the legalities. Navigating the legal requirements for starting a street food stall in the UK is a crucial step in the process. The UK's official food business registration page covers the basic information on how to legalise your business.
We’ve listed the highlights below:
- Street Trading Licences: You will need to obtain the appropriate licences from local authorities to operate your street food stall legally.
- Food Hygiene Certifications and Environmental Health Registration: Ensuring proper food hygiene practices and registering with the local environmental health department are essential for compliance.
- Handwashing Stations: Apart from the sink used for washing cooking utensils, you will need to provide handwashing stations for your staff and customers to maintain hygiene standards.
- Gas Safety Certificates and Electrical Licences: Ensuring that your cooking appliances comply with gas safety regulations and obtaining proper electrical licences are crucial for the safety of your stall and customers.
- Liability Insurance: Obtaining liability insurance for the public and employees will protect you and your business from potential legal and financial risks.
- Risk Assessment/HACCP Completion: Conducting a risk assessment and completing a Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) plan will help you identify and manage potential risks in your food business.
- Street Market Pitch: Finally, you will need to sign up for a street market pitch or obtain permission from the relevant authorities to set up your stall in a designated location.
One potential downside to a pop-up food stall is that its temporary nature makes it hard to attract long-term customers, as the stall isn’t necessarily in one place for any length of time. This is where using the right marketing tactics become a vital tool in allowing you to get the word out quickly and get as many customers as possible, as soon as possible.
You need to begin with the branding, which goes beyond just a logo on your business cards; it starts with your stall, and the bar is set very high. At the very least, your stall should have a nameplate with your business name that is easy to see and remember, as it will be the primary identifier for customers when you have no permanent location. You can also add lights and colours to decorate your stall, reflecting your brand identity.
The design of your stall directly impacts your overall branding. If you want to convey a sense of fun with a splash of colour, your stall will look different from a chic and minimalist design that exudes big flavours. Be intentional about carrying your branding over to your social media channels, packaging, and website.
Even if you're just starting out, ensure that your logos are consistent across all channels and something you'll be happy with for a while. Rebranding too early may cause customers to think you've disappeared from the scene, leading them to look elsewhere for tasty treats.
Social media
Beyond branding, there are plenty of other ways to get people to take notice. Street food stalls have traditionally relied on appealing to customers through their senses - the enticing smells, sizzles, and appearance of their food, along with little tasters to draw people in. However, with the advent of social media and the internet, customer reach has expanded even further. A strong online presence can attract customers to your stall before they even see it in person. That’s why it's crucial for all small businesses, especially pop-up food stalls, to have a presence on social media. An Instagram page filled with mouthwatering visuals can entice people to come to visit your stall, while a Facebook page can also help broaden your reach. Social media provides a significant opportunity to grow your business and attract more customers to your stall. Then it’s up to your food to get them to use their social media to tell their friends.
Launch events
Making a splash with your launch event is a good way to attract the right attention. For this in particular, it’s important to define your target audience, which consists of the people you want to attract to your pop-up and to craft your messaging accordingly. Consider how you want your brand to be perceived by your target audience and what key information you want them to know about your pop-up.
Other marketing tactics for your food business
Here are some other ways to market your pop-up food stall:
- Influencers - Instagram is full of foodie influencers. Leveraging influencer marketing can provide a significant boost to your pop-up restaurant. Look for local food influencers on social media and invite them to a soft opening event, where they can sample your food in exchange for posting about it on their social media channels. Most influencers are likely to request paid partnerships but the cost per post or ‘reel’ will depend on the size of the influencer so you’ll need to make sure you're working within your budget and have mutually agreed the terms. By collaborating with influencers, you can generate buzz, increase your visibility, and potentially attract new customers to your pop-up restaurant. It's important to establish clear expectations and mutually beneficial arrangements with influencers to ensure a successful partnership.
- Go old school with offline marketing - While online marketing is crucial for promoting your pop-up restaurant, don't underestimate the power of offline marketing. A simple yet effective idea to generate interest is to print flyers and distribute them in the local area. Include an appetising photo of your food and a discount coupon code to make the offer enticing. If you already own a restaurant and want to attract your loyal customers to your new pop-up, you can leverage our delivery heatmaps to identify high-density order areas and distribute your flyers there, where you know your regulars reside. This targeted approach can help you drive traffic to your new pop-up and leverage your existing customer base for increased success.
We hope you enjoyed our handy guide to opening your own pop up food stall guide. Bookmark this post to ensure you are fully prepared when it’s time to turn your concept into a reality.
Related posts

Can I park my food truck anywhere in the UK?

Card machines for small businesses: A complete guide.

A guide to food photography: Tips and tricks for restaurant owners
Business | Historic Markley Hotel will be redeveloped as…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
Baltimore Sun eNewspaper
- Real Estate
- Top Workplaces
- Best Reviews
Business | Historic Markley Hotel will be redeveloped as small-business, retail hub with student housing next door

People in Baltimore’s Lauraville and Beverly Hills neighborhoods have long known the sprawling brick building in the 4500 block of Harford Road as The Markley Hotel, though it’s not clear whether it ever hosted overnight guests.
A new chapter is starting for the former D. Markley Supply Co. seed and general store and warehouse as a community hub, with student housing for Morgan State University next door.
The historic Markley building, which sits on a 3-acre, former industrial tract that Baltimore-based MCB Real Estate purchased in 2022, would become a hub where food and retail entrepreneurs run stalls and kiosks. The $7 million project also involves transforming a second-floor loft into a gathering and event space for entrepreneurs and young professionals, along with offices. Construction is expected to start this summer.
Hamilton-Lauraville Main Street, which works to revitalize the Harford Road commercial corridor, began planning the 24,000-square-foot center after MCB donated the Markley building to the nonprofit group.
On the site’s remaining land, MCB is building a 151-unit Class A apartment building to house students from Morgan State’s campus less than a mile away. The apartments are expected to open by summer 2025.
Revitalization of the 4500 block, which has long struggled with vacant and deteriorating buildings, was seen as a critical link to Harford Road’s redevelopment, including new stores and restaurants, that has occurred both north and south of the site, said Daniel Doty, executive director of the Main Street group.
“There was just this huge property that was very difficult to do anything with,” Doty said. The redevelopment “is helping to bring life to the entire area.”
The Main Street group is redeveloping the Markley with the help of MCB and The Cube Cowork, an existing Harford Road-based business that calls itself the nation’s largest Black woman-run coworking space. The Cube will expand to the Markley and become the anchor tenant, leading the effort to attract and retain entrepreneurs. It will continue to run its current Harford Road location, where entrepreneurs lease its offices, co-working space, conference rooms and event space.

“Because the demand has been so high, in the sense of other services that entrepreneurs need, when we saw this space we thought that this would be a great expansion,” said Tammira Lucas, The Cube’s leader and small-business adviser. “This gives them a home. Something that they lack is a place where they can actually be stable but also not have the extreme overhead of a brick and mortar space.”
MCB, the development firm that purchased and is redeveloping Harborplace, decided to donate the Markley and work to repurpose it as part of its mission to foster overall neighborhood growth through its projects, said Amy Bonitz, MCB’s vice president of community development.
The idea for the new facility is to offer space for companies to grow and later potentially open their own stores or restaurants on Harford Road, Doty said. The vision includes offering affordable space for small retailers, food-based businesses, including a pop-up cafe, small media companies and other entrepreneurs.
“We aim to build something truly impactful here,” he said.
The group also is relying on help from the business and entrepreneurial programs at Morgan State’s Graves School of Business and Management.
The project was awarded a $2.5 million state historic tax credit as well as a $1 million grant from the Maryland Department of Housing and Community Development. Plans call for restoring the building’s signature two-story wraparound porch.
The property was initially used as a general store around the turn of the last century, selling farm seed and equipment to farmers on their way to markets in Baltimore, and a warehouse that supplied coal, said Reni Lawal, a development associate with MCB who researched the property’s history when applying for the historic tax credit. The Markley family once lived in upstairs quarters. Lawal said she believes the last member of the Markley family moved out in 1955.
The Markley was later used by a magazine, an adult day care program and a church. It has been vacant for about a decade.

More in Business

Business | Seven Black-owned businesses moving to Harborplace pavilions as temporary tenants

Restaurants, Food and Drink | Papi Cuisine, Ikonic Assembly Room win liquor license renewals despite complaints

Business | Retirement could come sooner than you think — how to plan for it

Business | FTC chief says tech advancements risk health care price fixing

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When writing the strategy section of a business plan for your street food stall, it is essential to include information about your competitive edge, pricing strategy, sales & marketing plan, milestones, and risks and mitigants. The competitive edge subsection should explain what sets your company apart from its competitors.
2. Write a business plan. Create a business plan that thoroughly explains your business model, operations, pricing strategy, and financial projections. 3. Handle health, safety, hygiene and legal compliance. Food and beverage is a highly regulated industry with additional legal, health, and safety requirements.
But even so, if you were to estimate, here's a general expense breakdown: Food Cart Business. $3,000 - $5000 on a fully equipped food cart. $500 - $700 on your ingredients & initial food stock, $400 - $ 600 on permits and registrations, $500 - upwards on marketing, $500 for the first month to park and clean the cart.
Explore potential locations for your food stall, assess competitor offerings, and gather insights into consumer demand to inform your business strategy and menu development. 3. Secure Permits and ...
Step 3: Set up your business. Once you've studied your market, you know where there's a hole that needs to be filled, and you've taken some time to create a business plan, you're ready to ...
6. Restaurant design. The design portion of your restaurant business plan is where you can really show off your thoughts and ideas to the investors. If you don't have professional mock-ups of your restaurant rendered, that's fine. Instead, put together a mood board to get your vision across.
The humble food stall has gone from a Sunday market add-on to a powerhouse of creativity, cuisine and style - having a favourite food stall is now expected of any self-respecting foodie. Take a whizz through these pointers - then start your food stall and see your dreams become a reality. Develop a food stall business plan
Develop a food stall business plan. ... Your 101 Guide to Building a Marketing Plan for Your Small Business. Jan 18, 2021 — 5 min read. Reaching Customers. A Beginner's Guide to Social Media Marketing for Businesses. Apr 28, 2021 — 4 min read. Tell us a little more about yourself to gain access to the resource.
Free Download: Sample Food and Beverage Business Plan Templates. The food and beverage sector is booming. Restaurant openings rose 10% in 2023 compared to 2022 — even higher than in pre-pandemic years. From fine dining to food trucks, farmers to brewers, and wholesalers to coffee makers, there are opportunities across the food and beverage ...
Starting a food business, like anything else, comes with its rewards and challenges. The global pandemic has led to a pent-up demand for visiting restaurants, bars and other food establishments. While most food businesses have shifted focus to curbside pickup and delivery, the restaurant industry's profits are expected to rise 15% in 2021.. The imminent boon is fantastic news, but one of the ...
Tacos are the perfect street stall food. They're small, delicious, and relatively simple to make. And with larger companies like Taco Bell setting up more stores in the UK, there's a proven market for them among the British public. 7. Loaded fries. Loaded fries, dirty fries, cheesy chips, or poutine.
Baby food. Homemade jams and jellies. Organic foods. Wine, beer, and spirits. Every food business has advantages and disadvantages, so consider what you'll be able to commit to and choose the food business idea that's best for you. To get started, here are 13 ideas for products and services to inspire you. 1.
The purpose of this business plan is to secure $50,000 in order to fund the purchase, marketing, and staffing requirements for Donny's Food Truck restaurant in Small Town, CT. Donny's Food Truck was founded by chef Donny O'Neal, and sous chef Miguel Sanchez, in 2020. The funds
This mock business plan focuses on a whipped topping business, but the format is appropriate for any small food business. fBusiness Plan Fancy's Foods, LLC. 2409 Oak Hollow Drive Antlers, OK 74523 (580) 298-2234 Keith Bean Marianne Bean December 1, 1998 fExecutive Summary Marianne and Keith Bean have been involved with the food industry for ...
Regarding business planning, the revenue from food stalls is typically irregular as it is usually a cash-only business. 15 Small Food Stall Business Ideas to Try Today. Here are ten small food stall business ideas to consider. These businesses will bring in a sustainable profit and can offer you a long-term income. 1. Meal Preparation
A financial plan for a street food stall enables you to look at your business in detail - from income to operating costs and investments - to evaluate its expected profitability and future cash flows. This gives you the visibility needed to plan future investments and expansion with confidence. And, when your trading environment gets tougher ...
Business&Plan& With goals and expectations in hand, a Business plan is the written document detailing how those goals will be achieved. The U.S. Small Business Association (SBA) aims to assist small businesses through access to capital and developmental resources. They define a business plan as "an essential roadmap for business success.
Pop-up food stalls are often used by food vendors or entrepreneurs to test a food concept, showcase a specific cuisine, or participate in events such as food festivals, farmers' markets, or street fairs. They're typically small and mobile, often consisting of a food cart or a portable structure, and they may serve a variety of food items such ...
The market size of the Hot Dog and Sausage Production industry is $19.2bn in 2023 and the industry is expected to increase by 3.6 percent going forward. 12. Crepe Restaurant Business Plan. A crepe restaurant is a niche restaurant that serves crepes (pancakes) as its main menu.
Identify the right location to start the business and its target audience. OBTAIN LICENSES AND PERMITS. Obtain all the licenses and registrations to start a food business. BUSINESS MODEL, VENDORS, TECH. Decide the business model, connect with vendors and set up the technology. KINDS OF FOOD SERVICE BUSINESSES.
6. Staffing. 7. Profits. Starting a food cart is one of the most ideal and affordable ways to enter the food industry. Lower risks and investment makes the business one of the most popular high-profit food business ideas among the various restaurant formats for opening a food business. However, for making your food cart business successful, you ...
A market stall is a temporary structure that you set up to sell your products or services. You can sell any type of product or service from handmade jewellery to fresh produce or clothing. Market stalls are one way for you to test your product with customers or expand your business. You'll likely need some type of registration, licence ...
The vision includes offering affordable space for small retailers, food-based businesses, including a pop-up cafe, small media companies and other entrepreneurs.
The subscription plan would allow Amazon's Prime members to get unlimited grocery delivery at $9.99 per month on orders over $35 from Whole Foods Market, Amazon Fresh, and other local grocery and ...